User login
Acalabrutinib extends PFS in advanced CLL
AMSTERDAM – For patients with relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), monotherapy with the Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor acalabrutinib (Calquence) was associated with better progression-free survival and a more tolerable safety profile than rituximab combined with either idelalisib (Zydelig) or bendamustine, an interim analysis from the phase 3 ASCEND trial showed.
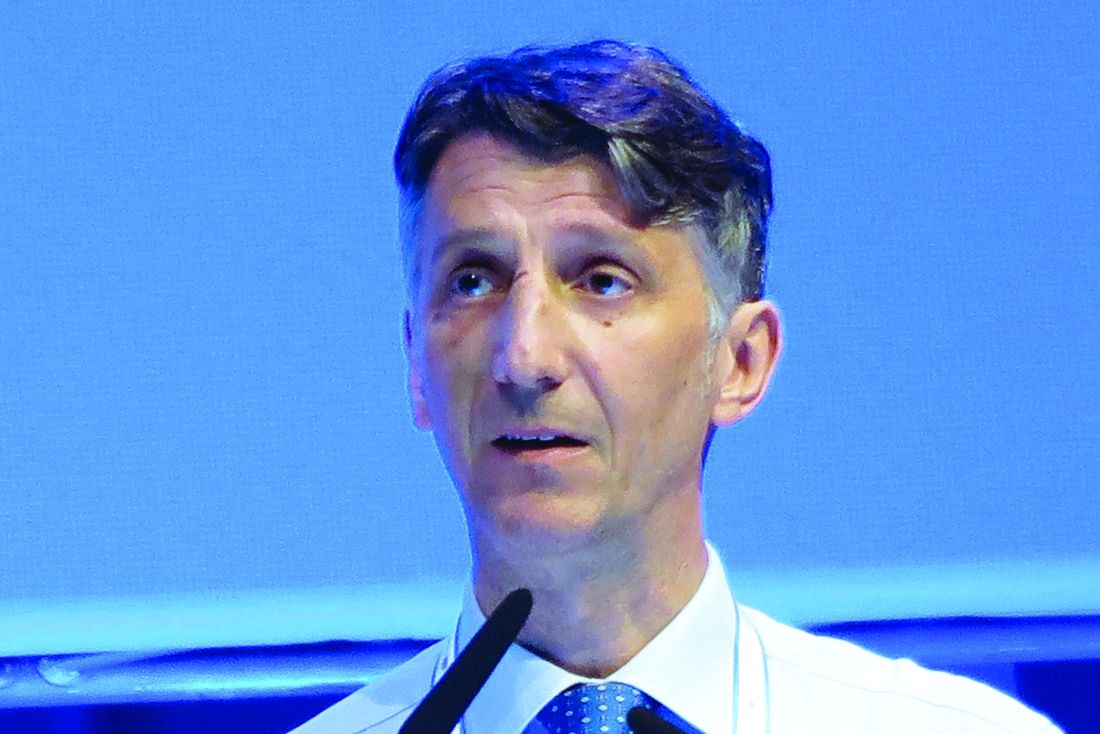
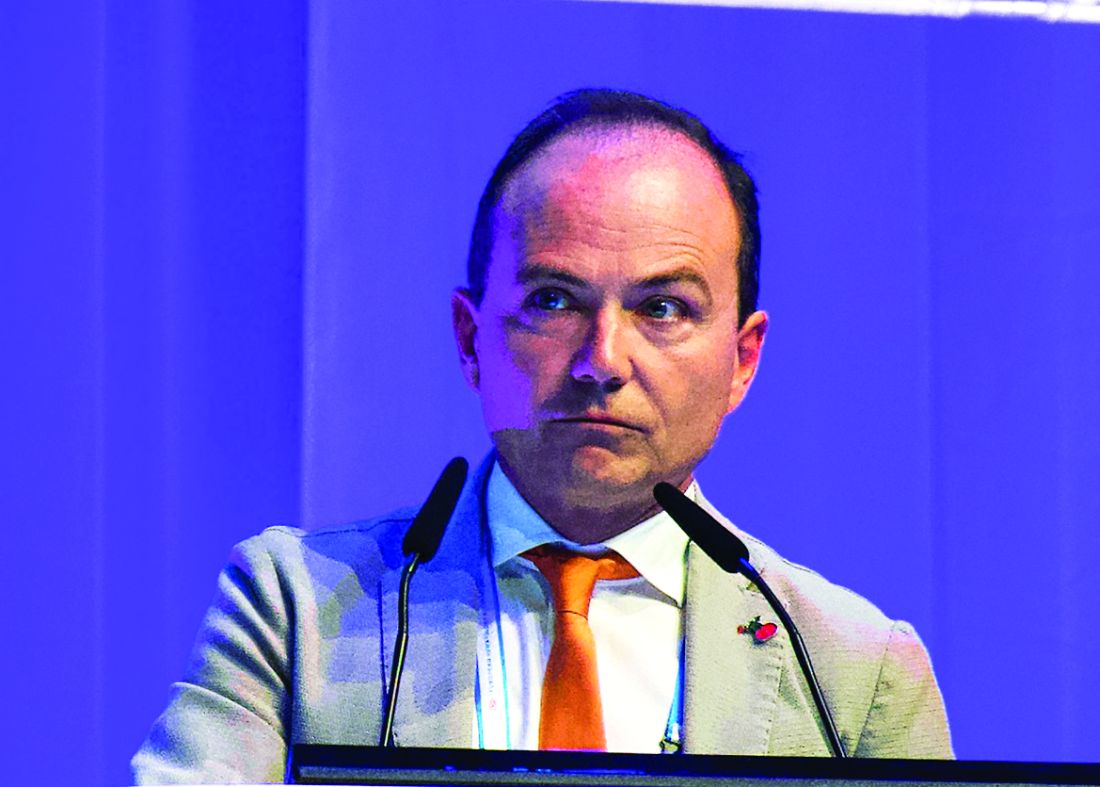
Among 310 patients with previously treated CLL followed for a median of 16.1 months, the primary endpoint of median progression-free survival (PFS), as assessed by independent reviewers, had not been reached for patients treated with acalabrutinib, compared with 16.5 months for patients treated with idelalisib and rituximab (IdR) or bendamustine and rituximab (BR), reported Paolo Ghia, MD, PhD, from Università Vita-Salute San Raffaele in Milan.
“We show that acalabrutinib improved progression-free survival across all groups, including those with high-risk features,” he said at the annual congress of the European Hematology Association.
Acalabrutinib is approved in the United States for treatment of mantle cell lymphoma that has progressed on at least one prior therapy. It has been shown in preclinical studies to be more selective for BTK than the first-in-class agent ibrutinib (Imbruvica), with less off-target kinase inhibition, Dr. Ghia said.
ASCEND was designed to see whether acalabrutinib monotherapy could offer superior PFS to IdR or BR in patients with CLL who had progressed or were refractory to at least one prior line of therapy.
Patients were randomly assigned, with 155 patients in each arm, to either acalabrutinib 100 mg orally twice daily or the investigator’s choice of either idelalisib 150 mg orally twice daily plus IV rituximab at an initial dose of 375 mg/m2, followed by up to seven doses at 500 mg/m2 delivered every 2 weeks for four infusions, then every 4 weeks for the remaining three infusions or IV bendamustine 70 mg/m2 on days 1 and 2 of each cycle, plus rituximab at the 375 mg/m2 dose on day 1 for the first cycle, followed by 500 mg/m2 for up to six total cycles.
Dr. Ghia presented results of an interim analysis planned for when two-thirds of the predicted PFS events (approximately 79) had occurred.
The baseline patient characteristics were generally similar, with a median age of 68 years in the acalabrutinib arm and 67 years in the comparison arm. Almost half of all patients in each arm had bulky disease, defined as 5 cm or greater. The majority of patients had two or more prior lines of therapy.
The primary endpoint of PFS as assessed by independent review favored acalabrutinib, with a hazard ratio of 0.31 (P less than .0001). Results were similar when acalabrutinib was compared with each of the regimens in the comparison arm (HR, 0.29 vs. IdR, 0.36 vs. BR; P less than .001 for each comparison).
Acalabrutinib was also superior in patients with high-risk cytogenetic features, compared with the other two regimens combined (HR, 0.27; P less than .001).
The benefit of the BTK inhibitor was consistent across all subgroups, including age, sex, performance status, Rai stage at screening, bulky/nonbulky disease, number of prior therapies, presence or absence of deletion 17p or TP53 mutation, mutated or unmutated immunoglobulin heavy chain, and complex/noncomplex karyotype.
Reviewer-assessed objective response rates were similar, occurring in 81% of patients on acalabrutinib and 76% of patients on other regimens.
There were no complete responses in the acalabrutinib arm, compared with two complete responses in the comparison arm. The majority of responses in each arm were partial responses (81% and 74%, respectively).
The median duration of response was not reached with acalabrutinib, compared with 13.6 months with the other therapies (HR, 0.33; P less than .0001).
In all, 85% of patients on acalabrutinib had a response lasting at least 12 months, compared with 60% of patients on the other regimens. There was no difference in overall survival at the 16.1-month median follow-up.
Adverse events of any grade occurred in 94% of patients on acalabrutinib, 99% on IdR, and 80% on BR; the respective incidences of serious adverse events were 29%, 56%, and 26%. Grade 3-4 adverse events occurred in 45%, 86%, and 43% of patients, respectively.
There were 13 treatment-related deaths. Six deaths in the acalabrutinib arm were caused by brain neoplasm, cachexia, cerebral ischemia, malignant lung tumor, neuroendocrine carcinoma, and sepsis. Five deaths among IdR-treated patients included chronic heart failure, cardiopulmonary disease, interstitial lung disease, MI, and pseudomonal pneumonia. Two deaths in BR-treated patients were attributed to acute cardiac failure and a gastric neoplasm.
The results show that “acalabrutinib has demonstrated efficacy in previously untreated and relapsed/refractory CLL and may be considered as an option in the future treatment paradigm,” Dr. Ghia said.
Acalabrutinib monotherapy is currently being compared with ibrutinib monotherapy in patients with relapsed/refractory CLL; in addition, the phase 3 ELEVATE-TN study investigating acalabrutinib in combination with obinutuzumab (Gazyva) versus obinutuzumab plus chlorambucil has reached its primary PFS endpoint and will be reported soon, Dr. Ghia said.
The ASCEND trial is sponsored by Acerta Pharma; AstraZeneca holds majority shares in the company. Dr. Ghia reported consulting fees and honoraria from AstraZeneca and other companies, and research funding from several different companies.
SOURCE: Ghia P et al. EHA Congress, Abstract LB2606.
AMSTERDAM – For patients with relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), monotherapy with the Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor acalabrutinib (Calquence) was associated with better progression-free survival and a more tolerable safety profile than rituximab combined with either idelalisib (Zydelig) or bendamustine, an interim analysis from the phase 3 ASCEND trial showed.
Among 310 patients with previously treated CLL followed for a median of 16.1 months, the primary endpoint of median progression-free survival (PFS), as assessed by independent reviewers, had not been reached for patients treated with acalabrutinib, compared with 16.5 months for patients treated with idelalisib and rituximab (IdR) or bendamustine and rituximab (BR), reported Paolo Ghia, MD, PhD, from Università Vita-Salute San Raffaele in Milan.
“We show that acalabrutinib improved progression-free survival across all groups, including those with high-risk features,” he said at the annual congress of the European Hematology Association.
Acalabrutinib is approved in the United States for treatment of mantle cell lymphoma that has progressed on at least one prior therapy. It has been shown in preclinical studies to be more selective for BTK than the first-in-class agent ibrutinib (Imbruvica), with less off-target kinase inhibition, Dr. Ghia said.
ASCEND was designed to see whether acalabrutinib monotherapy could offer superior PFS to IdR or BR in patients with CLL who had progressed or were refractory to at least one prior line of therapy.
Patients were randomly assigned, with 155 patients in each arm, to either acalabrutinib 100 mg orally twice daily or the investigator’s choice of either idelalisib 150 mg orally twice daily plus IV rituximab at an initial dose of 375 mg/m2, followed by up to seven doses at 500 mg/m2 delivered every 2 weeks for four infusions, then every 4 weeks for the remaining three infusions or IV bendamustine 70 mg/m2 on days 1 and 2 of each cycle, plus rituximab at the 375 mg/m2 dose on day 1 for the first cycle, followed by 500 mg/m2 for up to six total cycles.
Dr. Ghia presented results of an interim analysis planned for when two-thirds of the predicted PFS events (approximately 79) had occurred.
The baseline patient characteristics were generally similar, with a median age of 68 years in the acalabrutinib arm and 67 years in the comparison arm. Almost half of all patients in each arm had bulky disease, defined as 5 cm or greater. The majority of patients had two or more prior lines of therapy.
The primary endpoint of PFS as assessed by independent review favored acalabrutinib, with a hazard ratio of 0.31 (P less than .0001). Results were similar when acalabrutinib was compared with each of the regimens in the comparison arm (HR, 0.29 vs. IdR, 0.36 vs. BR; P less than .001 for each comparison).
Acalabrutinib was also superior in patients with high-risk cytogenetic features, compared with the other two regimens combined (HR, 0.27; P less than .001).
The benefit of the BTK inhibitor was consistent across all subgroups, including age, sex, performance status, Rai stage at screening, bulky/nonbulky disease, number of prior therapies, presence or absence of deletion 17p or TP53 mutation, mutated or unmutated immunoglobulin heavy chain, and complex/noncomplex karyotype.
Reviewer-assessed objective response rates were similar, occurring in 81% of patients on acalabrutinib and 76% of patients on other regimens.
There were no complete responses in the acalabrutinib arm, compared with two complete responses in the comparison arm. The majority of responses in each arm were partial responses (81% and 74%, respectively).
The median duration of response was not reached with acalabrutinib, compared with 13.6 months with the other therapies (HR, 0.33; P less than .0001).
In all, 85% of patients on acalabrutinib had a response lasting at least 12 months, compared with 60% of patients on the other regimens. There was no difference in overall survival at the 16.1-month median follow-up.
Adverse events of any grade occurred in 94% of patients on acalabrutinib, 99% on IdR, and 80% on BR; the respective incidences of serious adverse events were 29%, 56%, and 26%. Grade 3-4 adverse events occurred in 45%, 86%, and 43% of patients, respectively.
There were 13 treatment-related deaths. Six deaths in the acalabrutinib arm were caused by brain neoplasm, cachexia, cerebral ischemia, malignant lung tumor, neuroendocrine carcinoma, and sepsis. Five deaths among IdR-treated patients included chronic heart failure, cardiopulmonary disease, interstitial lung disease, MI, and pseudomonal pneumonia. Two deaths in BR-treated patients were attributed to acute cardiac failure and a gastric neoplasm.
The results show that “acalabrutinib has demonstrated efficacy in previously untreated and relapsed/refractory CLL and may be considered as an option in the future treatment paradigm,” Dr. Ghia said.
Acalabrutinib monotherapy is currently being compared with ibrutinib monotherapy in patients with relapsed/refractory CLL; in addition, the phase 3 ELEVATE-TN study investigating acalabrutinib in combination with obinutuzumab (Gazyva) versus obinutuzumab plus chlorambucil has reached its primary PFS endpoint and will be reported soon, Dr. Ghia said.
The ASCEND trial is sponsored by Acerta Pharma; AstraZeneca holds majority shares in the company. Dr. Ghia reported consulting fees and honoraria from AstraZeneca and other companies, and research funding from several different companies.
SOURCE: Ghia P et al. EHA Congress, Abstract LB2606.
AMSTERDAM – For patients with relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), monotherapy with the Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor acalabrutinib (Calquence) was associated with better progression-free survival and a more tolerable safety profile than rituximab combined with either idelalisib (Zydelig) or bendamustine, an interim analysis from the phase 3 ASCEND trial showed.
Among 310 patients with previously treated CLL followed for a median of 16.1 months, the primary endpoint of median progression-free survival (PFS), as assessed by independent reviewers, had not been reached for patients treated with acalabrutinib, compared with 16.5 months for patients treated with idelalisib and rituximab (IdR) or bendamustine and rituximab (BR), reported Paolo Ghia, MD, PhD, from Università Vita-Salute San Raffaele in Milan.
“We show that acalabrutinib improved progression-free survival across all groups, including those with high-risk features,” he said at the annual congress of the European Hematology Association.
Acalabrutinib is approved in the United States for treatment of mantle cell lymphoma that has progressed on at least one prior therapy. It has been shown in preclinical studies to be more selective for BTK than the first-in-class agent ibrutinib (Imbruvica), with less off-target kinase inhibition, Dr. Ghia said.
ASCEND was designed to see whether acalabrutinib monotherapy could offer superior PFS to IdR or BR in patients with CLL who had progressed or were refractory to at least one prior line of therapy.
Patients were randomly assigned, with 155 patients in each arm, to either acalabrutinib 100 mg orally twice daily or the investigator’s choice of either idelalisib 150 mg orally twice daily plus IV rituximab at an initial dose of 375 mg/m2, followed by up to seven doses at 500 mg/m2 delivered every 2 weeks for four infusions, then every 4 weeks for the remaining three infusions or IV bendamustine 70 mg/m2 on days 1 and 2 of each cycle, plus rituximab at the 375 mg/m2 dose on day 1 for the first cycle, followed by 500 mg/m2 for up to six total cycles.
Dr. Ghia presented results of an interim analysis planned for when two-thirds of the predicted PFS events (approximately 79) had occurred.
The baseline patient characteristics were generally similar, with a median age of 68 years in the acalabrutinib arm and 67 years in the comparison arm. Almost half of all patients in each arm had bulky disease, defined as 5 cm or greater. The majority of patients had two or more prior lines of therapy.
The primary endpoint of PFS as assessed by independent review favored acalabrutinib, with a hazard ratio of 0.31 (P less than .0001). Results were similar when acalabrutinib was compared with each of the regimens in the comparison arm (HR, 0.29 vs. IdR, 0.36 vs. BR; P less than .001 for each comparison).
Acalabrutinib was also superior in patients with high-risk cytogenetic features, compared with the other two regimens combined (HR, 0.27; P less than .001).
The benefit of the BTK inhibitor was consistent across all subgroups, including age, sex, performance status, Rai stage at screening, bulky/nonbulky disease, number of prior therapies, presence or absence of deletion 17p or TP53 mutation, mutated or unmutated immunoglobulin heavy chain, and complex/noncomplex karyotype.
Reviewer-assessed objective response rates were similar, occurring in 81% of patients on acalabrutinib and 76% of patients on other regimens.
There were no complete responses in the acalabrutinib arm, compared with two complete responses in the comparison arm. The majority of responses in each arm were partial responses (81% and 74%, respectively).
The median duration of response was not reached with acalabrutinib, compared with 13.6 months with the other therapies (HR, 0.33; P less than .0001).
In all, 85% of patients on acalabrutinib had a response lasting at least 12 months, compared with 60% of patients on the other regimens. There was no difference in overall survival at the 16.1-month median follow-up.
Adverse events of any grade occurred in 94% of patients on acalabrutinib, 99% on IdR, and 80% on BR; the respective incidences of serious adverse events were 29%, 56%, and 26%. Grade 3-4 adverse events occurred in 45%, 86%, and 43% of patients, respectively.
There were 13 treatment-related deaths. Six deaths in the acalabrutinib arm were caused by brain neoplasm, cachexia, cerebral ischemia, malignant lung tumor, neuroendocrine carcinoma, and sepsis. Five deaths among IdR-treated patients included chronic heart failure, cardiopulmonary disease, interstitial lung disease, MI, and pseudomonal pneumonia. Two deaths in BR-treated patients were attributed to acute cardiac failure and a gastric neoplasm.
The results show that “acalabrutinib has demonstrated efficacy in previously untreated and relapsed/refractory CLL and may be considered as an option in the future treatment paradigm,” Dr. Ghia said.
Acalabrutinib monotherapy is currently being compared with ibrutinib monotherapy in patients with relapsed/refractory CLL; in addition, the phase 3 ELEVATE-TN study investigating acalabrutinib in combination with obinutuzumab (Gazyva) versus obinutuzumab plus chlorambucil has reached its primary PFS endpoint and will be reported soon, Dr. Ghia said.
The ASCEND trial is sponsored by Acerta Pharma; AstraZeneca holds majority shares in the company. Dr. Ghia reported consulting fees and honoraria from AstraZeneca and other companies, and research funding from several different companies.
SOURCE: Ghia P et al. EHA Congress, Abstract LB2606.
REPORTING FROM EHA CONGRESS
Ibrutinib tops chlorambucil against CLL
AMSTERDAM – After 5 years, a large majority of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia treated with front-line ibrutinib (Imbruvica) have not experienced disease progression, and the median progression-free survival has still not been reached, long-term follow-up from the RESONATE-2 shows.
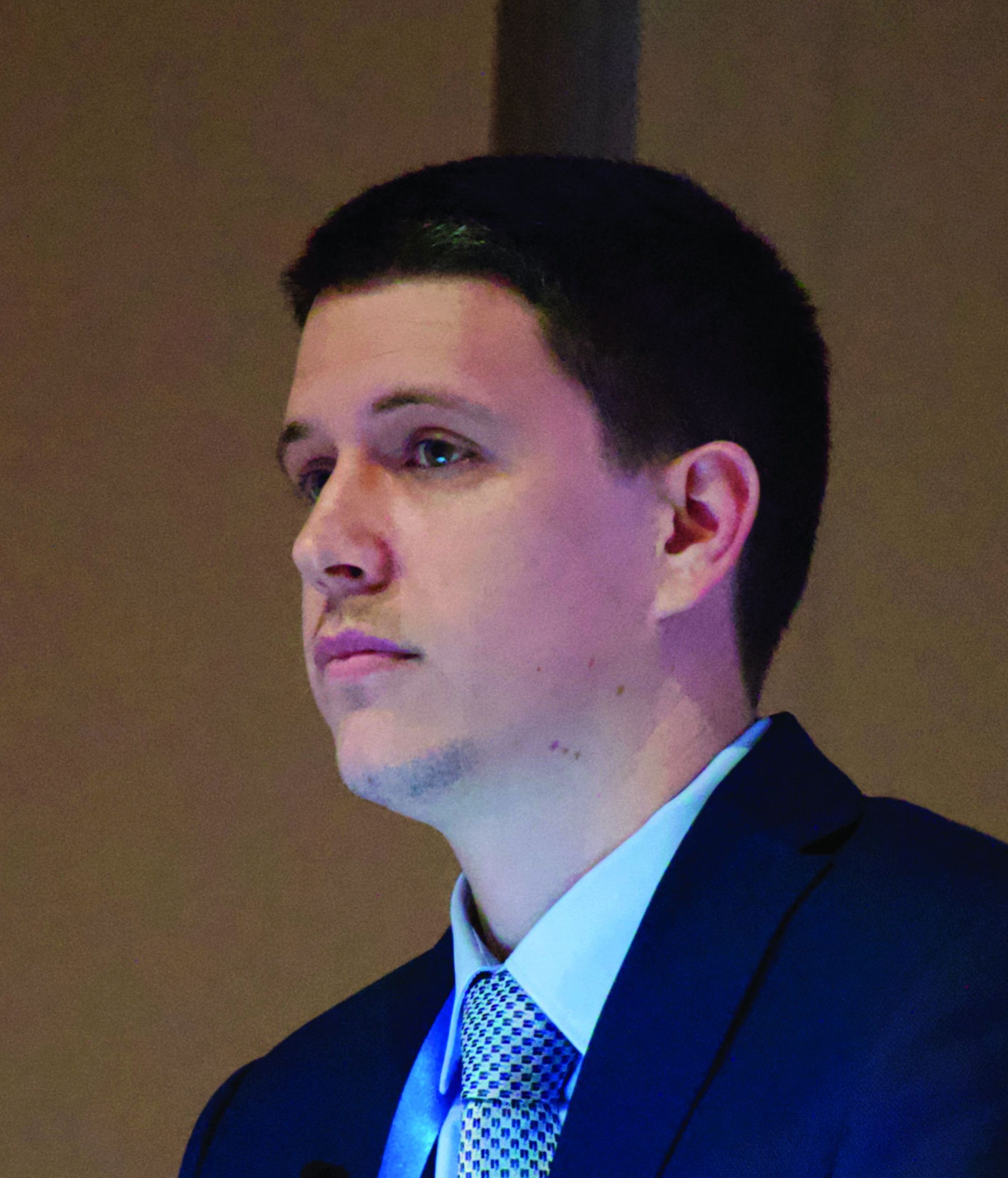
The 5-year estimated progression-free survival (PFS) rates were 70% for patients who had been randomized to receive ibrutinib monotherapy, compared with 12% for patients randomized to chlorambucil, reported Alessandra Tedeschi, MD, from Azienda Ospedaliera Niguarda Ca’ Granda in Milan.
Ibrutinib was also associated with a halving of risk for death, compared with chlorambucil, she said at the annual congress of the European Hematology Association.
“Importantly, the rate of progression during ibrutinib treatment was very low; only 8 – that is, 6% of patients” – experienced disease progression while receiving ibrutinib, she noted.
In the RESONATE-2 (PCYC-1115) trial, investigators enrolled 269 adults aged 65 years and older with previously untreated CLL/small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL). Patients at the younger end of the age range (65-69 years) had to have comorbidities that would have made them ineligible for the FCR chemotherapy regimen (fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab). Additionally, patients with the deleterious 17p deletion were excluded.
Patients were stratified by performance status and Rai stage and then randomized to receive either ibrutinib 420 mg once daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity (136 patients) or chlorambucil 0.5 mg/kg to a maximum of 0.8 mg/kg for up to 12 cycles (133 patients). The trial also had an extension study for patients who had disease progression as confirmed by an independent review committee or who had completed the RESONATE-2 trial. Of the 133 patients in the chlorambucil arm, 76 (57% of the intention-to-treat population) were crossed over to ibrutinib following disease progression.
The median duration of ibrutinib treatment was 57.1 months, with 73% of patients being on it for more than 3 years, 65% for more than 4 years, and 27% for more than 5 years. As of the data cutoff, 79 patients (58%) were continuing with ibrutinib on study.
At 5 years, 70% of ibrutinib-treated patients and 12% of chlorambucil-treated patients were estimated to be progression-free and alive (hazard ratio for PFS with ibrutinib 0.146 (95% confidence interval, 0.10-0.22). The benefit of ibrutinib was consistent for patients with high-risk genomic features, including the 11q deletion and unmutated immunoglobulin heavy-chain variable genes.
Estimated 5-year overall survival was also better with ibrutinib, at 83% vs. 68% (hazard ratio, 0.45; 95% CI, 0.266-0.761).
The most common grade 3 or greater adverse events occurring with ibrutinib were neutropenia (13%), pneumonia (12%), hypertension (8%), anemia (7%), hyponatremia (6%), atrial fibrillation (5%), and cataract (5%). The rates of most adverse events decreased over time, and dose reductions because of adverse events also diminished over time, from 5% of patients in the first year down to zero in years 4 through 5.
Patients responded to subsequent CLL therapies following ibrutinib discontinuation, including chemoimmunotherapy and other kinase inhibitors, Dr. Tedeschi said.
The trial was sponsored by Pharmacyclics with collaboration from Janssen Research & Development. Dr. Tedeschi reported advisory board activities with Janssen, AbbVie, and BeiGene.
SOURCE: Tedeschi A et al. EHA Congress, Abstract S107.
AMSTERDAM – After 5 years, a large majority of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia treated with front-line ibrutinib (Imbruvica) have not experienced disease progression, and the median progression-free survival has still not been reached, long-term follow-up from the RESONATE-2 shows.
The 5-year estimated progression-free survival (PFS) rates were 70% for patients who had been randomized to receive ibrutinib monotherapy, compared with 12% for patients randomized to chlorambucil, reported Alessandra Tedeschi, MD, from Azienda Ospedaliera Niguarda Ca’ Granda in Milan.
Ibrutinib was also associated with a halving of risk for death, compared with chlorambucil, she said at the annual congress of the European Hematology Association.
“Importantly, the rate of progression during ibrutinib treatment was very low; only 8 – that is, 6% of patients” – experienced disease progression while receiving ibrutinib, she noted.
In the RESONATE-2 (PCYC-1115) trial, investigators enrolled 269 adults aged 65 years and older with previously untreated CLL/small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL). Patients at the younger end of the age range (65-69 years) had to have comorbidities that would have made them ineligible for the FCR chemotherapy regimen (fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab). Additionally, patients with the deleterious 17p deletion were excluded.
Patients were stratified by performance status and Rai stage and then randomized to receive either ibrutinib 420 mg once daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity (136 patients) or chlorambucil 0.5 mg/kg to a maximum of 0.8 mg/kg for up to 12 cycles (133 patients). The trial also had an extension study for patients who had disease progression as confirmed by an independent review committee or who had completed the RESONATE-2 trial. Of the 133 patients in the chlorambucil arm, 76 (57% of the intention-to-treat population) were crossed over to ibrutinib following disease progression.
The median duration of ibrutinib treatment was 57.1 months, with 73% of patients being on it for more than 3 years, 65% for more than 4 years, and 27% for more than 5 years. As of the data cutoff, 79 patients (58%) were continuing with ibrutinib on study.
At 5 years, 70% of ibrutinib-treated patients and 12% of chlorambucil-treated patients were estimated to be progression-free and alive (hazard ratio for PFS with ibrutinib 0.146 (95% confidence interval, 0.10-0.22). The benefit of ibrutinib was consistent for patients with high-risk genomic features, including the 11q deletion and unmutated immunoglobulin heavy-chain variable genes.
Estimated 5-year overall survival was also better with ibrutinib, at 83% vs. 68% (hazard ratio, 0.45; 95% CI, 0.266-0.761).
The most common grade 3 or greater adverse events occurring with ibrutinib were neutropenia (13%), pneumonia (12%), hypertension (8%), anemia (7%), hyponatremia (6%), atrial fibrillation (5%), and cataract (5%). The rates of most adverse events decreased over time, and dose reductions because of adverse events also diminished over time, from 5% of patients in the first year down to zero in years 4 through 5.
Patients responded to subsequent CLL therapies following ibrutinib discontinuation, including chemoimmunotherapy and other kinase inhibitors, Dr. Tedeschi said.
The trial was sponsored by Pharmacyclics with collaboration from Janssen Research & Development. Dr. Tedeschi reported advisory board activities with Janssen, AbbVie, and BeiGene.
SOURCE: Tedeschi A et al. EHA Congress, Abstract S107.
AMSTERDAM – After 5 years, a large majority of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia treated with front-line ibrutinib (Imbruvica) have not experienced disease progression, and the median progression-free survival has still not been reached, long-term follow-up from the RESONATE-2 shows.
The 5-year estimated progression-free survival (PFS) rates were 70% for patients who had been randomized to receive ibrutinib monotherapy, compared with 12% for patients randomized to chlorambucil, reported Alessandra Tedeschi, MD, from Azienda Ospedaliera Niguarda Ca’ Granda in Milan.
Ibrutinib was also associated with a halving of risk for death, compared with chlorambucil, she said at the annual congress of the European Hematology Association.
“Importantly, the rate of progression during ibrutinib treatment was very low; only 8 – that is, 6% of patients” – experienced disease progression while receiving ibrutinib, she noted.
In the RESONATE-2 (PCYC-1115) trial, investigators enrolled 269 adults aged 65 years and older with previously untreated CLL/small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL). Patients at the younger end of the age range (65-69 years) had to have comorbidities that would have made them ineligible for the FCR chemotherapy regimen (fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab). Additionally, patients with the deleterious 17p deletion were excluded.
Patients were stratified by performance status and Rai stage and then randomized to receive either ibrutinib 420 mg once daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity (136 patients) or chlorambucil 0.5 mg/kg to a maximum of 0.8 mg/kg for up to 12 cycles (133 patients). The trial also had an extension study for patients who had disease progression as confirmed by an independent review committee or who had completed the RESONATE-2 trial. Of the 133 patients in the chlorambucil arm, 76 (57% of the intention-to-treat population) were crossed over to ibrutinib following disease progression.
The median duration of ibrutinib treatment was 57.1 months, with 73% of patients being on it for more than 3 years, 65% for more than 4 years, and 27% for more than 5 years. As of the data cutoff, 79 patients (58%) were continuing with ibrutinib on study.
At 5 years, 70% of ibrutinib-treated patients and 12% of chlorambucil-treated patients were estimated to be progression-free and alive (hazard ratio for PFS with ibrutinib 0.146 (95% confidence interval, 0.10-0.22). The benefit of ibrutinib was consistent for patients with high-risk genomic features, including the 11q deletion and unmutated immunoglobulin heavy-chain variable genes.
Estimated 5-year overall survival was also better with ibrutinib, at 83% vs. 68% (hazard ratio, 0.45; 95% CI, 0.266-0.761).
The most common grade 3 or greater adverse events occurring with ibrutinib were neutropenia (13%), pneumonia (12%), hypertension (8%), anemia (7%), hyponatremia (6%), atrial fibrillation (5%), and cataract (5%). The rates of most adverse events decreased over time, and dose reductions because of adverse events also diminished over time, from 5% of patients in the first year down to zero in years 4 through 5.
Patients responded to subsequent CLL therapies following ibrutinib discontinuation, including chemoimmunotherapy and other kinase inhibitors, Dr. Tedeschi said.
The trial was sponsored by Pharmacyclics with collaboration from Janssen Research & Development. Dr. Tedeschi reported advisory board activities with Janssen, AbbVie, and BeiGene.
SOURCE: Tedeschi A et al. EHA Congress, Abstract S107.
REPORTING FROM EHA CONGRESS
R2-CHOP doesn’t improve survival in DLBCL
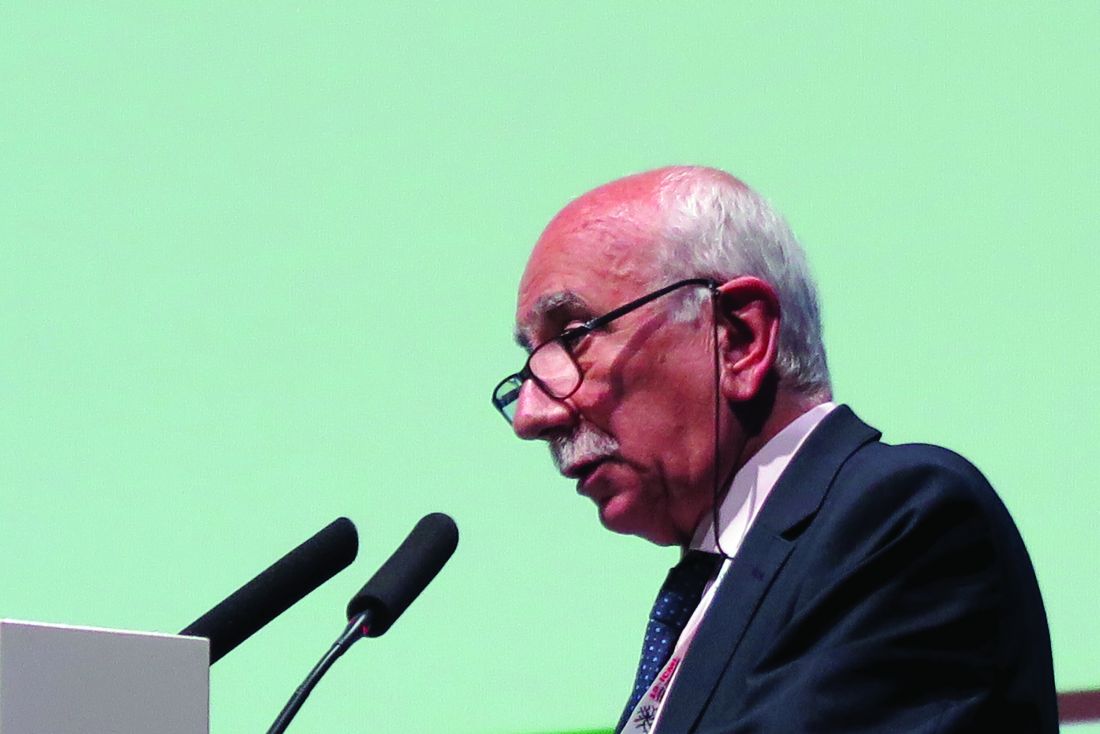
LUGANO, Switzerland – Adding the immunomodulator lenalidomide (Revlimid) to standard chemotherapy for patients with newly diagnosed ABC-type diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) – the so-called R2-CHOP regimen – did not significantly improve either progression-free or overall survival, compared with R-CHOP alone, investigators in the phase 3 ROBUST trial found.
Among 570 patients with activated B-cell (ABC) type DLBCL followed for a median of 27.1 months, median progression-free survival (PFS) – the primary endpoint – had not been reached either for patients randomized to R-CHOP (rituximab, cyclophosphamide, vincristine, doxorubicin and prednisone) plus lenalidomide (R2-CHOP) or R-CHOP plus placebo.
The 1-year and 2-year PFS rate with R2-CHOP was 77%, compared with 75% for R-CHOP, and 2-year PFS rates were 67% and 64%, respectively, and neither comparison was statistically significant reported Umberto Vitolo, MD, from the Citta della Salute e della Scienzia Hospital and University in Turin, Italy.“The future direction is that promising preclinical data with next-generation immunomodulatory agents will be evaluated in future DLBCL clinical trials,” he said at the International Conference on Malignant Lymphoma.
The ROBUST trial is the latest in a long line of studies that failed to show improvement in outcomes with the addition of a novel agent to R-CHOP.
The rationale for adding lenalidomide to R-CHOP came from in-vitro studies showing antiproliferative and immunomodulatory action of lenalidomide against DLBCL, as well as two proof-of-concept clinical studies (REAL07 and MC078E) indicating efficacy against non–germinal center–like B (GCB) type DLBCL, Dr. Vitolo said.
In the ROBUST trial, investigators across 257 global sites enrolled 570 patients with ABC-type DLBCL, stratified them by International Prognostic Index (IPI) score (2 vs. 3 or greater), bulky disease (less than 7 cm vs. 7 cm or more), and age (younger than 65 years vs. 65 years and older) and randomly assigned them to receive R-CHOP with either oral lenalidomide 15 mg or placebo daily on days 1-14 of each 21-day cycle for six cycles.
All patients were required to have neutropenia prophylaxis according to local practice, with either a granulocyte- or granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor.
The efficacy analysis was by intention-to-treat and included 285 patients in each arm.
The investigators found no significant difference in the primary endpoint of PFS. Overall response rates (ORR) and complete response (CR) rates were high in both arms. The ORR was 91% in each arm, and the CR rate was 69% for R2-CHOP and 65% for R-CHOP.
Event-free survival (EFS) – a composite of first disease progression, death, or relapse after CR or start of second-line therapy – also did not differ significantly between the groups. The 1-year and 2-year EFS rates were 68% vs. 71% and 59% vs. 61%, respectively. The median EFS was not reached in either arm.
Similarly, overall survival did not differ between the groups. At 48 months of follow-up, 57 patients in the R2-CHOP arm and 62 patients in the R-CHOP arm had died. Respective 1- and 2-year overall survival rates were 91% vs. 90%, and 79% vs. 80%.
In the safety analysis, which included 283 patients in the R2-CHOP arm and 284 in the placebo/R-CHOP arm, there were no new safety signals observed. In all, 78% of patients in the lenalidomide arm and 71% in the placebo arm had at least one grade 3 or greater adverse events. The most common adverse events were hematologic, including neutropenia, febrile neutropenia, anemia, thrombocytopenia, and leukopenia.
The ROBUST study was funded by Celgene. Dr. Vitolo reported consulting and speaker’s bureau fees and research funding from the company.
SOURCE: Vitolo U et al. 15-ICML, Abstract 005.
LUGANO, Switzerland – Adding the immunomodulator lenalidomide (Revlimid) to standard chemotherapy for patients with newly diagnosed ABC-type diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) – the so-called R2-CHOP regimen – did not significantly improve either progression-free or overall survival, compared with R-CHOP alone, investigators in the phase 3 ROBUST trial found.
Among 570 patients with activated B-cell (ABC) type DLBCL followed for a median of 27.1 months, median progression-free survival (PFS) – the primary endpoint – had not been reached either for patients randomized to R-CHOP (rituximab, cyclophosphamide, vincristine, doxorubicin and prednisone) plus lenalidomide (R2-CHOP) or R-CHOP plus placebo.
The 1-year and 2-year PFS rate with R2-CHOP was 77%, compared with 75% for R-CHOP, and 2-year PFS rates were 67% and 64%, respectively, and neither comparison was statistically significant reported Umberto Vitolo, MD, from the Citta della Salute e della Scienzia Hospital and University in Turin, Italy.“The future direction is that promising preclinical data with next-generation immunomodulatory agents will be evaluated in future DLBCL clinical trials,” he said at the International Conference on Malignant Lymphoma.
The ROBUST trial is the latest in a long line of studies that failed to show improvement in outcomes with the addition of a novel agent to R-CHOP.
The rationale for adding lenalidomide to R-CHOP came from in-vitro studies showing antiproliferative and immunomodulatory action of lenalidomide against DLBCL, as well as two proof-of-concept clinical studies (REAL07 and MC078E) indicating efficacy against non–germinal center–like B (GCB) type DLBCL, Dr. Vitolo said.
In the ROBUST trial, investigators across 257 global sites enrolled 570 patients with ABC-type DLBCL, stratified them by International Prognostic Index (IPI) score (2 vs. 3 or greater), bulky disease (less than 7 cm vs. 7 cm or more), and age (younger than 65 years vs. 65 years and older) and randomly assigned them to receive R-CHOP with either oral lenalidomide 15 mg or placebo daily on days 1-14 of each 21-day cycle for six cycles.
All patients were required to have neutropenia prophylaxis according to local practice, with either a granulocyte- or granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor.
The efficacy analysis was by intention-to-treat and included 285 patients in each arm.
The investigators found no significant difference in the primary endpoint of PFS. Overall response rates (ORR) and complete response (CR) rates were high in both arms. The ORR was 91% in each arm, and the CR rate was 69% for R2-CHOP and 65% for R-CHOP.
Event-free survival (EFS) – a composite of first disease progression, death, or relapse after CR or start of second-line therapy – also did not differ significantly between the groups. The 1-year and 2-year EFS rates were 68% vs. 71% and 59% vs. 61%, respectively. The median EFS was not reached in either arm.
Similarly, overall survival did not differ between the groups. At 48 months of follow-up, 57 patients in the R2-CHOP arm and 62 patients in the R-CHOP arm had died. Respective 1- and 2-year overall survival rates were 91% vs. 90%, and 79% vs. 80%.
In the safety analysis, which included 283 patients in the R2-CHOP arm and 284 in the placebo/R-CHOP arm, there were no new safety signals observed. In all, 78% of patients in the lenalidomide arm and 71% in the placebo arm had at least one grade 3 or greater adverse events. The most common adverse events were hematologic, including neutropenia, febrile neutropenia, anemia, thrombocytopenia, and leukopenia.
The ROBUST study was funded by Celgene. Dr. Vitolo reported consulting and speaker’s bureau fees and research funding from the company.
SOURCE: Vitolo U et al. 15-ICML, Abstract 005.
LUGANO, Switzerland – Adding the immunomodulator lenalidomide (Revlimid) to standard chemotherapy for patients with newly diagnosed ABC-type diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) – the so-called R2-CHOP regimen – did not significantly improve either progression-free or overall survival, compared with R-CHOP alone, investigators in the phase 3 ROBUST trial found.
Among 570 patients with activated B-cell (ABC) type DLBCL followed for a median of 27.1 months, median progression-free survival (PFS) – the primary endpoint – had not been reached either for patients randomized to R-CHOP (rituximab, cyclophosphamide, vincristine, doxorubicin and prednisone) plus lenalidomide (R2-CHOP) or R-CHOP plus placebo.
The 1-year and 2-year PFS rate with R2-CHOP was 77%, compared with 75% for R-CHOP, and 2-year PFS rates were 67% and 64%, respectively, and neither comparison was statistically significant reported Umberto Vitolo, MD, from the Citta della Salute e della Scienzia Hospital and University in Turin, Italy.“The future direction is that promising preclinical data with next-generation immunomodulatory agents will be evaluated in future DLBCL clinical trials,” he said at the International Conference on Malignant Lymphoma.
The ROBUST trial is the latest in a long line of studies that failed to show improvement in outcomes with the addition of a novel agent to R-CHOP.
The rationale for adding lenalidomide to R-CHOP came from in-vitro studies showing antiproliferative and immunomodulatory action of lenalidomide against DLBCL, as well as two proof-of-concept clinical studies (REAL07 and MC078E) indicating efficacy against non–germinal center–like B (GCB) type DLBCL, Dr. Vitolo said.
In the ROBUST trial, investigators across 257 global sites enrolled 570 patients with ABC-type DLBCL, stratified them by International Prognostic Index (IPI) score (2 vs. 3 or greater), bulky disease (less than 7 cm vs. 7 cm or more), and age (younger than 65 years vs. 65 years and older) and randomly assigned them to receive R-CHOP with either oral lenalidomide 15 mg or placebo daily on days 1-14 of each 21-day cycle for six cycles.
All patients were required to have neutropenia prophylaxis according to local practice, with either a granulocyte- or granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor.
The efficacy analysis was by intention-to-treat and included 285 patients in each arm.
The investigators found no significant difference in the primary endpoint of PFS. Overall response rates (ORR) and complete response (CR) rates were high in both arms. The ORR was 91% in each arm, and the CR rate was 69% for R2-CHOP and 65% for R-CHOP.
Event-free survival (EFS) – a composite of first disease progression, death, or relapse after CR or start of second-line therapy – also did not differ significantly between the groups. The 1-year and 2-year EFS rates were 68% vs. 71% and 59% vs. 61%, respectively. The median EFS was not reached in either arm.
Similarly, overall survival did not differ between the groups. At 48 months of follow-up, 57 patients in the R2-CHOP arm and 62 patients in the R-CHOP arm had died. Respective 1- and 2-year overall survival rates were 91% vs. 90%, and 79% vs. 80%.
In the safety analysis, which included 283 patients in the R2-CHOP arm and 284 in the placebo/R-CHOP arm, there were no new safety signals observed. In all, 78% of patients in the lenalidomide arm and 71% in the placebo arm had at least one grade 3 or greater adverse events. The most common adverse events were hematologic, including neutropenia, febrile neutropenia, anemia, thrombocytopenia, and leukopenia.
The ROBUST study was funded by Celgene. Dr. Vitolo reported consulting and speaker’s bureau fees and research funding from the company.
SOURCE: Vitolo U et al. 15-ICML, Abstract 005.
REPORTING FROM 15-ICML
CNS-directed therapy appears more effective for synDLBCL
Controlling CNS disease is “paramount” in treating diffuse large B-cell lymphoma with synchronous CNS and systemic disease (synDLBCL), according to researchers.
In a retrospective study, the CNS was the most common site of relapse in patients with synDLBCL, and patients had better outcomes when they received CNS-directed therapy.
The 2-year progression-free survival rate was 50% in patients who received CNS-intensive therapy and 31% in those who received CNS-conservative therapy. The 2-year overall survival rate was 54% and 44%, respectively.
Dr. Joel C. Wight, of Austin Health in Heidelberg, Australia, and colleagues conducted this study and recounted their findings in the British Journal of Haematology.
The researchers retrospectively analyzed 80 patients with synDLBCL treated at 10 centers in Australia and the United Kingdom. Patients had DLBCL not otherwise specified (n = 67); high-grade B-cell lymphoma, including double-hit lymphoma (n = 12); or T-cell histiocyte-rich DLBCL (n = 1).
At baseline, all patients were treatment-naive, they had a median age of 64 years (range, 18-87 years), and 68% were male. Seventy percent of patients had high-risk disease according to the CNS International Prognostic Index (IPI), and 96% had non-CNS extranodal disease. The median number of extranodal sites outside the CNS was 2 (range, 0 to more than 10).
Patients were divided into those who received CNS-intensive therapy (n = 38) and those given CNS-conservative therapy (n = 42). The CNS-conservative group was significantly older (P less than .001), significantly more likely to have high-risk disease according to the National Comprehensive Cancer Network IPI (P = .009) or CNS IPI (P = .01) and significantly more likely to have leptomeningeal disease only (P less than .001).
Treatment
CNS-intensive therapy was defined as any established multiagent IV chemotherapy regimen with two or more CNS-penetrating drugs and cytarabine, with or without intrathecal chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy.
CNS-conservative therapy was defined as one or fewer IV CNS-penetrating chemotherapy agents in induction, with or without intrathecal chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy.
Systemic induction in the CNS-intensive group consisted of R-HyperCVAD (rituximab, hyperfractionated cyclophosphamide, vincristine, doxorubicin, and dexamethasone alternating with IV methotrexate and cytarabine) in 66% of patients and R-CODOX-M/IVAC (rituximab, hyperfractionated cyclophosphamide, vincristine, doxorubicin, methotrexate/ifosfamide, etoposide, cytarabine) in 24% of patients.
The most common systemic induction regimens in the CNS-conservative group were R-CHOP (rituximab plus cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisolone) or CHOP-like regimens, given to 83% of patients.
CNS-directed IV therapy was given to 100% of the CNS-intensive group and 60% of the CNS-conservative group. This consisted of IV methotrexate plus cytarabine (97%) or MATRix (methotrexate, cytarabine, and thiotepa; 3%) in the CNS-intensive group and high-dose methotrexate in the conservative group.
Intrathecal chemotherapy was given to 97% of the CNS-intensive group and 60% of the CNS-conservative group. CNS-directed radiation was given to 32% and 19%, respectively.
Thirteen patients in the CNS-intensive group and one in the CNS-conservative group underwent autologous transplant as consolidation.
Outcomes
Dose reductions were more frequent in the CNS-conservative group than in the CNS-intensive group, at 48% and 18% (P = .009), as was early cessation of chemotherapy, at 52% and 18% (P = .002). Rates of treatment-related mortality were similar, at 13% in the CNS-intensive group and 12% in the CNS-conservative group.
At the end of induction, the complete response rate was 69% in the CNS-intensive group and 51% in the CNS-conservative group (P = .16). Primary refractory disease was observed in 19% and 38% of patients, respectively (P = .07).
The CNS was the most common site of relapse or progression (n = 28). CNS progression or relapse occurred in 25% of the CNS-intensive group and 49% of the CNS-conservative group (P = .03).
The 2-year progression-free survival rate was 50% for the CNS-intensive group and 31% for the CNS-conservative group (P = .006). The 2-year overall survival rate was 54% and 44%, respectively (P = .037).
When patients were matched for induction outcomes, consolidative transplant did not improve survival.
“The most significant factor affecting survival was the ability to control the CNS disease, which was improved by the addition of IV cytarabine to [high-dose methotrexate],” the researchers wrote.
“Whilst the younger age and more intensive systemic treatment of the CNS-intensive group may have contributed to the improved survival, it is clear that CNS disease control was substantially improved by the addition of cytarabine with lower rates of CNS relapse/progression observed.”
The researchers noted that “adequate control of the CNS disease is paramount and is best achieved by intensive CNS-directed induction.”
There was no formal funding for this study, and the researchers did not provide financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Wight JC et al. Br J Haematol. 2019 Jun 24. doi: 10.1111/bjh.16064.
Controlling CNS disease is “paramount” in treating diffuse large B-cell lymphoma with synchronous CNS and systemic disease (synDLBCL), according to researchers.
In a retrospective study, the CNS was the most common site of relapse in patients with synDLBCL, and patients had better outcomes when they received CNS-directed therapy.
The 2-year progression-free survival rate was 50% in patients who received CNS-intensive therapy and 31% in those who received CNS-conservative therapy. The 2-year overall survival rate was 54% and 44%, respectively.
Dr. Joel C. Wight, of Austin Health in Heidelberg, Australia, and colleagues conducted this study and recounted their findings in the British Journal of Haematology.
The researchers retrospectively analyzed 80 patients with synDLBCL treated at 10 centers in Australia and the United Kingdom. Patients had DLBCL not otherwise specified (n = 67); high-grade B-cell lymphoma, including double-hit lymphoma (n = 12); or T-cell histiocyte-rich DLBCL (n = 1).
At baseline, all patients were treatment-naive, they had a median age of 64 years (range, 18-87 years), and 68% were male. Seventy percent of patients had high-risk disease according to the CNS International Prognostic Index (IPI), and 96% had non-CNS extranodal disease. The median number of extranodal sites outside the CNS was 2 (range, 0 to more than 10).
Patients were divided into those who received CNS-intensive therapy (n = 38) and those given CNS-conservative therapy (n = 42). The CNS-conservative group was significantly older (P less than .001), significantly more likely to have high-risk disease according to the National Comprehensive Cancer Network IPI (P = .009) or CNS IPI (P = .01) and significantly more likely to have leptomeningeal disease only (P less than .001).
Treatment
CNS-intensive therapy was defined as any established multiagent IV chemotherapy regimen with two or more CNS-penetrating drugs and cytarabine, with or without intrathecal chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy.
CNS-conservative therapy was defined as one or fewer IV CNS-penetrating chemotherapy agents in induction, with or without intrathecal chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy.
Systemic induction in the CNS-intensive group consisted of R-HyperCVAD (rituximab, hyperfractionated cyclophosphamide, vincristine, doxorubicin, and dexamethasone alternating with IV methotrexate and cytarabine) in 66% of patients and R-CODOX-M/IVAC (rituximab, hyperfractionated cyclophosphamide, vincristine, doxorubicin, methotrexate/ifosfamide, etoposide, cytarabine) in 24% of patients.
The most common systemic induction regimens in the CNS-conservative group were R-CHOP (rituximab plus cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisolone) or CHOP-like regimens, given to 83% of patients.
CNS-directed IV therapy was given to 100% of the CNS-intensive group and 60% of the CNS-conservative group. This consisted of IV methotrexate plus cytarabine (97%) or MATRix (methotrexate, cytarabine, and thiotepa; 3%) in the CNS-intensive group and high-dose methotrexate in the conservative group.
Intrathecal chemotherapy was given to 97% of the CNS-intensive group and 60% of the CNS-conservative group. CNS-directed radiation was given to 32% and 19%, respectively.
Thirteen patients in the CNS-intensive group and one in the CNS-conservative group underwent autologous transplant as consolidation.
Outcomes
Dose reductions were more frequent in the CNS-conservative group than in the CNS-intensive group, at 48% and 18% (P = .009), as was early cessation of chemotherapy, at 52% and 18% (P = .002). Rates of treatment-related mortality were similar, at 13% in the CNS-intensive group and 12% in the CNS-conservative group.
At the end of induction, the complete response rate was 69% in the CNS-intensive group and 51% in the CNS-conservative group (P = .16). Primary refractory disease was observed in 19% and 38% of patients, respectively (P = .07).
The CNS was the most common site of relapse or progression (n = 28). CNS progression or relapse occurred in 25% of the CNS-intensive group and 49% of the CNS-conservative group (P = .03).
The 2-year progression-free survival rate was 50% for the CNS-intensive group and 31% for the CNS-conservative group (P = .006). The 2-year overall survival rate was 54% and 44%, respectively (P = .037).
When patients were matched for induction outcomes, consolidative transplant did not improve survival.
“The most significant factor affecting survival was the ability to control the CNS disease, which was improved by the addition of IV cytarabine to [high-dose methotrexate],” the researchers wrote.
“Whilst the younger age and more intensive systemic treatment of the CNS-intensive group may have contributed to the improved survival, it is clear that CNS disease control was substantially improved by the addition of cytarabine with lower rates of CNS relapse/progression observed.”
The researchers noted that “adequate control of the CNS disease is paramount and is best achieved by intensive CNS-directed induction.”
There was no formal funding for this study, and the researchers did not provide financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Wight JC et al. Br J Haematol. 2019 Jun 24. doi: 10.1111/bjh.16064.
Controlling CNS disease is “paramount” in treating diffuse large B-cell lymphoma with synchronous CNS and systemic disease (synDLBCL), according to researchers.
In a retrospective study, the CNS was the most common site of relapse in patients with synDLBCL, and patients had better outcomes when they received CNS-directed therapy.
The 2-year progression-free survival rate was 50% in patients who received CNS-intensive therapy and 31% in those who received CNS-conservative therapy. The 2-year overall survival rate was 54% and 44%, respectively.
Dr. Joel C. Wight, of Austin Health in Heidelberg, Australia, and colleagues conducted this study and recounted their findings in the British Journal of Haematology.
The researchers retrospectively analyzed 80 patients with synDLBCL treated at 10 centers in Australia and the United Kingdom. Patients had DLBCL not otherwise specified (n = 67); high-grade B-cell lymphoma, including double-hit lymphoma (n = 12); or T-cell histiocyte-rich DLBCL (n = 1).
At baseline, all patients were treatment-naive, they had a median age of 64 years (range, 18-87 years), and 68% were male. Seventy percent of patients had high-risk disease according to the CNS International Prognostic Index (IPI), and 96% had non-CNS extranodal disease. The median number of extranodal sites outside the CNS was 2 (range, 0 to more than 10).
Patients were divided into those who received CNS-intensive therapy (n = 38) and those given CNS-conservative therapy (n = 42). The CNS-conservative group was significantly older (P less than .001), significantly more likely to have high-risk disease according to the National Comprehensive Cancer Network IPI (P = .009) or CNS IPI (P = .01) and significantly more likely to have leptomeningeal disease only (P less than .001).
Treatment
CNS-intensive therapy was defined as any established multiagent IV chemotherapy regimen with two or more CNS-penetrating drugs and cytarabine, with or without intrathecal chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy.
CNS-conservative therapy was defined as one or fewer IV CNS-penetrating chemotherapy agents in induction, with or without intrathecal chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy.
Systemic induction in the CNS-intensive group consisted of R-HyperCVAD (rituximab, hyperfractionated cyclophosphamide, vincristine, doxorubicin, and dexamethasone alternating with IV methotrexate and cytarabine) in 66% of patients and R-CODOX-M/IVAC (rituximab, hyperfractionated cyclophosphamide, vincristine, doxorubicin, methotrexate/ifosfamide, etoposide, cytarabine) in 24% of patients.
The most common systemic induction regimens in the CNS-conservative group were R-CHOP (rituximab plus cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisolone) or CHOP-like regimens, given to 83% of patients.
CNS-directed IV therapy was given to 100% of the CNS-intensive group and 60% of the CNS-conservative group. This consisted of IV methotrexate plus cytarabine (97%) or MATRix (methotrexate, cytarabine, and thiotepa; 3%) in the CNS-intensive group and high-dose methotrexate in the conservative group.
Intrathecal chemotherapy was given to 97% of the CNS-intensive group and 60% of the CNS-conservative group. CNS-directed radiation was given to 32% and 19%, respectively.
Thirteen patients in the CNS-intensive group and one in the CNS-conservative group underwent autologous transplant as consolidation.
Outcomes
Dose reductions were more frequent in the CNS-conservative group than in the CNS-intensive group, at 48% and 18% (P = .009), as was early cessation of chemotherapy, at 52% and 18% (P = .002). Rates of treatment-related mortality were similar, at 13% in the CNS-intensive group and 12% in the CNS-conservative group.
At the end of induction, the complete response rate was 69% in the CNS-intensive group and 51% in the CNS-conservative group (P = .16). Primary refractory disease was observed in 19% and 38% of patients, respectively (P = .07).
The CNS was the most common site of relapse or progression (n = 28). CNS progression or relapse occurred in 25% of the CNS-intensive group and 49% of the CNS-conservative group (P = .03).
The 2-year progression-free survival rate was 50% for the CNS-intensive group and 31% for the CNS-conservative group (P = .006). The 2-year overall survival rate was 54% and 44%, respectively (P = .037).
When patients were matched for induction outcomes, consolidative transplant did not improve survival.
“The most significant factor affecting survival was the ability to control the CNS disease, which was improved by the addition of IV cytarabine to [high-dose methotrexate],” the researchers wrote.
“Whilst the younger age and more intensive systemic treatment of the CNS-intensive group may have contributed to the improved survival, it is clear that CNS disease control was substantially improved by the addition of cytarabine with lower rates of CNS relapse/progression observed.”
The researchers noted that “adequate control of the CNS disease is paramount and is best achieved by intensive CNS-directed induction.”
There was no formal funding for this study, and the researchers did not provide financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Wight JC et al. Br J Haematol. 2019 Jun 24. doi: 10.1111/bjh.16064.
FROM BRITISH JOURNAL OF HAEMATOLOGY
No benefit with rituximab after first CR in DLBCL
AMSTERDAM – Rituximab maintenance therapy did not significantly prolong disease-free survival among patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in complete remission after induction chemotherapy, investigators in the HOVON-Nordic trial collaboration found.
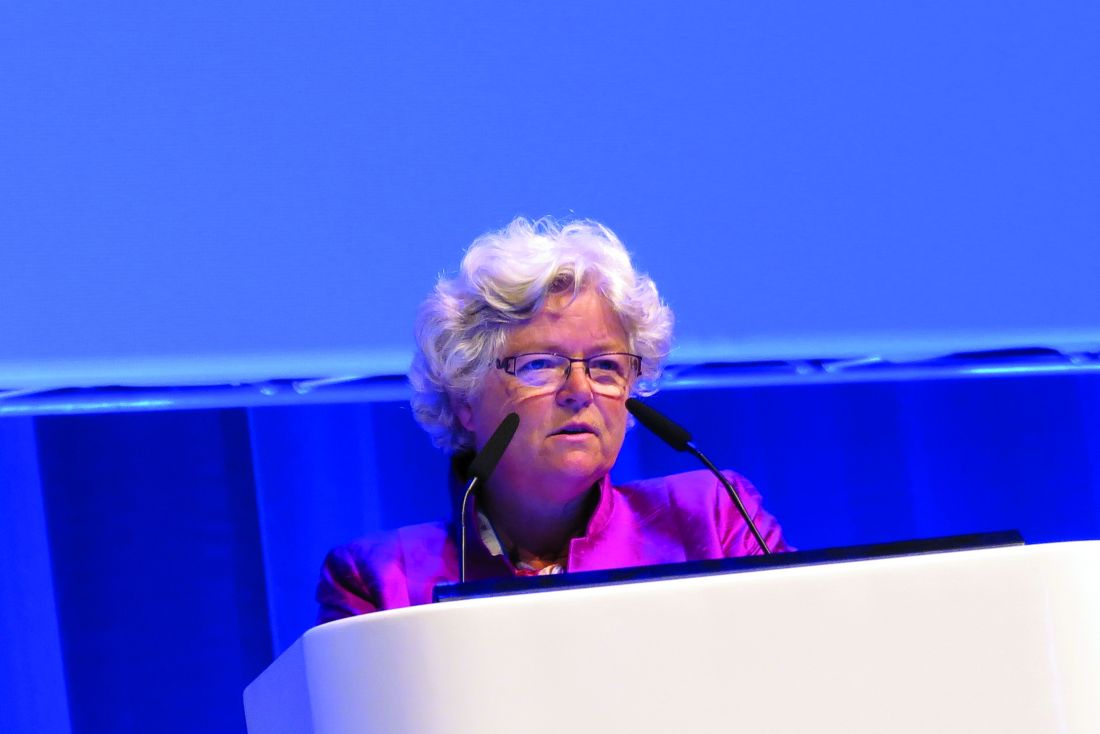
Among 380 patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) in complete remission following induction chemotherapy with R-CHOP (rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone), the median disease-free survival (DFS) after a median follow-up of 79.9 months had not been reached for patients randomized to either rituximab maintenance therapy or observation alone, reported Pieternella J. Lugtenburg, MD, PhD, from Erasmus Medical Center in Rotterdam, the Netherlands.
“In patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in first complete remission after R-CHOP induction therapy, rituximab maintenance therapy does not prolong disease-free survival, and we could not identify a clinical subgroup that benefited,” she said at the annual congress of the European Hematology Association.
The randomized, phase 3 HOVON-Nordic LG trial compared R-CHOP-14 with rituximab delivered on day 1 for four cycles in one arm, and on days 1 and 8 in the comparison arm (R2-CHOP). Patients were assessed for response after four cycles, and those with progressive disease were taken off the study. The remaining patients continued on their assigned regimen for an additional four cycles and second assessment, and those who had complete responses then underwent a second randomization to rituximab maintenance or observation. Patients randomized to maintenance could receive up to 12 8-week cycles.
The second randomization was stratified by age (18-65 vs. 66-80 years), age-adjusted International Prognostic Index score, and R-CHOP regimen (one or two infusions per cycle in the first randomization).
The induction phase found no significant benefit for the additional rituximab infusion for the primary endpoint of progression-free survival, with 3-year PFS rates of 74% for R-CHOP and 71% for R2-CHOP. Respective 5-year PFS rates were 68% and 62%.
There were no differences between the arms by any of the stratification factors, and no difference in overall survival.
Dr. Lugtenburg presented results of the maintenance phase, which included all patients in complete remission at least 4 weeks after the last cycle of R-CHOP-14 who did not have rituximab-related adverse events or active infections.
A total of 195 patients were randomized to observation, and 185 to maintenance. Of this latter group, 149 patients received all 12 cycles, with a median duration of exposure of 22.5 months.
As noted, DFS, the primary endpoint for the maintenance phase, was not significantly different between the arms, with 136 events in the maintenance arm versus 134 in the observation arm. A total of 21 patients assigned to maintenance died, and 22 patients assigned to observation died during follow-up.
The respective 5-year DFS rates were 79% and 74%, a difference that was not statistically significant.
There were no significant differences between the arms in either time to relapse or death, and no difference in overall survival.
In the question-and-answer section following her talk, Marek Trnený, MD, from Charles University in Prague, pointed out that, in the NHL 13 study, which looked at rituximab maintenance for patients with DLBCL or follicular lymphoma in first remission, there was an apparent clinical benefit with rituximab maintenance for men with low International Prognostic Index scores, and asked whether Dr. Lugtenburg and colleagues had seen similar trends.
“We knew about this finding, and we really didn’t see any differences between males and females, not only in terms of efficacy, but also in terms of toxicity, they had actually the same rates of toxicity,” she said.
In NHL 13, women had a significantly higher incidence of grade 3-4 adverse events, compared with men.
The study was sponsored by HOVON, the HematoOncology Foundation for Adults in the Netherlands, with additional support from Roche. Dr. Lugtenburg reported consultancy for and research funding from Roche and others. Dr. Trnený reported advisory board activity, research support, and honoraria from Roche and others.
SOURCE: Lugtenburg PJ et al. EHA 2019, Abstract S1559.
AMSTERDAM – Rituximab maintenance therapy did not significantly prolong disease-free survival among patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in complete remission after induction chemotherapy, investigators in the HOVON-Nordic trial collaboration found.
Among 380 patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) in complete remission following induction chemotherapy with R-CHOP (rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone), the median disease-free survival (DFS) after a median follow-up of 79.9 months had not been reached for patients randomized to either rituximab maintenance therapy or observation alone, reported Pieternella J. Lugtenburg, MD, PhD, from Erasmus Medical Center in Rotterdam, the Netherlands.
“In patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in first complete remission after R-CHOP induction therapy, rituximab maintenance therapy does not prolong disease-free survival, and we could not identify a clinical subgroup that benefited,” she said at the annual congress of the European Hematology Association.
The randomized, phase 3 HOVON-Nordic LG trial compared R-CHOP-14 with rituximab delivered on day 1 for four cycles in one arm, and on days 1 and 8 in the comparison arm (R2-CHOP). Patients were assessed for response after four cycles, and those with progressive disease were taken off the study. The remaining patients continued on their assigned regimen for an additional four cycles and second assessment, and those who had complete responses then underwent a second randomization to rituximab maintenance or observation. Patients randomized to maintenance could receive up to 12 8-week cycles.
The second randomization was stratified by age (18-65 vs. 66-80 years), age-adjusted International Prognostic Index score, and R-CHOP regimen (one or two infusions per cycle in the first randomization).
The induction phase found no significant benefit for the additional rituximab infusion for the primary endpoint of progression-free survival, with 3-year PFS rates of 74% for R-CHOP and 71% for R2-CHOP. Respective 5-year PFS rates were 68% and 62%.
There were no differences between the arms by any of the stratification factors, and no difference in overall survival.
Dr. Lugtenburg presented results of the maintenance phase, which included all patients in complete remission at least 4 weeks after the last cycle of R-CHOP-14 who did not have rituximab-related adverse events or active infections.
A total of 195 patients were randomized to observation, and 185 to maintenance. Of this latter group, 149 patients received all 12 cycles, with a median duration of exposure of 22.5 months.
As noted, DFS, the primary endpoint for the maintenance phase, was not significantly different between the arms, with 136 events in the maintenance arm versus 134 in the observation arm. A total of 21 patients assigned to maintenance died, and 22 patients assigned to observation died during follow-up.
The respective 5-year DFS rates were 79% and 74%, a difference that was not statistically significant.
There were no significant differences between the arms in either time to relapse or death, and no difference in overall survival.
In the question-and-answer section following her talk, Marek Trnený, MD, from Charles University in Prague, pointed out that, in the NHL 13 study, which looked at rituximab maintenance for patients with DLBCL or follicular lymphoma in first remission, there was an apparent clinical benefit with rituximab maintenance for men with low International Prognostic Index scores, and asked whether Dr. Lugtenburg and colleagues had seen similar trends.
“We knew about this finding, and we really didn’t see any differences between males and females, not only in terms of efficacy, but also in terms of toxicity, they had actually the same rates of toxicity,” she said.
In NHL 13, women had a significantly higher incidence of grade 3-4 adverse events, compared with men.
The study was sponsored by HOVON, the HematoOncology Foundation for Adults in the Netherlands, with additional support from Roche. Dr. Lugtenburg reported consultancy for and research funding from Roche and others. Dr. Trnený reported advisory board activity, research support, and honoraria from Roche and others.
SOURCE: Lugtenburg PJ et al. EHA 2019, Abstract S1559.
AMSTERDAM – Rituximab maintenance therapy did not significantly prolong disease-free survival among patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in complete remission after induction chemotherapy, investigators in the HOVON-Nordic trial collaboration found.
Among 380 patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) in complete remission following induction chemotherapy with R-CHOP (rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone), the median disease-free survival (DFS) after a median follow-up of 79.9 months had not been reached for patients randomized to either rituximab maintenance therapy or observation alone, reported Pieternella J. Lugtenburg, MD, PhD, from Erasmus Medical Center in Rotterdam, the Netherlands.
“In patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in first complete remission after R-CHOP induction therapy, rituximab maintenance therapy does not prolong disease-free survival, and we could not identify a clinical subgroup that benefited,” she said at the annual congress of the European Hematology Association.
The randomized, phase 3 HOVON-Nordic LG trial compared R-CHOP-14 with rituximab delivered on day 1 for four cycles in one arm, and on days 1 and 8 in the comparison arm (R2-CHOP). Patients were assessed for response after four cycles, and those with progressive disease were taken off the study. The remaining patients continued on their assigned regimen for an additional four cycles and second assessment, and those who had complete responses then underwent a second randomization to rituximab maintenance or observation. Patients randomized to maintenance could receive up to 12 8-week cycles.
The second randomization was stratified by age (18-65 vs. 66-80 years), age-adjusted International Prognostic Index score, and R-CHOP regimen (one or two infusions per cycle in the first randomization).
The induction phase found no significant benefit for the additional rituximab infusion for the primary endpoint of progression-free survival, with 3-year PFS rates of 74% for R-CHOP and 71% for R2-CHOP. Respective 5-year PFS rates were 68% and 62%.
There were no differences between the arms by any of the stratification factors, and no difference in overall survival.
Dr. Lugtenburg presented results of the maintenance phase, which included all patients in complete remission at least 4 weeks after the last cycle of R-CHOP-14 who did not have rituximab-related adverse events or active infections.
A total of 195 patients were randomized to observation, and 185 to maintenance. Of this latter group, 149 patients received all 12 cycles, with a median duration of exposure of 22.5 months.
As noted, DFS, the primary endpoint for the maintenance phase, was not significantly different between the arms, with 136 events in the maintenance arm versus 134 in the observation arm. A total of 21 patients assigned to maintenance died, and 22 patients assigned to observation died during follow-up.
The respective 5-year DFS rates were 79% and 74%, a difference that was not statistically significant.
There were no significant differences between the arms in either time to relapse or death, and no difference in overall survival.
In the question-and-answer section following her talk, Marek Trnený, MD, from Charles University in Prague, pointed out that, in the NHL 13 study, which looked at rituximab maintenance for patients with DLBCL or follicular lymphoma in first remission, there was an apparent clinical benefit with rituximab maintenance for men with low International Prognostic Index scores, and asked whether Dr. Lugtenburg and colleagues had seen similar trends.
“We knew about this finding, and we really didn’t see any differences between males and females, not only in terms of efficacy, but also in terms of toxicity, they had actually the same rates of toxicity,” she said.
In NHL 13, women had a significantly higher incidence of grade 3-4 adverse events, compared with men.
The study was sponsored by HOVON, the HematoOncology Foundation for Adults in the Netherlands, with additional support from Roche. Dr. Lugtenburg reported consultancy for and research funding from Roche and others. Dr. Trnený reported advisory board activity, research support, and honoraria from Roche and others.
SOURCE: Lugtenburg PJ et al. EHA 2019, Abstract S1559.
REPORTING FROM EHA 2019
Radiation bridging with axi-cel appears safe in DLBCL
according to results from a case series.
“Effective bridging strategies may be needed to provide patients with aggressive disease access to CAR T therapy,” wrote Austin J. Sim MD, JD, of Moffitt Cancer Center in Tampa and colleagues. The findings were reported in the International Journal of Radiation Oncology, Biology, Physics.
The study included a total of 12 patients planned to receive bridging treatment with radiation prior to axicabtagene ciloleucel infusion. The cohort consisted of patients with highly aggressive disease, including six with double-hit lymphoma and six with disease 10 cm or greater in diameter.
Study participants received a radiation dose between 2 and 4 Gy per fraction to a median of 20 Gy (range, 6-36.5 Gy) and half of the participants received 20 Gy in 5 fractions or 30 Gy in 10 fractions. Of the 12 patients, 7 were administered concomitant chemotherapy.
“One patient who underwent apheresis and radiation therapy ultimately did not proceed with CAR T infusion, but was still included in our analysis,” the researchers noted.
After analysis, the researchers reported that, during bridging radiation therapy, no patients had significant toxicities or in-field disease progression of disease prior to CAR T infusion.
Post CAR T infusion, 27% of patients experienced neurotoxicity or severe cytokine release syndrome.
At 30 days, the objective response rate was 81.8%, with 27% attaining complete response. At final follow-up, the best response rate was 81.8%, with complete response achieved in 45% of patients.
The researchers acknowledged that a key limitation of the study was the retrospective design. As a result, radiation dosing was not uniform and the optimal dose and fractionation remains unclear.
In addition, Dr. Sim and colleagues advised that caution should be taken if irradiation is initiated before T-cell apheresis, and if so, blood counts should be monitored closely.
“Future investigation is warranted to optimize the use of bridging radiation before CAR T therapy,” they concluded.
No funding sources were reported. The authors reported financial affiliations with Atara Biotherapeutics, AstraZeneca, Celgene, GlaxoSmithKline, Novartis, Precision Biosciences, and several others.
SOURCE: Sim AJ et al. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2019 Jun 5. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2019.05.065.
according to results from a case series.
“Effective bridging strategies may be needed to provide patients with aggressive disease access to CAR T therapy,” wrote Austin J. Sim MD, JD, of Moffitt Cancer Center in Tampa and colleagues. The findings were reported in the International Journal of Radiation Oncology, Biology, Physics.
The study included a total of 12 patients planned to receive bridging treatment with radiation prior to axicabtagene ciloleucel infusion. The cohort consisted of patients with highly aggressive disease, including six with double-hit lymphoma and six with disease 10 cm or greater in diameter.
Study participants received a radiation dose between 2 and 4 Gy per fraction to a median of 20 Gy (range, 6-36.5 Gy) and half of the participants received 20 Gy in 5 fractions or 30 Gy in 10 fractions. Of the 12 patients, 7 were administered concomitant chemotherapy.
“One patient who underwent apheresis and radiation therapy ultimately did not proceed with CAR T infusion, but was still included in our analysis,” the researchers noted.
After analysis, the researchers reported that, during bridging radiation therapy, no patients had significant toxicities or in-field disease progression of disease prior to CAR T infusion.
Post CAR T infusion, 27% of patients experienced neurotoxicity or severe cytokine release syndrome.
At 30 days, the objective response rate was 81.8%, with 27% attaining complete response. At final follow-up, the best response rate was 81.8%, with complete response achieved in 45% of patients.
The researchers acknowledged that a key limitation of the study was the retrospective design. As a result, radiation dosing was not uniform and the optimal dose and fractionation remains unclear.
In addition, Dr. Sim and colleagues advised that caution should be taken if irradiation is initiated before T-cell apheresis, and if so, blood counts should be monitored closely.
“Future investigation is warranted to optimize the use of bridging radiation before CAR T therapy,” they concluded.
No funding sources were reported. The authors reported financial affiliations with Atara Biotherapeutics, AstraZeneca, Celgene, GlaxoSmithKline, Novartis, Precision Biosciences, and several others.
SOURCE: Sim AJ et al. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2019 Jun 5. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2019.05.065.
according to results from a case series.
“Effective bridging strategies may be needed to provide patients with aggressive disease access to CAR T therapy,” wrote Austin J. Sim MD, JD, of Moffitt Cancer Center in Tampa and colleagues. The findings were reported in the International Journal of Radiation Oncology, Biology, Physics.
The study included a total of 12 patients planned to receive bridging treatment with radiation prior to axicabtagene ciloleucel infusion. The cohort consisted of patients with highly aggressive disease, including six with double-hit lymphoma and six with disease 10 cm or greater in diameter.
Study participants received a radiation dose between 2 and 4 Gy per fraction to a median of 20 Gy (range, 6-36.5 Gy) and half of the participants received 20 Gy in 5 fractions or 30 Gy in 10 fractions. Of the 12 patients, 7 were administered concomitant chemotherapy.
“One patient who underwent apheresis and radiation therapy ultimately did not proceed with CAR T infusion, but was still included in our analysis,” the researchers noted.
After analysis, the researchers reported that, during bridging radiation therapy, no patients had significant toxicities or in-field disease progression of disease prior to CAR T infusion.
Post CAR T infusion, 27% of patients experienced neurotoxicity or severe cytokine release syndrome.
At 30 days, the objective response rate was 81.8%, with 27% attaining complete response. At final follow-up, the best response rate was 81.8%, with complete response achieved in 45% of patients.
The researchers acknowledged that a key limitation of the study was the retrospective design. As a result, radiation dosing was not uniform and the optimal dose and fractionation remains unclear.
In addition, Dr. Sim and colleagues advised that caution should be taken if irradiation is initiated before T-cell apheresis, and if so, blood counts should be monitored closely.
“Future investigation is warranted to optimize the use of bridging radiation before CAR T therapy,” they concluded.
No funding sources were reported. The authors reported financial affiliations with Atara Biotherapeutics, AstraZeneca, Celgene, GlaxoSmithKline, Novartis, Precision Biosciences, and several others.
SOURCE: Sim AJ et al. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2019 Jun 5. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2019.05.065.
FROM THE INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RADIATION ONCOLOGY, BIOLOGY, PHYSICS
Polatuzumab vedotin combo shows promise in DLBCL
according to preliminary results from a phase 1b-2 trial.
Polatuzumab vedotin has already shown single-agent activity in relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, Hervé Tilly, MD, PhD, of the University of Rouen (France), and colleagues wrote in Lancet Oncology. “We explored the combination of polatuzumab vedotin with either rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and prednisone [R-CHP] or obinutuzumab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and prednisone [G-CHP].”
With respect to polatuzumab vedotin dosing, the maximum investigated dose was 1.8 mg/kg. The novel agent was infused on day 2 of cycles 1 and 2 and subsequently on day 1 of each cycle thereafter for a total of 6-8 cycles, with each cycle lasting of 21 days.
The primary outcomes of this ongoing study were treatment safety and tolerability, as well as the establishment of recommended phase 2 dosing. Secondary endpoints included overall response rate, complete response=, among others.
A total of 82 patients were included in final analysis, 25 in the phase 1b dose escalation phase and 57 in the expansion phase.
After analysis, Dr. Tilly and his colleagues reported two dose-limiting toxicities: One patient experienced a grade 4 pulmonary embolism (1.8 mg/kg plus R-CHP) and another had grade 4 febrile neutropenia and grade 3 thrombocytopenia (1.4 mg/kg plus G-CHP).
At a median follow-up of 21.5 months, the overall response rate was 89% in study participants, including 77% of patients who achieved a complete response and 12% who had a partial response.
The recommended phase 2 dose of polatuzumab vedotin was 1.8 mg/kg. At this dose, the most common grade 3 or higher toxicities were neutropenia (30%), febrile neutropenia (18%), and thrombocytopenia (9%).
The researchers acknowledged a key limitation of the study was the nonrandomized design. As a result, dose and regimen comparisons could not be made.
The study was funded by F. Hoffmann-La Roche and Genentech. The authors reported financial affiliations with AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Gilead, Janssen, Merck, Pfizer, and others.
SOURCE: Tilly H et al. Lancet Oncol. 2019 May 14. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(19)30091-9.
according to preliminary results from a phase 1b-2 trial.
Polatuzumab vedotin has already shown single-agent activity in relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, Hervé Tilly, MD, PhD, of the University of Rouen (France), and colleagues wrote in Lancet Oncology. “We explored the combination of polatuzumab vedotin with either rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and prednisone [R-CHP] or obinutuzumab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and prednisone [G-CHP].”
With respect to polatuzumab vedotin dosing, the maximum investigated dose was 1.8 mg/kg. The novel agent was infused on day 2 of cycles 1 and 2 and subsequently on day 1 of each cycle thereafter for a total of 6-8 cycles, with each cycle lasting of 21 days.
The primary outcomes of this ongoing study were treatment safety and tolerability, as well as the establishment of recommended phase 2 dosing. Secondary endpoints included overall response rate, complete response=, among others.
A total of 82 patients were included in final analysis, 25 in the phase 1b dose escalation phase and 57 in the expansion phase.
After analysis, Dr. Tilly and his colleagues reported two dose-limiting toxicities: One patient experienced a grade 4 pulmonary embolism (1.8 mg/kg plus R-CHP) and another had grade 4 febrile neutropenia and grade 3 thrombocytopenia (1.4 mg/kg plus G-CHP).
At a median follow-up of 21.5 months, the overall response rate was 89% in study participants, including 77% of patients who achieved a complete response and 12% who had a partial response.
The recommended phase 2 dose of polatuzumab vedotin was 1.8 mg/kg. At this dose, the most common grade 3 or higher toxicities were neutropenia (30%), febrile neutropenia (18%), and thrombocytopenia (9%).
The researchers acknowledged a key limitation of the study was the nonrandomized design. As a result, dose and regimen comparisons could not be made.
The study was funded by F. Hoffmann-La Roche and Genentech. The authors reported financial affiliations with AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Gilead, Janssen, Merck, Pfizer, and others.
SOURCE: Tilly H et al. Lancet Oncol. 2019 May 14. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(19)30091-9.
according to preliminary results from a phase 1b-2 trial.
Polatuzumab vedotin has already shown single-agent activity in relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, Hervé Tilly, MD, PhD, of the University of Rouen (France), and colleagues wrote in Lancet Oncology. “We explored the combination of polatuzumab vedotin with either rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and prednisone [R-CHP] or obinutuzumab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and prednisone [G-CHP].”
With respect to polatuzumab vedotin dosing, the maximum investigated dose was 1.8 mg/kg. The novel agent was infused on day 2 of cycles 1 and 2 and subsequently on day 1 of each cycle thereafter for a total of 6-8 cycles, with each cycle lasting of 21 days.
The primary outcomes of this ongoing study were treatment safety and tolerability, as well as the establishment of recommended phase 2 dosing. Secondary endpoints included overall response rate, complete response=, among others.
A total of 82 patients were included in final analysis, 25 in the phase 1b dose escalation phase and 57 in the expansion phase.
After analysis, Dr. Tilly and his colleagues reported two dose-limiting toxicities: One patient experienced a grade 4 pulmonary embolism (1.8 mg/kg plus R-CHP) and another had grade 4 febrile neutropenia and grade 3 thrombocytopenia (1.4 mg/kg plus G-CHP).
At a median follow-up of 21.5 months, the overall response rate was 89% in study participants, including 77% of patients who achieved a complete response and 12% who had a partial response.
The recommended phase 2 dose of polatuzumab vedotin was 1.8 mg/kg. At this dose, the most common grade 3 or higher toxicities were neutropenia (30%), febrile neutropenia (18%), and thrombocytopenia (9%).
The researchers acknowledged a key limitation of the study was the nonrandomized design. As a result, dose and regimen comparisons could not be made.
The study was funded by F. Hoffmann-La Roche and Genentech. The authors reported financial affiliations with AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Gilead, Janssen, Merck, Pfizer, and others.
SOURCE: Tilly H et al. Lancet Oncol. 2019 May 14. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(19)30091-9.
FROM LANCET ONCOLOGY
Influenza vaccination status in DLBCL poorly documented
Annual influenza vaccination rates and documentation of vaccination status appear to be suboptimal among patients with newly diagnosed diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, based on a retrospective analysis of data in the state of Georgia.
The researchers reviewed medical records of patients with a new diagnosis of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma at three Georgia hospitals. Documentation related to vaccine administration, refusal, and patient counseling was collected between Feb. 1, 2015, and Oct. 31, 2017, Andres Chang, MD, PhD, of Emory University, Atlanta, and colleagues wrote. The findings were published in Clinical Lymphoma, Myeloma & Leukemia.
Vaccination status within 1 year of diagnosis was documented for 61 of 107 patients. Among the 61 patients with documentation of influenza vaccination status, 35 (57%) were vaccinated. No reason was documented for vaccine refusal, and there was no follow-up documentation on vaccine counseling by nursing staff, physicians, or advanced practice providers in any of these admitted patients.
Nearly all documentation of influenza vaccination status came from the nursing staff. Only 4 of the 61 patients had documentation provided by primary oncologists or advanced practice providers, and those patients also had documentation from the outpatient nursing staff who subsequently administered the influenza vaccine.
“Routine outpatient vaccination screening and strategies for sharing and linking patient vaccination status between providers in different health care systems at the state and national levels could improve vaccination documentation in patients with lymphoma and provide opportunities to improve compliance,” the researchers wrote.
A key limitation of the study was the lack of adequate documentation, they explained. As a result, the reported vaccination rates were not more rigorously evaluated.
The study was funded by the Winship Cancer Institute and the National Institutes of Health. The authors reported financial affiliations with AbbVie, Acerta Pharma, Celgene, Gilead, Janssen, Pharmacyclics, and others.
SOURCE: Chang A et al. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2019 Jan 2. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2018.12.018.
Annual influenza vaccination rates and documentation of vaccination status appear to be suboptimal among patients with newly diagnosed diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, based on a retrospective analysis of data in the state of Georgia.
The researchers reviewed medical records of patients with a new diagnosis of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma at three Georgia hospitals. Documentation related to vaccine administration, refusal, and patient counseling was collected between Feb. 1, 2015, and Oct. 31, 2017, Andres Chang, MD, PhD, of Emory University, Atlanta, and colleagues wrote. The findings were published in Clinical Lymphoma, Myeloma & Leukemia.
Vaccination status within 1 year of diagnosis was documented for 61 of 107 patients. Among the 61 patients with documentation of influenza vaccination status, 35 (57%) were vaccinated. No reason was documented for vaccine refusal, and there was no follow-up documentation on vaccine counseling by nursing staff, physicians, or advanced practice providers in any of these admitted patients.
Nearly all documentation of influenza vaccination status came from the nursing staff. Only 4 of the 61 patients had documentation provided by primary oncologists or advanced practice providers, and those patients also had documentation from the outpatient nursing staff who subsequently administered the influenza vaccine.
“Routine outpatient vaccination screening and strategies for sharing and linking patient vaccination status between providers in different health care systems at the state and national levels could improve vaccination documentation in patients with lymphoma and provide opportunities to improve compliance,” the researchers wrote.
A key limitation of the study was the lack of adequate documentation, they explained. As a result, the reported vaccination rates were not more rigorously evaluated.
The study was funded by the Winship Cancer Institute and the National Institutes of Health. The authors reported financial affiliations with AbbVie, Acerta Pharma, Celgene, Gilead, Janssen, Pharmacyclics, and others.
SOURCE: Chang A et al. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2019 Jan 2. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2018.12.018.
Annual influenza vaccination rates and documentation of vaccination status appear to be suboptimal among patients with newly diagnosed diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, based on a retrospective analysis of data in the state of Georgia.
The researchers reviewed medical records of patients with a new diagnosis of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma at three Georgia hospitals. Documentation related to vaccine administration, refusal, and patient counseling was collected between Feb. 1, 2015, and Oct. 31, 2017, Andres Chang, MD, PhD, of Emory University, Atlanta, and colleagues wrote. The findings were published in Clinical Lymphoma, Myeloma & Leukemia.
Vaccination status within 1 year of diagnosis was documented for 61 of 107 patients. Among the 61 patients with documentation of influenza vaccination status, 35 (57%) were vaccinated. No reason was documented for vaccine refusal, and there was no follow-up documentation on vaccine counseling by nursing staff, physicians, or advanced practice providers in any of these admitted patients.
Nearly all documentation of influenza vaccination status came from the nursing staff. Only 4 of the 61 patients had documentation provided by primary oncologists or advanced practice providers, and those patients also had documentation from the outpatient nursing staff who subsequently administered the influenza vaccine.
“Routine outpatient vaccination screening and strategies for sharing and linking patient vaccination status between providers in different health care systems at the state and national levels could improve vaccination documentation in patients with lymphoma and provide opportunities to improve compliance,” the researchers wrote.
A key limitation of the study was the lack of adequate documentation, they explained. As a result, the reported vaccination rates were not more rigorously evaluated.
The study was funded by the Winship Cancer Institute and the National Institutes of Health. The authors reported financial affiliations with AbbVie, Acerta Pharma, Celgene, Gilead, Janssen, Pharmacyclics, and others.
SOURCE: Chang A et al. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2019 Jan 2. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2018.12.018.
FROM CLINICAL LYMPHOMA, MYELOMA & LEUKEMIA
Rituximab and vemurafenib could challenge frontline chemotherapy for HCL
AMSTERDAM – A combination of rituximab and the BRAF inhibitor vemurafenib could be the one-two punch needed for relapsed or refractory hairy cell leukemia (HCL), according to investigators.
Among evaluable patients treated with this combination, 96% achieved complete remission, reported lead author, Enrico Tiacci, MD, of the University and Hospital of Perugia, Italy.
This level of efficacy is “clearly superior to historical results with either agent alone,” Dr. Tiacci said during a presentation at the annual congress of the European Hematology Association, citing previous complete response rates with vemurafenib alone of 35%-40%. “[This combination] has potential for challenging chemotherapy in the frontline setting,” he said.
The phase 2 trial involved 31 patients with relapsed or refractory HCL who had received a median of three previous therapies. Eight of the patients (26%) had primary refractory disease. Patients received vemurafenib 960 mg, twice daily for 8 weeks and rituximab 375 mg/m2, every 2 weeks. After finishing vemurafenib, patients received rituximab four more times, keeping the interval of 2 weeks. Complete remission was defined as a normal blood count, no leukemic cells in bone marrow biopsies and blood smears, and no palpable splenomegaly.
Out of 31 patients, 27 were evaluable at data cutoff. Of these, 26 (96%) achieved complete remission. The investigators noted that two complete responders had incomplete platelet recovery at the end of treatment that resolved soon after, and two patients had persistent splenomegaly, but were considered to be in complete remission at 22.5 and 25 months after finishing therapy.
All of the complete responders had previously received purine analogs, while a few had been refractory to a prior BRAF inhibitor (n = 7) and/or rituximab (n = 5).
The investigators also pointed out that 15 out of 24 evaluable patients (63%) achieved complete remission just 4 weeks after starting the trial regimen. Almost two-thirds of patients (65%) were negative for minimal residual disease (MRD). The rate of progression-free survival at a median follow-up of 29.5 months was 83%. Disease progression occurred exclusively in patients who were MRD positive.
The combination was well tolerated; most adverse events were of grade 1 or 2, overlapping with the safety profile of each agent alone.
Reflecting on the study findings, Dr. Tiacci suggested that the combination could be most effective if delivered immediately, instead of after BRAF failure.
“Interestingly,” he said, “the relapse-free survival in patients naive to a BRAF inhibitor remained significantly longer than the relapse-free interval that patients previously exposed to a BRAF inhibitor enjoyed, both following monotherapy with a BRAF inhibitor and following subsequent combination with rituximab, potentially suggesting that vemurafenib should be used directly in combination with rituximab rather than being delivered first as a monotherapy and then added to rituximab at relapse.”
Randomized testing of the combination against the chemotherapy-based standard of care in the frontline setting is warranted, the investigators concluded.
Dr. Tiacci reported financial relationships with Roche, AbbVie, and Shire.
SOURCE: Tiacci E et al. EHA Congress, Abstract S104.
AMSTERDAM – A combination of rituximab and the BRAF inhibitor vemurafenib could be the one-two punch needed for relapsed or refractory hairy cell leukemia (HCL), according to investigators.
Among evaluable patients treated with this combination, 96% achieved complete remission, reported lead author, Enrico Tiacci, MD, of the University and Hospital of Perugia, Italy.
This level of efficacy is “clearly superior to historical results with either agent alone,” Dr. Tiacci said during a presentation at the annual congress of the European Hematology Association, citing previous complete response rates with vemurafenib alone of 35%-40%. “[This combination] has potential for challenging chemotherapy in the frontline setting,” he said.
The phase 2 trial involved 31 patients with relapsed or refractory HCL who had received a median of three previous therapies. Eight of the patients (26%) had primary refractory disease. Patients received vemurafenib 960 mg, twice daily for 8 weeks and rituximab 375 mg/m2, every 2 weeks. After finishing vemurafenib, patients received rituximab four more times, keeping the interval of 2 weeks. Complete remission was defined as a normal blood count, no leukemic cells in bone marrow biopsies and blood smears, and no palpable splenomegaly.
Out of 31 patients, 27 were evaluable at data cutoff. Of these, 26 (96%) achieved complete remission. The investigators noted that two complete responders had incomplete platelet recovery at the end of treatment that resolved soon after, and two patients had persistent splenomegaly, but were considered to be in complete remission at 22.5 and 25 months after finishing therapy.
All of the complete responders had previously received purine analogs, while a few had been refractory to a prior BRAF inhibitor (n = 7) and/or rituximab (n = 5).
The investigators also pointed out that 15 out of 24 evaluable patients (63%) achieved complete remission just 4 weeks after starting the trial regimen. Almost two-thirds of patients (65%) were negative for minimal residual disease (MRD). The rate of progression-free survival at a median follow-up of 29.5 months was 83%. Disease progression occurred exclusively in patients who were MRD positive.
The combination was well tolerated; most adverse events were of grade 1 or 2, overlapping with the safety profile of each agent alone.
Reflecting on the study findings, Dr. Tiacci suggested that the combination could be most effective if delivered immediately, instead of after BRAF failure.
“Interestingly,” he said, “the relapse-free survival in patients naive to a BRAF inhibitor remained significantly longer than the relapse-free interval that patients previously exposed to a BRAF inhibitor enjoyed, both following monotherapy with a BRAF inhibitor and following subsequent combination with rituximab, potentially suggesting that vemurafenib should be used directly in combination with rituximab rather than being delivered first as a monotherapy and then added to rituximab at relapse.”
Randomized testing of the combination against the chemotherapy-based standard of care in the frontline setting is warranted, the investigators concluded.
Dr. Tiacci reported financial relationships with Roche, AbbVie, and Shire.
SOURCE: Tiacci E et al. EHA Congress, Abstract S104.
AMSTERDAM – A combination of rituximab and the BRAF inhibitor vemurafenib could be the one-two punch needed for relapsed or refractory hairy cell leukemia (HCL), according to investigators.
Among evaluable patients treated with this combination, 96% achieved complete remission, reported lead author, Enrico Tiacci, MD, of the University and Hospital of Perugia, Italy.
This level of efficacy is “clearly superior to historical results with either agent alone,” Dr. Tiacci said during a presentation at the annual congress of the European Hematology Association, citing previous complete response rates with vemurafenib alone of 35%-40%. “[This combination] has potential for challenging chemotherapy in the frontline setting,” he said.
The phase 2 trial involved 31 patients with relapsed or refractory HCL who had received a median of three previous therapies. Eight of the patients (26%) had primary refractory disease. Patients received vemurafenib 960 mg, twice daily for 8 weeks and rituximab 375 mg/m2, every 2 weeks. After finishing vemurafenib, patients received rituximab four more times, keeping the interval of 2 weeks. Complete remission was defined as a normal blood count, no leukemic cells in bone marrow biopsies and blood smears, and no palpable splenomegaly.
Out of 31 patients, 27 were evaluable at data cutoff. Of these, 26 (96%) achieved complete remission. The investigators noted that two complete responders had incomplete platelet recovery at the end of treatment that resolved soon after, and two patients had persistent splenomegaly, but were considered to be in complete remission at 22.5 and 25 months after finishing therapy.
All of the complete responders had previously received purine analogs, while a few had been refractory to a prior BRAF inhibitor (n = 7) and/or rituximab (n = 5).
The investigators also pointed out that 15 out of 24 evaluable patients (63%) achieved complete remission just 4 weeks after starting the trial regimen. Almost two-thirds of patients (65%) were negative for minimal residual disease (MRD). The rate of progression-free survival at a median follow-up of 29.5 months was 83%. Disease progression occurred exclusively in patients who were MRD positive.
The combination was well tolerated; most adverse events were of grade 1 or 2, overlapping with the safety profile of each agent alone.
Reflecting on the study findings, Dr. Tiacci suggested that the combination could be most effective if delivered immediately, instead of after BRAF failure.
“Interestingly,” he said, “the relapse-free survival in patients naive to a BRAF inhibitor remained significantly longer than the relapse-free interval that patients previously exposed to a BRAF inhibitor enjoyed, both following monotherapy with a BRAF inhibitor and following subsequent combination with rituximab, potentially suggesting that vemurafenib should be used directly in combination with rituximab rather than being delivered first as a monotherapy and then added to rituximab at relapse.”
Randomized testing of the combination against the chemotherapy-based standard of care in the frontline setting is warranted, the investigators concluded.
Dr. Tiacci reported financial relationships with Roche, AbbVie, and Shire.
SOURCE: Tiacci E et al. EHA Congress, Abstract S104.
REPORTING FROM EHA CONGRESS
Cell count ratios appear to predict thromboembolism in lymphoma
AMSTERDAM – When predicting the risk of thromboembolism in lymphoma patients receiving chemotherapy, clinicians can rely on a routine diagnostic tool: complete blood count, investigators reported.
A recent study found that high neutrophil to lymphocyte (NLR) and platelet to lymphocyte (PLR) ratios were prognostic for thromboembolism in this setting, reported lead author Vladimir Otasevic, MD, of the Clinical Centre of Serbia in Belgrade.
“Because of the presence of a broad spectrum of risk factors [in patients with lymphoma undergoing chemotherapy], some authors have published risk-assessment models for prediction of thromboembolism,” Dr. Otasevic said during a presentation at the annual congress of the European Hematology Association. While the underlying pathophysiology that precedes thromboembolism is complex, Dr. Otasevic suggested that risk prediction may not have to be, noting that NLR and PLR were recently proposed as risk biomarkers.
To test the utility of these potential biomarkers, Dr. Otasevic and his colleagues retrospectively analyzed data from 484 patients with non-Hodgkin and Hodgkin lymphoma who had undergone at least one cycle of chemotherapy at the Clinic for Hematology, Clinical Centre of Serbia. Patients were followed for venous and arterial thromboembolic events from the time of diagnosis to 3 months beyond their final cycle of chemotherapy. NLR and PLR ratios were calculated from complete blood count. Thromboembolism was diagnosed by radiography, clinical exam, and laboratory evaluation, with probable diagnoses reviewed by an internist and radiologist.
The median patient age was 53 years with a range from 18 to 89 years. Most patients were recently diagnosed with advanced disease (21.1% stage III and 42.5% stage IV). Half of the population had high-grade non-Hodgkin lymphoma (50.0%) and slightly more than a quarter had low-grade non-Hodgkin lymphoma (28.3%). Low-grade Hodgkin lymphoma was less common (17.4%) and followed distantly by other forms (4.3%).
Thirty-five patients (7.2%) developed thromboembolic events; of these, 30 had venous thromboembolism (6.2%), 6 had arterial thromboembolism (1.2%), and 1 had both. Patients who experienced thromboembolic events had significantly higher NLR and PLR than patients without thromboembolism, and both ratios were significantly associated with one another.
A positive NLR, defined as a ratio of 3.1 or more, was associated with a relative risk of 4.1 for thromboembolism (P less than .001), while a positive PLR, defined as a ratio of 10 or more, was associated with a relative risk of 2.9 (P = .008). Using a multivariate model, a positive NLR was associated with an even higher relative risk (RR = 4.5; P less than .001).
“NLR and PLR demonstrated significant powerfulness in prediction of future risk of [thromboembolism] in lymphoma patients,” the investigators concluded. “Simplicity, effectiveness, modesty, and practicability qualify these new tools for routine [thromboembolism] prognostic assessment.”
Dr. Otasevic said that he and his colleagues have plans to build on these findings with further analysis involving progression-free and overall survival.
The investigators reported no disclosures.
SOURCE: Otasevic V et al. EHA Congress, Abstract S1645.
AMSTERDAM – When predicting the risk of thromboembolism in lymphoma patients receiving chemotherapy, clinicians can rely on a routine diagnostic tool: complete blood count, investigators reported.
A recent study found that high neutrophil to lymphocyte (NLR) and platelet to lymphocyte (PLR) ratios were prognostic for thromboembolism in this setting, reported lead author Vladimir Otasevic, MD, of the Clinical Centre of Serbia in Belgrade.
“Because of the presence of a broad spectrum of risk factors [in patients with lymphoma undergoing chemotherapy], some authors have published risk-assessment models for prediction of thromboembolism,” Dr. Otasevic said during a presentation at the annual congress of the European Hematology Association. While the underlying pathophysiology that precedes thromboembolism is complex, Dr. Otasevic suggested that risk prediction may not have to be, noting that NLR and PLR were recently proposed as risk biomarkers.
To test the utility of these potential biomarkers, Dr. Otasevic and his colleagues retrospectively analyzed data from 484 patients with non-Hodgkin and Hodgkin lymphoma who had undergone at least one cycle of chemotherapy at the Clinic for Hematology, Clinical Centre of Serbia. Patients were followed for venous and arterial thromboembolic events from the time of diagnosis to 3 months beyond their final cycle of chemotherapy. NLR and PLR ratios were calculated from complete blood count. Thromboembolism was diagnosed by radiography, clinical exam, and laboratory evaluation, with probable diagnoses reviewed by an internist and radiologist.
The median patient age was 53 years with a range from 18 to 89 years. Most patients were recently diagnosed with advanced disease (21.1% stage III and 42.5% stage IV). Half of the population had high-grade non-Hodgkin lymphoma (50.0%) and slightly more than a quarter had low-grade non-Hodgkin lymphoma (28.3%). Low-grade Hodgkin lymphoma was less common (17.4%) and followed distantly by other forms (4.3%).
Thirty-five patients (7.2%) developed thromboembolic events; of these, 30 had venous thromboembolism (6.2%), 6 had arterial thromboembolism (1.2%), and 1 had both. Patients who experienced thromboembolic events had significantly higher NLR and PLR than patients without thromboembolism, and both ratios were significantly associated with one another.
A positive NLR, defined as a ratio of 3.1 or more, was associated with a relative risk of 4.1 for thromboembolism (P less than .001), while a positive PLR, defined as a ratio of 10 or more, was associated with a relative risk of 2.9 (P = .008). Using a multivariate model, a positive NLR was associated with an even higher relative risk (RR = 4.5; P less than .001).
“NLR and PLR demonstrated significant powerfulness in prediction of future risk of [thromboembolism] in lymphoma patients,” the investigators concluded. “Simplicity, effectiveness, modesty, and practicability qualify these new tools for routine [thromboembolism] prognostic assessment.”
Dr. Otasevic said that he and his colleagues have plans to build on these findings with further analysis involving progression-free and overall survival.
The investigators reported no disclosures.
SOURCE: Otasevic V et al. EHA Congress, Abstract S1645.
AMSTERDAM – When predicting the risk of thromboembolism in lymphoma patients receiving chemotherapy, clinicians can rely on a routine diagnostic tool: complete blood count, investigators reported.
A recent study found that high neutrophil to lymphocyte (NLR) and platelet to lymphocyte (PLR) ratios were prognostic for thromboembolism in this setting, reported lead author Vladimir Otasevic, MD, of the Clinical Centre of Serbia in Belgrade.
“Because of the presence of a broad spectrum of risk factors [in patients with lymphoma undergoing chemotherapy], some authors have published risk-assessment models for prediction of thromboembolism,” Dr. Otasevic said during a presentation at the annual congress of the European Hematology Association. While the underlying pathophysiology that precedes thromboembolism is complex, Dr. Otasevic suggested that risk prediction may not have to be, noting that NLR and PLR were recently proposed as risk biomarkers.
To test the utility of these potential biomarkers, Dr. Otasevic and his colleagues retrospectively analyzed data from 484 patients with non-Hodgkin and Hodgkin lymphoma who had undergone at least one cycle of chemotherapy at the Clinic for Hematology, Clinical Centre of Serbia. Patients were followed for venous and arterial thromboembolic events from the time of diagnosis to 3 months beyond their final cycle of chemotherapy. NLR and PLR ratios were calculated from complete blood count. Thromboembolism was diagnosed by radiography, clinical exam, and laboratory evaluation, with probable diagnoses reviewed by an internist and radiologist.
The median patient age was 53 years with a range from 18 to 89 years. Most patients were recently diagnosed with advanced disease (21.1% stage III and 42.5% stage IV). Half of the population had high-grade non-Hodgkin lymphoma (50.0%) and slightly more than a quarter had low-grade non-Hodgkin lymphoma (28.3%). Low-grade Hodgkin lymphoma was less common (17.4%) and followed distantly by other forms (4.3%).
Thirty-five patients (7.2%) developed thromboembolic events; of these, 30 had venous thromboembolism (6.2%), 6 had arterial thromboembolism (1.2%), and 1 had both. Patients who experienced thromboembolic events had significantly higher NLR and PLR than patients without thromboembolism, and both ratios were significantly associated with one another.
A positive NLR, defined as a ratio of 3.1 or more, was associated with a relative risk of 4.1 for thromboembolism (P less than .001), while a positive PLR, defined as a ratio of 10 or more, was associated with a relative risk of 2.9 (P = .008). Using a multivariate model, a positive NLR was associated with an even higher relative risk (RR = 4.5; P less than .001).
“NLR and PLR demonstrated significant powerfulness in prediction of future risk of [thromboembolism] in lymphoma patients,” the investigators concluded. “Simplicity, effectiveness, modesty, and practicability qualify these new tools for routine [thromboembolism] prognostic assessment.”
Dr. Otasevic said that he and his colleagues have plans to build on these findings with further analysis involving progression-free and overall survival.
The investigators reported no disclosures.
SOURCE: Otasevic V et al. EHA Congress, Abstract S1645.
REPORTING FROM EHA CONGRESS