User login
Surgeon volume tied to mitral valve surgery outcomes
CHICAGO – A total annual surgeon volume of fewer than 25 operations was associated with increased 1-year mortality and reoperation rates, according to a study presented at the 2017 American Association for Thoracic Surgery Centennial.
Improvements in repair rates, survival, and freedom from reoperation increased with increasing surgeon case volumes, Joanna Chikwe, MD, and her colleagues at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, stated.
The researchers compared repair rates, long-term survival, and risk of postrepair reoperation in patients with degenerative disease according to total annual surgeon volume, which was defined as any mitral valve operation for any cause during the study period. The study was simultaneously published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology (2017 May 16;69[19]:2397-406).
Mitral valve repair is the preferred treatment, compared with valve replacement, for the treatment of severe mitral valve regurgitation in patients who have degenerative valve disease with mitral valve prolapse, and both U.S. and European guidelines strongly recommend valve repair whenever possible, according to Dr. Chikwe and her colleagues.
But, “mitral valve replacement unfortunately remains relatively common in patients with degenerative valve disease,” they stated.
A total of 313 surgeons from 41 institutions met the study eligibility criteria, according to the researchers. They performed a median of 10 mitral valve operations per year (range, 1-230). The median annual institutional mitral valve volume was 59 mitral valve operations, ranging from a minimum of 6 to a maximum of 310 operations. Repair rates for primary mitral valve operations for any cause at all 41 institutions varied from 15% to 83%, and repair rates for degenerative mitral valve operations varied from 25% to 100%.
In the study cohort, surgeons with a total annual volume of less than 25 operations carried out 25% of procedures.
After multivariable adjustment, total annual surgeon volume was independently associated with the probability of mitral valve repair. The chance of repair increased significantly by 13% for every 10-case increment in total annual surgeon volume (P less than .001).
In addition, compared with patients operated on by surgeons with a total annual surgeon volume of 10 or fewer operations, patients operated on by surgeons with a total annual surgeon volume of greater than 50 operations were more than three times as likely to undergo mitral valve repair rather than replacement.
A total annual surgeon volume of less than 25 operations was associated with lower mitral valve repair rates and with increased 1-year mortality and mitral valve reoperation rates. Improvements in repair rates, survival, and freedom from reoperation increased with increasing surgeon case volumes.
After 1 year of repair or replacement, the actuarial survival of patients with degenerative mitral valve disease who were operated on by surgeons performing greater than 50 operations per year was 97.8%, compared with 94.1% for patients operated on by surgeons performing less than or equal to 10 operations a year.
Compared with replacement, mitral repair was significantly associated with better survival, but total annual surgeon volume still remained a significant independent predictor (P less than .001). In addition, for those patients who underwent mitral valve repair, total annual surgeon volume was a significant independent predictor of late death.
The results are important, the investigators noted, given that the median number of mitral valve operations performed annually by individual surgeons in the United States was five, according to an analysis of the Society of Thoracic Surgeons database – and that, in New York state, most surgeons actually performed less than one mitral operation per month.
There were significant differences seen in the patient characteristics across surgeons’ case volume groups. The prevalence of congestive heart failure was significantly higher in patients operated on by surgeons with lower volumes, and the proportion of patients undergoing urgent surgery was also significantly higher for lower-volume surgeons.
“This leads to a double jeopardy, where sicker patients are adversely affected by the lower repair rates and poorer outcomes seen with lower-volume surgeons, and it underscores the need to refer the highest-risk patients to high-volume surgeons,” said Dr. Chickwe and her colleagues.
However, “even among high-volume surgeons, there was an observed variability of degenerative disease repair rates, ranging from 19% to nearly 100%,” they added. “This finding reflects that surgeon volume is not the only factor for better outcomes, and it emphasizes the need for more transparency of surgeon-related factors and outcomes of degenerative mitral valve surgery for patients and referring cardiologists.
“Considering that there was an incremental improvement in survival and probability of repair with increasing volume over 25 operations, one could make the argument that a minimum volume target of 50, or even more, operations would be optimal,” the researchers noted. “Developing more very high-volume surgeons experienced in mitral valve repair would likely be particularly beneficial for patients with complex but repairable mitral valve disease, and for asymptomatic patients whose repair feasibility would optimally approach 100%.”
Dr. David Adams is the national coprincipal investigator of the Core Valve United States Pivotal Trial, supported by Medtronic. Dr. Chikwe received speaker honoraria from Edwards Lifesciences. The other coauthors had no disclosures to report.
CHICAGO – A total annual surgeon volume of fewer than 25 operations was associated with increased 1-year mortality and reoperation rates, according to a study presented at the 2017 American Association for Thoracic Surgery Centennial.
Improvements in repair rates, survival, and freedom from reoperation increased with increasing surgeon case volumes, Joanna Chikwe, MD, and her colleagues at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, stated.
The researchers compared repair rates, long-term survival, and risk of postrepair reoperation in patients with degenerative disease according to total annual surgeon volume, which was defined as any mitral valve operation for any cause during the study period. The study was simultaneously published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology (2017 May 16;69[19]:2397-406).
Mitral valve repair is the preferred treatment, compared with valve replacement, for the treatment of severe mitral valve regurgitation in patients who have degenerative valve disease with mitral valve prolapse, and both U.S. and European guidelines strongly recommend valve repair whenever possible, according to Dr. Chikwe and her colleagues.
But, “mitral valve replacement unfortunately remains relatively common in patients with degenerative valve disease,” they stated.
A total of 313 surgeons from 41 institutions met the study eligibility criteria, according to the researchers. They performed a median of 10 mitral valve operations per year (range, 1-230). The median annual institutional mitral valve volume was 59 mitral valve operations, ranging from a minimum of 6 to a maximum of 310 operations. Repair rates for primary mitral valve operations for any cause at all 41 institutions varied from 15% to 83%, and repair rates for degenerative mitral valve operations varied from 25% to 100%.
In the study cohort, surgeons with a total annual volume of less than 25 operations carried out 25% of procedures.
After multivariable adjustment, total annual surgeon volume was independently associated with the probability of mitral valve repair. The chance of repair increased significantly by 13% for every 10-case increment in total annual surgeon volume (P less than .001).
In addition, compared with patients operated on by surgeons with a total annual surgeon volume of 10 or fewer operations, patients operated on by surgeons with a total annual surgeon volume of greater than 50 operations were more than three times as likely to undergo mitral valve repair rather than replacement.
A total annual surgeon volume of less than 25 operations was associated with lower mitral valve repair rates and with increased 1-year mortality and mitral valve reoperation rates. Improvements in repair rates, survival, and freedom from reoperation increased with increasing surgeon case volumes.
After 1 year of repair or replacement, the actuarial survival of patients with degenerative mitral valve disease who were operated on by surgeons performing greater than 50 operations per year was 97.8%, compared with 94.1% for patients operated on by surgeons performing less than or equal to 10 operations a year.
Compared with replacement, mitral repair was significantly associated with better survival, but total annual surgeon volume still remained a significant independent predictor (P less than .001). In addition, for those patients who underwent mitral valve repair, total annual surgeon volume was a significant independent predictor of late death.
The results are important, the investigators noted, given that the median number of mitral valve operations performed annually by individual surgeons in the United States was five, according to an analysis of the Society of Thoracic Surgeons database – and that, in New York state, most surgeons actually performed less than one mitral operation per month.
There were significant differences seen in the patient characteristics across surgeons’ case volume groups. The prevalence of congestive heart failure was significantly higher in patients operated on by surgeons with lower volumes, and the proportion of patients undergoing urgent surgery was also significantly higher for lower-volume surgeons.
“This leads to a double jeopardy, where sicker patients are adversely affected by the lower repair rates and poorer outcomes seen with lower-volume surgeons, and it underscores the need to refer the highest-risk patients to high-volume surgeons,” said Dr. Chickwe and her colleagues.
However, “even among high-volume surgeons, there was an observed variability of degenerative disease repair rates, ranging from 19% to nearly 100%,” they added. “This finding reflects that surgeon volume is not the only factor for better outcomes, and it emphasizes the need for more transparency of surgeon-related factors and outcomes of degenerative mitral valve surgery for patients and referring cardiologists.
“Considering that there was an incremental improvement in survival and probability of repair with increasing volume over 25 operations, one could make the argument that a minimum volume target of 50, or even more, operations would be optimal,” the researchers noted. “Developing more very high-volume surgeons experienced in mitral valve repair would likely be particularly beneficial for patients with complex but repairable mitral valve disease, and for asymptomatic patients whose repair feasibility would optimally approach 100%.”
Dr. David Adams is the national coprincipal investigator of the Core Valve United States Pivotal Trial, supported by Medtronic. Dr. Chikwe received speaker honoraria from Edwards Lifesciences. The other coauthors had no disclosures to report.
CHICAGO – A total annual surgeon volume of fewer than 25 operations was associated with increased 1-year mortality and reoperation rates, according to a study presented at the 2017 American Association for Thoracic Surgery Centennial.
Improvements in repair rates, survival, and freedom from reoperation increased with increasing surgeon case volumes, Joanna Chikwe, MD, and her colleagues at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, stated.
The researchers compared repair rates, long-term survival, and risk of postrepair reoperation in patients with degenerative disease according to total annual surgeon volume, which was defined as any mitral valve operation for any cause during the study period. The study was simultaneously published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology (2017 May 16;69[19]:2397-406).
Mitral valve repair is the preferred treatment, compared with valve replacement, for the treatment of severe mitral valve regurgitation in patients who have degenerative valve disease with mitral valve prolapse, and both U.S. and European guidelines strongly recommend valve repair whenever possible, according to Dr. Chikwe and her colleagues.
But, “mitral valve replacement unfortunately remains relatively common in patients with degenerative valve disease,” they stated.
A total of 313 surgeons from 41 institutions met the study eligibility criteria, according to the researchers. They performed a median of 10 mitral valve operations per year (range, 1-230). The median annual institutional mitral valve volume was 59 mitral valve operations, ranging from a minimum of 6 to a maximum of 310 operations. Repair rates for primary mitral valve operations for any cause at all 41 institutions varied from 15% to 83%, and repair rates for degenerative mitral valve operations varied from 25% to 100%.
In the study cohort, surgeons with a total annual volume of less than 25 operations carried out 25% of procedures.
After multivariable adjustment, total annual surgeon volume was independently associated with the probability of mitral valve repair. The chance of repair increased significantly by 13% for every 10-case increment in total annual surgeon volume (P less than .001).
In addition, compared with patients operated on by surgeons with a total annual surgeon volume of 10 or fewer operations, patients operated on by surgeons with a total annual surgeon volume of greater than 50 operations were more than three times as likely to undergo mitral valve repair rather than replacement.
A total annual surgeon volume of less than 25 operations was associated with lower mitral valve repair rates and with increased 1-year mortality and mitral valve reoperation rates. Improvements in repair rates, survival, and freedom from reoperation increased with increasing surgeon case volumes.
After 1 year of repair or replacement, the actuarial survival of patients with degenerative mitral valve disease who were operated on by surgeons performing greater than 50 operations per year was 97.8%, compared with 94.1% for patients operated on by surgeons performing less than or equal to 10 operations a year.
Compared with replacement, mitral repair was significantly associated with better survival, but total annual surgeon volume still remained a significant independent predictor (P less than .001). In addition, for those patients who underwent mitral valve repair, total annual surgeon volume was a significant independent predictor of late death.
The results are important, the investigators noted, given that the median number of mitral valve operations performed annually by individual surgeons in the United States was five, according to an analysis of the Society of Thoracic Surgeons database – and that, in New York state, most surgeons actually performed less than one mitral operation per month.
There were significant differences seen in the patient characteristics across surgeons’ case volume groups. The prevalence of congestive heart failure was significantly higher in patients operated on by surgeons with lower volumes, and the proportion of patients undergoing urgent surgery was also significantly higher for lower-volume surgeons.
“This leads to a double jeopardy, where sicker patients are adversely affected by the lower repair rates and poorer outcomes seen with lower-volume surgeons, and it underscores the need to refer the highest-risk patients to high-volume surgeons,” said Dr. Chickwe and her colleagues.
However, “even among high-volume surgeons, there was an observed variability of degenerative disease repair rates, ranging from 19% to nearly 100%,” they added. “This finding reflects that surgeon volume is not the only factor for better outcomes, and it emphasizes the need for more transparency of surgeon-related factors and outcomes of degenerative mitral valve surgery for patients and referring cardiologists.
“Considering that there was an incremental improvement in survival and probability of repair with increasing volume over 25 operations, one could make the argument that a minimum volume target of 50, or even more, operations would be optimal,” the researchers noted. “Developing more very high-volume surgeons experienced in mitral valve repair would likely be particularly beneficial for patients with complex but repairable mitral valve disease, and for asymptomatic patients whose repair feasibility would optimally approach 100%.”
Dr. David Adams is the national coprincipal investigator of the Core Valve United States Pivotal Trial, supported by Medtronic. Dr. Chikwe received speaker honoraria from Edwards Lifesciences. The other coauthors had no disclosures to report.
FROM THE AATS ANNUAL MEETING AND THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN COLLEGE OF CARDIOLOGY
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Mitral valve reoperation rates steadily decreased with increasing surgeon volume until 25 operations per year, coupled to an improved 1-year survival for every 10 additional operations more than that.
Data source: A mandatory New York state database containing 5,475 patients who underwent mitral valve repair between 2002 and 2013.
Disclosures: Dr. David Adams is the national coprincipal investigator of the Core Valve United States Pivotal Trial, supported by Medtronic. Dr. Joanna Chikwe received speaker honoraria from Edwards Lifesciences. The other coauthors had no disclosures to report.
Points/Counterpoint: Should surgeons operate on functional tricuspid regurgitation?
Yes, functional TR is worth repairing (David H. Adams, MD)
Functional tricuspid regurgitation is a common finding in patients undergoing degenerative mitral valve repair. Severe tricuspid regurgitation is unusual, and clearly there is little debate on the merits of concomitant tricuspid repair for these patients. Moderate tricuspid regurgitation is identified preoperatively in around 15% of patients undergoing degenerative mitral repair (J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2011;142:608-13), and concomitant tricuspid repair in these patients is certainly supported by both the American and European guidelines (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2017. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2017.03.011; Eur Heart J. 2012;33:2451-96).
What experience and evidence has led us to a more aggressive approach? One of the most important influences on our early adoption of tricuspid repair at the time of mitral surgery was linked to observations that tricuspid regurgitation (TR) sometimes progressed after isolated mitral valve repair (MVR), with some patients developing moderate or worse insufficiency. Certainly, the impact of significant tricuspid regurgitation on the quality and length of patients’ lives and the challenges of reoperation for isolated tricuspid regurgitation are well known to all surgeons.
Consequently, the importance of treating significant annular dilatation, even without significant tricuspid regurgitation, is supported by the guidelines. Our own experience with an aggressive approach to functional tricuspid regurgitation (FTR) at the time of mitral surgery put an exclamation point on this (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2015;65:1931-8). We found that concomitant tricuspid repair in patients who were worse off before surgery with more TR and higher rates of atrial fibrillation and right-sided dysfunction, actually did better during 5 years of follow-up than the isolated mitral repair patients who started with completely normal tricuspid valve anatomy and ventricular function.
Benign neglect is always an option (J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2017;154:125-6), but we agree with Roberto Dion, MD – despite our friends’ opinions in Toronto and Rochester – we would much prefer to have minimal TR and a normal sized tricuspid valve after MVR. Ask yourself: would you rather have no TR and a normal sized tricuspid valve after you undergo a mitral operation, or a very dilated annulus and perhaps moderate FTR? I am pretty sure I know the answer, but if you are not sure, read our paper.
Dr. Adams is cardiac surgeon-in-chief, Mount Sinai Health System, and Marie-Josée and Henry R. Kravis Professor and Chairman, department of cardiovascular surgery, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and The Mount Sinai Hospital, and president-elect of the American Association for Thoracic Surgery. He disclosed he is the national co-principal investigator for the Medtronic NeoChord trial, and receives royalties from Medtronic and Edwards Lifesciences. The Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai receives royalty payments from Edwards Lifesciences and Medtronic for intellectual property related to Dr. Adams’ involvement in the development of 2 mitral valve repair rings and 1 tricuspid valve repair ring.
No, a patient with FTR does not necessarily need repair (Tirone David, MD)
In our clinic, a patient who undergoes MVR and has FTR generally goes home without an annuloplasty. We now have 12 years or more of follow-up in these patients, and they do not develop TR if their MVR is competent. We have reported that preoperative TR in patients who had MVR is associated with mitral valve disease and often improves after the operation (J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2017;154:110-22). New postoperative TR is uncommon.
Ninety percent of my mitral valve repair patients today have no symptoms. Of those patients, a small proportion have moderate TR.
Dr. David is a professor of surgery at Toronto General Hospital. He reported no financial relationships.
Yes, but repair of FTR requires caution (Gilles Dreyfus, MD)
The controversy surrounding the legitimacy of concomitant tricuspid annuloplasty for functional TR during MVR begs for a clinical trial, but before we can conduct a clinical trial, we must define the primary and secondary endpoints. We’ve seen recent prospective, randomized trials that have reported faulty conclusions because the primary endpoints were wrong.
We need a strong debate to agree on those endpoints. Mortality as an endpoint will probably take a very long time to arrive at.
We’re mixing up many different factors. We’re mixing up TR grading, and we know that grading is unreliable. We have all seen patients with full-fledged TR, and after we put them on Lasix (furosemide, Sanofi), 3 days later they have mild TR. So the same patient with no treatment becomes let’s say a “Dreyfus indication,” and then suddenly in 3 days the patient doesn’t need surgery. At any further stage of his life this patient can experience severe TR again; tricuspid annuloplasty will prevent that from happening.
Moderate TR according to the common definition does not exist. If you look at the reports in echocardiography and if you ask any cardiologist, everything between no TR and severe TR is considered moderate. We have proposed a new staging system for evaluating FTR that uses three factors: TR severity; annular dilatation; and extent of tethering, or mode of leaflet coaptation (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2015;65:2331-6).
Dr. Dreyfus is director of the medical and surgical team at the Cardiothoracic Centre of Monaco in Monte Carlo and professor of cardiothoracic surgery at Paris V University and the Imperial College of London. He disclosed receiving speaker fees from Edwards Lifesciences, LivaNova, and Medtronic.
No, few FTR patients at risk after MVR (Hartzell Schaff, MD)
Echocardiography can provide a great deal of information about when concomitant repair for TR is indicated during MVR. We’ve found that if the patient has no right-sided signs, has normal right atrial pressure, and has mild or mild/moderate TR at the time of repair to the journey mitral valve, the chance of him returning for a tricuspid valve procedure is near zero.
A few patients do return after MVR. They develop atrial fibrillation and may need a pacemaker, but we see very few patients return for tricuspid surgery.
It’s fair to say we cannot demonstrate any benefit of correcting functional mitral regurgitation. Why would we think there’s a benefit of correcting FTR? We can say we’re going to look at grade of TR down the road, or we could look at some other endpoint, but think about it this way: If we cannot prove that correcting functional mitral regurgitation is helpful, why is correcting FTR going to help?
Dr. Schaff is a cardiothoracic surgeon at Mayo Clinic Foundation, Rochester, Minn. He reported no financial relationships.
Yes, functional TR is worth repairing (David H. Adams, MD)
Functional tricuspid regurgitation is a common finding in patients undergoing degenerative mitral valve repair. Severe tricuspid regurgitation is unusual, and clearly there is little debate on the merits of concomitant tricuspid repair for these patients. Moderate tricuspid regurgitation is identified preoperatively in around 15% of patients undergoing degenerative mitral repair (J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2011;142:608-13), and concomitant tricuspid repair in these patients is certainly supported by both the American and European guidelines (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2017. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2017.03.011; Eur Heart J. 2012;33:2451-96).
What experience and evidence has led us to a more aggressive approach? One of the most important influences on our early adoption of tricuspid repair at the time of mitral surgery was linked to observations that tricuspid regurgitation (TR) sometimes progressed after isolated mitral valve repair (MVR), with some patients developing moderate or worse insufficiency. Certainly, the impact of significant tricuspid regurgitation on the quality and length of patients’ lives and the challenges of reoperation for isolated tricuspid regurgitation are well known to all surgeons.
Consequently, the importance of treating significant annular dilatation, even without significant tricuspid regurgitation, is supported by the guidelines. Our own experience with an aggressive approach to functional tricuspid regurgitation (FTR) at the time of mitral surgery put an exclamation point on this (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2015;65:1931-8). We found that concomitant tricuspid repair in patients who were worse off before surgery with more TR and higher rates of atrial fibrillation and right-sided dysfunction, actually did better during 5 years of follow-up than the isolated mitral repair patients who started with completely normal tricuspid valve anatomy and ventricular function.
Benign neglect is always an option (J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2017;154:125-6), but we agree with Roberto Dion, MD – despite our friends’ opinions in Toronto and Rochester – we would much prefer to have minimal TR and a normal sized tricuspid valve after MVR. Ask yourself: would you rather have no TR and a normal sized tricuspid valve after you undergo a mitral operation, or a very dilated annulus and perhaps moderate FTR? I am pretty sure I know the answer, but if you are not sure, read our paper.
Dr. Adams is cardiac surgeon-in-chief, Mount Sinai Health System, and Marie-Josée and Henry R. Kravis Professor and Chairman, department of cardiovascular surgery, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and The Mount Sinai Hospital, and president-elect of the American Association for Thoracic Surgery. He disclosed he is the national co-principal investigator for the Medtronic NeoChord trial, and receives royalties from Medtronic and Edwards Lifesciences. The Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai receives royalty payments from Edwards Lifesciences and Medtronic for intellectual property related to Dr. Adams’ involvement in the development of 2 mitral valve repair rings and 1 tricuspid valve repair ring.
No, a patient with FTR does not necessarily need repair (Tirone David, MD)
In our clinic, a patient who undergoes MVR and has FTR generally goes home without an annuloplasty. We now have 12 years or more of follow-up in these patients, and they do not develop TR if their MVR is competent. We have reported that preoperative TR in patients who had MVR is associated with mitral valve disease and often improves after the operation (J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2017;154:110-22). New postoperative TR is uncommon.
Ninety percent of my mitral valve repair patients today have no symptoms. Of those patients, a small proportion have moderate TR.
Dr. David is a professor of surgery at Toronto General Hospital. He reported no financial relationships.
Yes, but repair of FTR requires caution (Gilles Dreyfus, MD)
The controversy surrounding the legitimacy of concomitant tricuspid annuloplasty for functional TR during MVR begs for a clinical trial, but before we can conduct a clinical trial, we must define the primary and secondary endpoints. We’ve seen recent prospective, randomized trials that have reported faulty conclusions because the primary endpoints were wrong.
We need a strong debate to agree on those endpoints. Mortality as an endpoint will probably take a very long time to arrive at.
We’re mixing up many different factors. We’re mixing up TR grading, and we know that grading is unreliable. We have all seen patients with full-fledged TR, and after we put them on Lasix (furosemide, Sanofi), 3 days later they have mild TR. So the same patient with no treatment becomes let’s say a “Dreyfus indication,” and then suddenly in 3 days the patient doesn’t need surgery. At any further stage of his life this patient can experience severe TR again; tricuspid annuloplasty will prevent that from happening.
Moderate TR according to the common definition does not exist. If you look at the reports in echocardiography and if you ask any cardiologist, everything between no TR and severe TR is considered moderate. We have proposed a new staging system for evaluating FTR that uses three factors: TR severity; annular dilatation; and extent of tethering, or mode of leaflet coaptation (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2015;65:2331-6).
Dr. Dreyfus is director of the medical and surgical team at the Cardiothoracic Centre of Monaco in Monte Carlo and professor of cardiothoracic surgery at Paris V University and the Imperial College of London. He disclosed receiving speaker fees from Edwards Lifesciences, LivaNova, and Medtronic.
No, few FTR patients at risk after MVR (Hartzell Schaff, MD)
Echocardiography can provide a great deal of information about when concomitant repair for TR is indicated during MVR. We’ve found that if the patient has no right-sided signs, has normal right atrial pressure, and has mild or mild/moderate TR at the time of repair to the journey mitral valve, the chance of him returning for a tricuspid valve procedure is near zero.
A few patients do return after MVR. They develop atrial fibrillation and may need a pacemaker, but we see very few patients return for tricuspid surgery.
It’s fair to say we cannot demonstrate any benefit of correcting functional mitral regurgitation. Why would we think there’s a benefit of correcting FTR? We can say we’re going to look at grade of TR down the road, or we could look at some other endpoint, but think about it this way: If we cannot prove that correcting functional mitral regurgitation is helpful, why is correcting FTR going to help?
Dr. Schaff is a cardiothoracic surgeon at Mayo Clinic Foundation, Rochester, Minn. He reported no financial relationships.
Yes, functional TR is worth repairing (David H. Adams, MD)
Functional tricuspid regurgitation is a common finding in patients undergoing degenerative mitral valve repair. Severe tricuspid regurgitation is unusual, and clearly there is little debate on the merits of concomitant tricuspid repair for these patients. Moderate tricuspid regurgitation is identified preoperatively in around 15% of patients undergoing degenerative mitral repair (J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2011;142:608-13), and concomitant tricuspid repair in these patients is certainly supported by both the American and European guidelines (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2017. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2017.03.011; Eur Heart J. 2012;33:2451-96).
What experience and evidence has led us to a more aggressive approach? One of the most important influences on our early adoption of tricuspid repair at the time of mitral surgery was linked to observations that tricuspid regurgitation (TR) sometimes progressed after isolated mitral valve repair (MVR), with some patients developing moderate or worse insufficiency. Certainly, the impact of significant tricuspid regurgitation on the quality and length of patients’ lives and the challenges of reoperation for isolated tricuspid regurgitation are well known to all surgeons.
Consequently, the importance of treating significant annular dilatation, even without significant tricuspid regurgitation, is supported by the guidelines. Our own experience with an aggressive approach to functional tricuspid regurgitation (FTR) at the time of mitral surgery put an exclamation point on this (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2015;65:1931-8). We found that concomitant tricuspid repair in patients who were worse off before surgery with more TR and higher rates of atrial fibrillation and right-sided dysfunction, actually did better during 5 years of follow-up than the isolated mitral repair patients who started with completely normal tricuspid valve anatomy and ventricular function.
Benign neglect is always an option (J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2017;154:125-6), but we agree with Roberto Dion, MD – despite our friends’ opinions in Toronto and Rochester – we would much prefer to have minimal TR and a normal sized tricuspid valve after MVR. Ask yourself: would you rather have no TR and a normal sized tricuspid valve after you undergo a mitral operation, or a very dilated annulus and perhaps moderate FTR? I am pretty sure I know the answer, but if you are not sure, read our paper.
Dr. Adams is cardiac surgeon-in-chief, Mount Sinai Health System, and Marie-Josée and Henry R. Kravis Professor and Chairman, department of cardiovascular surgery, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and The Mount Sinai Hospital, and president-elect of the American Association for Thoracic Surgery. He disclosed he is the national co-principal investigator for the Medtronic NeoChord trial, and receives royalties from Medtronic and Edwards Lifesciences. The Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai receives royalty payments from Edwards Lifesciences and Medtronic for intellectual property related to Dr. Adams’ involvement in the development of 2 mitral valve repair rings and 1 tricuspid valve repair ring.
No, a patient with FTR does not necessarily need repair (Tirone David, MD)
In our clinic, a patient who undergoes MVR and has FTR generally goes home without an annuloplasty. We now have 12 years or more of follow-up in these patients, and they do not develop TR if their MVR is competent. We have reported that preoperative TR in patients who had MVR is associated with mitral valve disease and often improves after the operation (J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2017;154:110-22). New postoperative TR is uncommon.
Ninety percent of my mitral valve repair patients today have no symptoms. Of those patients, a small proportion have moderate TR.
Dr. David is a professor of surgery at Toronto General Hospital. He reported no financial relationships.
Yes, but repair of FTR requires caution (Gilles Dreyfus, MD)
The controversy surrounding the legitimacy of concomitant tricuspid annuloplasty for functional TR during MVR begs for a clinical trial, but before we can conduct a clinical trial, we must define the primary and secondary endpoints. We’ve seen recent prospective, randomized trials that have reported faulty conclusions because the primary endpoints were wrong.
We need a strong debate to agree on those endpoints. Mortality as an endpoint will probably take a very long time to arrive at.
We’re mixing up many different factors. We’re mixing up TR grading, and we know that grading is unreliable. We have all seen patients with full-fledged TR, and after we put them on Lasix (furosemide, Sanofi), 3 days later they have mild TR. So the same patient with no treatment becomes let’s say a “Dreyfus indication,” and then suddenly in 3 days the patient doesn’t need surgery. At any further stage of his life this patient can experience severe TR again; tricuspid annuloplasty will prevent that from happening.
Moderate TR according to the common definition does not exist. If you look at the reports in echocardiography and if you ask any cardiologist, everything between no TR and severe TR is considered moderate. We have proposed a new staging system for evaluating FTR that uses three factors: TR severity; annular dilatation; and extent of tethering, or mode of leaflet coaptation (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2015;65:2331-6).
Dr. Dreyfus is director of the medical and surgical team at the Cardiothoracic Centre of Monaco in Monte Carlo and professor of cardiothoracic surgery at Paris V University and the Imperial College of London. He disclosed receiving speaker fees from Edwards Lifesciences, LivaNova, and Medtronic.
No, few FTR patients at risk after MVR (Hartzell Schaff, MD)
Echocardiography can provide a great deal of information about when concomitant repair for TR is indicated during MVR. We’ve found that if the patient has no right-sided signs, has normal right atrial pressure, and has mild or mild/moderate TR at the time of repair to the journey mitral valve, the chance of him returning for a tricuspid valve procedure is near zero.
A few patients do return after MVR. They develop atrial fibrillation and may need a pacemaker, but we see very few patients return for tricuspid surgery.
It’s fair to say we cannot demonstrate any benefit of correcting functional mitral regurgitation. Why would we think there’s a benefit of correcting FTR? We can say we’re going to look at grade of TR down the road, or we could look at some other endpoint, but think about it this way: If we cannot prove that correcting functional mitral regurgitation is helpful, why is correcting FTR going to help?
Dr. Schaff is a cardiothoracic surgeon at Mayo Clinic Foundation, Rochester, Minn. He reported no financial relationships.
AT THE AATS MITRAL CONCLAVE 2017
Shift to minimally invasive MV surgery picks up
NEW YORK – An analysis of a Society of Thoracic Surgeons database has identified a significant increase in volumes for isolated mitral valve surgery and leaflet prolapse this decade, with a shift toward minimally invasive approaches, according to a study of trends in mitral valve surgery in the United States presented here at the American Association for Thoracic Surgery Mitral Conclave 2017.
James Gammie, MD, of the University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore, reported on the analysis of the STS Adult Cardiac Surgery Database in which more than 90% of the adult cardiac surgery centers in North America participate.
“Degenerative disease remains the most common reason patients are referred for surgery,” Dr. Gammie said, noting that 60.7% of patients with an identified etiology had degenerative leaflet prolapse (etiology was unknown in 31% of the patients in the dataset).
“The operative approach has changed and continues to shift toward a less invasive approach,” Dr. Gammie said. Overall, 74.1% of operations involved sternotomy, but only 67.5% of those in the leaflet prolapse subgroup, with less invasive operations comprising 23% of all operations and 29.1% of those in the leaflet prolapse subgroup. From 2011 to 2016, total mitral surgical volume grew at a rate of 1.1% annually, but the volume for isolated MV operations grew 4.4% annually while leaflet prolapse procedures increased 7.6% annually, Dr. Gammie said.
Dr. Gammie described surgeons’ decision to perform ablation for preoperative AF during MV surgery a “coin toss.” One-third (34%) had AF, but only 51.2% of patients with AF in the total cohort and 54.4% of those in the leaflet prolapse subgroup got ablation. The overall MV repair rate was 65% for the total cohort but 83% for those with leaflet prolapse. For those who had MV replacement, the share of bioprosthetic devices increased steadily through the study period, from around 65% to 75.8%, Dr. Gammie said.
In the leaflet prolapse subgroup, 96.1% had annuloplasty and 29.2% had artificial chords implanted, with an average of two chords per operation. “There’s an increasing use of artificial ePTFE chords,” Dr. Gammie said. He noted the leaflet prolapse subgroup was composed of low-risk healthy patients. The mean ejection fraction (EF) for the cohort was 57%, and 47% of patients had EF of less than 60%. The overwhelming majority of patients (88%) had Class I indications for surgery with the remainder having Class IIa indications.
Dr. Gammie noted a few other emerging trends of MV surgery during the study period. “Patients with functional mitral regurgitation are rarely referred for operation: these patients made up fewer than 5% of patients undergoing mitral valve operations during the study period,” he said.;
With regard to outcomes, Dr. Gammie said, “There remain substantial differences between repair and replacement.” Replacement had almost twice the rate of reoperation for bleeding than repair (4.1% vs. 2.1%) and renal failure (3.4% vs. 1.4%).
“We observed that a substantial number of patients have an unsuccessful attempt at mitral valve repair before undergoing replacement – 16 % of the overall replacement group and 27% of patients having replacement for degenerative leaflet prolapse,” he said. “This does not appear to penalize patients in terms of outcome.”
The rate of permanent pacemaker was also significantly higher in the replacement cohort, 9.8% vs. 3.8% for repair operations, as was operative mortality, 3.7% vs. 1.1%. Said Dr. Gammie.
“This is something to think about as we move to less invasive approaches and overall operative mortality remains over threefold higher for replacement than repair.”
The leaflet prolapse subgroup showed similar disparities between replacement and repair groups. “The increased application of repair when feasible will be of value to improve outcomes, as will referral of patients earlier in the disease process ,” Dr. Gammie said.
“In our own STS database, about one-third of patients who were coded as having AF had no evidence of it, and that’s why in our institution they don’t get treated.” He added, “I’m not that surprised at the low repair rate when the average surgeon in the United States does five mitral repairs a year.”
Dr. Gammie disclosed that he is a consultant to Edwards Lifesciences and has an ownership interest in Harpoon Medical. Dr. Damiano disclosed that he is a speaker for LivaNova and a consultant to and a research grant recipient of Atricure.
NEW YORK – An analysis of a Society of Thoracic Surgeons database has identified a significant increase in volumes for isolated mitral valve surgery and leaflet prolapse this decade, with a shift toward minimally invasive approaches, according to a study of trends in mitral valve surgery in the United States presented here at the American Association for Thoracic Surgery Mitral Conclave 2017.
James Gammie, MD, of the University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore, reported on the analysis of the STS Adult Cardiac Surgery Database in which more than 90% of the adult cardiac surgery centers in North America participate.
“Degenerative disease remains the most common reason patients are referred for surgery,” Dr. Gammie said, noting that 60.7% of patients with an identified etiology had degenerative leaflet prolapse (etiology was unknown in 31% of the patients in the dataset).
“The operative approach has changed and continues to shift toward a less invasive approach,” Dr. Gammie said. Overall, 74.1% of operations involved sternotomy, but only 67.5% of those in the leaflet prolapse subgroup, with less invasive operations comprising 23% of all operations and 29.1% of those in the leaflet prolapse subgroup. From 2011 to 2016, total mitral surgical volume grew at a rate of 1.1% annually, but the volume for isolated MV operations grew 4.4% annually while leaflet prolapse procedures increased 7.6% annually, Dr. Gammie said.
Dr. Gammie described surgeons’ decision to perform ablation for preoperative AF during MV surgery a “coin toss.” One-third (34%) had AF, but only 51.2% of patients with AF in the total cohort and 54.4% of those in the leaflet prolapse subgroup got ablation. The overall MV repair rate was 65% for the total cohort but 83% for those with leaflet prolapse. For those who had MV replacement, the share of bioprosthetic devices increased steadily through the study period, from around 65% to 75.8%, Dr. Gammie said.
In the leaflet prolapse subgroup, 96.1% had annuloplasty and 29.2% had artificial chords implanted, with an average of two chords per operation. “There’s an increasing use of artificial ePTFE chords,” Dr. Gammie said. He noted the leaflet prolapse subgroup was composed of low-risk healthy patients. The mean ejection fraction (EF) for the cohort was 57%, and 47% of patients had EF of less than 60%. The overwhelming majority of patients (88%) had Class I indications for surgery with the remainder having Class IIa indications.
Dr. Gammie noted a few other emerging trends of MV surgery during the study period. “Patients with functional mitral regurgitation are rarely referred for operation: these patients made up fewer than 5% of patients undergoing mitral valve operations during the study period,” he said.;
With regard to outcomes, Dr. Gammie said, “There remain substantial differences between repair and replacement.” Replacement had almost twice the rate of reoperation for bleeding than repair (4.1% vs. 2.1%) and renal failure (3.4% vs. 1.4%).
“We observed that a substantial number of patients have an unsuccessful attempt at mitral valve repair before undergoing replacement – 16 % of the overall replacement group and 27% of patients having replacement for degenerative leaflet prolapse,” he said. “This does not appear to penalize patients in terms of outcome.”
The rate of permanent pacemaker was also significantly higher in the replacement cohort, 9.8% vs. 3.8% for repair operations, as was operative mortality, 3.7% vs. 1.1%. Said Dr. Gammie.
“This is something to think about as we move to less invasive approaches and overall operative mortality remains over threefold higher for replacement than repair.”
The leaflet prolapse subgroup showed similar disparities between replacement and repair groups. “The increased application of repair when feasible will be of value to improve outcomes, as will referral of patients earlier in the disease process ,” Dr. Gammie said.
“In our own STS database, about one-third of patients who were coded as having AF had no evidence of it, and that’s why in our institution they don’t get treated.” He added, “I’m not that surprised at the low repair rate when the average surgeon in the United States does five mitral repairs a year.”
Dr. Gammie disclosed that he is a consultant to Edwards Lifesciences and has an ownership interest in Harpoon Medical. Dr. Damiano disclosed that he is a speaker for LivaNova and a consultant to and a research grant recipient of Atricure.
NEW YORK – An analysis of a Society of Thoracic Surgeons database has identified a significant increase in volumes for isolated mitral valve surgery and leaflet prolapse this decade, with a shift toward minimally invasive approaches, according to a study of trends in mitral valve surgery in the United States presented here at the American Association for Thoracic Surgery Mitral Conclave 2017.
James Gammie, MD, of the University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore, reported on the analysis of the STS Adult Cardiac Surgery Database in which more than 90% of the adult cardiac surgery centers in North America participate.
“Degenerative disease remains the most common reason patients are referred for surgery,” Dr. Gammie said, noting that 60.7% of patients with an identified etiology had degenerative leaflet prolapse (etiology was unknown in 31% of the patients in the dataset).
“The operative approach has changed and continues to shift toward a less invasive approach,” Dr. Gammie said. Overall, 74.1% of operations involved sternotomy, but only 67.5% of those in the leaflet prolapse subgroup, with less invasive operations comprising 23% of all operations and 29.1% of those in the leaflet prolapse subgroup. From 2011 to 2016, total mitral surgical volume grew at a rate of 1.1% annually, but the volume for isolated MV operations grew 4.4% annually while leaflet prolapse procedures increased 7.6% annually, Dr. Gammie said.
Dr. Gammie described surgeons’ decision to perform ablation for preoperative AF during MV surgery a “coin toss.” One-third (34%) had AF, but only 51.2% of patients with AF in the total cohort and 54.4% of those in the leaflet prolapse subgroup got ablation. The overall MV repair rate was 65% for the total cohort but 83% for those with leaflet prolapse. For those who had MV replacement, the share of bioprosthetic devices increased steadily through the study period, from around 65% to 75.8%, Dr. Gammie said.
In the leaflet prolapse subgroup, 96.1% had annuloplasty and 29.2% had artificial chords implanted, with an average of two chords per operation. “There’s an increasing use of artificial ePTFE chords,” Dr. Gammie said. He noted the leaflet prolapse subgroup was composed of low-risk healthy patients. The mean ejection fraction (EF) for the cohort was 57%, and 47% of patients had EF of less than 60%. The overwhelming majority of patients (88%) had Class I indications for surgery with the remainder having Class IIa indications.
Dr. Gammie noted a few other emerging trends of MV surgery during the study period. “Patients with functional mitral regurgitation are rarely referred for operation: these patients made up fewer than 5% of patients undergoing mitral valve operations during the study period,” he said.;
With regard to outcomes, Dr. Gammie said, “There remain substantial differences between repair and replacement.” Replacement had almost twice the rate of reoperation for bleeding than repair (4.1% vs. 2.1%) and renal failure (3.4% vs. 1.4%).
“We observed that a substantial number of patients have an unsuccessful attempt at mitral valve repair before undergoing replacement – 16 % of the overall replacement group and 27% of patients having replacement for degenerative leaflet prolapse,” he said. “This does not appear to penalize patients in terms of outcome.”
The rate of permanent pacemaker was also significantly higher in the replacement cohort, 9.8% vs. 3.8% for repair operations, as was operative mortality, 3.7% vs. 1.1%. Said Dr. Gammie.
“This is something to think about as we move to less invasive approaches and overall operative mortality remains over threefold higher for replacement than repair.”
The leaflet prolapse subgroup showed similar disparities between replacement and repair groups. “The increased application of repair when feasible will be of value to improve outcomes, as will referral of patients earlier in the disease process ,” Dr. Gammie said.
“In our own STS database, about one-third of patients who were coded as having AF had no evidence of it, and that’s why in our institution they don’t get treated.” He added, “I’m not that surprised at the low repair rate when the average surgeon in the United States does five mitral repairs a year.”
Dr. Gammie disclosed that he is a consultant to Edwards Lifesciences and has an ownership interest in Harpoon Medical. Dr. Damiano disclosed that he is a speaker for LivaNova and a consultant to and a research grant recipient of Atricure.
AT THE AATS MITRAL CONCLAVE 2017
Key clinical point: The volume of mitral valve surgery has increased substantially, according to an analysis of the Society for Thoracic Surgery database, and an increasing percentage of procedures are minimally invasive in nature.
Major finding: Sternotomy continues to be the most widely used approach for mitral valve surgery, but less invasive options most recently comprised 23% of the overall group and 29.1% of those with isolated leaflet prolapse.
Data source: Retrospective study of 15,360 isolated mitral valve operations performed from July 2011 to September 2016 in the Society of Thoracic Surgeons database.
Disclosures: Dr. Gammie reported being a consultant to Edwards Lifesciences and having an ownership interest in Harpoon Medical.
Fewer early neurologic complications with TAVR than SAVR
PARIS – Patients with severe aortic stenosis at intermediate operative risk have a significantly lower 30-day risk of stroke and other neurologic complications with transcatheter aortic valve replacement than with surgical replacement, according to new results from the landmark SURTAVI trial.
“This is the first time the stroke rate has been shown to be lower with TAVR than with surgery,” A. Pieter Kappetein, MD, noted in presenting the results at the annual congress of the European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions.
It’s a finding that adds to the momentum for studying TAVR in low-surgical-risk patients, he added.
“As we move toward lower-risk patients it will become even more important to see whether there is a difference in stroke. Suppose the stroke rate in SURTAVI had been a little higher with TAVR than SAVR? It would really make us more cautious about moving toward lower-risk patients. Now that we see that in intermediate-risk patients the stroke rate is actually a little bit lower than with surgery, I think we’ll feel more comfortable moving toward lower-risk patients,” according to Dr. Kappetein, professor of cardiothoracic surgery at Erasmus University Medical Center in Rotterdam.
SURTAVI (Surgical Replacement and Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation) involved randomization of 1,660 patients with severe symptomatic aortic stenosis to TAVR or SAVR. All participants were deemed to be at intermediate operative risk based upon a predicted surgical mortality of 3%-15%. The primary outcome -- a composite of all-cause mortality and disabling stroke at 2 years -- was presented at the 2017 meeting of the American College of Cardiology and simultaneously published (N Engl J Med. 2017 Apr 6;376(14):1321-1331). The rate was 12.6% with TAVR using the self-expanding CoreValve or Evolut R bioprosthesis and noninferior at 14% with SAVR.
Dr. Kappetein presented a prespecified secondary analysis of the 30-day rate of all neurologic complications, including nondisabling strokes and encephalopathy. He and the other SURTAVI organizers felt this was an important outcome because these early neurologic events have a major impact upon quality of life, including whether a patient will be discharged home or to a rehabilitation clinic or skilled nursing facility following aortic valve replacement.
The 30-day incidence of all stroke was 3.3% in the TAVR patients, significantly lower than the 5.4% rate in the SAVR group. By the 2-year mark, however, the difference was no longer statistically significant, with a rate of 6.3% in the TAVR group compared with 8.0% with SAVR.
Ninety-five percent of the early strokes were ischemic.
The 30-day incidence of disabling stroke was 1.2% with TAVR and 2.4% with SAVR, a difference that was not significant (P=0.057). The 2-year rate was 2.4% in the TAVR arm and 4.5% with SAVR, again not significantly different.
Half of the strokes in the TAVR group had a modified Rankin score of 0-1 at 30 days, meaning no or only minimal signs of stroke. In contrast, most of the strokes in the SAVR group were disabling, with a modified Rankin score of 2-6.
Only 36% of patients who had an early stroke were discharged home, compared with 87% of patients without a stroke. Not surprisingly, quality of life as assessed using the SF-36 physical summary was significantly worse in the early-stroke group. However, with or without stroke, TAVR patients recovered quality of life faster than SAVR patients.
He noted that the timing of the early strokes differed between the two groups. The great majority of both disabling and nondisabling strokes in the TAVR patients were periprocedural, occurring on the day of TAVR or the next day. Strokes in the SAVR group occurred then as well, but also on days 2-6.
One reason why SURTAVI is the first study to show a lower stroke risk with TAVR is that it was the first TAVR-versus-SAVR study to feature comprehensive neurologic testing pre- and post-procedure, along with evaluation of all suspected events by a neurologist or stroke specialist, according to Dr. Kappetein.
“As surgeons we all have said the stroke rate after SAVR is 1%-1.5%, but only when the patient wasn’t waving to us the next morning would we say, ‘Oh, that patient may have a stroke.’ Then we would call a neurologist. So there were many more subtle strokes that we never actually detected. If you do a proper examination of the patient before and after the procedure you’ll find many more strokes,” he said.
He and his coinvestigators systematically searched in vain for predictors of increased stroke risk among the TAVR and SAVR patients.
“Actually, the stroke risk is present for every patient we treat with TAVR or SAVR,” the surgeon continued.
However, discussant Adnan Kastrati, MD, chief physician at the German Heart Center in Munich, thought he spied in the SURTAVI data a potential opportunity to reduce early strokes in SAVR patients. He noted that new-onset atrial fibrillation is consistently more common in SAVR than TAVR patients, and that many of the strokes in the SAVR group occurred on days 2-6. When do heart surgeons typically start oral anticoagulation in their patients with postsurgical atrial fibrillation? he asked.
Not until after 48 hours, Dr. Kappetein replied.
“Those strokes on days 4, 5, and 6 might have to do with atrial fibrillation, and we may need to be more aggressive as surgeons in anticoagulating patients with atrial fibrillation after surgery,” he said.
Dr. Kappetein reported receiving research grant support from Medtronic, sponsor of SURTAVI.
This article was updated July 28, 2107.
PARIS – Patients with severe aortic stenosis at intermediate operative risk have a significantly lower 30-day risk of stroke and other neurologic complications with transcatheter aortic valve replacement than with surgical replacement, according to new results from the landmark SURTAVI trial.
“This is the first time the stroke rate has been shown to be lower with TAVR than with surgery,” A. Pieter Kappetein, MD, noted in presenting the results at the annual congress of the European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions.
It’s a finding that adds to the momentum for studying TAVR in low-surgical-risk patients, he added.
“As we move toward lower-risk patients it will become even more important to see whether there is a difference in stroke. Suppose the stroke rate in SURTAVI had been a little higher with TAVR than SAVR? It would really make us more cautious about moving toward lower-risk patients. Now that we see that in intermediate-risk patients the stroke rate is actually a little bit lower than with surgery, I think we’ll feel more comfortable moving toward lower-risk patients,” according to Dr. Kappetein, professor of cardiothoracic surgery at Erasmus University Medical Center in Rotterdam.
SURTAVI (Surgical Replacement and Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation) involved randomization of 1,660 patients with severe symptomatic aortic stenosis to TAVR or SAVR. All participants were deemed to be at intermediate operative risk based upon a predicted surgical mortality of 3%-15%. The primary outcome -- a composite of all-cause mortality and disabling stroke at 2 years -- was presented at the 2017 meeting of the American College of Cardiology and simultaneously published (N Engl J Med. 2017 Apr 6;376(14):1321-1331). The rate was 12.6% with TAVR using the self-expanding CoreValve or Evolut R bioprosthesis and noninferior at 14% with SAVR.
Dr. Kappetein presented a prespecified secondary analysis of the 30-day rate of all neurologic complications, including nondisabling strokes and encephalopathy. He and the other SURTAVI organizers felt this was an important outcome because these early neurologic events have a major impact upon quality of life, including whether a patient will be discharged home or to a rehabilitation clinic or skilled nursing facility following aortic valve replacement.
The 30-day incidence of all stroke was 3.3% in the TAVR patients, significantly lower than the 5.4% rate in the SAVR group. By the 2-year mark, however, the difference was no longer statistically significant, with a rate of 6.3% in the TAVR group compared with 8.0% with SAVR.
Ninety-five percent of the early strokes were ischemic.
The 30-day incidence of disabling stroke was 1.2% with TAVR and 2.4% with SAVR, a difference that was not significant (P=0.057). The 2-year rate was 2.4% in the TAVR arm and 4.5% with SAVR, again not significantly different.
Half of the strokes in the TAVR group had a modified Rankin score of 0-1 at 30 days, meaning no or only minimal signs of stroke. In contrast, most of the strokes in the SAVR group were disabling, with a modified Rankin score of 2-6.
Only 36% of patients who had an early stroke were discharged home, compared with 87% of patients without a stroke. Not surprisingly, quality of life as assessed using the SF-36 physical summary was significantly worse in the early-stroke group. However, with or without stroke, TAVR patients recovered quality of life faster than SAVR patients.
He noted that the timing of the early strokes differed between the two groups. The great majority of both disabling and nondisabling strokes in the TAVR patients were periprocedural, occurring on the day of TAVR or the next day. Strokes in the SAVR group occurred then as well, but also on days 2-6.
One reason why SURTAVI is the first study to show a lower stroke risk with TAVR is that it was the first TAVR-versus-SAVR study to feature comprehensive neurologic testing pre- and post-procedure, along with evaluation of all suspected events by a neurologist or stroke specialist, according to Dr. Kappetein.
“As surgeons we all have said the stroke rate after SAVR is 1%-1.5%, but only when the patient wasn’t waving to us the next morning would we say, ‘Oh, that patient may have a stroke.’ Then we would call a neurologist. So there were many more subtle strokes that we never actually detected. If you do a proper examination of the patient before and after the procedure you’ll find many more strokes,” he said.
He and his coinvestigators systematically searched in vain for predictors of increased stroke risk among the TAVR and SAVR patients.
“Actually, the stroke risk is present for every patient we treat with TAVR or SAVR,” the surgeon continued.
However, discussant Adnan Kastrati, MD, chief physician at the German Heart Center in Munich, thought he spied in the SURTAVI data a potential opportunity to reduce early strokes in SAVR patients. He noted that new-onset atrial fibrillation is consistently more common in SAVR than TAVR patients, and that many of the strokes in the SAVR group occurred on days 2-6. When do heart surgeons typically start oral anticoagulation in their patients with postsurgical atrial fibrillation? he asked.
Not until after 48 hours, Dr. Kappetein replied.
“Those strokes on days 4, 5, and 6 might have to do with atrial fibrillation, and we may need to be more aggressive as surgeons in anticoagulating patients with atrial fibrillation after surgery,” he said.
Dr. Kappetein reported receiving research grant support from Medtronic, sponsor of SURTAVI.
This article was updated July 28, 2107.
PARIS – Patients with severe aortic stenosis at intermediate operative risk have a significantly lower 30-day risk of stroke and other neurologic complications with transcatheter aortic valve replacement than with surgical replacement, according to new results from the landmark SURTAVI trial.
“This is the first time the stroke rate has been shown to be lower with TAVR than with surgery,” A. Pieter Kappetein, MD, noted in presenting the results at the annual congress of the European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions.
It’s a finding that adds to the momentum for studying TAVR in low-surgical-risk patients, he added.
“As we move toward lower-risk patients it will become even more important to see whether there is a difference in stroke. Suppose the stroke rate in SURTAVI had been a little higher with TAVR than SAVR? It would really make us more cautious about moving toward lower-risk patients. Now that we see that in intermediate-risk patients the stroke rate is actually a little bit lower than with surgery, I think we’ll feel more comfortable moving toward lower-risk patients,” according to Dr. Kappetein, professor of cardiothoracic surgery at Erasmus University Medical Center in Rotterdam.
SURTAVI (Surgical Replacement and Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation) involved randomization of 1,660 patients with severe symptomatic aortic stenosis to TAVR or SAVR. All participants were deemed to be at intermediate operative risk based upon a predicted surgical mortality of 3%-15%. The primary outcome -- a composite of all-cause mortality and disabling stroke at 2 years -- was presented at the 2017 meeting of the American College of Cardiology and simultaneously published (N Engl J Med. 2017 Apr 6;376(14):1321-1331). The rate was 12.6% with TAVR using the self-expanding CoreValve or Evolut R bioprosthesis and noninferior at 14% with SAVR.
Dr. Kappetein presented a prespecified secondary analysis of the 30-day rate of all neurologic complications, including nondisabling strokes and encephalopathy. He and the other SURTAVI organizers felt this was an important outcome because these early neurologic events have a major impact upon quality of life, including whether a patient will be discharged home or to a rehabilitation clinic or skilled nursing facility following aortic valve replacement.
The 30-day incidence of all stroke was 3.3% in the TAVR patients, significantly lower than the 5.4% rate in the SAVR group. By the 2-year mark, however, the difference was no longer statistically significant, with a rate of 6.3% in the TAVR group compared with 8.0% with SAVR.
Ninety-five percent of the early strokes were ischemic.
The 30-day incidence of disabling stroke was 1.2% with TAVR and 2.4% with SAVR, a difference that was not significant (P=0.057). The 2-year rate was 2.4% in the TAVR arm and 4.5% with SAVR, again not significantly different.
Half of the strokes in the TAVR group had a modified Rankin score of 0-1 at 30 days, meaning no or only minimal signs of stroke. In contrast, most of the strokes in the SAVR group were disabling, with a modified Rankin score of 2-6.
Only 36% of patients who had an early stroke were discharged home, compared with 87% of patients without a stroke. Not surprisingly, quality of life as assessed using the SF-36 physical summary was significantly worse in the early-stroke group. However, with or without stroke, TAVR patients recovered quality of life faster than SAVR patients.
He noted that the timing of the early strokes differed between the two groups. The great majority of both disabling and nondisabling strokes in the TAVR patients were periprocedural, occurring on the day of TAVR or the next day. Strokes in the SAVR group occurred then as well, but also on days 2-6.
One reason why SURTAVI is the first study to show a lower stroke risk with TAVR is that it was the first TAVR-versus-SAVR study to feature comprehensive neurologic testing pre- and post-procedure, along with evaluation of all suspected events by a neurologist or stroke specialist, according to Dr. Kappetein.
“As surgeons we all have said the stroke rate after SAVR is 1%-1.5%, but only when the patient wasn’t waving to us the next morning would we say, ‘Oh, that patient may have a stroke.’ Then we would call a neurologist. So there were many more subtle strokes that we never actually detected. If you do a proper examination of the patient before and after the procedure you’ll find many more strokes,” he said.
He and his coinvestigators systematically searched in vain for predictors of increased stroke risk among the TAVR and SAVR patients.
“Actually, the stroke risk is present for every patient we treat with TAVR or SAVR,” the surgeon continued.
However, discussant Adnan Kastrati, MD, chief physician at the German Heart Center in Munich, thought he spied in the SURTAVI data a potential opportunity to reduce early strokes in SAVR patients. He noted that new-onset atrial fibrillation is consistently more common in SAVR than TAVR patients, and that many of the strokes in the SAVR group occurred on days 2-6. When do heart surgeons typically start oral anticoagulation in their patients with postsurgical atrial fibrillation? he asked.
Not until after 48 hours, Dr. Kappetein replied.
“Those strokes on days 4, 5, and 6 might have to do with atrial fibrillation, and we may need to be more aggressive as surgeons in anticoagulating patients with atrial fibrillation after surgery,” he said.
Dr. Kappetein reported receiving research grant support from Medtronic, sponsor of SURTAVI.
This article was updated July 28, 2107.
AT EUROPCR
Key clinical point:
Major finding: The combined incidence of disabling and nondisabling stroke within 30 days of TAVR was 3.3%, significantly better than the 5.4% rate in patients who underwent SAVR.
Data source: SURTAVI was a multicenter trial which included 1,660 patients with severe aortic stenosis who were at intermediate operative risk and were randomized to TAVR or SAVR.
Disclosures: The study presenter reported receiving research grant support from Medtronic, sponsor of the SURTAVI trial.
In 8 years, TMVR means more procedures
NEW YORK – Since the commercialization of transcatheter mitral valve repair, the share of these procedures among all mitral operations has grown exponentially and has also contributed to an increase in the number of overall mitral procedures, including surgical repair, according to an analysis of a national German database reported at the American Association for Thoracic Surgery Mitral Conclave here.
Transcatheter mitral valve repair (TMVR) using the MitraClip device (Abbott Vascular) was first commercialized in Germany in 2008, and in the years since the share of TMVR procedures among all mitral operations increased from 0.3% to 18.1% in 2015 throughout Germany, said Lenard Conradi, MD, surgical director of minimally-invasive and transcatheter heart valve procedures at the University Heart Center Hamburg.
The goal of the study was to gain insights into how cardiothoracic surgeons in Germany and at Dr. Conradi’s center in particular were approaching TMVR and what types of patients were having the procedure, Dr. Conradi said.
“While the EuroSCORE I of patients we operated on didn’t change at all between these two time frames, there were subtle changes in the patients that we operated on,” he said. “Before the commercialization of TMVR, we tended to have a ratio of organic vs. functional MR [mitral regurgitation] of 50-50; after commercialization of TMVR, many of the functional MR patients were allocated to TMVR.”
Dr. Conradi noted the profile of patients who had mitral valve repair also changed once the transcatheter approach became available. “Ischemic disease with coronary artery disease, previous infarction, or previous cardiac surgery – mostly coronary artery bypass grafting – were much less prevalent in this surgery population after TMVR became available,” he said.
The study also found that 30-day mortality declined from 7% to 4% during the study period. “That was probably due to more adequate patient selection because we had a more appropriate treatment that we could offer these high-risk patients as an alternative to high-risk surgical approaches,” Dr. Conradi said.
The analysis stratified procedure volumes and growth by four age groups: younger than 65 years; 65-74; 75-84; and greater than ore equal to 85. Older patients were more likely to have TMVR. Surgical procedure volumes increased most in the less than 65 group and least in the greater than or equal to 85 group.
In Germany, transcatheter mitral valve procedures are reimbursed at a higher rate than surgical procedures, but that doesn’t fully explain the uptake in TMVR, Dr. Conradi said. “The patients receiving the transcatheter approach vs. surgery still differ fundamentally, but the addition of an interventional program decreases the surgical patient’s mean risk profile and thus optimizes surgical results,” he said. “I think this can only happen if surgeons are closely involved. The indications will broaden for these therapies. There’s no doubt about that.”
Dr. Conradi disclosed receiving travel support and lecture fees from Abbott Vascular.
NEW YORK – Since the commercialization of transcatheter mitral valve repair, the share of these procedures among all mitral operations has grown exponentially and has also contributed to an increase in the number of overall mitral procedures, including surgical repair, according to an analysis of a national German database reported at the American Association for Thoracic Surgery Mitral Conclave here.
Transcatheter mitral valve repair (TMVR) using the MitraClip device (Abbott Vascular) was first commercialized in Germany in 2008, and in the years since the share of TMVR procedures among all mitral operations increased from 0.3% to 18.1% in 2015 throughout Germany, said Lenard Conradi, MD, surgical director of minimally-invasive and transcatheter heart valve procedures at the University Heart Center Hamburg.
The goal of the study was to gain insights into how cardiothoracic surgeons in Germany and at Dr. Conradi’s center in particular were approaching TMVR and what types of patients were having the procedure, Dr. Conradi said.
“While the EuroSCORE I of patients we operated on didn’t change at all between these two time frames, there were subtle changes in the patients that we operated on,” he said. “Before the commercialization of TMVR, we tended to have a ratio of organic vs. functional MR [mitral regurgitation] of 50-50; after commercialization of TMVR, many of the functional MR patients were allocated to TMVR.”
Dr. Conradi noted the profile of patients who had mitral valve repair also changed once the transcatheter approach became available. “Ischemic disease with coronary artery disease, previous infarction, or previous cardiac surgery – mostly coronary artery bypass grafting – were much less prevalent in this surgery population after TMVR became available,” he said.
The study also found that 30-day mortality declined from 7% to 4% during the study period. “That was probably due to more adequate patient selection because we had a more appropriate treatment that we could offer these high-risk patients as an alternative to high-risk surgical approaches,” Dr. Conradi said.
The analysis stratified procedure volumes and growth by four age groups: younger than 65 years; 65-74; 75-84; and greater than ore equal to 85. Older patients were more likely to have TMVR. Surgical procedure volumes increased most in the less than 65 group and least in the greater than or equal to 85 group.
In Germany, transcatheter mitral valve procedures are reimbursed at a higher rate than surgical procedures, but that doesn’t fully explain the uptake in TMVR, Dr. Conradi said. “The patients receiving the transcatheter approach vs. surgery still differ fundamentally, but the addition of an interventional program decreases the surgical patient’s mean risk profile and thus optimizes surgical results,” he said. “I think this can only happen if surgeons are closely involved. The indications will broaden for these therapies. There’s no doubt about that.”
Dr. Conradi disclosed receiving travel support and lecture fees from Abbott Vascular.
NEW YORK – Since the commercialization of transcatheter mitral valve repair, the share of these procedures among all mitral operations has grown exponentially and has also contributed to an increase in the number of overall mitral procedures, including surgical repair, according to an analysis of a national German database reported at the American Association for Thoracic Surgery Mitral Conclave here.
Transcatheter mitral valve repair (TMVR) using the MitraClip device (Abbott Vascular) was first commercialized in Germany in 2008, and in the years since the share of TMVR procedures among all mitral operations increased from 0.3% to 18.1% in 2015 throughout Germany, said Lenard Conradi, MD, surgical director of minimally-invasive and transcatheter heart valve procedures at the University Heart Center Hamburg.
The goal of the study was to gain insights into how cardiothoracic surgeons in Germany and at Dr. Conradi’s center in particular were approaching TMVR and what types of patients were having the procedure, Dr. Conradi said.
“While the EuroSCORE I of patients we operated on didn’t change at all between these two time frames, there were subtle changes in the patients that we operated on,” he said. “Before the commercialization of TMVR, we tended to have a ratio of organic vs. functional MR [mitral regurgitation] of 50-50; after commercialization of TMVR, many of the functional MR patients were allocated to TMVR.”
Dr. Conradi noted the profile of patients who had mitral valve repair also changed once the transcatheter approach became available. “Ischemic disease with coronary artery disease, previous infarction, or previous cardiac surgery – mostly coronary artery bypass grafting – were much less prevalent in this surgery population after TMVR became available,” he said.
The study also found that 30-day mortality declined from 7% to 4% during the study period. “That was probably due to more adequate patient selection because we had a more appropriate treatment that we could offer these high-risk patients as an alternative to high-risk surgical approaches,” Dr. Conradi said.
The analysis stratified procedure volumes and growth by four age groups: younger than 65 years; 65-74; 75-84; and greater than ore equal to 85. Older patients were more likely to have TMVR. Surgical procedure volumes increased most in the less than 65 group and least in the greater than or equal to 85 group.
In Germany, transcatheter mitral valve procedures are reimbursed at a higher rate than surgical procedures, but that doesn’t fully explain the uptake in TMVR, Dr. Conradi said. “The patients receiving the transcatheter approach vs. surgery still differ fundamentally, but the addition of an interventional program decreases the surgical patient’s mean risk profile and thus optimizes surgical results,” he said. “I think this can only happen if surgeons are closely involved. The indications will broaden for these therapies. There’s no doubt about that.”
Dr. Conradi disclosed receiving travel support and lecture fees from Abbott Vascular.
AT THE AATS MITRAL CONCLAVE 2017
Key clinical point: Since its commercialization, transcatheter mitral valve repair (TMVR) has accounted for an increasing share of all mitral surgeries in Germany and driven greater mitral surgery volume overall.
Major finding: Volume of surgical mitral valve procedures increased 70% overall and TMVR procedures 57% in Germany since 2008.
Data source: Analysis of data from German Federal statistics office.
Disclosures: Dr. Conradi reported receiving travel support and lecture fees from Abbott Vascular.
Low-dose aspirin bests dual-antiplatelet therapy in TAVR
PARIS – Single-antiplatelet therapy with low-dose aspirin following transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) reduced the occurrence of major adverse events, compared with guideline-recommended dual-antiplatelet therapy (DAPT), in the randomized ARTE trial.
The TAVR guideline recommendation for DAPT with low-dose aspirin plus clopidogrel is not based on evidence. It relies on expert opinion. ARTE (Aspirin Versus Aspirin + Clopidogrel Following TAVR) is the first sizable randomized trial to address the safety and efficacy of aspirin alone versus DAPT in the setting of TAVR, Josep Rodés-Cabau, MD, noted in presenting the ARTE results at the annual congress of the European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions.
ARTE was a multicenter, prospective, international open-label study of 222 TAVR patients who were randomized to 3 months of single-antiplatelet therapy (SAPT) with aspirin at 80-100 mg/day or to DAPT with aspirin at 80-100 mg/day plus clopidogrel at 75 mg/day after a single 300-mg loading dose. Participants had a mean Society of Thoracic Surgery Predicted Risk of Mortality score of 6.3%. The vast majority of participants received the balloon-expandable Edwards Lifesciences Sapien XT valve. The remainder got the Sapien 3 valve.
The primary outcome was the 3-month composite of death, MI, major or life-threatening bleeding, or stroke or transient ischemic attack. It occurred in 15.3% of the DAPT group and 7.2% on SAPT, a difference that didn’t reach statistical significance (P = .065) because of small patient numbers.
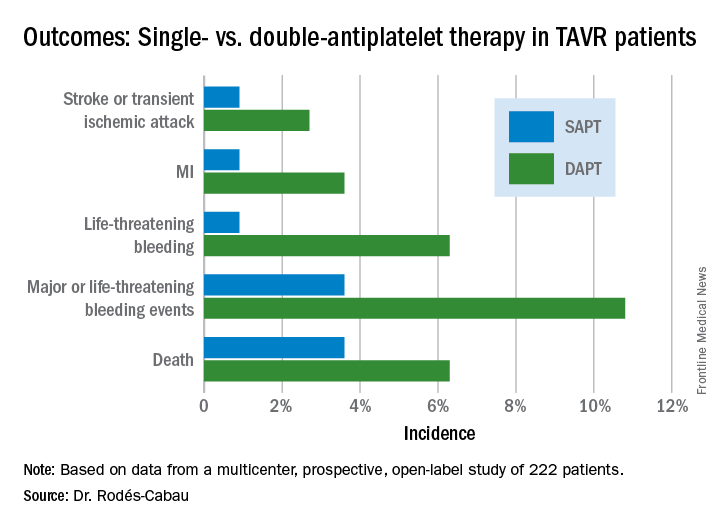
All subjects were on a proton pump inhibitor. The type, timing, and severity of bleeding events differed between the two study arms. All 4 bleeding events in the SAPT group were vascular in nature, while 5 of the 12 in the DAPT group were gastrointestinal. All the bleeding events in the SAPT group occurred within 72 hours after TAVR, whereas 5 of 12 in the DAPT recipients occurred later. Only one patient on SAPT experienced life-threatening bleeding, compared with seven DAPT patients who did.
“There were two prior smaller studies before ours,” according to Dr. Rodés-Cabau of Laval University in Quebec City. “One showed no differences, and an Italian one showed a tendency toward more bleeding with DAPT. So, I think there has been no sign to date that adding clopidogrel protects this group of patients from anything.”
Discussant Luis Nombela-Franco, MD, an interventional cardiologist at San Carlos Hospital in Madrid, pronounced the ARTE trial guideline-changing despite its limitations.
ARTE was supported by grants from Edwards Lifesciences and the Quebec Heart and Lung Institute.
Simultaneous with Dr. Rodés-Cabau’s presentation in Paris, the ARTE trial was published online (JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2017 May 11. pii: S1936-8798[17]30812-9).
PARIS – Single-antiplatelet therapy with low-dose aspirin following transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) reduced the occurrence of major adverse events, compared with guideline-recommended dual-antiplatelet therapy (DAPT), in the randomized ARTE trial.
The TAVR guideline recommendation for DAPT with low-dose aspirin plus clopidogrel is not based on evidence. It relies on expert opinion. ARTE (Aspirin Versus Aspirin + Clopidogrel Following TAVR) is the first sizable randomized trial to address the safety and efficacy of aspirin alone versus DAPT in the setting of TAVR, Josep Rodés-Cabau, MD, noted in presenting the ARTE results at the annual congress of the European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions.
ARTE was a multicenter, prospective, international open-label study of 222 TAVR patients who were randomized to 3 months of single-antiplatelet therapy (SAPT) with aspirin at 80-100 mg/day or to DAPT with aspirin at 80-100 mg/day plus clopidogrel at 75 mg/day after a single 300-mg loading dose. Participants had a mean Society of Thoracic Surgery Predicted Risk of Mortality score of 6.3%. The vast majority of participants received the balloon-expandable Edwards Lifesciences Sapien XT valve. The remainder got the Sapien 3 valve.
The primary outcome was the 3-month composite of death, MI, major or life-threatening bleeding, or stroke or transient ischemic attack. It occurred in 15.3% of the DAPT group and 7.2% on SAPT, a difference that didn’t reach statistical significance (P = .065) because of small patient numbers.

All subjects were on a proton pump inhibitor. The type, timing, and severity of bleeding events differed between the two study arms. All 4 bleeding events in the SAPT group were vascular in nature, while 5 of the 12 in the DAPT group were gastrointestinal. All the bleeding events in the SAPT group occurred within 72 hours after TAVR, whereas 5 of 12 in the DAPT recipients occurred later. Only one patient on SAPT experienced life-threatening bleeding, compared with seven DAPT patients who did.
“There were two prior smaller studies before ours,” according to Dr. Rodés-Cabau of Laval University in Quebec City. “One showed no differences, and an Italian one showed a tendency toward more bleeding with DAPT. So, I think there has been no sign to date that adding clopidogrel protects this group of patients from anything.”
Discussant Luis Nombela-Franco, MD, an interventional cardiologist at San Carlos Hospital in Madrid, pronounced the ARTE trial guideline-changing despite its limitations.
ARTE was supported by grants from Edwards Lifesciences and the Quebec Heart and Lung Institute.
Simultaneous with Dr. Rodés-Cabau’s presentation in Paris, the ARTE trial was published online (JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2017 May 11. pii: S1936-8798[17]30812-9).
PARIS – Single-antiplatelet therapy with low-dose aspirin following transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) reduced the occurrence of major adverse events, compared with guideline-recommended dual-antiplatelet therapy (DAPT), in the randomized ARTE trial.
The TAVR guideline recommendation for DAPT with low-dose aspirin plus clopidogrel is not based on evidence. It relies on expert opinion. ARTE (Aspirin Versus Aspirin + Clopidogrel Following TAVR) is the first sizable randomized trial to address the safety and efficacy of aspirin alone versus DAPT in the setting of TAVR, Josep Rodés-Cabau, MD, noted in presenting the ARTE results at the annual congress of the European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions.
ARTE was a multicenter, prospective, international open-label study of 222 TAVR patients who were randomized to 3 months of single-antiplatelet therapy (SAPT) with aspirin at 80-100 mg/day or to DAPT with aspirin at 80-100 mg/day plus clopidogrel at 75 mg/day after a single 300-mg loading dose. Participants had a mean Society of Thoracic Surgery Predicted Risk of Mortality score of 6.3%. The vast majority of participants received the balloon-expandable Edwards Lifesciences Sapien XT valve. The remainder got the Sapien 3 valve.
The primary outcome was the 3-month composite of death, MI, major or life-threatening bleeding, or stroke or transient ischemic attack. It occurred in 15.3% of the DAPT group and 7.2% on SAPT, a difference that didn’t reach statistical significance (P = .065) because of small patient numbers.

All subjects were on a proton pump inhibitor. The type, timing, and severity of bleeding events differed between the two study arms. All 4 bleeding events in the SAPT group were vascular in nature, while 5 of the 12 in the DAPT group were gastrointestinal. All the bleeding events in the SAPT group occurred within 72 hours after TAVR, whereas 5 of 12 in the DAPT recipients occurred later. Only one patient on SAPT experienced life-threatening bleeding, compared with seven DAPT patients who did.
“There were two prior smaller studies before ours,” according to Dr. Rodés-Cabau of Laval University in Quebec City. “One showed no differences, and an Italian one showed a tendency toward more bleeding with DAPT. So, I think there has been no sign to date that adding clopidogrel protects this group of patients from anything.”
Discussant Luis Nombela-Franco, MD, an interventional cardiologist at San Carlos Hospital in Madrid, pronounced the ARTE trial guideline-changing despite its limitations.
ARTE was supported by grants from Edwards Lifesciences and the Quebec Heart and Lung Institute.
Simultaneous with Dr. Rodés-Cabau’s presentation in Paris, the ARTE trial was published online (JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2017 May 11. pii: S1936-8798[17]30812-9).
AT EUROPCR
Key clinical point:
Major finding: The 3-month composite of death, MI, major or life-threatening bleeding, or stroke or transient ischemic attack occurred in 15.3% of TAVR patients randomized to DAPT with low-dose aspirin plus clopidogrel, compared with 7.2% on aspirin only.
Data source: A randomized, multicenter, international, prospective open-label trial in 222 TAVR patients.
Disclosures: The presenter reported receiving research grants from Edwards Lifesciences and the Quebec Heart and Lung Institute, which supported the ARTE trial.
FDA approves Sapien 3 transcatheter valve for bioprosthetic valve failure
The Food and Drug Administration announced June 5 the approval of an expanded indication for the Sapien 3 Transcatheter Heart Valve (THV) for patients with symptomatic heart disease caused by failure of a previously placed bioprosthetic aortic or mitral valve who have a risk of death or severe complications from repeat surgery.
This is the first FDA approval for the expanded use of the Sapien 3 THV as a valve-in-valve treatment. Such procedures provide an alternative to repeat surgery.
“For the first time, a regulatory agency is approving a transcatheter heart valve as a valve-in-valve treatment when bioprosthetic mitral or aortic valves fail in patients who are at high or greater risk of complications from repeat surgery,” Bram Zuckerman, MD, director of the division of cardiovascular devices at the FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health, said in a press release. “This new approval offers U.S. patients with failing surgical bioprosthetic aortic or mitral valves a less-invasive treatment option.”
Originally, the FDA approved the Sapien 3 THV for transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) as an alternative to surgical aortic valve replacement for patients with native aortic stenosis whose risk for death or severe complications from surgery is high or greater. Then in 2016, the FDA expanded the TAVR indication for Sapien 3 THV to include patients who are at intermediate surgical risk for death or complications.
Read the full press release on the FDA’s website.
The Food and Drug Administration announced June 5 the approval of an expanded indication for the Sapien 3 Transcatheter Heart Valve (THV) for patients with symptomatic heart disease caused by failure of a previously placed bioprosthetic aortic or mitral valve who have a risk of death or severe complications from repeat surgery.
This is the first FDA approval for the expanded use of the Sapien 3 THV as a valve-in-valve treatment. Such procedures provide an alternative to repeat surgery.
“For the first time, a regulatory agency is approving a transcatheter heart valve as a valve-in-valve treatment when bioprosthetic mitral or aortic valves fail in patients who are at high or greater risk of complications from repeat surgery,” Bram Zuckerman, MD, director of the division of cardiovascular devices at the FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health, said in a press release. “This new approval offers U.S. patients with failing surgical bioprosthetic aortic or mitral valves a less-invasive treatment option.”
Originally, the FDA approved the Sapien 3 THV for transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) as an alternative to surgical aortic valve replacement for patients with native aortic stenosis whose risk for death or severe complications from surgery is high or greater. Then in 2016, the FDA expanded the TAVR indication for Sapien 3 THV to include patients who are at intermediate surgical risk for death or complications.
Read the full press release on the FDA’s website.
The Food and Drug Administration announced June 5 the approval of an expanded indication for the Sapien 3 Transcatheter Heart Valve (THV) for patients with symptomatic heart disease caused by failure of a previously placed bioprosthetic aortic or mitral valve who have a risk of death or severe complications from repeat surgery.
This is the first FDA approval for the expanded use of the Sapien 3 THV as a valve-in-valve treatment. Such procedures provide an alternative to repeat surgery.
“For the first time, a regulatory agency is approving a transcatheter heart valve as a valve-in-valve treatment when bioprosthetic mitral or aortic valves fail in patients who are at high or greater risk of complications from repeat surgery,” Bram Zuckerman, MD, director of the division of cardiovascular devices at the FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health, said in a press release. “This new approval offers U.S. patients with failing surgical bioprosthetic aortic or mitral valves a less-invasive treatment option.”
Originally, the FDA approved the Sapien 3 THV for transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) as an alternative to surgical aortic valve replacement for patients with native aortic stenosis whose risk for death or severe complications from surgery is high or greater. Then in 2016, the FDA expanded the TAVR indication for Sapien 3 THV to include patients who are at intermediate surgical risk for death or complications.
Read the full press release on the FDA’s website.
BIO-RESORT: A mandate to prescreen PCI patients for silent diabetes
PARIS – Undetected diabetes and prediabetes are pervasive in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention, and they’re associated with a sharply increased risk of major adverse cardiovascular events, according to the results of the potentially practice-changing BIO-RESORT Silent Diabetes Study, Clemens von Birgelen, MD, PhD, reported at the annual congress of the European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions.
“Our data support screening PCI all-comers for silent diabetes, which may help identify patients with an increased event risk and improve their therapy,” said Dr. von Birgelen, professor of cardiology at the Thoraxcentrum of Twente, a high-volume center for cardiac interventions in Enschede, the Netherlands.
A substantial one-third of subjects turned out to have abnormal glucose tolerance according to World Health Organization criteria and an International Expert Committee Report (Diabetes Care. 2009 Jul;32[7]:1327-34). In a multivariate analysis, their 1-year rate of the primary study endpoint – target vessel failure, a composite of cardiac death, target vessel-related MI, or target vessel revascularization – was an adjusted 2.2 times greater than in the 788 normoglycemic patients.
Moreover, among the 7% of study participants who met diagnostic criteria for silent diabetes, the risk of target vessel failure was more than 4.4 times greater than in the normoglycemic group.
“To a very great extent, periprocedural MI is the driving force behind this difference that we saw. From a biological point of view, I think that the vulnerability of the vessel in the diabetic or prediabetic patient features more brittle plaque with a higher risk of cholesterol embolization, and with more plaque mass that can be pushed to the side so that side branch vessels can become occluded, leading to periprocedural MI,” he observed.
Glucose metabolism was assessed in all participants by two methods using the conventional cutoffs: a 2-hour oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT), and the combination of fasting plasma glucose and hemoglobin A1c. By OGTT, 7% of patients had silent, previously unrecognized diabetes and another 13% had prediabetes. Using the combination of fasting plasma glucose and HbA1c, a total of 25% of subjects had silent diabetes or prediabetes. Fully 33% of participants had abnormal glucose metabolism by one yardstick or the other.
“What we have seen is there is a group of patients that are missed with either. With the OGTT you don’t see all the diabetics, and with HbA1c and fasting blood glucose you also miss some patients,” said Dr. von Birgelen.
The 1-year cumulative incidence of target vessel failure was 13.2% in patients with silent diabetes as identified by the OGTT and 12.1% in those detected by the alternative method, compared with rates of 2.8% and 3.1%, respectively, in normoglycemic PCI patients. The event rate was 6.1% in patients with prediabetes by OGTT and similar at 5.5% in those found to be prediabetic based on fasting blood glucose and HbA1c, versus rates of 2.8% and 3.1%, respectively, in normoglycemic patients.
“The findings of this study suggest that post-PCI event risk associated with hyperglycemia is a continuum without a clear threshold effect, extending well beyond the threshold that currently defines diabetes,” Dr. von Birgelen said.
Once again, it’s worth emphasizing that the elevated target vessel failure rates seen in patients with abnormal glucose metabolism were due mostly to increased rates of acute MI within the first 24 hours after PCI. The target vessel–related MI rate was 10.3% in patients with silent diabetes, compared with just 1.8% in normoglycemic controls.
Asked what the take-home message for clinicians is from this study, he noted that the Netherlands has a relatively low prevalence of diabetes, and a highly developed primary care medicine system.
“We have a very good one-to-one relationship between the patient and the GP. So if we find 7% silent diabetes and up to one-third of patients with undetected abnormal glucose tolerance in a country with a relatively low prevalence of diabetes, you may expect that in other countries with a higher prevalence and perhaps a less developed primary care system the rate may be much, much higher,” Dr. von Birgelen cautioned.
The implications for the daily clinical practice of interventional cardiology are clear, he continued: “We’ve seen in several trials that the new stents are doing a fantastic job. So if we want to further improve the outcomes in our patients we have to do something else. We should look for subgroups of our PCI patients who have a particularly high risk. And we all realize that diabetics are such a problem, but I think we have shown that the prediabetic patients are also important. So we should identify and pretreat these patients, perhaps with aggressive lipid-lowering therapy during the weeks before a scheduled elective PCI.”
“There are data showing that with aggressive lipid-lowering you might reduce the risk of periprocedural MI,” the cardiologist noted.
As a practical matter, screening via fasting blood glucose and HbA1c is probably the way to go in clinical practice, according to Dr. von Birgelen.
“In this study, we performed the OGTT because it is still considered by many the gold standard. But there is increasing evidence favoring HbA1c data and fasting blood glucose,” he said.
Other possible pre-PCI interventions worthy of consideration in patients found to have previously unsuspected abnormal glucose tolerance might include medical therapy aimed at normalizing glucose metabolism, as well as perhaps resorting to the most potent forms of dual-antiplatelet therapy in patients with stable angina who have impaired glucose tolerance. However, these are possibilities that should be tested in randomized controlled trials before widespread adoption, he added.
The BIO-RESORT Silent Diabetes Study, which will continue for 5 years of post-PCI follow-up, is a prespecified substudy of the previously reported BIO-RESORT trial, which addressed another issue entirely. It was a three-arm, patient-blinded clinical trial comparing 1-year safety and efficacy outcomes in nearly 3,500 PCI patients randomized to PCI with very thin strut biodegradable polymer everolimus- or sirolimus-eluting stents or a durable polymer zotarolimus-eluting stent. Outcomes proved noninferior across the three treatment groups (Lancet. 2016 Nov 26;388[10060]:2607-17).
Dr. von Birgelen observed that the silent diabetes study broke new ground. Prior studies of PCI outcomes in patients with unrecognized diabetes were limited to recipients of plain old balloon angioplasty, bare metal, or first-generation drug-eluting stents. And studies of PCI in patients with unrecognized prediabetes are virtually nonexistent.
As the principal investigator for both the parent BIO-RESORT trial and the silent diabetes substudy, Dr. von Birgelen received research grants from Biotronik, Boston Scientific, and Medtronic, the cosponsors. He applauded the three companies for funding the silent diabetes substudy in the interest of science even though it had no commercial relevance to their stent businesses.
PARIS – Undetected diabetes and prediabetes are pervasive in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention, and they’re associated with a sharply increased risk of major adverse cardiovascular events, according to the results of the potentially practice-changing BIO-RESORT Silent Diabetes Study, Clemens von Birgelen, MD, PhD, reported at the annual congress of the European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions.
“Our data support screening PCI all-comers for silent diabetes, which may help identify patients with an increased event risk and improve their therapy,” said Dr. von Birgelen, professor of cardiology at the Thoraxcentrum of Twente, a high-volume center for cardiac interventions in Enschede, the Netherlands.
A substantial one-third of subjects turned out to have abnormal glucose tolerance according to World Health Organization criteria and an International Expert Committee Report (Diabetes Care. 2009 Jul;32[7]:1327-34). In a multivariate analysis, their 1-year rate of the primary study endpoint – target vessel failure, a composite of cardiac death, target vessel-related MI, or target vessel revascularization – was an adjusted 2.2 times greater than in the 788 normoglycemic patients.
Moreover, among the 7% of study participants who met diagnostic criteria for silent diabetes, the risk of target vessel failure was more than 4.4 times greater than in the normoglycemic group.
“To a very great extent, periprocedural MI is the driving force behind this difference that we saw. From a biological point of view, I think that the vulnerability of the vessel in the diabetic or prediabetic patient features more brittle plaque with a higher risk of cholesterol embolization, and with more plaque mass that can be pushed to the side so that side branch vessels can become occluded, leading to periprocedural MI,” he observed.
Glucose metabolism was assessed in all participants by two methods using the conventional cutoffs: a 2-hour oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT), and the combination of fasting plasma glucose and hemoglobin A1c. By OGTT, 7% of patients had silent, previously unrecognized diabetes and another 13% had prediabetes. Using the combination of fasting plasma glucose and HbA1c, a total of 25% of subjects had silent diabetes or prediabetes. Fully 33% of participants had abnormal glucose metabolism by one yardstick or the other.
“What we have seen is there is a group of patients that are missed with either. With the OGTT you don’t see all the diabetics, and with HbA1c and fasting blood glucose you also miss some patients,” said Dr. von Birgelen.
The 1-year cumulative incidence of target vessel failure was 13.2% in patients with silent diabetes as identified by the OGTT and 12.1% in those detected by the alternative method, compared with rates of 2.8% and 3.1%, respectively, in normoglycemic PCI patients. The event rate was 6.1% in patients with prediabetes by OGTT and similar at 5.5% in those found to be prediabetic based on fasting blood glucose and HbA1c, versus rates of 2.8% and 3.1%, respectively, in normoglycemic patients.
“The findings of this study suggest that post-PCI event risk associated with hyperglycemia is a continuum without a clear threshold effect, extending well beyond the threshold that currently defines diabetes,” Dr. von Birgelen said.
Once again, it’s worth emphasizing that the elevated target vessel failure rates seen in patients with abnormal glucose metabolism were due mostly to increased rates of acute MI within the first 24 hours after PCI. The target vessel–related MI rate was 10.3% in patients with silent diabetes, compared with just 1.8% in normoglycemic controls.
Asked what the take-home message for clinicians is from this study, he noted that the Netherlands has a relatively low prevalence of diabetes, and a highly developed primary care medicine system.
“We have a very good one-to-one relationship between the patient and the GP. So if we find 7% silent diabetes and up to one-third of patients with undetected abnormal glucose tolerance in a country with a relatively low prevalence of diabetes, you may expect that in other countries with a higher prevalence and perhaps a less developed primary care system the rate may be much, much higher,” Dr. von Birgelen cautioned.
The implications for the daily clinical practice of interventional cardiology are clear, he continued: “We’ve seen in several trials that the new stents are doing a fantastic job. So if we want to further improve the outcomes in our patients we have to do something else. We should look for subgroups of our PCI patients who have a particularly high risk. And we all realize that diabetics are such a problem, but I think we have shown that the prediabetic patients are also important. So we should identify and pretreat these patients, perhaps with aggressive lipid-lowering therapy during the weeks before a scheduled elective PCI.”
“There are data showing that with aggressive lipid-lowering you might reduce the risk of periprocedural MI,” the cardiologist noted.
As a practical matter, screening via fasting blood glucose and HbA1c is probably the way to go in clinical practice, according to Dr. von Birgelen.
“In this study, we performed the OGTT because it is still considered by many the gold standard. But there is increasing evidence favoring HbA1c data and fasting blood glucose,” he said.
Other possible pre-PCI interventions worthy of consideration in patients found to have previously unsuspected abnormal glucose tolerance might include medical therapy aimed at normalizing glucose metabolism, as well as perhaps resorting to the most potent forms of dual-antiplatelet therapy in patients with stable angina who have impaired glucose tolerance. However, these are possibilities that should be tested in randomized controlled trials before widespread adoption, he added.
The BIO-RESORT Silent Diabetes Study, which will continue for 5 years of post-PCI follow-up, is a prespecified substudy of the previously reported BIO-RESORT trial, which addressed another issue entirely. It was a three-arm, patient-blinded clinical trial comparing 1-year safety and efficacy outcomes in nearly 3,500 PCI patients randomized to PCI with very thin strut biodegradable polymer everolimus- or sirolimus-eluting stents or a durable polymer zotarolimus-eluting stent. Outcomes proved noninferior across the three treatment groups (Lancet. 2016 Nov 26;388[10060]:2607-17).
Dr. von Birgelen observed that the silent diabetes study broke new ground. Prior studies of PCI outcomes in patients with unrecognized diabetes were limited to recipients of plain old balloon angioplasty, bare metal, or first-generation drug-eluting stents. And studies of PCI in patients with unrecognized prediabetes are virtually nonexistent.
As the principal investigator for both the parent BIO-RESORT trial and the silent diabetes substudy, Dr. von Birgelen received research grants from Biotronik, Boston Scientific, and Medtronic, the cosponsors. He applauded the three companies for funding the silent diabetes substudy in the interest of science even though it had no commercial relevance to their stent businesses.
PARIS – Undetected diabetes and prediabetes are pervasive in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention, and they’re associated with a sharply increased risk of major adverse cardiovascular events, according to the results of the potentially practice-changing BIO-RESORT Silent Diabetes Study, Clemens von Birgelen, MD, PhD, reported at the annual congress of the European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions.
“Our data support screening PCI all-comers for silent diabetes, which may help identify patients with an increased event risk and improve their therapy,” said Dr. von Birgelen, professor of cardiology at the Thoraxcentrum of Twente, a high-volume center for cardiac interventions in Enschede, the Netherlands.
A substantial one-third of subjects turned out to have abnormal glucose tolerance according to World Health Organization criteria and an International Expert Committee Report (Diabetes Care. 2009 Jul;32[7]:1327-34). In a multivariate analysis, their 1-year rate of the primary study endpoint – target vessel failure, a composite of cardiac death, target vessel-related MI, or target vessel revascularization – was an adjusted 2.2 times greater than in the 788 normoglycemic patients.
Moreover, among the 7% of study participants who met diagnostic criteria for silent diabetes, the risk of target vessel failure was more than 4.4 times greater than in the normoglycemic group.
“To a very great extent, periprocedural MI is the driving force behind this difference that we saw. From a biological point of view, I think that the vulnerability of the vessel in the diabetic or prediabetic patient features more brittle plaque with a higher risk of cholesterol embolization, and with more plaque mass that can be pushed to the side so that side branch vessels can become occluded, leading to periprocedural MI,” he observed.
Glucose metabolism was assessed in all participants by two methods using the conventional cutoffs: a 2-hour oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT), and the combination of fasting plasma glucose and hemoglobin A1c. By OGTT, 7% of patients had silent, previously unrecognized diabetes and another 13% had prediabetes. Using the combination of fasting plasma glucose and HbA1c, a total of 25% of subjects had silent diabetes or prediabetes. Fully 33% of participants had abnormal glucose metabolism by one yardstick or the other.
“What we have seen is there is a group of patients that are missed with either. With the OGTT you don’t see all the diabetics, and with HbA1c and fasting blood glucose you also miss some patients,” said Dr. von Birgelen.
The 1-year cumulative incidence of target vessel failure was 13.2% in patients with silent diabetes as identified by the OGTT and 12.1% in those detected by the alternative method, compared with rates of 2.8% and 3.1%, respectively, in normoglycemic PCI patients. The event rate was 6.1% in patients with prediabetes by OGTT and similar at 5.5% in those found to be prediabetic based on fasting blood glucose and HbA1c, versus rates of 2.8% and 3.1%, respectively, in normoglycemic patients.
“The findings of this study suggest that post-PCI event risk associated with hyperglycemia is a continuum without a clear threshold effect, extending well beyond the threshold that currently defines diabetes,” Dr. von Birgelen said.
Once again, it’s worth emphasizing that the elevated target vessel failure rates seen in patients with abnormal glucose metabolism were due mostly to increased rates of acute MI within the first 24 hours after PCI. The target vessel–related MI rate was 10.3% in patients with silent diabetes, compared with just 1.8% in normoglycemic controls.
Asked what the take-home message for clinicians is from this study, he noted that the Netherlands has a relatively low prevalence of diabetes, and a highly developed primary care medicine system.
“We have a very good one-to-one relationship between the patient and the GP. So if we find 7% silent diabetes and up to one-third of patients with undetected abnormal glucose tolerance in a country with a relatively low prevalence of diabetes, you may expect that in other countries with a higher prevalence and perhaps a less developed primary care system the rate may be much, much higher,” Dr. von Birgelen cautioned.
The implications for the daily clinical practice of interventional cardiology are clear, he continued: “We’ve seen in several trials that the new stents are doing a fantastic job. So if we want to further improve the outcomes in our patients we have to do something else. We should look for subgroups of our PCI patients who have a particularly high risk. And we all realize that diabetics are such a problem, but I think we have shown that the prediabetic patients are also important. So we should identify and pretreat these patients, perhaps with aggressive lipid-lowering therapy during the weeks before a scheduled elective PCI.”
“There are data showing that with aggressive lipid-lowering you might reduce the risk of periprocedural MI,” the cardiologist noted.
As a practical matter, screening via fasting blood glucose and HbA1c is probably the way to go in clinical practice, according to Dr. von Birgelen.
“In this study, we performed the OGTT because it is still considered by many the gold standard. But there is increasing evidence favoring HbA1c data and fasting blood glucose,” he said.
Other possible pre-PCI interventions worthy of consideration in patients found to have previously unsuspected abnormal glucose tolerance might include medical therapy aimed at normalizing glucose metabolism, as well as perhaps resorting to the most potent forms of dual-antiplatelet therapy in patients with stable angina who have impaired glucose tolerance. However, these are possibilities that should be tested in randomized controlled trials before widespread adoption, he added.
The BIO-RESORT Silent Diabetes Study, which will continue for 5 years of post-PCI follow-up, is a prespecified substudy of the previously reported BIO-RESORT trial, which addressed another issue entirely. It was a three-arm, patient-blinded clinical trial comparing 1-year safety and efficacy outcomes in nearly 3,500 PCI patients randomized to PCI with very thin strut biodegradable polymer everolimus- or sirolimus-eluting stents or a durable polymer zotarolimus-eluting stent. Outcomes proved noninferior across the three treatment groups (Lancet. 2016 Nov 26;388[10060]:2607-17).
Dr. von Birgelen observed that the silent diabetes study broke new ground. Prior studies of PCI outcomes in patients with unrecognized diabetes were limited to recipients of plain old balloon angioplasty, bare metal, or first-generation drug-eluting stents. And studies of PCI in patients with unrecognized prediabetes are virtually nonexistent.
As the principal investigator for both the parent BIO-RESORT trial and the silent diabetes substudy, Dr. von Birgelen received research grants from Biotronik, Boston Scientific, and Medtronic, the cosponsors. He applauded the three companies for funding the silent diabetes substudy in the interest of science even though it had no commercial relevance to their stent businesses.
AT EUROPCR
Key clinical point:
Major finding: One-third of patients undergoing PCI have unsuspected silent diabetes or prediabetes, placing them at increased risk for major adverse cardiac events.
Data source: This prospective observational study included 988 patients not known to have diabetes who underwent screening for abnormal glucose tolerance 6 weeks after PCI with stenting.
Disclosures: The study was cosponsored by Biotronik, Boston Scientific, and Medtronic.
VIDEO: Lack of heart teams impact prevalence of PCI
BOSTON – Data show a marked bias in referral patterns for coronary revascularization in stand-alone interventional cardiology units lacking a heart team.
More patients underwent percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) in hospitals without on-site cardiac surgery than patients at hospitals with on-site cardiac surgery, according to the analysis presented at the annual meeting of the American Association for Thoracic Surgery. The multivariate logistic regression analysis showed that the absence of on-site cardiac surgery and a heart team was an independent predictor for PCI.
In this video, Ehud Raanani, MD, of Tel Aviv University in Israel discusses referral patterns for coronary revascularization in stand-alone interventional cardiology units lacking a heart team and how this phenomenon could affect patients.
The video associated with this article is no longer available on this site. Please view all of our videos on the MDedge YouTube channel
[email protected]
On Twitter @legal_med
BOSTON – Data show a marked bias in referral patterns for coronary revascularization in stand-alone interventional cardiology units lacking a heart team.
More patients underwent percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) in hospitals without on-site cardiac surgery than patients at hospitals with on-site cardiac surgery, according to the analysis presented at the annual meeting of the American Association for Thoracic Surgery. The multivariate logistic regression analysis showed that the absence of on-site cardiac surgery and a heart team was an independent predictor for PCI.
In this video, Ehud Raanani, MD, of Tel Aviv University in Israel discusses referral patterns for coronary revascularization in stand-alone interventional cardiology units lacking a heart team and how this phenomenon could affect patients.
The video associated with this article is no longer available on this site. Please view all of our videos on the MDedge YouTube channel
[email protected]
On Twitter @legal_med
BOSTON – Data show a marked bias in referral patterns for coronary revascularization in stand-alone interventional cardiology units lacking a heart team.
More patients underwent percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) in hospitals without on-site cardiac surgery than patients at hospitals with on-site cardiac surgery, according to the analysis presented at the annual meeting of the American Association for Thoracic Surgery. The multivariate logistic regression analysis showed that the absence of on-site cardiac surgery and a heart team was an independent predictor for PCI.
In this video, Ehud Raanani, MD, of Tel Aviv University in Israel discusses referral patterns for coronary revascularization in stand-alone interventional cardiology units lacking a heart team and how this phenomenon could affect patients.
The video associated with this article is no longer available on this site. Please view all of our videos on the MDedge YouTube channel
[email protected]
On Twitter @legal_med
AT THE AATS ANNUAL MEETING
Novel Lotus valve outperforms CoreValve in REPRISE III
PARIS – The investigational mechanically expandable Lotus valve system for transcatheter aortic valve replacement proved significantly more effective than the commercially available CoreValve platform in patients with severe aortic stenosis deemed at high or extreme surgical risk in the randomized pivotal phase III REPRISE III trial, Ted E. Feldman, MD, reported at the annual congress of the European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions.
The 1-year composite primary effectiveness endpoint comprised of all-cause mortality, disabling stroke, and moderate or greater paravalvular leak (PVL) occurred in 17% of patients randomized to the Lotus transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) device, compared with 29% of those in the CoreValve group, said Dr. Feldman, director of the cardiac catheterization laboratory at NorthShore University HealthSystem in Evanston, Ill.
A key finding was that the Lotus valve group had a 1-year rate of moderate or greater PVL of just 2% as assessed in a central core lab, compared with an 11% rate in patients randomized to the classic CoreValve or the subsequent-generation Evolut R device, he observed.
“With the Lotus valve there was no or only trace PVL in over 85% of patients. This is probably even more important than the low rate of moderate or severe PVL. The valve really does result in virtually no PVL in the vast majority of patients. That’s unique to this platform,” the cardiologist said in an interview.
The unprecedented low rate of moderate or severe PVL at 1 year postprocedure is attributable to the polymer seal delivered via the Lotus system for that express purpose, he explained.
REPRISE III was the first large randomized comparative clinical trial featuring two TAVR valves, an event that reflects the rapid expansion of the field. All previous major trials had compared TAVR with surgical aortic valve replacement.
REPRISE III randomized 912 TAVR patients at 55 centers 2:1 to the Lotus valve in its 23-, 25-, or 27-mm configurations or to a CoreValve at 26, 29, or 31 mm. Roughly half of the CoreValve group got the newer repositionable and retrievable Evolut R valve, while the earlier enrollees received the nonrepositionable classic CoreValve.
The Lotus valve group proved noninferior to the CoreValve recipients for the primary safety endpoint, a 30-day composite of all-cause mortality, stroke, major or life-threatening bleeding, major vascular complications, and stage 2 or 3 acute kidney injury. The rates were 20.3% in the Lotus arm and 17.2% with CoreValve.
The 1-year rate of disabling stroke was 3.6% in the Lotus group versus 7.3% in the CoreValve group. Dr. Feldman downplayed the importance of this difference, even though it was statistically significant. The Lotus valve performed as expected, but the disabling stroke rate in the CoreValve group was higher than in earlier studies for reasons unknown, most likely simply the play of chance, he said.
“I think the real message here is that the Lotus valve performed very well,” the cardiologist said. “There have been concerns that repositioning the valve into a better position during the deployment process might create excess stroke. It appears clear that’s not the case.”
The ability to reposition the Lotus device resulted in a significantly lower rate of repeat procedures at 1 year: 0.2% versus 2% with the CoreValve, as well as zero cases of aortic valve malposition and valve-in-valve deployment.
The need for a new pacemaker within 30 days after TAVR was strikingly more common in the Lotus valve group: 36%, compared with 20% with the CoreValve. Dr. Feldman attributed the high new pacemaker rate in the Lotus arm partly to the operators’ limited experience with the novel valve along with the fact that REPRISE III used a first-iteration device deployment mechanism. An improved deployment mechanism designed to minimize problematic contact with the left ventricular outflow tract was developed too late for inclusion in the trial. But in a recent European study using this proprietary deployment system, known as Depth Guard, the new pacemaker rate was below 20%.
The learning curve for the new Lotus valve system is “not at all challenging,” according to the cardiologist. He noted that U.S. operators participating in REPRISE III, who had no prior experience with the device, were allowed only two initial cases in order to gain experience; after that, every patient counted in the clinical trial results.
The REPRISE III results will be offered to the Food and Drug Administration to support regulatory approval of the device in high-surgical-risk patients. Dr. Feldman said Boston Scientific plans to conduct an additional clinical trial of the Lotus valve, this time in intermediate-risk patients, with the goal of gaining an expanded indication. This, too, will be a head-to-head comparison with a commercially available TAVR valve, probably the Edwards Sapien 3 valve.
REPRISE III was sponsored by Boston Scientific. Dr. Feldman reported serving as a consultant to that company, Abbott, and Edwards Lifesciences, and having received institutional research grants from those companies as well.
[email protected]
PARIS – The investigational mechanically expandable Lotus valve system for transcatheter aortic valve replacement proved significantly more effective than the commercially available CoreValve platform in patients with severe aortic stenosis deemed at high or extreme surgical risk in the randomized pivotal phase III REPRISE III trial, Ted E. Feldman, MD, reported at the annual congress of the European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions.
The 1-year composite primary effectiveness endpoint comprised of all-cause mortality, disabling stroke, and moderate or greater paravalvular leak (PVL) occurred in 17% of patients randomized to the Lotus transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) device, compared with 29% of those in the CoreValve group, said Dr. Feldman, director of the cardiac catheterization laboratory at NorthShore University HealthSystem in Evanston, Ill.
A key finding was that the Lotus valve group had a 1-year rate of moderate or greater PVL of just 2% as assessed in a central core lab, compared with an 11% rate in patients randomized to the classic CoreValve or the subsequent-generation Evolut R device, he observed.
“With the Lotus valve there was no or only trace PVL in over 85% of patients. This is probably even more important than the low rate of moderate or severe PVL. The valve really does result in virtually no PVL in the vast majority of patients. That’s unique to this platform,” the cardiologist said in an interview.
The unprecedented low rate of moderate or severe PVL at 1 year postprocedure is attributable to the polymer seal delivered via the Lotus system for that express purpose, he explained.
REPRISE III was the first large randomized comparative clinical trial featuring two TAVR valves, an event that reflects the rapid expansion of the field. All previous major trials had compared TAVR with surgical aortic valve replacement.
REPRISE III randomized 912 TAVR patients at 55 centers 2:1 to the Lotus valve in its 23-, 25-, or 27-mm configurations or to a CoreValve at 26, 29, or 31 mm. Roughly half of the CoreValve group got the newer repositionable and retrievable Evolut R valve, while the earlier enrollees received the nonrepositionable classic CoreValve.
The Lotus valve group proved noninferior to the CoreValve recipients for the primary safety endpoint, a 30-day composite of all-cause mortality, stroke, major or life-threatening bleeding, major vascular complications, and stage 2 or 3 acute kidney injury. The rates were 20.3% in the Lotus arm and 17.2% with CoreValve.
The 1-year rate of disabling stroke was 3.6% in the Lotus group versus 7.3% in the CoreValve group. Dr. Feldman downplayed the importance of this difference, even though it was statistically significant. The Lotus valve performed as expected, but the disabling stroke rate in the CoreValve group was higher than in earlier studies for reasons unknown, most likely simply the play of chance, he said.
“I think the real message here is that the Lotus valve performed very well,” the cardiologist said. “There have been concerns that repositioning the valve into a better position during the deployment process might create excess stroke. It appears clear that’s not the case.”
The ability to reposition the Lotus device resulted in a significantly lower rate of repeat procedures at 1 year: 0.2% versus 2% with the CoreValve, as well as zero cases of aortic valve malposition and valve-in-valve deployment.
The need for a new pacemaker within 30 days after TAVR was strikingly more common in the Lotus valve group: 36%, compared with 20% with the CoreValve. Dr. Feldman attributed the high new pacemaker rate in the Lotus arm partly to the operators’ limited experience with the novel valve along with the fact that REPRISE III used a first-iteration device deployment mechanism. An improved deployment mechanism designed to minimize problematic contact with the left ventricular outflow tract was developed too late for inclusion in the trial. But in a recent European study using this proprietary deployment system, known as Depth Guard, the new pacemaker rate was below 20%.
The learning curve for the new Lotus valve system is “not at all challenging,” according to the cardiologist. He noted that U.S. operators participating in REPRISE III, who had no prior experience with the device, were allowed only two initial cases in order to gain experience; after that, every patient counted in the clinical trial results.
The REPRISE III results will be offered to the Food and Drug Administration to support regulatory approval of the device in high-surgical-risk patients. Dr. Feldman said Boston Scientific plans to conduct an additional clinical trial of the Lotus valve, this time in intermediate-risk patients, with the goal of gaining an expanded indication. This, too, will be a head-to-head comparison with a commercially available TAVR valve, probably the Edwards Sapien 3 valve.
REPRISE III was sponsored by Boston Scientific. Dr. Feldman reported serving as a consultant to that company, Abbott, and Edwards Lifesciences, and having received institutional research grants from those companies as well.
[email protected]
PARIS – The investigational mechanically expandable Lotus valve system for transcatheter aortic valve replacement proved significantly more effective than the commercially available CoreValve platform in patients with severe aortic stenosis deemed at high or extreme surgical risk in the randomized pivotal phase III REPRISE III trial, Ted E. Feldman, MD, reported at the annual congress of the European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions.
The 1-year composite primary effectiveness endpoint comprised of all-cause mortality, disabling stroke, and moderate or greater paravalvular leak (PVL) occurred in 17% of patients randomized to the Lotus transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) device, compared with 29% of those in the CoreValve group, said Dr. Feldman, director of the cardiac catheterization laboratory at NorthShore University HealthSystem in Evanston, Ill.
A key finding was that the Lotus valve group had a 1-year rate of moderate or greater PVL of just 2% as assessed in a central core lab, compared with an 11% rate in patients randomized to the classic CoreValve or the subsequent-generation Evolut R device, he observed.
“With the Lotus valve there was no or only trace PVL in over 85% of patients. This is probably even more important than the low rate of moderate or severe PVL. The valve really does result in virtually no PVL in the vast majority of patients. That’s unique to this platform,” the cardiologist said in an interview.
The unprecedented low rate of moderate or severe PVL at 1 year postprocedure is attributable to the polymer seal delivered via the Lotus system for that express purpose, he explained.
REPRISE III was the first large randomized comparative clinical trial featuring two TAVR valves, an event that reflects the rapid expansion of the field. All previous major trials had compared TAVR with surgical aortic valve replacement.
REPRISE III randomized 912 TAVR patients at 55 centers 2:1 to the Lotus valve in its 23-, 25-, or 27-mm configurations or to a CoreValve at 26, 29, or 31 mm. Roughly half of the CoreValve group got the newer repositionable and retrievable Evolut R valve, while the earlier enrollees received the nonrepositionable classic CoreValve.
The Lotus valve group proved noninferior to the CoreValve recipients for the primary safety endpoint, a 30-day composite of all-cause mortality, stroke, major or life-threatening bleeding, major vascular complications, and stage 2 or 3 acute kidney injury. The rates were 20.3% in the Lotus arm and 17.2% with CoreValve.
The 1-year rate of disabling stroke was 3.6% in the Lotus group versus 7.3% in the CoreValve group. Dr. Feldman downplayed the importance of this difference, even though it was statistically significant. The Lotus valve performed as expected, but the disabling stroke rate in the CoreValve group was higher than in earlier studies for reasons unknown, most likely simply the play of chance, he said.
“I think the real message here is that the Lotus valve performed very well,” the cardiologist said. “There have been concerns that repositioning the valve into a better position during the deployment process might create excess stroke. It appears clear that’s not the case.”
The ability to reposition the Lotus device resulted in a significantly lower rate of repeat procedures at 1 year: 0.2% versus 2% with the CoreValve, as well as zero cases of aortic valve malposition and valve-in-valve deployment.
The need for a new pacemaker within 30 days after TAVR was strikingly more common in the Lotus valve group: 36%, compared with 20% with the CoreValve. Dr. Feldman attributed the high new pacemaker rate in the Lotus arm partly to the operators’ limited experience with the novel valve along with the fact that REPRISE III used a first-iteration device deployment mechanism. An improved deployment mechanism designed to minimize problematic contact with the left ventricular outflow tract was developed too late for inclusion in the trial. But in a recent European study using this proprietary deployment system, known as Depth Guard, the new pacemaker rate was below 20%.
The learning curve for the new Lotus valve system is “not at all challenging,” according to the cardiologist. He noted that U.S. operators participating in REPRISE III, who had no prior experience with the device, were allowed only two initial cases in order to gain experience; after that, every patient counted in the clinical trial results.
The REPRISE III results will be offered to the Food and Drug Administration to support regulatory approval of the device in high-surgical-risk patients. Dr. Feldman said Boston Scientific plans to conduct an additional clinical trial of the Lotus valve, this time in intermediate-risk patients, with the goal of gaining an expanded indication. This, too, will be a head-to-head comparison with a commercially available TAVR valve, probably the Edwards Sapien 3 valve.
REPRISE III was sponsored by Boston Scientific. Dr. Feldman reported serving as a consultant to that company, Abbott, and Edwards Lifesciences, and having received institutional research grants from those companies as well.
[email protected]
AT EUROPCR
Key clinical point:
Major finding: The rate of the 1-year composite primary effectiveness endpoint comprised of all-cause mortality, disabling stroke, and moderate or greater paravalvular leak was 17% in patients randomized to the investigational Lotus transcatheter aortic valve replacement system, compared with 29% in recipients of the CoreValve.
Data source: REPRISE III, a prospective, multicenter, international clinical trial randomized 912 patients with severe aortic stenosis who were at high surgical risk to TAVR with the investigational Lotus valve or a commercially available CoreValve.
Disclosures: REPRISE III was sponsored by Boston Scientific. The study presenter reported serving as a consultant to that company as well as for Abbott and Edwards Lifesciences. He has also received institutional research grants from those companies.