User login
9/11 responders show increased risk of leukemia, other cancers
New data suggest an increased risk of leukemia among responders who worked at the World Trade Center site after the attacks on Sept. 11, 2001.
Previous studies have shown that 9/11 responders have a higher incidence of cancers than does the general population. The current study is the first to show a higher incidence of leukemia among responders. It also shows a higher incidence of thyroid and prostate cancers as well as all cancer types combined.
These findings were published in JNCI Cancer Spectrum.
“This study showed increased incidence of several cancer types compared to previously conducted studies with shorter follow-up periods,” study author Susan L, Teitelbaum, PhD, of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, said in a press release.
“Because of the long latency period of many types of cancer, it is possible that increased rates of other cancers, as well as World Trade Center exposure health issues, may emerge after longer periods of study.”
Dr. Teitelbaum and colleagues evaluated responders enrolled in the World Trade Center Health Program General Responder Cohort from when it was established in July 2002 through the end of follow-up, which was Dec. 31, 2013, for New York residents and Dec. 31, 2012, for residents of other states.
To be eligible for the cohort, responders must have worked on the World Trade Center rescue and recovery effort a minimum of 4 hours in the first 4 days from Sept. 11, 2001, 24 hours in September 2001, or 80 hours from September through December 2001. Responders also had to complete at least one monitoring visit.
Responders’ data were linked to data from cancer registries in New York, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, and Connecticut (where most responders lived at the time of the attacks), as well as Florida and North Carolina (where responders were known to retire). The responders were linked to the registries using probabilistic matching algorithms, which made use of information such as patient name, address, social security number, sex, race, and birth date.
The researchers noted that patients who enrolled in the General Responder Cohort had their cancer certified for federally funded treatment, and this factor might result in “sicker members disproportionately self-selecting into the program.” To reduce this potential bias, the researchers conducted a restricted analysis in which counts of cancer cases and person-years of observation began 6 months after responder enrollment.
The researchers analyzed data on 28,729 responders who primarily worked in protective services (49.0%) and construction (20.8%). Responders spent a median of 52 days on the rescue and recovery effort, and 44.4% of them had some exposure to the dust cloud caused by the collapse of the towers.
In the restricted analysis, there were 1,072 cancers observed in 999 responders. Compared with the general population, responders had a significantly higher incidence of all cancers combined, with a standardized incidence ratio (SIR) of 1.09.
Responders had a significantly higher incidence of prostate cancer (SIR,1.25), thyroid cancer (SIR, 2.19), and leukemia (SIR, 1.41). The leukemia category included acute myeloid leukemia (SIR,1.58) and chronic lymphocytic leukemia (SIR, 1.08).
“Although other studies have revealed elevated SIRs for other hematologic malignancies, this is the first reported, statistically significant, elevated SIR for leukemia,” the researchers wrote. “Leukemia is known to occur after exposure to occupational carcinogens, including benzene (burning jet fuel and other sources at the [World Trade Center] site), possibly at low levels of exposure and with a latency of several years from exposure.”
A multivariate analysis showed no association between cancer incidence and the length of time responders spent on the rescue and recovery effort or the intensity of their exposure to the dust cloud or debris pile.
The analysis did show an elevated risk of all cancers combined with each 1-year increase in responder age (hazard ratio, 1.09), among male responders (HR, 1.21), and among responders who smoked at baseline (HR, 1.29).
This research was supported by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention/National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health. The researchers disclosed no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Shapiro MZ et al. JNCI Cancer Spectr. 2020 Jan 14. doi: 10.1093/jncics/pkz090.
New data suggest an increased risk of leukemia among responders who worked at the World Trade Center site after the attacks on Sept. 11, 2001.
Previous studies have shown that 9/11 responders have a higher incidence of cancers than does the general population. The current study is the first to show a higher incidence of leukemia among responders. It also shows a higher incidence of thyroid and prostate cancers as well as all cancer types combined.
These findings were published in JNCI Cancer Spectrum.
“This study showed increased incidence of several cancer types compared to previously conducted studies with shorter follow-up periods,” study author Susan L, Teitelbaum, PhD, of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, said in a press release.
“Because of the long latency period of many types of cancer, it is possible that increased rates of other cancers, as well as World Trade Center exposure health issues, may emerge after longer periods of study.”
Dr. Teitelbaum and colleagues evaluated responders enrolled in the World Trade Center Health Program General Responder Cohort from when it was established in July 2002 through the end of follow-up, which was Dec. 31, 2013, for New York residents and Dec. 31, 2012, for residents of other states.
To be eligible for the cohort, responders must have worked on the World Trade Center rescue and recovery effort a minimum of 4 hours in the first 4 days from Sept. 11, 2001, 24 hours in September 2001, or 80 hours from September through December 2001. Responders also had to complete at least one monitoring visit.
Responders’ data were linked to data from cancer registries in New York, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, and Connecticut (where most responders lived at the time of the attacks), as well as Florida and North Carolina (where responders were known to retire). The responders were linked to the registries using probabilistic matching algorithms, which made use of information such as patient name, address, social security number, sex, race, and birth date.
The researchers noted that patients who enrolled in the General Responder Cohort had their cancer certified for federally funded treatment, and this factor might result in “sicker members disproportionately self-selecting into the program.” To reduce this potential bias, the researchers conducted a restricted analysis in which counts of cancer cases and person-years of observation began 6 months after responder enrollment.
The researchers analyzed data on 28,729 responders who primarily worked in protective services (49.0%) and construction (20.8%). Responders spent a median of 52 days on the rescue and recovery effort, and 44.4% of them had some exposure to the dust cloud caused by the collapse of the towers.
In the restricted analysis, there were 1,072 cancers observed in 999 responders. Compared with the general population, responders had a significantly higher incidence of all cancers combined, with a standardized incidence ratio (SIR) of 1.09.
Responders had a significantly higher incidence of prostate cancer (SIR,1.25), thyroid cancer (SIR, 2.19), and leukemia (SIR, 1.41). The leukemia category included acute myeloid leukemia (SIR,1.58) and chronic lymphocytic leukemia (SIR, 1.08).
“Although other studies have revealed elevated SIRs for other hematologic malignancies, this is the first reported, statistically significant, elevated SIR for leukemia,” the researchers wrote. “Leukemia is known to occur after exposure to occupational carcinogens, including benzene (burning jet fuel and other sources at the [World Trade Center] site), possibly at low levels of exposure and with a latency of several years from exposure.”
A multivariate analysis showed no association between cancer incidence and the length of time responders spent on the rescue and recovery effort or the intensity of their exposure to the dust cloud or debris pile.
The analysis did show an elevated risk of all cancers combined with each 1-year increase in responder age (hazard ratio, 1.09), among male responders (HR, 1.21), and among responders who smoked at baseline (HR, 1.29).
This research was supported by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention/National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health. The researchers disclosed no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Shapiro MZ et al. JNCI Cancer Spectr. 2020 Jan 14. doi: 10.1093/jncics/pkz090.
New data suggest an increased risk of leukemia among responders who worked at the World Trade Center site after the attacks on Sept. 11, 2001.
Previous studies have shown that 9/11 responders have a higher incidence of cancers than does the general population. The current study is the first to show a higher incidence of leukemia among responders. It also shows a higher incidence of thyroid and prostate cancers as well as all cancer types combined.
These findings were published in JNCI Cancer Spectrum.
“This study showed increased incidence of several cancer types compared to previously conducted studies with shorter follow-up periods,” study author Susan L, Teitelbaum, PhD, of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, said in a press release.
“Because of the long latency period of many types of cancer, it is possible that increased rates of other cancers, as well as World Trade Center exposure health issues, may emerge after longer periods of study.”
Dr. Teitelbaum and colleagues evaluated responders enrolled in the World Trade Center Health Program General Responder Cohort from when it was established in July 2002 through the end of follow-up, which was Dec. 31, 2013, for New York residents and Dec. 31, 2012, for residents of other states.
To be eligible for the cohort, responders must have worked on the World Trade Center rescue and recovery effort a minimum of 4 hours in the first 4 days from Sept. 11, 2001, 24 hours in September 2001, or 80 hours from September through December 2001. Responders also had to complete at least one monitoring visit.
Responders’ data were linked to data from cancer registries in New York, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, and Connecticut (where most responders lived at the time of the attacks), as well as Florida and North Carolina (where responders were known to retire). The responders were linked to the registries using probabilistic matching algorithms, which made use of information such as patient name, address, social security number, sex, race, and birth date.
The researchers noted that patients who enrolled in the General Responder Cohort had their cancer certified for federally funded treatment, and this factor might result in “sicker members disproportionately self-selecting into the program.” To reduce this potential bias, the researchers conducted a restricted analysis in which counts of cancer cases and person-years of observation began 6 months after responder enrollment.
The researchers analyzed data on 28,729 responders who primarily worked in protective services (49.0%) and construction (20.8%). Responders spent a median of 52 days on the rescue and recovery effort, and 44.4% of them had some exposure to the dust cloud caused by the collapse of the towers.
In the restricted analysis, there were 1,072 cancers observed in 999 responders. Compared with the general population, responders had a significantly higher incidence of all cancers combined, with a standardized incidence ratio (SIR) of 1.09.
Responders had a significantly higher incidence of prostate cancer (SIR,1.25), thyroid cancer (SIR, 2.19), and leukemia (SIR, 1.41). The leukemia category included acute myeloid leukemia (SIR,1.58) and chronic lymphocytic leukemia (SIR, 1.08).
“Although other studies have revealed elevated SIRs for other hematologic malignancies, this is the first reported, statistically significant, elevated SIR for leukemia,” the researchers wrote. “Leukemia is known to occur after exposure to occupational carcinogens, including benzene (burning jet fuel and other sources at the [World Trade Center] site), possibly at low levels of exposure and with a latency of several years from exposure.”
A multivariate analysis showed no association between cancer incidence and the length of time responders spent on the rescue and recovery effort or the intensity of their exposure to the dust cloud or debris pile.
The analysis did show an elevated risk of all cancers combined with each 1-year increase in responder age (hazard ratio, 1.09), among male responders (HR, 1.21), and among responders who smoked at baseline (HR, 1.29).
This research was supported by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention/National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health. The researchers disclosed no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Shapiro MZ et al. JNCI Cancer Spectr. 2020 Jan 14. doi: 10.1093/jncics/pkz090.
FROM JNCI CANCER SPECTRUM
CAR T-cell therapy advances in CLL
ORLANDO – Lisocabtagene maraleucel (liso-cel), a CD19-directed chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy, has demonstrated manageable toxicity and promising clinical activity in the phase 1 portion of a trial enrolling heavily pretreated patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma, according to an investigator.
The overall response rate exceeded 80%, and most patients in response at 6 months had maintained that response at the 9-month mark, said Tanya Siddiqi, MD, of City of Hope National Medical Center, Duarte, Calif.
“Clinical responses were rapid, improved with time, and were deep and durable,” Dr. Siddiqi said at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
These findings have provided justification for conducting the phase 2 portion of the study, which is currently enrolling at the higher of two dose levels evaluated in phase 1, she added.
Dr. Siddiqi reported on a total of 23 patients enrolled in the study, known as TRANSCEND CLL 004. All patients had relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma (CLL/SLL), and had received at least two prior therapies, including ibrutinib, while about one-third had failed venetoclax as well.
The median patient age was 66 years, and 83% had high-risk features, according to Dr. Siddiqi, who said patients had received a median of five prior lines of therapy.
Nine patients were treated at dose level 1, or 50 x 106 CAR+ T cells, while 14 were treated at dose level 2, or 100 x 106 CAR+ T cells. Two patients experienced grade 3 or 4 dose-limiting toxicities at the second level, including hypertension in one patient, and encephalopathy, muscle weakness, and tumor lysis syndrome (TLS) in the other.
Cytokine release syndrome (CRS) occurred in 17 patients, though only two cases reached grade 3. Neurologic adverse events were seen in nine patients, of which five were grade 3 or 4.
Partial or complete responses were noted in 81.5%, or 18 of 22 evaluable patients, including 10 (45.5%) who had complete remission. In the subset of nine patients who had failed both ibrutinib and venetoclax, that overall response rate was a “very impressive” 89% (eight of nine patients), said Dr. Siddiqi, including 67% complete remissions (six patients).
Undetectable minimal residual disease (MRD) was reported in 65% and 75% of patients, depending on the method used to evaluate it.
About two-thirds of the patients had responses by day 30 evaluation, and responses deepened over time in about one-quarter, according to Dr. Siddiqi. Of 12 patients with a response at 6 months, 10 (83%) were still in response at 9 months, and 8 patients have been in response for 12 months or longer, she reported.
Neurologic adverse events seen in the CLL/SLL patients in this study were associated with higher lymph node tumor burden, and increased levels of interleukin(IL)-16 or tumor necrosis factor (TNF), according to further analysis presented by Dr. Siddiqi.
That raises the possibility that IL-16 or TNF may be a “good predictive biomarker” for neurotoxicity, which seems to be driven at least in part by lymphadenopathy. “If there was a way that we could combine the CAR T-cell with something like a novel agent that can shrink the tumor burden quickly, then maybe we can have even less toxicities with these CAR T cells,” Dr. Siddiqi said.
Dr. Siddiqi reported disclosures related to Kite, TG Therapeutics, Celgene, Janssen, Seattle Genetics, AstraZeneca, PCYC, Juno Therapeutics, and BeiGene.
SOURCE: Siddiqi T et al. ASH 2019, Abstract 503.
ORLANDO – Lisocabtagene maraleucel (liso-cel), a CD19-directed chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy, has demonstrated manageable toxicity and promising clinical activity in the phase 1 portion of a trial enrolling heavily pretreated patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma, according to an investigator.
The overall response rate exceeded 80%, and most patients in response at 6 months had maintained that response at the 9-month mark, said Tanya Siddiqi, MD, of City of Hope National Medical Center, Duarte, Calif.
“Clinical responses were rapid, improved with time, and were deep and durable,” Dr. Siddiqi said at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
These findings have provided justification for conducting the phase 2 portion of the study, which is currently enrolling at the higher of two dose levels evaluated in phase 1, she added.
Dr. Siddiqi reported on a total of 23 patients enrolled in the study, known as TRANSCEND CLL 004. All patients had relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma (CLL/SLL), and had received at least two prior therapies, including ibrutinib, while about one-third had failed venetoclax as well.
The median patient age was 66 years, and 83% had high-risk features, according to Dr. Siddiqi, who said patients had received a median of five prior lines of therapy.
Nine patients were treated at dose level 1, or 50 x 106 CAR+ T cells, while 14 were treated at dose level 2, or 100 x 106 CAR+ T cells. Two patients experienced grade 3 or 4 dose-limiting toxicities at the second level, including hypertension in one patient, and encephalopathy, muscle weakness, and tumor lysis syndrome (TLS) in the other.
Cytokine release syndrome (CRS) occurred in 17 patients, though only two cases reached grade 3. Neurologic adverse events were seen in nine patients, of which five were grade 3 or 4.
Partial or complete responses were noted in 81.5%, or 18 of 22 evaluable patients, including 10 (45.5%) who had complete remission. In the subset of nine patients who had failed both ibrutinib and venetoclax, that overall response rate was a “very impressive” 89% (eight of nine patients), said Dr. Siddiqi, including 67% complete remissions (six patients).
Undetectable minimal residual disease (MRD) was reported in 65% and 75% of patients, depending on the method used to evaluate it.
About two-thirds of the patients had responses by day 30 evaluation, and responses deepened over time in about one-quarter, according to Dr. Siddiqi. Of 12 patients with a response at 6 months, 10 (83%) were still in response at 9 months, and 8 patients have been in response for 12 months or longer, she reported.
Neurologic adverse events seen in the CLL/SLL patients in this study were associated with higher lymph node tumor burden, and increased levels of interleukin(IL)-16 or tumor necrosis factor (TNF), according to further analysis presented by Dr. Siddiqi.
That raises the possibility that IL-16 or TNF may be a “good predictive biomarker” for neurotoxicity, which seems to be driven at least in part by lymphadenopathy. “If there was a way that we could combine the CAR T-cell with something like a novel agent that can shrink the tumor burden quickly, then maybe we can have even less toxicities with these CAR T cells,” Dr. Siddiqi said.
Dr. Siddiqi reported disclosures related to Kite, TG Therapeutics, Celgene, Janssen, Seattle Genetics, AstraZeneca, PCYC, Juno Therapeutics, and BeiGene.
SOURCE: Siddiqi T et al. ASH 2019, Abstract 503.
ORLANDO – Lisocabtagene maraleucel (liso-cel), a CD19-directed chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy, has demonstrated manageable toxicity and promising clinical activity in the phase 1 portion of a trial enrolling heavily pretreated patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma, according to an investigator.
The overall response rate exceeded 80%, and most patients in response at 6 months had maintained that response at the 9-month mark, said Tanya Siddiqi, MD, of City of Hope National Medical Center, Duarte, Calif.
“Clinical responses were rapid, improved with time, and were deep and durable,” Dr. Siddiqi said at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
These findings have provided justification for conducting the phase 2 portion of the study, which is currently enrolling at the higher of two dose levels evaluated in phase 1, she added.
Dr. Siddiqi reported on a total of 23 patients enrolled in the study, known as TRANSCEND CLL 004. All patients had relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma (CLL/SLL), and had received at least two prior therapies, including ibrutinib, while about one-third had failed venetoclax as well.
The median patient age was 66 years, and 83% had high-risk features, according to Dr. Siddiqi, who said patients had received a median of five prior lines of therapy.
Nine patients were treated at dose level 1, or 50 x 106 CAR+ T cells, while 14 were treated at dose level 2, or 100 x 106 CAR+ T cells. Two patients experienced grade 3 or 4 dose-limiting toxicities at the second level, including hypertension in one patient, and encephalopathy, muscle weakness, and tumor lysis syndrome (TLS) in the other.
Cytokine release syndrome (CRS) occurred in 17 patients, though only two cases reached grade 3. Neurologic adverse events were seen in nine patients, of which five were grade 3 or 4.
Partial or complete responses were noted in 81.5%, or 18 of 22 evaluable patients, including 10 (45.5%) who had complete remission. In the subset of nine patients who had failed both ibrutinib and venetoclax, that overall response rate was a “very impressive” 89% (eight of nine patients), said Dr. Siddiqi, including 67% complete remissions (six patients).
Undetectable minimal residual disease (MRD) was reported in 65% and 75% of patients, depending on the method used to evaluate it.
About two-thirds of the patients had responses by day 30 evaluation, and responses deepened over time in about one-quarter, according to Dr. Siddiqi. Of 12 patients with a response at 6 months, 10 (83%) were still in response at 9 months, and 8 patients have been in response for 12 months or longer, she reported.
Neurologic adverse events seen in the CLL/SLL patients in this study were associated with higher lymph node tumor burden, and increased levels of interleukin(IL)-16 or tumor necrosis factor (TNF), according to further analysis presented by Dr. Siddiqi.
That raises the possibility that IL-16 or TNF may be a “good predictive biomarker” for neurotoxicity, which seems to be driven at least in part by lymphadenopathy. “If there was a way that we could combine the CAR T-cell with something like a novel agent that can shrink the tumor burden quickly, then maybe we can have even less toxicities with these CAR T cells,” Dr. Siddiqi said.
Dr. Siddiqi reported disclosures related to Kite, TG Therapeutics, Celgene, Janssen, Seattle Genetics, AstraZeneca, PCYC, Juno Therapeutics, and BeiGene.
SOURCE: Siddiqi T et al. ASH 2019, Abstract 503.
REPORTING FROM ASH 2019
LOXO-305: Next-gen BTK inhibitor safe and effective in B-cell malignancies
ORLANDO – A phase 1 trial of the next-generation Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor LOXO-305 has demonstrated safety and provided evidence of its efficacy in heavily pretreated patients with B-cell malignancies, including some with acquired resistance to other BTK inhibitors and venetoclax, according to an investigator.
The antitumor activity of this highly selective investigational oral BTK inhibitor was significant in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), with a rapid onset of action and resolution of lymphocytosis “consistent with effective BTK target inhibition,” said Anthony R. Mato, MD, of the Center for CLL at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York.
Responses were also seen in patients with BTK C481 mutations, the primary cause of progressive CLL after BTK inhibitor use, Dr. Mato said at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
The safety and tolerability profile of LOXO-305 is “consistent with highly selective drug design,” with no evidence of off-target effects, he said. “Collectively, these data demonstrate that BTK remains a highly actionable target despite progression on covalent BTK inhibitors.”
While BTK inhibitors have transformed treatment of B-cell malignancies, resistance remains a major problem, said Dr. Mato, citing 5-year ibrutinib discontinuation rates of 41% in the front line setting and 53.7% in the relapsed/refractory setting.
Key reasons for discontinuation are intolerance, events such as atrial fibrillation and major bleeding, progression of disease, and the appearance of BTK C481 mutations, which prevent covalent BTK inhibitors from achieving effective target inhibition, he said. In contrast, LOXO-305 is designed to non-covalently bind to BTK, regardless of C481 status.
Dr. Mato described results of the phase 1 BRUIN trial, in which 28 adult patients with CLL or B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas received once daily oral LOXO-305 at doses ranging from 25 mg to 200 mg. All patients had received at least two lines of prior therapy and had active disease in need of treatment.
For 13 evaluable CLL patients, the overall response rate was 77% (10 patients), Dr. Mato reported. Overall response rates for MCL and other B-cell malignancies were 50%, or three out of six MCL patients and two of four patients with Waldenström macroglobulinemia, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, or marginal zone lymphoma.
Though only a small subset of CLL patients have had multiple response assessments, the available data suggest that responses “deepen over time” with continued LOXO-305 treatment, Dr. Mato said.
With the median follow-up of 2.7 months, 24 of 28 patients remain on therapy, including all responders. “Some of the responses appear to be quite durable,” Dr. Mato said.
There have been no dose-limiting toxicities, the maximum tolerated dose has not been reached, and there have been no notable adverse events characteristic of covalent BTK inhibitors – namely atrial fibrillation or major bleeding – despite frequent monitoring, according to Dr. Mato.
There were two grade 3 events (leukocytosis and neutropenia), but the remaining treatment-emergent adverse events have been grade 1-2. “Having managed many of these patients, I can tell you that these adverse events were quite manageable,” Dr. Mato told attendees.
BRUIN is a global trial that continues to enroll patients at 18 sites in 3 countries, with a plan in 2020 to incorporate “rational combinations” of agents, according to the investigator.
Dr. Mato reported disclosures related to Gilead, Pharmacyclics, AstraZeneca, AbbVie, Sunesis, Johnson & Johnson, TG Therapeutics, LOXO, DTRM Biopharma, Genentech, Janssen, Acerta, Pharmacyclics, and Celgene.
SOURCE: Mato AR et al. ASH 2019, Abstract 501.
ORLANDO – A phase 1 trial of the next-generation Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor LOXO-305 has demonstrated safety and provided evidence of its efficacy in heavily pretreated patients with B-cell malignancies, including some with acquired resistance to other BTK inhibitors and venetoclax, according to an investigator.
The antitumor activity of this highly selective investigational oral BTK inhibitor was significant in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), with a rapid onset of action and resolution of lymphocytosis “consistent with effective BTK target inhibition,” said Anthony R. Mato, MD, of the Center for CLL at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York.
Responses were also seen in patients with BTK C481 mutations, the primary cause of progressive CLL after BTK inhibitor use, Dr. Mato said at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
The safety and tolerability profile of LOXO-305 is “consistent with highly selective drug design,” with no evidence of off-target effects, he said. “Collectively, these data demonstrate that BTK remains a highly actionable target despite progression on covalent BTK inhibitors.”
While BTK inhibitors have transformed treatment of B-cell malignancies, resistance remains a major problem, said Dr. Mato, citing 5-year ibrutinib discontinuation rates of 41% in the front line setting and 53.7% in the relapsed/refractory setting.
Key reasons for discontinuation are intolerance, events such as atrial fibrillation and major bleeding, progression of disease, and the appearance of BTK C481 mutations, which prevent covalent BTK inhibitors from achieving effective target inhibition, he said. In contrast, LOXO-305 is designed to non-covalently bind to BTK, regardless of C481 status.
Dr. Mato described results of the phase 1 BRUIN trial, in which 28 adult patients with CLL or B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas received once daily oral LOXO-305 at doses ranging from 25 mg to 200 mg. All patients had received at least two lines of prior therapy and had active disease in need of treatment.
For 13 evaluable CLL patients, the overall response rate was 77% (10 patients), Dr. Mato reported. Overall response rates for MCL and other B-cell malignancies were 50%, or three out of six MCL patients and two of four patients with Waldenström macroglobulinemia, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, or marginal zone lymphoma.
Though only a small subset of CLL patients have had multiple response assessments, the available data suggest that responses “deepen over time” with continued LOXO-305 treatment, Dr. Mato said.
With the median follow-up of 2.7 months, 24 of 28 patients remain on therapy, including all responders. “Some of the responses appear to be quite durable,” Dr. Mato said.
There have been no dose-limiting toxicities, the maximum tolerated dose has not been reached, and there have been no notable adverse events characteristic of covalent BTK inhibitors – namely atrial fibrillation or major bleeding – despite frequent monitoring, according to Dr. Mato.
There were two grade 3 events (leukocytosis and neutropenia), but the remaining treatment-emergent adverse events have been grade 1-2. “Having managed many of these patients, I can tell you that these adverse events were quite manageable,” Dr. Mato told attendees.
BRUIN is a global trial that continues to enroll patients at 18 sites in 3 countries, with a plan in 2020 to incorporate “rational combinations” of agents, according to the investigator.
Dr. Mato reported disclosures related to Gilead, Pharmacyclics, AstraZeneca, AbbVie, Sunesis, Johnson & Johnson, TG Therapeutics, LOXO, DTRM Biopharma, Genentech, Janssen, Acerta, Pharmacyclics, and Celgene.
SOURCE: Mato AR et al. ASH 2019, Abstract 501.
ORLANDO – A phase 1 trial of the next-generation Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor LOXO-305 has demonstrated safety and provided evidence of its efficacy in heavily pretreated patients with B-cell malignancies, including some with acquired resistance to other BTK inhibitors and venetoclax, according to an investigator.
The antitumor activity of this highly selective investigational oral BTK inhibitor was significant in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), with a rapid onset of action and resolution of lymphocytosis “consistent with effective BTK target inhibition,” said Anthony R. Mato, MD, of the Center for CLL at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York.
Responses were also seen in patients with BTK C481 mutations, the primary cause of progressive CLL after BTK inhibitor use, Dr. Mato said at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
The safety and tolerability profile of LOXO-305 is “consistent with highly selective drug design,” with no evidence of off-target effects, he said. “Collectively, these data demonstrate that BTK remains a highly actionable target despite progression on covalent BTK inhibitors.”
While BTK inhibitors have transformed treatment of B-cell malignancies, resistance remains a major problem, said Dr. Mato, citing 5-year ibrutinib discontinuation rates of 41% in the front line setting and 53.7% in the relapsed/refractory setting.
Key reasons for discontinuation are intolerance, events such as atrial fibrillation and major bleeding, progression of disease, and the appearance of BTK C481 mutations, which prevent covalent BTK inhibitors from achieving effective target inhibition, he said. In contrast, LOXO-305 is designed to non-covalently bind to BTK, regardless of C481 status.
Dr. Mato described results of the phase 1 BRUIN trial, in which 28 adult patients with CLL or B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas received once daily oral LOXO-305 at doses ranging from 25 mg to 200 mg. All patients had received at least two lines of prior therapy and had active disease in need of treatment.
For 13 evaluable CLL patients, the overall response rate was 77% (10 patients), Dr. Mato reported. Overall response rates for MCL and other B-cell malignancies were 50%, or three out of six MCL patients and two of four patients with Waldenström macroglobulinemia, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, or marginal zone lymphoma.
Though only a small subset of CLL patients have had multiple response assessments, the available data suggest that responses “deepen over time” with continued LOXO-305 treatment, Dr. Mato said.
With the median follow-up of 2.7 months, 24 of 28 patients remain on therapy, including all responders. “Some of the responses appear to be quite durable,” Dr. Mato said.
There have been no dose-limiting toxicities, the maximum tolerated dose has not been reached, and there have been no notable adverse events characteristic of covalent BTK inhibitors – namely atrial fibrillation or major bleeding – despite frequent monitoring, according to Dr. Mato.
There were two grade 3 events (leukocytosis and neutropenia), but the remaining treatment-emergent adverse events have been grade 1-2. “Having managed many of these patients, I can tell you that these adverse events were quite manageable,” Dr. Mato told attendees.
BRUIN is a global trial that continues to enroll patients at 18 sites in 3 countries, with a plan in 2020 to incorporate “rational combinations” of agents, according to the investigator.
Dr. Mato reported disclosures related to Gilead, Pharmacyclics, AstraZeneca, AbbVie, Sunesis, Johnson & Johnson, TG Therapeutics, LOXO, DTRM Biopharma, Genentech, Janssen, Acerta, Pharmacyclics, and Celgene.
SOURCE: Mato AR et al. ASH 2019, Abstract 501.
REPORTING FROM ASH 2019
Zanubrutinib achieved high response rate in del(17p) CLL cohort
ORLANDO – Zanubrutinib has produced a high overall response rate in one the largest cohorts of patients with treatment-naive 17p-deletion chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) studied to date.
An overall response rate of nearly 93% was seen in this 109-patient, high-risk cohort, enrolled as part of the phase 3 SEQUOIA study (BGB-3111-304), said Constantine S. Tam, MBBS, MD, of St. Vincent’s Hospital and Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre in Melbourne.
Tolerability of zanubrutinib was essentially consistent with previous reports of the agent as used in other B-cell malignancies, Dr. Tam said in an oral presentation of the results at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
Deletion of chromosome 17p13.1, or del(17p), is a marker of poor prognosis and poor response to chemotherapy in patients with CLL or small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL). For patients with del(17p) CLL, the first-generation Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor ibrutinib has become a standard of care, Dr. Tam said.
Zanubrutinib, a next-generation BTK inhibitor, was developed to improve BTK occupancy and minimize off-target inhibition of TEC and epidermal growth factor receptor kinases. “What this effectively means is that we are able to dose this drug at levels much higher than that achievable with ibrutinib, and not get intolerable side effects,” Dr. Tam said.
Zanubrutinib has been approved in the United States for previously treated mantle cell lymphoma, and generated durable responses among CLL/SLL patients with or without del(17p) in a phase 1/2 study, according to Dr. Tam.
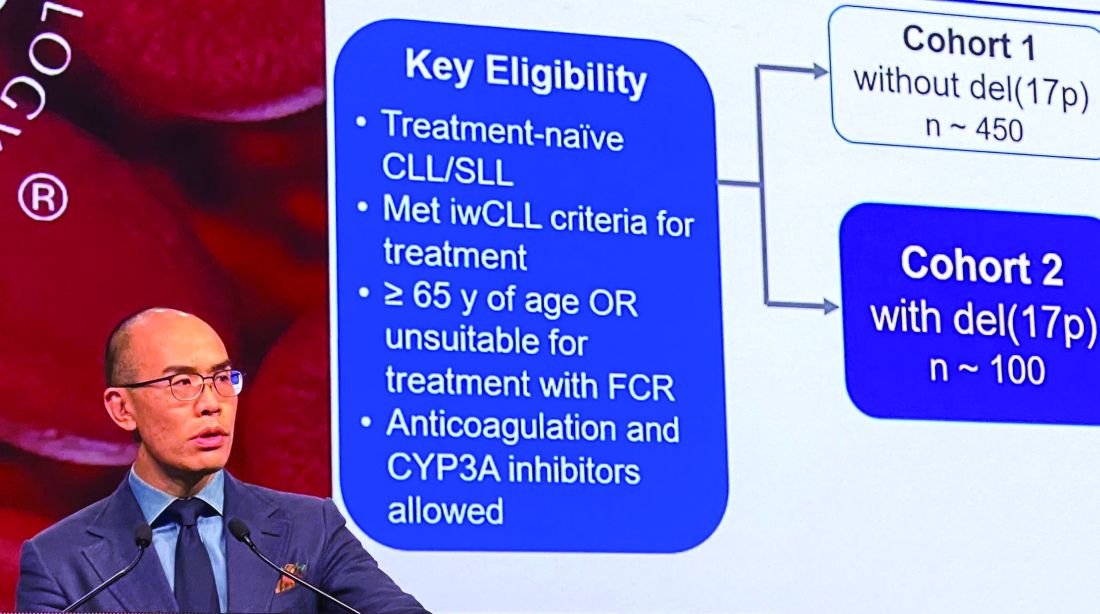
In the present study, which exclusively enrolled patients with del(17p) CLL/SLL, patients received 160 mg twice daily of zanubrutinib, Dr. Tam said. Out of 109 patients enrolled, 10 (9.2%) had SLL. All patients were aged at least 65 years or were deemed unsuitable for treatment with the combination of fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab.
Of 109 patients enrolled, 104 received on-study treatment. The median age was 70 years, Dr. Tam reported, and a number of patients had other high-risk markers beyond del(17p), including unmutated IgVH status in 61.5% of patients.
With a median follow-up of 10 months, the overall response rate was 92.7%, including 1.9% complete responses and 78.9% partial responses. “Only one patient had primary progressive disease after starting this drug,” Dr. Tam said.
Time to response was rapid, according to the investigator, at about 2.8 months; after 6 months, 95% of responders remained in response.
Further analysis showed that the response rate was consistent across subgroups. “There was not a single group that did not respond with a high response rate, including poor prognostic groups,” Dr. Tam said.
Most adverse events were grade 1-2 in severity, and the most common events included confusion and upper respiratory tract infection. The only common grade 3 event, according to Dr. Tam, was neutropenia. Rates of grade 3 major bleeding were low, he said, and the rate of grade 3 atrial fibrillation was 0.9%. One patient died due to pneumonia.
The ongoing SEQUOIA study, designed to compare zanubrutinib to the combination of bendamustine and rituximab in patients with previously untreated CLL or SLL, is sponsored by BeiGene. Dr. Tam reported disclosures related to Novartis, Pharmacyclics, AbbVie, BeiGene, Janssen, and Roche.
SOURCE: Tam C et al. ASH 2019, Abstract 499.
ORLANDO – Zanubrutinib has produced a high overall response rate in one the largest cohorts of patients with treatment-naive 17p-deletion chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) studied to date.
An overall response rate of nearly 93% was seen in this 109-patient, high-risk cohort, enrolled as part of the phase 3 SEQUOIA study (BGB-3111-304), said Constantine S. Tam, MBBS, MD, of St. Vincent’s Hospital and Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre in Melbourne.
Tolerability of zanubrutinib was essentially consistent with previous reports of the agent as used in other B-cell malignancies, Dr. Tam said in an oral presentation of the results at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
Deletion of chromosome 17p13.1, or del(17p), is a marker of poor prognosis and poor response to chemotherapy in patients with CLL or small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL). For patients with del(17p) CLL, the first-generation Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor ibrutinib has become a standard of care, Dr. Tam said.
Zanubrutinib, a next-generation BTK inhibitor, was developed to improve BTK occupancy and minimize off-target inhibition of TEC and epidermal growth factor receptor kinases. “What this effectively means is that we are able to dose this drug at levels much higher than that achievable with ibrutinib, and not get intolerable side effects,” Dr. Tam said.
Zanubrutinib has been approved in the United States for previously treated mantle cell lymphoma, and generated durable responses among CLL/SLL patients with or without del(17p) in a phase 1/2 study, according to Dr. Tam.
In the present study, which exclusively enrolled patients with del(17p) CLL/SLL, patients received 160 mg twice daily of zanubrutinib, Dr. Tam said. Out of 109 patients enrolled, 10 (9.2%) had SLL. All patients were aged at least 65 years or were deemed unsuitable for treatment with the combination of fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab.
Of 109 patients enrolled, 104 received on-study treatment. The median age was 70 years, Dr. Tam reported, and a number of patients had other high-risk markers beyond del(17p), including unmutated IgVH status in 61.5% of patients.
With a median follow-up of 10 months, the overall response rate was 92.7%, including 1.9% complete responses and 78.9% partial responses. “Only one patient had primary progressive disease after starting this drug,” Dr. Tam said.
Time to response was rapid, according to the investigator, at about 2.8 months; after 6 months, 95% of responders remained in response.
Further analysis showed that the response rate was consistent across subgroups. “There was not a single group that did not respond with a high response rate, including poor prognostic groups,” Dr. Tam said.
Most adverse events were grade 1-2 in severity, and the most common events included confusion and upper respiratory tract infection. The only common grade 3 event, according to Dr. Tam, was neutropenia. Rates of grade 3 major bleeding were low, he said, and the rate of grade 3 atrial fibrillation was 0.9%. One patient died due to pneumonia.
The ongoing SEQUOIA study, designed to compare zanubrutinib to the combination of bendamustine and rituximab in patients with previously untreated CLL or SLL, is sponsored by BeiGene. Dr. Tam reported disclosures related to Novartis, Pharmacyclics, AbbVie, BeiGene, Janssen, and Roche.
SOURCE: Tam C et al. ASH 2019, Abstract 499.
ORLANDO – Zanubrutinib has produced a high overall response rate in one the largest cohorts of patients with treatment-naive 17p-deletion chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) studied to date.
An overall response rate of nearly 93% was seen in this 109-patient, high-risk cohort, enrolled as part of the phase 3 SEQUOIA study (BGB-3111-304), said Constantine S. Tam, MBBS, MD, of St. Vincent’s Hospital and Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre in Melbourne.
Tolerability of zanubrutinib was essentially consistent with previous reports of the agent as used in other B-cell malignancies, Dr. Tam said in an oral presentation of the results at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
Deletion of chromosome 17p13.1, or del(17p), is a marker of poor prognosis and poor response to chemotherapy in patients with CLL or small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL). For patients with del(17p) CLL, the first-generation Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor ibrutinib has become a standard of care, Dr. Tam said.
Zanubrutinib, a next-generation BTK inhibitor, was developed to improve BTK occupancy and minimize off-target inhibition of TEC and epidermal growth factor receptor kinases. “What this effectively means is that we are able to dose this drug at levels much higher than that achievable with ibrutinib, and not get intolerable side effects,” Dr. Tam said.
Zanubrutinib has been approved in the United States for previously treated mantle cell lymphoma, and generated durable responses among CLL/SLL patients with or without del(17p) in a phase 1/2 study, according to Dr. Tam.
In the present study, which exclusively enrolled patients with del(17p) CLL/SLL, patients received 160 mg twice daily of zanubrutinib, Dr. Tam said. Out of 109 patients enrolled, 10 (9.2%) had SLL. All patients were aged at least 65 years or were deemed unsuitable for treatment with the combination of fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab.
Of 109 patients enrolled, 104 received on-study treatment. The median age was 70 years, Dr. Tam reported, and a number of patients had other high-risk markers beyond del(17p), including unmutated IgVH status in 61.5% of patients.
With a median follow-up of 10 months, the overall response rate was 92.7%, including 1.9% complete responses and 78.9% partial responses. “Only one patient had primary progressive disease after starting this drug,” Dr. Tam said.
Time to response was rapid, according to the investigator, at about 2.8 months; after 6 months, 95% of responders remained in response.
Further analysis showed that the response rate was consistent across subgroups. “There was not a single group that did not respond with a high response rate, including poor prognostic groups,” Dr. Tam said.
Most adverse events were grade 1-2 in severity, and the most common events included confusion and upper respiratory tract infection. The only common grade 3 event, according to Dr. Tam, was neutropenia. Rates of grade 3 major bleeding were low, he said, and the rate of grade 3 atrial fibrillation was 0.9%. One patient died due to pneumonia.
The ongoing SEQUOIA study, designed to compare zanubrutinib to the combination of bendamustine and rituximab in patients with previously untreated CLL or SLL, is sponsored by BeiGene. Dr. Tam reported disclosures related to Novartis, Pharmacyclics, AbbVie, BeiGene, Janssen, and Roche.
SOURCE: Tam C et al. ASH 2019, Abstract 499.
REPORTING FROM ASH 2019
Efficacy of postvenetoclax therapy may depend on prior agent exposure in CLL
ORLANDO – For a patient with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) who has discontinued venetoclax, choosing the best next therapy may depend on what novel agents the patient was exposed to and why they discontinued them, according to Anthony R. Mato, MD, with the Center for CLL at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York.
If the patient is Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor naive, then use of a BTK inhibitor after venetoclax would be supported, Dr. Mato said, by the high overall response rates and durable remissions that he and his coinvestigators documented in a retrospective, multicenter study designed specifically to address the gap in knowledge regarding what to use after venetoclax.
If the patient is BTK inhibitor exposed, then the reason for discontinuation needs to be considered before going with that venetoclax-to-BTK inhibitor sequence, Dr. Mato said during an oral presentation at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
“In patients with resistance to a BTK inhibitor, the sequence was not supported – it did not appear to be effective,” he said. “However, in the setting of intolerance, an alternate BTK inhibitor could be considered.”
The study did not support a venetoclax-to-PI3K inhibitor sequence in PI3K-naive patients, he added, noting that remissions did not appear to be durable, suggesting a potential overlap in resistance mechanisms between agents.
All told, the most effective therapies for in the postvenetoclax setting included the use of a BTK inhibitor in BTK inhibitor–naive or previously responsive patients, and allogeneic transplant following double novel-agent exposure.
“These data may provide support for venetoclax’s earlier use in the course of CLL, and may guide clinical practice and aid in the design of future clinical trials to address sequencing of novel agents,” Dr. Mato told attendees.
While prospective and real-world data clearly show that venetoclax is active in ibrutinib- or idelalisib-exposed patients, data are conversely “variable and limited” with regard to outcomes for next therapies following venetoclax.
“Current data addressing this key sequencing question, I feel, is a major limitation in supporting the sequence of venetoclax to a BTK inhibitor,” Dr. Mato said.
Accordingly, Dr. Mato and colleagues at 31 centers internationally planned and conducted this study, which included data on 326 patients treated with venetoclax who then discontinued for any reason.
“I wanted to highlight that 50% of the sites for this trial were recruited by a single tweet,” said Dr. Mato, adding that he and his coauthors received no funding to conduct this study and volunteered their time to complete it.
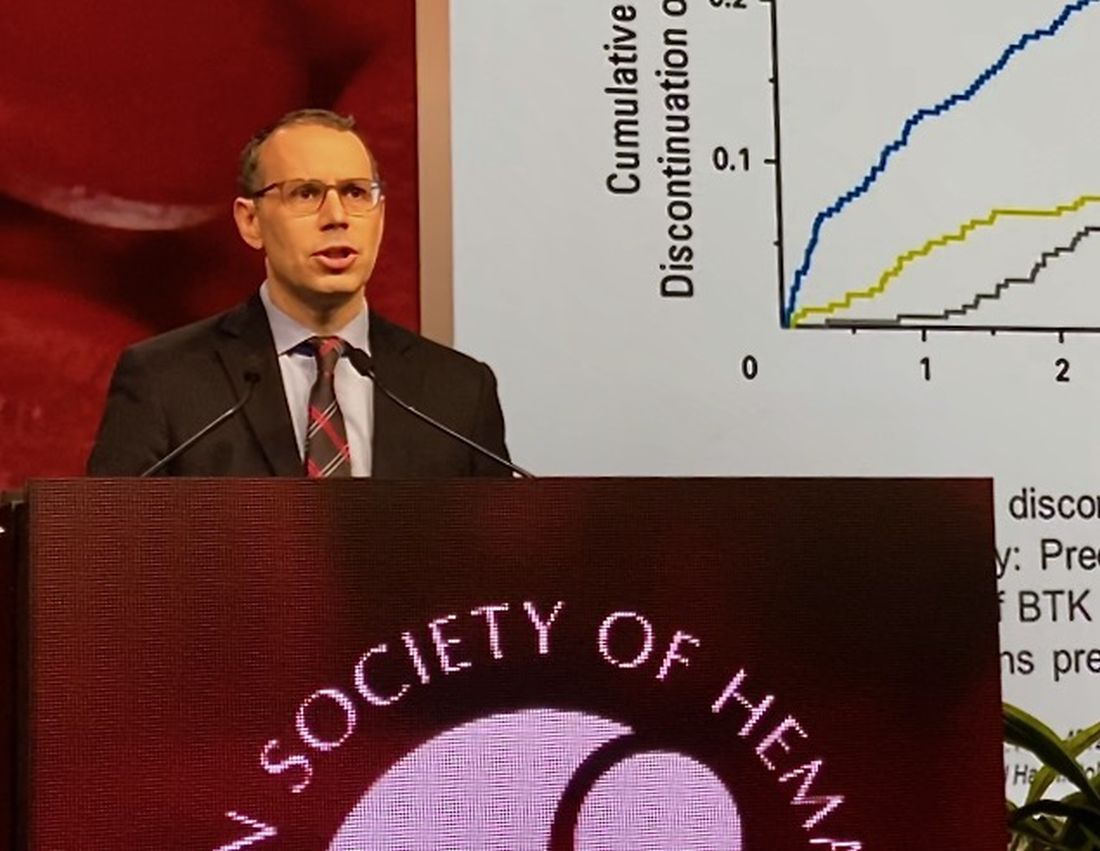
They found that, in BTK inhibitor–naive patients who discontinued venetoclax, subsequent BTK inhibitor treatment was associated with a high overall response rate and durable remissions, with a median progression-free survival (PFS) of 32 months.
In BTK inhibitor–exposed patients, response to postvenetoclax BTK inhibitor treatment depended on the reason for discontinuation, with a favorable result (PFS not reached with a mean follow-up of 7.7 months) in patients who were intolerant of the prior BTK inhibitor. By contrast, median PFS was only about 4 months for patients who were resistant to the prior BTK inhibitor.
PI3K inhibitors did not produce durable remissions after venetoclax, with a median PFS also of just 4 months, Dr. Mato reported.
However, cellular therapies appeared to be effective after venetoclax. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation was particularly effective, with the median PFS not reached, while chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy produced a PFS of 9 months.
Dr. Mato emphasized that the results of the retrospective trial were “hypothesis generating” and noted that patients in the study had received a median of 3, and up to 11, prior therapies. “This population are probably not our patients receiving venetoclax in clinical practice. They’re more heavily pretreated.”
Dr. Mato reported disclosures related to Gilead, AstraZeneca, AbbVie, Sunesis, Johnson & Johnson, TG Therapeutics, Loxo Oncology, DTRM Biopharma, Genentech, Janssen, Acerta Pharma, Pharmacyclics, and Celgene.
SOURCE: Mato AR et al. ASH 2019, Abstract 502.
ORLANDO – For a patient with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) who has discontinued venetoclax, choosing the best next therapy may depend on what novel agents the patient was exposed to and why they discontinued them, according to Anthony R. Mato, MD, with the Center for CLL at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York.
If the patient is Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor naive, then use of a BTK inhibitor after venetoclax would be supported, Dr. Mato said, by the high overall response rates and durable remissions that he and his coinvestigators documented in a retrospective, multicenter study designed specifically to address the gap in knowledge regarding what to use after venetoclax.
If the patient is BTK inhibitor exposed, then the reason for discontinuation needs to be considered before going with that venetoclax-to-BTK inhibitor sequence, Dr. Mato said during an oral presentation at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
“In patients with resistance to a BTK inhibitor, the sequence was not supported – it did not appear to be effective,” he said. “However, in the setting of intolerance, an alternate BTK inhibitor could be considered.”
The study did not support a venetoclax-to-PI3K inhibitor sequence in PI3K-naive patients, he added, noting that remissions did not appear to be durable, suggesting a potential overlap in resistance mechanisms between agents.
All told, the most effective therapies for in the postvenetoclax setting included the use of a BTK inhibitor in BTK inhibitor–naive or previously responsive patients, and allogeneic transplant following double novel-agent exposure.
“These data may provide support for venetoclax’s earlier use in the course of CLL, and may guide clinical practice and aid in the design of future clinical trials to address sequencing of novel agents,” Dr. Mato told attendees.
While prospective and real-world data clearly show that venetoclax is active in ibrutinib- or idelalisib-exposed patients, data are conversely “variable and limited” with regard to outcomes for next therapies following venetoclax.
“Current data addressing this key sequencing question, I feel, is a major limitation in supporting the sequence of venetoclax to a BTK inhibitor,” Dr. Mato said.
Accordingly, Dr. Mato and colleagues at 31 centers internationally planned and conducted this study, which included data on 326 patients treated with venetoclax who then discontinued for any reason.
“I wanted to highlight that 50% of the sites for this trial were recruited by a single tweet,” said Dr. Mato, adding that he and his coauthors received no funding to conduct this study and volunteered their time to complete it.
They found that, in BTK inhibitor–naive patients who discontinued venetoclax, subsequent BTK inhibitor treatment was associated with a high overall response rate and durable remissions, with a median progression-free survival (PFS) of 32 months.
In BTK inhibitor–exposed patients, response to postvenetoclax BTK inhibitor treatment depended on the reason for discontinuation, with a favorable result (PFS not reached with a mean follow-up of 7.7 months) in patients who were intolerant of the prior BTK inhibitor. By contrast, median PFS was only about 4 months for patients who were resistant to the prior BTK inhibitor.
PI3K inhibitors did not produce durable remissions after venetoclax, with a median PFS also of just 4 months, Dr. Mato reported.
However, cellular therapies appeared to be effective after venetoclax. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation was particularly effective, with the median PFS not reached, while chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy produced a PFS of 9 months.
Dr. Mato emphasized that the results of the retrospective trial were “hypothesis generating” and noted that patients in the study had received a median of 3, and up to 11, prior therapies. “This population are probably not our patients receiving venetoclax in clinical practice. They’re more heavily pretreated.”
Dr. Mato reported disclosures related to Gilead, AstraZeneca, AbbVie, Sunesis, Johnson & Johnson, TG Therapeutics, Loxo Oncology, DTRM Biopharma, Genentech, Janssen, Acerta Pharma, Pharmacyclics, and Celgene.
SOURCE: Mato AR et al. ASH 2019, Abstract 502.
ORLANDO – For a patient with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) who has discontinued venetoclax, choosing the best next therapy may depend on what novel agents the patient was exposed to and why they discontinued them, according to Anthony R. Mato, MD, with the Center for CLL at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York.
If the patient is Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor naive, then use of a BTK inhibitor after venetoclax would be supported, Dr. Mato said, by the high overall response rates and durable remissions that he and his coinvestigators documented in a retrospective, multicenter study designed specifically to address the gap in knowledge regarding what to use after venetoclax.
If the patient is BTK inhibitor exposed, then the reason for discontinuation needs to be considered before going with that venetoclax-to-BTK inhibitor sequence, Dr. Mato said during an oral presentation at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
“In patients with resistance to a BTK inhibitor, the sequence was not supported – it did not appear to be effective,” he said. “However, in the setting of intolerance, an alternate BTK inhibitor could be considered.”
The study did not support a venetoclax-to-PI3K inhibitor sequence in PI3K-naive patients, he added, noting that remissions did not appear to be durable, suggesting a potential overlap in resistance mechanisms between agents.
All told, the most effective therapies for in the postvenetoclax setting included the use of a BTK inhibitor in BTK inhibitor–naive or previously responsive patients, and allogeneic transplant following double novel-agent exposure.
“These data may provide support for venetoclax’s earlier use in the course of CLL, and may guide clinical practice and aid in the design of future clinical trials to address sequencing of novel agents,” Dr. Mato told attendees.
While prospective and real-world data clearly show that venetoclax is active in ibrutinib- or idelalisib-exposed patients, data are conversely “variable and limited” with regard to outcomes for next therapies following venetoclax.
“Current data addressing this key sequencing question, I feel, is a major limitation in supporting the sequence of venetoclax to a BTK inhibitor,” Dr. Mato said.
Accordingly, Dr. Mato and colleagues at 31 centers internationally planned and conducted this study, which included data on 326 patients treated with venetoclax who then discontinued for any reason.
“I wanted to highlight that 50% of the sites for this trial were recruited by a single tweet,” said Dr. Mato, adding that he and his coauthors received no funding to conduct this study and volunteered their time to complete it.
They found that, in BTK inhibitor–naive patients who discontinued venetoclax, subsequent BTK inhibitor treatment was associated with a high overall response rate and durable remissions, with a median progression-free survival (PFS) of 32 months.
In BTK inhibitor–exposed patients, response to postvenetoclax BTK inhibitor treatment depended on the reason for discontinuation, with a favorable result (PFS not reached with a mean follow-up of 7.7 months) in patients who were intolerant of the prior BTK inhibitor. By contrast, median PFS was only about 4 months for patients who were resistant to the prior BTK inhibitor.
PI3K inhibitors did not produce durable remissions after venetoclax, with a median PFS also of just 4 months, Dr. Mato reported.
However, cellular therapies appeared to be effective after venetoclax. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation was particularly effective, with the median PFS not reached, while chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy produced a PFS of 9 months.
Dr. Mato emphasized that the results of the retrospective trial were “hypothesis generating” and noted that patients in the study had received a median of 3, and up to 11, prior therapies. “This population are probably not our patients receiving venetoclax in clinical practice. They’re more heavily pretreated.”
Dr. Mato reported disclosures related to Gilead, AstraZeneca, AbbVie, Sunesis, Johnson & Johnson, TG Therapeutics, Loxo Oncology, DTRM Biopharma, Genentech, Janssen, Acerta Pharma, Pharmacyclics, and Celgene.
SOURCE: Mato AR et al. ASH 2019, Abstract 502.
REPORTING FROM ASH 2019
Off-the-shelf cellular therapy shows promise in the lab
ORLANDO – A cellular therapy called FT596 is active against B-cell malignancies and, when combined with rituximab, can be more effective than traditional chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells, preclinical research findings suggest.
FT596 is a universal, anti-CD19 CAR natural killer (NK) cell therapy derived from a master induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC) line.
FT596 reduced tumor growth in mouse models of leukemia and lymphoma. When combined with rituximab, FT596 was able to overcome CD19 antigen escape.
Jode P. Goodridge, PhD, of Fate Therapeutics in San Diego, presented these results at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
Dr. Goodridge explained that FT596 begins with a source material, such as a fibroblast, that is reprogrammed into an iPSC progenitor cell. That cell is sorted and expanded into a renewable, homogeneous, pluripotent master iPSC line. The iPSCs are differentiated into CD34 cells, which are differentiated into NK cells. The iPSC-derived NK cells are then modified with the following:
- An anti-CD19 CAR that is optimized for NK-cell biology and contains an NKG2D transmembrane domain, a 2B4 costimulatory domain, and a CD3-zeta signaling domain.
- An interleukin-15 receptor fusion that promotes cell survival and reduces the need for cytokine support.
- A high-affinity 158V, noncleavable CD16 Fc receptor that enhances antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity when FT596 is combined with a monoclonal antibody such as rituximab.
Dr. Goodridge presented results with FT596, both alone and in combination with rituximab, in vitro and in vivo.
When compared with no treatment, three doses of FT596 monotherapy reduced tumor growth in a mouse model of leukemia (Nalm6). FT596 plus rituximab reduced tumor growth in a mouse model of lymphoma (Raji), when compared with no treatment or rituximab alone.
Three doses of FT596 proved more effective than a single dose of CD19 CAR T-cell therapy in a mouse model of lymphoma (Raji). FT596 both reduced tumor growth and prolonged survival in the mice.
Lastly, in vitro experiments in Raji cells showed that FT596 plus rituximab can produce deeper responses than primary CAR-T cells, and the combination can prevent antigen escape.
Dr. Goodridge said these results support the phase 1 study of FT596, given as monotherapy or in combination with rituximab or obinutuzumab, in patients with relapsed/refractory B-cell lymphomas or chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
Dr. Goodridge is employed by Fate Therapeutics, the company developing FT596.
SOURCE: Goodridge JP et al. ASH 2019. Abstract 301.
ORLANDO – A cellular therapy called FT596 is active against B-cell malignancies and, when combined with rituximab, can be more effective than traditional chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells, preclinical research findings suggest.
FT596 is a universal, anti-CD19 CAR natural killer (NK) cell therapy derived from a master induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC) line.
FT596 reduced tumor growth in mouse models of leukemia and lymphoma. When combined with rituximab, FT596 was able to overcome CD19 antigen escape.
Jode P. Goodridge, PhD, of Fate Therapeutics in San Diego, presented these results at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
Dr. Goodridge explained that FT596 begins with a source material, such as a fibroblast, that is reprogrammed into an iPSC progenitor cell. That cell is sorted and expanded into a renewable, homogeneous, pluripotent master iPSC line. The iPSCs are differentiated into CD34 cells, which are differentiated into NK cells. The iPSC-derived NK cells are then modified with the following:
- An anti-CD19 CAR that is optimized for NK-cell biology and contains an NKG2D transmembrane domain, a 2B4 costimulatory domain, and a CD3-zeta signaling domain.
- An interleukin-15 receptor fusion that promotes cell survival and reduces the need for cytokine support.
- A high-affinity 158V, noncleavable CD16 Fc receptor that enhances antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity when FT596 is combined with a monoclonal antibody such as rituximab.
Dr. Goodridge presented results with FT596, both alone and in combination with rituximab, in vitro and in vivo.
When compared with no treatment, three doses of FT596 monotherapy reduced tumor growth in a mouse model of leukemia (Nalm6). FT596 plus rituximab reduced tumor growth in a mouse model of lymphoma (Raji), when compared with no treatment or rituximab alone.
Three doses of FT596 proved more effective than a single dose of CD19 CAR T-cell therapy in a mouse model of lymphoma (Raji). FT596 both reduced tumor growth and prolonged survival in the mice.
Lastly, in vitro experiments in Raji cells showed that FT596 plus rituximab can produce deeper responses than primary CAR-T cells, and the combination can prevent antigen escape.
Dr. Goodridge said these results support the phase 1 study of FT596, given as monotherapy or in combination with rituximab or obinutuzumab, in patients with relapsed/refractory B-cell lymphomas or chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
Dr. Goodridge is employed by Fate Therapeutics, the company developing FT596.
SOURCE: Goodridge JP et al. ASH 2019. Abstract 301.
ORLANDO – A cellular therapy called FT596 is active against B-cell malignancies and, when combined with rituximab, can be more effective than traditional chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells, preclinical research findings suggest.
FT596 is a universal, anti-CD19 CAR natural killer (NK) cell therapy derived from a master induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC) line.
FT596 reduced tumor growth in mouse models of leukemia and lymphoma. When combined with rituximab, FT596 was able to overcome CD19 antigen escape.
Jode P. Goodridge, PhD, of Fate Therapeutics in San Diego, presented these results at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
Dr. Goodridge explained that FT596 begins with a source material, such as a fibroblast, that is reprogrammed into an iPSC progenitor cell. That cell is sorted and expanded into a renewable, homogeneous, pluripotent master iPSC line. The iPSCs are differentiated into CD34 cells, which are differentiated into NK cells. The iPSC-derived NK cells are then modified with the following:
- An anti-CD19 CAR that is optimized for NK-cell biology and contains an NKG2D transmembrane domain, a 2B4 costimulatory domain, and a CD3-zeta signaling domain.
- An interleukin-15 receptor fusion that promotes cell survival and reduces the need for cytokine support.
- A high-affinity 158V, noncleavable CD16 Fc receptor that enhances antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity when FT596 is combined with a monoclonal antibody such as rituximab.
Dr. Goodridge presented results with FT596, both alone and in combination with rituximab, in vitro and in vivo.
When compared with no treatment, three doses of FT596 monotherapy reduced tumor growth in a mouse model of leukemia (Nalm6). FT596 plus rituximab reduced tumor growth in a mouse model of lymphoma (Raji), when compared with no treatment or rituximab alone.
Three doses of FT596 proved more effective than a single dose of CD19 CAR T-cell therapy in a mouse model of lymphoma (Raji). FT596 both reduced tumor growth and prolonged survival in the mice.
Lastly, in vitro experiments in Raji cells showed that FT596 plus rituximab can produce deeper responses than primary CAR-T cells, and the combination can prevent antigen escape.
Dr. Goodridge said these results support the phase 1 study of FT596, given as monotherapy or in combination with rituximab or obinutuzumab, in patients with relapsed/refractory B-cell lymphomas or chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
Dr. Goodridge is employed by Fate Therapeutics, the company developing FT596.
SOURCE: Goodridge JP et al. ASH 2019. Abstract 301.
REPORTING FROM ASH 2019
FDA approves acalabrutinib for CLL, SLL treatment
The Food and Drug Administration has approved acalabrutinib (Calquence) as initial or subsequent treatment for adults with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) or small lymphocytic leukemia (SLL).
The approval came as part of Project Orbis, a collaboration among the FDA, the Australian Therapeutic Goods Administration, and Health Canada. The program allows for the concurrent submission of review of oncology drug applications among the various agencies.
Acalabrutinib, a bruton tyrosin kinase inhibitor, is already approved in the United States for the treatment of adults with mantle cell lymphoma who have received at least one prior therapy. The FDA granted breakthrough therapy designation to acalabrutinib as a monotherapy for adults with CLL in August 2019, allowing for an expedited review.
The approval in CLL/SLL was based on results from two randomized clinical trials comparing acalabrutinib with other standard treatments. In the first trial, patients with previously untreated CLL who received acalabrutinib had a longer progression-free survival time, compared with patients who received standard treatment. A similar result was seen in the second trial among patients with previously treated CLL.
The most common adverse events associated with acalabrutinib include anemia, neutropenia, upper respiratory tract infection, thrombocytopenia, headache, diarrhea, and musculoskeletal pain. Patients receiving the drug should be monitored for symptoms of arrhythmia, serious infection, bleeding, and low blood count. Full prescribing information can be found on the FDA website.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved acalabrutinib (Calquence) as initial or subsequent treatment for adults with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) or small lymphocytic leukemia (SLL).
The approval came as part of Project Orbis, a collaboration among the FDA, the Australian Therapeutic Goods Administration, and Health Canada. The program allows for the concurrent submission of review of oncology drug applications among the various agencies.
Acalabrutinib, a bruton tyrosin kinase inhibitor, is already approved in the United States for the treatment of adults with mantle cell lymphoma who have received at least one prior therapy. The FDA granted breakthrough therapy designation to acalabrutinib as a monotherapy for adults with CLL in August 2019, allowing for an expedited review.
The approval in CLL/SLL was based on results from two randomized clinical trials comparing acalabrutinib with other standard treatments. In the first trial, patients with previously untreated CLL who received acalabrutinib had a longer progression-free survival time, compared with patients who received standard treatment. A similar result was seen in the second trial among patients with previously treated CLL.
The most common adverse events associated with acalabrutinib include anemia, neutropenia, upper respiratory tract infection, thrombocytopenia, headache, diarrhea, and musculoskeletal pain. Patients receiving the drug should be monitored for symptoms of arrhythmia, serious infection, bleeding, and low blood count. Full prescribing information can be found on the FDA website.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved acalabrutinib (Calquence) as initial or subsequent treatment for adults with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) or small lymphocytic leukemia (SLL).
The approval came as part of Project Orbis, a collaboration among the FDA, the Australian Therapeutic Goods Administration, and Health Canada. The program allows for the concurrent submission of review of oncology drug applications among the various agencies.
Acalabrutinib, a bruton tyrosin kinase inhibitor, is already approved in the United States for the treatment of adults with mantle cell lymphoma who have received at least one prior therapy. The FDA granted breakthrough therapy designation to acalabrutinib as a monotherapy for adults with CLL in August 2019, allowing for an expedited review.
The approval in CLL/SLL was based on results from two randomized clinical trials comparing acalabrutinib with other standard treatments. In the first trial, patients with previously untreated CLL who received acalabrutinib had a longer progression-free survival time, compared with patients who received standard treatment. A similar result was seen in the second trial among patients with previously treated CLL.
The most common adverse events associated with acalabrutinib include anemia, neutropenia, upper respiratory tract infection, thrombocytopenia, headache, diarrhea, and musculoskeletal pain. Patients receiving the drug should be monitored for symptoms of arrhythmia, serious infection, bleeding, and low blood count. Full prescribing information can be found on the FDA website.
Frontline ibrutinib saves money over chemoimmunotherapy
Ibrutinib monotherapy was associated with lower total health care costs compared with chemoimmunotherapy in the frontline treatment of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), according to a retrospective study.
“This study compared time to next treatment, health care resource utilization, and total direct costs among patients with CLL initiating front-line ibrutinib single agent or chemoimmunotherapy,” wrote Bruno Emond, of Analysis Group, Montreal, and colleagues. Their report is in Clinical Lymphoma, Myeloma & Leukemia.
The researchers retrospectively analyzed data from 1,161 patients with CLL who were started on ibrutinib monotherapy or chemoimmunotherapy from 2014 to 2017. Data were collected from the Optum Clinformatics Extended DataMart De-Identified Databases.
Between the two groups, differences in baseline characteristics were controlled for by way of inverse probability of treatment weighting. Two treatment periods were included in the study: the initial 6 months of treatment and entire duration of frontline therapy.
The team also conducted a subgroup analysis of patients treated with bendamustine and rituximab. This cohort was analyzed independently since the regimen is commonly used in clinical practice.
After analysis, the researchers found that ibrutinib monotherapy was associated with net monthly cost savings of $3,766 (P less than .0001), compared with chemoimmunotherapy and bendamustine/rituximab over the frontline therapy period.
Ibrutinib patients had fewer monthly days with outpatient services (rate ratio, 0.75; 95% confidence interval, 0.60-0.94; P = .0200), compared with those on chemoimmunotherapy; and were less likely to initiate a next line of treatment, compared with chemoimmunotherapy patients (hazard ratio, 0.54; 95% CI, 0.33-0.90; P = .0163).
“Cost savings and reductions in health care resource utilization were even more pronounced when considering only the first 6 months of front-line treatment,” the researchers wrote.
The researchers acknowledged that two key limitations of the study were the potential influence of unobserved confounding factors and the use of claims data, which could include errors and omissions.
“These results suggest that ibrutinib single-agent is associated with lower total costs driven by lower medical costs, despite higher pharmacy costs, compared with chemoimmunotherapy and bendamustine/rituximab,” they concluded.
The authors reported financial affiliations with Janssen Scientific Affairs, which funded the study, and other companies.
SOURCE: Emond B et al. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2019 Aug 26. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2019.08.004.
Ibrutinib monotherapy was associated with lower total health care costs compared with chemoimmunotherapy in the frontline treatment of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), according to a retrospective study.
“This study compared time to next treatment, health care resource utilization, and total direct costs among patients with CLL initiating front-line ibrutinib single agent or chemoimmunotherapy,” wrote Bruno Emond, of Analysis Group, Montreal, and colleagues. Their report is in Clinical Lymphoma, Myeloma & Leukemia.
The researchers retrospectively analyzed data from 1,161 patients with CLL who were started on ibrutinib monotherapy or chemoimmunotherapy from 2014 to 2017. Data were collected from the Optum Clinformatics Extended DataMart De-Identified Databases.
Between the two groups, differences in baseline characteristics were controlled for by way of inverse probability of treatment weighting. Two treatment periods were included in the study: the initial 6 months of treatment and entire duration of frontline therapy.
The team also conducted a subgroup analysis of patients treated with bendamustine and rituximab. This cohort was analyzed independently since the regimen is commonly used in clinical practice.
After analysis, the researchers found that ibrutinib monotherapy was associated with net monthly cost savings of $3,766 (P less than .0001), compared with chemoimmunotherapy and bendamustine/rituximab over the frontline therapy period.
Ibrutinib patients had fewer monthly days with outpatient services (rate ratio, 0.75; 95% confidence interval, 0.60-0.94; P = .0200), compared with those on chemoimmunotherapy; and were less likely to initiate a next line of treatment, compared with chemoimmunotherapy patients (hazard ratio, 0.54; 95% CI, 0.33-0.90; P = .0163).
“Cost savings and reductions in health care resource utilization were even more pronounced when considering only the first 6 months of front-line treatment,” the researchers wrote.
The researchers acknowledged that two key limitations of the study were the potential influence of unobserved confounding factors and the use of claims data, which could include errors and omissions.
“These results suggest that ibrutinib single-agent is associated with lower total costs driven by lower medical costs, despite higher pharmacy costs, compared with chemoimmunotherapy and bendamustine/rituximab,” they concluded.
The authors reported financial affiliations with Janssen Scientific Affairs, which funded the study, and other companies.
SOURCE: Emond B et al. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2019 Aug 26. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2019.08.004.
Ibrutinib monotherapy was associated with lower total health care costs compared with chemoimmunotherapy in the frontline treatment of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), according to a retrospective study.
“This study compared time to next treatment, health care resource utilization, and total direct costs among patients with CLL initiating front-line ibrutinib single agent or chemoimmunotherapy,” wrote Bruno Emond, of Analysis Group, Montreal, and colleagues. Their report is in Clinical Lymphoma, Myeloma & Leukemia.
The researchers retrospectively analyzed data from 1,161 patients with CLL who were started on ibrutinib monotherapy or chemoimmunotherapy from 2014 to 2017. Data were collected from the Optum Clinformatics Extended DataMart De-Identified Databases.
Between the two groups, differences in baseline characteristics were controlled for by way of inverse probability of treatment weighting. Two treatment periods were included in the study: the initial 6 months of treatment and entire duration of frontline therapy.
The team also conducted a subgroup analysis of patients treated with bendamustine and rituximab. This cohort was analyzed independently since the regimen is commonly used in clinical practice.
After analysis, the researchers found that ibrutinib monotherapy was associated with net monthly cost savings of $3,766 (P less than .0001), compared with chemoimmunotherapy and bendamustine/rituximab over the frontline therapy period.
Ibrutinib patients had fewer monthly days with outpatient services (rate ratio, 0.75; 95% confidence interval, 0.60-0.94; P = .0200), compared with those on chemoimmunotherapy; and were less likely to initiate a next line of treatment, compared with chemoimmunotherapy patients (hazard ratio, 0.54; 95% CI, 0.33-0.90; P = .0163).
“Cost savings and reductions in health care resource utilization were even more pronounced when considering only the first 6 months of front-line treatment,” the researchers wrote.
The researchers acknowledged that two key limitations of the study were the potential influence of unobserved confounding factors and the use of claims data, which could include errors and omissions.
“These results suggest that ibrutinib single-agent is associated with lower total costs driven by lower medical costs, despite higher pharmacy costs, compared with chemoimmunotherapy and bendamustine/rituximab,” they concluded.
The authors reported financial affiliations with Janssen Scientific Affairs, which funded the study, and other companies.
SOURCE: Emond B et al. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2019 Aug 26. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2019.08.004.
FROM CLINICAL LYMPHOMA, MYELOMA & LEUKEMIA
Gene signature may help guide initial CLL treatment choice
A novel 17-gene expression signature may help guide the choice of initial treatment in patients with IGHV-unmutated chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), according to findings of a retrospective dual cohort study.
“[Fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab] was the first regimen to improve progression-free survival and overall survival in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia, and has become a gold-standard chemoimmunotherapy regimen in physically fit patients,” wrote the investigators, who were led by Carmen D. Herling, MD, of the Center for Integrated Oncology, Cologne, Germany; and Kevin R. Coombes, PhD, of Ohio State University, Columbus.
While several studies demonstrate that young, fit patients with mutated IGHV gene and no high-risk cytogenetic abnormalities achieve durable remission with the FCR (fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab) regimen, there have been no studies to identify if this is true for patients with unmutated IGHV gene, they reported in the Lancet Oncology.
The investigators performed transcriptional profiling using peripheral blood samples collected from two cohorts of patients with CLL who were treated with frontline FCR.
The discovery and training cohort consisted of 101 patients (65% with IGHV-unmutated disease) treated at the MD Anderson Cancer Center who had a median follow-up of about 12 years. The validation cohort consisted of 109 patients with IGHV-unmutated disease treated on the German CLL8 single-arm trial who had a median follow-up of about 6 years.
A total of 1,136 genes showed a significant univariate association with time to progression. Ultimately, 17 of these genes – most of them involved in purine metabolism and oxidative phosphorylation – were included in the expression signature.
Among patients with IGHV-unmutated CLL, the 17-gene signature discriminated between two groups having differing time to progression after their frontline FCR chemoimmunotherapy: an unfavorable prognosis group and an intermediate prognosis group.
The unfavorable prognosis group had a significantly higher relative risk of progression in both the discovery/training cohort (hazard ratio, 3.83; P less than .0001) and the validation cohort (HR, 1.90; P = .008). In the validation cohort, the median time to progression was 39 months among patients with a signature-defined unfavorable prognosis, compared with 59 months among patients with a signature-defined intermediate prognosis.
“We would recommend testing the value of the 17-gene signature in a prospective study that compares FCR treatment with alternative therapies, such as ibrutinib, as part of a randomised clinical trial,” the investigators wrote.
Dr. Herling reported financial disclosures related to Hoffmann-La Roche, and Dr. Coombes reported grants from the National Institutes of Health. The study was funded by the Chronic Lymphocytic Leukaemia Global Research Foundation and the National Institutes of Health/National Cancer Institute.
SOURCE: Herling CD et al. Lancet Oncol. 2019;20(11):1576-86.
A novel 17-gene expression signature may help guide the choice of initial treatment in patients with IGHV-unmutated chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), according to findings of a retrospective dual cohort study.
“[Fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab] was the first regimen to improve progression-free survival and overall survival in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia, and has become a gold-standard chemoimmunotherapy regimen in physically fit patients,” wrote the investigators, who were led by Carmen D. Herling, MD, of the Center for Integrated Oncology, Cologne, Germany; and Kevin R. Coombes, PhD, of Ohio State University, Columbus.
While several studies demonstrate that young, fit patients with mutated IGHV gene and no high-risk cytogenetic abnormalities achieve durable remission with the FCR (fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab) regimen, there have been no studies to identify if this is true for patients with unmutated IGHV gene, they reported in the Lancet Oncology.
The investigators performed transcriptional profiling using peripheral blood samples collected from two cohorts of patients with CLL who were treated with frontline FCR.
The discovery and training cohort consisted of 101 patients (65% with IGHV-unmutated disease) treated at the MD Anderson Cancer Center who had a median follow-up of about 12 years. The validation cohort consisted of 109 patients with IGHV-unmutated disease treated on the German CLL8 single-arm trial who had a median follow-up of about 6 years.
A total of 1,136 genes showed a significant univariate association with time to progression. Ultimately, 17 of these genes – most of them involved in purine metabolism and oxidative phosphorylation – were included in the expression signature.
Among patients with IGHV-unmutated CLL, the 17-gene signature discriminated between two groups having differing time to progression after their frontline FCR chemoimmunotherapy: an unfavorable prognosis group and an intermediate prognosis group.
The unfavorable prognosis group had a significantly higher relative risk of progression in both the discovery/training cohort (hazard ratio, 3.83; P less than .0001) and the validation cohort (HR, 1.90; P = .008). In the validation cohort, the median time to progression was 39 months among patients with a signature-defined unfavorable prognosis, compared with 59 months among patients with a signature-defined intermediate prognosis.
“We would recommend testing the value of the 17-gene signature in a prospective study that compares FCR treatment with alternative therapies, such as ibrutinib, as part of a randomised clinical trial,” the investigators wrote.
Dr. Herling reported financial disclosures related to Hoffmann-La Roche, and Dr. Coombes reported grants from the National Institutes of Health. The study was funded by the Chronic Lymphocytic Leukaemia Global Research Foundation and the National Institutes of Health/National Cancer Institute.
SOURCE: Herling CD et al. Lancet Oncol. 2019;20(11):1576-86.
A novel 17-gene expression signature may help guide the choice of initial treatment in patients with IGHV-unmutated chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), according to findings of a retrospective dual cohort study.
“[Fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab] was the first regimen to improve progression-free survival and overall survival in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia, and has become a gold-standard chemoimmunotherapy regimen in physically fit patients,” wrote the investigators, who were led by Carmen D. Herling, MD, of the Center for Integrated Oncology, Cologne, Germany; and Kevin R. Coombes, PhD, of Ohio State University, Columbus.
While several studies demonstrate that young, fit patients with mutated IGHV gene and no high-risk cytogenetic abnormalities achieve durable remission with the FCR (fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab) regimen, there have been no studies to identify if this is true for patients with unmutated IGHV gene, they reported in the Lancet Oncology.
The investigators performed transcriptional profiling using peripheral blood samples collected from two cohorts of patients with CLL who were treated with frontline FCR.
The discovery and training cohort consisted of 101 patients (65% with IGHV-unmutated disease) treated at the MD Anderson Cancer Center who had a median follow-up of about 12 years. The validation cohort consisted of 109 patients with IGHV-unmutated disease treated on the German CLL8 single-arm trial who had a median follow-up of about 6 years.
A total of 1,136 genes showed a significant univariate association with time to progression. Ultimately, 17 of these genes – most of them involved in purine metabolism and oxidative phosphorylation – were included in the expression signature.
Among patients with IGHV-unmutated CLL, the 17-gene signature discriminated between two groups having differing time to progression after their frontline FCR chemoimmunotherapy: an unfavorable prognosis group and an intermediate prognosis group.
The unfavorable prognosis group had a significantly higher relative risk of progression in both the discovery/training cohort (hazard ratio, 3.83; P less than .0001) and the validation cohort (HR, 1.90; P = .008). In the validation cohort, the median time to progression was 39 months among patients with a signature-defined unfavorable prognosis, compared with 59 months among patients with a signature-defined intermediate prognosis.
“We would recommend testing the value of the 17-gene signature in a prospective study that compares FCR treatment with alternative therapies, such as ibrutinib, as part of a randomised clinical trial,” the investigators wrote.
Dr. Herling reported financial disclosures related to Hoffmann-La Roche, and Dr. Coombes reported grants from the National Institutes of Health. The study was funded by the Chronic Lymphocytic Leukaemia Global Research Foundation and the National Institutes of Health/National Cancer Institute.
SOURCE: Herling CD et al. Lancet Oncol. 2019;20(11):1576-86.
FROM LANCET ONCOLOGY
Consider renal function in TLS risk assessment of venetoclax-treated CLL
EDINBURGH – Impaired renal function may indicate excess risk of tumor lysis syndrome (TLS) in venetoclax-treated chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) patients and should be considered when assessing TLS risk, according to findings from a retrospective cohort study.
Complex karyotype may also affect TLS risk, Anthony Mato, MD, reported at the International Workshop on Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia.
Of 339 CLL patients who were treated with venetoclax, 38%, 34%, and 28% were considered to have low, medium, or high risk for TLS, respectively, according to the standard definition based on absolute lymphocyte count as a measure of tumor burden and/or lymph node size.
TLS occurred in 35 patients (10%), including 26 cases of laboratory-confirmed TLS and 9 clinical TLS cases; 1 patient required dialysis and 1 death occurred, which was attributable to the TLS, Dr. Mato of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, and colleagues reported in a poster at the workshop.
Univariate analysis was performed to “understand baseline factors associated with TLS development during dose escalation,” and it examined sex, creatinine clearance (CrCl), complex karyotype, immunoglobulin heavy chain variable mutation status, prior ibrutinib exposure, venetoclax monotherapy vs. combination therapy, and TLS risk group. The investigators observed no significant difference between the low- and medium-risk patients, therefore those two groups were combined and compared with the high-risk patients.
The univariate analysis showed significant associations between TLS and CrCl (odds ratio, 2.9 for 80 mL/min or less vs. greater than 80 mL/min), complex karyotype (OR, 2.2), and low/medium vs. high TLS risk based on the standard definition (OR, 2.56).
A multivariable analysis of the predictors identified as significant in the univariate analyses showed that standard TLS risk group and CrCl remained independent predictors of TLS.
“Although the odds ratio for complex karyotype suggested potential clinical significance, this did not meet the threshold for statistical significance and was not included in the final model,” they wrote.
The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve for a model including TLS risk group and CrCl was 74.6%, compared with 65% for the area under the ROC curve using the standard tumor burden/lymph node size approach for defining TLS risk, which is described in the venetoclax package insert.
Patients included in the study had a median age of 67 years at venetoclax initiation, 69% were men, 85% were white, and 13% were treated on a clinical trial. Complex karyotype was present in 39%, del(17p) in 43%, and 84% had immunoglobulin heavy chain variable–unmutated disease.
Most patients received venetoclax monotherapy (79%), had relapsed/refractory disease (94%), and had previously received ibrutinib (78%). The median number of prior therapies was 3, but the number ranged from 0-15, the investigators noted.
The findings of this study suggest that, in addition to defining risk based on absolute lymphocyte count and lymph node size, patients with CrCl less than 80 mL/min – indicating impaired renal function – have excess risk of TLS.
Although complex karyotype did not reach statistical significance as an independent predictor of TLS, the findings in this study suggest it “may impact TLS risk and is worthy of further study in larger samples,” they said, concluding that consideration of baseline renal function, and possibly karyotype, could “further guide practitioners in their approach to prophylaxis and patient counseling, allowing for improved safety in the use of this effective agent in CLL.”
Additional planned analyses will focus on TLS risk score development and further refinement of TLS risk stratification, they noted.
Dr. Mato has received grant support, consulting fees, and/or fees for serving on a data and safety monitoring board or advisory board from AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Celgene, Janssen, TG Therapeutics, Pharmacyclics, Loxo, Sunesis, prIME Oncology, Pfizer, Johnson & Johnson, and Regeneron.
EDINBURGH – Impaired renal function may indicate excess risk of tumor lysis syndrome (TLS) in venetoclax-treated chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) patients and should be considered when assessing TLS risk, according to findings from a retrospective cohort study.
Complex karyotype may also affect TLS risk, Anthony Mato, MD, reported at the International Workshop on Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia.
Of 339 CLL patients who were treated with venetoclax, 38%, 34%, and 28% were considered to have low, medium, or high risk for TLS, respectively, according to the standard definition based on absolute lymphocyte count as a measure of tumor burden and/or lymph node size.
TLS occurred in 35 patients (10%), including 26 cases of laboratory-confirmed TLS and 9 clinical TLS cases; 1 patient required dialysis and 1 death occurred, which was attributable to the TLS, Dr. Mato of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, and colleagues reported in a poster at the workshop.
Univariate analysis was performed to “understand baseline factors associated with TLS development during dose escalation,” and it examined sex, creatinine clearance (CrCl), complex karyotype, immunoglobulin heavy chain variable mutation status, prior ibrutinib exposure, venetoclax monotherapy vs. combination therapy, and TLS risk group. The investigators observed no significant difference between the low- and medium-risk patients, therefore those two groups were combined and compared with the high-risk patients.
The univariate analysis showed significant associations between TLS and CrCl (odds ratio, 2.9 for 80 mL/min or less vs. greater than 80 mL/min), complex karyotype (OR, 2.2), and low/medium vs. high TLS risk based on the standard definition (OR, 2.56).
A multivariable analysis of the predictors identified as significant in the univariate analyses showed that standard TLS risk group and CrCl remained independent predictors of TLS.
“Although the odds ratio for complex karyotype suggested potential clinical significance, this did not meet the threshold for statistical significance and was not included in the final model,” they wrote.
The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve for a model including TLS risk group and CrCl was 74.6%, compared with 65% for the area under the ROC curve using the standard tumor burden/lymph node size approach for defining TLS risk, which is described in the venetoclax package insert.
Patients included in the study had a median age of 67 years at venetoclax initiation, 69% were men, 85% were white, and 13% were treated on a clinical trial. Complex karyotype was present in 39%, del(17p) in 43%, and 84% had immunoglobulin heavy chain variable–unmutated disease.
Most patients received venetoclax monotherapy (79%), had relapsed/refractory disease (94%), and had previously received ibrutinib (78%). The median number of prior therapies was 3, but the number ranged from 0-15, the investigators noted.
The findings of this study suggest that, in addition to defining risk based on absolute lymphocyte count and lymph node size, patients with CrCl less than 80 mL/min – indicating impaired renal function – have excess risk of TLS.
Although complex karyotype did not reach statistical significance as an independent predictor of TLS, the findings in this study suggest it “may impact TLS risk and is worthy of further study in larger samples,” they said, concluding that consideration of baseline renal function, and possibly karyotype, could “further guide practitioners in their approach to prophylaxis and patient counseling, allowing for improved safety in the use of this effective agent in CLL.”
Additional planned analyses will focus on TLS risk score development and further refinement of TLS risk stratification, they noted.
Dr. Mato has received grant support, consulting fees, and/or fees for serving on a data and safety monitoring board or advisory board from AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Celgene, Janssen, TG Therapeutics, Pharmacyclics, Loxo, Sunesis, prIME Oncology, Pfizer, Johnson & Johnson, and Regeneron.
EDINBURGH – Impaired renal function may indicate excess risk of tumor lysis syndrome (TLS) in venetoclax-treated chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) patients and should be considered when assessing TLS risk, according to findings from a retrospective cohort study.
Complex karyotype may also affect TLS risk, Anthony Mato, MD, reported at the International Workshop on Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia.
Of 339 CLL patients who were treated with venetoclax, 38%, 34%, and 28% were considered to have low, medium, or high risk for TLS, respectively, according to the standard definition based on absolute lymphocyte count as a measure of tumor burden and/or lymph node size.
TLS occurred in 35 patients (10%), including 26 cases of laboratory-confirmed TLS and 9 clinical TLS cases; 1 patient required dialysis and 1 death occurred, which was attributable to the TLS, Dr. Mato of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, and colleagues reported in a poster at the workshop.
Univariate analysis was performed to “understand baseline factors associated with TLS development during dose escalation,” and it examined sex, creatinine clearance (CrCl), complex karyotype, immunoglobulin heavy chain variable mutation status, prior ibrutinib exposure, venetoclax monotherapy vs. combination therapy, and TLS risk group. The investigators observed no significant difference between the low- and medium-risk patients, therefore those two groups were combined and compared with the high-risk patients.
The univariate analysis showed significant associations between TLS and CrCl (odds ratio, 2.9 for 80 mL/min or less vs. greater than 80 mL/min), complex karyotype (OR, 2.2), and low/medium vs. high TLS risk based on the standard definition (OR, 2.56).
A multivariable analysis of the predictors identified as significant in the univariate analyses showed that standard TLS risk group and CrCl remained independent predictors of TLS.
“Although the odds ratio for complex karyotype suggested potential clinical significance, this did not meet the threshold for statistical significance and was not included in the final model,” they wrote.
The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve for a model including TLS risk group and CrCl was 74.6%, compared with 65% for the area under the ROC curve using the standard tumor burden/lymph node size approach for defining TLS risk, which is described in the venetoclax package insert.
Patients included in the study had a median age of 67 years at venetoclax initiation, 69% were men, 85% were white, and 13% were treated on a clinical trial. Complex karyotype was present in 39%, del(17p) in 43%, and 84% had immunoglobulin heavy chain variable–unmutated disease.
Most patients received venetoclax monotherapy (79%), had relapsed/refractory disease (94%), and had previously received ibrutinib (78%). The median number of prior therapies was 3, but the number ranged from 0-15, the investigators noted.
The findings of this study suggest that, in addition to defining risk based on absolute lymphocyte count and lymph node size, patients with CrCl less than 80 mL/min – indicating impaired renal function – have excess risk of TLS.
Although complex karyotype did not reach statistical significance as an independent predictor of TLS, the findings in this study suggest it “may impact TLS risk and is worthy of further study in larger samples,” they said, concluding that consideration of baseline renal function, and possibly karyotype, could “further guide practitioners in their approach to prophylaxis and patient counseling, allowing for improved safety in the use of this effective agent in CLL.”
Additional planned analyses will focus on TLS risk score development and further refinement of TLS risk stratification, they noted.
Dr. Mato has received grant support, consulting fees, and/or fees for serving on a data and safety monitoring board or advisory board from AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Celgene, Janssen, TG Therapeutics, Pharmacyclics, Loxo, Sunesis, prIME Oncology, Pfizer, Johnson & Johnson, and Regeneron.
REPORTING FROM iwCLL 2019