User login
Osteoporosis Drug Denosumab May Confer Lower Risk for Diabetes
TOPLINE:
Continued denosumab treatment is associated with a lower risk for diabetes in adults with osteoporosis older than 65 years, found a large-scale cohort study in Taiwan.
METHODOLOGY:
- Denosumab, used in osteoporosis treatment, has been suggested to improve glycemic parameters, but clinical evidence of its effects on diabetes risk is limited and inconsistent.
- Using data from Taiwan’s National Health Insurance Research Database (NHIRD), the study asked if continued denosumab treatment (60 mg) for osteoporosis reduced the risk for diabetes compared to those who discontinued denosumab.
- Researchers included all new users of denosumab between 2012 and 2019 who had no prior history of malignant neoplasms, Paget disease, or diabetes requiring antidiabetic medication.
- Patients in the treatment group (n = 34,255), who received a second dose of denosumab within 225 days, were 1:1 propensity matched with a control group (n = 34,255) of patients who had discontinued denosumab after the first dose.
- The 68,510 patients (mean age, 77.7 years; 84.3% women) were followed up for a mean of 1.9 years. The primary outcome was new-onset diabetes that required treatment with any antidiabetic drug.
TAKEAWAY:
- Continued denosumab treatment vs its discontinuation was associated with a lower risk for incident diabetes (hazard ratio [HR], 0.84; 95% CI, 0.78-0.90).
- In patients aged 65 years or older who were on continued treatment of denosumab, the risk for diabetes was lower (HR, 0.80; 95% CI, 0.75-0.85) but not among those younger than 65 years.
- A reduced risk for diabetes with continued denosumab treatment was observed in both men (HR, 0.85; 95% CI, 0.73-0.97) and women (HR, 0.81; 95% CI, 0.76-0.86).
- Lower diabetes risk with continued denosumab treatment was observed regardless of comorbidities, such as dyslipidemia, hypertension, ischemic heart disease, or kidney failure.
IN PRACTICE:
“Given the high osteoporosis prevalence, the extensive use of antiosteoporosis medications, and the negative effect of diabetes on both patient health and healthcare system burdens in the global aging population, our findings possess substantial clinical and public health significance,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Huei-Kai Huang, MD, Department of Family Medicine and Department of Medical Research, Hualien Tzu Chi Hospital, Buddhist Tzu Chi Medical Foundation, Hualien, Taiwan, and published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The research used claims-based data, so some clinical details, such as lifestyle, substance use, prediabetes weight status, and laboratory results, were not included. Owing to the anonymity policy of the NHIRD, patients could not be directly evaluated to validate incident diabetes. The study included the Taiwanese population, so the findings may not be generalizable to other populations. In Taiwan, the threshold for reimbursement of initiating denosumab treatment for osteoporosis includes below-normal bone density scores and a hip or vertebral fracture.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by grants from the National Science and Technology Council of Taiwan and the National Health Research Institutes of Taiwan and a grant from the Buddhist Tzu Chi Medical Foundation. The corresponding author and a coauthor disclosed receiving funds from Amgen, Novartis, Pfizer, Sanofi, Takeda, and AbbVie, all outside the submitted work.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Continued denosumab treatment is associated with a lower risk for diabetes in adults with osteoporosis older than 65 years, found a large-scale cohort study in Taiwan.
METHODOLOGY:
- Denosumab, used in osteoporosis treatment, has been suggested to improve glycemic parameters, but clinical evidence of its effects on diabetes risk is limited and inconsistent.
- Using data from Taiwan’s National Health Insurance Research Database (NHIRD), the study asked if continued denosumab treatment (60 mg) for osteoporosis reduced the risk for diabetes compared to those who discontinued denosumab.
- Researchers included all new users of denosumab between 2012 and 2019 who had no prior history of malignant neoplasms, Paget disease, or diabetes requiring antidiabetic medication.
- Patients in the treatment group (n = 34,255), who received a second dose of denosumab within 225 days, were 1:1 propensity matched with a control group (n = 34,255) of patients who had discontinued denosumab after the first dose.
- The 68,510 patients (mean age, 77.7 years; 84.3% women) were followed up for a mean of 1.9 years. The primary outcome was new-onset diabetes that required treatment with any antidiabetic drug.
TAKEAWAY:
- Continued denosumab treatment vs its discontinuation was associated with a lower risk for incident diabetes (hazard ratio [HR], 0.84; 95% CI, 0.78-0.90).
- In patients aged 65 years or older who were on continued treatment of denosumab, the risk for diabetes was lower (HR, 0.80; 95% CI, 0.75-0.85) but not among those younger than 65 years.
- A reduced risk for diabetes with continued denosumab treatment was observed in both men (HR, 0.85; 95% CI, 0.73-0.97) and women (HR, 0.81; 95% CI, 0.76-0.86).
- Lower diabetes risk with continued denosumab treatment was observed regardless of comorbidities, such as dyslipidemia, hypertension, ischemic heart disease, or kidney failure.
IN PRACTICE:
“Given the high osteoporosis prevalence, the extensive use of antiosteoporosis medications, and the negative effect of diabetes on both patient health and healthcare system burdens in the global aging population, our findings possess substantial clinical and public health significance,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Huei-Kai Huang, MD, Department of Family Medicine and Department of Medical Research, Hualien Tzu Chi Hospital, Buddhist Tzu Chi Medical Foundation, Hualien, Taiwan, and published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The research used claims-based data, so some clinical details, such as lifestyle, substance use, prediabetes weight status, and laboratory results, were not included. Owing to the anonymity policy of the NHIRD, patients could not be directly evaluated to validate incident diabetes. The study included the Taiwanese population, so the findings may not be generalizable to other populations. In Taiwan, the threshold for reimbursement of initiating denosumab treatment for osteoporosis includes below-normal bone density scores and a hip or vertebral fracture.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by grants from the National Science and Technology Council of Taiwan and the National Health Research Institutes of Taiwan and a grant from the Buddhist Tzu Chi Medical Foundation. The corresponding author and a coauthor disclosed receiving funds from Amgen, Novartis, Pfizer, Sanofi, Takeda, and AbbVie, all outside the submitted work.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Continued denosumab treatment is associated with a lower risk for diabetes in adults with osteoporosis older than 65 years, found a large-scale cohort study in Taiwan.
METHODOLOGY:
- Denosumab, used in osteoporosis treatment, has been suggested to improve glycemic parameters, but clinical evidence of its effects on diabetes risk is limited and inconsistent.
- Using data from Taiwan’s National Health Insurance Research Database (NHIRD), the study asked if continued denosumab treatment (60 mg) for osteoporosis reduced the risk for diabetes compared to those who discontinued denosumab.
- Researchers included all new users of denosumab between 2012 and 2019 who had no prior history of malignant neoplasms, Paget disease, or diabetes requiring antidiabetic medication.
- Patients in the treatment group (n = 34,255), who received a second dose of denosumab within 225 days, were 1:1 propensity matched with a control group (n = 34,255) of patients who had discontinued denosumab after the first dose.
- The 68,510 patients (mean age, 77.7 years; 84.3% women) were followed up for a mean of 1.9 years. The primary outcome was new-onset diabetes that required treatment with any antidiabetic drug.
TAKEAWAY:
- Continued denosumab treatment vs its discontinuation was associated with a lower risk for incident diabetes (hazard ratio [HR], 0.84; 95% CI, 0.78-0.90).
- In patients aged 65 years or older who were on continued treatment of denosumab, the risk for diabetes was lower (HR, 0.80; 95% CI, 0.75-0.85) but not among those younger than 65 years.
- A reduced risk for diabetes with continued denosumab treatment was observed in both men (HR, 0.85; 95% CI, 0.73-0.97) and women (HR, 0.81; 95% CI, 0.76-0.86).
- Lower diabetes risk with continued denosumab treatment was observed regardless of comorbidities, such as dyslipidemia, hypertension, ischemic heart disease, or kidney failure.
IN PRACTICE:
“Given the high osteoporosis prevalence, the extensive use of antiosteoporosis medications, and the negative effect of diabetes on both patient health and healthcare system burdens in the global aging population, our findings possess substantial clinical and public health significance,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Huei-Kai Huang, MD, Department of Family Medicine and Department of Medical Research, Hualien Tzu Chi Hospital, Buddhist Tzu Chi Medical Foundation, Hualien, Taiwan, and published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The research used claims-based data, so some clinical details, such as lifestyle, substance use, prediabetes weight status, and laboratory results, were not included. Owing to the anonymity policy of the NHIRD, patients could not be directly evaluated to validate incident diabetes. The study included the Taiwanese population, so the findings may not be generalizable to other populations. In Taiwan, the threshold for reimbursement of initiating denosumab treatment for osteoporosis includes below-normal bone density scores and a hip or vertebral fracture.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by grants from the National Science and Technology Council of Taiwan and the National Health Research Institutes of Taiwan and a grant from the Buddhist Tzu Chi Medical Foundation. The corresponding author and a coauthor disclosed receiving funds from Amgen, Novartis, Pfizer, Sanofi, Takeda, and AbbVie, all outside the submitted work.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Diabetes Basic Training Program: Empowering Veterans for Wellness
More than 37 million Americans (11.3%) have diabetes mellitus (DM), and 90% to 95% are diagnosed with type 2 DM, including nearly 1 in 4 veterans receiving Veterans Health Administration (VHA) care.1,2 DM is associated with serious negative health outcomes, including cardiovascular disease and subsequent complications as well as significant health care system utilization and cost.1,3
Group interventions have been identified as a possible method of improving DM outcomes. For example, shared medical appointments (SMAs) have been identified by the VHA as holding promise for improving care and efficiency for DM and other common health conditions.4 Although the precise structure and SMA process for managing DM has been noted to be heterogeneous, the appointment is typically led by an interdisciplinary health care team and includes individualized assessment including medication review and adjustment, group education, and troubleshooting challenges with management in a group format.5 Research suggests that DM SMAs are a worthwhile treatment approach.5 Several studies have found that SMAs were associated with decreased hemoglobin A1c (Hb A1c) levels and improvement in overall disease complications and severity.6
The high degree of SMA heterogeneity and lack of detailed description of structure and process of SMAs studied has made meta-analysis and other synthesis of the literature difficult.5 Consequently, there is inadequate empirically supported guidance for clinicians and health care organizations on how to best implement SMAs and similar group-based treatments. Edelman and colleagues recommended that future research should focus on more consistent and standardized intervention structures and real-world patient- and staff-centered outcomes to address gaps in the literature.5 They noted that a mental health professional was utilized in only a minority of SMAs studied.5 Additionally, we noted a paucity of studies examining patient satisfaction with SMAs.
Another group-based intervention found to be effective in improving DM outcomes is the 6-session Stanford Diabetes Self-Management Program (DSMP), a workshop led in part by trained peers with DM. The sessions focus on educating patients on DM care and self-management tools. The workshop encourages active practice in building DM self-management skills and confidence. DSMP participation has been associated with improvement in DM-related outcomes, including Hb A1c levels, amount of exercise, and medication adherence.7
While SMAs and DSMP have been shown to enhance clinical outcomes, they provide differing types of patient support. SMAs allow for frequent interaction with a health care professional (HCP) and less emphasis on behavioral health interventions. DSMPs include behavioral health professionals and peer leaders and emphasize higher levels of psychosocial support, but do not offer access to clinicians. It is possible that combining these interventions could result in better outcomes than what either could provide on their own.
In 2018, the Cincinnati Veterans Affairs Medical Center (VAMC) in Ohio offered Diabetes Basic Training, a structured DM intervention. Patients enrolled in the program participated in a 9-week intervention that included 3 SMAs and 6 DSMP sessions. During the SMAs, a clinical psychologist or psychology postdoctoral fellow skilled in motivational interviewing facilitated the group to enhance patient engagement and empowerment for improved self-management. In addition, patients participated in structured DSMP groups with an emphasis on action-planning, often surrounding nutrition, physical activity, and other health behavior change information reviewed during the SMAs.
Design and Referral
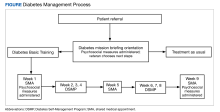
Self-management programs for chronic health conditions are often underutilized. Although HCPs may wish to connect veterans with available programs, time constraints may limit opportunities for detailed discussions with patients about specific aspects of each program. To simplify this process, a 2-hour orientation program was offered that explained individual and group DM self-management options (Figure). During this initial visit, patients met with an interdisciplinary care team (registered dietician, diabetes nurse practitioner, and behavioral health specialist) and were informed about Diabetes Basic Training, DM clinical care practices, and other related resources available at the Cincinnati VAMC (eg, cooking classes, food pantry). Patients received individualized referral recommendations and were urged to consult with their primary care practitioner to finalize their treatment plan.
Shared Medical Appointments
Diabetes Basic Training interventions had an average of 6 to 8 veterans participating in the weekly groups. The first, fifth, and final weeks were SMAs in which an interdisciplinary team collaboratively provided group-based health care for DM. The team consisted of a registered nurse, a prescriber (eg, nurse practitioner), a moderator (eg, psychologist), and a content expert (eg, nutritionist). Before each SMA began, the nurse checked-in patients in the SMA room and collected heart rate and blood pressure, and performed a diabetic foot check. Each SMA consisted of introductions, group-driven discussions (facilitated by an HCP) and troubleshooting DM self-management challenges. During group discussions, the prescriber initiated a 1-on-1 discussion with each patient in a private office regarding their recent laboratory results, medication regimen, and other aspects of DM care. The patient’s medications were refilled and/or adjusted as needed and other orders and referrals were submitted. If a patient had a medical question, the prescriber and moderator engaged the entire group so all individuals could benefit from generating and hearing answers. When discussion slowed, education was provided on topics generated by the group. Frequent topics included challenges managing DM, concerns, how DM impacted daily life and relationships, and sharing successes. As needed, HCPs spoke individually with patients following the SMA. Patients were sometimes asked, but never required, to do homework consistent with standard DM care (eg, recording what they eat or blood sugar levels). Each SMA session lasted about 2 hours.
Diabetes Self-Management Program
The second, third, fourth, sixth, seventh, and eighth weeks of the program were devoted to the DSMP. These sessions were delivered primarily by veteran peers who received appropriate training, observation, and certification. Each 2-hour educational program provided ample practice in many fundamental self-management skills, such as decision making, problem solving, and action planning. Patients were asked, but never required, to practice related skills during the sessions and to create weekly action plans to be completed between sessions that typically involved increasing exercise or improving diet. Patients were encouraged to follow up with HCPs at SMAs when they had questions requiring HCP expertise. If participants had more immediate concerns regarding their treatment plan and/or medications, they contacted their primary care practitioner prior to the next SMA.
As a part of participation in the program, psychosocial and health data and Hb A1c levels at baseline (the closest level to 90 days prior to start) and follow-up (the closest level to 90 days after the final session) were collected.8 In addition, Problem Areas in Diabetes (PAID), Patient Activation Measure (PAM)-13, and Diabetes Self-Management Questionnaire (DSMQ) were administered at 3 points: during the orientation, in the first week, and in the ninth week of the program.
PAID, a 20-item self-report questionnaire designed to capture
Observations
All measures were collected as part of traditional clinical care, and we present initial program evaluation data to demonstrate potential effectiveness of the clinic model. Paired samples t tests were used to examine differences between baseline and follow-up measures for the 24 veteran participants. The age of participants who completed the program ranged from 42 to 74 years (mean, 68 years); 29% of participants were Black veterans and 12% were female. Examination of clinical outcomes indicated that veterans reported significant increases in activation levels for managing their health increasing from a baseline mean (SD) 62.1 (12.3) to 68.4 (14.5) at follow up (t[23] = 2.15, P = .04). Hb A1c levels trended downward from a mean (SD) 8.6% (1.3) at baseline to 8.2% (1.2) at 90-day follow up (t[21] 1.05, P = .30). Similar nonsignificant trends in PAID scores were seen for pre- and postprogram reductions in emotional distress related to having DM from a mean (SD) 7.9 (5.0) at baseline to 6.3 (5.1) (t[18] = 11.51, P = .15), and enhanced self-management of glucose with a mean (SD) 6.5 (1.5) at baseline to 6.8 (1.3) at follow up (t[19] = 0.52, P = .61). The trends found in this study show promising outcomes for this pilot group-based DM treatment, though the small sample size (N = 24) limits statistical power. These findings support further exploration and expansion of interdisciplinary health programs supporting veteran self-management.
Discussion
DM is a condition of epidemic proportions that causes substantial negative health outcomes and costs at a national level. Current standards of DM care do not appear to be reversing these trends. Wider implementation of group-based treatment for DM could improve efficiency of care, increase access to quality care, and reduce burden on individual HCPs.
The VHA continues the transformation of its care system, which shifts toward a patient-centered, proactive focus on veteran well-being. This new whole health approach integrates conventional medical treatment with veteran self-empowerment in the pursuit of health goals based on individual veteran’s identified values.19 This approach emphasizes peer-led explorations of veterans’ aspirations, purpose, and individual mission, personalized health planning, and use of whole health coaches and well-being programs, with both allopathic and complementary and integrative clinical care centered around veterans’ identified goals and priorities.20
Including a program like Diabetes Basic Training as a part of whole health programming could offer several benefits. Diabetes Basic Training is unique in its integration of more traditional SMA structure with psychosocial interventions including values identification and motivational interviewing strategies to enhance patient engagement. Veterans can learn from each other’s experiences and concerns, leading to better DM management knowledge and skills. The group nature of the sessions enhances opportunities for emotional support and reduced isolation, as well as peer accountability for maintaining medication adherence.
By meeting with HCPs from multiple disciplines, veterans are exposed to different perspectives on self-management techniques, including behavioral approaches for overcoming barriers to behavior change. Clinicians have more time to engage with patients, building stronger relationships and trust. SMAs are cost-efficient and time efficient, allowing HCPs to see multiple patients at once, reducing wait times and increasing the number of patients treated in a given time frame.
The COVID-19 pandemic temporarily impacted the ongoing expansion of the program, when so many services were shifted from in-person to virtual classes. Due to staffing and other logistic issues, our pilot program was suspended during that time, but plans to resume the program by early 2024 are moving forward.
CONCLUSIONS
The Diabetes Basic Training program serves as a successful model for implementation within a VAMC. Although the number of veterans with complete data available for analysis was small, the trends exhibited in the preliminary outcome data are promising. We encourage other VAMCs to replicate this program with a larger participant base and evaluate its impact on veteran health outcomes. Next steps include comparing the clinical data from treatment as usual with outcomes from DM group participants. As the program resumes, we will reinitiate recruitment efforts to increase HCP referrals to this program.
1. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Diabetes Statistics. Updated February 2023. Accessed January 22, 2024. https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/health-statistics/diabetes-statistics
2. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Research and Development. VA research on diabetes. www.research.va.gov. Updated January 15, 2023. Accessed January 22, 2024. https://www.research.va.gov/topics/diabetes.cfm
3. Halter JB, Musi N, McFarland Horne F, et al. Diabetes and cardiovascular disease in older adults: current status and future directions. Diabetes. 2014;63(8):2578-2589. doi:10.2337/db14-0020
4. Kirsh S, Watts S, Schaub K, et al. VA shared medical appointments for patients with diabetes: maximizing patient and provider expertise to strengthen care management. Updated December 2010. Accessed January 22, 2024. https://www.vendorportal.ecms.va.gov/FBODocumentServer/DocumentServer.aspx?DocumentId=1513366&FileName=VA244-14-R-0025-011.pdf
5. Edelman D, Gierisch JM, McDuffie JR, Oddone E, Williams JW Jr. Shared medical appointments for patients with diabetes mellitus: a systematic review. J Gen Intern Med. 2015;30(1):99-106. doi:10.1007/s11606-014-2978-7
6. Watts SA, Strauss GJ, Pascuzzi K, et al. Shared medical appointments for patients with diabetes: glycemic reduction in high-risk patients. J Am Assoc Nurse Pract. 2015;27(8):450-456. doi:10.1002/2327-6924.12200
7. Lorig K, Ritter PL, Turner RM, English K, Laurent DD, Greenberg J. Benefits of diabetes self-management for health plan members: a 6-month translation study. J Med Internet Res. 2016;18(6):e164. Published 2016 Jun 24. doi:10.2196/jmir.5568
8. Gilstrap LG, Chernew ME, Nguyen CA, et al. Association between clinical practice group adherence to quality measures and adverse outcomes among adult patients with diabetes. JAMA Netw Open. 2019;2(8):e199139. Published 2019 Aug 2. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.9139
9. Venkataraman K, Tan LS, Bautista DC, et al. Psychometric properties of the Problem Areas in Diabetes (PAID) instrument in Singapore. PLoS One. 2015;10(9):e0136759. Published 2015 Sep 3. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0136759
10. Welch G, Weinger K, Anderson B, Polonsky WH. Responsiveness of the Problem Areas In Diabetes (PAID) questionnaire. Diabet Med. 2003;20(1):69-72. doi:10.1046/j.1464-5491.2003.00832.x
11. Hibbard JH, Mahoney ER, Stockard J, Tusler M. Development and testing of a short form of the patient activation measure. Health Serv Res. 2005;40(6 Pt 1):1918-1930. doi:10.1111/j.1475-6773.2005.00438.x
12. Hibbard JH, Stockard J, Mahoney ER, Tusler M. Development of the Patient Activation Measure (PAM): conceptualizing and measuring activation in patients and consumers. Health Serv Res. 2004;39(4 Pt 1):1005-1026. doi:10.1111/j.1475-6773.2004.00269.x
13. Ahn YH, Yi CH, Ham OK, Kim BJ. Psychometric properties of the Korean version of the “Patient Activation Measure 13” (PAM13-K) in patients with osteoarthritis. Eval Health Prof. 2015;38(2):255-264. doi:10.1177/0163278714540915
14. Brenk-Franz K, Hibbard JH, Herrmann WJ, et al. Validation of the German version of the patient activation measure 13 (PAM13-D) in an international multicentre study of primary care patients. PLoS One. 2013;8(9):e74786. Published 2013 Sep 30. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0074786
15. Zill JM, Dwinger S, Kriston L, Rohenkohl A, Härter M, Dirmaier J. Psychometric evaluation of the German version of the Patient Activation Measure (PAM13). BMC Public Health. 2013;13:1027. Published 2013 Oct 30. doi:10.1186/1471-2458-13-1027
16. Schmitt A, Gahr A, Hermanns N, Kulzer B, Huber J, Haak T. The Diabetes Self-Management Questionnaire (DSMQ): development and evaluation of an instrument to assess diabetes self-care activities associated with glycaemic control. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2013;11:138. Published 2013 Aug 13. doi:10.1186/1477-7525-11-138
17. Schmitt A, Reimer A, Hermanns N, et al. assessing diabetes self-management with the Diabetes Self-Management Questionnaire (DSMQ) can help analyse behavioural problems related to reduced glycaemic control. PLoS One. 2016;11(3):e0150774. Published 2016 Mar 3. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0150774
18. Bukhsh A, Lee SWH, Pusparajah P, Schmitt A, Khan TM. Psychometric properties of the Diabetes Self-Management Questionnaire (DSMQ) in Urdu. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2017;15(1):200. Published 2017 Oct 12. doi:10.1186/s12955-017-0776-8
19. Krejci LP, Carter K, Gaudet T. Whole health: the vision and implementation of personalized, proactive, patient-driven health care for veterans. Med Care. 2014;52(12 Suppl 5):S5-S8. doi:10.1097/MLR.0000000000000226
20. Bokhour BG, Haun JN, Hyde J, Charns M, Kligler B. Transforming the Veterans Affairs to a whole health system of care: time for action and research. Med Care. 2020;58(4):295-300. doi:10.1097/MLR.0000000000001316
More than 37 million Americans (11.3%) have diabetes mellitus (DM), and 90% to 95% are diagnosed with type 2 DM, including nearly 1 in 4 veterans receiving Veterans Health Administration (VHA) care.1,2 DM is associated with serious negative health outcomes, including cardiovascular disease and subsequent complications as well as significant health care system utilization and cost.1,3
Group interventions have been identified as a possible method of improving DM outcomes. For example, shared medical appointments (SMAs) have been identified by the VHA as holding promise for improving care and efficiency for DM and other common health conditions.4 Although the precise structure and SMA process for managing DM has been noted to be heterogeneous, the appointment is typically led by an interdisciplinary health care team and includes individualized assessment including medication review and adjustment, group education, and troubleshooting challenges with management in a group format.5 Research suggests that DM SMAs are a worthwhile treatment approach.5 Several studies have found that SMAs were associated with decreased hemoglobin A1c (Hb A1c) levels and improvement in overall disease complications and severity.6
The high degree of SMA heterogeneity and lack of detailed description of structure and process of SMAs studied has made meta-analysis and other synthesis of the literature difficult.5 Consequently, there is inadequate empirically supported guidance for clinicians and health care organizations on how to best implement SMAs and similar group-based treatments. Edelman and colleagues recommended that future research should focus on more consistent and standardized intervention structures and real-world patient- and staff-centered outcomes to address gaps in the literature.5 They noted that a mental health professional was utilized in only a minority of SMAs studied.5 Additionally, we noted a paucity of studies examining patient satisfaction with SMAs.
Another group-based intervention found to be effective in improving DM outcomes is the 6-session Stanford Diabetes Self-Management Program (DSMP), a workshop led in part by trained peers with DM. The sessions focus on educating patients on DM care and self-management tools. The workshop encourages active practice in building DM self-management skills and confidence. DSMP participation has been associated with improvement in DM-related outcomes, including Hb A1c levels, amount of exercise, and medication adherence.7
While SMAs and DSMP have been shown to enhance clinical outcomes, they provide differing types of patient support. SMAs allow for frequent interaction with a health care professional (HCP) and less emphasis on behavioral health interventions. DSMPs include behavioral health professionals and peer leaders and emphasize higher levels of psychosocial support, but do not offer access to clinicians. It is possible that combining these interventions could result in better outcomes than what either could provide on their own.
In 2018, the Cincinnati Veterans Affairs Medical Center (VAMC) in Ohio offered Diabetes Basic Training, a structured DM intervention. Patients enrolled in the program participated in a 9-week intervention that included 3 SMAs and 6 DSMP sessions. During the SMAs, a clinical psychologist or psychology postdoctoral fellow skilled in motivational interviewing facilitated the group to enhance patient engagement and empowerment for improved self-management. In addition, patients participated in structured DSMP groups with an emphasis on action-planning, often surrounding nutrition, physical activity, and other health behavior change information reviewed during the SMAs.
Design and Referral
Self-management programs for chronic health conditions are often underutilized. Although HCPs may wish to connect veterans with available programs, time constraints may limit opportunities for detailed discussions with patients about specific aspects of each program. To simplify this process, a 2-hour orientation program was offered that explained individual and group DM self-management options (Figure). During this initial visit, patients met with an interdisciplinary care team (registered dietician, diabetes nurse practitioner, and behavioral health specialist) and were informed about Diabetes Basic Training, DM clinical care practices, and other related resources available at the Cincinnati VAMC (eg, cooking classes, food pantry). Patients received individualized referral recommendations and were urged to consult with their primary care practitioner to finalize their treatment plan.
Shared Medical Appointments
Diabetes Basic Training interventions had an average of 6 to 8 veterans participating in the weekly groups. The first, fifth, and final weeks were SMAs in which an interdisciplinary team collaboratively provided group-based health care for DM. The team consisted of a registered nurse, a prescriber (eg, nurse practitioner), a moderator (eg, psychologist), and a content expert (eg, nutritionist). Before each SMA began, the nurse checked-in patients in the SMA room and collected heart rate and blood pressure, and performed a diabetic foot check. Each SMA consisted of introductions, group-driven discussions (facilitated by an HCP) and troubleshooting DM self-management challenges. During group discussions, the prescriber initiated a 1-on-1 discussion with each patient in a private office regarding their recent laboratory results, medication regimen, and other aspects of DM care. The patient’s medications were refilled and/or adjusted as needed and other orders and referrals were submitted. If a patient had a medical question, the prescriber and moderator engaged the entire group so all individuals could benefit from generating and hearing answers. When discussion slowed, education was provided on topics generated by the group. Frequent topics included challenges managing DM, concerns, how DM impacted daily life and relationships, and sharing successes. As needed, HCPs spoke individually with patients following the SMA. Patients were sometimes asked, but never required, to do homework consistent with standard DM care (eg, recording what they eat or blood sugar levels). Each SMA session lasted about 2 hours.
Diabetes Self-Management Program
The second, third, fourth, sixth, seventh, and eighth weeks of the program were devoted to the DSMP. These sessions were delivered primarily by veteran peers who received appropriate training, observation, and certification. Each 2-hour educational program provided ample practice in many fundamental self-management skills, such as decision making, problem solving, and action planning. Patients were asked, but never required, to practice related skills during the sessions and to create weekly action plans to be completed between sessions that typically involved increasing exercise or improving diet. Patients were encouraged to follow up with HCPs at SMAs when they had questions requiring HCP expertise. If participants had more immediate concerns regarding their treatment plan and/or medications, they contacted their primary care practitioner prior to the next SMA.
As a part of participation in the program, psychosocial and health data and Hb A1c levels at baseline (the closest level to 90 days prior to start) and follow-up (the closest level to 90 days after the final session) were collected.8 In addition, Problem Areas in Diabetes (PAID), Patient Activation Measure (PAM)-13, and Diabetes Self-Management Questionnaire (DSMQ) were administered at 3 points: during the orientation, in the first week, and in the ninth week of the program.
PAID, a 20-item self-report questionnaire designed to capture
Observations
All measures were collected as part of traditional clinical care, and we present initial program evaluation data to demonstrate potential effectiveness of the clinic model. Paired samples t tests were used to examine differences between baseline and follow-up measures for the 24 veteran participants. The age of participants who completed the program ranged from 42 to 74 years (mean, 68 years); 29% of participants were Black veterans and 12% were female. Examination of clinical outcomes indicated that veterans reported significant increases in activation levels for managing their health increasing from a baseline mean (SD) 62.1 (12.3) to 68.4 (14.5) at follow up (t[23] = 2.15, P = .04). Hb A1c levels trended downward from a mean (SD) 8.6% (1.3) at baseline to 8.2% (1.2) at 90-day follow up (t[21] 1.05, P = .30). Similar nonsignificant trends in PAID scores were seen for pre- and postprogram reductions in emotional distress related to having DM from a mean (SD) 7.9 (5.0) at baseline to 6.3 (5.1) (t[18] = 11.51, P = .15), and enhanced self-management of glucose with a mean (SD) 6.5 (1.5) at baseline to 6.8 (1.3) at follow up (t[19] = 0.52, P = .61). The trends found in this study show promising outcomes for this pilot group-based DM treatment, though the small sample size (N = 24) limits statistical power. These findings support further exploration and expansion of interdisciplinary health programs supporting veteran self-management.
Discussion
DM is a condition of epidemic proportions that causes substantial negative health outcomes and costs at a national level. Current standards of DM care do not appear to be reversing these trends. Wider implementation of group-based treatment for DM could improve efficiency of care, increase access to quality care, and reduce burden on individual HCPs.
The VHA continues the transformation of its care system, which shifts toward a patient-centered, proactive focus on veteran well-being. This new whole health approach integrates conventional medical treatment with veteran self-empowerment in the pursuit of health goals based on individual veteran’s identified values.19 This approach emphasizes peer-led explorations of veterans’ aspirations, purpose, and individual mission, personalized health planning, and use of whole health coaches and well-being programs, with both allopathic and complementary and integrative clinical care centered around veterans’ identified goals and priorities.20
Including a program like Diabetes Basic Training as a part of whole health programming could offer several benefits. Diabetes Basic Training is unique in its integration of more traditional SMA structure with psychosocial interventions including values identification and motivational interviewing strategies to enhance patient engagement. Veterans can learn from each other’s experiences and concerns, leading to better DM management knowledge and skills. The group nature of the sessions enhances opportunities for emotional support and reduced isolation, as well as peer accountability for maintaining medication adherence.
By meeting with HCPs from multiple disciplines, veterans are exposed to different perspectives on self-management techniques, including behavioral approaches for overcoming barriers to behavior change. Clinicians have more time to engage with patients, building stronger relationships and trust. SMAs are cost-efficient and time efficient, allowing HCPs to see multiple patients at once, reducing wait times and increasing the number of patients treated in a given time frame.
The COVID-19 pandemic temporarily impacted the ongoing expansion of the program, when so many services were shifted from in-person to virtual classes. Due to staffing and other logistic issues, our pilot program was suspended during that time, but plans to resume the program by early 2024 are moving forward.
CONCLUSIONS
The Diabetes Basic Training program serves as a successful model for implementation within a VAMC. Although the number of veterans with complete data available for analysis was small, the trends exhibited in the preliminary outcome data are promising. We encourage other VAMCs to replicate this program with a larger participant base and evaluate its impact on veteran health outcomes. Next steps include comparing the clinical data from treatment as usual with outcomes from DM group participants. As the program resumes, we will reinitiate recruitment efforts to increase HCP referrals to this program.
More than 37 million Americans (11.3%) have diabetes mellitus (DM), and 90% to 95% are diagnosed with type 2 DM, including nearly 1 in 4 veterans receiving Veterans Health Administration (VHA) care.1,2 DM is associated with serious negative health outcomes, including cardiovascular disease and subsequent complications as well as significant health care system utilization and cost.1,3
Group interventions have been identified as a possible method of improving DM outcomes. For example, shared medical appointments (SMAs) have been identified by the VHA as holding promise for improving care and efficiency for DM and other common health conditions.4 Although the precise structure and SMA process for managing DM has been noted to be heterogeneous, the appointment is typically led by an interdisciplinary health care team and includes individualized assessment including medication review and adjustment, group education, and troubleshooting challenges with management in a group format.5 Research suggests that DM SMAs are a worthwhile treatment approach.5 Several studies have found that SMAs were associated with decreased hemoglobin A1c (Hb A1c) levels and improvement in overall disease complications and severity.6
The high degree of SMA heterogeneity and lack of detailed description of structure and process of SMAs studied has made meta-analysis and other synthesis of the literature difficult.5 Consequently, there is inadequate empirically supported guidance for clinicians and health care organizations on how to best implement SMAs and similar group-based treatments. Edelman and colleagues recommended that future research should focus on more consistent and standardized intervention structures and real-world patient- and staff-centered outcomes to address gaps in the literature.5 They noted that a mental health professional was utilized in only a minority of SMAs studied.5 Additionally, we noted a paucity of studies examining patient satisfaction with SMAs.
Another group-based intervention found to be effective in improving DM outcomes is the 6-session Stanford Diabetes Self-Management Program (DSMP), a workshop led in part by trained peers with DM. The sessions focus on educating patients on DM care and self-management tools. The workshop encourages active practice in building DM self-management skills and confidence. DSMP participation has been associated with improvement in DM-related outcomes, including Hb A1c levels, amount of exercise, and medication adherence.7
While SMAs and DSMP have been shown to enhance clinical outcomes, they provide differing types of patient support. SMAs allow for frequent interaction with a health care professional (HCP) and less emphasis on behavioral health interventions. DSMPs include behavioral health professionals and peer leaders and emphasize higher levels of psychosocial support, but do not offer access to clinicians. It is possible that combining these interventions could result in better outcomes than what either could provide on their own.
In 2018, the Cincinnati Veterans Affairs Medical Center (VAMC) in Ohio offered Diabetes Basic Training, a structured DM intervention. Patients enrolled in the program participated in a 9-week intervention that included 3 SMAs and 6 DSMP sessions. During the SMAs, a clinical psychologist or psychology postdoctoral fellow skilled in motivational interviewing facilitated the group to enhance patient engagement and empowerment for improved self-management. In addition, patients participated in structured DSMP groups with an emphasis on action-planning, often surrounding nutrition, physical activity, and other health behavior change information reviewed during the SMAs.
Design and Referral
Self-management programs for chronic health conditions are often underutilized. Although HCPs may wish to connect veterans with available programs, time constraints may limit opportunities for detailed discussions with patients about specific aspects of each program. To simplify this process, a 2-hour orientation program was offered that explained individual and group DM self-management options (Figure). During this initial visit, patients met with an interdisciplinary care team (registered dietician, diabetes nurse practitioner, and behavioral health specialist) and were informed about Diabetes Basic Training, DM clinical care practices, and other related resources available at the Cincinnati VAMC (eg, cooking classes, food pantry). Patients received individualized referral recommendations and were urged to consult with their primary care practitioner to finalize their treatment plan.
Shared Medical Appointments
Diabetes Basic Training interventions had an average of 6 to 8 veterans participating in the weekly groups. The first, fifth, and final weeks were SMAs in which an interdisciplinary team collaboratively provided group-based health care for DM. The team consisted of a registered nurse, a prescriber (eg, nurse practitioner), a moderator (eg, psychologist), and a content expert (eg, nutritionist). Before each SMA began, the nurse checked-in patients in the SMA room and collected heart rate and blood pressure, and performed a diabetic foot check. Each SMA consisted of introductions, group-driven discussions (facilitated by an HCP) and troubleshooting DM self-management challenges. During group discussions, the prescriber initiated a 1-on-1 discussion with each patient in a private office regarding their recent laboratory results, medication regimen, and other aspects of DM care. The patient’s medications were refilled and/or adjusted as needed and other orders and referrals were submitted. If a patient had a medical question, the prescriber and moderator engaged the entire group so all individuals could benefit from generating and hearing answers. When discussion slowed, education was provided on topics generated by the group. Frequent topics included challenges managing DM, concerns, how DM impacted daily life and relationships, and sharing successes. As needed, HCPs spoke individually with patients following the SMA. Patients were sometimes asked, but never required, to do homework consistent with standard DM care (eg, recording what they eat or blood sugar levels). Each SMA session lasted about 2 hours.
Diabetes Self-Management Program
The second, third, fourth, sixth, seventh, and eighth weeks of the program were devoted to the DSMP. These sessions were delivered primarily by veteran peers who received appropriate training, observation, and certification. Each 2-hour educational program provided ample practice in many fundamental self-management skills, such as decision making, problem solving, and action planning. Patients were asked, but never required, to practice related skills during the sessions and to create weekly action plans to be completed between sessions that typically involved increasing exercise or improving diet. Patients were encouraged to follow up with HCPs at SMAs when they had questions requiring HCP expertise. If participants had more immediate concerns regarding their treatment plan and/or medications, they contacted their primary care practitioner prior to the next SMA.
As a part of participation in the program, psychosocial and health data and Hb A1c levels at baseline (the closest level to 90 days prior to start) and follow-up (the closest level to 90 days after the final session) were collected.8 In addition, Problem Areas in Diabetes (PAID), Patient Activation Measure (PAM)-13, and Diabetes Self-Management Questionnaire (DSMQ) were administered at 3 points: during the orientation, in the first week, and in the ninth week of the program.
PAID, a 20-item self-report questionnaire designed to capture
Observations
All measures were collected as part of traditional clinical care, and we present initial program evaluation data to demonstrate potential effectiveness of the clinic model. Paired samples t tests were used to examine differences between baseline and follow-up measures for the 24 veteran participants. The age of participants who completed the program ranged from 42 to 74 years (mean, 68 years); 29% of participants were Black veterans and 12% were female. Examination of clinical outcomes indicated that veterans reported significant increases in activation levels for managing their health increasing from a baseline mean (SD) 62.1 (12.3) to 68.4 (14.5) at follow up (t[23] = 2.15, P = .04). Hb A1c levels trended downward from a mean (SD) 8.6% (1.3) at baseline to 8.2% (1.2) at 90-day follow up (t[21] 1.05, P = .30). Similar nonsignificant trends in PAID scores were seen for pre- and postprogram reductions in emotional distress related to having DM from a mean (SD) 7.9 (5.0) at baseline to 6.3 (5.1) (t[18] = 11.51, P = .15), and enhanced self-management of glucose with a mean (SD) 6.5 (1.5) at baseline to 6.8 (1.3) at follow up (t[19] = 0.52, P = .61). The trends found in this study show promising outcomes for this pilot group-based DM treatment, though the small sample size (N = 24) limits statistical power. These findings support further exploration and expansion of interdisciplinary health programs supporting veteran self-management.
Discussion
DM is a condition of epidemic proportions that causes substantial negative health outcomes and costs at a national level. Current standards of DM care do not appear to be reversing these trends. Wider implementation of group-based treatment for DM could improve efficiency of care, increase access to quality care, and reduce burden on individual HCPs.
The VHA continues the transformation of its care system, which shifts toward a patient-centered, proactive focus on veteran well-being. This new whole health approach integrates conventional medical treatment with veteran self-empowerment in the pursuit of health goals based on individual veteran’s identified values.19 This approach emphasizes peer-led explorations of veterans’ aspirations, purpose, and individual mission, personalized health planning, and use of whole health coaches and well-being programs, with both allopathic and complementary and integrative clinical care centered around veterans’ identified goals and priorities.20
Including a program like Diabetes Basic Training as a part of whole health programming could offer several benefits. Diabetes Basic Training is unique in its integration of more traditional SMA structure with psychosocial interventions including values identification and motivational interviewing strategies to enhance patient engagement. Veterans can learn from each other’s experiences and concerns, leading to better DM management knowledge and skills. The group nature of the sessions enhances opportunities for emotional support and reduced isolation, as well as peer accountability for maintaining medication adherence.
By meeting with HCPs from multiple disciplines, veterans are exposed to different perspectives on self-management techniques, including behavioral approaches for overcoming barriers to behavior change. Clinicians have more time to engage with patients, building stronger relationships and trust. SMAs are cost-efficient and time efficient, allowing HCPs to see multiple patients at once, reducing wait times and increasing the number of patients treated in a given time frame.
The COVID-19 pandemic temporarily impacted the ongoing expansion of the program, when so many services were shifted from in-person to virtual classes. Due to staffing and other logistic issues, our pilot program was suspended during that time, but plans to resume the program by early 2024 are moving forward.
CONCLUSIONS
The Diabetes Basic Training program serves as a successful model for implementation within a VAMC. Although the number of veterans with complete data available for analysis was small, the trends exhibited in the preliminary outcome data are promising. We encourage other VAMCs to replicate this program with a larger participant base and evaluate its impact on veteran health outcomes. Next steps include comparing the clinical data from treatment as usual with outcomes from DM group participants. As the program resumes, we will reinitiate recruitment efforts to increase HCP referrals to this program.
1. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Diabetes Statistics. Updated February 2023. Accessed January 22, 2024. https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/health-statistics/diabetes-statistics
2. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Research and Development. VA research on diabetes. www.research.va.gov. Updated January 15, 2023. Accessed January 22, 2024. https://www.research.va.gov/topics/diabetes.cfm
3. Halter JB, Musi N, McFarland Horne F, et al. Diabetes and cardiovascular disease in older adults: current status and future directions. Diabetes. 2014;63(8):2578-2589. doi:10.2337/db14-0020
4. Kirsh S, Watts S, Schaub K, et al. VA shared medical appointments for patients with diabetes: maximizing patient and provider expertise to strengthen care management. Updated December 2010. Accessed January 22, 2024. https://www.vendorportal.ecms.va.gov/FBODocumentServer/DocumentServer.aspx?DocumentId=1513366&FileName=VA244-14-R-0025-011.pdf
5. Edelman D, Gierisch JM, McDuffie JR, Oddone E, Williams JW Jr. Shared medical appointments for patients with diabetes mellitus: a systematic review. J Gen Intern Med. 2015;30(1):99-106. doi:10.1007/s11606-014-2978-7
6. Watts SA, Strauss GJ, Pascuzzi K, et al. Shared medical appointments for patients with diabetes: glycemic reduction in high-risk patients. J Am Assoc Nurse Pract. 2015;27(8):450-456. doi:10.1002/2327-6924.12200
7. Lorig K, Ritter PL, Turner RM, English K, Laurent DD, Greenberg J. Benefits of diabetes self-management for health plan members: a 6-month translation study. J Med Internet Res. 2016;18(6):e164. Published 2016 Jun 24. doi:10.2196/jmir.5568
8. Gilstrap LG, Chernew ME, Nguyen CA, et al. Association between clinical practice group adherence to quality measures and adverse outcomes among adult patients with diabetes. JAMA Netw Open. 2019;2(8):e199139. Published 2019 Aug 2. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.9139
9. Venkataraman K, Tan LS, Bautista DC, et al. Psychometric properties of the Problem Areas in Diabetes (PAID) instrument in Singapore. PLoS One. 2015;10(9):e0136759. Published 2015 Sep 3. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0136759
10. Welch G, Weinger K, Anderson B, Polonsky WH. Responsiveness of the Problem Areas In Diabetes (PAID) questionnaire. Diabet Med. 2003;20(1):69-72. doi:10.1046/j.1464-5491.2003.00832.x
11. Hibbard JH, Mahoney ER, Stockard J, Tusler M. Development and testing of a short form of the patient activation measure. Health Serv Res. 2005;40(6 Pt 1):1918-1930. doi:10.1111/j.1475-6773.2005.00438.x
12. Hibbard JH, Stockard J, Mahoney ER, Tusler M. Development of the Patient Activation Measure (PAM): conceptualizing and measuring activation in patients and consumers. Health Serv Res. 2004;39(4 Pt 1):1005-1026. doi:10.1111/j.1475-6773.2004.00269.x
13. Ahn YH, Yi CH, Ham OK, Kim BJ. Psychometric properties of the Korean version of the “Patient Activation Measure 13” (PAM13-K) in patients with osteoarthritis. Eval Health Prof. 2015;38(2):255-264. doi:10.1177/0163278714540915
14. Brenk-Franz K, Hibbard JH, Herrmann WJ, et al. Validation of the German version of the patient activation measure 13 (PAM13-D) in an international multicentre study of primary care patients. PLoS One. 2013;8(9):e74786. Published 2013 Sep 30. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0074786
15. Zill JM, Dwinger S, Kriston L, Rohenkohl A, Härter M, Dirmaier J. Psychometric evaluation of the German version of the Patient Activation Measure (PAM13). BMC Public Health. 2013;13:1027. Published 2013 Oct 30. doi:10.1186/1471-2458-13-1027
16. Schmitt A, Gahr A, Hermanns N, Kulzer B, Huber J, Haak T. The Diabetes Self-Management Questionnaire (DSMQ): development and evaluation of an instrument to assess diabetes self-care activities associated with glycaemic control. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2013;11:138. Published 2013 Aug 13. doi:10.1186/1477-7525-11-138
17. Schmitt A, Reimer A, Hermanns N, et al. assessing diabetes self-management with the Diabetes Self-Management Questionnaire (DSMQ) can help analyse behavioural problems related to reduced glycaemic control. PLoS One. 2016;11(3):e0150774. Published 2016 Mar 3. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0150774
18. Bukhsh A, Lee SWH, Pusparajah P, Schmitt A, Khan TM. Psychometric properties of the Diabetes Self-Management Questionnaire (DSMQ) in Urdu. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2017;15(1):200. Published 2017 Oct 12. doi:10.1186/s12955-017-0776-8
19. Krejci LP, Carter K, Gaudet T. Whole health: the vision and implementation of personalized, proactive, patient-driven health care for veterans. Med Care. 2014;52(12 Suppl 5):S5-S8. doi:10.1097/MLR.0000000000000226
20. Bokhour BG, Haun JN, Hyde J, Charns M, Kligler B. Transforming the Veterans Affairs to a whole health system of care: time for action and research. Med Care. 2020;58(4):295-300. doi:10.1097/MLR.0000000000001316
1. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Diabetes Statistics. Updated February 2023. Accessed January 22, 2024. https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/health-statistics/diabetes-statistics
2. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Research and Development. VA research on diabetes. www.research.va.gov. Updated January 15, 2023. Accessed January 22, 2024. https://www.research.va.gov/topics/diabetes.cfm
3. Halter JB, Musi N, McFarland Horne F, et al. Diabetes and cardiovascular disease in older adults: current status and future directions. Diabetes. 2014;63(8):2578-2589. doi:10.2337/db14-0020
4. Kirsh S, Watts S, Schaub K, et al. VA shared medical appointments for patients with diabetes: maximizing patient and provider expertise to strengthen care management. Updated December 2010. Accessed January 22, 2024. https://www.vendorportal.ecms.va.gov/FBODocumentServer/DocumentServer.aspx?DocumentId=1513366&FileName=VA244-14-R-0025-011.pdf
5. Edelman D, Gierisch JM, McDuffie JR, Oddone E, Williams JW Jr. Shared medical appointments for patients with diabetes mellitus: a systematic review. J Gen Intern Med. 2015;30(1):99-106. doi:10.1007/s11606-014-2978-7
6. Watts SA, Strauss GJ, Pascuzzi K, et al. Shared medical appointments for patients with diabetes: glycemic reduction in high-risk patients. J Am Assoc Nurse Pract. 2015;27(8):450-456. doi:10.1002/2327-6924.12200
7. Lorig K, Ritter PL, Turner RM, English K, Laurent DD, Greenberg J. Benefits of diabetes self-management for health plan members: a 6-month translation study. J Med Internet Res. 2016;18(6):e164. Published 2016 Jun 24. doi:10.2196/jmir.5568
8. Gilstrap LG, Chernew ME, Nguyen CA, et al. Association between clinical practice group adherence to quality measures and adverse outcomes among adult patients with diabetes. JAMA Netw Open. 2019;2(8):e199139. Published 2019 Aug 2. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.9139
9. Venkataraman K, Tan LS, Bautista DC, et al. Psychometric properties of the Problem Areas in Diabetes (PAID) instrument in Singapore. PLoS One. 2015;10(9):e0136759. Published 2015 Sep 3. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0136759
10. Welch G, Weinger K, Anderson B, Polonsky WH. Responsiveness of the Problem Areas In Diabetes (PAID) questionnaire. Diabet Med. 2003;20(1):69-72. doi:10.1046/j.1464-5491.2003.00832.x
11. Hibbard JH, Mahoney ER, Stockard J, Tusler M. Development and testing of a short form of the patient activation measure. Health Serv Res. 2005;40(6 Pt 1):1918-1930. doi:10.1111/j.1475-6773.2005.00438.x
12. Hibbard JH, Stockard J, Mahoney ER, Tusler M. Development of the Patient Activation Measure (PAM): conceptualizing and measuring activation in patients and consumers. Health Serv Res. 2004;39(4 Pt 1):1005-1026. doi:10.1111/j.1475-6773.2004.00269.x
13. Ahn YH, Yi CH, Ham OK, Kim BJ. Psychometric properties of the Korean version of the “Patient Activation Measure 13” (PAM13-K) in patients with osteoarthritis. Eval Health Prof. 2015;38(2):255-264. doi:10.1177/0163278714540915
14. Brenk-Franz K, Hibbard JH, Herrmann WJ, et al. Validation of the German version of the patient activation measure 13 (PAM13-D) in an international multicentre study of primary care patients. PLoS One. 2013;8(9):e74786. Published 2013 Sep 30. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0074786
15. Zill JM, Dwinger S, Kriston L, Rohenkohl A, Härter M, Dirmaier J. Psychometric evaluation of the German version of the Patient Activation Measure (PAM13). BMC Public Health. 2013;13:1027. Published 2013 Oct 30. doi:10.1186/1471-2458-13-1027
16. Schmitt A, Gahr A, Hermanns N, Kulzer B, Huber J, Haak T. The Diabetes Self-Management Questionnaire (DSMQ): development and evaluation of an instrument to assess diabetes self-care activities associated with glycaemic control. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2013;11:138. Published 2013 Aug 13. doi:10.1186/1477-7525-11-138
17. Schmitt A, Reimer A, Hermanns N, et al. assessing diabetes self-management with the Diabetes Self-Management Questionnaire (DSMQ) can help analyse behavioural problems related to reduced glycaemic control. PLoS One. 2016;11(3):e0150774. Published 2016 Mar 3. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0150774
18. Bukhsh A, Lee SWH, Pusparajah P, Schmitt A, Khan TM. Psychometric properties of the Diabetes Self-Management Questionnaire (DSMQ) in Urdu. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2017;15(1):200. Published 2017 Oct 12. doi:10.1186/s12955-017-0776-8
19. Krejci LP, Carter K, Gaudet T. Whole health: the vision and implementation of personalized, proactive, patient-driven health care for veterans. Med Care. 2014;52(12 Suppl 5):S5-S8. doi:10.1097/MLR.0000000000000226
20. Bokhour BG, Haun JN, Hyde J, Charns M, Kligler B. Transforming the Veterans Affairs to a whole health system of care: time for action and research. Med Care. 2020;58(4):295-300. doi:10.1097/MLR.0000000000001316
FDA Removes Harmful Chemicals From Food Packaging
Issued on February 28, 2024, “this means the major source of dietary exposure to PFAS from food packaging like fast-food wrappers, microwave popcorn bags, take-out paperboard containers, and pet food bags is being eliminated,” the FDA said in a statement.
In 2020, the FDA had secured commitments from manufacturers to stop selling products containing PFAS used in the food packaging for grease-proofing. “Today’s announcement marks the fulfillment of these voluntary commitments,” according to the agency.
PFAS, a class of thousands of chemicals also called “forever chemicals” are widely used in consumer and industrial products. People may be exposed via contaminated food packaging (although perhaps no longer in the United States) or occupationally. Studies have found that some PFAS disrupt hormones including estrogen and testosterone, whereas others may impair thyroid function.
Endocrine Society Report Sounds the Alarm About PFAS and Others
The FDA’s announcement came just 2 days after the Endocrine Society issued a new alarm about the human health dangers from environmental EDCs including PFAS in a report covering the latest science.
“Endocrine disrupting chemicals” are individual substances or mixtures that can interfere with natural hormonal function, leading to disease or even death. Many are ubiquitous in the modern environment and contribute to a wide range of human diseases.
The new report Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals: Threats to Human Health was issued jointly with the International Pollutants Elimination Network (IPEN), a global advocacy organization. It’s an update to the Endocrine Society’s 2015 report, providing new data on the endocrine-disrupting substances previously covered and adding four EDCs not discussed in that document: Pesticides, plastics, PFAS, and children’s products containing arsenic.
At a briefing held during the United Nations Environment Assembly meeting in Nairobi, Kenya, last week, the new report’s lead author Andrea C. Gore, PhD, of the University of Texas at Austin, noted, “A well-established body of scientific research indicates that endocrine-disrupting chemicals that are part of our daily lives are making us more susceptible to reproductive disorders, cancer, diabetes, obesity, heart disease, and other serious health conditions.”
Added Dr. Gore, who is also a member of the Endocrine Society’s Board of Directors, “These chemicals pose particularly serious risks to pregnant women and children. Now is the time for the UN Environment Assembly and other global policymakers to take action to address this threat to public health.”
While the science has been emerging rapidly, global and national chemical control policies haven’t kept up, the authors said. Of particular concern is that EDCs behave differently from other chemicals in many ways, including that even very low-dose exposures can pose health threats, but policies thus far haven’t dealt with that aspect.
Moreover, “the effects of low doses cannot be predicted by the effects observed at high doses. This means there may be no safe dose for exposure to EDCs,” according to the report.
Exposures can come from household products, including furniture, toys, and food packages, as well as electronics building materials and cosmetics. These chemicals are also in the outdoor environment, via pesticides, air pollution, and industrial waste.
“IPEN and the Endocrine Society call for chemical regulations based on the most modern scientific understanding of how hormones act and how EDCs can perturb these actions. We work to educate policy makers in global, regional, and national government assemblies and help ensure that regulations correlate with current scientific understanding,” they said in the report.
New Data on Four Classes of EDCs
Chapters of the report summarized the latest information about the science of EDCs and their links to endocrine disease and real-world exposure. It included a special section about “EDCs throughout the plastics life cycle” and a summary of the links between EDCs and climate change.
The report reviewed three pesticides, including the world’s most heavily applied herbicide, glycophosphate. Exposures can occur directly from the air, water, dust, and food residues. Recent data linked glycophosphate to adverse reproductive health outcomes.
Two toxic plastic chemicals, phthalates and bisphenols, are present in personal care products, among others. Emerging evidence links them with impaired neurodevelopment, leading to impaired cognitive function, learning, attention, and impulsivity.
Arsenic has long been linked to human health conditions including cancer, but more recent evidence finds it can disrupt multiple endocrine systems and lead to metabolic conditions including diabetes, reproductive dysfunction, and cardiovascular and neurocognitive conditions.
The special section about plastics noted that they are made from fossil fuels and chemicals, including many toxic substances that are known or suspected EDCs. People who live near plastic production facilities or waste dumps may be at greatest risk, but anyone can be exposed using any plastic product. Plastic waste disposal is increasingly problematic and often foisted on lower- and middle-income countries.
‘Additional Education and Awareness-Raising Among Stakeholders Remain Necessary’
Policies aimed at reducing human health risks from EDCs have included the 2022 Plastics Treaty, a resolution adopted by 175 countries at the United Nations Environmental Assembly that “may be a significant step toward global control of plastics and elimination of threats from exposures to EDCs in plastics,” the report said.
The authors added, “While significant progress has been made in recent years connecting scientific advances on EDCs with health-protective policies, additional education and awareness-raising among stakeholders remain necessary to achieve a safer and more sustainable environment that minimizes exposure to these harmful chemicals.”
The document was produced with financial contributions from the Government of Sweden, the Tides Foundation, Passport Foundation, and other donors.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Issued on February 28, 2024, “this means the major source of dietary exposure to PFAS from food packaging like fast-food wrappers, microwave popcorn bags, take-out paperboard containers, and pet food bags is being eliminated,” the FDA said in a statement.
In 2020, the FDA had secured commitments from manufacturers to stop selling products containing PFAS used in the food packaging for grease-proofing. “Today’s announcement marks the fulfillment of these voluntary commitments,” according to the agency.
PFAS, a class of thousands of chemicals also called “forever chemicals” are widely used in consumer and industrial products. People may be exposed via contaminated food packaging (although perhaps no longer in the United States) or occupationally. Studies have found that some PFAS disrupt hormones including estrogen and testosterone, whereas others may impair thyroid function.
Endocrine Society Report Sounds the Alarm About PFAS and Others
The FDA’s announcement came just 2 days after the Endocrine Society issued a new alarm about the human health dangers from environmental EDCs including PFAS in a report covering the latest science.
“Endocrine disrupting chemicals” are individual substances or mixtures that can interfere with natural hormonal function, leading to disease or even death. Many are ubiquitous in the modern environment and contribute to a wide range of human diseases.
The new report Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals: Threats to Human Health was issued jointly with the International Pollutants Elimination Network (IPEN), a global advocacy organization. It’s an update to the Endocrine Society’s 2015 report, providing new data on the endocrine-disrupting substances previously covered and adding four EDCs not discussed in that document: Pesticides, plastics, PFAS, and children’s products containing arsenic.
At a briefing held during the United Nations Environment Assembly meeting in Nairobi, Kenya, last week, the new report’s lead author Andrea C. Gore, PhD, of the University of Texas at Austin, noted, “A well-established body of scientific research indicates that endocrine-disrupting chemicals that are part of our daily lives are making us more susceptible to reproductive disorders, cancer, diabetes, obesity, heart disease, and other serious health conditions.”
Added Dr. Gore, who is also a member of the Endocrine Society’s Board of Directors, “These chemicals pose particularly serious risks to pregnant women and children. Now is the time for the UN Environment Assembly and other global policymakers to take action to address this threat to public health.”
While the science has been emerging rapidly, global and national chemical control policies haven’t kept up, the authors said. Of particular concern is that EDCs behave differently from other chemicals in many ways, including that even very low-dose exposures can pose health threats, but policies thus far haven’t dealt with that aspect.
Moreover, “the effects of low doses cannot be predicted by the effects observed at high doses. This means there may be no safe dose for exposure to EDCs,” according to the report.
Exposures can come from household products, including furniture, toys, and food packages, as well as electronics building materials and cosmetics. These chemicals are also in the outdoor environment, via pesticides, air pollution, and industrial waste.
“IPEN and the Endocrine Society call for chemical regulations based on the most modern scientific understanding of how hormones act and how EDCs can perturb these actions. We work to educate policy makers in global, regional, and national government assemblies and help ensure that regulations correlate with current scientific understanding,” they said in the report.
New Data on Four Classes of EDCs
Chapters of the report summarized the latest information about the science of EDCs and their links to endocrine disease and real-world exposure. It included a special section about “EDCs throughout the plastics life cycle” and a summary of the links between EDCs and climate change.
The report reviewed three pesticides, including the world’s most heavily applied herbicide, glycophosphate. Exposures can occur directly from the air, water, dust, and food residues. Recent data linked glycophosphate to adverse reproductive health outcomes.
Two toxic plastic chemicals, phthalates and bisphenols, are present in personal care products, among others. Emerging evidence links them with impaired neurodevelopment, leading to impaired cognitive function, learning, attention, and impulsivity.
Arsenic has long been linked to human health conditions including cancer, but more recent evidence finds it can disrupt multiple endocrine systems and lead to metabolic conditions including diabetes, reproductive dysfunction, and cardiovascular and neurocognitive conditions.
The special section about plastics noted that they are made from fossil fuels and chemicals, including many toxic substances that are known or suspected EDCs. People who live near plastic production facilities or waste dumps may be at greatest risk, but anyone can be exposed using any plastic product. Plastic waste disposal is increasingly problematic and often foisted on lower- and middle-income countries.
‘Additional Education and Awareness-Raising Among Stakeholders Remain Necessary’
Policies aimed at reducing human health risks from EDCs have included the 2022 Plastics Treaty, a resolution adopted by 175 countries at the United Nations Environmental Assembly that “may be a significant step toward global control of plastics and elimination of threats from exposures to EDCs in plastics,” the report said.
The authors added, “While significant progress has been made in recent years connecting scientific advances on EDCs with health-protective policies, additional education and awareness-raising among stakeholders remain necessary to achieve a safer and more sustainable environment that minimizes exposure to these harmful chemicals.”
The document was produced with financial contributions from the Government of Sweden, the Tides Foundation, Passport Foundation, and other donors.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Issued on February 28, 2024, “this means the major source of dietary exposure to PFAS from food packaging like fast-food wrappers, microwave popcorn bags, take-out paperboard containers, and pet food bags is being eliminated,” the FDA said in a statement.
In 2020, the FDA had secured commitments from manufacturers to stop selling products containing PFAS used in the food packaging for grease-proofing. “Today’s announcement marks the fulfillment of these voluntary commitments,” according to the agency.
PFAS, a class of thousands of chemicals also called “forever chemicals” are widely used in consumer and industrial products. People may be exposed via contaminated food packaging (although perhaps no longer in the United States) or occupationally. Studies have found that some PFAS disrupt hormones including estrogen and testosterone, whereas others may impair thyroid function.
Endocrine Society Report Sounds the Alarm About PFAS and Others
The FDA’s announcement came just 2 days after the Endocrine Society issued a new alarm about the human health dangers from environmental EDCs including PFAS in a report covering the latest science.
“Endocrine disrupting chemicals” are individual substances or mixtures that can interfere with natural hormonal function, leading to disease or even death. Many are ubiquitous in the modern environment and contribute to a wide range of human diseases.
The new report Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals: Threats to Human Health was issued jointly with the International Pollutants Elimination Network (IPEN), a global advocacy organization. It’s an update to the Endocrine Society’s 2015 report, providing new data on the endocrine-disrupting substances previously covered and adding four EDCs not discussed in that document: Pesticides, plastics, PFAS, and children’s products containing arsenic.
At a briefing held during the United Nations Environment Assembly meeting in Nairobi, Kenya, last week, the new report’s lead author Andrea C. Gore, PhD, of the University of Texas at Austin, noted, “A well-established body of scientific research indicates that endocrine-disrupting chemicals that are part of our daily lives are making us more susceptible to reproductive disorders, cancer, diabetes, obesity, heart disease, and other serious health conditions.”
Added Dr. Gore, who is also a member of the Endocrine Society’s Board of Directors, “These chemicals pose particularly serious risks to pregnant women and children. Now is the time for the UN Environment Assembly and other global policymakers to take action to address this threat to public health.”
While the science has been emerging rapidly, global and national chemical control policies haven’t kept up, the authors said. Of particular concern is that EDCs behave differently from other chemicals in many ways, including that even very low-dose exposures can pose health threats, but policies thus far haven’t dealt with that aspect.
Moreover, “the effects of low doses cannot be predicted by the effects observed at high doses. This means there may be no safe dose for exposure to EDCs,” according to the report.
Exposures can come from household products, including furniture, toys, and food packages, as well as electronics building materials and cosmetics. These chemicals are also in the outdoor environment, via pesticides, air pollution, and industrial waste.
“IPEN and the Endocrine Society call for chemical regulations based on the most modern scientific understanding of how hormones act and how EDCs can perturb these actions. We work to educate policy makers in global, regional, and national government assemblies and help ensure that regulations correlate with current scientific understanding,” they said in the report.
New Data on Four Classes of EDCs
Chapters of the report summarized the latest information about the science of EDCs and their links to endocrine disease and real-world exposure. It included a special section about “EDCs throughout the plastics life cycle” and a summary of the links between EDCs and climate change.
The report reviewed three pesticides, including the world’s most heavily applied herbicide, glycophosphate. Exposures can occur directly from the air, water, dust, and food residues. Recent data linked glycophosphate to adverse reproductive health outcomes.
Two toxic plastic chemicals, phthalates and bisphenols, are present in personal care products, among others. Emerging evidence links them with impaired neurodevelopment, leading to impaired cognitive function, learning, attention, and impulsivity.
Arsenic has long been linked to human health conditions including cancer, but more recent evidence finds it can disrupt multiple endocrine systems and lead to metabolic conditions including diabetes, reproductive dysfunction, and cardiovascular and neurocognitive conditions.
The special section about plastics noted that they are made from fossil fuels and chemicals, including many toxic substances that are known or suspected EDCs. People who live near plastic production facilities or waste dumps may be at greatest risk, but anyone can be exposed using any plastic product. Plastic waste disposal is increasingly problematic and often foisted on lower- and middle-income countries.
‘Additional Education and Awareness-Raising Among Stakeholders Remain Necessary’
Policies aimed at reducing human health risks from EDCs have included the 2022 Plastics Treaty, a resolution adopted by 175 countries at the United Nations Environmental Assembly that “may be a significant step toward global control of plastics and elimination of threats from exposures to EDCs in plastics,” the report said.
The authors added, “While significant progress has been made in recent years connecting scientific advances on EDCs with health-protective policies, additional education and awareness-raising among stakeholders remain necessary to achieve a safer and more sustainable environment that minimizes exposure to these harmful chemicals.”
The document was produced with financial contributions from the Government of Sweden, the Tides Foundation, Passport Foundation, and other donors.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Is There a Connection Between Diabetes and Oral Health?
Emerging evidence suggests that oral health, often overlooked by clinicians, is closely connected with overall health — and this connection has important consequences for individuals with type 2 diabetes (T2D). While most studies are observational and can’t prove cause and effect, the associations are robust enough for researchers to conclude that the connection is real.
Endocrinologists and other specialists, as well as primary care physicians, should ask about oral health, if not look in the mouth directly, experts say. The ADA advocates for attention to oral health through its 2024 standards of care.
Systemic Impact
“Periodontitis is a probable risk factor for various problems connected to the cardiovascular, pulmonary, endocrine, musculoskeletal, central nervous, and reproductive systems,” wrote the authors of a recent review on the effects of periodontitis on major organ systems. While not specific to the diabetes connection, the review pinpoints some of the latest evidence that “oral health affects overall health, and…dental health should never be considered a distinct, remote, and lower significant part of health.”
In line with this perspective, and looking specifically at T2D, a recent study of more than 17,000 patients with T2D participating in a screening program in Korea found that periodontitis and an increased number of teeth with cavities were independent risk factors for cerebral or myocardial infarction (adjusted hazard ratios, 1.17 and 1.67, respectively).
Dental disease and poor oral hygiene were also associated with an increased risk for heart failure among people with T2D in a large cohort study, and the authors suggested that managing oral health may prevent heart failure development.
A recent review suggested that periodontitis exacerbates and promotes the progression of chronic kidney disease, a disorder that affects 1 in 3 people with diabetes.
Studies also have shown that diabetes is associated with cognitive decline, and a review of oral health and dementia progression concluded, “collectively, experimental findings indicate that the connection between oral health and cognition cannot be underestimated.”
Bidirectional Effects
Research has shown that the association between periodontal disease and T2D is likely bidirectional, although there is little awareness of this two-way relationship among patients and providers.
A recent review of this bidirectional relationship focused on microvascular complications, oral microbiota, pro- and anti-inflammatory factors in T2D and periodontal disease and concluded that “these two diseases require specific/complementary therapeutic solutions when they occur in association, with new clinical trials and epidemiological research being necessary for better control of this interdependent pathogenic topic.”
Yet an Australian study showed that 54% of 241 participants in a survey never received any information regarding the bidirectional relationship between periodontal disease and diabetes and lacked understanding of the association.
What’s the Mechanism?
How does T2D affect the teeth and vice versa? “Basically, people with T2D have high blood sugar, and the sugar comes out in the saliva and that promotes bacterial growth in the mouth and plaque formation on the teeth and gum disease,” Samir Malkani, MD, clinical chief of endocrinology and diabetes at UMass Chan School of Medicine in Worcester, Massachusetts, told this news organization.
“Patients get gingivitis, they get periodontitis, and since the gums and the jaw are a single unit, if the gum disease gets very severe, then there’s loss of jawbone and the teeth could fall out,” he said. There’s also inflammation in the mouth, and “when you have generalized inflammation, it affects the whole body.”
Recent research in Europe suggested that “although the mechanisms behind these associations are partially unclear, poor oral health is probably sustaining systemic inflammation.” Common oral infections, periodontal disease, and cavities are associated with inflammatory metabolic profiles related to an increased risk for cardiometabolic diseases, and they predict future adverse changes in metabolic profiles, according to the authors.
Awareness, Accessibility, Collaboration
Despite the evidence, the connection between oral health and diabetes (any type) is not front of mind with clinicians or patients, Dr. Malkani said. He pointed to a systematic review that included 28 studies of close to 28,000 people in 14 countries. The review found that people with diabetes have “inadequate oral health knowledge, poor oral health attitudes, and fewer dental visits, [and] rarely receive oral health education and dental referrals from their care providers.”
Social determinants of health have a “huge impact” on whether people will develop T2D and its related complications, including poor oral health, according to the National Clinical Care Commission Report presented to the US Congress in 2022. The commission was charged with making recommendations for federal policies and programs that could more effectively prevent and control diabetes and its complications.
The commission “approached its charge through the lens of a socioecological and an expanded chronic care model,” the report authors wrote. “It was clear that diabetes in the US cannot simply be viewed as a medical or healthcare problem but also must be addressed as a societal problem that cuts across many sectors, including food, housing, commerce, transportation, and the environment.”
Diabetes also is associated with higher dental costs, another factor affecting an individual’s ability to obtain care.
A recent questionnaire-based study from Denmark found that people with T2D were more likely than those without diabetes to rate their oral health as poor, and that the risk for self-rated poor oral health increased with lower educational attainment. Highest educational attainment and disposable household income were indicators of a high socioeconomic position, and a lower likelihood of rating their oral health as poor, again pointing out inequities.
The authors concluded that “diabetes and dental care providers should engage in multidisciplinary collaboration across healthcare sectors to ensure coherent treatment and management of diabetes.”
But such collaborations are easier said than done. “One of the challenges is our fragmented health system, where oral health and medical care are separate,” Dr. Gabbay said.
For the most part, the two are separate, Dr. Malkani agreed. “When we’re dealing with most complications of diabetes, like involvement of the heart or eyes or kidneys, we can have interdisciplinary care — everyone is within the overall discipline of medicine, and if I refer to a colleague in ophthalmology or a cardiologist or a vascular surgeon, they can all be within the same network from an insurance point of view, as well.”
But for dental care, referrals are interprofessional, not interdisciplinary. “I have to make sure that the patient has a dentist because dentists are usually not part of medical networks, and if the patient doesn’t have dental insurance, then cost and access can be a challenge.”
A recent systematic review from Australia on interprofessional education and interprofessional collaborative care found that more than a third of medical professionals were “ignorant” of the relationship between oral health and T2D. Furthermore, only 30% reported ever referring their patients for an oral health assessment. And there was little, if any, interprofessional collaborative care between medical and dental professionals while managing patients with T2D.
Treat the Teeth
“We always talk to our T2D patients about the importance of getting an eye exam, a foot exam, and a kidney test,” Dr. Malkani said. “But we also need to make sure that they’re going to the dentist. Normally, people get their teeth cleaned twice a year. But if you have diabetes and poor oral health, you might need to get your teeth cleaned every three months, and insurance often will pay for that.”
Furthermore, in keeping with the bidirectional connection, treating periodontitis can help glycemic control. The authors of a 2022 update of a Cochrane review on treating periodontitis for glycemic control wrote that they “doubled the number of included studies and participants” from the 2015 update to 35 studies randomizing 3249 participants to periodontal treatment or control. This “led to a change in our conclusions about the primary outcome of glycemic control and in our level of certainty in this conclusion.”
“We now have moderate‐certainty evidence that periodontal treatment using subgingival instrumentation improves glycemic control in people with both periodontitis and diabetes by a clinically significant amount when compared to no treatment or usual care. Further trials evaluating periodontal treatment vs no treatment/usual care are unlikely to change the overall conclusion reached in this review.”
“Dentists also have a responsibility,” Dr. Malkani added. “If they see someone with severe gum disease or cavities, especially at a younger age, they need to tell that person to get their blood sugar checked and make sure they don’t have T2D.”
In fact, a recent review found that complications of T2D such as xerostomia and periodontal problems adversely affect well-being, and that “dentists can play an essential role in the awareness of diabetic patients about these problems and improve their quality of life.”
Key Stats
The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention highlighted these facts about diabetes and oral health:
- Adults aged 20 years or older with diabetes are 40% more likely to have untreated cavities than similar adults without diabetes.
- About 60% of US adults with diabetes had a medical visit in the past year but no dental visit.
- Expanding healthcare coverage for periodontal treatment among people with diabetes could save each person about $6000 (2019 US dollars) over their lifetimes.
- Adults aged 50 years or older with diabetes lack functional dentition (have fewer than 20 teeth) 46% more often and have severe tooth loss (eight or fewer teeth) 56% more often than those without diabetes.
- Adults aged 50 years or older with diabetes are more likely to report that they have a hard time eating because of dental problems.
- Annual dental expenditures for an adult with diabetes are $77 (2017 US dollars) higher than for an adult without diabetes. This cost translates to $1.9 billion for the United States.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Emerging evidence suggests that oral health, often overlooked by clinicians, is closely connected with overall health — and this connection has important consequences for individuals with type 2 diabetes (T2D). While most studies are observational and can’t prove cause and effect, the associations are robust enough for researchers to conclude that the connection is real.
Endocrinologists and other specialists, as well as primary care physicians, should ask about oral health, if not look in the mouth directly, experts say. The ADA advocates for attention to oral health through its 2024 standards of care.
Systemic Impact
“Periodontitis is a probable risk factor for various problems connected to the cardiovascular, pulmonary, endocrine, musculoskeletal, central nervous, and reproductive systems,” wrote the authors of a recent review on the effects of periodontitis on major organ systems. While not specific to the diabetes connection, the review pinpoints some of the latest evidence that “oral health affects overall health, and…dental health should never be considered a distinct, remote, and lower significant part of health.”
In line with this perspective, and looking specifically at T2D, a recent study of more than 17,000 patients with T2D participating in a screening program in Korea found that periodontitis and an increased number of teeth with cavities were independent risk factors for cerebral or myocardial infarction (adjusted hazard ratios, 1.17 and 1.67, respectively).
Dental disease and poor oral hygiene were also associated with an increased risk for heart failure among people with T2D in a large cohort study, and the authors suggested that managing oral health may prevent heart failure development.
A recent review suggested that periodontitis exacerbates and promotes the progression of chronic kidney disease, a disorder that affects 1 in 3 people with diabetes.
Studies also have shown that diabetes is associated with cognitive decline, and a review of oral health and dementia progression concluded, “collectively, experimental findings indicate that the connection between oral health and cognition cannot be underestimated.”
Bidirectional Effects
Research has shown that the association between periodontal disease and T2D is likely bidirectional, although there is little awareness of this two-way relationship among patients and providers.
A recent review of this bidirectional relationship focused on microvascular complications, oral microbiota, pro- and anti-inflammatory factors in T2D and periodontal disease and concluded that “these two diseases require specific/complementary therapeutic solutions when they occur in association, with new clinical trials and epidemiological research being necessary for better control of this interdependent pathogenic topic.”
Yet an Australian study showed that 54% of 241 participants in a survey never received any information regarding the bidirectional relationship between periodontal disease and diabetes and lacked understanding of the association.
What’s the Mechanism?
How does T2D affect the teeth and vice versa? “Basically, people with T2D have high blood sugar, and the sugar comes out in the saliva and that promotes bacterial growth in the mouth and plaque formation on the teeth and gum disease,” Samir Malkani, MD, clinical chief of endocrinology and diabetes at UMass Chan School of Medicine in Worcester, Massachusetts, told this news organization.
“Patients get gingivitis, they get periodontitis, and since the gums and the jaw are a single unit, if the gum disease gets very severe, then there’s loss of jawbone and the teeth could fall out,” he said. There’s also inflammation in the mouth, and “when you have generalized inflammation, it affects the whole body.”
Recent research in Europe suggested that “although the mechanisms behind these associations are partially unclear, poor oral health is probably sustaining systemic inflammation.” Common oral infections, periodontal disease, and cavities are associated with inflammatory metabolic profiles related to an increased risk for cardiometabolic diseases, and they predict future adverse changes in metabolic profiles, according to the authors.
Awareness, Accessibility, Collaboration
Despite the evidence, the connection between oral health and diabetes (any type) is not front of mind with clinicians or patients, Dr. Malkani said. He pointed to a systematic review that included 28 studies of close to 28,000 people in 14 countries. The review found that people with diabetes have “inadequate oral health knowledge, poor oral health attitudes, and fewer dental visits, [and] rarely receive oral health education and dental referrals from their care providers.”
Social determinants of health have a “huge impact” on whether people will develop T2D and its related complications, including poor oral health, according to the National Clinical Care Commission Report presented to the US Congress in 2022. The commission was charged with making recommendations for federal policies and programs that could more effectively prevent and control diabetes and its complications.
The commission “approached its charge through the lens of a socioecological and an expanded chronic care model,” the report authors wrote. “It was clear that diabetes in the US cannot simply be viewed as a medical or healthcare problem but also must be addressed as a societal problem that cuts across many sectors, including food, housing, commerce, transportation, and the environment.”
Diabetes also is associated with higher dental costs, another factor affecting an individual’s ability to obtain care.
A recent questionnaire-based study from Denmark found that people with T2D were more likely than those without diabetes to rate their oral health as poor, and that the risk for self-rated poor oral health increased with lower educational attainment. Highest educational attainment and disposable household income were indicators of a high socioeconomic position, and a lower likelihood of rating their oral health as poor, again pointing out inequities.
The authors concluded that “diabetes and dental care providers should engage in multidisciplinary collaboration across healthcare sectors to ensure coherent treatment and management of diabetes.”
But such collaborations are easier said than done. “One of the challenges is our fragmented health system, where oral health and medical care are separate,” Dr. Gabbay said.
For the most part, the two are separate, Dr. Malkani agreed. “When we’re dealing with most complications of diabetes, like involvement of the heart or eyes or kidneys, we can have interdisciplinary care — everyone is within the overall discipline of medicine, and if I refer to a colleague in ophthalmology or a cardiologist or a vascular surgeon, they can all be within the same network from an insurance point of view, as well.”
But for dental care, referrals are interprofessional, not interdisciplinary. “I have to make sure that the patient has a dentist because dentists are usually not part of medical networks, and if the patient doesn’t have dental insurance, then cost and access can be a challenge.”
A recent systematic review from Australia on interprofessional education and interprofessional collaborative care found that more than a third of medical professionals were “ignorant” of the relationship between oral health and T2D. Furthermore, only 30% reported ever referring their patients for an oral health assessment. And there was little, if any, interprofessional collaborative care between medical and dental professionals while managing patients with T2D.
Treat the Teeth
“We always talk to our T2D patients about the importance of getting an eye exam, a foot exam, and a kidney test,” Dr. Malkani said. “But we also need to make sure that they’re going to the dentist. Normally, people get their teeth cleaned twice a year. But if you have diabetes and poor oral health, you might need to get your teeth cleaned every three months, and insurance often will pay for that.”
Furthermore, in keeping with the bidirectional connection, treating periodontitis can help glycemic control. The authors of a 2022 update of a Cochrane review on treating periodontitis for glycemic control wrote that they “doubled the number of included studies and participants” from the 2015 update to 35 studies randomizing 3249 participants to periodontal treatment or control. This “led to a change in our conclusions about the primary outcome of glycemic control and in our level of certainty in this conclusion.”
“We now have moderate‐certainty evidence that periodontal treatment using subgingival instrumentation improves glycemic control in people with both periodontitis and diabetes by a clinically significant amount when compared to no treatment or usual care. Further trials evaluating periodontal treatment vs no treatment/usual care are unlikely to change the overall conclusion reached in this review.”
“Dentists also have a responsibility,” Dr. Malkani added. “If they see someone with severe gum disease or cavities, especially at a younger age, they need to tell that person to get their blood sugar checked and make sure they don’t have T2D.”
In fact, a recent review found that complications of T2D such as xerostomia and periodontal problems adversely affect well-being, and that “dentists can play an essential role in the awareness of diabetic patients about these problems and improve their quality of life.”
Key Stats
The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention highlighted these facts about diabetes and oral health:
- Adults aged 20 years or older with diabetes are 40% more likely to have untreated cavities than similar adults without diabetes.
- About 60% of US adults with diabetes had a medical visit in the past year but no dental visit.
- Expanding healthcare coverage for periodontal treatment among people with diabetes could save each person about $6000 (2019 US dollars) over their lifetimes.
- Adults aged 50 years or older with diabetes lack functional dentition (have fewer than 20 teeth) 46% more often and have severe tooth loss (eight or fewer teeth) 56% more often than those without diabetes.
- Adults aged 50 years or older with diabetes are more likely to report that they have a hard time eating because of dental problems.
- Annual dental expenditures for an adult with diabetes are $77 (2017 US dollars) higher than for an adult without diabetes. This cost translates to $1.9 billion for the United States.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Emerging evidence suggests that oral health, often overlooked by clinicians, is closely connected with overall health — and this connection has important consequences for individuals with type 2 diabetes (T2D). While most studies are observational and can’t prove cause and effect, the associations are robust enough for researchers to conclude that the connection is real.
Endocrinologists and other specialists, as well as primary care physicians, should ask about oral health, if not look in the mouth directly, experts say. The ADA advocates for attention to oral health through its 2024 standards of care.
Systemic Impact
“Periodontitis is a probable risk factor for various problems connected to the cardiovascular, pulmonary, endocrine, musculoskeletal, central nervous, and reproductive systems,” wrote the authors of a recent review on the effects of periodontitis on major organ systems. While not specific to the diabetes connection, the review pinpoints some of the latest evidence that “oral health affects overall health, and…dental health should never be considered a distinct, remote, and lower significant part of health.”
In line with this perspective, and looking specifically at T2D, a recent study of more than 17,000 patients with T2D participating in a screening program in Korea found that periodontitis and an increased number of teeth with cavities were independent risk factors for cerebral or myocardial infarction (adjusted hazard ratios, 1.17 and 1.67, respectively).
Dental disease and poor oral hygiene were also associated with an increased risk for heart failure among people with T2D in a large cohort study, and the authors suggested that managing oral health may prevent heart failure development.
A recent review suggested that periodontitis exacerbates and promotes the progression of chronic kidney disease, a disorder that affects 1 in 3 people with diabetes.
Studies also have shown that diabetes is associated with cognitive decline, and a review of oral health and dementia progression concluded, “collectively, experimental findings indicate that the connection between oral health and cognition cannot be underestimated.”
Bidirectional Effects
Research has shown that the association between periodontal disease and T2D is likely bidirectional, although there is little awareness of this two-way relationship among patients and providers.
A recent review of this bidirectional relationship focused on microvascular complications, oral microbiota, pro- and anti-inflammatory factors in T2D and periodontal disease and concluded that “these two diseases require specific/complementary therapeutic solutions when they occur in association, with new clinical trials and epidemiological research being necessary for better control of this interdependent pathogenic topic.”
Yet an Australian study showed that 54% of 241 participants in a survey never received any information regarding the bidirectional relationship between periodontal disease and diabetes and lacked understanding of the association.
What’s the Mechanism?
How does T2D affect the teeth and vice versa? “Basically, people with T2D have high blood sugar, and the sugar comes out in the saliva and that promotes bacterial growth in the mouth and plaque formation on the teeth and gum disease,” Samir Malkani, MD, clinical chief of endocrinology and diabetes at UMass Chan School of Medicine in Worcester, Massachusetts, told this news organization.
“Patients get gingivitis, they get periodontitis, and since the gums and the jaw are a single unit, if the gum disease gets very severe, then there’s loss of jawbone and the teeth could fall out,” he said. There’s also inflammation in the mouth, and “when you have generalized inflammation, it affects the whole body.”
Recent research in Europe suggested that “although the mechanisms behind these associations are partially unclear, poor oral health is probably sustaining systemic inflammation.” Common oral infections, periodontal disease, and cavities are associated with inflammatory metabolic profiles related to an increased risk for cardiometabolic diseases, and they predict future adverse changes in metabolic profiles, according to the authors.
Awareness, Accessibility, Collaboration
Despite the evidence, the connection between oral health and diabetes (any type) is not front of mind with clinicians or patients, Dr. Malkani said. He pointed to a systematic review that included 28 studies of close to 28,000 people in 14 countries. The review found that people with diabetes have “inadequate oral health knowledge, poor oral health attitudes, and fewer dental visits, [and] rarely receive oral health education and dental referrals from their care providers.”
Social determinants of health have a “huge impact” on whether people will develop T2D and its related complications, including poor oral health, according to the National Clinical Care Commission Report presented to the US Congress in 2022. The commission was charged with making recommendations for federal policies and programs that could more effectively prevent and control diabetes and its complications.
The commission “approached its charge through the lens of a socioecological and an expanded chronic care model,” the report authors wrote. “It was clear that diabetes in the US cannot simply be viewed as a medical or healthcare problem but also must be addressed as a societal problem that cuts across many sectors, including food, housing, commerce, transportation, and the environment.”
Diabetes also is associated with higher dental costs, another factor affecting an individual’s ability to obtain care.
A recent questionnaire-based study from Denmark found that people with T2D were more likely than those without diabetes to rate their oral health as poor, and that the risk for self-rated poor oral health increased with lower educational attainment. Highest educational attainment and disposable household income were indicators of a high socioeconomic position, and a lower likelihood of rating their oral health as poor, again pointing out inequities.
The authors concluded that “diabetes and dental care providers should engage in multidisciplinary collaboration across healthcare sectors to ensure coherent treatment and management of diabetes.”
But such collaborations are easier said than done. “One of the challenges is our fragmented health system, where oral health and medical care are separate,” Dr. Gabbay said.
For the most part, the two are separate, Dr. Malkani agreed. “When we’re dealing with most complications of diabetes, like involvement of the heart or eyes or kidneys, we can have interdisciplinary care — everyone is within the overall discipline of medicine, and if I refer to a colleague in ophthalmology or a cardiologist or a vascular surgeon, they can all be within the same network from an insurance point of view, as well.”
But for dental care, referrals are interprofessional, not interdisciplinary. “I have to make sure that the patient has a dentist because dentists are usually not part of medical networks, and if the patient doesn’t have dental insurance, then cost and access can be a challenge.”
A recent systematic review from Australia on interprofessional education and interprofessional collaborative care found that more than a third of medical professionals were “ignorant” of the relationship between oral health and T2D. Furthermore, only 30% reported ever referring their patients for an oral health assessment. And there was little, if any, interprofessional collaborative care between medical and dental professionals while managing patients with T2D.
Treat the Teeth
“We always talk to our T2D patients about the importance of getting an eye exam, a foot exam, and a kidney test,” Dr. Malkani said. “But we also need to make sure that they’re going to the dentist. Normally, people get their teeth cleaned twice a year. But if you have diabetes and poor oral health, you might need to get your teeth cleaned every three months, and insurance often will pay for that.”
Furthermore, in keeping with the bidirectional connection, treating periodontitis can help glycemic control. The authors of a 2022 update of a Cochrane review on treating periodontitis for glycemic control wrote that they “doubled the number of included studies and participants” from the 2015 update to 35 studies randomizing 3249 participants to periodontal treatment or control. This “led to a change in our conclusions about the primary outcome of glycemic control and in our level of certainty in this conclusion.”
“We now have moderate‐certainty evidence that periodontal treatment using subgingival instrumentation improves glycemic control in people with both periodontitis and diabetes by a clinically significant amount when compared to no treatment or usual care. Further trials evaluating periodontal treatment vs no treatment/usual care are unlikely to change the overall conclusion reached in this review.”
“Dentists also have a responsibility,” Dr. Malkani added. “If they see someone with severe gum disease or cavities, especially at a younger age, they need to tell that person to get their blood sugar checked and make sure they don’t have T2D.”
In fact, a recent review found that complications of T2D such as xerostomia and periodontal problems adversely affect well-being, and that “dentists can play an essential role in the awareness of diabetic patients about these problems and improve their quality of life.”
Key Stats
The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention highlighted these facts about diabetes and oral health:
- Adults aged 20 years or older with diabetes are 40% more likely to have untreated cavities than similar adults without diabetes.
- About 60% of US adults with diabetes had a medical visit in the past year but no dental visit.
- Expanding healthcare coverage for periodontal treatment among people with diabetes could save each person about $6000 (2019 US dollars) over their lifetimes.
- Adults aged 50 years or older with diabetes lack functional dentition (have fewer than 20 teeth) 46% more often and have severe tooth loss (eight or fewer teeth) 56% more often than those without diabetes.
- Adults aged 50 years or older with diabetes are more likely to report that they have a hard time eating because of dental problems.
- Annual dental expenditures for an adult with diabetes are $77 (2017 US dollars) higher than for an adult without diabetes. This cost translates to $1.9 billion for the United States.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Is Metformin a ‘Drug for All Diseases’?
In 2021 alone, clinicians wrote more than 91 million orders for the medication — up from 40 million 2004.
But is metformin just getting started? Emerging evidence suggests the drug may be effective for a much broader range of conditions beyond managing high blood glucose, including various cancers, obesity, liver disease, cardiovascular, neurodegenerative, and renal diseases. As the evidence for diverse uses accumulates, many trials have launched, with researchers looking to expand metformin’s indications and validate or explore new directions.
Metformin’s long history as a pharmaceutical includes an herbal ancestry, recognition in 1918 for its ability to lower blood glucose, being cast aside because of toxicity fears in the 1930s, rediscovery and synthesis in Europe in the 1940s, the first reported use for diabetes in 1957, and approval in the United States in 1994.
The drug has maintained its place as the preferred first-line treatment for type 2 diabetes since 2011, when it was first included in the World Health Organization’s essential medicines list.
“The focus hitherto has been primarily on its insulin sensitization effects,” Akshay Jain, MD, a clinical and research endocrinologist at TLC Diabetes and Endocrinology, in Surrey, British Columbia, Canada, told this news organization.
“The recent surge of renewed interest is in part related to its postulated effects on multiple other receptors,” he said. “In my mind, the metformin data on coronary artery disease reduction and cancer-protective effects have come farther along than other disease states.”
Cardiovascular Outcomes
Gregory G. Schwartz, MD, PhD, chief of the cardiology section at Rocky Mountain Regional VA Medical Center and professor of medicine at the University of Colorado School of Medicine in Aurora, is leading the VA-IMPACT trial. Despite metformin’s long history and widespread use, he said his study is the first placebo-controlled cardiovascular outcomes trial of the drug.
Launched in 2023, the study tests the hypothesis that metformin reduces the risk for death or nonfatal ischemic cardiovascular events in patients with prediabetes and established coronary, cerebrovascular, or peripheral artery disease, Dr. Schwartz said. The trial is being conducted at roughly 40 VA medical centers, with a planned enrollment of 7410 patients. The estimated completion date is March 2029.
“The principal mechanism of action of metformin is through activation of AMP [adenosine monophosphate]–activated protein kinase, a central pathway in metabolic regulation, cell protection, and survival,” Dr. Schwartz explained. “Experimental data have demonstrated attenuated development of atherosclerosis, reduced myocardial infarct size, improved endothelial function, and antiarrhythmic actions — none of those dependent on the presence of diabetes.”
Dr. Schwartz and his colleagues decided to test their hypothesis in people with prediabetes, rather than diabetes, to create a “true placebo-controlled comparison,” he said.
“If patients with type 2 diabetes had been chosen, there would be potential for confounding because a placebo group would require more treatment with other active antihyperglycemic medications to achieve the same degree of glycemic control as a metformin group,” Dr. Schwartz said.
“If proven efficacious in the VA-IMPACT trial, metformin could provide an inexpensive, generally safe, and well-tolerated approach to reduce cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in a large segment of the population,” Dr. Schwartz added. “Perhaps the old dog can learn some new tricks.”
Other recruiting trials looking at cardiovascular-related outcomes include Met-PEF, LIMIT, and Metformin as an Adjunctive Therapy to Catheter Ablation in Atrial Fibrillation.
Reducing Cancer Risks
Sai Yendamuri, MD, chair of the Department of Thoracic Surgery and director of the Thoracic Surgery Laboratory at Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center in Buffalo, New York, is leading a phase 2 trial exploring whether metformin can prevent lung cancer in people with overweight or obesity who are at a high risk for the malignancy.
The study, which has accrued about 60% of its estimated enrollment, also will assess whether metformin can reprogram participants’ immune systems, with a view toward reducing the activity of regulatory T cells that are linked to development of tumors.
“In our preclinical and retrospective clinical data, we found that metformin had anticancer effects but only if the patients were overweight,” Dr. Yendamuri said. “In mice, we find that obesity increases regulatory T-cell function, which suppresses the immune system of the lungs. This effect is reversed by metformin.” The team is conducting the current study to examine if this happens in patients, as well. Results are expected next year.
Research is underway in other tumor types, including oral and endometrial, and brain cancers.
Preventing Alzheimer’s Disease
Cognitive function — or at least delaying its erosion — represents another front for metformin. José A. Luchsinger, MD, MPH, vice-chair for clinical and epidemiological research and director of the section on geriatrics, gerontology, and aging at Columbia University Irving Medical Center in New York City, is heading a phase 2/3 randomized controlled trial assessing the ability of the drug to prevent Alzheimer›s disease.
The study investigators hope to enroll 326 men and women aged 55-90 years with early and late mild cognitive impairment, overweight or obesity, and no diabetes.
“The hypothesis is that improving insulin and glucose levels can lead to lowering the risk of Alzheimer’s disease,” Dr. Luchsinger said. Recruitment should be complete by the end of 2024 and results are expected in late 2026.
Similar studies are underway in Europe and Asia.
Other areas of investigation, while tantalizing, are mostly in early stages, although bolstered by preclinical and mechanistic studies. The authors of a recent review on the potential mechanisms of action of metformin and existing evidence of the drug›s effectiveness — or lack thereof — in treating diseases other than diabetes, wrote: “Collectively, these data raise the question: Is metformin a drug for all diseases? It remains unclear as to whether all of these putative beneficial effects are secondary to its actions as an antihyperglycemic and insulin-sensitizing drug, or result from other cellular actions, including inhibition of mTOR (mammalian target for rapamycin), or direct antiviral actions.”
Off-Label Uses
Metformin currently is approved by the US Food and Drug Administration only for the treatment of type 2 diabetes, although it is also the only antidiabetic medication for prediabetes currently recommended by the American Diabetes Association.
Some studies currently are looking at its use in a variety of off-label indications, including obesity, gestational diabetes, weight gain from antipsychotics, and polycystic ovary syndrome.
For the most part, metformin is considered a safe drug, but it is not risk-free, Dr. Jain cautioned.
“Although it would certainly be helpful to see if this inexpensive medication that’s universally available can help in disease states, one shouldn’t overlook the potential risk of adverse effects, such as gastrointestinal, potential vitamin B12 deficiency, blunting of skeletal muscle development and the rare risk of lactic acidosis in those with kidney impairment,” he said.
“Similarly, with recent reports of the carcinogenic potential of certain formulations of long-acting metformin that contained NDMA [N-nitrosodimethylamine], it would be imperative that these kinks are removed before we incorporate metformin as the gift that keeps giving.”
Dr. Jain reported financial relationships with Abbott, Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Dexcom, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Medtronic, Merck, and Novo Nordisk. Dr. Yendamuri disclosed serving on the scientific advisory board member of Karkinos Healthcare and research funding from Lumeda for the metformin study. Dr. Luchsinger reported receiving donated metformin and matching placebo from EMD Serono, a subsidiary of Merck, for the MAP study. Dr. Schwartz received research support from the US Department of Veterans Affairs as National Chair of the VA-IMPACT trial.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
In 2021 alone, clinicians wrote more than 91 million orders for the medication — up from 40 million 2004.
But is metformin just getting started? Emerging evidence suggests the drug may be effective for a much broader range of conditions beyond managing high blood glucose, including various cancers, obesity, liver disease, cardiovascular, neurodegenerative, and renal diseases. As the evidence for diverse uses accumulates, many trials have launched, with researchers looking to expand metformin’s indications and validate or explore new directions.
Metformin’s long history as a pharmaceutical includes an herbal ancestry, recognition in 1918 for its ability to lower blood glucose, being cast aside because of toxicity fears in the 1930s, rediscovery and synthesis in Europe in the 1940s, the first reported use for diabetes in 1957, and approval in the United States in 1994.
The drug has maintained its place as the preferred first-line treatment for type 2 diabetes since 2011, when it was first included in the World Health Organization’s essential medicines list.
“The focus hitherto has been primarily on its insulin sensitization effects,” Akshay Jain, MD, a clinical and research endocrinologist at TLC Diabetes and Endocrinology, in Surrey, British Columbia, Canada, told this news organization.
“The recent surge of renewed interest is in part related to its postulated effects on multiple other receptors,” he said. “In my mind, the metformin data on coronary artery disease reduction and cancer-protective effects have come farther along than other disease states.”
Cardiovascular Outcomes
Gregory G. Schwartz, MD, PhD, chief of the cardiology section at Rocky Mountain Regional VA Medical Center and professor of medicine at the University of Colorado School of Medicine in Aurora, is leading the VA-IMPACT trial. Despite metformin’s long history and widespread use, he said his study is the first placebo-controlled cardiovascular outcomes trial of the drug.
Launched in 2023, the study tests the hypothesis that metformin reduces the risk for death or nonfatal ischemic cardiovascular events in patients with prediabetes and established coronary, cerebrovascular, or peripheral artery disease, Dr. Schwartz said. The trial is being conducted at roughly 40 VA medical centers, with a planned enrollment of 7410 patients. The estimated completion date is March 2029.
“The principal mechanism of action of metformin is through activation of AMP [adenosine monophosphate]–activated protein kinase, a central pathway in metabolic regulation, cell protection, and survival,” Dr. Schwartz explained. “Experimental data have demonstrated attenuated development of atherosclerosis, reduced myocardial infarct size, improved endothelial function, and antiarrhythmic actions — none of those dependent on the presence of diabetes.”
Dr. Schwartz and his colleagues decided to test their hypothesis in people with prediabetes, rather than diabetes, to create a “true placebo-controlled comparison,” he said.
“If patients with type 2 diabetes had been chosen, there would be potential for confounding because a placebo group would require more treatment with other active antihyperglycemic medications to achieve the same degree of glycemic control as a metformin group,” Dr. Schwartz said.
“If proven efficacious in the VA-IMPACT trial, metformin could provide an inexpensive, generally safe, and well-tolerated approach to reduce cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in a large segment of the population,” Dr. Schwartz added. “Perhaps the old dog can learn some new tricks.”
Other recruiting trials looking at cardiovascular-related outcomes include Met-PEF, LIMIT, and Metformin as an Adjunctive Therapy to Catheter Ablation in Atrial Fibrillation.
Reducing Cancer Risks
Sai Yendamuri, MD, chair of the Department of Thoracic Surgery and director of the Thoracic Surgery Laboratory at Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center in Buffalo, New York, is leading a phase 2 trial exploring whether metformin can prevent lung cancer in people with overweight or obesity who are at a high risk for the malignancy.
The study, which has accrued about 60% of its estimated enrollment, also will assess whether metformin can reprogram participants’ immune systems, with a view toward reducing the activity of regulatory T cells that are linked to development of tumors.
“In our preclinical and retrospective clinical data, we found that metformin had anticancer effects but only if the patients were overweight,” Dr. Yendamuri said. “In mice, we find that obesity increases regulatory T-cell function, which suppresses the immune system of the lungs. This effect is reversed by metformin.” The team is conducting the current study to examine if this happens in patients, as well. Results are expected next year.
Research is underway in other tumor types, including oral and endometrial, and brain cancers.
Preventing Alzheimer’s Disease
Cognitive function — or at least delaying its erosion — represents another front for metformin. José A. Luchsinger, MD, MPH, vice-chair for clinical and epidemiological research and director of the section on geriatrics, gerontology, and aging at Columbia University Irving Medical Center in New York City, is heading a phase 2/3 randomized controlled trial assessing the ability of the drug to prevent Alzheimer›s disease.
The study investigators hope to enroll 326 men and women aged 55-90 years with early and late mild cognitive impairment, overweight or obesity, and no diabetes.
“The hypothesis is that improving insulin and glucose levels can lead to lowering the risk of Alzheimer’s disease,” Dr. Luchsinger said. Recruitment should be complete by the end of 2024 and results are expected in late 2026.
Similar studies are underway in Europe and Asia.
Other areas of investigation, while tantalizing, are mostly in early stages, although bolstered by preclinical and mechanistic studies. The authors of a recent review on the potential mechanisms of action of metformin and existing evidence of the drug›s effectiveness — or lack thereof — in treating diseases other than diabetes, wrote: “Collectively, these data raise the question: Is metformin a drug for all diseases? It remains unclear as to whether all of these putative beneficial effects are secondary to its actions as an antihyperglycemic and insulin-sensitizing drug, or result from other cellular actions, including inhibition of mTOR (mammalian target for rapamycin), or direct antiviral actions.”
Off-Label Uses
Metformin currently is approved by the US Food and Drug Administration only for the treatment of type 2 diabetes, although it is also the only antidiabetic medication for prediabetes currently recommended by the American Diabetes Association.
Some studies currently are looking at its use in a variety of off-label indications, including obesity, gestational diabetes, weight gain from antipsychotics, and polycystic ovary syndrome.
For the most part, metformin is considered a safe drug, but it is not risk-free, Dr. Jain cautioned.
“Although it would certainly be helpful to see if this inexpensive medication that’s universally available can help in disease states, one shouldn’t overlook the potential risk of adverse effects, such as gastrointestinal, potential vitamin B12 deficiency, blunting of skeletal muscle development and the rare risk of lactic acidosis in those with kidney impairment,” he said.
“Similarly, with recent reports of the carcinogenic potential of certain formulations of long-acting metformin that contained NDMA [N-nitrosodimethylamine], it would be imperative that these kinks are removed before we incorporate metformin as the gift that keeps giving.”
Dr. Jain reported financial relationships with Abbott, Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Dexcom, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Medtronic, Merck, and Novo Nordisk. Dr. Yendamuri disclosed serving on the scientific advisory board member of Karkinos Healthcare and research funding from Lumeda for the metformin study. Dr. Luchsinger reported receiving donated metformin and matching placebo from EMD Serono, a subsidiary of Merck, for the MAP study. Dr. Schwartz received research support from the US Department of Veterans Affairs as National Chair of the VA-IMPACT trial.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
In 2021 alone, clinicians wrote more than 91 million orders for the medication — up from 40 million 2004.
But is metformin just getting started? Emerging evidence suggests the drug may be effective for a much broader range of conditions beyond managing high blood glucose, including various cancers, obesity, liver disease, cardiovascular, neurodegenerative, and renal diseases. As the evidence for diverse uses accumulates, many trials have launched, with researchers looking to expand metformin’s indications and validate or explore new directions.
Metformin’s long history as a pharmaceutical includes an herbal ancestry, recognition in 1918 for its ability to lower blood glucose, being cast aside because of toxicity fears in the 1930s, rediscovery and synthesis in Europe in the 1940s, the first reported use for diabetes in 1957, and approval in the United States in 1994.
The drug has maintained its place as the preferred first-line treatment for type 2 diabetes since 2011, when it was first included in the World Health Organization’s essential medicines list.
“The focus hitherto has been primarily on its insulin sensitization effects,” Akshay Jain, MD, a clinical and research endocrinologist at TLC Diabetes and Endocrinology, in Surrey, British Columbia, Canada, told this news organization.
“The recent surge of renewed interest is in part related to its postulated effects on multiple other receptors,” he said. “In my mind, the metformin data on coronary artery disease reduction and cancer-protective effects have come farther along than other disease states.”
Cardiovascular Outcomes
Gregory G. Schwartz, MD, PhD, chief of the cardiology section at Rocky Mountain Regional VA Medical Center and professor of medicine at the University of Colorado School of Medicine in Aurora, is leading the VA-IMPACT trial. Despite metformin’s long history and widespread use, he said his study is the first placebo-controlled cardiovascular outcomes trial of the drug.
Launched in 2023, the study tests the hypothesis that metformin reduces the risk for death or nonfatal ischemic cardiovascular events in patients with prediabetes and established coronary, cerebrovascular, or peripheral artery disease, Dr. Schwartz said. The trial is being conducted at roughly 40 VA medical centers, with a planned enrollment of 7410 patients. The estimated completion date is March 2029.
“The principal mechanism of action of metformin is through activation of AMP [adenosine monophosphate]–activated protein kinase, a central pathway in metabolic regulation, cell protection, and survival,” Dr. Schwartz explained. “Experimental data have demonstrated attenuated development of atherosclerosis, reduced myocardial infarct size, improved endothelial function, and antiarrhythmic actions — none of those dependent on the presence of diabetes.”
Dr. Schwartz and his colleagues decided to test their hypothesis in people with prediabetes, rather than diabetes, to create a “true placebo-controlled comparison,” he said.
“If patients with type 2 diabetes had been chosen, there would be potential for confounding because a placebo group would require more treatment with other active antihyperglycemic medications to achieve the same degree of glycemic control as a metformin group,” Dr. Schwartz said.
“If proven efficacious in the VA-IMPACT trial, metformin could provide an inexpensive, generally safe, and well-tolerated approach to reduce cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in a large segment of the population,” Dr. Schwartz added. “Perhaps the old dog can learn some new tricks.”
Other recruiting trials looking at cardiovascular-related outcomes include Met-PEF, LIMIT, and Metformin as an Adjunctive Therapy to Catheter Ablation in Atrial Fibrillation.
Reducing Cancer Risks
Sai Yendamuri, MD, chair of the Department of Thoracic Surgery and director of the Thoracic Surgery Laboratory at Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center in Buffalo, New York, is leading a phase 2 trial exploring whether metformin can prevent lung cancer in people with overweight or obesity who are at a high risk for the malignancy.
The study, which has accrued about 60% of its estimated enrollment, also will assess whether metformin can reprogram participants’ immune systems, with a view toward reducing the activity of regulatory T cells that are linked to development of tumors.
“In our preclinical and retrospective clinical data, we found that metformin had anticancer effects but only if the patients were overweight,” Dr. Yendamuri said. “In mice, we find that obesity increases regulatory T-cell function, which suppresses the immune system of the lungs. This effect is reversed by metformin.” The team is conducting the current study to examine if this happens in patients, as well. Results are expected next year.
Research is underway in other tumor types, including oral and endometrial, and brain cancers.
Preventing Alzheimer’s Disease
Cognitive function — or at least delaying its erosion — represents another front for metformin. José A. Luchsinger, MD, MPH, vice-chair for clinical and epidemiological research and director of the section on geriatrics, gerontology, and aging at Columbia University Irving Medical Center in New York City, is heading a phase 2/3 randomized controlled trial assessing the ability of the drug to prevent Alzheimer›s disease.
The study investigators hope to enroll 326 men and women aged 55-90 years with early and late mild cognitive impairment, overweight or obesity, and no diabetes.
“The hypothesis is that improving insulin and glucose levels can lead to lowering the risk of Alzheimer’s disease,” Dr. Luchsinger said. Recruitment should be complete by the end of 2024 and results are expected in late 2026.
Similar studies are underway in Europe and Asia.
Other areas of investigation, while tantalizing, are mostly in early stages, although bolstered by preclinical and mechanistic studies. The authors of a recent review on the potential mechanisms of action of metformin and existing evidence of the drug›s effectiveness — or lack thereof — in treating diseases other than diabetes, wrote: “Collectively, these data raise the question: Is metformin a drug for all diseases? It remains unclear as to whether all of these putative beneficial effects are secondary to its actions as an antihyperglycemic and insulin-sensitizing drug, or result from other cellular actions, including inhibition of mTOR (mammalian target for rapamycin), or direct antiviral actions.”
Off-Label Uses
Metformin currently is approved by the US Food and Drug Administration only for the treatment of type 2 diabetes, although it is also the only antidiabetic medication for prediabetes currently recommended by the American Diabetes Association.
Some studies currently are looking at its use in a variety of off-label indications, including obesity, gestational diabetes, weight gain from antipsychotics, and polycystic ovary syndrome.
For the most part, metformin is considered a safe drug, but it is not risk-free, Dr. Jain cautioned.
“Although it would certainly be helpful to see if this inexpensive medication that’s universally available can help in disease states, one shouldn’t overlook the potential risk of adverse effects, such as gastrointestinal, potential vitamin B12 deficiency, blunting of skeletal muscle development and the rare risk of lactic acidosis in those with kidney impairment,” he said.
“Similarly, with recent reports of the carcinogenic potential of certain formulations of long-acting metformin that contained NDMA [N-nitrosodimethylamine], it would be imperative that these kinks are removed before we incorporate metformin as the gift that keeps giving.”
Dr. Jain reported financial relationships with Abbott, Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Dexcom, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Medtronic, Merck, and Novo Nordisk. Dr. Yendamuri disclosed serving on the scientific advisory board member of Karkinos Healthcare and research funding from Lumeda for the metformin study. Dr. Luchsinger reported receiving donated metformin and matching placebo from EMD Serono, a subsidiary of Merck, for the MAP study. Dr. Schwartz received research support from the US Department of Veterans Affairs as National Chair of the VA-IMPACT trial.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Low-Glycemic Index Diet Benefits Mirror Fiber, Whole Grain
TOPLINE:
A diet with a low glycemic index (GI) had protective effects against diabetes and other chronic diseases similar to those of a diet high in fiber and whole grains.
METHODOLOGY:
- A 2019 Lancet report from the World Health Organization promoted fiber and whole grains to manage type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and cancer but rejected GI as a relevant dietary factor to prevent chronic diseases.
- This meta-analysis assessed the evidence of how GI and glycemic load are associated with four main outcomes and did the same for diets high in fiber and whole grain.
- Researchers identified 10 large prospective cohort studies (each including ≥ 100,000 participants) that assessed associations of GI, glycemic load, and fiber and whole grains with the outcomes of interest.
- The mean age was 56 years, and the mean follow-up duration was 12.6 years.
- The primary outcomes were incidence of type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular diseases and its components, diabetes-related cancers, and all-cause mortality.
TAKEAWAY:
- Compared with low-GI diets, high-GI diets were associated with an increased risk for:
- Type 2 diabetes (relative risk [RR], 1.27; P < .0001)
- Total cardiovascular disease (RR, 1.15; P < .0001)
- Diabetes-related cancers (RR, 1.05; P = .0001)
- All-cause mortality (RR, 1.08; P < .0001), statistically significant in women only.
- Foods with high glycemic load were associated with an increased risk for incident type 2 diabetes (RR, 1.15; P < .0001) and total cardiovascular disease (RR, 1.15; P < .0001) than foods with a low glycemic load.
- A diet high in fiber and whole grains reduced the risk for all four outcomes, with the association being similar to that observed for low-GI diet.
IN PRACTICE:
“These findings justify the combination of GI with fiber and whole grains in dietary recommendations to reduce the risk of diabetes and related chronic diseases,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by David J.A. Jenkins, MD, Department of Nutritional Sciences, Temerty Faculty of Medicine, University of Toronto, Ontario, Canada, and published online in The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology.
LIMITATIONS:
The lack of evaluation or absence of positive effects in some analyses may have led to a paucity of reported studies for some outcomes. Moreover, the findings for some outcomes may have had limited robustness because of a small difference in RR. Furthermore, only one or two cohorts were included to compare most disease outcomes related to GI with fiber and wholegrain exposure.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was funded by Banting and Best and the Karuna Foundation. The authors declared receiving research grants, payments, honoraria, and travel support from and having other ties with food and beverage growers, processors and manufacturers, as well as with foundations, chronic disease advocacy and research groups, professional societies, government organizations, and other sources.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
A diet with a low glycemic index (GI) had protective effects against diabetes and other chronic diseases similar to those of a diet high in fiber and whole grains.
METHODOLOGY:
- A 2019 Lancet report from the World Health Organization promoted fiber and whole grains to manage type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and cancer but rejected GI as a relevant dietary factor to prevent chronic diseases.
- This meta-analysis assessed the evidence of how GI and glycemic load are associated with four main outcomes and did the same for diets high in fiber and whole grain.
- Researchers identified 10 large prospective cohort studies (each including ≥ 100,000 participants) that assessed associations of GI, glycemic load, and fiber and whole grains with the outcomes of interest.
- The mean age was 56 years, and the mean follow-up duration was 12.6 years.
- The primary outcomes were incidence of type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular diseases and its components, diabetes-related cancers, and all-cause mortality.
TAKEAWAY:
- Compared with low-GI diets, high-GI diets were associated with an increased risk for:
- Type 2 diabetes (relative risk [RR], 1.27; P < .0001)
- Total cardiovascular disease (RR, 1.15; P < .0001)
- Diabetes-related cancers (RR, 1.05; P = .0001)
- All-cause mortality (RR, 1.08; P < .0001), statistically significant in women only.
- Foods with high glycemic load were associated with an increased risk for incident type 2 diabetes (RR, 1.15; P < .0001) and total cardiovascular disease (RR, 1.15; P < .0001) than foods with a low glycemic load.
- A diet high in fiber and whole grains reduced the risk for all four outcomes, with the association being similar to that observed for low-GI diet.
IN PRACTICE:
“These findings justify the combination of GI with fiber and whole grains in dietary recommendations to reduce the risk of diabetes and related chronic diseases,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by David J.A. Jenkins, MD, Department of Nutritional Sciences, Temerty Faculty of Medicine, University of Toronto, Ontario, Canada, and published online in The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology.
LIMITATIONS:
The lack of evaluation or absence of positive effects in some analyses may have led to a paucity of reported studies for some outcomes. Moreover, the findings for some outcomes may have had limited robustness because of a small difference in RR. Furthermore, only one or two cohorts were included to compare most disease outcomes related to GI with fiber and wholegrain exposure.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was funded by Banting and Best and the Karuna Foundation. The authors declared receiving research grants, payments, honoraria, and travel support from and having other ties with food and beverage growers, processors and manufacturers, as well as with foundations, chronic disease advocacy and research groups, professional societies, government organizations, and other sources.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
A diet with a low glycemic index (GI) had protective effects against diabetes and other chronic diseases similar to those of a diet high in fiber and whole grains.
METHODOLOGY:
- A 2019 Lancet report from the World Health Organization promoted fiber and whole grains to manage type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and cancer but rejected GI as a relevant dietary factor to prevent chronic diseases.
- This meta-analysis assessed the evidence of how GI and glycemic load are associated with four main outcomes and did the same for diets high in fiber and whole grain.
- Researchers identified 10 large prospective cohort studies (each including ≥ 100,000 participants) that assessed associations of GI, glycemic load, and fiber and whole grains with the outcomes of interest.
- The mean age was 56 years, and the mean follow-up duration was 12.6 years.
- The primary outcomes were incidence of type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular diseases and its components, diabetes-related cancers, and all-cause mortality.
TAKEAWAY:
- Compared with low-GI diets, high-GI diets were associated with an increased risk for:
- Type 2 diabetes (relative risk [RR], 1.27; P < .0001)
- Total cardiovascular disease (RR, 1.15; P < .0001)
- Diabetes-related cancers (RR, 1.05; P = .0001)
- All-cause mortality (RR, 1.08; P < .0001), statistically significant in women only.
- Foods with high glycemic load were associated with an increased risk for incident type 2 diabetes (RR, 1.15; P < .0001) and total cardiovascular disease (RR, 1.15; P < .0001) than foods with a low glycemic load.
- A diet high in fiber and whole grains reduced the risk for all four outcomes, with the association being similar to that observed for low-GI diet.
IN PRACTICE:
“These findings justify the combination of GI with fiber and whole grains in dietary recommendations to reduce the risk of diabetes and related chronic diseases,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by David J.A. Jenkins, MD, Department of Nutritional Sciences, Temerty Faculty of Medicine, University of Toronto, Ontario, Canada, and published online in The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology.
LIMITATIONS:
The lack of evaluation or absence of positive effects in some analyses may have led to a paucity of reported studies for some outcomes. Moreover, the findings for some outcomes may have had limited robustness because of a small difference in RR. Furthermore, only one or two cohorts were included to compare most disease outcomes related to GI with fiber and wholegrain exposure.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was funded by Banting and Best and the Karuna Foundation. The authors declared receiving research grants, payments, honoraria, and travel support from and having other ties with food and beverage growers, processors and manufacturers, as well as with foundations, chronic disease advocacy and research groups, professional societies, government organizations, and other sources.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
GLP-1s’ Next Target: Male Infertility?
The explosion of interest in glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs), such as semaglutide and tirzepatide, has raised questions about what therapeutic effects this class of medication might have beyond their current indications for type 2 diabetes and obesity.
Recent clinical trials have recently identified benefits from GLP-1 agents for the heart, liver, and kidneys, but the current evidence base is murkier regarding how the drugs may affect male fertility.
For starters, overweight and obesity are strongly associated with male infertility in several overlapping ways. Obesity can disrupt hormones linked to fertility, increase the risk for defective sperm, adversely affect semen quality, and even make sexual intercourse more difficult due to obesity’s link to erectile dysfunction. As a result, GLP-1 RAs should at least in theory boost male fertility in men who take the drugs to lose weight.
But animal studies and a handful of small trials and observational data point to the potential for GLP-1 RAs to improve male fertility in other ways.
A recent narrative review on GLP-1 RAs and male reproductive health, published in the journal Medicina in December 2023, surveyed the potential of the drugs for male infertility and offered reason for optimism.
Hossein Sadeghi-Nejad, MD, director of urology at NYU Langone Health, New York, and a coauthor of the article, said that one reason he and his colleagues conducted their analysis was the known association between weight loss and an increase in testosterone.
“Most of the animal studies that are out there show that this class of drugs does affect testosterone levels,” Dr. Sadeghi-Nejad said; they wanted to better understand what other evidence showed about GLP-1 agonists and other fertility factors.
Link Between Obesity and Fertility
The recent paper first reviews the well-established link between obesity and poorer fertility outcomes.
“Certainly, obesity poses a significant societal problem with substantial impacts on both overall health and economic aspects,” senior author Ranjith Ramasamy, MD, associate professor of urology and director of the reproductive urology Fellowship program at the University of Miami’s Miller School of Medicine, told this news organization. “The escalating global obesity rates raise concerns, especially in the field of male infertility, where excessive body fat induces intrinsic hormonal changes leading to alterations, eventually, in semen parameters.”
The authors noted that obesity has been linked in the research to worse assisted reproductive technology (ART) outcomes and to subfecundity, taking more than 12 months to achieve pregnancy. They also referenced a systematic review that found men with obesity were more likely to have lower sperm counts and less viable sperm.
“From our standpoint, I think the key point was to raise awareness about the fact that obesity, because of the aromatization of testosterone to estradiol [from excess adipose tissue], will affect the hormonal axis and the availability of testosterone and, therefore, indirectly affects spermatogenesis,” Dr. Sadeghi-Nejad said.
Obesity is also linked to lower levels of inhibin B, which stimulates testosterone secretion in Sertoli cells, which, when combined with the proinflammatory state of obesity, “results in a less favorable environment for sperm production,” he said. Finally, the link between obesity and poorer sexual function further inhibits fertility potential, he added.
Until recently, the primary treatments for obesity in men experiencing fertility problems have been lifestyle modifications or surgical interventions. But the recent approval of GLP-1 RA drugs for obesity present an additional option depending on how these drugs affect other fertility parameters.
Direct or Indirect Effects?
Most of the available evidence on GLP-RAs and sperm parameters comes from preclinical research. One of the few clinical trials, published last year in the Journal of Clinical Medicine, investigated the effects of liraglutide in men with metabolic hypogonadism, a body mass index between (BMI) 30 and 40, and severe erectile dysfunction.
Among the 110 men enrolled in the study, only the 35 participants who said that they were not seeking fatherhood received liraglutide. After 4 months of treatment, these men had significantly improved semen concentration, motility, and morphology than did those wanting to conceive who received conventional fertility treatment. Erectile dysfunction was also more improved in the liraglutide group, according to the researchers.
Though this study demonstrated the potential for liraglutide to treat metabolic hypogonadism, the men in that group also had greater weight loss and BMI reduction than the other participants. The review cited several other studies — albeit small ones — in which weight loss was associated with improvements in sperm parameters, including one randomized controlled trial in which one group lost weight with liraglutide and the other with lifestyle modifications; both groups showed increases in the concentration and number of sperm.
One of the key questions requiring further research, then, is whether GLP-1 agents have direct effects on male fertility independent of a reduction in obesity. The randomized controlled trials comparing liraglutide and lifestyle modifications failed to find additional effects on semen in the men taking liraglutide; however, the study had only 56 participants, and results from liraglutide cannot be generalized to potential effects of semaglutide or tirzepatide, Dr. Sadeghi-Nejad said.
“Determining the relative contributions of weight loss versus direct drug actions on fertility outcomes remains challenging without robust data,” Dr. Ramasamy said. “While acknowledged that diet and physical activity positively impact fertility, confirming the synergistic role of GLP-1 receptor agonists requires evidence from well-designed randomized clinical trials.”
Rodent studies suggest that GLP-1 RAs may independently affect testicular function because GLP-1 receptors exist in Sertoli and Leydig cells of the testes. In one study, for example, obese mice who received the GLP-1 agonist exenatide for 8 weeks had “improved sperm motility, DNA integrity, and decreased expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines,” the authors of the review reported. But the precise mechanisms aren’t well understood.
“We know that there are GLP-1 receptors in the reproductive tract, but the extent of the downstream effect of stimulating those receptors, I don’t think we know well,” said John P. Lindsey II, MD, MEng, assistant professor of urology at University of California San Francisco Health.
Other hormonal effects of GLP-1 agonists, such as stimulating insulin production and better regulating blood glucose levels, are better understood, said Raevti Bole, MD, a urologist at Cleveland Clinic, in Ohio, but still other effects of the drugs may not yet be identified.
“I think the really big unknown is whether these types of drugs have effects that are not hormonal on male fertility and what those effects are, and how those affect sperm,” Dr. Bole said. “For example, we know that these drugs slow gastric emptying. Is it possible that slow gastric emptying affects some of the nutrients that you absorb, and that could affect fertility?” Similarly, she said, it’s not clear whether GLP-1 agonists would have any effects on the thyroid that could then affect fertility.
Effects on Offspring
Another open question about GLP-1 RAs and male fertility is their potential effects on the offspring, said Sriram Machineni, MBBS, associate professor of endocrinology at the Albert Einstein College of Medicine in New York City. The clinical trials involving the drugs for treating type 2 diabetes and obesity required both men and women to use contraception. If sperm contributing to a pregnancy are exposed to a GLP-1 agent, “we don’t know what the consequences could be,” Dr. Machineni said. “Just increasing the fertility of the man is not enough. We need to make sure it’s safe long-term for the fetus.”
Dr. Bole also pointed out the need for understanding potential effects in the fetus.
“We know that there are epigenetic changes that can happen to sperm that are influenced by the lifestyle and the physical health and environment of the parent,” Dr. Bole said. “So how could these drugs potentially affect those epigenetic changes that then potentially are passed on to the offspring? We don’t know that.”
An ideal source for that data would be a cohort registry of people who are taking the medication and then cause a pregnancy. “They have a registry for pregnant women,” Dr. Machineni said, “but we need something similar for men.”
Dr. Sadeghi-Nejad said that he and his coauthors are working on developing a registry for men who take GLP-1 RAs that would enable long-term tracking of multiple andrologic outcomes, including fertility and sexual dysfunction. Such a registry could theoretically be useful in tracking pregnancy and offspring outcomes as well.
Too Soon for Prescribing
Additional options for treating fertility in men with obesity would be welcome. Current treatments include the selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) clomiphene citrate and the aromatase inhibitor anastrozole. But these have their drawbacks, Dr. Sadeghi-Nejad pointed out; in the overweight population in particular, they “are not necessarily ideal,” he said.
“Although both are viable treatments for enhancing hormonal balance and semen parameters, clomiphene citrate has rare but documented side effects, including thromboembolism, gastrointestinal distress and occasional weight gain in men,” Dr. Sadeghi-Nejad and his colleagues wrote. “Furthermore, despite clomiphene citrate’s association with significant increases in sperm concentration, it is not universally effective, with a meta-analysis indicating a significant increase in sperm concentration in approximately 60% of men.”
For men who have obesity and oligospermia but normal levels of testosterone and estradiol, “conventional pharmaceutical approaches like clomiphene may not be suitable,” the authors wrote.
Still, GLP-1 RAs may have a role to play for this population.
“I think it is within the wheelhouse of a reproductive urologist to consider those types of medications,” Dr. Lindsey said. For example, for a patient who has overweight or obesity, “does it make sense to think about doing clomiphene therapy, which we often do for someone who has low testosterone, in conjunction [with a GLP-1 agonist]? Maybe there’s a kind of an additive effect of having both on board.”
Dr. Ramasamy similarly noted that GLP-1 agonists cannot replace SERMs but may work “synergistically” with them.
“Despite the established popularity of GLP-1 receptor agonists, there may be some reluctance among urologists and fertility specialists to prescribe them, with some others advocating for their use to enhance semen parameters,” Dr. Ramasamy said. “However, robust scientific evidence is still lacking, necessitating caution and a wait for more substantial data.”
Even if GLP-1 RAs prove to have therapeutic benefit for fertility, considerations such as availability and cost may affect prescribing.
“We do currently have safe and effective drugs that we use for male fertility, and those are generally nowhere near as expensive,” Dr. Bole said. “When we start talking about another drug that we can add, we have to think about the efficacy and the potential side effect but also, is this affordable for patients?”
Eventually, once more evidence become available, all of the urologists who spoke with this news organization said that they expect discussion about the possible therapeutic utility of GLP-1 agonists to make its way into clinical guidelines.
“Obesity is such a huge impediment for fertility in the modern environment,” Dr. Machineni said. “We will have to clarify the use of these agents, so I think this will be a part of the guidelines some point, but I think we need more information.”
The research was funded by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases and the American Cancer Society. The review authors and other quoted physicians reported no disclosures. Dr. Machineni has consulted for Novo Nordisk and Lilly and has conducted clinical trials with semaglutide and tirzepatide for those companies.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The explosion of interest in glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs), such as semaglutide and tirzepatide, has raised questions about what therapeutic effects this class of medication might have beyond their current indications for type 2 diabetes and obesity.
Recent clinical trials have recently identified benefits from GLP-1 agents for the heart, liver, and kidneys, but the current evidence base is murkier regarding how the drugs may affect male fertility.
For starters, overweight and obesity are strongly associated with male infertility in several overlapping ways. Obesity can disrupt hormones linked to fertility, increase the risk for defective sperm, adversely affect semen quality, and even make sexual intercourse more difficult due to obesity’s link to erectile dysfunction. As a result, GLP-1 RAs should at least in theory boost male fertility in men who take the drugs to lose weight.
But animal studies and a handful of small trials and observational data point to the potential for GLP-1 RAs to improve male fertility in other ways.
A recent narrative review on GLP-1 RAs and male reproductive health, published in the journal Medicina in December 2023, surveyed the potential of the drugs for male infertility and offered reason for optimism.
Hossein Sadeghi-Nejad, MD, director of urology at NYU Langone Health, New York, and a coauthor of the article, said that one reason he and his colleagues conducted their analysis was the known association between weight loss and an increase in testosterone.
“Most of the animal studies that are out there show that this class of drugs does affect testosterone levels,” Dr. Sadeghi-Nejad said; they wanted to better understand what other evidence showed about GLP-1 agonists and other fertility factors.
Link Between Obesity and Fertility
The recent paper first reviews the well-established link between obesity and poorer fertility outcomes.
“Certainly, obesity poses a significant societal problem with substantial impacts on both overall health and economic aspects,” senior author Ranjith Ramasamy, MD, associate professor of urology and director of the reproductive urology Fellowship program at the University of Miami’s Miller School of Medicine, told this news organization. “The escalating global obesity rates raise concerns, especially in the field of male infertility, where excessive body fat induces intrinsic hormonal changes leading to alterations, eventually, in semen parameters.”
The authors noted that obesity has been linked in the research to worse assisted reproductive technology (ART) outcomes and to subfecundity, taking more than 12 months to achieve pregnancy. They also referenced a systematic review that found men with obesity were more likely to have lower sperm counts and less viable sperm.
“From our standpoint, I think the key point was to raise awareness about the fact that obesity, because of the aromatization of testosterone to estradiol [from excess adipose tissue], will affect the hormonal axis and the availability of testosterone and, therefore, indirectly affects spermatogenesis,” Dr. Sadeghi-Nejad said.
Obesity is also linked to lower levels of inhibin B, which stimulates testosterone secretion in Sertoli cells, which, when combined with the proinflammatory state of obesity, “results in a less favorable environment for sperm production,” he said. Finally, the link between obesity and poorer sexual function further inhibits fertility potential, he added.
Until recently, the primary treatments for obesity in men experiencing fertility problems have been lifestyle modifications or surgical interventions. But the recent approval of GLP-1 RA drugs for obesity present an additional option depending on how these drugs affect other fertility parameters.
Direct or Indirect Effects?
Most of the available evidence on GLP-RAs and sperm parameters comes from preclinical research. One of the few clinical trials, published last year in the Journal of Clinical Medicine, investigated the effects of liraglutide in men with metabolic hypogonadism, a body mass index between (BMI) 30 and 40, and severe erectile dysfunction.
Among the 110 men enrolled in the study, only the 35 participants who said that they were not seeking fatherhood received liraglutide. After 4 months of treatment, these men had significantly improved semen concentration, motility, and morphology than did those wanting to conceive who received conventional fertility treatment. Erectile dysfunction was also more improved in the liraglutide group, according to the researchers.
Though this study demonstrated the potential for liraglutide to treat metabolic hypogonadism, the men in that group also had greater weight loss and BMI reduction than the other participants. The review cited several other studies — albeit small ones — in which weight loss was associated with improvements in sperm parameters, including one randomized controlled trial in which one group lost weight with liraglutide and the other with lifestyle modifications; both groups showed increases in the concentration and number of sperm.
One of the key questions requiring further research, then, is whether GLP-1 agents have direct effects on male fertility independent of a reduction in obesity. The randomized controlled trials comparing liraglutide and lifestyle modifications failed to find additional effects on semen in the men taking liraglutide; however, the study had only 56 participants, and results from liraglutide cannot be generalized to potential effects of semaglutide or tirzepatide, Dr. Sadeghi-Nejad said.
“Determining the relative contributions of weight loss versus direct drug actions on fertility outcomes remains challenging without robust data,” Dr. Ramasamy said. “While acknowledged that diet and physical activity positively impact fertility, confirming the synergistic role of GLP-1 receptor agonists requires evidence from well-designed randomized clinical trials.”
Rodent studies suggest that GLP-1 RAs may independently affect testicular function because GLP-1 receptors exist in Sertoli and Leydig cells of the testes. In one study, for example, obese mice who received the GLP-1 agonist exenatide for 8 weeks had “improved sperm motility, DNA integrity, and decreased expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines,” the authors of the review reported. But the precise mechanisms aren’t well understood.
“We know that there are GLP-1 receptors in the reproductive tract, but the extent of the downstream effect of stimulating those receptors, I don’t think we know well,” said John P. Lindsey II, MD, MEng, assistant professor of urology at University of California San Francisco Health.
Other hormonal effects of GLP-1 agonists, such as stimulating insulin production and better regulating blood glucose levels, are better understood, said Raevti Bole, MD, a urologist at Cleveland Clinic, in Ohio, but still other effects of the drugs may not yet be identified.
“I think the really big unknown is whether these types of drugs have effects that are not hormonal on male fertility and what those effects are, and how those affect sperm,” Dr. Bole said. “For example, we know that these drugs slow gastric emptying. Is it possible that slow gastric emptying affects some of the nutrients that you absorb, and that could affect fertility?” Similarly, she said, it’s not clear whether GLP-1 agonists would have any effects on the thyroid that could then affect fertility.
Effects on Offspring
Another open question about GLP-1 RAs and male fertility is their potential effects on the offspring, said Sriram Machineni, MBBS, associate professor of endocrinology at the Albert Einstein College of Medicine in New York City. The clinical trials involving the drugs for treating type 2 diabetes and obesity required both men and women to use contraception. If sperm contributing to a pregnancy are exposed to a GLP-1 agent, “we don’t know what the consequences could be,” Dr. Machineni said. “Just increasing the fertility of the man is not enough. We need to make sure it’s safe long-term for the fetus.”
Dr. Bole also pointed out the need for understanding potential effects in the fetus.
“We know that there are epigenetic changes that can happen to sperm that are influenced by the lifestyle and the physical health and environment of the parent,” Dr. Bole said. “So how could these drugs potentially affect those epigenetic changes that then potentially are passed on to the offspring? We don’t know that.”
An ideal source for that data would be a cohort registry of people who are taking the medication and then cause a pregnancy. “They have a registry for pregnant women,” Dr. Machineni said, “but we need something similar for men.”
Dr. Sadeghi-Nejad said that he and his coauthors are working on developing a registry for men who take GLP-1 RAs that would enable long-term tracking of multiple andrologic outcomes, including fertility and sexual dysfunction. Such a registry could theoretically be useful in tracking pregnancy and offspring outcomes as well.
Too Soon for Prescribing
Additional options for treating fertility in men with obesity would be welcome. Current treatments include the selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) clomiphene citrate and the aromatase inhibitor anastrozole. But these have their drawbacks, Dr. Sadeghi-Nejad pointed out; in the overweight population in particular, they “are not necessarily ideal,” he said.
“Although both are viable treatments for enhancing hormonal balance and semen parameters, clomiphene citrate has rare but documented side effects, including thromboembolism, gastrointestinal distress and occasional weight gain in men,” Dr. Sadeghi-Nejad and his colleagues wrote. “Furthermore, despite clomiphene citrate’s association with significant increases in sperm concentration, it is not universally effective, with a meta-analysis indicating a significant increase in sperm concentration in approximately 60% of men.”
For men who have obesity and oligospermia but normal levels of testosterone and estradiol, “conventional pharmaceutical approaches like clomiphene may not be suitable,” the authors wrote.
Still, GLP-1 RAs may have a role to play for this population.
“I think it is within the wheelhouse of a reproductive urologist to consider those types of medications,” Dr. Lindsey said. For example, for a patient who has overweight or obesity, “does it make sense to think about doing clomiphene therapy, which we often do for someone who has low testosterone, in conjunction [with a GLP-1 agonist]? Maybe there’s a kind of an additive effect of having both on board.”
Dr. Ramasamy similarly noted that GLP-1 agonists cannot replace SERMs but may work “synergistically” with them.
“Despite the established popularity of GLP-1 receptor agonists, there may be some reluctance among urologists and fertility specialists to prescribe them, with some others advocating for their use to enhance semen parameters,” Dr. Ramasamy said. “However, robust scientific evidence is still lacking, necessitating caution and a wait for more substantial data.”
Even if GLP-1 RAs prove to have therapeutic benefit for fertility, considerations such as availability and cost may affect prescribing.
“We do currently have safe and effective drugs that we use for male fertility, and those are generally nowhere near as expensive,” Dr. Bole said. “When we start talking about another drug that we can add, we have to think about the efficacy and the potential side effect but also, is this affordable for patients?”
Eventually, once more evidence become available, all of the urologists who spoke with this news organization said that they expect discussion about the possible therapeutic utility of GLP-1 agonists to make its way into clinical guidelines.
“Obesity is such a huge impediment for fertility in the modern environment,” Dr. Machineni said. “We will have to clarify the use of these agents, so I think this will be a part of the guidelines some point, but I think we need more information.”
The research was funded by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases and the American Cancer Society. The review authors and other quoted physicians reported no disclosures. Dr. Machineni has consulted for Novo Nordisk and Lilly and has conducted clinical trials with semaglutide and tirzepatide for those companies.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The explosion of interest in glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs), such as semaglutide and tirzepatide, has raised questions about what therapeutic effects this class of medication might have beyond their current indications for type 2 diabetes and obesity.
Recent clinical trials have recently identified benefits from GLP-1 agents for the heart, liver, and kidneys, but the current evidence base is murkier regarding how the drugs may affect male fertility.
For starters, overweight and obesity are strongly associated with male infertility in several overlapping ways. Obesity can disrupt hormones linked to fertility, increase the risk for defective sperm, adversely affect semen quality, and even make sexual intercourse more difficult due to obesity’s link to erectile dysfunction. As a result, GLP-1 RAs should at least in theory boost male fertility in men who take the drugs to lose weight.
But animal studies and a handful of small trials and observational data point to the potential for GLP-1 RAs to improve male fertility in other ways.
A recent narrative review on GLP-1 RAs and male reproductive health, published in the journal Medicina in December 2023, surveyed the potential of the drugs for male infertility and offered reason for optimism.
Hossein Sadeghi-Nejad, MD, director of urology at NYU Langone Health, New York, and a coauthor of the article, said that one reason he and his colleagues conducted their analysis was the known association between weight loss and an increase in testosterone.
“Most of the animal studies that are out there show that this class of drugs does affect testosterone levels,” Dr. Sadeghi-Nejad said; they wanted to better understand what other evidence showed about GLP-1 agonists and other fertility factors.
Link Between Obesity and Fertility
The recent paper first reviews the well-established link between obesity and poorer fertility outcomes.
“Certainly, obesity poses a significant societal problem with substantial impacts on both overall health and economic aspects,” senior author Ranjith Ramasamy, MD, associate professor of urology and director of the reproductive urology Fellowship program at the University of Miami’s Miller School of Medicine, told this news organization. “The escalating global obesity rates raise concerns, especially in the field of male infertility, where excessive body fat induces intrinsic hormonal changes leading to alterations, eventually, in semen parameters.”
The authors noted that obesity has been linked in the research to worse assisted reproductive technology (ART) outcomes and to subfecundity, taking more than 12 months to achieve pregnancy. They also referenced a systematic review that found men with obesity were more likely to have lower sperm counts and less viable sperm.
“From our standpoint, I think the key point was to raise awareness about the fact that obesity, because of the aromatization of testosterone to estradiol [from excess adipose tissue], will affect the hormonal axis and the availability of testosterone and, therefore, indirectly affects spermatogenesis,” Dr. Sadeghi-Nejad said.
Obesity is also linked to lower levels of inhibin B, which stimulates testosterone secretion in Sertoli cells, which, when combined with the proinflammatory state of obesity, “results in a less favorable environment for sperm production,” he said. Finally, the link between obesity and poorer sexual function further inhibits fertility potential, he added.
Until recently, the primary treatments for obesity in men experiencing fertility problems have been lifestyle modifications or surgical interventions. But the recent approval of GLP-1 RA drugs for obesity present an additional option depending on how these drugs affect other fertility parameters.
Direct or Indirect Effects?
Most of the available evidence on GLP-RAs and sperm parameters comes from preclinical research. One of the few clinical trials, published last year in the Journal of Clinical Medicine, investigated the effects of liraglutide in men with metabolic hypogonadism, a body mass index between (BMI) 30 and 40, and severe erectile dysfunction.
Among the 110 men enrolled in the study, only the 35 participants who said that they were not seeking fatherhood received liraglutide. After 4 months of treatment, these men had significantly improved semen concentration, motility, and morphology than did those wanting to conceive who received conventional fertility treatment. Erectile dysfunction was also more improved in the liraglutide group, according to the researchers.
Though this study demonstrated the potential for liraglutide to treat metabolic hypogonadism, the men in that group also had greater weight loss and BMI reduction than the other participants. The review cited several other studies — albeit small ones — in which weight loss was associated with improvements in sperm parameters, including one randomized controlled trial in which one group lost weight with liraglutide and the other with lifestyle modifications; both groups showed increases in the concentration and number of sperm.
One of the key questions requiring further research, then, is whether GLP-1 agents have direct effects on male fertility independent of a reduction in obesity. The randomized controlled trials comparing liraglutide and lifestyle modifications failed to find additional effects on semen in the men taking liraglutide; however, the study had only 56 participants, and results from liraglutide cannot be generalized to potential effects of semaglutide or tirzepatide, Dr. Sadeghi-Nejad said.
“Determining the relative contributions of weight loss versus direct drug actions on fertility outcomes remains challenging without robust data,” Dr. Ramasamy said. “While acknowledged that diet and physical activity positively impact fertility, confirming the synergistic role of GLP-1 receptor agonists requires evidence from well-designed randomized clinical trials.”
Rodent studies suggest that GLP-1 RAs may independently affect testicular function because GLP-1 receptors exist in Sertoli and Leydig cells of the testes. In one study, for example, obese mice who received the GLP-1 agonist exenatide for 8 weeks had “improved sperm motility, DNA integrity, and decreased expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines,” the authors of the review reported. But the precise mechanisms aren’t well understood.
“We know that there are GLP-1 receptors in the reproductive tract, but the extent of the downstream effect of stimulating those receptors, I don’t think we know well,” said John P. Lindsey II, MD, MEng, assistant professor of urology at University of California San Francisco Health.
Other hormonal effects of GLP-1 agonists, such as stimulating insulin production and better regulating blood glucose levels, are better understood, said Raevti Bole, MD, a urologist at Cleveland Clinic, in Ohio, but still other effects of the drugs may not yet be identified.
“I think the really big unknown is whether these types of drugs have effects that are not hormonal on male fertility and what those effects are, and how those affect sperm,” Dr. Bole said. “For example, we know that these drugs slow gastric emptying. Is it possible that slow gastric emptying affects some of the nutrients that you absorb, and that could affect fertility?” Similarly, she said, it’s not clear whether GLP-1 agonists would have any effects on the thyroid that could then affect fertility.
Effects on Offspring
Another open question about GLP-1 RAs and male fertility is their potential effects on the offspring, said Sriram Machineni, MBBS, associate professor of endocrinology at the Albert Einstein College of Medicine in New York City. The clinical trials involving the drugs for treating type 2 diabetes and obesity required both men and women to use contraception. If sperm contributing to a pregnancy are exposed to a GLP-1 agent, “we don’t know what the consequences could be,” Dr. Machineni said. “Just increasing the fertility of the man is not enough. We need to make sure it’s safe long-term for the fetus.”
Dr. Bole also pointed out the need for understanding potential effects in the fetus.
“We know that there are epigenetic changes that can happen to sperm that are influenced by the lifestyle and the physical health and environment of the parent,” Dr. Bole said. “So how could these drugs potentially affect those epigenetic changes that then potentially are passed on to the offspring? We don’t know that.”
An ideal source for that data would be a cohort registry of people who are taking the medication and then cause a pregnancy. “They have a registry for pregnant women,” Dr. Machineni said, “but we need something similar for men.”
Dr. Sadeghi-Nejad said that he and his coauthors are working on developing a registry for men who take GLP-1 RAs that would enable long-term tracking of multiple andrologic outcomes, including fertility and sexual dysfunction. Such a registry could theoretically be useful in tracking pregnancy and offspring outcomes as well.
Too Soon for Prescribing
Additional options for treating fertility in men with obesity would be welcome. Current treatments include the selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) clomiphene citrate and the aromatase inhibitor anastrozole. But these have their drawbacks, Dr. Sadeghi-Nejad pointed out; in the overweight population in particular, they “are not necessarily ideal,” he said.
“Although both are viable treatments for enhancing hormonal balance and semen parameters, clomiphene citrate has rare but documented side effects, including thromboembolism, gastrointestinal distress and occasional weight gain in men,” Dr. Sadeghi-Nejad and his colleagues wrote. “Furthermore, despite clomiphene citrate’s association with significant increases in sperm concentration, it is not universally effective, with a meta-analysis indicating a significant increase in sperm concentration in approximately 60% of men.”
For men who have obesity and oligospermia but normal levels of testosterone and estradiol, “conventional pharmaceutical approaches like clomiphene may not be suitable,” the authors wrote.
Still, GLP-1 RAs may have a role to play for this population.
“I think it is within the wheelhouse of a reproductive urologist to consider those types of medications,” Dr. Lindsey said. For example, for a patient who has overweight or obesity, “does it make sense to think about doing clomiphene therapy, which we often do for someone who has low testosterone, in conjunction [with a GLP-1 agonist]? Maybe there’s a kind of an additive effect of having both on board.”
Dr. Ramasamy similarly noted that GLP-1 agonists cannot replace SERMs but may work “synergistically” with them.
“Despite the established popularity of GLP-1 receptor agonists, there may be some reluctance among urologists and fertility specialists to prescribe them, with some others advocating for their use to enhance semen parameters,” Dr. Ramasamy said. “However, robust scientific evidence is still lacking, necessitating caution and a wait for more substantial data.”
Even if GLP-1 RAs prove to have therapeutic benefit for fertility, considerations such as availability and cost may affect prescribing.
“We do currently have safe and effective drugs that we use for male fertility, and those are generally nowhere near as expensive,” Dr. Bole said. “When we start talking about another drug that we can add, we have to think about the efficacy and the potential side effect but also, is this affordable for patients?”
Eventually, once more evidence become available, all of the urologists who spoke with this news organization said that they expect discussion about the possible therapeutic utility of GLP-1 agonists to make its way into clinical guidelines.
“Obesity is such a huge impediment for fertility in the modern environment,” Dr. Machineni said. “We will have to clarify the use of these agents, so I think this will be a part of the guidelines some point, but I think we need more information.”
The research was funded by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases and the American Cancer Society. The review authors and other quoted physicians reported no disclosures. Dr. Machineni has consulted for Novo Nordisk and Lilly and has conducted clinical trials with semaglutide and tirzepatide for those companies.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA Warns Against Using Unauthorized Glucose Monitors
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is warning against the use of smartwatches and rings that are claimed to measure a person’s glucose levels without piercing the skin.
The warning doesn’t apply to authorized smartwatch applications that display glucose values from an FDA-approved continuous glucose monitor with a sensor implanted under the skin.
Rather, the warning pertains to watches or rings sold through online marketplaces or directly from sellers who claim that the devices measure blood sugar noninvasively without requiring the wearer to prick their finger or pierce their skin. These products are manufactured by dozens of companies and sold under many different brand names. The FDA’s warning applies to all of them.
These devices have not been evaluated by the FDA for safety and effectiveness, and their use by people with diabetes could result in inaccurate blood glucose measurements, with potentially serious consequences if relied upon for medication dosing.
“The FDA has not authorized, cleared, or approved any smartwatch or smart ring that is intended to measure or estimate blood glucose values on its own,” the agency said in a statement issued on February 21, 2024.
They added, “The agency is working to ensure that manufacturers, distributors, and sellers do not illegally market unauthorized smartwatches or smart rings that claim to measure blood glucose levels.”
People who experience any problems with inaccurate blood glucose measurement or experience any adverse events from using an unauthorized smartwatch or smart ring are urged to report it to the FDA through its MedWatch program.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is warning against the use of smartwatches and rings that are claimed to measure a person’s glucose levels without piercing the skin.
The warning doesn’t apply to authorized smartwatch applications that display glucose values from an FDA-approved continuous glucose monitor with a sensor implanted under the skin.
Rather, the warning pertains to watches or rings sold through online marketplaces or directly from sellers who claim that the devices measure blood sugar noninvasively without requiring the wearer to prick their finger or pierce their skin. These products are manufactured by dozens of companies and sold under many different brand names. The FDA’s warning applies to all of them.
These devices have not been evaluated by the FDA for safety and effectiveness, and their use by people with diabetes could result in inaccurate blood glucose measurements, with potentially serious consequences if relied upon for medication dosing.
“The FDA has not authorized, cleared, or approved any smartwatch or smart ring that is intended to measure or estimate blood glucose values on its own,” the agency said in a statement issued on February 21, 2024.
They added, “The agency is working to ensure that manufacturers, distributors, and sellers do not illegally market unauthorized smartwatches or smart rings that claim to measure blood glucose levels.”
People who experience any problems with inaccurate blood glucose measurement or experience any adverse events from using an unauthorized smartwatch or smart ring are urged to report it to the FDA through its MedWatch program.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is warning against the use of smartwatches and rings that are claimed to measure a person’s glucose levels without piercing the skin.
The warning doesn’t apply to authorized smartwatch applications that display glucose values from an FDA-approved continuous glucose monitor with a sensor implanted under the skin.
Rather, the warning pertains to watches or rings sold through online marketplaces or directly from sellers who claim that the devices measure blood sugar noninvasively without requiring the wearer to prick their finger or pierce their skin. These products are manufactured by dozens of companies and sold under many different brand names. The FDA’s warning applies to all of them.
These devices have not been evaluated by the FDA for safety and effectiveness, and their use by people with diabetes could result in inaccurate blood glucose measurements, with potentially serious consequences if relied upon for medication dosing.
“The FDA has not authorized, cleared, or approved any smartwatch or smart ring that is intended to measure or estimate blood glucose values on its own,” the agency said in a statement issued on February 21, 2024.
They added, “The agency is working to ensure that manufacturers, distributors, and sellers do not illegally market unauthorized smartwatches or smart rings that claim to measure blood glucose levels.”
People who experience any problems with inaccurate blood glucose measurement or experience any adverse events from using an unauthorized smartwatch or smart ring are urged to report it to the FDA through its MedWatch program.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Can Gargling With Mouthwash Help Manage Type 2 Diabetes?
TOPLINE:
in people with type 2 diabetes (T2D), especially younger adults.
METHODOLOGY:
- A total of 173 patients with T2D who had at least six total periodontopathic bacteria in their mouths and ≥ 6.5% were instructed to gargle with water three times a day for 6 months, followed by gargling with chlorhexidine gluconate mouthwash three times a day for the next 6 months.
- Saliva specimens were collected every 1-2 months at clinic visits totaling 6-12 samples per study period and bacterial DNA examined for three red complex species, namely, Porphyromonas gingivalis, Treponema denticola, and Tannerella forsythia.
TAKEAWAY:
- Twelve individuals who gargled once a day or less showed no significant reductions in red complex species after mouthwash or water gargling.
- By contrast, significant decreases in red complex bacteria were seen after 6 months of mouthwash gargling (P < .001) in the 80 who gargled twice a day and the 81 who did so three times a day compared with no changes after water gargling.
- Among the 161 individuals who gargled at least twice a day, the decrease in red species with mouthwash vs water gargling was highly significant (P < .0001).
- After adjustment for A1c seasonal variation, neither water gargling nor mouthwash gargling led to significant overall reduction in A1c levels.
- However, A1c levels were significantly lower in the 83 individuals aged ≤ 68 years than among the 78 aged ≥ 69 years after gargling with mouthwash (P < .05), with no change in either group after water gargling.
- Similarly, A1c levels were significantly reduced (P < .05) after mouthwash in the 69 with baseline A1c ≥ 7.5% compared with the 92 whose baseline A1c levels were ≤ 7.4%, with no changes in either after water.
IN PRACTICE:
“A bidirectional relationship between periodontitis and T2D has been reported. Patients with T2D are more susceptible to severe periodontitis than subjects without diabetes, and inflammatory periodontitis aggravates hyperglycemia, leading to inadequate glycemic control.” “Recently, it has been reported that patients with T2D treated for periodontitis have reduced periodontopathic bacteria and improved glycemic control. Patients with T2D complicated by periodontitis have more red complex species, and poor glycemic control is thought to be associated with increased levels of red complex species in the oral cavity.” “Further studies should be planned, taking into account various patient factors to determine the effect of mouthwash gargling on the amount of red complex species and A1c levels in patients with T2D.”
SOURCE:
This study was conducted by Saaya Matayoshi, of the Joint Research Laboratory of Science for Oral and Systemic Connection, Osaka University Graduate School of Dentistry, Osaka, Japan, and colleagues and published in Scientific Reports.
LIMITATIONS:
Only polymerase chain reaction used to detect periodontopathic bacteria so not quantified. No assessment of periodontal pocket depth. Saliva sampling conditions not standardized. Study conducted during COVID-19 pandemic; all patients wore masks. Heterogeneity in patient responses to the mouthwash.
DISCLOSURES:
This work was supported by the Fund for Scientific Promotion of Weltec Corp, Osaka, Japan. The authors declared no competing interests.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
in people with type 2 diabetes (T2D), especially younger adults.
METHODOLOGY:
- A total of 173 patients with T2D who had at least six total periodontopathic bacteria in their mouths and ≥ 6.5% were instructed to gargle with water three times a day for 6 months, followed by gargling with chlorhexidine gluconate mouthwash three times a day for the next 6 months.
- Saliva specimens were collected every 1-2 months at clinic visits totaling 6-12 samples per study period and bacterial DNA examined for three red complex species, namely, Porphyromonas gingivalis, Treponema denticola, and Tannerella forsythia.
TAKEAWAY:
- Twelve individuals who gargled once a day or less showed no significant reductions in red complex species after mouthwash or water gargling.
- By contrast, significant decreases in red complex bacteria were seen after 6 months of mouthwash gargling (P < .001) in the 80 who gargled twice a day and the 81 who did so three times a day compared with no changes after water gargling.
- Among the 161 individuals who gargled at least twice a day, the decrease in red species with mouthwash vs water gargling was highly significant (P < .0001).
- After adjustment for A1c seasonal variation, neither water gargling nor mouthwash gargling led to significant overall reduction in A1c levels.
- However, A1c levels were significantly lower in the 83 individuals aged ≤ 68 years than among the 78 aged ≥ 69 years after gargling with mouthwash (P < .05), with no change in either group after water gargling.
- Similarly, A1c levels were significantly reduced (P < .05) after mouthwash in the 69 with baseline A1c ≥ 7.5% compared with the 92 whose baseline A1c levels were ≤ 7.4%, with no changes in either after water.
IN PRACTICE:
“A bidirectional relationship between periodontitis and T2D has been reported. Patients with T2D are more susceptible to severe periodontitis than subjects without diabetes, and inflammatory periodontitis aggravates hyperglycemia, leading to inadequate glycemic control.” “Recently, it has been reported that patients with T2D treated for periodontitis have reduced periodontopathic bacteria and improved glycemic control. Patients with T2D complicated by periodontitis have more red complex species, and poor glycemic control is thought to be associated with increased levels of red complex species in the oral cavity.” “Further studies should be planned, taking into account various patient factors to determine the effect of mouthwash gargling on the amount of red complex species and A1c levels in patients with T2D.”
SOURCE:
This study was conducted by Saaya Matayoshi, of the Joint Research Laboratory of Science for Oral and Systemic Connection, Osaka University Graduate School of Dentistry, Osaka, Japan, and colleagues and published in Scientific Reports.
LIMITATIONS:
Only polymerase chain reaction used to detect periodontopathic bacteria so not quantified. No assessment of periodontal pocket depth. Saliva sampling conditions not standardized. Study conducted during COVID-19 pandemic; all patients wore masks. Heterogeneity in patient responses to the mouthwash.
DISCLOSURES:
This work was supported by the Fund for Scientific Promotion of Weltec Corp, Osaka, Japan. The authors declared no competing interests.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
in people with type 2 diabetes (T2D), especially younger adults.
METHODOLOGY:
- A total of 173 patients with T2D who had at least six total periodontopathic bacteria in their mouths and ≥ 6.5% were instructed to gargle with water three times a day for 6 months, followed by gargling with chlorhexidine gluconate mouthwash three times a day for the next 6 months.
- Saliva specimens were collected every 1-2 months at clinic visits totaling 6-12 samples per study period and bacterial DNA examined for three red complex species, namely, Porphyromonas gingivalis, Treponema denticola, and Tannerella forsythia.
TAKEAWAY:
- Twelve individuals who gargled once a day or less showed no significant reductions in red complex species after mouthwash or water gargling.
- By contrast, significant decreases in red complex bacteria were seen after 6 months of mouthwash gargling (P < .001) in the 80 who gargled twice a day and the 81 who did so three times a day compared with no changes after water gargling.
- Among the 161 individuals who gargled at least twice a day, the decrease in red species with mouthwash vs water gargling was highly significant (P < .0001).
- After adjustment for A1c seasonal variation, neither water gargling nor mouthwash gargling led to significant overall reduction in A1c levels.
- However, A1c levels were significantly lower in the 83 individuals aged ≤ 68 years than among the 78 aged ≥ 69 years after gargling with mouthwash (P < .05), with no change in either group after water gargling.
- Similarly, A1c levels were significantly reduced (P < .05) after mouthwash in the 69 with baseline A1c ≥ 7.5% compared with the 92 whose baseline A1c levels were ≤ 7.4%, with no changes in either after water.
IN PRACTICE:
“A bidirectional relationship between periodontitis and T2D has been reported. Patients with T2D are more susceptible to severe periodontitis than subjects without diabetes, and inflammatory periodontitis aggravates hyperglycemia, leading to inadequate glycemic control.” “Recently, it has been reported that patients with T2D treated for periodontitis have reduced periodontopathic bacteria and improved glycemic control. Patients with T2D complicated by periodontitis have more red complex species, and poor glycemic control is thought to be associated with increased levels of red complex species in the oral cavity.” “Further studies should be planned, taking into account various patient factors to determine the effect of mouthwash gargling on the amount of red complex species and A1c levels in patients with T2D.”
SOURCE:
This study was conducted by Saaya Matayoshi, of the Joint Research Laboratory of Science for Oral and Systemic Connection, Osaka University Graduate School of Dentistry, Osaka, Japan, and colleagues and published in Scientific Reports.
LIMITATIONS:
Only polymerase chain reaction used to detect periodontopathic bacteria so not quantified. No assessment of periodontal pocket depth. Saliva sampling conditions not standardized. Study conducted during COVID-19 pandemic; all patients wore masks. Heterogeneity in patient responses to the mouthwash.
DISCLOSURES:
This work was supported by the Fund for Scientific Promotion of Weltec Corp, Osaka, Japan. The authors declared no competing interests.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Lower Medication Costs Cut Diabetes Complications
TOPLINE:
A value-based medication plan that lowers out-of-pocket costs for antidiabetic medications reduces health complications in commercially insured individuals with diabetes, especially those living in lower-income areas.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers assessed the 1-year impact on type 2 diabetes outcomes from a preventive drug list (PDL), which employers can add to plans to reduce out-of-pocket costs (copayments or deductibles) for high-value preventive medications.
- Using data from a national insurer, they identified 10,588 members with diabetes newly enrolled in PDL plans between January 2004 and June 2017 (age, 12-64 years; 44.8% women; 45.5% from the South; 33.4% from employers with < 100 enrollees).
- The members with diabetes on a PDL plan for a full follow-up year were matched and weighted against 690,075 control participants whose employers did not offer PDL.
- In a subgroup analysis, health outcomes for members with diabetes residing in lower-income neighborhoods (53.1%) were evaluated.
- The primary outcome was acute, preventable diabetes complications, such as bacterial infections, neurovascular events, acute coronary disease, and diabetic ketoacidosis, measured as complication days per 1000 members per year.
TAKEAWAY:
- Out-of-pocket costs for noninsulin antidiabetic agents and insulin declined by 30.7% and 38.6%, respectively, in the PDL group vs controls.
- The 30-day prescription fills for noninsulin and insulin antidiabetic medication increased by 7.1% (95% CI, 5.0%-9.3%) and 5.3% (95% CI, 2.2%-8.4%), respectively, among PDL members and was slightly higher among PDL members residing in low-income areas.
- The PDL transition was associated with an 8.4% relative reduction (95% CI, −13.9% to −2.8%) in complication days overall (absolute reduction, −20.2 days per 1000 members per year).
- Among members from lower-income areas, PDL transition was associated with a 10.2% relative reduction (95% CI, −17.4% to −3.0%) in complication days (absolute reduction, −26.1 per 1000 members per year) compared with controls.
IN PRACTICE:
“Targeting out-of-pocket cost reductions to specific populations, in this case patients with diabetes from lower-income areas, might enhance health outcomes,” wrote the authors.
SOURCE:
The study was conducted by J. Franklin Wharam, MD, MPH, Department of Medicine, Duke University, Durham, North Carolina. It was published online in JAMA Health Forum.
LIMITATIONS:
The findings may be generalized only to patients with diabetes enrolled in commercial health plans. Instead of being randomized, the PDL coverage was chosen by certain employers. Moreover, only outcomes associated with new PDL enrollment over a single year were evaluated.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by grants from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. One of the authors reported receiving postmarket safety study stipends from Pfizer and GlaxoSmithKline outside the submitted work.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
A value-based medication plan that lowers out-of-pocket costs for antidiabetic medications reduces health complications in commercially insured individuals with diabetes, especially those living in lower-income areas.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers assessed the 1-year impact on type 2 diabetes outcomes from a preventive drug list (PDL), which employers can add to plans to reduce out-of-pocket costs (copayments or deductibles) for high-value preventive medications.
- Using data from a national insurer, they identified 10,588 members with diabetes newly enrolled in PDL plans between January 2004 and June 2017 (age, 12-64 years; 44.8% women; 45.5% from the South; 33.4% from employers with < 100 enrollees).
- The members with diabetes on a PDL plan for a full follow-up year were matched and weighted against 690,075 control participants whose employers did not offer PDL.
- In a subgroup analysis, health outcomes for members with diabetes residing in lower-income neighborhoods (53.1%) were evaluated.
- The primary outcome was acute, preventable diabetes complications, such as bacterial infections, neurovascular events, acute coronary disease, and diabetic ketoacidosis, measured as complication days per 1000 members per year.
TAKEAWAY:
- Out-of-pocket costs for noninsulin antidiabetic agents and insulin declined by 30.7% and 38.6%, respectively, in the PDL group vs controls.
- The 30-day prescription fills for noninsulin and insulin antidiabetic medication increased by 7.1% (95% CI, 5.0%-9.3%) and 5.3% (95% CI, 2.2%-8.4%), respectively, among PDL members and was slightly higher among PDL members residing in low-income areas.
- The PDL transition was associated with an 8.4% relative reduction (95% CI, −13.9% to −2.8%) in complication days overall (absolute reduction, −20.2 days per 1000 members per year).
- Among members from lower-income areas, PDL transition was associated with a 10.2% relative reduction (95% CI, −17.4% to −3.0%) in complication days (absolute reduction, −26.1 per 1000 members per year) compared with controls.
IN PRACTICE:
“Targeting out-of-pocket cost reductions to specific populations, in this case patients with diabetes from lower-income areas, might enhance health outcomes,” wrote the authors.
SOURCE:
The study was conducted by J. Franklin Wharam, MD, MPH, Department of Medicine, Duke University, Durham, North Carolina. It was published online in JAMA Health Forum.
LIMITATIONS:
The findings may be generalized only to patients with diabetes enrolled in commercial health plans. Instead of being randomized, the PDL coverage was chosen by certain employers. Moreover, only outcomes associated with new PDL enrollment over a single year were evaluated.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by grants from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. One of the authors reported receiving postmarket safety study stipends from Pfizer and GlaxoSmithKline outside the submitted work.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
A value-based medication plan that lowers out-of-pocket costs for antidiabetic medications reduces health complications in commercially insured individuals with diabetes, especially those living in lower-income areas.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers assessed the 1-year impact on type 2 diabetes outcomes from a preventive drug list (PDL), which employers can add to plans to reduce out-of-pocket costs (copayments or deductibles) for high-value preventive medications.
- Using data from a national insurer, they identified 10,588 members with diabetes newly enrolled in PDL plans between January 2004 and June 2017 (age, 12-64 years; 44.8% women; 45.5% from the South; 33.4% from employers with < 100 enrollees).
- The members with diabetes on a PDL plan for a full follow-up year were matched and weighted against 690,075 control participants whose employers did not offer PDL.
- In a subgroup analysis, health outcomes for members with diabetes residing in lower-income neighborhoods (53.1%) were evaluated.
- The primary outcome was acute, preventable diabetes complications, such as bacterial infections, neurovascular events, acute coronary disease, and diabetic ketoacidosis, measured as complication days per 1000 members per year.
TAKEAWAY:
- Out-of-pocket costs for noninsulin antidiabetic agents and insulin declined by 30.7% and 38.6%, respectively, in the PDL group vs controls.
- The 30-day prescription fills for noninsulin and insulin antidiabetic medication increased by 7.1% (95% CI, 5.0%-9.3%) and 5.3% (95% CI, 2.2%-8.4%), respectively, among PDL members and was slightly higher among PDL members residing in low-income areas.
- The PDL transition was associated with an 8.4% relative reduction (95% CI, −13.9% to −2.8%) in complication days overall (absolute reduction, −20.2 days per 1000 members per year).
- Among members from lower-income areas, PDL transition was associated with a 10.2% relative reduction (95% CI, −17.4% to −3.0%) in complication days (absolute reduction, −26.1 per 1000 members per year) compared with controls.
IN PRACTICE:
“Targeting out-of-pocket cost reductions to specific populations, in this case patients with diabetes from lower-income areas, might enhance health outcomes,” wrote the authors.
SOURCE:
The study was conducted by J. Franklin Wharam, MD, MPH, Department of Medicine, Duke University, Durham, North Carolina. It was published online in JAMA Health Forum.
LIMITATIONS:
The findings may be generalized only to patients with diabetes enrolled in commercial health plans. Instead of being randomized, the PDL coverage was chosen by certain employers. Moreover, only outcomes associated with new PDL enrollment over a single year were evaluated.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by grants from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. One of the authors reported receiving postmarket safety study stipends from Pfizer and GlaxoSmithKline outside the submitted work.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.