User login
Subcutaneous rituximab safe, effective for follicular lymphoma
Efficacy and safety profiles were similar for subcutaneous and standard IV rituximab when given as first-line therapy to adults with follicular lymphoma, based on results of a phase III clinical trial published online in Lancet Haematology.
Administering rituximab by IV infusion can take up to 6 hours to complete and requires continuous monitoring. Subcutaneous delivery takes approximately 6 minutes using a new rituximab formulation that is 12 times more concentrated to reduce the administered volume. The new formulation is expected to reduce the burden of treatment for patients, as well as for the health care system, said Andrew Davies, PhD, of the Cancer Research UK Centre, Southampton, and his associates.
They compared the two agents in an international open-label trial funded by Hoffmann-La Roche, maker of the subcutaneous formulation. Adult patients at 113 medical centers in 30 countries were randomly assigned to receive either IV (205 patients) or subcutaneous (205 patients) rituximab during induction therapy with six to eight cycles of CHOP (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone) or CVP (cyclophosphamide, vincristine, and prednisone). They continued with rituximab as maintenance therapy every 2 months for 2 years. The median duration of treatment was 27 months, and median follow-up was 37 months.
The primary efficacy end point – overall (complete or partial) response rate at the end of induction, based on investigator assessment confirmed by an independent review panel of radiologists – was 84.9% with IV and 84.4% with subcutaneous rituximab, a nonsignificant difference. Similarly, the overall response rate at the end of maintenance therapy was not significantly different between the two groups, at 78.1% and 77.9%, respectively.
Progression-free survival (hazard ratio, 0.84) and event-free survival (HR, 0.91) also did not differ significantly between the two study groups, the investigators said (Lancet Haematol. 2017 doi: 10.1016/S2352.3026(17)30078-9).
The rates of adverse events, grade 3 or higher adverse events, and serious adverse events also were similar for IV and subcutaneous formulations of rituximab. “Administration-related reactions were more common in the subcutaneous group but were predominantly mild-to-moderate local injection-site reactions, such as mild pain, swelling and erythema, reflecting the expected change in safety profile when switching to the subcutaneous route of administration,” Dr. Davies and his associates said.
These results indicate that subcutaneous administration of rituximab along with chemotherapy doesn’t compromise the agent’s antilymphoma activity, they added.
Efficacy and safety profiles were similar for subcutaneous and standard IV rituximab when given as first-line therapy to adults with follicular lymphoma, based on results of a phase III clinical trial published online in Lancet Haematology.
Administering rituximab by IV infusion can take up to 6 hours to complete and requires continuous monitoring. Subcutaneous delivery takes approximately 6 minutes using a new rituximab formulation that is 12 times more concentrated to reduce the administered volume. The new formulation is expected to reduce the burden of treatment for patients, as well as for the health care system, said Andrew Davies, PhD, of the Cancer Research UK Centre, Southampton, and his associates.
They compared the two agents in an international open-label trial funded by Hoffmann-La Roche, maker of the subcutaneous formulation. Adult patients at 113 medical centers in 30 countries were randomly assigned to receive either IV (205 patients) or subcutaneous (205 patients) rituximab during induction therapy with six to eight cycles of CHOP (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone) or CVP (cyclophosphamide, vincristine, and prednisone). They continued with rituximab as maintenance therapy every 2 months for 2 years. The median duration of treatment was 27 months, and median follow-up was 37 months.
The primary efficacy end point – overall (complete or partial) response rate at the end of induction, based on investigator assessment confirmed by an independent review panel of radiologists – was 84.9% with IV and 84.4% with subcutaneous rituximab, a nonsignificant difference. Similarly, the overall response rate at the end of maintenance therapy was not significantly different between the two groups, at 78.1% and 77.9%, respectively.
Progression-free survival (hazard ratio, 0.84) and event-free survival (HR, 0.91) also did not differ significantly between the two study groups, the investigators said (Lancet Haematol. 2017 doi: 10.1016/S2352.3026(17)30078-9).
The rates of adverse events, grade 3 or higher adverse events, and serious adverse events also were similar for IV and subcutaneous formulations of rituximab. “Administration-related reactions were more common in the subcutaneous group but were predominantly mild-to-moderate local injection-site reactions, such as mild pain, swelling and erythema, reflecting the expected change in safety profile when switching to the subcutaneous route of administration,” Dr. Davies and his associates said.
These results indicate that subcutaneous administration of rituximab along with chemotherapy doesn’t compromise the agent’s antilymphoma activity, they added.
Efficacy and safety profiles were similar for subcutaneous and standard IV rituximab when given as first-line therapy to adults with follicular lymphoma, based on results of a phase III clinical trial published online in Lancet Haematology.
Administering rituximab by IV infusion can take up to 6 hours to complete and requires continuous monitoring. Subcutaneous delivery takes approximately 6 minutes using a new rituximab formulation that is 12 times more concentrated to reduce the administered volume. The new formulation is expected to reduce the burden of treatment for patients, as well as for the health care system, said Andrew Davies, PhD, of the Cancer Research UK Centre, Southampton, and his associates.
They compared the two agents in an international open-label trial funded by Hoffmann-La Roche, maker of the subcutaneous formulation. Adult patients at 113 medical centers in 30 countries were randomly assigned to receive either IV (205 patients) or subcutaneous (205 patients) rituximab during induction therapy with six to eight cycles of CHOP (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone) or CVP (cyclophosphamide, vincristine, and prednisone). They continued with rituximab as maintenance therapy every 2 months for 2 years. The median duration of treatment was 27 months, and median follow-up was 37 months.
The primary efficacy end point – overall (complete or partial) response rate at the end of induction, based on investigator assessment confirmed by an independent review panel of radiologists – was 84.9% with IV and 84.4% with subcutaneous rituximab, a nonsignificant difference. Similarly, the overall response rate at the end of maintenance therapy was not significantly different between the two groups, at 78.1% and 77.9%, respectively.
Progression-free survival (hazard ratio, 0.84) and event-free survival (HR, 0.91) also did not differ significantly between the two study groups, the investigators said (Lancet Haematol. 2017 doi: 10.1016/S2352.3026(17)30078-9).
The rates of adverse events, grade 3 or higher adverse events, and serious adverse events also were similar for IV and subcutaneous formulations of rituximab. “Administration-related reactions were more common in the subcutaneous group but were predominantly mild-to-moderate local injection-site reactions, such as mild pain, swelling and erythema, reflecting the expected change in safety profile when switching to the subcutaneous route of administration,” Dr. Davies and his associates said.
These results indicate that subcutaneous administration of rituximab along with chemotherapy doesn’t compromise the agent’s antilymphoma activity, they added.
FROM LANCET HAEMATOLOGY
Key clinical point: Subcutaneous rituximab had efficacy and safety profiles similar to those of standard IV rituximab when given as first-line therapy to adults with follicular lymphoma.
Major finding: The primary efficacy end point – overall response rate at the end of induction – was 84.9% with IV and 84.4% with subcutaneous rituximab.
Data source: An international randomized controlled phase III trial involving 410 adults followed for 3 years.
Disclosures: This trial was funded by Hoffmann-La Roche, maker of the subcutaneous formulation of rituximab. The pharmaceutical company also was involved in the design and conduct of the trial, collection and interpretation of the data, and writing of the results. Dr. Davies reported ties to Hoffmann-La Roche and numerous other drug companies.
Ibrutinib monotherapy data in previously treated MZL is available
Ibrutinib is active in patients with previously treated marginal zone lymphoma (MZL) and has a good safety profile, the results of a multicenter, open-label phase II trial published in Blood suggest.
Nearly half of 63 patients responded to monotherapy with the once-daily oral inhibitor of Bruton tyrosine kinase, and ibrutinib was generally well tolerated, according to the study (Blood. 2017;129:2224-32). The results prompted the U.S. Food and Drug Administration to grant accelerated approval of ibrutinib for patients with MZL who were previously treated with at least one prior anti-CD20–based therapy.
“MZL is frequently linked to chronic infection, which may induce B-cell receptor (BCR) signaling, resulting in aberrant B-cell survival and proliferation,” note the investigators, who were led by Ariela Noy, MD, a hematologic oncologist with the Lymphoma Service at the Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, New York. “Single-agent ibrutinib induced durable responses with a favorable benefit–risk profile in patients with previously treated MZL, confirming the role of BCR signaling in this malignancy.”
“As the only approved therapy, ibrutinib provides a treatment option without chemotherapy for MZL,” they maintain. “Future studies will investigate ibrutinib in treatment-naive patients or as combination strategies in relapsed/refractory MZL.”
In the trial, which was funded by Pharmacyclics, an AbbVie Company, patients with MZL of all subtypes who had received at least one prior therapy with an anti-CD20 antibody–containing regimen were treated with 560 mg ibrutinib (Imbruvica) orally once daily. The median number of prior systemic therapies was two, and 63% had received prior chemoimmunotherapy.
The overall response rate, as assessed by an independent review committee using 2007 International Working Group criteria – the trial’s primary endpoint – was 48%, according to the published results. Benefit was similar across patients who differed regarding MZL subtype, number of prior regimen, and previous receipt of chemoimmunotherapy
After a 19.4-month median follow-up, the median duration of response was not reached, and median progression-free survival was 14.2 months.
The most common grade 3 or worse adverse events were anemia (14%), pneumonia (8%), and fatigue (6%). Serious adverse events of any grade affected 44% of patients. The most common was grade 3 or 4 pneumonia. Adverse events led to treatment discontinuation in 17% of patients and dose reductions in 10%.
“Due to evidence of pseudoprogression in our trial … biopsies may be warranted to differentiate between true lymphoma progression and immune-mediated antitumor response,” the investigators note.
Dr. Noy disclosed that she has received research funding from Pharmacyclics.
Putting these results into context, the efficacy of ibrutinib seems similar to that of other single agents evaluated in patients with relapsed marginal zone lymphoma, including other agents that target molecules downstream of the B-cell receptor.
The observed response rate is “modest” compared with that seen when the drug is used to treat other conditions for which it is approved, he notes. Therefore, additional correlative studies to identify biomarkers predicting benefit in marginal zone lymphoma would have been helpful.
Nonetheless, the study team should be congratulated, as the trial demonstrates the ability to investigate rare disease subtypes in multicenter collaborations. The results justify ibrutinib as the first FDA-approved therapy for this disease and form the basis for subsequent trials that combine ibrutinib with anti-CD20 monoclonal antibodies and other targeted agents.
Paul M. Barr, MD, of the Wilmot Cancer Institute at the University of Rochester in New York made his remarks in an accompanying editorial (Blood. 2017;129:2207-08). Dr. Barr disclosed that he has consulted for and received research funding from Pharmacyclics and AbbVie.
Putting these results into context, the efficacy of ibrutinib seems similar to that of other single agents evaluated in patients with relapsed marginal zone lymphoma, including other agents that target molecules downstream of the B-cell receptor.
The observed response rate is “modest” compared with that seen when the drug is used to treat other conditions for which it is approved, he notes. Therefore, additional correlative studies to identify biomarkers predicting benefit in marginal zone lymphoma would have been helpful.
Nonetheless, the study team should be congratulated, as the trial demonstrates the ability to investigate rare disease subtypes in multicenter collaborations. The results justify ibrutinib as the first FDA-approved therapy for this disease and form the basis for subsequent trials that combine ibrutinib with anti-CD20 monoclonal antibodies and other targeted agents.
Paul M. Barr, MD, of the Wilmot Cancer Institute at the University of Rochester in New York made his remarks in an accompanying editorial (Blood. 2017;129:2207-08). Dr. Barr disclosed that he has consulted for and received research funding from Pharmacyclics and AbbVie.
Putting these results into context, the efficacy of ibrutinib seems similar to that of other single agents evaluated in patients with relapsed marginal zone lymphoma, including other agents that target molecules downstream of the B-cell receptor.
The observed response rate is “modest” compared with that seen when the drug is used to treat other conditions for which it is approved, he notes. Therefore, additional correlative studies to identify biomarkers predicting benefit in marginal zone lymphoma would have been helpful.
Nonetheless, the study team should be congratulated, as the trial demonstrates the ability to investigate rare disease subtypes in multicenter collaborations. The results justify ibrutinib as the first FDA-approved therapy for this disease and form the basis for subsequent trials that combine ibrutinib with anti-CD20 monoclonal antibodies and other targeted agents.
Paul M. Barr, MD, of the Wilmot Cancer Institute at the University of Rochester in New York made his remarks in an accompanying editorial (Blood. 2017;129:2207-08). Dr. Barr disclosed that he has consulted for and received research funding from Pharmacyclics and AbbVie.
Ibrutinib is active in patients with previously treated marginal zone lymphoma (MZL) and has a good safety profile, the results of a multicenter, open-label phase II trial published in Blood suggest.
Nearly half of 63 patients responded to monotherapy with the once-daily oral inhibitor of Bruton tyrosine kinase, and ibrutinib was generally well tolerated, according to the study (Blood. 2017;129:2224-32). The results prompted the U.S. Food and Drug Administration to grant accelerated approval of ibrutinib for patients with MZL who were previously treated with at least one prior anti-CD20–based therapy.
“MZL is frequently linked to chronic infection, which may induce B-cell receptor (BCR) signaling, resulting in aberrant B-cell survival and proliferation,” note the investigators, who were led by Ariela Noy, MD, a hematologic oncologist with the Lymphoma Service at the Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, New York. “Single-agent ibrutinib induced durable responses with a favorable benefit–risk profile in patients with previously treated MZL, confirming the role of BCR signaling in this malignancy.”
“As the only approved therapy, ibrutinib provides a treatment option without chemotherapy for MZL,” they maintain. “Future studies will investigate ibrutinib in treatment-naive patients or as combination strategies in relapsed/refractory MZL.”
In the trial, which was funded by Pharmacyclics, an AbbVie Company, patients with MZL of all subtypes who had received at least one prior therapy with an anti-CD20 antibody–containing regimen were treated with 560 mg ibrutinib (Imbruvica) orally once daily. The median number of prior systemic therapies was two, and 63% had received prior chemoimmunotherapy.
The overall response rate, as assessed by an independent review committee using 2007 International Working Group criteria – the trial’s primary endpoint – was 48%, according to the published results. Benefit was similar across patients who differed regarding MZL subtype, number of prior regimen, and previous receipt of chemoimmunotherapy
After a 19.4-month median follow-up, the median duration of response was not reached, and median progression-free survival was 14.2 months.
The most common grade 3 or worse adverse events were anemia (14%), pneumonia (8%), and fatigue (6%). Serious adverse events of any grade affected 44% of patients. The most common was grade 3 or 4 pneumonia. Adverse events led to treatment discontinuation in 17% of patients and dose reductions in 10%.
“Due to evidence of pseudoprogression in our trial … biopsies may be warranted to differentiate between true lymphoma progression and immune-mediated antitumor response,” the investigators note.
Dr. Noy disclosed that she has received research funding from Pharmacyclics.
Ibrutinib is active in patients with previously treated marginal zone lymphoma (MZL) and has a good safety profile, the results of a multicenter, open-label phase II trial published in Blood suggest.
Nearly half of 63 patients responded to monotherapy with the once-daily oral inhibitor of Bruton tyrosine kinase, and ibrutinib was generally well tolerated, according to the study (Blood. 2017;129:2224-32). The results prompted the U.S. Food and Drug Administration to grant accelerated approval of ibrutinib for patients with MZL who were previously treated with at least one prior anti-CD20–based therapy.
“MZL is frequently linked to chronic infection, which may induce B-cell receptor (BCR) signaling, resulting in aberrant B-cell survival and proliferation,” note the investigators, who were led by Ariela Noy, MD, a hematologic oncologist with the Lymphoma Service at the Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, New York. “Single-agent ibrutinib induced durable responses with a favorable benefit–risk profile in patients with previously treated MZL, confirming the role of BCR signaling in this malignancy.”
“As the only approved therapy, ibrutinib provides a treatment option without chemotherapy for MZL,” they maintain. “Future studies will investigate ibrutinib in treatment-naive patients or as combination strategies in relapsed/refractory MZL.”
In the trial, which was funded by Pharmacyclics, an AbbVie Company, patients with MZL of all subtypes who had received at least one prior therapy with an anti-CD20 antibody–containing regimen were treated with 560 mg ibrutinib (Imbruvica) orally once daily. The median number of prior systemic therapies was two, and 63% had received prior chemoimmunotherapy.
The overall response rate, as assessed by an independent review committee using 2007 International Working Group criteria – the trial’s primary endpoint – was 48%, according to the published results. Benefit was similar across patients who differed regarding MZL subtype, number of prior regimen, and previous receipt of chemoimmunotherapy
After a 19.4-month median follow-up, the median duration of response was not reached, and median progression-free survival was 14.2 months.
The most common grade 3 or worse adverse events were anemia (14%), pneumonia (8%), and fatigue (6%). Serious adverse events of any grade affected 44% of patients. The most common was grade 3 or 4 pneumonia. Adverse events led to treatment discontinuation in 17% of patients and dose reductions in 10%.
“Due to evidence of pseudoprogression in our trial … biopsies may be warranted to differentiate between true lymphoma progression and immune-mediated antitumor response,” the investigators note.
Dr. Noy disclosed that she has received research funding from Pharmacyclics.
Key clinical point:
Major finding: The overall response rate was 48%, and the drug was well tolerated.
Data source: A multicenter, open-label phase II trial of ibrutinib in 63 patients with previously treated marginal zone lymphoma.
Disclosures: Dr. Noy disclosed that she has received research funding from Pharmacyclics. The trial was funded by Pharmacyclics, an AbbVie Company.
Waldenström macroglobulinemia panel advises on IgM paraproteinemic neuropathies
With optimal approaches still evolving for the diagnosis and management of peripheral neuropathies associated with Waldenström macroglobulinemia and other IgM paraproteinemias, new consensus recommendations from a multidisciplinary panel were recently published in the British Journal of Haematology.
Up to half of patients with IgM monoclonal gammopathies develop peripheral neuropathy, according to the 11-member panel (Br J Haematol. 2017 Mar;176[5]:728-42). The panel began deliberations at the eighth International Workshop on Waldenström Macroglobulinemia in London and was led by Shirley D’Sa, MD, of the Waldenström Clinic, Cancer Division, University College London Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust.
• Diagnostic evaluation: “The indications for invasive investigations such as cerebrospinal fluid analysis, nerve conduction tests, and sensory nerve biopsies are unclear,” according to the panelists.
When clinical examination identifies a neuropathy, neurophysiologic testing can ascertain its nature and inform additional work-up. Cerebrospinal fluid examination is not mandatory in cases of demyelinating neuropathy, but it is indicated when clinical evaluation is inconclusive and malignancy or CNS invasion is suspected.
Nerve biopsy carries substantial risk and is rarely indicated. It may be warranted when a comprehensive systemic work-up has not identified a cause and clinicians still suspect amyloid, vasculitis, or direct cellular invasion; in atypical cases not responding to treatment; or when the neuropathy is progressive and debilitating.
When it comes to imaging, “MRI of the neuraxis should be performed prior to lumbar puncture to avoid false positive meningeal enhancement,” they advised. “Prior discussion of likely sites of involvement with an experienced neuroradiologist will ensure that the correct sequences of the correct anatomical area are performed with appropriate gadolinium enhancement.”
• Clinical phenotypes and their treatment: IgM-associated neuropathies vary with respect to specific antibodies present and the likelihood that they are causally associated with the neuropathy, Dr. D’Sa and her colleagues noted. They provided a decision tree to help guide the work-up to determine the specific etiology.
“The presence of a neuropathy alone is not a justification for treatment, but steady progression with accumulating disability should prompt action,” they maintained.
Patients with antibody-negative peripheral neuropathy associated with IgM monoclonal gammopathies of undetermined significance who have mild disease and no hematologic reason for treatment can be managed with surveillance, according to the panelists.
However, immunosuppressive or immunomodulatory treatment should be considered when there is substantial or progressive disability associated with demyelination.
Patients with anti-MAG (myelin-associated glycoprotein) demyelinating neuropathy may benefit from rituximab (Rituxan). In those with more advanced disease, clinicians should consider immunosuppressive or immunomodulatory treatment instead.
Surveillance is also an option for Waldenström macroglobulinemia–associated peripheral neuropathy that is progressing slowly. When used, treatment should be tailored to severity of both systemic and neurologic disease.
• Treatment response assessment: “The optimum way to measure clinical response to treatment unknown,” Dr. D’Sa and her fellow panelists noted. A variety of measures of muscle strength, sensory function, and disability are used.
“The I-RODS [Inflammatory Rasch-Built Overall Disability Scale] more often captures clinically meaningful changes over time, with a greater magnitude of change, compared with the INCAT-ONLS [Inflammatory Neuropathy Cause and Treatment–Overall Neuropathy Limitation Scale] disability scale and its use is therefore suggested in future trials involving patients with inflammatory neuropathies,” they wrote.
• Model of care: Management of patients with IgM-associated neuropathies requires multidisciplinary care with good collaboration to optimize patient outcomes, the consensus panel said.
“A suggested model of care is a combined neurological and hematological clinic, in which patients are seen jointly by a specialist neurologist and hematologist and a decision can be made about the sequence of investigations, interventions, and the formulation of a treatment plan,” they proposed. “Appropriate and timely referral to physical, occupational, and orthotic professionals is recommended in order to maximize safety and function.”
• Future perspectives: “There is much to be done to improve outcomes for patients with IgM and [Waldenström macroglobulinemia]-associated peripheral neuropathies,” the panelists concluded.
Key areas of focus are “early recognition of the problem, appropriate causal attribution achieved through sensitive diagnostics that are not overly invasive, timely therapeutic intervention with effective and nonneurotoxic therapies, achievement of an appropriate degree of clonal reduction for optimum clinical outcomes, and the use of reproducible and readily applicable tools to measure outcomes.”
Dr. D’Sa disclosed that she receives honoraria from Janssen.
With optimal approaches still evolving for the diagnosis and management of peripheral neuropathies associated with Waldenström macroglobulinemia and other IgM paraproteinemias, new consensus recommendations from a multidisciplinary panel were recently published in the British Journal of Haematology.
Up to half of patients with IgM monoclonal gammopathies develop peripheral neuropathy, according to the 11-member panel (Br J Haematol. 2017 Mar;176[5]:728-42). The panel began deliberations at the eighth International Workshop on Waldenström Macroglobulinemia in London and was led by Shirley D’Sa, MD, of the Waldenström Clinic, Cancer Division, University College London Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust.
• Diagnostic evaluation: “The indications for invasive investigations such as cerebrospinal fluid analysis, nerve conduction tests, and sensory nerve biopsies are unclear,” according to the panelists.
When clinical examination identifies a neuropathy, neurophysiologic testing can ascertain its nature and inform additional work-up. Cerebrospinal fluid examination is not mandatory in cases of demyelinating neuropathy, but it is indicated when clinical evaluation is inconclusive and malignancy or CNS invasion is suspected.
Nerve biopsy carries substantial risk and is rarely indicated. It may be warranted when a comprehensive systemic work-up has not identified a cause and clinicians still suspect amyloid, vasculitis, or direct cellular invasion; in atypical cases not responding to treatment; or when the neuropathy is progressive and debilitating.
When it comes to imaging, “MRI of the neuraxis should be performed prior to lumbar puncture to avoid false positive meningeal enhancement,” they advised. “Prior discussion of likely sites of involvement with an experienced neuroradiologist will ensure that the correct sequences of the correct anatomical area are performed with appropriate gadolinium enhancement.”
• Clinical phenotypes and their treatment: IgM-associated neuropathies vary with respect to specific antibodies present and the likelihood that they are causally associated with the neuropathy, Dr. D’Sa and her colleagues noted. They provided a decision tree to help guide the work-up to determine the specific etiology.
“The presence of a neuropathy alone is not a justification for treatment, but steady progression with accumulating disability should prompt action,” they maintained.
Patients with antibody-negative peripheral neuropathy associated with IgM monoclonal gammopathies of undetermined significance who have mild disease and no hematologic reason for treatment can be managed with surveillance, according to the panelists.
However, immunosuppressive or immunomodulatory treatment should be considered when there is substantial or progressive disability associated with demyelination.
Patients with anti-MAG (myelin-associated glycoprotein) demyelinating neuropathy may benefit from rituximab (Rituxan). In those with more advanced disease, clinicians should consider immunosuppressive or immunomodulatory treatment instead.
Surveillance is also an option for Waldenström macroglobulinemia–associated peripheral neuropathy that is progressing slowly. When used, treatment should be tailored to severity of both systemic and neurologic disease.
• Treatment response assessment: “The optimum way to measure clinical response to treatment unknown,” Dr. D’Sa and her fellow panelists noted. A variety of measures of muscle strength, sensory function, and disability are used.
“The I-RODS [Inflammatory Rasch-Built Overall Disability Scale] more often captures clinically meaningful changes over time, with a greater magnitude of change, compared with the INCAT-ONLS [Inflammatory Neuropathy Cause and Treatment–Overall Neuropathy Limitation Scale] disability scale and its use is therefore suggested in future trials involving patients with inflammatory neuropathies,” they wrote.
• Model of care: Management of patients with IgM-associated neuropathies requires multidisciplinary care with good collaboration to optimize patient outcomes, the consensus panel said.
“A suggested model of care is a combined neurological and hematological clinic, in which patients are seen jointly by a specialist neurologist and hematologist and a decision can be made about the sequence of investigations, interventions, and the formulation of a treatment plan,” they proposed. “Appropriate and timely referral to physical, occupational, and orthotic professionals is recommended in order to maximize safety and function.”
• Future perspectives: “There is much to be done to improve outcomes for patients with IgM and [Waldenström macroglobulinemia]-associated peripheral neuropathies,” the panelists concluded.
Key areas of focus are “early recognition of the problem, appropriate causal attribution achieved through sensitive diagnostics that are not overly invasive, timely therapeutic intervention with effective and nonneurotoxic therapies, achievement of an appropriate degree of clonal reduction for optimum clinical outcomes, and the use of reproducible and readily applicable tools to measure outcomes.”
Dr. D’Sa disclosed that she receives honoraria from Janssen.
With optimal approaches still evolving for the diagnosis and management of peripheral neuropathies associated with Waldenström macroglobulinemia and other IgM paraproteinemias, new consensus recommendations from a multidisciplinary panel were recently published in the British Journal of Haematology.
Up to half of patients with IgM monoclonal gammopathies develop peripheral neuropathy, according to the 11-member panel (Br J Haematol. 2017 Mar;176[5]:728-42). The panel began deliberations at the eighth International Workshop on Waldenström Macroglobulinemia in London and was led by Shirley D’Sa, MD, of the Waldenström Clinic, Cancer Division, University College London Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust.
• Diagnostic evaluation: “The indications for invasive investigations such as cerebrospinal fluid analysis, nerve conduction tests, and sensory nerve biopsies are unclear,” according to the panelists.
When clinical examination identifies a neuropathy, neurophysiologic testing can ascertain its nature and inform additional work-up. Cerebrospinal fluid examination is not mandatory in cases of demyelinating neuropathy, but it is indicated when clinical evaluation is inconclusive and malignancy or CNS invasion is suspected.
Nerve biopsy carries substantial risk and is rarely indicated. It may be warranted when a comprehensive systemic work-up has not identified a cause and clinicians still suspect amyloid, vasculitis, or direct cellular invasion; in atypical cases not responding to treatment; or when the neuropathy is progressive and debilitating.
When it comes to imaging, “MRI of the neuraxis should be performed prior to lumbar puncture to avoid false positive meningeal enhancement,” they advised. “Prior discussion of likely sites of involvement with an experienced neuroradiologist will ensure that the correct sequences of the correct anatomical area are performed with appropriate gadolinium enhancement.”
• Clinical phenotypes and their treatment: IgM-associated neuropathies vary with respect to specific antibodies present and the likelihood that they are causally associated with the neuropathy, Dr. D’Sa and her colleagues noted. They provided a decision tree to help guide the work-up to determine the specific etiology.
“The presence of a neuropathy alone is not a justification for treatment, but steady progression with accumulating disability should prompt action,” they maintained.
Patients with antibody-negative peripheral neuropathy associated with IgM monoclonal gammopathies of undetermined significance who have mild disease and no hematologic reason for treatment can be managed with surveillance, according to the panelists.
However, immunosuppressive or immunomodulatory treatment should be considered when there is substantial or progressive disability associated with demyelination.
Patients with anti-MAG (myelin-associated glycoprotein) demyelinating neuropathy may benefit from rituximab (Rituxan). In those with more advanced disease, clinicians should consider immunosuppressive or immunomodulatory treatment instead.
Surveillance is also an option for Waldenström macroglobulinemia–associated peripheral neuropathy that is progressing slowly. When used, treatment should be tailored to severity of both systemic and neurologic disease.
• Treatment response assessment: “The optimum way to measure clinical response to treatment unknown,” Dr. D’Sa and her fellow panelists noted. A variety of measures of muscle strength, sensory function, and disability are used.
“The I-RODS [Inflammatory Rasch-Built Overall Disability Scale] more often captures clinically meaningful changes over time, with a greater magnitude of change, compared with the INCAT-ONLS [Inflammatory Neuropathy Cause and Treatment–Overall Neuropathy Limitation Scale] disability scale and its use is therefore suggested in future trials involving patients with inflammatory neuropathies,” they wrote.
• Model of care: Management of patients with IgM-associated neuropathies requires multidisciplinary care with good collaboration to optimize patient outcomes, the consensus panel said.
“A suggested model of care is a combined neurological and hematological clinic, in which patients are seen jointly by a specialist neurologist and hematologist and a decision can be made about the sequence of investigations, interventions, and the formulation of a treatment plan,” they proposed. “Appropriate and timely referral to physical, occupational, and orthotic professionals is recommended in order to maximize safety and function.”
• Future perspectives: “There is much to be done to improve outcomes for patients with IgM and [Waldenström macroglobulinemia]-associated peripheral neuropathies,” the panelists concluded.
Key areas of focus are “early recognition of the problem, appropriate causal attribution achieved through sensitive diagnostics that are not overly invasive, timely therapeutic intervention with effective and nonneurotoxic therapies, achievement of an appropriate degree of clonal reduction for optimum clinical outcomes, and the use of reproducible and readily applicable tools to measure outcomes.”
Dr. D’Sa disclosed that she receives honoraria from Janssen.
FROM THE BRITISH JOURNAL OF HAEMATOLOGY
Key clinical point:
Major finding: The indications for invasive testing and definitive answers about when and how to treat peripheral neuropathies due to Waldenström macroglobulinemia and other IgM paraproteinemias are unclear.
Data source: Recommendations from the eighth International Workshop on Waldenström Macroglobulinemia (IWWM-8) consensus panel.
Disclosures: Dr. D’Sa disclosed that she receives honoraria from Janssen.
Obinutuzumab vs. rituximab weighed as follicular lymphoma therapy
NEW YORK – Does obinutuzumab have a leg up over rituximab for treating follicular lymphoma?
A strict reading of the efficacy records of the two anti-CD20 antibodies when they went head-to-head suggests that obinutuzumab (Gazyva) edged out rituximab (Rituxan), but a broader view leaves the door open for rituximab as a still viable option depending on a patient’s status and priorities, experts said at the conference held by Imedex.
While conceding that quality of life correlates with progression-free survival (PFS), he stressed that it also correlates with treatment toxicities, treatment duration, and disease-related side effects.
Trial results have indicated that patients with newly diagnosed follicular lymphoma are reasonably treated with rituximab alone, or with rituximab plus bendamustine, without need for maintenance therapy, Dr. Leonard said.
In contrast, GALLIUM, a phase III trial that compared rituximab against obinutuzumab, used a maintenance phase of monotherapy with each of these two drugs following an induction phase when each of the drugs was combined with chemotherapy.
“If you use this approach [tested in GALLIUM] you need to use maintenance therapy,” and it was in GALLIUM that the most dramatic efficacy advantage for obinutuzumab over rituximab appeared, in the form of longer PFS although, so far, without demonstrated advantage in overall survival. The GALLIUM results, reported in December 2016 at the American Society of Hematology meeting, showed a 3-year PFS rate of 80% among patients treated with obinutuzumab and 73% among those treated with rituximab, a hazard ratio of 0.66 in favor of obinutuzumab that was statistically significant (P = .001) for the study’s primary endpoint (Blood. 2016 Dec 4;abstract 6).
“If you follow this study, you commit the patient to maintenance. We need to talk with patients about the pros and cons of maintenance, the pros and cons of chemotherapy, and the pros and cons of single agent therapy” with one of these anti-CD20 antibodies, Dr. Leonard said. “Right now, I think it’s unclear which antibody is best,” he concluded
To further buttress the case for obinutuzumab, he also cited the higher response rate among relapsed patients when single-agent obinutuzumab went against single-agent rituximab (J Clin Oncol. 2015 Oct 20:33[30]:3467-74), and the overall survival advantage that obinutuzumab gave patients when combined with bendamustine in patients refractory to rituximab (Blood. 2016 Dec 5; abstract 615).
Agreeing that the design of GALLIUM focused on combining an anti-CD20 antibody with chemotherapy, Dr. Friedberg acknowledged that, as initial therapy, “using rituximab monotherapy is very reasonable for many patients. I divide [follicular lymphoma] patients into those who are very symptomatic” (for example, those with hydronephrosis) “and need chemotherapy, and those who are not that symptomatic for whom single-agent rituximab is very reasonable,” he said in an interview.
Tumor aggressiveness is another way to identify patients who need chemotherapy plus an antibody, he added. “If the patient is not symptomatic, I generally first observe them, and if the growth is slow, you can sometimes intervene with rituximab alone, but, if the growth is fast, you also need chemotherapy,” Dr. Friedberg said.
Cost may soon become another consideration now that the U.S. patent on rituximab has expired leading to the ongoing development of several biosimilar versions of the antibody. If biosimilar formulations of rituximab soon appear on the U.S. market and if they result in a significant drop in drug price, it would introduce yet another significant variable. “Presuming biosimilar rituximab lowers the cost, that would be another important treatment decision,” he said.
Dr. Friedberg has been a consultant to Bayer. Dr. Leonard has been a consultant to 13 drug companies. Neither disclosed a relationship with the companies that market obinutuzumab or rituximab.
[email protected]
On Twitter @mitchelzoler
NEW YORK – Does obinutuzumab have a leg up over rituximab for treating follicular lymphoma?
A strict reading of the efficacy records of the two anti-CD20 antibodies when they went head-to-head suggests that obinutuzumab (Gazyva) edged out rituximab (Rituxan), but a broader view leaves the door open for rituximab as a still viable option depending on a patient’s status and priorities, experts said at the conference held by Imedex.
While conceding that quality of life correlates with progression-free survival (PFS), he stressed that it also correlates with treatment toxicities, treatment duration, and disease-related side effects.
Trial results have indicated that patients with newly diagnosed follicular lymphoma are reasonably treated with rituximab alone, or with rituximab plus bendamustine, without need for maintenance therapy, Dr. Leonard said.
In contrast, GALLIUM, a phase III trial that compared rituximab against obinutuzumab, used a maintenance phase of monotherapy with each of these two drugs following an induction phase when each of the drugs was combined with chemotherapy.
“If you use this approach [tested in GALLIUM] you need to use maintenance therapy,” and it was in GALLIUM that the most dramatic efficacy advantage for obinutuzumab over rituximab appeared, in the form of longer PFS although, so far, without demonstrated advantage in overall survival. The GALLIUM results, reported in December 2016 at the American Society of Hematology meeting, showed a 3-year PFS rate of 80% among patients treated with obinutuzumab and 73% among those treated with rituximab, a hazard ratio of 0.66 in favor of obinutuzumab that was statistically significant (P = .001) for the study’s primary endpoint (Blood. 2016 Dec 4;abstract 6).
“If you follow this study, you commit the patient to maintenance. We need to talk with patients about the pros and cons of maintenance, the pros and cons of chemotherapy, and the pros and cons of single agent therapy” with one of these anti-CD20 antibodies, Dr. Leonard said. “Right now, I think it’s unclear which antibody is best,” he concluded
To further buttress the case for obinutuzumab, he also cited the higher response rate among relapsed patients when single-agent obinutuzumab went against single-agent rituximab (J Clin Oncol. 2015 Oct 20:33[30]:3467-74), and the overall survival advantage that obinutuzumab gave patients when combined with bendamustine in patients refractory to rituximab (Blood. 2016 Dec 5; abstract 615).
Agreeing that the design of GALLIUM focused on combining an anti-CD20 antibody with chemotherapy, Dr. Friedberg acknowledged that, as initial therapy, “using rituximab monotherapy is very reasonable for many patients. I divide [follicular lymphoma] patients into those who are very symptomatic” (for example, those with hydronephrosis) “and need chemotherapy, and those who are not that symptomatic for whom single-agent rituximab is very reasonable,” he said in an interview.
Tumor aggressiveness is another way to identify patients who need chemotherapy plus an antibody, he added. “If the patient is not symptomatic, I generally first observe them, and if the growth is slow, you can sometimes intervene with rituximab alone, but, if the growth is fast, you also need chemotherapy,” Dr. Friedberg said.
Cost may soon become another consideration now that the U.S. patent on rituximab has expired leading to the ongoing development of several biosimilar versions of the antibody. If biosimilar formulations of rituximab soon appear on the U.S. market and if they result in a significant drop in drug price, it would introduce yet another significant variable. “Presuming biosimilar rituximab lowers the cost, that would be another important treatment decision,” he said.
Dr. Friedberg has been a consultant to Bayer. Dr. Leonard has been a consultant to 13 drug companies. Neither disclosed a relationship with the companies that market obinutuzumab or rituximab.
[email protected]
On Twitter @mitchelzoler
NEW YORK – Does obinutuzumab have a leg up over rituximab for treating follicular lymphoma?
A strict reading of the efficacy records of the two anti-CD20 antibodies when they went head-to-head suggests that obinutuzumab (Gazyva) edged out rituximab (Rituxan), but a broader view leaves the door open for rituximab as a still viable option depending on a patient’s status and priorities, experts said at the conference held by Imedex.
While conceding that quality of life correlates with progression-free survival (PFS), he stressed that it also correlates with treatment toxicities, treatment duration, and disease-related side effects.
Trial results have indicated that patients with newly diagnosed follicular lymphoma are reasonably treated with rituximab alone, or with rituximab plus bendamustine, without need for maintenance therapy, Dr. Leonard said.
In contrast, GALLIUM, a phase III trial that compared rituximab against obinutuzumab, used a maintenance phase of monotherapy with each of these two drugs following an induction phase when each of the drugs was combined with chemotherapy.
“If you use this approach [tested in GALLIUM] you need to use maintenance therapy,” and it was in GALLIUM that the most dramatic efficacy advantage for obinutuzumab over rituximab appeared, in the form of longer PFS although, so far, without demonstrated advantage in overall survival. The GALLIUM results, reported in December 2016 at the American Society of Hematology meeting, showed a 3-year PFS rate of 80% among patients treated with obinutuzumab and 73% among those treated with rituximab, a hazard ratio of 0.66 in favor of obinutuzumab that was statistically significant (P = .001) for the study’s primary endpoint (Blood. 2016 Dec 4;abstract 6).
“If you follow this study, you commit the patient to maintenance. We need to talk with patients about the pros and cons of maintenance, the pros and cons of chemotherapy, and the pros and cons of single agent therapy” with one of these anti-CD20 antibodies, Dr. Leonard said. “Right now, I think it’s unclear which antibody is best,” he concluded
To further buttress the case for obinutuzumab, he also cited the higher response rate among relapsed patients when single-agent obinutuzumab went against single-agent rituximab (J Clin Oncol. 2015 Oct 20:33[30]:3467-74), and the overall survival advantage that obinutuzumab gave patients when combined with bendamustine in patients refractory to rituximab (Blood. 2016 Dec 5; abstract 615).
Agreeing that the design of GALLIUM focused on combining an anti-CD20 antibody with chemotherapy, Dr. Friedberg acknowledged that, as initial therapy, “using rituximab monotherapy is very reasonable for many patients. I divide [follicular lymphoma] patients into those who are very symptomatic” (for example, those with hydronephrosis) “and need chemotherapy, and those who are not that symptomatic for whom single-agent rituximab is very reasonable,” he said in an interview.
Tumor aggressiveness is another way to identify patients who need chemotherapy plus an antibody, he added. “If the patient is not symptomatic, I generally first observe them, and if the growth is slow, you can sometimes intervene with rituximab alone, but, if the growth is fast, you also need chemotherapy,” Dr. Friedberg said.
Cost may soon become another consideration now that the U.S. patent on rituximab has expired leading to the ongoing development of several biosimilar versions of the antibody. If biosimilar formulations of rituximab soon appear on the U.S. market and if they result in a significant drop in drug price, it would introduce yet another significant variable. “Presuming biosimilar rituximab lowers the cost, that would be another important treatment decision,” he said.
Dr. Friedberg has been a consultant to Bayer. Dr. Leonard has been a consultant to 13 drug companies. Neither disclosed a relationship with the companies that market obinutuzumab or rituximab.
[email protected]
On Twitter @mitchelzoler
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM A MEETING ON HEMATOLOGIC MALIGNANCIES
Phase III trial: VZV protects auto-HCT patients
ORLANDO – An inactivated varicella zoster virus vaccine currently in development for adult patients undergoing autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation is efficacious and well tolerated, according to findings from a randomized, placebo-controlled, phase III trial.
During the course of the 2 1/2-year pivotal multicenter trial, confirmed herpes zoster infections occurred in 42 of 560 patients who were randomized to receive inactivated varicella zoster virus vaccine (ZVIN) consistency lot (overall incidence of 32.8 cases/1,000 patient-years), compared with 113 of 564 patients who received placebo (overall incidence of 91.8/1,000 patient-years). The estimated vaccine efficacy was 63.8% after adjusting for age and duration of antiviral prophylaxis, Drew J. Winston, MD, reported at the combined annual meetings of the Center for International Blood & Marrow Transplant Research and the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation.
The vaccine also was effective for reducing moderate and severe herpes zoster pain (estimated vaccine efficacy, 69.5%), for preventing postherpetic neuralgia (estimated vaccine efficacy, 83.7%), and for prevention of herpes zoster–related complications (estimated vaccine efficacy, 73.5%), he noted.
Study subjects were adults aged 18 years or older who were undergoing autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (auto-HCT) for a malignancy or other indication. The most common underlying diseases were lymphoma and multiple myeloma. All patients had a history of varicella infection or were seropositive for varicella zoster virus (VZV) antibody, and had no history of VZV vaccine or herpes zoster infection within the prior year.
They were randomized to receive a four-dose regimen of either ZVIN consistency lot, ZVIN high-antigen lot, or placebo. A group of 106 patients who received the ZVIN high-antigen lot were included in the safety analysis only. The first ZVIN dose was administered about a month before transplantation, and doses two through four were administered about 30, 60, and 90 days after transplantation. About 90% in each group received antiviral agents after transplantation, and the duration of the use of antivirals also was similar in the groups. All patients were followed for the duration of the study, and those who developed herpes zoster were followed for 6 months after onset.
Herpes zoster cases were confirmed by polymerase chain reaction or by blinded endpoint committee adjudication.
Serious adverse events and vaccine-related serious adverse events occurred in a similar proportion of patients in the treatment and placebo groups (32.9% and 32.7%, and 0.8% and 0.9%, respectively). Vaccine-related events were primarily injection-site reactions. Systemic adverse events that occurred up to 28 days after vaccination were mainly gastrointestinal side effects, such as diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting. Pyrexia, oral mucositis, thrombocytopenia, and febrile neutropenia also were reported.
The most common serious adverse events were infectious complications, such as febrile neutropenia and relapse of underlying disease.
The findings are notable, as patients undergoing auto-HCT have an increased risk of developing herpes zoster infection and its complications, including postherpetic neuralgia, secondary bacterial infections, and disseminated VZV infection, as well as an increased risk of hospitalization and mortality, Dr. Winston explained.
Herpes zoster infections are associated primarily with cell-mediated immunity, and in older studies done prior to the routine use of antiviral prophylaxis, the reported incidence in auto-HCT patients was between 16% and 25%. Because of this high risk, current guidelines call for antiviral prophylaxis during auto-HCT, but even in this current era of acyclovir or valacyclovir prophylaxis, infections occur at relatively high rates after auto-HCT, he noted.
“Now another approach to prevention of herpes zoster infection is vaccination,” he said.
The live attenuated vaccine currently on the market is generally contraindicated in immunocompromised patients – at least in early period after transplantation, but ZVIN showed promise with respect to safety in earlier studies, which led to the current trial.
“This study demonstrated that the inactivated varicella vaccine is very effective for preventing herpes zoster after autologous stem cell transplantation,” Dr. Winston said, noting that efficacy was observed both in those younger than age 50 years and in those aged 50 and older, and also in those who received prophylaxis for less than 3 months and for 3-6 months.
“Finally!” said one audience member, who noted during a discussion of the findings that there has long been a need for a vaccine to prevent herpes zoster in auto-HCT patients.
Dr. Winston reported receiving research funding from Oxford, and serving as a consultant to Merck and Chimerix.
ORLANDO – An inactivated varicella zoster virus vaccine currently in development for adult patients undergoing autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation is efficacious and well tolerated, according to findings from a randomized, placebo-controlled, phase III trial.
During the course of the 2 1/2-year pivotal multicenter trial, confirmed herpes zoster infections occurred in 42 of 560 patients who were randomized to receive inactivated varicella zoster virus vaccine (ZVIN) consistency lot (overall incidence of 32.8 cases/1,000 patient-years), compared with 113 of 564 patients who received placebo (overall incidence of 91.8/1,000 patient-years). The estimated vaccine efficacy was 63.8% after adjusting for age and duration of antiviral prophylaxis, Drew J. Winston, MD, reported at the combined annual meetings of the Center for International Blood & Marrow Transplant Research and the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation.
The vaccine also was effective for reducing moderate and severe herpes zoster pain (estimated vaccine efficacy, 69.5%), for preventing postherpetic neuralgia (estimated vaccine efficacy, 83.7%), and for prevention of herpes zoster–related complications (estimated vaccine efficacy, 73.5%), he noted.
Study subjects were adults aged 18 years or older who were undergoing autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (auto-HCT) for a malignancy or other indication. The most common underlying diseases were lymphoma and multiple myeloma. All patients had a history of varicella infection or were seropositive for varicella zoster virus (VZV) antibody, and had no history of VZV vaccine or herpes zoster infection within the prior year.
They were randomized to receive a four-dose regimen of either ZVIN consistency lot, ZVIN high-antigen lot, or placebo. A group of 106 patients who received the ZVIN high-antigen lot were included in the safety analysis only. The first ZVIN dose was administered about a month before transplantation, and doses two through four were administered about 30, 60, and 90 days after transplantation. About 90% in each group received antiviral agents after transplantation, and the duration of the use of antivirals also was similar in the groups. All patients were followed for the duration of the study, and those who developed herpes zoster were followed for 6 months after onset.
Herpes zoster cases were confirmed by polymerase chain reaction or by blinded endpoint committee adjudication.
Serious adverse events and vaccine-related serious adverse events occurred in a similar proportion of patients in the treatment and placebo groups (32.9% and 32.7%, and 0.8% and 0.9%, respectively). Vaccine-related events were primarily injection-site reactions. Systemic adverse events that occurred up to 28 days after vaccination were mainly gastrointestinal side effects, such as diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting. Pyrexia, oral mucositis, thrombocytopenia, and febrile neutropenia also were reported.
The most common serious adverse events were infectious complications, such as febrile neutropenia and relapse of underlying disease.
The findings are notable, as patients undergoing auto-HCT have an increased risk of developing herpes zoster infection and its complications, including postherpetic neuralgia, secondary bacterial infections, and disseminated VZV infection, as well as an increased risk of hospitalization and mortality, Dr. Winston explained.
Herpes zoster infections are associated primarily with cell-mediated immunity, and in older studies done prior to the routine use of antiviral prophylaxis, the reported incidence in auto-HCT patients was between 16% and 25%. Because of this high risk, current guidelines call for antiviral prophylaxis during auto-HCT, but even in this current era of acyclovir or valacyclovir prophylaxis, infections occur at relatively high rates after auto-HCT, he noted.
“Now another approach to prevention of herpes zoster infection is vaccination,” he said.
The live attenuated vaccine currently on the market is generally contraindicated in immunocompromised patients – at least in early period after transplantation, but ZVIN showed promise with respect to safety in earlier studies, which led to the current trial.
“This study demonstrated that the inactivated varicella vaccine is very effective for preventing herpes zoster after autologous stem cell transplantation,” Dr. Winston said, noting that efficacy was observed both in those younger than age 50 years and in those aged 50 and older, and also in those who received prophylaxis for less than 3 months and for 3-6 months.
“Finally!” said one audience member, who noted during a discussion of the findings that there has long been a need for a vaccine to prevent herpes zoster in auto-HCT patients.
Dr. Winston reported receiving research funding from Oxford, and serving as a consultant to Merck and Chimerix.
ORLANDO – An inactivated varicella zoster virus vaccine currently in development for adult patients undergoing autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation is efficacious and well tolerated, according to findings from a randomized, placebo-controlled, phase III trial.
During the course of the 2 1/2-year pivotal multicenter trial, confirmed herpes zoster infections occurred in 42 of 560 patients who were randomized to receive inactivated varicella zoster virus vaccine (ZVIN) consistency lot (overall incidence of 32.8 cases/1,000 patient-years), compared with 113 of 564 patients who received placebo (overall incidence of 91.8/1,000 patient-years). The estimated vaccine efficacy was 63.8% after adjusting for age and duration of antiviral prophylaxis, Drew J. Winston, MD, reported at the combined annual meetings of the Center for International Blood & Marrow Transplant Research and the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation.
The vaccine also was effective for reducing moderate and severe herpes zoster pain (estimated vaccine efficacy, 69.5%), for preventing postherpetic neuralgia (estimated vaccine efficacy, 83.7%), and for prevention of herpes zoster–related complications (estimated vaccine efficacy, 73.5%), he noted.
Study subjects were adults aged 18 years or older who were undergoing autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (auto-HCT) for a malignancy or other indication. The most common underlying diseases were lymphoma and multiple myeloma. All patients had a history of varicella infection or were seropositive for varicella zoster virus (VZV) antibody, and had no history of VZV vaccine or herpes zoster infection within the prior year.
They were randomized to receive a four-dose regimen of either ZVIN consistency lot, ZVIN high-antigen lot, or placebo. A group of 106 patients who received the ZVIN high-antigen lot were included in the safety analysis only. The first ZVIN dose was administered about a month before transplantation, and doses two through four were administered about 30, 60, and 90 days after transplantation. About 90% in each group received antiviral agents after transplantation, and the duration of the use of antivirals also was similar in the groups. All patients were followed for the duration of the study, and those who developed herpes zoster were followed for 6 months after onset.
Herpes zoster cases were confirmed by polymerase chain reaction or by blinded endpoint committee adjudication.
Serious adverse events and vaccine-related serious adverse events occurred in a similar proportion of patients in the treatment and placebo groups (32.9% and 32.7%, and 0.8% and 0.9%, respectively). Vaccine-related events were primarily injection-site reactions. Systemic adverse events that occurred up to 28 days after vaccination were mainly gastrointestinal side effects, such as diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting. Pyrexia, oral mucositis, thrombocytopenia, and febrile neutropenia also were reported.
The most common serious adverse events were infectious complications, such as febrile neutropenia and relapse of underlying disease.
The findings are notable, as patients undergoing auto-HCT have an increased risk of developing herpes zoster infection and its complications, including postherpetic neuralgia, secondary bacterial infections, and disseminated VZV infection, as well as an increased risk of hospitalization and mortality, Dr. Winston explained.
Herpes zoster infections are associated primarily with cell-mediated immunity, and in older studies done prior to the routine use of antiviral prophylaxis, the reported incidence in auto-HCT patients was between 16% and 25%. Because of this high risk, current guidelines call for antiviral prophylaxis during auto-HCT, but even in this current era of acyclovir or valacyclovir prophylaxis, infections occur at relatively high rates after auto-HCT, he noted.
“Now another approach to prevention of herpes zoster infection is vaccination,” he said.
The live attenuated vaccine currently on the market is generally contraindicated in immunocompromised patients – at least in early period after transplantation, but ZVIN showed promise with respect to safety in earlier studies, which led to the current trial.
“This study demonstrated that the inactivated varicella vaccine is very effective for preventing herpes zoster after autologous stem cell transplantation,” Dr. Winston said, noting that efficacy was observed both in those younger than age 50 years and in those aged 50 and older, and also in those who received prophylaxis for less than 3 months and for 3-6 months.
“Finally!” said one audience member, who noted during a discussion of the findings that there has long been a need for a vaccine to prevent herpes zoster in auto-HCT patients.
Dr. Winston reported receiving research funding from Oxford, and serving as a consultant to Merck and Chimerix.
AT THE 2017 BMT TANDEM MEETINGS
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Overall incidence of herpes zoster was 32.8 cases/1,000 patient-years vs. 91.8/1,000 patient-years in patients in the vaccine and placebo groups, respectively.
Data source: A randomized, placebo-controlled phase III trial involving 1,230 patients.
Disclosures: Dr. Winston reported receiving research funding from Oxford, and serving as a consultant to Merck and Chimerix.
Long view shows doubling of survival in non-Hodgkin lymphoma
Five-year survival for patients with non-Hodgkin lymphoma has more than doubled since the early 1950s, according to Ali H. Mokdad, PhD, and his associates.
Data from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program show that the 5-year relative survival rate for non-Hodgkin lymphoma in the United States went from 33% in 1950-1954 to 71.2% in 2008-2013, an increase of 116%, Dr. Mokdad and his associates reported (JAMA 2017;317[4]:388-406).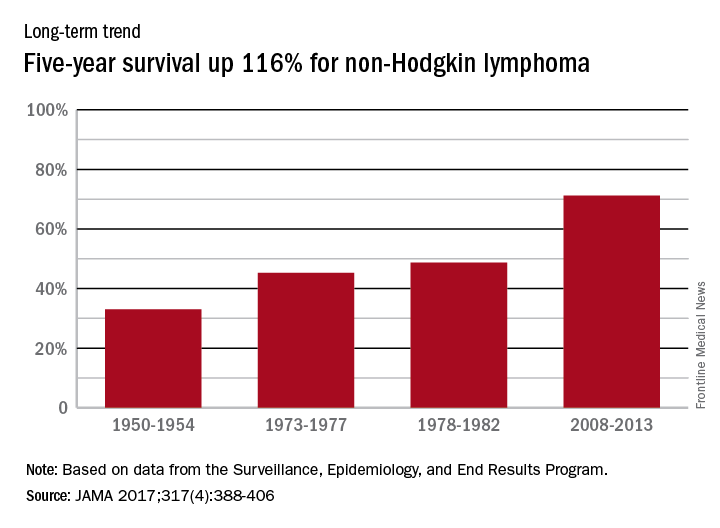
In 2014, mortality for non-Hodgkin lymphoma was the 7th highest among the 29 cancers included in the study, and more than 487,000 years of life were lost, which put it 6th among the 29 cancers, said Dr. Mokdad and his associates from the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation at the University of Washington, Seattle.
Five-year survival for patients with non-Hodgkin lymphoma has more than doubled since the early 1950s, according to Ali H. Mokdad, PhD, and his associates.
Data from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program show that the 5-year relative survival rate for non-Hodgkin lymphoma in the United States went from 33% in 1950-1954 to 71.2% in 2008-2013, an increase of 116%, Dr. Mokdad and his associates reported (JAMA 2017;317[4]:388-406).
In 2014, mortality for non-Hodgkin lymphoma was the 7th highest among the 29 cancers included in the study, and more than 487,000 years of life were lost, which put it 6th among the 29 cancers, said Dr. Mokdad and his associates from the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation at the University of Washington, Seattle.
Five-year survival for patients with non-Hodgkin lymphoma has more than doubled since the early 1950s, according to Ali H. Mokdad, PhD, and his associates.
Data from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program show that the 5-year relative survival rate for non-Hodgkin lymphoma in the United States went from 33% in 1950-1954 to 71.2% in 2008-2013, an increase of 116%, Dr. Mokdad and his associates reported (JAMA 2017;317[4]:388-406).
In 2014, mortality for non-Hodgkin lymphoma was the 7th highest among the 29 cancers included in the study, and more than 487,000 years of life were lost, which put it 6th among the 29 cancers, said Dr. Mokdad and his associates from the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation at the University of Washington, Seattle.
FROM JAMA
Hodgkin lymphoma survival has nearly tripled since the 1950s
Five-year relative survival for Hodgkin lymphoma increased 189% over the approximately 60 years from the early 1950s to 2013, according to investigators looking at data from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program.
During 1950-1954, the 5-year relative survival rate for Hodgkin lymphoma was 30%, compared with 86.6% in 2008-2013, said Ali H. Mokdad, PhD, and his associates at the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation at the University of Washington, Seattle.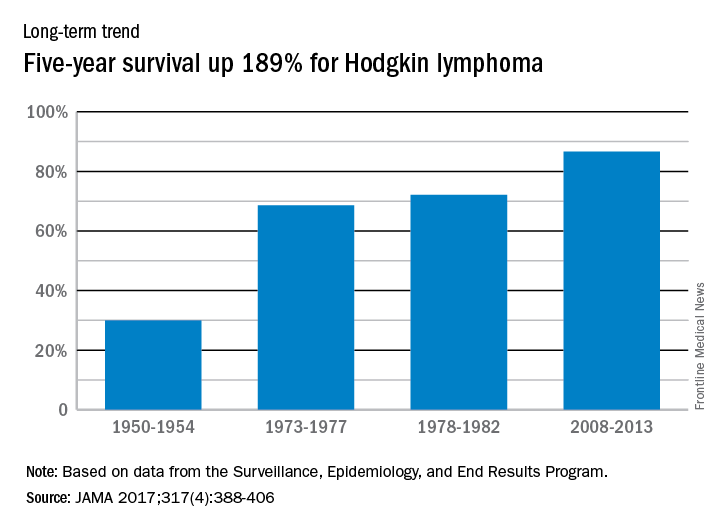
In 2014, mortality for Hodgkin lymphoma was 0.4 per 100,000 population, which put it 27th among the 29 included cancers, with about 36,000 years of life lost, which was 26th of the 29 cancers, Dr. Mokdad and his associates said. This part of their study used deidentified death records from the National Center for Health Statistics and population counts from the Census Bureau, the NCHS, and the Human Mortality Database.
Five-year relative survival for Hodgkin lymphoma increased 189% over the approximately 60 years from the early 1950s to 2013, according to investigators looking at data from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program.
During 1950-1954, the 5-year relative survival rate for Hodgkin lymphoma was 30%, compared with 86.6% in 2008-2013, said Ali H. Mokdad, PhD, and his associates at the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation at the University of Washington, Seattle.
In 2014, mortality for Hodgkin lymphoma was 0.4 per 100,000 population, which put it 27th among the 29 included cancers, with about 36,000 years of life lost, which was 26th of the 29 cancers, Dr. Mokdad and his associates said. This part of their study used deidentified death records from the National Center for Health Statistics and population counts from the Census Bureau, the NCHS, and the Human Mortality Database.
Five-year relative survival for Hodgkin lymphoma increased 189% over the approximately 60 years from the early 1950s to 2013, according to investigators looking at data from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program.
During 1950-1954, the 5-year relative survival rate for Hodgkin lymphoma was 30%, compared with 86.6% in 2008-2013, said Ali H. Mokdad, PhD, and his associates at the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation at the University of Washington, Seattle.
In 2014, mortality for Hodgkin lymphoma was 0.4 per 100,000 population, which put it 27th among the 29 included cancers, with about 36,000 years of life lost, which was 26th of the 29 cancers, Dr. Mokdad and his associates said. This part of their study used deidentified death records from the National Center for Health Statistics and population counts from the Census Bureau, the NCHS, and the Human Mortality Database.
FROM JAMA
FDA approves ibrutinib for refractory MZL
The Food and Drug Administration has approved ibrutinib for the treatment of patients with relapsed or refractory marginal zone lymphoma (MZL), the drug’s manufacturers report.
The approval marks the fifth indication for ibrutinib (Imbruvica) in just over 4 years, and ibrutinib is the first agent specifically approved for relapsed/refractory MZL, according to press releases issued by Janssen Biotech and Pharmacyclics, the two manufacturers that jointly developed and marketed the Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
After receiving various fast-track, breakthrough therapy, priority review, and accelerated approval designations from the FDA, ibrutinib was previously approved to treat mantle cell lymphoma; refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma (CLL/SLL); CLL/SLL with 17p deletion; and Waldenstrom’s macroglobulinemia, another rare form of non-Hodgkin lymphoma. The MCL and MZL approvals are based on overall response rates, and full approval is likely to require additional confirmatory data.
The new indication is based on data from a phase II, open-label, single-arm manufacturer-sponsored study that showed a 46% overall response rate (95% confidence interval, 33.4-59.1) in a cohort of 63 MZL patients who had failed one or more prior therapies. Of these, 3.2% had a complete response and 42.9% had a partial response. The median duration of response was not reached (NR) (range, 16.7 months–NR), with median follow-up of 19.4 months. The median time to initial response was 4.5 months (2.3-16.4 months).
All three MZL subtypes were represented in the cohort, and ibrutinib appeared to be effective across subtypes. Thrombocytopenia, fatigue, anemia, diarrhea, bruising, and musculoskeletal pain were commonly reported adverse events.
[email protected]
On Twitter @HematologyNews1
The Food and Drug Administration has approved ibrutinib for the treatment of patients with relapsed or refractory marginal zone lymphoma (MZL), the drug’s manufacturers report.
The approval marks the fifth indication for ibrutinib (Imbruvica) in just over 4 years, and ibrutinib is the first agent specifically approved for relapsed/refractory MZL, according to press releases issued by Janssen Biotech and Pharmacyclics, the two manufacturers that jointly developed and marketed the Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
After receiving various fast-track, breakthrough therapy, priority review, and accelerated approval designations from the FDA, ibrutinib was previously approved to treat mantle cell lymphoma; refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma (CLL/SLL); CLL/SLL with 17p deletion; and Waldenstrom’s macroglobulinemia, another rare form of non-Hodgkin lymphoma. The MCL and MZL approvals are based on overall response rates, and full approval is likely to require additional confirmatory data.
The new indication is based on data from a phase II, open-label, single-arm manufacturer-sponsored study that showed a 46% overall response rate (95% confidence interval, 33.4-59.1) in a cohort of 63 MZL patients who had failed one or more prior therapies. Of these, 3.2% had a complete response and 42.9% had a partial response. The median duration of response was not reached (NR) (range, 16.7 months–NR), with median follow-up of 19.4 months. The median time to initial response was 4.5 months (2.3-16.4 months).
All three MZL subtypes were represented in the cohort, and ibrutinib appeared to be effective across subtypes. Thrombocytopenia, fatigue, anemia, diarrhea, bruising, and musculoskeletal pain were commonly reported adverse events.
[email protected]
On Twitter @HematologyNews1
The Food and Drug Administration has approved ibrutinib for the treatment of patients with relapsed or refractory marginal zone lymphoma (MZL), the drug’s manufacturers report.
The approval marks the fifth indication for ibrutinib (Imbruvica) in just over 4 years, and ibrutinib is the first agent specifically approved for relapsed/refractory MZL, according to press releases issued by Janssen Biotech and Pharmacyclics, the two manufacturers that jointly developed and marketed the Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
After receiving various fast-track, breakthrough therapy, priority review, and accelerated approval designations from the FDA, ibrutinib was previously approved to treat mantle cell lymphoma; refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma (CLL/SLL); CLL/SLL with 17p deletion; and Waldenstrom’s macroglobulinemia, another rare form of non-Hodgkin lymphoma. The MCL and MZL approvals are based on overall response rates, and full approval is likely to require additional confirmatory data.
The new indication is based on data from a phase II, open-label, single-arm manufacturer-sponsored study that showed a 46% overall response rate (95% confidence interval, 33.4-59.1) in a cohort of 63 MZL patients who had failed one or more prior therapies. Of these, 3.2% had a complete response and 42.9% had a partial response. The median duration of response was not reached (NR) (range, 16.7 months–NR), with median follow-up of 19.4 months. The median time to initial response was 4.5 months (2.3-16.4 months).
All three MZL subtypes were represented in the cohort, and ibrutinib appeared to be effective across subtypes. Thrombocytopenia, fatigue, anemia, diarrhea, bruising, and musculoskeletal pain were commonly reported adverse events.
[email protected]
On Twitter @HematologyNews1
VIDEO: Obinutuzumab bests rituximab for PFS in follicular lymphoma
SAN DIEGO – For patients with indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma, adding the anti-CD20 antibody rituximab to a standard-combination chemotherapy regimen resulted in significant improvements in survival, compared with chemotherapy alone. Obinutuzumab (Gazyva), a second-generation anti-CD20 antibody touted as the heir apparent to rituximab, is being explored in various combinations for the treatment of indolent lymphomas, including follicular lymphoma and marginal zone lymphoma.
In this video interview from the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology, Robert Marcus, FRCP, of King’s College Hospital, London, discussed results of the phase III GALLIUM study, in which patients with untreated follicular lymphoma were randomly assigned to one of three chemotherapy regimens with either obinutuzumab or rituximab. The primary endpoint of investigator-assessed 3-year progression-free survival (PFS) at a median follow-up of 34.5 months was 80% for patients with follicular lymphoma treated with obinutuzumab and one of three standard chemotherapy regimens, compared with 73.3% for patients treated with rituximab and chemotherapy. This difference translated into a hazard ratio (HR) favoring obinutuzumab of 0.68 (P = .0012).
Respective 3-year overall survival rates at 3 years were similar, however, at 94% and 92.1% (HR, 0.75; P = .21).
The GALLIUM trial is sponsored by F. Hoffmann-La Roche. Dr. Marcus disclosed consulting with and receiving honoraria from the company, and relationships with other companies.
The video associated with this article is no longer available on this site. Please view all of our videos on the MDedge YouTube channel
SAN DIEGO – For patients with indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma, adding the anti-CD20 antibody rituximab to a standard-combination chemotherapy regimen resulted in significant improvements in survival, compared with chemotherapy alone. Obinutuzumab (Gazyva), a second-generation anti-CD20 antibody touted as the heir apparent to rituximab, is being explored in various combinations for the treatment of indolent lymphomas, including follicular lymphoma and marginal zone lymphoma.
In this video interview from the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology, Robert Marcus, FRCP, of King’s College Hospital, London, discussed results of the phase III GALLIUM study, in which patients with untreated follicular lymphoma were randomly assigned to one of three chemotherapy regimens with either obinutuzumab or rituximab. The primary endpoint of investigator-assessed 3-year progression-free survival (PFS) at a median follow-up of 34.5 months was 80% for patients with follicular lymphoma treated with obinutuzumab and one of three standard chemotherapy regimens, compared with 73.3% for patients treated with rituximab and chemotherapy. This difference translated into a hazard ratio (HR) favoring obinutuzumab of 0.68 (P = .0012).
Respective 3-year overall survival rates at 3 years were similar, however, at 94% and 92.1% (HR, 0.75; P = .21).
The GALLIUM trial is sponsored by F. Hoffmann-La Roche. Dr. Marcus disclosed consulting with and receiving honoraria from the company, and relationships with other companies.
The video associated with this article is no longer available on this site. Please view all of our videos on the MDedge YouTube channel
SAN DIEGO – For patients with indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma, adding the anti-CD20 antibody rituximab to a standard-combination chemotherapy regimen resulted in significant improvements in survival, compared with chemotherapy alone. Obinutuzumab (Gazyva), a second-generation anti-CD20 antibody touted as the heir apparent to rituximab, is being explored in various combinations for the treatment of indolent lymphomas, including follicular lymphoma and marginal zone lymphoma.
In this video interview from the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology, Robert Marcus, FRCP, of King’s College Hospital, London, discussed results of the phase III GALLIUM study, in which patients with untreated follicular lymphoma were randomly assigned to one of three chemotherapy regimens with either obinutuzumab or rituximab. The primary endpoint of investigator-assessed 3-year progression-free survival (PFS) at a median follow-up of 34.5 months was 80% for patients with follicular lymphoma treated with obinutuzumab and one of three standard chemotherapy regimens, compared with 73.3% for patients treated with rituximab and chemotherapy. This difference translated into a hazard ratio (HR) favoring obinutuzumab of 0.68 (P = .0012).
Respective 3-year overall survival rates at 3 years were similar, however, at 94% and 92.1% (HR, 0.75; P = .21).
The GALLIUM trial is sponsored by F. Hoffmann-La Roche. Dr. Marcus disclosed consulting with and receiving honoraria from the company, and relationships with other companies.
The video associated with this article is no longer available on this site. Please view all of our videos on the MDedge YouTube channel
AT ASH 2016
Antibody face-off in follicular lymphoma gives PFS, but not OS, edge to obinutuzumab
SAN DIEGO – Obinutuzumab, a second-generation anti-CD20 antibody touted as the heir apparent to rituximab, offered a progression-free survival (PFS) edge over rituximab when combined with standard chemotherapy in patients with previously untreated advanced follicular lymphoma.
But other clinicians and investigators who
attended the presentation of the GALLIUM data at a plenary session during the American Society of Hematology annual meeting indicated that despite the data, they weren’t ready to make a switch to the newer, costlier antibody.
“I feel that it is not convincing for practice-changing,” said Kanti R. Rai, MD, professor of medicine and molecular medicine at Hofstra University, Hempstead, N.Y.
“Unless we have evidence of a survival advantage in indolent disease, progression-free survivorship is not an adequate reason to jump to another antibody,” he said in an interview.
In GALLIUM, the primary endpoint of investigator-assessed 3-year PFS at a median follow-up of 34.5 months was 80% for patients with follicular lymphoma treated with obinutuzumab and one of three standard chemotherapy regimens, compared with 73.3% for patients treated with rituximab and chemotherapy. This difference translated into a hazard ratio of 0.68 favoring obinutuzumab (P = .0012).
Respective 3-year overall survival rates were similar, however, at 94% and 92.1% (HR, 0.75; P = .21).
Indolent lymphoma trial
The GALLIUM trial is a phase III study comparing obinutuzumab with rituximab when paired with one of three standard chemotherapy regimens for indolent non-Hodgkin lymphomas, including follicular lymphoma and splenic, nodal, or extranodal marginal zone lymphoma. Dr. Marcus presented data on patients with follicular lymphoma only.
The antibodies were delivered in combination with either CHOP (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine and prednisone; 33.1% of patients), CVP (cyclophosphamide, vincristine, prednisone; 9.8%) or bendamustine alone (B; 57.1%) as the chemotherapy backbone. The choice of regimen was at the discretion of the treating center.
A total of 1,202 patients with follicular lymphoma were enrolled and randomized to treatment and were included in an intention-to-treat analysis.
The treatment arms were well balanced with regard to distribution of patients characteristics, with approximately 21% in each arm having Follicular Lymphoma International Prognostic Index low-risk disease; 37% having intermediate-risk disease; and 34% having high-risk disease.
Roughly half of patients in each arm had bone marrow involvement, and two-thirds had extranodal involvement.
Obinutuzumab was dosed 1,000 mg IV on days 1, 8, and 15 of cycle one, and either on day 1 of cycles two through eight every 3 weeks, or every 4 weeks during cycles two through six.
Overall response rates at the end of induction were 86.9% with rituximab and 88.5% with obinutuzumab, with complete responses of 23.8% and 19.5%, respectively.
As noted before, investigator-assessed PFS favored obinutuzumab, as did PFS assessed by independent reviewer, at 81.9% vs. 77.9% for rituximab (HR, 0.71; P = .0138).
The newer antibody also had a slight edge in time to new treatment, with 87.1% of patients on obinutuzumab not starting on new therapy, compared with 81.2% of patients on rituximab.
More bendamustine deaths
Nearly all patients in each arm had an adverse event, with grade 3 or greater events occurring in 74.6% of patients on obinutuzumab vs. 67.8% on rituximab. Rates of neutropenia, leukopenia, febrile neutropenia, infusion reactions, and thrombocytopenia were all slightly higher with obinutuzumab. Grade 3 or greater infections occurred in 20% with obinutuzumab, compared with 15.6% with rituximab.
“What we did note, however, was a high level of mortality in patients receiving either obinutuzumab-based therapy or rituximab-based therapy, which were no different between the two arms and were somewhat higher than one might expect from patients receiving induction treatment in follicular lymphoma. Hence, we did a more detailed analysis of safety by treatment regimen,” Dr. Marcus said.
There were more deaths among patients treated with bendamustine (5.6% for patients in the B-obinutuzumab cohort, and 4.4% of patients in the B-rituximab cohort) vs. 1.6% and 2.0%, respectively, for patients on CHOP, and 1.6 and 1.8% for patients on CVP.
Dose effect?
John P. Leonard, MD, from Cornell University, New York , who introduced Dr. Marcus, commented that PFS may not be the ideal endpoint for patients with follicular lymphoma.
He pointed out that in trials comparing rituximab with obinutuzumab for other diseases, results have been mixed, with obinutuzumab showing superiority in chronic lymphocytic leukemia, but in data presented elsewhere at ASH 2016, obinutuzumab was not superior to rituximab for treatment of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.
“One question is whether obinutuzumab, which is generally administered at a higher mg dose to patients, is in fact a better antibody or if it is in fact a dose effect,” he said.
In response to a similar question following his presentation, Dr. Marcus replied that, despite sharing a target, the two antibodies are different, with different mechanisms of action. He also noted that there is no evidence to suggest that rituximab potency would be greater in follicular lymphoma if it were given at higher doses.
The GALLIUM trial is sponsored by Hoffmann-La Roche, Dr, Marcus disclosed consulting with and receiving honoraria from the company, and relationships with other companies.
SAN DIEGO – Obinutuzumab, a second-generation anti-CD20 antibody touted as the heir apparent to rituximab, offered a progression-free survival (PFS) edge over rituximab when combined with standard chemotherapy in patients with previously untreated advanced follicular lymphoma.
But other clinicians and investigators who
attended the presentation of the GALLIUM data at a plenary session during the American Society of Hematology annual meeting indicated that despite the data, they weren’t ready to make a switch to the newer, costlier antibody.
“I feel that it is not convincing for practice-changing,” said Kanti R. Rai, MD, professor of medicine and molecular medicine at Hofstra University, Hempstead, N.Y.
“Unless we have evidence of a survival advantage in indolent disease, progression-free survivorship is not an adequate reason to jump to another antibody,” he said in an interview.
In GALLIUM, the primary endpoint of investigator-assessed 3-year PFS at a median follow-up of 34.5 months was 80% for patients with follicular lymphoma treated with obinutuzumab and one of three standard chemotherapy regimens, compared with 73.3% for patients treated with rituximab and chemotherapy. This difference translated into a hazard ratio of 0.68 favoring obinutuzumab (P = .0012).
Respective 3-year overall survival rates were similar, however, at 94% and 92.1% (HR, 0.75; P = .21).
Indolent lymphoma trial
The GALLIUM trial is a phase III study comparing obinutuzumab with rituximab when paired with one of three standard chemotherapy regimens for indolent non-Hodgkin lymphomas, including follicular lymphoma and splenic, nodal, or extranodal marginal zone lymphoma. Dr. Marcus presented data on patients with follicular lymphoma only.
The antibodies were delivered in combination with either CHOP (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine and prednisone; 33.1% of patients), CVP (cyclophosphamide, vincristine, prednisone; 9.8%) or bendamustine alone (B; 57.1%) as the chemotherapy backbone. The choice of regimen was at the discretion of the treating center.
A total of 1,202 patients with follicular lymphoma were enrolled and randomized to treatment and were included in an intention-to-treat analysis.
The treatment arms were well balanced with regard to distribution of patients characteristics, with approximately 21% in each arm having Follicular Lymphoma International Prognostic Index low-risk disease; 37% having intermediate-risk disease; and 34% having high-risk disease.
Roughly half of patients in each arm had bone marrow involvement, and two-thirds had extranodal involvement.
Obinutuzumab was dosed 1,000 mg IV on days 1, 8, and 15 of cycle one, and either on day 1 of cycles two through eight every 3 weeks, or every 4 weeks during cycles two through six.
Overall response rates at the end of induction were 86.9% with rituximab and 88.5% with obinutuzumab, with complete responses of 23.8% and 19.5%, respectively.
As noted before, investigator-assessed PFS favored obinutuzumab, as did PFS assessed by independent reviewer, at 81.9% vs. 77.9% for rituximab (HR, 0.71; P = .0138).
The newer antibody also had a slight edge in time to new treatment, with 87.1% of patients on obinutuzumab not starting on new therapy, compared with 81.2% of patients on rituximab.
More bendamustine deaths
Nearly all patients in each arm had an adverse event, with grade 3 or greater events occurring in 74.6% of patients on obinutuzumab vs. 67.8% on rituximab. Rates of neutropenia, leukopenia, febrile neutropenia, infusion reactions, and thrombocytopenia were all slightly higher with obinutuzumab. Grade 3 or greater infections occurred in 20% with obinutuzumab, compared with 15.6% with rituximab.
“What we did note, however, was a high level of mortality in patients receiving either obinutuzumab-based therapy or rituximab-based therapy, which were no different between the two arms and were somewhat higher than one might expect from patients receiving induction treatment in follicular lymphoma. Hence, we did a more detailed analysis of safety by treatment regimen,” Dr. Marcus said.
There were more deaths among patients treated with bendamustine (5.6% for patients in the B-obinutuzumab cohort, and 4.4% of patients in the B-rituximab cohort) vs. 1.6% and 2.0%, respectively, for patients on CHOP, and 1.6 and 1.8% for patients on CVP.
Dose effect?
John P. Leonard, MD, from Cornell University, New York , who introduced Dr. Marcus, commented that PFS may not be the ideal endpoint for patients with follicular lymphoma.
He pointed out that in trials comparing rituximab with obinutuzumab for other diseases, results have been mixed, with obinutuzumab showing superiority in chronic lymphocytic leukemia, but in data presented elsewhere at ASH 2016, obinutuzumab was not superior to rituximab for treatment of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.
“One question is whether obinutuzumab, which is generally administered at a higher mg dose to patients, is in fact a better antibody or if it is in fact a dose effect,” he said.
In response to a similar question following his presentation, Dr. Marcus replied that, despite sharing a target, the two antibodies are different, with different mechanisms of action. He also noted that there is no evidence to suggest that rituximab potency would be greater in follicular lymphoma if it were given at higher doses.
The GALLIUM trial is sponsored by Hoffmann-La Roche, Dr, Marcus disclosed consulting with and receiving honoraria from the company, and relationships with other companies.
SAN DIEGO – Obinutuzumab, a second-generation anti-CD20 antibody touted as the heir apparent to rituximab, offered a progression-free survival (PFS) edge over rituximab when combined with standard chemotherapy in patients with previously untreated advanced follicular lymphoma.
But other clinicians and investigators who
attended the presentation of the GALLIUM data at a plenary session during the American Society of Hematology annual meeting indicated that despite the data, they weren’t ready to make a switch to the newer, costlier antibody.
“I feel that it is not convincing for practice-changing,” said Kanti R. Rai, MD, professor of medicine and molecular medicine at Hofstra University, Hempstead, N.Y.
“Unless we have evidence of a survival advantage in indolent disease, progression-free survivorship is not an adequate reason to jump to another antibody,” he said in an interview.
In GALLIUM, the primary endpoint of investigator-assessed 3-year PFS at a median follow-up of 34.5 months was 80% for patients with follicular lymphoma treated with obinutuzumab and one of three standard chemotherapy regimens, compared with 73.3% for patients treated with rituximab and chemotherapy. This difference translated into a hazard ratio of 0.68 favoring obinutuzumab (P = .0012).
Respective 3-year overall survival rates were similar, however, at 94% and 92.1% (HR, 0.75; P = .21).
Indolent lymphoma trial
The GALLIUM trial is a phase III study comparing obinutuzumab with rituximab when paired with one of three standard chemotherapy regimens for indolent non-Hodgkin lymphomas, including follicular lymphoma and splenic, nodal, or extranodal marginal zone lymphoma. Dr. Marcus presented data on patients with follicular lymphoma only.
The antibodies were delivered in combination with either CHOP (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine and prednisone; 33.1% of patients), CVP (cyclophosphamide, vincristine, prednisone; 9.8%) or bendamustine alone (B; 57.1%) as the chemotherapy backbone. The choice of regimen was at the discretion of the treating center.
A total of 1,202 patients with follicular lymphoma were enrolled and randomized to treatment and were included in an intention-to-treat analysis.
The treatment arms were well balanced with regard to distribution of patients characteristics, with approximately 21% in each arm having Follicular Lymphoma International Prognostic Index low-risk disease; 37% having intermediate-risk disease; and 34% having high-risk disease.
Roughly half of patients in each arm had bone marrow involvement, and two-thirds had extranodal involvement.
Obinutuzumab was dosed 1,000 mg IV on days 1, 8, and 15 of cycle one, and either on day 1 of cycles two through eight every 3 weeks, or every 4 weeks during cycles two through six.
Overall response rates at the end of induction were 86.9% with rituximab and 88.5% with obinutuzumab, with complete responses of 23.8% and 19.5%, respectively.
As noted before, investigator-assessed PFS favored obinutuzumab, as did PFS assessed by independent reviewer, at 81.9% vs. 77.9% for rituximab (HR, 0.71; P = .0138).
The newer antibody also had a slight edge in time to new treatment, with 87.1% of patients on obinutuzumab not starting on new therapy, compared with 81.2% of patients on rituximab.
More bendamustine deaths
Nearly all patients in each arm had an adverse event, with grade 3 or greater events occurring in 74.6% of patients on obinutuzumab vs. 67.8% on rituximab. Rates of neutropenia, leukopenia, febrile neutropenia, infusion reactions, and thrombocytopenia were all slightly higher with obinutuzumab. Grade 3 or greater infections occurred in 20% with obinutuzumab, compared with 15.6% with rituximab.
“What we did note, however, was a high level of mortality in patients receiving either obinutuzumab-based therapy or rituximab-based therapy, which were no different between the two arms and were somewhat higher than one might expect from patients receiving induction treatment in follicular lymphoma. Hence, we did a more detailed analysis of safety by treatment regimen,” Dr. Marcus said.
There were more deaths among patients treated with bendamustine (5.6% for patients in the B-obinutuzumab cohort, and 4.4% of patients in the B-rituximab cohort) vs. 1.6% and 2.0%, respectively, for patients on CHOP, and 1.6 and 1.8% for patients on CVP.
Dose effect?
John P. Leonard, MD, from Cornell University, New York , who introduced Dr. Marcus, commented that PFS may not be the ideal endpoint for patients with follicular lymphoma.
He pointed out that in trials comparing rituximab with obinutuzumab for other diseases, results have been mixed, with obinutuzumab showing superiority in chronic lymphocytic leukemia, but in data presented elsewhere at ASH 2016, obinutuzumab was not superior to rituximab for treatment of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.
“One question is whether obinutuzumab, which is generally administered at a higher mg dose to patients, is in fact a better antibody or if it is in fact a dose effect,” he said.
In response to a similar question following his presentation, Dr. Marcus replied that, despite sharing a target, the two antibodies are different, with different mechanisms of action. He also noted that there is no evidence to suggest that rituximab potency would be greater in follicular lymphoma if it were given at higher doses.
The GALLIUM trial is sponsored by Hoffmann-La Roche, Dr, Marcus disclosed consulting with and receiving honoraria from the company, and relationships with other companies.
AT ASH 2016
Key clinical point: Obinutuzumab plus chemotherapy was associated with better 3-year progression-free survival in patients with untreated follicular lymphoma.
Major finding: Obinutuzumab/chemo was associated with a hazard ratio for investigator-assessed PFS of 0.68 (P = .0012)
Data source: Randomized phase III trial in 1202 patients with previously untreated follicular lymphoma.
Disclosures: The GALLIUM trial was sponsored by Hoffmann-La Roche. Dr. Marcus disclosed consulting with and receiving honoraria from the company, and relationships with other companies.








