User login
How diet affects NASH-to-HCC progression
A new study sought to establish a new, clinically relevant mouse model of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) that closely reflects human disease as well as the multitissue dynamics involved in the progression and regression of the condition, according to the researchers. This study focused on the association between progression of NASH and consumption of a Western diet, as well as the development of HCC.
The study used a model consisting of hyperphagic mice that lacked a functional ALMS1 gene (Foz/Foz), in addition to wild-type littermates. The model ultimately defined “the key signaling and cytokine pathways that are critical for disease development and resolution” associated with NASH, wrote Souradipta Ganguly, PhD, of the University of California, San Diego, and colleagues. The report was published in Cellular and Molecular Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
According to the researchers, this study is unique given “current rodent models of NASH do not reproduce the complete spectrum of metabolic and histologic” nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) phenotypes. Likewise, the lack of “systemic studies in a single rodent model of NASH that closely recapitulates the human pathology” reinforces the importance of the new model, the researchers added.
Over time, NASH can progress to cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Studies that fed wild-type mice a Western diet have largely failed to mimic the full pathology of NASH to fibrosis to HCC. In addition, the models in these studies fail to reflect the multitissue injuries frequently observed in NASH.
To circumvent these challenges, Dr. Ganguly and colleagues used ALMS1-mutated mice to develop a rodent model of metabolic syndrome that included NASH with fibrosis, chronic kidney disease, and cardiovascular disease. The ALMS1 mutation also resulted in the mice becoming hyperphagic, which increases hunger and leads to early-onset obesity, among other conditions characteristic of metabolic syndrome.
Researchers fed the hyperphagic Foz/Foz mice and wild-type littermates a Western diet or standard diet during a 12-week period for NASH/fibrosis and a 24-week period for HCC. After NASH was established, mice were switched back to normal chow to see if the condition regressed.
Macronutrient distribution of the study’s Western diet included 40% fat, 15% protein, and 44% carbohydrates, based on total caloric content. In contrast, the standard chow included 12% fat, 23% protein, and 65% carbohydrates from total calories.
Within 1-2 weeks, Foz mice fed the Western diet were considered steatotic. These mice subsequently developed NASH by 4 weeks of the study and grade 3 fibrosis by 12 weeks. The researchers concurrently observed the development of chronic kidney injury in the animals. Mice continuing to the 24 weeks ultimately progressed to cirrhosis and HCC; these mice demonstrated reduced survival due to cardiac dysfunction.
Mice that developed NASH were then switched to a diet consisting of normal chow. Following this switch, NASH began to regress, and survival improved. These mice did not appear to develop HCC, and total liver weight was significantly reduced compared with the mice that didn’t enter the regression phase of the study. The researchers wrote that the resolution of hepatic steatosis was also consistent with improved glucose tolerance.
In transcriptomic and histologic analyses, the researchers found strong concordance between Foz/Foz mice NASH liver and human NASH.
The study also found that early disruption of gut barrier, microbial dysbiosis, lipopolysaccharide leakage, and intestinal inflammation preceded NASH in the Foz/Foz mice fed the Western diet, resulting in acute-phase liver inflammation. The early inflammation was reflected by an increase in several chemokines and cytokines by 1-2 weeks. As NASH progressed, the liver cytokine/chemokine profile continued to evolve, leading to monocyte recruitment predominance. “Further studies will elaborate the roles of these NASH-specific microbiomial features in the development and progression of NASH fibrosis,” wrote the researchers.
The study received financial support Janssen, in addition to funding from an ALF Liver Scholar award, ACTRI/National Institutes of Health, the SDDRC, and the NIAAA/National Institutes of Health. The authors disclosed no conflicts.
The prevalence and incidence of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and NASH-induced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) have rapidly increased worldwide in recent years. The growing number of patients with NASH and NASH-HCC poses a significant public health burden, further confounded by suboptimal approaches for disease management, including a lack of effective pharmacotherapy. To accelerate the development of novel treatment modalities, preclinical studies using animal models highly relevant to human disease are of utmost importance. The ideal experimental NASH model recapitulates the multifaceted human condition, including the etiology, underlying pathogenetic mechanisms, histologic features, and progression from NASH to NASH-related HCC.
Petra Hirsova, PharmD, PhD, is an assistant professor and investigator in the division of gastroenterology and hepatology at the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn. Dr. Hirsova reported having no disclosures.
The prevalence and incidence of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and NASH-induced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) have rapidly increased worldwide in recent years. The growing number of patients with NASH and NASH-HCC poses a significant public health burden, further confounded by suboptimal approaches for disease management, including a lack of effective pharmacotherapy. To accelerate the development of novel treatment modalities, preclinical studies using animal models highly relevant to human disease are of utmost importance. The ideal experimental NASH model recapitulates the multifaceted human condition, including the etiology, underlying pathogenetic mechanisms, histologic features, and progression from NASH to NASH-related HCC.
Petra Hirsova, PharmD, PhD, is an assistant professor and investigator in the division of gastroenterology and hepatology at the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn. Dr. Hirsova reported having no disclosures.
The prevalence and incidence of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and NASH-induced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) have rapidly increased worldwide in recent years. The growing number of patients with NASH and NASH-HCC poses a significant public health burden, further confounded by suboptimal approaches for disease management, including a lack of effective pharmacotherapy. To accelerate the development of novel treatment modalities, preclinical studies using animal models highly relevant to human disease are of utmost importance. The ideal experimental NASH model recapitulates the multifaceted human condition, including the etiology, underlying pathogenetic mechanisms, histologic features, and progression from NASH to NASH-related HCC.
Petra Hirsova, PharmD, PhD, is an assistant professor and investigator in the division of gastroenterology and hepatology at the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn. Dr. Hirsova reported having no disclosures.
A new study sought to establish a new, clinically relevant mouse model of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) that closely reflects human disease as well as the multitissue dynamics involved in the progression and regression of the condition, according to the researchers. This study focused on the association between progression of NASH and consumption of a Western diet, as well as the development of HCC.
The study used a model consisting of hyperphagic mice that lacked a functional ALMS1 gene (Foz/Foz), in addition to wild-type littermates. The model ultimately defined “the key signaling and cytokine pathways that are critical for disease development and resolution” associated with NASH, wrote Souradipta Ganguly, PhD, of the University of California, San Diego, and colleagues. The report was published in Cellular and Molecular Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
According to the researchers, this study is unique given “current rodent models of NASH do not reproduce the complete spectrum of metabolic and histologic” nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) phenotypes. Likewise, the lack of “systemic studies in a single rodent model of NASH that closely recapitulates the human pathology” reinforces the importance of the new model, the researchers added.
Over time, NASH can progress to cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Studies that fed wild-type mice a Western diet have largely failed to mimic the full pathology of NASH to fibrosis to HCC. In addition, the models in these studies fail to reflect the multitissue injuries frequently observed in NASH.
To circumvent these challenges, Dr. Ganguly and colleagues used ALMS1-mutated mice to develop a rodent model of metabolic syndrome that included NASH with fibrosis, chronic kidney disease, and cardiovascular disease. The ALMS1 mutation also resulted in the mice becoming hyperphagic, which increases hunger and leads to early-onset obesity, among other conditions characteristic of metabolic syndrome.
Researchers fed the hyperphagic Foz/Foz mice and wild-type littermates a Western diet or standard diet during a 12-week period for NASH/fibrosis and a 24-week period for HCC. After NASH was established, mice were switched back to normal chow to see if the condition regressed.
Macronutrient distribution of the study’s Western diet included 40% fat, 15% protein, and 44% carbohydrates, based on total caloric content. In contrast, the standard chow included 12% fat, 23% protein, and 65% carbohydrates from total calories.
Within 1-2 weeks, Foz mice fed the Western diet were considered steatotic. These mice subsequently developed NASH by 4 weeks of the study and grade 3 fibrosis by 12 weeks. The researchers concurrently observed the development of chronic kidney injury in the animals. Mice continuing to the 24 weeks ultimately progressed to cirrhosis and HCC; these mice demonstrated reduced survival due to cardiac dysfunction.
Mice that developed NASH were then switched to a diet consisting of normal chow. Following this switch, NASH began to regress, and survival improved. These mice did not appear to develop HCC, and total liver weight was significantly reduced compared with the mice that didn’t enter the regression phase of the study. The researchers wrote that the resolution of hepatic steatosis was also consistent with improved glucose tolerance.
In transcriptomic and histologic analyses, the researchers found strong concordance between Foz/Foz mice NASH liver and human NASH.
The study also found that early disruption of gut barrier, microbial dysbiosis, lipopolysaccharide leakage, and intestinal inflammation preceded NASH in the Foz/Foz mice fed the Western diet, resulting in acute-phase liver inflammation. The early inflammation was reflected by an increase in several chemokines and cytokines by 1-2 weeks. As NASH progressed, the liver cytokine/chemokine profile continued to evolve, leading to monocyte recruitment predominance. “Further studies will elaborate the roles of these NASH-specific microbiomial features in the development and progression of NASH fibrosis,” wrote the researchers.
The study received financial support Janssen, in addition to funding from an ALF Liver Scholar award, ACTRI/National Institutes of Health, the SDDRC, and the NIAAA/National Institutes of Health. The authors disclosed no conflicts.
A new study sought to establish a new, clinically relevant mouse model of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) that closely reflects human disease as well as the multitissue dynamics involved in the progression and regression of the condition, according to the researchers. This study focused on the association between progression of NASH and consumption of a Western diet, as well as the development of HCC.
The study used a model consisting of hyperphagic mice that lacked a functional ALMS1 gene (Foz/Foz), in addition to wild-type littermates. The model ultimately defined “the key signaling and cytokine pathways that are critical for disease development and resolution” associated with NASH, wrote Souradipta Ganguly, PhD, of the University of California, San Diego, and colleagues. The report was published in Cellular and Molecular Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
According to the researchers, this study is unique given “current rodent models of NASH do not reproduce the complete spectrum of metabolic and histologic” nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) phenotypes. Likewise, the lack of “systemic studies in a single rodent model of NASH that closely recapitulates the human pathology” reinforces the importance of the new model, the researchers added.
Over time, NASH can progress to cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Studies that fed wild-type mice a Western diet have largely failed to mimic the full pathology of NASH to fibrosis to HCC. In addition, the models in these studies fail to reflect the multitissue injuries frequently observed in NASH.
To circumvent these challenges, Dr. Ganguly and colleagues used ALMS1-mutated mice to develop a rodent model of metabolic syndrome that included NASH with fibrosis, chronic kidney disease, and cardiovascular disease. The ALMS1 mutation also resulted in the mice becoming hyperphagic, which increases hunger and leads to early-onset obesity, among other conditions characteristic of metabolic syndrome.
Researchers fed the hyperphagic Foz/Foz mice and wild-type littermates a Western diet or standard diet during a 12-week period for NASH/fibrosis and a 24-week period for HCC. After NASH was established, mice were switched back to normal chow to see if the condition regressed.
Macronutrient distribution of the study’s Western diet included 40% fat, 15% protein, and 44% carbohydrates, based on total caloric content. In contrast, the standard chow included 12% fat, 23% protein, and 65% carbohydrates from total calories.
Within 1-2 weeks, Foz mice fed the Western diet were considered steatotic. These mice subsequently developed NASH by 4 weeks of the study and grade 3 fibrosis by 12 weeks. The researchers concurrently observed the development of chronic kidney injury in the animals. Mice continuing to the 24 weeks ultimately progressed to cirrhosis and HCC; these mice demonstrated reduced survival due to cardiac dysfunction.
Mice that developed NASH were then switched to a diet consisting of normal chow. Following this switch, NASH began to regress, and survival improved. These mice did not appear to develop HCC, and total liver weight was significantly reduced compared with the mice that didn’t enter the regression phase of the study. The researchers wrote that the resolution of hepatic steatosis was also consistent with improved glucose tolerance.
In transcriptomic and histologic analyses, the researchers found strong concordance between Foz/Foz mice NASH liver and human NASH.
The study also found that early disruption of gut barrier, microbial dysbiosis, lipopolysaccharide leakage, and intestinal inflammation preceded NASH in the Foz/Foz mice fed the Western diet, resulting in acute-phase liver inflammation. The early inflammation was reflected by an increase in several chemokines and cytokines by 1-2 weeks. As NASH progressed, the liver cytokine/chemokine profile continued to evolve, leading to monocyte recruitment predominance. “Further studies will elaborate the roles of these NASH-specific microbiomial features in the development and progression of NASH fibrosis,” wrote the researchers.
The study received financial support Janssen, in addition to funding from an ALF Liver Scholar award, ACTRI/National Institutes of Health, the SDDRC, and the NIAAA/National Institutes of Health. The authors disclosed no conflicts.
FROM CELLULAR AND MOLECULAR GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY
HBV screening often incomplete or forgone when starting tocilizumab, tofacitinib
People beginning treatment with the immunosuppressive drugs tocilizumab (Actemra) or tofacitinib (Xeljanz) are infrequently screened for hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection, according to a new study of patients with rheumatic diseases who are starting one of the two treatments.
“Perhaps not unexpectedly, these screening patterns conform more with recommendations from the American College of Rheumatology, which do not explicitly stipulate universal HBV screening,” wrote lead author Amir M. Mohareb, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston. The study was published in The Journal of Rheumatology.
To determine the frequency of HBV screening among this specific population, the researchers conducted a retrospective, cross-sectional study of patients 18 years or older within the Mass General Brigham health system in the Boston area who initiated either of the two drugs before Dec. 31, 2018. Tocilizumab was approved by the Food and Drug Administration on Jan. 11, 2010, and tofacitinib was approved on Nov. 6, 2012.
The final study population included 678 patients on tocilizumab and 391 patients on tofacitinib. The mean age of the patients in each group was 61 years for tocilizumab and 60 years for tofacitinib. A large majority were female (78% of the tocilizumab group, 88% of the tofacitinib group) and 84% of patients in both groups were white. Their primary diagnosis was rheumatoid arthritis (53% of the tocilizumab group, 77% of the tofacitinib group), and most of them – 57% of patients on tocilizumab and 72% of patients on tofacitinib – had a history of being on both conventional synthetic and biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs).
HBV screening patterns were classified into three categories: complete (all three of the HBV surface antigen [HBsAg], total core antibody [anti-HBcAb], and surface antibody [HBsAb] tests); partial (any one to two tests); and none. Of the 678 patients on tocilizumab, 194 (29%) underwent complete screening, 307 (45%) underwent partial screening, and 177 (26%) had no screening. Of the 391 patients on tofacitinib, 94 (24%) underwent complete screening, 195 (50%) underwent partial screening, and 102 (26%) had none.
Inappropriate testing – defined as either HBV e-antigen (HBeAg), anti-HBcAb IgM, or HBV DNA without a positive HBsAg or total anti-HBcAb – occurred in 22% of patients on tocilizumab and 23% of patients on tofacitinib. After multivariable analysis, the authors found that Whites were less likely to undergo complete screening (odds ratio, 0.74; 95% confidence interval, 0.57-0.95) compared to non-Whites. Previous use of immunosuppressive agents such as conventional synthetic DMARDs (OR, 1.05; 95% CI, 0.72-1.55) and biologic DMARDs with or without prior csDMARDs (OR, 0.73; 95% CI, 0.48-1.12) was not associated with a likelihood of complete appropriate screening.
“These data add to the evidence indicating that clinicians are not completing pretreatment screening for latent infections prior to patients starting high-risk immunosuppressant drugs,” Gabriela Schmajuk, MD, of the University of California, San Francisco, said in an interview. “It can be dangerous, since a fraction of these patients may reactivate latent infections with HBV that can result in liver failure or death.
“On the bright side,” she added, “we have antivirals that can be given as prophylaxis against reactivation of latent HBV if patients do test positive.”
Dr. Schmajuk was previously the senior author of a similar study from the 2019 American College of Rheumatology annual meeting that found only a small percentage of patients who were new users of biologics or new synthetic DMARDs were screened for HBV or hepatitis C virus.
When asked if anything in the study stood out, she acknowledged being “somewhat surprised that patients with prior immunosuppression did not have higher rates of screening. One might expect that since those patients had more opportunities for screening – since they started new medications more times – they would have higher rates, but this did not appear to be the case.”
As a message to rheumatologists who may be starting their patients on any biologic or new synthetic DMARD, she reinforced that “we need universal HBV screening for patients starting these medications. Many clinicians are used to ordering a hepatitis B surface antigen test, but one key message is that we also need to be ordering hepatitis B core antibody tests. Patients with a positive core antibody are still at risk for reactivation.”
The authors noted their study’s limitations, including the data being retrospectively collected and some of the subjects potentially being screened in laboratories outside of the Mass General Brigham health system. In addition, they stated that their findings “may not be generalizable to nonrheumatologic settings or other immunomodulators,” although they added that studies of other patient populations have also uncovered “similarly low HBV screening frequencies.”
Several of the authors reported being supported by institutes within the National Institutes of Health. Beyond that, they declared no potential conflicts of interest.
People beginning treatment with the immunosuppressive drugs tocilizumab (Actemra) or tofacitinib (Xeljanz) are infrequently screened for hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection, according to a new study of patients with rheumatic diseases who are starting one of the two treatments.
“Perhaps not unexpectedly, these screening patterns conform more with recommendations from the American College of Rheumatology, which do not explicitly stipulate universal HBV screening,” wrote lead author Amir M. Mohareb, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston. The study was published in The Journal of Rheumatology.
To determine the frequency of HBV screening among this specific population, the researchers conducted a retrospective, cross-sectional study of patients 18 years or older within the Mass General Brigham health system in the Boston area who initiated either of the two drugs before Dec. 31, 2018. Tocilizumab was approved by the Food and Drug Administration on Jan. 11, 2010, and tofacitinib was approved on Nov. 6, 2012.
The final study population included 678 patients on tocilizumab and 391 patients on tofacitinib. The mean age of the patients in each group was 61 years for tocilizumab and 60 years for tofacitinib. A large majority were female (78% of the tocilizumab group, 88% of the tofacitinib group) and 84% of patients in both groups were white. Their primary diagnosis was rheumatoid arthritis (53% of the tocilizumab group, 77% of the tofacitinib group), and most of them – 57% of patients on tocilizumab and 72% of patients on tofacitinib – had a history of being on both conventional synthetic and biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs).
HBV screening patterns were classified into three categories: complete (all three of the HBV surface antigen [HBsAg], total core antibody [anti-HBcAb], and surface antibody [HBsAb] tests); partial (any one to two tests); and none. Of the 678 patients on tocilizumab, 194 (29%) underwent complete screening, 307 (45%) underwent partial screening, and 177 (26%) had no screening. Of the 391 patients on tofacitinib, 94 (24%) underwent complete screening, 195 (50%) underwent partial screening, and 102 (26%) had none.
Inappropriate testing – defined as either HBV e-antigen (HBeAg), anti-HBcAb IgM, or HBV DNA without a positive HBsAg or total anti-HBcAb – occurred in 22% of patients on tocilizumab and 23% of patients on tofacitinib. After multivariable analysis, the authors found that Whites were less likely to undergo complete screening (odds ratio, 0.74; 95% confidence interval, 0.57-0.95) compared to non-Whites. Previous use of immunosuppressive agents such as conventional synthetic DMARDs (OR, 1.05; 95% CI, 0.72-1.55) and biologic DMARDs with or without prior csDMARDs (OR, 0.73; 95% CI, 0.48-1.12) was not associated with a likelihood of complete appropriate screening.
“These data add to the evidence indicating that clinicians are not completing pretreatment screening for latent infections prior to patients starting high-risk immunosuppressant drugs,” Gabriela Schmajuk, MD, of the University of California, San Francisco, said in an interview. “It can be dangerous, since a fraction of these patients may reactivate latent infections with HBV that can result in liver failure or death.
“On the bright side,” she added, “we have antivirals that can be given as prophylaxis against reactivation of latent HBV if patients do test positive.”
Dr. Schmajuk was previously the senior author of a similar study from the 2019 American College of Rheumatology annual meeting that found only a small percentage of patients who were new users of biologics or new synthetic DMARDs were screened for HBV or hepatitis C virus.
When asked if anything in the study stood out, she acknowledged being “somewhat surprised that patients with prior immunosuppression did not have higher rates of screening. One might expect that since those patients had more opportunities for screening – since they started new medications more times – they would have higher rates, but this did not appear to be the case.”
As a message to rheumatologists who may be starting their patients on any biologic or new synthetic DMARD, she reinforced that “we need universal HBV screening for patients starting these medications. Many clinicians are used to ordering a hepatitis B surface antigen test, but one key message is that we also need to be ordering hepatitis B core antibody tests. Patients with a positive core antibody are still at risk for reactivation.”
The authors noted their study’s limitations, including the data being retrospectively collected and some of the subjects potentially being screened in laboratories outside of the Mass General Brigham health system. In addition, they stated that their findings “may not be generalizable to nonrheumatologic settings or other immunomodulators,” although they added that studies of other patient populations have also uncovered “similarly low HBV screening frequencies.”
Several of the authors reported being supported by institutes within the National Institutes of Health. Beyond that, they declared no potential conflicts of interest.
People beginning treatment with the immunosuppressive drugs tocilizumab (Actemra) or tofacitinib (Xeljanz) are infrequently screened for hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection, according to a new study of patients with rheumatic diseases who are starting one of the two treatments.
“Perhaps not unexpectedly, these screening patterns conform more with recommendations from the American College of Rheumatology, which do not explicitly stipulate universal HBV screening,” wrote lead author Amir M. Mohareb, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston. The study was published in The Journal of Rheumatology.
To determine the frequency of HBV screening among this specific population, the researchers conducted a retrospective, cross-sectional study of patients 18 years or older within the Mass General Brigham health system in the Boston area who initiated either of the two drugs before Dec. 31, 2018. Tocilizumab was approved by the Food and Drug Administration on Jan. 11, 2010, and tofacitinib was approved on Nov. 6, 2012.
The final study population included 678 patients on tocilizumab and 391 patients on tofacitinib. The mean age of the patients in each group was 61 years for tocilizumab and 60 years for tofacitinib. A large majority were female (78% of the tocilizumab group, 88% of the tofacitinib group) and 84% of patients in both groups were white. Their primary diagnosis was rheumatoid arthritis (53% of the tocilizumab group, 77% of the tofacitinib group), and most of them – 57% of patients on tocilizumab and 72% of patients on tofacitinib – had a history of being on both conventional synthetic and biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs).
HBV screening patterns were classified into three categories: complete (all three of the HBV surface antigen [HBsAg], total core antibody [anti-HBcAb], and surface antibody [HBsAb] tests); partial (any one to two tests); and none. Of the 678 patients on tocilizumab, 194 (29%) underwent complete screening, 307 (45%) underwent partial screening, and 177 (26%) had no screening. Of the 391 patients on tofacitinib, 94 (24%) underwent complete screening, 195 (50%) underwent partial screening, and 102 (26%) had none.
Inappropriate testing – defined as either HBV e-antigen (HBeAg), anti-HBcAb IgM, or HBV DNA without a positive HBsAg or total anti-HBcAb – occurred in 22% of patients on tocilizumab and 23% of patients on tofacitinib. After multivariable analysis, the authors found that Whites were less likely to undergo complete screening (odds ratio, 0.74; 95% confidence interval, 0.57-0.95) compared to non-Whites. Previous use of immunosuppressive agents such as conventional synthetic DMARDs (OR, 1.05; 95% CI, 0.72-1.55) and biologic DMARDs with or without prior csDMARDs (OR, 0.73; 95% CI, 0.48-1.12) was not associated with a likelihood of complete appropriate screening.
“These data add to the evidence indicating that clinicians are not completing pretreatment screening for latent infections prior to patients starting high-risk immunosuppressant drugs,” Gabriela Schmajuk, MD, of the University of California, San Francisco, said in an interview. “It can be dangerous, since a fraction of these patients may reactivate latent infections with HBV that can result in liver failure or death.
“On the bright side,” she added, “we have antivirals that can be given as prophylaxis against reactivation of latent HBV if patients do test positive.”
Dr. Schmajuk was previously the senior author of a similar study from the 2019 American College of Rheumatology annual meeting that found only a small percentage of patients who were new users of biologics or new synthetic DMARDs were screened for HBV or hepatitis C virus.
When asked if anything in the study stood out, she acknowledged being “somewhat surprised that patients with prior immunosuppression did not have higher rates of screening. One might expect that since those patients had more opportunities for screening – since they started new medications more times – they would have higher rates, but this did not appear to be the case.”
As a message to rheumatologists who may be starting their patients on any biologic or new synthetic DMARD, she reinforced that “we need universal HBV screening for patients starting these medications. Many clinicians are used to ordering a hepatitis B surface antigen test, but one key message is that we also need to be ordering hepatitis B core antibody tests. Patients with a positive core antibody are still at risk for reactivation.”
The authors noted their study’s limitations, including the data being retrospectively collected and some of the subjects potentially being screened in laboratories outside of the Mass General Brigham health system. In addition, they stated that their findings “may not be generalizable to nonrheumatologic settings or other immunomodulators,” although they added that studies of other patient populations have also uncovered “similarly low HBV screening frequencies.”
Several of the authors reported being supported by institutes within the National Institutes of Health. Beyond that, they declared no potential conflicts of interest.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF RHEUMATOLOGY
Call to Action: Multidisciplinary panel urges coordinated care for ‘NASH epidemic’
A multidisciplinary panel of U.S. experts released a “Call to Action” for improved screening, diagnosis, and treatment of patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) on July 26, an effort organized by the American Gastroenterological Association in collaboration with seven other U.S. medical organizations including several endocrinology groups.
The published statement, “Preparing for the NASH Epidemic: A Call to Action,” proposes several urgent steps for the U.S. clinical community to provide better-focused and better-coordinated care for patients at risk for developing or having NAFLD or NASH, particularly among “emerging” at-risk cohorts such as patients with diabetes and obesity. It appears in the journals Gastroenterology, Diabetes Care, Metabolism: Clinical and Experimental, and Obesity.
The statement’s central pitch is that improvements in care won’t be possible unless the several medical specialties that deal with affected or at-risk patients stop working “in separate silos,” and instead create “a collective action plan,” and also organize multidisciplinary teams that “integrate primary care, hepatology, obesity medicine, endocrinology, and diabetology via well-defined care pathways.”
“The overarching goal” is a “unified, international public health response to NAFLD and NASH,” said the statement, which stemmed from a conference held in July 2020 that included representatives from not only the lead gastroenterology group but also the American Diabetes Association, the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists, The Endocrine Society, The American Academy of Family Physicians, The Obesity Society, and the American College of Osteopathic Family Physicians.
The statement cites sobering prevalence numbers, with estimates that NAFLD exists in more than half the patients with type 2 diabetes, while NASH affects about a third, rates that translate into many millions of affected Americans, given recent estimates that the U.S. prevalence of type 2 diabetes exceeds 30 million people. And the numbers continue to rise along with increases in the prevalence of obesity and type 2 diabetes.
“It’s an enormously common disease, and there are not enough gastroenterologists, to say nothing of hepatologists, to care for every patient with NAFLD,” said Anna Mae Diehl, MD, a gastroenterologist and professor at Duke University in Durham, N.C., who was not involved with the conference nor in writing the statement.
Clinical care pathways coming soon
Another key part of this initiative is development of clinical care pathways that will have “careful explication of each step in screening, diagnosis, and treatment,” and will be designed to inform the practice of primary care physicians (PCPs) as well as clinicians from the various specialties that deal with these patients.
The clinical care pathways are on track to come out later in 2021, said Fasiha Kanwal, MD, a professor and chief of gastroenterology at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston, and lead author on the Call to Action document.
“The Pathways will include practical recommendations about whom to screen and when to refer, and the criteria primary care physicians can use for diagnosis and risk stratification,” Dr. Kanwal said in an interview. “Patients can benefit from a standardized approach.”
The new document also includes results from a recent survey about NAFLD and NASH management completed by 751 U.S. physicians, including 401 (53%) primary care physicians, 175 gastroenterologists, (23%) and 175 endocrinologists (23%; percentages total 99% because of rounding).
The results showed “significant gaps in knowledge about whom to screen and how to diagnose and treat patients at high risk for NASH,” concluded the statement’s authors. Barely more than a third of the respondents knew that almost all patients with severe obesity likely have NAFLD, and fewer than half the endocrinologists and the primary care physicians appreciated that NAFLD is very common among patients with type 2 diabetes.
‘Understanding of NAFLD is not there’
“I applaud this effort that calls attention to an emerging public health problem. This paper and survey are great ideas. The findings are not surprising, but they’re important,” said Dr. Diehl said in an interview. “Much more needs to be done” including changes in social behavior and government policies.
“The public’s understanding of NAFLD is not there,” and many physicians also have an incomplete understanding of NAFLD and more serious stages of metabolic liver disease. “Physicians know that patients with obesity are at risk for heart disease, diabetes, and stroke, but they may not always be aware that these patients can also have cirrhosis,” noted Dr. Diehl, who published in 2019 a call to action for NAFLD of her own with some associates.
“My referrals are fueled by primary care physicians who recognize patients with significant liver disease. It would be great to outline recommended practice; I have no doubt that providers will embrace this,” as well as the broader concept of multidisciplinary teams, another focus of the statement. Dr. Diehl cited the “Cancer Center model,” where an oncologist takes primary responsibility for caring for a cancer patient while coordinating care with other specialists, an approach facilitated by EMRs that allow seamless data and chart sharing and something that many health systems have either already adopted or are moving toward.
She said the NASH Call to Action may help catalyze broader application of this model to many more patients with NAFLD or NASH, and noted that some U.S. centers already use this approach – including Dr. Diehl’s program at Duke – which brings together her gastroenterology colleagues with cardiologists, radiologists, endocrinologists, and bariatric surgeons. But she noted that for most patients with metabolic liver disease, the hub clinician needs to be a PCP, especially for patients with earlier-stage disease, because the number of affected patients is so huge.
“Key steps toward establishing such teams include establishing protocols for risk stratification and referral, definition of roles and responsibilities, and buy-in from institutions and payers. Clearly a lot of work needs to occur to get to these multidisciplinary teams,” said Dr. Kanwal.
Ralph A. DeFronzo, MD, professor and deputy director of the Texas Diabetes Institute at UT Health San Antonio, who was not involved with the conference or statement, had a different take on what the future of NASH and NAFLD care may look like.
“Endocrinologists, hepatologists, and obesity experts will work within their individual specialties to diagnose and manage NASH,” he said in an interview. But he acknowledged that “an integrated effort by specialists would be important” to help “primary care physicians who are less familiar with the disease.”
Controversy over pioglitazone?
Dr. DeFronzo endorsed development of clinical care pathways as “important,” but also as a potential source of “controversy, especially with respect to treatment.”
The Call to Action statement cites lifestyle-based therapies, such as an appropriate diet; regular, moderate exercise; and elimination when possible of obesogenic medications as cornerstone interventions for patients with NAFLD or early-stage NASH, interventions that can be prescribed by PCPs. For patients with NASH and stage 2 or worse fibrosis, the statement endorses liver-directed pharmacotherapy. While noting that no agents currently carry a Food and Drug Administration–approved indication for treating NASH, the statement cites evidence that 800 IU/day of vitamin E improves steatosis in patients with NASH but not type 2 diabetes.
For patients with type 2 diabetes, the statement notes that results from five randomized trials indicated that pioglitazone could reverse steatohepatitis, findings that led to its recommendation in guidelines from a modest circle of medical groups, including the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. However, the 2021 Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes from the American Diabetes Association gives these agents limited endorsement, saying: “Pioglitazone, vitamin E treatment, and liraglutide treatment of biopsy-proven nonalcoholic steatohepatitis have each been shown to improve liver histology, but effects on longer-term clinical outcomes are not known.”
“The strongest evidence by far is for pioglitazone for treating NAFLD and NASH,” said Dr. DeFronzo, a vocal proponent of the drug for this indication. But he added that “hepatologists don’t feel comfortable with drugs from the thiazolidinedione class,” which includes pioglitazone.
“We don’t yet know how to optimally configure the health system for NAFLD and NASH to make it more efficient and helpful to patients, but models exist, and the approach is evolving,” said Dr. Diehl.
Dr. Diehl and Dr. Kanwal had no relevant disclosures. Dr. DeFronzo has been a speaker on behalf of AstraZeneca and Novo Nordisk, has been an adviser to AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Intarcia, and Janssen, and has received research funding from AstraZeneca, Janssen and Merck.
A multidisciplinary panel of U.S. experts released a “Call to Action” for improved screening, diagnosis, and treatment of patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) on July 26, an effort organized by the American Gastroenterological Association in collaboration with seven other U.S. medical organizations including several endocrinology groups.
The published statement, “Preparing for the NASH Epidemic: A Call to Action,” proposes several urgent steps for the U.S. clinical community to provide better-focused and better-coordinated care for patients at risk for developing or having NAFLD or NASH, particularly among “emerging” at-risk cohorts such as patients with diabetes and obesity. It appears in the journals Gastroenterology, Diabetes Care, Metabolism: Clinical and Experimental, and Obesity.
The statement’s central pitch is that improvements in care won’t be possible unless the several medical specialties that deal with affected or at-risk patients stop working “in separate silos,” and instead create “a collective action plan,” and also organize multidisciplinary teams that “integrate primary care, hepatology, obesity medicine, endocrinology, and diabetology via well-defined care pathways.”
“The overarching goal” is a “unified, international public health response to NAFLD and NASH,” said the statement, which stemmed from a conference held in July 2020 that included representatives from not only the lead gastroenterology group but also the American Diabetes Association, the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists, The Endocrine Society, The American Academy of Family Physicians, The Obesity Society, and the American College of Osteopathic Family Physicians.
The statement cites sobering prevalence numbers, with estimates that NAFLD exists in more than half the patients with type 2 diabetes, while NASH affects about a third, rates that translate into many millions of affected Americans, given recent estimates that the U.S. prevalence of type 2 diabetes exceeds 30 million people. And the numbers continue to rise along with increases in the prevalence of obesity and type 2 diabetes.
“It’s an enormously common disease, and there are not enough gastroenterologists, to say nothing of hepatologists, to care for every patient with NAFLD,” said Anna Mae Diehl, MD, a gastroenterologist and professor at Duke University in Durham, N.C., who was not involved with the conference nor in writing the statement.
Clinical care pathways coming soon
Another key part of this initiative is development of clinical care pathways that will have “careful explication of each step in screening, diagnosis, and treatment,” and will be designed to inform the practice of primary care physicians (PCPs) as well as clinicians from the various specialties that deal with these patients.
The clinical care pathways are on track to come out later in 2021, said Fasiha Kanwal, MD, a professor and chief of gastroenterology at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston, and lead author on the Call to Action document.
“The Pathways will include practical recommendations about whom to screen and when to refer, and the criteria primary care physicians can use for diagnosis and risk stratification,” Dr. Kanwal said in an interview. “Patients can benefit from a standardized approach.”
The new document also includes results from a recent survey about NAFLD and NASH management completed by 751 U.S. physicians, including 401 (53%) primary care physicians, 175 gastroenterologists, (23%) and 175 endocrinologists (23%; percentages total 99% because of rounding).
The results showed “significant gaps in knowledge about whom to screen and how to diagnose and treat patients at high risk for NASH,” concluded the statement’s authors. Barely more than a third of the respondents knew that almost all patients with severe obesity likely have NAFLD, and fewer than half the endocrinologists and the primary care physicians appreciated that NAFLD is very common among patients with type 2 diabetes.
‘Understanding of NAFLD is not there’
“I applaud this effort that calls attention to an emerging public health problem. This paper and survey are great ideas. The findings are not surprising, but they’re important,” said Dr. Diehl said in an interview. “Much more needs to be done” including changes in social behavior and government policies.
“The public’s understanding of NAFLD is not there,” and many physicians also have an incomplete understanding of NAFLD and more serious stages of metabolic liver disease. “Physicians know that patients with obesity are at risk for heart disease, diabetes, and stroke, but they may not always be aware that these patients can also have cirrhosis,” noted Dr. Diehl, who published in 2019 a call to action for NAFLD of her own with some associates.
“My referrals are fueled by primary care physicians who recognize patients with significant liver disease. It would be great to outline recommended practice; I have no doubt that providers will embrace this,” as well as the broader concept of multidisciplinary teams, another focus of the statement. Dr. Diehl cited the “Cancer Center model,” where an oncologist takes primary responsibility for caring for a cancer patient while coordinating care with other specialists, an approach facilitated by EMRs that allow seamless data and chart sharing and something that many health systems have either already adopted or are moving toward.
She said the NASH Call to Action may help catalyze broader application of this model to many more patients with NAFLD or NASH, and noted that some U.S. centers already use this approach – including Dr. Diehl’s program at Duke – which brings together her gastroenterology colleagues with cardiologists, radiologists, endocrinologists, and bariatric surgeons. But she noted that for most patients with metabolic liver disease, the hub clinician needs to be a PCP, especially for patients with earlier-stage disease, because the number of affected patients is so huge.
“Key steps toward establishing such teams include establishing protocols for risk stratification and referral, definition of roles and responsibilities, and buy-in from institutions and payers. Clearly a lot of work needs to occur to get to these multidisciplinary teams,” said Dr. Kanwal.
Ralph A. DeFronzo, MD, professor and deputy director of the Texas Diabetes Institute at UT Health San Antonio, who was not involved with the conference or statement, had a different take on what the future of NASH and NAFLD care may look like.
“Endocrinologists, hepatologists, and obesity experts will work within their individual specialties to diagnose and manage NASH,” he said in an interview. But he acknowledged that “an integrated effort by specialists would be important” to help “primary care physicians who are less familiar with the disease.”
Controversy over pioglitazone?
Dr. DeFronzo endorsed development of clinical care pathways as “important,” but also as a potential source of “controversy, especially with respect to treatment.”
The Call to Action statement cites lifestyle-based therapies, such as an appropriate diet; regular, moderate exercise; and elimination when possible of obesogenic medications as cornerstone interventions for patients with NAFLD or early-stage NASH, interventions that can be prescribed by PCPs. For patients with NASH and stage 2 or worse fibrosis, the statement endorses liver-directed pharmacotherapy. While noting that no agents currently carry a Food and Drug Administration–approved indication for treating NASH, the statement cites evidence that 800 IU/day of vitamin E improves steatosis in patients with NASH but not type 2 diabetes.
For patients with type 2 diabetes, the statement notes that results from five randomized trials indicated that pioglitazone could reverse steatohepatitis, findings that led to its recommendation in guidelines from a modest circle of medical groups, including the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. However, the 2021 Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes from the American Diabetes Association gives these agents limited endorsement, saying: “Pioglitazone, vitamin E treatment, and liraglutide treatment of biopsy-proven nonalcoholic steatohepatitis have each been shown to improve liver histology, but effects on longer-term clinical outcomes are not known.”
“The strongest evidence by far is for pioglitazone for treating NAFLD and NASH,” said Dr. DeFronzo, a vocal proponent of the drug for this indication. But he added that “hepatologists don’t feel comfortable with drugs from the thiazolidinedione class,” which includes pioglitazone.
“We don’t yet know how to optimally configure the health system for NAFLD and NASH to make it more efficient and helpful to patients, but models exist, and the approach is evolving,” said Dr. Diehl.
Dr. Diehl and Dr. Kanwal had no relevant disclosures. Dr. DeFronzo has been a speaker on behalf of AstraZeneca and Novo Nordisk, has been an adviser to AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Intarcia, and Janssen, and has received research funding from AstraZeneca, Janssen and Merck.
A multidisciplinary panel of U.S. experts released a “Call to Action” for improved screening, diagnosis, and treatment of patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) on July 26, an effort organized by the American Gastroenterological Association in collaboration with seven other U.S. medical organizations including several endocrinology groups.
The published statement, “Preparing for the NASH Epidemic: A Call to Action,” proposes several urgent steps for the U.S. clinical community to provide better-focused and better-coordinated care for patients at risk for developing or having NAFLD or NASH, particularly among “emerging” at-risk cohorts such as patients with diabetes and obesity. It appears in the journals Gastroenterology, Diabetes Care, Metabolism: Clinical and Experimental, and Obesity.
The statement’s central pitch is that improvements in care won’t be possible unless the several medical specialties that deal with affected or at-risk patients stop working “in separate silos,” and instead create “a collective action plan,” and also organize multidisciplinary teams that “integrate primary care, hepatology, obesity medicine, endocrinology, and diabetology via well-defined care pathways.”
“The overarching goal” is a “unified, international public health response to NAFLD and NASH,” said the statement, which stemmed from a conference held in July 2020 that included representatives from not only the lead gastroenterology group but also the American Diabetes Association, the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists, The Endocrine Society, The American Academy of Family Physicians, The Obesity Society, and the American College of Osteopathic Family Physicians.
The statement cites sobering prevalence numbers, with estimates that NAFLD exists in more than half the patients with type 2 diabetes, while NASH affects about a third, rates that translate into many millions of affected Americans, given recent estimates that the U.S. prevalence of type 2 diabetes exceeds 30 million people. And the numbers continue to rise along with increases in the prevalence of obesity and type 2 diabetes.
“It’s an enormously common disease, and there are not enough gastroenterologists, to say nothing of hepatologists, to care for every patient with NAFLD,” said Anna Mae Diehl, MD, a gastroenterologist and professor at Duke University in Durham, N.C., who was not involved with the conference nor in writing the statement.
Clinical care pathways coming soon
Another key part of this initiative is development of clinical care pathways that will have “careful explication of each step in screening, diagnosis, and treatment,” and will be designed to inform the practice of primary care physicians (PCPs) as well as clinicians from the various specialties that deal with these patients.
The clinical care pathways are on track to come out later in 2021, said Fasiha Kanwal, MD, a professor and chief of gastroenterology at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston, and lead author on the Call to Action document.
“The Pathways will include practical recommendations about whom to screen and when to refer, and the criteria primary care physicians can use for diagnosis and risk stratification,” Dr. Kanwal said in an interview. “Patients can benefit from a standardized approach.”
The new document also includes results from a recent survey about NAFLD and NASH management completed by 751 U.S. physicians, including 401 (53%) primary care physicians, 175 gastroenterologists, (23%) and 175 endocrinologists (23%; percentages total 99% because of rounding).
The results showed “significant gaps in knowledge about whom to screen and how to diagnose and treat patients at high risk for NASH,” concluded the statement’s authors. Barely more than a third of the respondents knew that almost all patients with severe obesity likely have NAFLD, and fewer than half the endocrinologists and the primary care physicians appreciated that NAFLD is very common among patients with type 2 diabetes.
‘Understanding of NAFLD is not there’
“I applaud this effort that calls attention to an emerging public health problem. This paper and survey are great ideas. The findings are not surprising, but they’re important,” said Dr. Diehl said in an interview. “Much more needs to be done” including changes in social behavior and government policies.
“The public’s understanding of NAFLD is not there,” and many physicians also have an incomplete understanding of NAFLD and more serious stages of metabolic liver disease. “Physicians know that patients with obesity are at risk for heart disease, diabetes, and stroke, but they may not always be aware that these patients can also have cirrhosis,” noted Dr. Diehl, who published in 2019 a call to action for NAFLD of her own with some associates.
“My referrals are fueled by primary care physicians who recognize patients with significant liver disease. It would be great to outline recommended practice; I have no doubt that providers will embrace this,” as well as the broader concept of multidisciplinary teams, another focus of the statement. Dr. Diehl cited the “Cancer Center model,” where an oncologist takes primary responsibility for caring for a cancer patient while coordinating care with other specialists, an approach facilitated by EMRs that allow seamless data and chart sharing and something that many health systems have either already adopted or are moving toward.
She said the NASH Call to Action may help catalyze broader application of this model to many more patients with NAFLD or NASH, and noted that some U.S. centers already use this approach – including Dr. Diehl’s program at Duke – which brings together her gastroenterology colleagues with cardiologists, radiologists, endocrinologists, and bariatric surgeons. But she noted that for most patients with metabolic liver disease, the hub clinician needs to be a PCP, especially for patients with earlier-stage disease, because the number of affected patients is so huge.
“Key steps toward establishing such teams include establishing protocols for risk stratification and referral, definition of roles and responsibilities, and buy-in from institutions and payers. Clearly a lot of work needs to occur to get to these multidisciplinary teams,” said Dr. Kanwal.
Ralph A. DeFronzo, MD, professor and deputy director of the Texas Diabetes Institute at UT Health San Antonio, who was not involved with the conference or statement, had a different take on what the future of NASH and NAFLD care may look like.
“Endocrinologists, hepatologists, and obesity experts will work within their individual specialties to diagnose and manage NASH,” he said in an interview. But he acknowledged that “an integrated effort by specialists would be important” to help “primary care physicians who are less familiar with the disease.”
Controversy over pioglitazone?
Dr. DeFronzo endorsed development of clinical care pathways as “important,” but also as a potential source of “controversy, especially with respect to treatment.”
The Call to Action statement cites lifestyle-based therapies, such as an appropriate diet; regular, moderate exercise; and elimination when possible of obesogenic medications as cornerstone interventions for patients with NAFLD or early-stage NASH, interventions that can be prescribed by PCPs. For patients with NASH and stage 2 or worse fibrosis, the statement endorses liver-directed pharmacotherapy. While noting that no agents currently carry a Food and Drug Administration–approved indication for treating NASH, the statement cites evidence that 800 IU/day of vitamin E improves steatosis in patients with NASH but not type 2 diabetes.
For patients with type 2 diabetes, the statement notes that results from five randomized trials indicated that pioglitazone could reverse steatohepatitis, findings that led to its recommendation in guidelines from a modest circle of medical groups, including the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. However, the 2021 Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes from the American Diabetes Association gives these agents limited endorsement, saying: “Pioglitazone, vitamin E treatment, and liraglutide treatment of biopsy-proven nonalcoholic steatohepatitis have each been shown to improve liver histology, but effects on longer-term clinical outcomes are not known.”
“The strongest evidence by far is for pioglitazone for treating NAFLD and NASH,” said Dr. DeFronzo, a vocal proponent of the drug for this indication. But he added that “hepatologists don’t feel comfortable with drugs from the thiazolidinedione class,” which includes pioglitazone.
“We don’t yet know how to optimally configure the health system for NAFLD and NASH to make it more efficient and helpful to patients, but models exist, and the approach is evolving,” said Dr. Diehl.
Dr. Diehl and Dr. Kanwal had no relevant disclosures. Dr. DeFronzo has been a speaker on behalf of AstraZeneca and Novo Nordisk, has been an adviser to AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Intarcia, and Janssen, and has received research funding from AstraZeneca, Janssen and Merck.
Good survival, outcomes with TARE for HCC in practice
Patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) can be offered transarterial radioembolization (TARE) as a safe and effective first-line treatment or adjunct to other locoregional therapies, authors of a large multicenter study reported.
Among 422 patients with HCC treated with TARE in eight European countries, the median overall survival was 16.5 months, with fewer than 10% of patients experiencing grade 3 or greater adverse events, reported Frank Kolligs, MD, from Helios Hospital Berlin-Buch.
“This exploratory study evaluated factors that can influence the application and outcome of transarterial radioembolization in clinical practice. TARE is generally applied according to guideline recommendations, and randomized, controlled trials are needed to confirm the effect of personalized dosimetry on the effectiveness of TARE,” he said in an oral abstract presented at the meeting sponsored by the European Association for the Study of the Liver.
Intriguingly, the investigators found evidence suggesting that patients whose treatments were planned using a partition model had better survival outcomes than those patients who treatments were based on calculated body surface area or measured BSA (mBSA), but this finding will need to be explored in more detail, Dr. Kolligs said.
The partition model incorporates variables such as tumor volume and liver volume, shunt fractions, the ratio of radiation uptake between tumor and normal tissues, vascular anatomy and other factors to estimate the optimal dose.
Study design
Dr. Kolligs and colleagues looked at prospective data from the Cardiovascular and Interventional Radiological Society of Europe (CIRSE) Registry for SIR-Spheres Therapy to evaluate the real-world clinical application of TARE with yttrium Y-90 resin microspheres in Europe, clinical outcomes, safety, and quality of life.
They selected data from centers with a minimum of 10 cases performed in the previous 12 months and at least 40 total cases overall.
The patients included adults 18 years and older scheduled for treatment with Y-90 resin microspheres for primary or metastatic liver tumors, with no specific exclusion criteria. The patients were followed for at least 24 months at recommended intervals of every 3 months. The first patient was enrolled in January 2015, and the last follow-up visit was in December 2019. A total of 422 registry patients had a diagnosis of HCC and were included in the study.
The median age was 68 years (range, 60-74), 80.8% were male, 70.9% had cirrhosis, 14.5% had ascites, and 8.5% had extrahepatic disease. About 32% of patients had one tumor nodule, 33% had two to five nodules, and the remainder had either more than five or an uncountable number.
In all, 14% of patients had Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer stage A disease, 51.4% had stage B, 33.6% had stage C, and 0.9% stage D.
About one-third of patients had portal vein occlusion. Tumors were in both left and right lobes in 35.5%, the left lobe alone in 12.1%, and the right lobe alone in 52.4%.
Half of all patients (50.2%) received TARE as first-line therapy, 44.8% had it following surgery (17.1%), ablation (14.7%), and/or transarterial chemoembolization (; 23%). In addition, 9.7% of patients received systemic therapy prior to TARE, primarily with sorafenib (Nexavar).
Treatment intent was palliative for 57.3% of patients, and tumor downsizing/downstaging in 32.5% (remainder unspecified).
Survival and prognostic factors
As noted before, median overall survival was 16.5 months. Median progression-free survival was 6.1 months, and median hepatic PFS was 6.7 months.
Factors prognostic for better overall survival included hepatitis B or C virus as the cirrhosis cause versus alcohol (hazard ratio for death, 0.51 for each; P = .0060 for HBV and P = .0007 for HCV); unilobar versus bilobar tumors (HR, 0.67; P = .0422 for left-lobe; HR 0.55; P < .0001 for right); prior surgery (HR, 0.67; P = .0258); prior ablation (HR, 0.65; P = .0394); and curative versus palliative intent (HR, 0.53; P < .0001).
Factors associated with worse overall survival were presence of ascites (HR 1.75, P = .001); presence of extrahepatic disease before TARE (HR, 1.81, P = .0037); tumor burden greater than 5 nodules (HR, 1.67; P = .0073); main portal vein occlusion (HR, 2.14; P = .0064); lobar portal vein occlusion (HR, 1.77; P = .0083); total bilirubin greater than 1.5 mg/dL (HR, 1.69; P = .0094); albumin-bilirubin grade A2 (HR, 1.66; P = .0005); ALB1 grade A3 (HR, 3.92; P < .0001); and BSA/mBSA versus partition-model dosimetry (HR, 1.89; P < .0001).
The safety analysis showed that 36.7% of patients had at least one adverse event, but only 7.1% had at least one grade 3 or greater event.
Grade 3 or greater events were abdominal pain (nine patients), fatigue (six), nausea (three), radioembolization-induced liver disease (three), vomiting (two), and GI ulceration (one). Fifteen additional patients had other unspecified events.
The investigators acknowledged broad inclusion criteria, relatively high rates of loss to follow-up, and differences in national guidelines and local standards of practice as potential limitations to their findings.
In the question-and-answer following the presentation, session comoderator María Varela, MD, PhD, a pathologist in the liver unit at the Hospital Universitario Central de Asturia, Oviedo, Spain, questioned why about one-third of patients received TARE for downstaging, but only 13 underwent subsequent surgical resection.
“We don’t have a detailed analysis of this subgroup of patients who received curative intent as yet, ” Dr. Kolligs said.
Pierre Nahon, MD, from the University of Paris and Hôpital Jean Verdier in Bondy, France, commented that, among this heterogenous population, one of the best indications for TARE is probably localized HCC with adjacent portal vein thrombosis.
He asked whether the investigators had examined overall survival among patients with localized unilobar HCC with adjacent small portal vein thrombosis.
“We find that patients with portal vein occlusion have a worse prognosis in the total group,” Dr. Kolligs replied. “To look into the question whether partial thrombosis with a small tumor might benefit is an interesting question, and we should look into that, but I don’t have any data on that yet.”
Another audience member asked: “According to your data, which patients are the best candidates for radioembolization?”
“According to these data, the best candidates are of course patients with good liver function, ascites should ideally not be present, and what is probably is important is that we identify or include patients without extrahepatic disease,” he said.
The study was sponsored by CIRSE. Dr. Kolligs disclosed speaking activities and consulting for several companies. Dr. Varela disclosed speaking for several companies and advisory board activity for Bayer. Dr. Nahon disclosed honoraria and consulting fees from several companies.
Patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) can be offered transarterial radioembolization (TARE) as a safe and effective first-line treatment or adjunct to other locoregional therapies, authors of a large multicenter study reported.
Among 422 patients with HCC treated with TARE in eight European countries, the median overall survival was 16.5 months, with fewer than 10% of patients experiencing grade 3 or greater adverse events, reported Frank Kolligs, MD, from Helios Hospital Berlin-Buch.
“This exploratory study evaluated factors that can influence the application and outcome of transarterial radioembolization in clinical practice. TARE is generally applied according to guideline recommendations, and randomized, controlled trials are needed to confirm the effect of personalized dosimetry on the effectiveness of TARE,” he said in an oral abstract presented at the meeting sponsored by the European Association for the Study of the Liver.
Intriguingly, the investigators found evidence suggesting that patients whose treatments were planned using a partition model had better survival outcomes than those patients who treatments were based on calculated body surface area or measured BSA (mBSA), but this finding will need to be explored in more detail, Dr. Kolligs said.
The partition model incorporates variables such as tumor volume and liver volume, shunt fractions, the ratio of radiation uptake between tumor and normal tissues, vascular anatomy and other factors to estimate the optimal dose.
Study design
Dr. Kolligs and colleagues looked at prospective data from the Cardiovascular and Interventional Radiological Society of Europe (CIRSE) Registry for SIR-Spheres Therapy to evaluate the real-world clinical application of TARE with yttrium Y-90 resin microspheres in Europe, clinical outcomes, safety, and quality of life.
They selected data from centers with a minimum of 10 cases performed in the previous 12 months and at least 40 total cases overall.
The patients included adults 18 years and older scheduled for treatment with Y-90 resin microspheres for primary or metastatic liver tumors, with no specific exclusion criteria. The patients were followed for at least 24 months at recommended intervals of every 3 months. The first patient was enrolled in January 2015, and the last follow-up visit was in December 2019. A total of 422 registry patients had a diagnosis of HCC and were included in the study.
The median age was 68 years (range, 60-74), 80.8% were male, 70.9% had cirrhosis, 14.5% had ascites, and 8.5% had extrahepatic disease. About 32% of patients had one tumor nodule, 33% had two to five nodules, and the remainder had either more than five or an uncountable number.
In all, 14% of patients had Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer stage A disease, 51.4% had stage B, 33.6% had stage C, and 0.9% stage D.
About one-third of patients had portal vein occlusion. Tumors were in both left and right lobes in 35.5%, the left lobe alone in 12.1%, and the right lobe alone in 52.4%.
Half of all patients (50.2%) received TARE as first-line therapy, 44.8% had it following surgery (17.1%), ablation (14.7%), and/or transarterial chemoembolization (; 23%). In addition, 9.7% of patients received systemic therapy prior to TARE, primarily with sorafenib (Nexavar).
Treatment intent was palliative for 57.3% of patients, and tumor downsizing/downstaging in 32.5% (remainder unspecified).
Survival and prognostic factors
As noted before, median overall survival was 16.5 months. Median progression-free survival was 6.1 months, and median hepatic PFS was 6.7 months.
Factors prognostic for better overall survival included hepatitis B or C virus as the cirrhosis cause versus alcohol (hazard ratio for death, 0.51 for each; P = .0060 for HBV and P = .0007 for HCV); unilobar versus bilobar tumors (HR, 0.67; P = .0422 for left-lobe; HR 0.55; P < .0001 for right); prior surgery (HR, 0.67; P = .0258); prior ablation (HR, 0.65; P = .0394); and curative versus palliative intent (HR, 0.53; P < .0001).
Factors associated with worse overall survival were presence of ascites (HR 1.75, P = .001); presence of extrahepatic disease before TARE (HR, 1.81, P = .0037); tumor burden greater than 5 nodules (HR, 1.67; P = .0073); main portal vein occlusion (HR, 2.14; P = .0064); lobar portal vein occlusion (HR, 1.77; P = .0083); total bilirubin greater than 1.5 mg/dL (HR, 1.69; P = .0094); albumin-bilirubin grade A2 (HR, 1.66; P = .0005); ALB1 grade A3 (HR, 3.92; P < .0001); and BSA/mBSA versus partition-model dosimetry (HR, 1.89; P < .0001).
The safety analysis showed that 36.7% of patients had at least one adverse event, but only 7.1% had at least one grade 3 or greater event.
Grade 3 or greater events were abdominal pain (nine patients), fatigue (six), nausea (three), radioembolization-induced liver disease (three), vomiting (two), and GI ulceration (one). Fifteen additional patients had other unspecified events.
The investigators acknowledged broad inclusion criteria, relatively high rates of loss to follow-up, and differences in national guidelines and local standards of practice as potential limitations to their findings.
In the question-and-answer following the presentation, session comoderator María Varela, MD, PhD, a pathologist in the liver unit at the Hospital Universitario Central de Asturia, Oviedo, Spain, questioned why about one-third of patients received TARE for downstaging, but only 13 underwent subsequent surgical resection.
“We don’t have a detailed analysis of this subgroup of patients who received curative intent as yet, ” Dr. Kolligs said.
Pierre Nahon, MD, from the University of Paris and Hôpital Jean Verdier in Bondy, France, commented that, among this heterogenous population, one of the best indications for TARE is probably localized HCC with adjacent portal vein thrombosis.
He asked whether the investigators had examined overall survival among patients with localized unilobar HCC with adjacent small portal vein thrombosis.
“We find that patients with portal vein occlusion have a worse prognosis in the total group,” Dr. Kolligs replied. “To look into the question whether partial thrombosis with a small tumor might benefit is an interesting question, and we should look into that, but I don’t have any data on that yet.”
Another audience member asked: “According to your data, which patients are the best candidates for radioembolization?”
“According to these data, the best candidates are of course patients with good liver function, ascites should ideally not be present, and what is probably is important is that we identify or include patients without extrahepatic disease,” he said.
The study was sponsored by CIRSE. Dr. Kolligs disclosed speaking activities and consulting for several companies. Dr. Varela disclosed speaking for several companies and advisory board activity for Bayer. Dr. Nahon disclosed honoraria and consulting fees from several companies.
Patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) can be offered transarterial radioembolization (TARE) as a safe and effective first-line treatment or adjunct to other locoregional therapies, authors of a large multicenter study reported.
Among 422 patients with HCC treated with TARE in eight European countries, the median overall survival was 16.5 months, with fewer than 10% of patients experiencing grade 3 or greater adverse events, reported Frank Kolligs, MD, from Helios Hospital Berlin-Buch.
“This exploratory study evaluated factors that can influence the application and outcome of transarterial radioembolization in clinical practice. TARE is generally applied according to guideline recommendations, and randomized, controlled trials are needed to confirm the effect of personalized dosimetry on the effectiveness of TARE,” he said in an oral abstract presented at the meeting sponsored by the European Association for the Study of the Liver.
Intriguingly, the investigators found evidence suggesting that patients whose treatments were planned using a partition model had better survival outcomes than those patients who treatments were based on calculated body surface area or measured BSA (mBSA), but this finding will need to be explored in more detail, Dr. Kolligs said.
The partition model incorporates variables such as tumor volume and liver volume, shunt fractions, the ratio of radiation uptake between tumor and normal tissues, vascular anatomy and other factors to estimate the optimal dose.
Study design
Dr. Kolligs and colleagues looked at prospective data from the Cardiovascular and Interventional Radiological Society of Europe (CIRSE) Registry for SIR-Spheres Therapy to evaluate the real-world clinical application of TARE with yttrium Y-90 resin microspheres in Europe, clinical outcomes, safety, and quality of life.
They selected data from centers with a minimum of 10 cases performed in the previous 12 months and at least 40 total cases overall.
The patients included adults 18 years and older scheduled for treatment with Y-90 resin microspheres for primary or metastatic liver tumors, with no specific exclusion criteria. The patients were followed for at least 24 months at recommended intervals of every 3 months. The first patient was enrolled in January 2015, and the last follow-up visit was in December 2019. A total of 422 registry patients had a diagnosis of HCC and were included in the study.
The median age was 68 years (range, 60-74), 80.8% were male, 70.9% had cirrhosis, 14.5% had ascites, and 8.5% had extrahepatic disease. About 32% of patients had one tumor nodule, 33% had two to five nodules, and the remainder had either more than five or an uncountable number.
In all, 14% of patients had Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer stage A disease, 51.4% had stage B, 33.6% had stage C, and 0.9% stage D.
About one-third of patients had portal vein occlusion. Tumors were in both left and right lobes in 35.5%, the left lobe alone in 12.1%, and the right lobe alone in 52.4%.
Half of all patients (50.2%) received TARE as first-line therapy, 44.8% had it following surgery (17.1%), ablation (14.7%), and/or transarterial chemoembolization (; 23%). In addition, 9.7% of patients received systemic therapy prior to TARE, primarily with sorafenib (Nexavar).
Treatment intent was palliative for 57.3% of patients, and tumor downsizing/downstaging in 32.5% (remainder unspecified).
Survival and prognostic factors
As noted before, median overall survival was 16.5 months. Median progression-free survival was 6.1 months, and median hepatic PFS was 6.7 months.
Factors prognostic for better overall survival included hepatitis B or C virus as the cirrhosis cause versus alcohol (hazard ratio for death, 0.51 for each; P = .0060 for HBV and P = .0007 for HCV); unilobar versus bilobar tumors (HR, 0.67; P = .0422 for left-lobe; HR 0.55; P < .0001 for right); prior surgery (HR, 0.67; P = .0258); prior ablation (HR, 0.65; P = .0394); and curative versus palliative intent (HR, 0.53; P < .0001).
Factors associated with worse overall survival were presence of ascites (HR 1.75, P = .001); presence of extrahepatic disease before TARE (HR, 1.81, P = .0037); tumor burden greater than 5 nodules (HR, 1.67; P = .0073); main portal vein occlusion (HR, 2.14; P = .0064); lobar portal vein occlusion (HR, 1.77; P = .0083); total bilirubin greater than 1.5 mg/dL (HR, 1.69; P = .0094); albumin-bilirubin grade A2 (HR, 1.66; P = .0005); ALB1 grade A3 (HR, 3.92; P < .0001); and BSA/mBSA versus partition-model dosimetry (HR, 1.89; P < .0001).
The safety analysis showed that 36.7% of patients had at least one adverse event, but only 7.1% had at least one grade 3 or greater event.
Grade 3 or greater events were abdominal pain (nine patients), fatigue (six), nausea (three), radioembolization-induced liver disease (three), vomiting (two), and GI ulceration (one). Fifteen additional patients had other unspecified events.
The investigators acknowledged broad inclusion criteria, relatively high rates of loss to follow-up, and differences in national guidelines and local standards of practice as potential limitations to their findings.
In the question-and-answer following the presentation, session comoderator María Varela, MD, PhD, a pathologist in the liver unit at the Hospital Universitario Central de Asturia, Oviedo, Spain, questioned why about one-third of patients received TARE for downstaging, but only 13 underwent subsequent surgical resection.
“We don’t have a detailed analysis of this subgroup of patients who received curative intent as yet, ” Dr. Kolligs said.
Pierre Nahon, MD, from the University of Paris and Hôpital Jean Verdier in Bondy, France, commented that, among this heterogenous population, one of the best indications for TARE is probably localized HCC with adjacent portal vein thrombosis.
He asked whether the investigators had examined overall survival among patients with localized unilobar HCC with adjacent small portal vein thrombosis.
“We find that patients with portal vein occlusion have a worse prognosis in the total group,” Dr. Kolligs replied. “To look into the question whether partial thrombosis with a small tumor might benefit is an interesting question, and we should look into that, but I don’t have any data on that yet.”
Another audience member asked: “According to your data, which patients are the best candidates for radioembolization?”
“According to these data, the best candidates are of course patients with good liver function, ascites should ideally not be present, and what is probably is important is that we identify or include patients without extrahepatic disease,” he said.
The study was sponsored by CIRSE. Dr. Kolligs disclosed speaking activities and consulting for several companies. Dr. Varela disclosed speaking for several companies and advisory board activity for Bayer. Dr. Nahon disclosed honoraria and consulting fees from several companies.
FROM ILC 2021
Fibrosis severity in ALD predicts survival
Moderate fibrosis in patients with alcoholic liver disease is not a benign condition, say investigators who studied the natural history of ALD according to biopsy-proven fibrosis stage.
In a study of 422 patients who were followed for a median of 43 months, 5.8% of patients with no or minimal fibrosis had a liver decompensation event. This compares with 21% (hazard ratio, 3.8; 95% confidence interval, 1.9-7.5; P < .01) of patients with significant fibrosis and 45% (HR, 9.6; 95% CI, 5.2-18.0; P < .01) of patients with advanced fibrosis, said Ditlev Nytoft Rasmussen, PhD, in an oral presentation at the meeting sponsored by the European Association for the Study of the Liver.
“The most obvious implication of this study is that the stage of fibrosis is a very strong predictor for the prognosis in early asymptomatic alcohol-related liver disease,” he said.
The findings suggest that gastroenterologists do not need to follow patients with no or only minor fibrosis, but patients with significant (F2) fibrosis, or greater, should be closely followed, said Dr. Rasmussen, who is with the FLASH Center for Liver Research at Odense (Denmark) University.
A gastroenterologist who was not involved in the study commented on the excess mortality the investigators saw.
“The really striking finding here to me is the excess mortality in the significant fibrosis group. They are not healthy, and some of that excess mortality does appear to be liver related, but some of it may not be liver related,“ said Esperance A. Schaefer, MD, MPH, of Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston.
“I think it will be important to be vigilant about the causes of death that are not liver related in patients with significant and advanced fibrosis, and the healthy group,” she said in an interview.
Ewan H. Forrest, MD, from the University of Glasgow, who was not involved in the study, said: “These are a challenging group of patients to identify with early disease. You quite rightly raise the question of how we should follow-up with these patients.”
Managing asymptomatic patients
Although noninvasive tests can identify ALD in the early fibrotic stage, it’s unclear how patients with early asymptomatic disease should be managed, Dr. Rasmussen said.
This uncertainty prompted FLASH investigators to study patients with ALD to determine how fibrosis affected outcomes such as decompensation, hospitalization, and death.
They looked at a prospective cohort of patients diagnosed with ALD by biopsy and transient elastography (FibroScan) from 2013 to 2018. Follow-up data for the patients were collected retrospectively from electronic health records or charts.
The patients, who all had alcohol overuse and no history of decompensation or other etiologies at baseline, were classified into three groups: 225 liver-healthy patients with minimal to no fibrosis (F1 or transient elastography <6 kPa kPa); 104 patients with significant fibrosis (F2); and, 93 patients with advanced fibrosis (F3 or F4).
The median patient age was 57 years, and 75% of the patients were men. The patients were followed for 1,149 patient-years.
Findings and outcomes
During follow-up, 53 patients died, and 51 had a decompensation event: overt hepatoencephalopathy, ascites, variceal bleeding, hepatorenal syndrome, or jaundice. Of the 51 patients, 27 died.
There was a protocol change during the study, with the new protocol stating that patients with transient elastography below 6 kPa could not undergo biopsy. Based on the 106 patients who had both a FibroScan and biopsy, of whom 20% had F2 fibrosis, the investigators calculated that 14 patients who did not undergo biopsy may have been incorrectly classified as having healthy livers, Dr. Rasmussen said.
Patients with healthy livers had a significantly better decompensation-free survival rates, with only 5.8% of those with healthy livers having a decompensation event out to 4.5 years, compared with 21% of patients with significant fibrosis or advanced fibrosis.
Within the first year of follow-up, 98% of patients with healthy livers were alive and free of decompensations, compared with 94% with significant fibrosis and 84% with advanced fibrosis. The respective rates at 3 years were 95%, 82%, and 55%.
The percentage of hospital admissions that were liver related was 5% in the healthy-liver group, 24% in the significant group, and 47% in the advanced group.
Ongoing alcohol use during follow-up was also a significant predictor of worse decompensation-free survival (HR, 1.6; P = .04), with two in three decompensation events occurring in patients with alcohol overuse. The effect of alcohol was less strong than fibrosis stage, however, Dr. Rasmussen noted.
Dr. Schaefer said that “we see individuals who with heavy alcohol use progress much more rapidly than you’d anticipate with the rule of thumb that you see in other diseases of one fibrosis stage every 5-7 years.”
Among the strengths of this study included the use of biopsy and the inclusion of all stages of fibrosis. The investigators acknowledged as potential limitations the retrospective collection of follow-up data, reliance on medical charts to estimate alcohol consumption, and the single-center design.
The study was supported by grants from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program and the Novo Nordisk Foundation Challenge program. Dr. Rasmussen, Dr. Schaefer, and Dr. Forrest reported no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Moderate fibrosis in patients with alcoholic liver disease is not a benign condition, say investigators who studied the natural history of ALD according to biopsy-proven fibrosis stage.
In a study of 422 patients who were followed for a median of 43 months, 5.8% of patients with no or minimal fibrosis had a liver decompensation event. This compares with 21% (hazard ratio, 3.8; 95% confidence interval, 1.9-7.5; P < .01) of patients with significant fibrosis and 45% (HR, 9.6; 95% CI, 5.2-18.0; P < .01) of patients with advanced fibrosis, said Ditlev Nytoft Rasmussen, PhD, in an oral presentation at the meeting sponsored by the European Association for the Study of the Liver.
“The most obvious implication of this study is that the stage of fibrosis is a very strong predictor for the prognosis in early asymptomatic alcohol-related liver disease,” he said.
The findings suggest that gastroenterologists do not need to follow patients with no or only minor fibrosis, but patients with significant (F2) fibrosis, or greater, should be closely followed, said Dr. Rasmussen, who is with the FLASH Center for Liver Research at Odense (Denmark) University.
A gastroenterologist who was not involved in the study commented on the excess mortality the investigators saw.
“The really striking finding here to me is the excess mortality in the significant fibrosis group. They are not healthy, and some of that excess mortality does appear to be liver related, but some of it may not be liver related,“ said Esperance A. Schaefer, MD, MPH, of Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston.
“I think it will be important to be vigilant about the causes of death that are not liver related in patients with significant and advanced fibrosis, and the healthy group,” she said in an interview.
Ewan H. Forrest, MD, from the University of Glasgow, who was not involved in the study, said: “These are a challenging group of patients to identify with early disease. You quite rightly raise the question of how we should follow-up with these patients.”
Managing asymptomatic patients
Although noninvasive tests can identify ALD in the early fibrotic stage, it’s unclear how patients with early asymptomatic disease should be managed, Dr. Rasmussen said.
This uncertainty prompted FLASH investigators to study patients with ALD to determine how fibrosis affected outcomes such as decompensation, hospitalization, and death.
They looked at a prospective cohort of patients diagnosed with ALD by biopsy and transient elastography (FibroScan) from 2013 to 2018. Follow-up data for the patients were collected retrospectively from electronic health records or charts.
The patients, who all had alcohol overuse and no history of decompensation or other etiologies at baseline, were classified into three groups: 225 liver-healthy patients with minimal to no fibrosis (F1 or transient elastography <6 kPa kPa); 104 patients with significant fibrosis (F2); and, 93 patients with advanced fibrosis (F3 or F4).
The median patient age was 57 years, and 75% of the patients were men. The patients were followed for 1,149 patient-years.
Findings and outcomes
During follow-up, 53 patients died, and 51 had a decompensation event: overt hepatoencephalopathy, ascites, variceal bleeding, hepatorenal syndrome, or jaundice. Of the 51 patients, 27 died.
There was a protocol change during the study, with the new protocol stating that patients with transient elastography below 6 kPa could not undergo biopsy. Based on the 106 patients who had both a FibroScan and biopsy, of whom 20% had F2 fibrosis, the investigators calculated that 14 patients who did not undergo biopsy may have been incorrectly classified as having healthy livers, Dr. Rasmussen said.
Patients with healthy livers had a significantly better decompensation-free survival rates, with only 5.8% of those with healthy livers having a decompensation event out to 4.5 years, compared with 21% of patients with significant fibrosis or advanced fibrosis.
Within the first year of follow-up, 98% of patients with healthy livers were alive and free of decompensations, compared with 94% with significant fibrosis and 84% with advanced fibrosis. The respective rates at 3 years were 95%, 82%, and 55%.
The percentage of hospital admissions that were liver related was 5% in the healthy-liver group, 24% in the significant group, and 47% in the advanced group.
Ongoing alcohol use during follow-up was also a significant predictor of worse decompensation-free survival (HR, 1.6; P = .04), with two in three decompensation events occurring in patients with alcohol overuse. The effect of alcohol was less strong than fibrosis stage, however, Dr. Rasmussen noted.
Dr. Schaefer said that “we see individuals who with heavy alcohol use progress much more rapidly than you’d anticipate with the rule of thumb that you see in other diseases of one fibrosis stage every 5-7 years.”
Among the strengths of this study included the use of biopsy and the inclusion of all stages of fibrosis. The investigators acknowledged as potential limitations the retrospective collection of follow-up data, reliance on medical charts to estimate alcohol consumption, and the single-center design.
The study was supported by grants from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program and the Novo Nordisk Foundation Challenge program. Dr. Rasmussen, Dr. Schaefer, and Dr. Forrest reported no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Moderate fibrosis in patients with alcoholic liver disease is not a benign condition, say investigators who studied the natural history of ALD according to biopsy-proven fibrosis stage.
In a study of 422 patients who were followed for a median of 43 months, 5.8% of patients with no or minimal fibrosis had a liver decompensation event. This compares with 21% (hazard ratio, 3.8; 95% confidence interval, 1.9-7.5; P < .01) of patients with significant fibrosis and 45% (HR, 9.6; 95% CI, 5.2-18.0; P < .01) of patients with advanced fibrosis, said Ditlev Nytoft Rasmussen, PhD, in an oral presentation at the meeting sponsored by the European Association for the Study of the Liver.
“The most obvious implication of this study is that the stage of fibrosis is a very strong predictor for the prognosis in early asymptomatic alcohol-related liver disease,” he said.
The findings suggest that gastroenterologists do not need to follow patients with no or only minor fibrosis, but patients with significant (F2) fibrosis, or greater, should be closely followed, said Dr. Rasmussen, who is with the FLASH Center for Liver Research at Odense (Denmark) University.
A gastroenterologist who was not involved in the study commented on the excess mortality the investigators saw.
“The really striking finding here to me is the excess mortality in the significant fibrosis group. They are not healthy, and some of that excess mortality does appear to be liver related, but some of it may not be liver related,“ said Esperance A. Schaefer, MD, MPH, of Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston.
“I think it will be important to be vigilant about the causes of death that are not liver related in patients with significant and advanced fibrosis, and the healthy group,” she said in an interview.
Ewan H. Forrest, MD, from the University of Glasgow, who was not involved in the study, said: “These are a challenging group of patients to identify with early disease. You quite rightly raise the question of how we should follow-up with these patients.”
Managing asymptomatic patients
Although noninvasive tests can identify ALD in the early fibrotic stage, it’s unclear how patients with early asymptomatic disease should be managed, Dr. Rasmussen said.
This uncertainty prompted FLASH investigators to study patients with ALD to determine how fibrosis affected outcomes such as decompensation, hospitalization, and death.
They looked at a prospective cohort of patients diagnosed with ALD by biopsy and transient elastography (FibroScan) from 2013 to 2018. Follow-up data for the patients were collected retrospectively from electronic health records or charts.
The patients, who all had alcohol overuse and no history of decompensation or other etiologies at baseline, were classified into three groups: 225 liver-healthy patients with minimal to no fibrosis (F1 or transient elastography <6 kPa kPa); 104 patients with significant fibrosis (F2); and, 93 patients with advanced fibrosis (F3 or F4).
The median patient age was 57 years, and 75% of the patients were men. The patients were followed for 1,149 patient-years.
Findings and outcomes
During follow-up, 53 patients died, and 51 had a decompensation event: overt hepatoencephalopathy, ascites, variceal bleeding, hepatorenal syndrome, or jaundice. Of the 51 patients, 27 died.
There was a protocol change during the study, with the new protocol stating that patients with transient elastography below 6 kPa could not undergo biopsy. Based on the 106 patients who had both a FibroScan and biopsy, of whom 20% had F2 fibrosis, the investigators calculated that 14 patients who did not undergo biopsy may have been incorrectly classified as having healthy livers, Dr. Rasmussen said.
Patients with healthy livers had a significantly better decompensation-free survival rates, with only 5.8% of those with healthy livers having a decompensation event out to 4.5 years, compared with 21% of patients with significant fibrosis or advanced fibrosis.
Within the first year of follow-up, 98% of patients with healthy livers were alive and free of decompensations, compared with 94% with significant fibrosis and 84% with advanced fibrosis. The respective rates at 3 years were 95%, 82%, and 55%.
The percentage of hospital admissions that were liver related was 5% in the healthy-liver group, 24% in the significant group, and 47% in the advanced group.
Ongoing alcohol use during follow-up was also a significant predictor of worse decompensation-free survival (HR, 1.6; P = .04), with two in three decompensation events occurring in patients with alcohol overuse. The effect of alcohol was less strong than fibrosis stage, however, Dr. Rasmussen noted.
Dr. Schaefer said that “we see individuals who with heavy alcohol use progress much more rapidly than you’d anticipate with the rule of thumb that you see in other diseases of one fibrosis stage every 5-7 years.”
Among the strengths of this study included the use of biopsy and the inclusion of all stages of fibrosis. The investigators acknowledged as potential limitations the retrospective collection of follow-up data, reliance on medical charts to estimate alcohol consumption, and the single-center design.
The study was supported by grants from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program and the Novo Nordisk Foundation Challenge program. Dr. Rasmussen, Dr. Schaefer, and Dr. Forrest reported no conflicts of interest to disclose.
FROM ILC 2021
Protein expression may predict HBV DNA suppression
Stopping nucleoside analog therapy in patients with hepatitis B viral (HBV) infections results in sustained viral suppression in only a minority of patients, but a new study suggests there are immune signatures that may serve as predictive biomarkers to help clinicians determine how to improve immune responses in these patients, according to investigators.
In a study of 359 patients enrolled in clinical trials of antiviral therapy for HBV infections, there were 29 immune-related proteins that were found in significantly higher levels among patients who continued to have viral suppression 24 weeks after the end of treatment, compared with patients who did not maintain viral suppression, reported Henry L.Y. Chan, MD, from the Chinese University of Hong Kong.
“In this study, plasma proteomics shows that sustained HBV suppression following treatment discontinuation is associated with higher levels of innate and adaptive immune responses during treatment, but whether these signatures vary by specific treatment regimens remains to be determined,” he said in an oral session at the meeting sponsored by the European Association for the Study of the Liver.
The clustering of proteins differed between patients treated with nucleoside analogs and those who received pegylated interferon (PEG-IFN), Dr. Chan noted.
Is it safe?
Although current international guidelines say that clinicians may consider stopping nucleoside analogs in certain patient populations with the goal of promoting sustained off-treatment responses, pooled data from four large phase 3 studies showed that only 10% of patients had sustained HBV DNA suppression, and only 32% had persistent low-level viremia, Dr. Chan said, citing a presentation from ILC in 2019.
Dr. Chan and colleagues sought to identify immune biomarkers that at the end of treatment predict HBV off-treatment response. This is important because existing treatments do not kill the virus which – even if suppressed – can lead to hepatocellular carcinoma.
The researchers examined plasma samples from patients with chronic hepatitis B who were enrolled in two studies: a registrational study comparing tenofovir disoproxil fumarate with adefovir followed by tenofovir maintenance (GS-US-174-0102) and one comparing TDF plus PEG-IFN with either drug alone (GS-US-174-0149).
They identified a total of 359 patients who had at least two treatment-free follow-up visits, were positive for the hepatitis B S antigen (HBsAg) at the end of the treatment, including patients who had antigen loss on treatment but subsequently seroverted, and had available plasma samples collected before the end of treatment.
The study outcomes were sustained viral suppression 24 weeks after the end of treatment, defined as HBV DNA less than 29 IU/mL, and a low replicative state defined as HBV DNA below 2,000 IU/mL with ALT levels at or below the upper limit of normal.
The median patient age was 39 years. In all, 67% of the population was male, and 70% were Asian.
Immune-related proteins
The investigators performed proteomic analyses looking for expression levels in serum or plasma proteins at the end of treatment.
A total of 25 patients had HBV DNA suppression at posttreatment week 24, 111 patients had a low replicative states, and 4 had HBsAg loss.
The patients with HBV DNA suppression had significantly higher expression of 29 immune-related proteins, the majority of which were related to the host immune response.
The proteins included myeloid cell markers, leukocyte-trafficking chemokines, natural killer cell markers, and extracellular matrix and/or extracellular matrix–associated proteins.
Among patients with HBV suppression, there was evidence of enrichment for extracellular remodeling pathways, as well as pathways involved in innate immune response to viral infections and immune regulation.
Among patients with low viral replication, there was a trend toward higher CD8a expression levels at the 24-week follow-up, but there were no proteins with significantly elevated expression levels.
“Assessment of unique protein signatures associated with HBsAg loss following treatment discontinuation is ongoing,” Dr. Chan said.
Timing of expression patterns
During the question-and-answer session following his presentation, comoderator Pablo Sarobe, MD, from the Clinica Universidad de Navarra (Spain), said: “I’ve seen that you have compared the different proteins which are detected in your cell samples 24 weeks after stopping treatment. Do you think that these differences are already relevant just at the end of treatment, or that these proteins are being expressed [during] the 24 weeks between the end of treatment and your determination?”
“We only have one time-point sample, so it’s hard to say,” Dr. Chan replied, but he speculated that the delay would not have a direct impact on protein expression, “so probably this expression should last after treatment has stopped. But we only have only posttreatment 24-week data, and we believe that some of the outcome measures may change with longer follow-up. After 1 year some patients in suppression may relapse.”
Asked by an audience member whether the investigators had performed a subanalysis of patients treated with nucleoside analogs, Dr. Chan noted that such an analysis was under consideration, although the patient numbers were relatively small. He did add, however, that protein expression patterns differed among patients treated with nucleoside analogs and PEG-IFN.
The study was funded by Gilead Sciences. Dr. Chan disclosed sponsored lecture activities and consulting for Gilead and others. Dr. Sarobe reported no conflicts of interest.
Stopping nucleoside analog therapy in patients with hepatitis B viral (HBV) infections results in sustained viral suppression in only a minority of patients, but a new study suggests there are immune signatures that may serve as predictive biomarkers to help clinicians determine how to improve immune responses in these patients, according to investigators.
In a study of 359 patients enrolled in clinical trials of antiviral therapy for HBV infections, there were 29 immune-related proteins that were found in significantly higher levels among patients who continued to have viral suppression 24 weeks after the end of treatment, compared with patients who did not maintain viral suppression, reported Henry L.Y. Chan, MD, from the Chinese University of Hong Kong.
“In this study, plasma proteomics shows that sustained HBV suppression following treatment discontinuation is associated with higher levels of innate and adaptive immune responses during treatment, but whether these signatures vary by specific treatment regimens remains to be determined,” he said in an oral session at the meeting sponsored by the European Association for the Study of the Liver.
The clustering of proteins differed between patients treated with nucleoside analogs and those who received pegylated interferon (PEG-IFN), Dr. Chan noted.
Is it safe?
Although current international guidelines say that clinicians may consider stopping nucleoside analogs in certain patient populations with the goal of promoting sustained off-treatment responses, pooled data from four large phase 3 studies showed that only 10% of patients had sustained HBV DNA suppression, and only 32% had persistent low-level viremia, Dr. Chan said, citing a presentation from ILC in 2019.
Dr. Chan and colleagues sought to identify immune biomarkers that at the end of treatment predict HBV off-treatment response. This is important because existing treatments do not kill the virus which – even if suppressed – can lead to hepatocellular carcinoma.
The researchers examined plasma samples from patients with chronic hepatitis B who were enrolled in two studies: a registrational study comparing tenofovir disoproxil fumarate with adefovir followed by tenofovir maintenance (GS-US-174-0102) and one comparing TDF plus PEG-IFN with either drug alone (GS-US-174-0149).
They identified a total of 359 patients who had at least two treatment-free follow-up visits, were positive for the hepatitis B S antigen (HBsAg) at the end of the treatment, including patients who had antigen loss on treatment but subsequently seroverted, and had available plasma samples collected before the end of treatment.
The study outcomes were sustained viral suppression 24 weeks after the end of treatment, defined as HBV DNA less than 29 IU/mL, and a low replicative state defined as HBV DNA below 2,000 IU/mL with ALT levels at or below the upper limit of normal.
The median patient age was 39 years. In all, 67% of the population was male, and 70% were Asian.
Immune-related proteins
The investigators performed proteomic analyses looking for expression levels in serum or plasma proteins at the end of treatment.
A total of 25 patients had HBV DNA suppression at posttreatment week 24, 111 patients had a low replicative states, and 4 had HBsAg loss.
The patients with HBV DNA suppression had significantly higher expression of 29 immune-related proteins, the majority of which were related to the host immune response.
The proteins included myeloid cell markers, leukocyte-trafficking chemokines, natural killer cell markers, and extracellular matrix and/or extracellular matrix–associated proteins.
Among patients with HBV suppression, there was evidence of enrichment for extracellular remodeling pathways, as well as pathways involved in innate immune response to viral infections and immune regulation.
Among patients with low viral replication, there was a trend toward higher CD8a expression levels at the 24-week follow-up, but there were no proteins with significantly elevated expression levels.
“Assessment of unique protein signatures associated with HBsAg loss following treatment discontinuation is ongoing,” Dr. Chan said.
Timing of expression patterns
During the question-and-answer session following his presentation, comoderator Pablo Sarobe, MD, from the Clinica Universidad de Navarra (Spain), said: “I’ve seen that you have compared the different proteins which are detected in your cell samples 24 weeks after stopping treatment. Do you think that these differences are already relevant just at the end of treatment, or that these proteins are being expressed [during] the 24 weeks between the end of treatment and your determination?”
“We only have one time-point sample, so it’s hard to say,” Dr. Chan replied, but he speculated that the delay would not have a direct impact on protein expression, “so probably this expression should last after treatment has stopped. But we only have only posttreatment 24-week data, and we believe that some of the outcome measures may change with longer follow-up. After 1 year some patients in suppression may relapse.”
Asked by an audience member whether the investigators had performed a subanalysis of patients treated with nucleoside analogs, Dr. Chan noted that such an analysis was under consideration, although the patient numbers were relatively small. He did add, however, that protein expression patterns differed among patients treated with nucleoside analogs and PEG-IFN.
The study was funded by Gilead Sciences. Dr. Chan disclosed sponsored lecture activities and consulting for Gilead and others. Dr. Sarobe reported no conflicts of interest.
Stopping nucleoside analog therapy in patients with hepatitis B viral (HBV) infections results in sustained viral suppression in only a minority of patients, but a new study suggests there are immune signatures that may serve as predictive biomarkers to help clinicians determine how to improve immune responses in these patients, according to investigators.
In a study of 359 patients enrolled in clinical trials of antiviral therapy for HBV infections, there were 29 immune-related proteins that were found in significantly higher levels among patients who continued to have viral suppression 24 weeks after the end of treatment, compared with patients who did not maintain viral suppression, reported Henry L.Y. Chan, MD, from the Chinese University of Hong Kong.
“In this study, plasma proteomics shows that sustained HBV suppression following treatment discontinuation is associated with higher levels of innate and adaptive immune responses during treatment, but whether these signatures vary by specific treatment regimens remains to be determined,” he said in an oral session at the meeting sponsored by the European Association for the Study of the Liver.
The clustering of proteins differed between patients treated with nucleoside analogs and those who received pegylated interferon (PEG-IFN), Dr. Chan noted.
Is it safe?
Although current international guidelines say that clinicians may consider stopping nucleoside analogs in certain patient populations with the goal of promoting sustained off-treatment responses, pooled data from four large phase 3 studies showed that only 10% of patients had sustained HBV DNA suppression, and only 32% had persistent low-level viremia, Dr. Chan said, citing a presentation from ILC in 2019.
Dr. Chan and colleagues sought to identify immune biomarkers that at the end of treatment predict HBV off-treatment response. This is important because existing treatments do not kill the virus which – even if suppressed – can lead to hepatocellular carcinoma.
The researchers examined plasma samples from patients with chronic hepatitis B who were enrolled in two studies: a registrational study comparing tenofovir disoproxil fumarate with adefovir followed by tenofovir maintenance (GS-US-174-0102) and one comparing TDF plus PEG-IFN with either drug alone (GS-US-174-0149).
They identified a total of 359 patients who had at least two treatment-free follow-up visits, were positive for the hepatitis B S antigen (HBsAg) at the end of the treatment, including patients who had antigen loss on treatment but subsequently seroverted, and had available plasma samples collected before the end of treatment.
The study outcomes were sustained viral suppression 24 weeks after the end of treatment, defined as HBV DNA less than 29 IU/mL, and a low replicative state defined as HBV DNA below 2,000 IU/mL with ALT levels at or below the upper limit of normal.
The median patient age was 39 years. In all, 67% of the population was male, and 70% were Asian.
Immune-related proteins
The investigators performed proteomic analyses looking for expression levels in serum or plasma proteins at the end of treatment.
A total of 25 patients had HBV DNA suppression at posttreatment week 24, 111 patients had a low replicative states, and 4 had HBsAg loss.
The patients with HBV DNA suppression had significantly higher expression of 29 immune-related proteins, the majority of which were related to the host immune response.
The proteins included myeloid cell markers, leukocyte-trafficking chemokines, natural killer cell markers, and extracellular matrix and/or extracellular matrix–associated proteins.
Among patients with HBV suppression, there was evidence of enrichment for extracellular remodeling pathways, as well as pathways involved in innate immune response to viral infections and immune regulation.
Among patients with low viral replication, there was a trend toward higher CD8a expression levels at the 24-week follow-up, but there were no proteins with significantly elevated expression levels.
“Assessment of unique protein signatures associated with HBsAg loss following treatment discontinuation is ongoing,” Dr. Chan said.
Timing of expression patterns
During the question-and-answer session following his presentation, comoderator Pablo Sarobe, MD, from the Clinica Universidad de Navarra (Spain), said: “I’ve seen that you have compared the different proteins which are detected in your cell samples 24 weeks after stopping treatment. Do you think that these differences are already relevant just at the end of treatment, or that these proteins are being expressed [during] the 24 weeks between the end of treatment and your determination?”
“We only have one time-point sample, so it’s hard to say,” Dr. Chan replied, but he speculated that the delay would not have a direct impact on protein expression, “so probably this expression should last after treatment has stopped. But we only have only posttreatment 24-week data, and we believe that some of the outcome measures may change with longer follow-up. After 1 year some patients in suppression may relapse.”
Asked by an audience member whether the investigators had performed a subanalysis of patients treated with nucleoside analogs, Dr. Chan noted that such an analysis was under consideration, although the patient numbers were relatively small. He did add, however, that protein expression patterns differed among patients treated with nucleoside analogs and PEG-IFN.
The study was funded by Gilead Sciences. Dr. Chan disclosed sponsored lecture activities and consulting for Gilead and others. Dr. Sarobe reported no conflicts of interest.
FROM ILC 2021
Does MELD need an update?
Dear colleagues and friends,
The Perspectives series continues! There are few issues in our discipline that are as challenging, and controversial, as liver transplant prioritization. The Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) has been the mainstay for organ allocation for nearly 2 decades, and there has been vigorous debate as to whether it should remain so. In this issue, Dr. Jasmohan Bajaj and Dr. Julie Heimbach discuss the strengths and limitations of MELD and provide a vision of upcoming developments. As always, I welcome your feedback and suggestions for future topics at [email protected].
Charles J. Kahi, MD, MS, AGAF, is professor of medicine at Indiana University, Indianapolis. He is an associate editor for GI & Hepatology News.
Yes, it’s time for an update
BY JASMOHAN S. BAJAJ, MD, AGAF
Since February 2002, the U.S.-based liver transplant system has adopted the MELD score for transplant priority. Initially developed to predict outcomes after transjugular intrahepatic porto-systemic shunt, it was modified to exclude etiology for the purpose of listing patients.1
There were several advantages with MELD including objectivity, ease of calculation using a website, and over time, a burgeoning experience nationwide that extended even beyond transplant. Moreover, it focused on “sickest-first,” did away with the extremely “manipulable” waiting list, and left off hepatic encephalopathy (HE) and ascites severity.1 However, even earlier on, there were concerns regarding not capturing hepatocellular cancer (HCC) and some complications of cirrhosis that required exceptions. The points awarded to all these exceptions also changed with time, with lower priority and reincorporation of the waiting list time for HCC. Over time, the addition of serum sodium led it to be converted to “MELD-Na,” which now remains the primary method for transplant listing priority.
But the population with cirrhosis that existed 20 years ago has shifted radically. Patients with cirrhosis currently tend to either be much older with more comorbid conditions that predispose them to chronic kidney disease and cerebrovascular and cardiovascular compromise or be younger with an earlier presentation of alcohol-associated hepatitis. Moreover, the widespread availability of hepatitis C virus (HCV) eradication has changed the landscape and stopped the progression of cirrhosis organically by virtually removing that etiology. This is relevant because a recent United Network for Organ Sharing (UNOS) analysis showed that the concordance between MELD score and 90-day mortality was the lowest in the rapidly increasing population with alcohol-related and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease etiologies, but conversely, this concordance was the highest in the population with hepatitis C–related cirrhosis.2 These demographic shifts in age and changes in etiology likely lessen the predictive power of the current MELD score iteration.
There is also increasing evidence that MELD is “stuck in the middle.” This means that both patients at low MELD score and those with organ failures may be underserved with respect to transplant listing with the current MELD score iteration.
Among patients with a MELD score disproportionately lower than their complications of cirrhosis several studies demonstrate the improvement in prognostication with addition of covert HE, history of overt HE, frailty, and sarcopenia indices. These are independently prognostic variables that affect daily function, affect patient-reported outcomes, and can influence readmissions. The burden of impending falls, readmissions, infections, and overall ill health is not captured even though relatively objective methods such as cognitive tests and documented admissions for overt HE can be utilized.3 This relative mistrust in including HE and covariables likely harkens back to a dramatic reduction in grade III/IV HE severity seen the year after MELD introduction, when compared with the year before, during which that designation was added to the listing priority.4 However, objective additions to the MELD score that capture the distress of patients and their families with multiple readmissions for HE worsened by sarcopenia are desperately needed (see table).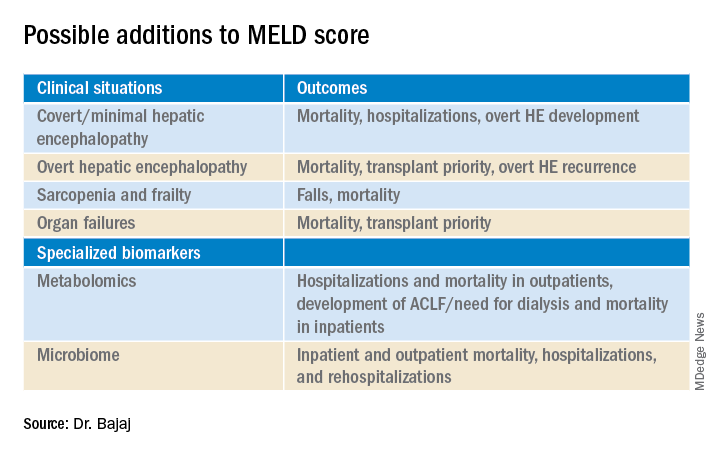
On the other extreme, there is an increasing recognition of acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF) and higher acceptability for transplanting alcohol-associated hepatitis (AAH).5 Prognostic variables in AAH have relied on Maddrey’s score and MELD score as well as the dynamic Lille score. The ability of MELD to predict outcomes is variable, but it is still required for listing these critical patients. A relatively newer entity, ACLF is defined variably across the world. In retrospective studies of the UNOS database in which patients were listed based on native MELD score rather than ACLF grades, there was a cut-off beyond which transplant was not useful. However, there is evidence that organ failures that do not involve creatinine or INR can influence survival independent of the MELD score.5 The rapidly increasing burden of critical illness may force a rethink of allocation policies, but a recent survey among U.S.-based transplant providers found little appetite to do so currently.
Objectivity is a major strength of the MELD score, but several systemic issues, including creatinine variability by sex, interlaboratory inconsistencies in laboratory results, and lack of accounting for international normalized ratio (INR) changes in those on warfarin or other INR-prolonging medications, to name a few that still exist.6 However, in our zeal to list patients and get the maximum chance for organ offers, there is a tendency to maximize or inflate the listing scores. This hope to provide the best care for patients under our specific care could come at the expense of patients listed elsewhere, but no score, however objective, is going to completely eliminate this possibility.
So, does this mean MELD-Na should be abandoned?
Absolutely not. An ecosystem of practitioners has now grown up under this system in the U.S., and it is rapidly being exported to other parts of the world. As with everything else, we need to keep up with the times, and for the popular MELD score, it needs to be responsive to issues at both extremes of cirrhosis severity. Studies on specialized markers such as serum, urine, and stool metabolomics as well as microbiome could be an objective addition to MELD score, but further studies are needed. It is also likely that artificial intelligence approaches could be used to not only improve access but also geographic equity that has plagued liver transplant in the U.S.
In the immortal words of Bob Dylan, “The times, they are a-changin’ …” We have to make sure the MELD score does too.
Jasmohan S. Bajaj, MD, AGAF, is with the division of gastroenterology, hepatology, and nutrition at Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, and Richmond VA Medical Center. He has no conflicts of interest.
References
1. Kamath PS and Kim WR. Hepatology. 2007;45:797-805.
2. Godfrey EL et al. Am J Transplant. 2019;19:3299-307.
3. Acharya C and Bajaj JS. Liver Transpl. 2021 May 21. doi:10.1002/lt.26099.
4. Bajaj JS and Saeian K. Dig Dis Sci 2005;50:753-6.
5. Artru F and Samuel D. JHEP Rep 2019 May;1(1):53-65.
6. Bernardi M et al. J Hepatol 2010 Dec 9;54:1297-306.
Maybe, but take it slow
BY JULIE K. HEIMBACH, MD
Even though 2020 was another record year for organ donation in the United States, a truly remarkable feat considering the profound impact of COVID-19 on health care as well as the population at large, there remains a critical shortage of available liver allografts.1 Last year in the U.S., of the approximately 13,000 patients waiting for a liver transplant, just under 9,000 patients underwent liver transplantation from a deceased or a living donor, while 2,345 either died waiting on the list or were removed for being too sick, and the rest remained waiting.1 In a perfect system, we would transplant every wait-listed patient at a time that would provide them the greatest benefit with the least amount of distress. However, because of the shortage of available organs for transplantation, an allocation system to rank wait-listed candidates is required. Because organ transplantation relies on the incredible altruism of individuals and their family members who make this ultimate gift on their behalf, it is crucial both for donor families and for waiting recipients that organ allocation be transparent, as fair and equitable as possible, and compliant with federal law, which is currently determined by the “Final Rule” that states that organ allocation be based in order of urgency.2
Since February 2002, U.S. liver allocation policy has been based on MELD.3 Prior to that time, liver allocation was based in part on the Child-Turcot-Pugh classification of liver disease, which included subjective components (ascites and encephalopathy) that are difficult to measure, as well as increased priority based on admission to the intensive care unit, also subjective and open to interpretation or abuse. Most crucially, the system defaulted to length of waiting time with large numbers of patients in the same category, which led to higher death rates for patients whose disease progressed more quickly or who were referred very late in their disease course.
MELD relies on a simple set of laboratory values that are easily obtained at any clinical lab and are already being routinely monitored as part of standard care for patients with end-stage liver disease.3 MELD initially required just three variables (bilirubin, creatinine, INR) and was updated to include just four variables with the adoption of MELD-Na in 2016, which added sodium levels. The MELD- and MELD-Na–based approach is a highly reliable, accurate way to rank patients who are most at risk of death in the next 3 months, with a C statistic of approximately 0.83-0.84.3,4 Perhaps the greatest testament to the strength of MELD is that, following the adoption of MELD-based liver allocation, MELD has gradually been adopted as the system of liver allocation by most countries around the world.
With the adoption of MELD and subsequently MELD-Na, which prioritize deceased donor liver allografts to the sickest patients first and is therefore compliant with the Final Rule, outcomes for patients waiting for liver transplant have steadily improved.3,4 In addition, MELD has provided an easily obtainable, objective measure to guide decisions about timing of liver transplant, especially in the setting of potential living donor liver transplantation. MELD is also predictive of outcome for patients undergoing nontransplant elective and emergent surgical procedures, and because of the ease in calculating the score, it allows for an objective comparison of patients with cirrhosis across a variety of clinical and research settings.
The MELD system has many additional strengths, though perhaps the most important is that it is adaptable. While the MELD score accurately predicts death from chronic liver disease, the MELD score is not able to predict mortality or risk of wait-list dropout due to disease progression from certain complications of chronic liver disease such as the development of HCC or hepatopulmonary syndrome, in which access to timely transplantation has been proven to be beneficial. This has required an adaption to the system whereby candidates with conditions, such as HCC, that meet specific criteria receive an assigned MELD score, rather than a calculated score. Determining which patients should qualify for MELD exceptions, as well as what the assigned priority score should be, has required careful analysis and ongoing revision. An additional issue for MELD, which was identified more than a decade ago and is overdue for adjustment, is the disparity in access to transplant for women who continue to experience a lower transplant rate (14.4% according to the most recent analysis) and approximately 8.6% higher death rate than men with the same MELD score.5 This is due, in part, to the use of creatinine in the MELD equation, which as a by-product of muscle metabolism, underestimates the degree of renal dysfunction in women and thus underestimates their risk of wait-list mortality.5 A potential modification to the MELD-Na score that corrects for this sex-based disparity is currently being studied by the OPTN Liver-Intestine committee, which is further evidence of the strength and adaptability of a MELD-based allocation system.
While it is tempting to conclude that a system that requires on-going monitoring and revision is best discarded in favor of a new model such as an artificial intelligence–based solution, policy development requires a tremendous amount of time for consensus-building, as well as effort to ensure that unexpected negative effects are not created. Whereas a novel system could be identified and determined to be superior down the road, the amount of effort and expense that would be needed to build consensus around such a new model should not be underestimated. Considering the challenges to health care and the population at large that are already occurring as we emerge from the COVID pandemic, as well as the short-term need to monitor the impact from the recent adoption of the acuity circle model which went live in February 2020 and allocates according to MELD but over a broader geographic area based on a circle around the donor hospital, building consensus around incremental changes to a MELD-based allocation system likely represents the best option in our continued quest for the optimal liver allocation system.
Julie K. Heimbach, MD, is a transplant surgeon and the surgical director of liver transplantation at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn. She has no conflicts to report.
References
1. Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network data. Available at https://optn.transplant.hrsa.gov/data/view-data-reports/national-data. Accessed May 1, 2021.
2. Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network. Final rule. Available at https://optn.transplant.hrsa.gov/governance/about-the-optn/final-rule. Accessed May 1, 2021.
3. Wiesner R et al; United Network for Organ Sharing Liver Disease Severity Score Committee. Gastroenterology. 2003 Jan;124(1):91-6.
4. Nagai S et al. Gastroenterology. 2018 Nov;155(5):1451-62.e3.
5. Locke JE et al. JAMA Surg. 2020 Jul 1;155(7):e201129.
Dear colleagues and friends,
The Perspectives series continues! There are few issues in our discipline that are as challenging, and controversial, as liver transplant prioritization. The Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) has been the mainstay for organ allocation for nearly 2 decades, and there has been vigorous debate as to whether it should remain so. In this issue, Dr. Jasmohan Bajaj and Dr. Julie Heimbach discuss the strengths and limitations of MELD and provide a vision of upcoming developments. As always, I welcome your feedback and suggestions for future topics at [email protected].
Charles J. Kahi, MD, MS, AGAF, is professor of medicine at Indiana University, Indianapolis. He is an associate editor for GI & Hepatology News.
Yes, it’s time for an update
BY JASMOHAN S. BAJAJ, MD, AGAF
Since February 2002, the U.S.-based liver transplant system has adopted the MELD score for transplant priority. Initially developed to predict outcomes after transjugular intrahepatic porto-systemic shunt, it was modified to exclude etiology for the purpose of listing patients.1
There were several advantages with MELD including objectivity, ease of calculation using a website, and over time, a burgeoning experience nationwide that extended even beyond transplant. Moreover, it focused on “sickest-first,” did away with the extremely “manipulable” waiting list, and left off hepatic encephalopathy (HE) and ascites severity.1 However, even earlier on, there were concerns regarding not capturing hepatocellular cancer (HCC) and some complications of cirrhosis that required exceptions. The points awarded to all these exceptions also changed with time, with lower priority and reincorporation of the waiting list time for HCC. Over time, the addition of serum sodium led it to be converted to “MELD-Na,” which now remains the primary method for transplant listing priority.
But the population with cirrhosis that existed 20 years ago has shifted radically. Patients with cirrhosis currently tend to either be much older with more comorbid conditions that predispose them to chronic kidney disease and cerebrovascular and cardiovascular compromise or be younger with an earlier presentation of alcohol-associated hepatitis. Moreover, the widespread availability of hepatitis C virus (HCV) eradication has changed the landscape and stopped the progression of cirrhosis organically by virtually removing that etiology. This is relevant because a recent United Network for Organ Sharing (UNOS) analysis showed that the concordance between MELD score and 90-day mortality was the lowest in the rapidly increasing population with alcohol-related and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease etiologies, but conversely, this concordance was the highest in the population with hepatitis C–related cirrhosis.2 These demographic shifts in age and changes in etiology likely lessen the predictive power of the current MELD score iteration.
There is also increasing evidence that MELD is “stuck in the middle.” This means that both patients at low MELD score and those with organ failures may be underserved with respect to transplant listing with the current MELD score iteration.
Among patients with a MELD score disproportionately lower than their complications of cirrhosis several studies demonstrate the improvement in prognostication with addition of covert HE, history of overt HE, frailty, and sarcopenia indices. These are independently prognostic variables that affect daily function, affect patient-reported outcomes, and can influence readmissions. The burden of impending falls, readmissions, infections, and overall ill health is not captured even though relatively objective methods such as cognitive tests and documented admissions for overt HE can be utilized.3 This relative mistrust in including HE and covariables likely harkens back to a dramatic reduction in grade III/IV HE severity seen the year after MELD introduction, when compared with the year before, during which that designation was added to the listing priority.4 However, objective additions to the MELD score that capture the distress of patients and their families with multiple readmissions for HE worsened by sarcopenia are desperately needed (see table).
On the other extreme, there is an increasing recognition of acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF) and higher acceptability for transplanting alcohol-associated hepatitis (AAH).5 Prognostic variables in AAH have relied on Maddrey’s score and MELD score as well as the dynamic Lille score. The ability of MELD to predict outcomes is variable, but it is still required for listing these critical patients. A relatively newer entity, ACLF is defined variably across the world. In retrospective studies of the UNOS database in which patients were listed based on native MELD score rather than ACLF grades, there was a cut-off beyond which transplant was not useful. However, there is evidence that organ failures that do not involve creatinine or INR can influence survival independent of the MELD score.5 The rapidly increasing burden of critical illness may force a rethink of allocation policies, but a recent survey among U.S.-based transplant providers found little appetite to do so currently.
Objectivity is a major strength of the MELD score, but several systemic issues, including creatinine variability by sex, interlaboratory inconsistencies in laboratory results, and lack of accounting for international normalized ratio (INR) changes in those on warfarin or other INR-prolonging medications, to name a few that still exist.6 However, in our zeal to list patients and get the maximum chance for organ offers, there is a tendency to maximize or inflate the listing scores. This hope to provide the best care for patients under our specific care could come at the expense of patients listed elsewhere, but no score, however objective, is going to completely eliminate this possibility.
So, does this mean MELD-Na should be abandoned?
Absolutely not. An ecosystem of practitioners has now grown up under this system in the U.S., and it is rapidly being exported to other parts of the world. As with everything else, we need to keep up with the times, and for the popular MELD score, it needs to be responsive to issues at both extremes of cirrhosis severity. Studies on specialized markers such as serum, urine, and stool metabolomics as well as microbiome could be an objective addition to MELD score, but further studies are needed. It is also likely that artificial intelligence approaches could be used to not only improve access but also geographic equity that has plagued liver transplant in the U.S.
In the immortal words of Bob Dylan, “The times, they are a-changin’ …” We have to make sure the MELD score does too.
Jasmohan S. Bajaj, MD, AGAF, is with the division of gastroenterology, hepatology, and nutrition at Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, and Richmond VA Medical Center. He has no conflicts of interest.
References
1. Kamath PS and Kim WR. Hepatology. 2007;45:797-805.
2. Godfrey EL et al. Am J Transplant. 2019;19:3299-307.
3. Acharya C and Bajaj JS. Liver Transpl. 2021 May 21. doi:10.1002/lt.26099.
4. Bajaj JS and Saeian K. Dig Dis Sci 2005;50:753-6.
5. Artru F and Samuel D. JHEP Rep 2019 May;1(1):53-65.
6. Bernardi M et al. J Hepatol 2010 Dec 9;54:1297-306.
Maybe, but take it slow
BY JULIE K. HEIMBACH, MD
Even though 2020 was another record year for organ donation in the United States, a truly remarkable feat considering the profound impact of COVID-19 on health care as well as the population at large, there remains a critical shortage of available liver allografts.1 Last year in the U.S., of the approximately 13,000 patients waiting for a liver transplant, just under 9,000 patients underwent liver transplantation from a deceased or a living donor, while 2,345 either died waiting on the list or were removed for being too sick, and the rest remained waiting.1 In a perfect system, we would transplant every wait-listed patient at a time that would provide them the greatest benefit with the least amount of distress. However, because of the shortage of available organs for transplantation, an allocation system to rank wait-listed candidates is required. Because organ transplantation relies on the incredible altruism of individuals and their family members who make this ultimate gift on their behalf, it is crucial both for donor families and for waiting recipients that organ allocation be transparent, as fair and equitable as possible, and compliant with federal law, which is currently determined by the “Final Rule” that states that organ allocation be based in order of urgency.2
Since February 2002, U.S. liver allocation policy has been based on MELD.3 Prior to that time, liver allocation was based in part on the Child-Turcot-Pugh classification of liver disease, which included subjective components (ascites and encephalopathy) that are difficult to measure, as well as increased priority based on admission to the intensive care unit, also subjective and open to interpretation or abuse. Most crucially, the system defaulted to length of waiting time with large numbers of patients in the same category, which led to higher death rates for patients whose disease progressed more quickly or who were referred very late in their disease course.
MELD relies on a simple set of laboratory values that are easily obtained at any clinical lab and are already being routinely monitored as part of standard care for patients with end-stage liver disease.3 MELD initially required just three variables (bilirubin, creatinine, INR) and was updated to include just four variables with the adoption of MELD-Na in 2016, which added sodium levels. The MELD- and MELD-Na–based approach is a highly reliable, accurate way to rank patients who are most at risk of death in the next 3 months, with a C statistic of approximately 0.83-0.84.3,4 Perhaps the greatest testament to the strength of MELD is that, following the adoption of MELD-based liver allocation, MELD has gradually been adopted as the system of liver allocation by most countries around the world.
With the adoption of MELD and subsequently MELD-Na, which prioritize deceased donor liver allografts to the sickest patients first and is therefore compliant with the Final Rule, outcomes for patients waiting for liver transplant have steadily improved.3,4 In addition, MELD has provided an easily obtainable, objective measure to guide decisions about timing of liver transplant, especially in the setting of potential living donor liver transplantation. MELD is also predictive of outcome for patients undergoing nontransplant elective and emergent surgical procedures, and because of the ease in calculating the score, it allows for an objective comparison of patients with cirrhosis across a variety of clinical and research settings.
The MELD system has many additional strengths, though perhaps the most important is that it is adaptable. While the MELD score accurately predicts death from chronic liver disease, the MELD score is not able to predict mortality or risk of wait-list dropout due to disease progression from certain complications of chronic liver disease such as the development of HCC or hepatopulmonary syndrome, in which access to timely transplantation has been proven to be beneficial. This has required an adaption to the system whereby candidates with conditions, such as HCC, that meet specific criteria receive an assigned MELD score, rather than a calculated score. Determining which patients should qualify for MELD exceptions, as well as what the assigned priority score should be, has required careful analysis and ongoing revision. An additional issue for MELD, which was identified more than a decade ago and is overdue for adjustment, is the disparity in access to transplant for women who continue to experience a lower transplant rate (14.4% according to the most recent analysis) and approximately 8.6% higher death rate than men with the same MELD score.5 This is due, in part, to the use of creatinine in the MELD equation, which as a by-product of muscle metabolism, underestimates the degree of renal dysfunction in women and thus underestimates their risk of wait-list mortality.5 A potential modification to the MELD-Na score that corrects for this sex-based disparity is currently being studied by the OPTN Liver-Intestine committee, which is further evidence of the strength and adaptability of a MELD-based allocation system.
While it is tempting to conclude that a system that requires on-going monitoring and revision is best discarded in favor of a new model such as an artificial intelligence–based solution, policy development requires a tremendous amount of time for consensus-building, as well as effort to ensure that unexpected negative effects are not created. Whereas a novel system could be identified and determined to be superior down the road, the amount of effort and expense that would be needed to build consensus around such a new model should not be underestimated. Considering the challenges to health care and the population at large that are already occurring as we emerge from the COVID pandemic, as well as the short-term need to monitor the impact from the recent adoption of the acuity circle model which went live in February 2020 and allocates according to MELD but over a broader geographic area based on a circle around the donor hospital, building consensus around incremental changes to a MELD-based allocation system likely represents the best option in our continued quest for the optimal liver allocation system.
Julie K. Heimbach, MD, is a transplant surgeon and the surgical director of liver transplantation at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn. She has no conflicts to report.
References
1. Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network data. Available at https://optn.transplant.hrsa.gov/data/view-data-reports/national-data. Accessed May 1, 2021.
2. Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network. Final rule. Available at https://optn.transplant.hrsa.gov/governance/about-the-optn/final-rule. Accessed May 1, 2021.
3. Wiesner R et al; United Network for Organ Sharing Liver Disease Severity Score Committee. Gastroenterology. 2003 Jan;124(1):91-6.
4. Nagai S et al. Gastroenterology. 2018 Nov;155(5):1451-62.e3.
5. Locke JE et al. JAMA Surg. 2020 Jul 1;155(7):e201129.
Dear colleagues and friends,
The Perspectives series continues! There are few issues in our discipline that are as challenging, and controversial, as liver transplant prioritization. The Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) has been the mainstay for organ allocation for nearly 2 decades, and there has been vigorous debate as to whether it should remain so. In this issue, Dr. Jasmohan Bajaj and Dr. Julie Heimbach discuss the strengths and limitations of MELD and provide a vision of upcoming developments. As always, I welcome your feedback and suggestions for future topics at [email protected].
Charles J. Kahi, MD, MS, AGAF, is professor of medicine at Indiana University, Indianapolis. He is an associate editor for GI & Hepatology News.
Yes, it’s time for an update
BY JASMOHAN S. BAJAJ, MD, AGAF
Since February 2002, the U.S.-based liver transplant system has adopted the MELD score for transplant priority. Initially developed to predict outcomes after transjugular intrahepatic porto-systemic shunt, it was modified to exclude etiology for the purpose of listing patients.1
There were several advantages with MELD including objectivity, ease of calculation using a website, and over time, a burgeoning experience nationwide that extended even beyond transplant. Moreover, it focused on “sickest-first,” did away with the extremely “manipulable” waiting list, and left off hepatic encephalopathy (HE) and ascites severity.1 However, even earlier on, there were concerns regarding not capturing hepatocellular cancer (HCC) and some complications of cirrhosis that required exceptions. The points awarded to all these exceptions also changed with time, with lower priority and reincorporation of the waiting list time for HCC. Over time, the addition of serum sodium led it to be converted to “MELD-Na,” which now remains the primary method for transplant listing priority.
But the population with cirrhosis that existed 20 years ago has shifted radically. Patients with cirrhosis currently tend to either be much older with more comorbid conditions that predispose them to chronic kidney disease and cerebrovascular and cardiovascular compromise or be younger with an earlier presentation of alcohol-associated hepatitis. Moreover, the widespread availability of hepatitis C virus (HCV) eradication has changed the landscape and stopped the progression of cirrhosis organically by virtually removing that etiology. This is relevant because a recent United Network for Organ Sharing (UNOS) analysis showed that the concordance between MELD score and 90-day mortality was the lowest in the rapidly increasing population with alcohol-related and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease etiologies, but conversely, this concordance was the highest in the population with hepatitis C–related cirrhosis.2 These demographic shifts in age and changes in etiology likely lessen the predictive power of the current MELD score iteration.
There is also increasing evidence that MELD is “stuck in the middle.” This means that both patients at low MELD score and those with organ failures may be underserved with respect to transplant listing with the current MELD score iteration.
Among patients with a MELD score disproportionately lower than their complications of cirrhosis several studies demonstrate the improvement in prognostication with addition of covert HE, history of overt HE, frailty, and sarcopenia indices. These are independently prognostic variables that affect daily function, affect patient-reported outcomes, and can influence readmissions. The burden of impending falls, readmissions, infections, and overall ill health is not captured even though relatively objective methods such as cognitive tests and documented admissions for overt HE can be utilized.3 This relative mistrust in including HE and covariables likely harkens back to a dramatic reduction in grade III/IV HE severity seen the year after MELD introduction, when compared with the year before, during which that designation was added to the listing priority.4 However, objective additions to the MELD score that capture the distress of patients and their families with multiple readmissions for HE worsened by sarcopenia are desperately needed (see table).
On the other extreme, there is an increasing recognition of acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF) and higher acceptability for transplanting alcohol-associated hepatitis (AAH).5 Prognostic variables in AAH have relied on Maddrey’s score and MELD score as well as the dynamic Lille score. The ability of MELD to predict outcomes is variable, but it is still required for listing these critical patients. A relatively newer entity, ACLF is defined variably across the world. In retrospective studies of the UNOS database in which patients were listed based on native MELD score rather than ACLF grades, there was a cut-off beyond which transplant was not useful. However, there is evidence that organ failures that do not involve creatinine or INR can influence survival independent of the MELD score.5 The rapidly increasing burden of critical illness may force a rethink of allocation policies, but a recent survey among U.S.-based transplant providers found little appetite to do so currently.
Objectivity is a major strength of the MELD score, but several systemic issues, including creatinine variability by sex, interlaboratory inconsistencies in laboratory results, and lack of accounting for international normalized ratio (INR) changes in those on warfarin or other INR-prolonging medications, to name a few that still exist.6 However, in our zeal to list patients and get the maximum chance for organ offers, there is a tendency to maximize or inflate the listing scores. This hope to provide the best care for patients under our specific care could come at the expense of patients listed elsewhere, but no score, however objective, is going to completely eliminate this possibility.
So, does this mean MELD-Na should be abandoned?
Absolutely not. An ecosystem of practitioners has now grown up under this system in the U.S., and it is rapidly being exported to other parts of the world. As with everything else, we need to keep up with the times, and for the popular MELD score, it needs to be responsive to issues at both extremes of cirrhosis severity. Studies on specialized markers such as serum, urine, and stool metabolomics as well as microbiome could be an objective addition to MELD score, but further studies are needed. It is also likely that artificial intelligence approaches could be used to not only improve access but also geographic equity that has plagued liver transplant in the U.S.
In the immortal words of Bob Dylan, “The times, they are a-changin’ …” We have to make sure the MELD score does too.
Jasmohan S. Bajaj, MD, AGAF, is with the division of gastroenterology, hepatology, and nutrition at Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, and Richmond VA Medical Center. He has no conflicts of interest.
References
1. Kamath PS and Kim WR. Hepatology. 2007;45:797-805.
2. Godfrey EL et al. Am J Transplant. 2019;19:3299-307.
3. Acharya C and Bajaj JS. Liver Transpl. 2021 May 21. doi:10.1002/lt.26099.
4. Bajaj JS and Saeian K. Dig Dis Sci 2005;50:753-6.
5. Artru F and Samuel D. JHEP Rep 2019 May;1(1):53-65.
6. Bernardi M et al. J Hepatol 2010 Dec 9;54:1297-306.
Maybe, but take it slow
BY JULIE K. HEIMBACH, MD
Even though 2020 was another record year for organ donation in the United States, a truly remarkable feat considering the profound impact of COVID-19 on health care as well as the population at large, there remains a critical shortage of available liver allografts.1 Last year in the U.S., of the approximately 13,000 patients waiting for a liver transplant, just under 9,000 patients underwent liver transplantation from a deceased or a living donor, while 2,345 either died waiting on the list or were removed for being too sick, and the rest remained waiting.1 In a perfect system, we would transplant every wait-listed patient at a time that would provide them the greatest benefit with the least amount of distress. However, because of the shortage of available organs for transplantation, an allocation system to rank wait-listed candidates is required. Because organ transplantation relies on the incredible altruism of individuals and their family members who make this ultimate gift on their behalf, it is crucial both for donor families and for waiting recipients that organ allocation be transparent, as fair and equitable as possible, and compliant with federal law, which is currently determined by the “Final Rule” that states that organ allocation be based in order of urgency.2
Since February 2002, U.S. liver allocation policy has been based on MELD.3 Prior to that time, liver allocation was based in part on the Child-Turcot-Pugh classification of liver disease, which included subjective components (ascites and encephalopathy) that are difficult to measure, as well as increased priority based on admission to the intensive care unit, also subjective and open to interpretation or abuse. Most crucially, the system defaulted to length of waiting time with large numbers of patients in the same category, which led to higher death rates for patients whose disease progressed more quickly or who were referred very late in their disease course.
MELD relies on a simple set of laboratory values that are easily obtained at any clinical lab and are already being routinely monitored as part of standard care for patients with end-stage liver disease.3 MELD initially required just three variables (bilirubin, creatinine, INR) and was updated to include just four variables with the adoption of MELD-Na in 2016, which added sodium levels. The MELD- and MELD-Na–based approach is a highly reliable, accurate way to rank patients who are most at risk of death in the next 3 months, with a C statistic of approximately 0.83-0.84.3,4 Perhaps the greatest testament to the strength of MELD is that, following the adoption of MELD-based liver allocation, MELD has gradually been adopted as the system of liver allocation by most countries around the world.
With the adoption of MELD and subsequently MELD-Na, which prioritize deceased donor liver allografts to the sickest patients first and is therefore compliant with the Final Rule, outcomes for patients waiting for liver transplant have steadily improved.3,4 In addition, MELD has provided an easily obtainable, objective measure to guide decisions about timing of liver transplant, especially in the setting of potential living donor liver transplantation. MELD is also predictive of outcome for patients undergoing nontransplant elective and emergent surgical procedures, and because of the ease in calculating the score, it allows for an objective comparison of patients with cirrhosis across a variety of clinical and research settings.
The MELD system has many additional strengths, though perhaps the most important is that it is adaptable. While the MELD score accurately predicts death from chronic liver disease, the MELD score is not able to predict mortality or risk of wait-list dropout due to disease progression from certain complications of chronic liver disease such as the development of HCC or hepatopulmonary syndrome, in which access to timely transplantation has been proven to be beneficial. This has required an adaption to the system whereby candidates with conditions, such as HCC, that meet specific criteria receive an assigned MELD score, rather than a calculated score. Determining which patients should qualify for MELD exceptions, as well as what the assigned priority score should be, has required careful analysis and ongoing revision. An additional issue for MELD, which was identified more than a decade ago and is overdue for adjustment, is the disparity in access to transplant for women who continue to experience a lower transplant rate (14.4% according to the most recent analysis) and approximately 8.6% higher death rate than men with the same MELD score.5 This is due, in part, to the use of creatinine in the MELD equation, which as a by-product of muscle metabolism, underestimates the degree of renal dysfunction in women and thus underestimates their risk of wait-list mortality.5 A potential modification to the MELD-Na score that corrects for this sex-based disparity is currently being studied by the OPTN Liver-Intestine committee, which is further evidence of the strength and adaptability of a MELD-based allocation system.
While it is tempting to conclude that a system that requires on-going monitoring and revision is best discarded in favor of a new model such as an artificial intelligence–based solution, policy development requires a tremendous amount of time for consensus-building, as well as effort to ensure that unexpected negative effects are not created. Whereas a novel system could be identified and determined to be superior down the road, the amount of effort and expense that would be needed to build consensus around such a new model should not be underestimated. Considering the challenges to health care and the population at large that are already occurring as we emerge from the COVID pandemic, as well as the short-term need to monitor the impact from the recent adoption of the acuity circle model which went live in February 2020 and allocates according to MELD but over a broader geographic area based on a circle around the donor hospital, building consensus around incremental changes to a MELD-based allocation system likely represents the best option in our continued quest for the optimal liver allocation system.
Julie K. Heimbach, MD, is a transplant surgeon and the surgical director of liver transplantation at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn. She has no conflicts to report.
References
1. Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network data. Available at https://optn.transplant.hrsa.gov/data/view-data-reports/national-data. Accessed May 1, 2021.
2. Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network. Final rule. Available at https://optn.transplant.hrsa.gov/governance/about-the-optn/final-rule. Accessed May 1, 2021.
3. Wiesner R et al; United Network for Organ Sharing Liver Disease Severity Score Committee. Gastroenterology. 2003 Jan;124(1):91-6.
4. Nagai S et al. Gastroenterology. 2018 Nov;155(5):1451-62.e3.
5. Locke JE et al. JAMA Surg. 2020 Jul 1;155(7):e201129.
Rapid core antigen HCV tests could expand accessibility
A proposed rapid diagnostic test for hepatitis C viral infections that combines an inexpensive but lower-sensitivity core-antigen test with lab RNA confirmation of negative tests could expand testing and same-day initiation of antiviral therapy in places where resources are limited, investigators said.
Applying the proposed method to the Republic of Georgia, with a hepatitis C virus (HCV) prevalence of 5.4% as reported by the World Health Organization, would result in a 95.4% diagnosis rate, compared with 78.8% for lab-based RNA testing, which is the standard of care. Applied to Malaysia, the proposed method would boost diagnosis rates from 57.0% to 91.2%, reported Madeline Adee, MPH, from Massachusetts General Hospital’s Institute for Technology Assessment in Boston and colleagues.
“We found that a novel core antigen rapid diagnostic test for HCV could improve the diagnosis rate and result in cost savings. Although not yet developed, such a test could be a game changer and have a substantial impact on the feasibility and cost of HCV elimination, especially in low and middle-income countries,” they wrote in a poster presented at the meeting sponsored by the European Association for the Study of the Liver.
Although rapid diagnostic tests for HCV can improve diagnosis and treatment rates, currently available molecular tests are expensive and require a solid clinical laboratory infrastructure, which can put such tests out of the reach for clinicians in low- or middle-income countries. Rapid immunoassays based on HCV core antigens are comparative bargains, but their sensitivity ranges from 70% to 90%; in contrast, the third-generation HCV enzyme immunoassay has about a 98% sensitivity.
Could it work?
The proposed testing method would be likely to improve diagnosis, but whether that would translate into increased treatment is uncertain, commented Lesley Miller, MD, who specializes in HCV screening and treatment in underserved populations at Emory University, Atlanta.
“When we’re talking about hepatitis C, it’s all about the care cascade, the drop-off at each step from those who have the disease and aren’t diagnosed, to those who are tested and only partially diagnosed because they don’t have a confirmed infection, to those that get into care, get treated, and get cured,” she said in an interview.
“It’s all about closing the gaps in the care cascade in order to achieve elimination of the virus, which is what we’re all trying to do,” she added.
She pointed that there are certain at-risk populations in the United States, such as injectable-drug users, who might be able to benefit from such a system.
“These folks often have less access to traditional care, so bringing rapid testing and care to where those folks are is really important, so if we can deploy mobile units to areas where there is high prevalence and do it at the point of care, it simplifies the entire process,” she said.
Thomas J. Hoerger, PhD, a senior fellow in health economics and financing at the nonprofit research group RTI International in Research Triangle Park, N.C., said in an interview that the proposed model could eliminate the step in testing in which patients are required to return for confirmation.
“People don’t always come back for further testing, so if you can do it immediately and have the results of a screening test, you might be able to get people to come back more quickly. You still have the problem of the high cost of treatment, but this would at least make it a little more convenient,” he said.
He noted that the success of the strategy would be dependent on the sensitivity of the rapid core antigen test, it’s cost relative to HCV RNA testing, and whether the availability of the rapid test would translate into an improvement in follow-up.
Neither Dr. Miller nor Dr. Hoerger were involved in the study.
Evaluating the approach
To determine whether a lower-cost rapid test could be cost effective, the researchers created a microsimulation model of the natural history of HCV to compare potential outcomes from either core antigen rapid diagnostic testing with a base case sensitivity for HCV viremia of 80% with lab-based RNA confirmation for negative results or the current standard of care with lab-based RNA confirmation only.
The model incorporated METAVIR stage F0-F4, decompensated cirrhosis, hepatocellular carcinoma, and liver-related death. The investigators determined the baseline characteristics of HCV patients in each country based on different distributions of sex, HCV genotype, and METAVIR fibrosis stage.
They simulated outcomes for 10,000 adults in the Republic of Georgia, with an HCV prevalence of 5.4%, and Malaysia, with an HCV prevalence of 1.5%.
The model considers costs from a health care payer’s perspective, and the investigations performed deterministic and probabilistic sensitivity analyses to evaluate how the cost-effectiveness of testing pathways might change when various factors were plugged into the model.
As noted before, the investigators determined that the core antigen rapid test algorithm would improve diagnosis rates in Georgia from 78.8% to 95.4% and in Malaysia from 57.9% to 91.2%.
The use of the rapid test would also increase quality-adjusted life-years in Georgia by 207 per 10,000 and in Malaysia by 146 per 10,000.
Cost savings, primarily from averting the costs of care for patients with HCV, begin within the first year of the model. Over 50 years, the lifetime horizon cost savings in Georgia would be $232,000 per 10,000 people, and the corresponding savings in Malaysia would be $504,000 per 10,000 people.
Even when allowing for variations in parameters, the core antigen rapid diagnostic test approach remained the preferred model, the investigators reported.
The study was supported by the global health agency Unitaid. The researchers, Dr. Miller, and Dr. Hoerger reported no conflicts of interest relevant to the study.
A proposed rapid diagnostic test for hepatitis C viral infections that combines an inexpensive but lower-sensitivity core-antigen test with lab RNA confirmation of negative tests could expand testing and same-day initiation of antiviral therapy in places where resources are limited, investigators said.
Applying the proposed method to the Republic of Georgia, with a hepatitis C virus (HCV) prevalence of 5.4% as reported by the World Health Organization, would result in a 95.4% diagnosis rate, compared with 78.8% for lab-based RNA testing, which is the standard of care. Applied to Malaysia, the proposed method would boost diagnosis rates from 57.0% to 91.2%, reported Madeline Adee, MPH, from Massachusetts General Hospital’s Institute for Technology Assessment in Boston and colleagues.
“We found that a novel core antigen rapid diagnostic test for HCV could improve the diagnosis rate and result in cost savings. Although not yet developed, such a test could be a game changer and have a substantial impact on the feasibility and cost of HCV elimination, especially in low and middle-income countries,” they wrote in a poster presented at the meeting sponsored by the European Association for the Study of the Liver.
Although rapid diagnostic tests for HCV can improve diagnosis and treatment rates, currently available molecular tests are expensive and require a solid clinical laboratory infrastructure, which can put such tests out of the reach for clinicians in low- or middle-income countries. Rapid immunoassays based on HCV core antigens are comparative bargains, but their sensitivity ranges from 70% to 90%; in contrast, the third-generation HCV enzyme immunoassay has about a 98% sensitivity.
Could it work?
The proposed testing method would be likely to improve diagnosis, but whether that would translate into increased treatment is uncertain, commented Lesley Miller, MD, who specializes in HCV screening and treatment in underserved populations at Emory University, Atlanta.
“When we’re talking about hepatitis C, it’s all about the care cascade, the drop-off at each step from those who have the disease and aren’t diagnosed, to those who are tested and only partially diagnosed because they don’t have a confirmed infection, to those that get into care, get treated, and get cured,” she said in an interview.
“It’s all about closing the gaps in the care cascade in order to achieve elimination of the virus, which is what we’re all trying to do,” she added.
She pointed that there are certain at-risk populations in the United States, such as injectable-drug users, who might be able to benefit from such a system.
“These folks often have less access to traditional care, so bringing rapid testing and care to where those folks are is really important, so if we can deploy mobile units to areas where there is high prevalence and do it at the point of care, it simplifies the entire process,” she said.
Thomas J. Hoerger, PhD, a senior fellow in health economics and financing at the nonprofit research group RTI International in Research Triangle Park, N.C., said in an interview that the proposed model could eliminate the step in testing in which patients are required to return for confirmation.
“People don’t always come back for further testing, so if you can do it immediately and have the results of a screening test, you might be able to get people to come back more quickly. You still have the problem of the high cost of treatment, but this would at least make it a little more convenient,” he said.
He noted that the success of the strategy would be dependent on the sensitivity of the rapid core antigen test, it’s cost relative to HCV RNA testing, and whether the availability of the rapid test would translate into an improvement in follow-up.
Neither Dr. Miller nor Dr. Hoerger were involved in the study.
Evaluating the approach
To determine whether a lower-cost rapid test could be cost effective, the researchers created a microsimulation model of the natural history of HCV to compare potential outcomes from either core antigen rapid diagnostic testing with a base case sensitivity for HCV viremia of 80% with lab-based RNA confirmation for negative results or the current standard of care with lab-based RNA confirmation only.
The model incorporated METAVIR stage F0-F4, decompensated cirrhosis, hepatocellular carcinoma, and liver-related death. The investigators determined the baseline characteristics of HCV patients in each country based on different distributions of sex, HCV genotype, and METAVIR fibrosis stage.
They simulated outcomes for 10,000 adults in the Republic of Georgia, with an HCV prevalence of 5.4%, and Malaysia, with an HCV prevalence of 1.5%.
The model considers costs from a health care payer’s perspective, and the investigations performed deterministic and probabilistic sensitivity analyses to evaluate how the cost-effectiveness of testing pathways might change when various factors were plugged into the model.
As noted before, the investigators determined that the core antigen rapid test algorithm would improve diagnosis rates in Georgia from 78.8% to 95.4% and in Malaysia from 57.9% to 91.2%.
The use of the rapid test would also increase quality-adjusted life-years in Georgia by 207 per 10,000 and in Malaysia by 146 per 10,000.
Cost savings, primarily from averting the costs of care for patients with HCV, begin within the first year of the model. Over 50 years, the lifetime horizon cost savings in Georgia would be $232,000 per 10,000 people, and the corresponding savings in Malaysia would be $504,000 per 10,000 people.
Even when allowing for variations in parameters, the core antigen rapid diagnostic test approach remained the preferred model, the investigators reported.
The study was supported by the global health agency Unitaid. The researchers, Dr. Miller, and Dr. Hoerger reported no conflicts of interest relevant to the study.
A proposed rapid diagnostic test for hepatitis C viral infections that combines an inexpensive but lower-sensitivity core-antigen test with lab RNA confirmation of negative tests could expand testing and same-day initiation of antiviral therapy in places where resources are limited, investigators said.
Applying the proposed method to the Republic of Georgia, with a hepatitis C virus (HCV) prevalence of 5.4% as reported by the World Health Organization, would result in a 95.4% diagnosis rate, compared with 78.8% for lab-based RNA testing, which is the standard of care. Applied to Malaysia, the proposed method would boost diagnosis rates from 57.0% to 91.2%, reported Madeline Adee, MPH, from Massachusetts General Hospital’s Institute for Technology Assessment in Boston and colleagues.
“We found that a novel core antigen rapid diagnostic test for HCV could improve the diagnosis rate and result in cost savings. Although not yet developed, such a test could be a game changer and have a substantial impact on the feasibility and cost of HCV elimination, especially in low and middle-income countries,” they wrote in a poster presented at the meeting sponsored by the European Association for the Study of the Liver.
Although rapid diagnostic tests for HCV can improve diagnosis and treatment rates, currently available molecular tests are expensive and require a solid clinical laboratory infrastructure, which can put such tests out of the reach for clinicians in low- or middle-income countries. Rapid immunoassays based on HCV core antigens are comparative bargains, but their sensitivity ranges from 70% to 90%; in contrast, the third-generation HCV enzyme immunoassay has about a 98% sensitivity.
Could it work?
The proposed testing method would be likely to improve diagnosis, but whether that would translate into increased treatment is uncertain, commented Lesley Miller, MD, who specializes in HCV screening and treatment in underserved populations at Emory University, Atlanta.
“When we’re talking about hepatitis C, it’s all about the care cascade, the drop-off at each step from those who have the disease and aren’t diagnosed, to those who are tested and only partially diagnosed because they don’t have a confirmed infection, to those that get into care, get treated, and get cured,” she said in an interview.
“It’s all about closing the gaps in the care cascade in order to achieve elimination of the virus, which is what we’re all trying to do,” she added.
She pointed that there are certain at-risk populations in the United States, such as injectable-drug users, who might be able to benefit from such a system.
“These folks often have less access to traditional care, so bringing rapid testing and care to where those folks are is really important, so if we can deploy mobile units to areas where there is high prevalence and do it at the point of care, it simplifies the entire process,” she said.
Thomas J. Hoerger, PhD, a senior fellow in health economics and financing at the nonprofit research group RTI International in Research Triangle Park, N.C., said in an interview that the proposed model could eliminate the step in testing in which patients are required to return for confirmation.
“People don’t always come back for further testing, so if you can do it immediately and have the results of a screening test, you might be able to get people to come back more quickly. You still have the problem of the high cost of treatment, but this would at least make it a little more convenient,” he said.
He noted that the success of the strategy would be dependent on the sensitivity of the rapid core antigen test, it’s cost relative to HCV RNA testing, and whether the availability of the rapid test would translate into an improvement in follow-up.
Neither Dr. Miller nor Dr. Hoerger were involved in the study.
Evaluating the approach
To determine whether a lower-cost rapid test could be cost effective, the researchers created a microsimulation model of the natural history of HCV to compare potential outcomes from either core antigen rapid diagnostic testing with a base case sensitivity for HCV viremia of 80% with lab-based RNA confirmation for negative results or the current standard of care with lab-based RNA confirmation only.
The model incorporated METAVIR stage F0-F4, decompensated cirrhosis, hepatocellular carcinoma, and liver-related death. The investigators determined the baseline characteristics of HCV patients in each country based on different distributions of sex, HCV genotype, and METAVIR fibrosis stage.
They simulated outcomes for 10,000 adults in the Republic of Georgia, with an HCV prevalence of 5.4%, and Malaysia, with an HCV prevalence of 1.5%.
The model considers costs from a health care payer’s perspective, and the investigations performed deterministic and probabilistic sensitivity analyses to evaluate how the cost-effectiveness of testing pathways might change when various factors were plugged into the model.
As noted before, the investigators determined that the core antigen rapid test algorithm would improve diagnosis rates in Georgia from 78.8% to 95.4% and in Malaysia from 57.9% to 91.2%.
The use of the rapid test would also increase quality-adjusted life-years in Georgia by 207 per 10,000 and in Malaysia by 146 per 10,000.
Cost savings, primarily from averting the costs of care for patients with HCV, begin within the first year of the model. Over 50 years, the lifetime horizon cost savings in Georgia would be $232,000 per 10,000 people, and the corresponding savings in Malaysia would be $504,000 per 10,000 people.
Even when allowing for variations in parameters, the core antigen rapid diagnostic test approach remained the preferred model, the investigators reported.
The study was supported by the global health agency Unitaid. The researchers, Dr. Miller, and Dr. Hoerger reported no conflicts of interest relevant to the study.
FROM ILC 2021
The pandemic hurt patients with liver disease in many ways
The COVID-19 pandemic has worsened the health of patients with liver disease worldwide, researchers say.
Not only does liver disease make people more vulnerable to the virus that causes COVID-19, precautions to prevent its spread have delayed health care and worsened alcohol abuse.
At this year’s virtual International Liver Congress (ILC) 2021, experts from around the world documented this toll on their patients.
Surgeons have seen a surge in patients needing transplants because of alcoholic liver disease, the campaign to snuff out hepatitis C slowed down, and procedures such as endoscopy and ultrasound exams postponed, said Mario Mondelli, MD, PhD, a professor and consultant physician of infectious diseases at the University of Pavia, Italy.
“We were able to ensure only emergency treatments, not routine surveillance,” he said in an interview.
Of 1,994 people with chronic liver disease who responded to a survey through the Global Liver Registry, 11% reported that the pandemic had affected their liver health.
This proportion was not statistically different for the 165 patients (8.2%) who had been diagnosed with COVID-19 compared with those who had not. But many of those who had been diagnosed with COVID-19 reported that it severely affected them. They reported worse overall heath, more mental illness, and greater need for supportive service than those who evaded the virus. Thirty-three respondents (20.8%) were hospitalized.
The global effort to eradicate hepatitis C slowed as a result of the pandemic. Already in 2019, the United States was behind the World Health Organization schedule for eliminating this virus. In 2020, it slipped further, with 25% fewer patients starting treatment for hepatitis C than in 2019, according to researchers at the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Similar delays in eliminating hepatitis C occurred around the world, Dr. Mondelli said, noting that the majority of countries will not be able to reach the WHO objectives.
One striking result of the pandemic was an uptick of patients needing liver transplants as a result of alcoholic liver disease, said George Cholankeril, MD, a liver transplant surgeon at Baylor College of Medicine, Houston.
Before the pandemic, he and his colleagues had noted an increase in the number of people needing liver transplants because of alcohol abuse. During the pandemic, that trend accelerated.
They defined the pre-COVID era as June 1, 2019, to Feb. 29, 2020, and the COVID era as after April 1, 2020. In the COVID era, alcoholic liver disease accounted for 40% of patients whom the hospital put on its list for liver transplant. Hepatitis C and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease combined accounted for only 36%.
The change has resulted in part from the effectiveness of hepatitis C treatments, which have reduced the number of patients with livers damaged by that virus. But the change also resulted from the increased severity of illness in the patients with alcoholic liver disease, Dr. Cholankeril said in an interview. Overall, Model for End-Stage Liver Disease scores – which are used to predict survival – worsened for patients with alcoholic liver disease but remained the same for patients with nonalcoholic liver disease.
In the pre-COVID era, patients with alcoholic liver disease had a 10% higher chance for undergoing transplant, compared with patients with nonalcoholic liver disease. In the COVID era, they had a 50% higher chance, a statistically significant change (P < .001).
The finding parallels those of other studies that have shown a spike in consults for alcohol-related gastrointestinal and liver diseases, as reported by this news organization.
“We feel that the increase in alcoholic hepatitis is possibly from binge drinking and alcoholic consumption during the pandemic,” said Dr. Cholankeril. “Anecdotally, I can’t tell you how many patients say that the video meetings for Alcoholic Anonymous just don’t work. It’s not the same as in person. They don’t feel that they’re getting the support that they need.”
In Europe, fewer of the people who need liver transplants may be receiving them, said Dr. Mondelli.
“There are several papers indicating, particularly in Italy, in France, and in the United Kingdom, that during the pandemic, the offer for organs significantly declined,” he said.
Other studies have shown increases in mortality from liver disease during the pandemic, Dr. Mondelli said. The same is true of myocardial infarction, cancer, and most other life-threatening illnesses, he pointed out.
“Because of the enormous tsunami that has affected hospital services during the peaks of the pandemic, there has been an increase in deceased patients from a variety of other diseases, not only liver disease,” he said.
But Dr. Mondelli also added that physicians had improved in their ability to safely care for their patients while protecting themselves over the course of the pandemic.
Dr. Mondelli and Dr. Cholankeril have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The COVID-19 pandemic has worsened the health of patients with liver disease worldwide, researchers say.
Not only does liver disease make people more vulnerable to the virus that causes COVID-19, precautions to prevent its spread have delayed health care and worsened alcohol abuse.
At this year’s virtual International Liver Congress (ILC) 2021, experts from around the world documented this toll on their patients.
Surgeons have seen a surge in patients needing transplants because of alcoholic liver disease, the campaign to snuff out hepatitis C slowed down, and procedures such as endoscopy and ultrasound exams postponed, said Mario Mondelli, MD, PhD, a professor and consultant physician of infectious diseases at the University of Pavia, Italy.
“We were able to ensure only emergency treatments, not routine surveillance,” he said in an interview.
Of 1,994 people with chronic liver disease who responded to a survey through the Global Liver Registry, 11% reported that the pandemic had affected their liver health.
This proportion was not statistically different for the 165 patients (8.2%) who had been diagnosed with COVID-19 compared with those who had not. But many of those who had been diagnosed with COVID-19 reported that it severely affected them. They reported worse overall heath, more mental illness, and greater need for supportive service than those who evaded the virus. Thirty-three respondents (20.8%) were hospitalized.
The global effort to eradicate hepatitis C slowed as a result of the pandemic. Already in 2019, the United States was behind the World Health Organization schedule for eliminating this virus. In 2020, it slipped further, with 25% fewer patients starting treatment for hepatitis C than in 2019, according to researchers at the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Similar delays in eliminating hepatitis C occurred around the world, Dr. Mondelli said, noting that the majority of countries will not be able to reach the WHO objectives.
One striking result of the pandemic was an uptick of patients needing liver transplants as a result of alcoholic liver disease, said George Cholankeril, MD, a liver transplant surgeon at Baylor College of Medicine, Houston.
Before the pandemic, he and his colleagues had noted an increase in the number of people needing liver transplants because of alcohol abuse. During the pandemic, that trend accelerated.
They defined the pre-COVID era as June 1, 2019, to Feb. 29, 2020, and the COVID era as after April 1, 2020. In the COVID era, alcoholic liver disease accounted for 40% of patients whom the hospital put on its list for liver transplant. Hepatitis C and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease combined accounted for only 36%.
The change has resulted in part from the effectiveness of hepatitis C treatments, which have reduced the number of patients with livers damaged by that virus. But the change also resulted from the increased severity of illness in the patients with alcoholic liver disease, Dr. Cholankeril said in an interview. Overall, Model for End-Stage Liver Disease scores – which are used to predict survival – worsened for patients with alcoholic liver disease but remained the same for patients with nonalcoholic liver disease.
In the pre-COVID era, patients with alcoholic liver disease had a 10% higher chance for undergoing transplant, compared with patients with nonalcoholic liver disease. In the COVID era, they had a 50% higher chance, a statistically significant change (P < .001).
The finding parallels those of other studies that have shown a spike in consults for alcohol-related gastrointestinal and liver diseases, as reported by this news organization.
“We feel that the increase in alcoholic hepatitis is possibly from binge drinking and alcoholic consumption during the pandemic,” said Dr. Cholankeril. “Anecdotally, I can’t tell you how many patients say that the video meetings for Alcoholic Anonymous just don’t work. It’s not the same as in person. They don’t feel that they’re getting the support that they need.”
In Europe, fewer of the people who need liver transplants may be receiving them, said Dr. Mondelli.
“There are several papers indicating, particularly in Italy, in France, and in the United Kingdom, that during the pandemic, the offer for organs significantly declined,” he said.
Other studies have shown increases in mortality from liver disease during the pandemic, Dr. Mondelli said. The same is true of myocardial infarction, cancer, and most other life-threatening illnesses, he pointed out.
“Because of the enormous tsunami that has affected hospital services during the peaks of the pandemic, there has been an increase in deceased patients from a variety of other diseases, not only liver disease,” he said.
But Dr. Mondelli also added that physicians had improved in their ability to safely care for their patients while protecting themselves over the course of the pandemic.
Dr. Mondelli and Dr. Cholankeril have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The COVID-19 pandemic has worsened the health of patients with liver disease worldwide, researchers say.
Not only does liver disease make people more vulnerable to the virus that causes COVID-19, precautions to prevent its spread have delayed health care and worsened alcohol abuse.
At this year’s virtual International Liver Congress (ILC) 2021, experts from around the world documented this toll on their patients.
Surgeons have seen a surge in patients needing transplants because of alcoholic liver disease, the campaign to snuff out hepatitis C slowed down, and procedures such as endoscopy and ultrasound exams postponed, said Mario Mondelli, MD, PhD, a professor and consultant physician of infectious diseases at the University of Pavia, Italy.
“We were able to ensure only emergency treatments, not routine surveillance,” he said in an interview.
Of 1,994 people with chronic liver disease who responded to a survey through the Global Liver Registry, 11% reported that the pandemic had affected their liver health.
This proportion was not statistically different for the 165 patients (8.2%) who had been diagnosed with COVID-19 compared with those who had not. But many of those who had been diagnosed with COVID-19 reported that it severely affected them. They reported worse overall heath, more mental illness, and greater need for supportive service than those who evaded the virus. Thirty-three respondents (20.8%) were hospitalized.
The global effort to eradicate hepatitis C slowed as a result of the pandemic. Already in 2019, the United States was behind the World Health Organization schedule for eliminating this virus. In 2020, it slipped further, with 25% fewer patients starting treatment for hepatitis C than in 2019, according to researchers at the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Similar delays in eliminating hepatitis C occurred around the world, Dr. Mondelli said, noting that the majority of countries will not be able to reach the WHO objectives.
One striking result of the pandemic was an uptick of patients needing liver transplants as a result of alcoholic liver disease, said George Cholankeril, MD, a liver transplant surgeon at Baylor College of Medicine, Houston.
Before the pandemic, he and his colleagues had noted an increase in the number of people needing liver transplants because of alcohol abuse. During the pandemic, that trend accelerated.
They defined the pre-COVID era as June 1, 2019, to Feb. 29, 2020, and the COVID era as after April 1, 2020. In the COVID era, alcoholic liver disease accounted for 40% of patients whom the hospital put on its list for liver transplant. Hepatitis C and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease combined accounted for only 36%.
The change has resulted in part from the effectiveness of hepatitis C treatments, which have reduced the number of patients with livers damaged by that virus. But the change also resulted from the increased severity of illness in the patients with alcoholic liver disease, Dr. Cholankeril said in an interview. Overall, Model for End-Stage Liver Disease scores – which are used to predict survival – worsened for patients with alcoholic liver disease but remained the same for patients with nonalcoholic liver disease.
In the pre-COVID era, patients with alcoholic liver disease had a 10% higher chance for undergoing transplant, compared with patients with nonalcoholic liver disease. In the COVID era, they had a 50% higher chance, a statistically significant change (P < .001).
The finding parallels those of other studies that have shown a spike in consults for alcohol-related gastrointestinal and liver diseases, as reported by this news organization.
“We feel that the increase in alcoholic hepatitis is possibly from binge drinking and alcoholic consumption during the pandemic,” said Dr. Cholankeril. “Anecdotally, I can’t tell you how many patients say that the video meetings for Alcoholic Anonymous just don’t work. It’s not the same as in person. They don’t feel that they’re getting the support that they need.”
In Europe, fewer of the people who need liver transplants may be receiving them, said Dr. Mondelli.
“There are several papers indicating, particularly in Italy, in France, and in the United Kingdom, that during the pandemic, the offer for organs significantly declined,” he said.
Other studies have shown increases in mortality from liver disease during the pandemic, Dr. Mondelli said. The same is true of myocardial infarction, cancer, and most other life-threatening illnesses, he pointed out.
“Because of the enormous tsunami that has affected hospital services during the peaks of the pandemic, there has been an increase in deceased patients from a variety of other diseases, not only liver disease,” he said.
But Dr. Mondelli also added that physicians had improved in their ability to safely care for their patients while protecting themselves over the course of the pandemic.
Dr. Mondelli and Dr. Cholankeril have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Novel liver dialysis device may safely curb ACLF
An investigational liver dialysis device (DIALIVE) was associated with significantly greater survival of patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF), compared with the standard of care in a multicenter randomized study.
Among 30 evaluable patients with ACLF from alcoholic cirrhosis randomized to treatment with the DIALIVE system or standard of care, two-thirds of patients assigned to DIALIVE had both survived and experienced resolution of ACLF by 28 days, compared with one-third of patients assigned to standard of care, reported Banwari Agarwal, MBBS, MD from the Royal Free Hospital in London at the meeting sponsored by the European Association for the Study of the Liver.
Different from MARS
The DIALIVE system differs from the Molecular Adsorbent Recirculating System (MARS) liver dialysis system in that DIALIVE removes and replaces albumin, including proinflammatory albumin, rather than filtering and recirculating it, he explained.
“It addresses systemic inflammation, which wasn’t quite the case with MARS,” he said in the question-and-answer portion of his presentation in a general session.
In patients with ACLF, the risk of 28-day mortality increases substantially as the grade of ACLF increases.
“ACLF, however, is potentially reversible, and the initial grade at presentation undergoes changes over time during the natural course of the illness, with some patients deteriorating, some improving, and some even achieving complete ACLF resolution. The final grade is reached by days 3-7, and it is this final grade which determines their future outcome trajectory. I therefore propose that ACLF resolution in itself is an important therapeutic target,” he said.
Study details
Dr. Agarwal and coinvestigators from eight centers in six European countries enrolled patients with a history indicative of alcohol-related cirrhosis, at least one acute decompensation event, and progression to ACLF grades 1, 2, or 3a.
Patients with an international normalized ratio above 3 were excluded, as were those with more than three organ failures, uncontrolled infections, patients with primary respiratory organ failure, and those with hemodynamic instability refractory to volume resuscitation and low-dose vasopressors.
A total of 32 patients, of whom 30 were evaluable, were randomized to receive liver dialysis in three to five DIALIVE sessions lasting 8-12 hours each (15 evaluable patients) or to standard of care at participating institutions (15 patients).
The investigators looked at safety of the device (the primary endpoint) in all patients who received at least one DIALIVE treatment (safety population), and a modified safety population of patients who received at least three DIALIVE treatments.
The median patient age in each arm was 49 years, and all patients had alcoholic cirrhosis, with alcoholic hepatitis accounting for at least one decompensation event. In addition, about 25% of patients in each arm had decompensation with infections and/or sepsis as precipitating factors.
Safety
Serious adverse events on days 1-10 occurred in 11 of 17 patients in the DIALIVE arm, and in 8 in the standard-of-care arm. In the DIALIVE arm, there were seven treatment-related serious device events, three unexpected serious device events (anemia, septic shock, and hypotension), and one patient discontinued dialysis after having unsafe levels of thrombocytopenia.
Four patients in the DIALIVE arm died on study. The first two died on day 1 one from hypotension, coagulopathy, and multiorgan failure, and this prompted a change in the protocol mandating that DIALIVE be conducted only in an ICU setting with more invasive monitoring and more frequent lab analysis of clotting and other biochemical parameters. Of the two other patients in the DIALIVE arm who on died on study, one died from non-MI cardiac arrest on day 8, and one patient with ACLF grade 3 and a European Foundation for the study of chronic liver failure (CLIF)–ACLF score of 68 died from multiorgan failure.
“I must emphasize that even this very sick patient tolerated the device very, very well,” Dr. Agarwal said.
In the standard-of-care arm, two patients died from progressive liver failure on days 17 and 27, respectively, and one died on day 17 from bacterial infections, bleeding, and progressive liver failure.
There were eight instances of filters clotting out of 64 filters used in total, and four episodes of device deficiency, including two instances where tubing could not be disconnected from an Oxiris filter during setup of the DIALIVE circuit, requiring use of new DIALIVE kits; one use of an incorrect dialysis fluid; and one incorrect setup of the DIALIVE circuit.
Significant improvements in many scores
In the DIALIVE group, there were significant improvements over baseline at day 10 in both liver scores (P < .05) and brain scores (P < .001). In contrast, in the standard-of-care group there were no improvements in individual organ scores, and respiration scores were significantly worse (P < .01).
DIALIVE was also associated with significant improvements in CLIF-C organ failure scores, compared with standard of care at day 5 and day 10 (P = .021 and .001, respectively); CLIF-C–ACLF scores at days 5 and 10 (P = .045 and .023); and Model for End-Stage Liver Disease scores at day 5 (P = .028).
In the DIALIVE group, 40% of patients had ACLF resolution by day 5, and 66.7% had resolution by day 10. In the standard-of-care arm, 15% had resolution on day 5, and 33.3% had resolution on day 10. DIALIVE was also associated with a significantly faster median time to resolution, compared with standard of care (10 days vs. not reached; P = .0307). At 28 days, 10 of 15 evaluable patients were alive and had resolution of ACLF with DIALIVE versus 5 of 15 with standard of care (P = .0281).
Dr. Agarwal said that the data justify the implementation of late-phase clinical trials of the liver dialysis device.
‘Hopeful’ findings
“It’s very early, but we’re really desperate in finding something to bridge to transplantation,” commented Tobias Boettler, MD, from the University of Freiburg (Germany), who was not involved in the study.
“I think this is very hopeful,” said Dr. Boettler, who moderated the briefing where Dr. Agarwal summarized the study findings.
In the question and answer following the talk in a general session, moderator Philip N. Newsome, MD, from University Hospitals Birmingham (England) asked whether patients who were not treated should have been included in the analysis.
Dr. Agarwal replied that “the whole idea behind this study was to understand what this device does to these patients, and how these patients react to this device, so really not looking at the efficacy.”
The study was supported by the European Union’s Horizon 2020 initiative. Dr. Agarwal received a study grant from the initiative, but had no other relevant disclosures. Dr. Boettler and Dr. Newsome had no disclosures relevant to the study.
An investigational liver dialysis device (DIALIVE) was associated with significantly greater survival of patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF), compared with the standard of care in a multicenter randomized study.
Among 30 evaluable patients with ACLF from alcoholic cirrhosis randomized to treatment with the DIALIVE system or standard of care, two-thirds of patients assigned to DIALIVE had both survived and experienced resolution of ACLF by 28 days, compared with one-third of patients assigned to standard of care, reported Banwari Agarwal, MBBS, MD from the Royal Free Hospital in London at the meeting sponsored by the European Association for the Study of the Liver.
Different from MARS
The DIALIVE system differs from the Molecular Adsorbent Recirculating System (MARS) liver dialysis system in that DIALIVE removes and replaces albumin, including proinflammatory albumin, rather than filtering and recirculating it, he explained.
“It addresses systemic inflammation, which wasn’t quite the case with MARS,” he said in the question-and-answer portion of his presentation in a general session.
In patients with ACLF, the risk of 28-day mortality increases substantially as the grade of ACLF increases.
“ACLF, however, is potentially reversible, and the initial grade at presentation undergoes changes over time during the natural course of the illness, with some patients deteriorating, some improving, and some even achieving complete ACLF resolution. The final grade is reached by days 3-7, and it is this final grade which determines their future outcome trajectory. I therefore propose that ACLF resolution in itself is an important therapeutic target,” he said.
Study details
Dr. Agarwal and coinvestigators from eight centers in six European countries enrolled patients with a history indicative of alcohol-related cirrhosis, at least one acute decompensation event, and progression to ACLF grades 1, 2, or 3a.
Patients with an international normalized ratio above 3 were excluded, as were those with more than three organ failures, uncontrolled infections, patients with primary respiratory organ failure, and those with hemodynamic instability refractory to volume resuscitation and low-dose vasopressors.
A total of 32 patients, of whom 30 were evaluable, were randomized to receive liver dialysis in three to five DIALIVE sessions lasting 8-12 hours each (15 evaluable patients) or to standard of care at participating institutions (15 patients).
The investigators looked at safety of the device (the primary endpoint) in all patients who received at least one DIALIVE treatment (safety population), and a modified safety population of patients who received at least three DIALIVE treatments.
The median patient age in each arm was 49 years, and all patients had alcoholic cirrhosis, with alcoholic hepatitis accounting for at least one decompensation event. In addition, about 25% of patients in each arm had decompensation with infections and/or sepsis as precipitating factors.
Safety
Serious adverse events on days 1-10 occurred in 11 of 17 patients in the DIALIVE arm, and in 8 in the standard-of-care arm. In the DIALIVE arm, there were seven treatment-related serious device events, three unexpected serious device events (anemia, septic shock, and hypotension), and one patient discontinued dialysis after having unsafe levels of thrombocytopenia.
Four patients in the DIALIVE arm died on study. The first two died on day 1 one from hypotension, coagulopathy, and multiorgan failure, and this prompted a change in the protocol mandating that DIALIVE be conducted only in an ICU setting with more invasive monitoring and more frequent lab analysis of clotting and other biochemical parameters. Of the two other patients in the DIALIVE arm who on died on study, one died from non-MI cardiac arrest on day 8, and one patient with ACLF grade 3 and a European Foundation for the study of chronic liver failure (CLIF)–ACLF score of 68 died from multiorgan failure.
“I must emphasize that even this very sick patient tolerated the device very, very well,” Dr. Agarwal said.
In the standard-of-care arm, two patients died from progressive liver failure on days 17 and 27, respectively, and one died on day 17 from bacterial infections, bleeding, and progressive liver failure.
There were eight instances of filters clotting out of 64 filters used in total, and four episodes of device deficiency, including two instances where tubing could not be disconnected from an Oxiris filter during setup of the DIALIVE circuit, requiring use of new DIALIVE kits; one use of an incorrect dialysis fluid; and one incorrect setup of the DIALIVE circuit.
Significant improvements in many scores
In the DIALIVE group, there were significant improvements over baseline at day 10 in both liver scores (P < .05) and brain scores (P < .001). In contrast, in the standard-of-care group there were no improvements in individual organ scores, and respiration scores were significantly worse (P < .01).
DIALIVE was also associated with significant improvements in CLIF-C organ failure scores, compared with standard of care at day 5 and day 10 (P = .021 and .001, respectively); CLIF-C–ACLF scores at days 5 and 10 (P = .045 and .023); and Model for End-Stage Liver Disease scores at day 5 (P = .028).
In the DIALIVE group, 40% of patients had ACLF resolution by day 5, and 66.7% had resolution by day 10. In the standard-of-care arm, 15% had resolution on day 5, and 33.3% had resolution on day 10. DIALIVE was also associated with a significantly faster median time to resolution, compared with standard of care (10 days vs. not reached; P = .0307). At 28 days, 10 of 15 evaluable patients were alive and had resolution of ACLF with DIALIVE versus 5 of 15 with standard of care (P = .0281).
Dr. Agarwal said that the data justify the implementation of late-phase clinical trials of the liver dialysis device.
‘Hopeful’ findings
“It’s very early, but we’re really desperate in finding something to bridge to transplantation,” commented Tobias Boettler, MD, from the University of Freiburg (Germany), who was not involved in the study.
“I think this is very hopeful,” said Dr. Boettler, who moderated the briefing where Dr. Agarwal summarized the study findings.
In the question and answer following the talk in a general session, moderator Philip N. Newsome, MD, from University Hospitals Birmingham (England) asked whether patients who were not treated should have been included in the analysis.
Dr. Agarwal replied that “the whole idea behind this study was to understand what this device does to these patients, and how these patients react to this device, so really not looking at the efficacy.”
The study was supported by the European Union’s Horizon 2020 initiative. Dr. Agarwal received a study grant from the initiative, but had no other relevant disclosures. Dr. Boettler and Dr. Newsome had no disclosures relevant to the study.
An investigational liver dialysis device (DIALIVE) was associated with significantly greater survival of patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF), compared with the standard of care in a multicenter randomized study.
Among 30 evaluable patients with ACLF from alcoholic cirrhosis randomized to treatment with the DIALIVE system or standard of care, two-thirds of patients assigned to DIALIVE had both survived and experienced resolution of ACLF by 28 days, compared with one-third of patients assigned to standard of care, reported Banwari Agarwal, MBBS, MD from the Royal Free Hospital in London at the meeting sponsored by the European Association for the Study of the Liver.
Different from MARS
The DIALIVE system differs from the Molecular Adsorbent Recirculating System (MARS) liver dialysis system in that DIALIVE removes and replaces albumin, including proinflammatory albumin, rather than filtering and recirculating it, he explained.
“It addresses systemic inflammation, which wasn’t quite the case with MARS,” he said in the question-and-answer portion of his presentation in a general session.
In patients with ACLF, the risk of 28-day mortality increases substantially as the grade of ACLF increases.
“ACLF, however, is potentially reversible, and the initial grade at presentation undergoes changes over time during the natural course of the illness, with some patients deteriorating, some improving, and some even achieving complete ACLF resolution. The final grade is reached by days 3-7, and it is this final grade which determines their future outcome trajectory. I therefore propose that ACLF resolution in itself is an important therapeutic target,” he said.
Study details
Dr. Agarwal and coinvestigators from eight centers in six European countries enrolled patients with a history indicative of alcohol-related cirrhosis, at least one acute decompensation event, and progression to ACLF grades 1, 2, or 3a.
Patients with an international normalized ratio above 3 were excluded, as were those with more than three organ failures, uncontrolled infections, patients with primary respiratory organ failure, and those with hemodynamic instability refractory to volume resuscitation and low-dose vasopressors.
A total of 32 patients, of whom 30 were evaluable, were randomized to receive liver dialysis in three to five DIALIVE sessions lasting 8-12 hours each (15 evaluable patients) or to standard of care at participating institutions (15 patients).
The investigators looked at safety of the device (the primary endpoint) in all patients who received at least one DIALIVE treatment (safety population), and a modified safety population of patients who received at least three DIALIVE treatments.
The median patient age in each arm was 49 years, and all patients had alcoholic cirrhosis, with alcoholic hepatitis accounting for at least one decompensation event. In addition, about 25% of patients in each arm had decompensation with infections and/or sepsis as precipitating factors.
Safety
Serious adverse events on days 1-10 occurred in 11 of 17 patients in the DIALIVE arm, and in 8 in the standard-of-care arm. In the DIALIVE arm, there were seven treatment-related serious device events, three unexpected serious device events (anemia, septic shock, and hypotension), and one patient discontinued dialysis after having unsafe levels of thrombocytopenia.
Four patients in the DIALIVE arm died on study. The first two died on day 1 one from hypotension, coagulopathy, and multiorgan failure, and this prompted a change in the protocol mandating that DIALIVE be conducted only in an ICU setting with more invasive monitoring and more frequent lab analysis of clotting and other biochemical parameters. Of the two other patients in the DIALIVE arm who on died on study, one died from non-MI cardiac arrest on day 8, and one patient with ACLF grade 3 and a European Foundation for the study of chronic liver failure (CLIF)–ACLF score of 68 died from multiorgan failure.
“I must emphasize that even this very sick patient tolerated the device very, very well,” Dr. Agarwal said.
In the standard-of-care arm, two patients died from progressive liver failure on days 17 and 27, respectively, and one died on day 17 from bacterial infections, bleeding, and progressive liver failure.
There were eight instances of filters clotting out of 64 filters used in total, and four episodes of device deficiency, including two instances where tubing could not be disconnected from an Oxiris filter during setup of the DIALIVE circuit, requiring use of new DIALIVE kits; one use of an incorrect dialysis fluid; and one incorrect setup of the DIALIVE circuit.
Significant improvements in many scores
In the DIALIVE group, there were significant improvements over baseline at day 10 in both liver scores (P < .05) and brain scores (P < .001). In contrast, in the standard-of-care group there were no improvements in individual organ scores, and respiration scores were significantly worse (P < .01).
DIALIVE was also associated with significant improvements in CLIF-C organ failure scores, compared with standard of care at day 5 and day 10 (P = .021 and .001, respectively); CLIF-C–ACLF scores at days 5 and 10 (P = .045 and .023); and Model for End-Stage Liver Disease scores at day 5 (P = .028).
In the DIALIVE group, 40% of patients had ACLF resolution by day 5, and 66.7% had resolution by day 10. In the standard-of-care arm, 15% had resolution on day 5, and 33.3% had resolution on day 10. DIALIVE was also associated with a significantly faster median time to resolution, compared with standard of care (10 days vs. not reached; P = .0307). At 28 days, 10 of 15 evaluable patients were alive and had resolution of ACLF with DIALIVE versus 5 of 15 with standard of care (P = .0281).
Dr. Agarwal said that the data justify the implementation of late-phase clinical trials of the liver dialysis device.
‘Hopeful’ findings
“It’s very early, but we’re really desperate in finding something to bridge to transplantation,” commented Tobias Boettler, MD, from the University of Freiburg (Germany), who was not involved in the study.
“I think this is very hopeful,” said Dr. Boettler, who moderated the briefing where Dr. Agarwal summarized the study findings.
In the question and answer following the talk in a general session, moderator Philip N. Newsome, MD, from University Hospitals Birmingham (England) asked whether patients who were not treated should have been included in the analysis.
Dr. Agarwal replied that “the whole idea behind this study was to understand what this device does to these patients, and how these patients react to this device, so really not looking at the efficacy.”
The study was supported by the European Union’s Horizon 2020 initiative. Dr. Agarwal received a study grant from the initiative, but had no other relevant disclosures. Dr. Boettler and Dr. Newsome had no disclosures relevant to the study.
FROM ILC 2021









