User login
Decoding biosimilar approvals
SAN FRANCISCO – Several factors must be considered when extrapolating biosimilar results, according to a speaker at the National Comprehensive Cancer Network Hematologic Malignancies Annual Congress.
In this context, “extrapolation” means expanding the use of an approved biosimilar from one indication to another, based on efficacy and safety data from the first indication, Andrew D. Zelenetz, MD, PhD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, explained at the meeting.
To determine if extrapolation is appropriate, regulatory agencies consider the biosimilar’s mechanism of action in each indication; pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and immunogenicity in the different patient populations; differences in expected toxicities for each condition and population; and any other factor that may affect safety or efficacy.
To illustrate the process, Dr. Zelenetz explained how results with a rituximab biosimilar in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) cannot be extrapolated to B‐cell non‐Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), but results with that same biosimilar in follicular lymphoma can be extrapolated to other types of B-cell NHL.
The biosimilar is rituximab-abbs (CT‐P10, Truxima). In a phase 1 trial of patients with RA, rituximab-abbs demonstrated biosimilarity to the reference product (Ann Rheum Dis. 2017;76[3]:566‐70).
The RA results cannot be extrapolated to B-cell NHL for a few reasons, according to Dr. Zelenetz. He noted that rituximab’s mechanism of action is antibody-dependent cell‐mediated cytotoxicity in both RA and NHL. However, the target in RA is the normal B cell, and the target in NHL is the malignant B cell.
In addition, the pharmacokinetics of rituximab are “drastically different” in RA and NHL, Dr. Zelenetz said. Differences in pharmacokinetics support different dosing approaches in the two diseases.
Another big difference is immunogenicity. Anti‐CD20 antibodies develop in 15%-17% of RA patients, Dr. Zelenetz said, but the risk of antibody development is less than 1% in lymphoma.
Though extrapolation from RA to B‐cell NHL was not possible, it was possible to extrapolate results with rituximab-abbs in follicular lymphoma to other B-cell NHLs.
The study used was a phase 3 trial comparing rituximab-abbs to rituximab – both in combination with cyclophosphamide, vincristine, and prednisone – in patients with newly diagnosed, advanced stage follicular lymphoma.
This study showed no difference in pharmacokinetics or pharmacodynamics between rituximab-abbs and rituximab. The two agents also had comparable safety profiles and produced similar response rates (Lancet Haematol. 2017 Jul 13;4:e362‐73).
Rituximab‐abbs was approved in the United States based on these data, and results from this trial were extrapolated to other types of B-cell NHL. The results were extrapolated because the mechanism of action, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and immunogenicity of rituximab are the same across B-cell NHLs, Dr. Zelenetz noted.
“Extrapolation is a critical part of biosimilarity development,” he said. “As long as scientific justification for extrapolation exists, I believe that extrapolation makes good sense.”
Dr. Zelenetz reported relationships with AbbVie, Adaptive Biotechnologies, Amgen, AstraZeneca, BeiGene, Celgene, Genentech, Gilead Sciences, Janssen, MEI Pharma, MorphoSys AG, Novartis, Pharmacyclics, and Roche.
SAN FRANCISCO – Several factors must be considered when extrapolating biosimilar results, according to a speaker at the National Comprehensive Cancer Network Hematologic Malignancies Annual Congress.
In this context, “extrapolation” means expanding the use of an approved biosimilar from one indication to another, based on efficacy and safety data from the first indication, Andrew D. Zelenetz, MD, PhD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, explained at the meeting.
To determine if extrapolation is appropriate, regulatory agencies consider the biosimilar’s mechanism of action in each indication; pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and immunogenicity in the different patient populations; differences in expected toxicities for each condition and population; and any other factor that may affect safety or efficacy.
To illustrate the process, Dr. Zelenetz explained how results with a rituximab biosimilar in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) cannot be extrapolated to B‐cell non‐Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), but results with that same biosimilar in follicular lymphoma can be extrapolated to other types of B-cell NHL.
The biosimilar is rituximab-abbs (CT‐P10, Truxima). In a phase 1 trial of patients with RA, rituximab-abbs demonstrated biosimilarity to the reference product (Ann Rheum Dis. 2017;76[3]:566‐70).
The RA results cannot be extrapolated to B-cell NHL for a few reasons, according to Dr. Zelenetz. He noted that rituximab’s mechanism of action is antibody-dependent cell‐mediated cytotoxicity in both RA and NHL. However, the target in RA is the normal B cell, and the target in NHL is the malignant B cell.
In addition, the pharmacokinetics of rituximab are “drastically different” in RA and NHL, Dr. Zelenetz said. Differences in pharmacokinetics support different dosing approaches in the two diseases.
Another big difference is immunogenicity. Anti‐CD20 antibodies develop in 15%-17% of RA patients, Dr. Zelenetz said, but the risk of antibody development is less than 1% in lymphoma.
Though extrapolation from RA to B‐cell NHL was not possible, it was possible to extrapolate results with rituximab-abbs in follicular lymphoma to other B-cell NHLs.
The study used was a phase 3 trial comparing rituximab-abbs to rituximab – both in combination with cyclophosphamide, vincristine, and prednisone – in patients with newly diagnosed, advanced stage follicular lymphoma.
This study showed no difference in pharmacokinetics or pharmacodynamics between rituximab-abbs and rituximab. The two agents also had comparable safety profiles and produced similar response rates (Lancet Haematol. 2017 Jul 13;4:e362‐73).
Rituximab‐abbs was approved in the United States based on these data, and results from this trial were extrapolated to other types of B-cell NHL. The results were extrapolated because the mechanism of action, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and immunogenicity of rituximab are the same across B-cell NHLs, Dr. Zelenetz noted.
“Extrapolation is a critical part of biosimilarity development,” he said. “As long as scientific justification for extrapolation exists, I believe that extrapolation makes good sense.”
Dr. Zelenetz reported relationships with AbbVie, Adaptive Biotechnologies, Amgen, AstraZeneca, BeiGene, Celgene, Genentech, Gilead Sciences, Janssen, MEI Pharma, MorphoSys AG, Novartis, Pharmacyclics, and Roche.
SAN FRANCISCO – Several factors must be considered when extrapolating biosimilar results, according to a speaker at the National Comprehensive Cancer Network Hematologic Malignancies Annual Congress.
In this context, “extrapolation” means expanding the use of an approved biosimilar from one indication to another, based on efficacy and safety data from the first indication, Andrew D. Zelenetz, MD, PhD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, explained at the meeting.
To determine if extrapolation is appropriate, regulatory agencies consider the biosimilar’s mechanism of action in each indication; pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and immunogenicity in the different patient populations; differences in expected toxicities for each condition and population; and any other factor that may affect safety or efficacy.
To illustrate the process, Dr. Zelenetz explained how results with a rituximab biosimilar in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) cannot be extrapolated to B‐cell non‐Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), but results with that same biosimilar in follicular lymphoma can be extrapolated to other types of B-cell NHL.
The biosimilar is rituximab-abbs (CT‐P10, Truxima). In a phase 1 trial of patients with RA, rituximab-abbs demonstrated biosimilarity to the reference product (Ann Rheum Dis. 2017;76[3]:566‐70).
The RA results cannot be extrapolated to B-cell NHL for a few reasons, according to Dr. Zelenetz. He noted that rituximab’s mechanism of action is antibody-dependent cell‐mediated cytotoxicity in both RA and NHL. However, the target in RA is the normal B cell, and the target in NHL is the malignant B cell.
In addition, the pharmacokinetics of rituximab are “drastically different” in RA and NHL, Dr. Zelenetz said. Differences in pharmacokinetics support different dosing approaches in the two diseases.
Another big difference is immunogenicity. Anti‐CD20 antibodies develop in 15%-17% of RA patients, Dr. Zelenetz said, but the risk of antibody development is less than 1% in lymphoma.
Though extrapolation from RA to B‐cell NHL was not possible, it was possible to extrapolate results with rituximab-abbs in follicular lymphoma to other B-cell NHLs.
The study used was a phase 3 trial comparing rituximab-abbs to rituximab – both in combination with cyclophosphamide, vincristine, and prednisone – in patients with newly diagnosed, advanced stage follicular lymphoma.
This study showed no difference in pharmacokinetics or pharmacodynamics between rituximab-abbs and rituximab. The two agents also had comparable safety profiles and produced similar response rates (Lancet Haematol. 2017 Jul 13;4:e362‐73).
Rituximab‐abbs was approved in the United States based on these data, and results from this trial were extrapolated to other types of B-cell NHL. The results were extrapolated because the mechanism of action, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and immunogenicity of rituximab are the same across B-cell NHLs, Dr. Zelenetz noted.
“Extrapolation is a critical part of biosimilarity development,” he said. “As long as scientific justification for extrapolation exists, I believe that extrapolation makes good sense.”
Dr. Zelenetz reported relationships with AbbVie, Adaptive Biotechnologies, Amgen, AstraZeneca, BeiGene, Celgene, Genentech, Gilead Sciences, Janssen, MEI Pharma, MorphoSys AG, Novartis, Pharmacyclics, and Roche.
REPORTING FROM NCCN HEMATOLOGIC MALIGNANCIES
Study finds no standard for treatment discontinuation in myeloma
BOSTON — There is “no standard of care and no clear pattern” for discontinuing treatment in multiple myeloma, according to a speaker at the International Myeloma Workshop.
Data from a large, observational study revealed that a wide range of treatment regimens are used for first-, second-, and third-line therapy in multiple myeloma. The duration of therapy and time to next treatment were shorter in this real-world study than in prior clinical trials, and reasons for treatment discontinuation varied by regimen and line of therapy.
Katja Weisel, MD, of University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf in Germany, presented these findings at the workshop, held by the International Myeloma Society.
The study, INSIGHT MM, is the largest global, prospective, observational study of multiple myeloma to date, according to Dr. Weisel. The study, which began July 1, 2016, has enrolled patients in the United States (n = 1,004), Europe (n = 1,612), Latin America (n = 367), and Asia (n = 218).
Dr. Weisel and her colleagues evaluated duration of therapy, reasons for treatment discontinuation, and subsequent therapies in a subset of patients on INSIGHT MM. The researchers’ analysis revealed “broad heterogeneity” across lines of therapy, Dr. Weisel said, adding that patients are receiving multiple regimens in addition to the most commonly prescribed regimens in myeloma.
First-line therapy
“In first-line treatment, we see predominantly bortezomib-based triplets ... regardless of transplant-eligible or transplant-ineligible patients,” Dr. Weisel said. “This is followed by doublets and other more rarely [applied] regimens.”
First-line therapies in 1,175 patients included:
- Bortezomib, cyclophosphamide, and dexamethasone (VCd) – 323 patients.
- Bortezomib, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone (VRd) – 321 patients.
- Bortezomib, thalidomide, and dexamethasone (VTd) – 200 patients.
- Bortezomib and dexamethasone (Vd) – 102 patients.
- Lenalidomide and dexamethasone (Rd) – 90 patients.
- Bortezomib, melphalan, and prednisone (VMP) – 53 patients.
- Carfilzomib, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone (KRd) – 47 patients.
- Daratumumab-based regimens (Dara) – 32 patients.
- Carfilzomib and dexamethasone (Kd) – 5 patients.
- Ixazomib, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone (IRd) – 2 patients.
Of the 1,175 newly diagnosed patients, 894 did not proceed to transplant after first-line therapy, but 281 did. Most of the patients who went on to transplant had received VRd (n = 82), VTd (n = 76), or VCd (n = 75).
Second- and third-line therapies
“In second-line treatment, we have still a dominance of the len-dex regimen all over the world,” Dr. Weisel said. “There is an emerging use of daratumumab in various combinations, and then you see the whole spectrum of approved triplet and doublet regimens.”
In the third line, the most commonly used regimens are daratumumab-based combinations and Rd.
There were 548 patients who received second-line treatment and 332 who received third-line therapy. The regimens used were:
- Rd – 130 patients second line, 71 third line.
- Dara – 121 patients second line, 105 third line.
- KRd – 61 patients second line, 17 third line.
- VCd – 57 patients second line, 19 third line.
- Vd – 48 patients second line, 29 third line.
- VRd – 36 patients second line, 8 third line.
- Kd – 33 patients for both second and third line.
- IRd – 29 patients second line, 43 third line.
- VTd – 25 patients second line, 4 third line.
- VMP – 8 patients second line, 3 third line.
Duration of therapy
Most transplant-eligible patients received any first-line therapy (VRd, VTd, or VCd) for longer than 12 months. Among transplant-ineligible patients, Rd was the first-line therapy most likely to be given for 12 months or more.
None of the second-line regimens lasted longer than 12 months in a majority of patients, but daratumumab-based regimens and IRd were the therapies most likely to exceed 12 months’ duration in both second- and third-line treatment.
Time to next treatment
“The vast majority of [transplant-eligible] patients, close to 90% ... do not need a second-line treatment during the first year of treatment,” Dr. Weisel said. “However, for transplant-ineligible patients, this accounts only for the most effective regimens, VMP and Rd.”
For second- and third-line therapies, a 12-month or longer time to next treatment was most likely among patients who received IRd or daratumumab-based regimens.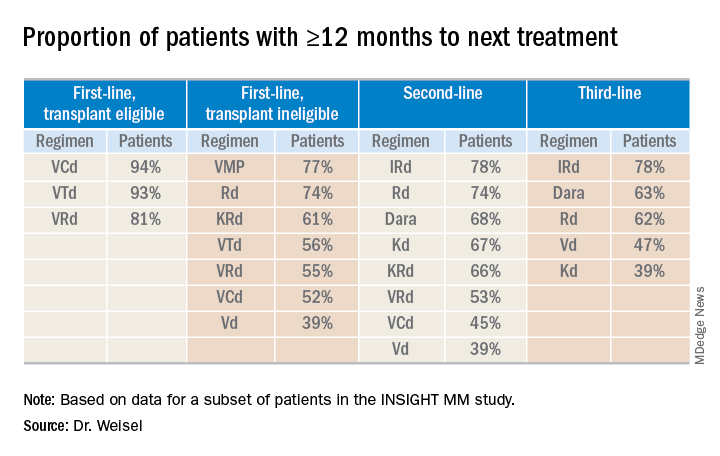
Reasons for discontinuation
“Planned end of therapy only accounts for a small proportion of treatment discontinuations, especially in the relapsed setting,” Dr. Weisel said. “Patients are discontinuing treatment due to reasons other than relapse, ultimately receiving fixed-duration therapy.”
The most common reasons for discontinuation of first-line therapy were:
- Relapse for VCd.
- Planned end of therapy for VRd.
- Adverse events (AEs) for VD and VTd.
- AEs and “other reasons” for Rd.
The most common reasons for discontinuation of second-line therapy were:
- Planned end of therapy for VCd.
- AEs, relapse, and other reasons for VRd.
- Relapse for VD, KRd, and Dara.
- AEs for Rd and IRd.
- AEs and other reasons for Kd.
The most common reasons for discontinuation of third-line therapy were:
- AEs for VCd, Vd, and KRd.
- Relapse for Kd, IRd, and Dara.
- Relapse and other reasons for VRd.
- AEs and other reasons for Rd.
The most common AE leading to discontinuation, across all treatment regimens, was peripheral neuropathy. This suggests peripheral neuropathy is still the “biggest impediment for continuous treatment,” Dr. Weisel said.
INSIGHT MM is sponsored by Takeda. Dr. Weisel reported relationships with Takeda and several other companies.
SOURCE: Weisel K et al. IMW 2019, Abstract OAB-005.
BOSTON — There is “no standard of care and no clear pattern” for discontinuing treatment in multiple myeloma, according to a speaker at the International Myeloma Workshop.
Data from a large, observational study revealed that a wide range of treatment regimens are used for first-, second-, and third-line therapy in multiple myeloma. The duration of therapy and time to next treatment were shorter in this real-world study than in prior clinical trials, and reasons for treatment discontinuation varied by regimen and line of therapy.
Katja Weisel, MD, of University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf in Germany, presented these findings at the workshop, held by the International Myeloma Society.
The study, INSIGHT MM, is the largest global, prospective, observational study of multiple myeloma to date, according to Dr. Weisel. The study, which began July 1, 2016, has enrolled patients in the United States (n = 1,004), Europe (n = 1,612), Latin America (n = 367), and Asia (n = 218).
Dr. Weisel and her colleagues evaluated duration of therapy, reasons for treatment discontinuation, and subsequent therapies in a subset of patients on INSIGHT MM. The researchers’ analysis revealed “broad heterogeneity” across lines of therapy, Dr. Weisel said, adding that patients are receiving multiple regimens in addition to the most commonly prescribed regimens in myeloma.
First-line therapy
“In first-line treatment, we see predominantly bortezomib-based triplets ... regardless of transplant-eligible or transplant-ineligible patients,” Dr. Weisel said. “This is followed by doublets and other more rarely [applied] regimens.”
First-line therapies in 1,175 patients included:
- Bortezomib, cyclophosphamide, and dexamethasone (VCd) – 323 patients.
- Bortezomib, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone (VRd) – 321 patients.
- Bortezomib, thalidomide, and dexamethasone (VTd) – 200 patients.
- Bortezomib and dexamethasone (Vd) – 102 patients.
- Lenalidomide and dexamethasone (Rd) – 90 patients.
- Bortezomib, melphalan, and prednisone (VMP) – 53 patients.
- Carfilzomib, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone (KRd) – 47 patients.
- Daratumumab-based regimens (Dara) – 32 patients.
- Carfilzomib and dexamethasone (Kd) – 5 patients.
- Ixazomib, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone (IRd) – 2 patients.
Of the 1,175 newly diagnosed patients, 894 did not proceed to transplant after first-line therapy, but 281 did. Most of the patients who went on to transplant had received VRd (n = 82), VTd (n = 76), or VCd (n = 75).
Second- and third-line therapies
“In second-line treatment, we have still a dominance of the len-dex regimen all over the world,” Dr. Weisel said. “There is an emerging use of daratumumab in various combinations, and then you see the whole spectrum of approved triplet and doublet regimens.”
In the third line, the most commonly used regimens are daratumumab-based combinations and Rd.
There were 548 patients who received second-line treatment and 332 who received third-line therapy. The regimens used were:
- Rd – 130 patients second line, 71 third line.
- Dara – 121 patients second line, 105 third line.
- KRd – 61 patients second line, 17 third line.
- VCd – 57 patients second line, 19 third line.
- Vd – 48 patients second line, 29 third line.
- VRd – 36 patients second line, 8 third line.
- Kd – 33 patients for both second and third line.
- IRd – 29 patients second line, 43 third line.
- VTd – 25 patients second line, 4 third line.
- VMP – 8 patients second line, 3 third line.
Duration of therapy
Most transplant-eligible patients received any first-line therapy (VRd, VTd, or VCd) for longer than 12 months. Among transplant-ineligible patients, Rd was the first-line therapy most likely to be given for 12 months or more.
None of the second-line regimens lasted longer than 12 months in a majority of patients, but daratumumab-based regimens and IRd were the therapies most likely to exceed 12 months’ duration in both second- and third-line treatment.
Time to next treatment
“The vast majority of [transplant-eligible] patients, close to 90% ... do not need a second-line treatment during the first year of treatment,” Dr. Weisel said. “However, for transplant-ineligible patients, this accounts only for the most effective regimens, VMP and Rd.”
For second- and third-line therapies, a 12-month or longer time to next treatment was most likely among patients who received IRd or daratumumab-based regimens.
Reasons for discontinuation
“Planned end of therapy only accounts for a small proportion of treatment discontinuations, especially in the relapsed setting,” Dr. Weisel said. “Patients are discontinuing treatment due to reasons other than relapse, ultimately receiving fixed-duration therapy.”
The most common reasons for discontinuation of first-line therapy were:
- Relapse for VCd.
- Planned end of therapy for VRd.
- Adverse events (AEs) for VD and VTd.
- AEs and “other reasons” for Rd.
The most common reasons for discontinuation of second-line therapy were:
- Planned end of therapy for VCd.
- AEs, relapse, and other reasons for VRd.
- Relapse for VD, KRd, and Dara.
- AEs for Rd and IRd.
- AEs and other reasons for Kd.
The most common reasons for discontinuation of third-line therapy were:
- AEs for VCd, Vd, and KRd.
- Relapse for Kd, IRd, and Dara.
- Relapse and other reasons for VRd.
- AEs and other reasons for Rd.
The most common AE leading to discontinuation, across all treatment regimens, was peripheral neuropathy. This suggests peripheral neuropathy is still the “biggest impediment for continuous treatment,” Dr. Weisel said.
INSIGHT MM is sponsored by Takeda. Dr. Weisel reported relationships with Takeda and several other companies.
SOURCE: Weisel K et al. IMW 2019, Abstract OAB-005.
BOSTON — There is “no standard of care and no clear pattern” for discontinuing treatment in multiple myeloma, according to a speaker at the International Myeloma Workshop.
Data from a large, observational study revealed that a wide range of treatment regimens are used for first-, second-, and third-line therapy in multiple myeloma. The duration of therapy and time to next treatment were shorter in this real-world study than in prior clinical trials, and reasons for treatment discontinuation varied by regimen and line of therapy.
Katja Weisel, MD, of University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf in Germany, presented these findings at the workshop, held by the International Myeloma Society.
The study, INSIGHT MM, is the largest global, prospective, observational study of multiple myeloma to date, according to Dr. Weisel. The study, which began July 1, 2016, has enrolled patients in the United States (n = 1,004), Europe (n = 1,612), Latin America (n = 367), and Asia (n = 218).
Dr. Weisel and her colleagues evaluated duration of therapy, reasons for treatment discontinuation, and subsequent therapies in a subset of patients on INSIGHT MM. The researchers’ analysis revealed “broad heterogeneity” across lines of therapy, Dr. Weisel said, adding that patients are receiving multiple regimens in addition to the most commonly prescribed regimens in myeloma.
First-line therapy
“In first-line treatment, we see predominantly bortezomib-based triplets ... regardless of transplant-eligible or transplant-ineligible patients,” Dr. Weisel said. “This is followed by doublets and other more rarely [applied] regimens.”
First-line therapies in 1,175 patients included:
- Bortezomib, cyclophosphamide, and dexamethasone (VCd) – 323 patients.
- Bortezomib, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone (VRd) – 321 patients.
- Bortezomib, thalidomide, and dexamethasone (VTd) – 200 patients.
- Bortezomib and dexamethasone (Vd) – 102 patients.
- Lenalidomide and dexamethasone (Rd) – 90 patients.
- Bortezomib, melphalan, and prednisone (VMP) – 53 patients.
- Carfilzomib, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone (KRd) – 47 patients.
- Daratumumab-based regimens (Dara) – 32 patients.
- Carfilzomib and dexamethasone (Kd) – 5 patients.
- Ixazomib, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone (IRd) – 2 patients.
Of the 1,175 newly diagnosed patients, 894 did not proceed to transplant after first-line therapy, but 281 did. Most of the patients who went on to transplant had received VRd (n = 82), VTd (n = 76), or VCd (n = 75).
Second- and third-line therapies
“In second-line treatment, we have still a dominance of the len-dex regimen all over the world,” Dr. Weisel said. “There is an emerging use of daratumumab in various combinations, and then you see the whole spectrum of approved triplet and doublet regimens.”
In the third line, the most commonly used regimens are daratumumab-based combinations and Rd.
There were 548 patients who received second-line treatment and 332 who received third-line therapy. The regimens used were:
- Rd – 130 patients second line, 71 third line.
- Dara – 121 patients second line, 105 third line.
- KRd – 61 patients second line, 17 third line.
- VCd – 57 patients second line, 19 third line.
- Vd – 48 patients second line, 29 third line.
- VRd – 36 patients second line, 8 third line.
- Kd – 33 patients for both second and third line.
- IRd – 29 patients second line, 43 third line.
- VTd – 25 patients second line, 4 third line.
- VMP – 8 patients second line, 3 third line.
Duration of therapy
Most transplant-eligible patients received any first-line therapy (VRd, VTd, or VCd) for longer than 12 months. Among transplant-ineligible patients, Rd was the first-line therapy most likely to be given for 12 months or more.
None of the second-line regimens lasted longer than 12 months in a majority of patients, but daratumumab-based regimens and IRd were the therapies most likely to exceed 12 months’ duration in both second- and third-line treatment.
Time to next treatment
“The vast majority of [transplant-eligible] patients, close to 90% ... do not need a second-line treatment during the first year of treatment,” Dr. Weisel said. “However, for transplant-ineligible patients, this accounts only for the most effective regimens, VMP and Rd.”
For second- and third-line therapies, a 12-month or longer time to next treatment was most likely among patients who received IRd or daratumumab-based regimens.
Reasons for discontinuation
“Planned end of therapy only accounts for a small proportion of treatment discontinuations, especially in the relapsed setting,” Dr. Weisel said. “Patients are discontinuing treatment due to reasons other than relapse, ultimately receiving fixed-duration therapy.”
The most common reasons for discontinuation of first-line therapy were:
- Relapse for VCd.
- Planned end of therapy for VRd.
- Adverse events (AEs) for VD and VTd.
- AEs and “other reasons” for Rd.
The most common reasons for discontinuation of second-line therapy were:
- Planned end of therapy for VCd.
- AEs, relapse, and other reasons for VRd.
- Relapse for VD, KRd, and Dara.
- AEs for Rd and IRd.
- AEs and other reasons for Kd.
The most common reasons for discontinuation of third-line therapy were:
- AEs for VCd, Vd, and KRd.
- Relapse for Kd, IRd, and Dara.
- Relapse and other reasons for VRd.
- AEs and other reasons for Rd.
The most common AE leading to discontinuation, across all treatment regimens, was peripheral neuropathy. This suggests peripheral neuropathy is still the “biggest impediment for continuous treatment,” Dr. Weisel said.
INSIGHT MM is sponsored by Takeda. Dr. Weisel reported relationships with Takeda and several other companies.
SOURCE: Weisel K et al. IMW 2019, Abstract OAB-005.
REPORTING FROM IMW 2019
Second-generation anti-BCMA CAR T-cell therapy shows promise in myeloma trial
BOSTON – CT053, a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy, has demonstrated efficacy and tolerability in a phase 1 trial of patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma.
CT053 produced an objective response rate of 87.5% and a complete response rate of 79.2%. All patients experienced grade 3 or higher adverse events (AEs), but none developed grade 3 or higher cytokine-release syndrome (CRS).
Siguo Hao, MD, of Xinhua Hospital, Shanghai (China) Jiaotong University, presented these results at the International Myeloma Workshop held by the International Myeloma Society.
Dr. Hao explained that CT053 consists of autologous T cells modified with a second-generation CAR that incorporates a fully human anti–B-cell maturation antigen single-chain fragment variant, a 4-1BB costimulatory domain, and a CD3-zeta–signaling domain.
In preclinical studies, CT053 induced dose-dependent cytotoxic effects on multiple myeloma cell lines and completely eradicated myeloma in mice.
Dr. Hao and his colleagues conducted the phase 1 study of CT053 at three sites (NCT03716856, NCT03302403, and NCT03380039). The study enrolled 30 patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma, and 24 ultimately received CT053.
In the 24 patients, the median age was 60.2 years (range, 38.5-70.0 years), and the median time since diagnosis was 3.5 years (range, 0.3-10.8 years). Nine patients had progressive disease at baseline.
The patients had received a median of 5 prior therapies (range, 2-12). All patients had received a proteasome inhibitor, 22 had received an immunomodulatory agent, 10 had undergone a transplant, and 5 had received an anti-CD38 monoclonal antibody.
For this study, patients received conditioning with fludarabine and cyclophosphamide, followed by a single infusion of CT053. Most patients (n = 21) received 1.5 x 108 cells, but three received 0.5 x 108, 1 x 108, and 1.8 x 108 cells, respectively.
The median follow-up was 333 days. CAR T cells were detectable 1-7 days after infusion and peaked at 7-21 days. The cells persisted for a median of 172 days (range, 21-341 days).
A total of 21 patients responded to treatment (87.5%). There were 19 patients with a complete response or stringent complete response, 1 patient with a very good partial response, and 1 with a partial response.
Dr. Hao noted that CT053 was effective even at the lowest dose. The patient who received 0.5 x 108 cells initially achieved a very good partial response that deepened to a stringent complete response on day 502 after infusion.
Ten patients still had a stringent complete response at last follow-up, and two had a complete response. Nine patients progressed, and one patient relapsed after achieving a complete response. Three patients died, two from disease progression and one from a serious AE (neutropenic infection).
All 24 patients experienced a treatment-related AE, and all had grade 3 or higher hematologic AEs. Six patients had grade 3 or higher fever, six had grade 3 or higher infections and infestations, and one had grade 3 or higher neurotoxicity.
Three patients had grade 1 CRS, and 12 had grade 2 CRS. None of the patients had grade 3 or higher CRS.
This trial was sponsored by Xinhua Hospital/Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, First Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang University, and First Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University in collaboration with Carsgen Therapeutics. Dr. Hao did not disclose any conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Hao S et al. IMW 2019, Abstract OAB-082.
BOSTON – CT053, a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy, has demonstrated efficacy and tolerability in a phase 1 trial of patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma.
CT053 produced an objective response rate of 87.5% and a complete response rate of 79.2%. All patients experienced grade 3 or higher adverse events (AEs), but none developed grade 3 or higher cytokine-release syndrome (CRS).
Siguo Hao, MD, of Xinhua Hospital, Shanghai (China) Jiaotong University, presented these results at the International Myeloma Workshop held by the International Myeloma Society.
Dr. Hao explained that CT053 consists of autologous T cells modified with a second-generation CAR that incorporates a fully human anti–B-cell maturation antigen single-chain fragment variant, a 4-1BB costimulatory domain, and a CD3-zeta–signaling domain.
In preclinical studies, CT053 induced dose-dependent cytotoxic effects on multiple myeloma cell lines and completely eradicated myeloma in mice.
Dr. Hao and his colleagues conducted the phase 1 study of CT053 at three sites (NCT03716856, NCT03302403, and NCT03380039). The study enrolled 30 patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma, and 24 ultimately received CT053.
In the 24 patients, the median age was 60.2 years (range, 38.5-70.0 years), and the median time since diagnosis was 3.5 years (range, 0.3-10.8 years). Nine patients had progressive disease at baseline.
The patients had received a median of 5 prior therapies (range, 2-12). All patients had received a proteasome inhibitor, 22 had received an immunomodulatory agent, 10 had undergone a transplant, and 5 had received an anti-CD38 monoclonal antibody.
For this study, patients received conditioning with fludarabine and cyclophosphamide, followed by a single infusion of CT053. Most patients (n = 21) received 1.5 x 108 cells, but three received 0.5 x 108, 1 x 108, and 1.8 x 108 cells, respectively.
The median follow-up was 333 days. CAR T cells were detectable 1-7 days after infusion and peaked at 7-21 days. The cells persisted for a median of 172 days (range, 21-341 days).
A total of 21 patients responded to treatment (87.5%). There were 19 patients with a complete response or stringent complete response, 1 patient with a very good partial response, and 1 with a partial response.
Dr. Hao noted that CT053 was effective even at the lowest dose. The patient who received 0.5 x 108 cells initially achieved a very good partial response that deepened to a stringent complete response on day 502 after infusion.
Ten patients still had a stringent complete response at last follow-up, and two had a complete response. Nine patients progressed, and one patient relapsed after achieving a complete response. Three patients died, two from disease progression and one from a serious AE (neutropenic infection).
All 24 patients experienced a treatment-related AE, and all had grade 3 or higher hematologic AEs. Six patients had grade 3 or higher fever, six had grade 3 or higher infections and infestations, and one had grade 3 or higher neurotoxicity.
Three patients had grade 1 CRS, and 12 had grade 2 CRS. None of the patients had grade 3 or higher CRS.
This trial was sponsored by Xinhua Hospital/Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, First Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang University, and First Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University in collaboration with Carsgen Therapeutics. Dr. Hao did not disclose any conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Hao S et al. IMW 2019, Abstract OAB-082.
BOSTON – CT053, a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy, has demonstrated efficacy and tolerability in a phase 1 trial of patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma.
CT053 produced an objective response rate of 87.5% and a complete response rate of 79.2%. All patients experienced grade 3 or higher adverse events (AEs), but none developed grade 3 or higher cytokine-release syndrome (CRS).
Siguo Hao, MD, of Xinhua Hospital, Shanghai (China) Jiaotong University, presented these results at the International Myeloma Workshop held by the International Myeloma Society.
Dr. Hao explained that CT053 consists of autologous T cells modified with a second-generation CAR that incorporates a fully human anti–B-cell maturation antigen single-chain fragment variant, a 4-1BB costimulatory domain, and a CD3-zeta–signaling domain.
In preclinical studies, CT053 induced dose-dependent cytotoxic effects on multiple myeloma cell lines and completely eradicated myeloma in mice.
Dr. Hao and his colleagues conducted the phase 1 study of CT053 at three sites (NCT03716856, NCT03302403, and NCT03380039). The study enrolled 30 patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma, and 24 ultimately received CT053.
In the 24 patients, the median age was 60.2 years (range, 38.5-70.0 years), and the median time since diagnosis was 3.5 years (range, 0.3-10.8 years). Nine patients had progressive disease at baseline.
The patients had received a median of 5 prior therapies (range, 2-12). All patients had received a proteasome inhibitor, 22 had received an immunomodulatory agent, 10 had undergone a transplant, and 5 had received an anti-CD38 monoclonal antibody.
For this study, patients received conditioning with fludarabine and cyclophosphamide, followed by a single infusion of CT053. Most patients (n = 21) received 1.5 x 108 cells, but three received 0.5 x 108, 1 x 108, and 1.8 x 108 cells, respectively.
The median follow-up was 333 days. CAR T cells were detectable 1-7 days after infusion and peaked at 7-21 days. The cells persisted for a median of 172 days (range, 21-341 days).
A total of 21 patients responded to treatment (87.5%). There were 19 patients with a complete response or stringent complete response, 1 patient with a very good partial response, and 1 with a partial response.
Dr. Hao noted that CT053 was effective even at the lowest dose. The patient who received 0.5 x 108 cells initially achieved a very good partial response that deepened to a stringent complete response on day 502 after infusion.
Ten patients still had a stringent complete response at last follow-up, and two had a complete response. Nine patients progressed, and one patient relapsed after achieving a complete response. Three patients died, two from disease progression and one from a serious AE (neutropenic infection).
All 24 patients experienced a treatment-related AE, and all had grade 3 or higher hematologic AEs. Six patients had grade 3 or higher fever, six had grade 3 or higher infections and infestations, and one had grade 3 or higher neurotoxicity.
Three patients had grade 1 CRS, and 12 had grade 2 CRS. None of the patients had grade 3 or higher CRS.
This trial was sponsored by Xinhua Hospital/Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, First Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang University, and First Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University in collaboration with Carsgen Therapeutics. Dr. Hao did not disclose any conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Hao S et al. IMW 2019, Abstract OAB-082.
REPORTING FROM IMW 2019
German CLLM1 study: 4-year data raise concerns about lenalidomide maintenance
EDINBURGH – Lenalidomide maintenance therapy after chemoimmunotherapy in high-risk chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) improved progression- and event-free survival, but not overall survival, and was associated with three unexpected cases of B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL), according to 4-year follow-up in the German, phase 3 CLLM1 study.
Given these findings, and in particular the B-ALL cases, lenalidomide cannot be generally recommended as maintenance therapy in high-risk CLL, Moritz Fürstenau, MD, of the University of Cologne, reported in a poster at the International Workshop on Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia.
At a median follow-up of 47.6 months, median progression-free survival (PFS) by investigator assessment was 54.7 months in 60 patients randomized to receive lenalidomide maintenance therapy, compared with 23.2 months for 29 who received placebo (hazard ratio, 0.22), and median event-free survival (EFS) was 46.2 months vs. 14.6 months in the groups, respectively (hazard ratio, 0.24), Dr. Fürstenau said during an oral poster presentation at the conference.
“So ... after 4 years of observation, we still see improvement in PFS, EFS, and time to next treatment,” he said, also noting that minimal residual disease (MRD) negativity was achieved by eight patients in the lenalidomide group, and in none of the patients in the placebo group.
However, overall survival was 79% and 87% in the lenalidomide and placebo groups, respectively (HR, 1.53). In total, 12 patients died, including 9 in the lenalidomide group from fatal infections, concomitant disease, CLL progression, or unknown causes. Three patients in the placebo group died from CLL progression or fatal infection.
In the lenalidomide group, hematological and solid tumor second primary malignancies were reported in three and four patients, respectively (5% and 7%), compared with zero and two patients, respectively (0% and 7%), in the placebo group.
The CLLM1 study of the German CLL Study Group evaluated maintenance with lenalidomide vs. placebo in patients with high risk of progression after first-line chemoimmunotherapy. Previously reported results also favored lenalidomide maintenance for PFS, but not OS, Dr. Fürstenau said, adding that the study was unblinded at a median follow-up of 17.9 months, and in November 2017 treatment was stopped when two cases of B-ALL were observed. A third case was reported in 2018.
The current analysis includes data available through December 2018, and the findings warrant further investigation to analyze the unexpectedly high incidence of B-ALL, he said.
The CLLM1 study was funded by Celgene.
[email protected]
EDINBURGH – Lenalidomide maintenance therapy after chemoimmunotherapy in high-risk chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) improved progression- and event-free survival, but not overall survival, and was associated with three unexpected cases of B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL), according to 4-year follow-up in the German, phase 3 CLLM1 study.
Given these findings, and in particular the B-ALL cases, lenalidomide cannot be generally recommended as maintenance therapy in high-risk CLL, Moritz Fürstenau, MD, of the University of Cologne, reported in a poster at the International Workshop on Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia.
At a median follow-up of 47.6 months, median progression-free survival (PFS) by investigator assessment was 54.7 months in 60 patients randomized to receive lenalidomide maintenance therapy, compared with 23.2 months for 29 who received placebo (hazard ratio, 0.22), and median event-free survival (EFS) was 46.2 months vs. 14.6 months in the groups, respectively (hazard ratio, 0.24), Dr. Fürstenau said during an oral poster presentation at the conference.
“So ... after 4 years of observation, we still see improvement in PFS, EFS, and time to next treatment,” he said, also noting that minimal residual disease (MRD) negativity was achieved by eight patients in the lenalidomide group, and in none of the patients in the placebo group.
However, overall survival was 79% and 87% in the lenalidomide and placebo groups, respectively (HR, 1.53). In total, 12 patients died, including 9 in the lenalidomide group from fatal infections, concomitant disease, CLL progression, or unknown causes. Three patients in the placebo group died from CLL progression or fatal infection.
In the lenalidomide group, hematological and solid tumor second primary malignancies were reported in three and four patients, respectively (5% and 7%), compared with zero and two patients, respectively (0% and 7%), in the placebo group.
The CLLM1 study of the German CLL Study Group evaluated maintenance with lenalidomide vs. placebo in patients with high risk of progression after first-line chemoimmunotherapy. Previously reported results also favored lenalidomide maintenance for PFS, but not OS, Dr. Fürstenau said, adding that the study was unblinded at a median follow-up of 17.9 months, and in November 2017 treatment was stopped when two cases of B-ALL were observed. A third case was reported in 2018.
The current analysis includes data available through December 2018, and the findings warrant further investigation to analyze the unexpectedly high incidence of B-ALL, he said.
The CLLM1 study was funded by Celgene.
[email protected]
EDINBURGH – Lenalidomide maintenance therapy after chemoimmunotherapy in high-risk chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) improved progression- and event-free survival, but not overall survival, and was associated with three unexpected cases of B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL), according to 4-year follow-up in the German, phase 3 CLLM1 study.
Given these findings, and in particular the B-ALL cases, lenalidomide cannot be generally recommended as maintenance therapy in high-risk CLL, Moritz Fürstenau, MD, of the University of Cologne, reported in a poster at the International Workshop on Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia.
At a median follow-up of 47.6 months, median progression-free survival (PFS) by investigator assessment was 54.7 months in 60 patients randomized to receive lenalidomide maintenance therapy, compared with 23.2 months for 29 who received placebo (hazard ratio, 0.22), and median event-free survival (EFS) was 46.2 months vs. 14.6 months in the groups, respectively (hazard ratio, 0.24), Dr. Fürstenau said during an oral poster presentation at the conference.
“So ... after 4 years of observation, we still see improvement in PFS, EFS, and time to next treatment,” he said, also noting that minimal residual disease (MRD) negativity was achieved by eight patients in the lenalidomide group, and in none of the patients in the placebo group.
However, overall survival was 79% and 87% in the lenalidomide and placebo groups, respectively (HR, 1.53). In total, 12 patients died, including 9 in the lenalidomide group from fatal infections, concomitant disease, CLL progression, or unknown causes. Three patients in the placebo group died from CLL progression or fatal infection.
In the lenalidomide group, hematological and solid tumor second primary malignancies were reported in three and four patients, respectively (5% and 7%), compared with zero and two patients, respectively (0% and 7%), in the placebo group.
The CLLM1 study of the German CLL Study Group evaluated maintenance with lenalidomide vs. placebo in patients with high risk of progression after first-line chemoimmunotherapy. Previously reported results also favored lenalidomide maintenance for PFS, but not OS, Dr. Fürstenau said, adding that the study was unblinded at a median follow-up of 17.9 months, and in November 2017 treatment was stopped when two cases of B-ALL were observed. A third case was reported in 2018.
The current analysis includes data available through December 2018, and the findings warrant further investigation to analyze the unexpectedly high incidence of B-ALL, he said.
The CLLM1 study was funded by Celgene.
[email protected]
REPORTING FROM iwCLL 2019
ICLL-07 trial: MRD-driven strategy yields prolonged survival
EDINBURGH – Treatment induction with obinutuzumab and ibrutinib followed by a minimal residual disease (MRD)–driven treatment strategy in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) yields a high long-term complete response rate and prolonged progression-free and overall survival, according to findings from the phase 2 ICLL-07 trial.
The intent-to-treat (ITT) complete response rate at 16 months in 135 patients who were treated with this strategy was 62%, Anne-Sophie Michallet, MD, reported at the International Workshop on Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia.
Patients in the multicenter, open-label trial conducted by the French Innovative Leukemia Organization (FILO) were previously untreated, medically fit patients with CLL and no 17p deletion. They were enrolled between November 2015 and May 2017 to receive eight 1,000 mg IV doses of obinutuzumab over six 4-week cycles along with oral Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor ibrutinib at a dose of 420 mg daily for 9 months.
Ten patients (7.7%) achieved complete response with bone marrow MRD less than 0.01% (undetectable) at 9 months and, by study protocol, continued on only the ibrutinib for 6 additional months. The remaining 120 evaluable patients received four 4-week cycles of fludarabine/cyclophosphamide along with the obinutuzumab and ibrutinib for 6 additional months, explained Dr. Michallet of Centre Léon Bérard, Lyon, France.
The ITT rate at 16 months – the primary endpoint of the study – was achieved with no more than four cycles of fludarabine/cyclophosphamide and obinutuzumab, and exceeded the primary objective of demonstrating a 30% or higher rate of complete response with bone marrow MRD less than 0.01% at the month 16 ITT analysis, she said.
“The ... strategy yielded an overall response rate of 100%, a complete response rate, according to iwCLL [criteria], of 73%, a bone marrow MRD–undetectable rate of 79% [in the ITT population],” she said, adding that the primary objective was achieved with a complete response with a peripheral blood and bone marrow MRD–undetectable rate of 62%.
Response assessments at months 9 and 16 involved whole-body computed tomography scans with tumor measurements and bone marrow trephine biopsy for patients in clinical complete response. MRD testing was performed by eight-color flow cytometry in both peripheral blood and bone marrow.
After month 16, response was clinically assessed every 3 months, and peripheral blood MRD was assessed every 6 months until month 40.
“With a median follow-up of 26.3 months, the 2-year progression-free survival and overall survival were, respectively, 97% and 97.5%,” Dr. Michallet said, noting that the longitudinal follow-up of peripheral blood MRD in the entire cohort showed durability of a deep response. The rate of peripheral blood MRD less than 0.01% at 22 months was 77% in the 10 patients who received only ibrutinib after the 9-month assessment, and 93% in those who received fludarabine/cyclophosphamide after the 9-month assessment.
In patients with immunoglobulin heavy gene variable (IGHV) mutations, the rate of peripheral blood MRD less than 0.01% at month 22 was 96%, and in those without IGHV mutations, the rate was 77%, she noted.
The findings demonstrate that the approach has merit in medically fit, treatment-naive patients with CLL and no 17p deletion, she said, explaining that the fixed-duration, MRD-driven strategy used in this study was developed to “avoid or at least reduce chemotherapy exposure” in the first-line treatment of such patients.
Indeed, the approach was associated with “a high [complete response] rate, a high level of undetectable bone marrow MRD, an acceptable safety profile, and a sustained MRD negativity rate at 12 months after the end of the treatment,” she said.
“This highly effective strategy combining a BTK inhibitor and abbreviated immunochemotherapy deserves further investigation with randomized trials,” she concluded.
ICLL-07 FILO was funded by Roche and Janssen. Dr. Michallet reported having no disclosures.
EDINBURGH – Treatment induction with obinutuzumab and ibrutinib followed by a minimal residual disease (MRD)–driven treatment strategy in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) yields a high long-term complete response rate and prolonged progression-free and overall survival, according to findings from the phase 2 ICLL-07 trial.
The intent-to-treat (ITT) complete response rate at 16 months in 135 patients who were treated with this strategy was 62%, Anne-Sophie Michallet, MD, reported at the International Workshop on Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia.
Patients in the multicenter, open-label trial conducted by the French Innovative Leukemia Organization (FILO) were previously untreated, medically fit patients with CLL and no 17p deletion. They were enrolled between November 2015 and May 2017 to receive eight 1,000 mg IV doses of obinutuzumab over six 4-week cycles along with oral Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor ibrutinib at a dose of 420 mg daily for 9 months.
Ten patients (7.7%) achieved complete response with bone marrow MRD less than 0.01% (undetectable) at 9 months and, by study protocol, continued on only the ibrutinib for 6 additional months. The remaining 120 evaluable patients received four 4-week cycles of fludarabine/cyclophosphamide along with the obinutuzumab and ibrutinib for 6 additional months, explained Dr. Michallet of Centre Léon Bérard, Lyon, France.
The ITT rate at 16 months – the primary endpoint of the study – was achieved with no more than four cycles of fludarabine/cyclophosphamide and obinutuzumab, and exceeded the primary objective of demonstrating a 30% or higher rate of complete response with bone marrow MRD less than 0.01% at the month 16 ITT analysis, she said.
“The ... strategy yielded an overall response rate of 100%, a complete response rate, according to iwCLL [criteria], of 73%, a bone marrow MRD–undetectable rate of 79% [in the ITT population],” she said, adding that the primary objective was achieved with a complete response with a peripheral blood and bone marrow MRD–undetectable rate of 62%.
Response assessments at months 9 and 16 involved whole-body computed tomography scans with tumor measurements and bone marrow trephine biopsy for patients in clinical complete response. MRD testing was performed by eight-color flow cytometry in both peripheral blood and bone marrow.
After month 16, response was clinically assessed every 3 months, and peripheral blood MRD was assessed every 6 months until month 40.
“With a median follow-up of 26.3 months, the 2-year progression-free survival and overall survival were, respectively, 97% and 97.5%,” Dr. Michallet said, noting that the longitudinal follow-up of peripheral blood MRD in the entire cohort showed durability of a deep response. The rate of peripheral blood MRD less than 0.01% at 22 months was 77% in the 10 patients who received only ibrutinib after the 9-month assessment, and 93% in those who received fludarabine/cyclophosphamide after the 9-month assessment.
In patients with immunoglobulin heavy gene variable (IGHV) mutations, the rate of peripheral blood MRD less than 0.01% at month 22 was 96%, and in those without IGHV mutations, the rate was 77%, she noted.
The findings demonstrate that the approach has merit in medically fit, treatment-naive patients with CLL and no 17p deletion, she said, explaining that the fixed-duration, MRD-driven strategy used in this study was developed to “avoid or at least reduce chemotherapy exposure” in the first-line treatment of such patients.
Indeed, the approach was associated with “a high [complete response] rate, a high level of undetectable bone marrow MRD, an acceptable safety profile, and a sustained MRD negativity rate at 12 months after the end of the treatment,” she said.
“This highly effective strategy combining a BTK inhibitor and abbreviated immunochemotherapy deserves further investigation with randomized trials,” she concluded.
ICLL-07 FILO was funded by Roche and Janssen. Dr. Michallet reported having no disclosures.
EDINBURGH – Treatment induction with obinutuzumab and ibrutinib followed by a minimal residual disease (MRD)–driven treatment strategy in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) yields a high long-term complete response rate and prolonged progression-free and overall survival, according to findings from the phase 2 ICLL-07 trial.
The intent-to-treat (ITT) complete response rate at 16 months in 135 patients who were treated with this strategy was 62%, Anne-Sophie Michallet, MD, reported at the International Workshop on Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia.
Patients in the multicenter, open-label trial conducted by the French Innovative Leukemia Organization (FILO) were previously untreated, medically fit patients with CLL and no 17p deletion. They were enrolled between November 2015 and May 2017 to receive eight 1,000 mg IV doses of obinutuzumab over six 4-week cycles along with oral Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor ibrutinib at a dose of 420 mg daily for 9 months.
Ten patients (7.7%) achieved complete response with bone marrow MRD less than 0.01% (undetectable) at 9 months and, by study protocol, continued on only the ibrutinib for 6 additional months. The remaining 120 evaluable patients received four 4-week cycles of fludarabine/cyclophosphamide along with the obinutuzumab and ibrutinib for 6 additional months, explained Dr. Michallet of Centre Léon Bérard, Lyon, France.
The ITT rate at 16 months – the primary endpoint of the study – was achieved with no more than four cycles of fludarabine/cyclophosphamide and obinutuzumab, and exceeded the primary objective of demonstrating a 30% or higher rate of complete response with bone marrow MRD less than 0.01% at the month 16 ITT analysis, she said.
“The ... strategy yielded an overall response rate of 100%, a complete response rate, according to iwCLL [criteria], of 73%, a bone marrow MRD–undetectable rate of 79% [in the ITT population],” she said, adding that the primary objective was achieved with a complete response with a peripheral blood and bone marrow MRD–undetectable rate of 62%.
Response assessments at months 9 and 16 involved whole-body computed tomography scans with tumor measurements and bone marrow trephine biopsy for patients in clinical complete response. MRD testing was performed by eight-color flow cytometry in both peripheral blood and bone marrow.
After month 16, response was clinically assessed every 3 months, and peripheral blood MRD was assessed every 6 months until month 40.
“With a median follow-up of 26.3 months, the 2-year progression-free survival and overall survival were, respectively, 97% and 97.5%,” Dr. Michallet said, noting that the longitudinal follow-up of peripheral blood MRD in the entire cohort showed durability of a deep response. The rate of peripheral blood MRD less than 0.01% at 22 months was 77% in the 10 patients who received only ibrutinib after the 9-month assessment, and 93% in those who received fludarabine/cyclophosphamide after the 9-month assessment.
In patients with immunoglobulin heavy gene variable (IGHV) mutations, the rate of peripheral blood MRD less than 0.01% at month 22 was 96%, and in those without IGHV mutations, the rate was 77%, she noted.
The findings demonstrate that the approach has merit in medically fit, treatment-naive patients with CLL and no 17p deletion, she said, explaining that the fixed-duration, MRD-driven strategy used in this study was developed to “avoid or at least reduce chemotherapy exposure” in the first-line treatment of such patients.
Indeed, the approach was associated with “a high [complete response] rate, a high level of undetectable bone marrow MRD, an acceptable safety profile, and a sustained MRD negativity rate at 12 months after the end of the treatment,” she said.
“This highly effective strategy combining a BTK inhibitor and abbreviated immunochemotherapy deserves further investigation with randomized trials,” she concluded.
ICLL-07 FILO was funded by Roche and Janssen. Dr. Michallet reported having no disclosures.
REPORTING FROM iwCLL 2019
Daratumumab approved in combo with VTd for transplant-eligible multiple myeloma
The Food and Drug Administration has approved daratumumab in combination with certain therapies for newly diagnosed patients with multiple myeloma who are eligible for autologous stem cell transplant.
The approval specifies combination of this CD38-directed antibody with bortezomib (Velcade), thalidomide, and dexamethasone (VTd), according to an announcement from Janssen.
The approval is based on results from the CASSIOPEIA study. The first part of the study randomized 1,085 patients (median age, 58 years) and showed that, compared with VTd alone, the daratumumab-VTd combination had significantly better postconsolidation stringent complete response (29% vs. 20%; odds ratio, 1.60; 95% confidence interval, 1.21-2.12; P = .001) and a 53% reduction in risk of disease progression or death (hazard ratio, 0.47; 95% CI, 0.33-0.67; P = .0001).
The most frequent adverse reactions with 5% greater frequency in the daratumumab-VTd group were infusion reactions (including anaphylaxis), nausea, pyrexia, upper respiratory tract infection, and bronchitis. Full prescribing information, including contraindications and warnings, can be found on the Janssen website.
Daratumumab was initially approved in 2015, and in June 2019, it received approval, in combination with lenalidomide and dexamethasone, for treatment of patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma who are ineligible for autologous stem cell transplant.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved daratumumab in combination with certain therapies for newly diagnosed patients with multiple myeloma who are eligible for autologous stem cell transplant.
The approval specifies combination of this CD38-directed antibody with bortezomib (Velcade), thalidomide, and dexamethasone (VTd), according to an announcement from Janssen.
The approval is based on results from the CASSIOPEIA study. The first part of the study randomized 1,085 patients (median age, 58 years) and showed that, compared with VTd alone, the daratumumab-VTd combination had significantly better postconsolidation stringent complete response (29% vs. 20%; odds ratio, 1.60; 95% confidence interval, 1.21-2.12; P = .001) and a 53% reduction in risk of disease progression or death (hazard ratio, 0.47; 95% CI, 0.33-0.67; P = .0001).
The most frequent adverse reactions with 5% greater frequency in the daratumumab-VTd group were infusion reactions (including anaphylaxis), nausea, pyrexia, upper respiratory tract infection, and bronchitis. Full prescribing information, including contraindications and warnings, can be found on the Janssen website.
Daratumumab was initially approved in 2015, and in June 2019, it received approval, in combination with lenalidomide and dexamethasone, for treatment of patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma who are ineligible for autologous stem cell transplant.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved daratumumab in combination with certain therapies for newly diagnosed patients with multiple myeloma who are eligible for autologous stem cell transplant.
The approval specifies combination of this CD38-directed antibody with bortezomib (Velcade), thalidomide, and dexamethasone (VTd), according to an announcement from Janssen.
The approval is based on results from the CASSIOPEIA study. The first part of the study randomized 1,085 patients (median age, 58 years) and showed that, compared with VTd alone, the daratumumab-VTd combination had significantly better postconsolidation stringent complete response (29% vs. 20%; odds ratio, 1.60; 95% confidence interval, 1.21-2.12; P = .001) and a 53% reduction in risk of disease progression or death (hazard ratio, 0.47; 95% CI, 0.33-0.67; P = .0001).
The most frequent adverse reactions with 5% greater frequency in the daratumumab-VTd group were infusion reactions (including anaphylaxis), nausea, pyrexia, upper respiratory tract infection, and bronchitis. Full prescribing information, including contraindications and warnings, can be found on the Janssen website.
Daratumumab was initially approved in 2015, and in June 2019, it received approval, in combination with lenalidomide and dexamethasone, for treatment of patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma who are ineligible for autologous stem cell transplant.
Subcutaneous and IV daratumumab combos appear comparable in myeloma
BOSTON – Subcutaneous daratumumab in combination with standard care is comparable to intravenous daratumumab plus standard care in patients with newly diagnosed or relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma, according to a speaker at the International Myeloma Workshop.
Overall response rates (ORRs) observed with subcutaneous daratumumab–based combinations in the phase 2 PLEIADES trial were similar to ORRs observed with intravenous daratumumab–based combinations in three other trials – GRIFFIN, ALCYONE, and POLLUX.
Ajai Chari, MD, of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, presented these findings at the workshop, which is held by the International Myeloma Society.
In the PLEIADES trial, researchers tested subcutaneous daratumumab (D) in combination with:
- Bortezomib, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone (VRd) in transplant-eligible patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma
- Bortezomib, melphalan, and prednisone (VMP) in transplant-ineligible patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma
- Lenalidomide and dexamethasone (Rd) in patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma who had received at least one prior line of therapy.
There were 67 patients in the D-VRd arm, and they had a median age of 59 years (range, 33-76 years). There were 67 patients in the D-VMP arm, and they had a median age of 75 years (range, 66-86 years). There were 65 patients in the D-Rd arm, they had a median age of 69 years (range, 33-82 years), and they had received a median of one (range, one to five) prior therapies.
Dr. Chari noted that baseline characteristics in this study were “pretty comparable” to characteristics in the studies of intravenous daratumumab. He also pointed out that the median administration time for subcutaneous daratumumab was 5 minutes in this study, which is “substantially” shorter than the typical administration time for intravenous daratumumab.
The median number of treatment cycles was 4 (range, 1-4) in the D-VRd arm, 8 (range, 1-10) in the D-VMP arm, and 12 (range, 1-15) in the D-Rd arm. The median duration of treatment was 2.6 months, 10.6 months, and 11.1 months, respectively.
The proportion of patients who discontinued treatment was 3% in the D-VRd arm, 10.4% in the D-VMP arm, and 20% in the D-Rd arm.
Response
Dr. Chari said response rates in the three arms of PLEAIDES were similar to response rates in corresponding groups from the studies of intravenous daratumumab–based combinations.
After four induction cycles, subcutaneous D-VRd produced an ORR of 97% in PLEAIDES, and intravenous D-VRd produced an ORR of 98% in the GRIFFIN trial (IMW 2019. Abstract OAB-087).
Subcutaneous D-VMP produced an ORR of 89.6% at a median follow-up of 11 months. In the ALCYONE trial, intravenous D-VMP produced an ORR of 90.9% at a median follow-up of 16.5 months (N Engl J Med. 2018; 378:518-28).
Subcutaneous D-Rd produced an ORR of 93.8% at a median follow-up of 11.2 months. In the POLLUX trial, intravenous D-Rd produced an ORR of 92.9% at a median follow-up of 13.5 months (N Engl J Med. 2016; 375:1319-31).
Safety
All patients in PLEIADES had treatment-related adverse events (TEAEs). The rate of serious TEAEs was 28.4% in the D-VRd arm, 38.8% in the D-VMP arm, and 47.7% in the D-Rd arm. The rate of grade 3/4 TEAEs was 56.7%, 68.7%, and 83.1%, respectively. There was one fatal TEAE in the D-VRd arm, two fatal TEAEs in the D-VMP arm, and two in the D-Rd arm.
Infusion-related reactions occurred in 7.5% of all patients (15/199). Most infusion-related reactions were grade 1/2. One patient had a grade 3 reaction, and there were no grade 4 reactions. The median time to onset was 3.3 hours.
“Daratumumab in combination with standard of care, when given subcutaneously, demonstrated comparable clinical activity and safety and corresponded to daratumumab intravenous–containing regimens,” Dr. Chari said. “These results support the use of flat-dose 1,800 mg [subcutaneous daratumumab] in combination with standard treatment regimens.”
The PLEIADES trial was sponsored by Janssen Research & Development. Dr. Chari reported relationships with Janssen and several other companies.
SOURCE: Chari A et al. IMW 2019, Abstract OAB-022.
BOSTON – Subcutaneous daratumumab in combination with standard care is comparable to intravenous daratumumab plus standard care in patients with newly diagnosed or relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma, according to a speaker at the International Myeloma Workshop.
Overall response rates (ORRs) observed with subcutaneous daratumumab–based combinations in the phase 2 PLEIADES trial were similar to ORRs observed with intravenous daratumumab–based combinations in three other trials – GRIFFIN, ALCYONE, and POLLUX.
Ajai Chari, MD, of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, presented these findings at the workshop, which is held by the International Myeloma Society.
In the PLEIADES trial, researchers tested subcutaneous daratumumab (D) in combination with:
- Bortezomib, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone (VRd) in transplant-eligible patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma
- Bortezomib, melphalan, and prednisone (VMP) in transplant-ineligible patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma
- Lenalidomide and dexamethasone (Rd) in patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma who had received at least one prior line of therapy.
There were 67 patients in the D-VRd arm, and they had a median age of 59 years (range, 33-76 years). There were 67 patients in the D-VMP arm, and they had a median age of 75 years (range, 66-86 years). There were 65 patients in the D-Rd arm, they had a median age of 69 years (range, 33-82 years), and they had received a median of one (range, one to five) prior therapies.
Dr. Chari noted that baseline characteristics in this study were “pretty comparable” to characteristics in the studies of intravenous daratumumab. He also pointed out that the median administration time for subcutaneous daratumumab was 5 minutes in this study, which is “substantially” shorter than the typical administration time for intravenous daratumumab.
The median number of treatment cycles was 4 (range, 1-4) in the D-VRd arm, 8 (range, 1-10) in the D-VMP arm, and 12 (range, 1-15) in the D-Rd arm. The median duration of treatment was 2.6 months, 10.6 months, and 11.1 months, respectively.
The proportion of patients who discontinued treatment was 3% in the D-VRd arm, 10.4% in the D-VMP arm, and 20% in the D-Rd arm.
Response
Dr. Chari said response rates in the three arms of PLEAIDES were similar to response rates in corresponding groups from the studies of intravenous daratumumab–based combinations.
After four induction cycles, subcutaneous D-VRd produced an ORR of 97% in PLEAIDES, and intravenous D-VRd produced an ORR of 98% in the GRIFFIN trial (IMW 2019. Abstract OAB-087).
Subcutaneous D-VMP produced an ORR of 89.6% at a median follow-up of 11 months. In the ALCYONE trial, intravenous D-VMP produced an ORR of 90.9% at a median follow-up of 16.5 months (N Engl J Med. 2018; 378:518-28).
Subcutaneous D-Rd produced an ORR of 93.8% at a median follow-up of 11.2 months. In the POLLUX trial, intravenous D-Rd produced an ORR of 92.9% at a median follow-up of 13.5 months (N Engl J Med. 2016; 375:1319-31).
Safety
All patients in PLEIADES had treatment-related adverse events (TEAEs). The rate of serious TEAEs was 28.4% in the D-VRd arm, 38.8% in the D-VMP arm, and 47.7% in the D-Rd arm. The rate of grade 3/4 TEAEs was 56.7%, 68.7%, and 83.1%, respectively. There was one fatal TEAE in the D-VRd arm, two fatal TEAEs in the D-VMP arm, and two in the D-Rd arm.
Infusion-related reactions occurred in 7.5% of all patients (15/199). Most infusion-related reactions were grade 1/2. One patient had a grade 3 reaction, and there were no grade 4 reactions. The median time to onset was 3.3 hours.
“Daratumumab in combination with standard of care, when given subcutaneously, demonstrated comparable clinical activity and safety and corresponded to daratumumab intravenous–containing regimens,” Dr. Chari said. “These results support the use of flat-dose 1,800 mg [subcutaneous daratumumab] in combination with standard treatment regimens.”
The PLEIADES trial was sponsored by Janssen Research & Development. Dr. Chari reported relationships with Janssen and several other companies.
SOURCE: Chari A et al. IMW 2019, Abstract OAB-022.
BOSTON – Subcutaneous daratumumab in combination with standard care is comparable to intravenous daratumumab plus standard care in patients with newly diagnosed or relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma, according to a speaker at the International Myeloma Workshop.
Overall response rates (ORRs) observed with subcutaneous daratumumab–based combinations in the phase 2 PLEIADES trial were similar to ORRs observed with intravenous daratumumab–based combinations in three other trials – GRIFFIN, ALCYONE, and POLLUX.
Ajai Chari, MD, of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, presented these findings at the workshop, which is held by the International Myeloma Society.
In the PLEIADES trial, researchers tested subcutaneous daratumumab (D) in combination with:
- Bortezomib, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone (VRd) in transplant-eligible patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma
- Bortezomib, melphalan, and prednisone (VMP) in transplant-ineligible patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma
- Lenalidomide and dexamethasone (Rd) in patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma who had received at least one prior line of therapy.
There were 67 patients in the D-VRd arm, and they had a median age of 59 years (range, 33-76 years). There were 67 patients in the D-VMP arm, and they had a median age of 75 years (range, 66-86 years). There were 65 patients in the D-Rd arm, they had a median age of 69 years (range, 33-82 years), and they had received a median of one (range, one to five) prior therapies.
Dr. Chari noted that baseline characteristics in this study were “pretty comparable” to characteristics in the studies of intravenous daratumumab. He also pointed out that the median administration time for subcutaneous daratumumab was 5 minutes in this study, which is “substantially” shorter than the typical administration time for intravenous daratumumab.
The median number of treatment cycles was 4 (range, 1-4) in the D-VRd arm, 8 (range, 1-10) in the D-VMP arm, and 12 (range, 1-15) in the D-Rd arm. The median duration of treatment was 2.6 months, 10.6 months, and 11.1 months, respectively.
The proportion of patients who discontinued treatment was 3% in the D-VRd arm, 10.4% in the D-VMP arm, and 20% in the D-Rd arm.
Response
Dr. Chari said response rates in the three arms of PLEAIDES were similar to response rates in corresponding groups from the studies of intravenous daratumumab–based combinations.
After four induction cycles, subcutaneous D-VRd produced an ORR of 97% in PLEAIDES, and intravenous D-VRd produced an ORR of 98% in the GRIFFIN trial (IMW 2019. Abstract OAB-087).
Subcutaneous D-VMP produced an ORR of 89.6% at a median follow-up of 11 months. In the ALCYONE trial, intravenous D-VMP produced an ORR of 90.9% at a median follow-up of 16.5 months (N Engl J Med. 2018; 378:518-28).
Subcutaneous D-Rd produced an ORR of 93.8% at a median follow-up of 11.2 months. In the POLLUX trial, intravenous D-Rd produced an ORR of 92.9% at a median follow-up of 13.5 months (N Engl J Med. 2016; 375:1319-31).
Safety
All patients in PLEIADES had treatment-related adverse events (TEAEs). The rate of serious TEAEs was 28.4% in the D-VRd arm, 38.8% in the D-VMP arm, and 47.7% in the D-Rd arm. The rate of grade 3/4 TEAEs was 56.7%, 68.7%, and 83.1%, respectively. There was one fatal TEAE in the D-VRd arm, two fatal TEAEs in the D-VMP arm, and two in the D-Rd arm.
Infusion-related reactions occurred in 7.5% of all patients (15/199). Most infusion-related reactions were grade 1/2. One patient had a grade 3 reaction, and there were no grade 4 reactions. The median time to onset was 3.3 hours.
“Daratumumab in combination with standard of care, when given subcutaneously, demonstrated comparable clinical activity and safety and corresponded to daratumumab intravenous–containing regimens,” Dr. Chari said. “These results support the use of flat-dose 1,800 mg [subcutaneous daratumumab] in combination with standard treatment regimens.”
The PLEIADES trial was sponsored by Janssen Research & Development. Dr. Chari reported relationships with Janssen and several other companies.
SOURCE: Chari A et al. IMW 2019, Abstract OAB-022.
REPORTING FROM IMW 2019
Quadruplet prolongs progression-free survival in newly diagnosed myeloma
BOSTON – A carfilzomib-based quadruplet can improve outcomes in transplant-eligible patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma, a phase 3 trial suggests.
In the Myeloma XI trial, carfilzomib plus cyclophosphamide, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone (KCRD) significantly prolonged progression-free survival (PFS), compared with cyclophosphamide-lenalidomide-dexamethasone (CRD) or cyclophosphamide-thalidomide-dexamethasone (CTD).
“KCRD was associated with a very high response rate and a high MRD [minimal residual disease]-negative rate at the end of induction, and it significantly improved progression-free survival compared to the triplet combinations,” said Charlotte Pawlyn, PhD, of The Institute of Cancer Research in London.
Dr. Pawlyn reported these findings at the International Myeloma Workshop held by the International Myeloma Society.
The phase 3 Myeloma XI trial enrolled 1,056 patients with newly diagnosed myeloma who were eligible for transplant. The patients were randomized to receive KCRD (n = 526), CRD (n = 265), or CTD (n = 265) as induction.
Baseline characteristics were well balanced between the treatment arms. The median age was 61 years in the KCRD and CTD arms and 62 years in the CRD arm (overall range, 33-75 years). Roughly 60% of patients in each arm were men.
About 50%-60% of patients in each arm had standard-risk cytogenetics, which was defined as the absence of any cytogenetic lesions. About 30%-40% of patients in each arm had high-risk cytogenetics, meaning they had one of the following lesions: t(4;14), t(14;16), t(14;20), del (17p), or gain(1q). About 10% of patients in each arm had ultra-high-risk cytogenetics, which was defined as having more than one lesion.
Treatment
For induction, patients were randomized to KCRD, CRD, or CTD. All patients in the KCRD arm and patients in the CRD/CTD arms who achieved a partial response or better went straight to autologous transplant after induction. Nonresponders in the CTD and CRD arms received intensification with cyclophosphamide, bortezomib, and dexamethasone before transplant.
After transplant, all eligible patients were randomized to lenalidomide maintenance or observation. Patients were eligible for this randomization if they didn’t respond to induction, had progressive disease, or had previous or concurrent active malignancies.
The median follow-up was 34.5 months. The median number of induction cycles completed was 4 (range, 1-12) in the KCRD arm, 5 (range, 1-15) in the CRD arm, and 6 (range, 1-13) in the CTD arm.
Response
At the end of induction, the rate of very good partial response or better was 82.3% in the KCRD arm, 64.9% in the CRD arm, 52.8% in the CTD arm, and 58.9% in the CTD-CRD arms combined. The odds ratio for the KCRD group compared to the triplets combined was 4.35 (P less than .0001).
At 100 days after transplant, the rate of very good partial response or better was 91.9% in the KCRD arm, 82.1% in the CRD arm, 76.1% in the CTD arm, and 79.3% in the CTD-CRD arms combined. The odds ratio for the KCRD group compared to the triplets combined was 3.01 (P less than .0001).
KCRD produced a higher proportion of MRD-negative responses both before and after transplant. After induction, the rate of MRD-negative response was 11% in the CTD arm, 21% in the CRD arm, and 55% in the KCRD arm. After transplant, the rates were 51%, 49%, and 77%, respectively.
Survival
KCRD improved PFS. The 3-year PFS rate was 64.5% in the KCRD arm and 50.3% in the CTD-CRD arms combined. The hazard ratio (HR) was 0.63 (P less than .0001).
The PFS benefit with KCRD was present in all patient subgroups. For example, KCRD improved PFS, compared with CTD-CRD, in patients with standard-risk (HR = 0.62), high-risk (HR = 0.68), and ultra-high-risk (HR = 0.50) cytogenetics.
Patients who achieved an MRD-negative response had better PFS, and early achievement of MRD negativity was associated with improved PFS, Dr. Pawlyn noted.
“But what’s also notable ... is that those patients who received KCRD and achieved MRD negativity ... had better outcomes than patients who achieved MRD negativity whilst receiving a triplet combination,” Dr. Pawlyn said. “So this suggests that the induction regimen delivered is important, not just the achievement of MRD negativity at a defined cutoff.”
Dr. Pawlyn added that overall survival data from this study are not yet mature, but the researchers did assess PFS2. PFS2 was defined as the time from randomization to second disease progression. The 3-year PFS2 was 81.8% in the KCRD arm and 75.1% in the CTD-CRD arms combined. The HR was 0.75 (P = .0451).
Myeloma XI is sponsored by University of Leeds in collaboration with Celgene, Merck Sharp & Dohme, and Amgen. Dr. Pawlyn reported relationships with Amgen, Celgene, and other companies.
SOURCE: Pawlyn C et al. IMW 2019, Abstract OAB-002.
BOSTON – A carfilzomib-based quadruplet can improve outcomes in transplant-eligible patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma, a phase 3 trial suggests.
In the Myeloma XI trial, carfilzomib plus cyclophosphamide, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone (KCRD) significantly prolonged progression-free survival (PFS), compared with cyclophosphamide-lenalidomide-dexamethasone (CRD) or cyclophosphamide-thalidomide-dexamethasone (CTD).
“KCRD was associated with a very high response rate and a high MRD [minimal residual disease]-negative rate at the end of induction, and it significantly improved progression-free survival compared to the triplet combinations,” said Charlotte Pawlyn, PhD, of The Institute of Cancer Research in London.
Dr. Pawlyn reported these findings at the International Myeloma Workshop held by the International Myeloma Society.
The phase 3 Myeloma XI trial enrolled 1,056 patients with newly diagnosed myeloma who were eligible for transplant. The patients were randomized to receive KCRD (n = 526), CRD (n = 265), or CTD (n = 265) as induction.
Baseline characteristics were well balanced between the treatment arms. The median age was 61 years in the KCRD and CTD arms and 62 years in the CRD arm (overall range, 33-75 years). Roughly 60% of patients in each arm were men.
About 50%-60% of patients in each arm had standard-risk cytogenetics, which was defined as the absence of any cytogenetic lesions. About 30%-40% of patients in each arm had high-risk cytogenetics, meaning they had one of the following lesions: t(4;14), t(14;16), t(14;20), del (17p), or gain(1q). About 10% of patients in each arm had ultra-high-risk cytogenetics, which was defined as having more than one lesion.
Treatment
For induction, patients were randomized to KCRD, CRD, or CTD. All patients in the KCRD arm and patients in the CRD/CTD arms who achieved a partial response or better went straight to autologous transplant after induction. Nonresponders in the CTD and CRD arms received intensification with cyclophosphamide, bortezomib, and dexamethasone before transplant.
After transplant, all eligible patients were randomized to lenalidomide maintenance or observation. Patients were eligible for this randomization if they didn’t respond to induction, had progressive disease, or had previous or concurrent active malignancies.
The median follow-up was 34.5 months. The median number of induction cycles completed was 4 (range, 1-12) in the KCRD arm, 5 (range, 1-15) in the CRD arm, and 6 (range, 1-13) in the CTD arm.
Response
At the end of induction, the rate of very good partial response or better was 82.3% in the KCRD arm, 64.9% in the CRD arm, 52.8% in the CTD arm, and 58.9% in the CTD-CRD arms combined. The odds ratio for the KCRD group compared to the triplets combined was 4.35 (P less than .0001).
At 100 days after transplant, the rate of very good partial response or better was 91.9% in the KCRD arm, 82.1% in the CRD arm, 76.1% in the CTD arm, and 79.3% in the CTD-CRD arms combined. The odds ratio for the KCRD group compared to the triplets combined was 3.01 (P less than .0001).
KCRD produced a higher proportion of MRD-negative responses both before and after transplant. After induction, the rate of MRD-negative response was 11% in the CTD arm, 21% in the CRD arm, and 55% in the KCRD arm. After transplant, the rates were 51%, 49%, and 77%, respectively.
Survival
KCRD improved PFS. The 3-year PFS rate was 64.5% in the KCRD arm and 50.3% in the CTD-CRD arms combined. The hazard ratio (HR) was 0.63 (P less than .0001).
The PFS benefit with KCRD was present in all patient subgroups. For example, KCRD improved PFS, compared with CTD-CRD, in patients with standard-risk (HR = 0.62), high-risk (HR = 0.68), and ultra-high-risk (HR = 0.50) cytogenetics.
Patients who achieved an MRD-negative response had better PFS, and early achievement of MRD negativity was associated with improved PFS, Dr. Pawlyn noted.
“But what’s also notable ... is that those patients who received KCRD and achieved MRD negativity ... had better outcomes than patients who achieved MRD negativity whilst receiving a triplet combination,” Dr. Pawlyn said. “So this suggests that the induction regimen delivered is important, not just the achievement of MRD negativity at a defined cutoff.”
Dr. Pawlyn added that overall survival data from this study are not yet mature, but the researchers did assess PFS2. PFS2 was defined as the time from randomization to second disease progression. The 3-year PFS2 was 81.8% in the KCRD arm and 75.1% in the CTD-CRD arms combined. The HR was 0.75 (P = .0451).
Myeloma XI is sponsored by University of Leeds in collaboration with Celgene, Merck Sharp & Dohme, and Amgen. Dr. Pawlyn reported relationships with Amgen, Celgene, and other companies.
SOURCE: Pawlyn C et al. IMW 2019, Abstract OAB-002.
BOSTON – A carfilzomib-based quadruplet can improve outcomes in transplant-eligible patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma, a phase 3 trial suggests.
In the Myeloma XI trial, carfilzomib plus cyclophosphamide, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone (KCRD) significantly prolonged progression-free survival (PFS), compared with cyclophosphamide-lenalidomide-dexamethasone (CRD) or cyclophosphamide-thalidomide-dexamethasone (CTD).
“KCRD was associated with a very high response rate and a high MRD [minimal residual disease]-negative rate at the end of induction, and it significantly improved progression-free survival compared to the triplet combinations,” said Charlotte Pawlyn, PhD, of The Institute of Cancer Research in London.
Dr. Pawlyn reported these findings at the International Myeloma Workshop held by the International Myeloma Society.
The phase 3 Myeloma XI trial enrolled 1,056 patients with newly diagnosed myeloma who were eligible for transplant. The patients were randomized to receive KCRD (n = 526), CRD (n = 265), or CTD (n = 265) as induction.
Baseline characteristics were well balanced between the treatment arms. The median age was 61 years in the KCRD and CTD arms and 62 years in the CRD arm (overall range, 33-75 years). Roughly 60% of patients in each arm were men.
About 50%-60% of patients in each arm had standard-risk cytogenetics, which was defined as the absence of any cytogenetic lesions. About 30%-40% of patients in each arm had high-risk cytogenetics, meaning they had one of the following lesions: t(4;14), t(14;16), t(14;20), del (17p), or gain(1q). About 10% of patients in each arm had ultra-high-risk cytogenetics, which was defined as having more than one lesion.
Treatment
For induction, patients were randomized to KCRD, CRD, or CTD. All patients in the KCRD arm and patients in the CRD/CTD arms who achieved a partial response or better went straight to autologous transplant after induction. Nonresponders in the CTD and CRD arms received intensification with cyclophosphamide, bortezomib, and dexamethasone before transplant.
After transplant, all eligible patients were randomized to lenalidomide maintenance or observation. Patients were eligible for this randomization if they didn’t respond to induction, had progressive disease, or had previous or concurrent active malignancies.
The median follow-up was 34.5 months. The median number of induction cycles completed was 4 (range, 1-12) in the KCRD arm, 5 (range, 1-15) in the CRD arm, and 6 (range, 1-13) in the CTD arm.
Response
At the end of induction, the rate of very good partial response or better was 82.3% in the KCRD arm, 64.9% in the CRD arm, 52.8% in the CTD arm, and 58.9% in the CTD-CRD arms combined. The odds ratio for the KCRD group compared to the triplets combined was 4.35 (P less than .0001).
At 100 days after transplant, the rate of very good partial response or better was 91.9% in the KCRD arm, 82.1% in the CRD arm, 76.1% in the CTD arm, and 79.3% in the CTD-CRD arms combined. The odds ratio for the KCRD group compared to the triplets combined was 3.01 (P less than .0001).
KCRD produced a higher proportion of MRD-negative responses both before and after transplant. After induction, the rate of MRD-negative response was 11% in the CTD arm, 21% in the CRD arm, and 55% in the KCRD arm. After transplant, the rates were 51%, 49%, and 77%, respectively.
Survival
KCRD improved PFS. The 3-year PFS rate was 64.5% in the KCRD arm and 50.3% in the CTD-CRD arms combined. The hazard ratio (HR) was 0.63 (P less than .0001).
The PFS benefit with KCRD was present in all patient subgroups. For example, KCRD improved PFS, compared with CTD-CRD, in patients with standard-risk (HR = 0.62), high-risk (HR = 0.68), and ultra-high-risk (HR = 0.50) cytogenetics.
Patients who achieved an MRD-negative response had better PFS, and early achievement of MRD negativity was associated with improved PFS, Dr. Pawlyn noted.
“But what’s also notable ... is that those patients who received KCRD and achieved MRD negativity ... had better outcomes than patients who achieved MRD negativity whilst receiving a triplet combination,” Dr. Pawlyn said. “So this suggests that the induction regimen delivered is important, not just the achievement of MRD negativity at a defined cutoff.”
Dr. Pawlyn added that overall survival data from this study are not yet mature, but the researchers did assess PFS2. PFS2 was defined as the time from randomization to second disease progression. The 3-year PFS2 was 81.8% in the KCRD arm and 75.1% in the CTD-CRD arms combined. The HR was 0.75 (P = .0451).
Myeloma XI is sponsored by University of Leeds in collaboration with Celgene, Merck Sharp & Dohme, and Amgen. Dr. Pawlyn reported relationships with Amgen, Celgene, and other companies.
SOURCE: Pawlyn C et al. IMW 2019, Abstract OAB-002.
REPORTING FROM IMW 2019
GALACTIC CLL trial: Obinutuzumab consolidation helps eradicate MRD
EDINBURGH – Consolidation therapy with obinutuzumab after chemoimmunotherapy for B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLL) was highly effective for eradicating minimal residual disease (MRD) within 6 months following randomization in the seamless phase 2/3 GALACTIC trial.
Of 14 patients who were MRD positive after chemoimmunotherapy and randomized to consolidation with the type II monoclonal antibody targeting the CD20 antigen, 10 achieved MRD negativity in the bone marrow by 6 months, and 13 achieved MRD negativity in the peripheral blood by 6 months, Talha Munir, MD, reported at the International Workshop on Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia.
“And that translated into [progression-free survival] improvement in the consolidation arm,” said Dr. Munir of St. James’s University, Leeds, England.
The median progression-free survival in that arm was not reached, whereas progression-free survival in 15 MRD-positive patients randomized to the nonconsolidation arm was 16.6 months, he said.
Further, no difference was seen in median progression-free survival, overall survival, or MRD duration between the consolidation arm and 19 patients who were not randomized because of MRD negativity after chemoimmunotherapy, he noted.
Achieving MRD negativity in CLL confers a survival advantage, and obinutuzumab has shown greater efficacy with respect to MRD in CLL when compared with previous anti-CD20 antibodies, and it is less immune suppressive than the anti-CD52 antibody alemtuzumab, he explained.
The GALACTIC trial was designed to assess the safety and efficacy of obinutuzumab consolidation for eradicating MRD and whether its effects would prolong progression-free survival in patients with B-CLL who recently responded to chemoimmunotherapy. Those achieving complete response or partial response at 3-24 months after chemoimmunotherapy, and who remained MRD-positive, were eligible for randomization.
The planned sample size was 188 patients, but the trial was closed early in February 2017 because of poor recruitment; a total of 48 patients were enrolled, including the 19 nonrandomized, MRD-negative patients.
Patients randomized to consolidation received 1,000 mg of obinutuzumab weekly for the first four doses, and then every other week for four additional doses.
Obinutuzumab was well tolerated with minimal infusion-related reactions and toxicity, Dr. Munir said.
Despite the low recruitment, both the phase 2 and 3 endpoints were assessed as positive, because the consolidation strategy was so efficacious, Dr. Munir noted, concluding that the findings provide further evidence of the value of MRD negativity for improving outcomes in CLL.
The GALACTIC trial was developed by the GALACTIC Trial Management Group with the support of the UKCLL/NCRI CLL Clinical Trials Subgroup. The trial is funded by Cancer Research UK and Roche and sponsored by the University of Leeds. Dr. Munir reported having no disclosures.
[email protected]
EDINBURGH – Consolidation therapy with obinutuzumab after chemoimmunotherapy for B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLL) was highly effective for eradicating minimal residual disease (MRD) within 6 months following randomization in the seamless phase 2/3 GALACTIC trial.
Of 14 patients who were MRD positive after chemoimmunotherapy and randomized to consolidation with the type II monoclonal antibody targeting the CD20 antigen, 10 achieved MRD negativity in the bone marrow by 6 months, and 13 achieved MRD negativity in the peripheral blood by 6 months, Talha Munir, MD, reported at the International Workshop on Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia.
“And that translated into [progression-free survival] improvement in the consolidation arm,” said Dr. Munir of St. James’s University, Leeds, England.
The median progression-free survival in that arm was not reached, whereas progression-free survival in 15 MRD-positive patients randomized to the nonconsolidation arm was 16.6 months, he said.
Further, no difference was seen in median progression-free survival, overall survival, or MRD duration between the consolidation arm and 19 patients who were not randomized because of MRD negativity after chemoimmunotherapy, he noted.
Achieving MRD negativity in CLL confers a survival advantage, and obinutuzumab has shown greater efficacy with respect to MRD in CLL when compared with previous anti-CD20 antibodies, and it is less immune suppressive than the anti-CD52 antibody alemtuzumab, he explained.
The GALACTIC trial was designed to assess the safety and efficacy of obinutuzumab consolidation for eradicating MRD and whether its effects would prolong progression-free survival in patients with B-CLL who recently responded to chemoimmunotherapy. Those achieving complete response or partial response at 3-24 months after chemoimmunotherapy, and who remained MRD-positive, were eligible for randomization.
The planned sample size was 188 patients, but the trial was closed early in February 2017 because of poor recruitment; a total of 48 patients were enrolled, including the 19 nonrandomized, MRD-negative patients.
Patients randomized to consolidation received 1,000 mg of obinutuzumab weekly for the first four doses, and then every other week for four additional doses.
Obinutuzumab was well tolerated with minimal infusion-related reactions and toxicity, Dr. Munir said.
Despite the low recruitment, both the phase 2 and 3 endpoints were assessed as positive, because the consolidation strategy was so efficacious, Dr. Munir noted, concluding that the findings provide further evidence of the value of MRD negativity for improving outcomes in CLL.
The GALACTIC trial was developed by the GALACTIC Trial Management Group with the support of the UKCLL/NCRI CLL Clinical Trials Subgroup. The trial is funded by Cancer Research UK and Roche and sponsored by the University of Leeds. Dr. Munir reported having no disclosures.
[email protected]
EDINBURGH – Consolidation therapy with obinutuzumab after chemoimmunotherapy for B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLL) was highly effective for eradicating minimal residual disease (MRD) within 6 months following randomization in the seamless phase 2/3 GALACTIC trial.
Of 14 patients who were MRD positive after chemoimmunotherapy and randomized to consolidation with the type II monoclonal antibody targeting the CD20 antigen, 10 achieved MRD negativity in the bone marrow by 6 months, and 13 achieved MRD negativity in the peripheral blood by 6 months, Talha Munir, MD, reported at the International Workshop on Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia.
“And that translated into [progression-free survival] improvement in the consolidation arm,” said Dr. Munir of St. James’s University, Leeds, England.
The median progression-free survival in that arm was not reached, whereas progression-free survival in 15 MRD-positive patients randomized to the nonconsolidation arm was 16.6 months, he said.
Further, no difference was seen in median progression-free survival, overall survival, or MRD duration between the consolidation arm and 19 patients who were not randomized because of MRD negativity after chemoimmunotherapy, he noted.
Achieving MRD negativity in CLL confers a survival advantage, and obinutuzumab has shown greater efficacy with respect to MRD in CLL when compared with previous anti-CD20 antibodies, and it is less immune suppressive than the anti-CD52 antibody alemtuzumab, he explained.
The GALACTIC trial was designed to assess the safety and efficacy of obinutuzumab consolidation for eradicating MRD and whether its effects would prolong progression-free survival in patients with B-CLL who recently responded to chemoimmunotherapy. Those achieving complete response or partial response at 3-24 months after chemoimmunotherapy, and who remained MRD-positive, were eligible for randomization.
The planned sample size was 188 patients, but the trial was closed early in February 2017 because of poor recruitment; a total of 48 patients were enrolled, including the 19 nonrandomized, MRD-negative patients.
Patients randomized to consolidation received 1,000 mg of obinutuzumab weekly for the first four doses, and then every other week for four additional doses.
Obinutuzumab was well tolerated with minimal infusion-related reactions and toxicity, Dr. Munir said.
Despite the low recruitment, both the phase 2 and 3 endpoints were assessed as positive, because the consolidation strategy was so efficacious, Dr. Munir noted, concluding that the findings provide further evidence of the value of MRD negativity for improving outcomes in CLL.
The GALACTIC trial was developed by the GALACTIC Trial Management Group with the support of the UKCLL/NCRI CLL Clinical Trials Subgroup. The trial is funded by Cancer Research UK and Roche and sponsored by the University of Leeds. Dr. Munir reported having no disclosures.
[email protected]
REPORTING FROM iwCLL 2019
ASCT may cure follicular lymphoma for some rituximab-naive patients
Prompt autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT) is often curative in rituximab-naive patients with follicular lymphoma who have experienced early failure of first-line therapy and achieved a response to second-line therapy, suggest results from a registry-based study conducted by GELTAMO (the Spanish Lymphoma and Bone Marrow Transplant Group).
“Overall, our results suggest that, whereas some patients might benefit from more aggressive therapies, such as allogenic stem cell transplantations, or novel drugs, such as immunomodulatory agents, monoclonal antibodies, phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibitors, or even the application of bispecific T-cell engagers and chimeric antigen receptor T cells, there are a considerable number of patients in this high-risk [early therapy failure] subgroup that can be cured with ASCT, even in the absence of rituximab,” Ana Jiménez-Ubieto, MD, PhD, of the Hospital Universitario, 12 de Octubre, Madrid, Spain, and colleagues wrote.
The results are more favorable when ASCT is performed in patients experiencing early therapy failure, with less than 1 year from first relapse after primary treatment to ASCT.
“Early ASCT could be a hopeful option in patients with difficult access to rituximab,” the researchers wrote in Hematology/Oncology and Stem Cell Therapy.
Patients with follicular lymphoma who experience relapse or progression during or soon after first-line therapy have poor overall survival, and there is no standard therapy for this population, according to the researchers. Previous research has shown that ASCT prolongs survival in those who have received rituximab before transplantation, but benefit in the absence of this agent is unknown.
Dr. Jiménez-Ubieto and colleagues conducted a multicenter registry-based retrospective cohort study of 134 patients with nontransformed follicular lymphoma who underwent ASCT during 1989-2007 while in second complete or partial response to rescue chemotherapy and had not received rituximab.
Overall, 65% of the patients had experienced early therapy failure (relapse or progression within 2 years of starting first-line chemotherapy). Within this group, 78% underwent ASCT within 1 year, and 67% underwent ASCT while in second complete response. Median posttransplantation follow-up for the entire study cohort was 13.4 years.
Study results showed that patients who had experienced early therapy failure versus who had not had poorer 5-year progression-free survival (43% vs. 57%; P = .048) but similar 5-year overall survival (69% vs. 77%; P = .4). However, those patients with early therapy failure who underwent ASCT within 1 year had a statistically indistinguishable 5-year progression-free survival relative to counterparts without early therapy failure (48% vs. 66%; P = .44).
Additionally, the 48% progression-free survival seen in this subset was almost identical to the 49% seen in a historical cohort of patients with early therapy failure who similarly underwent ASCT within 1 year of first relapse but received rituximab before transplantation (Hematol Oncol. 2018;36[5]:765-72). This suggests “that the possible synergistic effect of rituximab plus ASCT is not as relevant if ASCT is offered soon in the course of the disease,” the researchers wrote.
Patients who had experienced early therapy failure achieved better overall survival if they underwent ASCT while in second complete response, as opposed to second partial response. Notably, 56% of those who underwent ASCT while in second complete response were alive at 13.7 years of follow-up and remained so long term.
The study was funded by the Foundation Research Institute at the Hospital Universitario 12 de Octubre. The researchers reported having no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Jiménez-Ubieto A et al. Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Ther. 2019 Jul 9. doi: 10.1016/j.hemonc.2019.06.001.
Prompt autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT) is often curative in rituximab-naive patients with follicular lymphoma who have experienced early failure of first-line therapy and achieved a response to second-line therapy, suggest results from a registry-based study conducted by GELTAMO (the Spanish Lymphoma and Bone Marrow Transplant Group).
“Overall, our results suggest that, whereas some patients might benefit from more aggressive therapies, such as allogenic stem cell transplantations, or novel drugs, such as immunomodulatory agents, monoclonal antibodies, phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibitors, or even the application of bispecific T-cell engagers and chimeric antigen receptor T cells, there are a considerable number of patients in this high-risk [early therapy failure] subgroup that can be cured with ASCT, even in the absence of rituximab,” Ana Jiménez-Ubieto, MD, PhD, of the Hospital Universitario, 12 de Octubre, Madrid, Spain, and colleagues wrote.
The results are more favorable when ASCT is performed in patients experiencing early therapy failure, with less than 1 year from first relapse after primary treatment to ASCT.
“Early ASCT could be a hopeful option in patients with difficult access to rituximab,” the researchers wrote in Hematology/Oncology and Stem Cell Therapy.
Patients with follicular lymphoma who experience relapse or progression during or soon after first-line therapy have poor overall survival, and there is no standard therapy for this population, according to the researchers. Previous research has shown that ASCT prolongs survival in those who have received rituximab before transplantation, but benefit in the absence of this agent is unknown.
Dr. Jiménez-Ubieto and colleagues conducted a multicenter registry-based retrospective cohort study of 134 patients with nontransformed follicular lymphoma who underwent ASCT during 1989-2007 while in second complete or partial response to rescue chemotherapy and had not received rituximab.
Overall, 65% of the patients had experienced early therapy failure (relapse or progression within 2 years of starting first-line chemotherapy). Within this group, 78% underwent ASCT within 1 year, and 67% underwent ASCT while in second complete response. Median posttransplantation follow-up for the entire study cohort was 13.4 years.
Study results showed that patients who had experienced early therapy failure versus who had not had poorer 5-year progression-free survival (43% vs. 57%; P = .048) but similar 5-year overall survival (69% vs. 77%; P = .4). However, those patients with early therapy failure who underwent ASCT within 1 year had a statistically indistinguishable 5-year progression-free survival relative to counterparts without early therapy failure (48% vs. 66%; P = .44).
Additionally, the 48% progression-free survival seen in this subset was almost identical to the 49% seen in a historical cohort of patients with early therapy failure who similarly underwent ASCT within 1 year of first relapse but received rituximab before transplantation (Hematol Oncol. 2018;36[5]:765-72). This suggests “that the possible synergistic effect of rituximab plus ASCT is not as relevant if ASCT is offered soon in the course of the disease,” the researchers wrote.
Patients who had experienced early therapy failure achieved better overall survival if they underwent ASCT while in second complete response, as opposed to second partial response. Notably, 56% of those who underwent ASCT while in second complete response were alive at 13.7 years of follow-up and remained so long term.
The study was funded by the Foundation Research Institute at the Hospital Universitario 12 de Octubre. The researchers reported having no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Jiménez-Ubieto A et al. Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Ther. 2019 Jul 9. doi: 10.1016/j.hemonc.2019.06.001.
Prompt autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT) is often curative in rituximab-naive patients with follicular lymphoma who have experienced early failure of first-line therapy and achieved a response to second-line therapy, suggest results from a registry-based study conducted by GELTAMO (the Spanish Lymphoma and Bone Marrow Transplant Group).
“Overall, our results suggest that, whereas some patients might benefit from more aggressive therapies, such as allogenic stem cell transplantations, or novel drugs, such as immunomodulatory agents, monoclonal antibodies, phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibitors, or even the application of bispecific T-cell engagers and chimeric antigen receptor T cells, there are a considerable number of patients in this high-risk [early therapy failure] subgroup that can be cured with ASCT, even in the absence of rituximab,” Ana Jiménez-Ubieto, MD, PhD, of the Hospital Universitario, 12 de Octubre, Madrid, Spain, and colleagues wrote.
The results are more favorable when ASCT is performed in patients experiencing early therapy failure, with less than 1 year from first relapse after primary treatment to ASCT.
“Early ASCT could be a hopeful option in patients with difficult access to rituximab,” the researchers wrote in Hematology/Oncology and Stem Cell Therapy.
Patients with follicular lymphoma who experience relapse or progression during or soon after first-line therapy have poor overall survival, and there is no standard therapy for this population, according to the researchers. Previous research has shown that ASCT prolongs survival in those who have received rituximab before transplantation, but benefit in the absence of this agent is unknown.
Dr. Jiménez-Ubieto and colleagues conducted a multicenter registry-based retrospective cohort study of 134 patients with nontransformed follicular lymphoma who underwent ASCT during 1989-2007 while in second complete or partial response to rescue chemotherapy and had not received rituximab.
Overall, 65% of the patients had experienced early therapy failure (relapse or progression within 2 years of starting first-line chemotherapy). Within this group, 78% underwent ASCT within 1 year, and 67% underwent ASCT while in second complete response. Median posttransplantation follow-up for the entire study cohort was 13.4 years.
Study results showed that patients who had experienced early therapy failure versus who had not had poorer 5-year progression-free survival (43% vs. 57%; P = .048) but similar 5-year overall survival (69% vs. 77%; P = .4). However, those patients with early therapy failure who underwent ASCT within 1 year had a statistically indistinguishable 5-year progression-free survival relative to counterparts without early therapy failure (48% vs. 66%; P = .44).
Additionally, the 48% progression-free survival seen in this subset was almost identical to the 49% seen in a historical cohort of patients with early therapy failure who similarly underwent ASCT within 1 year of first relapse but received rituximab before transplantation (Hematol Oncol. 2018;36[5]:765-72). This suggests “that the possible synergistic effect of rituximab plus ASCT is not as relevant if ASCT is offered soon in the course of the disease,” the researchers wrote.
Patients who had experienced early therapy failure achieved better overall survival if they underwent ASCT while in second complete response, as opposed to second partial response. Notably, 56% of those who underwent ASCT while in second complete response were alive at 13.7 years of follow-up and remained so long term.
The study was funded by the Foundation Research Institute at the Hospital Universitario 12 de Octubre. The researchers reported having no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Jiménez-Ubieto A et al. Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Ther. 2019 Jul 9. doi: 10.1016/j.hemonc.2019.06.001.
FROM HEMATOLOGY/ONCOLOGY AND STEM CELL THERAPY