User login
FDA proposes new breast implant labeling with a boxed warning
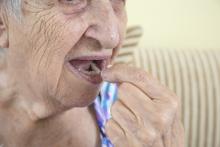
Breast implants sold in the United States may soon require a boxed warning in their label, along with other label changes proposed by the Food and Drug Administration aimed at better informing prospective patients and clinicians of the potential risks from breast implants.
Other elements of the proposed labeling changes include creation of a patient-decision checklist, new recommendations for follow-up imaging to monitor for implant rupture, inclusion of detailed and understandable information about materials in the device, and provision of a device card to each patient with details on the specific implant they received.
These labeling changes all stemmed from a breast implant hearing held by the agency’s General and Plastic Surgery Devices Panel in March 2019, according to the draft guidance document officially released by the FDA on Oct. 24.
The proposed labeling changes were generally welcomed by patient advocates and by clinicians as a reasonable response to the concerns discussed at the March hearing. In an earlier move to address issues brought up at the hearing, the FDA in July arranged for a recall for certain Allergan models of textured breast implants because of their link with the development of breast implant–associated anaplastic large cell lymphoma (BIA-ALCL).
The boxed warning proposed by the FDA would highlight four specific facts that patients, physicians, and surgeons should know about breast implants: They are not considered lifetime devices, the chance of developing complications from implants increases over time, some complications require additional surgery, and placement of breast implants has been associated with development of BIA-ALCL and may also be associated with certain systemic symptoms.
The FDA also proposed four other notable labeling changes:
- Creation of a patient-decision checklist to better systematize the informed consent process and make sure that certain aspects of breast implant placement are clearly brought to patients’ attention. The FDA proposed that patients sign their checklist attesting to having read and understood the information and that patients receive a take-home copy for their future reference. Proposed elements of the checklist include situations to not use breast implants; considerations for successful implant recipients; the risks of breast implant surgery; the importance of appropriate physician education, training, and experience; the risk for developing BIA-ALCL or systemic symptoms; and discussion of options other than breast implants.
- A new scheme for systematically and serially using imaging to screen for implant rupture that designates for the first time that ultrasound is an acceptable alternative to MRI and relies on a schedule by which either method initially screens the implant 5-6 years post operatively and then every 2 years thereafter.
- Detailed and understandable information about each material component of the implant with further information on possible adverse health effects of these compounds.
- A device card that patients should receive after their surgery with the implant’s name, serial number, and other identifiers; the boxed warning information; and a web link for accessing more up-to-date information.
The patient group Breast Implant Victim Advocacy praised the draft guidance. “The March Advisory Committee meeting seems to have prompted a shift by the FDA, surgeons, and industry,” said Jamee Cook, cofounder of the group. “We are definitely seeing a change in patient engagement. The FDA has been cooperating with patients and listening to our concerns. We still have a long way to go in raising public awareness of breast implant issues, but progress over the past 1-2 years has been amazing.”
Diana Zuckerman, PhD, president of the National Center for Health Research in Washington, gave the draft guidance a mixed review. “The FDA’s draft includes the types of information that we had proposed to the FDA in recent months in our work with patient advocates and plastic surgeons,” she said. “However, it is not as informative as it should be in describing well-designed studies indicating a risk of systemic illnesses. Patients deserve to make better-informed decisions in the future than most women considering breast implants have been able to make” in the past.
Patricia McGuire, MD, a St. Louis plastic surgeon who specializes in breast surgery and has studied breast implant illness, declared the guidance to be “reasonable.”
“I think the changes address the concerns expressed by patients during the [March] hearing; I agree with everything the FDA proposed in the guidance document,” Dr. McGuire said. “The boxed warning is reasonable and needs to be part of the informed consent process. I also agree with the changes in screening implants postoperatively. Most patients do not get MRI examinations. High-resolution ultrasound is more convenient and cost effective.”
The boxed warning was rated as “reasonably strong” and “the most serious step the FDA can take short of taking a device off the market,” but in the case of breast implants, a wider recall of textured implants than what the FDA arranged last July would be even more appropriate, commented Sidney M. Wolfe, MD, founder and senior adviser to Public Citizen. He also faulted the agency for not taking quicker action in mandating inclusion of the proposed boxed warning.
Issuing the labeling changes as draft guidance “is a ministep forward,” but also a process that “guarantees delay” and “creeps along at a dangerously slow pace,” Dr. Wolfe said. “The FDA is delaying what should be inevitable. The agency could put the boxed warning in place right now if they had the guts to do it.”
Dr. McGuire has been a consultant to Allergan, Establishment Labs, and Hans Biomed. Ms. Cook, Dr. Zuckerman, and Dr. Wolfe reported having no commercial disclosures.
Breast implants sold in the United States may soon require a boxed warning in their label, along with other label changes proposed by the Food and Drug Administration aimed at better informing prospective patients and clinicians of the potential risks from breast implants.
Other elements of the proposed labeling changes include creation of a patient-decision checklist, new recommendations for follow-up imaging to monitor for implant rupture, inclusion of detailed and understandable information about materials in the device, and provision of a device card to each patient with details on the specific implant they received.
These labeling changes all stemmed from a breast implant hearing held by the agency’s General and Plastic Surgery Devices Panel in March 2019, according to the draft guidance document officially released by the FDA on Oct. 24.
The proposed labeling changes were generally welcomed by patient advocates and by clinicians as a reasonable response to the concerns discussed at the March hearing. In an earlier move to address issues brought up at the hearing, the FDA in July arranged for a recall for certain Allergan models of textured breast implants because of their link with the development of breast implant–associated anaplastic large cell lymphoma (BIA-ALCL).
The boxed warning proposed by the FDA would highlight four specific facts that patients, physicians, and surgeons should know about breast implants: They are not considered lifetime devices, the chance of developing complications from implants increases over time, some complications require additional surgery, and placement of breast implants has been associated with development of BIA-ALCL and may also be associated with certain systemic symptoms.
The FDA also proposed four other notable labeling changes:
- Creation of a patient-decision checklist to better systematize the informed consent process and make sure that certain aspects of breast implant placement are clearly brought to patients’ attention. The FDA proposed that patients sign their checklist attesting to having read and understood the information and that patients receive a take-home copy for their future reference. Proposed elements of the checklist include situations to not use breast implants; considerations for successful implant recipients; the risks of breast implant surgery; the importance of appropriate physician education, training, and experience; the risk for developing BIA-ALCL or systemic symptoms; and discussion of options other than breast implants.
- A new scheme for systematically and serially using imaging to screen for implant rupture that designates for the first time that ultrasound is an acceptable alternative to MRI and relies on a schedule by which either method initially screens the implant 5-6 years post operatively and then every 2 years thereafter.
- Detailed and understandable information about each material component of the implant with further information on possible adverse health effects of these compounds.
- A device card that patients should receive after their surgery with the implant’s name, serial number, and other identifiers; the boxed warning information; and a web link for accessing more up-to-date information.
The patient group Breast Implant Victim Advocacy praised the draft guidance. “The March Advisory Committee meeting seems to have prompted a shift by the FDA, surgeons, and industry,” said Jamee Cook, cofounder of the group. “We are definitely seeing a change in patient engagement. The FDA has been cooperating with patients and listening to our concerns. We still have a long way to go in raising public awareness of breast implant issues, but progress over the past 1-2 years has been amazing.”
Diana Zuckerman, PhD, president of the National Center for Health Research in Washington, gave the draft guidance a mixed review. “The FDA’s draft includes the types of information that we had proposed to the FDA in recent months in our work with patient advocates and plastic surgeons,” she said. “However, it is not as informative as it should be in describing well-designed studies indicating a risk of systemic illnesses. Patients deserve to make better-informed decisions in the future than most women considering breast implants have been able to make” in the past.
Patricia McGuire, MD, a St. Louis plastic surgeon who specializes in breast surgery and has studied breast implant illness, declared the guidance to be “reasonable.”
“I think the changes address the concerns expressed by patients during the [March] hearing; I agree with everything the FDA proposed in the guidance document,” Dr. McGuire said. “The boxed warning is reasonable and needs to be part of the informed consent process. I also agree with the changes in screening implants postoperatively. Most patients do not get MRI examinations. High-resolution ultrasound is more convenient and cost effective.”
The boxed warning was rated as “reasonably strong” and “the most serious step the FDA can take short of taking a device off the market,” but in the case of breast implants, a wider recall of textured implants than what the FDA arranged last July would be even more appropriate, commented Sidney M. Wolfe, MD, founder and senior adviser to Public Citizen. He also faulted the agency for not taking quicker action in mandating inclusion of the proposed boxed warning.
Issuing the labeling changes as draft guidance “is a ministep forward,” but also a process that “guarantees delay” and “creeps along at a dangerously slow pace,” Dr. Wolfe said. “The FDA is delaying what should be inevitable. The agency could put the boxed warning in place right now if they had the guts to do it.”
Dr. McGuire has been a consultant to Allergan, Establishment Labs, and Hans Biomed. Ms. Cook, Dr. Zuckerman, and Dr. Wolfe reported having no commercial disclosures.
Breast implants sold in the United States may soon require a boxed warning in their label, along with other label changes proposed by the Food and Drug Administration aimed at better informing prospective patients and clinicians of the potential risks from breast implants.
Other elements of the proposed labeling changes include creation of a patient-decision checklist, new recommendations for follow-up imaging to monitor for implant rupture, inclusion of detailed and understandable information about materials in the device, and provision of a device card to each patient with details on the specific implant they received.
These labeling changes all stemmed from a breast implant hearing held by the agency’s General and Plastic Surgery Devices Panel in March 2019, according to the draft guidance document officially released by the FDA on Oct. 24.
The proposed labeling changes were generally welcomed by patient advocates and by clinicians as a reasonable response to the concerns discussed at the March hearing. In an earlier move to address issues brought up at the hearing, the FDA in July arranged for a recall for certain Allergan models of textured breast implants because of their link with the development of breast implant–associated anaplastic large cell lymphoma (BIA-ALCL).
The boxed warning proposed by the FDA would highlight four specific facts that patients, physicians, and surgeons should know about breast implants: They are not considered lifetime devices, the chance of developing complications from implants increases over time, some complications require additional surgery, and placement of breast implants has been associated with development of BIA-ALCL and may also be associated with certain systemic symptoms.
The FDA also proposed four other notable labeling changes:
- Creation of a patient-decision checklist to better systematize the informed consent process and make sure that certain aspects of breast implant placement are clearly brought to patients’ attention. The FDA proposed that patients sign their checklist attesting to having read and understood the information and that patients receive a take-home copy for their future reference. Proposed elements of the checklist include situations to not use breast implants; considerations for successful implant recipients; the risks of breast implant surgery; the importance of appropriate physician education, training, and experience; the risk for developing BIA-ALCL or systemic symptoms; and discussion of options other than breast implants.
- A new scheme for systematically and serially using imaging to screen for implant rupture that designates for the first time that ultrasound is an acceptable alternative to MRI and relies on a schedule by which either method initially screens the implant 5-6 years post operatively and then every 2 years thereafter.
- Detailed and understandable information about each material component of the implant with further information on possible adverse health effects of these compounds.
- A device card that patients should receive after their surgery with the implant’s name, serial number, and other identifiers; the boxed warning information; and a web link for accessing more up-to-date information.
The patient group Breast Implant Victim Advocacy praised the draft guidance. “The March Advisory Committee meeting seems to have prompted a shift by the FDA, surgeons, and industry,” said Jamee Cook, cofounder of the group. “We are definitely seeing a change in patient engagement. The FDA has been cooperating with patients and listening to our concerns. We still have a long way to go in raising public awareness of breast implant issues, but progress over the past 1-2 years has been amazing.”
Diana Zuckerman, PhD, president of the National Center for Health Research in Washington, gave the draft guidance a mixed review. “The FDA’s draft includes the types of information that we had proposed to the FDA in recent months in our work with patient advocates and plastic surgeons,” she said. “However, it is not as informative as it should be in describing well-designed studies indicating a risk of systemic illnesses. Patients deserve to make better-informed decisions in the future than most women considering breast implants have been able to make” in the past.
Patricia McGuire, MD, a St. Louis plastic surgeon who specializes in breast surgery and has studied breast implant illness, declared the guidance to be “reasonable.”
“I think the changes address the concerns expressed by patients during the [March] hearing; I agree with everything the FDA proposed in the guidance document,” Dr. McGuire said. “The boxed warning is reasonable and needs to be part of the informed consent process. I also agree with the changes in screening implants postoperatively. Most patients do not get MRI examinations. High-resolution ultrasound is more convenient and cost effective.”
The boxed warning was rated as “reasonably strong” and “the most serious step the FDA can take short of taking a device off the market,” but in the case of breast implants, a wider recall of textured implants than what the FDA arranged last July would be even more appropriate, commented Sidney M. Wolfe, MD, founder and senior adviser to Public Citizen. He also faulted the agency for not taking quicker action in mandating inclusion of the proposed boxed warning.
Issuing the labeling changes as draft guidance “is a ministep forward,” but also a process that “guarantees delay” and “creeps along at a dangerously slow pace,” Dr. Wolfe said. “The FDA is delaying what should be inevitable. The agency could put the boxed warning in place right now if they had the guts to do it.”
Dr. McGuire has been a consultant to Allergan, Establishment Labs, and Hans Biomed. Ms. Cook, Dr. Zuckerman, and Dr. Wolfe reported having no commercial disclosures.
SEER analysis reveals medication adherence factors in newly diagnosed myeloma
Black race, polypharmacy, and increasing age were associated with poor adherence to lenalidomide in older patients with newly-diagnosed multiple myeloma, according to an analysis of Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER)–Medicare linked data.
The objective of the study was to examine factors affecting adherence in older adults who received lenalidomide.
Of 793 patients diagnosed and treated between 2007 and 2014, 302 (38%) had poor adherence to lenalidomide, reported Hira Mian, MD, of McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont., and colleagues. The findings were published in Clinical Lymphoma, Myeloma & Leukemia.
The researchers studied patients 65 years and older who had received at least two lenalidomide prescriptions in the first year following diagnosis. Only patients who filled a prescription for lenalidomide within 60 days of a myeloma diagnosis were included.
The median age of the patients was 73 years; 43% were aged 75 years or older. Most of the patients included in the analysis were white.
The medication possession ratio, defined as the “ratio of the number of days the patient had pills in their possession to the number of days in the observation period,” was used to evaluate adherence to therapy. A ratio of less than 90% was deemed poor adherence by the researchers.
After analysis, the researchers found that black race (adjusted odds ratio, 1.72; P = .022), polypharmacy (aOR, 1.04 per drug; P = .008), and increasing age (aOR, 1.03 per year; P = .024) were all significantly associated with poor adherence to lenalidomide.
The mean medication possession ratio among study patients was 89.5%. Overall, 38% of patients in the study had poor adherence to lenalidomide, while just 7% of patients in the study had a medication possession ratio of 100%, indicating “perfect adherence.”
There was a trend toward inferior overall survival among patients with poor adherence to lenalidomide, but it was not statistically significant (hazard ratio 1.10, 95% confidence interval, 0.88-1.38).
“Our study emphasizes the need for both better clinical monitoring of adherence and for future prospective studies in accurately understanding the rates and predictors of adherence while simultaneously developing strategies for improving adherence for patients that are at high risk of nonadherence,” the researchers wrote.
The National Institutes of Health funded the study. No conflicts of interest were reported.
SOURCE: Mian H et al. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2019 Oct 9. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2019.09.618.
Black race, polypharmacy, and increasing age were associated with poor adherence to lenalidomide in older patients with newly-diagnosed multiple myeloma, according to an analysis of Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER)–Medicare linked data.
The objective of the study was to examine factors affecting adherence in older adults who received lenalidomide.
Of 793 patients diagnosed and treated between 2007 and 2014, 302 (38%) had poor adherence to lenalidomide, reported Hira Mian, MD, of McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont., and colleagues. The findings were published in Clinical Lymphoma, Myeloma & Leukemia.
The researchers studied patients 65 years and older who had received at least two lenalidomide prescriptions in the first year following diagnosis. Only patients who filled a prescription for lenalidomide within 60 days of a myeloma diagnosis were included.
The median age of the patients was 73 years; 43% were aged 75 years or older. Most of the patients included in the analysis were white.
The medication possession ratio, defined as the “ratio of the number of days the patient had pills in their possession to the number of days in the observation period,” was used to evaluate adherence to therapy. A ratio of less than 90% was deemed poor adherence by the researchers.
After analysis, the researchers found that black race (adjusted odds ratio, 1.72; P = .022), polypharmacy (aOR, 1.04 per drug; P = .008), and increasing age (aOR, 1.03 per year; P = .024) were all significantly associated with poor adherence to lenalidomide.
The mean medication possession ratio among study patients was 89.5%. Overall, 38% of patients in the study had poor adherence to lenalidomide, while just 7% of patients in the study had a medication possession ratio of 100%, indicating “perfect adherence.”
There was a trend toward inferior overall survival among patients with poor adherence to lenalidomide, but it was not statistically significant (hazard ratio 1.10, 95% confidence interval, 0.88-1.38).
“Our study emphasizes the need for both better clinical monitoring of adherence and for future prospective studies in accurately understanding the rates and predictors of adherence while simultaneously developing strategies for improving adherence for patients that are at high risk of nonadherence,” the researchers wrote.
The National Institutes of Health funded the study. No conflicts of interest were reported.
SOURCE: Mian H et al. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2019 Oct 9. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2019.09.618.
Black race, polypharmacy, and increasing age were associated with poor adherence to lenalidomide in older patients with newly-diagnosed multiple myeloma, according to an analysis of Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER)–Medicare linked data.
The objective of the study was to examine factors affecting adherence in older adults who received lenalidomide.
Of 793 patients diagnosed and treated between 2007 and 2014, 302 (38%) had poor adherence to lenalidomide, reported Hira Mian, MD, of McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont., and colleagues. The findings were published in Clinical Lymphoma, Myeloma & Leukemia.
The researchers studied patients 65 years and older who had received at least two lenalidomide prescriptions in the first year following diagnosis. Only patients who filled a prescription for lenalidomide within 60 days of a myeloma diagnosis were included.
The median age of the patients was 73 years; 43% were aged 75 years or older. Most of the patients included in the analysis were white.
The medication possession ratio, defined as the “ratio of the number of days the patient had pills in their possession to the number of days in the observation period,” was used to evaluate adherence to therapy. A ratio of less than 90% was deemed poor adherence by the researchers.
After analysis, the researchers found that black race (adjusted odds ratio, 1.72; P = .022), polypharmacy (aOR, 1.04 per drug; P = .008), and increasing age (aOR, 1.03 per year; P = .024) were all significantly associated with poor adherence to lenalidomide.
The mean medication possession ratio among study patients was 89.5%. Overall, 38% of patients in the study had poor adherence to lenalidomide, while just 7% of patients in the study had a medication possession ratio of 100%, indicating “perfect adherence.”
There was a trend toward inferior overall survival among patients with poor adherence to lenalidomide, but it was not statistically significant (hazard ratio 1.10, 95% confidence interval, 0.88-1.38).
“Our study emphasizes the need for both better clinical monitoring of adherence and for future prospective studies in accurately understanding the rates and predictors of adherence while simultaneously developing strategies for improving adherence for patients that are at high risk of nonadherence,” the researchers wrote.
The National Institutes of Health funded the study. No conflicts of interest were reported.
SOURCE: Mian H et al. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2019 Oct 9. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2019.09.618.
FROM CLINICAL LYMPHOMA, MYELOMA & LEUKEMIA
Pembrolizumab shows promise for relapsed/refractory PMBCL
The programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) inhibitor pembrolizumab showed manageable safety and promising clinical activity in patients with relapsed/refractory primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma (PMBCL), according to results from two early-phase studies.
The phase 1b KEYNOTE-013 study included an expansion cohort that evaluated pembrolizumab monotherapy in patients with relapsed/refractory PMBCL. Based on preliminary findings from KEYNOTE-013, the phase 2 KEYNOTE-170 study was initiated to validate these results.
Philippe Armand, MD, PhD, of Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, and colleagues reported results from 53 patients in KEYNOTE-170 and extended follow-up of 21 patients in KEYNOTE-013. Data from these two trials formed the basis of an accelerated approval by the Food and Drug Administration of pembrolizumab in patients with relapsed/refractory PMBCL in June 2018.
“Frequent amplification and translocation events occur at 9p24.1 in PMBCL, resulting in tumor expression of the programmed cell death-1 (PD-1) ligands PD-L1 and PD-L2. This suggests susceptibility of PMBCL to PD-1 blockade,” the researchers wrote in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
KEYNOTE-170 included patients with relapsed or refractory disease who were transplant-ineligible and had failed a minimum of two prior lines of treatment. KEYNOTE-013 enrolled patients who relapsed following autologous stem cell transplantation or were ineligible for transplant.
Among patients in KEYNOTE-013 and KEYNOTE-170, the objective response rates were 48% and 45%, respectively. In total, 33% of patients in KEYNOTE-013 and 13% of patients in KEYNOTE-170 achieved a complete response. Among these patients, no disease progression was observed.
The median progression-free survival in KEYNOTE-170 was 5.5 months and 10.4 months in KEYNOTE-013. In KEYNOTE-170, median overall survival was not reached, while in KEYNOTE-013, the median overall survival was 31.4 months.
After a median follow-up time of 29.1 months in KEYNOTE-013 and 12.5 months in KEYNOTE-170, the median duration of response was not reached in either trial, the researchers reported.
With respect to safety, pembrolizumab-related grade 3 or 4 adverse events were observed in 23% and 24% of patients in KEYNOTE-170 and KEYNOTE-013, respectively. The most common adverse event in both trials was neutropenia. No deaths related to pembrolizumab were observed.
Response rates were lower in KEYNOTE-170, compared with KEYNOTE-013, but the researchers noted that longer follow-up could change these results.
“Although the small numbers allow only a tentative hypothesis, they raise the question of whether PD-1 blockade in this setting might resensitize tumors to chemotherapy, as recently suggested. If this can be further validated, it could have profound implication for the management of patients with [relapsed/refractory] PMBCL,” the researchers wrote.
The study was supported by Merck Sharp & Dohme, the Harold and Virginia Lash Foundation, the Leukemia and Lymphoma Society, and the Center for Immuno-Oncology of the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute. The authors reported financial affiliations with Merck Sharp & Dohme and several other companies.
SOURCE: Armand P et al. J Clin Oncol. 2019 Sep 10. doi: 10.1200/JCO.19.01389.
The programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) inhibitor pembrolizumab showed manageable safety and promising clinical activity in patients with relapsed/refractory primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma (PMBCL), according to results from two early-phase studies.
The phase 1b KEYNOTE-013 study included an expansion cohort that evaluated pembrolizumab monotherapy in patients with relapsed/refractory PMBCL. Based on preliminary findings from KEYNOTE-013, the phase 2 KEYNOTE-170 study was initiated to validate these results.
Philippe Armand, MD, PhD, of Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, and colleagues reported results from 53 patients in KEYNOTE-170 and extended follow-up of 21 patients in KEYNOTE-013. Data from these two trials formed the basis of an accelerated approval by the Food and Drug Administration of pembrolizumab in patients with relapsed/refractory PMBCL in June 2018.
“Frequent amplification and translocation events occur at 9p24.1 in PMBCL, resulting in tumor expression of the programmed cell death-1 (PD-1) ligands PD-L1 and PD-L2. This suggests susceptibility of PMBCL to PD-1 blockade,” the researchers wrote in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
KEYNOTE-170 included patients with relapsed or refractory disease who were transplant-ineligible and had failed a minimum of two prior lines of treatment. KEYNOTE-013 enrolled patients who relapsed following autologous stem cell transplantation or were ineligible for transplant.
Among patients in KEYNOTE-013 and KEYNOTE-170, the objective response rates were 48% and 45%, respectively. In total, 33% of patients in KEYNOTE-013 and 13% of patients in KEYNOTE-170 achieved a complete response. Among these patients, no disease progression was observed.
The median progression-free survival in KEYNOTE-170 was 5.5 months and 10.4 months in KEYNOTE-013. In KEYNOTE-170, median overall survival was not reached, while in KEYNOTE-013, the median overall survival was 31.4 months.
After a median follow-up time of 29.1 months in KEYNOTE-013 and 12.5 months in KEYNOTE-170, the median duration of response was not reached in either trial, the researchers reported.
With respect to safety, pembrolizumab-related grade 3 or 4 adverse events were observed in 23% and 24% of patients in KEYNOTE-170 and KEYNOTE-013, respectively. The most common adverse event in both trials was neutropenia. No deaths related to pembrolizumab were observed.
Response rates were lower in KEYNOTE-170, compared with KEYNOTE-013, but the researchers noted that longer follow-up could change these results.
“Although the small numbers allow only a tentative hypothesis, they raise the question of whether PD-1 blockade in this setting might resensitize tumors to chemotherapy, as recently suggested. If this can be further validated, it could have profound implication for the management of patients with [relapsed/refractory] PMBCL,” the researchers wrote.
The study was supported by Merck Sharp & Dohme, the Harold and Virginia Lash Foundation, the Leukemia and Lymphoma Society, and the Center for Immuno-Oncology of the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute. The authors reported financial affiliations with Merck Sharp & Dohme and several other companies.
SOURCE: Armand P et al. J Clin Oncol. 2019 Sep 10. doi: 10.1200/JCO.19.01389.
The programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) inhibitor pembrolizumab showed manageable safety and promising clinical activity in patients with relapsed/refractory primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma (PMBCL), according to results from two early-phase studies.
The phase 1b KEYNOTE-013 study included an expansion cohort that evaluated pembrolizumab monotherapy in patients with relapsed/refractory PMBCL. Based on preliminary findings from KEYNOTE-013, the phase 2 KEYNOTE-170 study was initiated to validate these results.
Philippe Armand, MD, PhD, of Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, and colleagues reported results from 53 patients in KEYNOTE-170 and extended follow-up of 21 patients in KEYNOTE-013. Data from these two trials formed the basis of an accelerated approval by the Food and Drug Administration of pembrolizumab in patients with relapsed/refractory PMBCL in June 2018.
“Frequent amplification and translocation events occur at 9p24.1 in PMBCL, resulting in tumor expression of the programmed cell death-1 (PD-1) ligands PD-L1 and PD-L2. This suggests susceptibility of PMBCL to PD-1 blockade,” the researchers wrote in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
KEYNOTE-170 included patients with relapsed or refractory disease who were transplant-ineligible and had failed a minimum of two prior lines of treatment. KEYNOTE-013 enrolled patients who relapsed following autologous stem cell transplantation or were ineligible for transplant.
Among patients in KEYNOTE-013 and KEYNOTE-170, the objective response rates were 48% and 45%, respectively. In total, 33% of patients in KEYNOTE-013 and 13% of patients in KEYNOTE-170 achieved a complete response. Among these patients, no disease progression was observed.
The median progression-free survival in KEYNOTE-170 was 5.5 months and 10.4 months in KEYNOTE-013. In KEYNOTE-170, median overall survival was not reached, while in KEYNOTE-013, the median overall survival was 31.4 months.
After a median follow-up time of 29.1 months in KEYNOTE-013 and 12.5 months in KEYNOTE-170, the median duration of response was not reached in either trial, the researchers reported.
With respect to safety, pembrolizumab-related grade 3 or 4 adverse events were observed in 23% and 24% of patients in KEYNOTE-170 and KEYNOTE-013, respectively. The most common adverse event in both trials was neutropenia. No deaths related to pembrolizumab were observed.
Response rates were lower in KEYNOTE-170, compared with KEYNOTE-013, but the researchers noted that longer follow-up could change these results.
“Although the small numbers allow only a tentative hypothesis, they raise the question of whether PD-1 blockade in this setting might resensitize tumors to chemotherapy, as recently suggested. If this can be further validated, it could have profound implication for the management of patients with [relapsed/refractory] PMBCL,” the researchers wrote.
The study was supported by Merck Sharp & Dohme, the Harold and Virginia Lash Foundation, the Leukemia and Lymphoma Society, and the Center for Immuno-Oncology of the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute. The authors reported financial affiliations with Merck Sharp & Dohme and several other companies.
SOURCE: Armand P et al. J Clin Oncol. 2019 Sep 10. doi: 10.1200/JCO.19.01389.
FROM JOURNAL OF CLINICAL ONCOLOGY
ASCO to award $50,000 young investigator grant to study MCL
Early-career researchers who are interested in studying
The young investigator grant is for a 1-year period and the award is used to fund a project focused on clinical or translational research on the clinical biology, natural history, prevention, screening, diagnosis, therapy, or epidemiology of MCL.
The purpose of this annual award, according to ASCO, is to fund physicians during the transition from a fellowship program to a faculty appointment.
Eligible applicants must be physicians currently in the last 2 years of final subspecialty training and within 10 years of having obtained his or her medical degree. Additionally, applicants must be planning a research career in clinical oncology, with a focus on MCL.
The grant selection committee’s primary criteria include the significance and originality of the proposed study and hypothesis, the feasibility of the experiment and methodology, whether it has an appropriate and detailed statistical analysis plan, and if the research is patient oriented.
The application deadline is Jan. 7, 2020, and the award term is July 1, 2020–June 30, 2021.
Application instructions are available on the ASCO website.
Early-career researchers who are interested in studying
The young investigator grant is for a 1-year period and the award is used to fund a project focused on clinical or translational research on the clinical biology, natural history, prevention, screening, diagnosis, therapy, or epidemiology of MCL.
The purpose of this annual award, according to ASCO, is to fund physicians during the transition from a fellowship program to a faculty appointment.
Eligible applicants must be physicians currently in the last 2 years of final subspecialty training and within 10 years of having obtained his or her medical degree. Additionally, applicants must be planning a research career in clinical oncology, with a focus on MCL.
The grant selection committee’s primary criteria include the significance and originality of the proposed study and hypothesis, the feasibility of the experiment and methodology, whether it has an appropriate and detailed statistical analysis plan, and if the research is patient oriented.
The application deadline is Jan. 7, 2020, and the award term is July 1, 2020–June 30, 2021.
Application instructions are available on the ASCO website.
Early-career researchers who are interested in studying
The young investigator grant is for a 1-year period and the award is used to fund a project focused on clinical or translational research on the clinical biology, natural history, prevention, screening, diagnosis, therapy, or epidemiology of MCL.
The purpose of this annual award, according to ASCO, is to fund physicians during the transition from a fellowship program to a faculty appointment.
Eligible applicants must be physicians currently in the last 2 years of final subspecialty training and within 10 years of having obtained his or her medical degree. Additionally, applicants must be planning a research career in clinical oncology, with a focus on MCL.
The grant selection committee’s primary criteria include the significance and originality of the proposed study and hypothesis, the feasibility of the experiment and methodology, whether it has an appropriate and detailed statistical analysis plan, and if the research is patient oriented.
The application deadline is Jan. 7, 2020, and the award term is July 1, 2020–June 30, 2021.
Application instructions are available on the ASCO website.
Vitamin D deficiency appears to worsen survival in Hodgkin lymphoma
Vitamin D deficiency is associated with worse progression-free and overall survival among patients with Hodgkin lymphoma, according to new study findings.
Sven Borchmann, MD, of the University of Cologne (Germany) and German Hodgkin Study Group and coauthors conducted a case-control study of 351 patients enrolled in the German Hodgkin Study Group trials who had available baseline serum samples. Pretreatment vitamin D levels were assessed and categorized as deficient (less than 30 nmol/L), insufficient (30-49 nmol/L), or sufficient (50 nmol/L or greater). The findings were published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
The researchers found that before starting treatment, 50% of patients were vitamin D deficient.
Patients with baseline vitamin D deficiency had significantly lower progression-free survival – 10.2% lower at 5 years and 17.6% lower at 10 years – compared with patients with either sufficient or insufficient vitamin D levels (P less than .001). They also had 2% lower overall survival at 5 years and 11.1% lower overall survival at 10 years (P less than .001).
The researchers also conducted preclinical studies in effort to understand the effect of vitamin D on Hodgkin lymphoma cells and in Hodgkin lymphoma tumor models.
They explored the effect of vitamin D on cultured Hodgkin lymphoma cell lines and saw a dose-response effect of calcitriol in reducing cell proliferation rates. They then looked at the effect of calcitriol on cell lines that were also exposed to doxorubicin or etoposide, and found calcitriol improved the cytotoxicity of these chemotherapy agents, especially at lower doses.
Finally, they conducted an in-vivo mouse study using Hodgkin lymphoma xenografts, and looked at whether vitamin D supplementation increased the effect of doxorubicin or etoposide. This revealed that chemotherapy and vitamin D supplementation together were significantly better at controlling tumor growth, compared with monotherapy with either vitamin D or doxorubicin and compared with placebo.
“On the basis of our study results and the limited toxicity of vitamin D replacement therapy, we would advocate for vitamin D deficiency screening and replacement to be incorporated into future randomized clinical trials to properly clarify the role of vitamin D replacement in HL [Hodgkin lymphoma],” the researchers wrote. “The goal of these trials should be to determine whether vitamin D replacement in HL improves outcome.”
No study funding information was reported. Dr. Borchmann reported honoraria and research funding from Takeda. Other authors reported financial disclosures related to Takeda, Roche, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and other companies.
SOURCE: Borchmann S et al. J Clin Oncol. 2019 Oct 17. doi:10.1200/JCO.19.00985.
Vitamin D deficiency is associated with worse progression-free and overall survival among patients with Hodgkin lymphoma, according to new study findings.
Sven Borchmann, MD, of the University of Cologne (Germany) and German Hodgkin Study Group and coauthors conducted a case-control study of 351 patients enrolled in the German Hodgkin Study Group trials who had available baseline serum samples. Pretreatment vitamin D levels were assessed and categorized as deficient (less than 30 nmol/L), insufficient (30-49 nmol/L), or sufficient (50 nmol/L or greater). The findings were published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
The researchers found that before starting treatment, 50% of patients were vitamin D deficient.
Patients with baseline vitamin D deficiency had significantly lower progression-free survival – 10.2% lower at 5 years and 17.6% lower at 10 years – compared with patients with either sufficient or insufficient vitamin D levels (P less than .001). They also had 2% lower overall survival at 5 years and 11.1% lower overall survival at 10 years (P less than .001).
The researchers also conducted preclinical studies in effort to understand the effect of vitamin D on Hodgkin lymphoma cells and in Hodgkin lymphoma tumor models.
They explored the effect of vitamin D on cultured Hodgkin lymphoma cell lines and saw a dose-response effect of calcitriol in reducing cell proliferation rates. They then looked at the effect of calcitriol on cell lines that were also exposed to doxorubicin or etoposide, and found calcitriol improved the cytotoxicity of these chemotherapy agents, especially at lower doses.
Finally, they conducted an in-vivo mouse study using Hodgkin lymphoma xenografts, and looked at whether vitamin D supplementation increased the effect of doxorubicin or etoposide. This revealed that chemotherapy and vitamin D supplementation together were significantly better at controlling tumor growth, compared with monotherapy with either vitamin D or doxorubicin and compared with placebo.
“On the basis of our study results and the limited toxicity of vitamin D replacement therapy, we would advocate for vitamin D deficiency screening and replacement to be incorporated into future randomized clinical trials to properly clarify the role of vitamin D replacement in HL [Hodgkin lymphoma],” the researchers wrote. “The goal of these trials should be to determine whether vitamin D replacement in HL improves outcome.”
No study funding information was reported. Dr. Borchmann reported honoraria and research funding from Takeda. Other authors reported financial disclosures related to Takeda, Roche, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and other companies.
SOURCE: Borchmann S et al. J Clin Oncol. 2019 Oct 17. doi:10.1200/JCO.19.00985.
Vitamin D deficiency is associated with worse progression-free and overall survival among patients with Hodgkin lymphoma, according to new study findings.
Sven Borchmann, MD, of the University of Cologne (Germany) and German Hodgkin Study Group and coauthors conducted a case-control study of 351 patients enrolled in the German Hodgkin Study Group trials who had available baseline serum samples. Pretreatment vitamin D levels were assessed and categorized as deficient (less than 30 nmol/L), insufficient (30-49 nmol/L), or sufficient (50 nmol/L or greater). The findings were published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
The researchers found that before starting treatment, 50% of patients were vitamin D deficient.
Patients with baseline vitamin D deficiency had significantly lower progression-free survival – 10.2% lower at 5 years and 17.6% lower at 10 years – compared with patients with either sufficient or insufficient vitamin D levels (P less than .001). They also had 2% lower overall survival at 5 years and 11.1% lower overall survival at 10 years (P less than .001).
The researchers also conducted preclinical studies in effort to understand the effect of vitamin D on Hodgkin lymphoma cells and in Hodgkin lymphoma tumor models.
They explored the effect of vitamin D on cultured Hodgkin lymphoma cell lines and saw a dose-response effect of calcitriol in reducing cell proliferation rates. They then looked at the effect of calcitriol on cell lines that were also exposed to doxorubicin or etoposide, and found calcitriol improved the cytotoxicity of these chemotherapy agents, especially at lower doses.
Finally, they conducted an in-vivo mouse study using Hodgkin lymphoma xenografts, and looked at whether vitamin D supplementation increased the effect of doxorubicin or etoposide. This revealed that chemotherapy and vitamin D supplementation together were significantly better at controlling tumor growth, compared with monotherapy with either vitamin D or doxorubicin and compared with placebo.
“On the basis of our study results and the limited toxicity of vitamin D replacement therapy, we would advocate for vitamin D deficiency screening and replacement to be incorporated into future randomized clinical trials to properly clarify the role of vitamin D replacement in HL [Hodgkin lymphoma],” the researchers wrote. “The goal of these trials should be to determine whether vitamin D replacement in HL improves outcome.”
No study funding information was reported. Dr. Borchmann reported honoraria and research funding from Takeda. Other authors reported financial disclosures related to Takeda, Roche, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and other companies.
SOURCE: Borchmann S et al. J Clin Oncol. 2019 Oct 17. doi:10.1200/JCO.19.00985.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL ONCOLOGY
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Patients with Hodgkin lymphoma and vitamin D deficiency had a 17.6% lower progression-free survival at 10 years, compared with patients who were not vitamin D deficient (P less than .001).
Study details: A case-control study in 351 patients with Hodgkin lymphoma.
Disclosures: No study funding information was reported. Dr. Borchmann reported honoraria and research funding from Takeda. Other authors reported financial disclosures related to Takeda, Roche, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and other companies.
Source: Borchmann S et al. J Clin Oncol. 2019 Oct 17. doi: 10.1200/JCO.19.00985.
Ibrutinib linked to hypertension in B-cell malignancies
The incidence and severity of hypertension was considerably higher in patients with B-cell malignancies treated with ibrutinib, according to a retrospective analysis.
Additionally, new or worsening hypertension was associated with a greater risk of major adverse cardiac events (MACE), including stroke, myocardial infarction, and cardiovascular-related death (hazard ratio, 2.17; 95% confidence interval, 1.08-4.38; P = .03).
“Despite ibrutinib’s benefits, cardiotoxicity has emerged as an increasingly important complication of this life-saving therapy,” Tyler Dickerson, PhD, of the Ohio State University, Columbus, and colleagues wrote in Blood.
The researchers retrospectively studied 562 consecutive patients with a lymphoid malignancy who received ibrutinib. Data was collected from patients treated at The Ohio State University’s Comprehensive Cancer Center during 2009-2016.
The mean age of study participants was 63.8 years, with a mean body mass index of 28.0 kg/m2. Most of the patients included in the analysis were men.
The team assessed rates of new or worsening hypertension, as well as rates of other MACE. The observed rates were compared with Framingham Heart Study–predicted incident-hypertension rates. The effects of various antihypertensive drugs on ibrutinib-linked hypertension were also evaluated.
After a median follow-up of 30 months, 78.3% of patients who received ibrutinib had new or worsening hypertension using a systolic blood pressure cutoff of 130 mm Hg. Of these, 84.8% of cases had an “at least probable association with ibrutinib,” they reported.
Among the 215 patients with no baseline hypertension, 71.6% developed hypertension while on ibrutinib, with a mean increase in systolic blood pressure of 13.4 mm Hg. Among the 347 patients with baseline hypertension, 82.4% experienced a worsening of their hypertension.
“This relationship remained even after accounting for ibrutinib dose, and was not attenuated by the use of any specific anti-hypertensive class,” the researchers wrote.
The researchers observed MACE among 93 patients. This included 84 patients with new or worsening hypertension and 9 patients with stable or no hypertension. Most MACE events were of at least probable ibrutinib association, the researchers reported.
Overall, the cumulative incidence of new hypertension at 1 year was 442 per 1,000 person-years in the current study. This value is 12.9-fold higher than the Framingham Heart Study risk–predicted rate of 34 per 1,000 person-years.
“Given the expected continued increase in ibrutinib use, further studies characterizing the mechanisms, treatment, and implications of [hypertension] during ibrutinib use are needed,” the researchers wrote.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health, the D. Warren Brown Family Foundation, the Four Winds Foundation, and the Connie Brown CLL Research Fund. The authors reported financial affiliations with Janssen, Pharmacyclics, and other companies.
SOURCE: Dickerson T et al. Blood. 2019 Oct 3. doi: 10.1182/blood.2019000840.
The incidence and severity of hypertension was considerably higher in patients with B-cell malignancies treated with ibrutinib, according to a retrospective analysis.
Additionally, new or worsening hypertension was associated with a greater risk of major adverse cardiac events (MACE), including stroke, myocardial infarction, and cardiovascular-related death (hazard ratio, 2.17; 95% confidence interval, 1.08-4.38; P = .03).
“Despite ibrutinib’s benefits, cardiotoxicity has emerged as an increasingly important complication of this life-saving therapy,” Tyler Dickerson, PhD, of the Ohio State University, Columbus, and colleagues wrote in Blood.
The researchers retrospectively studied 562 consecutive patients with a lymphoid malignancy who received ibrutinib. Data was collected from patients treated at The Ohio State University’s Comprehensive Cancer Center during 2009-2016.
The mean age of study participants was 63.8 years, with a mean body mass index of 28.0 kg/m2. Most of the patients included in the analysis were men.
The team assessed rates of new or worsening hypertension, as well as rates of other MACE. The observed rates were compared with Framingham Heart Study–predicted incident-hypertension rates. The effects of various antihypertensive drugs on ibrutinib-linked hypertension were also evaluated.
After a median follow-up of 30 months, 78.3% of patients who received ibrutinib had new or worsening hypertension using a systolic blood pressure cutoff of 130 mm Hg. Of these, 84.8% of cases had an “at least probable association with ibrutinib,” they reported.
Among the 215 patients with no baseline hypertension, 71.6% developed hypertension while on ibrutinib, with a mean increase in systolic blood pressure of 13.4 mm Hg. Among the 347 patients with baseline hypertension, 82.4% experienced a worsening of their hypertension.
“This relationship remained even after accounting for ibrutinib dose, and was not attenuated by the use of any specific anti-hypertensive class,” the researchers wrote.
The researchers observed MACE among 93 patients. This included 84 patients with new or worsening hypertension and 9 patients with stable or no hypertension. Most MACE events were of at least probable ibrutinib association, the researchers reported.
Overall, the cumulative incidence of new hypertension at 1 year was 442 per 1,000 person-years in the current study. This value is 12.9-fold higher than the Framingham Heart Study risk–predicted rate of 34 per 1,000 person-years.
“Given the expected continued increase in ibrutinib use, further studies characterizing the mechanisms, treatment, and implications of [hypertension] during ibrutinib use are needed,” the researchers wrote.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health, the D. Warren Brown Family Foundation, the Four Winds Foundation, and the Connie Brown CLL Research Fund. The authors reported financial affiliations with Janssen, Pharmacyclics, and other companies.
SOURCE: Dickerson T et al. Blood. 2019 Oct 3. doi: 10.1182/blood.2019000840.
The incidence and severity of hypertension was considerably higher in patients with B-cell malignancies treated with ibrutinib, according to a retrospective analysis.
Additionally, new or worsening hypertension was associated with a greater risk of major adverse cardiac events (MACE), including stroke, myocardial infarction, and cardiovascular-related death (hazard ratio, 2.17; 95% confidence interval, 1.08-4.38; P = .03).
“Despite ibrutinib’s benefits, cardiotoxicity has emerged as an increasingly important complication of this life-saving therapy,” Tyler Dickerson, PhD, of the Ohio State University, Columbus, and colleagues wrote in Blood.
The researchers retrospectively studied 562 consecutive patients with a lymphoid malignancy who received ibrutinib. Data was collected from patients treated at The Ohio State University’s Comprehensive Cancer Center during 2009-2016.
The mean age of study participants was 63.8 years, with a mean body mass index of 28.0 kg/m2. Most of the patients included in the analysis were men.
The team assessed rates of new or worsening hypertension, as well as rates of other MACE. The observed rates were compared with Framingham Heart Study–predicted incident-hypertension rates. The effects of various antihypertensive drugs on ibrutinib-linked hypertension were also evaluated.
After a median follow-up of 30 months, 78.3% of patients who received ibrutinib had new or worsening hypertension using a systolic blood pressure cutoff of 130 mm Hg. Of these, 84.8% of cases had an “at least probable association with ibrutinib,” they reported.
Among the 215 patients with no baseline hypertension, 71.6% developed hypertension while on ibrutinib, with a mean increase in systolic blood pressure of 13.4 mm Hg. Among the 347 patients with baseline hypertension, 82.4% experienced a worsening of their hypertension.
“This relationship remained even after accounting for ibrutinib dose, and was not attenuated by the use of any specific anti-hypertensive class,” the researchers wrote.
The researchers observed MACE among 93 patients. This included 84 patients with new or worsening hypertension and 9 patients with stable or no hypertension. Most MACE events were of at least probable ibrutinib association, the researchers reported.
Overall, the cumulative incidence of new hypertension at 1 year was 442 per 1,000 person-years in the current study. This value is 12.9-fold higher than the Framingham Heart Study risk–predicted rate of 34 per 1,000 person-years.
“Given the expected continued increase in ibrutinib use, further studies characterizing the mechanisms, treatment, and implications of [hypertension] during ibrutinib use are needed,” the researchers wrote.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health, the D. Warren Brown Family Foundation, the Four Winds Foundation, and the Connie Brown CLL Research Fund. The authors reported financial affiliations with Janssen, Pharmacyclics, and other companies.
SOURCE: Dickerson T et al. Blood. 2019 Oct 3. doi: 10.1182/blood.2019000840.
FROM BLOOD
Best treatment approach for early stage follicular lymphoma is unclear
Randomized trials are needed to determine the optimal treatment approach for early stage follicular lymphoma (FL), according to researchers.
A retrospective study showed similar outcomes among patients who received radiotherapy, immunochemotherapy, combined modality treatment (CMT), and watchful waiting (WW).
There were some differences in progression-free survival (PFS) according to treatment approach. However, there were no significant differences in overall survival (OS) between any of the active treatments or between patients who received active treatment and those managed with WW.
Joshua W. D. Tobin, MD, of Princess Alexandra Hospital in Brisbane, Queensland, Australia, and colleagues conducted this research and reported the results in Blood Advances.
The researchers analyzed 365 patients with newly diagnosed, stage I/II FL. The patients had a median age of 63 years and more than half were men. They were diagnosed between 2005 and 2017, and the median follow-up was 45 months.
Most patients (n = 280) received active treatment, but 85 were managed with WW. The WW patients were older and had more extranodal involvement.
Types of active treatment included radiotherapy alone (n = 171), immunochemotherapy alone (n = 63), and CMT (n = 46). Compared with the other groups, patients who received radiotherapy alone had less bulk, fewer nodal sites, and fewer B symptoms, and were more likely to have stage I disease. Patients who received CMT had fewer B symptoms and lower FLIPI scores compared with patients who received immunochemotherapy.
The immunochemotherapy regimens used were largely rituximab based. In all, 106 patients received rituximab (alone or in combination) for induction, and 49 received maintenance rituximab (37 in the immunochemotherapy group and 12 in the CMT group).
Results
Response rates were similar among the active treatment groups. The overall response rate was 95% in the radiotherapy group, 96% in the immunochemotherapy group, and 95% in the CMT group (P = .87).
There was a significant difference in PFS between the radiotherapy, immunochemotherapy, and CMT groups (P = .023), but there was no difference in OS between these groups (P = .38).
There was no significant difference in PFS between the immunochemotherapy and CMT groups (hazard ratio [HR], 1.78; P = .24), so the researchers combined these groups into a single group called “systemic therapy.” The patients treated with systemic therapy had PFS (HR, 1.32; P = .96) and OS (HR, 0.46; P = .21) similar to that of patients treated with radiotherapy alone.
Maintenance rituximab was associated with prolonged PFS among patients treated with systemic therapy (HR, 0.24; P = .017). However, there was no significant difference in OS between patients who received maintenance and those who did not (HR, 0.89; P = .90).
Relapse was less common among patients who received maintenance, and there were no cases of transformation in that group. Relapse occurred in 24.6% of the radiotherapy group, 18.3% of the systemic therapy group, and 4.1% of the group that received systemic therapy plus maintenance (P = .006). Transformation was less likely in the systemic therapy group (1.8%) than in the radiotherapy (6.4%) and WW (9.4%) groups (HR, 0.20; P = .034).
Overall, the active treatment group had better PFS than the WW group (HR, 0.52; P = .002), but there was no significant difference in OS between the groups (HR, 0.94; P = .90).
“Based on our comparable OS between WW and actively treated patients, WW could be considered as an initial management strategy in early stage FL,” Dr. Tobin and colleagues wrote. “However, long-term follow-up is required to determine if a survival benefit exists favoring active treatment.”
The researchers reported relationships with many pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Tobin JWD et al. Blood Adv. 2019 Oct 8;3(19):2804-11.
Randomized trials are needed to determine the optimal treatment approach for early stage follicular lymphoma (FL), according to researchers.
A retrospective study showed similar outcomes among patients who received radiotherapy, immunochemotherapy, combined modality treatment (CMT), and watchful waiting (WW).
There were some differences in progression-free survival (PFS) according to treatment approach. However, there were no significant differences in overall survival (OS) between any of the active treatments or between patients who received active treatment and those managed with WW.
Joshua W. D. Tobin, MD, of Princess Alexandra Hospital in Brisbane, Queensland, Australia, and colleagues conducted this research and reported the results in Blood Advances.
The researchers analyzed 365 patients with newly diagnosed, stage I/II FL. The patients had a median age of 63 years and more than half were men. They were diagnosed between 2005 and 2017, and the median follow-up was 45 months.
Most patients (n = 280) received active treatment, but 85 were managed with WW. The WW patients were older and had more extranodal involvement.
Types of active treatment included radiotherapy alone (n = 171), immunochemotherapy alone (n = 63), and CMT (n = 46). Compared with the other groups, patients who received radiotherapy alone had less bulk, fewer nodal sites, and fewer B symptoms, and were more likely to have stage I disease. Patients who received CMT had fewer B symptoms and lower FLIPI scores compared with patients who received immunochemotherapy.
The immunochemotherapy regimens used were largely rituximab based. In all, 106 patients received rituximab (alone or in combination) for induction, and 49 received maintenance rituximab (37 in the immunochemotherapy group and 12 in the CMT group).
Results
Response rates were similar among the active treatment groups. The overall response rate was 95% in the radiotherapy group, 96% in the immunochemotherapy group, and 95% in the CMT group (P = .87).
There was a significant difference in PFS between the radiotherapy, immunochemotherapy, and CMT groups (P = .023), but there was no difference in OS between these groups (P = .38).
There was no significant difference in PFS between the immunochemotherapy and CMT groups (hazard ratio [HR], 1.78; P = .24), so the researchers combined these groups into a single group called “systemic therapy.” The patients treated with systemic therapy had PFS (HR, 1.32; P = .96) and OS (HR, 0.46; P = .21) similar to that of patients treated with radiotherapy alone.
Maintenance rituximab was associated with prolonged PFS among patients treated with systemic therapy (HR, 0.24; P = .017). However, there was no significant difference in OS between patients who received maintenance and those who did not (HR, 0.89; P = .90).
Relapse was less common among patients who received maintenance, and there were no cases of transformation in that group. Relapse occurred in 24.6% of the radiotherapy group, 18.3% of the systemic therapy group, and 4.1% of the group that received systemic therapy plus maintenance (P = .006). Transformation was less likely in the systemic therapy group (1.8%) than in the radiotherapy (6.4%) and WW (9.4%) groups (HR, 0.20; P = .034).
Overall, the active treatment group had better PFS than the WW group (HR, 0.52; P = .002), but there was no significant difference in OS between the groups (HR, 0.94; P = .90).
“Based on our comparable OS between WW and actively treated patients, WW could be considered as an initial management strategy in early stage FL,” Dr. Tobin and colleagues wrote. “However, long-term follow-up is required to determine if a survival benefit exists favoring active treatment.”
The researchers reported relationships with many pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Tobin JWD et al. Blood Adv. 2019 Oct 8;3(19):2804-11.
Randomized trials are needed to determine the optimal treatment approach for early stage follicular lymphoma (FL), according to researchers.
A retrospective study showed similar outcomes among patients who received radiotherapy, immunochemotherapy, combined modality treatment (CMT), and watchful waiting (WW).
There were some differences in progression-free survival (PFS) according to treatment approach. However, there were no significant differences in overall survival (OS) between any of the active treatments or between patients who received active treatment and those managed with WW.
Joshua W. D. Tobin, MD, of Princess Alexandra Hospital in Brisbane, Queensland, Australia, and colleagues conducted this research and reported the results in Blood Advances.
The researchers analyzed 365 patients with newly diagnosed, stage I/II FL. The patients had a median age of 63 years and more than half were men. They were diagnosed between 2005 and 2017, and the median follow-up was 45 months.
Most patients (n = 280) received active treatment, but 85 were managed with WW. The WW patients were older and had more extranodal involvement.
Types of active treatment included radiotherapy alone (n = 171), immunochemotherapy alone (n = 63), and CMT (n = 46). Compared with the other groups, patients who received radiotherapy alone had less bulk, fewer nodal sites, and fewer B symptoms, and were more likely to have stage I disease. Patients who received CMT had fewer B symptoms and lower FLIPI scores compared with patients who received immunochemotherapy.
The immunochemotherapy regimens used were largely rituximab based. In all, 106 patients received rituximab (alone or in combination) for induction, and 49 received maintenance rituximab (37 in the immunochemotherapy group and 12 in the CMT group).
Results
Response rates were similar among the active treatment groups. The overall response rate was 95% in the radiotherapy group, 96% in the immunochemotherapy group, and 95% in the CMT group (P = .87).
There was a significant difference in PFS between the radiotherapy, immunochemotherapy, and CMT groups (P = .023), but there was no difference in OS between these groups (P = .38).
There was no significant difference in PFS between the immunochemotherapy and CMT groups (hazard ratio [HR], 1.78; P = .24), so the researchers combined these groups into a single group called “systemic therapy.” The patients treated with systemic therapy had PFS (HR, 1.32; P = .96) and OS (HR, 0.46; P = .21) similar to that of patients treated with radiotherapy alone.
Maintenance rituximab was associated with prolonged PFS among patients treated with systemic therapy (HR, 0.24; P = .017). However, there was no significant difference in OS between patients who received maintenance and those who did not (HR, 0.89; P = .90).
Relapse was less common among patients who received maintenance, and there were no cases of transformation in that group. Relapse occurred in 24.6% of the radiotherapy group, 18.3% of the systemic therapy group, and 4.1% of the group that received systemic therapy plus maintenance (P = .006). Transformation was less likely in the systemic therapy group (1.8%) than in the radiotherapy (6.4%) and WW (9.4%) groups (HR, 0.20; P = .034).
Overall, the active treatment group had better PFS than the WW group (HR, 0.52; P = .002), but there was no significant difference in OS between the groups (HR, 0.94; P = .90).
“Based on our comparable OS between WW and actively treated patients, WW could be considered as an initial management strategy in early stage FL,” Dr. Tobin and colleagues wrote. “However, long-term follow-up is required to determine if a survival benefit exists favoring active treatment.”
The researchers reported relationships with many pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Tobin JWD et al. Blood Adv. 2019 Oct 8;3(19):2804-11.
FROM BLOOD ADVANCES
Follow-up shows favorable results with acalabrutinib in MCL
Acalabrutinib monotherapy can produce durable responses in relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), according to updated results from a phase 2 trial.
The drug produced an overall response rate (ORR) of 81%, and the median duration of response was 26 months.
These are the highest such figures reported “among all approved single-agent therapies for the treatment of relapsed/refractory MCL,” Michael Wang, MD, of the MD Anderson Cancer Center at the University of Texas in Houston and colleagues wrote in a letter in Leukemia.
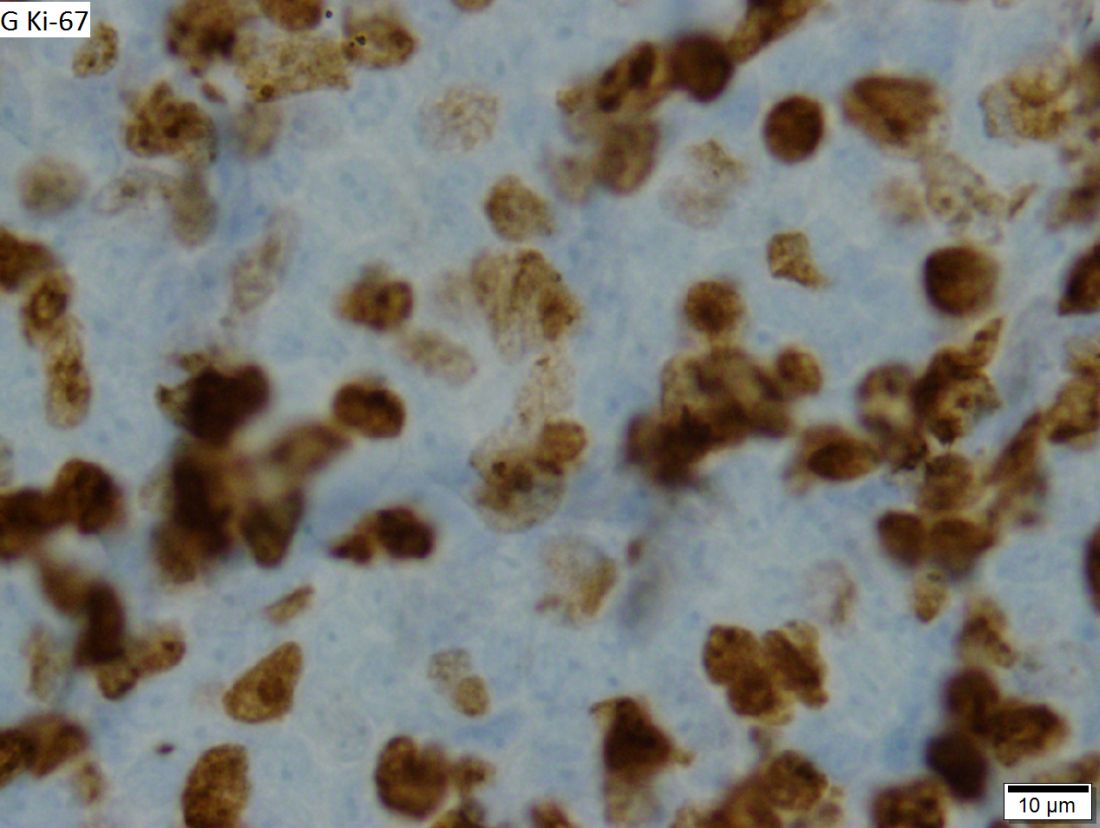
Dr. Wang and colleagues reported updated results in 124 patients treated on the ACE-LY-004 trial. At baseline, the patients had a median age of 68 years (range, 42-90 years), and 80% were men. Three-quarters of patients had stage IV disease, 72% had extranodal disease, 21% had blastoid/pleomorphic MCL, and 26% had a Ki-67 proliferation index of 50% or greater.
At a median follow-up of 26 months, 40% (n = 49) of patients were still on acalabrutinib, and 61% (n = 76) were still in follow-up for survival. Six patients went on to allogeneic transplant at a median of 19 days after stopping acalabrutinib.
The ORR was 81% (100/124), and the complete response (CR) rate was 43% (n = 53). Four patients who initially had a partial response converted to a CR with longer follow-up. The estimated 24-month duration of response was 52.4%.
“ORR was consistent across patients with refractory disease and those with blastoid/pleomorphic MCL, despite those patients having a higher mean Ki-67 index [of 50% or greater], suggesting that some patients with poorer prognosis may also benefit from acalabrutinib,” Dr. Wang and colleagues wrote.
There were 29 patients evaluable for minimal residual disease (MRD) assessment. Seven patients (24%) had MRD-negative disease in the peripheral blood after they achieved a CR. An additional patient with a CR became MRD negative when a second blood sample was taken about 6 months after the first.
“Despite limited samples, these results demonstrate that continued use of acalabrutinib can lead to undetectable MRD in patients with CR,” Dr. Wang and his colleagues wrote. “Since most patients with MRD data are still on treatment (27/29), relationships between MRD negativity and durability of response cannot be made at this time.”
The median progression-free survival was 20 months, and the median overall survival was not reached. The estimated 24-month progression-free survival rate was 49.0%, and the estimated 24-month overall survival rate was 72.4%. Patients with low/intermediate Mantle Cell Lymphoma International Prognostic Index scores, classical MCL, and a Ki-67 index less than 50% had a longer duration of response and survival.
The adverse event profile was “largely consistent with earlier reporting,” Dr. Wang and colleagues wrote. The most frequent adverse events were headache (38%), diarrhea (36%), fatigue (28%), cough (22%), and myalgia (21%). The most common grade 3/4 adverse events were anemia (10%), neutropenia (10%), and pneumonia (6%).
Ten patients developed second primary cancers. There were no new atrial fibrillation events and no new hypertension events. The frequency of infections decreased over time, as did the number of bleeding events. However, two of three major hemorrhage events occurred after the previous report was published.
There were 43 deaths (35%), 29 of them because of disease progression. Six patients died of adverse events, two died of unknown causes, and two died of secondary acute myeloid leukemia. Other causes of death included multiorgan failure, intestinal obstruction, lung cancer, and graft-versus-host disease.
This study was sponsored by Acerta Pharma, a member of the AstraZeneca Group. The researchers reported relationships with AstraZeneca/Acerta Pharma and many other companies.
SOURCE: Wang M et al. Leukemia. 2019 Sep 26. doi: 10.1038/s41375-019-0575-9.
Acalabrutinib monotherapy can produce durable responses in relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), according to updated results from a phase 2 trial.
The drug produced an overall response rate (ORR) of 81%, and the median duration of response was 26 months.
These are the highest such figures reported “among all approved single-agent therapies for the treatment of relapsed/refractory MCL,” Michael Wang, MD, of the MD Anderson Cancer Center at the University of Texas in Houston and colleagues wrote in a letter in Leukemia.
Dr. Wang and colleagues reported updated results in 124 patients treated on the ACE-LY-004 trial. At baseline, the patients had a median age of 68 years (range, 42-90 years), and 80% were men. Three-quarters of patients had stage IV disease, 72% had extranodal disease, 21% had blastoid/pleomorphic MCL, and 26% had a Ki-67 proliferation index of 50% or greater.
At a median follow-up of 26 months, 40% (n = 49) of patients were still on acalabrutinib, and 61% (n = 76) were still in follow-up for survival. Six patients went on to allogeneic transplant at a median of 19 days after stopping acalabrutinib.
The ORR was 81% (100/124), and the complete response (CR) rate was 43% (n = 53). Four patients who initially had a partial response converted to a CR with longer follow-up. The estimated 24-month duration of response was 52.4%.
“ORR was consistent across patients with refractory disease and those with blastoid/pleomorphic MCL, despite those patients having a higher mean Ki-67 index [of 50% or greater], suggesting that some patients with poorer prognosis may also benefit from acalabrutinib,” Dr. Wang and colleagues wrote.
There were 29 patients evaluable for minimal residual disease (MRD) assessment. Seven patients (24%) had MRD-negative disease in the peripheral blood after they achieved a CR. An additional patient with a CR became MRD negative when a second blood sample was taken about 6 months after the first.
“Despite limited samples, these results demonstrate that continued use of acalabrutinib can lead to undetectable MRD in patients with CR,” Dr. Wang and his colleagues wrote. “Since most patients with MRD data are still on treatment (27/29), relationships between MRD negativity and durability of response cannot be made at this time.”
The median progression-free survival was 20 months, and the median overall survival was not reached. The estimated 24-month progression-free survival rate was 49.0%, and the estimated 24-month overall survival rate was 72.4%. Patients with low/intermediate Mantle Cell Lymphoma International Prognostic Index scores, classical MCL, and a Ki-67 index less than 50% had a longer duration of response and survival.
The adverse event profile was “largely consistent with earlier reporting,” Dr. Wang and colleagues wrote. The most frequent adverse events were headache (38%), diarrhea (36%), fatigue (28%), cough (22%), and myalgia (21%). The most common grade 3/4 adverse events were anemia (10%), neutropenia (10%), and pneumonia (6%).
Ten patients developed second primary cancers. There were no new atrial fibrillation events and no new hypertension events. The frequency of infections decreased over time, as did the number of bleeding events. However, two of three major hemorrhage events occurred after the previous report was published.
There were 43 deaths (35%), 29 of them because of disease progression. Six patients died of adverse events, two died of unknown causes, and two died of secondary acute myeloid leukemia. Other causes of death included multiorgan failure, intestinal obstruction, lung cancer, and graft-versus-host disease.
This study was sponsored by Acerta Pharma, a member of the AstraZeneca Group. The researchers reported relationships with AstraZeneca/Acerta Pharma and many other companies.
SOURCE: Wang M et al. Leukemia. 2019 Sep 26. doi: 10.1038/s41375-019-0575-9.
Acalabrutinib monotherapy can produce durable responses in relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), according to updated results from a phase 2 trial.
The drug produced an overall response rate (ORR) of 81%, and the median duration of response was 26 months.
These are the highest such figures reported “among all approved single-agent therapies for the treatment of relapsed/refractory MCL,” Michael Wang, MD, of the MD Anderson Cancer Center at the University of Texas in Houston and colleagues wrote in a letter in Leukemia.
Dr. Wang and colleagues reported updated results in 124 patients treated on the ACE-LY-004 trial. At baseline, the patients had a median age of 68 years (range, 42-90 years), and 80% were men. Three-quarters of patients had stage IV disease, 72% had extranodal disease, 21% had blastoid/pleomorphic MCL, and 26% had a Ki-67 proliferation index of 50% or greater.
At a median follow-up of 26 months, 40% (n = 49) of patients were still on acalabrutinib, and 61% (n = 76) were still in follow-up for survival. Six patients went on to allogeneic transplant at a median of 19 days after stopping acalabrutinib.
The ORR was 81% (100/124), and the complete response (CR) rate was 43% (n = 53). Four patients who initially had a partial response converted to a CR with longer follow-up. The estimated 24-month duration of response was 52.4%.
“ORR was consistent across patients with refractory disease and those with blastoid/pleomorphic MCL, despite those patients having a higher mean Ki-67 index [of 50% or greater], suggesting that some patients with poorer prognosis may also benefit from acalabrutinib,” Dr. Wang and colleagues wrote.
There were 29 patients evaluable for minimal residual disease (MRD) assessment. Seven patients (24%) had MRD-negative disease in the peripheral blood after they achieved a CR. An additional patient with a CR became MRD negative when a second blood sample was taken about 6 months after the first.
“Despite limited samples, these results demonstrate that continued use of acalabrutinib can lead to undetectable MRD in patients with CR,” Dr. Wang and his colleagues wrote. “Since most patients with MRD data are still on treatment (27/29), relationships between MRD negativity and durability of response cannot be made at this time.”
The median progression-free survival was 20 months, and the median overall survival was not reached. The estimated 24-month progression-free survival rate was 49.0%, and the estimated 24-month overall survival rate was 72.4%. Patients with low/intermediate Mantle Cell Lymphoma International Prognostic Index scores, classical MCL, and a Ki-67 index less than 50% had a longer duration of response and survival.
The adverse event profile was “largely consistent with earlier reporting,” Dr. Wang and colleagues wrote. The most frequent adverse events were headache (38%), diarrhea (36%), fatigue (28%), cough (22%), and myalgia (21%). The most common grade 3/4 adverse events were anemia (10%), neutropenia (10%), and pneumonia (6%).
Ten patients developed second primary cancers. There were no new atrial fibrillation events and no new hypertension events. The frequency of infections decreased over time, as did the number of bleeding events. However, two of three major hemorrhage events occurred after the previous report was published.
There were 43 deaths (35%), 29 of them because of disease progression. Six patients died of adverse events, two died of unknown causes, and two died of secondary acute myeloid leukemia. Other causes of death included multiorgan failure, intestinal obstruction, lung cancer, and graft-versus-host disease.
This study was sponsored by Acerta Pharma, a member of the AstraZeneca Group. The researchers reported relationships with AstraZeneca/Acerta Pharma and many other companies.
SOURCE: Wang M et al. Leukemia. 2019 Sep 26. doi: 10.1038/s41375-019-0575-9.
FROM LEUKEMIA
What is the optimal duration of maintenance in myeloma?
SAN FRANCISCO – Should patients with multiple myeloma receive maintenance therapy until progression?
Yvonne A. Efebera, MD, of The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center – Arthur G. James Cancer Hospital in Columbus, and Nina Shah, MD, of the University of California San Francisco Health, faced off on this question at the National Comprehensive Cancer Network Hematologic Malignancies Annual Congress.
Dr. Shah said maintenance therapy improves survival in myeloma patients, so it follows that treating them until progression would confer a survival advantage. While Dr. Efebera agreed that maintenance can improve survival, she said the optimal duration of that treatment is unknown.
Treat until progression
Dr. Shah cited studies suggesting that maintenance improves progression-free survival (PFS) and may prolong overall survival (OS) in multiple myeloma.
A meta-analysis of data from the IFM 2005-02, CALGB 100104, and GIMEMA RV-MM-PI-209 trials showed that lenalidomide maintenance prolonged PFS and OS. The median PFS was 52.8 months in patients who received maintenance and 23.5 months in those who received placebo or observation (hazard ratio [HR], 0.48). At a median follow-up of 79.5 months, the median OS was not reached for the maintenance group and was 86.0 months for the no-maintenance group (HR, 0.75; P = .001; J Clin Oncol. 2017 Oct 10;35[29]:3279-89).
In the Myeloma XI trial, maintenance improved PFS, but not OS, in both transplant-eligible and ineligible patients. Overall, the median PFS was 39 months in the lenalidomide maintenance arm and 20 months in the observation arm (P less than .0001). Among transplant-eligible patients, the median PFS was 57 months and 30 months, respectively (P less than .0001). Among transplant-ineligible patients, the median PFS was 26 months and 11 months, respectively (P less than .0001; Lancet Oncol. 2019 Jan;20[1]:57-73).
These data suggest maintenance can improve survival, “but the question is, how long should we have therapy,” Dr. Shah said. “No one has looked at this in a prospective manner, so we really have to look at our retrospective data.”
One study suggested a longer duration of lenalidomide maintenance improves PFS. The HR for progression or death was 0.39 for patients who received maintenance for 12-24 months, compared with those who received maintenance for less than 12 months. The HR was 0.13 for patients who received maintenance for more than 24 months, compared with less than 12 months (Leuk Lymphoma. 2019 Feb;60[2]:511-4).
Dr. Shah also cited a pooled analysis of three phase 3 trials suggesting that continuous therapy is superior to fixed-duration therapy in patients with newly diagnosed myeloma. The median PFS was 32 months with continuous therapy and 16 months with fixed-duration therapy (P less than .001). The 4-year OS was 69% and 60%, respectively (P = .003; J Clin Oncol. 2015 Oct 20;33[30]:3459-66).
These data suggest that “continuous therapy, more therapy, has a survival advantage,” Dr. Shah said.
Don’t treat until progression
Dr. Efebera also discussed data from studies showing that lenalidomide maintenance can prolong survival in multiple myeloma. However, she said, it’s unclear how long maintenance should last.
Different durations of maintenance have proved effective in different trials. In the CALGB 100104 trial, the median duration of maintenance was 31 months (Lancet Haematol. 2017 Sep;4[9]:e431-e442). In the meta-analysis of the CALGB, IFM, and GIMEMA trials, the median duration was 22 months. And in Myeloma XI, the median duration was 18 months.
As there is no randomized trial comparing different durations of maintenance, Dr. Efebera proposed that researchers conduct one. She said this “perfect study” would involve induction with an immunomodulatory agent, a proteasome inhibitor, dexamethasone, and perhaps an anti-CD38 therapy. Transplant-eligible patients would receive four cycles of induction before transplant. Transplant-ineligible patients would receive eight cycles of induction. Then, all patients would be randomized to lenalidomide maintenance for 3 years, 5 years, or 7-10 years.
Until a trial like this reveals the optimal duration of maintenance, we cannot conclude that treating patients until progression is better, Dr. Efebera said.
She added that maintenance has been shown to have detrimental effects, and these should be taken into consideration. For instance, neutropenia, other hematologic adverse events, and second primary malignancies have been shown to be more common among patients who receive lenalidomide maintenance (N Engl J Med. 2012; 366:1782-91).
The cost of maintenance is another factor to consider. Researchers analyzed data from the CALGB 100104 and IFM 2005-02 trials to compare the cost of lenalidomide maintenance with no maintenance. In the CALGB 100104 trial, patients who received lenalidomide maintenance had 5.72 quality-adjusted life years (QALYs), and those who received no maintenance had 4.61 QALYs. The incremental cost-utility ratio (ICUR) was more than 277,000 euros per QALY.
In the IFM2005-02 trial, patients in the lenalidomide group had 5.13 QALYs, and those who didn’t receive maintenance had 4.98 QALYs. The ICUR was more than 1.5 million euros per QALY. The researchers said the high ICURs and budgetary impact add “uncertainty about the maximum prudent duration of the treatment” (Bone Marrow Transplant. 2019 May 31. doi: 10.1038/s41409-019-0574-5).
Dr. Efebera reported relationships with Akcea Therapeutics, Janssen, and Takeda. Dr. Shah reported having no relevant financial relationships.
SAN FRANCISCO – Should patients with multiple myeloma receive maintenance therapy until progression?
Yvonne A. Efebera, MD, of The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center – Arthur G. James Cancer Hospital in Columbus, and Nina Shah, MD, of the University of California San Francisco Health, faced off on this question at the National Comprehensive Cancer Network Hematologic Malignancies Annual Congress.
Dr. Shah said maintenance therapy improves survival in myeloma patients, so it follows that treating them until progression would confer a survival advantage. While Dr. Efebera agreed that maintenance can improve survival, she said the optimal duration of that treatment is unknown.
Treat until progression
Dr. Shah cited studies suggesting that maintenance improves progression-free survival (PFS) and may prolong overall survival (OS) in multiple myeloma.
A meta-analysis of data from the IFM 2005-02, CALGB 100104, and GIMEMA RV-MM-PI-209 trials showed that lenalidomide maintenance prolonged PFS and OS. The median PFS was 52.8 months in patients who received maintenance and 23.5 months in those who received placebo or observation (hazard ratio [HR], 0.48). At a median follow-up of 79.5 months, the median OS was not reached for the maintenance group and was 86.0 months for the no-maintenance group (HR, 0.75; P = .001; J Clin Oncol. 2017 Oct 10;35[29]:3279-89).
In the Myeloma XI trial, maintenance improved PFS, but not OS, in both transplant-eligible and ineligible patients. Overall, the median PFS was 39 months in the lenalidomide maintenance arm and 20 months in the observation arm (P less than .0001). Among transplant-eligible patients, the median PFS was 57 months and 30 months, respectively (P less than .0001). Among transplant-ineligible patients, the median PFS was 26 months and 11 months, respectively (P less than .0001; Lancet Oncol. 2019 Jan;20[1]:57-73).
These data suggest maintenance can improve survival, “but the question is, how long should we have therapy,” Dr. Shah said. “No one has looked at this in a prospective manner, so we really have to look at our retrospective data.”
One study suggested a longer duration of lenalidomide maintenance improves PFS. The HR for progression or death was 0.39 for patients who received maintenance for 12-24 months, compared with those who received maintenance for less than 12 months. The HR was 0.13 for patients who received maintenance for more than 24 months, compared with less than 12 months (Leuk Lymphoma. 2019 Feb;60[2]:511-4).
Dr. Shah also cited a pooled analysis of three phase 3 trials suggesting that continuous therapy is superior to fixed-duration therapy in patients with newly diagnosed myeloma. The median PFS was 32 months with continuous therapy and 16 months with fixed-duration therapy (P less than .001). The 4-year OS was 69% and 60%, respectively (P = .003; J Clin Oncol. 2015 Oct 20;33[30]:3459-66).
These data suggest that “continuous therapy, more therapy, has a survival advantage,” Dr. Shah said.
Don’t treat until progression
Dr. Efebera also discussed data from studies showing that lenalidomide maintenance can prolong survival in multiple myeloma. However, she said, it’s unclear how long maintenance should last.
Different durations of maintenance have proved effective in different trials. In the CALGB 100104 trial, the median duration of maintenance was 31 months (Lancet Haematol. 2017 Sep;4[9]:e431-e442). In the meta-analysis of the CALGB, IFM, and GIMEMA trials, the median duration was 22 months. And in Myeloma XI, the median duration was 18 months.
As there is no randomized trial comparing different durations of maintenance, Dr. Efebera proposed that researchers conduct one. She said this “perfect study” would involve induction with an immunomodulatory agent, a proteasome inhibitor, dexamethasone, and perhaps an anti-CD38 therapy. Transplant-eligible patients would receive four cycles of induction before transplant. Transplant-ineligible patients would receive eight cycles of induction. Then, all patients would be randomized to lenalidomide maintenance for 3 years, 5 years, or 7-10 years.
Until a trial like this reveals the optimal duration of maintenance, we cannot conclude that treating patients until progression is better, Dr. Efebera said.
She added that maintenance has been shown to have detrimental effects, and these should be taken into consideration. For instance, neutropenia, other hematologic adverse events, and second primary malignancies have been shown to be more common among patients who receive lenalidomide maintenance (N Engl J Med. 2012; 366:1782-91).
The cost of maintenance is another factor to consider. Researchers analyzed data from the CALGB 100104 and IFM 2005-02 trials to compare the cost of lenalidomide maintenance with no maintenance. In the CALGB 100104 trial, patients who received lenalidomide maintenance had 5.72 quality-adjusted life years (QALYs), and those who received no maintenance had 4.61 QALYs. The incremental cost-utility ratio (ICUR) was more than 277,000 euros per QALY.
In the IFM2005-02 trial, patients in the lenalidomide group had 5.13 QALYs, and those who didn’t receive maintenance had 4.98 QALYs. The ICUR was more than 1.5 million euros per QALY. The researchers said the high ICURs and budgetary impact add “uncertainty about the maximum prudent duration of the treatment” (Bone Marrow Transplant. 2019 May 31. doi: 10.1038/s41409-019-0574-5).
Dr. Efebera reported relationships with Akcea Therapeutics, Janssen, and Takeda. Dr. Shah reported having no relevant financial relationships.
SAN FRANCISCO – Should patients with multiple myeloma receive maintenance therapy until progression?
Yvonne A. Efebera, MD, of The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center – Arthur G. James Cancer Hospital in Columbus, and Nina Shah, MD, of the University of California San Francisco Health, faced off on this question at the National Comprehensive Cancer Network Hematologic Malignancies Annual Congress.
Dr. Shah said maintenance therapy improves survival in myeloma patients, so it follows that treating them until progression would confer a survival advantage. While Dr. Efebera agreed that maintenance can improve survival, she said the optimal duration of that treatment is unknown.
Treat until progression
Dr. Shah cited studies suggesting that maintenance improves progression-free survival (PFS) and may prolong overall survival (OS) in multiple myeloma.
A meta-analysis of data from the IFM 2005-02, CALGB 100104, and GIMEMA RV-MM-PI-209 trials showed that lenalidomide maintenance prolonged PFS and OS. The median PFS was 52.8 months in patients who received maintenance and 23.5 months in those who received placebo or observation (hazard ratio [HR], 0.48). At a median follow-up of 79.5 months, the median OS was not reached for the maintenance group and was 86.0 months for the no-maintenance group (HR, 0.75; P = .001; J Clin Oncol. 2017 Oct 10;35[29]:3279-89).
In the Myeloma XI trial, maintenance improved PFS, but not OS, in both transplant-eligible and ineligible patients. Overall, the median PFS was 39 months in the lenalidomide maintenance arm and 20 months in the observation arm (P less than .0001). Among transplant-eligible patients, the median PFS was 57 months and 30 months, respectively (P less than .0001). Among transplant-ineligible patients, the median PFS was 26 months and 11 months, respectively (P less than .0001; Lancet Oncol. 2019 Jan;20[1]:57-73).
These data suggest maintenance can improve survival, “but the question is, how long should we have therapy,” Dr. Shah said. “No one has looked at this in a prospective manner, so we really have to look at our retrospective data.”
One study suggested a longer duration of lenalidomide maintenance improves PFS. The HR for progression or death was 0.39 for patients who received maintenance for 12-24 months, compared with those who received maintenance for less than 12 months. The HR was 0.13 for patients who received maintenance for more than 24 months, compared with less than 12 months (Leuk Lymphoma. 2019 Feb;60[2]:511-4).
Dr. Shah also cited a pooled analysis of three phase 3 trials suggesting that continuous therapy is superior to fixed-duration therapy in patients with newly diagnosed myeloma. The median PFS was 32 months with continuous therapy and 16 months with fixed-duration therapy (P less than .001). The 4-year OS was 69% and 60%, respectively (P = .003; J Clin Oncol. 2015 Oct 20;33[30]:3459-66).
These data suggest that “continuous therapy, more therapy, has a survival advantage,” Dr. Shah said.
Don’t treat until progression
Dr. Efebera also discussed data from studies showing that lenalidomide maintenance can prolong survival in multiple myeloma. However, she said, it’s unclear how long maintenance should last.
Different durations of maintenance have proved effective in different trials. In the CALGB 100104 trial, the median duration of maintenance was 31 months (Lancet Haematol. 2017 Sep;4[9]:e431-e442). In the meta-analysis of the CALGB, IFM, and GIMEMA trials, the median duration was 22 months. And in Myeloma XI, the median duration was 18 months.
As there is no randomized trial comparing different durations of maintenance, Dr. Efebera proposed that researchers conduct one. She said this “perfect study” would involve induction with an immunomodulatory agent, a proteasome inhibitor, dexamethasone, and perhaps an anti-CD38 therapy. Transplant-eligible patients would receive four cycles of induction before transplant. Transplant-ineligible patients would receive eight cycles of induction. Then, all patients would be randomized to lenalidomide maintenance for 3 years, 5 years, or 7-10 years.
Until a trial like this reveals the optimal duration of maintenance, we cannot conclude that treating patients until progression is better, Dr. Efebera said.
She added that maintenance has been shown to have detrimental effects, and these should be taken into consideration. For instance, neutropenia, other hematologic adverse events, and second primary malignancies have been shown to be more common among patients who receive lenalidomide maintenance (N Engl J Med. 2012; 366:1782-91).
The cost of maintenance is another factor to consider. Researchers analyzed data from the CALGB 100104 and IFM 2005-02 trials to compare the cost of lenalidomide maintenance with no maintenance. In the CALGB 100104 trial, patients who received lenalidomide maintenance had 5.72 quality-adjusted life years (QALYs), and those who received no maintenance had 4.61 QALYs. The incremental cost-utility ratio (ICUR) was more than 277,000 euros per QALY.
In the IFM2005-02 trial, patients in the lenalidomide group had 5.13 QALYs, and those who didn’t receive maintenance had 4.98 QALYs. The ICUR was more than 1.5 million euros per QALY. The researchers said the high ICURs and budgetary impact add “uncertainty about the maximum prudent duration of the treatment” (Bone Marrow Transplant. 2019 May 31. doi: 10.1038/s41409-019-0574-5).
Dr. Efebera reported relationships with Akcea Therapeutics, Janssen, and Takeda. Dr. Shah reported having no relevant financial relationships.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM NCCN HEMATOLOGIC MALIGNANCIES
Targeted agents vs. chemoimmunotherapy as first-line treatment of CLL
SAN FRANCISCO – Should targeted agents replace chemoimmunotherapy (CIT) as first-line treatment for chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)? A recent debate suggests there’s no consensus.
William G. Wierda, MD, PhD, of The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston, and Jennifer R. Brown, MD, PhD, of Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston, debated the topic at the National Comprehensive Cancer Network Hematologic Malignancies Annual Congress.
Dr. Wierda argued that CLL patients should receive a BTK inhibitor or BCL2 inhibitor, with or without obinutuzumab, as first-line therapy because these targeted agents have been shown to provide better progression-free survival (PFS) than CIT, and the targeted therapies may prolong overall survival (OS) as well.
Dr. Brown countered that targeted agents don’t improve PFS for all CLL patients, improved PFS doesn’t always translate to improved OS, and targeted agents cost more than CIT.
No role for CIT as first-line treatment
“We have two approaches right now, with nonchemoimmunotherapy-based treatment,” Dr. Wierda said. “One approach, with small-molecule inhibitors, is to have a sustained and durable period of disease control, particularly with BTK inhibitors. The other strategy that has emerged is deep remissions with fixed-duration treatment with BCL2 small-molecule inhibitor-based therapy, which, I would argue, is better than being exposed to genotoxic chemoimmunotherapy.”
Dr. Wierda went on to explain that the BTK inhibitor ibrutinib has been shown to improve PFS, compared with CIT, in phase 3 trials.
In the iLLUMINATE trial, researchers compared ibrutinib plus obinutuzumab to chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab as first-line treatment in CLL. At a median follow-up of 31.3 months, the median PFS was not reached in the ibrutinib arm and was 19 months in the chlorambucil arm (P less than .0001; Lancet Oncol. 2019 Jan;20[1]:43-56).
In the A041202 study, researchers compared ibrutinib alone (Ib) or in combination with rituximab (Ib-R) to bendamustine plus rituximab (BR) in untreated, older patients with CLL. The 2-year PFS estimates were 74% in the BR arm, 87% in the Ib arm, and 88% in the Ib-R arm (P less than .001 for BR vs. Ib or Ib-R; N Engl J Med. 2018; 379:2517-28).
In the E1912 trial, researchers compared Ib-R to fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab (FCR) in younger, untreated CLL patients. The 3-year PFS was 89.4% with Ib-R and 72.9% with FCR (P less than .001; N Engl J Med. 2019 Aug 1;381:432-43).
Dr. Wierda noted that the E1912 trial also showed superior OS with Ib-R. The 3-year OS rate was 98.8% with Ib-R and 91.5% with FCR (P less than .001). However, there was no significant difference in OS between the treatment arms in the A041202 trial or the iLLUMINATE trial.
“But I would argue that is, in part, because of short follow-up,” Dr. Wierda said. “The trials were all designed to look at progression-free survival, not overall survival. With longer follow-up, we may see differences in overall survival emerging.”
Dr. Wierda went on to say that fixed‐duration treatment with the BCL2 inhibitor venetoclax can improve PFS over CIT.
In the phase 3 CLL14 trial, researchers compared fixed-duration treatment with venetoclax plus obinutuzumab to chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab in previously untreated CLL patients with comorbidities. The estimated PFS at 2 years was 88.2% in the venetoclax group and 64.1% in the chlorambucil group (P less than .001; N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:2225-36).
“[There was] no difference in overall survival,” Dr. Wierda noted. “But, again, I would argue ... that follow-up is relatively limited. We may ultimately see a difference in overall survival.”
Based on these findings, Dr. Wierda made the following treatment recommendations:
- Any CLL patient with del(17p) or TP53 mutation, and older, unfit patients with unmutated IGHV should receive a BTK inhibitor, with or without obinutuzumab.
- All young, fit patients, and older, unfit patients with mutated IGHV should receive a BCL2 inhibitor plus obinutuzumab.
Dr. Wierda also noted that ibrutinib and venetoclax in combination have shown early promise for patients with previously untreated CLL (N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:2095-2103).
CIT still has a role as first-line treatment
Dr. Brown suggested that a PFS benefit may not be enough to recommend targeted agents over CIT. For one thing, the PFS benefit doesn’t apply to all patients, as the IGHV-mutated subgroup does equally well with CIT and targeted agents.
In the IGHV-mutated group from the E1912 trial, the 3-year PFS was 88% for patients who received Ib-R and those who received FCR (N Engl J Med. 2019 Aug 1;381:432-43). In the A041202 study, the 2-year PFS among IGHV-mutated patients was 87% in the BR arm, 86% in the Ib arm, and 88% in the Ib-R arm (N Engl J Med. 2018; 379:2517-28).
In the CLL14 trial, PFS rates were similar among IGHV-mutated patients who received chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab and IGHV-mutated or unmutated patients who received venetoclax and obinutuzumab (N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:2225-36).
Dr. Brown also noted that the overall improvement in PFS observed with ibrutinib and venetoclax doesn’t always translate to improved OS.
In the A041202 study, there was no significant difference in OS between the Ib, Ib-R, and BR arms (N Engl J Med. 2018; 379:2517-28). There was no significant difference in OS between the ibrutinib and chlorambucil arms in the iLLUMINATE trial (Lancet Oncol. 2019 Jan;20[1]:43-56). And there was no significant difference in OS between the venetoclax and chlorambucil arms in the CLL14 trial (N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:2225-36).
However, in the RESONATE-2 trial, ibrutinib provided an OS benefit over chlorambucil. The 2-year OS was 95% and 84%, respectively (P = .0145; Haematologica. Sept 2018;103:1502-10). Dr. Brown said the OS advantage in this study was due to the “very poor comparator of chlorambucil and very limited crossover.”
As Dr. Wierda mentioned, the OS rate was higher with Ib-R than with FCR in the E1912 trial. The 3-year OS rate was 98.8% and 91.5%, respectively (P less than .001; N Engl J Med. 2019 Aug 1;381:432-43). Dr. Brown noted, however, that there were few deaths in this study, and many of them “were not clearly related to the disease or its treatment.”
Dr. Brown also pointed out that FCR has been shown to have curative potential in IGHV-mutated CLL in both the FCR300 trial (Blood. 2016 127:303-9) and the CLL8 trial (Blood. 2016 127:208-15).
Another factor to consider is the greater cost of targeted agents. One analysis suggested the per-patient lifetime cost of CLL treatment in the United States will increase from $147,000 to $604,000 as targeted therapies overtake CIT as first-line treatment (J Clin Oncol. 2017 Jan 10;35[2]:166-174).
“Given all of the above, chemoimmunotherapy is going to remain part of the treatment repertoire for CLL,” Dr. Brown said. “It’s our only known potential cure for the fit, mutated patients ... and can also result in prolonged treatment-free intervals for patients who are older. As we manage CLL as a chronic disease over a lifetime, we need to continue to have this in our armamentarium.”
Specifically, Dr. Brown said CIT is appropriate for patients who don’t have del(17p) or mutated TP53. FCR should be given to young, fit patients with IGHV-mutated CLL, and FCR or BR should be given to older patients and young, fit patients with IGHV-unmutated CLL.
Dr. Brown and Dr. Wierda reported financial ties to multiple pharmaceutical companies, including makers of CLL treatments.
SAN FRANCISCO – Should targeted agents replace chemoimmunotherapy (CIT) as first-line treatment for chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)? A recent debate suggests there’s no consensus.
William G. Wierda, MD, PhD, of The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston, and Jennifer R. Brown, MD, PhD, of Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston, debated the topic at the National Comprehensive Cancer Network Hematologic Malignancies Annual Congress.
Dr. Wierda argued that CLL patients should receive a BTK inhibitor or BCL2 inhibitor, with or without obinutuzumab, as first-line therapy because these targeted agents have been shown to provide better progression-free survival (PFS) than CIT, and the targeted therapies may prolong overall survival (OS) as well.
Dr. Brown countered that targeted agents don’t improve PFS for all CLL patients, improved PFS doesn’t always translate to improved OS, and targeted agents cost more than CIT.
No role for CIT as first-line treatment
“We have two approaches right now, with nonchemoimmunotherapy-based treatment,” Dr. Wierda said. “One approach, with small-molecule inhibitors, is to have a sustained and durable period of disease control, particularly with BTK inhibitors. The other strategy that has emerged is deep remissions with fixed-duration treatment with BCL2 small-molecule inhibitor-based therapy, which, I would argue, is better than being exposed to genotoxic chemoimmunotherapy.”
Dr. Wierda went on to explain that the BTK inhibitor ibrutinib has been shown to improve PFS, compared with CIT, in phase 3 trials.
In the iLLUMINATE trial, researchers compared ibrutinib plus obinutuzumab to chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab as first-line treatment in CLL. At a median follow-up of 31.3 months, the median PFS was not reached in the ibrutinib arm and was 19 months in the chlorambucil arm (P less than .0001; Lancet Oncol. 2019 Jan;20[1]:43-56).
In the A041202 study, researchers compared ibrutinib alone (Ib) or in combination with rituximab (Ib-R) to bendamustine plus rituximab (BR) in untreated, older patients with CLL. The 2-year PFS estimates were 74% in the BR arm, 87% in the Ib arm, and 88% in the Ib-R arm (P less than .001 for BR vs. Ib or Ib-R; N Engl J Med. 2018; 379:2517-28).
In the E1912 trial, researchers compared Ib-R to fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab (FCR) in younger, untreated CLL patients. The 3-year PFS was 89.4% with Ib-R and 72.9% with FCR (P less than .001; N Engl J Med. 2019 Aug 1;381:432-43).
Dr. Wierda noted that the E1912 trial also showed superior OS with Ib-R. The 3-year OS rate was 98.8% with Ib-R and 91.5% with FCR (P less than .001). However, there was no significant difference in OS between the treatment arms in the A041202 trial or the iLLUMINATE trial.
“But I would argue that is, in part, because of short follow-up,” Dr. Wierda said. “The trials were all designed to look at progression-free survival, not overall survival. With longer follow-up, we may see differences in overall survival emerging.”
Dr. Wierda went on to say that fixed‐duration treatment with the BCL2 inhibitor venetoclax can improve PFS over CIT.
In the phase 3 CLL14 trial, researchers compared fixed-duration treatment with venetoclax plus obinutuzumab to chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab in previously untreated CLL patients with comorbidities. The estimated PFS at 2 years was 88.2% in the venetoclax group and 64.1% in the chlorambucil group (P less than .001; N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:2225-36).
“[There was] no difference in overall survival,” Dr. Wierda noted. “But, again, I would argue ... that follow-up is relatively limited. We may ultimately see a difference in overall survival.”
Based on these findings, Dr. Wierda made the following treatment recommendations:
- Any CLL patient with del(17p) or TP53 mutation, and older, unfit patients with unmutated IGHV should receive a BTK inhibitor, with or without obinutuzumab.
- All young, fit patients, and older, unfit patients with mutated IGHV should receive a BCL2 inhibitor plus obinutuzumab.
Dr. Wierda also noted that ibrutinib and venetoclax in combination have shown early promise for patients with previously untreated CLL (N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:2095-2103).
CIT still has a role as first-line treatment
Dr. Brown suggested that a PFS benefit may not be enough to recommend targeted agents over CIT. For one thing, the PFS benefit doesn’t apply to all patients, as the IGHV-mutated subgroup does equally well with CIT and targeted agents.
In the IGHV-mutated group from the E1912 trial, the 3-year PFS was 88% for patients who received Ib-R and those who received FCR (N Engl J Med. 2019 Aug 1;381:432-43). In the A041202 study, the 2-year PFS among IGHV-mutated patients was 87% in the BR arm, 86% in the Ib arm, and 88% in the Ib-R arm (N Engl J Med. 2018; 379:2517-28).
In the CLL14 trial, PFS rates were similar among IGHV-mutated patients who received chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab and IGHV-mutated or unmutated patients who received venetoclax and obinutuzumab (N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:2225-36).
Dr. Brown also noted that the overall improvement in PFS observed with ibrutinib and venetoclax doesn’t always translate to improved OS.
In the A041202 study, there was no significant difference in OS between the Ib, Ib-R, and BR arms (N Engl J Med. 2018; 379:2517-28). There was no significant difference in OS between the ibrutinib and chlorambucil arms in the iLLUMINATE trial (Lancet Oncol. 2019 Jan;20[1]:43-56). And there was no significant difference in OS between the venetoclax and chlorambucil arms in the CLL14 trial (N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:2225-36).
However, in the RESONATE-2 trial, ibrutinib provided an OS benefit over chlorambucil. The 2-year OS was 95% and 84%, respectively (P = .0145; Haematologica. Sept 2018;103:1502-10). Dr. Brown said the OS advantage in this study was due to the “very poor comparator of chlorambucil and very limited crossover.”
As Dr. Wierda mentioned, the OS rate was higher with Ib-R than with FCR in the E1912 trial. The 3-year OS rate was 98.8% and 91.5%, respectively (P less than .001; N Engl J Med. 2019 Aug 1;381:432-43). Dr. Brown noted, however, that there were few deaths in this study, and many of them “were not clearly related to the disease or its treatment.”
Dr. Brown also pointed out that FCR has been shown to have curative potential in IGHV-mutated CLL in both the FCR300 trial (Blood. 2016 127:303-9) and the CLL8 trial (Blood. 2016 127:208-15).
Another factor to consider is the greater cost of targeted agents. One analysis suggested the per-patient lifetime cost of CLL treatment in the United States will increase from $147,000 to $604,000 as targeted therapies overtake CIT as first-line treatment (J Clin Oncol. 2017 Jan 10;35[2]:166-174).
“Given all of the above, chemoimmunotherapy is going to remain part of the treatment repertoire for CLL,” Dr. Brown said. “It’s our only known potential cure for the fit, mutated patients ... and can also result in prolonged treatment-free intervals for patients who are older. As we manage CLL as a chronic disease over a lifetime, we need to continue to have this in our armamentarium.”
Specifically, Dr. Brown said CIT is appropriate for patients who don’t have del(17p) or mutated TP53. FCR should be given to young, fit patients with IGHV-mutated CLL, and FCR or BR should be given to older patients and young, fit patients with IGHV-unmutated CLL.
Dr. Brown and Dr. Wierda reported financial ties to multiple pharmaceutical companies, including makers of CLL treatments.
SAN FRANCISCO – Should targeted agents replace chemoimmunotherapy (CIT) as first-line treatment for chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)? A recent debate suggests there’s no consensus.
William G. Wierda, MD, PhD, of The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston, and Jennifer R. Brown, MD, PhD, of Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston, debated the topic at the National Comprehensive Cancer Network Hematologic Malignancies Annual Congress.
Dr. Wierda argued that CLL patients should receive a BTK inhibitor or BCL2 inhibitor, with or without obinutuzumab, as first-line therapy because these targeted agents have been shown to provide better progression-free survival (PFS) than CIT, and the targeted therapies may prolong overall survival (OS) as well.
Dr. Brown countered that targeted agents don’t improve PFS for all CLL patients, improved PFS doesn’t always translate to improved OS, and targeted agents cost more than CIT.
No role for CIT as first-line treatment
“We have two approaches right now, with nonchemoimmunotherapy-based treatment,” Dr. Wierda said. “One approach, with small-molecule inhibitors, is to have a sustained and durable period of disease control, particularly with BTK inhibitors. The other strategy that has emerged is deep remissions with fixed-duration treatment with BCL2 small-molecule inhibitor-based therapy, which, I would argue, is better than being exposed to genotoxic chemoimmunotherapy.”
Dr. Wierda went on to explain that the BTK inhibitor ibrutinib has been shown to improve PFS, compared with CIT, in phase 3 trials.
In the iLLUMINATE trial, researchers compared ibrutinib plus obinutuzumab to chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab as first-line treatment in CLL. At a median follow-up of 31.3 months, the median PFS was not reached in the ibrutinib arm and was 19 months in the chlorambucil arm (P less than .0001; Lancet Oncol. 2019 Jan;20[1]:43-56).
In the A041202 study, researchers compared ibrutinib alone (Ib) or in combination with rituximab (Ib-R) to bendamustine plus rituximab (BR) in untreated, older patients with CLL. The 2-year PFS estimates were 74% in the BR arm, 87% in the Ib arm, and 88% in the Ib-R arm (P less than .001 for BR vs. Ib or Ib-R; N Engl J Med. 2018; 379:2517-28).
In the E1912 trial, researchers compared Ib-R to fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab (FCR) in younger, untreated CLL patients. The 3-year PFS was 89.4% with Ib-R and 72.9% with FCR (P less than .001; N Engl J Med. 2019 Aug 1;381:432-43).
Dr. Wierda noted that the E1912 trial also showed superior OS with Ib-R. The 3-year OS rate was 98.8% with Ib-R and 91.5% with FCR (P less than .001). However, there was no significant difference in OS between the treatment arms in the A041202 trial or the iLLUMINATE trial.
“But I would argue that is, in part, because of short follow-up,” Dr. Wierda said. “The trials were all designed to look at progression-free survival, not overall survival. With longer follow-up, we may see differences in overall survival emerging.”
Dr. Wierda went on to say that fixed‐duration treatment with the BCL2 inhibitor venetoclax can improve PFS over CIT.
In the phase 3 CLL14 trial, researchers compared fixed-duration treatment with venetoclax plus obinutuzumab to chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab in previously untreated CLL patients with comorbidities. The estimated PFS at 2 years was 88.2% in the venetoclax group and 64.1% in the chlorambucil group (P less than .001; N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:2225-36).
“[There was] no difference in overall survival,” Dr. Wierda noted. “But, again, I would argue ... that follow-up is relatively limited. We may ultimately see a difference in overall survival.”
Based on these findings, Dr. Wierda made the following treatment recommendations:
- Any CLL patient with del(17p) or TP53 mutation, and older, unfit patients with unmutated IGHV should receive a BTK inhibitor, with or without obinutuzumab.
- All young, fit patients, and older, unfit patients with mutated IGHV should receive a BCL2 inhibitor plus obinutuzumab.
Dr. Wierda also noted that ibrutinib and venetoclax in combination have shown early promise for patients with previously untreated CLL (N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:2095-2103).
CIT still has a role as first-line treatment
Dr. Brown suggested that a PFS benefit may not be enough to recommend targeted agents over CIT. For one thing, the PFS benefit doesn’t apply to all patients, as the IGHV-mutated subgroup does equally well with CIT and targeted agents.
In the IGHV-mutated group from the E1912 trial, the 3-year PFS was 88% for patients who received Ib-R and those who received FCR (N Engl J Med. 2019 Aug 1;381:432-43). In the A041202 study, the 2-year PFS among IGHV-mutated patients was 87% in the BR arm, 86% in the Ib arm, and 88% in the Ib-R arm (N Engl J Med. 2018; 379:2517-28).
In the CLL14 trial, PFS rates were similar among IGHV-mutated patients who received chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab and IGHV-mutated or unmutated patients who received venetoclax and obinutuzumab (N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:2225-36).
Dr. Brown also noted that the overall improvement in PFS observed with ibrutinib and venetoclax doesn’t always translate to improved OS.
In the A041202 study, there was no significant difference in OS between the Ib, Ib-R, and BR arms (N Engl J Med. 2018; 379:2517-28). There was no significant difference in OS between the ibrutinib and chlorambucil arms in the iLLUMINATE trial (Lancet Oncol. 2019 Jan;20[1]:43-56). And there was no significant difference in OS between the venetoclax and chlorambucil arms in the CLL14 trial (N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:2225-36).
However, in the RESONATE-2 trial, ibrutinib provided an OS benefit over chlorambucil. The 2-year OS was 95% and 84%, respectively (P = .0145; Haematologica. Sept 2018;103:1502-10). Dr. Brown said the OS advantage in this study was due to the “very poor comparator of chlorambucil and very limited crossover.”
As Dr. Wierda mentioned, the OS rate was higher with Ib-R than with FCR in the E1912 trial. The 3-year OS rate was 98.8% and 91.5%, respectively (P less than .001; N Engl J Med. 2019 Aug 1;381:432-43). Dr. Brown noted, however, that there were few deaths in this study, and many of them “were not clearly related to the disease or its treatment.”
Dr. Brown also pointed out that FCR has been shown to have curative potential in IGHV-mutated CLL in both the FCR300 trial (Blood. 2016 127:303-9) and the CLL8 trial (Blood. 2016 127:208-15).
Another factor to consider is the greater cost of targeted agents. One analysis suggested the per-patient lifetime cost of CLL treatment in the United States will increase from $147,000 to $604,000 as targeted therapies overtake CIT as first-line treatment (J Clin Oncol. 2017 Jan 10;35[2]:166-174).
“Given all of the above, chemoimmunotherapy is going to remain part of the treatment repertoire for CLL,” Dr. Brown said. “It’s our only known potential cure for the fit, mutated patients ... and can also result in prolonged treatment-free intervals for patients who are older. As we manage CLL as a chronic disease over a lifetime, we need to continue to have this in our armamentarium.”
Specifically, Dr. Brown said CIT is appropriate for patients who don’t have del(17p) or mutated TP53. FCR should be given to young, fit patients with IGHV-mutated CLL, and FCR or BR should be given to older patients and young, fit patients with IGHV-unmutated CLL.
Dr. Brown and Dr. Wierda reported financial ties to multiple pharmaceutical companies, including makers of CLL treatments.
REPORTING FROM NCCN HEMATOLOGIC MALIGNANCIES