User login
Myeloma therapies raise cardiovascular risks
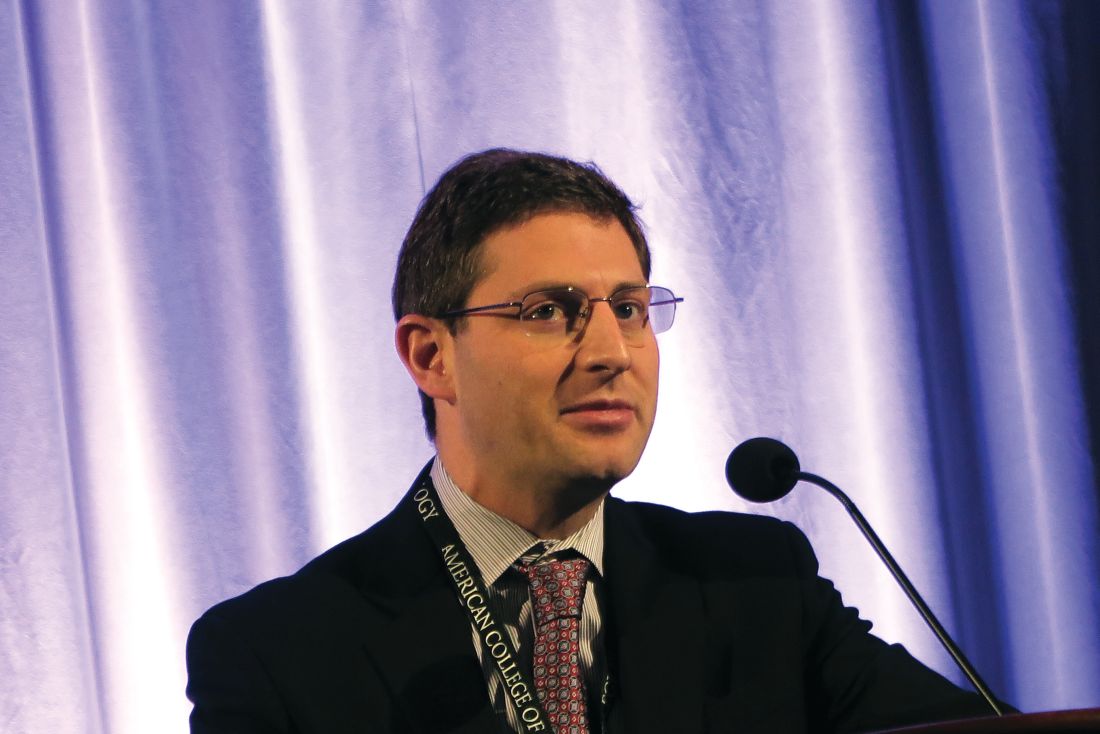
WASHINGTON – Proteasome inhibitors are essential components of therapeutic regimens for multiple myeloma, but at least one member of this class of life-extending agents, carfilzomib (Kyprolis), is also associated with a significant increase in risk of heart failure, cautioned a specialist in plasma cell disorders.
In addition, immunomodulating agents such as lenalidomide (Revlimid) and pomalidomide (Pomalyst) are associated with increased risk for thromboembolic events, said R. Frank Cornell, MD, clinical director of plasma cell disorders at Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, Tenn.
In an ongoing, prospective study comparing rates of cardiac adverse events in patients receiving carfilzomib or another proteasome inhibitor, bortezomib (Velcade), Dr. Cornell and his colleagues found that while there were no significant differences in progression-free survival (PFS) or overall survival (OS) between the treatments, “patients who experienced a cardiovascular event had significantly worse progression-free and overall survival compared to those that did not have a cardiovascular event,” he said at the American College of Cardiology’s Advancing the Cardiovascular Care of the Oncology Patient meeting.
The Prospective Observation of Cardiac Safety With Proteasome Inhibition (PROTECT) trial, scheduled for completion in August 2019, enrolled 95 patients with relapsed multiple myeloma and randomly assigned them on a 2:1 basis to receive carfilzomib or bortezomib.
The investigators found that cardiovascular adverse events occurred in 33 of the 65 patients (51%) randomized to carfilzomib, compared with 5 of 30 patients (17%) assigned to bortezomib.
The events included grade 1 or 2 heart failure (HF) in 12 patients on carfilzomib vs. 2 on bortezomib, and grade 3 or 4 HF in 11 vs. 1, respectively. Hypertension was significantly more frequent among patients on carfilzomib, and one patient on carfilzomib died from the acute coronary syndrome 24 hours after receiving carfilzomib in the second week of treatment.
The investigators found that both B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) and N-terminal pro b-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) were highly predictive of cardiovascular adverse events. Patients on carfilzomib who had levels of the markers above normal at baseline had an odds ratio (OR) for cardiovascular events of 7.39 (P less than .0001), and those with BNP or NT-proBNP increases at week 2 or 3 during cycle 1 had an OR for a cardiovascular adverse event of 63.5 (P less than .001).
In multivariate analysis, the risk for cardiovascular events for patients treated with carfilzomib was significantly lower for patients with one or no traditional cardiovascular risk factors, compared with patients with two or more.
“Prospective monitoring with natriuretic peptides should be considered, particularly early in treatment,” Dr. Cornell said.
IMiDs and thromboembolism
In early clinical trials of immunomodulators (IMiDs) for multiple myeloma, investigators saw that the incidence of thromboembolic events was lower among patients who received thromboprophylaxis than among those who did not, Dr. Cornell noted.
“From this, certain guidelines have been developed such that all patients considered to be at risk should at least receive an aspirin, 81-325 mg, and patients at higher risk for thromboembolism should receive low-molecular-weight heparin or therapeutic-dose warfarin,” he said.
There is little guidance, however, about the use of direct oral anticoagulants in this population, he added, a fact that prompted him and his colleagues in oncology and cardiology to perform a pilot study of apixaban (Eliquis) for primary prevention of venous thromboembolism (VTE) in patients with multiple myeloma who were receiving immunodulatory drugs.
Results of the pilot study, reported in a poster session at the 2018 annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology, showed that among 50 patients who received apixaban 2.5 mg twice daily for 6 months during IMiD therapy, there were no VTEs, stroke, or myocardial infarction, and no episodes of major bleeding. There were just three nonmajor bleeding events, and one early withdrawal from apixaban due to an allergic reaction manifesting as generalized edema.
“Further study is needed to validate this as a potential primary prophylaxis in patients receiving IMiDs for multiple myeloma,” Dr. Cornell said.
He reported having no financial disclosures. Millennium Pharmaceuticals is a sponsor of the PROTECT trial.
WASHINGTON – Proteasome inhibitors are essential components of therapeutic regimens for multiple myeloma, but at least one member of this class of life-extending agents, carfilzomib (Kyprolis), is also associated with a significant increase in risk of heart failure, cautioned a specialist in plasma cell disorders.
In addition, immunomodulating agents such as lenalidomide (Revlimid) and pomalidomide (Pomalyst) are associated with increased risk for thromboembolic events, said R. Frank Cornell, MD, clinical director of plasma cell disorders at Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, Tenn.
In an ongoing, prospective study comparing rates of cardiac adverse events in patients receiving carfilzomib or another proteasome inhibitor, bortezomib (Velcade), Dr. Cornell and his colleagues found that while there were no significant differences in progression-free survival (PFS) or overall survival (OS) between the treatments, “patients who experienced a cardiovascular event had significantly worse progression-free and overall survival compared to those that did not have a cardiovascular event,” he said at the American College of Cardiology’s Advancing the Cardiovascular Care of the Oncology Patient meeting.
The Prospective Observation of Cardiac Safety With Proteasome Inhibition (PROTECT) trial, scheduled for completion in August 2019, enrolled 95 patients with relapsed multiple myeloma and randomly assigned them on a 2:1 basis to receive carfilzomib or bortezomib.
The investigators found that cardiovascular adverse events occurred in 33 of the 65 patients (51%) randomized to carfilzomib, compared with 5 of 30 patients (17%) assigned to bortezomib.
The events included grade 1 or 2 heart failure (HF) in 12 patients on carfilzomib vs. 2 on bortezomib, and grade 3 or 4 HF in 11 vs. 1, respectively. Hypertension was significantly more frequent among patients on carfilzomib, and one patient on carfilzomib died from the acute coronary syndrome 24 hours after receiving carfilzomib in the second week of treatment.
The investigators found that both B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) and N-terminal pro b-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) were highly predictive of cardiovascular adverse events. Patients on carfilzomib who had levels of the markers above normal at baseline had an odds ratio (OR) for cardiovascular events of 7.39 (P less than .0001), and those with BNP or NT-proBNP increases at week 2 or 3 during cycle 1 had an OR for a cardiovascular adverse event of 63.5 (P less than .001).
In multivariate analysis, the risk for cardiovascular events for patients treated with carfilzomib was significantly lower for patients with one or no traditional cardiovascular risk factors, compared with patients with two or more.
“Prospective monitoring with natriuretic peptides should be considered, particularly early in treatment,” Dr. Cornell said.
IMiDs and thromboembolism
In early clinical trials of immunomodulators (IMiDs) for multiple myeloma, investigators saw that the incidence of thromboembolic events was lower among patients who received thromboprophylaxis than among those who did not, Dr. Cornell noted.
“From this, certain guidelines have been developed such that all patients considered to be at risk should at least receive an aspirin, 81-325 mg, and patients at higher risk for thromboembolism should receive low-molecular-weight heparin or therapeutic-dose warfarin,” he said.
There is little guidance, however, about the use of direct oral anticoagulants in this population, he added, a fact that prompted him and his colleagues in oncology and cardiology to perform a pilot study of apixaban (Eliquis) for primary prevention of venous thromboembolism (VTE) in patients with multiple myeloma who were receiving immunodulatory drugs.
Results of the pilot study, reported in a poster session at the 2018 annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology, showed that among 50 patients who received apixaban 2.5 mg twice daily for 6 months during IMiD therapy, there were no VTEs, stroke, or myocardial infarction, and no episodes of major bleeding. There were just three nonmajor bleeding events, and one early withdrawal from apixaban due to an allergic reaction manifesting as generalized edema.
“Further study is needed to validate this as a potential primary prophylaxis in patients receiving IMiDs for multiple myeloma,” Dr. Cornell said.
He reported having no financial disclosures. Millennium Pharmaceuticals is a sponsor of the PROTECT trial.
WASHINGTON – Proteasome inhibitors are essential components of therapeutic regimens for multiple myeloma, but at least one member of this class of life-extending agents, carfilzomib (Kyprolis), is also associated with a significant increase in risk of heart failure, cautioned a specialist in plasma cell disorders.
In addition, immunomodulating agents such as lenalidomide (Revlimid) and pomalidomide (Pomalyst) are associated with increased risk for thromboembolic events, said R. Frank Cornell, MD, clinical director of plasma cell disorders at Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, Tenn.
In an ongoing, prospective study comparing rates of cardiac adverse events in patients receiving carfilzomib or another proteasome inhibitor, bortezomib (Velcade), Dr. Cornell and his colleagues found that while there were no significant differences in progression-free survival (PFS) or overall survival (OS) between the treatments, “patients who experienced a cardiovascular event had significantly worse progression-free and overall survival compared to those that did not have a cardiovascular event,” he said at the American College of Cardiology’s Advancing the Cardiovascular Care of the Oncology Patient meeting.
The Prospective Observation of Cardiac Safety With Proteasome Inhibition (PROTECT) trial, scheduled for completion in August 2019, enrolled 95 patients with relapsed multiple myeloma and randomly assigned them on a 2:1 basis to receive carfilzomib or bortezomib.
The investigators found that cardiovascular adverse events occurred in 33 of the 65 patients (51%) randomized to carfilzomib, compared with 5 of 30 patients (17%) assigned to bortezomib.
The events included grade 1 or 2 heart failure (HF) in 12 patients on carfilzomib vs. 2 on bortezomib, and grade 3 or 4 HF in 11 vs. 1, respectively. Hypertension was significantly more frequent among patients on carfilzomib, and one patient on carfilzomib died from the acute coronary syndrome 24 hours after receiving carfilzomib in the second week of treatment.
The investigators found that both B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) and N-terminal pro b-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) were highly predictive of cardiovascular adverse events. Patients on carfilzomib who had levels of the markers above normal at baseline had an odds ratio (OR) for cardiovascular events of 7.39 (P less than .0001), and those with BNP or NT-proBNP increases at week 2 or 3 during cycle 1 had an OR for a cardiovascular adverse event of 63.5 (P less than .001).
In multivariate analysis, the risk for cardiovascular events for patients treated with carfilzomib was significantly lower for patients with one or no traditional cardiovascular risk factors, compared with patients with two or more.
“Prospective monitoring with natriuretic peptides should be considered, particularly early in treatment,” Dr. Cornell said.
IMiDs and thromboembolism
In early clinical trials of immunomodulators (IMiDs) for multiple myeloma, investigators saw that the incidence of thromboembolic events was lower among patients who received thromboprophylaxis than among those who did not, Dr. Cornell noted.
“From this, certain guidelines have been developed such that all patients considered to be at risk should at least receive an aspirin, 81-325 mg, and patients at higher risk for thromboembolism should receive low-molecular-weight heparin or therapeutic-dose warfarin,” he said.
There is little guidance, however, about the use of direct oral anticoagulants in this population, he added, a fact that prompted him and his colleagues in oncology and cardiology to perform a pilot study of apixaban (Eliquis) for primary prevention of venous thromboembolism (VTE) in patients with multiple myeloma who were receiving immunodulatory drugs.
Results of the pilot study, reported in a poster session at the 2018 annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology, showed that among 50 patients who received apixaban 2.5 mg twice daily for 6 months during IMiD therapy, there were no VTEs, stroke, or myocardial infarction, and no episodes of major bleeding. There were just three nonmajor bleeding events, and one early withdrawal from apixaban due to an allergic reaction manifesting as generalized edema.
“Further study is needed to validate this as a potential primary prophylaxis in patients receiving IMiDs for multiple myeloma,” Dr. Cornell said.
He reported having no financial disclosures. Millennium Pharmaceuticals is a sponsor of the PROTECT trial.
REPORTING FROM ACC CARDIO-ONCOLOGY
Selinexor hits FDA stumbling block
Karyopharm Therapeutics must finish a randomized phase 3 trial of selinexor plus dexamethasone before the Food and Drug Administration will proceed with a safety and tolerability assessment for the first-in-class multiple myeloma drug.
By an 8-5 vote, the FDA Oncologic Drugs Advisory Committee said that data from STORM 2, Karyopharm’s single-arm phase 2b trial, didn’t sufficiently show that selinexor exerted any significant benefit over dexamethasone alone, used because the company claims it potentiates selinexor’s action.
Committee members also expressed concerns about the drug’s challenging adverse event profile. In STORM Part 2, 60% of patients experienced serious treatment-emergent adverse events and 10 died from them.
“This trial design is not adequate to assess tolerability and efficacy,” and move the drug along, said Christian S. Hinrichs, MD, of the National Cancer Institute. For that to happen, “we’d be looking for several things. We’d be looking for a subset of patients who benefited profoundly, which could be somewhat compelling despite a lower overall response rate. Next we might be looking for durable response, and here we see 4-month responses. And finally, what we look for in a single-arm trial is a really favorable side effect profile, like we see in checkpoint inhibitors. That is clearly not the case with this drug. So, on the basis of both the trial design and the results, I find it hard to conclude that these data allow for an adequate assessment that safety and efficacy are proven.”
The decision came despite the pleas of 15 patients and one patient advocate who said the drug improved clinical status and quality of life, and even extended life beyond what anyone expected. However, several committee members noted that Karyopharm paid for speakers’ travel and that patients who had negative experiences would probably be too sick to attend.
Selinexor is a completely new therapeutic option for relapsed multiple myeloma patients. It is a twice-weekly, oral tablet that inhibits nuclear export protein Exportin 1 (XPO1), which regulates the localization of tumor suppressor proteins and is associated with poor prognosis. Aberrant XPO1 expression causes tumor suppressors to locate away from their targets, allowing tumors to grow. Inhibiting it with selinexor blocks signal transduction pathways, interrupting tumor cell proliferation and inducing apoptosis while sparing normal cells.
Karyopharm is seeking approval of selinexor in combination with low-dose dexamethasone for the treatment of patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma who have received at least three prior therapies and whose disease is refractory to at least one proteasome inhibitor, at least one immunomodulatory imide drug, and an anti-CD38 monoclonal antibody.
This disease is referred to as “triple-class refractory” multiple myeloma. At this stage, patients have exhausted every effective treatment option and are faced with the choice of supportive care or recycling previously successful drugs. Their median overall survival time is 3-5 months.
Karyopharm submitted its the New Drug Application using the Accelerated Approval pathway, arguing that the drug meets an unmet medical need and can be approved on surrogate endpoints – in this case, overall response rate.
The modified intent-to-treat analysis comprised 122 patients. The overall response rate was 25.4% with a median response duration of 4.4 months. Two patients had a complete response; six had a very good partial response; and 23 had a partial response.
Some committee members, however, said it would be impossible to tease out how much of the response could be due to the co-administration of 20 mg dexamethasone with each dose. In a phase 1 dose-ranging study of selinexor as monotherapy, it produced only one partial response in 56 patients. And, FDA pointed out, historical studies have shown response rates of 10%-27% for high-dose dexamethasone.
However, those in favor of the drug pointed out that the STORM patients were steroid-refractory, and that a 25% response rate would be unlikely on low-dose dexamethasone alone. This is proof of the company’s claim that the steroid works synergistically with selinexor, they said.
These members also pointed out that even a few years ago, there simply were no patients like the STORM cohort. Only recently have these patients lived long enough to develop resistance against all therapeutic lines, so it’s unrealistic to use historical data to judge what a reasonable response rate looks like in this situation.
Committee members also choked on STORM’s adverse event (AE) profile. All patients experienced at least one treatment-emergent AE, and 60% had at least one serious AE. Most (88.6%) required a dose modification due to an AE, and 28.5% discontinued due to one. The most common AEs were thrombocytopenia, anemia, nausea, fatigue, and decreased appetite. The company said these were “typically reversible and manageable with dose reductions.”
Additionally, there were 23 deaths in the trial. About half (13) were due to disease progression, but the remainder were due to a fatal treatment-emergent AE. Two of these (one pneumonia and one sepsis) were directly due to selinexor, the company said.
Despite the committee’s concerns, 16 of the 17 speakers described positive experiences with selinexor. They universally acknowledged that “it’s a hard drug to take,” and that side effects need to be managed proactively. But they also said, universally, that the drug has brought them additional months of good-quality life, decreased lengthy hospital stays, enabled them to participate in important family events, and even travel. Some also expressed the hope that selinexor would be a bridge drug, decreasing their disease burden enough that they could qualify for other clinical trials of new investigational drugs.
Only Stephanie Fox-Rawlings, PhD, of the National Center for Health Research, urged a delay. “Even if these adverse events are manageable, they harm patients’ quality of life,” she said. “This may be acceptable to some, but if the drug can’t provide a meaningful benefit then they are not worth it and in this clinical trial there was no improvement noted in quality of life. This drug has serious risks and we don’t know if it works.”
Dr. Fox said she was “very glad” that Karyopharm has completed recruitment for its phase 3 randomized study, dubbed BOSTON. BOSTON will assign active patients to once-weekly 100 mg selinexor plus weight-dosed bortezomib, plus twice-weekly 20 mg dexamethasone. The comparator group will receive weight-based bortezomib twice a week and 20 mg dexamethasone four times a week. Patients who progress can cross over to the active arm. The company hopes for even better results, saying that the proteasome inhibitor has also shown a synergistic effect with selinexor. Results are expected in 2020.
“The BOSTON study doesn’t solve anything,” retorted committee member David Harrington, PhD, emeritus professor of biostatistics at the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute. “It’s a different clinical profile, different dosing, a different combination of agents, and it doesn’t isolate the single-arm activity of selinexor.”
Karyopharm Therapeutics must finish a randomized phase 3 trial of selinexor plus dexamethasone before the Food and Drug Administration will proceed with a safety and tolerability assessment for the first-in-class multiple myeloma drug.
By an 8-5 vote, the FDA Oncologic Drugs Advisory Committee said that data from STORM 2, Karyopharm’s single-arm phase 2b trial, didn’t sufficiently show that selinexor exerted any significant benefit over dexamethasone alone, used because the company claims it potentiates selinexor’s action.
Committee members also expressed concerns about the drug’s challenging adverse event profile. In STORM Part 2, 60% of patients experienced serious treatment-emergent adverse events and 10 died from them.
“This trial design is not adequate to assess tolerability and efficacy,” and move the drug along, said Christian S. Hinrichs, MD, of the National Cancer Institute. For that to happen, “we’d be looking for several things. We’d be looking for a subset of patients who benefited profoundly, which could be somewhat compelling despite a lower overall response rate. Next we might be looking for durable response, and here we see 4-month responses. And finally, what we look for in a single-arm trial is a really favorable side effect profile, like we see in checkpoint inhibitors. That is clearly not the case with this drug. So, on the basis of both the trial design and the results, I find it hard to conclude that these data allow for an adequate assessment that safety and efficacy are proven.”
The decision came despite the pleas of 15 patients and one patient advocate who said the drug improved clinical status and quality of life, and even extended life beyond what anyone expected. However, several committee members noted that Karyopharm paid for speakers’ travel and that patients who had negative experiences would probably be too sick to attend.
Selinexor is a completely new therapeutic option for relapsed multiple myeloma patients. It is a twice-weekly, oral tablet that inhibits nuclear export protein Exportin 1 (XPO1), which regulates the localization of tumor suppressor proteins and is associated with poor prognosis. Aberrant XPO1 expression causes tumor suppressors to locate away from their targets, allowing tumors to grow. Inhibiting it with selinexor blocks signal transduction pathways, interrupting tumor cell proliferation and inducing apoptosis while sparing normal cells.
Karyopharm is seeking approval of selinexor in combination with low-dose dexamethasone for the treatment of patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma who have received at least three prior therapies and whose disease is refractory to at least one proteasome inhibitor, at least one immunomodulatory imide drug, and an anti-CD38 monoclonal antibody.
This disease is referred to as “triple-class refractory” multiple myeloma. At this stage, patients have exhausted every effective treatment option and are faced with the choice of supportive care or recycling previously successful drugs. Their median overall survival time is 3-5 months.
Karyopharm submitted its the New Drug Application using the Accelerated Approval pathway, arguing that the drug meets an unmet medical need and can be approved on surrogate endpoints – in this case, overall response rate.
The modified intent-to-treat analysis comprised 122 patients. The overall response rate was 25.4% with a median response duration of 4.4 months. Two patients had a complete response; six had a very good partial response; and 23 had a partial response.
Some committee members, however, said it would be impossible to tease out how much of the response could be due to the co-administration of 20 mg dexamethasone with each dose. In a phase 1 dose-ranging study of selinexor as monotherapy, it produced only one partial response in 56 patients. And, FDA pointed out, historical studies have shown response rates of 10%-27% for high-dose dexamethasone.
However, those in favor of the drug pointed out that the STORM patients were steroid-refractory, and that a 25% response rate would be unlikely on low-dose dexamethasone alone. This is proof of the company’s claim that the steroid works synergistically with selinexor, they said.
These members also pointed out that even a few years ago, there simply were no patients like the STORM cohort. Only recently have these patients lived long enough to develop resistance against all therapeutic lines, so it’s unrealistic to use historical data to judge what a reasonable response rate looks like in this situation.
Committee members also choked on STORM’s adverse event (AE) profile. All patients experienced at least one treatment-emergent AE, and 60% had at least one serious AE. Most (88.6%) required a dose modification due to an AE, and 28.5% discontinued due to one. The most common AEs were thrombocytopenia, anemia, nausea, fatigue, and decreased appetite. The company said these were “typically reversible and manageable with dose reductions.”
Additionally, there were 23 deaths in the trial. About half (13) were due to disease progression, but the remainder were due to a fatal treatment-emergent AE. Two of these (one pneumonia and one sepsis) were directly due to selinexor, the company said.
Despite the committee’s concerns, 16 of the 17 speakers described positive experiences with selinexor. They universally acknowledged that “it’s a hard drug to take,” and that side effects need to be managed proactively. But they also said, universally, that the drug has brought them additional months of good-quality life, decreased lengthy hospital stays, enabled them to participate in important family events, and even travel. Some also expressed the hope that selinexor would be a bridge drug, decreasing their disease burden enough that they could qualify for other clinical trials of new investigational drugs.
Only Stephanie Fox-Rawlings, PhD, of the National Center for Health Research, urged a delay. “Even if these adverse events are manageable, they harm patients’ quality of life,” she said. “This may be acceptable to some, but if the drug can’t provide a meaningful benefit then they are not worth it and in this clinical trial there was no improvement noted in quality of life. This drug has serious risks and we don’t know if it works.”
Dr. Fox said she was “very glad” that Karyopharm has completed recruitment for its phase 3 randomized study, dubbed BOSTON. BOSTON will assign active patients to once-weekly 100 mg selinexor plus weight-dosed bortezomib, plus twice-weekly 20 mg dexamethasone. The comparator group will receive weight-based bortezomib twice a week and 20 mg dexamethasone four times a week. Patients who progress can cross over to the active arm. The company hopes for even better results, saying that the proteasome inhibitor has also shown a synergistic effect with selinexor. Results are expected in 2020.
“The BOSTON study doesn’t solve anything,” retorted committee member David Harrington, PhD, emeritus professor of biostatistics at the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute. “It’s a different clinical profile, different dosing, a different combination of agents, and it doesn’t isolate the single-arm activity of selinexor.”
Karyopharm Therapeutics must finish a randomized phase 3 trial of selinexor plus dexamethasone before the Food and Drug Administration will proceed with a safety and tolerability assessment for the first-in-class multiple myeloma drug.
By an 8-5 vote, the FDA Oncologic Drugs Advisory Committee said that data from STORM 2, Karyopharm’s single-arm phase 2b trial, didn’t sufficiently show that selinexor exerted any significant benefit over dexamethasone alone, used because the company claims it potentiates selinexor’s action.
Committee members also expressed concerns about the drug’s challenging adverse event profile. In STORM Part 2, 60% of patients experienced serious treatment-emergent adverse events and 10 died from them.
“This trial design is not adequate to assess tolerability and efficacy,” and move the drug along, said Christian S. Hinrichs, MD, of the National Cancer Institute. For that to happen, “we’d be looking for several things. We’d be looking for a subset of patients who benefited profoundly, which could be somewhat compelling despite a lower overall response rate. Next we might be looking for durable response, and here we see 4-month responses. And finally, what we look for in a single-arm trial is a really favorable side effect profile, like we see in checkpoint inhibitors. That is clearly not the case with this drug. So, on the basis of both the trial design and the results, I find it hard to conclude that these data allow for an adequate assessment that safety and efficacy are proven.”
The decision came despite the pleas of 15 patients and one patient advocate who said the drug improved clinical status and quality of life, and even extended life beyond what anyone expected. However, several committee members noted that Karyopharm paid for speakers’ travel and that patients who had negative experiences would probably be too sick to attend.
Selinexor is a completely new therapeutic option for relapsed multiple myeloma patients. It is a twice-weekly, oral tablet that inhibits nuclear export protein Exportin 1 (XPO1), which regulates the localization of tumor suppressor proteins and is associated with poor prognosis. Aberrant XPO1 expression causes tumor suppressors to locate away from their targets, allowing tumors to grow. Inhibiting it with selinexor blocks signal transduction pathways, interrupting tumor cell proliferation and inducing apoptosis while sparing normal cells.
Karyopharm is seeking approval of selinexor in combination with low-dose dexamethasone for the treatment of patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma who have received at least three prior therapies and whose disease is refractory to at least one proteasome inhibitor, at least one immunomodulatory imide drug, and an anti-CD38 monoclonal antibody.
This disease is referred to as “triple-class refractory” multiple myeloma. At this stage, patients have exhausted every effective treatment option and are faced with the choice of supportive care or recycling previously successful drugs. Their median overall survival time is 3-5 months.
Karyopharm submitted its the New Drug Application using the Accelerated Approval pathway, arguing that the drug meets an unmet medical need and can be approved on surrogate endpoints – in this case, overall response rate.
The modified intent-to-treat analysis comprised 122 patients. The overall response rate was 25.4% with a median response duration of 4.4 months. Two patients had a complete response; six had a very good partial response; and 23 had a partial response.
Some committee members, however, said it would be impossible to tease out how much of the response could be due to the co-administration of 20 mg dexamethasone with each dose. In a phase 1 dose-ranging study of selinexor as monotherapy, it produced only one partial response in 56 patients. And, FDA pointed out, historical studies have shown response rates of 10%-27% for high-dose dexamethasone.
However, those in favor of the drug pointed out that the STORM patients were steroid-refractory, and that a 25% response rate would be unlikely on low-dose dexamethasone alone. This is proof of the company’s claim that the steroid works synergistically with selinexor, they said.
These members also pointed out that even a few years ago, there simply were no patients like the STORM cohort. Only recently have these patients lived long enough to develop resistance against all therapeutic lines, so it’s unrealistic to use historical data to judge what a reasonable response rate looks like in this situation.
Committee members also choked on STORM’s adverse event (AE) profile. All patients experienced at least one treatment-emergent AE, and 60% had at least one serious AE. Most (88.6%) required a dose modification due to an AE, and 28.5% discontinued due to one. The most common AEs were thrombocytopenia, anemia, nausea, fatigue, and decreased appetite. The company said these were “typically reversible and manageable with dose reductions.”
Additionally, there were 23 deaths in the trial. About half (13) were due to disease progression, but the remainder were due to a fatal treatment-emergent AE. Two of these (one pneumonia and one sepsis) were directly due to selinexor, the company said.
Despite the committee’s concerns, 16 of the 17 speakers described positive experiences with selinexor. They universally acknowledged that “it’s a hard drug to take,” and that side effects need to be managed proactively. But they also said, universally, that the drug has brought them additional months of good-quality life, decreased lengthy hospital stays, enabled them to participate in important family events, and even travel. Some also expressed the hope that selinexor would be a bridge drug, decreasing their disease burden enough that they could qualify for other clinical trials of new investigational drugs.
Only Stephanie Fox-Rawlings, PhD, of the National Center for Health Research, urged a delay. “Even if these adverse events are manageable, they harm patients’ quality of life,” she said. “This may be acceptable to some, but if the drug can’t provide a meaningful benefit then they are not worth it and in this clinical trial there was no improvement noted in quality of life. This drug has serious risks and we don’t know if it works.”
Dr. Fox said she was “very glad” that Karyopharm has completed recruitment for its phase 3 randomized study, dubbed BOSTON. BOSTON will assign active patients to once-weekly 100 mg selinexor plus weight-dosed bortezomib, plus twice-weekly 20 mg dexamethasone. The comparator group will receive weight-based bortezomib twice a week and 20 mg dexamethasone four times a week. Patients who progress can cross over to the active arm. The company hopes for even better results, saying that the proteasome inhibitor has also shown a synergistic effect with selinexor. Results are expected in 2020.
“The BOSTON study doesn’t solve anything,” retorted committee member David Harrington, PhD, emeritus professor of biostatistics at the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute. “It’s a different clinical profile, different dosing, a different combination of agents, and it doesn’t isolate the single-arm activity of selinexor.”
ZUMA-1 update: Axi-cel responses persist at 2 years
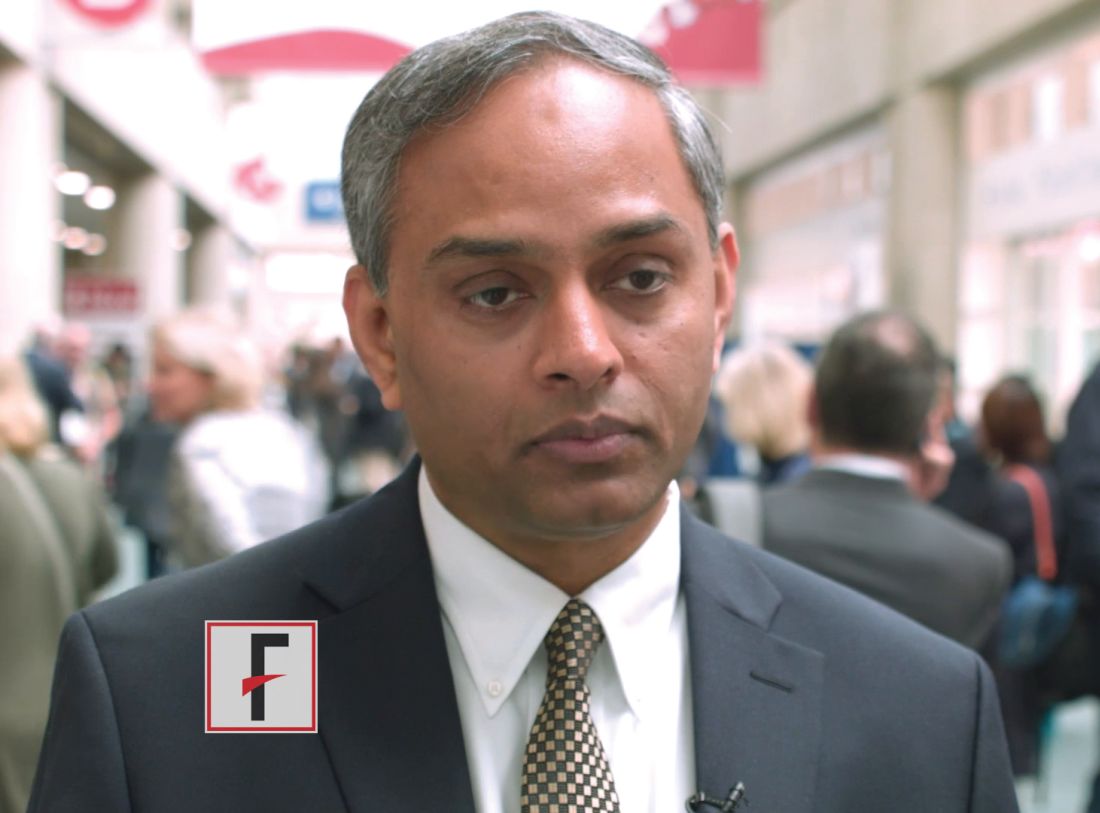
HOUSTON – With a median follow-up now exceeding 2 years, 39% of refractory large B-cell lymphoma patients enrolled in the pivotal ZUMA-1 trial have maintained ongoing response to axicabtagene ciloleucel, according to an investigator involved in the study.
Median duration of response to axi-cel and median overall survival have not yet been reached, while a recent subset analysis showed that nearly half of patients with certain high-risk characteristics had a durable response, said investigator Sattva S. Neelapu, MD, of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston.
Evidence of B-cell recovery and a decrease in detectable, gene-marked CAR T cells have been noted in further follow-up, suggesting that functional CAR T-cell persistence may not be required for long-term remissions, Dr. Neelapu added.
“These data support [the conclusion] that axi-cel induces durable remissions in patients with large B-cell lymphoma who otherwise lack curative options,” Dr. Neelapu said at the Transplantation & Cellular Therapy Meetings.
The update on the phase 1/2 ZUMA-1 study included 108 patients with refractory large B-cell lymphoma who received axi-cel, the CD19-directed autologous chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy.
In a previously reported 1-year update on the trial, 42% of patients had ongoing responses, Dr. Neelapu said. In the present update, with a median follow-up of 27.1 months, ongoing responses were seen in 39%, most of whom (37%) were in complete response, according to the data presented.
Thirty-three patients in the phase 2 portion of ZUMA-1 were known to have double-expressor or high-grade B-cell lymphoma, according to the investigator. In this high-risk subset, 48% were in ongoing complete response at the 2-year follow-up.
Progression-free survival in ZUMA-1 plateaued at the 6 month-follow-up, according to Dr. Neelapu, who said that plateau has been largely maintained, with just 10 patients progressing since then. Median progression-free survival is 5.9 months and median overall survival has not been reached, with a 24-month overall survival of 51%.
Late-onset serious adverse events mainly consisted of manageable infections, none of which were considered related to axi-cel treatment, according to Dr. Neelapu.
The proportion of ongoing responders with detectable CAR T-cells has decreased over time, from 95% at 3 months to 66% at 24 months, Dr. Neelapu reported. Meanwhile, the proportion of ongoing responders with detectable B cells after axi-cel treatment has gone from 17% to 75%.
More details on the 2-year follow-up data from ZUMA-1 were reported recently in the Lancet Oncology (2019 Jan;20[1]:31-42).
Funding for ZUMA-1 came from Kite and the Leukemia & Lymphoma Society. Dr. Neelapu reported disclosures related to Kite, Celgene, Cellectis, Merck, Poseida, Acerta, Karus, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Novartis, and Unum Therapeutics.
The meeting was held by the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation and the Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research. At its meeting, the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation announced a new name for the society: American Society for Transplantation and Cellular Therapy (ASTCT).
SOURCE: Neelapu SS et al. TCT 2019, Abstract 82.
HOUSTON – With a median follow-up now exceeding 2 years, 39% of refractory large B-cell lymphoma patients enrolled in the pivotal ZUMA-1 trial have maintained ongoing response to axicabtagene ciloleucel, according to an investigator involved in the study.
Median duration of response to axi-cel and median overall survival have not yet been reached, while a recent subset analysis showed that nearly half of patients with certain high-risk characteristics had a durable response, said investigator Sattva S. Neelapu, MD, of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston.
Evidence of B-cell recovery and a decrease in detectable, gene-marked CAR T cells have been noted in further follow-up, suggesting that functional CAR T-cell persistence may not be required for long-term remissions, Dr. Neelapu added.
“These data support [the conclusion] that axi-cel induces durable remissions in patients with large B-cell lymphoma who otherwise lack curative options,” Dr. Neelapu said at the Transplantation & Cellular Therapy Meetings.
The update on the phase 1/2 ZUMA-1 study included 108 patients with refractory large B-cell lymphoma who received axi-cel, the CD19-directed autologous chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy.
In a previously reported 1-year update on the trial, 42% of patients had ongoing responses, Dr. Neelapu said. In the present update, with a median follow-up of 27.1 months, ongoing responses were seen in 39%, most of whom (37%) were in complete response, according to the data presented.
Thirty-three patients in the phase 2 portion of ZUMA-1 were known to have double-expressor or high-grade B-cell lymphoma, according to the investigator. In this high-risk subset, 48% were in ongoing complete response at the 2-year follow-up.
Progression-free survival in ZUMA-1 plateaued at the 6 month-follow-up, according to Dr. Neelapu, who said that plateau has been largely maintained, with just 10 patients progressing since then. Median progression-free survival is 5.9 months and median overall survival has not been reached, with a 24-month overall survival of 51%.
Late-onset serious adverse events mainly consisted of manageable infections, none of which were considered related to axi-cel treatment, according to Dr. Neelapu.
The proportion of ongoing responders with detectable CAR T-cells has decreased over time, from 95% at 3 months to 66% at 24 months, Dr. Neelapu reported. Meanwhile, the proportion of ongoing responders with detectable B cells after axi-cel treatment has gone from 17% to 75%.
More details on the 2-year follow-up data from ZUMA-1 were reported recently in the Lancet Oncology (2019 Jan;20[1]:31-42).
Funding for ZUMA-1 came from Kite and the Leukemia & Lymphoma Society. Dr. Neelapu reported disclosures related to Kite, Celgene, Cellectis, Merck, Poseida, Acerta, Karus, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Novartis, and Unum Therapeutics.
The meeting was held by the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation and the Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research. At its meeting, the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation announced a new name for the society: American Society for Transplantation and Cellular Therapy (ASTCT).
SOURCE: Neelapu SS et al. TCT 2019, Abstract 82.
HOUSTON – With a median follow-up now exceeding 2 years, 39% of refractory large B-cell lymphoma patients enrolled in the pivotal ZUMA-1 trial have maintained ongoing response to axicabtagene ciloleucel, according to an investigator involved in the study.
Median duration of response to axi-cel and median overall survival have not yet been reached, while a recent subset analysis showed that nearly half of patients with certain high-risk characteristics had a durable response, said investigator Sattva S. Neelapu, MD, of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston.
Evidence of B-cell recovery and a decrease in detectable, gene-marked CAR T cells have been noted in further follow-up, suggesting that functional CAR T-cell persistence may not be required for long-term remissions, Dr. Neelapu added.
“These data support [the conclusion] that axi-cel induces durable remissions in patients with large B-cell lymphoma who otherwise lack curative options,” Dr. Neelapu said at the Transplantation & Cellular Therapy Meetings.
The update on the phase 1/2 ZUMA-1 study included 108 patients with refractory large B-cell lymphoma who received axi-cel, the CD19-directed autologous chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy.
In a previously reported 1-year update on the trial, 42% of patients had ongoing responses, Dr. Neelapu said. In the present update, with a median follow-up of 27.1 months, ongoing responses were seen in 39%, most of whom (37%) were in complete response, according to the data presented.
Thirty-three patients in the phase 2 portion of ZUMA-1 were known to have double-expressor or high-grade B-cell lymphoma, according to the investigator. In this high-risk subset, 48% were in ongoing complete response at the 2-year follow-up.
Progression-free survival in ZUMA-1 plateaued at the 6 month-follow-up, according to Dr. Neelapu, who said that plateau has been largely maintained, with just 10 patients progressing since then. Median progression-free survival is 5.9 months and median overall survival has not been reached, with a 24-month overall survival of 51%.
Late-onset serious adverse events mainly consisted of manageable infections, none of which were considered related to axi-cel treatment, according to Dr. Neelapu.
The proportion of ongoing responders with detectable CAR T-cells has decreased over time, from 95% at 3 months to 66% at 24 months, Dr. Neelapu reported. Meanwhile, the proportion of ongoing responders with detectable B cells after axi-cel treatment has gone from 17% to 75%.
More details on the 2-year follow-up data from ZUMA-1 were reported recently in the Lancet Oncology (2019 Jan;20[1]:31-42).
Funding for ZUMA-1 came from Kite and the Leukemia & Lymphoma Society. Dr. Neelapu reported disclosures related to Kite, Celgene, Cellectis, Merck, Poseida, Acerta, Karus, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Novartis, and Unum Therapeutics.
The meeting was held by the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation and the Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research. At its meeting, the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation announced a new name for the society: American Society for Transplantation and Cellular Therapy (ASTCT).
SOURCE: Neelapu SS et al. TCT 2019, Abstract 82.
REPORTING FROM TCT 2019
Dual-targeted CAR T shows ‘clinical signal’ in NHL
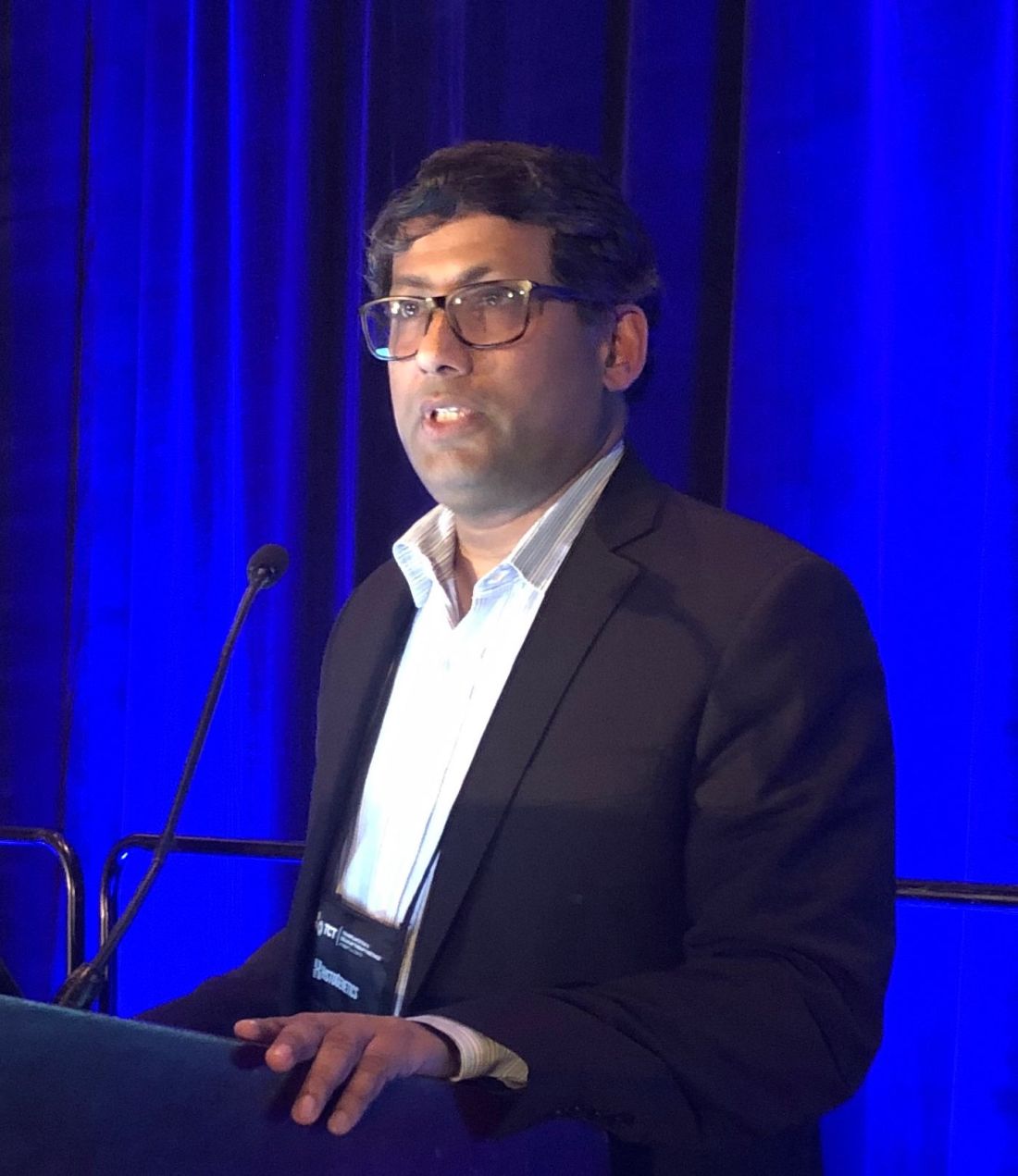
HOUSTON – A dual-targeted, locally manufactured, anti-CD19/CD20 chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy was safe and produced ongoing complete responses in a phase 1 study of heavily pretreated non-Hodgkin lymphoma patients, an investigator reported.
The bispecific CAR T-cell product, designed to limit relapses due to loss of target antigen, was produced at the point of care with a 100% success rate for these heavily pretreated patients, the first of whom has now maintained a complete response for 19 months, said Parameswaran Hari, MD, of the Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee.
“So far, this trial has demonstrated safety for this bispecific vector and suggests a clinical signal, with 7 out of 12 patients with ongoing CR, and with minimal toxicity,” Dr. Hari said at the Transplantation & Cellular Therapy Meetings.
“Point of care delivery, we think, allowed patients to have fresh infusion of CAR T cells, with the avoidance of cryopreservation,” added Dr. Hari, who presented the results on behalf of coinvestigators at the Medical College of Wisconsin and Lentigen Technology.
There was no grade 3 or 4 neurotoxicity or cytokine release syndrome among the 12 patients reported to date in the phase 1, dose-escalation trial, and no patient required intensive care, according to Dr. Hari. Grade 1 and 2 neurotoxicity occurred in two and one patients, respectively, while grade 1 and 2 cytokine release syndrome was observed in three patients each.
Among the 12 patients treated to date, the overall response rate was 81% at day 28, Dr. Hari said, noting that of 6 patients treated at the goal dose of 2.5 x 106 cells/kg, 5 remain in ongoing complete remission.
The median age of patients enrolled in the study was 55 years. Six patients had diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, five had mantle cell lymphoma, and two had chronic lymphocytic leukemia. All but one patient underwent fludarabine/cyclophosphamide lymphodepletion prior to receiving the inpatient CAR T-cell infusions, given over the course of 2 days.
Dr. Hari specifically highlighted the mantle cell lymphoma patient subset, noting that four out of five patients were in complete remission at day 28, and remained in ongoing complete remission at times ranging from 1 to 16 months.
With a set manufacturing time of 14 days, production was successful in all 12 patients, and 10 were able to receive fresh product, while 3 received cryopreserved product due to illness-related delays and a holiday, according to the investigators.
“The time to actual delivery of CAR T cell in the patient is actually shortened dramatically,” Dr. Hari said. “We hope to get it down to day 10.”
Local manufacturing can also reduce some costs associated with CAR T-cell production, such as shipping and courier costs, he added.
Taken together, these findings suggest that locally manufactured anti-CD19/CD20 CAR T cells could improve clinical outcomes for patients with relapsed and refractory B-cell NHL, with efficiency through point-of-care delivery, Dr. Hari concluded.
Further studies are planned to evaluate the efficacy of the product and to investigate the mechanism of relapse or progression in patients who experience treatment failure, he said.
Dr. Hari reported disclosures related to Juno, Kite, Spectrum, Janssen, Takeda, Celgene, and BMS. Several study coauthors reported that they were employed by Lentigen Technology, a Miltenyi Biotec Company.
The meeting was held by the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation and the Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research. At its meeting, the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation announced a new name for the society: American Society for Transplantation and Cellular Therapy (ASTCT).
SOURCE: Shah NN et al. TCT 2019, Abstract 80.
HOUSTON – A dual-targeted, locally manufactured, anti-CD19/CD20 chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy was safe and produced ongoing complete responses in a phase 1 study of heavily pretreated non-Hodgkin lymphoma patients, an investigator reported.
The bispecific CAR T-cell product, designed to limit relapses due to loss of target antigen, was produced at the point of care with a 100% success rate for these heavily pretreated patients, the first of whom has now maintained a complete response for 19 months, said Parameswaran Hari, MD, of the Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee.
“So far, this trial has demonstrated safety for this bispecific vector and suggests a clinical signal, with 7 out of 12 patients with ongoing CR, and with minimal toxicity,” Dr. Hari said at the Transplantation & Cellular Therapy Meetings.
“Point of care delivery, we think, allowed patients to have fresh infusion of CAR T cells, with the avoidance of cryopreservation,” added Dr. Hari, who presented the results on behalf of coinvestigators at the Medical College of Wisconsin and Lentigen Technology.
There was no grade 3 or 4 neurotoxicity or cytokine release syndrome among the 12 patients reported to date in the phase 1, dose-escalation trial, and no patient required intensive care, according to Dr. Hari. Grade 1 and 2 neurotoxicity occurred in two and one patients, respectively, while grade 1 and 2 cytokine release syndrome was observed in three patients each.
Among the 12 patients treated to date, the overall response rate was 81% at day 28, Dr. Hari said, noting that of 6 patients treated at the goal dose of 2.5 x 106 cells/kg, 5 remain in ongoing complete remission.
The median age of patients enrolled in the study was 55 years. Six patients had diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, five had mantle cell lymphoma, and two had chronic lymphocytic leukemia. All but one patient underwent fludarabine/cyclophosphamide lymphodepletion prior to receiving the inpatient CAR T-cell infusions, given over the course of 2 days.
Dr. Hari specifically highlighted the mantle cell lymphoma patient subset, noting that four out of five patients were in complete remission at day 28, and remained in ongoing complete remission at times ranging from 1 to 16 months.
With a set manufacturing time of 14 days, production was successful in all 12 patients, and 10 were able to receive fresh product, while 3 received cryopreserved product due to illness-related delays and a holiday, according to the investigators.
“The time to actual delivery of CAR T cell in the patient is actually shortened dramatically,” Dr. Hari said. “We hope to get it down to day 10.”
Local manufacturing can also reduce some costs associated with CAR T-cell production, such as shipping and courier costs, he added.
Taken together, these findings suggest that locally manufactured anti-CD19/CD20 CAR T cells could improve clinical outcomes for patients with relapsed and refractory B-cell NHL, with efficiency through point-of-care delivery, Dr. Hari concluded.
Further studies are planned to evaluate the efficacy of the product and to investigate the mechanism of relapse or progression in patients who experience treatment failure, he said.
Dr. Hari reported disclosures related to Juno, Kite, Spectrum, Janssen, Takeda, Celgene, and BMS. Several study coauthors reported that they were employed by Lentigen Technology, a Miltenyi Biotec Company.
The meeting was held by the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation and the Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research. At its meeting, the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation announced a new name for the society: American Society for Transplantation and Cellular Therapy (ASTCT).
SOURCE: Shah NN et al. TCT 2019, Abstract 80.
HOUSTON – A dual-targeted, locally manufactured, anti-CD19/CD20 chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy was safe and produced ongoing complete responses in a phase 1 study of heavily pretreated non-Hodgkin lymphoma patients, an investigator reported.
The bispecific CAR T-cell product, designed to limit relapses due to loss of target antigen, was produced at the point of care with a 100% success rate for these heavily pretreated patients, the first of whom has now maintained a complete response for 19 months, said Parameswaran Hari, MD, of the Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee.
“So far, this trial has demonstrated safety for this bispecific vector and suggests a clinical signal, with 7 out of 12 patients with ongoing CR, and with minimal toxicity,” Dr. Hari said at the Transplantation & Cellular Therapy Meetings.
“Point of care delivery, we think, allowed patients to have fresh infusion of CAR T cells, with the avoidance of cryopreservation,” added Dr. Hari, who presented the results on behalf of coinvestigators at the Medical College of Wisconsin and Lentigen Technology.
There was no grade 3 or 4 neurotoxicity or cytokine release syndrome among the 12 patients reported to date in the phase 1, dose-escalation trial, and no patient required intensive care, according to Dr. Hari. Grade 1 and 2 neurotoxicity occurred in two and one patients, respectively, while grade 1 and 2 cytokine release syndrome was observed in three patients each.
Among the 12 patients treated to date, the overall response rate was 81% at day 28, Dr. Hari said, noting that of 6 patients treated at the goal dose of 2.5 x 106 cells/kg, 5 remain in ongoing complete remission.
The median age of patients enrolled in the study was 55 years. Six patients had diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, five had mantle cell lymphoma, and two had chronic lymphocytic leukemia. All but one patient underwent fludarabine/cyclophosphamide lymphodepletion prior to receiving the inpatient CAR T-cell infusions, given over the course of 2 days.
Dr. Hari specifically highlighted the mantle cell lymphoma patient subset, noting that four out of five patients were in complete remission at day 28, and remained in ongoing complete remission at times ranging from 1 to 16 months.
With a set manufacturing time of 14 days, production was successful in all 12 patients, and 10 were able to receive fresh product, while 3 received cryopreserved product due to illness-related delays and a holiday, according to the investigators.
“The time to actual delivery of CAR T cell in the patient is actually shortened dramatically,” Dr. Hari said. “We hope to get it down to day 10.”
Local manufacturing can also reduce some costs associated with CAR T-cell production, such as shipping and courier costs, he added.
Taken together, these findings suggest that locally manufactured anti-CD19/CD20 CAR T cells could improve clinical outcomes for patients with relapsed and refractory B-cell NHL, with efficiency through point-of-care delivery, Dr. Hari concluded.
Further studies are planned to evaluate the efficacy of the product and to investigate the mechanism of relapse or progression in patients who experience treatment failure, he said.
Dr. Hari reported disclosures related to Juno, Kite, Spectrum, Janssen, Takeda, Celgene, and BMS. Several study coauthors reported that they were employed by Lentigen Technology, a Miltenyi Biotec Company.
The meeting was held by the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation and the Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research. At its meeting, the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation announced a new name for the society: American Society for Transplantation and Cellular Therapy (ASTCT).
SOURCE: Shah NN et al. TCT 2019, Abstract 80.
REPORTING FROM TCT 2019
MRD negativity linked to survival in MM after auto-HCT
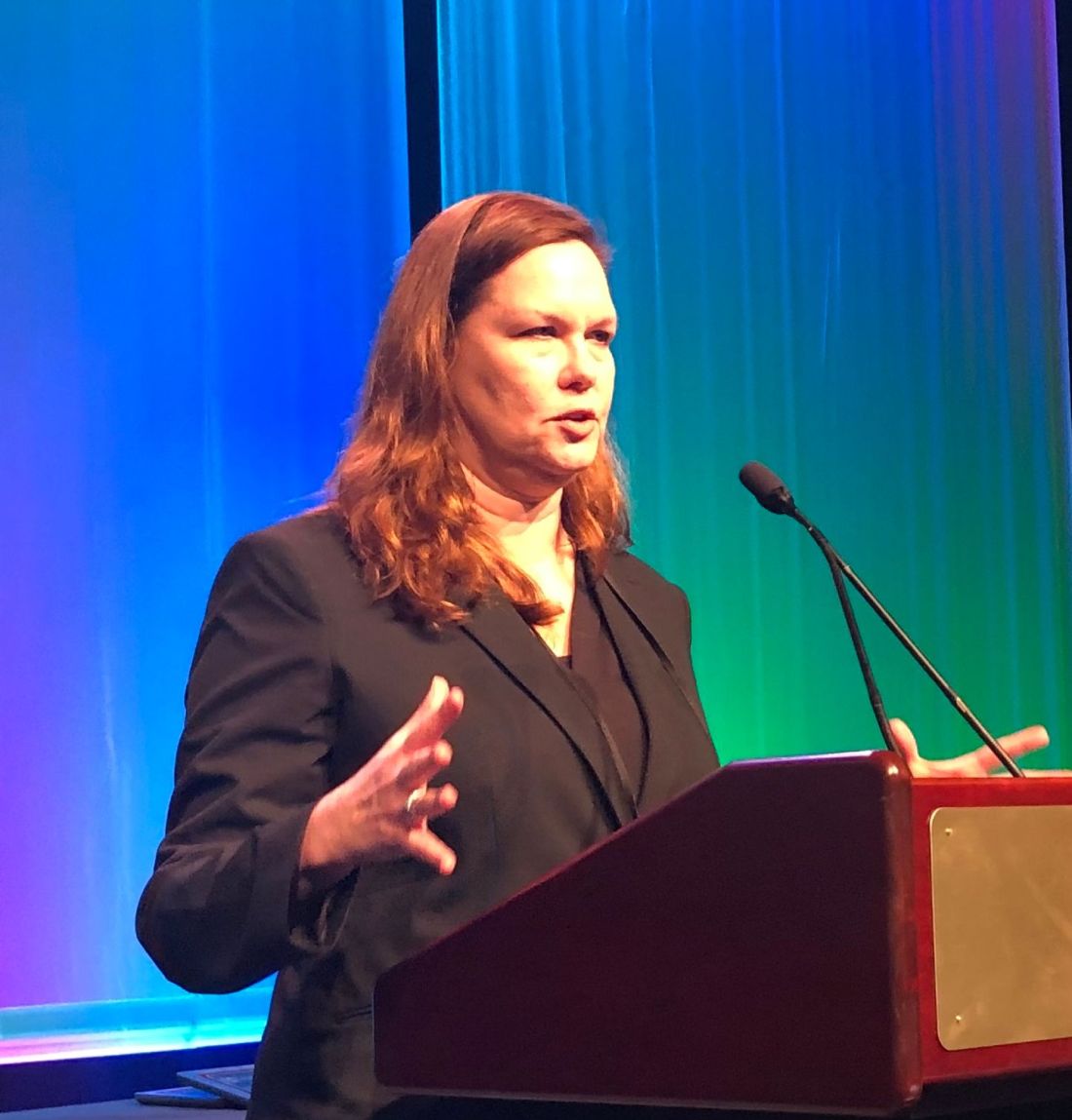
HOUSTON – Minimal residual disease (MRD) negativity by multiparameter flow cytometry was linked to survival benefit in multiple myeloma patients undergoing autologous transplantation, according to results of the first U.S.-based study evaluating this endpoint as part of a national randomized clinical trial.
MRD-negative status was prognostic for improved progression-free survival at all time points measured over the course of 1 year post transplant, in this ancillary study of patients in the randomized, 3-arm STAMiNA trial.
Moreover, there was an overall survival benefit for MRD-negative status at 1 year post transplant, investigator Theresa A. Hahn, PhD, of Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center, Buffalo, N.Y., reported at the Transplantation & Cellular Therapy Meetings.
There was no significant difference in rate of conversion to MRD negativity in the arms of the trial, which evaluated several different upfront approaches to autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HCT).
Assessments of MRD beyond 1 year post transplant may be valuable in future trials, Dr. Hahn said.
“Trials are needed incorporating MRD as an endpoint for treatment decisions to augment, change, or discontinue therapy,” she added.
Results of the ancillary study known as PRIMeR (Prognostic Immunophenotyping for Myeloma Response) included 445 patients from STAMiNA who underwent MRD assessment at baseline, prior to maintenance, and at 1 year post transplantation.
As part of the overall STAMiNA trial, they were randomized to single autologous hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT); autologous HCT followed by a second autologous HCT (tandem autologous HCT); or single autologous HCT followed by four cycles of consolidation with lenalidomide, bortezomib, and dexamethasone (RVD). All three arms continued on lenalidomide maintenance after those interventions.
Overall results of the STAMiNA trial, previously reported, showed no significant differences in progression-free survival or overall survival among the three transplant strategies (J Clin Oncol. 2019 Jan 17. doi: 10.1200/JCO.18.00685).
In this PRIMeR substudy, by contrast, progression-free survival was significantly increased for patients who were MRD negative at all three time points measured, Dr. Hahn reported, while overall survival was significantly improved based on MRD status measured at the 1-year time point.
The rate of MRD negativity did not differ significantly between arms at baseline or premaintenance time points, Dr. Hahn said. Those rates were 42%, 47%, and 40%, respectively, for the single transplant, tandem transplant, and single transplant plus consolidation arms, while the premaintenance MRD negativity rates were 77%, 83%, and 76%.
At 1 year, MRD negativity rates were significantly different between arms, but only in the intent-to-treat analysis.
Most of the difference was due to an increased rate of MRD negativity in the tandem-transplant arm, compared to a single auto-transplant. However, about 30% of patients in the tandem transplant arm did not receive the therapy, so in the analysis by actual treatment received, the rates of MRD negativity were 81% for single transplant, 90% for tandem transplant, and 85% for single transplant plus consolidation (P = 0.2).
Dr. Hahn said she and her colleagues will be updating their analysis of the PRIMeR study to assess the predictive value of MRD status in patients who were negative at all time points evaluated, versus those who converted to MRD negativity at the 1-year analysis.
The MRD assessments used in this trial have been incorporated into the recently completed BMT CTN 1401 trial and the ongoing BMT CTN 1302 study of allogeneic HCT plus ixazomib in high-risk myeloma, she added.
Dr. Hahn reported research funding from Celgene and the National Institutes of Health.
The meeting was held by the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation and the Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research. At its meeting, the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation announced a new name for the society: American Society for Transplantation and Cellular Therapy (ASTCT).
SOURCE: Hahn TE et al. TCT 2019, Abstract 6.
HOUSTON – Minimal residual disease (MRD) negativity by multiparameter flow cytometry was linked to survival benefit in multiple myeloma patients undergoing autologous transplantation, according to results of the first U.S.-based study evaluating this endpoint as part of a national randomized clinical trial.
MRD-negative status was prognostic for improved progression-free survival at all time points measured over the course of 1 year post transplant, in this ancillary study of patients in the randomized, 3-arm STAMiNA trial.
Moreover, there was an overall survival benefit for MRD-negative status at 1 year post transplant, investigator Theresa A. Hahn, PhD, of Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center, Buffalo, N.Y., reported at the Transplantation & Cellular Therapy Meetings.
There was no significant difference in rate of conversion to MRD negativity in the arms of the trial, which evaluated several different upfront approaches to autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HCT).
Assessments of MRD beyond 1 year post transplant may be valuable in future trials, Dr. Hahn said.
“Trials are needed incorporating MRD as an endpoint for treatment decisions to augment, change, or discontinue therapy,” she added.
Results of the ancillary study known as PRIMeR (Prognostic Immunophenotyping for Myeloma Response) included 445 patients from STAMiNA who underwent MRD assessment at baseline, prior to maintenance, and at 1 year post transplantation.
As part of the overall STAMiNA trial, they were randomized to single autologous hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT); autologous HCT followed by a second autologous HCT (tandem autologous HCT); or single autologous HCT followed by four cycles of consolidation with lenalidomide, bortezomib, and dexamethasone (RVD). All three arms continued on lenalidomide maintenance after those interventions.
Overall results of the STAMiNA trial, previously reported, showed no significant differences in progression-free survival or overall survival among the three transplant strategies (J Clin Oncol. 2019 Jan 17. doi: 10.1200/JCO.18.00685).
In this PRIMeR substudy, by contrast, progression-free survival was significantly increased for patients who were MRD negative at all three time points measured, Dr. Hahn reported, while overall survival was significantly improved based on MRD status measured at the 1-year time point.
The rate of MRD negativity did not differ significantly between arms at baseline or premaintenance time points, Dr. Hahn said. Those rates were 42%, 47%, and 40%, respectively, for the single transplant, tandem transplant, and single transplant plus consolidation arms, while the premaintenance MRD negativity rates were 77%, 83%, and 76%.
At 1 year, MRD negativity rates were significantly different between arms, but only in the intent-to-treat analysis.
Most of the difference was due to an increased rate of MRD negativity in the tandem-transplant arm, compared to a single auto-transplant. However, about 30% of patients in the tandem transplant arm did not receive the therapy, so in the analysis by actual treatment received, the rates of MRD negativity were 81% for single transplant, 90% for tandem transplant, and 85% for single transplant plus consolidation (P = 0.2).
Dr. Hahn said she and her colleagues will be updating their analysis of the PRIMeR study to assess the predictive value of MRD status in patients who were negative at all time points evaluated, versus those who converted to MRD negativity at the 1-year analysis.
The MRD assessments used in this trial have been incorporated into the recently completed BMT CTN 1401 trial and the ongoing BMT CTN 1302 study of allogeneic HCT plus ixazomib in high-risk myeloma, she added.
Dr. Hahn reported research funding from Celgene and the National Institutes of Health.
The meeting was held by the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation and the Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research. At its meeting, the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation announced a new name for the society: American Society for Transplantation and Cellular Therapy (ASTCT).
SOURCE: Hahn TE et al. TCT 2019, Abstract 6.
HOUSTON – Minimal residual disease (MRD) negativity by multiparameter flow cytometry was linked to survival benefit in multiple myeloma patients undergoing autologous transplantation, according to results of the first U.S.-based study evaluating this endpoint as part of a national randomized clinical trial.
MRD-negative status was prognostic for improved progression-free survival at all time points measured over the course of 1 year post transplant, in this ancillary study of patients in the randomized, 3-arm STAMiNA trial.
Moreover, there was an overall survival benefit for MRD-negative status at 1 year post transplant, investigator Theresa A. Hahn, PhD, of Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center, Buffalo, N.Y., reported at the Transplantation & Cellular Therapy Meetings.
There was no significant difference in rate of conversion to MRD negativity in the arms of the trial, which evaluated several different upfront approaches to autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HCT).
Assessments of MRD beyond 1 year post transplant may be valuable in future trials, Dr. Hahn said.
“Trials are needed incorporating MRD as an endpoint for treatment decisions to augment, change, or discontinue therapy,” she added.
Results of the ancillary study known as PRIMeR (Prognostic Immunophenotyping for Myeloma Response) included 445 patients from STAMiNA who underwent MRD assessment at baseline, prior to maintenance, and at 1 year post transplantation.
As part of the overall STAMiNA trial, they were randomized to single autologous hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT); autologous HCT followed by a second autologous HCT (tandem autologous HCT); or single autologous HCT followed by four cycles of consolidation with lenalidomide, bortezomib, and dexamethasone (RVD). All three arms continued on lenalidomide maintenance after those interventions.
Overall results of the STAMiNA trial, previously reported, showed no significant differences in progression-free survival or overall survival among the three transplant strategies (J Clin Oncol. 2019 Jan 17. doi: 10.1200/JCO.18.00685).
In this PRIMeR substudy, by contrast, progression-free survival was significantly increased for patients who were MRD negative at all three time points measured, Dr. Hahn reported, while overall survival was significantly improved based on MRD status measured at the 1-year time point.
The rate of MRD negativity did not differ significantly between arms at baseline or premaintenance time points, Dr. Hahn said. Those rates were 42%, 47%, and 40%, respectively, for the single transplant, tandem transplant, and single transplant plus consolidation arms, while the premaintenance MRD negativity rates were 77%, 83%, and 76%.
At 1 year, MRD negativity rates were significantly different between arms, but only in the intent-to-treat analysis.
Most of the difference was due to an increased rate of MRD negativity in the tandem-transplant arm, compared to a single auto-transplant. However, about 30% of patients in the tandem transplant arm did not receive the therapy, so in the analysis by actual treatment received, the rates of MRD negativity were 81% for single transplant, 90% for tandem transplant, and 85% for single transplant plus consolidation (P = 0.2).
Dr. Hahn said she and her colleagues will be updating their analysis of the PRIMeR study to assess the predictive value of MRD status in patients who were negative at all time points evaluated, versus those who converted to MRD negativity at the 1-year analysis.
The MRD assessments used in this trial have been incorporated into the recently completed BMT CTN 1401 trial and the ongoing BMT CTN 1302 study of allogeneic HCT plus ixazomib in high-risk myeloma, she added.
Dr. Hahn reported research funding from Celgene and the National Institutes of Health.
The meeting was held by the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation and the Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research. At its meeting, the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation announced a new name for the society: American Society for Transplantation and Cellular Therapy (ASTCT).
SOURCE: Hahn TE et al. TCT 2019, Abstract 6.
REPORTING FROM TCT 2019
Similar results for once- or twice-weekly carfilzomib in MM
Patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma have similar outcomes whether they receive carfilzomib once or twice a week, according to a pooled analysis of trial data.
Researchers found no significant difference in safety, progression-free survival (PFS), or overall survival (OS) whether patients received carfilzomib at 70 mg/m2 once a week or 36 mg/m2 twice a week.
Sara Bringhen, MD, PhD, of University of Turin, Italy, and her colleagues conducted this analysis and detailed the results in Haematologica.
The researchers pooled data from a phase 1/2 trial (NCT01857115) and a phase 2 trial (NCT01346787), both enrolling transplant-ineligible patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma.
In both studies, induction consisted of nine 4-week cycles of carfilzomib (given once or twice weekly), cyclophosphamide (300 mg on days 1, 8, and 15), and dexamethasone (40 mg on days 1, 8, 15, and 22). After induction, patients received carfilzomib maintenance (at either dose) until progression or intolerable toxicity.
The pooled analysis included 121 patients: 63 who received carfilzomib at 70 mg/m2 once weekly and 58 who received carfilzomib at 36 mg/m2 twice weekly.
There were no significant differences in baseline characteristics between the dosing groups. For the entire cohort, the median age at diagnosis was 72 years (range, 55-86), and the median follow-up was 39 months.
A total of 119 patients started induction (63 in the once-weekly group and 56 in the twice-weekly group), and 90 patients received maintenance (47 and 43, respectively). Patients received maintenance for a median of 17 months in the once-weekly group and 20 months in the twice-weekly group (P = .17).
There was no significant difference between the groups with regard to PFS or OS, either from enrollment or the start of maintenance.
From enrollment, the median PFS was 35.7 months in the once-weekly group and 35.5 months in the twice-weekly group (hazard ratio [HR] = 1.39; P = .26). The 3-year OS was 70% and 72%, respectively (HR = 1.27; P = .5).
From the start of maintenance, the 3-year PFS was 47% in the once-weekly group and 51% in the twice-weekly group (HR = 1.04; P = .92). The 3-year OS was 72% and 73%, respectively (HR = 0.82; P = .71).
There were no significant between-group differences in the rates of grade 3-5 adverse events (AEs) or the need for carfilzomib dose reduction or discontinuation.
Grade 3-5 hematologic AEs occurred in 24% of patients in the once-weekly group and 30% of those in the twice-weekly group. Grade 3-5 nonhematologic AEs occurred in 38% and 41%, respectively.
Twenty-nine percent of patients in the once-weekly group required a reduction in carfilzomib dose, as did 30% of patients in the twice-weekly group. Common AEs leading to dose reduction were acute kidney injury, infections, and hypertension.
AEs leading to carfilzomib discontinuation occurred in 27% of patients in the once-weekly group and 30% of those in the twice-weekly group. Common AEs leading to discontinuation were cardiac injury, infections, and thromboembolism.
Both trials were sponsored by Stichting Hemato-Oncologie voor Volwassenen Nederland in collaboration with Fondazione Neoplasie Sangue ONLUS and supported by funding from Amgen (Onyx Pharmaceuticals). Dr. Bringhen reported relationships with Amgen and other companies. Coauthor Antonio Palumbo, MD, is an employee of Takeda, and other authors reported relationships with a range of companies.
SOURCE: Bringhen S et al. Haematologica. 2019 Feb 7. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2018.208272.
Patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma have similar outcomes whether they receive carfilzomib once or twice a week, according to a pooled analysis of trial data.
Researchers found no significant difference in safety, progression-free survival (PFS), or overall survival (OS) whether patients received carfilzomib at 70 mg/m2 once a week or 36 mg/m2 twice a week.
Sara Bringhen, MD, PhD, of University of Turin, Italy, and her colleagues conducted this analysis and detailed the results in Haematologica.
The researchers pooled data from a phase 1/2 trial (NCT01857115) and a phase 2 trial (NCT01346787), both enrolling transplant-ineligible patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma.
In both studies, induction consisted of nine 4-week cycles of carfilzomib (given once or twice weekly), cyclophosphamide (300 mg on days 1, 8, and 15), and dexamethasone (40 mg on days 1, 8, 15, and 22). After induction, patients received carfilzomib maintenance (at either dose) until progression or intolerable toxicity.
The pooled analysis included 121 patients: 63 who received carfilzomib at 70 mg/m2 once weekly and 58 who received carfilzomib at 36 mg/m2 twice weekly.
There were no significant differences in baseline characteristics between the dosing groups. For the entire cohort, the median age at diagnosis was 72 years (range, 55-86), and the median follow-up was 39 months.
A total of 119 patients started induction (63 in the once-weekly group and 56 in the twice-weekly group), and 90 patients received maintenance (47 and 43, respectively). Patients received maintenance for a median of 17 months in the once-weekly group and 20 months in the twice-weekly group (P = .17).
There was no significant difference between the groups with regard to PFS or OS, either from enrollment or the start of maintenance.
From enrollment, the median PFS was 35.7 months in the once-weekly group and 35.5 months in the twice-weekly group (hazard ratio [HR] = 1.39; P = .26). The 3-year OS was 70% and 72%, respectively (HR = 1.27; P = .5).
From the start of maintenance, the 3-year PFS was 47% in the once-weekly group and 51% in the twice-weekly group (HR = 1.04; P = .92). The 3-year OS was 72% and 73%, respectively (HR = 0.82; P = .71).
There were no significant between-group differences in the rates of grade 3-5 adverse events (AEs) or the need for carfilzomib dose reduction or discontinuation.
Grade 3-5 hematologic AEs occurred in 24% of patients in the once-weekly group and 30% of those in the twice-weekly group. Grade 3-5 nonhematologic AEs occurred in 38% and 41%, respectively.
Twenty-nine percent of patients in the once-weekly group required a reduction in carfilzomib dose, as did 30% of patients in the twice-weekly group. Common AEs leading to dose reduction were acute kidney injury, infections, and hypertension.
AEs leading to carfilzomib discontinuation occurred in 27% of patients in the once-weekly group and 30% of those in the twice-weekly group. Common AEs leading to discontinuation were cardiac injury, infections, and thromboembolism.
Both trials were sponsored by Stichting Hemato-Oncologie voor Volwassenen Nederland in collaboration with Fondazione Neoplasie Sangue ONLUS and supported by funding from Amgen (Onyx Pharmaceuticals). Dr. Bringhen reported relationships with Amgen and other companies. Coauthor Antonio Palumbo, MD, is an employee of Takeda, and other authors reported relationships with a range of companies.
SOURCE: Bringhen S et al. Haematologica. 2019 Feb 7. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2018.208272.
Patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma have similar outcomes whether they receive carfilzomib once or twice a week, according to a pooled analysis of trial data.
Researchers found no significant difference in safety, progression-free survival (PFS), or overall survival (OS) whether patients received carfilzomib at 70 mg/m2 once a week or 36 mg/m2 twice a week.
Sara Bringhen, MD, PhD, of University of Turin, Italy, and her colleagues conducted this analysis and detailed the results in Haematologica.
The researchers pooled data from a phase 1/2 trial (NCT01857115) and a phase 2 trial (NCT01346787), both enrolling transplant-ineligible patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma.
In both studies, induction consisted of nine 4-week cycles of carfilzomib (given once or twice weekly), cyclophosphamide (300 mg on days 1, 8, and 15), and dexamethasone (40 mg on days 1, 8, 15, and 22). After induction, patients received carfilzomib maintenance (at either dose) until progression or intolerable toxicity.
The pooled analysis included 121 patients: 63 who received carfilzomib at 70 mg/m2 once weekly and 58 who received carfilzomib at 36 mg/m2 twice weekly.
There were no significant differences in baseline characteristics between the dosing groups. For the entire cohort, the median age at diagnosis was 72 years (range, 55-86), and the median follow-up was 39 months.
A total of 119 patients started induction (63 in the once-weekly group and 56 in the twice-weekly group), and 90 patients received maintenance (47 and 43, respectively). Patients received maintenance for a median of 17 months in the once-weekly group and 20 months in the twice-weekly group (P = .17).
There was no significant difference between the groups with regard to PFS or OS, either from enrollment or the start of maintenance.
From enrollment, the median PFS was 35.7 months in the once-weekly group and 35.5 months in the twice-weekly group (hazard ratio [HR] = 1.39; P = .26). The 3-year OS was 70% and 72%, respectively (HR = 1.27; P = .5).
From the start of maintenance, the 3-year PFS was 47% in the once-weekly group and 51% in the twice-weekly group (HR = 1.04; P = .92). The 3-year OS was 72% and 73%, respectively (HR = 0.82; P = .71).
There were no significant between-group differences in the rates of grade 3-5 adverse events (AEs) or the need for carfilzomib dose reduction or discontinuation.
Grade 3-5 hematologic AEs occurred in 24% of patients in the once-weekly group and 30% of those in the twice-weekly group. Grade 3-5 nonhematologic AEs occurred in 38% and 41%, respectively.
Twenty-nine percent of patients in the once-weekly group required a reduction in carfilzomib dose, as did 30% of patients in the twice-weekly group. Common AEs leading to dose reduction were acute kidney injury, infections, and hypertension.
AEs leading to carfilzomib discontinuation occurred in 27% of patients in the once-weekly group and 30% of those in the twice-weekly group. Common AEs leading to discontinuation were cardiac injury, infections, and thromboembolism.
Both trials were sponsored by Stichting Hemato-Oncologie voor Volwassenen Nederland in collaboration with Fondazione Neoplasie Sangue ONLUS and supported by funding from Amgen (Onyx Pharmaceuticals). Dr. Bringhen reported relationships with Amgen and other companies. Coauthor Antonio Palumbo, MD, is an employee of Takeda, and other authors reported relationships with a range of companies.
SOURCE: Bringhen S et al. Haematologica. 2019 Feb 7. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2018.208272.
FROM HAEMATOLOGICA
Alisertib response rate in PTCL patients was 33%
An open-label randomized phase 3 trial of oral alisertib for relapsed/refractory peripheral T-cell lymphoma (rrPTCL) was terminated in 2015 after it became clear that it was not going to prove significantly superior to options already on the market.
A new report explains what happened. Oral Alisertib was compared to two agents approved for rrPTCL: intravenous pralatrexate (Folotyn) and romidepsin (Istodax), as well as a common off-label option, intravenous gemcitabine (Gemzar). In all, 138 adults were randomized to alisertib 50 mg two times per day on days 1-7, with a median of four 21-day cycles; 133 were randomized to a comparator, the majority to gemcitabine, and again with repeated cycles as tolerated (J Clin Oncol. 2019 Feb 1. doi: 10.1200/JCO.18.00899).
Overall response rate (ORR) was 33% for alisertib versus 45% for the comparator arm (odds ratio, 0.60; 95% confidence interval, 0.33-1.08). Median progression-free survival was 115 days for alisertib versus 104 days for the comparators, a non–statistically significant difference (hazard ratio, 0.87; 95% CI, 0.637-1.178). Median overall survival was 415 days in the alisertib arm versus 367 days in the comparator arm, also not statistically significant (HR, 0.98; 95% CI, 0.707-1.369).
In patients with rrPTCL, alisertib “did not demonstrate superior efficacy over comparators,” concluded investigators led by oncologist Owen A. O’Connor, MD, PhD, of the Columbia University Medical Center, New York.
Another downside to this drug is that it was associated with adverse events in more than half of patients who took it. While 53% of alisertib patients developed anemia and 47% became neutropenic, in the comparator arm, only 34% and 31% developed anemia and neutropenia, respectively. Further, three deaths in the trial were judged to have be related to alisertib. An additional two deaths occurred in this trial; those were judged to have been related to the rival treatments.
Despite alisertib’s less than great results, the story of this drug’s use for rrPTCL may not be over.
There were hints of benefits for rrPCLT, which might play out in a more focused trial, maybe “in a subgroup of patients with PTCL who responded poorly to comparator agents,” perhaps as a last ditch option. There’s also “potential for treatment combinations of alisertib with novel agents,” the investigators said.
The ORR differences were driven mostly by better performance with the approved agents: ORR was 61% with romidepsin and 43% with pralatrexate; however, alisertib’s ORR (33%) was similar to that for gemcitabine (35%) with “the potential benefits of ... oral administration,” the researchers said.
Also, the number of patients who discontinued treatment because of adverse events was higher in the comparator arm (14%) than in the alisertib group (9%), and more comparator patients required dose reductions (33% versus 28%) because of drug side effects.
Alisertib binds to and inhibits Aurora A kinase (AAK), which is essential for mitosis; studies have demonstrated overexpression in PTCL, which supports AAK inhibition as a novel therapeutic strategy. Research on alisertib for other cancer indications continues, including breast and lung cancer and leukemia.
Most of the subjects in both study arms were white, and about two-thirds were men; the median age was 63 years in both arms.
The work was funded by alisertib maker Millennium Pharmaceuticals, a subsidiary of Takeda. Dr. O’Connor and other investigators reported various ties to Millennium and Takeda, including research funding, honoraria, and consulting work. The study included employees of the companies.
SOURCE: O’Connor OA et al. J Clin Oncol. 2019 Feb 1. doi: 10.1200/JCO.18.00899.
An open-label randomized phase 3 trial of oral alisertib for relapsed/refractory peripheral T-cell lymphoma (rrPTCL) was terminated in 2015 after it became clear that it was not going to prove significantly superior to options already on the market.
A new report explains what happened. Oral Alisertib was compared to two agents approved for rrPTCL: intravenous pralatrexate (Folotyn) and romidepsin (Istodax), as well as a common off-label option, intravenous gemcitabine (Gemzar). In all, 138 adults were randomized to alisertib 50 mg two times per day on days 1-7, with a median of four 21-day cycles; 133 were randomized to a comparator, the majority to gemcitabine, and again with repeated cycles as tolerated (J Clin Oncol. 2019 Feb 1. doi: 10.1200/JCO.18.00899).
Overall response rate (ORR) was 33% for alisertib versus 45% for the comparator arm (odds ratio, 0.60; 95% confidence interval, 0.33-1.08). Median progression-free survival was 115 days for alisertib versus 104 days for the comparators, a non–statistically significant difference (hazard ratio, 0.87; 95% CI, 0.637-1.178). Median overall survival was 415 days in the alisertib arm versus 367 days in the comparator arm, also not statistically significant (HR, 0.98; 95% CI, 0.707-1.369).
In patients with rrPTCL, alisertib “did not demonstrate superior efficacy over comparators,” concluded investigators led by oncologist Owen A. O’Connor, MD, PhD, of the Columbia University Medical Center, New York.
Another downside to this drug is that it was associated with adverse events in more than half of patients who took it. While 53% of alisertib patients developed anemia and 47% became neutropenic, in the comparator arm, only 34% and 31% developed anemia and neutropenia, respectively. Further, three deaths in the trial were judged to have be related to alisertib. An additional two deaths occurred in this trial; those were judged to have been related to the rival treatments.
Despite alisertib’s less than great results, the story of this drug’s use for rrPTCL may not be over.
There were hints of benefits for rrPCLT, which might play out in a more focused trial, maybe “in a subgroup of patients with PTCL who responded poorly to comparator agents,” perhaps as a last ditch option. There’s also “potential for treatment combinations of alisertib with novel agents,” the investigators said.
The ORR differences were driven mostly by better performance with the approved agents: ORR was 61% with romidepsin and 43% with pralatrexate; however, alisertib’s ORR (33%) was similar to that for gemcitabine (35%) with “the potential benefits of ... oral administration,” the researchers said.
Also, the number of patients who discontinued treatment because of adverse events was higher in the comparator arm (14%) than in the alisertib group (9%), and more comparator patients required dose reductions (33% versus 28%) because of drug side effects.
Alisertib binds to and inhibits Aurora A kinase (AAK), which is essential for mitosis; studies have demonstrated overexpression in PTCL, which supports AAK inhibition as a novel therapeutic strategy. Research on alisertib for other cancer indications continues, including breast and lung cancer and leukemia.
Most of the subjects in both study arms were white, and about two-thirds were men; the median age was 63 years in both arms.
The work was funded by alisertib maker Millennium Pharmaceuticals, a subsidiary of Takeda. Dr. O’Connor and other investigators reported various ties to Millennium and Takeda, including research funding, honoraria, and consulting work. The study included employees of the companies.
SOURCE: O’Connor OA et al. J Clin Oncol. 2019 Feb 1. doi: 10.1200/JCO.18.00899.
An open-label randomized phase 3 trial of oral alisertib for relapsed/refractory peripheral T-cell lymphoma (rrPTCL) was terminated in 2015 after it became clear that it was not going to prove significantly superior to options already on the market.
A new report explains what happened. Oral Alisertib was compared to two agents approved for rrPTCL: intravenous pralatrexate (Folotyn) and romidepsin (Istodax), as well as a common off-label option, intravenous gemcitabine (Gemzar). In all, 138 adults were randomized to alisertib 50 mg two times per day on days 1-7, with a median of four 21-day cycles; 133 were randomized to a comparator, the majority to gemcitabine, and again with repeated cycles as tolerated (J Clin Oncol. 2019 Feb 1. doi: 10.1200/JCO.18.00899).
Overall response rate (ORR) was 33% for alisertib versus 45% for the comparator arm (odds ratio, 0.60; 95% confidence interval, 0.33-1.08). Median progression-free survival was 115 days for alisertib versus 104 days for the comparators, a non–statistically significant difference (hazard ratio, 0.87; 95% CI, 0.637-1.178). Median overall survival was 415 days in the alisertib arm versus 367 days in the comparator arm, also not statistically significant (HR, 0.98; 95% CI, 0.707-1.369).
In patients with rrPTCL, alisertib “did not demonstrate superior efficacy over comparators,” concluded investigators led by oncologist Owen A. O’Connor, MD, PhD, of the Columbia University Medical Center, New York.
Another downside to this drug is that it was associated with adverse events in more than half of patients who took it. While 53% of alisertib patients developed anemia and 47% became neutropenic, in the comparator arm, only 34% and 31% developed anemia and neutropenia, respectively. Further, three deaths in the trial were judged to have be related to alisertib. An additional two deaths occurred in this trial; those were judged to have been related to the rival treatments.
Despite alisertib’s less than great results, the story of this drug’s use for rrPTCL may not be over.
There were hints of benefits for rrPCLT, which might play out in a more focused trial, maybe “in a subgroup of patients with PTCL who responded poorly to comparator agents,” perhaps as a last ditch option. There’s also “potential for treatment combinations of alisertib with novel agents,” the investigators said.
The ORR differences were driven mostly by better performance with the approved agents: ORR was 61% with romidepsin and 43% with pralatrexate; however, alisertib’s ORR (33%) was similar to that for gemcitabine (35%) with “the potential benefits of ... oral administration,” the researchers said.
Also, the number of patients who discontinued treatment because of adverse events was higher in the comparator arm (14%) than in the alisertib group (9%), and more comparator patients required dose reductions (33% versus 28%) because of drug side effects.
Alisertib binds to and inhibits Aurora A kinase (AAK), which is essential for mitosis; studies have demonstrated overexpression in PTCL, which supports AAK inhibition as a novel therapeutic strategy. Research on alisertib for other cancer indications continues, including breast and lung cancer and leukemia.
Most of the subjects in both study arms were white, and about two-thirds were men; the median age was 63 years in both arms.
The work was funded by alisertib maker Millennium Pharmaceuticals, a subsidiary of Takeda. Dr. O’Connor and other investigators reported various ties to Millennium and Takeda, including research funding, honoraria, and consulting work. The study included employees of the companies.
SOURCE: O’Connor OA et al. J Clin Oncol. 2019 Feb 1. doi: 10.1200/JCO.18.00899.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL ONCOLOGY
Regimen shows promise as salvage for classical HL
A retrospective study suggests a four-drug regimen can be effective salvage therapy for patients with relapsed or refractory classical Hodgkin lymphoma.
The regimen – brentuximab vedotin plus ifosfamide, gemcitabine, and vinorelbine (BV-IGEV) – produced responses in 27 of 28 patients studied, allowing them to undergo autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT).
After HSCT, the estimated 2-year progression-free survival (PFS) was 87.1% and the overall survival (OS) was 73.5%.
Though this study was limited by its small population and retrospective nature, the results “warrant further investigation,” according to Khadega A. Abuelgasim, MD, of King Abdullah International Medical Research Center in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, and colleagues.
The researchers reported the results in a letter to Bone Marrow Transplantation.
The study included 28 patients with classical Hodgkin lymphoma, 15 of them male. The patients’ median age at HSCT was 25 years (range, 15-49 years). Twenty patients (71%) had constitutional symptoms at diagnosis, and eight (29%) had bulky disease.
Twenty-three patients (82%) received doxorubicin, bleomycin, vinblastine, and dacarbazine (ABVD) as frontline therapy, and four (14%) received ABVD followed by escalated bleomycin, etoposide, doxorubicin, cyclophosphamide, vincristine, procarbazine, and prednisone. One patient received a different frontline regimen.
The median time to relapse was 7.9 months (range, 1.9-133 months), and 12 patients (43%) were refractory to frontline treatment.
Half of patients (n = 14) received BV-IGEV as first salvage. The regimen was given as follows: ifosfamide at 2,000 mg/m2 on days 1-4, gemcitabine at 800 mg/m2 on days 1 and 4, vinorelbine at 20 mg/m2 on day 1, prednisolone at 100 mg on days 1-4, and BV at a dose of 1.8 mg/kg on day 1 of each 3-week IGEV course.
All patients received at least two cycles of BV-IGEV and were assessed for response after one or two cycles. The median follow-up was 17 months (range, 0-65 months).
Twenty patients (71%) had a complete metabolic response to BV-IGEV, seven (25%) had a partial metabolic response, and one patient (4%) had stable disease. The patient with stable disease went on to receive another salvage regimen and achieved a partial response to that regimen.
The most common adverse events during BV-IGEV treatment were grade 3-4 neutropenia (n = 27; 96%) and thrombocytopenia (n = 25; 89%). Febrile neutropenia was also common (n = 16; 57%), as were mucositis (n = 6; 21%) and diarrhea (n = 6; 21%). Six patients had a reduction in BV dose because of an adverse event.
All patients underwent autologous HSCT. They received carmustine, etoposide, cytarabine, and melphalan as conditioning beforehand, and 18 patients (64%) received consolidative BV after transplant.
PFS and OS were calculated from the date of stem cell infusion. The estimated 2-year PFS was 87.1%, and the estimated 2-year OS was 73.5%.
Patients who received BV-IGEV as first salvage fared better than those who received the regimen as second salvage. The PFS rates were 100% and 75%, respectively (P = .0078), and OS rates were 100% and 50%, respectively (P = .08).
Six patients relapsed after HSCT, and three died. Two patients died of progressive disease and one died of pulmonary infection.
These results suggest BV-IGEV can produce high response rates without compromising stem cell mobilization, but the combination should be investigated further, according to the researchers.
The researchers reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Abuelgasim KA et al. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2019 Jan 30. doi: 10.1038/s41409-019-0454-z.
A retrospective study suggests a four-drug regimen can be effective salvage therapy for patients with relapsed or refractory classical Hodgkin lymphoma.
The regimen – brentuximab vedotin plus ifosfamide, gemcitabine, and vinorelbine (BV-IGEV) – produced responses in 27 of 28 patients studied, allowing them to undergo autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT).
After HSCT, the estimated 2-year progression-free survival (PFS) was 87.1% and the overall survival (OS) was 73.5%.
Though this study was limited by its small population and retrospective nature, the results “warrant further investigation,” according to Khadega A. Abuelgasim, MD, of King Abdullah International Medical Research Center in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, and colleagues.
The researchers reported the results in a letter to Bone Marrow Transplantation.
The study included 28 patients with classical Hodgkin lymphoma, 15 of them male. The patients’ median age at HSCT was 25 years (range, 15-49 years). Twenty patients (71%) had constitutional symptoms at diagnosis, and eight (29%) had bulky disease.
Twenty-three patients (82%) received doxorubicin, bleomycin, vinblastine, and dacarbazine (ABVD) as frontline therapy, and four (14%) received ABVD followed by escalated bleomycin, etoposide, doxorubicin, cyclophosphamide, vincristine, procarbazine, and prednisone. One patient received a different frontline regimen.
The median time to relapse was 7.9 months (range, 1.9-133 months), and 12 patients (43%) were refractory to frontline treatment.
Half of patients (n = 14) received BV-IGEV as first salvage. The regimen was given as follows: ifosfamide at 2,000 mg/m2 on days 1-4, gemcitabine at 800 mg/m2 on days 1 and 4, vinorelbine at 20 mg/m2 on day 1, prednisolone at 100 mg on days 1-4, and BV at a dose of 1.8 mg/kg on day 1 of each 3-week IGEV course.
All patients received at least two cycles of BV-IGEV and were assessed for response after one or two cycles. The median follow-up was 17 months (range, 0-65 months).
Twenty patients (71%) had a complete metabolic response to BV-IGEV, seven (25%) had a partial metabolic response, and one patient (4%) had stable disease. The patient with stable disease went on to receive another salvage regimen and achieved a partial response to that regimen.
The most common adverse events during BV-IGEV treatment were grade 3-4 neutropenia (n = 27; 96%) and thrombocytopenia (n = 25; 89%). Febrile neutropenia was also common (n = 16; 57%), as were mucositis (n = 6; 21%) and diarrhea (n = 6; 21%). Six patients had a reduction in BV dose because of an adverse event.
All patients underwent autologous HSCT. They received carmustine, etoposide, cytarabine, and melphalan as conditioning beforehand, and 18 patients (64%) received consolidative BV after transplant.
PFS and OS were calculated from the date of stem cell infusion. The estimated 2-year PFS was 87.1%, and the estimated 2-year OS was 73.5%.
Patients who received BV-IGEV as first salvage fared better than those who received the regimen as second salvage. The PFS rates were 100% and 75%, respectively (P = .0078), and OS rates were 100% and 50%, respectively (P = .08).
Six patients relapsed after HSCT, and three died. Two patients died of progressive disease and one died of pulmonary infection.
These results suggest BV-IGEV can produce high response rates without compromising stem cell mobilization, but the combination should be investigated further, according to the researchers.
The researchers reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Abuelgasim KA et al. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2019 Jan 30. doi: 10.1038/s41409-019-0454-z.
A retrospective study suggests a four-drug regimen can be effective salvage therapy for patients with relapsed or refractory classical Hodgkin lymphoma.
The regimen – brentuximab vedotin plus ifosfamide, gemcitabine, and vinorelbine (BV-IGEV) – produced responses in 27 of 28 patients studied, allowing them to undergo autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT).
After HSCT, the estimated 2-year progression-free survival (PFS) was 87.1% and the overall survival (OS) was 73.5%.
Though this study was limited by its small population and retrospective nature, the results “warrant further investigation,” according to Khadega A. Abuelgasim, MD, of King Abdullah International Medical Research Center in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, and colleagues.
The researchers reported the results in a letter to Bone Marrow Transplantation.
The study included 28 patients with classical Hodgkin lymphoma, 15 of them male. The patients’ median age at HSCT was 25 years (range, 15-49 years). Twenty patients (71%) had constitutional symptoms at diagnosis, and eight (29%) had bulky disease.
Twenty-three patients (82%) received doxorubicin, bleomycin, vinblastine, and dacarbazine (ABVD) as frontline therapy, and four (14%) received ABVD followed by escalated bleomycin, etoposide, doxorubicin, cyclophosphamide, vincristine, procarbazine, and prednisone. One patient received a different frontline regimen.
The median time to relapse was 7.9 months (range, 1.9-133 months), and 12 patients (43%) were refractory to frontline treatment.
Half of patients (n = 14) received BV-IGEV as first salvage. The regimen was given as follows: ifosfamide at 2,000 mg/m2 on days 1-4, gemcitabine at 800 mg/m2 on days 1 and 4, vinorelbine at 20 mg/m2 on day 1, prednisolone at 100 mg on days 1-4, and BV at a dose of 1.8 mg/kg on day 1 of each 3-week IGEV course.
All patients received at least two cycles of BV-IGEV and were assessed for response after one or two cycles. The median follow-up was 17 months (range, 0-65 months).
Twenty patients (71%) had a complete metabolic response to BV-IGEV, seven (25%) had a partial metabolic response, and one patient (4%) had stable disease. The patient with stable disease went on to receive another salvage regimen and achieved a partial response to that regimen.
The most common adverse events during BV-IGEV treatment were grade 3-4 neutropenia (n = 27; 96%) and thrombocytopenia (n = 25; 89%). Febrile neutropenia was also common (n = 16; 57%), as were mucositis (n = 6; 21%) and diarrhea (n = 6; 21%). Six patients had a reduction in BV dose because of an adverse event.
All patients underwent autologous HSCT. They received carmustine, etoposide, cytarabine, and melphalan as conditioning beforehand, and 18 patients (64%) received consolidative BV after transplant.
PFS and OS were calculated from the date of stem cell infusion. The estimated 2-year PFS was 87.1%, and the estimated 2-year OS was 73.5%.
Patients who received BV-IGEV as first salvage fared better than those who received the regimen as second salvage. The PFS rates were 100% and 75%, respectively (P = .0078), and OS rates were 100% and 50%, respectively (P = .08).
Six patients relapsed after HSCT, and three died. Two patients died of progressive disease and one died of pulmonary infection.
These results suggest BV-IGEV can produce high response rates without compromising stem cell mobilization, but the combination should be investigated further, according to the researchers.
The researchers reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Abuelgasim KA et al. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2019 Jan 30. doi: 10.1038/s41409-019-0454-z.
FROM BONE MARROW TRANSPLANTATION
Haplo-HCT shows viability in DLBCL
For patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) who need allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (allo-HCT), a haploidentical family member could be a viable donor, according to a retrospective study of 1,438 patients.
When combined with nonmyeloablative/reduced intensity conditioning (NMC/RIC) and posttransplant cyclophosphamide (PTCy), patients treated with haploidentical HCT (haplo-HCT) had outcomes similar to those seen in patients with matched donors, reported Peter Dreger, MD, of the University of Heidelberg (Germany) and his colleagues.
“Using well-matched sibling donors (MSDs) or unrelated donors (MUDs), allo-HCT can result in sustained disease control in 30% to 45% of patients with DLBCL who have early disease recurrence after standard chemoimmunotherapy or have failed auto-HCT [autologous HCT],” the investigators wrote in Blood Advances. “However, the search for a well-matched unrelated donor could be time-consuming and unsuccessful in up to 50% of the patients in need.”
But the present findings suggest that haplo-HCT may one day improve these odds by providing a larger pool of potential donors.
The patients in the study were divided into four treatment groups: haplo-HCT (n = 132), MSD (n = 525), MUD with T-cell depletion (n = 403), and MUD without T-cell depletion (n = 378). For graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) prophylaxis, patients in the haplo-HCT group received PTCy, with or without a calcineurin inhibitor and mycophenolate mofetil, whereas all patients with matched donors received a calcineurin inhibitor. T-cell depletion was accomplished by in vivo antithymocyte globulin and alemtuzumab.
The primary end point was overall survival (OS). Secondary end points were progression-free survival (PFS), progression/relapse, and nonrelapse mortality (NRM).
After a median follow-up of 4.1 years, all groups had similar outcomes, without statistical differences in multivariable analysis.
In the haplo-HCT group, the 3-year OS rate was 46%, the NRM rate was 22%, the PFS rate was 38%, and the relapse/progression rate was 41%.
Of note, patients receiving haplo-HCT did have a lower cumulative incidence of chronic GVHD, at 15% after 1 year and 18% after 2 years. These rates were significantly lower than the other groups’ 1- and 2-year GVHD rates, which were as follows: MSD, 41% and 48%; MUD with T-cell depletion, 23% and 27%; and MUD without T-cell depletion, 48% and 57%.
The investigators noted that these disparities may actually be caused by the use of bone marrow grafts in the haplo-HCT group instead of peripheral blood grafts, which were used in most of the patients in the other groups.
Overall, the findings were encouraging, but the investigators cautioned that “additional studies are needed before haploidentical donors can be considered as equivalent to well-matched related or unrelated donors in patients with DLBCL.”
The study was funded by the Center for International Blood & Marrow Transplant Research (CIBMTR) and the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. CIBMTR is supported by grants from the U.S. government and the pharmaceutical industry. The authors reported having no competing financial interests.
SOURCE: Dreger P et al. Blood Adv. 2019 Feb 12;3(3):360-9.
For patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) who need allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (allo-HCT), a haploidentical family member could be a viable donor, according to a retrospective study of 1,438 patients.
When combined with nonmyeloablative/reduced intensity conditioning (NMC/RIC) and posttransplant cyclophosphamide (PTCy), patients treated with haploidentical HCT (haplo-HCT) had outcomes similar to those seen in patients with matched donors, reported Peter Dreger, MD, of the University of Heidelberg (Germany) and his colleagues.
“Using well-matched sibling donors (MSDs) or unrelated donors (MUDs), allo-HCT can result in sustained disease control in 30% to 45% of patients with DLBCL who have early disease recurrence after standard chemoimmunotherapy or have failed auto-HCT [autologous HCT],” the investigators wrote in Blood Advances. “However, the search for a well-matched unrelated donor could be time-consuming and unsuccessful in up to 50% of the patients in need.”
But the present findings suggest that haplo-HCT may one day improve these odds by providing a larger pool of potential donors.
The patients in the study were divided into four treatment groups: haplo-HCT (n = 132), MSD (n = 525), MUD with T-cell depletion (n = 403), and MUD without T-cell depletion (n = 378). For graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) prophylaxis, patients in the haplo-HCT group received PTCy, with or without a calcineurin inhibitor and mycophenolate mofetil, whereas all patients with matched donors received a calcineurin inhibitor. T-cell depletion was accomplished by in vivo antithymocyte globulin and alemtuzumab.
The primary end point was overall survival (OS). Secondary end points were progression-free survival (PFS), progression/relapse, and nonrelapse mortality (NRM).
After a median follow-up of 4.1 years, all groups had similar outcomes, without statistical differences in multivariable analysis.
In the haplo-HCT group, the 3-year OS rate was 46%, the NRM rate was 22%, the PFS rate was 38%, and the relapse/progression rate was 41%.
Of note, patients receiving haplo-HCT did have a lower cumulative incidence of chronic GVHD, at 15% after 1 year and 18% after 2 years. These rates were significantly lower than the other groups’ 1- and 2-year GVHD rates, which were as follows: MSD, 41% and 48%; MUD with T-cell depletion, 23% and 27%; and MUD without T-cell depletion, 48% and 57%.
The investigators noted that these disparities may actually be caused by the use of bone marrow grafts in the haplo-HCT group instead of peripheral blood grafts, which were used in most of the patients in the other groups.
Overall, the findings were encouraging, but the investigators cautioned that “additional studies are needed before haploidentical donors can be considered as equivalent to well-matched related or unrelated donors in patients with DLBCL.”
The study was funded by the Center for International Blood & Marrow Transplant Research (CIBMTR) and the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. CIBMTR is supported by grants from the U.S. government and the pharmaceutical industry. The authors reported having no competing financial interests.
SOURCE: Dreger P et al. Blood Adv. 2019 Feb 12;3(3):360-9.
For patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) who need allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (allo-HCT), a haploidentical family member could be a viable donor, according to a retrospective study of 1,438 patients.
When combined with nonmyeloablative/reduced intensity conditioning (NMC/RIC) and posttransplant cyclophosphamide (PTCy), patients treated with haploidentical HCT (haplo-HCT) had outcomes similar to those seen in patients with matched donors, reported Peter Dreger, MD, of the University of Heidelberg (Germany) and his colleagues.
“Using well-matched sibling donors (MSDs) or unrelated donors (MUDs), allo-HCT can result in sustained disease control in 30% to 45% of patients with DLBCL who have early disease recurrence after standard chemoimmunotherapy or have failed auto-HCT [autologous HCT],” the investigators wrote in Blood Advances. “However, the search for a well-matched unrelated donor could be time-consuming and unsuccessful in up to 50% of the patients in need.”
But the present findings suggest that haplo-HCT may one day improve these odds by providing a larger pool of potential donors.
The patients in the study were divided into four treatment groups: haplo-HCT (n = 132), MSD (n = 525), MUD with T-cell depletion (n = 403), and MUD without T-cell depletion (n = 378). For graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) prophylaxis, patients in the haplo-HCT group received PTCy, with or without a calcineurin inhibitor and mycophenolate mofetil, whereas all patients with matched donors received a calcineurin inhibitor. T-cell depletion was accomplished by in vivo antithymocyte globulin and alemtuzumab.
The primary end point was overall survival (OS). Secondary end points were progression-free survival (PFS), progression/relapse, and nonrelapse mortality (NRM).
After a median follow-up of 4.1 years, all groups had similar outcomes, without statistical differences in multivariable analysis.
In the haplo-HCT group, the 3-year OS rate was 46%, the NRM rate was 22%, the PFS rate was 38%, and the relapse/progression rate was 41%.
Of note, patients receiving haplo-HCT did have a lower cumulative incidence of chronic GVHD, at 15% after 1 year and 18% after 2 years. These rates were significantly lower than the other groups’ 1- and 2-year GVHD rates, which were as follows: MSD, 41% and 48%; MUD with T-cell depletion, 23% and 27%; and MUD without T-cell depletion, 48% and 57%.
The investigators noted that these disparities may actually be caused by the use of bone marrow grafts in the haplo-HCT group instead of peripheral blood grafts, which were used in most of the patients in the other groups.
Overall, the findings were encouraging, but the investigators cautioned that “additional studies are needed before haploidentical donors can be considered as equivalent to well-matched related or unrelated donors in patients with DLBCL.”
The study was funded by the Center for International Blood & Marrow Transplant Research (CIBMTR) and the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. CIBMTR is supported by grants from the U.S. government and the pharmaceutical industry. The authors reported having no competing financial interests.
SOURCE: Dreger P et al. Blood Adv. 2019 Feb 12;3(3):360-9.
FROM BLOOD ADVANCES
FDA grants priority review to polatuzumab vedotin for DLBCL
With this BLA, Genentech is seeking approval for polatuzumab vedotin in combination with bendamustine and rituximab (BR) to treat patients with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
The FDA grants priority review to applications for products that are expected to provide significant improvements in the treatment, diagnosis, or prevention of serious conditions. The agency aims to take action on a priority review application within 6 months, rather than the standard 10 months.
The FDA is expected to make a decision on this BLA by Aug. 19, 2019.
The BLA is supported by a phase 1b/2 trial (NCT02257567) of patients with relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma or DLBCL who received polatuzumab vedotin in combination with BR or obinutuzumab.
The trial’s phase 2 stage included 80 DLBCL patients who were randomized to receive BR or BR plus polatuzumab vedotin, according to Genentech.
The complete response rate was 40% in the polatuzumab vedotin arm and 18% in the BR arm. The median duration of response was 10.3 months and 4.1 months, respectively (hazard ratio [HR] = 0.44).
The median progression-free survival was 7.6 months in the polatuzumab vedotin arm and 2.0 months in the BR arm (HR = 0.34).
Among patients who were ineligible for a transplant, the median overall survival (an exploratory endpoint) was 12.4 months in the polatuzumab vedotin arm and 4.7 months in the BR arm (HR = 0.42).
Patients who received polatuzumab vedotin had higher rates of grade 3-4 cytopenias, compared with patients who received BR alone. Rates of infection and transfusion were similar between the arms.
With this BLA, Genentech is seeking approval for polatuzumab vedotin in combination with bendamustine and rituximab (BR) to treat patients with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
The FDA grants priority review to applications for products that are expected to provide significant improvements in the treatment, diagnosis, or prevention of serious conditions. The agency aims to take action on a priority review application within 6 months, rather than the standard 10 months.
The FDA is expected to make a decision on this BLA by Aug. 19, 2019.
The BLA is supported by a phase 1b/2 trial (NCT02257567) of patients with relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma or DLBCL who received polatuzumab vedotin in combination with BR or obinutuzumab.
The trial’s phase 2 stage included 80 DLBCL patients who were randomized to receive BR or BR plus polatuzumab vedotin, according to Genentech.
The complete response rate was 40% in the polatuzumab vedotin arm and 18% in the BR arm. The median duration of response was 10.3 months and 4.1 months, respectively (hazard ratio [HR] = 0.44).
The median progression-free survival was 7.6 months in the polatuzumab vedotin arm and 2.0 months in the BR arm (HR = 0.34).
Among patients who were ineligible for a transplant, the median overall survival (an exploratory endpoint) was 12.4 months in the polatuzumab vedotin arm and 4.7 months in the BR arm (HR = 0.42).
Patients who received polatuzumab vedotin had higher rates of grade 3-4 cytopenias, compared with patients who received BR alone. Rates of infection and transfusion were similar between the arms.
With this BLA, Genentech is seeking approval for polatuzumab vedotin in combination with bendamustine and rituximab (BR) to treat patients with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
The FDA grants priority review to applications for products that are expected to provide significant improvements in the treatment, diagnosis, or prevention of serious conditions. The agency aims to take action on a priority review application within 6 months, rather than the standard 10 months.
The FDA is expected to make a decision on this BLA by Aug. 19, 2019.
The BLA is supported by a phase 1b/2 trial (NCT02257567) of patients with relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma or DLBCL who received polatuzumab vedotin in combination with BR or obinutuzumab.
The trial’s phase 2 stage included 80 DLBCL patients who were randomized to receive BR or BR plus polatuzumab vedotin, according to Genentech.
The complete response rate was 40% in the polatuzumab vedotin arm and 18% in the BR arm. The median duration of response was 10.3 months and 4.1 months, respectively (hazard ratio [HR] = 0.44).
The median progression-free survival was 7.6 months in the polatuzumab vedotin arm and 2.0 months in the BR arm (HR = 0.34).
Among patients who were ineligible for a transplant, the median overall survival (an exploratory endpoint) was 12.4 months in the polatuzumab vedotin arm and 4.7 months in the BR arm (HR = 0.42).
Patients who received polatuzumab vedotin had higher rates of grade 3-4 cytopenias, compared with patients who received BR alone. Rates of infection and transfusion were similar between the arms.