User login
Ibrutinib plus venetoclax is active in mantle cell lymphoma
In mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), ibrutinib plus venetoclax significantly improved the complete response rate, compared with what has been previously reported for ibrutinib alone, according to results of a phase 2 study.
Clinical outcomes with the combination seem superior to previously reported results for either treatment alone, said lead investigator Constantine S. Tam, MBBS, MD, of the Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre, Melbourne, and his coinvestigators.
“The results of our study, which used a historical cohort as a control, are consistent with the notion that the combination of ibrutinib and venetoclax is highly effective in mantle-cell lymphoma,” the investigators wrote in the New England Journal of Medicine.
The BTK inhibitor ibrutinib and the BCL2 inhibitor venetoclax are two of the most active agents for this B-cell cancer, investigators reported. The rationale for combining the agents is “compelling” because they affect different critical pathways in the malignant B cell.
Both agents have demonstrated complete response rates of 21% in previous studies of relapsed or refractory MCL, and preclinical studies suggest the combination of ibrutinib and venetoclax would be synergistic.
In the present single-group, phase 2 study, 24 patients with MCL (23 relapsed or refractory, 1 previously untreated) started ibrutinib 560 mg daily; at 4 weeks, venetoclax was started at a low dose and increased to 400 mg daily.
The study primary end point – complete response rate at week 16 assessed by CT – was 42%, compared with 9% for ibrutinib monotherapy in the phase 2 PCYC-1104-CA study (P less than .001).
Computed tomography assessment was used for the primary end point to allow comparison to the ibrutinib monotherapy study, which did not use positron emission tomography for restaging. “Our study was designed to have 80% power to reject a complete response rate of 9% (at a one-sided alpha level of 0.05) if the rate of complete response was at least 30%,” the investigators noted.
Complete response rate assessed by positron emission tomography at week 16 was 62%, and was 71% overall.
In all, 67% of patients had absence of minimal residual disease by flow cytometry. At 15 months, 78% of the responses were ongoing, and at 18 months, 57% of patients were alive and progression free.
“Such outcomes appear to be substantially better than those that have been reported for ibrutinib or venetoclax monotherapy,” the investigators wrote.
The combination had side effects that are “acceptable to both patients and physicians,” investigators wrote. Side effects, usually low grade, included diarrhea in 83% of patients, fatigue in 75%, and nausea or vomiting in 71%. Tumor lysis syndrome was seen in two patients.
Whether ibrutinib plus venetoclax is superior to ibrutinib alone is being formally evaluated in an ongoing phase 3 study.
Janssen and AbbVie partially funded the current phase 2 study. Dr. Tam reported financial ties to Janssen, AbbVie, and Pharmacyclics. Other study authors reported financial ties to various pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Tam C et al. N Engl J Med. 2018;378:1211-23.
In mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), ibrutinib plus venetoclax significantly improved the complete response rate, compared with what has been previously reported for ibrutinib alone, according to results of a phase 2 study.
Clinical outcomes with the combination seem superior to previously reported results for either treatment alone, said lead investigator Constantine S. Tam, MBBS, MD, of the Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre, Melbourne, and his coinvestigators.
“The results of our study, which used a historical cohort as a control, are consistent with the notion that the combination of ibrutinib and venetoclax is highly effective in mantle-cell lymphoma,” the investigators wrote in the New England Journal of Medicine.
The BTK inhibitor ibrutinib and the BCL2 inhibitor venetoclax are two of the most active agents for this B-cell cancer, investigators reported. The rationale for combining the agents is “compelling” because they affect different critical pathways in the malignant B cell.
Both agents have demonstrated complete response rates of 21% in previous studies of relapsed or refractory MCL, and preclinical studies suggest the combination of ibrutinib and venetoclax would be synergistic.
In the present single-group, phase 2 study, 24 patients with MCL (23 relapsed or refractory, 1 previously untreated) started ibrutinib 560 mg daily; at 4 weeks, venetoclax was started at a low dose and increased to 400 mg daily.
The study primary end point – complete response rate at week 16 assessed by CT – was 42%, compared with 9% for ibrutinib monotherapy in the phase 2 PCYC-1104-CA study (P less than .001).
Computed tomography assessment was used for the primary end point to allow comparison to the ibrutinib monotherapy study, which did not use positron emission tomography for restaging. “Our study was designed to have 80% power to reject a complete response rate of 9% (at a one-sided alpha level of 0.05) if the rate of complete response was at least 30%,” the investigators noted.
Complete response rate assessed by positron emission tomography at week 16 was 62%, and was 71% overall.
In all, 67% of patients had absence of minimal residual disease by flow cytometry. At 15 months, 78% of the responses were ongoing, and at 18 months, 57% of patients were alive and progression free.
“Such outcomes appear to be substantially better than those that have been reported for ibrutinib or venetoclax monotherapy,” the investigators wrote.
The combination had side effects that are “acceptable to both patients and physicians,” investigators wrote. Side effects, usually low grade, included diarrhea in 83% of patients, fatigue in 75%, and nausea or vomiting in 71%. Tumor lysis syndrome was seen in two patients.
Whether ibrutinib plus venetoclax is superior to ibrutinib alone is being formally evaluated in an ongoing phase 3 study.
Janssen and AbbVie partially funded the current phase 2 study. Dr. Tam reported financial ties to Janssen, AbbVie, and Pharmacyclics. Other study authors reported financial ties to various pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Tam C et al. N Engl J Med. 2018;378:1211-23.
In mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), ibrutinib plus venetoclax significantly improved the complete response rate, compared with what has been previously reported for ibrutinib alone, according to results of a phase 2 study.
Clinical outcomes with the combination seem superior to previously reported results for either treatment alone, said lead investigator Constantine S. Tam, MBBS, MD, of the Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre, Melbourne, and his coinvestigators.
“The results of our study, which used a historical cohort as a control, are consistent with the notion that the combination of ibrutinib and venetoclax is highly effective in mantle-cell lymphoma,” the investigators wrote in the New England Journal of Medicine.
The BTK inhibitor ibrutinib and the BCL2 inhibitor venetoclax are two of the most active agents for this B-cell cancer, investigators reported. The rationale for combining the agents is “compelling” because they affect different critical pathways in the malignant B cell.
Both agents have demonstrated complete response rates of 21% in previous studies of relapsed or refractory MCL, and preclinical studies suggest the combination of ibrutinib and venetoclax would be synergistic.
In the present single-group, phase 2 study, 24 patients with MCL (23 relapsed or refractory, 1 previously untreated) started ibrutinib 560 mg daily; at 4 weeks, venetoclax was started at a low dose and increased to 400 mg daily.
The study primary end point – complete response rate at week 16 assessed by CT – was 42%, compared with 9% for ibrutinib monotherapy in the phase 2 PCYC-1104-CA study (P less than .001).
Computed tomography assessment was used for the primary end point to allow comparison to the ibrutinib monotherapy study, which did not use positron emission tomography for restaging. “Our study was designed to have 80% power to reject a complete response rate of 9% (at a one-sided alpha level of 0.05) if the rate of complete response was at least 30%,” the investigators noted.
Complete response rate assessed by positron emission tomography at week 16 was 62%, and was 71% overall.
In all, 67% of patients had absence of minimal residual disease by flow cytometry. At 15 months, 78% of the responses were ongoing, and at 18 months, 57% of patients were alive and progression free.
“Such outcomes appear to be substantially better than those that have been reported for ibrutinib or venetoclax monotherapy,” the investigators wrote.
The combination had side effects that are “acceptable to both patients and physicians,” investigators wrote. Side effects, usually low grade, included diarrhea in 83% of patients, fatigue in 75%, and nausea or vomiting in 71%. Tumor lysis syndrome was seen in two patients.
Whether ibrutinib plus venetoclax is superior to ibrutinib alone is being formally evaluated in an ongoing phase 3 study.
Janssen and AbbVie partially funded the current phase 2 study. Dr. Tam reported financial ties to Janssen, AbbVie, and Pharmacyclics. Other study authors reported financial ties to various pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Tam C et al. N Engl J Med. 2018;378:1211-23.
FROM THE NEW ENGLAND JOURNAL OF MEDICINE
Key clinical point: Dual targeting of BTK and BCL2 with ibrutinib and venetoclax may improve complete response rate versus ibrutinib alone in patients with mantle cell lymphoma.
Major finding: Complete response rate at week 16 as assessed by CT was 42%, compared with 9% with ibrutinib monotherapy in a previous study (P less than .001).
Study details: A single-group phase 2 study of daily oral ibrutinib and venetoclax in 24 patients with mantle cell lymphoma (23 relapsed or refractory, 1 previously untreated), as compared with historical controls.
Disclosures: Janssen and AbbVie partially funded the study. Dr. Tam reported financial ties to Janssen, Abbvie, and Pharmacyclics. Other study authors reported financial ties to various pharmaceutical companies.
Source: Tam C et al. N Engl J Med. 2018;378:1211-23.
Time to rethink MCL treatment, trial design
Classic mantle cell lymphoma (cMCL) has long been treated as a uniformly aggressive disease in need of similarly aggressive treatment, but that approach may be leading to overtreatment, according to one expert.
“The cMCL encompasses a broad category of lymphomas with highly variable clinical behaviors. A contemporary categorization of cMCL as a predominantly aggressive entity is misleading, as only an estimated 20% to 25% of patients with cMCL present with a symptomatic or aggressively behaving disease,” Leonid L. Yavorkovsky, MD, PhD, of the Kaiser Permanente San Jose Medical Center (Calif.), wrote in a commentary in JAMA Oncology.
While groups like the National Comprehensive Cancer Network and the European Society for Medical Oncology recommend that only older patients and those with significant comorbidities should be exempted from intensive therapy, Dr. Yavorkovsky said to identify asymptomatic patients who might be able to safely delay aggressive treatment. He also called for more risk-adapted patient assignment to cMCL clinical trials.
“The failure to recognize the erratic nature of cMCL in clinical studies may confound the outcome gains and, ultimately, undermine the ensuing treatment recommendations,” Dr. Yavorkovsky wrote.
Read his full commentary in JAMA Oncology.
SOURCE: Yavorkovsky L, JAMA Oncology. 2018 Mar 1. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2017.5685.
Classic mantle cell lymphoma (cMCL) has long been treated as a uniformly aggressive disease in need of similarly aggressive treatment, but that approach may be leading to overtreatment, according to one expert.
“The cMCL encompasses a broad category of lymphomas with highly variable clinical behaviors. A contemporary categorization of cMCL as a predominantly aggressive entity is misleading, as only an estimated 20% to 25% of patients with cMCL present with a symptomatic or aggressively behaving disease,” Leonid L. Yavorkovsky, MD, PhD, of the Kaiser Permanente San Jose Medical Center (Calif.), wrote in a commentary in JAMA Oncology.
While groups like the National Comprehensive Cancer Network and the European Society for Medical Oncology recommend that only older patients and those with significant comorbidities should be exempted from intensive therapy, Dr. Yavorkovsky said to identify asymptomatic patients who might be able to safely delay aggressive treatment. He also called for more risk-adapted patient assignment to cMCL clinical trials.
“The failure to recognize the erratic nature of cMCL in clinical studies may confound the outcome gains and, ultimately, undermine the ensuing treatment recommendations,” Dr. Yavorkovsky wrote.
Read his full commentary in JAMA Oncology.
SOURCE: Yavorkovsky L, JAMA Oncology. 2018 Mar 1. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2017.5685.
Classic mantle cell lymphoma (cMCL) has long been treated as a uniformly aggressive disease in need of similarly aggressive treatment, but that approach may be leading to overtreatment, according to one expert.
“The cMCL encompasses a broad category of lymphomas with highly variable clinical behaviors. A contemporary categorization of cMCL as a predominantly aggressive entity is misleading, as only an estimated 20% to 25% of patients with cMCL present with a symptomatic or aggressively behaving disease,” Leonid L. Yavorkovsky, MD, PhD, of the Kaiser Permanente San Jose Medical Center (Calif.), wrote in a commentary in JAMA Oncology.
While groups like the National Comprehensive Cancer Network and the European Society for Medical Oncology recommend that only older patients and those with significant comorbidities should be exempted from intensive therapy, Dr. Yavorkovsky said to identify asymptomatic patients who might be able to safely delay aggressive treatment. He also called for more risk-adapted patient assignment to cMCL clinical trials.
“The failure to recognize the erratic nature of cMCL in clinical studies may confound the outcome gains and, ultimately, undermine the ensuing treatment recommendations,” Dr. Yavorkovsky wrote.
Read his full commentary in JAMA Oncology.
SOURCE: Yavorkovsky L, JAMA Oncology. 2018 Mar 1. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2017.5685.
FROM JAMA ONCOLOGY
Outpatient CAR T infusions feasible using liso-cel
SALT LAKE CITY – A CD19-directed 4-1BB chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell product showed efficacy and a low rate of cytokine release syndrome and neurotoxicity in patients with aggressive lymphomas and poor prognoses, raising the possibility of outpatient administration and fewer hospitalization days in this high-risk group.
A total of 86 patients who received inpatient infusions of lisocabtagene maraleucel (liso-cel, also known as JCAR017) had a mean 15.6 days of hospitalization, compared with 9.3 days for 8 outpatient recipients, said Jeremy Abramson, MD, speaking at a top abstracts session of the combined annual meetings of the Center for International Blood & Marrow Transplant Research and the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation.
As of October 2017, eight patients had received liso-cel infusion as outpatients with at least 28 days of postinfusion data, Dr. Abramson said.
Although all but one required hospital admission, at a median of 5 days postinfusion (range, 4-22 days), there had been no intensive care unit admissions, and no outpatient recipients had experienced severe cytokine release syndrome (CRS) or neurotoxicity. All admitted patients presented with fever.
Among the study population, “Cytokine release syndrome was only seen in 35% of our entire dataset,” with neurologic toxicity seen in 19% of participants, Dr. Abramson said. “The majority of subjects had no CRS and no toxicity,” he said. Severe CRS occurred in 1% of the study population, and severe neurotoxicity in 12%. There were no deaths related to either complication.
Dr. Abramson reported these results from the TRANSCEND NHL 001 trial, a seamless design phase 1 pivotal trial of liso-cel enrolling patients with relapsed and refractory aggressive B cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL). Liso-cel delivers CD19-directed CD4 and CD8 CAR T cells in a 1:1 ratio, said Dr. Abramson, director of the lymphoma program at the Massachusetts General Hospital Cancer Center, Boston.
A total of 91 patients were randomized to one of the three dose-finding cohorts of the multicenter trial of liso-cel. One cohort received 5 x 107 cells in a single dose; a second cohort received the same number of cells but in two doses administered 14 days apart; the third cohort received a single dose of 1 x 108 cells.
The seamless trial design then moved to dose expansion, using the two single doses established in the dose-finding phase of the study. Ultimately, Dr. Abramson said, the third and pivotal diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) cohort received the higher single dose, since a dose-response relationship was seen in the earlier cohorts. No increase in cytokine release syndrome or neurotoxicity has been seen with the higher dose in patients evaluated to date.
Patients (median age, 61 years) were eligible to participate in the trial if they had relapsed or refractory DLBCL, primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma, grade 3B follicular lymphoma, or mantle cell lymphoma. Patients with a failed prior allogeneic stem cell transplant or secondary central nervous system involvement were eligible, but all patients had to have an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status of 0-2.
As the trial moved to the core pivotal phase, eligibility requirements shifted slightly to include patients with ECOG status 0 or 1, and lymphoma diagnoses narrowed to include only DLBCL not otherwise specified (NOS), transformed follicular lymphoma, and high-grade B-cell lymphoma with double- and triple-hit cytogenetics. The core group was nearing completion of accrual at the time of the presentation, which presented preliminary results from this phase of the trial.
Among the 88 evaluable patients in the initial population with DLBCL receiving any of three dose levels, the best overall response rate (ORR) was 74% (95% confidence interval, 63%-83%); 52% of these patients achieved complete response (CR; 95% CI, 41%-63%).
For patients receiving the higher dose of liso-cel, the ORR was 81% (95% CI, 62%-94%), with a 63% CR rate (95% CI, 42%-81%), bearing out the dose-response rate that had been seen earlier in the trial, Dr. Abramson said.
The median duration of response in all TRANSCEND patients was 9.2 months; the median duration of remission has not been reached, he said. “We see evidence of durable response at 3 months in all our high-risk subsets, and that includes double- and triple-hit lymphomas, double-expresser lymphomas, patients who’ve never achieved prior complete remission, and patients with refractory disease.”
“The overall results are similarly encouraging,” Dr. Abramson said, with 86% of all patients alive at 6 months. Among the complete responders, 94% are alive at the 6-month mark. “The median duration of complete responders has not been reached in this cohort,” he said.
These results are notable, Dr. Abramson said, since about 90% of study participants have at least one disease risk factor that would predict median overall survival of 3-6 months.
During the period after leukapheresis while the CAR T cells were in production, patients could have ongoing treatment, but received PET scans to confirm disease before continuing enrollment in the trial and receiving liso-cel. The time from apheresis to product release for the pivotal cohort is now under 21 days, he said.
The study was supported by Juno Therapeutics, which plans to market liso-cel. Dr. Abramson reported ties with Celgene, Gilead, Seattle Genetics, Novartis, and Genentech.
SOURCE: Abramson J et al. Abstract 5.
SALT LAKE CITY – A CD19-directed 4-1BB chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell product showed efficacy and a low rate of cytokine release syndrome and neurotoxicity in patients with aggressive lymphomas and poor prognoses, raising the possibility of outpatient administration and fewer hospitalization days in this high-risk group.
A total of 86 patients who received inpatient infusions of lisocabtagene maraleucel (liso-cel, also known as JCAR017) had a mean 15.6 days of hospitalization, compared with 9.3 days for 8 outpatient recipients, said Jeremy Abramson, MD, speaking at a top abstracts session of the combined annual meetings of the Center for International Blood & Marrow Transplant Research and the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation.
As of October 2017, eight patients had received liso-cel infusion as outpatients with at least 28 days of postinfusion data, Dr. Abramson said.
Although all but one required hospital admission, at a median of 5 days postinfusion (range, 4-22 days), there had been no intensive care unit admissions, and no outpatient recipients had experienced severe cytokine release syndrome (CRS) or neurotoxicity. All admitted patients presented with fever.
Among the study population, “Cytokine release syndrome was only seen in 35% of our entire dataset,” with neurologic toxicity seen in 19% of participants, Dr. Abramson said. “The majority of subjects had no CRS and no toxicity,” he said. Severe CRS occurred in 1% of the study population, and severe neurotoxicity in 12%. There were no deaths related to either complication.
Dr. Abramson reported these results from the TRANSCEND NHL 001 trial, a seamless design phase 1 pivotal trial of liso-cel enrolling patients with relapsed and refractory aggressive B cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL). Liso-cel delivers CD19-directed CD4 and CD8 CAR T cells in a 1:1 ratio, said Dr. Abramson, director of the lymphoma program at the Massachusetts General Hospital Cancer Center, Boston.
A total of 91 patients were randomized to one of the three dose-finding cohorts of the multicenter trial of liso-cel. One cohort received 5 x 107 cells in a single dose; a second cohort received the same number of cells but in two doses administered 14 days apart; the third cohort received a single dose of 1 x 108 cells.
The seamless trial design then moved to dose expansion, using the two single doses established in the dose-finding phase of the study. Ultimately, Dr. Abramson said, the third and pivotal diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) cohort received the higher single dose, since a dose-response relationship was seen in the earlier cohorts. No increase in cytokine release syndrome or neurotoxicity has been seen with the higher dose in patients evaluated to date.
Patients (median age, 61 years) were eligible to participate in the trial if they had relapsed or refractory DLBCL, primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma, grade 3B follicular lymphoma, or mantle cell lymphoma. Patients with a failed prior allogeneic stem cell transplant or secondary central nervous system involvement were eligible, but all patients had to have an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status of 0-2.
As the trial moved to the core pivotal phase, eligibility requirements shifted slightly to include patients with ECOG status 0 or 1, and lymphoma diagnoses narrowed to include only DLBCL not otherwise specified (NOS), transformed follicular lymphoma, and high-grade B-cell lymphoma with double- and triple-hit cytogenetics. The core group was nearing completion of accrual at the time of the presentation, which presented preliminary results from this phase of the trial.
Among the 88 evaluable patients in the initial population with DLBCL receiving any of three dose levels, the best overall response rate (ORR) was 74% (95% confidence interval, 63%-83%); 52% of these patients achieved complete response (CR; 95% CI, 41%-63%).
For patients receiving the higher dose of liso-cel, the ORR was 81% (95% CI, 62%-94%), with a 63% CR rate (95% CI, 42%-81%), bearing out the dose-response rate that had been seen earlier in the trial, Dr. Abramson said.
The median duration of response in all TRANSCEND patients was 9.2 months; the median duration of remission has not been reached, he said. “We see evidence of durable response at 3 months in all our high-risk subsets, and that includes double- and triple-hit lymphomas, double-expresser lymphomas, patients who’ve never achieved prior complete remission, and patients with refractory disease.”
“The overall results are similarly encouraging,” Dr. Abramson said, with 86% of all patients alive at 6 months. Among the complete responders, 94% are alive at the 6-month mark. “The median duration of complete responders has not been reached in this cohort,” he said.
These results are notable, Dr. Abramson said, since about 90% of study participants have at least one disease risk factor that would predict median overall survival of 3-6 months.
During the period after leukapheresis while the CAR T cells were in production, patients could have ongoing treatment, but received PET scans to confirm disease before continuing enrollment in the trial and receiving liso-cel. The time from apheresis to product release for the pivotal cohort is now under 21 days, he said.
The study was supported by Juno Therapeutics, which plans to market liso-cel. Dr. Abramson reported ties with Celgene, Gilead, Seattle Genetics, Novartis, and Genentech.
SOURCE: Abramson J et al. Abstract 5.
SALT LAKE CITY – A CD19-directed 4-1BB chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell product showed efficacy and a low rate of cytokine release syndrome and neurotoxicity in patients with aggressive lymphomas and poor prognoses, raising the possibility of outpatient administration and fewer hospitalization days in this high-risk group.
A total of 86 patients who received inpatient infusions of lisocabtagene maraleucel (liso-cel, also known as JCAR017) had a mean 15.6 days of hospitalization, compared with 9.3 days for 8 outpatient recipients, said Jeremy Abramson, MD, speaking at a top abstracts session of the combined annual meetings of the Center for International Blood & Marrow Transplant Research and the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation.
As of October 2017, eight patients had received liso-cel infusion as outpatients with at least 28 days of postinfusion data, Dr. Abramson said.
Although all but one required hospital admission, at a median of 5 days postinfusion (range, 4-22 days), there had been no intensive care unit admissions, and no outpatient recipients had experienced severe cytokine release syndrome (CRS) or neurotoxicity. All admitted patients presented with fever.
Among the study population, “Cytokine release syndrome was only seen in 35% of our entire dataset,” with neurologic toxicity seen in 19% of participants, Dr. Abramson said. “The majority of subjects had no CRS and no toxicity,” he said. Severe CRS occurred in 1% of the study population, and severe neurotoxicity in 12%. There were no deaths related to either complication.
Dr. Abramson reported these results from the TRANSCEND NHL 001 trial, a seamless design phase 1 pivotal trial of liso-cel enrolling patients with relapsed and refractory aggressive B cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL). Liso-cel delivers CD19-directed CD4 and CD8 CAR T cells in a 1:1 ratio, said Dr. Abramson, director of the lymphoma program at the Massachusetts General Hospital Cancer Center, Boston.
A total of 91 patients were randomized to one of the three dose-finding cohorts of the multicenter trial of liso-cel. One cohort received 5 x 107 cells in a single dose; a second cohort received the same number of cells but in two doses administered 14 days apart; the third cohort received a single dose of 1 x 108 cells.
The seamless trial design then moved to dose expansion, using the two single doses established in the dose-finding phase of the study. Ultimately, Dr. Abramson said, the third and pivotal diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) cohort received the higher single dose, since a dose-response relationship was seen in the earlier cohorts. No increase in cytokine release syndrome or neurotoxicity has been seen with the higher dose in patients evaluated to date.
Patients (median age, 61 years) were eligible to participate in the trial if they had relapsed or refractory DLBCL, primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma, grade 3B follicular lymphoma, or mantle cell lymphoma. Patients with a failed prior allogeneic stem cell transplant or secondary central nervous system involvement were eligible, but all patients had to have an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status of 0-2.
As the trial moved to the core pivotal phase, eligibility requirements shifted slightly to include patients with ECOG status 0 or 1, and lymphoma diagnoses narrowed to include only DLBCL not otherwise specified (NOS), transformed follicular lymphoma, and high-grade B-cell lymphoma with double- and triple-hit cytogenetics. The core group was nearing completion of accrual at the time of the presentation, which presented preliminary results from this phase of the trial.
Among the 88 evaluable patients in the initial population with DLBCL receiving any of three dose levels, the best overall response rate (ORR) was 74% (95% confidence interval, 63%-83%); 52% of these patients achieved complete response (CR; 95% CI, 41%-63%).
For patients receiving the higher dose of liso-cel, the ORR was 81% (95% CI, 62%-94%), with a 63% CR rate (95% CI, 42%-81%), bearing out the dose-response rate that had been seen earlier in the trial, Dr. Abramson said.
The median duration of response in all TRANSCEND patients was 9.2 months; the median duration of remission has not been reached, he said. “We see evidence of durable response at 3 months in all our high-risk subsets, and that includes double- and triple-hit lymphomas, double-expresser lymphomas, patients who’ve never achieved prior complete remission, and patients with refractory disease.”
“The overall results are similarly encouraging,” Dr. Abramson said, with 86% of all patients alive at 6 months. Among the complete responders, 94% are alive at the 6-month mark. “The median duration of complete responders has not been reached in this cohort,” he said.
These results are notable, Dr. Abramson said, since about 90% of study participants have at least one disease risk factor that would predict median overall survival of 3-6 months.
During the period after leukapheresis while the CAR T cells were in production, patients could have ongoing treatment, but received PET scans to confirm disease before continuing enrollment in the trial and receiving liso-cel. The time from apheresis to product release for the pivotal cohort is now under 21 days, he said.
The study was supported by Juno Therapeutics, which plans to market liso-cel. Dr. Abramson reported ties with Celgene, Gilead, Seattle Genetics, Novartis, and Genentech.
SOURCE: Abramson J et al. Abstract 5.
REPORTING FROM THE 2018 BMT TANDEM MEETINGS
Key clinical point:
Major finding: High-risk lymphoma patients had more than 6 fewer inpatient days with outpatient CAR T infusion.
Study details: Seamless phase 1 trial initially evaluating 91 patients with relapsed/refractory diffuse large B cell lymphoma.
Disclosures: Juno Therapeutics sponsored the study. Dr. Abramson reported ties with Celgene, Gilead, Seattle Genetics, Novartis, and Genentech.
Source: Abramson J et al. Abstract 5.
Ibrutinib linked to invasive fungal infections
The tyrosine kinase inhibitor ibrutinib (Imbruvica) may be associated with early-onset invasive fungal infections (IFI) in patients with hematologic malignancies, investigators caution.
French investigators identified 33 cases of invasive fungal infections occurring among patients who had been treated with ibrutinib as monotherapy or in combination with other agents. Of the 33 cases, 27 were invasive aspergillosis, and 40% of these were localized in the central nervous system. The findings were published in the journal Blood.
“IFI tend to occur within the first months of treatment and are infrequent thereafter. Whilst it seems difficult at this point to advocate for systematic antifungal prophylaxis in all patients, an increased awareness about the potential risk of IFI after initiating ibrutinib is warranted, especially when other predisposing factors are associated,” wrote David Ghez, MD, PhD, and colleagues at the Gustave Roussy Institute in Villejuif and other centers in France.
Although ibrutinib, an inhibitor of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase, is generally considered to be less immunosuppressive than other therapies, it was associated with five cases of Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) treated with ibrutinib monotherapy in a 2016 report (Blood. 2016;128:1940-3). Of these five patients, four were treatment naive, suggesting that ibrutinib itself could increase risk for invasive opportunistic infections, Dr. Ghez and his colleagues noted.
Based on this finding and on case reports of invasive infections in other patients being treated with ibrutinib, the authors conducted a retrospective survey of centers in the French Innovative Leukemia Organization CLL group.
They identified 33 cases, including 30 patients with CLL (15 of whom had deleterious 17p deletions), 1 with mantle cell lymphoma, and 2 with Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia.
Invasive aspergillosis accounted for 27 of the 33 cases, and 11 cases had CNS localization. There were four cases of disseminated cryptococcosis, and one each of mucormycosis and pneumocystis pneumonia.
The median time between the start of ibrutinib therapy and a diagnosis of invasive fungal infection was 3 months, with some cases occurring as early as 1 month, and others occurring 30 months out. However, the majority of cases – 28 – were diagnosed within 6 months of the start of therapy, including 20 that occurred within 3 months of ibrutinib initiation.
In 21 patients, the diagnosis of an invasive fungal infection led to drug discontinuation. In the remaining patients, the drug was either resumed after resolution of the IFI, or continued at a lower dose because of potential for interaction between ibrutinib and the antifungal agent voriconazole.
Dr. Ghez reported receiving a research grant from Janssen, and coauthor Loic Ysebaert, MD, PhD, reported consultancy fees from the company. All other authors declared no competing financial interests.
SOURCE: Ghez D et al., Blood. 2018 Feb 1. doi: 10.1182/blood-2017-11-818286.
The tyrosine kinase inhibitor ibrutinib (Imbruvica) may be associated with early-onset invasive fungal infections (IFI) in patients with hematologic malignancies, investigators caution.
French investigators identified 33 cases of invasive fungal infections occurring among patients who had been treated with ibrutinib as monotherapy or in combination with other agents. Of the 33 cases, 27 were invasive aspergillosis, and 40% of these were localized in the central nervous system. The findings were published in the journal Blood.
“IFI tend to occur within the first months of treatment and are infrequent thereafter. Whilst it seems difficult at this point to advocate for systematic antifungal prophylaxis in all patients, an increased awareness about the potential risk of IFI after initiating ibrutinib is warranted, especially when other predisposing factors are associated,” wrote David Ghez, MD, PhD, and colleagues at the Gustave Roussy Institute in Villejuif and other centers in France.
Although ibrutinib, an inhibitor of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase, is generally considered to be less immunosuppressive than other therapies, it was associated with five cases of Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) treated with ibrutinib monotherapy in a 2016 report (Blood. 2016;128:1940-3). Of these five patients, four were treatment naive, suggesting that ibrutinib itself could increase risk for invasive opportunistic infections, Dr. Ghez and his colleagues noted.
Based on this finding and on case reports of invasive infections in other patients being treated with ibrutinib, the authors conducted a retrospective survey of centers in the French Innovative Leukemia Organization CLL group.
They identified 33 cases, including 30 patients with CLL (15 of whom had deleterious 17p deletions), 1 with mantle cell lymphoma, and 2 with Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia.
Invasive aspergillosis accounted for 27 of the 33 cases, and 11 cases had CNS localization. There were four cases of disseminated cryptococcosis, and one each of mucormycosis and pneumocystis pneumonia.
The median time between the start of ibrutinib therapy and a diagnosis of invasive fungal infection was 3 months, with some cases occurring as early as 1 month, and others occurring 30 months out. However, the majority of cases – 28 – were diagnosed within 6 months of the start of therapy, including 20 that occurred within 3 months of ibrutinib initiation.
In 21 patients, the diagnosis of an invasive fungal infection led to drug discontinuation. In the remaining patients, the drug was either resumed after resolution of the IFI, or continued at a lower dose because of potential for interaction between ibrutinib and the antifungal agent voriconazole.
Dr. Ghez reported receiving a research grant from Janssen, and coauthor Loic Ysebaert, MD, PhD, reported consultancy fees from the company. All other authors declared no competing financial interests.
SOURCE: Ghez D et al., Blood. 2018 Feb 1. doi: 10.1182/blood-2017-11-818286.
The tyrosine kinase inhibitor ibrutinib (Imbruvica) may be associated with early-onset invasive fungal infections (IFI) in patients with hematologic malignancies, investigators caution.
French investigators identified 33 cases of invasive fungal infections occurring among patients who had been treated with ibrutinib as monotherapy or in combination with other agents. Of the 33 cases, 27 were invasive aspergillosis, and 40% of these were localized in the central nervous system. The findings were published in the journal Blood.
“IFI tend to occur within the first months of treatment and are infrequent thereafter. Whilst it seems difficult at this point to advocate for systematic antifungal prophylaxis in all patients, an increased awareness about the potential risk of IFI after initiating ibrutinib is warranted, especially when other predisposing factors are associated,” wrote David Ghez, MD, PhD, and colleagues at the Gustave Roussy Institute in Villejuif and other centers in France.
Although ibrutinib, an inhibitor of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase, is generally considered to be less immunosuppressive than other therapies, it was associated with five cases of Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) treated with ibrutinib monotherapy in a 2016 report (Blood. 2016;128:1940-3). Of these five patients, four were treatment naive, suggesting that ibrutinib itself could increase risk for invasive opportunistic infections, Dr. Ghez and his colleagues noted.
Based on this finding and on case reports of invasive infections in other patients being treated with ibrutinib, the authors conducted a retrospective survey of centers in the French Innovative Leukemia Organization CLL group.
They identified 33 cases, including 30 patients with CLL (15 of whom had deleterious 17p deletions), 1 with mantle cell lymphoma, and 2 with Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia.
Invasive aspergillosis accounted for 27 of the 33 cases, and 11 cases had CNS localization. There were four cases of disseminated cryptococcosis, and one each of mucormycosis and pneumocystis pneumonia.
The median time between the start of ibrutinib therapy and a diagnosis of invasive fungal infection was 3 months, with some cases occurring as early as 1 month, and others occurring 30 months out. However, the majority of cases – 28 – were diagnosed within 6 months of the start of therapy, including 20 that occurred within 3 months of ibrutinib initiation.
In 21 patients, the diagnosis of an invasive fungal infection led to drug discontinuation. In the remaining patients, the drug was either resumed after resolution of the IFI, or continued at a lower dose because of potential for interaction between ibrutinib and the antifungal agent voriconazole.
Dr. Ghez reported receiving a research grant from Janssen, and coauthor Loic Ysebaert, MD, PhD, reported consultancy fees from the company. All other authors declared no competing financial interests.
SOURCE: Ghez D et al., Blood. 2018 Feb 1. doi: 10.1182/blood-2017-11-818286.
FROM BLOOD
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Of 33 identified cases, 27 were invasive aspergillosis.
Study details: Retrospective review of case reports from 16 French centers.
Disclosures: Dr. Ghez reported receiving a research grant from Janssen, and coauthor Loic Ysebaert, MD, PhD, reported consultancy fees with the company. All other authors declared no competing financial interests.
Source: Ghez D et al. Blood. 2018 Feb 1. doi: 10.1182/blood-2017-11-818286.
Acalabrutinib shows less off-target activity in mantle cell lymphoma
A new Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor has shown a high response rate and favorable safety profile in the treatment of patients with mantle cell lymphoma.
Researchers reported the results of an open-label, phase 2 study of oral acalabrutinib (100 mg, twice daily) in 124 patients with relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma in The Lancet. Acalabrutinib (Calquence) received accelerated approval from the Food and Drug Administration in October 2017 for treatment of adults with mantle cell lymphoma who have received at least one prior therapy.
The Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor ibrutinib (Imbruvica), which was approved in 2013 for the treatment of mantle cell lymphoma, has been associated with side effects including atrial fibrillation, infections and bleeding, likely due to its off-target activity against other kinases. But acalabrutinib (ACP-196) “is a highly selective, potent BTK inhibitor developed to minimise off-target activity,” wrote Michael Wang, MD, of the department of lymphoma and myeloma at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, and his colleagues.
After a median follow-up of 15.2 months, 81% of patients in the study achieved an investigator-assessed overall response based on Lugano classification, with 40% achieving a complete response. The results were similar according to an independent review committee evaluation of responses based on CT and PET scans, bone-marrow biopsy specimens, endoscopy results, and clinical data.
There was also a reduction in lymphadenopathy seen in 94% of patients. The patients who showed a complete response took a median of 3.4 months to get there, and the median time to best response was 1.9 months.
The researchers also looked at response rates across a number of prespecified subgroups. Patients with Ann Arbor stage IV disease, those with bone marrow involvement, and those with extranodal disease were less likely to achieve a complete response (29%, 14% and 28% respectively). Patients with lymph nodes 5 cm or larger in diameter showed a 78% response rate.
While the Kaplan-Meier estimated medians for duration of response, progression-free survival, and overall survival were not reached, 87% of patients achieved 12-month overall survival and 67% of patients achieved progression-free survival at 12 months.
Most of the adverse events were grade 1 or 2, and included headache, diarrhea, fatigue, and myalgia.
There were no grade 4 or 5 adverse events, but 10% of patients experienced neutropenia, 9% experienced anemia and 5% experienced pneumonia. There was also one case of grade 3 or worse hemorrhage, but no cases of atrial fibrillation. Lymphocytosis was seen in 31% of patients.
Nearly half of patients (44%) discontinued treatment, mostly because of progressive disease (31%) but 6% discontinued the treatment because of adverse events.
“Overall, treatment with acalabrutinib demonstrated a favourable benefit-risk profile and represents a promising treatment option for patients with relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma,” the researchers wrote. “Data from the ongoing ACE-CL-006 trial directly comparing acalabrutinib with ibrutinib in previously treated patients with high-risk chronic lymphocytic leukaemia will further differentiate the safety profiles of the two treatments.”
The researchers noted a decrease in plasma levels of tumor necrosis factor alpha, the cytokine CXCL13, and other cytokines known to be involved in inflammation and cell trafficking.
“These findings add to the growing body of evidence indicating that BTK inhibition disrupts the tumour microenvironment, limiting the supply of cytokines and chemokines necessary for complex interactions with stromal and accessory cells important for tumour growth and survival.”
The study was sponsored by Acerta Pharma, a member of the AstraZeneca Group. Several study authors reported grants, personal fees and other support from the pharmaceutical industry, including Acerta Pharma, most outside the submitted work. Several authors were also employees of Acerta and some had acalabrutinib patents pending or issued.
SOURCE: Wang M et al., Lancet. 2018;391:659-67.
A new Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor has shown a high response rate and favorable safety profile in the treatment of patients with mantle cell lymphoma.
Researchers reported the results of an open-label, phase 2 study of oral acalabrutinib (100 mg, twice daily) in 124 patients with relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma in The Lancet. Acalabrutinib (Calquence) received accelerated approval from the Food and Drug Administration in October 2017 for treatment of adults with mantle cell lymphoma who have received at least one prior therapy.
The Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor ibrutinib (Imbruvica), which was approved in 2013 for the treatment of mantle cell lymphoma, has been associated with side effects including atrial fibrillation, infections and bleeding, likely due to its off-target activity against other kinases. But acalabrutinib (ACP-196) “is a highly selective, potent BTK inhibitor developed to minimise off-target activity,” wrote Michael Wang, MD, of the department of lymphoma and myeloma at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, and his colleagues.
After a median follow-up of 15.2 months, 81% of patients in the study achieved an investigator-assessed overall response based on Lugano classification, with 40% achieving a complete response. The results were similar according to an independent review committee evaluation of responses based on CT and PET scans, bone-marrow biopsy specimens, endoscopy results, and clinical data.
There was also a reduction in lymphadenopathy seen in 94% of patients. The patients who showed a complete response took a median of 3.4 months to get there, and the median time to best response was 1.9 months.
The researchers also looked at response rates across a number of prespecified subgroups. Patients with Ann Arbor stage IV disease, those with bone marrow involvement, and those with extranodal disease were less likely to achieve a complete response (29%, 14% and 28% respectively). Patients with lymph nodes 5 cm or larger in diameter showed a 78% response rate.
While the Kaplan-Meier estimated medians for duration of response, progression-free survival, and overall survival were not reached, 87% of patients achieved 12-month overall survival and 67% of patients achieved progression-free survival at 12 months.
Most of the adverse events were grade 1 or 2, and included headache, diarrhea, fatigue, and myalgia.
There were no grade 4 or 5 adverse events, but 10% of patients experienced neutropenia, 9% experienced anemia and 5% experienced pneumonia. There was also one case of grade 3 or worse hemorrhage, but no cases of atrial fibrillation. Lymphocytosis was seen in 31% of patients.
Nearly half of patients (44%) discontinued treatment, mostly because of progressive disease (31%) but 6% discontinued the treatment because of adverse events.
“Overall, treatment with acalabrutinib demonstrated a favourable benefit-risk profile and represents a promising treatment option for patients with relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma,” the researchers wrote. “Data from the ongoing ACE-CL-006 trial directly comparing acalabrutinib with ibrutinib in previously treated patients with high-risk chronic lymphocytic leukaemia will further differentiate the safety profiles of the two treatments.”
The researchers noted a decrease in plasma levels of tumor necrosis factor alpha, the cytokine CXCL13, and other cytokines known to be involved in inflammation and cell trafficking.
“These findings add to the growing body of evidence indicating that BTK inhibition disrupts the tumour microenvironment, limiting the supply of cytokines and chemokines necessary for complex interactions with stromal and accessory cells important for tumour growth and survival.”
The study was sponsored by Acerta Pharma, a member of the AstraZeneca Group. Several study authors reported grants, personal fees and other support from the pharmaceutical industry, including Acerta Pharma, most outside the submitted work. Several authors were also employees of Acerta and some had acalabrutinib patents pending or issued.
SOURCE: Wang M et al., Lancet. 2018;391:659-67.
A new Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor has shown a high response rate and favorable safety profile in the treatment of patients with mantle cell lymphoma.
Researchers reported the results of an open-label, phase 2 study of oral acalabrutinib (100 mg, twice daily) in 124 patients with relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma in The Lancet. Acalabrutinib (Calquence) received accelerated approval from the Food and Drug Administration in October 2017 for treatment of adults with mantle cell lymphoma who have received at least one prior therapy.
The Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor ibrutinib (Imbruvica), which was approved in 2013 for the treatment of mantle cell lymphoma, has been associated with side effects including atrial fibrillation, infections and bleeding, likely due to its off-target activity against other kinases. But acalabrutinib (ACP-196) “is a highly selective, potent BTK inhibitor developed to minimise off-target activity,” wrote Michael Wang, MD, of the department of lymphoma and myeloma at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, and his colleagues.
After a median follow-up of 15.2 months, 81% of patients in the study achieved an investigator-assessed overall response based on Lugano classification, with 40% achieving a complete response. The results were similar according to an independent review committee evaluation of responses based on CT and PET scans, bone-marrow biopsy specimens, endoscopy results, and clinical data.
There was also a reduction in lymphadenopathy seen in 94% of patients. The patients who showed a complete response took a median of 3.4 months to get there, and the median time to best response was 1.9 months.
The researchers also looked at response rates across a number of prespecified subgroups. Patients with Ann Arbor stage IV disease, those with bone marrow involvement, and those with extranodal disease were less likely to achieve a complete response (29%, 14% and 28% respectively). Patients with lymph nodes 5 cm or larger in diameter showed a 78% response rate.
While the Kaplan-Meier estimated medians for duration of response, progression-free survival, and overall survival were not reached, 87% of patients achieved 12-month overall survival and 67% of patients achieved progression-free survival at 12 months.
Most of the adverse events were grade 1 or 2, and included headache, diarrhea, fatigue, and myalgia.
There were no grade 4 or 5 adverse events, but 10% of patients experienced neutropenia, 9% experienced anemia and 5% experienced pneumonia. There was also one case of grade 3 or worse hemorrhage, but no cases of atrial fibrillation. Lymphocytosis was seen in 31% of patients.
Nearly half of patients (44%) discontinued treatment, mostly because of progressive disease (31%) but 6% discontinued the treatment because of adverse events.
“Overall, treatment with acalabrutinib demonstrated a favourable benefit-risk profile and represents a promising treatment option for patients with relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma,” the researchers wrote. “Data from the ongoing ACE-CL-006 trial directly comparing acalabrutinib with ibrutinib in previously treated patients with high-risk chronic lymphocytic leukaemia will further differentiate the safety profiles of the two treatments.”
The researchers noted a decrease in plasma levels of tumor necrosis factor alpha, the cytokine CXCL13, and other cytokines known to be involved in inflammation and cell trafficking.
“These findings add to the growing body of evidence indicating that BTK inhibition disrupts the tumour microenvironment, limiting the supply of cytokines and chemokines necessary for complex interactions with stromal and accessory cells important for tumour growth and survival.”
The study was sponsored by Acerta Pharma, a member of the AstraZeneca Group. Several study authors reported grants, personal fees and other support from the pharmaceutical industry, including Acerta Pharma, most outside the submitted work. Several authors were also employees of Acerta and some had acalabrutinib patents pending or issued.
SOURCE: Wang M et al., Lancet. 2018;391:659-67.
FROM THE LANCET
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Eighty-one percent of patients with relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma showed a partial or complete response to Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor acalabrutinib.
Study details: An open-label, phase 2 study in 124 patients with relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma.
Disclosures: The study was sponsored by Acerta Pharma, a member of the AstraZeneca Group. Several study authors reported grants, personal fees and other support from the pharmaceutical industry, including Acerta Pharma, most outside the submitted work. Several authors were also employees of Acerta and some had acalabrutinib patents pending or issued.
Source: Wang M et al. Lancet. 2018;391:659-67.
NF-kappaB pathway could help solve resistance problem in mantle cell lymphoma
B-cell receptor (BCR) resistance is a significant treatment obstacle in mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), but a new study highlights the potential protective role for cells expressing specific ligands.
Hilka Rauert-Wunderlich, of the University of Würzburg and Comprehensive Cancer Center, Germany, and her colleagues stimulated the REC-1, MAVER-1, and L-929 cell lines to show the role of the alternative nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-kappaB) pathway and the tumor necrosis factor ligand CD40L.
Viability assays showed a protective effect of CD40L prestimulation on BCR inhibitor treatment. The effect was detectable and significant in the REC-1 cell line for both ibrutinib and sotrastaurin at “clinically relevant concentrations” and in the resistant MAVER-1 cell line at “nonphysiologically high” sotrastaurin concentrations. CD40L stimulation also induced alternative NF-kappaB pathway signaling in both REC-1 and MAVER-1 cell lines.
“The data presented in this study argue for the protective potential of microenvironmentally mediated activation of the alternative [NF-kappaB] pathway in MCL cell against BCR signaling-associated drugs, which might represent a physiologic niche for MCL relapse. Additionally, these data provide evidence for the potential of the alternative [NF-kappaB] pathway as a possible therapeutic target in MCL,” the researchers wrote in Cell Death & Disease.
The researchers reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Rauert-Wunderlich H et al. Cell Death Dis. 2018 Jan 24. doi: 10.1038/s41419-017-0157-6.
B-cell receptor (BCR) resistance is a significant treatment obstacle in mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), but a new study highlights the potential protective role for cells expressing specific ligands.
Hilka Rauert-Wunderlich, of the University of Würzburg and Comprehensive Cancer Center, Germany, and her colleagues stimulated the REC-1, MAVER-1, and L-929 cell lines to show the role of the alternative nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-kappaB) pathway and the tumor necrosis factor ligand CD40L.
Viability assays showed a protective effect of CD40L prestimulation on BCR inhibitor treatment. The effect was detectable and significant in the REC-1 cell line for both ibrutinib and sotrastaurin at “clinically relevant concentrations” and in the resistant MAVER-1 cell line at “nonphysiologically high” sotrastaurin concentrations. CD40L stimulation also induced alternative NF-kappaB pathway signaling in both REC-1 and MAVER-1 cell lines.
“The data presented in this study argue for the protective potential of microenvironmentally mediated activation of the alternative [NF-kappaB] pathway in MCL cell against BCR signaling-associated drugs, which might represent a physiologic niche for MCL relapse. Additionally, these data provide evidence for the potential of the alternative [NF-kappaB] pathway as a possible therapeutic target in MCL,” the researchers wrote in Cell Death & Disease.
The researchers reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Rauert-Wunderlich H et al. Cell Death Dis. 2018 Jan 24. doi: 10.1038/s41419-017-0157-6.
B-cell receptor (BCR) resistance is a significant treatment obstacle in mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), but a new study highlights the potential protective role for cells expressing specific ligands.
Hilka Rauert-Wunderlich, of the University of Würzburg and Comprehensive Cancer Center, Germany, and her colleagues stimulated the REC-1, MAVER-1, and L-929 cell lines to show the role of the alternative nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-kappaB) pathway and the tumor necrosis factor ligand CD40L.
Viability assays showed a protective effect of CD40L prestimulation on BCR inhibitor treatment. The effect was detectable and significant in the REC-1 cell line for both ibrutinib and sotrastaurin at “clinically relevant concentrations” and in the resistant MAVER-1 cell line at “nonphysiologically high” sotrastaurin concentrations. CD40L stimulation also induced alternative NF-kappaB pathway signaling in both REC-1 and MAVER-1 cell lines.
“The data presented in this study argue for the protective potential of microenvironmentally mediated activation of the alternative [NF-kappaB] pathway in MCL cell against BCR signaling-associated drugs, which might represent a physiologic niche for MCL relapse. Additionally, these data provide evidence for the potential of the alternative [NF-kappaB] pathway as a possible therapeutic target in MCL,” the researchers wrote in Cell Death & Disease.
The researchers reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Rauert-Wunderlich H et al. Cell Death Dis. 2018 Jan 24. doi: 10.1038/s41419-017-0157-6.
FROM CELL DEATH & DISEASE
Triple therapy ups response in refractory mantle cell lymphoma
A combination of ibrutinib, lenalidomide, and rituximab produced an overall response rate of 76% at 17.8 months median follow-up among 50 adults with relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma, according to an open-label, single-arm, phase 2 trial.
There were complete responses in 28 patients (56%) and partial responses in 10 (20%). Median progression-free survival was 16 months and median overall survival was 22 months. Similar proportions of patients, with and without TP53 mutations, had overall and complete responses, suggesting that triple therapy might be particularly useful in patients with high-risk genetic features.
“Our results provide preliminary evidence that the triplet combination of ibrutinib, lenalidomide, and rituximab is an active regimen in patients with relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma, and should be evaluated in a prospective randomized controlled trial,” wrote Mats Jerkeman, MD, of Lund University, Sweden, and colleagues. The report was published in The Lancet Haematology.
“Addition of lenalidomide to ibrutinib and rituximab might increase the proportion of patients who have complete remission ... Previous studies reported complete responses in 44% of patients on ibrutinib and rituximab, in 36% of patients on rituximab and lenalidomide, and in 19% of patients on ibrutinib alone,” they wrote.
Treatment was divided into an induction phase of 12 cycles of 28 days with all three drugs and a maintenance phase with ibrutinib and rituximab only, given until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. All the patients had previously been treated with at least one rituximab-containing regimen.
Janssen and Celgene funded the work. Dr. Jerkeman reported ties to Janssen and Celgene, as well as AbbVie and Gilead.
SOURCE: Jerkeman M et al. Lancet Haematol. 2018 Jan 29. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3026(18)30018-8.
A combination of ibrutinib, lenalidomide, and rituximab produced an overall response rate of 76% at 17.8 months median follow-up among 50 adults with relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma, according to an open-label, single-arm, phase 2 trial.
There were complete responses in 28 patients (56%) and partial responses in 10 (20%). Median progression-free survival was 16 months and median overall survival was 22 months. Similar proportions of patients, with and without TP53 mutations, had overall and complete responses, suggesting that triple therapy might be particularly useful in patients with high-risk genetic features.
“Our results provide preliminary evidence that the triplet combination of ibrutinib, lenalidomide, and rituximab is an active regimen in patients with relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma, and should be evaluated in a prospective randomized controlled trial,” wrote Mats Jerkeman, MD, of Lund University, Sweden, and colleagues. The report was published in The Lancet Haematology.
“Addition of lenalidomide to ibrutinib and rituximab might increase the proportion of patients who have complete remission ... Previous studies reported complete responses in 44% of patients on ibrutinib and rituximab, in 36% of patients on rituximab and lenalidomide, and in 19% of patients on ibrutinib alone,” they wrote.
Treatment was divided into an induction phase of 12 cycles of 28 days with all three drugs and a maintenance phase with ibrutinib and rituximab only, given until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. All the patients had previously been treated with at least one rituximab-containing regimen.
Janssen and Celgene funded the work. Dr. Jerkeman reported ties to Janssen and Celgene, as well as AbbVie and Gilead.
SOURCE: Jerkeman M et al. Lancet Haematol. 2018 Jan 29. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3026(18)30018-8.
A combination of ibrutinib, lenalidomide, and rituximab produced an overall response rate of 76% at 17.8 months median follow-up among 50 adults with relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma, according to an open-label, single-arm, phase 2 trial.
There were complete responses in 28 patients (56%) and partial responses in 10 (20%). Median progression-free survival was 16 months and median overall survival was 22 months. Similar proportions of patients, with and without TP53 mutations, had overall and complete responses, suggesting that triple therapy might be particularly useful in patients with high-risk genetic features.
“Our results provide preliminary evidence that the triplet combination of ibrutinib, lenalidomide, and rituximab is an active regimen in patients with relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma, and should be evaluated in a prospective randomized controlled trial,” wrote Mats Jerkeman, MD, of Lund University, Sweden, and colleagues. The report was published in The Lancet Haematology.
“Addition of lenalidomide to ibrutinib and rituximab might increase the proportion of patients who have complete remission ... Previous studies reported complete responses in 44% of patients on ibrutinib and rituximab, in 36% of patients on rituximab and lenalidomide, and in 19% of patients on ibrutinib alone,” they wrote.
Treatment was divided into an induction phase of 12 cycles of 28 days with all three drugs and a maintenance phase with ibrutinib and rituximab only, given until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. All the patients had previously been treated with at least one rituximab-containing regimen.
Janssen and Celgene funded the work. Dr. Jerkeman reported ties to Janssen and Celgene, as well as AbbVie and Gilead.
SOURCE: Jerkeman M et al. Lancet Haematol. 2018 Jan 29. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3026(18)30018-8.
FROM THE LANCET HAEMATOLOGY
Key clinical point:
Major finding: The overall response from for the combination of the three drugs was 76% at 17.8 months median follow-up.
Study details: An open-label, single-arm, phase 2 trial of 50 adults with relapsed/refractory MCL.
Disclosures: Janssen and Celgene funded the work. Dr. Jerkeman reported ties to Janssen and Celgene, as well as AbbVie and Gilead.
Source: Jerkeman M et al. Lancet Haematol. 2018 Jan 29. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3026(18)30018-8.
VcR-CVAD yields high responses, ‘excellent’ survival in MCL
Adding rituximab and bortezomib to a moderate-intensity chemotherapy regimen and following it up with maintenance rituximab produced high response rates and “excellent” survival outcomes for adults with previously untreated mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), investigators reported in long-term follow-up of a small study.
The objective response rate (ORR) among 30 patients with MCL treated with VcR-CVAD – bortezomib (Velcade), rituximab, and hyperCVAD (hyper-fractionated cyclophosphamide, vincristine, doxorubicin, and dexamethasone) followed by rituximab maintenance – was 90%, including a high proportion of complete responses (CR) or unconfirmed complete responses.
After a median follow-up of 7.8 years, the rates of 6-year progression-free and overall survival (PFS and OS) were 53% and 70%, respectively, with patients older and younger than 60 years having equally good outcomes, according to Julie E. Chang, MD, of the Wisconsin Institute of Medical Research in Madison, and her colleagues.
VcR-CVAD is a moderate-intensity regimen with a favorable toxicity profile that allowed tolerability even in an older population, the investigators noted. “An important lesson illustrated by VcR-CVAD is that long-term remissions are achievable in some patients without intensive inductions or consolidation,” they wrote in Clinical Lymphoma, Myeloma & Leukemia.
The investigators previously reported that after a median follow-up of 42 months, the 3-year PFS and OS were 63% and 86%, respectively, and that these outcomes were comparable to those reported with more intensive regimens (Br J Haematol. 2011 Oct;155[2]:190-7).
As noted, the ORR was 90%, including 77% CR/unconfirmed CR, 6-year PFS was 53%, and 6-year OS was 70%.
A univariate analysis showed a significant interaction between lactate dehydrogenase levels and age for PFS, and a trend, albeit not significant, toward an interaction with LDH levels and age for OS.
In multivariate analysis, worse Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status at baseline showed a nonsignificant trend toward worse OS. In contrast, an increase of one in the number of extranodal disease sites was associated with better OS (relative risk 0.66, 95% confidence interval 0.01-0.66).
The investigators noted that the advent of new agents with activity against MCL and the use of prognostic information, such as minimal residual disease measurements, could help clinicians develop induction and maintenance strategies with better efficacy and lower toxicity than VcR-CVAD.
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health, Millennium Pharmaceuticals, and the University of Wisconsin Forward Lymphoma Research Fund. Dr. Chang reported research funding from Genentech. One coauthor disclosed consulting work for Genentech and Millennium and research funding from Genentech.
SOURCE: Chang J et al. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2018 Jan;18(1):e61-e67. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2017.10.006.
Adding rituximab and bortezomib to a moderate-intensity chemotherapy regimen and following it up with maintenance rituximab produced high response rates and “excellent” survival outcomes for adults with previously untreated mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), investigators reported in long-term follow-up of a small study.
The objective response rate (ORR) among 30 patients with MCL treated with VcR-CVAD – bortezomib (Velcade), rituximab, and hyperCVAD (hyper-fractionated cyclophosphamide, vincristine, doxorubicin, and dexamethasone) followed by rituximab maintenance – was 90%, including a high proportion of complete responses (CR) or unconfirmed complete responses.
After a median follow-up of 7.8 years, the rates of 6-year progression-free and overall survival (PFS and OS) were 53% and 70%, respectively, with patients older and younger than 60 years having equally good outcomes, according to Julie E. Chang, MD, of the Wisconsin Institute of Medical Research in Madison, and her colleagues.
VcR-CVAD is a moderate-intensity regimen with a favorable toxicity profile that allowed tolerability even in an older population, the investigators noted. “An important lesson illustrated by VcR-CVAD is that long-term remissions are achievable in some patients without intensive inductions or consolidation,” they wrote in Clinical Lymphoma, Myeloma & Leukemia.
The investigators previously reported that after a median follow-up of 42 months, the 3-year PFS and OS were 63% and 86%, respectively, and that these outcomes were comparable to those reported with more intensive regimens (Br J Haematol. 2011 Oct;155[2]:190-7).
As noted, the ORR was 90%, including 77% CR/unconfirmed CR, 6-year PFS was 53%, and 6-year OS was 70%.
A univariate analysis showed a significant interaction between lactate dehydrogenase levels and age for PFS, and a trend, albeit not significant, toward an interaction with LDH levels and age for OS.
In multivariate analysis, worse Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status at baseline showed a nonsignificant trend toward worse OS. In contrast, an increase of one in the number of extranodal disease sites was associated with better OS (relative risk 0.66, 95% confidence interval 0.01-0.66).
The investigators noted that the advent of new agents with activity against MCL and the use of prognostic information, such as minimal residual disease measurements, could help clinicians develop induction and maintenance strategies with better efficacy and lower toxicity than VcR-CVAD.
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health, Millennium Pharmaceuticals, and the University of Wisconsin Forward Lymphoma Research Fund. Dr. Chang reported research funding from Genentech. One coauthor disclosed consulting work for Genentech and Millennium and research funding from Genentech.
SOURCE: Chang J et al. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2018 Jan;18(1):e61-e67. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2017.10.006.
Adding rituximab and bortezomib to a moderate-intensity chemotherapy regimen and following it up with maintenance rituximab produced high response rates and “excellent” survival outcomes for adults with previously untreated mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), investigators reported in long-term follow-up of a small study.
The objective response rate (ORR) among 30 patients with MCL treated with VcR-CVAD – bortezomib (Velcade), rituximab, and hyperCVAD (hyper-fractionated cyclophosphamide, vincristine, doxorubicin, and dexamethasone) followed by rituximab maintenance – was 90%, including a high proportion of complete responses (CR) or unconfirmed complete responses.
After a median follow-up of 7.8 years, the rates of 6-year progression-free and overall survival (PFS and OS) were 53% and 70%, respectively, with patients older and younger than 60 years having equally good outcomes, according to Julie E. Chang, MD, of the Wisconsin Institute of Medical Research in Madison, and her colleagues.
VcR-CVAD is a moderate-intensity regimen with a favorable toxicity profile that allowed tolerability even in an older population, the investigators noted. “An important lesson illustrated by VcR-CVAD is that long-term remissions are achievable in some patients without intensive inductions or consolidation,” they wrote in Clinical Lymphoma, Myeloma & Leukemia.
The investigators previously reported that after a median follow-up of 42 months, the 3-year PFS and OS were 63% and 86%, respectively, and that these outcomes were comparable to those reported with more intensive regimens (Br J Haematol. 2011 Oct;155[2]:190-7).
As noted, the ORR was 90%, including 77% CR/unconfirmed CR, 6-year PFS was 53%, and 6-year OS was 70%.
A univariate analysis showed a significant interaction between lactate dehydrogenase levels and age for PFS, and a trend, albeit not significant, toward an interaction with LDH levels and age for OS.
In multivariate analysis, worse Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status at baseline showed a nonsignificant trend toward worse OS. In contrast, an increase of one in the number of extranodal disease sites was associated with better OS (relative risk 0.66, 95% confidence interval 0.01-0.66).
The investigators noted that the advent of new agents with activity against MCL and the use of prognostic information, such as minimal residual disease measurements, could help clinicians develop induction and maintenance strategies with better efficacy and lower toxicity than VcR-CVAD.
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health, Millennium Pharmaceuticals, and the University of Wisconsin Forward Lymphoma Research Fund. Dr. Chang reported research funding from Genentech. One coauthor disclosed consulting work for Genentech and Millennium and research funding from Genentech.
SOURCE: Chang J et al. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2018 Jan;18(1):e61-e67. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2017.10.006.
FROM CLINICAL LYMPHOMA, MYELOMA & LEUKEMIA
Key clinical point:
Major finding: The objective response rate was 90%, including 77% complete or unconfirmed complete responses.
Study details: Open-label study of 30 patients with previously untreated MCL.
Disclosures: The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health, Millennium Pharmaceuticals, and the University of Wisconsin Forward Lymphoma Research Fund. Dr. Chang reported research funding from Genentech. A coauthor reported consulting work for Genentech and Millennium and research funding from Genentech.
Source: Chang J et al. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2018 Jan;18(1):e61-e67. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2017.10.006.
BTK inhibitor zanubrutinib active in non-Hodgkin lymphomas
ATLANTA – , according to data presented at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
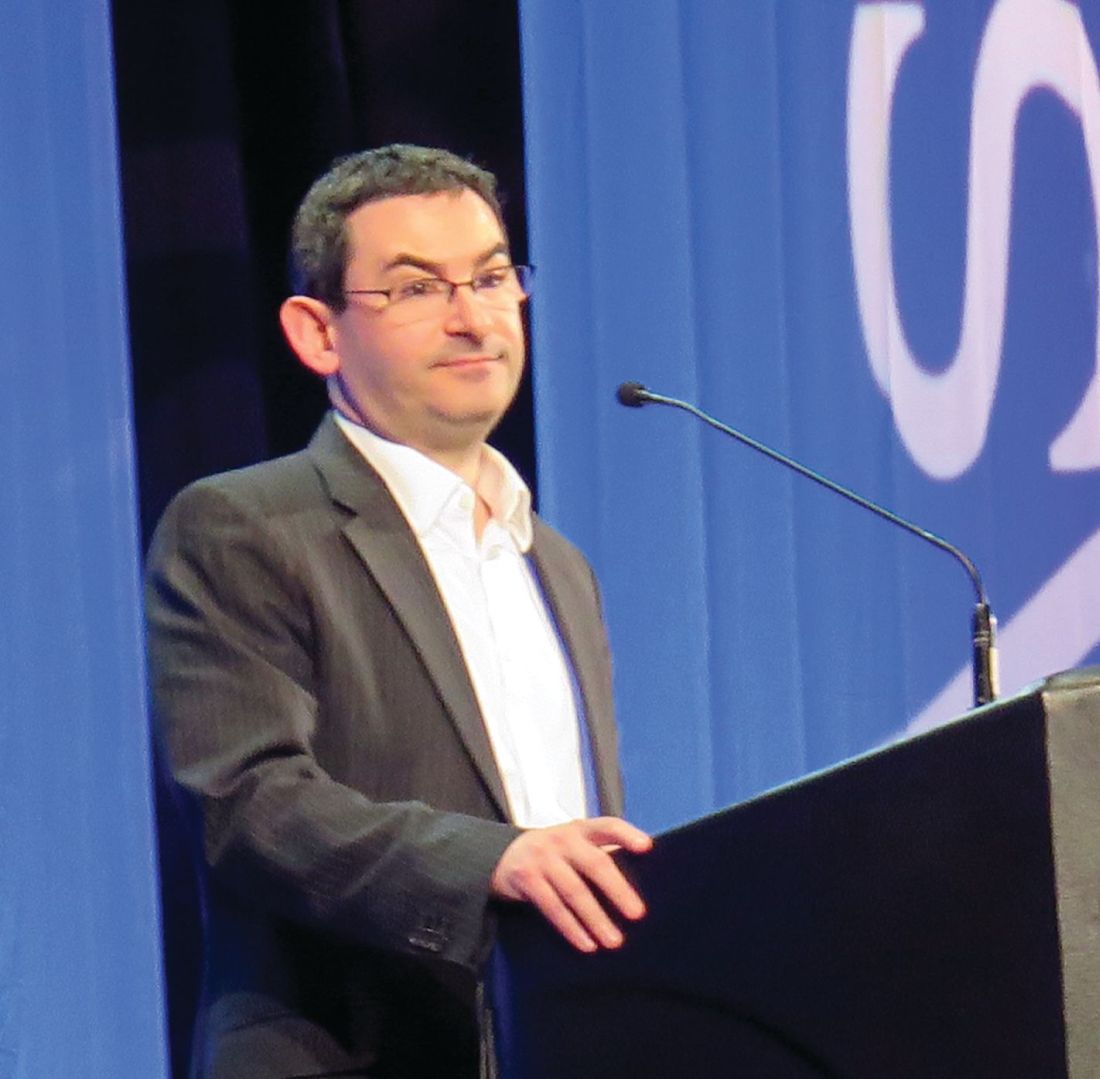
Response rates ranged from 31% to 88% depending on the lymphoma subtype. Overall, approximately 10% of patients discontinued the drug because of adverse events, reported Constantine S. Tam, MBBS, MD, of Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre & St. Vincent’s Hospital, Melbourne.
“There was encouraging activity against all the spectrum of indolent and aggressive NHL subtypes … and durable responses were observed across a variety of histologies,” Dr. Tam said.
Zanubrutinib is a second-generation BTK inhibitor that, based on biochemical assays, has higher selectivity against BTK than ibrutinib, Dr. Tam said.
He presented results of an open-label, multicenter, phase 1b study of daily or twice-daily zanubrutinib in patients with B-cell malignancies, most of them relapsed or refractory to prior therapies. The lymphoma subtypes he presented included diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), follicular lymphoma (FL), mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), and marginal zone lymphoma (MZL).
For 34 patients with indolent lymphomas (FL and MZL), the most frequent adverse events were petechiae/purpura/contusion and upper respiratory tract infection. Eleven grade 3-5 adverse events were reported, including neutropenia, infection, nausea, urinary tract infection, and abdominal pain.
Atrial fibrillation was observed in two patients in the aggressive NHL cohort, for an overall AF rate of approximately 2%, Dr. Tam said.
For 65 patients with aggressive lymphomas (DLBCL and MCL), the most frequent adverse events were petechiae/purpura/contusion and diarrhea; 27 grade 3-5 adverse events were reported, including neutropenia, pneumonia, and anemia.
The highest overall response rate reported was for MCL, at 88% (28 of 32 patients) followed by MZL at 78% (7 of 9 patients), FL at 41% (7 of 17 patients), and DLBCL 31% (8 of 26 patients).
The recommended phase 2 dose for zanubrutinib is either 320 mg/day once daily or a split dose of 160 mg twice daily, Dr. Tam said.
Based on this experience, investigators started a registration trial of zanubrutinib in combination with obinutuzumab for FL, and additional trials are planned, according to Dr. Tam.
There are also registration trials in Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia and chronic lymphocytic leukemia based on other data suggesting activity of zanubrutinib in those disease types, he added.
Zanubrutinib is a product of BeiGene. Dr. Tam reported disclosures related to Roche, Janssen Cilag, Abbvie, Celgene, Pharmacyclics, Onyx, and Amgen.
SOURCE: Tam C et al, ASH 2017, Abstract 152
ATLANTA – , according to data presented at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
Response rates ranged from 31% to 88% depending on the lymphoma subtype. Overall, approximately 10% of patients discontinued the drug because of adverse events, reported Constantine S. Tam, MBBS, MD, of Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre & St. Vincent’s Hospital, Melbourne.
“There was encouraging activity against all the spectrum of indolent and aggressive NHL subtypes … and durable responses were observed across a variety of histologies,” Dr. Tam said.
Zanubrutinib is a second-generation BTK inhibitor that, based on biochemical assays, has higher selectivity against BTK than ibrutinib, Dr. Tam said.
He presented results of an open-label, multicenter, phase 1b study of daily or twice-daily zanubrutinib in patients with B-cell malignancies, most of them relapsed or refractory to prior therapies. The lymphoma subtypes he presented included diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), follicular lymphoma (FL), mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), and marginal zone lymphoma (MZL).
For 34 patients with indolent lymphomas (FL and MZL), the most frequent adverse events were petechiae/purpura/contusion and upper respiratory tract infection. Eleven grade 3-5 adverse events were reported, including neutropenia, infection, nausea, urinary tract infection, and abdominal pain.
Atrial fibrillation was observed in two patients in the aggressive NHL cohort, for an overall AF rate of approximately 2%, Dr. Tam said.
For 65 patients with aggressive lymphomas (DLBCL and MCL), the most frequent adverse events were petechiae/purpura/contusion and diarrhea; 27 grade 3-5 adverse events were reported, including neutropenia, pneumonia, and anemia.
The highest overall response rate reported was for MCL, at 88% (28 of 32 patients) followed by MZL at 78% (7 of 9 patients), FL at 41% (7 of 17 patients), and DLBCL 31% (8 of 26 patients).
The recommended phase 2 dose for zanubrutinib is either 320 mg/day once daily or a split dose of 160 mg twice daily, Dr. Tam said.
Based on this experience, investigators started a registration trial of zanubrutinib in combination with obinutuzumab for FL, and additional trials are planned, according to Dr. Tam.
There are also registration trials in Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia and chronic lymphocytic leukemia based on other data suggesting activity of zanubrutinib in those disease types, he added.
Zanubrutinib is a product of BeiGene. Dr. Tam reported disclosures related to Roche, Janssen Cilag, Abbvie, Celgene, Pharmacyclics, Onyx, and Amgen.
SOURCE: Tam C et al, ASH 2017, Abstract 152
ATLANTA – , according to data presented at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
Response rates ranged from 31% to 88% depending on the lymphoma subtype. Overall, approximately 10% of patients discontinued the drug because of adverse events, reported Constantine S. Tam, MBBS, MD, of Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre & St. Vincent’s Hospital, Melbourne.
“There was encouraging activity against all the spectrum of indolent and aggressive NHL subtypes … and durable responses were observed across a variety of histologies,” Dr. Tam said.
Zanubrutinib is a second-generation BTK inhibitor that, based on biochemical assays, has higher selectivity against BTK than ibrutinib, Dr. Tam said.
He presented results of an open-label, multicenter, phase 1b study of daily or twice-daily zanubrutinib in patients with B-cell malignancies, most of them relapsed or refractory to prior therapies. The lymphoma subtypes he presented included diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), follicular lymphoma (FL), mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), and marginal zone lymphoma (MZL).
For 34 patients with indolent lymphomas (FL and MZL), the most frequent adverse events were petechiae/purpura/contusion and upper respiratory tract infection. Eleven grade 3-5 adverse events were reported, including neutropenia, infection, nausea, urinary tract infection, and abdominal pain.
Atrial fibrillation was observed in two patients in the aggressive NHL cohort, for an overall AF rate of approximately 2%, Dr. Tam said.
For 65 patients with aggressive lymphomas (DLBCL and MCL), the most frequent adverse events were petechiae/purpura/contusion and diarrhea; 27 grade 3-5 adverse events were reported, including neutropenia, pneumonia, and anemia.
The highest overall response rate reported was for MCL, at 88% (28 of 32 patients) followed by MZL at 78% (7 of 9 patients), FL at 41% (7 of 17 patients), and DLBCL 31% (8 of 26 patients).
The recommended phase 2 dose for zanubrutinib is either 320 mg/day once daily or a split dose of 160 mg twice daily, Dr. Tam said.
Based on this experience, investigators started a registration trial of zanubrutinib in combination with obinutuzumab for FL, and additional trials are planned, according to Dr. Tam.
There are also registration trials in Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia and chronic lymphocytic leukemia based on other data suggesting activity of zanubrutinib in those disease types, he added.
Zanubrutinib is a product of BeiGene. Dr. Tam reported disclosures related to Roche, Janssen Cilag, Abbvie, Celgene, Pharmacyclics, Onyx, and Amgen.
SOURCE: Tam C et al, ASH 2017, Abstract 152
REPORTING FROM ASH 2017
Key clinical point: Monotherapy with the BTK inhibitor zanubrutinib (BGB-3111) was active and well tolerated in patients with a variety of non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) subtypes.
Major finding: Response rates ranged from 31% to 88% depending on the lymphoma subtype.
Data source: Preliminary results of an open-label, multicenter, phase 1b study including 99 patients with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, follicular lymphoma, mantle cell lymphoma, or marginal zone lymphoma.
Disclosures: Zanubrutinib is a product of BeiGene. Constantine S. Tam, MBBS, MD, reported disclosures related to Roche, Janssen Cilag, Abbvie, Celgene, Pharmacyclics, Onyx, and Amgen.
Source: Tam C et al. ASH 2017, Abstract 152.
VIDEO - New lymphoma drug approvals: Clinical use, future directions
ATLANTA – 2017 was a banner year for the approval of new drugs to treat hematologic disorders.
At a special interest session at the annual meeting of American Society of Hematology, representatives from the Food and Drug Administration joined forces with clinicians to discuss the use of the newly approved treatments in the real-world setting.
In this video interview,
“This is extremely exciting,” she said regarding the pace of new approvals for hematologic malignancies.
The video associated with this article is no longer available on this site. Please view all of our videos on the MDedge YouTube channel
Axicabtagene ciloleucel, a CAR T-cell product approved in October for the treatment of relapsed/refractory large B-cell lymphoma in adults, is particularly interesting, she said.
“The data shows that if you look at a population of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients, that historically have a very poor outcome, there is definitely an impressive response rate and improved survival, compared to the natural history cohort,” said Dr. Heslop of Baylor College of Medicine, Houston.
However, while the findings are encouraging, only 30%-40% are having a durable response, she added.
“So I think there’ll be lots of efforts to try and improve the response rate by combination with other agents such as checkpoint inhibitors or other immunomodulators,” she said.
With respect to the second-generation Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor acalabrutinib, which was approved in October for adults with mantle cell lymphoma who have been treated with at least one prior therapy, she discussed the potential for improved outcomes and the importance of looking further into its use in patients who have failed ibrutinib therapy, as well as its use in combination with other agents, such as bendamustine and rituximab early in the course of disease.
Copanlisib, a PI3 kinase inhibitor approved in September, is an addition to the armamentarium for adult patients with relapsed follicular lymphoma after two lines of previous therapy.
“It still does have some side effects, as do other drugs in this class, so I think it’s place will still need to be defined,” Dr. Heslop said.
She reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
ATLANTA – 2017 was a banner year for the approval of new drugs to treat hematologic disorders.
At a special interest session at the annual meeting of American Society of Hematology, representatives from the Food and Drug Administration joined forces with clinicians to discuss the use of the newly approved treatments in the real-world setting.
In this video interview,
“This is extremely exciting,” she said regarding the pace of new approvals for hematologic malignancies.
The video associated with this article is no longer available on this site. Please view all of our videos on the MDedge YouTube channel
Axicabtagene ciloleucel, a CAR T-cell product approved in October for the treatment of relapsed/refractory large B-cell lymphoma in adults, is particularly interesting, she said.
“The data shows that if you look at a population of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients, that historically have a very poor outcome, there is definitely an impressive response rate and improved survival, compared to the natural history cohort,” said Dr. Heslop of Baylor College of Medicine, Houston.
However, while the findings are encouraging, only 30%-40% are having a durable response, she added.
“So I think there’ll be lots of efforts to try and improve the response rate by combination with other agents such as checkpoint inhibitors or other immunomodulators,” she said.
With respect to the second-generation Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor acalabrutinib, which was approved in October for adults with mantle cell lymphoma who have been treated with at least one prior therapy, she discussed the potential for improved outcomes and the importance of looking further into its use in patients who have failed ibrutinib therapy, as well as its use in combination with other agents, such as bendamustine and rituximab early in the course of disease.
Copanlisib, a PI3 kinase inhibitor approved in September, is an addition to the armamentarium for adult patients with relapsed follicular lymphoma after two lines of previous therapy.
“It still does have some side effects, as do other drugs in this class, so I think it’s place will still need to be defined,” Dr. Heslop said.
She reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
ATLANTA – 2017 was a banner year for the approval of new drugs to treat hematologic disorders.
At a special interest session at the annual meeting of American Society of Hematology, representatives from the Food and Drug Administration joined forces with clinicians to discuss the use of the newly approved treatments in the real-world setting.
In this video interview,
“This is extremely exciting,” she said regarding the pace of new approvals for hematologic malignancies.
The video associated with this article is no longer available on this site. Please view all of our videos on the MDedge YouTube channel
Axicabtagene ciloleucel, a CAR T-cell product approved in October for the treatment of relapsed/refractory large B-cell lymphoma in adults, is particularly interesting, she said.
“The data shows that if you look at a population of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients, that historically have a very poor outcome, there is definitely an impressive response rate and improved survival, compared to the natural history cohort,” said Dr. Heslop of Baylor College of Medicine, Houston.
However, while the findings are encouraging, only 30%-40% are having a durable response, she added.
“So I think there’ll be lots of efforts to try and improve the response rate by combination with other agents such as checkpoint inhibitors or other immunomodulators,” she said.
With respect to the second-generation Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor acalabrutinib, which was approved in October for adults with mantle cell lymphoma who have been treated with at least one prior therapy, she discussed the potential for improved outcomes and the importance of looking further into its use in patients who have failed ibrutinib therapy, as well as its use in combination with other agents, such as bendamustine and rituximab early in the course of disease.
Copanlisib, a PI3 kinase inhibitor approved in September, is an addition to the armamentarium for adult patients with relapsed follicular lymphoma after two lines of previous therapy.
“It still does have some side effects, as do other drugs in this class, so I think it’s place will still need to be defined,” Dr. Heslop said.
She reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
REPORTING FROM ASH 2017