User login
Medical, Endoscopic, and Surgical Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
Introduction
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a frequently encountered condition, and rising annually.1 A recent meta-analysis suggests nearly 14% (1.03 billion) of the population are affected worldwide. Differences may range by region from 12% in Latin America to 20% in North America, and by country from 4% in China to 23% in Turkey.1 In the United States, 21% of the population are afflicted with weekly GERD symptoms.2 Novel medical therapies and endoscopic options provide clinicians with opportunities to help patients with GERD.3
Diagnosis
Definition
GERD was originally defined by the Montreal consensus as a condition that develops when the reflux of stomach contents causes troublesome symptoms and/or complications.4 Heartburn and regurgitation are common symptoms of GERD, with a sensitivity of 30%-76% and specificity of 62%-96% for erosive esophagitis (EE), which occurs when the reflux of stomach content causes esophageal mucosal breaks.5 The presence of characteristic mucosal injury observed during an upper endoscopy or abnormal esophageal acid exposure on ambulatory reflux monitoring are objective evidence of GERD. A trial of a proton pump inhibitor (PPI) may function as a diagnostic test for patients exhibiting the typical symptoms of GERD without any alarm symptoms.3,6
Endoscopic Evaluation and Confirmation
The 2022 American Gastroenterological Association (AGA) clinical practice update recommends diagnostic endoscopy, after PPIs are stopped for 2-4 weeks, in patients whose GERD symptoms do not respond adequately to an empiric trial of a PPI.3 Those with GERD and alarm symptoms such as dysphagia, weight loss, bleeding, and vomiting should undergo endoscopy as soon as possible. Endoscopic findings of EE (Los Angeles Grade B or more severe) and long-segment Barrett’s esophagus (> 3-cm segment with intestinal metaplasia on biopsy) are diagnostic of GERD.3
Reflux Monitoring
With ambulatory reflux monitoring (pH or impedance-pH), esophageal acid exposure (or neutral refluxate in impedance testing) can be measured to confirm GERD diagnosis and to correlate symptoms with reflux episodes. Patients with atypical GERD symptoms or patients with a confirmed diagnosis of GERD whose symptoms have not improved sufficiently with twice-daily PPI therapy should have esophageal impedance-pH monitoring while on PPIs.6,7
Esophageal Manometry
High-resolution esophageal manometry can be used to assess motility abnormalities associated with GERD.
Although no manometric abnormality is unique to GERD, weak lower esophageal sphincter (LES) resting pressure and ineffective esophageal motility frequently coexist with severe GERD.6
Manometry is particularly useful in patients considering surgical or endoscopic anti-reflux procedures to evaluate for achalasia,3 an important contraindication to surgery.
Medical Management
Management of GERD requires a multidisciplinary and personalized approach based on symptom presentation, body mass index, endoscopic findings (e.g., presence of EE, Barrett’s esophagus, hiatal hernia), and physiological abnormalities (e.g., gastroparesis or ineffective motility).3
Lifestyle Modifications
Recommended lifestyle modifications include weight loss for patients with obesity, stress reduction, tobacco and alcohol cessation, elevating the head of the bed, staying upright during and after meals, avoidance of food intake < 3 hours before bedtime, and cessation of foods that potentially aggravate reflux symptoms such as coffee, chocolate, carbonated beverages, spicy foods, acidic foods, and foods with high fat content.6,8
Medications
Pharmacologic therapy for GERD includes medications that primarily aim to neutralize or reduce gastric acid -- we summarize options in Table 1.3,8
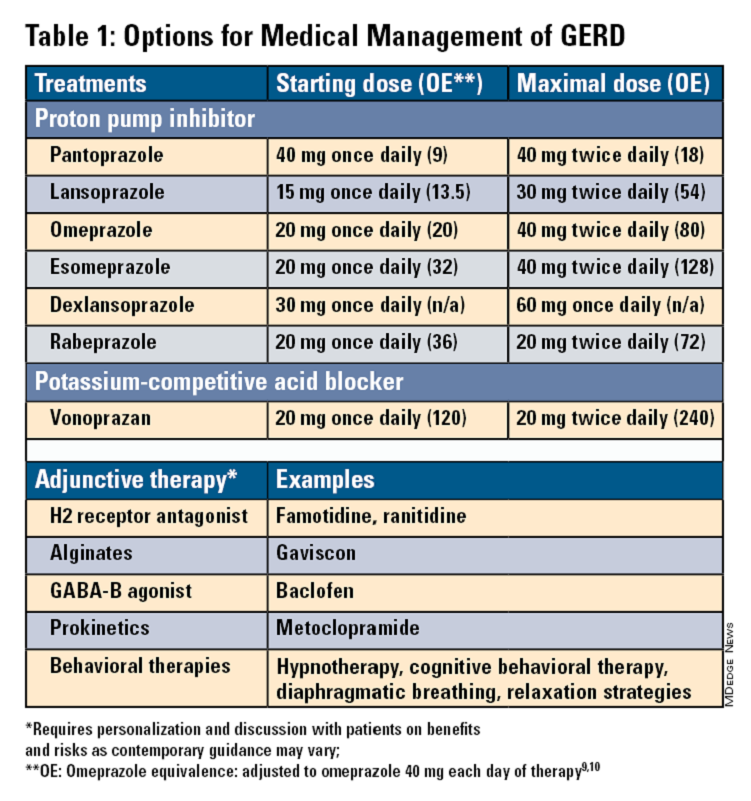
Proton Pump Inhibitors
Most guidelines suggest a trial of 4-8 weeks of once-daily enteric-coated PPI before meals in patients with typical GERD symptoms and no alarm symptoms. Escalation to double-dose PPI may be considered in the case of persistent symptoms. The relative potencies of standard-dose pantoprazole, lansoprazole, esomeprazole, and rabeprazole are presented in Table 1.9 When a PPI switch is needed, rabeprazole may be considered as it is a PPI that does not rely on CYP2C19 for primary metabolism.9
Acid suppression should be weaned down to the lowest effective dose or converted to H2RAs or other antacids once symptoms are sufficiently controlled unless patients have EE, Barrett’s esophagus, or peptic stricture.3 Patients with severe GERD may require long-term PPI therapy or an invasive anti-reflux procedure.
Recent studies have shown that potassium-competitive acid blockers (PCAB) like vonoprazan may offer more effective gastric acid inhibition. While not included in the latest clinical practice update, vonoprazan is thought to be superior to lansoprazole for those with LA Grade C/D esophagitis for both symptom relief and healing at 2 weeks.10
Adjunctive Therapies
Alginates can function as a physical barrier to even neutral reflux and may be helpful for patients with postprandial or nighttime symptoms as well as those with hiatal hernia.3 H2RAs can also help mitigate nighttime symptoms.3 Baclofen is a gamma-aminobutyric acid–B agonist which inhibits transient lower esophageal sphincter relaxation (TLESR) and may be effective for patients with belching.3 Prokinetics may be helpful for GERD with concomitant gastroparesis.3 Sucralfate is a mucosal protective agent, but there is a lack of data supporting its efficacy in GERD treatment. Consider referral to a behavioral therapist for supplemental therapies, hypnotherapy, cognitive-behavior therapy, diaphragmatic breathing, and relaxation strategies for functional heartburn or reflux-associated esophageal hypervigilance or reflux hypersensitivity.3
When to Refer to Higher Level of Care
For patients who do not wish to remain on longer-term pharmacologic therapy or would benefit from anatomic repair, clinicians should have a discussion of risks and benefits prior to consideration of referral for anti-reflux procedures.3,6,8 We advise this conversation should include review of patient health status, postsurgical side effects such as increased flatus, bloating and dysphagia as well as the potential need to still resume PPI post operation.8
Endoscopic Management
Patient Selection And Evaluation
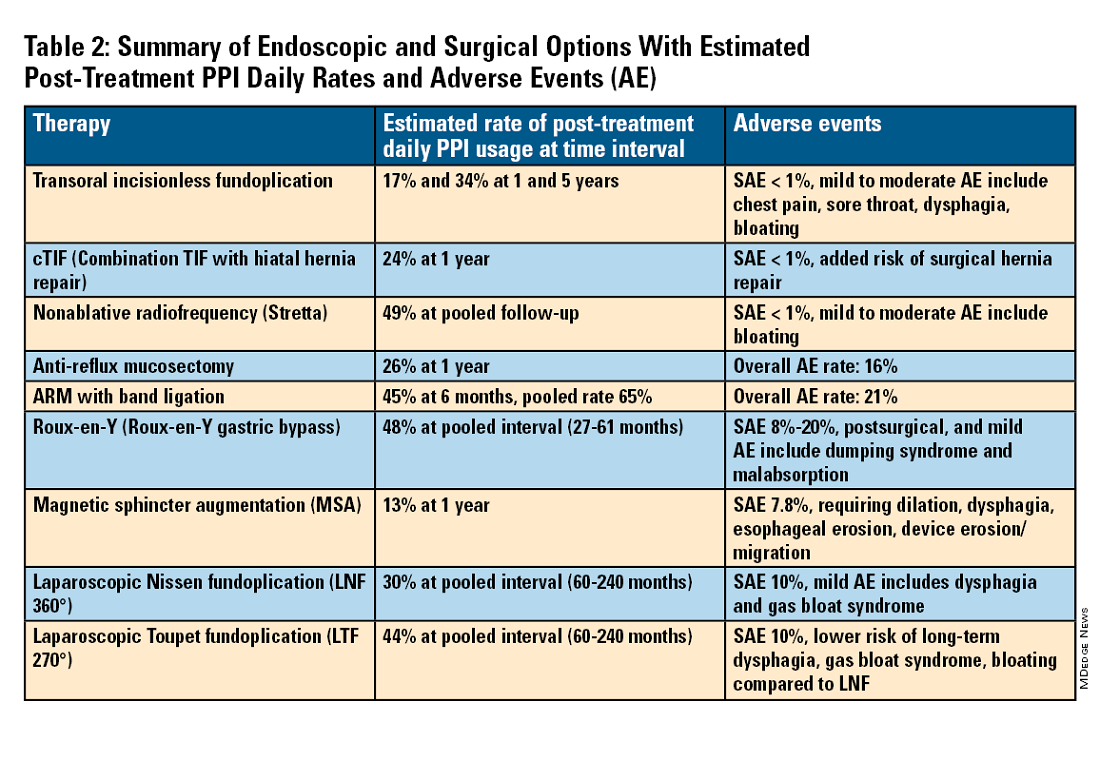
For the groups indicated for a higher level of care, we agree with AGA recommendations, multi-society guidelines, and expert review,3,7,11,12 and highlight potential options in Table 2. Step-up options should be based on patient characteristics and reviewed carefully with patients. Endoscopic therapies are less invasive than surgery and may be considered for those who do not require anatomic repair of hiatal hernia, do not want surgery, or are not suitable for surgery.
The pathophysiology of GERD is from a loss of the anti-reflux barrier of the esophageal gastric junction (EGJ) at the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) leading to unintended retrograde movement of gastric contents.6 Anatomically, the LES is composed of muscles of the distal esophagus and sling fibers of the proximal stomach, the “external valve” from the diaphragmatic crura, and the “internal valve” from the gastroesophageal flap valve (GEFV). GERD occurs from mechanical failure of the LES. First, there may be disproportional dilation of the diaphragmatic crura as categorized by Hill Grade of the GEFV as seen by a retroflexed view of EGJ after 30-45 seconds of insufflation.13 Second, there may be a migration of the LES away from the diaphragmatic crura as in the case of a hiatal hernia. Provocative maneuvers may reveal a sliding hernia by gentle retraction of the endoscope while under retroflexed view.13 Third, there may be more frequent TLESR associated with GERD.12
The aim of most interventions is to restore competency of the LES by reconstruction of the GEFV via suture or staple-based approximation of tissue.11,12 Intraluminal therapy may only target the GEFV at the internal valve. Therefore, most endoscopic interventions are limited to patients with intact diaphragmatic crura (ie, small to no hiatal hernia and GEFV Hill Grade 1 to 2). Contraindications for endoscopic therapy are moderate to severe reflux (ie, LA Grade C/ D), hiatus hernia 2 cm or larger, strictures, or long-segment Barrett’s esophagus.
Utility, Safety, and Outcomes of TIF
Historically, endoscopic therapy targeting endoscopic fundoplication started with EndoLuminal gastro-gastric fundoplication (ELF, 2005) which was a proof of concept of safe manipulation and suture for gastro-gastric plication to below the Z-line. Transoral incisionless fundoplication (TIF) 1.0 was suggested in 2007 for clinical application by proposing a longitudinal oriented esophago-gastric plication 1 cm above the Z-line.
In 2009, TIF2.0 was proposed as a rotational 270° wrap of the cardia and fundus to a full-thickness esophago-gastric fundoplication around 2-4 cm of the distal esophagus. Like a surgical fundoplication, this reinforces sling fibers, increases the Angle of His and improves the cardiac notch. TIF 2.0 is indicated for those with small (< 2 cm) or no hiatal hernia and a GEFV Hill Grade 1 or 2. The present iteration of TIF2.0 uses EsophyX-Z (EndoGastric Solutions; Redmond, Washington) which features dual fastener deployment and a simplified firing mechanism. Plication is secured via nonresorbable polypropylene T-fasteners with strength equivalence of 3-0 sutures.
Compared with the original, TIF2.0 represents a decrease of severe adverse events from 2%-2.5% to 0.4%-1%.11,14 Based on longitudinal TEMPO data, patient satisfaction ranges between 70% and 90% and rates of patients reverting to daily PPI use are 17% and 34% at 1 and 5 years. A 5% reintervention rate was noted to be comparable with surgical reoperation for fundoplication.15 One retrospective evaluation of patients with failed TIF followed by successful cTIF noted that in all failures there was a documented underestimation of a much larger crura defect at time of index procedure.16 Chest pain is common post procedure and patients and collaborating providers should be counseled on the expected course. In our practice, we admit patients for at least 1 postprocedure day and consider scheduling symptom control medications for those with significant pain.
TIF2.0 for Special Populations
Indications for TIF2.0 continue to evolve. In 2017, concomitant TIF2.0 with hiatal hernia repair (cTIF or HH-TIF) for hernia > 2 cm was accepted for expanded use. In one study, cTIF has been shown to have similar outcomes for postprocedural PPI use, dysphagia, wrap disruption, and hiatal hernia recurrence, compared with hiatal hernia repair paired with laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication with possibly shorter postadmission stay, serious adverse events, and bloating.17 A cTIF may be performed in a single general anesthetic session typically with a surgical hiatal hernia repair followed by TIF2.0.
Other Endoscopic Procedures
Several other endoscopic interventions have been proposed for GERD management. The following procedures are under continuous study and should be considered only by those with expertise.
Stretta
The Stretta device (Restech; Houston, Texas) was approved in 2000 for use of a radiofrequency (RF) generator and catheter applied to the squamocolumnar junction under irrigation. Ideal candidates for this nonablative procedure may include patients with confirmed GERD, low-grade EE, without Barrett’s esophagus, small hiatal hernia, and a competent LES with pressure > 5 mmHg. Meta-analysis has yielded conflicting results in terms of its efficacy, compared with TIF2.0, and recent multi-society guidance suggests fundoplication over Stretta.7
ARM, MASE, and RAP
Anti-reflux mucosectomy (ARM) has been proposed based on the observation that patients undergoing mucosectomy for neoplasms in the cardia had improvement of reflux symptoms.11,12 Systematic review has suggested a clinical response of 80% of either PPI discontinuation or reduction, but 17% of adverse events include development of strictures. Iterations of ARM continue to be studied including ARM with band ligation (L-ARM) and endoscopic submucosal dissection for GERD (ESD-G).12
Experts have proposed incorporating endoscopic suturing of the EGJ to modulate the LES. Mucosal ablation and suturing of the EG junction (MASE) has been proposed by first priming tissue via argon plasma coagulation (APC) prior to endoscopic overstitch of two to three interrupted sutures below the EGJ to narrow and elongate the EGJ. The resection and plication (RAP) procedure performs a mucosal resection prior to full-thickness plication of the LES and cardia.11,12 Expert opinion has suggested that RAP may be used in patients with altered anatomy whereas MASE may be used when resection is not possible (eg, prior scarring, resection or ablation).12
Surgical Management
We agree with a recent multi-society guideline recommending that an interdisciplinary consultation with surgery for indicated patients with refractory GERD and underlying hiatal hernia, or who do not want lifelong medical therapy.
Fundoplication creates a surgical wrap to reinforce the LES and may be performed laparoscopically. Contraindications include body mass index (BMI) >35 kg/m2 and significantly impaired dysmotility. Fundoplication of 180°, 270°, and 360° may achieve comparable outcomes, but a laparoscopic toupet fundoplication (LTF 270°) may have fewer postsurgical issues of dysphagia and bloating. Advantages for both anterior and posterior partial fundoplications have been demonstrated by network meta-analysis. Therefore, a multi-society guideline for GERD suggests partial over complete fundoplication.7 Compared with posterior techniques, anterior fundoplication (Watson fundoplication) led to more recurrent reflux symptoms but less dysphagia and other side effects.19
Magnetic sphincter augmentation (MSA) is a surgical option that strengthens the LES with magnets to improve sphincter competence. In addition to listed contraindications of fundoplication, patients with an allergy to nickel and/or titanium are also contraindicated to receive MSA.7 MSA has been suggested to be equivalent to LNF although there may be less gas bloat and greater ability to belch on follow up.20
Surgical Options for Special Populations
Patients with medically refractory GERD and a BMI ≥ 35 kg/m2 may benefit from either Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) or fundoplication, however sleeve gastrectomy is not advised.7 In patients with BMI > 50 kg/m2, RYGB may provide an optimal choice. We agree with consultation with a bariatric surgeon when reviewing these situations.
Conclusion
Patients with GERD are commonly encountered worldwide. Empiric PPI are effective mainstays for medical treatment of GERD. Novel PCABs (e.g., vonoprazan) may present new options for GERD with LA Grade C/D esophagitis EE and merit more study. In refractory cases or for patients who do not want long term medical therapy, step-up therapy may be considered via endoscopic or surgical interventions. Patient anatomy and comorbidities should be considered by the clinician to inform treatment options. Surgery may have the most durable outcomes for those requiring step-up therapy. Improvements in technique, devices and patient selection have allowed TIF2.0 to grow as a viable offering with excellent 5-year outcomes for indicated patients.
Dr. Chang, Dr. Tintara, and Dr. Phan are based in the Division of Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease at the University of Southern California in Los Angeles. They have no conflicts of interest to declare.
References
1. Richter JE andRubenstein JH. Gastroenterology. 2018 Jan. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.07.045.
2. El-Serag HB et al. Gut. 2014 Jun. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2012-304269.
3. Yadlapati R et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 May. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2022.01.025.
4. Vakil N et al. Am J Gastroenterol. 2006 Aug. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2006.00630.x.
5. Numans ME et al. Ann Intern Med. 2004 Apr. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-140-7-200404060-00011.
6. Kahrilas PJ et al. Gastroenterology. 2008 Oct. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2008.08.045.
7. Slater BJ et al. Surg Endosc. 2023 Feb. doi: 10.1007/s00464-022-09817-3.
8. Gyawali CP et al. Gut. 2018 Jul. doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2017-314722.
9. Graham DY and Tansel A. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018 Jun. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2017.09.033.
10. Graham DY and Dore MP. Gastroenterology. 2018 Feb. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2018.01.018.
11. Haseeb M and Thompson CC. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2023 Sep. doi: 10.1097/MOG.0000000000000968.
12. Kolb JM and Chang KJ. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2023 Jul. doi:10.1097/MOG.0000000000000944.
13. Nguyen NT et al. Foregut. 2022 Sep. doi: 10.1177/26345161221126961.
14. Mazzoleni G et al. Endosc Int Open. 2021 Feb. doi: 10.1055/a-1322-2209.
15. Trad KS et al. Surg Innov. 2018 Apr. doi: 10.1177/1553350618755214.
16. Kolb JM et al. Gastroenterology. 2021 May. doi: 10.1016/S0016-5085(21)02953-X.
17. Jaruvongvanich VK et al. Endosc Int Open. 2023 Jan. doi: 10.1055/a-1972-9190.
18. Lee Y et al. Surg Endosc. 2023 Jul. doi: 10.1007/s00464-023-10151-5.
19. Andreou A et al. Surg Endosc. 2020 Feb. doi: 10.1007/s00464-019-07208-9.
20. Guidozzi N et al. Dis Esophagus. 2019 Nov. doi: 10.1093/dote/doz031.
Introduction
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a frequently encountered condition, and rising annually.1 A recent meta-analysis suggests nearly 14% (1.03 billion) of the population are affected worldwide. Differences may range by region from 12% in Latin America to 20% in North America, and by country from 4% in China to 23% in Turkey.1 In the United States, 21% of the population are afflicted with weekly GERD symptoms.2 Novel medical therapies and endoscopic options provide clinicians with opportunities to help patients with GERD.3
Diagnosis
Definition
GERD was originally defined by the Montreal consensus as a condition that develops when the reflux of stomach contents causes troublesome symptoms and/or complications.4 Heartburn and regurgitation are common symptoms of GERD, with a sensitivity of 30%-76% and specificity of 62%-96% for erosive esophagitis (EE), which occurs when the reflux of stomach content causes esophageal mucosal breaks.5 The presence of characteristic mucosal injury observed during an upper endoscopy or abnormal esophageal acid exposure on ambulatory reflux monitoring are objective evidence of GERD. A trial of a proton pump inhibitor (PPI) may function as a diagnostic test for patients exhibiting the typical symptoms of GERD without any alarm symptoms.3,6
Endoscopic Evaluation and Confirmation
The 2022 American Gastroenterological Association (AGA) clinical practice update recommends diagnostic endoscopy, after PPIs are stopped for 2-4 weeks, in patients whose GERD symptoms do not respond adequately to an empiric trial of a PPI.3 Those with GERD and alarm symptoms such as dysphagia, weight loss, bleeding, and vomiting should undergo endoscopy as soon as possible. Endoscopic findings of EE (Los Angeles Grade B or more severe) and long-segment Barrett’s esophagus (> 3-cm segment with intestinal metaplasia on biopsy) are diagnostic of GERD.3
Reflux Monitoring
With ambulatory reflux monitoring (pH or impedance-pH), esophageal acid exposure (or neutral refluxate in impedance testing) can be measured to confirm GERD diagnosis and to correlate symptoms with reflux episodes. Patients with atypical GERD symptoms or patients with a confirmed diagnosis of GERD whose symptoms have not improved sufficiently with twice-daily PPI therapy should have esophageal impedance-pH monitoring while on PPIs.6,7
Esophageal Manometry
High-resolution esophageal manometry can be used to assess motility abnormalities associated with GERD.
Although no manometric abnormality is unique to GERD, weak lower esophageal sphincter (LES) resting pressure and ineffective esophageal motility frequently coexist with severe GERD.6
Manometry is particularly useful in patients considering surgical or endoscopic anti-reflux procedures to evaluate for achalasia,3 an important contraindication to surgery.
Medical Management
Management of GERD requires a multidisciplinary and personalized approach based on symptom presentation, body mass index, endoscopic findings (e.g., presence of EE, Barrett’s esophagus, hiatal hernia), and physiological abnormalities (e.g., gastroparesis or ineffective motility).3
Lifestyle Modifications
Recommended lifestyle modifications include weight loss for patients with obesity, stress reduction, tobacco and alcohol cessation, elevating the head of the bed, staying upright during and after meals, avoidance of food intake < 3 hours before bedtime, and cessation of foods that potentially aggravate reflux symptoms such as coffee, chocolate, carbonated beverages, spicy foods, acidic foods, and foods with high fat content.6,8
Medications
Pharmacologic therapy for GERD includes medications that primarily aim to neutralize or reduce gastric acid -- we summarize options in Table 1.3,8

Proton Pump Inhibitors
Most guidelines suggest a trial of 4-8 weeks of once-daily enteric-coated PPI before meals in patients with typical GERD symptoms and no alarm symptoms. Escalation to double-dose PPI may be considered in the case of persistent symptoms. The relative potencies of standard-dose pantoprazole, lansoprazole, esomeprazole, and rabeprazole are presented in Table 1.9 When a PPI switch is needed, rabeprazole may be considered as it is a PPI that does not rely on CYP2C19 for primary metabolism.9
Acid suppression should be weaned down to the lowest effective dose or converted to H2RAs or other antacids once symptoms are sufficiently controlled unless patients have EE, Barrett’s esophagus, or peptic stricture.3 Patients with severe GERD may require long-term PPI therapy or an invasive anti-reflux procedure.
Recent studies have shown that potassium-competitive acid blockers (PCAB) like vonoprazan may offer more effective gastric acid inhibition. While not included in the latest clinical practice update, vonoprazan is thought to be superior to lansoprazole for those with LA Grade C/D esophagitis for both symptom relief and healing at 2 weeks.10
Adjunctive Therapies
Alginates can function as a physical barrier to even neutral reflux and may be helpful for patients with postprandial or nighttime symptoms as well as those with hiatal hernia.3 H2RAs can also help mitigate nighttime symptoms.3 Baclofen is a gamma-aminobutyric acid–B agonist which inhibits transient lower esophageal sphincter relaxation (TLESR) and may be effective for patients with belching.3 Prokinetics may be helpful for GERD with concomitant gastroparesis.3 Sucralfate is a mucosal protective agent, but there is a lack of data supporting its efficacy in GERD treatment. Consider referral to a behavioral therapist for supplemental therapies, hypnotherapy, cognitive-behavior therapy, diaphragmatic breathing, and relaxation strategies for functional heartburn or reflux-associated esophageal hypervigilance or reflux hypersensitivity.3
When to Refer to Higher Level of Care
For patients who do not wish to remain on longer-term pharmacologic therapy or would benefit from anatomic repair, clinicians should have a discussion of risks and benefits prior to consideration of referral for anti-reflux procedures.3,6,8 We advise this conversation should include review of patient health status, postsurgical side effects such as increased flatus, bloating and dysphagia as well as the potential need to still resume PPI post operation.8
Endoscopic Management
Patient Selection And Evaluation
For the groups indicated for a higher level of care, we agree with AGA recommendations, multi-society guidelines, and expert review,3,7,11,12 and highlight potential options in Table 2. Step-up options should be based on patient characteristics and reviewed carefully with patients. Endoscopic therapies are less invasive than surgery and may be considered for those who do not require anatomic repair of hiatal hernia, do not want surgery, or are not suitable for surgery.

The pathophysiology of GERD is from a loss of the anti-reflux barrier of the esophageal gastric junction (EGJ) at the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) leading to unintended retrograde movement of gastric contents.6 Anatomically, the LES is composed of muscles of the distal esophagus and sling fibers of the proximal stomach, the “external valve” from the diaphragmatic crura, and the “internal valve” from the gastroesophageal flap valve (GEFV). GERD occurs from mechanical failure of the LES. First, there may be disproportional dilation of the diaphragmatic crura as categorized by Hill Grade of the GEFV as seen by a retroflexed view of EGJ after 30-45 seconds of insufflation.13 Second, there may be a migration of the LES away from the diaphragmatic crura as in the case of a hiatal hernia. Provocative maneuvers may reveal a sliding hernia by gentle retraction of the endoscope while under retroflexed view.13 Third, there may be more frequent TLESR associated with GERD.12
The aim of most interventions is to restore competency of the LES by reconstruction of the GEFV via suture or staple-based approximation of tissue.11,12 Intraluminal therapy may only target the GEFV at the internal valve. Therefore, most endoscopic interventions are limited to patients with intact diaphragmatic crura (ie, small to no hiatal hernia and GEFV Hill Grade 1 to 2). Contraindications for endoscopic therapy are moderate to severe reflux (ie, LA Grade C/ D), hiatus hernia 2 cm or larger, strictures, or long-segment Barrett’s esophagus.
Utility, Safety, and Outcomes of TIF
Historically, endoscopic therapy targeting endoscopic fundoplication started with EndoLuminal gastro-gastric fundoplication (ELF, 2005) which was a proof of concept of safe manipulation and suture for gastro-gastric plication to below the Z-line. Transoral incisionless fundoplication (TIF) 1.0 was suggested in 2007 for clinical application by proposing a longitudinal oriented esophago-gastric plication 1 cm above the Z-line.
In 2009, TIF2.0 was proposed as a rotational 270° wrap of the cardia and fundus to a full-thickness esophago-gastric fundoplication around 2-4 cm of the distal esophagus. Like a surgical fundoplication, this reinforces sling fibers, increases the Angle of His and improves the cardiac notch. TIF 2.0 is indicated for those with small (< 2 cm) or no hiatal hernia and a GEFV Hill Grade 1 or 2. The present iteration of TIF2.0 uses EsophyX-Z (EndoGastric Solutions; Redmond, Washington) which features dual fastener deployment and a simplified firing mechanism. Plication is secured via nonresorbable polypropylene T-fasteners with strength equivalence of 3-0 sutures.
Compared with the original, TIF2.0 represents a decrease of severe adverse events from 2%-2.5% to 0.4%-1%.11,14 Based on longitudinal TEMPO data, patient satisfaction ranges between 70% and 90% and rates of patients reverting to daily PPI use are 17% and 34% at 1 and 5 years. A 5% reintervention rate was noted to be comparable with surgical reoperation for fundoplication.15 One retrospective evaluation of patients with failed TIF followed by successful cTIF noted that in all failures there was a documented underestimation of a much larger crura defect at time of index procedure.16 Chest pain is common post procedure and patients and collaborating providers should be counseled on the expected course. In our practice, we admit patients for at least 1 postprocedure day and consider scheduling symptom control medications for those with significant pain.
TIF2.0 for Special Populations
Indications for TIF2.0 continue to evolve. In 2017, concomitant TIF2.0 with hiatal hernia repair (cTIF or HH-TIF) for hernia > 2 cm was accepted for expanded use. In one study, cTIF has been shown to have similar outcomes for postprocedural PPI use, dysphagia, wrap disruption, and hiatal hernia recurrence, compared with hiatal hernia repair paired with laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication with possibly shorter postadmission stay, serious adverse events, and bloating.17 A cTIF may be performed in a single general anesthetic session typically with a surgical hiatal hernia repair followed by TIF2.0.
Other Endoscopic Procedures
Several other endoscopic interventions have been proposed for GERD management. The following procedures are under continuous study and should be considered only by those with expertise.
Stretta
The Stretta device (Restech; Houston, Texas) was approved in 2000 for use of a radiofrequency (RF) generator and catheter applied to the squamocolumnar junction under irrigation. Ideal candidates for this nonablative procedure may include patients with confirmed GERD, low-grade EE, without Barrett’s esophagus, small hiatal hernia, and a competent LES with pressure > 5 mmHg. Meta-analysis has yielded conflicting results in terms of its efficacy, compared with TIF2.0, and recent multi-society guidance suggests fundoplication over Stretta.7
ARM, MASE, and RAP
Anti-reflux mucosectomy (ARM) has been proposed based on the observation that patients undergoing mucosectomy for neoplasms in the cardia had improvement of reflux symptoms.11,12 Systematic review has suggested a clinical response of 80% of either PPI discontinuation or reduction, but 17% of adverse events include development of strictures. Iterations of ARM continue to be studied including ARM with band ligation (L-ARM) and endoscopic submucosal dissection for GERD (ESD-G).12
Experts have proposed incorporating endoscopic suturing of the EGJ to modulate the LES. Mucosal ablation and suturing of the EG junction (MASE) has been proposed by first priming tissue via argon plasma coagulation (APC) prior to endoscopic overstitch of two to three interrupted sutures below the EGJ to narrow and elongate the EGJ. The resection and plication (RAP) procedure performs a mucosal resection prior to full-thickness plication of the LES and cardia.11,12 Expert opinion has suggested that RAP may be used in patients with altered anatomy whereas MASE may be used when resection is not possible (eg, prior scarring, resection or ablation).12
Surgical Management
We agree with a recent multi-society guideline recommending that an interdisciplinary consultation with surgery for indicated patients with refractory GERD and underlying hiatal hernia, or who do not want lifelong medical therapy.
Fundoplication creates a surgical wrap to reinforce the LES and may be performed laparoscopically. Contraindications include body mass index (BMI) >35 kg/m2 and significantly impaired dysmotility. Fundoplication of 180°, 270°, and 360° may achieve comparable outcomes, but a laparoscopic toupet fundoplication (LTF 270°) may have fewer postsurgical issues of dysphagia and bloating. Advantages for both anterior and posterior partial fundoplications have been demonstrated by network meta-analysis. Therefore, a multi-society guideline for GERD suggests partial over complete fundoplication.7 Compared with posterior techniques, anterior fundoplication (Watson fundoplication) led to more recurrent reflux symptoms but less dysphagia and other side effects.19
Magnetic sphincter augmentation (MSA) is a surgical option that strengthens the LES with magnets to improve sphincter competence. In addition to listed contraindications of fundoplication, patients with an allergy to nickel and/or titanium are also contraindicated to receive MSA.7 MSA has been suggested to be equivalent to LNF although there may be less gas bloat and greater ability to belch on follow up.20
Surgical Options for Special Populations
Patients with medically refractory GERD and a BMI ≥ 35 kg/m2 may benefit from either Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) or fundoplication, however sleeve gastrectomy is not advised.7 In patients with BMI > 50 kg/m2, RYGB may provide an optimal choice. We agree with consultation with a bariatric surgeon when reviewing these situations.
Conclusion
Patients with GERD are commonly encountered worldwide. Empiric PPI are effective mainstays for medical treatment of GERD. Novel PCABs (e.g., vonoprazan) may present new options for GERD with LA Grade C/D esophagitis EE and merit more study. In refractory cases or for patients who do not want long term medical therapy, step-up therapy may be considered via endoscopic or surgical interventions. Patient anatomy and comorbidities should be considered by the clinician to inform treatment options. Surgery may have the most durable outcomes for those requiring step-up therapy. Improvements in technique, devices and patient selection have allowed TIF2.0 to grow as a viable offering with excellent 5-year outcomes for indicated patients.
Dr. Chang, Dr. Tintara, and Dr. Phan are based in the Division of Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease at the University of Southern California in Los Angeles. They have no conflicts of interest to declare.
References
1. Richter JE andRubenstein JH. Gastroenterology. 2018 Jan. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.07.045.
2. El-Serag HB et al. Gut. 2014 Jun. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2012-304269.
3. Yadlapati R et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 May. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2022.01.025.
4. Vakil N et al. Am J Gastroenterol. 2006 Aug. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2006.00630.x.
5. Numans ME et al. Ann Intern Med. 2004 Apr. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-140-7-200404060-00011.
6. Kahrilas PJ et al. Gastroenterology. 2008 Oct. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2008.08.045.
7. Slater BJ et al. Surg Endosc. 2023 Feb. doi: 10.1007/s00464-022-09817-3.
8. Gyawali CP et al. Gut. 2018 Jul. doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2017-314722.
9. Graham DY and Tansel A. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018 Jun. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2017.09.033.
10. Graham DY and Dore MP. Gastroenterology. 2018 Feb. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2018.01.018.
11. Haseeb M and Thompson CC. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2023 Sep. doi: 10.1097/MOG.0000000000000968.
12. Kolb JM and Chang KJ. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2023 Jul. doi:10.1097/MOG.0000000000000944.
13. Nguyen NT et al. Foregut. 2022 Sep. doi: 10.1177/26345161221126961.
14. Mazzoleni G et al. Endosc Int Open. 2021 Feb. doi: 10.1055/a-1322-2209.
15. Trad KS et al. Surg Innov. 2018 Apr. doi: 10.1177/1553350618755214.
16. Kolb JM et al. Gastroenterology. 2021 May. doi: 10.1016/S0016-5085(21)02953-X.
17. Jaruvongvanich VK et al. Endosc Int Open. 2023 Jan. doi: 10.1055/a-1972-9190.
18. Lee Y et al. Surg Endosc. 2023 Jul. doi: 10.1007/s00464-023-10151-5.
19. Andreou A et al. Surg Endosc. 2020 Feb. doi: 10.1007/s00464-019-07208-9.
20. Guidozzi N et al. Dis Esophagus. 2019 Nov. doi: 10.1093/dote/doz031.
Introduction
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a frequently encountered condition, and rising annually.1 A recent meta-analysis suggests nearly 14% (1.03 billion) of the population are affected worldwide. Differences may range by region from 12% in Latin America to 20% in North America, and by country from 4% in China to 23% in Turkey.1 In the United States, 21% of the population are afflicted with weekly GERD symptoms.2 Novel medical therapies and endoscopic options provide clinicians with opportunities to help patients with GERD.3
Diagnosis
Definition
GERD was originally defined by the Montreal consensus as a condition that develops when the reflux of stomach contents causes troublesome symptoms and/or complications.4 Heartburn and regurgitation are common symptoms of GERD, with a sensitivity of 30%-76% and specificity of 62%-96% for erosive esophagitis (EE), which occurs when the reflux of stomach content causes esophageal mucosal breaks.5 The presence of characteristic mucosal injury observed during an upper endoscopy or abnormal esophageal acid exposure on ambulatory reflux monitoring are objective evidence of GERD. A trial of a proton pump inhibitor (PPI) may function as a diagnostic test for patients exhibiting the typical symptoms of GERD without any alarm symptoms.3,6
Endoscopic Evaluation and Confirmation
The 2022 American Gastroenterological Association (AGA) clinical practice update recommends diagnostic endoscopy, after PPIs are stopped for 2-4 weeks, in patients whose GERD symptoms do not respond adequately to an empiric trial of a PPI.3 Those with GERD and alarm symptoms such as dysphagia, weight loss, bleeding, and vomiting should undergo endoscopy as soon as possible. Endoscopic findings of EE (Los Angeles Grade B or more severe) and long-segment Barrett’s esophagus (> 3-cm segment with intestinal metaplasia on biopsy) are diagnostic of GERD.3
Reflux Monitoring
With ambulatory reflux monitoring (pH or impedance-pH), esophageal acid exposure (or neutral refluxate in impedance testing) can be measured to confirm GERD diagnosis and to correlate symptoms with reflux episodes. Patients with atypical GERD symptoms or patients with a confirmed diagnosis of GERD whose symptoms have not improved sufficiently with twice-daily PPI therapy should have esophageal impedance-pH monitoring while on PPIs.6,7
Esophageal Manometry
High-resolution esophageal manometry can be used to assess motility abnormalities associated with GERD.
Although no manometric abnormality is unique to GERD, weak lower esophageal sphincter (LES) resting pressure and ineffective esophageal motility frequently coexist with severe GERD.6
Manometry is particularly useful in patients considering surgical or endoscopic anti-reflux procedures to evaluate for achalasia,3 an important contraindication to surgery.
Medical Management
Management of GERD requires a multidisciplinary and personalized approach based on symptom presentation, body mass index, endoscopic findings (e.g., presence of EE, Barrett’s esophagus, hiatal hernia), and physiological abnormalities (e.g., gastroparesis or ineffective motility).3
Lifestyle Modifications
Recommended lifestyle modifications include weight loss for patients with obesity, stress reduction, tobacco and alcohol cessation, elevating the head of the bed, staying upright during and after meals, avoidance of food intake < 3 hours before bedtime, and cessation of foods that potentially aggravate reflux symptoms such as coffee, chocolate, carbonated beverages, spicy foods, acidic foods, and foods with high fat content.6,8
Medications
Pharmacologic therapy for GERD includes medications that primarily aim to neutralize or reduce gastric acid -- we summarize options in Table 1.3,8

Proton Pump Inhibitors
Most guidelines suggest a trial of 4-8 weeks of once-daily enteric-coated PPI before meals in patients with typical GERD symptoms and no alarm symptoms. Escalation to double-dose PPI may be considered in the case of persistent symptoms. The relative potencies of standard-dose pantoprazole, lansoprazole, esomeprazole, and rabeprazole are presented in Table 1.9 When a PPI switch is needed, rabeprazole may be considered as it is a PPI that does not rely on CYP2C19 for primary metabolism.9
Acid suppression should be weaned down to the lowest effective dose or converted to H2RAs or other antacids once symptoms are sufficiently controlled unless patients have EE, Barrett’s esophagus, or peptic stricture.3 Patients with severe GERD may require long-term PPI therapy or an invasive anti-reflux procedure.
Recent studies have shown that potassium-competitive acid blockers (PCAB) like vonoprazan may offer more effective gastric acid inhibition. While not included in the latest clinical practice update, vonoprazan is thought to be superior to lansoprazole for those with LA Grade C/D esophagitis for both symptom relief and healing at 2 weeks.10
Adjunctive Therapies
Alginates can function as a physical barrier to even neutral reflux and may be helpful for patients with postprandial or nighttime symptoms as well as those with hiatal hernia.3 H2RAs can also help mitigate nighttime symptoms.3 Baclofen is a gamma-aminobutyric acid–B agonist which inhibits transient lower esophageal sphincter relaxation (TLESR) and may be effective for patients with belching.3 Prokinetics may be helpful for GERD with concomitant gastroparesis.3 Sucralfate is a mucosal protective agent, but there is a lack of data supporting its efficacy in GERD treatment. Consider referral to a behavioral therapist for supplemental therapies, hypnotherapy, cognitive-behavior therapy, diaphragmatic breathing, and relaxation strategies for functional heartburn or reflux-associated esophageal hypervigilance or reflux hypersensitivity.3
When to Refer to Higher Level of Care
For patients who do not wish to remain on longer-term pharmacologic therapy or would benefit from anatomic repair, clinicians should have a discussion of risks and benefits prior to consideration of referral for anti-reflux procedures.3,6,8 We advise this conversation should include review of patient health status, postsurgical side effects such as increased flatus, bloating and dysphagia as well as the potential need to still resume PPI post operation.8
Endoscopic Management
Patient Selection And Evaluation
For the groups indicated for a higher level of care, we agree with AGA recommendations, multi-society guidelines, and expert review,3,7,11,12 and highlight potential options in Table 2. Step-up options should be based on patient characteristics and reviewed carefully with patients. Endoscopic therapies are less invasive than surgery and may be considered for those who do not require anatomic repair of hiatal hernia, do not want surgery, or are not suitable for surgery.

The pathophysiology of GERD is from a loss of the anti-reflux barrier of the esophageal gastric junction (EGJ) at the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) leading to unintended retrograde movement of gastric contents.6 Anatomically, the LES is composed of muscles of the distal esophagus and sling fibers of the proximal stomach, the “external valve” from the diaphragmatic crura, and the “internal valve” from the gastroesophageal flap valve (GEFV). GERD occurs from mechanical failure of the LES. First, there may be disproportional dilation of the diaphragmatic crura as categorized by Hill Grade of the GEFV as seen by a retroflexed view of EGJ after 30-45 seconds of insufflation.13 Second, there may be a migration of the LES away from the diaphragmatic crura as in the case of a hiatal hernia. Provocative maneuvers may reveal a sliding hernia by gentle retraction of the endoscope while under retroflexed view.13 Third, there may be more frequent TLESR associated with GERD.12
The aim of most interventions is to restore competency of the LES by reconstruction of the GEFV via suture or staple-based approximation of tissue.11,12 Intraluminal therapy may only target the GEFV at the internal valve. Therefore, most endoscopic interventions are limited to patients with intact diaphragmatic crura (ie, small to no hiatal hernia and GEFV Hill Grade 1 to 2). Contraindications for endoscopic therapy are moderate to severe reflux (ie, LA Grade C/ D), hiatus hernia 2 cm or larger, strictures, or long-segment Barrett’s esophagus.
Utility, Safety, and Outcomes of TIF
Historically, endoscopic therapy targeting endoscopic fundoplication started with EndoLuminal gastro-gastric fundoplication (ELF, 2005) which was a proof of concept of safe manipulation and suture for gastro-gastric plication to below the Z-line. Transoral incisionless fundoplication (TIF) 1.0 was suggested in 2007 for clinical application by proposing a longitudinal oriented esophago-gastric plication 1 cm above the Z-line.
In 2009, TIF2.0 was proposed as a rotational 270° wrap of the cardia and fundus to a full-thickness esophago-gastric fundoplication around 2-4 cm of the distal esophagus. Like a surgical fundoplication, this reinforces sling fibers, increases the Angle of His and improves the cardiac notch. TIF 2.0 is indicated for those with small (< 2 cm) or no hiatal hernia and a GEFV Hill Grade 1 or 2. The present iteration of TIF2.0 uses EsophyX-Z (EndoGastric Solutions; Redmond, Washington) which features dual fastener deployment and a simplified firing mechanism. Plication is secured via nonresorbable polypropylene T-fasteners with strength equivalence of 3-0 sutures.
Compared with the original, TIF2.0 represents a decrease of severe adverse events from 2%-2.5% to 0.4%-1%.11,14 Based on longitudinal TEMPO data, patient satisfaction ranges between 70% and 90% and rates of patients reverting to daily PPI use are 17% and 34% at 1 and 5 years. A 5% reintervention rate was noted to be comparable with surgical reoperation for fundoplication.15 One retrospective evaluation of patients with failed TIF followed by successful cTIF noted that in all failures there was a documented underestimation of a much larger crura defect at time of index procedure.16 Chest pain is common post procedure and patients and collaborating providers should be counseled on the expected course. In our practice, we admit patients for at least 1 postprocedure day and consider scheduling symptom control medications for those with significant pain.
TIF2.0 for Special Populations
Indications for TIF2.0 continue to evolve. In 2017, concomitant TIF2.0 with hiatal hernia repair (cTIF or HH-TIF) for hernia > 2 cm was accepted for expanded use. In one study, cTIF has been shown to have similar outcomes for postprocedural PPI use, dysphagia, wrap disruption, and hiatal hernia recurrence, compared with hiatal hernia repair paired with laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication with possibly shorter postadmission stay, serious adverse events, and bloating.17 A cTIF may be performed in a single general anesthetic session typically with a surgical hiatal hernia repair followed by TIF2.0.
Other Endoscopic Procedures
Several other endoscopic interventions have been proposed for GERD management. The following procedures are under continuous study and should be considered only by those with expertise.
Stretta
The Stretta device (Restech; Houston, Texas) was approved in 2000 for use of a radiofrequency (RF) generator and catheter applied to the squamocolumnar junction under irrigation. Ideal candidates for this nonablative procedure may include patients with confirmed GERD, low-grade EE, without Barrett’s esophagus, small hiatal hernia, and a competent LES with pressure > 5 mmHg. Meta-analysis has yielded conflicting results in terms of its efficacy, compared with TIF2.0, and recent multi-society guidance suggests fundoplication over Stretta.7
ARM, MASE, and RAP
Anti-reflux mucosectomy (ARM) has been proposed based on the observation that patients undergoing mucosectomy for neoplasms in the cardia had improvement of reflux symptoms.11,12 Systematic review has suggested a clinical response of 80% of either PPI discontinuation or reduction, but 17% of adverse events include development of strictures. Iterations of ARM continue to be studied including ARM with band ligation (L-ARM) and endoscopic submucosal dissection for GERD (ESD-G).12
Experts have proposed incorporating endoscopic suturing of the EGJ to modulate the LES. Mucosal ablation and suturing of the EG junction (MASE) has been proposed by first priming tissue via argon plasma coagulation (APC) prior to endoscopic overstitch of two to three interrupted sutures below the EGJ to narrow and elongate the EGJ. The resection and plication (RAP) procedure performs a mucosal resection prior to full-thickness plication of the LES and cardia.11,12 Expert opinion has suggested that RAP may be used in patients with altered anatomy whereas MASE may be used when resection is not possible (eg, prior scarring, resection or ablation).12
Surgical Management
We agree with a recent multi-society guideline recommending that an interdisciplinary consultation with surgery for indicated patients with refractory GERD and underlying hiatal hernia, or who do not want lifelong medical therapy.
Fundoplication creates a surgical wrap to reinforce the LES and may be performed laparoscopically. Contraindications include body mass index (BMI) >35 kg/m2 and significantly impaired dysmotility. Fundoplication of 180°, 270°, and 360° may achieve comparable outcomes, but a laparoscopic toupet fundoplication (LTF 270°) may have fewer postsurgical issues of dysphagia and bloating. Advantages for both anterior and posterior partial fundoplications have been demonstrated by network meta-analysis. Therefore, a multi-society guideline for GERD suggests partial over complete fundoplication.7 Compared with posterior techniques, anterior fundoplication (Watson fundoplication) led to more recurrent reflux symptoms but less dysphagia and other side effects.19
Magnetic sphincter augmentation (MSA) is a surgical option that strengthens the LES with magnets to improve sphincter competence. In addition to listed contraindications of fundoplication, patients with an allergy to nickel and/or titanium are also contraindicated to receive MSA.7 MSA has been suggested to be equivalent to LNF although there may be less gas bloat and greater ability to belch on follow up.20
Surgical Options for Special Populations
Patients with medically refractory GERD and a BMI ≥ 35 kg/m2 may benefit from either Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) or fundoplication, however sleeve gastrectomy is not advised.7 In patients with BMI > 50 kg/m2, RYGB may provide an optimal choice. We agree with consultation with a bariatric surgeon when reviewing these situations.
Conclusion
Patients with GERD are commonly encountered worldwide. Empiric PPI are effective mainstays for medical treatment of GERD. Novel PCABs (e.g., vonoprazan) may present new options for GERD with LA Grade C/D esophagitis EE and merit more study. In refractory cases or for patients who do not want long term medical therapy, step-up therapy may be considered via endoscopic or surgical interventions. Patient anatomy and comorbidities should be considered by the clinician to inform treatment options. Surgery may have the most durable outcomes for those requiring step-up therapy. Improvements in technique, devices and patient selection have allowed TIF2.0 to grow as a viable offering with excellent 5-year outcomes for indicated patients.
Dr. Chang, Dr. Tintara, and Dr. Phan are based in the Division of Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease at the University of Southern California in Los Angeles. They have no conflicts of interest to declare.
References
1. Richter JE andRubenstein JH. Gastroenterology. 2018 Jan. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.07.045.
2. El-Serag HB et al. Gut. 2014 Jun. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2012-304269.
3. Yadlapati R et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 May. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2022.01.025.
4. Vakil N et al. Am J Gastroenterol. 2006 Aug. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2006.00630.x.
5. Numans ME et al. Ann Intern Med. 2004 Apr. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-140-7-200404060-00011.
6. Kahrilas PJ et al. Gastroenterology. 2008 Oct. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2008.08.045.
7. Slater BJ et al. Surg Endosc. 2023 Feb. doi: 10.1007/s00464-022-09817-3.
8. Gyawali CP et al. Gut. 2018 Jul. doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2017-314722.
9. Graham DY and Tansel A. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018 Jun. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2017.09.033.
10. Graham DY and Dore MP. Gastroenterology. 2018 Feb. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2018.01.018.
11. Haseeb M and Thompson CC. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2023 Sep. doi: 10.1097/MOG.0000000000000968.
12. Kolb JM and Chang KJ. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2023 Jul. doi:10.1097/MOG.0000000000000944.
13. Nguyen NT et al. Foregut. 2022 Sep. doi: 10.1177/26345161221126961.
14. Mazzoleni G et al. Endosc Int Open. 2021 Feb. doi: 10.1055/a-1322-2209.
15. Trad KS et al. Surg Innov. 2018 Apr. doi: 10.1177/1553350618755214.
16. Kolb JM et al. Gastroenterology. 2021 May. doi: 10.1016/S0016-5085(21)02953-X.
17. Jaruvongvanich VK et al. Endosc Int Open. 2023 Jan. doi: 10.1055/a-1972-9190.
18. Lee Y et al. Surg Endosc. 2023 Jul. doi: 10.1007/s00464-023-10151-5.
19. Andreou A et al. Surg Endosc. 2020 Feb. doi: 10.1007/s00464-019-07208-9.
20. Guidozzi N et al. Dis Esophagus. 2019 Nov. doi: 10.1093/dote/doz031.
Cendakimab That Targets IL-13 Shows Promise in Eosinophilic Esophagitis
VIENNA — , according to interim results of a pivotal phase 3 trial.
Treatment with cendakimab also improved key endoscopic and histologic features, even in patients who had an inadequate response or intolerance to steroids, reported Alain Schoepfer, MD, gastroenterologist from Centre Hospitalier Universitaire Vaudois and University of Lausanne, in Switzerland.
The drug was generally safe and well tolerated up to 24 weeks of treatment, added Schoepfer, who presented the results during a presentation at the United European Gastroenterology (UEG) Week 2024.
Targeting IL-13 Shows ‘Surprisingly Good Results’
EoE is a chronic, progressive, immune-mediated, inflammatory disease that is mainly driven by the cytokine, IL-13.
In a prior phase 2 study, cendakimab, which selectively binds to IL-13 and blocks its interaction with both the IL-13Ra1 and the IL-13Ra2 receptors, was shown to improve symptoms and endoscopic features of EoE.
For the current phase 3 trial, participants were required to have a peak eosinophil count (PEC) of ≥ 15 eosinophils (eos)/high power field (hpf) and 4 or more days of dysphagia over the 2 weeks prior to the start of the study. In addition, they had to have shown a complete lack of response to proton pump inhibitor (PPI) treatment for 8 weeks or more.
A total of 430 patients were randomized 1:1:1 to subcutaneous cendakimab (360 mg) once weekly for 48 weeks; subcutaneous cendakimab (360 mg) once weekly for 24 weeks, then once every 2 weeks for a further 24 weeks; or subcutaneous placebo once weekly for 48 weeks.
Patient characteristics were similar across randomization groups. The majority of participants were men, with a mean age of 35 years (range, 12-75 years); adolescents comprised 6%-11% of the total. The disease duration was around 5-6 years for all participants, of which 45% were on a stable PPI dosage and around 65% had steroid intolerance or an inadequate response. The endoscopic reference score was around 10 across all groups. The mean PEC was around 160 eos/hpf in the cendakimab arms vs 200 eos/hpf in the placebo arm.
Schoepfer reported results for the coprimary endpoints — the mean change from baseline in dysphagia days and the proportion of patients with eosinophil histologic response (PEC ≤ 6 eos/hpf) — at week 24. At this point, a total of 286 patients had received treatment with 360 mg of cendakimab once weekly, and 143 had received placebo.
The change in dysphagia days was −6.1 in patients on cendakimab once weekly vs −4.2 in patients on placebo (P = .0005). The proportion of patients with eosinophil histologic response was 28.6% in the treatment arm vs 2.2% in the placebo arm.
The results were similar for patients who were classified as having had a steroid inadequate response. The change in dysphagia days was −6.3 in the cendakimab group vs −4.7 in the placebo group (P = .0156). The eosinophil histologic response was 29.5% in the treatment group vs 2.1% in the placebo group (P < .0001).
Endoscopic response, a key secondary endpoint, showed a change from baseline to week 24 in the endoscopic features of EoE. The total endoscopic reference scores were −5.2 for patients on cendakimab once weekly and −1.2 for patients on placebo (P < .0001).
The safety profile of cendakimab was “unspectacular,” Schoepfer said, with adverse events related to the study drug occurring in 30% of patients in the treatment arm vs 18.9% of those in the placebo arm. He noted that as the trial was conducted during the COVID pandemic, there were some infections.
Serious adverse events, which were assessed by investigators to not be related to the study drug, occurred in 1.8% and 2.8% of patients on cendakimab and placebo, respectively. Drug discontinuation occurred in 1.4% in the cendakimab group and 0.7% in the placebo group. There were no deaths.
“We really need drugs for this disease, given that there are very few alternatives to steroids and PPIs,” Co-moderator Ram Dickman, MD, Division of Gastroenterology, Rabin Medical Center, Petah Tikva, Israel, said in an interview.
Right now, we have dupilumab, which targets two receptors: IL-4 and IL-13. But targeting IL-13 by itself “is showing surprisingly good results,” so cendakimab is a good candidate to be in “the first line of biologic treatments,” Dickman said.
“It’s safe and works rapidly,” he added. “Given this is a phase 3 study, I believe we’ll see it on the market.”
Schoepfer has served as a consultant for Regeneron/Sanofi, Adare/Ellodi, AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Celgene/Receptos/Bristol Myers Squibb, Dr. Falk Pharma, Gossamer Bio, GSK, Janssen, MSD, Pfizer, Regeneron/Sanofi, Takeda, and Vifor; received grant/research support from Adare/Ellodi, Celgene/Receptos/Bristol Myers Squibb, GSK, and Regeneron/Sanofi. Dickman has declared no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
VIENNA — , according to interim results of a pivotal phase 3 trial.
Treatment with cendakimab also improved key endoscopic and histologic features, even in patients who had an inadequate response or intolerance to steroids, reported Alain Schoepfer, MD, gastroenterologist from Centre Hospitalier Universitaire Vaudois and University of Lausanne, in Switzerland.
The drug was generally safe and well tolerated up to 24 weeks of treatment, added Schoepfer, who presented the results during a presentation at the United European Gastroenterology (UEG) Week 2024.
Targeting IL-13 Shows ‘Surprisingly Good Results’
EoE is a chronic, progressive, immune-mediated, inflammatory disease that is mainly driven by the cytokine, IL-13.
In a prior phase 2 study, cendakimab, which selectively binds to IL-13 and blocks its interaction with both the IL-13Ra1 and the IL-13Ra2 receptors, was shown to improve symptoms and endoscopic features of EoE.
For the current phase 3 trial, participants were required to have a peak eosinophil count (PEC) of ≥ 15 eosinophils (eos)/high power field (hpf) and 4 or more days of dysphagia over the 2 weeks prior to the start of the study. In addition, they had to have shown a complete lack of response to proton pump inhibitor (PPI) treatment for 8 weeks or more.
A total of 430 patients were randomized 1:1:1 to subcutaneous cendakimab (360 mg) once weekly for 48 weeks; subcutaneous cendakimab (360 mg) once weekly for 24 weeks, then once every 2 weeks for a further 24 weeks; or subcutaneous placebo once weekly for 48 weeks.
Patient characteristics were similar across randomization groups. The majority of participants were men, with a mean age of 35 years (range, 12-75 years); adolescents comprised 6%-11% of the total. The disease duration was around 5-6 years for all participants, of which 45% were on a stable PPI dosage and around 65% had steroid intolerance or an inadequate response. The endoscopic reference score was around 10 across all groups. The mean PEC was around 160 eos/hpf in the cendakimab arms vs 200 eos/hpf in the placebo arm.
Schoepfer reported results for the coprimary endpoints — the mean change from baseline in dysphagia days and the proportion of patients with eosinophil histologic response (PEC ≤ 6 eos/hpf) — at week 24. At this point, a total of 286 patients had received treatment with 360 mg of cendakimab once weekly, and 143 had received placebo.
The change in dysphagia days was −6.1 in patients on cendakimab once weekly vs −4.2 in patients on placebo (P = .0005). The proportion of patients with eosinophil histologic response was 28.6% in the treatment arm vs 2.2% in the placebo arm.
The results were similar for patients who were classified as having had a steroid inadequate response. The change in dysphagia days was −6.3 in the cendakimab group vs −4.7 in the placebo group (P = .0156). The eosinophil histologic response was 29.5% in the treatment group vs 2.1% in the placebo group (P < .0001).
Endoscopic response, a key secondary endpoint, showed a change from baseline to week 24 in the endoscopic features of EoE. The total endoscopic reference scores were −5.2 for patients on cendakimab once weekly and −1.2 for patients on placebo (P < .0001).
The safety profile of cendakimab was “unspectacular,” Schoepfer said, with adverse events related to the study drug occurring in 30% of patients in the treatment arm vs 18.9% of those in the placebo arm. He noted that as the trial was conducted during the COVID pandemic, there were some infections.
Serious adverse events, which were assessed by investigators to not be related to the study drug, occurred in 1.8% and 2.8% of patients on cendakimab and placebo, respectively. Drug discontinuation occurred in 1.4% in the cendakimab group and 0.7% in the placebo group. There were no deaths.
“We really need drugs for this disease, given that there are very few alternatives to steroids and PPIs,” Co-moderator Ram Dickman, MD, Division of Gastroenterology, Rabin Medical Center, Petah Tikva, Israel, said in an interview.
Right now, we have dupilumab, which targets two receptors: IL-4 and IL-13. But targeting IL-13 by itself “is showing surprisingly good results,” so cendakimab is a good candidate to be in “the first line of biologic treatments,” Dickman said.
“It’s safe and works rapidly,” he added. “Given this is a phase 3 study, I believe we’ll see it on the market.”
Schoepfer has served as a consultant for Regeneron/Sanofi, Adare/Ellodi, AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Celgene/Receptos/Bristol Myers Squibb, Dr. Falk Pharma, Gossamer Bio, GSK, Janssen, MSD, Pfizer, Regeneron/Sanofi, Takeda, and Vifor; received grant/research support from Adare/Ellodi, Celgene/Receptos/Bristol Myers Squibb, GSK, and Regeneron/Sanofi. Dickman has declared no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
VIENNA — , according to interim results of a pivotal phase 3 trial.
Treatment with cendakimab also improved key endoscopic and histologic features, even in patients who had an inadequate response or intolerance to steroids, reported Alain Schoepfer, MD, gastroenterologist from Centre Hospitalier Universitaire Vaudois and University of Lausanne, in Switzerland.
The drug was generally safe and well tolerated up to 24 weeks of treatment, added Schoepfer, who presented the results during a presentation at the United European Gastroenterology (UEG) Week 2024.
Targeting IL-13 Shows ‘Surprisingly Good Results’
EoE is a chronic, progressive, immune-mediated, inflammatory disease that is mainly driven by the cytokine, IL-13.
In a prior phase 2 study, cendakimab, which selectively binds to IL-13 and blocks its interaction with both the IL-13Ra1 and the IL-13Ra2 receptors, was shown to improve symptoms and endoscopic features of EoE.
For the current phase 3 trial, participants were required to have a peak eosinophil count (PEC) of ≥ 15 eosinophils (eos)/high power field (hpf) and 4 or more days of dysphagia over the 2 weeks prior to the start of the study. In addition, they had to have shown a complete lack of response to proton pump inhibitor (PPI) treatment for 8 weeks or more.
A total of 430 patients were randomized 1:1:1 to subcutaneous cendakimab (360 mg) once weekly for 48 weeks; subcutaneous cendakimab (360 mg) once weekly for 24 weeks, then once every 2 weeks for a further 24 weeks; or subcutaneous placebo once weekly for 48 weeks.
Patient characteristics were similar across randomization groups. The majority of participants were men, with a mean age of 35 years (range, 12-75 years); adolescents comprised 6%-11% of the total. The disease duration was around 5-6 years for all participants, of which 45% were on a stable PPI dosage and around 65% had steroid intolerance or an inadequate response. The endoscopic reference score was around 10 across all groups. The mean PEC was around 160 eos/hpf in the cendakimab arms vs 200 eos/hpf in the placebo arm.
Schoepfer reported results for the coprimary endpoints — the mean change from baseline in dysphagia days and the proportion of patients with eosinophil histologic response (PEC ≤ 6 eos/hpf) — at week 24. At this point, a total of 286 patients had received treatment with 360 mg of cendakimab once weekly, and 143 had received placebo.
The change in dysphagia days was −6.1 in patients on cendakimab once weekly vs −4.2 in patients on placebo (P = .0005). The proportion of patients with eosinophil histologic response was 28.6% in the treatment arm vs 2.2% in the placebo arm.
The results were similar for patients who were classified as having had a steroid inadequate response. The change in dysphagia days was −6.3 in the cendakimab group vs −4.7 in the placebo group (P = .0156). The eosinophil histologic response was 29.5% in the treatment group vs 2.1% in the placebo group (P < .0001).
Endoscopic response, a key secondary endpoint, showed a change from baseline to week 24 in the endoscopic features of EoE. The total endoscopic reference scores were −5.2 for patients on cendakimab once weekly and −1.2 for patients on placebo (P < .0001).
The safety profile of cendakimab was “unspectacular,” Schoepfer said, with adverse events related to the study drug occurring in 30% of patients in the treatment arm vs 18.9% of those in the placebo arm. He noted that as the trial was conducted during the COVID pandemic, there were some infections.
Serious adverse events, which were assessed by investigators to not be related to the study drug, occurred in 1.8% and 2.8% of patients on cendakimab and placebo, respectively. Drug discontinuation occurred in 1.4% in the cendakimab group and 0.7% in the placebo group. There were no deaths.
“We really need drugs for this disease, given that there are very few alternatives to steroids and PPIs,” Co-moderator Ram Dickman, MD, Division of Gastroenterology, Rabin Medical Center, Petah Tikva, Israel, said in an interview.
Right now, we have dupilumab, which targets two receptors: IL-4 and IL-13. But targeting IL-13 by itself “is showing surprisingly good results,” so cendakimab is a good candidate to be in “the first line of biologic treatments,” Dickman said.
“It’s safe and works rapidly,” he added. “Given this is a phase 3 study, I believe we’ll see it on the market.”
Schoepfer has served as a consultant for Regeneron/Sanofi, Adare/Ellodi, AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Celgene/Receptos/Bristol Myers Squibb, Dr. Falk Pharma, Gossamer Bio, GSK, Janssen, MSD, Pfizer, Regeneron/Sanofi, Takeda, and Vifor; received grant/research support from Adare/Ellodi, Celgene/Receptos/Bristol Myers Squibb, GSK, and Regeneron/Sanofi. Dickman has declared no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM UEG 2024
Vonoprazan Offers PPI Alternative for Heartburn with Non-Erosive Reflux
according to investigators.
Benefits of vonoprazan were seen as soon as the first day of treatment and persisted through the 20-week extension period, lead author Loren Laine, MD, AGAF, of Yale School of Medicine, New Haven, Connecticut, and colleagues reported.
“A potential alternative to PPI therapy is a potassium-competitive acid blocker, a new class of antisecretory agents that provide more potent inhibition of gastric acid secretion than PPIs,” the investigators wrote in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
While a small observational study found that 18 out of 26 patients (69%) with PPI-resistant NERD had improved symptoms with vonoprazan, subsequent randomized trials in Japan failed to meet their primary endpoints, Laine and colleagues noted. The present randomized trial was therefore conducted to determine how vonoprazan might help a US patient population.
The study involved 772 patients who reported heartburn at least 4 days per week during screening, but without erosive esophagitis on endoscopy. Participants were randomized into three groups: placebo, vonoprazan 10 mg, or vonoprazan 20 mg. These protocols were administered for 4 weeks, followed by a 20-week extension, in which placebo patients were rerandomized to receive one of the two vonoprazan dose levels.
The primary endpoint was the percentage of days without daytime or nighttime heartburn (24-hour heartburn-free days) during the initial 4-week treatment period. The secondary endpoint, assessed during the same timeframe, was percentage of days without need for a rescue antacid.
In the 4-week placebo-controlled period, patients treated with vonoprazan 10 mg and 20 mg showed a significant improvement in heartburn-free days, compared with placebo. The percentage of 24-hour heartburn-free days was 27.7% in the placebo group vs 44.8% in the 10-mg vonoprazan group (least squares mean difference 17.1%; P < .0001) and 44.4% in the 20 mg vonoprazan group (least squares mean difference 16.7%; P < .0001).
Benefits of vonoprazan were seen as early as the first day of treatment, with 8.3% and 11.6% more patients in the 10-mg and 20-mg groups, respectively, experiencing a heartburn-free day, compared with placebo. By day 2, these differences increased to 18.1% and 23.2%, respectively.
The percentage of days without rescue antacid use was also significantly higher in both vonoprazan groups. Patients in the 10 mg and 20 mg groups had 63.3% and 61.2% of days without antacid use, respectively, compared with 47.6% in the placebo group (P < .0001 for both comparisons).
These benefits persisted throughout the 20-week extension period, with similar percentages of heartburn-free days across all groups. Mean percentages of 24-hour heartburn-free days ranged from 61% to 63% in the extension phase, while median percentages spanned 76%-79%.
Adverse events were infrequent and comparable across all groups. The most common adverse event was nausea, occurring slightly more frequently in the vonoprazan groups (2.3% in the 10-mg group and 3.1% in the 20-mg group) vs placebo (0.4%). Serious adverse events were rare and were deemed unrelated to treatment. No new safety signals were identified during the 20-week extension period. Increases in serum gastrin levels, a marker of acid suppression, returned to near baseline after discontinuation of vonoprazan.
“In conclusion, the potassium-competitive acid blocker vonoprazan was efficacious in reducing heartburn symptoms in patients with NERD, with the benefit appearing to begin as early as the first day of therapy,” Laine and colleagues wrote.
In July 2024, the Food and Drug Administration approved vonoprazan for treating heartburn in patients with nonerosive gastroesophageal reflux disease.This study was funded by Phathom Pharmaceuticals. The investigators disclosed additional relationships with Takeda, Medtronic, Carnot, and others.
Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) have revolutionized the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). One might ask what the reason would be to challenge this giant of the pharmacopeia with another medication for GERD.
In this important study by Laine et al, vonoprazan is expectedly efficacious in treating nonerosive GERD (NERD) but notably less so when compared with the authors’ trial for erosive GERD. This is not surprising owing to the multiple and common acid independent etiologies of NERD, such as esophageal hypersensitivity. The high placebo response supports this. Two notable results, however, merit emphasis in potential advantages over PPIs.
First, vonoprazan is effective at day 1 of therapy by eliminating the need for loading. Second, nocturnal reflux, a purer form of GERD, is better controlled with a morning dose of vonopazan mitigating against nocturnal acid breakthrough and the need for twice-daily dosing with PPIs and/or addition of an H2 antagonist. These results by no means advocate for replacement of PPIs with PCABs, but at least suggest specific populations of GERD patients who may specifically benefit from PCAB use. The study also indirectly emphasizes that careful selection of NERD patients whose GERD symptoms are predominantly caused by increased esophageal acid exposure are the most appropriate candidates. The ultimate answer as to where vonoprazan will be used in our practice is evolving.
David Katzka, MD, is based in the Division of Digestive and Liver Diseases, Columbia University Medical Center, New York City. He has received research support from Takeda, Sanofi, and Regeneron. He is also an associate editor for GI & Hepatology News.
Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) have revolutionized the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). One might ask what the reason would be to challenge this giant of the pharmacopeia with another medication for GERD.
In this important study by Laine et al, vonoprazan is expectedly efficacious in treating nonerosive GERD (NERD) but notably less so when compared with the authors’ trial for erosive GERD. This is not surprising owing to the multiple and common acid independent etiologies of NERD, such as esophageal hypersensitivity. The high placebo response supports this. Two notable results, however, merit emphasis in potential advantages over PPIs.
First, vonoprazan is effective at day 1 of therapy by eliminating the need for loading. Second, nocturnal reflux, a purer form of GERD, is better controlled with a morning dose of vonopazan mitigating against nocturnal acid breakthrough and the need for twice-daily dosing with PPIs and/or addition of an H2 antagonist. These results by no means advocate for replacement of PPIs with PCABs, but at least suggest specific populations of GERD patients who may specifically benefit from PCAB use. The study also indirectly emphasizes that careful selection of NERD patients whose GERD symptoms are predominantly caused by increased esophageal acid exposure are the most appropriate candidates. The ultimate answer as to where vonoprazan will be used in our practice is evolving.
David Katzka, MD, is based in the Division of Digestive and Liver Diseases, Columbia University Medical Center, New York City. He has received research support from Takeda, Sanofi, and Regeneron. He is also an associate editor for GI & Hepatology News.
Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) have revolutionized the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). One might ask what the reason would be to challenge this giant of the pharmacopeia with another medication for GERD.
In this important study by Laine et al, vonoprazan is expectedly efficacious in treating nonerosive GERD (NERD) but notably less so when compared with the authors’ trial for erosive GERD. This is not surprising owing to the multiple and common acid independent etiologies of NERD, such as esophageal hypersensitivity. The high placebo response supports this. Two notable results, however, merit emphasis in potential advantages over PPIs.
First, vonoprazan is effective at day 1 of therapy by eliminating the need for loading. Second, nocturnal reflux, a purer form of GERD, is better controlled with a morning dose of vonopazan mitigating against nocturnal acid breakthrough and the need for twice-daily dosing with PPIs and/or addition of an H2 antagonist. These results by no means advocate for replacement of PPIs with PCABs, but at least suggest specific populations of GERD patients who may specifically benefit from PCAB use. The study also indirectly emphasizes that careful selection of NERD patients whose GERD symptoms are predominantly caused by increased esophageal acid exposure are the most appropriate candidates. The ultimate answer as to where vonoprazan will be used in our practice is evolving.
David Katzka, MD, is based in the Division of Digestive and Liver Diseases, Columbia University Medical Center, New York City. He has received research support from Takeda, Sanofi, and Regeneron. He is also an associate editor for GI & Hepatology News.
according to investigators.
Benefits of vonoprazan were seen as soon as the first day of treatment and persisted through the 20-week extension period, lead author Loren Laine, MD, AGAF, of Yale School of Medicine, New Haven, Connecticut, and colleagues reported.
“A potential alternative to PPI therapy is a potassium-competitive acid blocker, a new class of antisecretory agents that provide more potent inhibition of gastric acid secretion than PPIs,” the investigators wrote in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
While a small observational study found that 18 out of 26 patients (69%) with PPI-resistant NERD had improved symptoms with vonoprazan, subsequent randomized trials in Japan failed to meet their primary endpoints, Laine and colleagues noted. The present randomized trial was therefore conducted to determine how vonoprazan might help a US patient population.
The study involved 772 patients who reported heartburn at least 4 days per week during screening, but without erosive esophagitis on endoscopy. Participants were randomized into three groups: placebo, vonoprazan 10 mg, or vonoprazan 20 mg. These protocols were administered for 4 weeks, followed by a 20-week extension, in which placebo patients were rerandomized to receive one of the two vonoprazan dose levels.
The primary endpoint was the percentage of days without daytime or nighttime heartburn (24-hour heartburn-free days) during the initial 4-week treatment period. The secondary endpoint, assessed during the same timeframe, was percentage of days without need for a rescue antacid.
In the 4-week placebo-controlled period, patients treated with vonoprazan 10 mg and 20 mg showed a significant improvement in heartburn-free days, compared with placebo. The percentage of 24-hour heartburn-free days was 27.7% in the placebo group vs 44.8% in the 10-mg vonoprazan group (least squares mean difference 17.1%; P < .0001) and 44.4% in the 20 mg vonoprazan group (least squares mean difference 16.7%; P < .0001).
Benefits of vonoprazan were seen as early as the first day of treatment, with 8.3% and 11.6% more patients in the 10-mg and 20-mg groups, respectively, experiencing a heartburn-free day, compared with placebo. By day 2, these differences increased to 18.1% and 23.2%, respectively.
The percentage of days without rescue antacid use was also significantly higher in both vonoprazan groups. Patients in the 10 mg and 20 mg groups had 63.3% and 61.2% of days without antacid use, respectively, compared with 47.6% in the placebo group (P < .0001 for both comparisons).
These benefits persisted throughout the 20-week extension period, with similar percentages of heartburn-free days across all groups. Mean percentages of 24-hour heartburn-free days ranged from 61% to 63% in the extension phase, while median percentages spanned 76%-79%.
Adverse events were infrequent and comparable across all groups. The most common adverse event was nausea, occurring slightly more frequently in the vonoprazan groups (2.3% in the 10-mg group and 3.1% in the 20-mg group) vs placebo (0.4%). Serious adverse events were rare and were deemed unrelated to treatment. No new safety signals were identified during the 20-week extension period. Increases in serum gastrin levels, a marker of acid suppression, returned to near baseline after discontinuation of vonoprazan.
“In conclusion, the potassium-competitive acid blocker vonoprazan was efficacious in reducing heartburn symptoms in patients with NERD, with the benefit appearing to begin as early as the first day of therapy,” Laine and colleagues wrote.
In July 2024, the Food and Drug Administration approved vonoprazan for treating heartburn in patients with nonerosive gastroesophageal reflux disease.This study was funded by Phathom Pharmaceuticals. The investigators disclosed additional relationships with Takeda, Medtronic, Carnot, and others.
according to investigators.
Benefits of vonoprazan were seen as soon as the first day of treatment and persisted through the 20-week extension period, lead author Loren Laine, MD, AGAF, of Yale School of Medicine, New Haven, Connecticut, and colleagues reported.
“A potential alternative to PPI therapy is a potassium-competitive acid blocker, a new class of antisecretory agents that provide more potent inhibition of gastric acid secretion than PPIs,” the investigators wrote in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
While a small observational study found that 18 out of 26 patients (69%) with PPI-resistant NERD had improved symptoms with vonoprazan, subsequent randomized trials in Japan failed to meet their primary endpoints, Laine and colleagues noted. The present randomized trial was therefore conducted to determine how vonoprazan might help a US patient population.
The study involved 772 patients who reported heartburn at least 4 days per week during screening, but without erosive esophagitis on endoscopy. Participants were randomized into three groups: placebo, vonoprazan 10 mg, or vonoprazan 20 mg. These protocols were administered for 4 weeks, followed by a 20-week extension, in which placebo patients were rerandomized to receive one of the two vonoprazan dose levels.
The primary endpoint was the percentage of days without daytime or nighttime heartburn (24-hour heartburn-free days) during the initial 4-week treatment period. The secondary endpoint, assessed during the same timeframe, was percentage of days without need for a rescue antacid.
In the 4-week placebo-controlled period, patients treated with vonoprazan 10 mg and 20 mg showed a significant improvement in heartburn-free days, compared with placebo. The percentage of 24-hour heartburn-free days was 27.7% in the placebo group vs 44.8% in the 10-mg vonoprazan group (least squares mean difference 17.1%; P < .0001) and 44.4% in the 20 mg vonoprazan group (least squares mean difference 16.7%; P < .0001).
Benefits of vonoprazan were seen as early as the first day of treatment, with 8.3% and 11.6% more patients in the 10-mg and 20-mg groups, respectively, experiencing a heartburn-free day, compared with placebo. By day 2, these differences increased to 18.1% and 23.2%, respectively.
The percentage of days without rescue antacid use was also significantly higher in both vonoprazan groups. Patients in the 10 mg and 20 mg groups had 63.3% and 61.2% of days without antacid use, respectively, compared with 47.6% in the placebo group (P < .0001 for both comparisons).
These benefits persisted throughout the 20-week extension period, with similar percentages of heartburn-free days across all groups. Mean percentages of 24-hour heartburn-free days ranged from 61% to 63% in the extension phase, while median percentages spanned 76%-79%.
Adverse events were infrequent and comparable across all groups. The most common adverse event was nausea, occurring slightly more frequently in the vonoprazan groups (2.3% in the 10-mg group and 3.1% in the 20-mg group) vs placebo (0.4%). Serious adverse events were rare and were deemed unrelated to treatment. No new safety signals were identified during the 20-week extension period. Increases in serum gastrin levels, a marker of acid suppression, returned to near baseline after discontinuation of vonoprazan.
“In conclusion, the potassium-competitive acid blocker vonoprazan was efficacious in reducing heartburn symptoms in patients with NERD, with the benefit appearing to begin as early as the first day of therapy,” Laine and colleagues wrote.
In July 2024, the Food and Drug Administration approved vonoprazan for treating heartburn in patients with nonerosive gastroesophageal reflux disease.This study was funded by Phathom Pharmaceuticals. The investigators disclosed additional relationships with Takeda, Medtronic, Carnot, and others.
FROM CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY
Celiac Screening in Kids Appears Cost-Effective
If these screening strategies are deemed feasible by clinicians and patients, then implementation in routine care is needed, lead author Jan Heijdra Suasnabar, MSc, of Leiden University Medical Centre in the Netherlands, and colleagues reported.
“Cohort studies have shown that CD likely develops early in life and can be easily diagnosed by detection of CD-specific antibodies against the enzyme tissue transglutaminase type 2 (IgA-TG2),” the investigators wrote in Gastroenterology.
Despite the ease of diagnosis, as few as one in five cases of CD are detected using current clinical strategies, meaning many cases are diagnosed years after symptom onset.
“Such high rates of missed/delayed diagnoses have been attributed to CD’s varied and nonspecific symptoms, lack of awareness, and the resource-intensive process necessary to establish the diagnosis,” Heijdra Suasnabar and colleagues wrote. “From an economic perspective, the burden of CD translates into substantial excess healthcare and societal costs.”
These practice gaps prompted the present study, which explored the long-term cost effectiveness of mass CD screening and active case finding among pediatric patients.
The investigators employed a model-based cost-effectiveness analysis with a hypothetical cohort representing all children with CD in the Netherlands. Iterations of this model evaluated long-term costs as these children moved through the healthcare system along various CD detection strategies.
The first strategy was based on the current Dutch approach, which is the same as that in the United States: Patients are only evaluated for CD if they present with symptoms that prompt suspicion of disease. Based on data from population-based studies, the model assumed that approximately one in three cases would be detected using this strategy.
The second strategy involved mass screening using IgA-TG2 point-of-care testing (sensitivity, 0.94; specificity, 0.944) via youth health care clinics, regardless of symptoms.
The third strategy, called “active case finding,” represented something of an intermediate approach, in which children with at least 1 CD-related symptom underwent point-of-care antibody testing.
For both mass screening and active case finding strategies, a positive antibody test was followed with confirmatory diagnostic testing.
Compared with current clinical approach, mass screening added 7.46 more quality-adjusted life-years (QALYs) per CD patient with an increased cost of €28,635 per CD patient. Active case finding gained 4.33 QALYs per CD patient while incurring an additional cost of €15,585 per CD patient.
Based on a willingness-to-pay threshold of €20,000 per QALY, the investigators deemed both strategies “highly cost effective,” compared with current standard of care. Some of these costs were offset by “substantial” reductions in productivity losses, they noted, including CD-related absences from work and school.
“Our results illustrate how an earlier detection of CD through screening or case finding, although more costly, leads to improved health outcomes and a reduction in disease burden, compared with current care,” Heijdra Suasnabar and colleagues wrote.
Their concluding remarks highlighted the conservative scenarios built into their model, and suggested that their findings offer solid evidence for implementing new CD-testing strategies.
“If found to be feasible and acceptable by clinicians and patients, these strategies should be implemented in the Netherlands,” they wrote.This study was supported by the Netherlands Organization for Health Research and Development. The investigators disclosed no conflicts of interest.
Celiac disease (CD) is common, affecting about 1% of the population, but it remains underdiagnosed because of its heterogeneous presentation and limited provider awareness. Most cases are detected only after patients develop gastrointestinal symptoms or laboratory abnormalities.
In this cost-effectiveness analysis, Suasnabar and colleagues demonstrate that screening children for celiac disease would be highly cost-effective relative to the current practice of clinical detection. They modeled point-of-care-testing using tissue transglutaminase IgA in all 3-year-old children in the Netherlands. While both mass screening and case-finding (via a standardized questionnaire) would increase healthcare costs relative to current care, both strategies would improve quality of life (QoL), reduce long-term complications (such as osteoporosis and non-Hodgkin lymphoma), and minimize productivity losses in individuals with CD. In sensitivity analyses accounting for uncertainty in QoL inputs and in the utility of diagnosing and treating asymptomatic CD, each screening strategy remained well below accepted willingness-to-pay thresholds.
John B. Doyle, MD, is a gastroenterology fellow in the Division of Digestive and Liver Diseases at Columbia University Medical Center, New York City. Benjamin Lebwohl, MD, MS, AGAF, is professor of medicine and epidemiology at Columbia University Medical Center and director of clinical research at The Celiac Disease Center at Columbia. They have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Celiac disease (CD) is common, affecting about 1% of the population, but it remains underdiagnosed because of its heterogeneous presentation and limited provider awareness. Most cases are detected only after patients develop gastrointestinal symptoms or laboratory abnormalities.
In this cost-effectiveness analysis, Suasnabar and colleagues demonstrate that screening children for celiac disease would be highly cost-effective relative to the current practice of clinical detection. They modeled point-of-care-testing using tissue transglutaminase IgA in all 3-year-old children in the Netherlands. While both mass screening and case-finding (via a standardized questionnaire) would increase healthcare costs relative to current care, both strategies would improve quality of life (QoL), reduce long-term complications (such as osteoporosis and non-Hodgkin lymphoma), and minimize productivity losses in individuals with CD. In sensitivity analyses accounting for uncertainty in QoL inputs and in the utility of diagnosing and treating asymptomatic CD, each screening strategy remained well below accepted willingness-to-pay thresholds.
John B. Doyle, MD, is a gastroenterology fellow in the Division of Digestive and Liver Diseases at Columbia University Medical Center, New York City. Benjamin Lebwohl, MD, MS, AGAF, is professor of medicine and epidemiology at Columbia University Medical Center and director of clinical research at The Celiac Disease Center at Columbia. They have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Celiac disease (CD) is common, affecting about 1% of the population, but it remains underdiagnosed because of its heterogeneous presentation and limited provider awareness. Most cases are detected only after patients develop gastrointestinal symptoms or laboratory abnormalities.
In this cost-effectiveness analysis, Suasnabar and colleagues demonstrate that screening children for celiac disease would be highly cost-effective relative to the current practice of clinical detection. They modeled point-of-care-testing using tissue transglutaminase IgA in all 3-year-old children in the Netherlands. While both mass screening and case-finding (via a standardized questionnaire) would increase healthcare costs relative to current care, both strategies would improve quality of life (QoL), reduce long-term complications (such as osteoporosis and non-Hodgkin lymphoma), and minimize productivity losses in individuals with CD. In sensitivity analyses accounting for uncertainty in QoL inputs and in the utility of diagnosing and treating asymptomatic CD, each screening strategy remained well below accepted willingness-to-pay thresholds.
John B. Doyle, MD, is a gastroenterology fellow in the Division of Digestive and Liver Diseases at Columbia University Medical Center, New York City. Benjamin Lebwohl, MD, MS, AGAF, is professor of medicine and epidemiology at Columbia University Medical Center and director of clinical research at The Celiac Disease Center at Columbia. They have no conflicts of interest to declare.
If these screening strategies are deemed feasible by clinicians and patients, then implementation in routine care is needed, lead author Jan Heijdra Suasnabar, MSc, of Leiden University Medical Centre in the Netherlands, and colleagues reported.
“Cohort studies have shown that CD likely develops early in life and can be easily diagnosed by detection of CD-specific antibodies against the enzyme tissue transglutaminase type 2 (IgA-TG2),” the investigators wrote in Gastroenterology.
Despite the ease of diagnosis, as few as one in five cases of CD are detected using current clinical strategies, meaning many cases are diagnosed years after symptom onset.
“Such high rates of missed/delayed diagnoses have been attributed to CD’s varied and nonspecific symptoms, lack of awareness, and the resource-intensive process necessary to establish the diagnosis,” Heijdra Suasnabar and colleagues wrote. “From an economic perspective, the burden of CD translates into substantial excess healthcare and societal costs.”
These practice gaps prompted the present study, which explored the long-term cost effectiveness of mass CD screening and active case finding among pediatric patients.
The investigators employed a model-based cost-effectiveness analysis with a hypothetical cohort representing all children with CD in the Netherlands. Iterations of this model evaluated long-term costs as these children moved through the healthcare system along various CD detection strategies.
The first strategy was based on the current Dutch approach, which is the same as that in the United States: Patients are only evaluated for CD if they present with symptoms that prompt suspicion of disease. Based on data from population-based studies, the model assumed that approximately one in three cases would be detected using this strategy.
The second strategy involved mass screening using IgA-TG2 point-of-care testing (sensitivity, 0.94; specificity, 0.944) via youth health care clinics, regardless of symptoms.
The third strategy, called “active case finding,” represented something of an intermediate approach, in which children with at least 1 CD-related symptom underwent point-of-care antibody testing.
For both mass screening and active case finding strategies, a positive antibody test was followed with confirmatory diagnostic testing.
Compared with current clinical approach, mass screening added 7.46 more quality-adjusted life-years (QALYs) per CD patient with an increased cost of €28,635 per CD patient. Active case finding gained 4.33 QALYs per CD patient while incurring an additional cost of €15,585 per CD patient.
Based on a willingness-to-pay threshold of €20,000 per QALY, the investigators deemed both strategies “highly cost effective,” compared with current standard of care. Some of these costs were offset by “substantial” reductions in productivity losses, they noted, including CD-related absences from work and school.
“Our results illustrate how an earlier detection of CD through screening or case finding, although more costly, leads to improved health outcomes and a reduction in disease burden, compared with current care,” Heijdra Suasnabar and colleagues wrote.
Their concluding remarks highlighted the conservative scenarios built into their model, and suggested that their findings offer solid evidence for implementing new CD-testing strategies.
“If found to be feasible and acceptable by clinicians and patients, these strategies should be implemented in the Netherlands,” they wrote.This study was supported by the Netherlands Organization for Health Research and Development. The investigators disclosed no conflicts of interest.
If these screening strategies are deemed feasible by clinicians and patients, then implementation in routine care is needed, lead author Jan Heijdra Suasnabar, MSc, of Leiden University Medical Centre in the Netherlands, and colleagues reported.
“Cohort studies have shown that CD likely develops early in life and can be easily diagnosed by detection of CD-specific antibodies against the enzyme tissue transglutaminase type 2 (IgA-TG2),” the investigators wrote in Gastroenterology.
Despite the ease of diagnosis, as few as one in five cases of CD are detected using current clinical strategies, meaning many cases are diagnosed years after symptom onset.
“Such high rates of missed/delayed diagnoses have been attributed to CD’s varied and nonspecific symptoms, lack of awareness, and the resource-intensive process necessary to establish the diagnosis,” Heijdra Suasnabar and colleagues wrote. “From an economic perspective, the burden of CD translates into substantial excess healthcare and societal costs.”
These practice gaps prompted the present study, which explored the long-term cost effectiveness of mass CD screening and active case finding among pediatric patients.
The investigators employed a model-based cost-effectiveness analysis with a hypothetical cohort representing all children with CD in the Netherlands. Iterations of this model evaluated long-term costs as these children moved through the healthcare system along various CD detection strategies.
The first strategy was based on the current Dutch approach, which is the same as that in the United States: Patients are only evaluated for CD if they present with symptoms that prompt suspicion of disease. Based on data from population-based studies, the model assumed that approximately one in three cases would be detected using this strategy.
The second strategy involved mass screening using IgA-TG2 point-of-care testing (sensitivity, 0.94; specificity, 0.944) via youth health care clinics, regardless of symptoms.
The third strategy, called “active case finding,” represented something of an intermediate approach, in which children with at least 1 CD-related symptom underwent point-of-care antibody testing.
For both mass screening and active case finding strategies, a positive antibody test was followed with confirmatory diagnostic testing.
Compared with current clinical approach, mass screening added 7.46 more quality-adjusted life-years (QALYs) per CD patient with an increased cost of €28,635 per CD patient. Active case finding gained 4.33 QALYs per CD patient while incurring an additional cost of €15,585 per CD patient.
Based on a willingness-to-pay threshold of €20,000 per QALY, the investigators deemed both strategies “highly cost effective,” compared with current standard of care. Some of these costs were offset by “substantial” reductions in productivity losses, they noted, including CD-related absences from work and school.
“Our results illustrate how an earlier detection of CD through screening or case finding, although more costly, leads to improved health outcomes and a reduction in disease burden, compared with current care,” Heijdra Suasnabar and colleagues wrote.
Their concluding remarks highlighted the conservative scenarios built into their model, and suggested that their findings offer solid evidence for implementing new CD-testing strategies.
“If found to be feasible and acceptable by clinicians and patients, these strategies should be implemented in the Netherlands,” they wrote.This study was supported by the Netherlands Organization for Health Research and Development. The investigators disclosed no conflicts of interest.
FROM GASTROENTEROLOGY
Navigating Ethical and Clinical Considerations Relating to Percutaneous Gastrostomy (PEG) Tubes
Cases
Consults for percutaneous gastrostomy (PEG) tube placement for a patient ...
- With dysphagia after stroke: A 70-year-old female with a history of hypertension presented to the hospital with altered mental status and left-sided weakness. She was previously active and independently living. MRI of the brain revealed a right basal ganglia infarct. As a result, she developed dysphagia. She was evaluated by speech and language pathology and underwent a modified barium swallow. Given concerns for aspiration, the recommendation was made for gastroenterology (GI) consultation to place PEG tube for nutrition and medication administration.
- With advanced dementia: An 85-year-old male with an extensive medical history including advanced dementia was admitted from his nursing home for decreased oral intake. His baseline mental status is awake and alert, but he is nonverbal and does not follow commands. Upon 72-hour calorie count, the nutrition consultants determined that he cannot independently meet his nutrition goals. His family wants “everything done” and are asking about a “feeding tube.” The primary team has now consulted GI for PEG tube placement.
- Who is being discharged to a long-term care facility: A 45-year-old male was admitted to the ICU after a heroin overdose. CPR was initiated in the field and return of spontaneous circulation was obtained after 25 minutes. The patient has minimal brainstem reflexes. He is ventilator dependent. He has no family, and now is status-post tracheostomy placement by two-physician consent. The patient is ready for discharge to a long-term care facility that will not accept patients with nasogastric tubes. GI is consulted for PEG tube placement.
Discussion
Gastroenterologists are often consulted for PEG tube placement. However, This is rooted in the fact that, as one expert wrote, “feeding, unlike any other medical treatment, has a moral and emotional significance derived from culture.”1 Understanding the evidence, ethical considerations, and team dynamic behind PEG tube placement is critical for every gastroenterologist. Herein we review these topics and offer guidelines for having patient-centered conversations involving these fundamental concepts.
First, the gastroenterologist should understand the evidence to debunk myths and clarify truths surrounding PEG tube placement. While PEG tubes may help patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis stabilize their weight and can even be prophylactically placed in select patients with head and neck cancer,2,3 they are not always appropriate in patients in early recovery from stroke and have not been shown to improve outcomes in patients with advanced dementia. At least 50% of stroke-related dysphagia resolves within 1-2 weeks, and so the American Heart Association Stroke Council recommends continuing nasogastric tube feeding for 2-3 weeks in patients such as the one presented in case 1 before considering PEG tube placement.4
In situations of advanced dementia such as in case,2 several studies demonstrate that PEG tubes do not reduce or prevent aspiration pneumonia, prevent consequences of malnutrition, prolong life, reduce pressure ulcers, reduce urinary of gastrointestinal tract infections, lead to functional improvement, mitigate decline, or even improve comfort or quality of life for patients or their caregivers.5-7 Despite this evidence, as demonstrated in case,3 it is true that many American skilled nursing facilities will not accept a patient without a PEG if enteral feeding is needed. This restriction may vary by state: One study found that skilled nursing facilities in New York City are much less likely to accept patients with nasogastric feeding tubes than randomly selected skilled nursing facilities throughout the country.6 Nonetheless, gastroenterologists should look to the literature to understand the outcomes of populations of patients after PEG tube placement and use that data to guide decision-making.
Secondly, the five ethical principles that inform all medical decision making – autonomy, beneficence, nonmaleficence, justice, and futility – should also inform the gastroenterologist’s rationale in offering PEG placement.8
Autonomy implies that the medical team has determined who is able to make the decision regarding PEG tube placement for the patient. Beneficence connects the patient’s medical diagnosis and technical parameters of PEG tube placement with his or her goals of care. Nonmaleficence ensures the decision-making party understands the benefits and risks of the procedure, including anticipatory guidance on possible PEG tube management, complications, risks, and need for replacement. Justice incorporates the context of the patient’s life, including family dynamics, religious, cultural, and financial factors. Futility connects the patient’s prognosis with practical aspects of having a PEG tube.
The complexity of PEG placement lies in the fact that these ethical principles are often at odds with each other. For example, case 2 highlights the conflicting principles of autonomy and futility for elderly dementia patients: While PEG tube placements do not improve comfort or quality of life in advanced dementia (futility), the family representing the patient has stated they want everything done for his care, including PEG tube placement (autonomy). Navigating these ethical principles can be difficult, but having a framework to organize the different factors offers sound guidance for the gastroenterologist.
Finally, the gastroenterologist should recognize the roles of the multidisciplinary team members, including the patient and their representatives, regarding PEG tube placement consults. While gastroenterologists can be viewed as the technicians consulted to simply “place the tube,” they must seek to understand the members of the team representing the patient to be stewards of their skill set. Consulting team physicians carry great responsibility in organizing the medical and psychosocial aspects of each patient’s care, and their proper goals to relieve suffering and prevent death may color their judgment regarding who they believe is a candidate for a PEG tube. Nutritionists, speech therapists, and case managers can help provide objective data on the practicality and feasibility of a PEG tube in their patients. The healthcare system may influence the decision to consult heavily, as seen in the rules of the long-term care facility in case.3 While it is the job of the multidisciplinary medical team to explain the evidence and ethical considerations of PEG tube placement in a patient-centered manner, ultimately the decision belongs to the patient and their family or representatives.
The moral burden of not pursuing PEG placement may supersede the medical advice in many situations. There is an emotionally taxing perception that withholding nutrition via PEG is “starving the patient,” despite literature showing many terminally ill patients do not experience thirst or hunger, and those who do have alleviation of these symptoms with small amounts of food or liquid, not with PEG placement.5 As every patient is unique, PEG tube consultation guidelines created with input from all stakeholders have been utilized to ensure that patients are medically optimized for PEG tube placement and that evidence and ethics-based considerations are evaluated by the multidisciplinary team. An example of such a guideline is shown in Figure 1.
If the gastroenterologist encounters more contentious consultations, there are ways to build consensus to both alleviate patient and family suffering as well as elevate the discussions between teams.
First, identify the type of consult that is repeatedly bringing differing viewpoints and differing ethical principles into play. Second, get representatives from teams together in a neutral environment to understand stakeholders needs. New data suggest, in stroke cases like case 1, there may be dramatic benefit in long-term ability to recover if patients can get early intensive rehabilitation.9 This intense daily rehabilitation is not available within the hospital setting at many locations, and facilitation of discharge may be requested earlier than usually advised tube placement. Third, build a common language for requests and responses between teams. For instance, neurologists can identify and document which patients have less likelihood of early spontaneous recovery, and this can allow gastroenterologists to understand that those patients with little potential for early swallowing recovery can safely be targeted for PEG earlier during the hospital course. Other patients described as having a potential for spontaneous improvement should be given time to recover before an intervention is considered.10 Having a common understanding of goals and a better-informed decision pathway helps each team member feel fulfilled and rewarded, which will ultimately help reduce compassion fatigue and moral burden on providers.
In conclusion, PEG tube placement can be a challenging consultation for gastroenterologists because of the clinical, social, and ethical ramifications at stake for the patient. Even when PEG tube placement is technically feasible, the gastroenterologist should feel empowered to address the evidence-based outcomes of PEG tube placement, discuss the ethical principles of the decision-making process, and communicate with a multidisciplinary team using guidelines as set forth by this paper to best serve the patient.
Dr. Seltzer is based in the Department of Internal Medicine, Mount Sinai Morningside-West, New York City. Dr. Pusateri is based in the Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition, Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus. Dr. Nguyen is based in the Division of Gastroenterology and Center for Esophageal Diseases, Baylor Scott & White Health, Dallas, Texas. Dr. Stein is based in the Division of Gastroenterology, Robert Wood Johnson University Hospital, Rutgers University, New Brunswick, New Jersey. All authors contributed equally to this manuscript, and have no disclosures related to this article.
References
1. Mackie S. Gastroenterol Nurs. 2001 May-Jun;24(3):138-42.
2. Miller RG et al. Neurology. 2009 Oct. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181bc0141.
3. Colevas AD et al. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2018 May. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2018.0026.
4. Holloway RG et al. Stroke. 2014 Jun. doi: 10.1161/STR.0000000000000015.
5. Finucane TE et al. JAMA. 1999 Oct. doi: 10.1001/jama.282.14.1365.
6. Burgermaster M et al. Nutr Clin Pract. 2016 Jun. doi: 10.1177/0884533616629636.
7. American Geriatrics Society Ethics C, Clinical P, Models of Care C. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2014 Aug. doi: 10.1111/jgs.12924.
8. Beauchamp TL. Principlism in Bioethics. In: Serna P, eds. Bioethical Decision Making and Argumentation. International Library of Ethics, Law, and the New Medicine, vol 70. Springer; Cham. 2016 Sept:1-16. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-43419-3_1.
9. Powers WJ et al. Stroke. 2019 Oct. doi: 10.1161/STR.0000000000000211.
10. Galovic M et al. JAMA Neurol. 2019 May. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2018.4858.
Cases
Consults for percutaneous gastrostomy (PEG) tube placement for a patient ...
- With dysphagia after stroke: A 70-year-old female with a history of hypertension presented to the hospital with altered mental status and left-sided weakness. She was previously active and independently living. MRI of the brain revealed a right basal ganglia infarct. As a result, she developed dysphagia. She was evaluated by speech and language pathology and underwent a modified barium swallow. Given concerns for aspiration, the recommendation was made for gastroenterology (GI) consultation to place PEG tube for nutrition and medication administration.
- With advanced dementia: An 85-year-old male with an extensive medical history including advanced dementia was admitted from his nursing home for decreased oral intake. His baseline mental status is awake and alert, but he is nonverbal and does not follow commands. Upon 72-hour calorie count, the nutrition consultants determined that he cannot independently meet his nutrition goals. His family wants “everything done” and are asking about a “feeding tube.” The primary team has now consulted GI for PEG tube placement.
- Who is being discharged to a long-term care facility: A 45-year-old male was admitted to the ICU after a heroin overdose. CPR was initiated in the field and return of spontaneous circulation was obtained after 25 minutes. The patient has minimal brainstem reflexes. He is ventilator dependent. He has no family, and now is status-post tracheostomy placement by two-physician consent. The patient is ready for discharge to a long-term care facility that will not accept patients with nasogastric tubes. GI is consulted for PEG tube placement.
Discussion
Gastroenterologists are often consulted for PEG tube placement. However, This is rooted in the fact that, as one expert wrote, “feeding, unlike any other medical treatment, has a moral and emotional significance derived from culture.”1 Understanding the evidence, ethical considerations, and team dynamic behind PEG tube placement is critical for every gastroenterologist. Herein we review these topics and offer guidelines for having patient-centered conversations involving these fundamental concepts.
First, the gastroenterologist should understand the evidence to debunk myths and clarify truths surrounding PEG tube placement. While PEG tubes may help patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis stabilize their weight and can even be prophylactically placed in select patients with head and neck cancer,2,3 they are not always appropriate in patients in early recovery from stroke and have not been shown to improve outcomes in patients with advanced dementia. At least 50% of stroke-related dysphagia resolves within 1-2 weeks, and so the American Heart Association Stroke Council recommends continuing nasogastric tube feeding for 2-3 weeks in patients such as the one presented in case 1 before considering PEG tube placement.4
In situations of advanced dementia such as in case,2 several studies demonstrate that PEG tubes do not reduce or prevent aspiration pneumonia, prevent consequences of malnutrition, prolong life, reduce pressure ulcers, reduce urinary of gastrointestinal tract infections, lead to functional improvement, mitigate decline, or even improve comfort or quality of life for patients or their caregivers.5-7 Despite this evidence, as demonstrated in case,3 it is true that many American skilled nursing facilities will not accept a patient without a PEG if enteral feeding is needed. This restriction may vary by state: One study found that skilled nursing facilities in New York City are much less likely to accept patients with nasogastric feeding tubes than randomly selected skilled nursing facilities throughout the country.6 Nonetheless, gastroenterologists should look to the literature to understand the outcomes of populations of patients after PEG tube placement and use that data to guide decision-making.
Secondly, the five ethical principles that inform all medical decision making – autonomy, beneficence, nonmaleficence, justice, and futility – should also inform the gastroenterologist’s rationale in offering PEG placement.8
Autonomy implies that the medical team has determined who is able to make the decision regarding PEG tube placement for the patient. Beneficence connects the patient’s medical diagnosis and technical parameters of PEG tube placement with his or her goals of care. Nonmaleficence ensures the decision-making party understands the benefits and risks of the procedure, including anticipatory guidance on possible PEG tube management, complications, risks, and need for replacement. Justice incorporates the context of the patient’s life, including family dynamics, religious, cultural, and financial factors. Futility connects the patient’s prognosis with practical aspects of having a PEG tube.
The complexity of PEG placement lies in the fact that these ethical principles are often at odds with each other. For example, case 2 highlights the conflicting principles of autonomy and futility for elderly dementia patients: While PEG tube placements do not improve comfort or quality of life in advanced dementia (futility), the family representing the patient has stated they want everything done for his care, including PEG tube placement (autonomy). Navigating these ethical principles can be difficult, but having a framework to organize the different factors offers sound guidance for the gastroenterologist.
Finally, the gastroenterologist should recognize the roles of the multidisciplinary team members, including the patient and their representatives, regarding PEG tube placement consults. While gastroenterologists can be viewed as the technicians consulted to simply “place the tube,” they must seek to understand the members of the team representing the patient to be stewards of their skill set. Consulting team physicians carry great responsibility in organizing the medical and psychosocial aspects of each patient’s care, and their proper goals to relieve suffering and prevent death may color their judgment regarding who they believe is a candidate for a PEG tube. Nutritionists, speech therapists, and case managers can help provide objective data on the practicality and feasibility of a PEG tube in their patients. The healthcare system may influence the decision to consult heavily, as seen in the rules of the long-term care facility in case.3 While it is the job of the multidisciplinary medical team to explain the evidence and ethical considerations of PEG tube placement in a patient-centered manner, ultimately the decision belongs to the patient and their family or representatives.
The moral burden of not pursuing PEG placement may supersede the medical advice in many situations. There is an emotionally taxing perception that withholding nutrition via PEG is “starving the patient,” despite literature showing many terminally ill patients do not experience thirst or hunger, and those who do have alleviation of these symptoms with small amounts of food or liquid, not with PEG placement.5 As every patient is unique, PEG tube consultation guidelines created with input from all stakeholders have been utilized to ensure that patients are medically optimized for PEG tube placement and that evidence and ethics-based considerations are evaluated by the multidisciplinary team. An example of such a guideline is shown in Figure 1.
If the gastroenterologist encounters more contentious consultations, there are ways to build consensus to both alleviate patient and family suffering as well as elevate the discussions between teams.
First, identify the type of consult that is repeatedly bringing differing viewpoints and differing ethical principles into play. Second, get representatives from teams together in a neutral environment to understand stakeholders needs. New data suggest, in stroke cases like case 1, there may be dramatic benefit in long-term ability to recover if patients can get early intensive rehabilitation.9 This intense daily rehabilitation is not available within the hospital setting at many locations, and facilitation of discharge may be requested earlier than usually advised tube placement. Third, build a common language for requests and responses between teams. For instance, neurologists can identify and document which patients have less likelihood of early spontaneous recovery, and this can allow gastroenterologists to understand that those patients with little potential for early swallowing recovery can safely be targeted for PEG earlier during the hospital course. Other patients described as having a potential for spontaneous improvement should be given time to recover before an intervention is considered.10 Having a common understanding of goals and a better-informed decision pathway helps each team member feel fulfilled and rewarded, which will ultimately help reduce compassion fatigue and moral burden on providers.
In conclusion, PEG tube placement can be a challenging consultation for gastroenterologists because of the clinical, social, and ethical ramifications at stake for the patient. Even when PEG tube placement is technically feasible, the gastroenterologist should feel empowered to address the evidence-based outcomes of PEG tube placement, discuss the ethical principles of the decision-making process, and communicate with a multidisciplinary team using guidelines as set forth by this paper to best serve the patient.
Dr. Seltzer is based in the Department of Internal Medicine, Mount Sinai Morningside-West, New York City. Dr. Pusateri is based in the Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition, Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus. Dr. Nguyen is based in the Division of Gastroenterology and Center for Esophageal Diseases, Baylor Scott & White Health, Dallas, Texas. Dr. Stein is based in the Division of Gastroenterology, Robert Wood Johnson University Hospital, Rutgers University, New Brunswick, New Jersey. All authors contributed equally to this manuscript, and have no disclosures related to this article.
References
1. Mackie S. Gastroenterol Nurs. 2001 May-Jun;24(3):138-42.
2. Miller RG et al. Neurology. 2009 Oct. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181bc0141.
3. Colevas AD et al. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2018 May. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2018.0026.
4. Holloway RG et al. Stroke. 2014 Jun. doi: 10.1161/STR.0000000000000015.
5. Finucane TE et al. JAMA. 1999 Oct. doi: 10.1001/jama.282.14.1365.
6. Burgermaster M et al. Nutr Clin Pract. 2016 Jun. doi: 10.1177/0884533616629636.
7. American Geriatrics Society Ethics C, Clinical P, Models of Care C. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2014 Aug. doi: 10.1111/jgs.12924.
8. Beauchamp TL. Principlism in Bioethics. In: Serna P, eds. Bioethical Decision Making and Argumentation. International Library of Ethics, Law, and the New Medicine, vol 70. Springer; Cham. 2016 Sept:1-16. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-43419-3_1.
9. Powers WJ et al. Stroke. 2019 Oct. doi: 10.1161/STR.0000000000000211.
10. Galovic M et al. JAMA Neurol. 2019 May. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2018.4858.
Cases
Consults for percutaneous gastrostomy (PEG) tube placement for a patient ...
- With dysphagia after stroke: A 70-year-old female with a history of hypertension presented to the hospital with altered mental status and left-sided weakness. She was previously active and independently living. MRI of the brain revealed a right basal ganglia infarct. As a result, she developed dysphagia. She was evaluated by speech and language pathology and underwent a modified barium swallow. Given concerns for aspiration, the recommendation was made for gastroenterology (GI) consultation to place PEG tube for nutrition and medication administration.
- With advanced dementia: An 85-year-old male with an extensive medical history including advanced dementia was admitted from his nursing home for decreased oral intake. His baseline mental status is awake and alert, but he is nonverbal and does not follow commands. Upon 72-hour calorie count, the nutrition consultants determined that he cannot independently meet his nutrition goals. His family wants “everything done” and are asking about a “feeding tube.” The primary team has now consulted GI for PEG tube placement.
- Who is being discharged to a long-term care facility: A 45-year-old male was admitted to the ICU after a heroin overdose. CPR was initiated in the field and return of spontaneous circulation was obtained after 25 minutes. The patient has minimal brainstem reflexes. He is ventilator dependent. He has no family, and now is status-post tracheostomy placement by two-physician consent. The patient is ready for discharge to a long-term care facility that will not accept patients with nasogastric tubes. GI is consulted for PEG tube placement.
Discussion
Gastroenterologists are often consulted for PEG tube placement. However, This is rooted in the fact that, as one expert wrote, “feeding, unlike any other medical treatment, has a moral and emotional significance derived from culture.”1 Understanding the evidence, ethical considerations, and team dynamic behind PEG tube placement is critical for every gastroenterologist. Herein we review these topics and offer guidelines for having patient-centered conversations involving these fundamental concepts.
First, the gastroenterologist should understand the evidence to debunk myths and clarify truths surrounding PEG tube placement. While PEG tubes may help patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis stabilize their weight and can even be prophylactically placed in select patients with head and neck cancer,2,3 they are not always appropriate in patients in early recovery from stroke and have not been shown to improve outcomes in patients with advanced dementia. At least 50% of stroke-related dysphagia resolves within 1-2 weeks, and so the American Heart Association Stroke Council recommends continuing nasogastric tube feeding for 2-3 weeks in patients such as the one presented in case 1 before considering PEG tube placement.4
In situations of advanced dementia such as in case,2 several studies demonstrate that PEG tubes do not reduce or prevent aspiration pneumonia, prevent consequences of malnutrition, prolong life, reduce pressure ulcers, reduce urinary of gastrointestinal tract infections, lead to functional improvement, mitigate decline, or even improve comfort or quality of life for patients or their caregivers.5-7 Despite this evidence, as demonstrated in case,3 it is true that many American skilled nursing facilities will not accept a patient without a PEG if enteral feeding is needed. This restriction may vary by state: One study found that skilled nursing facilities in New York City are much less likely to accept patients with nasogastric feeding tubes than randomly selected skilled nursing facilities throughout the country.6 Nonetheless, gastroenterologists should look to the literature to understand the outcomes of populations of patients after PEG tube placement and use that data to guide decision-making.
Secondly, the five ethical principles that inform all medical decision making – autonomy, beneficence, nonmaleficence, justice, and futility – should also inform the gastroenterologist’s rationale in offering PEG placement.8
Autonomy implies that the medical team has determined who is able to make the decision regarding PEG tube placement for the patient. Beneficence connects the patient’s medical diagnosis and technical parameters of PEG tube placement with his or her goals of care. Nonmaleficence ensures the decision-making party understands the benefits and risks of the procedure, including anticipatory guidance on possible PEG tube management, complications, risks, and need for replacement. Justice incorporates the context of the patient’s life, including family dynamics, religious, cultural, and financial factors. Futility connects the patient’s prognosis with practical aspects of having a PEG tube.
The complexity of PEG placement lies in the fact that these ethical principles are often at odds with each other. For example, case 2 highlights the conflicting principles of autonomy and futility for elderly dementia patients: While PEG tube placements do not improve comfort or quality of life in advanced dementia (futility), the family representing the patient has stated they want everything done for his care, including PEG tube placement (autonomy). Navigating these ethical principles can be difficult, but having a framework to organize the different factors offers sound guidance for the gastroenterologist.
Finally, the gastroenterologist should recognize the roles of the multidisciplinary team members, including the patient and their representatives, regarding PEG tube placement consults. While gastroenterologists can be viewed as the technicians consulted to simply “place the tube,” they must seek to understand the members of the team representing the patient to be stewards of their skill set. Consulting team physicians carry great responsibility in organizing the medical and psychosocial aspects of each patient’s care, and their proper goals to relieve suffering and prevent death may color their judgment regarding who they believe is a candidate for a PEG tube. Nutritionists, speech therapists, and case managers can help provide objective data on the practicality and feasibility of a PEG tube in their patients. The healthcare system may influence the decision to consult heavily, as seen in the rules of the long-term care facility in case.3 While it is the job of the multidisciplinary medical team to explain the evidence and ethical considerations of PEG tube placement in a patient-centered manner, ultimately the decision belongs to the patient and their family or representatives.
The moral burden of not pursuing PEG placement may supersede the medical advice in many situations. There is an emotionally taxing perception that withholding nutrition via PEG is “starving the patient,” despite literature showing many terminally ill patients do not experience thirst or hunger, and those who do have alleviation of these symptoms with small amounts of food or liquid, not with PEG placement.5 As every patient is unique, PEG tube consultation guidelines created with input from all stakeholders have been utilized to ensure that patients are medically optimized for PEG tube placement and that evidence and ethics-based considerations are evaluated by the multidisciplinary team. An example of such a guideline is shown in Figure 1.
If the gastroenterologist encounters more contentious consultations, there are ways to build consensus to both alleviate patient and family suffering as well as elevate the discussions between teams.
First, identify the type of consult that is repeatedly bringing differing viewpoints and differing ethical principles into play. Second, get representatives from teams together in a neutral environment to understand stakeholders needs. New data suggest, in stroke cases like case 1, there may be dramatic benefit in long-term ability to recover if patients can get early intensive rehabilitation.9 This intense daily rehabilitation is not available within the hospital setting at many locations, and facilitation of discharge may be requested earlier than usually advised tube placement. Third, build a common language for requests and responses between teams. For instance, neurologists can identify and document which patients have less likelihood of early spontaneous recovery, and this can allow gastroenterologists to understand that those patients with little potential for early swallowing recovery can safely be targeted for PEG earlier during the hospital course. Other patients described as having a potential for spontaneous improvement should be given time to recover before an intervention is considered.10 Having a common understanding of goals and a better-informed decision pathway helps each team member feel fulfilled and rewarded, which will ultimately help reduce compassion fatigue and moral burden on providers.
In conclusion, PEG tube placement can be a challenging consultation for gastroenterologists because of the clinical, social, and ethical ramifications at stake for the patient. Even when PEG tube placement is technically feasible, the gastroenterologist should feel empowered to address the evidence-based outcomes of PEG tube placement, discuss the ethical principles of the decision-making process, and communicate with a multidisciplinary team using guidelines as set forth by this paper to best serve the patient.
Dr. Seltzer is based in the Department of Internal Medicine, Mount Sinai Morningside-West, New York City. Dr. Pusateri is based in the Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition, Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus. Dr. Nguyen is based in the Division of Gastroenterology and Center for Esophageal Diseases, Baylor Scott & White Health, Dallas, Texas. Dr. Stein is based in the Division of Gastroenterology, Robert Wood Johnson University Hospital, Rutgers University, New Brunswick, New Jersey. All authors contributed equally to this manuscript, and have no disclosures related to this article.
References
1. Mackie S. Gastroenterol Nurs. 2001 May-Jun;24(3):138-42.
2. Miller RG et al. Neurology. 2009 Oct. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181bc0141.
3. Colevas AD et al. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2018 May. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2018.0026.
4. Holloway RG et al. Stroke. 2014 Jun. doi: 10.1161/STR.0000000000000015.
5. Finucane TE et al. JAMA. 1999 Oct. doi: 10.1001/jama.282.14.1365.
6. Burgermaster M et al. Nutr Clin Pract. 2016 Jun. doi: 10.1177/0884533616629636.
7. American Geriatrics Society Ethics C, Clinical P, Models of Care C. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2014 Aug. doi: 10.1111/jgs.12924.
8. Beauchamp TL. Principlism in Bioethics. In: Serna P, eds. Bioethical Decision Making and Argumentation. International Library of Ethics, Law, and the New Medicine, vol 70. Springer; Cham. 2016 Sept:1-16. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-43419-3_1.
9. Powers WJ et al. Stroke. 2019 Oct. doi: 10.1161/STR.0000000000000211.
10. Galovic M et al. JAMA Neurol. 2019 May. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2018.4858.
PPI Prophylaxis Prevents GI Bleed in Ventilated Patients
according to a randomized trial and a systematic review led by researchers at McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontario, Canada.
Patients in the intensive care unit (ICU) who need mechanical ventilation typically are given a PPI, such as pantoprazole, to prevent upper GI bleeding caused by stress-induced stomach ulcers, but some evidence suggested that their use might increase the risk for pneumonia and death in the most severely ill patients.
As a result, recent guidelines have issued only weak recommendations for stress ulcer prophylaxis, especially with PPIs, in critically ill patients at a high risk for bleeding, Deborah Cook, MD, professor of medicine at McMaster University, and colleagues noted.
To address clinical questions, they investigated the efficacy and safety of PPIs to prevent upper GI bleeding in critically ill patients.
Both the randomized trial in The New England Journal of Medicine and the systematic review in NEJM Evidence were published online in June.
Significantly Lower Bleeding Risk
The REVISE trial, conducted in eight countries, compared pantoprazole 40 mg daily with placebo in critically ill adults on mechanical ventilation.
The primary efficacy outcome was clinically important upper GI bleeding in the ICU at 90 days, and the primary safety outcome was death from any cause at 90 days.
A total of 4821 patients in 68 ICUs were randomly assigned to the pantoprazole group or placebo group.
Clinically important upper GI bleeding occurred in 25 patients (1%) receiving pantoprazole and in 84 patients (3.5%) receiving placebo. At 90 days, 696 patients (29.1%) in the pantoprazole group died, as did 734 (30.9%) in the placebo group.
No significant differences were found on key secondary outcomes, including ventilator-associated pneumonia and Clostridioides difficile infection in the hospital.
The authors concluded that pantoprazole resulted in a significantly lower risk for clinically important upper GI bleeding than placebo, and it had no significant effect on mortality.
Disease Severity as a Possible Factor
The systematic review included 12 randomized controlled trials comparing PPIs with placebo or no prophylaxis for stress ulcers in a total of 9533 critically ill adults. The researchers performed meta-analyses and assessed the certainty of the evidence. They also conducted a subgroup analysis combining within-trial subgroup data from the two largest trials.
They found that PPIs were associated with a reduced incidence of clinically important upper GI bleeding (relative risk [RR], 0.51, with high certainty evidence) and may have little or no effect on mortality (RR, 0.99, with low-certainty evidence).
However, the within-trial subgroup analysis with intermediate credibility suggested that the effect of PPIs on mortality may differ based on disease severity. The results also raised the possibility that PPI use may decrease 90-day mortality in less severely ill patients (RR, 0.89) and increase mortality in more severely ill patients (RR, 1.08). The mechanisms behind this possible signal are likely multifactorial, the authors noted.
In addition, the review found that PPIs may have no effect on pneumonia, duration of ICU stay, or duration of hospital stay, and little or no effect on C difficile infection or duration of mechanical ventilation (low-certainty evidence).
“Physicians, nurses, and pharmacists working in the ICU setting will use this information in practice right away, and the trial results and the updated meta-analysis will be incorporated into international practice guidelines,” Dr. Cook said.
Both studies had limitations. The REVISE trial did not include patient-reported disability outcomes, and the results may not be generalizable to patients with unassisted breathing. The systematic review included studies with diverse definitions of bleeding and pneumonia, and with mortality reported at different milestones, without considering competing risk analyses. Patient-important GI bleeding was available in only one trial. Other potential side effects of PPIs, such as infection with multidrug-resistant organisms, were not reported.
In an editorial accompanying both studies, Samuel M. Brown, MD, a pulmonologist and vice president of research at Intermountain Health, Salt Lake City, Utah, said that the REVISE trial was “well designed and executed, with generalizable eligibility criteria and excellent experimental separation.” He said the researchers had shown that PPIs “slightly but significantly” decrease the risk of important GI bleeding and have a “decent chance” of slightly decreasing mortality in less severely ill patients during mechanical ventilation. At the same time, he noted, PPIs “do not decrease — and may slightly increase — mortality” in severely ill patients.
Dr. Brown wrote that, in his own practice, he intends to prescribe prophylactic PPIs to patients during mechanical ventilation “if they have an APACHE II score of less than 25” or a reasonable equivalent. The APACHE II scoring system is a point-based system that estimates a patient’s risk of death while in an ICU.
“For sicker patients, I would probably reserve the use of proton-pump inhibitors for those who are being treated with antiplatelet agents, especially in the presence of therapeutic anticoagulants,” he added.
REVISE was supported by numerous grants from organizations in several countries. No funding was specified for the systematic review. Author disclosures and other supplementary materials are available with the full text of the article.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to a randomized trial and a systematic review led by researchers at McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontario, Canada.
Patients in the intensive care unit (ICU) who need mechanical ventilation typically are given a PPI, such as pantoprazole, to prevent upper GI bleeding caused by stress-induced stomach ulcers, but some evidence suggested that their use might increase the risk for pneumonia and death in the most severely ill patients.
As a result, recent guidelines have issued only weak recommendations for stress ulcer prophylaxis, especially with PPIs, in critically ill patients at a high risk for bleeding, Deborah Cook, MD, professor of medicine at McMaster University, and colleagues noted.
To address clinical questions, they investigated the efficacy and safety of PPIs to prevent upper GI bleeding in critically ill patients.
Both the randomized trial in The New England Journal of Medicine and the systematic review in NEJM Evidence were published online in June.
Significantly Lower Bleeding Risk
The REVISE trial, conducted in eight countries, compared pantoprazole 40 mg daily with placebo in critically ill adults on mechanical ventilation.
The primary efficacy outcome was clinically important upper GI bleeding in the ICU at 90 days, and the primary safety outcome was death from any cause at 90 days.
A total of 4821 patients in 68 ICUs were randomly assigned to the pantoprazole group or placebo group.
Clinically important upper GI bleeding occurred in 25 patients (1%) receiving pantoprazole and in 84 patients (3.5%) receiving placebo. At 90 days, 696 patients (29.1%) in the pantoprazole group died, as did 734 (30.9%) in the placebo group.
No significant differences were found on key secondary outcomes, including ventilator-associated pneumonia and Clostridioides difficile infection in the hospital.
The authors concluded that pantoprazole resulted in a significantly lower risk for clinically important upper GI bleeding than placebo, and it had no significant effect on mortality.
Disease Severity as a Possible Factor
The systematic review included 12 randomized controlled trials comparing PPIs with placebo or no prophylaxis for stress ulcers in a total of 9533 critically ill adults. The researchers performed meta-analyses and assessed the certainty of the evidence. They also conducted a subgroup analysis combining within-trial subgroup data from the two largest trials.
They found that PPIs were associated with a reduced incidence of clinically important upper GI bleeding (relative risk [RR], 0.51, with high certainty evidence) and may have little or no effect on mortality (RR, 0.99, with low-certainty evidence).
However, the within-trial subgroup analysis with intermediate credibility suggested that the effect of PPIs on mortality may differ based on disease severity. The results also raised the possibility that PPI use may decrease 90-day mortality in less severely ill patients (RR, 0.89) and increase mortality in more severely ill patients (RR, 1.08). The mechanisms behind this possible signal are likely multifactorial, the authors noted.
In addition, the review found that PPIs may have no effect on pneumonia, duration of ICU stay, or duration of hospital stay, and little or no effect on C difficile infection or duration of mechanical ventilation (low-certainty evidence).
“Physicians, nurses, and pharmacists working in the ICU setting will use this information in practice right away, and the trial results and the updated meta-analysis will be incorporated into international practice guidelines,” Dr. Cook said.
Both studies had limitations. The REVISE trial did not include patient-reported disability outcomes, and the results may not be generalizable to patients with unassisted breathing. The systematic review included studies with diverse definitions of bleeding and pneumonia, and with mortality reported at different milestones, without considering competing risk analyses. Patient-important GI bleeding was available in only one trial. Other potential side effects of PPIs, such as infection with multidrug-resistant organisms, were not reported.
In an editorial accompanying both studies, Samuel M. Brown, MD, a pulmonologist and vice president of research at Intermountain Health, Salt Lake City, Utah, said that the REVISE trial was “well designed and executed, with generalizable eligibility criteria and excellent experimental separation.” He said the researchers had shown that PPIs “slightly but significantly” decrease the risk of important GI bleeding and have a “decent chance” of slightly decreasing mortality in less severely ill patients during mechanical ventilation. At the same time, he noted, PPIs “do not decrease — and may slightly increase — mortality” in severely ill patients.
Dr. Brown wrote that, in his own practice, he intends to prescribe prophylactic PPIs to patients during mechanical ventilation “if they have an APACHE II score of less than 25” or a reasonable equivalent. The APACHE II scoring system is a point-based system that estimates a patient’s risk of death while in an ICU.
“For sicker patients, I would probably reserve the use of proton-pump inhibitors for those who are being treated with antiplatelet agents, especially in the presence of therapeutic anticoagulants,” he added.
REVISE was supported by numerous grants from organizations in several countries. No funding was specified for the systematic review. Author disclosures and other supplementary materials are available with the full text of the article.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to a randomized trial and a systematic review led by researchers at McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontario, Canada.
Patients in the intensive care unit (ICU) who need mechanical ventilation typically are given a PPI, such as pantoprazole, to prevent upper GI bleeding caused by stress-induced stomach ulcers, but some evidence suggested that their use might increase the risk for pneumonia and death in the most severely ill patients.
As a result, recent guidelines have issued only weak recommendations for stress ulcer prophylaxis, especially with PPIs, in critically ill patients at a high risk for bleeding, Deborah Cook, MD, professor of medicine at McMaster University, and colleagues noted.
To address clinical questions, they investigated the efficacy and safety of PPIs to prevent upper GI bleeding in critically ill patients.
Both the randomized trial in The New England Journal of Medicine and the systematic review in NEJM Evidence were published online in June.
Significantly Lower Bleeding Risk
The REVISE trial, conducted in eight countries, compared pantoprazole 40 mg daily with placebo in critically ill adults on mechanical ventilation.
The primary efficacy outcome was clinically important upper GI bleeding in the ICU at 90 days, and the primary safety outcome was death from any cause at 90 days.
A total of 4821 patients in 68 ICUs were randomly assigned to the pantoprazole group or placebo group.
Clinically important upper GI bleeding occurred in 25 patients (1%) receiving pantoprazole and in 84 patients (3.5%) receiving placebo. At 90 days, 696 patients (29.1%) in the pantoprazole group died, as did 734 (30.9%) in the placebo group.
No significant differences were found on key secondary outcomes, including ventilator-associated pneumonia and Clostridioides difficile infection in the hospital.
The authors concluded that pantoprazole resulted in a significantly lower risk for clinically important upper GI bleeding than placebo, and it had no significant effect on mortality.
Disease Severity as a Possible Factor
The systematic review included 12 randomized controlled trials comparing PPIs with placebo or no prophylaxis for stress ulcers in a total of 9533 critically ill adults. The researchers performed meta-analyses and assessed the certainty of the evidence. They also conducted a subgroup analysis combining within-trial subgroup data from the two largest trials.
They found that PPIs were associated with a reduced incidence of clinically important upper GI bleeding (relative risk [RR], 0.51, with high certainty evidence) and may have little or no effect on mortality (RR, 0.99, with low-certainty evidence).
However, the within-trial subgroup analysis with intermediate credibility suggested that the effect of PPIs on mortality may differ based on disease severity. The results also raised the possibility that PPI use may decrease 90-day mortality in less severely ill patients (RR, 0.89) and increase mortality in more severely ill patients (RR, 1.08). The mechanisms behind this possible signal are likely multifactorial, the authors noted.
In addition, the review found that PPIs may have no effect on pneumonia, duration of ICU stay, or duration of hospital stay, and little or no effect on C difficile infection or duration of mechanical ventilation (low-certainty evidence).
“Physicians, nurses, and pharmacists working in the ICU setting will use this information in practice right away, and the trial results and the updated meta-analysis will be incorporated into international practice guidelines,” Dr. Cook said.
Both studies had limitations. The REVISE trial did not include patient-reported disability outcomes, and the results may not be generalizable to patients with unassisted breathing. The systematic review included studies with diverse definitions of bleeding and pneumonia, and with mortality reported at different milestones, without considering competing risk analyses. Patient-important GI bleeding was available in only one trial. Other potential side effects of PPIs, such as infection with multidrug-resistant organisms, were not reported.
In an editorial accompanying both studies, Samuel M. Brown, MD, a pulmonologist and vice president of research at Intermountain Health, Salt Lake City, Utah, said that the REVISE trial was “well designed and executed, with generalizable eligibility criteria and excellent experimental separation.” He said the researchers had shown that PPIs “slightly but significantly” decrease the risk of important GI bleeding and have a “decent chance” of slightly decreasing mortality in less severely ill patients during mechanical ventilation. At the same time, he noted, PPIs “do not decrease — and may slightly increase — mortality” in severely ill patients.
Dr. Brown wrote that, in his own practice, he intends to prescribe prophylactic PPIs to patients during mechanical ventilation “if they have an APACHE II score of less than 25” or a reasonable equivalent. The APACHE II scoring system is a point-based system that estimates a patient’s risk of death while in an ICU.
“For sicker patients, I would probably reserve the use of proton-pump inhibitors for those who are being treated with antiplatelet agents, especially in the presence of therapeutic anticoagulants,” he added.
REVISE was supported by numerous grants from organizations in several countries. No funding was specified for the systematic review. Author disclosures and other supplementary materials are available with the full text of the article.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE NEW ENGLAND JOURNAL OF MEDICINE
August 2024 – ICYMI
Gastroenterology
April 2024
Shah I, et al. Disparities in Colorectal Cancer Screening Among Asian American Populations and Strategies to Address These Disparities. Gastroenterology. 2024 Apr;166(4):549-552. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2024.02.009. PMID: 38521575.
Shiha MG, et al. Accuracy of the No-Biopsy Approach for the Diagnosis of Celiac Disease in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Gastroenterology. 2024 Apr;166(4):620-630. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.12.023. Epub 2024 Jan 2. PMID: 38176661.
Goltstein LCMJ, et al. Standard of Care Versus Octreotide in Angiodysplasia-Related Bleeding (the OCEAN Study): A Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial. Gastroenterology. 2024 Apr;166(4):690-703. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.12.020. Epub 2023 Dec 28. PMID: 38158089.
May 2024
Robertson DJ, et al. Colonoscopy vs the Fecal Immunochemical Test: Which is Best? Gastroenterology. 2024 May;166(5):758-771. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.12.027. Epub 2024 Feb 9. PMID: 38342196.
Mårild K, et al. Histologic Remission in Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Female Fertility: A Nationwide Study. Gastroenterology. 2024 May;166(5):802-814.e18. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2024.01.018. Epub 2024 Feb 6. PMID: 38331202.
June 2024
Trivedi PJ, et al. Immunopathogenesis of Primary Biliary Cholangitis, Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis and Autoimmune Hepatitis: Themes and Concepts. Gastroenterology. 2024 Jun;166(6):995-1019. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2024.01.049. Epub 2024 Feb 10. PMID: 38342195.
Rubenstein JH, et al. AGA Clinical Practice Guideline on Endoscopic Eradication Therapy of Barrett’s Esophagus and Related Neoplasia. Gastroenterology. 2024 Jun;166(6):1020-1055. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2024.03.019. PMID: 38763697.
Ridtitid W, et al. Endoscopic Gallbladder Stenting to Prevent Recurrent Cholecystitis in Deferred Cholecystectomy: A Randomized Trial. Gastroenterology. 2024 Jun;166(6):1145-1155. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2024.02.007. Epub 2024 Feb 14. PMID: 38360274.
Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology
April 2024
Berwald G, et al. The Diagnostic Performance of Fecal Immunochemical Tests for Detecting Advanced Neoplasia at Surveillance Colonoscopy. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Apr;22(4):878-885.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2023.09.016. Epub 2023 Sep 22. PMID: 37743036.
Hashash JG, et al. AGA Rapid Clinical Practice Update on the Management of Patients Taking GLP-1 Receptor Agonists Prior to Endoscopy: Communication. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Apr;22(4):705-707. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2023.11.002. Epub 2023 Nov 7. PMID: 37944573.
Sharma R, et al. Statins Are Associated With a Decreased Risk of Severe Liver Disease in Individuals With Noncirrhotic Chronic Liver Disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Apr;22(4):749-759.e19. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2023.04.017. Epub 2023 Apr 28. PMID: 37121528.
May 2024
Overbeek KA, et al; PrescrAIP Study Group. Type 1 Autoimmune Pancreatitis in Europe: Clinical Profile and Response to Treatment. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 May;22(5):994-1004.e10. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2023.12.010. Epub 2024 Jan 5. Erratum in: Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Jun 1:S1542-3565(24)00446-4. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2024.05.005. PMID: 38184096.
Jairath V, et al. ENTERPRET: A Randomized Controlled Trial of Vedolizumab Dose Optimization in Patients With Ulcerative Colitis Who Have Early Nonresponse. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 May;22(5):1077-1086.e13. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2023.10.029. Epub 2023 Nov 10. PMID: 37951560.
Gunby SA, et al. Smoking and Alcohol Consumption and Risk of Incident Diverticulitis in Women. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 May;22(5):1108-1116. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2023.11.036. Epub 2023 Dec 19. PMID: 38122959; PMCID: PMC11045313.
June 2024
Krause AJ, et al. Validated Clinical Score to Predict Gastroesophageal Reflux in Patients With Chronic Laryngeal Symptoms: COuGH RefluX. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Jun;22(6):1200-1209.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2024.01.021. Epub 2024 Feb 2. PMID: 38309491; PMCID: PMC11128352.
Peng X, et al. Efficacy and Safety of Vonoprazan-Amoxicillin Dual Regimen With Varying Dose and Duration for Helicobacter pylori Eradication: A Multicenter, Prospective, Randomized Study. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Jun;22(6):1210-1216. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2024.01.022. Epub 2024 Feb 1. PMID: 38309492.
Kedia S, et al. Coconut Water Induces Clinical Remission in Mild to Moderate Ulcerative Colitis: Double-blind Placebo-controlled Trial. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Jun;22(6):1295-1306.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2024.01.013. Epub 2024 Jan 24. PMID: 38278200.
Techniques and Innovations in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy
Ogura T, et al. Step-Up Strategy for Endoscopic Hemostasis Using PuraStat After Endoscopic Sphincterotomy Bleeding (STOP Trial). Tech Innov Gastrointest Endosc. 2024 March 16. doi: 10.1016/j.tige.2024.03.005.
Nakai Y, et al. Cyst Detection Rate: A Quality Indicator in the Era of Pancreatic Screening Endoscopic Ultrasonography. Tech Innov Gastrointest Endosc. 2024 May. doi: 10.1016/j.tige.2024.04.001.
Gastro Hep Advances
Kimura Y, et al. Early Sonographic Improvement Predicts Clinical Remission and Mucosal Healing With Molecular-Targeted Drugs in Ulcerative Colitis. Gastro Hep Adv. 2024 April 22. doi: 10.1016/j.gastha.2024.04.007.
Hunaut T, et al. Long-Term Neoplastic Risk Associated With Colorectal Strictures in Crohn’s Disease: A Multicenter Study. Gastro Hep Adv. 2024 May 15. doi: 10.1016/j.gastha.2024.05.003.
Gastroenterology
April 2024
Shah I, et al. Disparities in Colorectal Cancer Screening Among Asian American Populations and Strategies to Address These Disparities. Gastroenterology. 2024 Apr;166(4):549-552. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2024.02.009. PMID: 38521575.
Shiha MG, et al. Accuracy of the No-Biopsy Approach for the Diagnosis of Celiac Disease in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Gastroenterology. 2024 Apr;166(4):620-630. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.12.023. Epub 2024 Jan 2. PMID: 38176661.
Goltstein LCMJ, et al. Standard of Care Versus Octreotide in Angiodysplasia-Related Bleeding (the OCEAN Study): A Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial. Gastroenterology. 2024 Apr;166(4):690-703. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.12.020. Epub 2023 Dec 28. PMID: 38158089.
May 2024
Robertson DJ, et al. Colonoscopy vs the Fecal Immunochemical Test: Which is Best? Gastroenterology. 2024 May;166(5):758-771. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.12.027. Epub 2024 Feb 9. PMID: 38342196.
Mårild K, et al. Histologic Remission in Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Female Fertility: A Nationwide Study. Gastroenterology. 2024 May;166(5):802-814.e18. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2024.01.018. Epub 2024 Feb 6. PMID: 38331202.
June 2024
Trivedi PJ, et al. Immunopathogenesis of Primary Biliary Cholangitis, Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis and Autoimmune Hepatitis: Themes and Concepts. Gastroenterology. 2024 Jun;166(6):995-1019. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2024.01.049. Epub 2024 Feb 10. PMID: 38342195.
Rubenstein JH, et al. AGA Clinical Practice Guideline on Endoscopic Eradication Therapy of Barrett’s Esophagus and Related Neoplasia. Gastroenterology. 2024 Jun;166(6):1020-1055. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2024.03.019. PMID: 38763697.
Ridtitid W, et al. Endoscopic Gallbladder Stenting to Prevent Recurrent Cholecystitis in Deferred Cholecystectomy: A Randomized Trial. Gastroenterology. 2024 Jun;166(6):1145-1155. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2024.02.007. Epub 2024 Feb 14. PMID: 38360274.
Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology
April 2024
Berwald G, et al. The Diagnostic Performance of Fecal Immunochemical Tests for Detecting Advanced Neoplasia at Surveillance Colonoscopy. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Apr;22(4):878-885.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2023.09.016. Epub 2023 Sep 22. PMID: 37743036.
Hashash JG, et al. AGA Rapid Clinical Practice Update on the Management of Patients Taking GLP-1 Receptor Agonists Prior to Endoscopy: Communication. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Apr;22(4):705-707. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2023.11.002. Epub 2023 Nov 7. PMID: 37944573.
Sharma R, et al. Statins Are Associated With a Decreased Risk of Severe Liver Disease in Individuals With Noncirrhotic Chronic Liver Disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Apr;22(4):749-759.e19. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2023.04.017. Epub 2023 Apr 28. PMID: 37121528.
May 2024
Overbeek KA, et al; PrescrAIP Study Group. Type 1 Autoimmune Pancreatitis in Europe: Clinical Profile and Response to Treatment. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 May;22(5):994-1004.e10. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2023.12.010. Epub 2024 Jan 5. Erratum in: Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Jun 1:S1542-3565(24)00446-4. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2024.05.005. PMID: 38184096.
Jairath V, et al. ENTERPRET: A Randomized Controlled Trial of Vedolizumab Dose Optimization in Patients With Ulcerative Colitis Who Have Early Nonresponse. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 May;22(5):1077-1086.e13. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2023.10.029. Epub 2023 Nov 10. PMID: 37951560.
Gunby SA, et al. Smoking and Alcohol Consumption and Risk of Incident Diverticulitis in Women. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 May;22(5):1108-1116. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2023.11.036. Epub 2023 Dec 19. PMID: 38122959; PMCID: PMC11045313.
June 2024
Krause AJ, et al. Validated Clinical Score to Predict Gastroesophageal Reflux in Patients With Chronic Laryngeal Symptoms: COuGH RefluX. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Jun;22(6):1200-1209.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2024.01.021. Epub 2024 Feb 2. PMID: 38309491; PMCID: PMC11128352.
Peng X, et al. Efficacy and Safety of Vonoprazan-Amoxicillin Dual Regimen With Varying Dose and Duration for Helicobacter pylori Eradication: A Multicenter, Prospective, Randomized Study. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Jun;22(6):1210-1216. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2024.01.022. Epub 2024 Feb 1. PMID: 38309492.
Kedia S, et al. Coconut Water Induces Clinical Remission in Mild to Moderate Ulcerative Colitis: Double-blind Placebo-controlled Trial. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Jun;22(6):1295-1306.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2024.01.013. Epub 2024 Jan 24. PMID: 38278200.
Techniques and Innovations in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy
Ogura T, et al. Step-Up Strategy for Endoscopic Hemostasis Using PuraStat After Endoscopic Sphincterotomy Bleeding (STOP Trial). Tech Innov Gastrointest Endosc. 2024 March 16. doi: 10.1016/j.tige.2024.03.005.
Nakai Y, et al. Cyst Detection Rate: A Quality Indicator in the Era of Pancreatic Screening Endoscopic Ultrasonography. Tech Innov Gastrointest Endosc. 2024 May. doi: 10.1016/j.tige.2024.04.001.
Gastro Hep Advances
Kimura Y, et al. Early Sonographic Improvement Predicts Clinical Remission and Mucosal Healing With Molecular-Targeted Drugs in Ulcerative Colitis. Gastro Hep Adv. 2024 April 22. doi: 10.1016/j.gastha.2024.04.007.
Hunaut T, et al. Long-Term Neoplastic Risk Associated With Colorectal Strictures in Crohn’s Disease: A Multicenter Study. Gastro Hep Adv. 2024 May 15. doi: 10.1016/j.gastha.2024.05.003.
Gastroenterology
April 2024
Shah I, et al. Disparities in Colorectal Cancer Screening Among Asian American Populations and Strategies to Address These Disparities. Gastroenterology. 2024 Apr;166(4):549-552. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2024.02.009. PMID: 38521575.
Shiha MG, et al. Accuracy of the No-Biopsy Approach for the Diagnosis of Celiac Disease in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Gastroenterology. 2024 Apr;166(4):620-630. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.12.023. Epub 2024 Jan 2. PMID: 38176661.
Goltstein LCMJ, et al. Standard of Care Versus Octreotide in Angiodysplasia-Related Bleeding (the OCEAN Study): A Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial. Gastroenterology. 2024 Apr;166(4):690-703. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.12.020. Epub 2023 Dec 28. PMID: 38158089.
May 2024
Robertson DJ, et al. Colonoscopy vs the Fecal Immunochemical Test: Which is Best? Gastroenterology. 2024 May;166(5):758-771. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.12.027. Epub 2024 Feb 9. PMID: 38342196.
Mårild K, et al. Histologic Remission in Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Female Fertility: A Nationwide Study. Gastroenterology. 2024 May;166(5):802-814.e18. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2024.01.018. Epub 2024 Feb 6. PMID: 38331202.
June 2024
Trivedi PJ, et al. Immunopathogenesis of Primary Biliary Cholangitis, Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis and Autoimmune Hepatitis: Themes and Concepts. Gastroenterology. 2024 Jun;166(6):995-1019. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2024.01.049. Epub 2024 Feb 10. PMID: 38342195.
Rubenstein JH, et al. AGA Clinical Practice Guideline on Endoscopic Eradication Therapy of Barrett’s Esophagus and Related Neoplasia. Gastroenterology. 2024 Jun;166(6):1020-1055. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2024.03.019. PMID: 38763697.
Ridtitid W, et al. Endoscopic Gallbladder Stenting to Prevent Recurrent Cholecystitis in Deferred Cholecystectomy: A Randomized Trial. Gastroenterology. 2024 Jun;166(6):1145-1155. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2024.02.007. Epub 2024 Feb 14. PMID: 38360274.
Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology
April 2024
Berwald G, et al. The Diagnostic Performance of Fecal Immunochemical Tests for Detecting Advanced Neoplasia at Surveillance Colonoscopy. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Apr;22(4):878-885.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2023.09.016. Epub 2023 Sep 22. PMID: 37743036.
Hashash JG, et al. AGA Rapid Clinical Practice Update on the Management of Patients Taking GLP-1 Receptor Agonists Prior to Endoscopy: Communication. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Apr;22(4):705-707. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2023.11.002. Epub 2023 Nov 7. PMID: 37944573.
Sharma R, et al. Statins Are Associated With a Decreased Risk of Severe Liver Disease in Individuals With Noncirrhotic Chronic Liver Disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Apr;22(4):749-759.e19. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2023.04.017. Epub 2023 Apr 28. PMID: 37121528.
May 2024
Overbeek KA, et al; PrescrAIP Study Group. Type 1 Autoimmune Pancreatitis in Europe: Clinical Profile and Response to Treatment. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 May;22(5):994-1004.e10. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2023.12.010. Epub 2024 Jan 5. Erratum in: Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Jun 1:S1542-3565(24)00446-4. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2024.05.005. PMID: 38184096.
Jairath V, et al. ENTERPRET: A Randomized Controlled Trial of Vedolizumab Dose Optimization in Patients With Ulcerative Colitis Who Have Early Nonresponse. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 May;22(5):1077-1086.e13. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2023.10.029. Epub 2023 Nov 10. PMID: 37951560.
Gunby SA, et al. Smoking and Alcohol Consumption and Risk of Incident Diverticulitis in Women. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 May;22(5):1108-1116. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2023.11.036. Epub 2023 Dec 19. PMID: 38122959; PMCID: PMC11045313.
June 2024
Krause AJ, et al. Validated Clinical Score to Predict Gastroesophageal Reflux in Patients With Chronic Laryngeal Symptoms: COuGH RefluX. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Jun;22(6):1200-1209.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2024.01.021. Epub 2024 Feb 2. PMID: 38309491; PMCID: PMC11128352.
Peng X, et al. Efficacy and Safety of Vonoprazan-Amoxicillin Dual Regimen With Varying Dose and Duration for Helicobacter pylori Eradication: A Multicenter, Prospective, Randomized Study. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Jun;22(6):1210-1216. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2024.01.022. Epub 2024 Feb 1. PMID: 38309492.
Kedia S, et al. Coconut Water Induces Clinical Remission in Mild to Moderate Ulcerative Colitis: Double-blind Placebo-controlled Trial. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Jun;22(6):1295-1306.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2024.01.013. Epub 2024 Jan 24. PMID: 38278200.
Techniques and Innovations in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy
Ogura T, et al. Step-Up Strategy for Endoscopic Hemostasis Using PuraStat After Endoscopic Sphincterotomy Bleeding (STOP Trial). Tech Innov Gastrointest Endosc. 2024 March 16. doi: 10.1016/j.tige.2024.03.005.
Nakai Y, et al. Cyst Detection Rate: A Quality Indicator in the Era of Pancreatic Screening Endoscopic Ultrasonography. Tech Innov Gastrointest Endosc. 2024 May. doi: 10.1016/j.tige.2024.04.001.
Gastro Hep Advances
Kimura Y, et al. Early Sonographic Improvement Predicts Clinical Remission and Mucosal Healing With Molecular-Targeted Drugs in Ulcerative Colitis. Gastro Hep Adv. 2024 April 22. doi: 10.1016/j.gastha.2024.04.007.
Hunaut T, et al. Long-Term Neoplastic Risk Associated With Colorectal Strictures in Crohn’s Disease: A Multicenter Study. Gastro Hep Adv. 2024 May 15. doi: 10.1016/j.gastha.2024.05.003.
A Paradigm Shift in Evaluating and Investigating the Etiology of Bloating
Introduction
Abdominal bloating is a common condition affecting up to 3.5% of people globally (4.6% in women and 2.4% in men),1 with 13.9% of the US population reporting bloating in the past 7 days.2 The prevalence of bloating and distention exceeds 50% when linked to disorders of gut-brain interaction (DGBIs) such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), constipation, gastroparesis, and functional dyspepsia (FD).3,4 According to the Rome IV criteria, functional bloating and distention (FABD) patients are characterized by recurrent symptoms of abdominal fullness or pressure (bloating), or a visible increase in abdominal girth (distention) occurring at least 1 day per week for 3 consecutive months with an onset of 6 months and without predominant pain or altered bowel habits.5
Prolonged abdominal bloating and distention (ABD) can significantly impact quality of life and work productivity and can lead to increased medical consultations.2 Multiple pathophysiological mechanisms are involved in ABD that complicate the clinical management.4 There is an unmet need to understand the underlying mechanisms that lead to the development of ABD such as, food intolerance, abnormal viscerosomatic reflex, visceral hypersensitivity, and gut microbial dysbiosis. Recent advancements and acceptance of a multidisciplinary management of ABD have shifted the paradigm from merely treating symptoms to subtyping the condition and identifying overlaps with other DGBIs in order to individualize treatment that addresses the underlying pathophysiological mechanism. The recent American Gastroenterological Association (AGA) clinical update provided insights into the best practice advice for evaluating and managing ABD based on a review of current literature and on expert opinion of coauthors.6 This article aims to deliberate a practical approach to diagnostic strategies and treatment options based on etiology to refine clinical care of patients with ABD.
Pathophysiological Mechanisms
ABD can result from various pathophysiological mechanisms. This section highlights the major causes (illustrated in Figure 1).
Food intolerances
Understanding food intolerances is crucial for diagnosing and managing patients with ABD. Disaccharidase deficiency is common (e.g., lactase deficiency is found in 35%-40% of adults).7 It can be undiagnosed in patients presenting with IBS symptoms, given the overlap in presentation with a prevalence of 9% of pan-disaccharidase deficiency. Sucrase-deficient patients must often adjust sugar and carbohydrate/starch intake to relieve symptoms.7 Deficiencies in lactase and sucrase activity, along with the consumption of some artificial sweeteners (e.g., sugar alcohols and sorbitol) and fructans can lead to bloating and distention. These substances increase osmotic load, fluid retention, microbial fermentation, and visceral hypersensitivity, leading to gas production and abdominal distention. One prospective study of symptomatic patients with various DGBIs (n = 1372) reported a prevalence of lactose intolerance and malabsorption at 51% and 32%, respectively.8 Furthermore, fructose intolerance and malabsorption prevalence were 60% and 45%, respectively.8 Notably, lactase deficiency does not always cause ABD, as not all individuals with lactase deficiency experience these symptoms after consuming lactose. Patients with celiac disease (CD), non-celiac gluten sensitivity (NCGS), and gluten intolerance can also experience bloating and distention, with or without changes in bowel habits.9 In some patients with self-reported NCGS, symptoms may be due to fructans in gluten-rich foods rather than gluten itself, thus recommending the elimination of fructans may help improve symptoms.9
Visceral hypersensitivity
Visceral hypersensitivity is explained by an increased perception of gut mechano-chemical stimulation, which typically manifests in an aggravated feeling of pain, nausea, distension, and ABD.10 In the gut, food particles and gut bacteria and their derived molecules interact with neuroimmune and enteroendocrine cells causing visceral sensitivity by the proximity of gut’s neurons to immune cells activated by them and leading to inflammatory reactions (Figure 1).
Pelvic floor dysfunction
Patients with anorectal motor dysfunction often experience difficulty in effectively evacuating both gas and stool, leading to ABD.12 Impaired ability to expel gas and stool results in prolonged balloon expulsion times, which correlates with symptoms of distention in patients with constipation.
Abdominophrenic dyssynergia
Abdominophrenic dyssynergia is characterized as a paradoxical viscerosomatic reflex response to minimal gaseous distention in individuals with FABD.13 In this condition, the diaphragm contracts (descends), and the anterior abdominal wall muscles relax in response to the presence of gas. This response is opposite to the normal physiological response to increased intraluminal gas, where the diaphragm relaxes and the anterior abdominal muscles contract to increase the craniocaudal capacity of the abdominal cavity without causing abdominal protrusion.13 Patients with FABD exhibit significant abdominal wall protrusion and diaphragmatic descent even with relatively small increases in intraluminal gas.11 Understanding the role of abdominophrenic dyssynergia in abdominal bloating and distention is essential for effective diagnosis and management of the patients.
Gut dysmotility
Gut dysmotility is a crucial factor that can contribute to FABD. Gut dysmotility affects the movement of contents through the GI tract, accumulating gas and stool, directly contributing to bloating and distention. A prospective study involving over 2000 patients with functional constipation and constipation predominant-IBS (IBS-C) found that more than 90% of these patients reported symptoms of bloating.14 Furthermore, in IBS-C patients, those with prolonged colonic transit exhibited greater abdominal distention compared to those with normal gut transit times. In patients with gastroparesis, delayed gastric emptying resulting in prolonged retention of stomach contents is the main factor in the generation of bloating symptoms.4
Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO)
SIBO is overrepresented in various conditions, including IBS, FD, diabetes, gastrointestinal (GI) surgery patients and obesity, and can play an important role in generating ABD. Excess bacteria in the small intestine ferment carbohydrates, producing gas that stretches and distends the small intestine, leading to these symptoms. Additionally, altered sensation and abnormal viscerosomatic reflexes may contribute to SIBO-related bloating.4 One recent study noted decreased duodenal phylogenetic diversity in individuals who developed postprandial bloating.15 Increased methane levels caused by intestinal methanogen overgrowth, primarily the archaea Methanobrevibacter smithii, is possibly responsible for ABD in patients with IBS-C.16 Testing for SIBO in patients with ABD is generally only recommended if there are clear risk factors or severe symptoms warranting a test-and-treat approach.
Practical Diagnosis
Diagnosing ABD typically does not require extensive laboratory testing, imaging, or endoscopy unless there are alarm features or significant changes in symptoms. Here is the AGA clinical update on best practice advice6 for when to conduct further testing:
Diagnostic tests should be considered if patients exhibit:
- Recent onset or worsening of dyspepsia or abdominal pain
- Vomiting
- GI bleeding
- Unintentional weight loss exceeding 10% of body weight
- Chronic diarrhea
- Family history of GI malignancy, celiac disease, or inflammatory bowel disease
Physical examination
If visible abdominal distention is present, a thorough abdominal examination can help identify potential issues:
- Tympany to percussion suggests bowel dilation.
- Abnormal bowel sounds may indicate obstruction or ileus.
- A succussion splash could indicate the presence of ascites and obstruction.
- Any abnormalities discovered during the physical exam should prompt further investigation with imaging, such as a computed tomography (CT) scan or ultrasound, to evaluate for ascites, masses, or increased bowel gas due to ileus, obstruction, or pseudo-obstruction.
Radiologic imaging, laboratory testing and endoscopy
- An abdominal x-ray may reveal an increased stool burden, suggesting the need for further evaluation of slow transit constipation or a pelvic floor disorder, particularly in patients with functional constipation, IBS-mixed, or IBS-C.
- Hyperglycemia, weight gain, and bloating can be a presenting sign of ovarian cancer therefore all women should continue pelvic exams as dictated by the gynecologic societies. The need for an annual pelvic exam should be discussed with health care professionals especially in those with family history of ovarian cancer.
- An upper endoscopy may be warranted for patients over 40 years old with dyspeptic symptoms and abdominal bloating or distention, especially in regions with a high prevalence of Helicobacter pylori.
- Chronic pancreatitis, indicated by bloating and pain, may necessitate fecal elastase testing to assess pancreatic function.
The expert review in the AGA clinical update provides step-by-step advice regarding the best practices6 for diagnosis and identifying who to test for ABD.
Treatment Options
The following sections highlight recent best practice advice on therapeutic approaches for treating ABD.
Dietary interventions
Specific foods may trigger bloating and abdominal distention, especially in patients with overlapping DGBIs. However, only a few studies have evaluated dietary restriction specifically for patients with primary ABD. Restricting non-absorbable sugars led to symptomatic improvement in 81% of patients with FABD who had documented sugar malabsorption.17 Two studies have shown that IBS patients treated with a low-fermentable, oligo-, di-, and monosaccharides (FODMAP) diet noted improvement in ABD and that restricting fructans initially may be the most optimal.18 A recent study showed that the Mediterranean diet improved IBS symptoms, including abdominal pain and bloating.19 It should be noted restrictive diets are efficacious but come with short- and long-term challenges. If empiric treatment and/or therapeutic testing do not resolve symptoms, a referral to a dietitian can be useful. Dietitians can provide tailored dietary advice, ensuring patients avoid trigger foods while maintaining a balanced and nutritious diet.
Prokinetics and laxatives
Prokinetic agents are used to treat symptoms of FD, gastroparesis, chronic idiopathic constipation (CIC), and IBS. A meta-analysis of 13 trials found all constipation medications superior to placebo for treating abdominal bloating in patients with IBS-C.20
Probiotics
Treatment with probiotics is recommended for bloating or distention. One double-blind placebo-controlled trial with two separate probiotics, Bifidobacterium lactis and Lactobacillus acidophilus, showed improvements in global GI symptoms of patients with DGBI at 8 weeks versus placebo, with improvements in bloating symptoms.21
Antibiotics
The most commonly studied antibiotic for treating bloating is rifaximin.22 Global symptomatic improvement in IBS patients treated with antibiotics has correlated with the normalization of hydrogen levels in lactulose hydrogen breath tests.22 Patients with non-constipation IBS randomized to rifaximin 550 mg three times daily for 14 days had a greater proportion of relief of IBS-related bloating compared to placebo for at least 2 of the first 4 weeks after treatment.22 Future research warrants use of narrow-spectrum antibiotics study for FABD as the use of broad-spectrum antibiotics may deplete commensals forever, resulting in metabolic disorders.
Biofeedback therapy
Anorectal biofeedback therapy may help with ABD, particularly in patients with IBS-C and chronic constipation. One study noted that post-biofeedback therapy, myoelectric activity of the intercostals and diaphragm decreased, and internal oblique myoelectric activity increased.23 This study also showed ascent of the diaphragm and decreased girth, improving distention.
Central neuromodulators
As bloating results from multiple disturbed mechanisms, including altered gut-brain interaction, these symptoms can be amplified by psychological states such as anxiety, depression, or somatization. Central neuromodulators reduce the perception of visceral signals, re-regulate brain-gut control mechanisms, and improve psychological comorbidities.6 A large study of FD patients demonstrated that both amitriptyline (50 mg daily) and escitalopram (10 mg daily) significantly improved postprandial bloating compared to placebo.24 Antidepressants that activate noradrenergic and serotonergic pathways, including tricyclic antidepressants (e.g., amitriptyline) and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (e.g., duloxetine and venlafaxine), show the greatest benefit in reducing visceral sensations.6
Brain-gut behavioral therapies
A recent multidisciplinary consensus report supports a myriad of potential brain-gut behavioral therapies (BGBTs) for treating DGBI.25 These therapies, including hypnotherapy, cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), and other modalities, may be combined with central neuromodulators and other GI treatments in a safe, noninvasive, and complementary fashion. BGBTs do not need to be symptom-specific, as they improve overall quality of life, anxiety, stress, and the burden associated with DGBIs. To date, none of the BGBTs have focused exclusively on FABD; however, prescription-based psychological therapies are now FDA-approved for use on smart apps, improving global symptoms that include bloating in IBS and FD.
Recent AGA clinical update best practices should be considered for the clinical care of patients with ABD.6
Conclusion and Future Perspectives
ABD are highly prevalent and significantly impact patients with various GI and metabolic disorders. Although our understanding of these symptoms is still evolving, evidence increasingly points to the dysregulation of the gut-brain axis and supports the application of the biopsychosocial model in treatment. This model addresses diet, motility, visceral sensitivity, pelvic floor disorders and psychosocial factors, providing a comprehensive approach to patient care.
Physician-scientists around the globe face numerous challenges when evaluating patients with these symptoms. However, the recent AGA clinical update on the best practice guidelines offers step-by-step diagnostic tests and treatment options to assist physicians in making informed decisions. . More comprehensive, large-scale, and longitudinal studies using metabolomics, capsule technologies for discovery of dysbiosis, mass spectrometry, and imaging data are needed to identify the exact contributors to disease pathogenesis, particularly those that can be targeted with pharmacologic agents. Collaborative work between gastroenterologists, dietitians, gut-brain behavioral therapists, endocrinologists, is crucial for clinical care of patients with ABD.
Careful attention to the patient’s primary symptoms and physical examination, combined with advancements in targeted diagnostics like the analysis of microbial markers, metabolites, and molecular signals, can significantly enhance patient clinical outcomes. Additionally, education and effective communication using a patient-centered care model are essential for guiding practical evaluation and individualized treatment.
Dr. Singh is assistant professor (research) at the University of Nevada, Reno, School of Medicine. Dr. Moshiree is director of motility at Atrium Health, and clinical professor of medicine, Wake Forest Medical University, Charlotte, North Carolina.
References
1. Ballou S et al. Prevalence and associated factors of bloating: Results from the Rome Foundation Global Epidemiology Study. Gastroenterology. 2023 June. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.05.049.
2. Oh JE et al. Abdominal bloating in the United States: Results of a survey of 88,795 Americans examining prevalence and healthcare seeking. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023 Aug. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2022.10.031.
3. Drossman DA et al. Neuromodulators for functional gastrointestinal disorders (disorders of gut-brain interaction): A Rome Foundation Working Team Report. Gastroenterology. 2018 Mar. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.11.279.
4. Lacy BE et al. Management of chronic abdominal distension and bloating. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021 Feb. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2020.03.056.
5. Mearin F et al. Bowel disorders. Gastroenterology. 2016 Feb. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2016.02.031.
6. Moshiree B et al. AGA Clinical Practice Update on evaluation and management of belching, abdominal bloating, and distention: expert review. Gastroenterology. 2023 Sep. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.04.039.
7. Viswanathan L and Rao SS. Intestinal disaccharidase deficiency in adults: evaluation and treatment. Curr Gastroenterol Rep 2023 May. doi: 10.1007/s11894-023-00870-z.
8. Wilder-Smith CH et al. Fructose and lactose intolerance and malabsorption testing: the relationship with symptoms in functional gastrointestinal disorders. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2013 Jun. doi: 10.1111/apt.12306.
9. Skodje GI et al. Fructan, rather than gluten, induces symptoms in patients with self-reported non-celiac gluten sensitivity. Gastroenterology. 2018 Feb. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.10.040.
10. Singh R et al. Current treatment options and therapeutic insights for gastrointestinal dysmotility and functional gastrointestinal disorders. Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jan. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.808195.
11. Accarino A et al. Abdominal distention results from caudo-ventral redistribution of contents. Gastroenterology 2009 May. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2009.01.067.
12. Shim L et al. Prolonged balloon expulsion is predictive of abdominal distension in bloating. Am J Gastroenterol. 2010 Apr. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2010.54.
13. Villoria A et al. Abdomino-phrenic dyssynergia in patients with abdominal bloating and distension. Am J Gastroenterol. 2011 May. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2010.408.
14. Neri L and Iovino P. Laxative Inadequate Relief Survey Group. Bloating is associated with worse quality of life, treatment satisfaction, and treatment responsiveness among patients with constipation-predominant irritable bowel syndrome and functional constipation. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2016 Apr. doi: 10.1111/nmo.12758.
15. Saffouri GB et al. Small intestinal microbial dysbiosis underlies symptoms associated with functional gastrointestinal disorders. Nat Commun. 2019 May. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-09964-7.
16. Villanueva-Millan MJ et al. Methanogens and hydrogen sulfide producing bacteria guide distinct gut microbe profiles and irritable bowel syndrome subtypes. Am J Gastroenterol. 2022 Dec. doi: 10.14309/ajg.0000000000001997.
17. Fernández-Bañares F et al. Sugar malabsorption in functional abdominal bloating: a pilot study on the long-term effect of dietary treatment. Clin Nutr. 2006 Oct. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2005.11.010.
18. Böhn L et al. Diet low in FODMAPs reduces symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome as well as traditional dietary advice: a randomized controlled trial. Gastroenterology. 2015 Nov. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2015.07.054.
19. Staudacher HM et al. Clinical trial: A Mediterranean diet is feasible and improves gastrointestinal and psychological symptoms in irritable bowel syndrome. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2024 Feb. doi: 10.1111/apt.17791.
20. Nelson AD et al. Systematic review and network meta-analysis: efficacy of licensed drugs for abdominal bloating in irritable bowel syndrome with constipation. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2021 Jul. doi: 10.1111/apt.16437.
21. Ringel-Kulka T et al. Probiotic bacteria Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM and Bifidobacterium lactis Bi-07 versus placebo for the symptoms of bloating in patients with functional bowel disorders: a double-blind study. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2011 Jul. doi: 10.1097/MCG.0b013e31820ca4d6.
22. Pimentel M et al. Rifaximin therapy for patients with irritable bowel syndrome without constipation. N Engl J Med. 2011 Jan. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1004409.
23. Iovino P et al. Pelvic floor biofeedback is an effective treatment for severe bloating in disorders of gut-brain interaction with outlet dysfunction. Neurogastroenterol Motil 2022 May. doi: 10.1111/nmo.14264.
24. Talley NJ et al. Effect of amitriptyline and escitalopram on functional dyspepsia: A multicenter, randomized controlled study. Gastroenterology. 2015 Aug. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2015.04.020.
25. Keefer L et al. A Rome Working Team Report on brain-gut behavior therapies for disorders of gut-brain interaction. Gastroenterology. 2022 Jan. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.09.015.
Introduction
Abdominal bloating is a common condition affecting up to 3.5% of people globally (4.6% in women and 2.4% in men),1 with 13.9% of the US population reporting bloating in the past 7 days.2 The prevalence of bloating and distention exceeds 50% when linked to disorders of gut-brain interaction (DGBIs) such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), constipation, gastroparesis, and functional dyspepsia (FD).3,4 According to the Rome IV criteria, functional bloating and distention (FABD) patients are characterized by recurrent symptoms of abdominal fullness or pressure (bloating), or a visible increase in abdominal girth (distention) occurring at least 1 day per week for 3 consecutive months with an onset of 6 months and without predominant pain or altered bowel habits.5
Prolonged abdominal bloating and distention (ABD) can significantly impact quality of life and work productivity and can lead to increased medical consultations.2 Multiple pathophysiological mechanisms are involved in ABD that complicate the clinical management.4 There is an unmet need to understand the underlying mechanisms that lead to the development of ABD such as, food intolerance, abnormal viscerosomatic reflex, visceral hypersensitivity, and gut microbial dysbiosis. Recent advancements and acceptance of a multidisciplinary management of ABD have shifted the paradigm from merely treating symptoms to subtyping the condition and identifying overlaps with other DGBIs in order to individualize treatment that addresses the underlying pathophysiological mechanism. The recent American Gastroenterological Association (AGA) clinical update provided insights into the best practice advice for evaluating and managing ABD based on a review of current literature and on expert opinion of coauthors.6 This article aims to deliberate a practical approach to diagnostic strategies and treatment options based on etiology to refine clinical care of patients with ABD.
Pathophysiological Mechanisms
ABD can result from various pathophysiological mechanisms. This section highlights the major causes (illustrated in Figure 1).
Food intolerances
Understanding food intolerances is crucial for diagnosing and managing patients with ABD. Disaccharidase deficiency is common (e.g., lactase deficiency is found in 35%-40% of adults).7 It can be undiagnosed in patients presenting with IBS symptoms, given the overlap in presentation with a prevalence of 9% of pan-disaccharidase deficiency. Sucrase-deficient patients must often adjust sugar and carbohydrate/starch intake to relieve symptoms.7 Deficiencies in lactase and sucrase activity, along with the consumption of some artificial sweeteners (e.g., sugar alcohols and sorbitol) and fructans can lead to bloating and distention. These substances increase osmotic load, fluid retention, microbial fermentation, and visceral hypersensitivity, leading to gas production and abdominal distention. One prospective study of symptomatic patients with various DGBIs (n = 1372) reported a prevalence of lactose intolerance and malabsorption at 51% and 32%, respectively.8 Furthermore, fructose intolerance and malabsorption prevalence were 60% and 45%, respectively.8 Notably, lactase deficiency does not always cause ABD, as not all individuals with lactase deficiency experience these symptoms after consuming lactose. Patients with celiac disease (CD), non-celiac gluten sensitivity (NCGS), and gluten intolerance can also experience bloating and distention, with or without changes in bowel habits.9 In some patients with self-reported NCGS, symptoms may be due to fructans in gluten-rich foods rather than gluten itself, thus recommending the elimination of fructans may help improve symptoms.9
Visceral hypersensitivity
Visceral hypersensitivity is explained by an increased perception of gut mechano-chemical stimulation, which typically manifests in an aggravated feeling of pain, nausea, distension, and ABD.10 In the gut, food particles and gut bacteria and their derived molecules interact with neuroimmune and enteroendocrine cells causing visceral sensitivity by the proximity of gut’s neurons to immune cells activated by them and leading to inflammatory reactions (Figure 1).

Pelvic floor dysfunction
Patients with anorectal motor dysfunction often experience difficulty in effectively evacuating both gas and stool, leading to ABD.12 Impaired ability to expel gas and stool results in prolonged balloon expulsion times, which correlates with symptoms of distention in patients with constipation.
Abdominophrenic dyssynergia
Abdominophrenic dyssynergia is characterized as a paradoxical viscerosomatic reflex response to minimal gaseous distention in individuals with FABD.13 In this condition, the diaphragm contracts (descends), and the anterior abdominal wall muscles relax in response to the presence of gas. This response is opposite to the normal physiological response to increased intraluminal gas, where the diaphragm relaxes and the anterior abdominal muscles contract to increase the craniocaudal capacity of the abdominal cavity without causing abdominal protrusion.13 Patients with FABD exhibit significant abdominal wall protrusion and diaphragmatic descent even with relatively small increases in intraluminal gas.11 Understanding the role of abdominophrenic dyssynergia in abdominal bloating and distention is essential for effective diagnosis and management of the patients.
Gut dysmotility
Gut dysmotility is a crucial factor that can contribute to FABD. Gut dysmotility affects the movement of contents through the GI tract, accumulating gas and stool, directly contributing to bloating and distention. A prospective study involving over 2000 patients with functional constipation and constipation predominant-IBS (IBS-C) found that more than 90% of these patients reported symptoms of bloating.14 Furthermore, in IBS-C patients, those with prolonged colonic transit exhibited greater abdominal distention compared to those with normal gut transit times. In patients with gastroparesis, delayed gastric emptying resulting in prolonged retention of stomach contents is the main factor in the generation of bloating symptoms.4
Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO)
SIBO is overrepresented in various conditions, including IBS, FD, diabetes, gastrointestinal (GI) surgery patients and obesity, and can play an important role in generating ABD. Excess bacteria in the small intestine ferment carbohydrates, producing gas that stretches and distends the small intestine, leading to these symptoms. Additionally, altered sensation and abnormal viscerosomatic reflexes may contribute to SIBO-related bloating.4 One recent study noted decreased duodenal phylogenetic diversity in individuals who developed postprandial bloating.15 Increased methane levels caused by intestinal methanogen overgrowth, primarily the archaea Methanobrevibacter smithii, is possibly responsible for ABD in patients with IBS-C.16 Testing for SIBO in patients with ABD is generally only recommended if there are clear risk factors or severe symptoms warranting a test-and-treat approach.
Practical Diagnosis
Diagnosing ABD typically does not require extensive laboratory testing, imaging, or endoscopy unless there are alarm features or significant changes in symptoms. Here is the AGA clinical update on best practice advice6 for when to conduct further testing:
Diagnostic tests should be considered if patients exhibit:
- Recent onset or worsening of dyspepsia or abdominal pain
- Vomiting
- GI bleeding
- Unintentional weight loss exceeding 10% of body weight
- Chronic diarrhea
- Family history of GI malignancy, celiac disease, or inflammatory bowel disease
Physical examination
If visible abdominal distention is present, a thorough abdominal examination can help identify potential issues:
- Tympany to percussion suggests bowel dilation.
- Abnormal bowel sounds may indicate obstruction or ileus.
- A succussion splash could indicate the presence of ascites and obstruction.
- Any abnormalities discovered during the physical exam should prompt further investigation with imaging, such as a computed tomography (CT) scan or ultrasound, to evaluate for ascites, masses, or increased bowel gas due to ileus, obstruction, or pseudo-obstruction.
Radiologic imaging, laboratory testing and endoscopy
- An abdominal x-ray may reveal an increased stool burden, suggesting the need for further evaluation of slow transit constipation or a pelvic floor disorder, particularly in patients with functional constipation, IBS-mixed, or IBS-C.
- Hyperglycemia, weight gain, and bloating can be a presenting sign of ovarian cancer therefore all women should continue pelvic exams as dictated by the gynecologic societies. The need for an annual pelvic exam should be discussed with health care professionals especially in those with family history of ovarian cancer.
- An upper endoscopy may be warranted for patients over 40 years old with dyspeptic symptoms and abdominal bloating or distention, especially in regions with a high prevalence of Helicobacter pylori.
- Chronic pancreatitis, indicated by bloating and pain, may necessitate fecal elastase testing to assess pancreatic function.
The expert review in the AGA clinical update provides step-by-step advice regarding the best practices6 for diagnosis and identifying who to test for ABD.
Treatment Options
The following sections highlight recent best practice advice on therapeutic approaches for treating ABD.
Dietary interventions
Specific foods may trigger bloating and abdominal distention, especially in patients with overlapping DGBIs. However, only a few studies have evaluated dietary restriction specifically for patients with primary ABD. Restricting non-absorbable sugars led to symptomatic improvement in 81% of patients with FABD who had documented sugar malabsorption.17 Two studies have shown that IBS patients treated with a low-fermentable, oligo-, di-, and monosaccharides (FODMAP) diet noted improvement in ABD and that restricting fructans initially may be the most optimal.18 A recent study showed that the Mediterranean diet improved IBS symptoms, including abdominal pain and bloating.19 It should be noted restrictive diets are efficacious but come with short- and long-term challenges. If empiric treatment and/or therapeutic testing do not resolve symptoms, a referral to a dietitian can be useful. Dietitians can provide tailored dietary advice, ensuring patients avoid trigger foods while maintaining a balanced and nutritious diet.
Prokinetics and laxatives
Prokinetic agents are used to treat symptoms of FD, gastroparesis, chronic idiopathic constipation (CIC), and IBS. A meta-analysis of 13 trials found all constipation medications superior to placebo for treating abdominal bloating in patients with IBS-C.20
Probiotics
Treatment with probiotics is recommended for bloating or distention. One double-blind placebo-controlled trial with two separate probiotics, Bifidobacterium lactis and Lactobacillus acidophilus, showed improvements in global GI symptoms of patients with DGBI at 8 weeks versus placebo, with improvements in bloating symptoms.21
Antibiotics
The most commonly studied antibiotic for treating bloating is rifaximin.22 Global symptomatic improvement in IBS patients treated with antibiotics has correlated with the normalization of hydrogen levels in lactulose hydrogen breath tests.22 Patients with non-constipation IBS randomized to rifaximin 550 mg three times daily for 14 days had a greater proportion of relief of IBS-related bloating compared to placebo for at least 2 of the first 4 weeks after treatment.22 Future research warrants use of narrow-spectrum antibiotics study for FABD as the use of broad-spectrum antibiotics may deplete commensals forever, resulting in metabolic disorders.
Biofeedback therapy
Anorectal biofeedback therapy may help with ABD, particularly in patients with IBS-C and chronic constipation. One study noted that post-biofeedback therapy, myoelectric activity of the intercostals and diaphragm decreased, and internal oblique myoelectric activity increased.23 This study also showed ascent of the diaphragm and decreased girth, improving distention.
Central neuromodulators
As bloating results from multiple disturbed mechanisms, including altered gut-brain interaction, these symptoms can be amplified by psychological states such as anxiety, depression, or somatization. Central neuromodulators reduce the perception of visceral signals, re-regulate brain-gut control mechanisms, and improve psychological comorbidities.6 A large study of FD patients demonstrated that both amitriptyline (50 mg daily) and escitalopram (10 mg daily) significantly improved postprandial bloating compared to placebo.24 Antidepressants that activate noradrenergic and serotonergic pathways, including tricyclic antidepressants (e.g., amitriptyline) and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (e.g., duloxetine and venlafaxine), show the greatest benefit in reducing visceral sensations.6
Brain-gut behavioral therapies
A recent multidisciplinary consensus report supports a myriad of potential brain-gut behavioral therapies (BGBTs) for treating DGBI.25 These therapies, including hypnotherapy, cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), and other modalities, may be combined with central neuromodulators and other GI treatments in a safe, noninvasive, and complementary fashion. BGBTs do not need to be symptom-specific, as they improve overall quality of life, anxiety, stress, and the burden associated with DGBIs. To date, none of the BGBTs have focused exclusively on FABD; however, prescription-based psychological therapies are now FDA-approved for use on smart apps, improving global symptoms that include bloating in IBS and FD.
Recent AGA clinical update best practices should be considered for the clinical care of patients with ABD.6
Conclusion and Future Perspectives
ABD are highly prevalent and significantly impact patients with various GI and metabolic disorders. Although our understanding of these symptoms is still evolving, evidence increasingly points to the dysregulation of the gut-brain axis and supports the application of the biopsychosocial model in treatment. This model addresses diet, motility, visceral sensitivity, pelvic floor disorders and psychosocial factors, providing a comprehensive approach to patient care.
Physician-scientists around the globe face numerous challenges when evaluating patients with these symptoms. However, the recent AGA clinical update on the best practice guidelines offers step-by-step diagnostic tests and treatment options to assist physicians in making informed decisions. . More comprehensive, large-scale, and longitudinal studies using metabolomics, capsule technologies for discovery of dysbiosis, mass spectrometry, and imaging data are needed to identify the exact contributors to disease pathogenesis, particularly those that can be targeted with pharmacologic agents. Collaborative work between gastroenterologists, dietitians, gut-brain behavioral therapists, endocrinologists, is crucial for clinical care of patients with ABD.
Careful attention to the patient’s primary symptoms and physical examination, combined with advancements in targeted diagnostics like the analysis of microbial markers, metabolites, and molecular signals, can significantly enhance patient clinical outcomes. Additionally, education and effective communication using a patient-centered care model are essential for guiding practical evaluation and individualized treatment.
Dr. Singh is assistant professor (research) at the University of Nevada, Reno, School of Medicine. Dr. Moshiree is director of motility at Atrium Health, and clinical professor of medicine, Wake Forest Medical University, Charlotte, North Carolina.
References
1. Ballou S et al. Prevalence and associated factors of bloating: Results from the Rome Foundation Global Epidemiology Study. Gastroenterology. 2023 June. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.05.049.
2. Oh JE et al. Abdominal bloating in the United States: Results of a survey of 88,795 Americans examining prevalence and healthcare seeking. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023 Aug. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2022.10.031.
3. Drossman DA et al. Neuromodulators for functional gastrointestinal disorders (disorders of gut-brain interaction): A Rome Foundation Working Team Report. Gastroenterology. 2018 Mar. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.11.279.
4. Lacy BE et al. Management of chronic abdominal distension and bloating. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021 Feb. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2020.03.056.
5. Mearin F et al. Bowel disorders. Gastroenterology. 2016 Feb. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2016.02.031.
6. Moshiree B et al. AGA Clinical Practice Update on evaluation and management of belching, abdominal bloating, and distention: expert review. Gastroenterology. 2023 Sep. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.04.039.
7. Viswanathan L and Rao SS. Intestinal disaccharidase deficiency in adults: evaluation and treatment. Curr Gastroenterol Rep 2023 May. doi: 10.1007/s11894-023-00870-z.
8. Wilder-Smith CH et al. Fructose and lactose intolerance and malabsorption testing: the relationship with symptoms in functional gastrointestinal disorders. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2013 Jun. doi: 10.1111/apt.12306.
9. Skodje GI et al. Fructan, rather than gluten, induces symptoms in patients with self-reported non-celiac gluten sensitivity. Gastroenterology. 2018 Feb. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.10.040.
10. Singh R et al. Current treatment options and therapeutic insights for gastrointestinal dysmotility and functional gastrointestinal disorders. Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jan. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.808195.
11. Accarino A et al. Abdominal distention results from caudo-ventral redistribution of contents. Gastroenterology 2009 May. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2009.01.067.
12. Shim L et al. Prolonged balloon expulsion is predictive of abdominal distension in bloating. Am J Gastroenterol. 2010 Apr. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2010.54.
13. Villoria A et al. Abdomino-phrenic dyssynergia in patients with abdominal bloating and distension. Am J Gastroenterol. 2011 May. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2010.408.
14. Neri L and Iovino P. Laxative Inadequate Relief Survey Group. Bloating is associated with worse quality of life, treatment satisfaction, and treatment responsiveness among patients with constipation-predominant irritable bowel syndrome and functional constipation. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2016 Apr. doi: 10.1111/nmo.12758.
15. Saffouri GB et al. Small intestinal microbial dysbiosis underlies symptoms associated with functional gastrointestinal disorders. Nat Commun. 2019 May. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-09964-7.
16. Villanueva-Millan MJ et al. Methanogens and hydrogen sulfide producing bacteria guide distinct gut microbe profiles and irritable bowel syndrome subtypes. Am J Gastroenterol. 2022 Dec. doi: 10.14309/ajg.0000000000001997.
17. Fernández-Bañares F et al. Sugar malabsorption in functional abdominal bloating: a pilot study on the long-term effect of dietary treatment. Clin Nutr. 2006 Oct. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2005.11.010.
18. Böhn L et al. Diet low in FODMAPs reduces symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome as well as traditional dietary advice: a randomized controlled trial. Gastroenterology. 2015 Nov. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2015.07.054.
19. Staudacher HM et al. Clinical trial: A Mediterranean diet is feasible and improves gastrointestinal and psychological symptoms in irritable bowel syndrome. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2024 Feb. doi: 10.1111/apt.17791.
20. Nelson AD et al. Systematic review and network meta-analysis: efficacy of licensed drugs for abdominal bloating in irritable bowel syndrome with constipation. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2021 Jul. doi: 10.1111/apt.16437.
21. Ringel-Kulka T et al. Probiotic bacteria Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM and Bifidobacterium lactis Bi-07 versus placebo for the symptoms of bloating in patients with functional bowel disorders: a double-blind study. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2011 Jul. doi: 10.1097/MCG.0b013e31820ca4d6.
22. Pimentel M et al. Rifaximin therapy for patients with irritable bowel syndrome without constipation. N Engl J Med. 2011 Jan. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1004409.
23. Iovino P et al. Pelvic floor biofeedback is an effective treatment for severe bloating in disorders of gut-brain interaction with outlet dysfunction. Neurogastroenterol Motil 2022 May. doi: 10.1111/nmo.14264.
24. Talley NJ et al. Effect of amitriptyline and escitalopram on functional dyspepsia: A multicenter, randomized controlled study. Gastroenterology. 2015 Aug. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2015.04.020.
25. Keefer L et al. A Rome Working Team Report on brain-gut behavior therapies for disorders of gut-brain interaction. Gastroenterology. 2022 Jan. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.09.015.
Introduction
Abdominal bloating is a common condition affecting up to 3.5% of people globally (4.6% in women and 2.4% in men),1 with 13.9% of the US population reporting bloating in the past 7 days.2 The prevalence of bloating and distention exceeds 50% when linked to disorders of gut-brain interaction (DGBIs) such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), constipation, gastroparesis, and functional dyspepsia (FD).3,4 According to the Rome IV criteria, functional bloating and distention (FABD) patients are characterized by recurrent symptoms of abdominal fullness or pressure (bloating), or a visible increase in abdominal girth (distention) occurring at least 1 day per week for 3 consecutive months with an onset of 6 months and without predominant pain or altered bowel habits.5
Prolonged abdominal bloating and distention (ABD) can significantly impact quality of life and work productivity and can lead to increased medical consultations.2 Multiple pathophysiological mechanisms are involved in ABD that complicate the clinical management.4 There is an unmet need to understand the underlying mechanisms that lead to the development of ABD such as, food intolerance, abnormal viscerosomatic reflex, visceral hypersensitivity, and gut microbial dysbiosis. Recent advancements and acceptance of a multidisciplinary management of ABD have shifted the paradigm from merely treating symptoms to subtyping the condition and identifying overlaps with other DGBIs in order to individualize treatment that addresses the underlying pathophysiological mechanism. The recent American Gastroenterological Association (AGA) clinical update provided insights into the best practice advice for evaluating and managing ABD based on a review of current literature and on expert opinion of coauthors.6 This article aims to deliberate a practical approach to diagnostic strategies and treatment options based on etiology to refine clinical care of patients with ABD.
Pathophysiological Mechanisms
ABD can result from various pathophysiological mechanisms. This section highlights the major causes (illustrated in Figure 1).
Food intolerances
Understanding food intolerances is crucial for diagnosing and managing patients with ABD. Disaccharidase deficiency is common (e.g., lactase deficiency is found in 35%-40% of adults).7 It can be undiagnosed in patients presenting with IBS symptoms, given the overlap in presentation with a prevalence of 9% of pan-disaccharidase deficiency. Sucrase-deficient patients must often adjust sugar and carbohydrate/starch intake to relieve symptoms.7 Deficiencies in lactase and sucrase activity, along with the consumption of some artificial sweeteners (e.g., sugar alcohols and sorbitol) and fructans can lead to bloating and distention. These substances increase osmotic load, fluid retention, microbial fermentation, and visceral hypersensitivity, leading to gas production and abdominal distention. One prospective study of symptomatic patients with various DGBIs (n = 1372) reported a prevalence of lactose intolerance and malabsorption at 51% and 32%, respectively.8 Furthermore, fructose intolerance and malabsorption prevalence were 60% and 45%, respectively.8 Notably, lactase deficiency does not always cause ABD, as not all individuals with lactase deficiency experience these symptoms after consuming lactose. Patients with celiac disease (CD), non-celiac gluten sensitivity (NCGS), and gluten intolerance can also experience bloating and distention, with or without changes in bowel habits.9 In some patients with self-reported NCGS, symptoms may be due to fructans in gluten-rich foods rather than gluten itself, thus recommending the elimination of fructans may help improve symptoms.9
Visceral hypersensitivity
Visceral hypersensitivity is explained by an increased perception of gut mechano-chemical stimulation, which typically manifests in an aggravated feeling of pain, nausea, distension, and ABD.10 In the gut, food particles and gut bacteria and their derived molecules interact with neuroimmune and enteroendocrine cells causing visceral sensitivity by the proximity of gut’s neurons to immune cells activated by them and leading to inflammatory reactions (Figure 1).

Pelvic floor dysfunction
Patients with anorectal motor dysfunction often experience difficulty in effectively evacuating both gas and stool, leading to ABD.12 Impaired ability to expel gas and stool results in prolonged balloon expulsion times, which correlates with symptoms of distention in patients with constipation.
Abdominophrenic dyssynergia
Abdominophrenic dyssynergia is characterized as a paradoxical viscerosomatic reflex response to minimal gaseous distention in individuals with FABD.13 In this condition, the diaphragm contracts (descends), and the anterior abdominal wall muscles relax in response to the presence of gas. This response is opposite to the normal physiological response to increased intraluminal gas, where the diaphragm relaxes and the anterior abdominal muscles contract to increase the craniocaudal capacity of the abdominal cavity without causing abdominal protrusion.13 Patients with FABD exhibit significant abdominal wall protrusion and diaphragmatic descent even with relatively small increases in intraluminal gas.11 Understanding the role of abdominophrenic dyssynergia in abdominal bloating and distention is essential for effective diagnosis and management of the patients.
Gut dysmotility
Gut dysmotility is a crucial factor that can contribute to FABD. Gut dysmotility affects the movement of contents through the GI tract, accumulating gas and stool, directly contributing to bloating and distention. A prospective study involving over 2000 patients with functional constipation and constipation predominant-IBS (IBS-C) found that more than 90% of these patients reported symptoms of bloating.14 Furthermore, in IBS-C patients, those with prolonged colonic transit exhibited greater abdominal distention compared to those with normal gut transit times. In patients with gastroparesis, delayed gastric emptying resulting in prolonged retention of stomach contents is the main factor in the generation of bloating symptoms.4
Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO)
SIBO is overrepresented in various conditions, including IBS, FD, diabetes, gastrointestinal (GI) surgery patients and obesity, and can play an important role in generating ABD. Excess bacteria in the small intestine ferment carbohydrates, producing gas that stretches and distends the small intestine, leading to these symptoms. Additionally, altered sensation and abnormal viscerosomatic reflexes may contribute to SIBO-related bloating.4 One recent study noted decreased duodenal phylogenetic diversity in individuals who developed postprandial bloating.15 Increased methane levels caused by intestinal methanogen overgrowth, primarily the archaea Methanobrevibacter smithii, is possibly responsible for ABD in patients with IBS-C.16 Testing for SIBO in patients with ABD is generally only recommended if there are clear risk factors or severe symptoms warranting a test-and-treat approach.
Practical Diagnosis
Diagnosing ABD typically does not require extensive laboratory testing, imaging, or endoscopy unless there are alarm features or significant changes in symptoms. Here is the AGA clinical update on best practice advice6 for when to conduct further testing:
Diagnostic tests should be considered if patients exhibit:
- Recent onset or worsening of dyspepsia or abdominal pain
- Vomiting
- GI bleeding
- Unintentional weight loss exceeding 10% of body weight
- Chronic diarrhea
- Family history of GI malignancy, celiac disease, or inflammatory bowel disease
Physical examination
If visible abdominal distention is present, a thorough abdominal examination can help identify potential issues:
- Tympany to percussion suggests bowel dilation.
- Abnormal bowel sounds may indicate obstruction or ileus.
- A succussion splash could indicate the presence of ascites and obstruction.
- Any abnormalities discovered during the physical exam should prompt further investigation with imaging, such as a computed tomography (CT) scan or ultrasound, to evaluate for ascites, masses, or increased bowel gas due to ileus, obstruction, or pseudo-obstruction.
Radiologic imaging, laboratory testing and endoscopy
- An abdominal x-ray may reveal an increased stool burden, suggesting the need for further evaluation of slow transit constipation or a pelvic floor disorder, particularly in patients with functional constipation, IBS-mixed, or IBS-C.
- Hyperglycemia, weight gain, and bloating can be a presenting sign of ovarian cancer therefore all women should continue pelvic exams as dictated by the gynecologic societies. The need for an annual pelvic exam should be discussed with health care professionals especially in those with family history of ovarian cancer.
- An upper endoscopy may be warranted for patients over 40 years old with dyspeptic symptoms and abdominal bloating or distention, especially in regions with a high prevalence of Helicobacter pylori.
- Chronic pancreatitis, indicated by bloating and pain, may necessitate fecal elastase testing to assess pancreatic function.
The expert review in the AGA clinical update provides step-by-step advice regarding the best practices6 for diagnosis and identifying who to test for ABD.
Treatment Options
The following sections highlight recent best practice advice on therapeutic approaches for treating ABD.
Dietary interventions
Specific foods may trigger bloating and abdominal distention, especially in patients with overlapping DGBIs. However, only a few studies have evaluated dietary restriction specifically for patients with primary ABD. Restricting non-absorbable sugars led to symptomatic improvement in 81% of patients with FABD who had documented sugar malabsorption.17 Two studies have shown that IBS patients treated with a low-fermentable, oligo-, di-, and monosaccharides (FODMAP) diet noted improvement in ABD and that restricting fructans initially may be the most optimal.18 A recent study showed that the Mediterranean diet improved IBS symptoms, including abdominal pain and bloating.19 It should be noted restrictive diets are efficacious but come with short- and long-term challenges. If empiric treatment and/or therapeutic testing do not resolve symptoms, a referral to a dietitian can be useful. Dietitians can provide tailored dietary advice, ensuring patients avoid trigger foods while maintaining a balanced and nutritious diet.
Prokinetics and laxatives
Prokinetic agents are used to treat symptoms of FD, gastroparesis, chronic idiopathic constipation (CIC), and IBS. A meta-analysis of 13 trials found all constipation medications superior to placebo for treating abdominal bloating in patients with IBS-C.20
Probiotics
Treatment with probiotics is recommended for bloating or distention. One double-blind placebo-controlled trial with two separate probiotics, Bifidobacterium lactis and Lactobacillus acidophilus, showed improvements in global GI symptoms of patients with DGBI at 8 weeks versus placebo, with improvements in bloating symptoms.21
Antibiotics
The most commonly studied antibiotic for treating bloating is rifaximin.22 Global symptomatic improvement in IBS patients treated with antibiotics has correlated with the normalization of hydrogen levels in lactulose hydrogen breath tests.22 Patients with non-constipation IBS randomized to rifaximin 550 mg three times daily for 14 days had a greater proportion of relief of IBS-related bloating compared to placebo for at least 2 of the first 4 weeks after treatment.22 Future research warrants use of narrow-spectrum antibiotics study for FABD as the use of broad-spectrum antibiotics may deplete commensals forever, resulting in metabolic disorders.
Biofeedback therapy
Anorectal biofeedback therapy may help with ABD, particularly in patients with IBS-C and chronic constipation. One study noted that post-biofeedback therapy, myoelectric activity of the intercostals and diaphragm decreased, and internal oblique myoelectric activity increased.23 This study also showed ascent of the diaphragm and decreased girth, improving distention.
Central neuromodulators
As bloating results from multiple disturbed mechanisms, including altered gut-brain interaction, these symptoms can be amplified by psychological states such as anxiety, depression, or somatization. Central neuromodulators reduce the perception of visceral signals, re-regulate brain-gut control mechanisms, and improve psychological comorbidities.6 A large study of FD patients demonstrated that both amitriptyline (50 mg daily) and escitalopram (10 mg daily) significantly improved postprandial bloating compared to placebo.24 Antidepressants that activate noradrenergic and serotonergic pathways, including tricyclic antidepressants (e.g., amitriptyline) and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (e.g., duloxetine and venlafaxine), show the greatest benefit in reducing visceral sensations.6
Brain-gut behavioral therapies
A recent multidisciplinary consensus report supports a myriad of potential brain-gut behavioral therapies (BGBTs) for treating DGBI.25 These therapies, including hypnotherapy, cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), and other modalities, may be combined with central neuromodulators and other GI treatments in a safe, noninvasive, and complementary fashion. BGBTs do not need to be symptom-specific, as they improve overall quality of life, anxiety, stress, and the burden associated with DGBIs. To date, none of the BGBTs have focused exclusively on FABD; however, prescription-based psychological therapies are now FDA-approved for use on smart apps, improving global symptoms that include bloating in IBS and FD.
Recent AGA clinical update best practices should be considered for the clinical care of patients with ABD.6
Conclusion and Future Perspectives
ABD are highly prevalent and significantly impact patients with various GI and metabolic disorders. Although our understanding of these symptoms is still evolving, evidence increasingly points to the dysregulation of the gut-brain axis and supports the application of the biopsychosocial model in treatment. This model addresses diet, motility, visceral sensitivity, pelvic floor disorders and psychosocial factors, providing a comprehensive approach to patient care.
Physician-scientists around the globe face numerous challenges when evaluating patients with these symptoms. However, the recent AGA clinical update on the best practice guidelines offers step-by-step diagnostic tests and treatment options to assist physicians in making informed decisions. . More comprehensive, large-scale, and longitudinal studies using metabolomics, capsule technologies for discovery of dysbiosis, mass spectrometry, and imaging data are needed to identify the exact contributors to disease pathogenesis, particularly those that can be targeted with pharmacologic agents. Collaborative work between gastroenterologists, dietitians, gut-brain behavioral therapists, endocrinologists, is crucial for clinical care of patients with ABD.
Careful attention to the patient’s primary symptoms and physical examination, combined with advancements in targeted diagnostics like the analysis of microbial markers, metabolites, and molecular signals, can significantly enhance patient clinical outcomes. Additionally, education and effective communication using a patient-centered care model are essential for guiding practical evaluation and individualized treatment.
Dr. Singh is assistant professor (research) at the University of Nevada, Reno, School of Medicine. Dr. Moshiree is director of motility at Atrium Health, and clinical professor of medicine, Wake Forest Medical University, Charlotte, North Carolina.
References
1. Ballou S et al. Prevalence and associated factors of bloating: Results from the Rome Foundation Global Epidemiology Study. Gastroenterology. 2023 June. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.05.049.
2. Oh JE et al. Abdominal bloating in the United States: Results of a survey of 88,795 Americans examining prevalence and healthcare seeking. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023 Aug. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2022.10.031.
3. Drossman DA et al. Neuromodulators for functional gastrointestinal disorders (disorders of gut-brain interaction): A Rome Foundation Working Team Report. Gastroenterology. 2018 Mar. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.11.279.
4. Lacy BE et al. Management of chronic abdominal distension and bloating. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021 Feb. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2020.03.056.
5. Mearin F et al. Bowel disorders. Gastroenterology. 2016 Feb. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2016.02.031.
6. Moshiree B et al. AGA Clinical Practice Update on evaluation and management of belching, abdominal bloating, and distention: expert review. Gastroenterology. 2023 Sep. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.04.039.
7. Viswanathan L and Rao SS. Intestinal disaccharidase deficiency in adults: evaluation and treatment. Curr Gastroenterol Rep 2023 May. doi: 10.1007/s11894-023-00870-z.
8. Wilder-Smith CH et al. Fructose and lactose intolerance and malabsorption testing: the relationship with symptoms in functional gastrointestinal disorders. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2013 Jun. doi: 10.1111/apt.12306.
9. Skodje GI et al. Fructan, rather than gluten, induces symptoms in patients with self-reported non-celiac gluten sensitivity. Gastroenterology. 2018 Feb. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.10.040.
10. Singh R et al. Current treatment options and therapeutic insights for gastrointestinal dysmotility and functional gastrointestinal disorders. Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jan. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.808195.
11. Accarino A et al. Abdominal distention results from caudo-ventral redistribution of contents. Gastroenterology 2009 May. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2009.01.067.
12. Shim L et al. Prolonged balloon expulsion is predictive of abdominal distension in bloating. Am J Gastroenterol. 2010 Apr. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2010.54.
13. Villoria A et al. Abdomino-phrenic dyssynergia in patients with abdominal bloating and distension. Am J Gastroenterol. 2011 May. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2010.408.
14. Neri L and Iovino P. Laxative Inadequate Relief Survey Group. Bloating is associated with worse quality of life, treatment satisfaction, and treatment responsiveness among patients with constipation-predominant irritable bowel syndrome and functional constipation. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2016 Apr. doi: 10.1111/nmo.12758.
15. Saffouri GB et al. Small intestinal microbial dysbiosis underlies symptoms associated with functional gastrointestinal disorders. Nat Commun. 2019 May. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-09964-7.
16. Villanueva-Millan MJ et al. Methanogens and hydrogen sulfide producing bacteria guide distinct gut microbe profiles and irritable bowel syndrome subtypes. Am J Gastroenterol. 2022 Dec. doi: 10.14309/ajg.0000000000001997.
17. Fernández-Bañares F et al. Sugar malabsorption in functional abdominal bloating: a pilot study on the long-term effect of dietary treatment. Clin Nutr. 2006 Oct. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2005.11.010.
18. Böhn L et al. Diet low in FODMAPs reduces symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome as well as traditional dietary advice: a randomized controlled trial. Gastroenterology. 2015 Nov. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2015.07.054.
19. Staudacher HM et al. Clinical trial: A Mediterranean diet is feasible and improves gastrointestinal and psychological symptoms in irritable bowel syndrome. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2024 Feb. doi: 10.1111/apt.17791.
20. Nelson AD et al. Systematic review and network meta-analysis: efficacy of licensed drugs for abdominal bloating in irritable bowel syndrome with constipation. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2021 Jul. doi: 10.1111/apt.16437.
21. Ringel-Kulka T et al. Probiotic bacteria Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM and Bifidobacterium lactis Bi-07 versus placebo for the symptoms of bloating in patients with functional bowel disorders: a double-blind study. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2011 Jul. doi: 10.1097/MCG.0b013e31820ca4d6.
22. Pimentel M et al. Rifaximin therapy for patients with irritable bowel syndrome without constipation. N Engl J Med. 2011 Jan. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1004409.
23. Iovino P et al. Pelvic floor biofeedback is an effective treatment for severe bloating in disorders of gut-brain interaction with outlet dysfunction. Neurogastroenterol Motil 2022 May. doi: 10.1111/nmo.14264.
24. Talley NJ et al. Effect of amitriptyline and escitalopram on functional dyspepsia: A multicenter, randomized controlled study. Gastroenterology. 2015 Aug. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2015.04.020.
25. Keefer L et al. A Rome Working Team Report on brain-gut behavior therapies for disorders of gut-brain interaction. Gastroenterology. 2022 Jan. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.09.015.
AGA Issues Guidance on Identifying, Treating Cyclic Vomiting Syndrome
, according to a new clinical practice update from the American Gastroenterological Association.
CVS affects up to 2% of U.S. adults and is more common in women, young adults, and those with a personal or family history of migraine headaches. However, most patients don’t receive a diagnosis or often experience years of delay in receiving effective treatment.
“A diagnosis is a powerful tool. Not only does it help patients make sense of debilitating symptoms, but it allows healthcare providers to create an effective treatment plan,” said author David J. Levinthal, MD, AGAF, director of the Neurogastroenterology and Motility Center at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center.
The update was published online in Gastroenterology.
Understanding Cyclic Vomiting Syndrome
CVS is a chronic disorder of gut-brain interaction (DGBI), which is characterized by acute episodes of nausea and vomiting, separated by time without symptoms. Patients can usually identify a pattern of symptoms that show up during and between episodes.
CVS can vary, ranging from mild — with less than four episodes per year and lasting less than 2 days — to moderate-severe — with more than four episodes per year, lasting more than 2 days, and requiring at least one emergency department visit or hospitalization.
The disorder has four distinct phases — inter-episodic, prodromal, emetic, and recovery — that align with distinct treatment and management strategies. Between episodes, patients typically don’t experience repetitive vomiting but may experience symptoms such as mild nausea, indigestion, and occasional vomiting. Although CVS episodes can happen at any time, most tend to occur in the early morning.
For diagnosis, clinicians should consider CVS in adults presenting with episodic bouts of repetitive vomiting, following criteria established by the Rome Foundation. Rome IV criteria include acute-onset vomiting lasting less than 7 days, at least three discrete episodes in a year with two in the previous 6 months, and an absence of vomiting between episodes separated by at least 1 week of baseline health.

About 65% of patients with CVS experience prodromal symptoms, which last for about an hour before the onset of vomiting and may include panic, a sense of doom, and an inability to communicate effectively. During prodromal or emetic phases, patients have also reported fatigue, brain fog, restlessness, anxiety, headache, bowel urgency, abdominal pain, flushing, or shakiness.
As with migraines, CVS episodes may often be triggered by psychological and physiological factors, particularly stress. Episodes can stem from both negative stress, such as a death or relationship conflicts, as well as positive stress, such as birthdays and vacations. Other triggers include sleep deprivation, hormonal fluctuations linked to the menstrual cycle, travel, motion sickness, or acute infections.
Adult CVS is associated with several conditions, particularly mood disorders, including anxiety, depression, and panic disorder. Patients may also experience migraines, seizure disorders, or autonomic imbalances, such as postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome, which may indicate pathophysiological mechanisms and routes for management.
The American Neurogastroenterology and Motility Society recommends testing to rule out similar or overlapping conditions, such as Addison’s disease, hypothyroidism, and hepatic porphyria. Diagnostic workup should include blood work, urinalysis, and one-time esophagogastroduodenoscopy or upper gastrointestinal imaging. Repeated imaging and gastric emptying scans should be avoided.
Providing Treatment and Prevention
For treatment, knowing the CVS phase is “essential,” the authors wrote. For instance, during the prodromal phase, abortive therapies can halt the transition to the emetic phase, and earlier intervention is associated with a higher probability of stopping an episode. The authors recommend intranasal sumatriptan, ondansetron, antihistamines, and sedatives.
During the emetic phase, supportive therapy can help terminate the episode. This may include continuing the abortive regimen and going to the emergency department for hydration and antiemetic medications. Patients may also find relief in a quiet, darker room in the emergency department, along with IV benzodiazepines, with the goal of inducing sedation.
During the recovery phase, patients should rest and focus on rehydration and nutrition to return to the well phase.
During the well or inter-episodic phase, patients can follow lifestyle measures to identify and avoid triggers, such as taking prophylactic medication (tricyclic antidepressants, anticonvulsants, and neurokinin-1 receptor antagonists such as aprepitant), reducing stress, and implementing a good sleep routine.
As part of patient education, clinicians can discuss the four phases and rehearse the actions to take to prevent or stop an episode.
“CVS has a significant impact on patients, families, and the healthcare system. The unpredictable and disruptive nature of episodes can result in reduced health-related quality of life, job loss precipitated by work absenteeism, and even divorce,” said Rosita Frazier, MD, a gastroenterologist at Mayo Clinic Arizona in Scottsdale who specializes in DGBI and CVS. Dr. Frazier, who wasn’t involved with the clinical practice update, has previously written about CVS diagnosis and management.
“Providing an individualized care plan for all patients could potentially address this problem and improve the physician-patient interaction,” she said. “Educational efforts to raise awareness among the medical community and increase both patient and provider engagement can optimize outcomes and are needed to address this critical problem.”
The authors received no specific funding for this update. Dr. Levinthal is a consultant for Takeda Pharmaceuticals and Mahana. Dr. Frazier reported no relevant financial disclosures.
, according to a new clinical practice update from the American Gastroenterological Association.
CVS affects up to 2% of U.S. adults and is more common in women, young adults, and those with a personal or family history of migraine headaches. However, most patients don’t receive a diagnosis or often experience years of delay in receiving effective treatment.
“A diagnosis is a powerful tool. Not only does it help patients make sense of debilitating symptoms, but it allows healthcare providers to create an effective treatment plan,” said author David J. Levinthal, MD, AGAF, director of the Neurogastroenterology and Motility Center at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center.
The update was published online in Gastroenterology.
Understanding Cyclic Vomiting Syndrome
CVS is a chronic disorder of gut-brain interaction (DGBI), which is characterized by acute episodes of nausea and vomiting, separated by time without symptoms. Patients can usually identify a pattern of symptoms that show up during and between episodes.
CVS can vary, ranging from mild — with less than four episodes per year and lasting less than 2 days — to moderate-severe — with more than four episodes per year, lasting more than 2 days, and requiring at least one emergency department visit or hospitalization.
The disorder has four distinct phases — inter-episodic, prodromal, emetic, and recovery — that align with distinct treatment and management strategies. Between episodes, patients typically don’t experience repetitive vomiting but may experience symptoms such as mild nausea, indigestion, and occasional vomiting. Although CVS episodes can happen at any time, most tend to occur in the early morning.
For diagnosis, clinicians should consider CVS in adults presenting with episodic bouts of repetitive vomiting, following criteria established by the Rome Foundation. Rome IV criteria include acute-onset vomiting lasting less than 7 days, at least three discrete episodes in a year with two in the previous 6 months, and an absence of vomiting between episodes separated by at least 1 week of baseline health.

About 65% of patients with CVS experience prodromal symptoms, which last for about an hour before the onset of vomiting and may include panic, a sense of doom, and an inability to communicate effectively. During prodromal or emetic phases, patients have also reported fatigue, brain fog, restlessness, anxiety, headache, bowel urgency, abdominal pain, flushing, or shakiness.
As with migraines, CVS episodes may often be triggered by psychological and physiological factors, particularly stress. Episodes can stem from both negative stress, such as a death or relationship conflicts, as well as positive stress, such as birthdays and vacations. Other triggers include sleep deprivation, hormonal fluctuations linked to the menstrual cycle, travel, motion sickness, or acute infections.
Adult CVS is associated with several conditions, particularly mood disorders, including anxiety, depression, and panic disorder. Patients may also experience migraines, seizure disorders, or autonomic imbalances, such as postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome, which may indicate pathophysiological mechanisms and routes for management.
The American Neurogastroenterology and Motility Society recommends testing to rule out similar or overlapping conditions, such as Addison’s disease, hypothyroidism, and hepatic porphyria. Diagnostic workup should include blood work, urinalysis, and one-time esophagogastroduodenoscopy or upper gastrointestinal imaging. Repeated imaging and gastric emptying scans should be avoided.
Providing Treatment and Prevention
For treatment, knowing the CVS phase is “essential,” the authors wrote. For instance, during the prodromal phase, abortive therapies can halt the transition to the emetic phase, and earlier intervention is associated with a higher probability of stopping an episode. The authors recommend intranasal sumatriptan, ondansetron, antihistamines, and sedatives.
During the emetic phase, supportive therapy can help terminate the episode. This may include continuing the abortive regimen and going to the emergency department for hydration and antiemetic medications. Patients may also find relief in a quiet, darker room in the emergency department, along with IV benzodiazepines, with the goal of inducing sedation.
During the recovery phase, patients should rest and focus on rehydration and nutrition to return to the well phase.
During the well or inter-episodic phase, patients can follow lifestyle measures to identify and avoid triggers, such as taking prophylactic medication (tricyclic antidepressants, anticonvulsants, and neurokinin-1 receptor antagonists such as aprepitant), reducing stress, and implementing a good sleep routine.
As part of patient education, clinicians can discuss the four phases and rehearse the actions to take to prevent or stop an episode.
“CVS has a significant impact on patients, families, and the healthcare system. The unpredictable and disruptive nature of episodes can result in reduced health-related quality of life, job loss precipitated by work absenteeism, and even divorce,” said Rosita Frazier, MD, a gastroenterologist at Mayo Clinic Arizona in Scottsdale who specializes in DGBI and CVS. Dr. Frazier, who wasn’t involved with the clinical practice update, has previously written about CVS diagnosis and management.
“Providing an individualized care plan for all patients could potentially address this problem and improve the physician-patient interaction,” she said. “Educational efforts to raise awareness among the medical community and increase both patient and provider engagement can optimize outcomes and are needed to address this critical problem.”
The authors received no specific funding for this update. Dr. Levinthal is a consultant for Takeda Pharmaceuticals and Mahana. Dr. Frazier reported no relevant financial disclosures.
, according to a new clinical practice update from the American Gastroenterological Association.
CVS affects up to 2% of U.S. adults and is more common in women, young adults, and those with a personal or family history of migraine headaches. However, most patients don’t receive a diagnosis or often experience years of delay in receiving effective treatment.
“A diagnosis is a powerful tool. Not only does it help patients make sense of debilitating symptoms, but it allows healthcare providers to create an effective treatment plan,” said author David J. Levinthal, MD, AGAF, director of the Neurogastroenterology and Motility Center at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center.
The update was published online in Gastroenterology.
Understanding Cyclic Vomiting Syndrome
CVS is a chronic disorder of gut-brain interaction (DGBI), which is characterized by acute episodes of nausea and vomiting, separated by time without symptoms. Patients can usually identify a pattern of symptoms that show up during and between episodes.
CVS can vary, ranging from mild — with less than four episodes per year and lasting less than 2 days — to moderate-severe — with more than four episodes per year, lasting more than 2 days, and requiring at least one emergency department visit or hospitalization.
The disorder has four distinct phases — inter-episodic, prodromal, emetic, and recovery — that align with distinct treatment and management strategies. Between episodes, patients typically don’t experience repetitive vomiting but may experience symptoms such as mild nausea, indigestion, and occasional vomiting. Although CVS episodes can happen at any time, most tend to occur in the early morning.
For diagnosis, clinicians should consider CVS in adults presenting with episodic bouts of repetitive vomiting, following criteria established by the Rome Foundation. Rome IV criteria include acute-onset vomiting lasting less than 7 days, at least three discrete episodes in a year with two in the previous 6 months, and an absence of vomiting between episodes separated by at least 1 week of baseline health.

About 65% of patients with CVS experience prodromal symptoms, which last for about an hour before the onset of vomiting and may include panic, a sense of doom, and an inability to communicate effectively. During prodromal or emetic phases, patients have also reported fatigue, brain fog, restlessness, anxiety, headache, bowel urgency, abdominal pain, flushing, or shakiness.
As with migraines, CVS episodes may often be triggered by psychological and physiological factors, particularly stress. Episodes can stem from both negative stress, such as a death or relationship conflicts, as well as positive stress, such as birthdays and vacations. Other triggers include sleep deprivation, hormonal fluctuations linked to the menstrual cycle, travel, motion sickness, or acute infections.
Adult CVS is associated with several conditions, particularly mood disorders, including anxiety, depression, and panic disorder. Patients may also experience migraines, seizure disorders, or autonomic imbalances, such as postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome, which may indicate pathophysiological mechanisms and routes for management.
The American Neurogastroenterology and Motility Society recommends testing to rule out similar or overlapping conditions, such as Addison’s disease, hypothyroidism, and hepatic porphyria. Diagnostic workup should include blood work, urinalysis, and one-time esophagogastroduodenoscopy or upper gastrointestinal imaging. Repeated imaging and gastric emptying scans should be avoided.
Providing Treatment and Prevention
For treatment, knowing the CVS phase is “essential,” the authors wrote. For instance, during the prodromal phase, abortive therapies can halt the transition to the emetic phase, and earlier intervention is associated with a higher probability of stopping an episode. The authors recommend intranasal sumatriptan, ondansetron, antihistamines, and sedatives.
During the emetic phase, supportive therapy can help terminate the episode. This may include continuing the abortive regimen and going to the emergency department for hydration and antiemetic medications. Patients may also find relief in a quiet, darker room in the emergency department, along with IV benzodiazepines, with the goal of inducing sedation.
During the recovery phase, patients should rest and focus on rehydration and nutrition to return to the well phase.
During the well or inter-episodic phase, patients can follow lifestyle measures to identify and avoid triggers, such as taking prophylactic medication (tricyclic antidepressants, anticonvulsants, and neurokinin-1 receptor antagonists such as aprepitant), reducing stress, and implementing a good sleep routine.
As part of patient education, clinicians can discuss the four phases and rehearse the actions to take to prevent or stop an episode.
“CVS has a significant impact on patients, families, and the healthcare system. The unpredictable and disruptive nature of episodes can result in reduced health-related quality of life, job loss precipitated by work absenteeism, and even divorce,” said Rosita Frazier, MD, a gastroenterologist at Mayo Clinic Arizona in Scottsdale who specializes in DGBI and CVS. Dr. Frazier, who wasn’t involved with the clinical practice update, has previously written about CVS diagnosis and management.
“Providing an individualized care plan for all patients could potentially address this problem and improve the physician-patient interaction,” she said. “Educational efforts to raise awareness among the medical community and increase both patient and provider engagement can optimize outcomes and are needed to address this critical problem.”
The authors received no specific funding for this update. Dr. Levinthal is a consultant for Takeda Pharmaceuticals and Mahana. Dr. Frazier reported no relevant financial disclosures.
FROM GASTROENTEROLOGY
FDA OKs Voquezna for Heartburn Relief in Nonerosive Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
It represents the third indication for the potassium-competitive acid blocker, which is already approved to treat all severities of erosive esophagitis and to eradicate Helicobacter pylori infection in combination with antibiotics.
The approval in nonerosive GERD was supported by results of the PHALCON-nonerosive GERD-301 study, a phase 3 randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, multicenter study evaluating the safety and efficacy of once-daily Voquezna in more than 700 adults with nonerosive GERD experiencing at least 4 days of heartburn per week.
“Vonoprazan was efficacious in reducing heartburn symptoms in patients with [nonerosive GERD], with the benefit appearing to begin as early as the first day of therapy. This treatment effect persisted after the initial 4-week placebo-controlled period throughout the 20-week extension period,” the study team wrote in a paper published online in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology , and reported on by this news organization.
Voquezna “provides physicians with a novel, first-in-class treatment that can quickly and significantly reduce heartburn for many adult patients” with nonerosive GERD, Colin W. Howden, MD, AGAF, professor emeritus, University of Tennessee College of Medicine in Memphis, said in a news release.
The most common adverse events reported in patients treated with Voquezna during the 4-week placebo-controlled period were abdominal pain, constipation, diarrhea, nausea, and urinary tract infection.
Upper respiratory tract infection and sinusitis were also reported in patients who taking Voquezna in the 20-week extension phase of the trial.
Full prescribing information is available online.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
It represents the third indication for the potassium-competitive acid blocker, which is already approved to treat all severities of erosive esophagitis and to eradicate Helicobacter pylori infection in combination with antibiotics.
The approval in nonerosive GERD was supported by results of the PHALCON-nonerosive GERD-301 study, a phase 3 randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, multicenter study evaluating the safety and efficacy of once-daily Voquezna in more than 700 adults with nonerosive GERD experiencing at least 4 days of heartburn per week.
“Vonoprazan was efficacious in reducing heartburn symptoms in patients with [nonerosive GERD], with the benefit appearing to begin as early as the first day of therapy. This treatment effect persisted after the initial 4-week placebo-controlled period throughout the 20-week extension period,” the study team wrote in a paper published online in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology , and reported on by this news organization.
Voquezna “provides physicians with a novel, first-in-class treatment that can quickly and significantly reduce heartburn for many adult patients” with nonerosive GERD, Colin W. Howden, MD, AGAF, professor emeritus, University of Tennessee College of Medicine in Memphis, said in a news release.
The most common adverse events reported in patients treated with Voquezna during the 4-week placebo-controlled period were abdominal pain, constipation, diarrhea, nausea, and urinary tract infection.
Upper respiratory tract infection and sinusitis were also reported in patients who taking Voquezna in the 20-week extension phase of the trial.
Full prescribing information is available online.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
It represents the third indication for the potassium-competitive acid blocker, which is already approved to treat all severities of erosive esophagitis and to eradicate Helicobacter pylori infection in combination with antibiotics.
The approval in nonerosive GERD was supported by results of the PHALCON-nonerosive GERD-301 study, a phase 3 randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, multicenter study evaluating the safety and efficacy of once-daily Voquezna in more than 700 adults with nonerosive GERD experiencing at least 4 days of heartburn per week.
“Vonoprazan was efficacious in reducing heartburn symptoms in patients with [nonerosive GERD], with the benefit appearing to begin as early as the first day of therapy. This treatment effect persisted after the initial 4-week placebo-controlled period throughout the 20-week extension period,” the study team wrote in a paper published online in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology , and reported on by this news organization.
Voquezna “provides physicians with a novel, first-in-class treatment that can quickly and significantly reduce heartburn for many adult patients” with nonerosive GERD, Colin W. Howden, MD, AGAF, professor emeritus, University of Tennessee College of Medicine in Memphis, said in a news release.
The most common adverse events reported in patients treated with Voquezna during the 4-week placebo-controlled period were abdominal pain, constipation, diarrhea, nausea, and urinary tract infection.
Upper respiratory tract infection and sinusitis were also reported in patients who taking Voquezna in the 20-week extension phase of the trial.
Full prescribing information is available online.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.