User login
Piperacillin/Tazobactam Use vs Cefepime May Be Associated With Acute Decompensated Heart Failure
Piperacillin/tazobactam (PTZ) is a combination IV antibiotic comprised of the semisynthetic antipseudomonal β-lactam, piperacillin sodium, and the β-lactamase inhibitor, tazobactam sodium.1 PTZ is extensively prescribed in the hospital setting for a multitude of infections including but not limited to the US Food and Drug Administration–approved indications: intra-abdominal infection, skin and skin structure infection (SSTI), urinary tract infection (UTI), and pneumonia. Given its broad spectrum of activity and relative safety profile, PTZ is a mainstay of many empiric IV antibiotic regimens. The primary elimination pathway for PTZ is renal excretion, and dosage adjustments are recommended with reduced creatinine clearance. Additionally, PTZ use has been associated with acute renal injury and delayed renal recovery.1-3
There are various mechanisms through which medications can contribute to acute decomopensated heart failure (ADHF).4 These mechanisms include direct cardiotoxicity; negative inotropic, lusitropic, or chronotropic effects; exacerbating hypertension; sodium loading; and drug-drug interactions that limit the benefits of heart failure (HF) medications. One potentially overlooked constituent of PTZ is the sodium content, with the standard formulation containing 65 mg of sodium per gram of piperacillin.1-3 Furthermore, PTZ must be diluted in 50 to 150 mL of diluent, commonly 0.9% sodium chloride, which can contribute an additional 177 to 531 mg of sodium per dose. PTZ prescribing information advises caution for use in patients with decreased renal, hepatic, and/or cardiac function and notes that geriatric patients, particularly with HF, may be at risk of impaired natriuresis in the setting of large sodium doses.
It is estimated that roughly 6.2 million adults in the United States have HF and prevalence continues to rise.5,6 Mortality rates after hospitalization due to HF are 20% to 25% at 1 year. Health care expenditures for the management of HF surpass $30 billion per year in the US, with most of this cost attributed to hospitalizations. Consequently, it is important to continue to identify and practice preventative strategies when managing patients with HF.
Methods
This single-center, retrospective, cohort study was conducted at James H. Quillen Veterans Affairs Medical Center (JHQVAMC) in Mountain Home, Tennessee, a 174-bed tertiary medical center. The purpose of this study was to compare the incidence of ADHF in patients who received PTZ vs cefepime (CFP). This project was reviewed by the JHQVAMC Institutional Review Board and deemed exempt as a clinical process improvement operations activity.
The antimicrobial stewardship team at JHQVAMC reviewed the use of PTZ in veterans between January 1, 2018, to December 31, 2019, and compared baseline demographics, history of HF, and outcomes in patients receiving analogous broad-spectrum empiric antibiotic therapy with CFP.
Statistical Analysis
Analysis was conducted with R Software. Pearson χ2 and t tests were used to compare baseline demographics, length of stay, readmission, and mortality. Significance used was α = .05.
Results
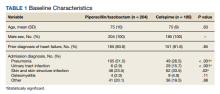
A retrospective chart review was performed on 389 veterans. Of the 389, 204 patients received at least 24 hours of PTZ, and 185 patients received CFP. The mean age in both groups was 75 years. Patients in the PTZ group were more likely to have been admitted with the diagnosis of pneumonia (105 vs 49, P < .001). However, 29 patients (15.7%) in the CFP group were admitted with a UTI diagnosis compared with 6 patients (2.9%) in the PTZ group (P < .001) and 62 patients (33.5%) in the CFP group were admitted with a SSTI diagnosis compared with 48 patients (23.5%) in the PTZ group (P = .03). Otherwise, there were no differences between other admitting diagnoses. Additionally, there was no difference in prior history of HF between groups (Table 1).
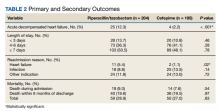
Twenty-five patients (12.3%) in the PTZ group and 4 patients (2.2%) in the CFP group were subsequently diagnosed with ADHF (P < .001). Hospital readmissions due to HF were higher in the PTZ group compared with the CFP group (11 vs 2, P = .02). Hospital readmission due to other causes was not significantly different between groups. Hospital readmission due to infection occurred in 18 patients who received PTZ and 25 who received CFP (8.8% vs 13.5%, P = .14). Hospital readmission due to any other indication occurred in 24 patients who received PTZ and 24 who received CFP (11.8% vs 13.0%, P = .72). There was no statistically significant difference in all-cause mortality during the associated admission or within 6 months of discharge between groups, with 59 total deaths in the PTZ group and 50 in the CFP group (28.9% vs 27.0%, P = .63).
There was no difference in length of stay outcomes between patients receiving PTZ compared with CFP. Twenty-eight patients in the PTZ group and 20 in the CFP group had a length of stay duration of < 3 days (13.7% vs 10.8%, P = .46). Seventy-three patients in the PTZ group and 76 in the CFP group had a length of stay duration of 4 to 6 days (36.3% vs 41.1%, P = .28). One hundred three patients in the PTZ group and 89 in the CFP group had a length of stay duration ≥ 7 days (50.5% vs 48.1%, P = .78). Table 2 includes a complete overview of primary and secondary endpoint results.
Discussion
The American Heart Association (AHA) lists PTZ as a medication that may cause or exacerbate HF, though no studies have identified a clear association between PTZ use and ADHF.4 Sodium restriction is consistently recommended as an important strategy for the prevention of ADHF. Accordingly, PTZ prescribing information and the AHA advise careful consideration with PTZ use in this patient population.1,4
The specific mechanism responsible for the association of PTZ with cardiac-related adverse outcomes is unclear. It is easy to presume that the sodium content of PTZ is solely responsible; however, other antibiotic regimens not included as agents of concern by the AHA, such as meropenem, can approach similar overall daily sodium amounts.4,7 Additionally, total sodium and volume can also be contributed by various IV medications and fluids. This study did not evaluate total sodium intake from all sources, but it is notable that this study identified a possible trend toward the risk of ADHF with PTZ use in a routine practice environment. It is reasonable to postulate additional intrinsic properties of PTZ may be contributing to the development of ADHF, such as its association with renal injury possibly resulting in increased fluid retainment and subsequent fluid volume overload.1,2,4 Other hypothesized mechanisms may include those previously described, such as direct myocardial toxicity; negative inotropic, lusitropic, or chronotropic effects; exacerbating hypertension; and drug-drug interactions that limit the benefits of HF medications, although these have not been overtly associated with PTZ in the literature to date.4,8
ADHF can present similarly to other acute pulmonary conditions, including pneumonia.9,10 It is important to acknowledge the challenge this creates for diagnosticians to differentiate between these conditions rapidly and precisely. As a result, this patient population is likely at increased risk of IV antibiotic exposure. Other studies have identified worse outcomes in patients who receive potentially unwarranted IV antibiotics in patients with ADHF.9,10 The results of this study further emphasize the importance of careful considerate antibiotic selection and overall avoidance of unnecessary antibiotic exposure to limit potential adverse outcomes.
Limitations
There are various limitations to this study. Firstly, no women were included due to the predominantly male population within the Veterans Health Administration system. Secondly, this study was retrospective in design and was therefore limited to the completeness and accuracy of the available data collected. Additionally, this study evaluated any ADHF episode during the associated hospitalization as the primary endpoint. The time to diagnosis of ADHF in relation to PTZ initiation was not evaluated, which may have helped better elucidate this possible association. Furthermore, while a significant statistical difference was identified, the smaller sample size may have limited the ability to accurately identify differences in lower event rate outcomes.
Conclusions
This study identifies an association between PTZ use and significant cardiac-related adverse outcomes, including increased incidence of ADHF and readmission due to HF exacerbation. While more research is needed to define the exact mechanisms by which PTZ may precipitate acute decompensation in patients with HF, it is judicious to consider close monitoring or the avoidance of PTZ when appropriate antibiotic alternatives are available in patients with a known history of HF.
1. Zosyn. Package insert. Wyeth Pharmaceuticals; 2020.
2. Jensen JU, Hein L, Lundgren B, et al. Kidney failure related to broad-spectrum antibiotics in critically ill patients: secondary end point results from a 1200 patient randomised trial. BMJ Open. 2012;2(2):e000635. Published 2012 Mar 11. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2011-000635
3. Kadomura S, Takekuma Y, Sato Y, et al. Higher incidence of acute kidney injury in patients treated with piperacillin/tazobactam than in patients treated with cefepime: a single-center retrospective cohort study. J Pharm Health Care Sci. 2019;5:13. Published 2019 Jun 12. doi:10.1186/s40780-019-0142-6
4. Page RL 2nd, O’Bryant CL, Cheng D, et al. Drugs that may cause or exacerbate heart failure: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2016;134(6):e32-e69. doi:10.1161/CIR.0000000000000426
5. Bozkurt B, Hershberger RE, Butler J, et al. 2021 ACC/AHA key data elements and definitions for heart failure: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association task force on clinical data standards. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2021;77(16):2053-2150.
6. Virani SS, Alonso A, Aparicio HJ, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2021 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2021;143(8):e254-e743. doi:10.1161/CIR.0000000000000950
7. Merrem. Package insert. Pfizer Labs; 2021.
8. Keller GA, Alvarez PA, Ponte ML, et al. Drug-induced QTc interval prolongation: a multicenter study to detect drugs and clinical factors involved in every day practice. Curr Drug Saf. 2016;11(1):86-98. doi:10.2174/1574886311207040262
9. Wu S, Alikhil M, Forsyth R, Allen B. Impact of potentially unwarranted intravenous antibiotics targeting pulmonary infections in acute decompensated heart failure. J Pharm Technol. 2021;37(6):298-303. doi:10.1177/87551225211038020
10. Frisbee J, Heidel RH, Rasnake MS. Adverse outcomes associated with potentially inappropriate antibiotic use in heart failure admissions. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2019;6(6):ofz220. doi:10.1093/ofid/ofz220
Piperacillin/tazobactam (PTZ) is a combination IV antibiotic comprised of the semisynthetic antipseudomonal β-lactam, piperacillin sodium, and the β-lactamase inhibitor, tazobactam sodium.1 PTZ is extensively prescribed in the hospital setting for a multitude of infections including but not limited to the US Food and Drug Administration–approved indications: intra-abdominal infection, skin and skin structure infection (SSTI), urinary tract infection (UTI), and pneumonia. Given its broad spectrum of activity and relative safety profile, PTZ is a mainstay of many empiric IV antibiotic regimens. The primary elimination pathway for PTZ is renal excretion, and dosage adjustments are recommended with reduced creatinine clearance. Additionally, PTZ use has been associated with acute renal injury and delayed renal recovery.1-3
There are various mechanisms through which medications can contribute to acute decomopensated heart failure (ADHF).4 These mechanisms include direct cardiotoxicity; negative inotropic, lusitropic, or chronotropic effects; exacerbating hypertension; sodium loading; and drug-drug interactions that limit the benefits of heart failure (HF) medications. One potentially overlooked constituent of PTZ is the sodium content, with the standard formulation containing 65 mg of sodium per gram of piperacillin.1-3 Furthermore, PTZ must be diluted in 50 to 150 mL of diluent, commonly 0.9% sodium chloride, which can contribute an additional 177 to 531 mg of sodium per dose. PTZ prescribing information advises caution for use in patients with decreased renal, hepatic, and/or cardiac function and notes that geriatric patients, particularly with HF, may be at risk of impaired natriuresis in the setting of large sodium doses.
It is estimated that roughly 6.2 million adults in the United States have HF and prevalence continues to rise.5,6 Mortality rates after hospitalization due to HF are 20% to 25% at 1 year. Health care expenditures for the management of HF surpass $30 billion per year in the US, with most of this cost attributed to hospitalizations. Consequently, it is important to continue to identify and practice preventative strategies when managing patients with HF.
Methods
This single-center, retrospective, cohort study was conducted at James H. Quillen Veterans Affairs Medical Center (JHQVAMC) in Mountain Home, Tennessee, a 174-bed tertiary medical center. The purpose of this study was to compare the incidence of ADHF in patients who received PTZ vs cefepime (CFP). This project was reviewed by the JHQVAMC Institutional Review Board and deemed exempt as a clinical process improvement operations activity.
The antimicrobial stewardship team at JHQVAMC reviewed the use of PTZ in veterans between January 1, 2018, to December 31, 2019, and compared baseline demographics, history of HF, and outcomes in patients receiving analogous broad-spectrum empiric antibiotic therapy with CFP.
Statistical Analysis
Analysis was conducted with R Software. Pearson χ2 and t tests were used to compare baseline demographics, length of stay, readmission, and mortality. Significance used was α = .05.
Results
A retrospective chart review was performed on 389 veterans. Of the 389, 204 patients received at least 24 hours of PTZ, and 185 patients received CFP. The mean age in both groups was 75 years. Patients in the PTZ group were more likely to have been admitted with the diagnosis of pneumonia (105 vs 49, P < .001). However, 29 patients (15.7%) in the CFP group were admitted with a UTI diagnosis compared with 6 patients (2.9%) in the PTZ group (P < .001) and 62 patients (33.5%) in the CFP group were admitted with a SSTI diagnosis compared with 48 patients (23.5%) in the PTZ group (P = .03). Otherwise, there were no differences between other admitting diagnoses. Additionally, there was no difference in prior history of HF between groups (Table 1).
Twenty-five patients (12.3%) in the PTZ group and 4 patients (2.2%) in the CFP group were subsequently diagnosed with ADHF (P < .001). Hospital readmissions due to HF were higher in the PTZ group compared with the CFP group (11 vs 2, P = .02). Hospital readmission due to other causes was not significantly different between groups. Hospital readmission due to infection occurred in 18 patients who received PTZ and 25 who received CFP (8.8% vs 13.5%, P = .14). Hospital readmission due to any other indication occurred in 24 patients who received PTZ and 24 who received CFP (11.8% vs 13.0%, P = .72). There was no statistically significant difference in all-cause mortality during the associated admission or within 6 months of discharge between groups, with 59 total deaths in the PTZ group and 50 in the CFP group (28.9% vs 27.0%, P = .63).
There was no difference in length of stay outcomes between patients receiving PTZ compared with CFP. Twenty-eight patients in the PTZ group and 20 in the CFP group had a length of stay duration of < 3 days (13.7% vs 10.8%, P = .46). Seventy-three patients in the PTZ group and 76 in the CFP group had a length of stay duration of 4 to 6 days (36.3% vs 41.1%, P = .28). One hundred three patients in the PTZ group and 89 in the CFP group had a length of stay duration ≥ 7 days (50.5% vs 48.1%, P = .78). Table 2 includes a complete overview of primary and secondary endpoint results.
Discussion
The American Heart Association (AHA) lists PTZ as a medication that may cause or exacerbate HF, though no studies have identified a clear association between PTZ use and ADHF.4 Sodium restriction is consistently recommended as an important strategy for the prevention of ADHF. Accordingly, PTZ prescribing information and the AHA advise careful consideration with PTZ use in this patient population.1,4
The specific mechanism responsible for the association of PTZ with cardiac-related adverse outcomes is unclear. It is easy to presume that the sodium content of PTZ is solely responsible; however, other antibiotic regimens not included as agents of concern by the AHA, such as meropenem, can approach similar overall daily sodium amounts.4,7 Additionally, total sodium and volume can also be contributed by various IV medications and fluids. This study did not evaluate total sodium intake from all sources, but it is notable that this study identified a possible trend toward the risk of ADHF with PTZ use in a routine practice environment. It is reasonable to postulate additional intrinsic properties of PTZ may be contributing to the development of ADHF, such as its association with renal injury possibly resulting in increased fluid retainment and subsequent fluid volume overload.1,2,4 Other hypothesized mechanisms may include those previously described, such as direct myocardial toxicity; negative inotropic, lusitropic, or chronotropic effects; exacerbating hypertension; and drug-drug interactions that limit the benefits of HF medications, although these have not been overtly associated with PTZ in the literature to date.4,8
ADHF can present similarly to other acute pulmonary conditions, including pneumonia.9,10 It is important to acknowledge the challenge this creates for diagnosticians to differentiate between these conditions rapidly and precisely. As a result, this patient population is likely at increased risk of IV antibiotic exposure. Other studies have identified worse outcomes in patients who receive potentially unwarranted IV antibiotics in patients with ADHF.9,10 The results of this study further emphasize the importance of careful considerate antibiotic selection and overall avoidance of unnecessary antibiotic exposure to limit potential adverse outcomes.
Limitations
There are various limitations to this study. Firstly, no women were included due to the predominantly male population within the Veterans Health Administration system. Secondly, this study was retrospective in design and was therefore limited to the completeness and accuracy of the available data collected. Additionally, this study evaluated any ADHF episode during the associated hospitalization as the primary endpoint. The time to diagnosis of ADHF in relation to PTZ initiation was not evaluated, which may have helped better elucidate this possible association. Furthermore, while a significant statistical difference was identified, the smaller sample size may have limited the ability to accurately identify differences in lower event rate outcomes.
Conclusions
This study identifies an association between PTZ use and significant cardiac-related adverse outcomes, including increased incidence of ADHF and readmission due to HF exacerbation. While more research is needed to define the exact mechanisms by which PTZ may precipitate acute decompensation in patients with HF, it is judicious to consider close monitoring or the avoidance of PTZ when appropriate antibiotic alternatives are available in patients with a known history of HF.
Piperacillin/tazobactam (PTZ) is a combination IV antibiotic comprised of the semisynthetic antipseudomonal β-lactam, piperacillin sodium, and the β-lactamase inhibitor, tazobactam sodium.1 PTZ is extensively prescribed in the hospital setting for a multitude of infections including but not limited to the US Food and Drug Administration–approved indications: intra-abdominal infection, skin and skin structure infection (SSTI), urinary tract infection (UTI), and pneumonia. Given its broad spectrum of activity and relative safety profile, PTZ is a mainstay of many empiric IV antibiotic regimens. The primary elimination pathway for PTZ is renal excretion, and dosage adjustments are recommended with reduced creatinine clearance. Additionally, PTZ use has been associated with acute renal injury and delayed renal recovery.1-3
There are various mechanisms through which medications can contribute to acute decomopensated heart failure (ADHF).4 These mechanisms include direct cardiotoxicity; negative inotropic, lusitropic, or chronotropic effects; exacerbating hypertension; sodium loading; and drug-drug interactions that limit the benefits of heart failure (HF) medications. One potentially overlooked constituent of PTZ is the sodium content, with the standard formulation containing 65 mg of sodium per gram of piperacillin.1-3 Furthermore, PTZ must be diluted in 50 to 150 mL of diluent, commonly 0.9% sodium chloride, which can contribute an additional 177 to 531 mg of sodium per dose. PTZ prescribing information advises caution for use in patients with decreased renal, hepatic, and/or cardiac function and notes that geriatric patients, particularly with HF, may be at risk of impaired natriuresis in the setting of large sodium doses.
It is estimated that roughly 6.2 million adults in the United States have HF and prevalence continues to rise.5,6 Mortality rates after hospitalization due to HF are 20% to 25% at 1 year. Health care expenditures for the management of HF surpass $30 billion per year in the US, with most of this cost attributed to hospitalizations. Consequently, it is important to continue to identify and practice preventative strategies when managing patients with HF.
Methods
This single-center, retrospective, cohort study was conducted at James H. Quillen Veterans Affairs Medical Center (JHQVAMC) in Mountain Home, Tennessee, a 174-bed tertiary medical center. The purpose of this study was to compare the incidence of ADHF in patients who received PTZ vs cefepime (CFP). This project was reviewed by the JHQVAMC Institutional Review Board and deemed exempt as a clinical process improvement operations activity.
The antimicrobial stewardship team at JHQVAMC reviewed the use of PTZ in veterans between January 1, 2018, to December 31, 2019, and compared baseline demographics, history of HF, and outcomes in patients receiving analogous broad-spectrum empiric antibiotic therapy with CFP.
Statistical Analysis
Analysis was conducted with R Software. Pearson χ2 and t tests were used to compare baseline demographics, length of stay, readmission, and mortality. Significance used was α = .05.
Results
A retrospective chart review was performed on 389 veterans. Of the 389, 204 patients received at least 24 hours of PTZ, and 185 patients received CFP. The mean age in both groups was 75 years. Patients in the PTZ group were more likely to have been admitted with the diagnosis of pneumonia (105 vs 49, P < .001). However, 29 patients (15.7%) in the CFP group were admitted with a UTI diagnosis compared with 6 patients (2.9%) in the PTZ group (P < .001) and 62 patients (33.5%) in the CFP group were admitted with a SSTI diagnosis compared with 48 patients (23.5%) in the PTZ group (P = .03). Otherwise, there were no differences between other admitting diagnoses. Additionally, there was no difference in prior history of HF between groups (Table 1).
Twenty-five patients (12.3%) in the PTZ group and 4 patients (2.2%) in the CFP group were subsequently diagnosed with ADHF (P < .001). Hospital readmissions due to HF were higher in the PTZ group compared with the CFP group (11 vs 2, P = .02). Hospital readmission due to other causes was not significantly different between groups. Hospital readmission due to infection occurred in 18 patients who received PTZ and 25 who received CFP (8.8% vs 13.5%, P = .14). Hospital readmission due to any other indication occurred in 24 patients who received PTZ and 24 who received CFP (11.8% vs 13.0%, P = .72). There was no statistically significant difference in all-cause mortality during the associated admission or within 6 months of discharge between groups, with 59 total deaths in the PTZ group and 50 in the CFP group (28.9% vs 27.0%, P = .63).
There was no difference in length of stay outcomes between patients receiving PTZ compared with CFP. Twenty-eight patients in the PTZ group and 20 in the CFP group had a length of stay duration of < 3 days (13.7% vs 10.8%, P = .46). Seventy-three patients in the PTZ group and 76 in the CFP group had a length of stay duration of 4 to 6 days (36.3% vs 41.1%, P = .28). One hundred three patients in the PTZ group and 89 in the CFP group had a length of stay duration ≥ 7 days (50.5% vs 48.1%, P = .78). Table 2 includes a complete overview of primary and secondary endpoint results.
Discussion
The American Heart Association (AHA) lists PTZ as a medication that may cause or exacerbate HF, though no studies have identified a clear association between PTZ use and ADHF.4 Sodium restriction is consistently recommended as an important strategy for the prevention of ADHF. Accordingly, PTZ prescribing information and the AHA advise careful consideration with PTZ use in this patient population.1,4
The specific mechanism responsible for the association of PTZ with cardiac-related adverse outcomes is unclear. It is easy to presume that the sodium content of PTZ is solely responsible; however, other antibiotic regimens not included as agents of concern by the AHA, such as meropenem, can approach similar overall daily sodium amounts.4,7 Additionally, total sodium and volume can also be contributed by various IV medications and fluids. This study did not evaluate total sodium intake from all sources, but it is notable that this study identified a possible trend toward the risk of ADHF with PTZ use in a routine practice environment. It is reasonable to postulate additional intrinsic properties of PTZ may be contributing to the development of ADHF, such as its association with renal injury possibly resulting in increased fluid retainment and subsequent fluid volume overload.1,2,4 Other hypothesized mechanisms may include those previously described, such as direct myocardial toxicity; negative inotropic, lusitropic, or chronotropic effects; exacerbating hypertension; and drug-drug interactions that limit the benefits of HF medications, although these have not been overtly associated with PTZ in the literature to date.4,8
ADHF can present similarly to other acute pulmonary conditions, including pneumonia.9,10 It is important to acknowledge the challenge this creates for diagnosticians to differentiate between these conditions rapidly and precisely. As a result, this patient population is likely at increased risk of IV antibiotic exposure. Other studies have identified worse outcomes in patients who receive potentially unwarranted IV antibiotics in patients with ADHF.9,10 The results of this study further emphasize the importance of careful considerate antibiotic selection and overall avoidance of unnecessary antibiotic exposure to limit potential adverse outcomes.
Limitations
There are various limitations to this study. Firstly, no women were included due to the predominantly male population within the Veterans Health Administration system. Secondly, this study was retrospective in design and was therefore limited to the completeness and accuracy of the available data collected. Additionally, this study evaluated any ADHF episode during the associated hospitalization as the primary endpoint. The time to diagnosis of ADHF in relation to PTZ initiation was not evaluated, which may have helped better elucidate this possible association. Furthermore, while a significant statistical difference was identified, the smaller sample size may have limited the ability to accurately identify differences in lower event rate outcomes.
Conclusions
This study identifies an association between PTZ use and significant cardiac-related adverse outcomes, including increased incidence of ADHF and readmission due to HF exacerbation. While more research is needed to define the exact mechanisms by which PTZ may precipitate acute decompensation in patients with HF, it is judicious to consider close monitoring or the avoidance of PTZ when appropriate antibiotic alternatives are available in patients with a known history of HF.
1. Zosyn. Package insert. Wyeth Pharmaceuticals; 2020.
2. Jensen JU, Hein L, Lundgren B, et al. Kidney failure related to broad-spectrum antibiotics in critically ill patients: secondary end point results from a 1200 patient randomised trial. BMJ Open. 2012;2(2):e000635. Published 2012 Mar 11. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2011-000635
3. Kadomura S, Takekuma Y, Sato Y, et al. Higher incidence of acute kidney injury in patients treated with piperacillin/tazobactam than in patients treated with cefepime: a single-center retrospective cohort study. J Pharm Health Care Sci. 2019;5:13. Published 2019 Jun 12. doi:10.1186/s40780-019-0142-6
4. Page RL 2nd, O’Bryant CL, Cheng D, et al. Drugs that may cause or exacerbate heart failure: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2016;134(6):e32-e69. doi:10.1161/CIR.0000000000000426
5. Bozkurt B, Hershberger RE, Butler J, et al. 2021 ACC/AHA key data elements and definitions for heart failure: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association task force on clinical data standards. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2021;77(16):2053-2150.
6. Virani SS, Alonso A, Aparicio HJ, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2021 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2021;143(8):e254-e743. doi:10.1161/CIR.0000000000000950
7. Merrem. Package insert. Pfizer Labs; 2021.
8. Keller GA, Alvarez PA, Ponte ML, et al. Drug-induced QTc interval prolongation: a multicenter study to detect drugs and clinical factors involved in every day practice. Curr Drug Saf. 2016;11(1):86-98. doi:10.2174/1574886311207040262
9. Wu S, Alikhil M, Forsyth R, Allen B. Impact of potentially unwarranted intravenous antibiotics targeting pulmonary infections in acute decompensated heart failure. J Pharm Technol. 2021;37(6):298-303. doi:10.1177/87551225211038020
10. Frisbee J, Heidel RH, Rasnake MS. Adverse outcomes associated with potentially inappropriate antibiotic use in heart failure admissions. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2019;6(6):ofz220. doi:10.1093/ofid/ofz220
1. Zosyn. Package insert. Wyeth Pharmaceuticals; 2020.
2. Jensen JU, Hein L, Lundgren B, et al. Kidney failure related to broad-spectrum antibiotics in critically ill patients: secondary end point results from a 1200 patient randomised trial. BMJ Open. 2012;2(2):e000635. Published 2012 Mar 11. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2011-000635
3. Kadomura S, Takekuma Y, Sato Y, et al. Higher incidence of acute kidney injury in patients treated with piperacillin/tazobactam than in patients treated with cefepime: a single-center retrospective cohort study. J Pharm Health Care Sci. 2019;5:13. Published 2019 Jun 12. doi:10.1186/s40780-019-0142-6
4. Page RL 2nd, O’Bryant CL, Cheng D, et al. Drugs that may cause or exacerbate heart failure: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2016;134(6):e32-e69. doi:10.1161/CIR.0000000000000426
5. Bozkurt B, Hershberger RE, Butler J, et al. 2021 ACC/AHA key data elements and definitions for heart failure: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association task force on clinical data standards. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2021;77(16):2053-2150.
6. Virani SS, Alonso A, Aparicio HJ, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2021 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2021;143(8):e254-e743. doi:10.1161/CIR.0000000000000950
7. Merrem. Package insert. Pfizer Labs; 2021.
8. Keller GA, Alvarez PA, Ponte ML, et al. Drug-induced QTc interval prolongation: a multicenter study to detect drugs and clinical factors involved in every day practice. Curr Drug Saf. 2016;11(1):86-98. doi:10.2174/1574886311207040262
9. Wu S, Alikhil M, Forsyth R, Allen B. Impact of potentially unwarranted intravenous antibiotics targeting pulmonary infections in acute decompensated heart failure. J Pharm Technol. 2021;37(6):298-303. doi:10.1177/87551225211038020
10. Frisbee J, Heidel RH, Rasnake MS. Adverse outcomes associated with potentially inappropriate antibiotic use in heart failure admissions. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2019;6(6):ofz220. doi:10.1093/ofid/ofz220
Implementing Trustworthy AI in VA High Reliability Health Care Organizations
Artificial intelligence (AI) has lagged in health care but has considerable potential to improve quality, safety, clinician experience, and access to care. It is being tested in areas like billing, hospital operations, and preventing adverse events (eg, sepsis mortality) with some early success. However, there are still many barriers preventing the widespread use of AI, such as data problems, mismatched rewards, and workplace obstacles. Innovative projects, partnerships, better rewards, and more investment could remove barriers. Implemented reliably and safely, AI can add to what clinicians know, help them work faster, cut costs, and, most importantly, improve patient care.1
AI can potentially bring several clinical benefits, such as reducing the administrative strain on clinicians and granting them more time for direct patient care. It can also improve diagnostic accuracy by analyzing patient data and diagnostic images, providing differential diagnoses, and increasing access to care by providing medical information and essential online services to patients.2
High Reliability Organizations
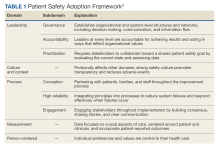
High reliability health care organizations have considerable experience safely launching new programs. For example, the Patient Safety Adoption Framework gives practical tips for smoothly rolling out safety initiatives (Table 1). Developed with experts and diverse views, this framework has 5 key areas: leadership, culture and context, process, measurement, and person-centeredness. These address adoption problems, guide leaders step-by-step, and focus on leadership buy-in, safety culture, cooperation, and local customization. Checklists and tools make it systematic to go from ideas to action on patient safety.3
Leadership involves establishing organizational commitment behind new safety programs. This visible commitment signals importance and priorities to others. Leaders model desired behaviors and language around safety, allocate resources, remove obstacles, and keep initiatives energized over time through consistent messaging.4 Culture and context recognizes that safety culture differs across units and facilities. Local input tailors programs to fit and examines strengths to build on, like psychological safety. Surveys gauge the existing culture and its need for change. Process details how to plan, design, test, implement, and improve new safety practices and provides a phased roadmap from idea to results. Measurement collects data to drive improvement and show impact. Metrics track progress and allow benchmarking. Person-centeredness puts patients first in safety efforts through participation, education, and transparency.
The Veterans Health Administration piloted a comprehensive high reliability hospital (HRH) model. Over 3 years, the Veterans Health Administration focused on leadership, culture, and process improvement at a hospital. After initiating the model, the pilot hospital improved its safety culture, reported more minor safety issues, and reduced deaths and complications better than other hospitals. The high-reliability approach successfully instilled principles and improved culture and outcomes. The HRH model is set to be expanded to 18 more US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) sites for further evaluation across diverse settings.5
Trustworthy AI Framework
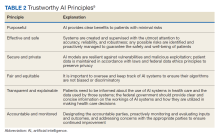
AI systems are growing more powerful and widespread, including in health care. Unfortunately, irresponsible AI can introduce new harm. ChatGPT and other large language models, for example, sometimes are known to provide erroneous information in a compelling way. Clinicians and patients who use such programs can act on such information, which would lead to unforeseen negative consequences. Several frameworks on ethical AI have come from governmental groups.6-9 In 2023, the VA National AI Institute suggested a Trustworthy AI Framework based on core principles tailored for federal health care. The framework has 6 key principles: purposeful, effective and safe, secure and private, fair and equitable, transparent and explainable, and accountable and monitored (Table 2).10
First, AI must clearly help veterans while minimizing risks. To ensure purpose, the VA will assess patient and clinician needs and design AI that targets meaningful problems to avoid scope creep or feature bloat. For example, adding new features to the AI software after release can clutter and complicate the interface, making it difficult to use. Rigorous testing will confirm that AI meets intent prior to deployment. Second, AI is designed and checked for effectiveness, safety, and reliability. The VA pledges to monitor AI’s impact to ensure it performs as expected without unintended consequences. Algorithms will be stress tested across representative datasets and approval processes will screen for safety issues. Third, AI models are secured from vulnerabilities and misuse. Technical controls will prevent unauthorized access or changes to AI systems. Audits will check for appropriate internal usage per policies. Continual patches and upgrades will maintain security. Fourth, the VA manages AI for fairness, avoiding bias. They will proactively assess datasets and algorithms for potential biases based on protected attributes like race, gender, or age. Biased outputs will be addressed through techniques such as data augmentation, reweighting, and algorithm tweaks. Fifth, transparency explains AI’s role in care. Documentation will detail an AI system’s data sources, methodology, testing, limitations, and integration with clinical workflows. Clinicians and patients will receive education on interpreting AI outputs. Finally, the VA pledges to closely monitor AI systems to sustain trust. The VA will establish oversight processes to quickly identify any declines in reliability or unfair impacts on subgroups. AI models will be retrained as needed based on incoming data patterns.
Each Trustworthy AI Framework principle connects to others in existing frameworks. The purpose principle aligns with human-centric AI focused on benefits. Effectiveness and safety link to technical robustness and risk management principles. Security maps to privacy protection principles. Fairness connects to principles of avoiding bias and discrimination. Transparency corresponds with accountable and explainable AI. Monitoring and accountability tie back to governance principles. Overall, the VA framework aims to guide ethical AI based on context. It offers a model for managing risks and building trust in health care AI.
Combining VA principles with high-reliability safety principles can ensure that AI benefits veterans. The leadership and culture aspects will drive commitment to trustworthy AI practices. Leaders will communicate the importance of responsible AI through words and actions. Culture surveys can assess baseline awareness of AI ethics issues to target education. AI security and fairness will be emphasized as safety critical. The process aspect will institute policies and procedures to uphold AI principles through the project lifecycle. For example, structured testing processes will validate safety. Measurement will collect data on principles like transparency and fairness. Dashboards can track metrics like explainability and biases. A patient-centered approach will incorporate veteran perspectives on AI through participatory design and advisory councils. They can give input on AI explainability and potential biases based on their diverse backgrounds.
Conclusions
Joint principles will lead to successful AI that improves care while proactively managing risks. Involve leaders to stress the necessity of eliminating biases. Build security into the AI development process. Co-design AI transparency features with end users. Closely monitor the impact of AI across safety, fairness, and other principles. Adhering to both Trustworthy AI and high reliability organizations principles will earn veterans’ confidence. Health care organizations like the VA can integrate ethical AI safely via established frameworks. With responsible design and implementation, AI’s potential to enhance care quality, safety, and access can be realized.
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge Joshua Mueller, Theo Tiffney, John Zachary, and Gil Alterovitz for their excellent work creating the VA Trustworthy Principles. This material is the result of work supported by resources and the use of facilities at the James A. Haley Veterans’ Hospital.
1. Sahni NR, Carrus B. Artificial intelligence in U.S. health care delivery. N Engl J Med. 2023;389(4):348-358. doi:10.1056/NEJMra2204673
2. Borkowski AA, Jakey CE, Mastorides SM, et al. Applications of ChatGPT and large language models in medicine and health care: benefits and pitfalls. Fed Pract. 2023;40(6):170-173. doi:10.12788/fp.0386
3. Moyal-Smith R, Margo J, Maloney FL, et al. The patient safety adoption framework: a practical framework to bridge the know-do gap. J Patient Saf. 2023;19(4):243-248. doi:10.1097/PTS.0000000000001118
4. Isaacks DB, Anderson TM, Moore SC, Patterson W, Govindan S. High reliability organization principles improve VA workplace burnout: the Truman THRIVE2 model. Am J Med Qual. 2021;36(6):422-428. doi:10.1097/01.JMQ.0000735516.35323.97
5. Sculli GL, Pendley-Louis R, Neily J, et al. A high-reliability organization framework for health care: a multiyear implementation strategy and associated outcomes. J Patient Saf. 2022;18(1):64-70. doi:10.1097/PTS.0000000000000788
6. National Institute of Standards and Technology. AI risk management framework. Accessed January 2, 2024. https://www.nist.gov/itl/ai-risk-management-framework
7. Executive Office of the President, Office of Science and Technology Policy. Blueprint for an AI Bill of Rights. Accessed January 11, 2024. https://www.whitehouse.gov/ostp/ai-bill-of-rights
8. Executive Office of the President. Executive Order 13960: promoting the use of trustworthy artificial intelligence in the federal government. Fed Regist. 2020;89(236):78939-78943.
9. Biden JR. Executive Order on the safe, secure, and trustworthy development and use of artificial intelligence. Published October 30, 2023. Accessed January 11, 2024. https://www.whitehouse.gov/briefing-room/presidential-actions/2023/10/30/executive-order-on-the-safe-secure-and-trustworthy-development-and-use-of-artificial-intelligence/
10. US Department of Veterans Affairs. Trustworthy AI. Accessed January 11, 2024. https://department.va.gov/ai/trustworthy/
Artificial intelligence (AI) has lagged in health care but has considerable potential to improve quality, safety, clinician experience, and access to care. It is being tested in areas like billing, hospital operations, and preventing adverse events (eg, sepsis mortality) with some early success. However, there are still many barriers preventing the widespread use of AI, such as data problems, mismatched rewards, and workplace obstacles. Innovative projects, partnerships, better rewards, and more investment could remove barriers. Implemented reliably and safely, AI can add to what clinicians know, help them work faster, cut costs, and, most importantly, improve patient care.1
AI can potentially bring several clinical benefits, such as reducing the administrative strain on clinicians and granting them more time for direct patient care. It can also improve diagnostic accuracy by analyzing patient data and diagnostic images, providing differential diagnoses, and increasing access to care by providing medical information and essential online services to patients.2
High Reliability Organizations
High reliability health care organizations have considerable experience safely launching new programs. For example, the Patient Safety Adoption Framework gives practical tips for smoothly rolling out safety initiatives (Table 1). Developed with experts and diverse views, this framework has 5 key areas: leadership, culture and context, process, measurement, and person-centeredness. These address adoption problems, guide leaders step-by-step, and focus on leadership buy-in, safety culture, cooperation, and local customization. Checklists and tools make it systematic to go from ideas to action on patient safety.3
Leadership involves establishing organizational commitment behind new safety programs. This visible commitment signals importance and priorities to others. Leaders model desired behaviors and language around safety, allocate resources, remove obstacles, and keep initiatives energized over time through consistent messaging.4 Culture and context recognizes that safety culture differs across units and facilities. Local input tailors programs to fit and examines strengths to build on, like psychological safety. Surveys gauge the existing culture and its need for change. Process details how to plan, design, test, implement, and improve new safety practices and provides a phased roadmap from idea to results. Measurement collects data to drive improvement and show impact. Metrics track progress and allow benchmarking. Person-centeredness puts patients first in safety efforts through participation, education, and transparency.
The Veterans Health Administration piloted a comprehensive high reliability hospital (HRH) model. Over 3 years, the Veterans Health Administration focused on leadership, culture, and process improvement at a hospital. After initiating the model, the pilot hospital improved its safety culture, reported more minor safety issues, and reduced deaths and complications better than other hospitals. The high-reliability approach successfully instilled principles and improved culture and outcomes. The HRH model is set to be expanded to 18 more US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) sites for further evaluation across diverse settings.5
Trustworthy AI Framework
AI systems are growing more powerful and widespread, including in health care. Unfortunately, irresponsible AI can introduce new harm. ChatGPT and other large language models, for example, sometimes are known to provide erroneous information in a compelling way. Clinicians and patients who use such programs can act on such information, which would lead to unforeseen negative consequences. Several frameworks on ethical AI have come from governmental groups.6-9 In 2023, the VA National AI Institute suggested a Trustworthy AI Framework based on core principles tailored for federal health care. The framework has 6 key principles: purposeful, effective and safe, secure and private, fair and equitable, transparent and explainable, and accountable and monitored (Table 2).10
First, AI must clearly help veterans while minimizing risks. To ensure purpose, the VA will assess patient and clinician needs and design AI that targets meaningful problems to avoid scope creep or feature bloat. For example, adding new features to the AI software after release can clutter and complicate the interface, making it difficult to use. Rigorous testing will confirm that AI meets intent prior to deployment. Second, AI is designed and checked for effectiveness, safety, and reliability. The VA pledges to monitor AI’s impact to ensure it performs as expected without unintended consequences. Algorithms will be stress tested across representative datasets and approval processes will screen for safety issues. Third, AI models are secured from vulnerabilities and misuse. Technical controls will prevent unauthorized access or changes to AI systems. Audits will check for appropriate internal usage per policies. Continual patches and upgrades will maintain security. Fourth, the VA manages AI for fairness, avoiding bias. They will proactively assess datasets and algorithms for potential biases based on protected attributes like race, gender, or age. Biased outputs will be addressed through techniques such as data augmentation, reweighting, and algorithm tweaks. Fifth, transparency explains AI’s role in care. Documentation will detail an AI system’s data sources, methodology, testing, limitations, and integration with clinical workflows. Clinicians and patients will receive education on interpreting AI outputs. Finally, the VA pledges to closely monitor AI systems to sustain trust. The VA will establish oversight processes to quickly identify any declines in reliability or unfair impacts on subgroups. AI models will be retrained as needed based on incoming data patterns.
Each Trustworthy AI Framework principle connects to others in existing frameworks. The purpose principle aligns with human-centric AI focused on benefits. Effectiveness and safety link to technical robustness and risk management principles. Security maps to privacy protection principles. Fairness connects to principles of avoiding bias and discrimination. Transparency corresponds with accountable and explainable AI. Monitoring and accountability tie back to governance principles. Overall, the VA framework aims to guide ethical AI based on context. It offers a model for managing risks and building trust in health care AI.
Combining VA principles with high-reliability safety principles can ensure that AI benefits veterans. The leadership and culture aspects will drive commitment to trustworthy AI practices. Leaders will communicate the importance of responsible AI through words and actions. Culture surveys can assess baseline awareness of AI ethics issues to target education. AI security and fairness will be emphasized as safety critical. The process aspect will institute policies and procedures to uphold AI principles through the project lifecycle. For example, structured testing processes will validate safety. Measurement will collect data on principles like transparency and fairness. Dashboards can track metrics like explainability and biases. A patient-centered approach will incorporate veteran perspectives on AI through participatory design and advisory councils. They can give input on AI explainability and potential biases based on their diverse backgrounds.
Conclusions
Joint principles will lead to successful AI that improves care while proactively managing risks. Involve leaders to stress the necessity of eliminating biases. Build security into the AI development process. Co-design AI transparency features with end users. Closely monitor the impact of AI across safety, fairness, and other principles. Adhering to both Trustworthy AI and high reliability organizations principles will earn veterans’ confidence. Health care organizations like the VA can integrate ethical AI safely via established frameworks. With responsible design and implementation, AI’s potential to enhance care quality, safety, and access can be realized.
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge Joshua Mueller, Theo Tiffney, John Zachary, and Gil Alterovitz for their excellent work creating the VA Trustworthy Principles. This material is the result of work supported by resources and the use of facilities at the James A. Haley Veterans’ Hospital.
Artificial intelligence (AI) has lagged in health care but has considerable potential to improve quality, safety, clinician experience, and access to care. It is being tested in areas like billing, hospital operations, and preventing adverse events (eg, sepsis mortality) with some early success. However, there are still many barriers preventing the widespread use of AI, such as data problems, mismatched rewards, and workplace obstacles. Innovative projects, partnerships, better rewards, and more investment could remove barriers. Implemented reliably and safely, AI can add to what clinicians know, help them work faster, cut costs, and, most importantly, improve patient care.1
AI can potentially bring several clinical benefits, such as reducing the administrative strain on clinicians and granting them more time for direct patient care. It can also improve diagnostic accuracy by analyzing patient data and diagnostic images, providing differential diagnoses, and increasing access to care by providing medical information and essential online services to patients.2
High Reliability Organizations
High reliability health care organizations have considerable experience safely launching new programs. For example, the Patient Safety Adoption Framework gives practical tips for smoothly rolling out safety initiatives (Table 1). Developed with experts and diverse views, this framework has 5 key areas: leadership, culture and context, process, measurement, and person-centeredness. These address adoption problems, guide leaders step-by-step, and focus on leadership buy-in, safety culture, cooperation, and local customization. Checklists and tools make it systematic to go from ideas to action on patient safety.3
Leadership involves establishing organizational commitment behind new safety programs. This visible commitment signals importance and priorities to others. Leaders model desired behaviors and language around safety, allocate resources, remove obstacles, and keep initiatives energized over time through consistent messaging.4 Culture and context recognizes that safety culture differs across units and facilities. Local input tailors programs to fit and examines strengths to build on, like psychological safety. Surveys gauge the existing culture and its need for change. Process details how to plan, design, test, implement, and improve new safety practices and provides a phased roadmap from idea to results. Measurement collects data to drive improvement and show impact. Metrics track progress and allow benchmarking. Person-centeredness puts patients first in safety efforts through participation, education, and transparency.
The Veterans Health Administration piloted a comprehensive high reliability hospital (HRH) model. Over 3 years, the Veterans Health Administration focused on leadership, culture, and process improvement at a hospital. After initiating the model, the pilot hospital improved its safety culture, reported more minor safety issues, and reduced deaths and complications better than other hospitals. The high-reliability approach successfully instilled principles and improved culture and outcomes. The HRH model is set to be expanded to 18 more US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) sites for further evaluation across diverse settings.5
Trustworthy AI Framework
AI systems are growing more powerful and widespread, including in health care. Unfortunately, irresponsible AI can introduce new harm. ChatGPT and other large language models, for example, sometimes are known to provide erroneous information in a compelling way. Clinicians and patients who use such programs can act on such information, which would lead to unforeseen negative consequences. Several frameworks on ethical AI have come from governmental groups.6-9 In 2023, the VA National AI Institute suggested a Trustworthy AI Framework based on core principles tailored for federal health care. The framework has 6 key principles: purposeful, effective and safe, secure and private, fair and equitable, transparent and explainable, and accountable and monitored (Table 2).10
First, AI must clearly help veterans while minimizing risks. To ensure purpose, the VA will assess patient and clinician needs and design AI that targets meaningful problems to avoid scope creep or feature bloat. For example, adding new features to the AI software after release can clutter and complicate the interface, making it difficult to use. Rigorous testing will confirm that AI meets intent prior to deployment. Second, AI is designed and checked for effectiveness, safety, and reliability. The VA pledges to monitor AI’s impact to ensure it performs as expected without unintended consequences. Algorithms will be stress tested across representative datasets and approval processes will screen for safety issues. Third, AI models are secured from vulnerabilities and misuse. Technical controls will prevent unauthorized access or changes to AI systems. Audits will check for appropriate internal usage per policies. Continual patches and upgrades will maintain security. Fourth, the VA manages AI for fairness, avoiding bias. They will proactively assess datasets and algorithms for potential biases based on protected attributes like race, gender, or age. Biased outputs will be addressed through techniques such as data augmentation, reweighting, and algorithm tweaks. Fifth, transparency explains AI’s role in care. Documentation will detail an AI system’s data sources, methodology, testing, limitations, and integration with clinical workflows. Clinicians and patients will receive education on interpreting AI outputs. Finally, the VA pledges to closely monitor AI systems to sustain trust. The VA will establish oversight processes to quickly identify any declines in reliability or unfair impacts on subgroups. AI models will be retrained as needed based on incoming data patterns.
Each Trustworthy AI Framework principle connects to others in existing frameworks. The purpose principle aligns with human-centric AI focused on benefits. Effectiveness and safety link to technical robustness and risk management principles. Security maps to privacy protection principles. Fairness connects to principles of avoiding bias and discrimination. Transparency corresponds with accountable and explainable AI. Monitoring and accountability tie back to governance principles. Overall, the VA framework aims to guide ethical AI based on context. It offers a model for managing risks and building trust in health care AI.
Combining VA principles with high-reliability safety principles can ensure that AI benefits veterans. The leadership and culture aspects will drive commitment to trustworthy AI practices. Leaders will communicate the importance of responsible AI through words and actions. Culture surveys can assess baseline awareness of AI ethics issues to target education. AI security and fairness will be emphasized as safety critical. The process aspect will institute policies and procedures to uphold AI principles through the project lifecycle. For example, structured testing processes will validate safety. Measurement will collect data on principles like transparency and fairness. Dashboards can track metrics like explainability and biases. A patient-centered approach will incorporate veteran perspectives on AI through participatory design and advisory councils. They can give input on AI explainability and potential biases based on their diverse backgrounds.
Conclusions
Joint principles will lead to successful AI that improves care while proactively managing risks. Involve leaders to stress the necessity of eliminating biases. Build security into the AI development process. Co-design AI transparency features with end users. Closely monitor the impact of AI across safety, fairness, and other principles. Adhering to both Trustworthy AI and high reliability organizations principles will earn veterans’ confidence. Health care organizations like the VA can integrate ethical AI safely via established frameworks. With responsible design and implementation, AI’s potential to enhance care quality, safety, and access can be realized.
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge Joshua Mueller, Theo Tiffney, John Zachary, and Gil Alterovitz for their excellent work creating the VA Trustworthy Principles. This material is the result of work supported by resources and the use of facilities at the James A. Haley Veterans’ Hospital.
1. Sahni NR, Carrus B. Artificial intelligence in U.S. health care delivery. N Engl J Med. 2023;389(4):348-358. doi:10.1056/NEJMra2204673
2. Borkowski AA, Jakey CE, Mastorides SM, et al. Applications of ChatGPT and large language models in medicine and health care: benefits and pitfalls. Fed Pract. 2023;40(6):170-173. doi:10.12788/fp.0386
3. Moyal-Smith R, Margo J, Maloney FL, et al. The patient safety adoption framework: a practical framework to bridge the know-do gap. J Patient Saf. 2023;19(4):243-248. doi:10.1097/PTS.0000000000001118
4. Isaacks DB, Anderson TM, Moore SC, Patterson W, Govindan S. High reliability organization principles improve VA workplace burnout: the Truman THRIVE2 model. Am J Med Qual. 2021;36(6):422-428. doi:10.1097/01.JMQ.0000735516.35323.97
5. Sculli GL, Pendley-Louis R, Neily J, et al. A high-reliability organization framework for health care: a multiyear implementation strategy and associated outcomes. J Patient Saf. 2022;18(1):64-70. doi:10.1097/PTS.0000000000000788
6. National Institute of Standards and Technology. AI risk management framework. Accessed January 2, 2024. https://www.nist.gov/itl/ai-risk-management-framework
7. Executive Office of the President, Office of Science and Technology Policy. Blueprint for an AI Bill of Rights. Accessed January 11, 2024. https://www.whitehouse.gov/ostp/ai-bill-of-rights
8. Executive Office of the President. Executive Order 13960: promoting the use of trustworthy artificial intelligence in the federal government. Fed Regist. 2020;89(236):78939-78943.
9. Biden JR. Executive Order on the safe, secure, and trustworthy development and use of artificial intelligence. Published October 30, 2023. Accessed January 11, 2024. https://www.whitehouse.gov/briefing-room/presidential-actions/2023/10/30/executive-order-on-the-safe-secure-and-trustworthy-development-and-use-of-artificial-intelligence/
10. US Department of Veterans Affairs. Trustworthy AI. Accessed January 11, 2024. https://department.va.gov/ai/trustworthy/
1. Sahni NR, Carrus B. Artificial intelligence in U.S. health care delivery. N Engl J Med. 2023;389(4):348-358. doi:10.1056/NEJMra2204673
2. Borkowski AA, Jakey CE, Mastorides SM, et al. Applications of ChatGPT and large language models in medicine and health care: benefits and pitfalls. Fed Pract. 2023;40(6):170-173. doi:10.12788/fp.0386
3. Moyal-Smith R, Margo J, Maloney FL, et al. The patient safety adoption framework: a practical framework to bridge the know-do gap. J Patient Saf. 2023;19(4):243-248. doi:10.1097/PTS.0000000000001118
4. Isaacks DB, Anderson TM, Moore SC, Patterson W, Govindan S. High reliability organization principles improve VA workplace burnout: the Truman THRIVE2 model. Am J Med Qual. 2021;36(6):422-428. doi:10.1097/01.JMQ.0000735516.35323.97
5. Sculli GL, Pendley-Louis R, Neily J, et al. A high-reliability organization framework for health care: a multiyear implementation strategy and associated outcomes. J Patient Saf. 2022;18(1):64-70. doi:10.1097/PTS.0000000000000788
6. National Institute of Standards and Technology. AI risk management framework. Accessed January 2, 2024. https://www.nist.gov/itl/ai-risk-management-framework
7. Executive Office of the President, Office of Science and Technology Policy. Blueprint for an AI Bill of Rights. Accessed January 11, 2024. https://www.whitehouse.gov/ostp/ai-bill-of-rights
8. Executive Office of the President. Executive Order 13960: promoting the use of trustworthy artificial intelligence in the federal government. Fed Regist. 2020;89(236):78939-78943.
9. Biden JR. Executive Order on the safe, secure, and trustworthy development and use of artificial intelligence. Published October 30, 2023. Accessed January 11, 2024. https://www.whitehouse.gov/briefing-room/presidential-actions/2023/10/30/executive-order-on-the-safe-secure-and-trustworthy-development-and-use-of-artificial-intelligence/
10. US Department of Veterans Affairs. Trustworthy AI. Accessed January 11, 2024. https://department.va.gov/ai/trustworthy/
Psychogenic Purpura
To the Editor:
A 14-year-old Black adolescent girl presented with episodic, painful, edematous plaques that occurred symmetrically on the arms and legs of 5 years’ duration. The plaques evolved into hyperpigmented patches within 24 to 48 hours before eventually resolving. Fatigue, headache, arthralgias of the arms and legs, chest pain, abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting variably accompanied these episodes.
Prior to visiting our clinic, the patient had been seen by numerous specialists. A review of her medical records revealed an initial diagnosis of Henoch-Schönlein purpura (HSP), then urticarial vasculitis. She had been treated with antihistamines, topical and systemic steroids, hydroxychloroquine, mycophenolate mofetil, dapsone, azathioprine, and gabapentin. All treatments were ineffectual. She underwent extensive diagnostic testing and imaging, which were normal or noncontributory, including type I allergy testing; multiple exhaustive batteries of hematologic testing; and computed tomography/magnetic resonance imaging/magnetic resonance angiography of the brain, chest, abdomen, and pelvic region. Biopsies from symptomatic segments of the gastrointestinal tract were normal.
Chronic treatment with systemic steroids over 9 months resulted in gastritis and an episode of hematemesis requiring emergent hospitalization. A lengthy multidisciplinary evaluation was conducted at the patient’s local community hospital; the team concluded that she had an urticarial-type rash with accompanying symptoms that did not have an autoimmune, rheumatologic, or inflammatory basis.
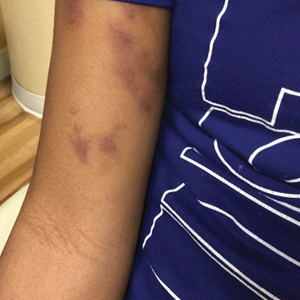
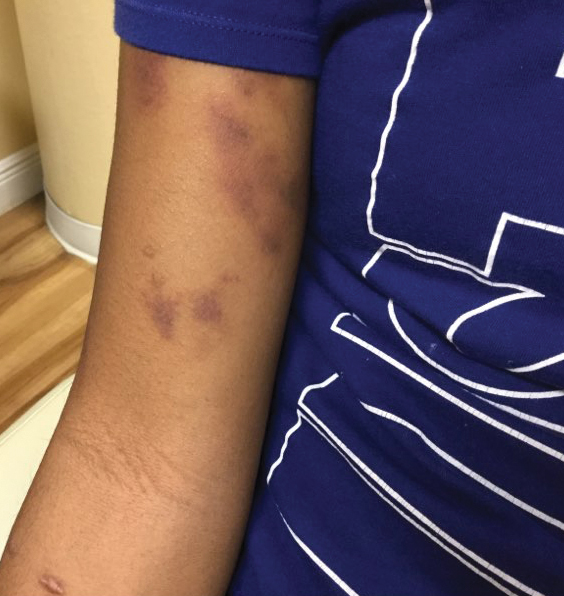
The patient’s medical history was remarkable for recent-onset panic attacks. Her family medical history was noncontributory. Physical examination revealed multiple violaceous hyperpigmented patches diffusely located on the proximal upper arms (Figure 1). There were no additional findings on physical examination.
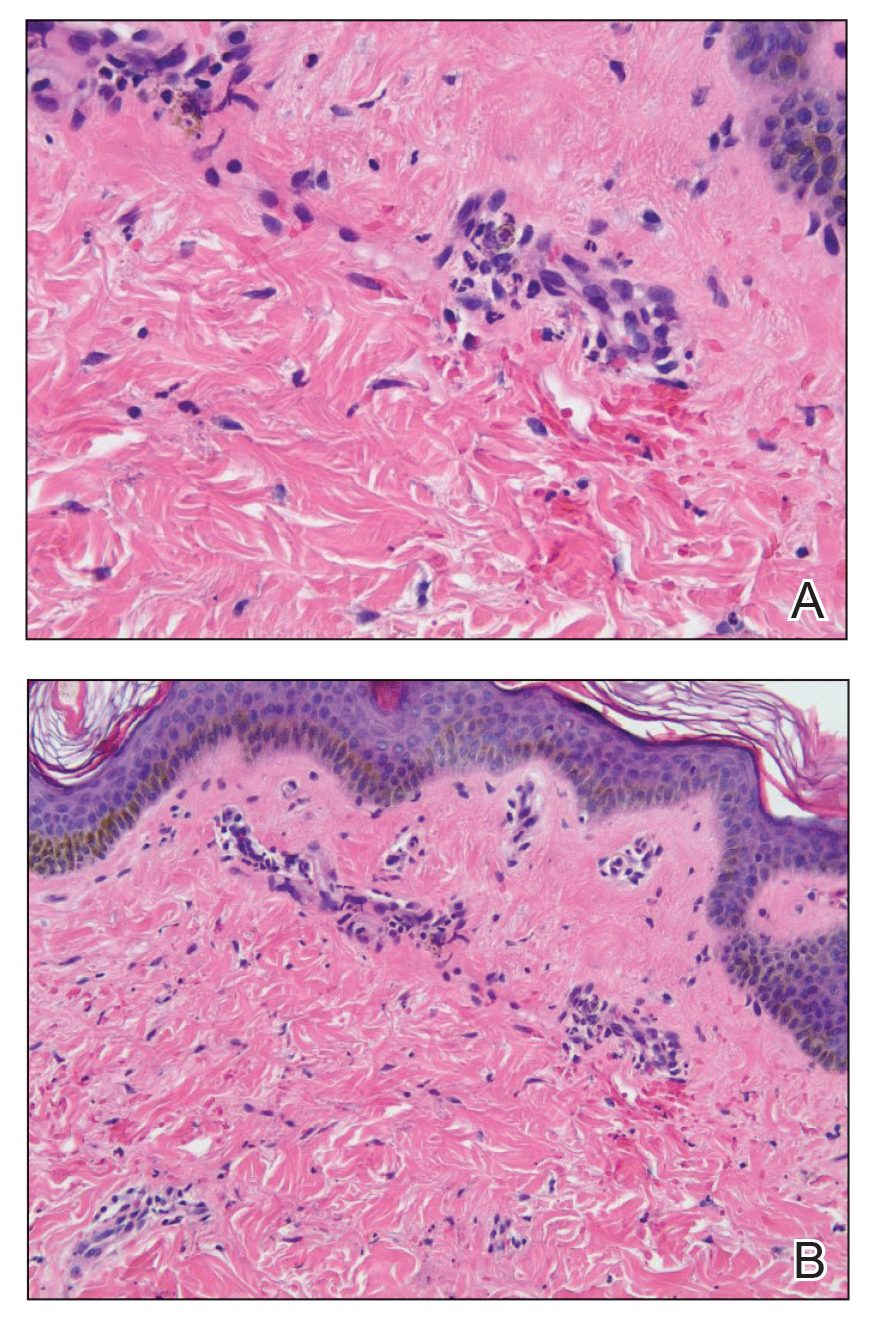
Punch biopsies were performed on lesional areas of the arm. Histopathology indicated a mild superficial perivascular dermal mixed infiltrate and extravasated erythrocytes (Figure 2). Direct immunofluorescence (DIF) testing was negative for vasculitis. Immunohistochemical stains for CD117 and tryptase demonstrated a slight increase in the number of dermal mast cells; however, the increase was not sufficient to diagnose cutaneous mastocytosis, which was in the differential. We proposed a diagnosis of psychogenic purpura (PP)(also known as Gardner-Diamond syndrome). She was treated with gabapentin, a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor, and cognitive therapy. Unfortunately, after starting therapy the patient was lost to follow-up.
Psychogenic purpura is a rare vasculopathy of unknown etiology that may be a special form of factitious disorder.1,2 In one study, PP occurred predominantly in females aged 15 to 66 years, with a median onset age of 33 years.3 A prodrome of localized itching, burning, and/or pain precedes the development of edematous plaques. The plaques evolve into painful ecchymoses within 1 to 2 days and resolve in 10 days or fewer without treatment. Lesions most commonly occur on the extremities but may occur anywhere on the body. The most common associated finding is an underlying depressive disorder. Episodes may be accompanied by headache, dizziness, fatigue, fever, arthralgia, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, menstrual irregularities, myalgia, and urologic conditions.
In 1955, Gardner and Diamond4 described the first cases of PP in 4 female patients at Peter Bent Brigham Hospital in Boston, Massachusetts. The investigators were able to replicate the painful ecchymoses with intradermal injection of the patient’s own erythrocytes into the skin. They proposed that the underlying pathogenesis involved autosensitization to erythrocyte stroma.4 Since then, others have suggested that the pathogenesis may include autosensitization to erythrocyte phosphatidylserine, tonus dysregulation of venous capillaries, abnormal endothelial fibrin synthesis, and capillary wall instability.5-7
Histopathology typically reveals superficial and deep perivascular inflammation with extravasated erythrocytes. Direct immunofluorescence is negative for vasculitis.8 Diagnostics and laboratory findings for underlying systemic illness are negative or noncontributory. Cutaneous injection of 1 mL of the patient’s own washed erythrocytes may result in the formation of the characteristic painful plaques within 24 hours; however, this test is limited by lack of standardization and low sensitivity.3
Psychogenic purpura may share clinical features with cutaneous small vessel vasculitis, such as HSP or urticarial vasculitis. Some of the findings that our patient was experiencing, including purpura, arthralgia, and abdominal pain, are associated with HSP. However, HSP typically is self-limiting and classically features palpable purpura distributed across the lower extremities and buttocks. Histopathology demonstrates the classic findings of leukocytoclastic vasculitis; DIF typically is positive for perivascular IgA and C3 deposition. Increased serum IgA may be present.9 Urticarial vasculitis appears as erythematous indurated wheals that favor a proximal extremity and truncal distribution. They characteristically last longer than 24 hours, are frequently associated with nonprodromal pain or burning, and resolve with hyperpigmentation. Arthralgia and gastrointestinal, renal, pulmonary, cardiac, and neurologic symptoms may be present, especially in patients with low complement levels.10 Skin biopsy demonstrates leukocytoclasia that must be accompanied by vessel wall necrosis. Fibrinoid deposition, erythrocyte extravasation, or perivascular inflammation may be present. In 70% of cases revealing perivascular immunoglobulin, C3, and fibrinogen deposition, DIF is positive. Serum C1q autoantibody may be associated with the hypocomplementemic form.10
The classic histopathologic findings in leukocytoclastic vasculitis include transmural neutrophilic infiltration of the walls of small vessels, fibrinoid necrosis of vessel walls, leukocytoclasia, extravasated erythrocytes, and signs of endothelial cell damage.9 A prior punch biopsy in this patient demonstrated rare neutrophilic nuclear debris within the vessel walls without fibrin deposition. Although the presence of nuclear debris and extravasated erythrocytes could be compatible with a manifestation of urticarial vasculitis, the lack of direct evidence of vessel wall necrosis combined with subsequent biopsies unequivocally ruled out cutaneous small vessel vasculitis in our patient.
Psychogenic purpura has been reported to occur frequently in the background of psycho-emotional distress. In 1989, Ratnoff11 noted that many of the patients he was treating at the University Hospitals of Cleveland, Ohio, had a depressive syndrome. A review of patients treated at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota, illustrated concomitant psychiatric illnesses in 41 of 76 (54%) patients treated for PP, most commonly depressive, personality, and anxiety disorders.3
There is no consensus on therapy for PP. Treatment is based on providing symptomatic relief and relieving underlying psychiatric distress. Block et al12 found the use of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, tricyclic antidepressants, and psychotherapy to be successful in improving symptoms and reducing lesions at follow-up visits.
- Piette WW. Purpura: mechanisms and differential diagnosis. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2018:376-389.
- Harth W, Taube KM, Gieler U. Factitious disorders in dermatology. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2010;8:361-372.
- Sridharan M, Ali U, Hook CC, et al. The Mayo Clinic experience with psychogenic purpura (Gardner-Diamond syndrome). Am J Med Sci. 2019;357:411‐420.
- Gardner FH, Diamond LK. Autoerythrocyte sensitization; a form of purpura producing painful bruising following autosensitization to red blood cells in certain women. Blood. 1955;10:675-690.
- Groch GS, Finch SC, Rogoway W, et al. Studies in the pathogenesis of autoerythrocyte sensitization syndrome. Blood. 1966;28:19-33.
- Strunecká A, Krpejsová L, Palecek J, et al. Transbilayer redistribution of phosphatidylserine in erythrocytes of a patient with autoerythrocyte sensitization syndrome (psychogenic purpura). Folia Haematol Int Mag Klin Morphol Blutforsch. 1990;117:829-841.
- Merlen JF. Ecchymotic patches of the fingers and Gardner-Diamond vascular purpura. Phlebologie. 1987;40:473-487.
- Ivanov OL, Lvov AN, Michenko AV, et al. Autoerythrocyte sensitization syndrome (Gardner-Diamond syndrome): review of the literature. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2009;23:499-504.
- Wetter DA, Dutz JP, Shinkai K, et al. Cutaneous vasculitis. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2018:409-439.
- Hamad A, Jithpratuck W, Krishnaswamy G. Urticarial vasculitis and associated disorders. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2017;118:394-398.
- Ratnoff OD. Psychogenic purpura (autoerythrocyte sensitization): an unsolved dilemma. Am J Med. 1989;87:16N-21N.
- Block ME, Sitenga JL, Lehrer M, et al. Gardner‐Diamond syndrome: a systematic review of treatment options for a rare psychodermatological disorder. Int J Dermatol. 2019;58:782-787.
To the Editor:
A 14-year-old Black adolescent girl presented with episodic, painful, edematous plaques that occurred symmetrically on the arms and legs of 5 years’ duration. The plaques evolved into hyperpigmented patches within 24 to 48 hours before eventually resolving. Fatigue, headache, arthralgias of the arms and legs, chest pain, abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting variably accompanied these episodes.
Prior to visiting our clinic, the patient had been seen by numerous specialists. A review of her medical records revealed an initial diagnosis of Henoch-Schönlein purpura (HSP), then urticarial vasculitis. She had been treated with antihistamines, topical and systemic steroids, hydroxychloroquine, mycophenolate mofetil, dapsone, azathioprine, and gabapentin. All treatments were ineffectual. She underwent extensive diagnostic testing and imaging, which were normal or noncontributory, including type I allergy testing; multiple exhaustive batteries of hematologic testing; and computed tomography/magnetic resonance imaging/magnetic resonance angiography of the brain, chest, abdomen, and pelvic region. Biopsies from symptomatic segments of the gastrointestinal tract were normal.
Chronic treatment with systemic steroids over 9 months resulted in gastritis and an episode of hematemesis requiring emergent hospitalization. A lengthy multidisciplinary evaluation was conducted at the patient’s local community hospital; the team concluded that she had an urticarial-type rash with accompanying symptoms that did not have an autoimmune, rheumatologic, or inflammatory basis.
The patient’s medical history was remarkable for recent-onset panic attacks. Her family medical history was noncontributory. Physical examination revealed multiple violaceous hyperpigmented patches diffusely located on the proximal upper arms (Figure 1). There were no additional findings on physical examination.

Punch biopsies were performed on lesional areas of the arm. Histopathology indicated a mild superficial perivascular dermal mixed infiltrate and extravasated erythrocytes (Figure 2). Direct immunofluorescence (DIF) testing was negative for vasculitis. Immunohistochemical stains for CD117 and tryptase demonstrated a slight increase in the number of dermal mast cells; however, the increase was not sufficient to diagnose cutaneous mastocytosis, which was in the differential. We proposed a diagnosis of psychogenic purpura (PP)(also known as Gardner-Diamond syndrome). She was treated with gabapentin, a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor, and cognitive therapy. Unfortunately, after starting therapy the patient was lost to follow-up.

Psychogenic purpura is a rare vasculopathy of unknown etiology that may be a special form of factitious disorder.1,2 In one study, PP occurred predominantly in females aged 15 to 66 years, with a median onset age of 33 years.3 A prodrome of localized itching, burning, and/or pain precedes the development of edematous plaques. The plaques evolve into painful ecchymoses within 1 to 2 days and resolve in 10 days or fewer without treatment. Lesions most commonly occur on the extremities but may occur anywhere on the body. The most common associated finding is an underlying depressive disorder. Episodes may be accompanied by headache, dizziness, fatigue, fever, arthralgia, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, menstrual irregularities, myalgia, and urologic conditions.
In 1955, Gardner and Diamond4 described the first cases of PP in 4 female patients at Peter Bent Brigham Hospital in Boston, Massachusetts. The investigators were able to replicate the painful ecchymoses with intradermal injection of the patient’s own erythrocytes into the skin. They proposed that the underlying pathogenesis involved autosensitization to erythrocyte stroma.4 Since then, others have suggested that the pathogenesis may include autosensitization to erythrocyte phosphatidylserine, tonus dysregulation of venous capillaries, abnormal endothelial fibrin synthesis, and capillary wall instability.5-7
Histopathology typically reveals superficial and deep perivascular inflammation with extravasated erythrocytes. Direct immunofluorescence is negative for vasculitis.8 Diagnostics and laboratory findings for underlying systemic illness are negative or noncontributory. Cutaneous injection of 1 mL of the patient’s own washed erythrocytes may result in the formation of the characteristic painful plaques within 24 hours; however, this test is limited by lack of standardization and low sensitivity.3
Psychogenic purpura may share clinical features with cutaneous small vessel vasculitis, such as HSP or urticarial vasculitis. Some of the findings that our patient was experiencing, including purpura, arthralgia, and abdominal pain, are associated with HSP. However, HSP typically is self-limiting and classically features palpable purpura distributed across the lower extremities and buttocks. Histopathology demonstrates the classic findings of leukocytoclastic vasculitis; DIF typically is positive for perivascular IgA and C3 deposition. Increased serum IgA may be present.9 Urticarial vasculitis appears as erythematous indurated wheals that favor a proximal extremity and truncal distribution. They characteristically last longer than 24 hours, are frequently associated with nonprodromal pain or burning, and resolve with hyperpigmentation. Arthralgia and gastrointestinal, renal, pulmonary, cardiac, and neurologic symptoms may be present, especially in patients with low complement levels.10 Skin biopsy demonstrates leukocytoclasia that must be accompanied by vessel wall necrosis. Fibrinoid deposition, erythrocyte extravasation, or perivascular inflammation may be present. In 70% of cases revealing perivascular immunoglobulin, C3, and fibrinogen deposition, DIF is positive. Serum C1q autoantibody may be associated with the hypocomplementemic form.10
The classic histopathologic findings in leukocytoclastic vasculitis include transmural neutrophilic infiltration of the walls of small vessels, fibrinoid necrosis of vessel walls, leukocytoclasia, extravasated erythrocytes, and signs of endothelial cell damage.9 A prior punch biopsy in this patient demonstrated rare neutrophilic nuclear debris within the vessel walls without fibrin deposition. Although the presence of nuclear debris and extravasated erythrocytes could be compatible with a manifestation of urticarial vasculitis, the lack of direct evidence of vessel wall necrosis combined with subsequent biopsies unequivocally ruled out cutaneous small vessel vasculitis in our patient.
Psychogenic purpura has been reported to occur frequently in the background of psycho-emotional distress. In 1989, Ratnoff11 noted that many of the patients he was treating at the University Hospitals of Cleveland, Ohio, had a depressive syndrome. A review of patients treated at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota, illustrated concomitant psychiatric illnesses in 41 of 76 (54%) patients treated for PP, most commonly depressive, personality, and anxiety disorders.3
There is no consensus on therapy for PP. Treatment is based on providing symptomatic relief and relieving underlying psychiatric distress. Block et al12 found the use of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, tricyclic antidepressants, and psychotherapy to be successful in improving symptoms and reducing lesions at follow-up visits.
To the Editor:
A 14-year-old Black adolescent girl presented with episodic, painful, edematous plaques that occurred symmetrically on the arms and legs of 5 years’ duration. The plaques evolved into hyperpigmented patches within 24 to 48 hours before eventually resolving. Fatigue, headache, arthralgias of the arms and legs, chest pain, abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting variably accompanied these episodes.
Prior to visiting our clinic, the patient had been seen by numerous specialists. A review of her medical records revealed an initial diagnosis of Henoch-Schönlein purpura (HSP), then urticarial vasculitis. She had been treated with antihistamines, topical and systemic steroids, hydroxychloroquine, mycophenolate mofetil, dapsone, azathioprine, and gabapentin. All treatments were ineffectual. She underwent extensive diagnostic testing and imaging, which were normal or noncontributory, including type I allergy testing; multiple exhaustive batteries of hematologic testing; and computed tomography/magnetic resonance imaging/magnetic resonance angiography of the brain, chest, abdomen, and pelvic region. Biopsies from symptomatic segments of the gastrointestinal tract were normal.
Chronic treatment with systemic steroids over 9 months resulted in gastritis and an episode of hematemesis requiring emergent hospitalization. A lengthy multidisciplinary evaluation was conducted at the patient’s local community hospital; the team concluded that she had an urticarial-type rash with accompanying symptoms that did not have an autoimmune, rheumatologic, or inflammatory basis.
The patient’s medical history was remarkable for recent-onset panic attacks. Her family medical history was noncontributory. Physical examination revealed multiple violaceous hyperpigmented patches diffusely located on the proximal upper arms (Figure 1). There were no additional findings on physical examination.

Punch biopsies were performed on lesional areas of the arm. Histopathology indicated a mild superficial perivascular dermal mixed infiltrate and extravasated erythrocytes (Figure 2). Direct immunofluorescence (DIF) testing was negative for vasculitis. Immunohistochemical stains for CD117 and tryptase demonstrated a slight increase in the number of dermal mast cells; however, the increase was not sufficient to diagnose cutaneous mastocytosis, which was in the differential. We proposed a diagnosis of psychogenic purpura (PP)(also known as Gardner-Diamond syndrome). She was treated with gabapentin, a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor, and cognitive therapy. Unfortunately, after starting therapy the patient was lost to follow-up.

Psychogenic purpura is a rare vasculopathy of unknown etiology that may be a special form of factitious disorder.1,2 In one study, PP occurred predominantly in females aged 15 to 66 years, with a median onset age of 33 years.3 A prodrome of localized itching, burning, and/or pain precedes the development of edematous plaques. The plaques evolve into painful ecchymoses within 1 to 2 days and resolve in 10 days or fewer without treatment. Lesions most commonly occur on the extremities but may occur anywhere on the body. The most common associated finding is an underlying depressive disorder. Episodes may be accompanied by headache, dizziness, fatigue, fever, arthralgia, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, menstrual irregularities, myalgia, and urologic conditions.
In 1955, Gardner and Diamond4 described the first cases of PP in 4 female patients at Peter Bent Brigham Hospital in Boston, Massachusetts. The investigators were able to replicate the painful ecchymoses with intradermal injection of the patient’s own erythrocytes into the skin. They proposed that the underlying pathogenesis involved autosensitization to erythrocyte stroma.4 Since then, others have suggested that the pathogenesis may include autosensitization to erythrocyte phosphatidylserine, tonus dysregulation of venous capillaries, abnormal endothelial fibrin synthesis, and capillary wall instability.5-7
Histopathology typically reveals superficial and deep perivascular inflammation with extravasated erythrocytes. Direct immunofluorescence is negative for vasculitis.8 Diagnostics and laboratory findings for underlying systemic illness are negative or noncontributory. Cutaneous injection of 1 mL of the patient’s own washed erythrocytes may result in the formation of the characteristic painful plaques within 24 hours; however, this test is limited by lack of standardization and low sensitivity.3
Psychogenic purpura may share clinical features with cutaneous small vessel vasculitis, such as HSP or urticarial vasculitis. Some of the findings that our patient was experiencing, including purpura, arthralgia, and abdominal pain, are associated with HSP. However, HSP typically is self-limiting and classically features palpable purpura distributed across the lower extremities and buttocks. Histopathology demonstrates the classic findings of leukocytoclastic vasculitis; DIF typically is positive for perivascular IgA and C3 deposition. Increased serum IgA may be present.9 Urticarial vasculitis appears as erythematous indurated wheals that favor a proximal extremity and truncal distribution. They characteristically last longer than 24 hours, are frequently associated with nonprodromal pain or burning, and resolve with hyperpigmentation. Arthralgia and gastrointestinal, renal, pulmonary, cardiac, and neurologic symptoms may be present, especially in patients with low complement levels.10 Skin biopsy demonstrates leukocytoclasia that must be accompanied by vessel wall necrosis. Fibrinoid deposition, erythrocyte extravasation, or perivascular inflammation may be present. In 70% of cases revealing perivascular immunoglobulin, C3, and fibrinogen deposition, DIF is positive. Serum C1q autoantibody may be associated with the hypocomplementemic form.10
The classic histopathologic findings in leukocytoclastic vasculitis include transmural neutrophilic infiltration of the walls of small vessels, fibrinoid necrosis of vessel walls, leukocytoclasia, extravasated erythrocytes, and signs of endothelial cell damage.9 A prior punch biopsy in this patient demonstrated rare neutrophilic nuclear debris within the vessel walls without fibrin deposition. Although the presence of nuclear debris and extravasated erythrocytes could be compatible with a manifestation of urticarial vasculitis, the lack of direct evidence of vessel wall necrosis combined with subsequent biopsies unequivocally ruled out cutaneous small vessel vasculitis in our patient.
Psychogenic purpura has been reported to occur frequently in the background of psycho-emotional distress. In 1989, Ratnoff11 noted that many of the patients he was treating at the University Hospitals of Cleveland, Ohio, had a depressive syndrome. A review of patients treated at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota, illustrated concomitant psychiatric illnesses in 41 of 76 (54%) patients treated for PP, most commonly depressive, personality, and anxiety disorders.3
There is no consensus on therapy for PP. Treatment is based on providing symptomatic relief and relieving underlying psychiatric distress. Block et al12 found the use of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, tricyclic antidepressants, and psychotherapy to be successful in improving symptoms and reducing lesions at follow-up visits.
- Piette WW. Purpura: mechanisms and differential diagnosis. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2018:376-389.
- Harth W, Taube KM, Gieler U. Factitious disorders in dermatology. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2010;8:361-372.
- Sridharan M, Ali U, Hook CC, et al. The Mayo Clinic experience with psychogenic purpura (Gardner-Diamond syndrome). Am J Med Sci. 2019;357:411‐420.
- Gardner FH, Diamond LK. Autoerythrocyte sensitization; a form of purpura producing painful bruising following autosensitization to red blood cells in certain women. Blood. 1955;10:675-690.
- Groch GS, Finch SC, Rogoway W, et al. Studies in the pathogenesis of autoerythrocyte sensitization syndrome. Blood. 1966;28:19-33.
- Strunecká A, Krpejsová L, Palecek J, et al. Transbilayer redistribution of phosphatidylserine in erythrocytes of a patient with autoerythrocyte sensitization syndrome (psychogenic purpura). Folia Haematol Int Mag Klin Morphol Blutforsch. 1990;117:829-841.
- Merlen JF. Ecchymotic patches of the fingers and Gardner-Diamond vascular purpura. Phlebologie. 1987;40:473-487.
- Ivanov OL, Lvov AN, Michenko AV, et al. Autoerythrocyte sensitization syndrome (Gardner-Diamond syndrome): review of the literature. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2009;23:499-504.
- Wetter DA, Dutz JP, Shinkai K, et al. Cutaneous vasculitis. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2018:409-439.
- Hamad A, Jithpratuck W, Krishnaswamy G. Urticarial vasculitis and associated disorders. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2017;118:394-398.
- Ratnoff OD. Psychogenic purpura (autoerythrocyte sensitization): an unsolved dilemma. Am J Med. 1989;87:16N-21N.
- Block ME, Sitenga JL, Lehrer M, et al. Gardner‐Diamond syndrome: a systematic review of treatment options for a rare psychodermatological disorder. Int J Dermatol. 2019;58:782-787.
- Piette WW. Purpura: mechanisms and differential diagnosis. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2018:376-389.
- Harth W, Taube KM, Gieler U. Factitious disorders in dermatology. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2010;8:361-372.
- Sridharan M, Ali U, Hook CC, et al. The Mayo Clinic experience with psychogenic purpura (Gardner-Diamond syndrome). Am J Med Sci. 2019;357:411‐420.
- Gardner FH, Diamond LK. Autoerythrocyte sensitization; a form of purpura producing painful bruising following autosensitization to red blood cells in certain women. Blood. 1955;10:675-690.
- Groch GS, Finch SC, Rogoway W, et al. Studies in the pathogenesis of autoerythrocyte sensitization syndrome. Blood. 1966;28:19-33.
- Strunecká A, Krpejsová L, Palecek J, et al. Transbilayer redistribution of phosphatidylserine in erythrocytes of a patient with autoerythrocyte sensitization syndrome (psychogenic purpura). Folia Haematol Int Mag Klin Morphol Blutforsch. 1990;117:829-841.
- Merlen JF. Ecchymotic patches of the fingers and Gardner-Diamond vascular purpura. Phlebologie. 1987;40:473-487.
- Ivanov OL, Lvov AN, Michenko AV, et al. Autoerythrocyte sensitization syndrome (Gardner-Diamond syndrome): review of the literature. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2009;23:499-504.
- Wetter DA, Dutz JP, Shinkai K, et al. Cutaneous vasculitis. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2018:409-439.
- Hamad A, Jithpratuck W, Krishnaswamy G. Urticarial vasculitis and associated disorders. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2017;118:394-398.
- Ratnoff OD. Psychogenic purpura (autoerythrocyte sensitization): an unsolved dilemma. Am J Med. 1989;87:16N-21N.
- Block ME, Sitenga JL, Lehrer M, et al. Gardner‐Diamond syndrome: a systematic review of treatment options for a rare psychodermatological disorder. Int J Dermatol. 2019;58:782-787.
PRACTICE POINTS
- Psychogenic purpura is a rare vasculopathy characterized by painful recurrent episodes of purpura. It is a diagnosis of exclusion that may manifest with signs similar to cutaneous small vessel vasculitis.
- Awareness of this condition could help prevent unnecessary diagnostics, medications, and adverse events.
What’s Eating You? Rhipicephalus Ticks Revisited
Characteristics
Rhipicephalus ticks belong to the Ixodidae family of hard-bodied ticks. They are large and teardrop shaped with an inornate scutum (hard dorsal plate) and relatively short mouthparts attached at a hexagonal basis capitulum (base of the head to which mouthparts are attached)(Figure).1 Widely spaced eyes and festoons also are present. The first pair of coxae—attachment base for the first pair of legs—are characteristically bifid; males have a pair of sclerotized adanal plates on the ventral surface adjacent to the anus as well as accessory adanal shields.2 Rhipicephalus (formerly Boophilus) microplus (the so-called cattle tick) is a newly added species; it lacks posterior festoons, and the anal groove is absent.3

Almost all Rhipicephalus ticks, except for R microplus, are 3-host ticks in which a single blood meal is consumed from a vertebrate host at each active life stage—larva, nymph, and adult—to complete development.4,5 In contrast to most ixodid ticks, which are exophilic (living outside of human habitation), the Rhipicephalus sanguineus sensu lato species (the brown dog tick) is highly endophilic (adapted to indoor living) and often can be found hidden in cracks and crevices of walls in homes and peridomestic structures.6 It is predominately monotropic (all developmental stages feed on the same host species) and has a strong host preference for dogs, though it occasionally feeds on other hosts (eg, humans).7 Although most common in tropical and subtropical climates, they can be found anywhere there are dogs due to their ability to colonize indoor dwellings.8 In contrast, R microplus ticks have a predilection for cattle and livestock rather than humans, posing a notable concern to livestock worldwide. Infestation results in transmission of disease-causing pathogens, such as Babesia and Anaplasma species, which costs the cattle industry billions of dollars annually.9
Clinical Manifestations and Treatment
Tick bites usually manifest as intensely pruritic, erythematous papules at the site of tick attachment due to a local type IV hypersensitivity reaction to antigens in the tick’s saliva. This reaction can be long-lasting. In addition to pruritic papules following a bite, an attached tick can be mistaken for a skin neoplasm or nevus. Given that ticks are small, especially during the larval stage, dermoscopy may be helpful in making a diagnosis.10 Symptomatic relief usually can be achieved with topical antipruritics or oral antihistamines.
Of public health concern, brown dog ticks are important vectors of Rickettsia rickettsii (the causative organism of Rocky Mountain spotted fever [RMSF]) in the Western hemisphere, and Rickettsia conorii (the causative organism of Mediterranean spotted fever [MSF][also known as Boutonneuse fever]) in the Eastern hemisphere.11 Bites by ticks carrying rickettsial disease classically manifest with early symptoms of fever, headache, and myalgia, followed by a rash or by a localized eschar or tache noire (a black, necrotic, scabbed lesion) that represents direct endothelial invasion and vascular damage by Rickettsia.12 Rocky Mountain spotted fever and MSF are more prevalent during summer, likely due, in part, to the combination of increased outdoor activity and a higher rate of tick-questing (host-seeking) behavior in warmer climates.4,7
Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever—Dermacentor variabilis is the primary vector of RMSF in the southeastern United States; Dermacentor andersoni is the major vector of RMSF in Rocky Mountain states. Rhipicephalus sanguineus sensu lato is an important vector of RMSF in the southwestern United States, Mexico, and Central America.11,13
Early symptoms of RMSF are nonspecific and can include fever, headache, arthralgia, myalgia, and malaise. Gastrointestinal tract symptoms (eg, nausea, vomiting, anorexia) may occur; notable abdominal pain occurs in some patients, particularly children. A characteristic petechial rash occurs in as many as 90% of patients, typically at the third to fifth day of illness, and classically begins on the wrists and ankles, with progression to the palms and soles before spreading centripetally to the arms, legs, and trunk.14 An eschar at the inoculation site is uncommon in RMSF; when present, it is more suggestive of MSF.15
The classic triad of fever, headache, and rash is present in 3% of patients during the first 3 days after a tick bite and in 60% to 70% within 2 weeks.16 A rash often is absent when patients first seek medical attention and may not develop (absent in 9% to 12% of cases; so-called spotless RMSF). Therefore, absence of rash should not be a reason to withhold treatment.16 Empiric treatment with doxycycline should be started promptly for all suspected cases of RMSF because of the rapid progression of disease and an increased risk for morbidity and mortality with delayed diagnosis.
Patients do not become antibody positive until 7 to 10 days after symptoms begin; therefore, treatment should not be delayed while awaiting serologic test results. The case fatality rate in the United States is estimated to be 5% to 10% overall and as high as 40% to 50% among patients who are not treated until day 8 or 9 of illness.17
Cutaneous complications include skin necrosis and gangrene due to continuous tissue damage in severe cases.16 Severe infection also may manifest with signs of multiorgan system damage, including altered mental status, cerebral edema, meningismus, transient deafness, myocarditis, pulmonary hemorrhage and edema, conjunctivitis, retinal abnormalities, and acute renal failure.14,16 Risk factors for more severe illness include delayed treatment, age 40 years or older or younger than 10 years, and underlying medical conditions such as alcoholic liver disease and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency. However, even some healthy young patients die of this disease.17
Mediterranean Spotted Fever—Rhipicephalus sanguineus sensu lato is the primary vector of MSF, which is prevalent in areas adjacent to the Mediterranean Sea, including southern Europe, Africa, and Central Asia; Sicily is the most highly affected region.18 Findings with MSF are nearly identical to those of RMSF, except that tache noire is more common, present in as many as 70% of cases at the site of the inoculating tick bite, and MSF typically follows a less severe clinical course.12 Similar to other rickettsial diseases, the pathogenesis of MSF involves direct injury to vascular endothelial cells, causing a vasculitis that is responsible for the clinical abnormalities observed.
Patients with severe MSF experience complications similar to severe RMSF, including neurologic manifestations and multiorgan damage.18 Risk factors include advanced age, immunocompromised state, cardiac disease, chronic alcoholism, diabetes mellitus, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency, respiratory insufficiency, and delayed treatment.18
Treatment—For all spotted fever group rickettsial infections, doxycycline is the treatment of choice for all patients, including children and pregnant women. Treatment should be started without delay; recommended dosages are 100 mg twice daily for children weighing more than 45 kg and adults, and 2.2 mg/kg twice daily for children weighing 45 kg or less.12
Rhipicephalus tick bites rarely can result in paralysis; however, Dermacentor ticks are responsible for most cases of tick-related paralysis in North America. Other pathogens proven or reputed to be transmitted by Rhipicephalus sanguineus sensu lato with zoonotic potential include but are not limited to Rickettsia massiliae, Coxiella burnetti, Anaplasma platys, Leishmania infantum, and Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus (Nairovirus).19
Environmental Treatment and Prevention
The most effective way to prevent tick-borne illness is avoidance of tick bites. Primary prevention methods include vector control, use of repellents (eg, N,N-diethyl-meta-toluamide [DEET]), picaridin, permethrin), avoidance of areas with a high tick burden, use of protective clothing, and detection and removal of ticks as soon as possible.
Environmental and veterinary controls also are important methods of tick-bite prevention. A veterinarian can recommend a variety of agents for dogs and cats that prevent attachment of ticks. Environmental controls include synthetic or natural product-based chemical acaricides and nonchemical methods, such as landscape management (eg, sealing cracks and crevices in homes and controlling tall grasses, weeds, and leaf debris) to minimize potential tick habitat.20 Secondary prevention includes antibiotics for prophylaxis or for treatment of tick-borne disease, when indicated.
Numerous tick repellents are available commercially; others are being studied. DEET, the most widely used topical repellent, has a broad spectrum of activity against many tick species.21 In addition, DEET has a well-known safety and toxicity profile, with rare adverse effects, and is safe for use in pregnant women and children older than 2 years. Alternative repellents, such as those containing picaridin, ethyl butylacetylaminopropionate (IR3535 [Merck]), oil of lemon eucalyptus, and 2-undecanone can be effective; some show efficacy comparable to that of DEET.22 Permethrin, a synthetic pyrethroid, is a highly efficacious tick repellent and insecticide, especially when used in conjunction with a topical repellent such as DEET. Unlike topically applied repellents, permethrin spray is applied to fabric (eg, clothing, shoes, bed nets, camping gear), not to skin.
Indiscriminate use of acaricides worldwide has led to increasing selection of acaricide resistance in Rhipicephalus tick species, which is especially true with the use of acaricides in controlling R microplus livestock infestations; several tick populations now show resistance to all major classes of these compounds.23-25 For that reason, there has been an increasing effort to develop new chemical and nonchemical approaches to tick control that are more environmentally sustainable and strategies to minimize development and progression of resistance such as rotation of acaricides; reducing the frequency of their application; use of pesticide mixtures, synergists, or both; and increasing use of nonacaricidal methods of control.26
Prompt removal of ticks is important for preventing the transmission of tick-borne disease. Proper removal involves rubbing the tick in a circular motion with a moist gauze pad or using fine-tipped tweezers to grasp the tick as close to the skin surface as possible and pulling upward with a steady pressure.17,27 It is important not to jerk, twist, squeeze, smash, or burn the tick, as this can result in insufficient removal of mouthparts or spread contaminated tick fluids to mucous membranes, increasing the risk for infection. Application of petroleum jelly or nail polish to aid in tick removal have not been shown to be effective and are not recommended.16,28
- Dantas-Torres F. The brown dog tick, Rhipicephalus sanguineus (Latreille, 1806) (Acari: Ixodidae): from taxonomy to control. Vet Parasitol. 2008;152:173-185. doi:10.1016/j.vetpar.2007.12.030
- Madder M, Fourie JJ, Schetters TPM. Arachnida, Metastigmata, Ixodidae (except Ixodes holocyclus). In: Marchiondo AA, Cruthers LR, Fourie JJ, eds. Parasiticide Screening: In Vitro and In Vivo Tests With Relevant Parasite Rearing and Host Infection/Infestation Methods. Volume 1. Elsevier Academic Press; 2019:19-20.
- Burger TD, Shao R, Barker SC. Phylogenetic analysis of mitochondrial genome sequences indicates that the cattle tick, Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus, contains a cryptic species. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2014;76:241-253. doi:10.1016/j.ympev.2014.03.017
- Gray J, Dantas-Torres F, Estrada-Peña A, et al. Systematics and ecology of the brown dog tick, Rhipicephalus sanguineus. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2013;4:171-180. doi:10.1016/j.ttbdis.2012.12.003
- Tian Y, Lord CC, Kaufman PE. Brown dog tick, Rhipicephalus Sanguineus Latrielle (Arachnida: Acari: Ixodidae): EENY-221/IN378. EDIS. March 26, 2020. Accessed January 3, 2024. https://doi.org/10.32473/edis-in378-2020
- Saleh MN, Allen KE, Lineberry MW, et al. Ticks infesting dogs and cats in North America: biology, geographic distribution, and pathogen transmission. Vet Parasitol. 2021;294:109392. doi:10.1016/j.vetpar.2021.109392
- Dantas-Torres F. Biology and ecology of the brown dog tick, Rhipicephalus sanguineus. Parasit Vectors. 2010;3:26. doi:10.1186/1756-3305-3-26
- Dryden MW, Payne PA. Biology and control of ticks infesting dogs and cats in North America. Vet Ther. 2004;5:139-154.
- Nyangiwe N, Yawa M, Muchenje V. Driving forces for changes in geographic range of cattle ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) in Africa: a Review. S Afr J Anim Sci. 2018;48:829. doi:10.4314/sajas.v48i5.4
- Ramot Y, Zlotogorski A, Mumcuoglu KY. Brown dog tick (Rhipicephalus sanguineus) infestation of the penis detected by dermoscopy. Int J Dermatol. 2012;51:1402-1403. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2010.04756.x
- Tucker NSG, Weeks ENI, Beati L, et al. Prevalence and distribution of pathogen infection and permethrin resistance in tropical and temperate populations of Rhipicephalus sanguineus s.l. collected worldwide. Med Vet Entomol. 2021;35:147-157. doi:10.1111/mve.12479
- McClain MT, Sexton DJ, Hall KK, eds. Other spotted fever group rickettsial infections. UpToDate. Updated October 10, 2022. Accessed January 3, 2024. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/other-spotted-fever-group-rickettsial-infections
- Ribeiro CM, Carvalho JLB, Bastos PAS, et al. Prevalence of Rickettsia rickettsii in ticks: systematic review and meta-analysis. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2021;21:557-565. doi:10.1089/vbz.2021.0004
- Pace EJ, O’Reilly M. Tickborne diseases: diagnosis and management. Am Fam Physician. 2020;101:530-540.
- Patterson JW. Weedon’s Skin Pathology. 5th ed. Elsevier; 2020.
- Dantas-Torres F. Rocky Mountain spotted fever. Lancet Infect Dis. 2007;7:724-732. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(07)70261-X
- Biggs HM, Behravesh CB, Bradley KK, et al. Diagnosis and management of tickborne rickettsial diseases: Rocky Mountain spotted fever and other spotted fever group rickettsioses, ehrlichioses, and anaplasmosis—United States. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2016;65:1-44. doi:10.15585/mmwr.rr6502a1
- Rossio R, Conalbi V, Castagna V, et al. Mediterranean spotted fever and hearing impairment: a rare complication. Int J Infect Dis. 2015;35:34-36. doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2015.04.005
- Dantas-Torres F, Otranto D. Further thoughts on the taxonomy and vector role of Rhipicephalus sanguineus group ticks. Vet Parasitol. 2015;208:9-13. doi:10.1016/j.vetpar.2014.12.014
- Eisen RJ, Kugeler KJ, Eisen L, et al. Tick-borne zoonoses in the United States: persistent and emerging threats to human health. ILAR J. 2017;58:319-335. doi:10.1093/ilar/ilx005
- Nguyen QD, Vu MN, Hebert AA. Insect repellents: an updated review for the clinician. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;88:123-130. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.10.053
- Pages F, Dautel H, Duvallet G, et al. Tick repellents for human use: prevention of tick bites and tick-borne diseases. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2014;14:85-93. doi:10.1089/vbz.2013.1410
- Rodriguez-Vivas RI, Alonso-Díaz MA, et al. Prevalence and potential risk factors for organophosphate and pyrethroid resistance in Boophilus microplus ticks on cattle ranches from the State of Yucatan, Mexico. Vet Parasitol. 2006;136:335-342. doi:10.1016/j.vetpar.2005.05.069
- Rodríguez-Vivas RI, Rodríguez-Arevalo F, Alonso-Díaz MA, et al. Prevalence and potential risk factors for amitraz resistance in Boophilus microplus ticks in cattle farms in the State of Yucatan, Mexico. Prev Vet Med. 2006;75:280-286. doi:10.1016/j.prevetmed.2006.04.001
- Perez-Cogollo LC, Rodriguez-Vivas RI, Ramirez-Cruz GT, et al. First report of the cattle tick Rhipicephalus microplus resistant to ivermectin in Mexico. Vet Parasitol. 2010;168:165-169. doi:10.1016/j.vetpar.2009.10.021
- Rodriguez-Vivas RI, Jonsson NN, Bhushan C. Strategies for the control of Rhipicephalus microplus ticks in a world of conventional acaricide and macrocyclic lactone resistance. Parasitol Res.2018;117:3-29. doi:10.1007/s00436-017-5677-6
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Tick removal. Updated May 13, 2022. Accessed January 3, 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/ticks/removing_a_tick.html
- Diaz JH. Chemical and plant-based insect repellents: efficacy, safety, and toxicity. Wilderness Environ Med. 2016;27:153-163. doi:10.1016/j.wem.2015.11.007
Characteristics
Rhipicephalus ticks belong to the Ixodidae family of hard-bodied ticks. They are large and teardrop shaped with an inornate scutum (hard dorsal plate) and relatively short mouthparts attached at a hexagonal basis capitulum (base of the head to which mouthparts are attached)(Figure).1 Widely spaced eyes and festoons also are present. The first pair of coxae—attachment base for the first pair of legs—are characteristically bifid; males have a pair of sclerotized adanal plates on the ventral surface adjacent to the anus as well as accessory adanal shields.2 Rhipicephalus (formerly Boophilus) microplus (the so-called cattle tick) is a newly added species; it lacks posterior festoons, and the anal groove is absent.3

Almost all Rhipicephalus ticks, except for R microplus, are 3-host ticks in which a single blood meal is consumed from a vertebrate host at each active life stage—larva, nymph, and adult—to complete development.4,5 In contrast to most ixodid ticks, which are exophilic (living outside of human habitation), the Rhipicephalus sanguineus sensu lato species (the brown dog tick) is highly endophilic (adapted to indoor living) and often can be found hidden in cracks and crevices of walls in homes and peridomestic structures.6 It is predominately monotropic (all developmental stages feed on the same host species) and has a strong host preference for dogs, though it occasionally feeds on other hosts (eg, humans).7 Although most common in tropical and subtropical climates, they can be found anywhere there are dogs due to their ability to colonize indoor dwellings.8 In contrast, R microplus ticks have a predilection for cattle and livestock rather than humans, posing a notable concern to livestock worldwide. Infestation results in transmission of disease-causing pathogens, such as Babesia and Anaplasma species, which costs the cattle industry billions of dollars annually.9
Clinical Manifestations and Treatment
Tick bites usually manifest as intensely pruritic, erythematous papules at the site of tick attachment due to a local type IV hypersensitivity reaction to antigens in the tick’s saliva. This reaction can be long-lasting. In addition to pruritic papules following a bite, an attached tick can be mistaken for a skin neoplasm or nevus. Given that ticks are small, especially during the larval stage, dermoscopy may be helpful in making a diagnosis.10 Symptomatic relief usually can be achieved with topical antipruritics or oral antihistamines.
Of public health concern, brown dog ticks are important vectors of Rickettsia rickettsii (the causative organism of Rocky Mountain spotted fever [RMSF]) in the Western hemisphere, and Rickettsia conorii (the causative organism of Mediterranean spotted fever [MSF][also known as Boutonneuse fever]) in the Eastern hemisphere.11 Bites by ticks carrying rickettsial disease classically manifest with early symptoms of fever, headache, and myalgia, followed by a rash or by a localized eschar or tache noire (a black, necrotic, scabbed lesion) that represents direct endothelial invasion and vascular damage by Rickettsia.12 Rocky Mountain spotted fever and MSF are more prevalent during summer, likely due, in part, to the combination of increased outdoor activity and a higher rate of tick-questing (host-seeking) behavior in warmer climates.4,7
Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever—Dermacentor variabilis is the primary vector of RMSF in the southeastern United States; Dermacentor andersoni is the major vector of RMSF in Rocky Mountain states. Rhipicephalus sanguineus sensu lato is an important vector of RMSF in the southwestern United States, Mexico, and Central America.11,13
Early symptoms of RMSF are nonspecific and can include fever, headache, arthralgia, myalgia, and malaise. Gastrointestinal tract symptoms (eg, nausea, vomiting, anorexia) may occur; notable abdominal pain occurs in some patients, particularly children. A characteristic petechial rash occurs in as many as 90% of patients, typically at the third to fifth day of illness, and classically begins on the wrists and ankles, with progression to the palms and soles before spreading centripetally to the arms, legs, and trunk.14 An eschar at the inoculation site is uncommon in RMSF; when present, it is more suggestive of MSF.15
The classic triad of fever, headache, and rash is present in 3% of patients during the first 3 days after a tick bite and in 60% to 70% within 2 weeks.16 A rash often is absent when patients first seek medical attention and may not develop (absent in 9% to 12% of cases; so-called spotless RMSF). Therefore, absence of rash should not be a reason to withhold treatment.16 Empiric treatment with doxycycline should be started promptly for all suspected cases of RMSF because of the rapid progression of disease and an increased risk for morbidity and mortality with delayed diagnosis.
Patients do not become antibody positive until 7 to 10 days after symptoms begin; therefore, treatment should not be delayed while awaiting serologic test results. The case fatality rate in the United States is estimated to be 5% to 10% overall and as high as 40% to 50% among patients who are not treated until day 8 or 9 of illness.17
Cutaneous complications include skin necrosis and gangrene due to continuous tissue damage in severe cases.16 Severe infection also may manifest with signs of multiorgan system damage, including altered mental status, cerebral edema, meningismus, transient deafness, myocarditis, pulmonary hemorrhage and edema, conjunctivitis, retinal abnormalities, and acute renal failure.14,16 Risk factors for more severe illness include delayed treatment, age 40 years or older or younger than 10 years, and underlying medical conditions such as alcoholic liver disease and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency. However, even some healthy young patients die of this disease.17
Mediterranean Spotted Fever—Rhipicephalus sanguineus sensu lato is the primary vector of MSF, which is prevalent in areas adjacent to the Mediterranean Sea, including southern Europe, Africa, and Central Asia; Sicily is the most highly affected region.18 Findings with MSF are nearly identical to those of RMSF, except that tache noire is more common, present in as many as 70% of cases at the site of the inoculating tick bite, and MSF typically follows a less severe clinical course.12 Similar to other rickettsial diseases, the pathogenesis of MSF involves direct injury to vascular endothelial cells, causing a vasculitis that is responsible for the clinical abnormalities observed.
Patients with severe MSF experience complications similar to severe RMSF, including neurologic manifestations and multiorgan damage.18 Risk factors include advanced age, immunocompromised state, cardiac disease, chronic alcoholism, diabetes mellitus, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency, respiratory insufficiency, and delayed treatment.18
Treatment—For all spotted fever group rickettsial infections, doxycycline is the treatment of choice for all patients, including children and pregnant women. Treatment should be started without delay; recommended dosages are 100 mg twice daily for children weighing more than 45 kg and adults, and 2.2 mg/kg twice daily for children weighing 45 kg or less.12
Rhipicephalus tick bites rarely can result in paralysis; however, Dermacentor ticks are responsible for most cases of tick-related paralysis in North America. Other pathogens proven or reputed to be transmitted by Rhipicephalus sanguineus sensu lato with zoonotic potential include but are not limited to Rickettsia massiliae, Coxiella burnetti, Anaplasma platys, Leishmania infantum, and Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus (Nairovirus).19
Environmental Treatment and Prevention
The most effective way to prevent tick-borne illness is avoidance of tick bites. Primary prevention methods include vector control, use of repellents (eg, N,N-diethyl-meta-toluamide [DEET]), picaridin, permethrin), avoidance of areas with a high tick burden, use of protective clothing, and detection and removal of ticks as soon as possible.
Environmental and veterinary controls also are important methods of tick-bite prevention. A veterinarian can recommend a variety of agents for dogs and cats that prevent attachment of ticks. Environmental controls include synthetic or natural product-based chemical acaricides and nonchemical methods, such as landscape management (eg, sealing cracks and crevices in homes and controlling tall grasses, weeds, and leaf debris) to minimize potential tick habitat.20 Secondary prevention includes antibiotics for prophylaxis or for treatment of tick-borne disease, when indicated.
Numerous tick repellents are available commercially; others are being studied. DEET, the most widely used topical repellent, has a broad spectrum of activity against many tick species.21 In addition, DEET has a well-known safety and toxicity profile, with rare adverse effects, and is safe for use in pregnant women and children older than 2 years. Alternative repellents, such as those containing picaridin, ethyl butylacetylaminopropionate (IR3535 [Merck]), oil of lemon eucalyptus, and 2-undecanone can be effective; some show efficacy comparable to that of DEET.22 Permethrin, a synthetic pyrethroid, is a highly efficacious tick repellent and insecticide, especially when used in conjunction with a topical repellent such as DEET. Unlike topically applied repellents, permethrin spray is applied to fabric (eg, clothing, shoes, bed nets, camping gear), not to skin.
Indiscriminate use of acaricides worldwide has led to increasing selection of acaricide resistance in Rhipicephalus tick species, which is especially true with the use of acaricides in controlling R microplus livestock infestations; several tick populations now show resistance to all major classes of these compounds.23-25 For that reason, there has been an increasing effort to develop new chemical and nonchemical approaches to tick control that are more environmentally sustainable and strategies to minimize development and progression of resistance such as rotation of acaricides; reducing the frequency of their application; use of pesticide mixtures, synergists, or both; and increasing use of nonacaricidal methods of control.26
Prompt removal of ticks is important for preventing the transmission of tick-borne disease. Proper removal involves rubbing the tick in a circular motion with a moist gauze pad or using fine-tipped tweezers to grasp the tick as close to the skin surface as possible and pulling upward with a steady pressure.17,27 It is important not to jerk, twist, squeeze, smash, or burn the tick, as this can result in insufficient removal of mouthparts or spread contaminated tick fluids to mucous membranes, increasing the risk for infection. Application of petroleum jelly or nail polish to aid in tick removal have not been shown to be effective and are not recommended.16,28
Characteristics
Rhipicephalus ticks belong to the Ixodidae family of hard-bodied ticks. They are large and teardrop shaped with an inornate scutum (hard dorsal plate) and relatively short mouthparts attached at a hexagonal basis capitulum (base of the head to which mouthparts are attached)(Figure).1 Widely spaced eyes and festoons also are present. The first pair of coxae—attachment base for the first pair of legs—are characteristically bifid; males have a pair of sclerotized adanal plates on the ventral surface adjacent to the anus as well as accessory adanal shields.2 Rhipicephalus (formerly Boophilus) microplus (the so-called cattle tick) is a newly added species; it lacks posterior festoons, and the anal groove is absent.3

Almost all Rhipicephalus ticks, except for R microplus, are 3-host ticks in which a single blood meal is consumed from a vertebrate host at each active life stage—larva, nymph, and adult—to complete development.4,5 In contrast to most ixodid ticks, which are exophilic (living outside of human habitation), the Rhipicephalus sanguineus sensu lato species (the brown dog tick) is highly endophilic (adapted to indoor living) and often can be found hidden in cracks and crevices of walls in homes and peridomestic structures.6 It is predominately monotropic (all developmental stages feed on the same host species) and has a strong host preference for dogs, though it occasionally feeds on other hosts (eg, humans).7 Although most common in tropical and subtropical climates, they can be found anywhere there are dogs due to their ability to colonize indoor dwellings.8 In contrast, R microplus ticks have a predilection for cattle and livestock rather than humans, posing a notable concern to livestock worldwide. Infestation results in transmission of disease-causing pathogens, such as Babesia and Anaplasma species, which costs the cattle industry billions of dollars annually.9
Clinical Manifestations and Treatment
Tick bites usually manifest as intensely pruritic, erythematous papules at the site of tick attachment due to a local type IV hypersensitivity reaction to antigens in the tick’s saliva. This reaction can be long-lasting. In addition to pruritic papules following a bite, an attached tick can be mistaken for a skin neoplasm or nevus. Given that ticks are small, especially during the larval stage, dermoscopy may be helpful in making a diagnosis.10 Symptomatic relief usually can be achieved with topical antipruritics or oral antihistamines.
Of public health concern, brown dog ticks are important vectors of Rickettsia rickettsii (the causative organism of Rocky Mountain spotted fever [RMSF]) in the Western hemisphere, and Rickettsia conorii (the causative organism of Mediterranean spotted fever [MSF][also known as Boutonneuse fever]) in the Eastern hemisphere.11 Bites by ticks carrying rickettsial disease classically manifest with early symptoms of fever, headache, and myalgia, followed by a rash or by a localized eschar or tache noire (a black, necrotic, scabbed lesion) that represents direct endothelial invasion and vascular damage by Rickettsia.12 Rocky Mountain spotted fever and MSF are more prevalent during summer, likely due, in part, to the combination of increased outdoor activity and a higher rate of tick-questing (host-seeking) behavior in warmer climates.4,7
Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever—Dermacentor variabilis is the primary vector of RMSF in the southeastern United States; Dermacentor andersoni is the major vector of RMSF in Rocky Mountain states. Rhipicephalus sanguineus sensu lato is an important vector of RMSF in the southwestern United States, Mexico, and Central America.11,13
Early symptoms of RMSF are nonspecific and can include fever, headache, arthralgia, myalgia, and malaise. Gastrointestinal tract symptoms (eg, nausea, vomiting, anorexia) may occur; notable abdominal pain occurs in some patients, particularly children. A characteristic petechial rash occurs in as many as 90% of patients, typically at the third to fifth day of illness, and classically begins on the wrists and ankles, with progression to the palms and soles before spreading centripetally to the arms, legs, and trunk.14 An eschar at the inoculation site is uncommon in RMSF; when present, it is more suggestive of MSF.15
The classic triad of fever, headache, and rash is present in 3% of patients during the first 3 days after a tick bite and in 60% to 70% within 2 weeks.16 A rash often is absent when patients first seek medical attention and may not develop (absent in 9% to 12% of cases; so-called spotless RMSF). Therefore, absence of rash should not be a reason to withhold treatment.16 Empiric treatment with doxycycline should be started promptly for all suspected cases of RMSF because of the rapid progression of disease and an increased risk for morbidity and mortality with delayed diagnosis.
Patients do not become antibody positive until 7 to 10 days after symptoms begin; therefore, treatment should not be delayed while awaiting serologic test results. The case fatality rate in the United States is estimated to be 5% to 10% overall and as high as 40% to 50% among patients who are not treated until day 8 or 9 of illness.17
Cutaneous complications include skin necrosis and gangrene due to continuous tissue damage in severe cases.16 Severe infection also may manifest with signs of multiorgan system damage, including altered mental status, cerebral edema, meningismus, transient deafness, myocarditis, pulmonary hemorrhage and edema, conjunctivitis, retinal abnormalities, and acute renal failure.14,16 Risk factors for more severe illness include delayed treatment, age 40 years or older or younger than 10 years, and underlying medical conditions such as alcoholic liver disease and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency. However, even some healthy young patients die of this disease.17
Mediterranean Spotted Fever—Rhipicephalus sanguineus sensu lato is the primary vector of MSF, which is prevalent in areas adjacent to the Mediterranean Sea, including southern Europe, Africa, and Central Asia; Sicily is the most highly affected region.18 Findings with MSF are nearly identical to those of RMSF, except that tache noire is more common, present in as many as 70% of cases at the site of the inoculating tick bite, and MSF typically follows a less severe clinical course.12 Similar to other rickettsial diseases, the pathogenesis of MSF involves direct injury to vascular endothelial cells, causing a vasculitis that is responsible for the clinical abnormalities observed.
Patients with severe MSF experience complications similar to severe RMSF, including neurologic manifestations and multiorgan damage.18 Risk factors include advanced age, immunocompromised state, cardiac disease, chronic alcoholism, diabetes mellitus, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency, respiratory insufficiency, and delayed treatment.18
Treatment—For all spotted fever group rickettsial infections, doxycycline is the treatment of choice for all patients, including children and pregnant women. Treatment should be started without delay; recommended dosages are 100 mg twice daily for children weighing more than 45 kg and adults, and 2.2 mg/kg twice daily for children weighing 45 kg or less.12
Rhipicephalus tick bites rarely can result in paralysis; however, Dermacentor ticks are responsible for most cases of tick-related paralysis in North America. Other pathogens proven or reputed to be transmitted by Rhipicephalus sanguineus sensu lato with zoonotic potential include but are not limited to Rickettsia massiliae, Coxiella burnetti, Anaplasma platys, Leishmania infantum, and Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus (Nairovirus).19
Environmental Treatment and Prevention
The most effective way to prevent tick-borne illness is avoidance of tick bites. Primary prevention methods include vector control, use of repellents (eg, N,N-diethyl-meta-toluamide [DEET]), picaridin, permethrin), avoidance of areas with a high tick burden, use of protective clothing, and detection and removal of ticks as soon as possible.
Environmental and veterinary controls also are important methods of tick-bite prevention. A veterinarian can recommend a variety of agents for dogs and cats that prevent attachment of ticks. Environmental controls include synthetic or natural product-based chemical acaricides and nonchemical methods, such as landscape management (eg, sealing cracks and crevices in homes and controlling tall grasses, weeds, and leaf debris) to minimize potential tick habitat.20 Secondary prevention includes antibiotics for prophylaxis or for treatment of tick-borne disease, when indicated.
Numerous tick repellents are available commercially; others are being studied. DEET, the most widely used topical repellent, has a broad spectrum of activity against many tick species.21 In addition, DEET has a well-known safety and toxicity profile, with rare adverse effects, and is safe for use in pregnant women and children older than 2 years. Alternative repellents, such as those containing picaridin, ethyl butylacetylaminopropionate (IR3535 [Merck]), oil of lemon eucalyptus, and 2-undecanone can be effective; some show efficacy comparable to that of DEET.22 Permethrin, a synthetic pyrethroid, is a highly efficacious tick repellent and insecticide, especially when used in conjunction with a topical repellent such as DEET. Unlike topically applied repellents, permethrin spray is applied to fabric (eg, clothing, shoes, bed nets, camping gear), not to skin.
Indiscriminate use of acaricides worldwide has led to increasing selection of acaricide resistance in Rhipicephalus tick species, which is especially true with the use of acaricides in controlling R microplus livestock infestations; several tick populations now show resistance to all major classes of these compounds.23-25 For that reason, there has been an increasing effort to develop new chemical and nonchemical approaches to tick control that are more environmentally sustainable and strategies to minimize development and progression of resistance such as rotation of acaricides; reducing the frequency of their application; use of pesticide mixtures, synergists, or both; and increasing use of nonacaricidal methods of control.26
Prompt removal of ticks is important for preventing the transmission of tick-borne disease. Proper removal involves rubbing the tick in a circular motion with a moist gauze pad or using fine-tipped tweezers to grasp the tick as close to the skin surface as possible and pulling upward with a steady pressure.17,27 It is important not to jerk, twist, squeeze, smash, or burn the tick, as this can result in insufficient removal of mouthparts or spread contaminated tick fluids to mucous membranes, increasing the risk for infection. Application of petroleum jelly or nail polish to aid in tick removal have not been shown to be effective and are not recommended.16,28
- Dantas-Torres F. The brown dog tick, Rhipicephalus sanguineus (Latreille, 1806) (Acari: Ixodidae): from taxonomy to control. Vet Parasitol. 2008;152:173-185. doi:10.1016/j.vetpar.2007.12.030
- Madder M, Fourie JJ, Schetters TPM. Arachnida, Metastigmata, Ixodidae (except Ixodes holocyclus). In: Marchiondo AA, Cruthers LR, Fourie JJ, eds. Parasiticide Screening: In Vitro and In Vivo Tests With Relevant Parasite Rearing and Host Infection/Infestation Methods. Volume 1. Elsevier Academic Press; 2019:19-20.
- Burger TD, Shao R, Barker SC. Phylogenetic analysis of mitochondrial genome sequences indicates that the cattle tick, Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus, contains a cryptic species. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2014;76:241-253. doi:10.1016/j.ympev.2014.03.017
- Gray J, Dantas-Torres F, Estrada-Peña A, et al. Systematics and ecology of the brown dog tick, Rhipicephalus sanguineus. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2013;4:171-180. doi:10.1016/j.ttbdis.2012.12.003
- Tian Y, Lord CC, Kaufman PE. Brown dog tick, Rhipicephalus Sanguineus Latrielle (Arachnida: Acari: Ixodidae): EENY-221/IN378. EDIS. March 26, 2020. Accessed January 3, 2024. https://doi.org/10.32473/edis-in378-2020
- Saleh MN, Allen KE, Lineberry MW, et al. Ticks infesting dogs and cats in North America: biology, geographic distribution, and pathogen transmission. Vet Parasitol. 2021;294:109392. doi:10.1016/j.vetpar.2021.109392
- Dantas-Torres F. Biology and ecology of the brown dog tick, Rhipicephalus sanguineus. Parasit Vectors. 2010;3:26. doi:10.1186/1756-3305-3-26
- Dryden MW, Payne PA. Biology and control of ticks infesting dogs and cats in North America. Vet Ther. 2004;5:139-154.
- Nyangiwe N, Yawa M, Muchenje V. Driving forces for changes in geographic range of cattle ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) in Africa: a Review. S Afr J Anim Sci. 2018;48:829. doi:10.4314/sajas.v48i5.4
- Ramot Y, Zlotogorski A, Mumcuoglu KY. Brown dog tick (Rhipicephalus sanguineus) infestation of the penis detected by dermoscopy. Int J Dermatol. 2012;51:1402-1403. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2010.04756.x
- Tucker NSG, Weeks ENI, Beati L, et al. Prevalence and distribution of pathogen infection and permethrin resistance in tropical and temperate populations of Rhipicephalus sanguineus s.l. collected worldwide. Med Vet Entomol. 2021;35:147-157. doi:10.1111/mve.12479
- McClain MT, Sexton DJ, Hall KK, eds. Other spotted fever group rickettsial infections. UpToDate. Updated October 10, 2022. Accessed January 3, 2024. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/other-spotted-fever-group-rickettsial-infections
- Ribeiro CM, Carvalho JLB, Bastos PAS, et al. Prevalence of Rickettsia rickettsii in ticks: systematic review and meta-analysis. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2021;21:557-565. doi:10.1089/vbz.2021.0004
- Pace EJ, O’Reilly M. Tickborne diseases: diagnosis and management. Am Fam Physician. 2020;101:530-540.
- Patterson JW. Weedon’s Skin Pathology. 5th ed. Elsevier; 2020.
- Dantas-Torres F. Rocky Mountain spotted fever. Lancet Infect Dis. 2007;7:724-732. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(07)70261-X
- Biggs HM, Behravesh CB, Bradley KK, et al. Diagnosis and management of tickborne rickettsial diseases: Rocky Mountain spotted fever and other spotted fever group rickettsioses, ehrlichioses, and anaplasmosis—United States. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2016;65:1-44. doi:10.15585/mmwr.rr6502a1
- Rossio R, Conalbi V, Castagna V, et al. Mediterranean spotted fever and hearing impairment: a rare complication. Int J Infect Dis. 2015;35:34-36. doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2015.04.005
- Dantas-Torres F, Otranto D. Further thoughts on the taxonomy and vector role of Rhipicephalus sanguineus group ticks. Vet Parasitol. 2015;208:9-13. doi:10.1016/j.vetpar.2014.12.014
- Eisen RJ, Kugeler KJ, Eisen L, et al. Tick-borne zoonoses in the United States: persistent and emerging threats to human health. ILAR J. 2017;58:319-335. doi:10.1093/ilar/ilx005
- Nguyen QD, Vu MN, Hebert AA. Insect repellents: an updated review for the clinician. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;88:123-130. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.10.053
- Pages F, Dautel H, Duvallet G, et al. Tick repellents for human use: prevention of tick bites and tick-borne diseases. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2014;14:85-93. doi:10.1089/vbz.2013.1410
- Rodriguez-Vivas RI, Alonso-Díaz MA, et al. Prevalence and potential risk factors for organophosphate and pyrethroid resistance in Boophilus microplus ticks on cattle ranches from the State of Yucatan, Mexico. Vet Parasitol. 2006;136:335-342. doi:10.1016/j.vetpar.2005.05.069
- Rodríguez-Vivas RI, Rodríguez-Arevalo F, Alonso-Díaz MA, et al. Prevalence and potential risk factors for amitraz resistance in Boophilus microplus ticks in cattle farms in the State of Yucatan, Mexico. Prev Vet Med. 2006;75:280-286. doi:10.1016/j.prevetmed.2006.04.001
- Perez-Cogollo LC, Rodriguez-Vivas RI, Ramirez-Cruz GT, et al. First report of the cattle tick Rhipicephalus microplus resistant to ivermectin in Mexico. Vet Parasitol. 2010;168:165-169. doi:10.1016/j.vetpar.2009.10.021
- Rodriguez-Vivas RI, Jonsson NN, Bhushan C. Strategies for the control of Rhipicephalus microplus ticks in a world of conventional acaricide and macrocyclic lactone resistance. Parasitol Res.2018;117:3-29. doi:10.1007/s00436-017-5677-6
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Tick removal. Updated May 13, 2022. Accessed January 3, 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/ticks/removing_a_tick.html
- Diaz JH. Chemical and plant-based insect repellents: efficacy, safety, and toxicity. Wilderness Environ Med. 2016;27:153-163. doi:10.1016/j.wem.2015.11.007
- Dantas-Torres F. The brown dog tick, Rhipicephalus sanguineus (Latreille, 1806) (Acari: Ixodidae): from taxonomy to control. Vet Parasitol. 2008;152:173-185. doi:10.1016/j.vetpar.2007.12.030
- Madder M, Fourie JJ, Schetters TPM. Arachnida, Metastigmata, Ixodidae (except Ixodes holocyclus). In: Marchiondo AA, Cruthers LR, Fourie JJ, eds. Parasiticide Screening: In Vitro and In Vivo Tests With Relevant Parasite Rearing and Host Infection/Infestation Methods. Volume 1. Elsevier Academic Press; 2019:19-20.
- Burger TD, Shao R, Barker SC. Phylogenetic analysis of mitochondrial genome sequences indicates that the cattle tick, Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus, contains a cryptic species. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2014;76:241-253. doi:10.1016/j.ympev.2014.03.017
- Gray J, Dantas-Torres F, Estrada-Peña A, et al. Systematics and ecology of the brown dog tick, Rhipicephalus sanguineus. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2013;4:171-180. doi:10.1016/j.ttbdis.2012.12.003
- Tian Y, Lord CC, Kaufman PE. Brown dog tick, Rhipicephalus Sanguineus Latrielle (Arachnida: Acari: Ixodidae): EENY-221/IN378. EDIS. March 26, 2020. Accessed January 3, 2024. https://doi.org/10.32473/edis-in378-2020
- Saleh MN, Allen KE, Lineberry MW, et al. Ticks infesting dogs and cats in North America: biology, geographic distribution, and pathogen transmission. Vet Parasitol. 2021;294:109392. doi:10.1016/j.vetpar.2021.109392
- Dantas-Torres F. Biology and ecology of the brown dog tick, Rhipicephalus sanguineus. Parasit Vectors. 2010;3:26. doi:10.1186/1756-3305-3-26
- Dryden MW, Payne PA. Biology and control of ticks infesting dogs and cats in North America. Vet Ther. 2004;5:139-154.
- Nyangiwe N, Yawa M, Muchenje V. Driving forces for changes in geographic range of cattle ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) in Africa: a Review. S Afr J Anim Sci. 2018;48:829. doi:10.4314/sajas.v48i5.4
- Ramot Y, Zlotogorski A, Mumcuoglu KY. Brown dog tick (Rhipicephalus sanguineus) infestation of the penis detected by dermoscopy. Int J Dermatol. 2012;51:1402-1403. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2010.04756.x
- Tucker NSG, Weeks ENI, Beati L, et al. Prevalence and distribution of pathogen infection and permethrin resistance in tropical and temperate populations of Rhipicephalus sanguineus s.l. collected worldwide. Med Vet Entomol. 2021;35:147-157. doi:10.1111/mve.12479
- McClain MT, Sexton DJ, Hall KK, eds. Other spotted fever group rickettsial infections. UpToDate. Updated October 10, 2022. Accessed January 3, 2024. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/other-spotted-fever-group-rickettsial-infections
- Ribeiro CM, Carvalho JLB, Bastos PAS, et al. Prevalence of Rickettsia rickettsii in ticks: systematic review and meta-analysis. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2021;21:557-565. doi:10.1089/vbz.2021.0004
- Pace EJ, O’Reilly M. Tickborne diseases: diagnosis and management. Am Fam Physician. 2020;101:530-540.
- Patterson JW. Weedon’s Skin Pathology. 5th ed. Elsevier; 2020.
- Dantas-Torres F. Rocky Mountain spotted fever. Lancet Infect Dis. 2007;7:724-732. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(07)70261-X
- Biggs HM, Behravesh CB, Bradley KK, et al. Diagnosis and management of tickborne rickettsial diseases: Rocky Mountain spotted fever and other spotted fever group rickettsioses, ehrlichioses, and anaplasmosis—United States. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2016;65:1-44. doi:10.15585/mmwr.rr6502a1
- Rossio R, Conalbi V, Castagna V, et al. Mediterranean spotted fever and hearing impairment: a rare complication. Int J Infect Dis. 2015;35:34-36. doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2015.04.005
- Dantas-Torres F, Otranto D. Further thoughts on the taxonomy and vector role of Rhipicephalus sanguineus group ticks. Vet Parasitol. 2015;208:9-13. doi:10.1016/j.vetpar.2014.12.014
- Eisen RJ, Kugeler KJ, Eisen L, et al. Tick-borne zoonoses in the United States: persistent and emerging threats to human health. ILAR J. 2017;58:319-335. doi:10.1093/ilar/ilx005
- Nguyen QD, Vu MN, Hebert AA. Insect repellents: an updated review for the clinician. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;88:123-130. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.10.053
- Pages F, Dautel H, Duvallet G, et al. Tick repellents for human use: prevention of tick bites and tick-borne diseases. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2014;14:85-93. doi:10.1089/vbz.2013.1410
- Rodriguez-Vivas RI, Alonso-Díaz MA, et al. Prevalence and potential risk factors for organophosphate and pyrethroid resistance in Boophilus microplus ticks on cattle ranches from the State of Yucatan, Mexico. Vet Parasitol. 2006;136:335-342. doi:10.1016/j.vetpar.2005.05.069
- Rodríguez-Vivas RI, Rodríguez-Arevalo F, Alonso-Díaz MA, et al. Prevalence and potential risk factors for amitraz resistance in Boophilus microplus ticks in cattle farms in the State of Yucatan, Mexico. Prev Vet Med. 2006;75:280-286. doi:10.1016/j.prevetmed.2006.04.001
- Perez-Cogollo LC, Rodriguez-Vivas RI, Ramirez-Cruz GT, et al. First report of the cattle tick Rhipicephalus microplus resistant to ivermectin in Mexico. Vet Parasitol. 2010;168:165-169. doi:10.1016/j.vetpar.2009.10.021
- Rodriguez-Vivas RI, Jonsson NN, Bhushan C. Strategies for the control of Rhipicephalus microplus ticks in a world of conventional acaricide and macrocyclic lactone resistance. Parasitol Res.2018;117:3-29. doi:10.1007/s00436-017-5677-6
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Tick removal. Updated May 13, 2022. Accessed January 3, 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/ticks/removing_a_tick.html
- Diaz JH. Chemical and plant-based insect repellents: efficacy, safety, and toxicity. Wilderness Environ Med. 2016;27:153-163. doi:10.1016/j.wem.2015.11.007
PRACTICE POINTS
- Rhipicephalus ticks are vectors of a variety of diseases, including the rickettsial diseases Rocky Mountain spotted fever and Mediterranean spotted fever.
- Presenting symptoms of a tick bite include intensely pruritic, erythematous papules and nodules at the site of tick attachment.
- If rickettsial disease is suspected, treatment with doxycycline should be initiated immediately; do not delay treatment to await results of confirmatory tests or because of the absence of a rash.
- Primary methods of prevention of tick-borne disease include repellents, protective clothing, vector control, and prompt removal of the tick.
Commentary: PsA in Women, February 2024
Another study investigated the persistence of targeted therapies for PsA in women compared with men. In a nationwide cohort study using administrative information from French health insurance, the study looked at 14,778 patients (57% women) with PsA who were new users of targeted therapies. The study showed that women had 20%-40% lower treatment persistence rates than men for tumour necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR] 1.4; 99% CI 1.3-1.5) and interleukin (IL)-17 inhibitors (aHR 1.2; 99% CI 1.1-1.3). However, the treatment persistence between both sexes was comparable for IL-12/23 inhibitor (aHR 1.1; 99% CI 0.9-1.3), IL-23 inhibitor (aHR 1.1; 99% CI 0.7-1.5), and Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor (aHR 1.2; 99% CI 0.9-1.6) therapies. The paradigm that women have lower treatment persistence is based on studies done primarily in patients treated with TNF inhibitors. This study and a few other recent studies challenge this paradigm by indicating that other targeted therapies, especially JAK inhibitors, may not have lower persistence in women. Sex should be taken into consideration while choosing and counseling women about PsA therapies.
There are few studies on exercise and its impact on PsA. Functional training (FT) and resistance training (RT) may improve functional capacity and quality of life of patients with PsA. The safety of exercise is also not known, given that (micro)trauma is a risk factor for PsA. To evaluate this, Silva and colleagues conducted a 12-week, single-blind trial including 41 patients with PsA who were randomly assigned to undergo FT with elastic bands or RT with weight machines. They demonstrated that FT and RT led to similar improvements in functional capacity measured by the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Functional Index (P = .919), functional status measured by the Health Assessment Questionnaire for Spondyloarthritis (P = .932), disease activity measured by the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (P = .700), and muscle strength. No adverse events occurred in either group. Thus, FT and RT improved functional capacity, functional status, disease activity, and muscle strength to a comparable extent in patients with PsA, with no adverse events. Both modalities may be recommended for PsA patients.
Finally, a cross-sectional study that included 503 patients with PsA, of whom 160 patients underwent treatment escalation, evaluated whether the patient-reported outcome (PsA Impact of Disease questionnaire [PsAID-12]) affected treatment decisions by the treating rheumatologist. Coyle and colleagues demonstrated that although PsAID-12 scores were higher in patients who did vs did not have a treatment escalation, physicians relied more on their assessment of disease activity rather than the PsAID-12 scores when making treatment-related decisions. Of note, physicians also reported that PsAID-12 scores influenced treatment reduction decisions.
Another study investigated the persistence of targeted therapies for PsA in women compared with men. In a nationwide cohort study using administrative information from French health insurance, the study looked at 14,778 patients (57% women) with PsA who were new users of targeted therapies. The study showed that women had 20%-40% lower treatment persistence rates than men for tumour necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR] 1.4; 99% CI 1.3-1.5) and interleukin (IL)-17 inhibitors (aHR 1.2; 99% CI 1.1-1.3). However, the treatment persistence between both sexes was comparable for IL-12/23 inhibitor (aHR 1.1; 99% CI 0.9-1.3), IL-23 inhibitor (aHR 1.1; 99% CI 0.7-1.5), and Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor (aHR 1.2; 99% CI 0.9-1.6) therapies. The paradigm that women have lower treatment persistence is based on studies done primarily in patients treated with TNF inhibitors. This study and a few other recent studies challenge this paradigm by indicating that other targeted therapies, especially JAK inhibitors, may not have lower persistence in women. Sex should be taken into consideration while choosing and counseling women about PsA therapies.
There are few studies on exercise and its impact on PsA. Functional training (FT) and resistance training (RT) may improve functional capacity and quality of life of patients with PsA. The safety of exercise is also not known, given that (micro)trauma is a risk factor for PsA. To evaluate this, Silva and colleagues conducted a 12-week, single-blind trial including 41 patients with PsA who were randomly assigned to undergo FT with elastic bands or RT with weight machines. They demonstrated that FT and RT led to similar improvements in functional capacity measured by the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Functional Index (P = .919), functional status measured by the Health Assessment Questionnaire for Spondyloarthritis (P = .932), disease activity measured by the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (P = .700), and muscle strength. No adverse events occurred in either group. Thus, FT and RT improved functional capacity, functional status, disease activity, and muscle strength to a comparable extent in patients with PsA, with no adverse events. Both modalities may be recommended for PsA patients.
Finally, a cross-sectional study that included 503 patients with PsA, of whom 160 patients underwent treatment escalation, evaluated whether the patient-reported outcome (PsA Impact of Disease questionnaire [PsAID-12]) affected treatment decisions by the treating rheumatologist. Coyle and colleagues demonstrated that although PsAID-12 scores were higher in patients who did vs did not have a treatment escalation, physicians relied more on their assessment of disease activity rather than the PsAID-12 scores when making treatment-related decisions. Of note, physicians also reported that PsAID-12 scores influenced treatment reduction decisions.
Another study investigated the persistence of targeted therapies for PsA in women compared with men. In a nationwide cohort study using administrative information from French health insurance, the study looked at 14,778 patients (57% women) with PsA who were new users of targeted therapies. The study showed that women had 20%-40% lower treatment persistence rates than men for tumour necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR] 1.4; 99% CI 1.3-1.5) and interleukin (IL)-17 inhibitors (aHR 1.2; 99% CI 1.1-1.3). However, the treatment persistence between both sexes was comparable for IL-12/23 inhibitor (aHR 1.1; 99% CI 0.9-1.3), IL-23 inhibitor (aHR 1.1; 99% CI 0.7-1.5), and Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor (aHR 1.2; 99% CI 0.9-1.6) therapies. The paradigm that women have lower treatment persistence is based on studies done primarily in patients treated with TNF inhibitors. This study and a few other recent studies challenge this paradigm by indicating that other targeted therapies, especially JAK inhibitors, may not have lower persistence in women. Sex should be taken into consideration while choosing and counseling women about PsA therapies.
There are few studies on exercise and its impact on PsA. Functional training (FT) and resistance training (RT) may improve functional capacity and quality of life of patients with PsA. The safety of exercise is also not known, given that (micro)trauma is a risk factor for PsA. To evaluate this, Silva and colleagues conducted a 12-week, single-blind trial including 41 patients with PsA who were randomly assigned to undergo FT with elastic bands or RT with weight machines. They demonstrated that FT and RT led to similar improvements in functional capacity measured by the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Functional Index (P = .919), functional status measured by the Health Assessment Questionnaire for Spondyloarthritis (P = .932), disease activity measured by the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (P = .700), and muscle strength. No adverse events occurred in either group. Thus, FT and RT improved functional capacity, functional status, disease activity, and muscle strength to a comparable extent in patients with PsA, with no adverse events. Both modalities may be recommended for PsA patients.
Finally, a cross-sectional study that included 503 patients with PsA, of whom 160 patients underwent treatment escalation, evaluated whether the patient-reported outcome (PsA Impact of Disease questionnaire [PsAID-12]) affected treatment decisions by the treating rheumatologist. Coyle and colleagues demonstrated that although PsAID-12 scores were higher in patients who did vs did not have a treatment escalation, physicians relied more on their assessment of disease activity rather than the PsAID-12 scores when making treatment-related decisions. Of note, physicians also reported that PsAID-12 scores influenced treatment reduction decisions.
Commentary: Benign Breast Disease, PD-L1+ TNBC, and Exercise in BC, February 2024
The benefit of immunotherapy in combination with chemotherapy for programmed death–ligand 1–positive (PD-L1+) metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (mTNBC) has been shown in both the IMpassion130 and KEYNOTE-355 trials.[2,3] However, the IMpassion131 trial, which evaluated atezolizumab plus paclitaxel, did not show a progression-free survival (PFS) or overall survival (OS) benefit vs paclitaxel alone in PD-L1+ mTNBC.[4] Various explanations for these divergent results have been proposed, including the inherent properties of the chemotherapy backbone, patient populations, and the heterogenous nature of TNBC, which can affect response to immunotherapy. Of present, the various KEYNOTE-355 regimens (pembrolizumab plus investigator's choice chemotherapy [nab-paclitaxel, paclitaxel, or gemcitabine-carboplatin]) are US Food and Drug Administration approved for PD-L1+ mTNBC in the first-line setting. The phase 2 randomized TBCRC 043 trial investigated the effect of atezolizumab with carboplatin in patients with mTNBC and further looked at clinical and molecular correlates of response (Lehmann et al). A total of 106 patients were randomly assigned to carboplatin or carboplatin plus atezolizumab; the combination improved PFS (median PFS, 4.1 vs 2.2 mo; hazard ratio [HR] 0.66; P = .05) and OS (12.6 vs 8.6 mo; HR 0.60; P = .03). Grade 3/4 serious adverse events were more common with carboplatin-atezolizumab vs carboplatin alone (41% vs 8%). In addition, an association of better responses with PD-L1 immunotherapy was seen in patients with obesity, uncontrolled blood glucose levels, high tumor mutation burden, and increased tumor infiltrating lymphocytes. These data support the role of immunotherapy in mTNBC, highlight tumor heterogeneity within this subtype and encourage correlative studies to better define which patients benefit from immunotherapy.
Various studies have demonstrated the favorable impact of physical activity on breast cancer risk in postmenopausal women.[5] However, data in premenopausal women is less clear. Various mechanisms connecting physical activity to premenopausal breast cancer risk have been proposed including the effect of exercise on sex steroid hormones, fasting insulin levels, and inflammation.[6] A pooled analysis from 19 cohort studies including 547,601 premenopausal women, with 10,231 incident cases of breast cancer, aimed to examine the relationship between leisure-time physical activity (sports, exercise, recreational walking) and breast cancer risk in young women (Timmins et al). Higher (90th percentile) vs lower (10th percentile) levels of leisure-time physical activity were associated with a 10% reduction in breast cancer risk after adjustment for body mass index (BMI; adjusted HR 0.90; 95% CI 0.85-0.95; P < .001). They also found a significant reduction in risk: 32% (HR 0.68; P = .01) and 9% (HR 0.91; P = .005) for women with underweight (BMI < 18.5) and with average weight (BMI 18.5-24.9), respectively. Further, the effect of physical activity was most pronounced in the human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)–enriched breast cancer subtype, wherein higher vs lower levels of activity were associated with an estimated 45% reduction in breast cancer risk (adjusted HR 0.55; 95% CI 0.37-0.82). These findings support the beneficial role of aerobic exercise and healthy body weight on breast cancer risk among premenopausal women and highlight the value of incorporating this information into counseling for our patients.
Additional References
- Figueroa JD, Gierach GL, Duggan MA, et al. Risk factors for breast cancer development by tumor characteristics among women with benign breast disease. Breast Cancer Res. 2021;23:34. doi: 10.1186/s13058-021-01410-1 Source
- Schmid P, Adams S, Rugo HS, et al, for the IMpassion130 Trial Investigators. Atezolizumab and nab-paclitaxel in advanced triple-negative breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2018;379:2108-2121. doi: 10.1056/nejmoa1809615 Source
- Cortes J, Rugo HS, Cescon DW, et al, for the KEYNOTE-355 Investigators. Pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy in advanced triple-negative breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2022;387:217-226. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2202809 Source
- Miles D, Gligorov J, André F, et al, on behalf of the IMpassion131 investigators. Primary results from IMpassion131, a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomised phase III trial of first-line paclitaxel with or without atezolizumab for unresectable locally advanced/metastatic triple-negative breast cancer. Ann Oncol. 2021;32:994-1004. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2021.05.801 Source
- Eliassen AH, Hankinson SE, Rosner B, et al. Physical activity and risk of breast cancer among postmenopausal women. Arch Intern Med. 2010;170:1758-1764. doi: 10.1001/archinternmed.2010.363 Source
- Swain CTV, Drummond AE, Boing L, et al. Linking physical activity to breast cancer via sex hormones, part 1: The effect of physical activity on sex steroid hormones. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2022;31:16-27. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-21-0437 Source
The benefit of immunotherapy in combination with chemotherapy for programmed death–ligand 1–positive (PD-L1+) metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (mTNBC) has been shown in both the IMpassion130 and KEYNOTE-355 trials.[2,3] However, the IMpassion131 trial, which evaluated atezolizumab plus paclitaxel, did not show a progression-free survival (PFS) or overall survival (OS) benefit vs paclitaxel alone in PD-L1+ mTNBC.[4] Various explanations for these divergent results have been proposed, including the inherent properties of the chemotherapy backbone, patient populations, and the heterogenous nature of TNBC, which can affect response to immunotherapy. Of present, the various KEYNOTE-355 regimens (pembrolizumab plus investigator's choice chemotherapy [nab-paclitaxel, paclitaxel, or gemcitabine-carboplatin]) are US Food and Drug Administration approved for PD-L1+ mTNBC in the first-line setting. The phase 2 randomized TBCRC 043 trial investigated the effect of atezolizumab with carboplatin in patients with mTNBC and further looked at clinical and molecular correlates of response (Lehmann et al). A total of 106 patients were randomly assigned to carboplatin or carboplatin plus atezolizumab; the combination improved PFS (median PFS, 4.1 vs 2.2 mo; hazard ratio [HR] 0.66; P = .05) and OS (12.6 vs 8.6 mo; HR 0.60; P = .03). Grade 3/4 serious adverse events were more common with carboplatin-atezolizumab vs carboplatin alone (41% vs 8%). In addition, an association of better responses with PD-L1 immunotherapy was seen in patients with obesity, uncontrolled blood glucose levels, high tumor mutation burden, and increased tumor infiltrating lymphocytes. These data support the role of immunotherapy in mTNBC, highlight tumor heterogeneity within this subtype and encourage correlative studies to better define which patients benefit from immunotherapy.
Various studies have demonstrated the favorable impact of physical activity on breast cancer risk in postmenopausal women.[5] However, data in premenopausal women is less clear. Various mechanisms connecting physical activity to premenopausal breast cancer risk have been proposed including the effect of exercise on sex steroid hormones, fasting insulin levels, and inflammation.[6] A pooled analysis from 19 cohort studies including 547,601 premenopausal women, with 10,231 incident cases of breast cancer, aimed to examine the relationship between leisure-time physical activity (sports, exercise, recreational walking) and breast cancer risk in young women (Timmins et al). Higher (90th percentile) vs lower (10th percentile) levels of leisure-time physical activity were associated with a 10% reduction in breast cancer risk after adjustment for body mass index (BMI; adjusted HR 0.90; 95% CI 0.85-0.95; P < .001). They also found a significant reduction in risk: 32% (HR 0.68; P = .01) and 9% (HR 0.91; P = .005) for women with underweight (BMI < 18.5) and with average weight (BMI 18.5-24.9), respectively. Further, the effect of physical activity was most pronounced in the human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)–enriched breast cancer subtype, wherein higher vs lower levels of activity were associated with an estimated 45% reduction in breast cancer risk (adjusted HR 0.55; 95% CI 0.37-0.82). These findings support the beneficial role of aerobic exercise and healthy body weight on breast cancer risk among premenopausal women and highlight the value of incorporating this information into counseling for our patients.
Additional References
- Figueroa JD, Gierach GL, Duggan MA, et al. Risk factors for breast cancer development by tumor characteristics among women with benign breast disease. Breast Cancer Res. 2021;23:34. doi: 10.1186/s13058-021-01410-1 Source
- Schmid P, Adams S, Rugo HS, et al, for the IMpassion130 Trial Investigators. Atezolizumab and nab-paclitaxel in advanced triple-negative breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2018;379:2108-2121. doi: 10.1056/nejmoa1809615 Source
- Cortes J, Rugo HS, Cescon DW, et al, for the KEYNOTE-355 Investigators. Pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy in advanced triple-negative breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2022;387:217-226. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2202809 Source
- Miles D, Gligorov J, André F, et al, on behalf of the IMpassion131 investigators. Primary results from IMpassion131, a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomised phase III trial of first-line paclitaxel with or without atezolizumab for unresectable locally advanced/metastatic triple-negative breast cancer. Ann Oncol. 2021;32:994-1004. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2021.05.801 Source
- Eliassen AH, Hankinson SE, Rosner B, et al. Physical activity and risk of breast cancer among postmenopausal women. Arch Intern Med. 2010;170:1758-1764. doi: 10.1001/archinternmed.2010.363 Source
- Swain CTV, Drummond AE, Boing L, et al. Linking physical activity to breast cancer via sex hormones, part 1: The effect of physical activity on sex steroid hormones. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2022;31:16-27. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-21-0437 Source
The benefit of immunotherapy in combination with chemotherapy for programmed death–ligand 1–positive (PD-L1+) metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (mTNBC) has been shown in both the IMpassion130 and KEYNOTE-355 trials.[2,3] However, the IMpassion131 trial, which evaluated atezolizumab plus paclitaxel, did not show a progression-free survival (PFS) or overall survival (OS) benefit vs paclitaxel alone in PD-L1+ mTNBC.[4] Various explanations for these divergent results have been proposed, including the inherent properties of the chemotherapy backbone, patient populations, and the heterogenous nature of TNBC, which can affect response to immunotherapy. Of present, the various KEYNOTE-355 regimens (pembrolizumab plus investigator's choice chemotherapy [nab-paclitaxel, paclitaxel, or gemcitabine-carboplatin]) are US Food and Drug Administration approved for PD-L1+ mTNBC in the first-line setting. The phase 2 randomized TBCRC 043 trial investigated the effect of atezolizumab with carboplatin in patients with mTNBC and further looked at clinical and molecular correlates of response (Lehmann et al). A total of 106 patients were randomly assigned to carboplatin or carboplatin plus atezolizumab; the combination improved PFS (median PFS, 4.1 vs 2.2 mo; hazard ratio [HR] 0.66; P = .05) and OS (12.6 vs 8.6 mo; HR 0.60; P = .03). Grade 3/4 serious adverse events were more common with carboplatin-atezolizumab vs carboplatin alone (41% vs 8%). In addition, an association of better responses with PD-L1 immunotherapy was seen in patients with obesity, uncontrolled blood glucose levels, high tumor mutation burden, and increased tumor infiltrating lymphocytes. These data support the role of immunotherapy in mTNBC, highlight tumor heterogeneity within this subtype and encourage correlative studies to better define which patients benefit from immunotherapy.
Various studies have demonstrated the favorable impact of physical activity on breast cancer risk in postmenopausal women.[5] However, data in premenopausal women is less clear. Various mechanisms connecting physical activity to premenopausal breast cancer risk have been proposed including the effect of exercise on sex steroid hormones, fasting insulin levels, and inflammation.[6] A pooled analysis from 19 cohort studies including 547,601 premenopausal women, with 10,231 incident cases of breast cancer, aimed to examine the relationship between leisure-time physical activity (sports, exercise, recreational walking) and breast cancer risk in young women (Timmins et al). Higher (90th percentile) vs lower (10th percentile) levels of leisure-time physical activity were associated with a 10% reduction in breast cancer risk after adjustment for body mass index (BMI; adjusted HR 0.90; 95% CI 0.85-0.95; P < .001). They also found a significant reduction in risk: 32% (HR 0.68; P = .01) and 9% (HR 0.91; P = .005) for women with underweight (BMI < 18.5) and with average weight (BMI 18.5-24.9), respectively. Further, the effect of physical activity was most pronounced in the human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)–enriched breast cancer subtype, wherein higher vs lower levels of activity were associated with an estimated 45% reduction in breast cancer risk (adjusted HR 0.55; 95% CI 0.37-0.82). These findings support the beneficial role of aerobic exercise and healthy body weight on breast cancer risk among premenopausal women and highlight the value of incorporating this information into counseling for our patients.
Additional References
- Figueroa JD, Gierach GL, Duggan MA, et al. Risk factors for breast cancer development by tumor characteristics among women with benign breast disease. Breast Cancer Res. 2021;23:34. doi: 10.1186/s13058-021-01410-1 Source
- Schmid P, Adams S, Rugo HS, et al, for the IMpassion130 Trial Investigators. Atezolizumab and nab-paclitaxel in advanced triple-negative breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2018;379:2108-2121. doi: 10.1056/nejmoa1809615 Source
- Cortes J, Rugo HS, Cescon DW, et al, for the KEYNOTE-355 Investigators. Pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy in advanced triple-negative breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2022;387:217-226. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2202809 Source
- Miles D, Gligorov J, André F, et al, on behalf of the IMpassion131 investigators. Primary results from IMpassion131, a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomised phase III trial of first-line paclitaxel with or without atezolizumab for unresectable locally advanced/metastatic triple-negative breast cancer. Ann Oncol. 2021;32:994-1004. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2021.05.801 Source
- Eliassen AH, Hankinson SE, Rosner B, et al. Physical activity and risk of breast cancer among postmenopausal women. Arch Intern Med. 2010;170:1758-1764. doi: 10.1001/archinternmed.2010.363 Source
- Swain CTV, Drummond AE, Boing L, et al. Linking physical activity to breast cancer via sex hormones, part 1: The effect of physical activity on sex steroid hormones. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2022;31:16-27. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-21-0437 Source
Noduloplaque on the Forehead
The Diagnosis: Giant Apocrine Hidrocystoma
Histopathology of the noduloplaque revealed an unremarkable epidermis with multilocular cystic spaces centered in the dermis. The cysts had a double-lined epithelium with inner columnar to cuboidal cells and outer myoepithelial cells (bottom quiz image). Columnar cells showing decapitation secretion could be appreciated at places indicating apocrine secretion (Figure). A final diagnosis of apocrine hidrocystoma was made.
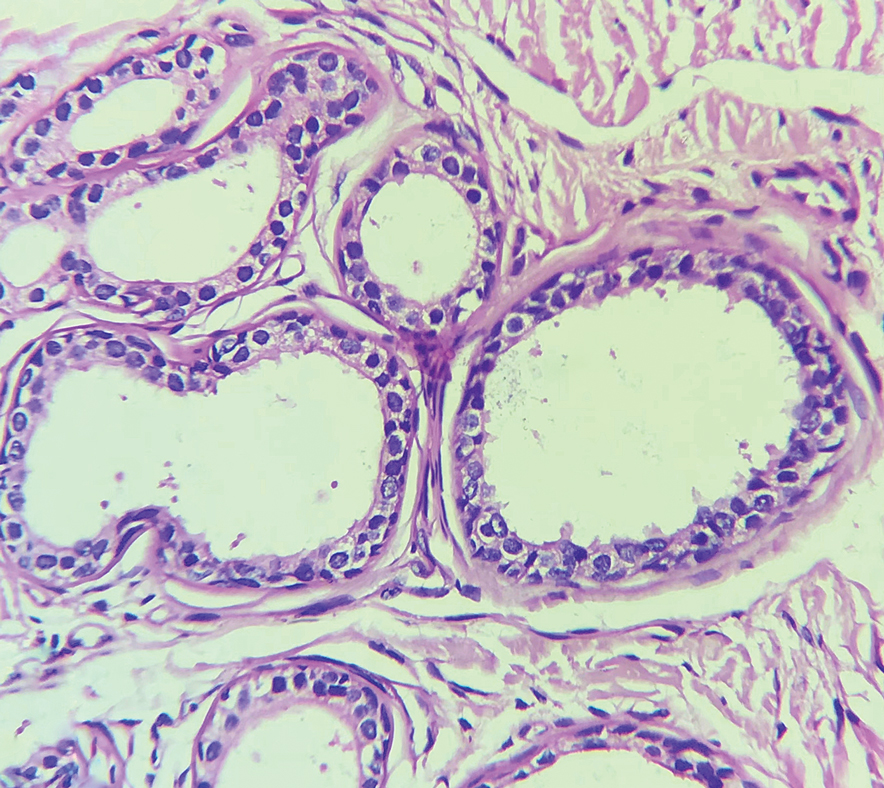
Hidrocystomas are rare, benign, cystic lesions derived either from apocrine or eccrine glands.1 Apocrine hidrocystoma usually manifests as asymptomatic, solitary, dome-shaped papules or nodules with a predilection for the head and neck region. Hidrocystomas can vary from flesh colored to blue, brown, or black. Pigmentation in hidrocystoma is seen in 5% to 80% of cases and is attributed to the Tyndall effect.1 The tumor usually is less than 20 mm in diameter; larger lesions are termed giant apocrine hidrocystoma.2 Apocrine hidrocystoma manifesting with multiple lesions and a size greater than 10 mm, as seen in our case, is uncommon.
Zaballos et al3 described dermoscopy of apocrine hidrocystoma in 22 patients. Hallmark dermoscopic findings were the presence of a homogeneous flesh-colored, yellowish, blue to pinkish-blue area involving the entire lesion with arborizing vessels and whitish structures.3 Similar dermoscopic findings were present in our patient. The homogeneous area histologically correlates to the multiloculated cysts located in the dermis. The exact reason for white structures is unknown; however, their visualization in apocrine hidrocystoma could be attributed to the alternation in collagen orientation secondary to the presence of large or multiple cysts in the dermis.
The presence of shiny white dots arranged in a square resembling a four-leaf clover (also known as white rosettes) was a unique dermoscopic finding in our patient. These rosettes can be appreciated only with polarized dermoscopy, and they have been described in actinic keratosis, seborrheic keratosis, squamous cell carcinoma, and basal cell carcinoma.4 The exact morphologic correlate of white rosettes is unknown but is postulated to be secondary to material inside adnexal openings in small rosettes and concentric perifollicular fibrosis in larger rosettes.4 In our patient, we believe the white rosettes can be attributed to the accumulated secretions in the dermal glands, which also were seen via histopathology. Dermoscopy also revealed increased peripheral, brown, networklike pigmentation, which was unique and could be secondary to the patient’s darker skin phenotype.
Differential diagnoses of apocrine hidrocystoma include both melanocytic and nonmelanocytic conditions such as epidermal cyst, nodular melanoma, nodular hidradenoma, syringoma, blue nevus, pilomatricoma, eccrine poroma, nodular Kaposi sarcoma, and venous lake.1 Histopathology showing large unilocular or multilocular dermal cysts with double lining comprising outer myoepithelial cells and inner columnar or cuboidal cell with decapitation secretion is paramount in confirming the diagnosis of apocrine hidrocystoma.
Dermoscopy can act as a valuable noninvasive modality in differentiating apocrine hidrocystoma from its melanocytic and nonmelanocytic differential diagnoses (Table).5-8 In our patient, the presence of a homogeneous pink to bluish area involving the entire lesion, linear branched vessels, and whitish structures on dermoscopy pointed to the diagnosis of apocrine hidrocystoma, which was further confirmed by characteristic histopathologic findings.
The treatment of apocrine hidrocystoma includes surgical excision for solitary lesions, with electrodesiccation and curettage, chemical cautery, and CO2 laser ablation employed for multiple lesions.1 Our patient was scheduled for CO2 laser ablation, considering the multiple lesions and size of the apocrine hidrocystoma but was subsequently lost to follow-up.
- Nguyen HP, Barker HS, Bloomquist L, et al. Giant pigmented apocrine hidrocystoma of the scalp [published online August 15, 2020]. Dermatol Online J. 2020;26:13030/qt7rt3s4pp.
- Anzai S, Goto M, Fujiwara S, et al. Apocrine hidrocystoma: a case report and analysis of 167 Japanese cases. Int J Dermatol. 2005;44:702-703. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2005.02512.x
- Zaballos P, Bañuls J, Medina C, et al. Dermoscopy of apocrine hidrocystomas: a morphological study. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2014;28:378-381. doi:10.1111/jdv.12044
- Haspeslagh M, Noë M, De Wispelaere I, et al. Rosettes and other white shiny structures in polarized dermoscopy: histological correlate and optical explanation. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2016;30:311-313. doi:10.1111/jdv.13080
- Suh KS, Kang DY, Park JB, et al. Usefulness of dermoscopy in the differential diagnosis of ruptured and unruptured epidermal cysts. Ann Dermatol. 2017;29:33-38. doi:10.5021/ad.2017.29.1.33
- Serrano P, Lallas A, Del Pozo LJ, et al. Dermoscopy of nodular hidradenoma, a great masquerader: a morphological study of 28 cases. Dermatology. 2016;232:78-82. doi:10.1159/000441218
- Russo T, Piccolo V, Lallas A, et al. Dermoscopy of malignant skin tumours: what’s new? Dermatology. 2017;233:64-73. doi:10.1159/000472253
- Zaballos P, Llambrich A, Puig S, et al. Dermoscopic findings of pilomatricomas. Dermatology. 2008;217:225-230. doi:10.1159 /000148248
The Diagnosis: Giant Apocrine Hidrocystoma
Histopathology of the noduloplaque revealed an unremarkable epidermis with multilocular cystic spaces centered in the dermis. The cysts had a double-lined epithelium with inner columnar to cuboidal cells and outer myoepithelial cells (bottom quiz image). Columnar cells showing decapitation secretion could be appreciated at places indicating apocrine secretion (Figure). A final diagnosis of apocrine hidrocystoma was made.

Hidrocystomas are rare, benign, cystic lesions derived either from apocrine or eccrine glands.1 Apocrine hidrocystoma usually manifests as asymptomatic, solitary, dome-shaped papules or nodules with a predilection for the head and neck region. Hidrocystomas can vary from flesh colored to blue, brown, or black. Pigmentation in hidrocystoma is seen in 5% to 80% of cases and is attributed to the Tyndall effect.1 The tumor usually is less than 20 mm in diameter; larger lesions are termed giant apocrine hidrocystoma.2 Apocrine hidrocystoma manifesting with multiple lesions and a size greater than 10 mm, as seen in our case, is uncommon.
Zaballos et al3 described dermoscopy of apocrine hidrocystoma in 22 patients. Hallmark dermoscopic findings were the presence of a homogeneous flesh-colored, yellowish, blue to pinkish-blue area involving the entire lesion with arborizing vessels and whitish structures.3 Similar dermoscopic findings were present in our patient. The homogeneous area histologically correlates to the multiloculated cysts located in the dermis. The exact reason for white structures is unknown; however, their visualization in apocrine hidrocystoma could be attributed to the alternation in collagen orientation secondary to the presence of large or multiple cysts in the dermis.
The presence of shiny white dots arranged in a square resembling a four-leaf clover (also known as white rosettes) was a unique dermoscopic finding in our patient. These rosettes can be appreciated only with polarized dermoscopy, and they have been described in actinic keratosis, seborrheic keratosis, squamous cell carcinoma, and basal cell carcinoma.4 The exact morphologic correlate of white rosettes is unknown but is postulated to be secondary to material inside adnexal openings in small rosettes and concentric perifollicular fibrosis in larger rosettes.4 In our patient, we believe the white rosettes can be attributed to the accumulated secretions in the dermal glands, which also were seen via histopathology. Dermoscopy also revealed increased peripheral, brown, networklike pigmentation, which was unique and could be secondary to the patient’s darker skin phenotype.
Differential diagnoses of apocrine hidrocystoma include both melanocytic and nonmelanocytic conditions such as epidermal cyst, nodular melanoma, nodular hidradenoma, syringoma, blue nevus, pilomatricoma, eccrine poroma, nodular Kaposi sarcoma, and venous lake.1 Histopathology showing large unilocular or multilocular dermal cysts with double lining comprising outer myoepithelial cells and inner columnar or cuboidal cell with decapitation secretion is paramount in confirming the diagnosis of apocrine hidrocystoma.
Dermoscopy can act as a valuable noninvasive modality in differentiating apocrine hidrocystoma from its melanocytic and nonmelanocytic differential diagnoses (Table).5-8 In our patient, the presence of a homogeneous pink to bluish area involving the entire lesion, linear branched vessels, and whitish structures on dermoscopy pointed to the diagnosis of apocrine hidrocystoma, which was further confirmed by characteristic histopathologic findings.

The treatment of apocrine hidrocystoma includes surgical excision for solitary lesions, with electrodesiccation and curettage, chemical cautery, and CO2 laser ablation employed for multiple lesions.1 Our patient was scheduled for CO2 laser ablation, considering the multiple lesions and size of the apocrine hidrocystoma but was subsequently lost to follow-up.
The Diagnosis: Giant Apocrine Hidrocystoma
Histopathology of the noduloplaque revealed an unremarkable epidermis with multilocular cystic spaces centered in the dermis. The cysts had a double-lined epithelium with inner columnar to cuboidal cells and outer myoepithelial cells (bottom quiz image). Columnar cells showing decapitation secretion could be appreciated at places indicating apocrine secretion (Figure). A final diagnosis of apocrine hidrocystoma was made.

Hidrocystomas are rare, benign, cystic lesions derived either from apocrine or eccrine glands.1 Apocrine hidrocystoma usually manifests as asymptomatic, solitary, dome-shaped papules or nodules with a predilection for the head and neck region. Hidrocystomas can vary from flesh colored to blue, brown, or black. Pigmentation in hidrocystoma is seen in 5% to 80% of cases and is attributed to the Tyndall effect.1 The tumor usually is less than 20 mm in diameter; larger lesions are termed giant apocrine hidrocystoma.2 Apocrine hidrocystoma manifesting with multiple lesions and a size greater than 10 mm, as seen in our case, is uncommon.
Zaballos et al3 described dermoscopy of apocrine hidrocystoma in 22 patients. Hallmark dermoscopic findings were the presence of a homogeneous flesh-colored, yellowish, blue to pinkish-blue area involving the entire lesion with arborizing vessels and whitish structures.3 Similar dermoscopic findings were present in our patient. The homogeneous area histologically correlates to the multiloculated cysts located in the dermis. The exact reason for white structures is unknown; however, their visualization in apocrine hidrocystoma could be attributed to the alternation in collagen orientation secondary to the presence of large or multiple cysts in the dermis.
The presence of shiny white dots arranged in a square resembling a four-leaf clover (also known as white rosettes) was a unique dermoscopic finding in our patient. These rosettes can be appreciated only with polarized dermoscopy, and they have been described in actinic keratosis, seborrheic keratosis, squamous cell carcinoma, and basal cell carcinoma.4 The exact morphologic correlate of white rosettes is unknown but is postulated to be secondary to material inside adnexal openings in small rosettes and concentric perifollicular fibrosis in larger rosettes.4 In our patient, we believe the white rosettes can be attributed to the accumulated secretions in the dermal glands, which also were seen via histopathology. Dermoscopy also revealed increased peripheral, brown, networklike pigmentation, which was unique and could be secondary to the patient’s darker skin phenotype.
Differential diagnoses of apocrine hidrocystoma include both melanocytic and nonmelanocytic conditions such as epidermal cyst, nodular melanoma, nodular hidradenoma, syringoma, blue nevus, pilomatricoma, eccrine poroma, nodular Kaposi sarcoma, and venous lake.1 Histopathology showing large unilocular or multilocular dermal cysts with double lining comprising outer myoepithelial cells and inner columnar or cuboidal cell with decapitation secretion is paramount in confirming the diagnosis of apocrine hidrocystoma.
Dermoscopy can act as a valuable noninvasive modality in differentiating apocrine hidrocystoma from its melanocytic and nonmelanocytic differential diagnoses (Table).5-8 In our patient, the presence of a homogeneous pink to bluish area involving the entire lesion, linear branched vessels, and whitish structures on dermoscopy pointed to the diagnosis of apocrine hidrocystoma, which was further confirmed by characteristic histopathologic findings.

The treatment of apocrine hidrocystoma includes surgical excision for solitary lesions, with electrodesiccation and curettage, chemical cautery, and CO2 laser ablation employed for multiple lesions.1 Our patient was scheduled for CO2 laser ablation, considering the multiple lesions and size of the apocrine hidrocystoma but was subsequently lost to follow-up.
- Nguyen HP, Barker HS, Bloomquist L, et al. Giant pigmented apocrine hidrocystoma of the scalp [published online August 15, 2020]. Dermatol Online J. 2020;26:13030/qt7rt3s4pp.
- Anzai S, Goto M, Fujiwara S, et al. Apocrine hidrocystoma: a case report and analysis of 167 Japanese cases. Int J Dermatol. 2005;44:702-703. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2005.02512.x
- Zaballos P, Bañuls J, Medina C, et al. Dermoscopy of apocrine hidrocystomas: a morphological study. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2014;28:378-381. doi:10.1111/jdv.12044
- Haspeslagh M, Noë M, De Wispelaere I, et al. Rosettes and other white shiny structures in polarized dermoscopy: histological correlate and optical explanation. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2016;30:311-313. doi:10.1111/jdv.13080
- Suh KS, Kang DY, Park JB, et al. Usefulness of dermoscopy in the differential diagnosis of ruptured and unruptured epidermal cysts. Ann Dermatol. 2017;29:33-38. doi:10.5021/ad.2017.29.1.33
- Serrano P, Lallas A, Del Pozo LJ, et al. Dermoscopy of nodular hidradenoma, a great masquerader: a morphological study of 28 cases. Dermatology. 2016;232:78-82. doi:10.1159/000441218
- Russo T, Piccolo V, Lallas A, et al. Dermoscopy of malignant skin tumours: what’s new? Dermatology. 2017;233:64-73. doi:10.1159/000472253
- Zaballos P, Llambrich A, Puig S, et al. Dermoscopic findings of pilomatricomas. Dermatology. 2008;217:225-230. doi:10.1159 /000148248
- Nguyen HP, Barker HS, Bloomquist L, et al. Giant pigmented apocrine hidrocystoma of the scalp [published online August 15, 2020]. Dermatol Online J. 2020;26:13030/qt7rt3s4pp.
- Anzai S, Goto M, Fujiwara S, et al. Apocrine hidrocystoma: a case report and analysis of 167 Japanese cases. Int J Dermatol. 2005;44:702-703. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2005.02512.x
- Zaballos P, Bañuls J, Medina C, et al. Dermoscopy of apocrine hidrocystomas: a morphological study. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2014;28:378-381. doi:10.1111/jdv.12044
- Haspeslagh M, Noë M, De Wispelaere I, et al. Rosettes and other white shiny structures in polarized dermoscopy: histological correlate and optical explanation. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2016;30:311-313. doi:10.1111/jdv.13080
- Suh KS, Kang DY, Park JB, et al. Usefulness of dermoscopy in the differential diagnosis of ruptured and unruptured epidermal cysts. Ann Dermatol. 2017;29:33-38. doi:10.5021/ad.2017.29.1.33
- Serrano P, Lallas A, Del Pozo LJ, et al. Dermoscopy of nodular hidradenoma, a great masquerader: a morphological study of 28 cases. Dermatology. 2016;232:78-82. doi:10.1159/000441218
- Russo T, Piccolo V, Lallas A, et al. Dermoscopy of malignant skin tumours: what’s new? Dermatology. 2017;233:64-73. doi:10.1159/000472253
- Zaballos P, Llambrich A, Puig S, et al. Dermoscopic findings of pilomatricomas. Dermatology. 2008;217:225-230. doi:10.1159 /000148248
A 21-year-old man presented with a raised lesion on the forehead that had started as a single papule 16 years prior and gradually increased in number and size. There were no associated symptoms and no history of seasonal variation in the size of the lesions. Physical examination revealed multiple erythematous to slightly bluish translucent papules that coalesced to form a 3×3-cm noduloplaque with cystic consistency on the right side of the forehead (top). Dermoscopic examination (middle) (polarized noncontact mode) revealed a homogeneous pink to bluish background, scattered linear vessels with branches (black arrows), multiple chrysalislike shiny white lines (blue arrows), and dots arranged in a 4-dot pattern (black circle) resembling a four-leaf clover. Increased peripheral, brown, networklike pigmentation (black stars) also was noted on dermoscopy. Histopathologic examination of the noduloplaque was performed (bottom).
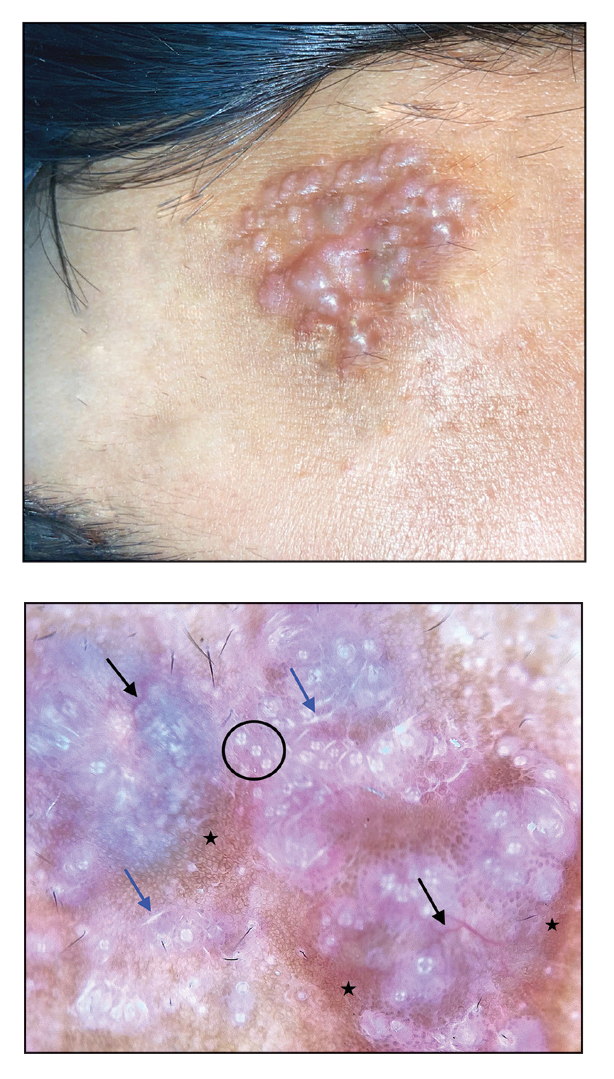
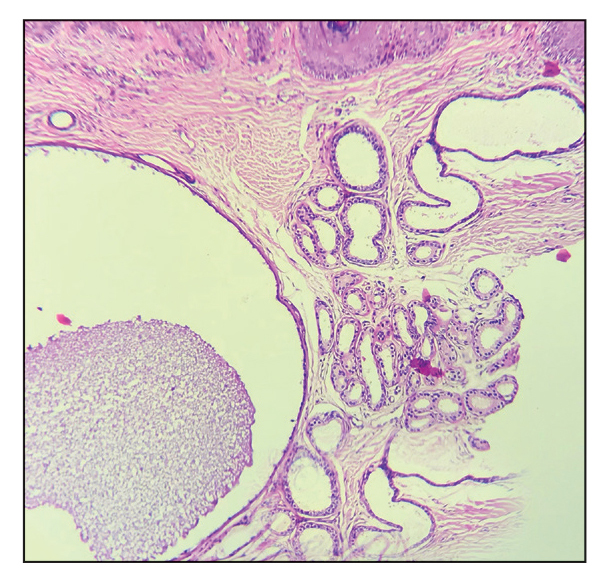
Nonblanching, Erythematous, Cerebriform Plaques on the Foot
The Diagnosis: Coral Dermatitis
At 3-week follow-up, the patient demonstrated remarkable improvement in the intensity and size of the erythematous cerebriform plaques following daily application of triamcinolone acetonide cream 0.1% (Figure). The lesion disappeared after several months and did not recur. The delayed presentation of symptoms with a history of incidental coral contact during snorkeling most likely represents the type IV hypersensitivity reaction seen in the diagnosis of coral dermatitis, an extraordinarily rare form of contact dermatitis.1 Not all coral trigger skin reactions. Species of coral that contain nematocysts in their tentacles (aptly named stinging capsules) are responsible for the sting preceding coral dermatitis, as the nematocysts eject a coiled filament in response to human tactile stimulation that injects toxins into the epidermis.2
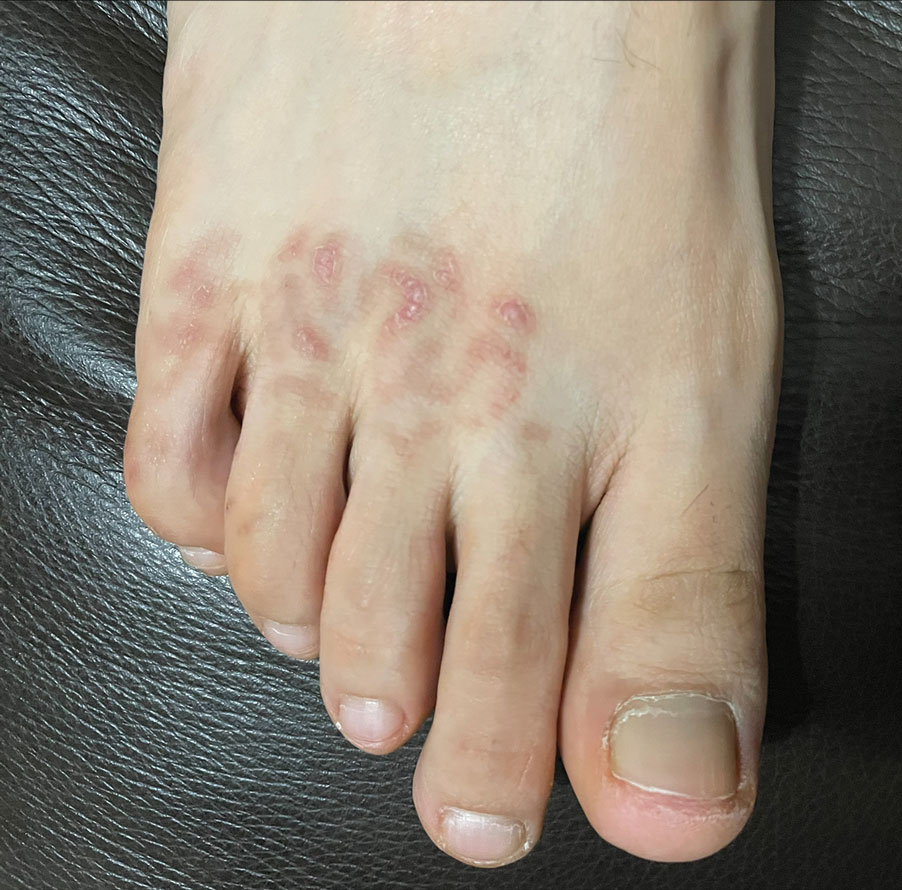
Acute, delayed, or chronic cutaneous changes follow envenomation. Acute responses arise immediately to a few hours after initial contact and are considered an irritant contact dermatitis.3 Local tissue histamine release and cascades of cytotoxic reactions often result in the characteristic urticarial or vesiculobullous plaques in addition to necrosis, piloerection, and localized lymphadenopathy.2-4 Although relatively uncommon, there may be rapid onset of systemic symptoms such as fever, malaise, hives, nausea, or emesis. Cardiopulmonary events, hepatotoxicity, renal failure, or anaphylaxis are rare.2 Histopathology of biopsy specimens reveals epidermal spongiosis with microvesicles and papillary dermal edema.1,5 In comparison, delayed reactions occur within days to weeks and exhibit epidermal parakeratosis, spongiosis, basal layer vacuolization, focal necrosis, lymphocyte exocytosis, and papillary dermal edema with extravasated erythrocytes.1,6 Clinically, it may present as linear rows of erythematous papules with burning and pruritus.6 Chronic reactions manifest after months as difficult-to-treat, persistent lichenoid dermatitis occasionally accompanied by granulomatous changes.1,2,4 Primary prevention measures after initial contact include an acetic acid rinse and cold compression to wash away residual nematocysts in the affected area.4,7,8 If a rash develops, topical steroids are the mainstay of treatment.3,8
In tandem with toxic nematocysts, the rigid calcified bodies of coral provide an additional self-defense mechanism against human contact.2,4 The irregular haphazard nature of coral may catch novice divers off guard and lead to laceration of a mispositioned limb, thereby increasing the risk for secondary infections due to the introduction of calcium carbonate and toxic mucinous deposits at the wound site, warranting antibiotic treatment.2,4,7 Because tropical locales are home to other natural dangers that inflict disease and mimic early signs of coral dermatitis, reaching an accurate diagnosis can be difficult, particularly for lower limb lesions. In summary, the diagnosis of coral dermatitis can be rendered based on morphology of the lesion and clinical context (exposure to corals and delayed symptoms) as well as response to topical steroids.
The differential diagnosis includes accidental trauma. Variations in impact force and patient skin integrity lead to a number of possible cutaneous manifestations seen in accidental trauma,9 which includes contusions resulting from burst capillaries underneath intact skin, abrasions due to the superficial epidermis scuffing away, and lacerations caused by enough force to rip and split the skin, leaving subcutaneous tissue between the intact tissue.9,10 Typically, the pattern of injury can provide hints to match what object or organism caused the wound.9 However, delayed response and worsening symptoms, as seen in coral dermatitis, would be unusual in accidental trauma unless it is complicated by secondary infection (infectious dermatitis), which does not respond to topical steroids and requires antibiotic treatment.
Another differential diagnosis includes cutaneous larva migrans, which infests domesticated and stray animals. For example, hookworm larvae propagate their eggs inside the intestines of their host before fecal-soil transmission in sandy locales.11 Unexpecting beachgoers travel barefoot on this contaminated soil, offering ample opportunity for the parasite to burrow into the upper dermis.11,12 The clinical presentation includes signs and symptoms of creeping eruption such as pruritic, linear, serpiginous tracks. Topical treatment with thiabendazole requires application 3 times daily for 15 days, which increases the risk for nonadherence, yet this therapy proves advantageous if a patient does not tolerate oral agents due to systemic adverse effects.11,12 Oral agents (eg, ivermectin, albendazole) offer improved adherence with a single dose11,13; the cure rate was higher with a single dose of ivermectin 12 mg vs a single dose of albendazole 400 mg.13 The current suggested treatment is ivermectin 200 μg/kg by mouth daily for 1 or 2 days.14
The incidence of seabather’s eruption (also known as chinkui dermatitis) is highest during the summer season and fluctuates between epidemic and nonepidemic years.15,16 It occurs sporadically worldwide mostly in tropical climates due to trapping of larvae spawn of sea animals such as crustaceans in swimwear. Initially, it presents as a pruritic and burning sensation after exiting the water, manifesting as a macular, papular, or maculopapular rash on areas covered by the swimsuit.15,16 The sensation is worse in areas that are tightly banded on the swimsuit, including the waistband and elastic straps.15 Commonly, the affected individual will seek relief via a shower, which intensifies the burning, especially if the swimsuit has not been removed. The contaminated swimwear should be immediately discarded, as the trapped sea larvae’s nematocysts activate with the pressure and friction of movement.15 Seabather’s eruption typically resolves spontaneously within a week, but symptom management can be achieved with topical steroids (triamcinolone 0.1% or clobetasol 0.05%).15,16 Unlike coral dermatitis, in seabather’s eruption the symptoms are immediate and the location of the eruption coincides with areas covered by the swimsuit.
- Ahn HS, Yoon SY, Park HJ, et al. A patient with delayed contact dermatitis to coral and she displayed superficial granuloma. Ann Dermatol. 2009;21:95-97. doi:10.5021/ad.2009.21.1.95
- Haddad V Jr, Lupi O, Lonza JP, et al. Tropical dermatology: marine and aquatic dermatology. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;61:733-752. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2009.01.046
- Salik J, Tang R. Images in clinical medicine. Coral dermatitis. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:E2. doi:10.1056/NEJMicm1412907
- Reese E, Depenbrock P. Water envenomations and stings. Curr Sports Med Rep. 2014;13:126-131. doi:10.1249/JSR.0000000000000042
- Addy JH. Red sea coral contact dermatitis. Int J Dermatol. 1991; 30:271-273. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4362.1991.tb04636.x
- Miracco C, Lalinga AV, Sbano P, et al. Delayed skin reaction to Red Sea coral injury showing superficial granulomas and atypical CD30+ lymphocytes: report of a case. Br J Dermatol. 2001;145:849-851. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2133.2001.04454.x
- Ceponis PJ, Cable R, Weaver LK. Don’t kick the coral! Wilderness Environ Med. 2017;28:153-155. doi:10.1016/j.wem.2017.01.025
- Tlougan BE, Podjasek JO, Adams BB. Aquatic sports dematoses. part 2-in the water: saltwater dermatoses. Int J Dermatol. 2010;49:994-1002. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2010.04476.x
- Simon LV, Lopez RA, King KC. Blunt force trauma. StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing; 2023. Accessed January 12, 2034. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470338/
- Gentile S, Kneubuehl BP, Barrera V, et al. Fracture energy threshold in parry injuries due to sharp and blunt force. Int J Legal Med. 2019;133:1429-1435.
- Caumes E. Treatment of cutaneous larva migrans. Clin Infect Dis. 2000;30:811-814. doi:10.1086/313787
- Davies HD, Sakuls P, Keystone JS. Creeping eruption. A review of clinical presentation and management of 60 cases presenting to a tropical disease unit. Arch Dermatol. 1993;129:588-591. doi:10.1001 /archderm.129.5.588
- Caumes E, Carriere J, Datry A, et al. A randomized trial of ivermectin versus albendazole for the treatment of cutaneous larva migrans. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1993;49:641-644. doi:10.4269 /ajtmh.1993.49.641
- Schuster A, Lesshafft H, Reichert F, et al. Hookworm-related cutaneous larva migrans in northern Brazil: resolution of clinical pathology after a single dose of ivermectin. Clin Infect Dis. 2013;57:1155-1157. doi:10.1093/cid/cit440
- Freudenthal AR, Joseph PR. Seabather’s eruption. N Engl J Med. 1993;329:542-544. doi:10.1056/NEJM199308193290805
- Odagawa S, Watari T, Yoshida M. Chinkui dermatitis: the sea bather’s eruption. QJM. 2022;115:100-101. doi:10.1093/qjmed/hcab277
The Diagnosis: Coral Dermatitis
At 3-week follow-up, the patient demonstrated remarkable improvement in the intensity and size of the erythematous cerebriform plaques following daily application of triamcinolone acetonide cream 0.1% (Figure). The lesion disappeared after several months and did not recur. The delayed presentation of symptoms with a history of incidental coral contact during snorkeling most likely represents the type IV hypersensitivity reaction seen in the diagnosis of coral dermatitis, an extraordinarily rare form of contact dermatitis.1 Not all coral trigger skin reactions. Species of coral that contain nematocysts in their tentacles (aptly named stinging capsules) are responsible for the sting preceding coral dermatitis, as the nematocysts eject a coiled filament in response to human tactile stimulation that injects toxins into the epidermis.2

Acute, delayed, or chronic cutaneous changes follow envenomation. Acute responses arise immediately to a few hours after initial contact and are considered an irritant contact dermatitis.3 Local tissue histamine release and cascades of cytotoxic reactions often result in the characteristic urticarial or vesiculobullous plaques in addition to necrosis, piloerection, and localized lymphadenopathy.2-4 Although relatively uncommon, there may be rapid onset of systemic symptoms such as fever, malaise, hives, nausea, or emesis. Cardiopulmonary events, hepatotoxicity, renal failure, or anaphylaxis are rare.2 Histopathology of biopsy specimens reveals epidermal spongiosis with microvesicles and papillary dermal edema.1,5 In comparison, delayed reactions occur within days to weeks and exhibit epidermal parakeratosis, spongiosis, basal layer vacuolization, focal necrosis, lymphocyte exocytosis, and papillary dermal edema with extravasated erythrocytes.1,6 Clinically, it may present as linear rows of erythematous papules with burning and pruritus.6 Chronic reactions manifest after months as difficult-to-treat, persistent lichenoid dermatitis occasionally accompanied by granulomatous changes.1,2,4 Primary prevention measures after initial contact include an acetic acid rinse and cold compression to wash away residual nematocysts in the affected area.4,7,8 If a rash develops, topical steroids are the mainstay of treatment.3,8
In tandem with toxic nematocysts, the rigid calcified bodies of coral provide an additional self-defense mechanism against human contact.2,4 The irregular haphazard nature of coral may catch novice divers off guard and lead to laceration of a mispositioned limb, thereby increasing the risk for secondary infections due to the introduction of calcium carbonate and toxic mucinous deposits at the wound site, warranting antibiotic treatment.2,4,7 Because tropical locales are home to other natural dangers that inflict disease and mimic early signs of coral dermatitis, reaching an accurate diagnosis can be difficult, particularly for lower limb lesions. In summary, the diagnosis of coral dermatitis can be rendered based on morphology of the lesion and clinical context (exposure to corals and delayed symptoms) as well as response to topical steroids.
The differential diagnosis includes accidental trauma. Variations in impact force and patient skin integrity lead to a number of possible cutaneous manifestations seen in accidental trauma,9 which includes contusions resulting from burst capillaries underneath intact skin, abrasions due to the superficial epidermis scuffing away, and lacerations caused by enough force to rip and split the skin, leaving subcutaneous tissue between the intact tissue.9,10 Typically, the pattern of injury can provide hints to match what object or organism caused the wound.9 However, delayed response and worsening symptoms, as seen in coral dermatitis, would be unusual in accidental trauma unless it is complicated by secondary infection (infectious dermatitis), which does not respond to topical steroids and requires antibiotic treatment.
Another differential diagnosis includes cutaneous larva migrans, which infests domesticated and stray animals. For example, hookworm larvae propagate their eggs inside the intestines of their host before fecal-soil transmission in sandy locales.11 Unexpecting beachgoers travel barefoot on this contaminated soil, offering ample opportunity for the parasite to burrow into the upper dermis.11,12 The clinical presentation includes signs and symptoms of creeping eruption such as pruritic, linear, serpiginous tracks. Topical treatment with thiabendazole requires application 3 times daily for 15 days, which increases the risk for nonadherence, yet this therapy proves advantageous if a patient does not tolerate oral agents due to systemic adverse effects.11,12 Oral agents (eg, ivermectin, albendazole) offer improved adherence with a single dose11,13; the cure rate was higher with a single dose of ivermectin 12 mg vs a single dose of albendazole 400 mg.13 The current suggested treatment is ivermectin 200 μg/kg by mouth daily for 1 or 2 days.14
The incidence of seabather’s eruption (also known as chinkui dermatitis) is highest during the summer season and fluctuates between epidemic and nonepidemic years.15,16 It occurs sporadically worldwide mostly in tropical climates due to trapping of larvae spawn of sea animals such as crustaceans in swimwear. Initially, it presents as a pruritic and burning sensation after exiting the water, manifesting as a macular, papular, or maculopapular rash on areas covered by the swimsuit.15,16 The sensation is worse in areas that are tightly banded on the swimsuit, including the waistband and elastic straps.15 Commonly, the affected individual will seek relief via a shower, which intensifies the burning, especially if the swimsuit has not been removed. The contaminated swimwear should be immediately discarded, as the trapped sea larvae’s nematocysts activate with the pressure and friction of movement.15 Seabather’s eruption typically resolves spontaneously within a week, but symptom management can be achieved with topical steroids (triamcinolone 0.1% or clobetasol 0.05%).15,16 Unlike coral dermatitis, in seabather’s eruption the symptoms are immediate and the location of the eruption coincides with areas covered by the swimsuit.
The Diagnosis: Coral Dermatitis
At 3-week follow-up, the patient demonstrated remarkable improvement in the intensity and size of the erythematous cerebriform plaques following daily application of triamcinolone acetonide cream 0.1% (Figure). The lesion disappeared after several months and did not recur. The delayed presentation of symptoms with a history of incidental coral contact during snorkeling most likely represents the type IV hypersensitivity reaction seen in the diagnosis of coral dermatitis, an extraordinarily rare form of contact dermatitis.1 Not all coral trigger skin reactions. Species of coral that contain nematocysts in their tentacles (aptly named stinging capsules) are responsible for the sting preceding coral dermatitis, as the nematocysts eject a coiled filament in response to human tactile stimulation that injects toxins into the epidermis.2

Acute, delayed, or chronic cutaneous changes follow envenomation. Acute responses arise immediately to a few hours after initial contact and are considered an irritant contact dermatitis.3 Local tissue histamine release and cascades of cytotoxic reactions often result in the characteristic urticarial or vesiculobullous plaques in addition to necrosis, piloerection, and localized lymphadenopathy.2-4 Although relatively uncommon, there may be rapid onset of systemic symptoms such as fever, malaise, hives, nausea, or emesis. Cardiopulmonary events, hepatotoxicity, renal failure, or anaphylaxis are rare.2 Histopathology of biopsy specimens reveals epidermal spongiosis with microvesicles and papillary dermal edema.1,5 In comparison, delayed reactions occur within days to weeks and exhibit epidermal parakeratosis, spongiosis, basal layer vacuolization, focal necrosis, lymphocyte exocytosis, and papillary dermal edema with extravasated erythrocytes.1,6 Clinically, it may present as linear rows of erythematous papules with burning and pruritus.6 Chronic reactions manifest after months as difficult-to-treat, persistent lichenoid dermatitis occasionally accompanied by granulomatous changes.1,2,4 Primary prevention measures after initial contact include an acetic acid rinse and cold compression to wash away residual nematocysts in the affected area.4,7,8 If a rash develops, topical steroids are the mainstay of treatment.3,8
In tandem with toxic nematocysts, the rigid calcified bodies of coral provide an additional self-defense mechanism against human contact.2,4 The irregular haphazard nature of coral may catch novice divers off guard and lead to laceration of a mispositioned limb, thereby increasing the risk for secondary infections due to the introduction of calcium carbonate and toxic mucinous deposits at the wound site, warranting antibiotic treatment.2,4,7 Because tropical locales are home to other natural dangers that inflict disease and mimic early signs of coral dermatitis, reaching an accurate diagnosis can be difficult, particularly for lower limb lesions. In summary, the diagnosis of coral dermatitis can be rendered based on morphology of the lesion and clinical context (exposure to corals and delayed symptoms) as well as response to topical steroids.
The differential diagnosis includes accidental trauma. Variations in impact force and patient skin integrity lead to a number of possible cutaneous manifestations seen in accidental trauma,9 which includes contusions resulting from burst capillaries underneath intact skin, abrasions due to the superficial epidermis scuffing away, and lacerations caused by enough force to rip and split the skin, leaving subcutaneous tissue between the intact tissue.9,10 Typically, the pattern of injury can provide hints to match what object or organism caused the wound.9 However, delayed response and worsening symptoms, as seen in coral dermatitis, would be unusual in accidental trauma unless it is complicated by secondary infection (infectious dermatitis), which does not respond to topical steroids and requires antibiotic treatment.
Another differential diagnosis includes cutaneous larva migrans, which infests domesticated and stray animals. For example, hookworm larvae propagate their eggs inside the intestines of their host before fecal-soil transmission in sandy locales.11 Unexpecting beachgoers travel barefoot on this contaminated soil, offering ample opportunity for the parasite to burrow into the upper dermis.11,12 The clinical presentation includes signs and symptoms of creeping eruption such as pruritic, linear, serpiginous tracks. Topical treatment with thiabendazole requires application 3 times daily for 15 days, which increases the risk for nonadherence, yet this therapy proves advantageous if a patient does not tolerate oral agents due to systemic adverse effects.11,12 Oral agents (eg, ivermectin, albendazole) offer improved adherence with a single dose11,13; the cure rate was higher with a single dose of ivermectin 12 mg vs a single dose of albendazole 400 mg.13 The current suggested treatment is ivermectin 200 μg/kg by mouth daily for 1 or 2 days.14
The incidence of seabather’s eruption (also known as chinkui dermatitis) is highest during the summer season and fluctuates between epidemic and nonepidemic years.15,16 It occurs sporadically worldwide mostly in tropical climates due to trapping of larvae spawn of sea animals such as crustaceans in swimwear. Initially, it presents as a pruritic and burning sensation after exiting the water, manifesting as a macular, papular, or maculopapular rash on areas covered by the swimsuit.15,16 The sensation is worse in areas that are tightly banded on the swimsuit, including the waistband and elastic straps.15 Commonly, the affected individual will seek relief via a shower, which intensifies the burning, especially if the swimsuit has not been removed. The contaminated swimwear should be immediately discarded, as the trapped sea larvae’s nematocysts activate with the pressure and friction of movement.15 Seabather’s eruption typically resolves spontaneously within a week, but symptom management can be achieved with topical steroids (triamcinolone 0.1% or clobetasol 0.05%).15,16 Unlike coral dermatitis, in seabather’s eruption the symptoms are immediate and the location of the eruption coincides with areas covered by the swimsuit.
- Ahn HS, Yoon SY, Park HJ, et al. A patient with delayed contact dermatitis to coral and she displayed superficial granuloma. Ann Dermatol. 2009;21:95-97. doi:10.5021/ad.2009.21.1.95
- Haddad V Jr, Lupi O, Lonza JP, et al. Tropical dermatology: marine and aquatic dermatology. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;61:733-752. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2009.01.046
- Salik J, Tang R. Images in clinical medicine. Coral dermatitis. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:E2. doi:10.1056/NEJMicm1412907
- Reese E, Depenbrock P. Water envenomations and stings. Curr Sports Med Rep. 2014;13:126-131. doi:10.1249/JSR.0000000000000042
- Addy JH. Red sea coral contact dermatitis. Int J Dermatol. 1991; 30:271-273. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4362.1991.tb04636.x
- Miracco C, Lalinga AV, Sbano P, et al. Delayed skin reaction to Red Sea coral injury showing superficial granulomas and atypical CD30+ lymphocytes: report of a case. Br J Dermatol. 2001;145:849-851. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2133.2001.04454.x
- Ceponis PJ, Cable R, Weaver LK. Don’t kick the coral! Wilderness Environ Med. 2017;28:153-155. doi:10.1016/j.wem.2017.01.025
- Tlougan BE, Podjasek JO, Adams BB. Aquatic sports dematoses. part 2-in the water: saltwater dermatoses. Int J Dermatol. 2010;49:994-1002. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2010.04476.x
- Simon LV, Lopez RA, King KC. Blunt force trauma. StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing; 2023. Accessed January 12, 2034. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470338/
- Gentile S, Kneubuehl BP, Barrera V, et al. Fracture energy threshold in parry injuries due to sharp and blunt force. Int J Legal Med. 2019;133:1429-1435.
- Caumes E. Treatment of cutaneous larva migrans. Clin Infect Dis. 2000;30:811-814. doi:10.1086/313787
- Davies HD, Sakuls P, Keystone JS. Creeping eruption. A review of clinical presentation and management of 60 cases presenting to a tropical disease unit. Arch Dermatol. 1993;129:588-591. doi:10.1001 /archderm.129.5.588
- Caumes E, Carriere J, Datry A, et al. A randomized trial of ivermectin versus albendazole for the treatment of cutaneous larva migrans. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1993;49:641-644. doi:10.4269 /ajtmh.1993.49.641
- Schuster A, Lesshafft H, Reichert F, et al. Hookworm-related cutaneous larva migrans in northern Brazil: resolution of clinical pathology after a single dose of ivermectin. Clin Infect Dis. 2013;57:1155-1157. doi:10.1093/cid/cit440
- Freudenthal AR, Joseph PR. Seabather’s eruption. N Engl J Med. 1993;329:542-544. doi:10.1056/NEJM199308193290805
- Odagawa S, Watari T, Yoshida M. Chinkui dermatitis: the sea bather’s eruption. QJM. 2022;115:100-101. doi:10.1093/qjmed/hcab277
- Ahn HS, Yoon SY, Park HJ, et al. A patient with delayed contact dermatitis to coral and she displayed superficial granuloma. Ann Dermatol. 2009;21:95-97. doi:10.5021/ad.2009.21.1.95
- Haddad V Jr, Lupi O, Lonza JP, et al. Tropical dermatology: marine and aquatic dermatology. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;61:733-752. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2009.01.046
- Salik J, Tang R. Images in clinical medicine. Coral dermatitis. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:E2. doi:10.1056/NEJMicm1412907
- Reese E, Depenbrock P. Water envenomations and stings. Curr Sports Med Rep. 2014;13:126-131. doi:10.1249/JSR.0000000000000042
- Addy JH. Red sea coral contact dermatitis. Int J Dermatol. 1991; 30:271-273. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4362.1991.tb04636.x
- Miracco C, Lalinga AV, Sbano P, et al. Delayed skin reaction to Red Sea coral injury showing superficial granulomas and atypical CD30+ lymphocytes: report of a case. Br J Dermatol. 2001;145:849-851. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2133.2001.04454.x
- Ceponis PJ, Cable R, Weaver LK. Don’t kick the coral! Wilderness Environ Med. 2017;28:153-155. doi:10.1016/j.wem.2017.01.025
- Tlougan BE, Podjasek JO, Adams BB. Aquatic sports dematoses. part 2-in the water: saltwater dermatoses. Int J Dermatol. 2010;49:994-1002. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2010.04476.x
- Simon LV, Lopez RA, King KC. Blunt force trauma. StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing; 2023. Accessed January 12, 2034. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470338/
- Gentile S, Kneubuehl BP, Barrera V, et al. Fracture energy threshold in parry injuries due to sharp and blunt force. Int J Legal Med. 2019;133:1429-1435.
- Caumes E. Treatment of cutaneous larva migrans. Clin Infect Dis. 2000;30:811-814. doi:10.1086/313787
- Davies HD, Sakuls P, Keystone JS. Creeping eruption. A review of clinical presentation and management of 60 cases presenting to a tropical disease unit. Arch Dermatol. 1993;129:588-591. doi:10.1001 /archderm.129.5.588
- Caumes E, Carriere J, Datry A, et al. A randomized trial of ivermectin versus albendazole for the treatment of cutaneous larva migrans. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1993;49:641-644. doi:10.4269 /ajtmh.1993.49.641
- Schuster A, Lesshafft H, Reichert F, et al. Hookworm-related cutaneous larva migrans in northern Brazil: resolution of clinical pathology after a single dose of ivermectin. Clin Infect Dis. 2013;57:1155-1157. doi:10.1093/cid/cit440
- Freudenthal AR, Joseph PR. Seabather’s eruption. N Engl J Med. 1993;329:542-544. doi:10.1056/NEJM199308193290805
- Odagawa S, Watari T, Yoshida M. Chinkui dermatitis: the sea bather’s eruption. QJM. 2022;115:100-101. doi:10.1093/qjmed/hcab277
A 48-year-old otherwise healthy man presented with a tender lesion on the dorsal aspect of the right foot with dysesthesia and progressive pruritus that he originally noticed 9 days prior after snorkeling in the Caribbean. He recalled kicking what he assumed was a rock while swimming. Initially there was negligible discomfort; however, on day 7 the symptoms started to worsen and the lesion started to swell. Application of a gauze pad soaked in hydrogen peroxide 3% failed to alleviate symptoms. Physical examination revealed a 4-cm region of well-demarcated, nonblanching, erythematous plaques in a lattice pattern accompanied by edematous and bullous changes. Triamcinolone acetonide cream 0.1% was prescribed.
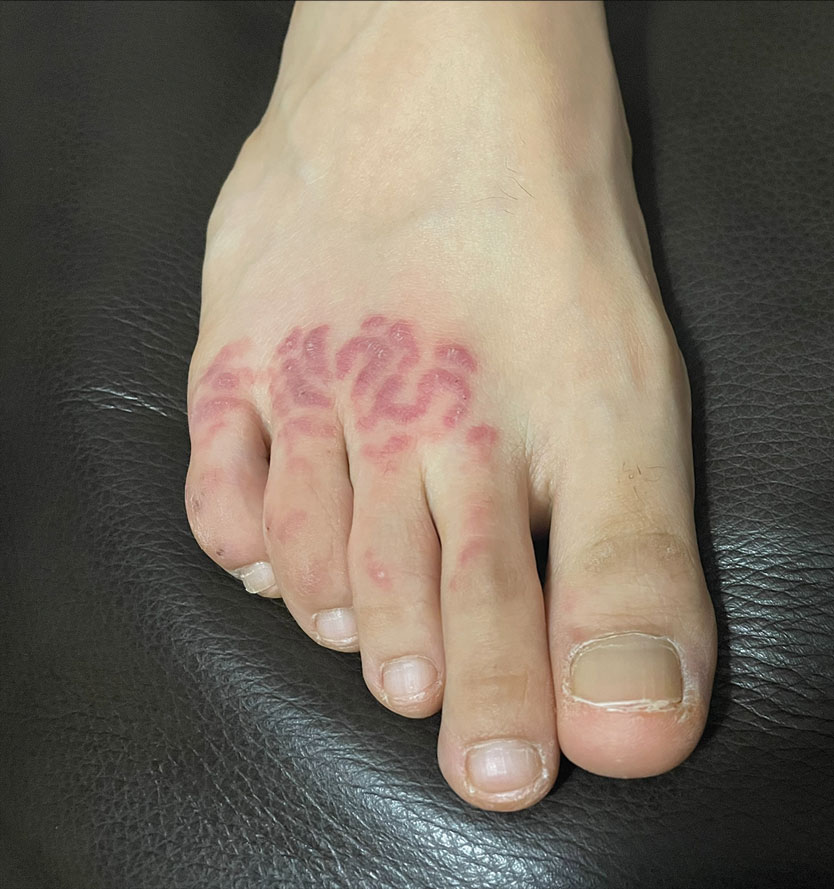
Annular Erythematous Plaques on the Back
The Diagnosis: Granuloma Annulare
The biopsies revealed palisading granulomatous dermatitis consistent with granuloma annulare (GA). This diagnosis was supported by the clinical presentation and histopathologic findings. Although the pathogenesis of GA is unclear, it is a benign, self-limiting condition. Primarily affected sites include the trunk and forearms. Generalized GA (or GA with ≥10 lesions) may warrant workup for malignancy, as it may represent a paraneoplastic process.1 Histopathology reveals granulomas comprising a dermal lymphohistiocytic infiltrate as well as central mucin and nuclear debris. There are a few histologic subtypes of GA, including palisading and interstitial, which refer to the distribution of the histiocytic infiltrate.2,3 This case—with palisading histiocytes lining the collection of necrobiosis and mucin (bottom quiz image)—features palisading GA. Notably, GA exhibits central rather than diffuse mucin.4
Erythema gyratum repens is a paraneoplastic arcuate erythema that manifests as erythematous figurate, gyrate, or annular plaques exhibiting a trailing scale. Clinically, erythema gyratum repens spreads rapidly—as quickly as 1 cm/d—and can be extensive (as in this case). Histopathology ruled out this diagnosis in our patient. Nonspecific findings of acanthosis, parakeratosis, and superficial spongiosis can be found in erythema gyratum repens. A superficial and deep perivascular lymphohistiocytic infiltrate may be seen in figurate erythemas (Figure 1).5 Unlike GA, this infiltrate does not form granulomas, is more superficial, and does not contain mucin.
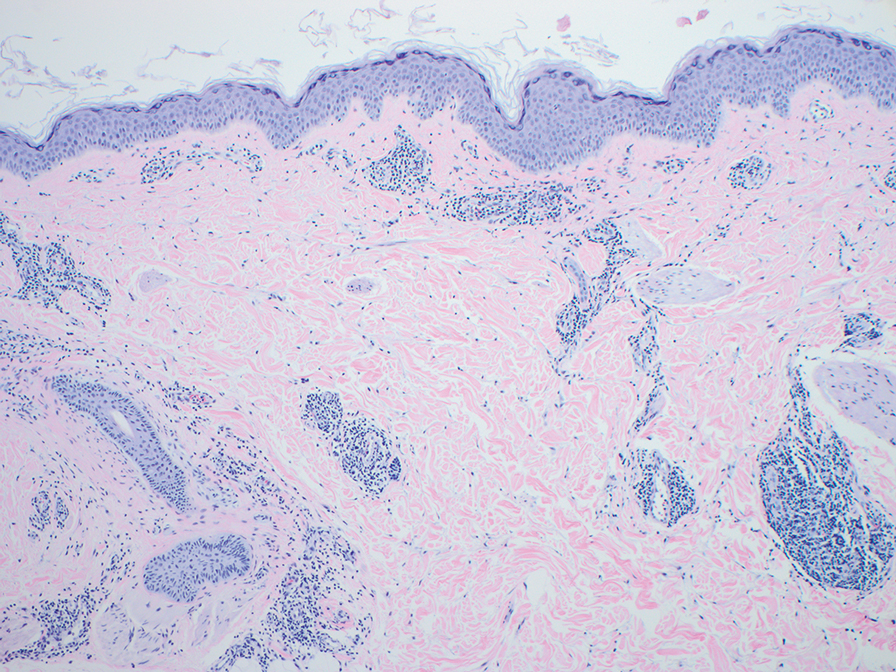
Histopathology also can help establish the diagnosis of leprosy and its specific subtype, as leprosy exists on a spectrum from tuberculoid to lepromatous, with a great deal of overlap in between.6 Lepromatous leprosy has many cutaneous clinical presentations but typically manifests as erythematous papules or nodules. It is multibacillary, and these mycobacteria form clumps known as globi that can be seen on Fite stain.7 In lepromatous leprosy, there is a characteristic dense lymphohistiocytic infiltrate (Figure 2) above which a Grenz zone can be seen.4,8 There are no well-formed granulomas in lepromatous leprosy, unlike in tuberculoid leprosy, which is paucibacillary and creates a granulomatous response surrounding nerves and adnexal structures.6
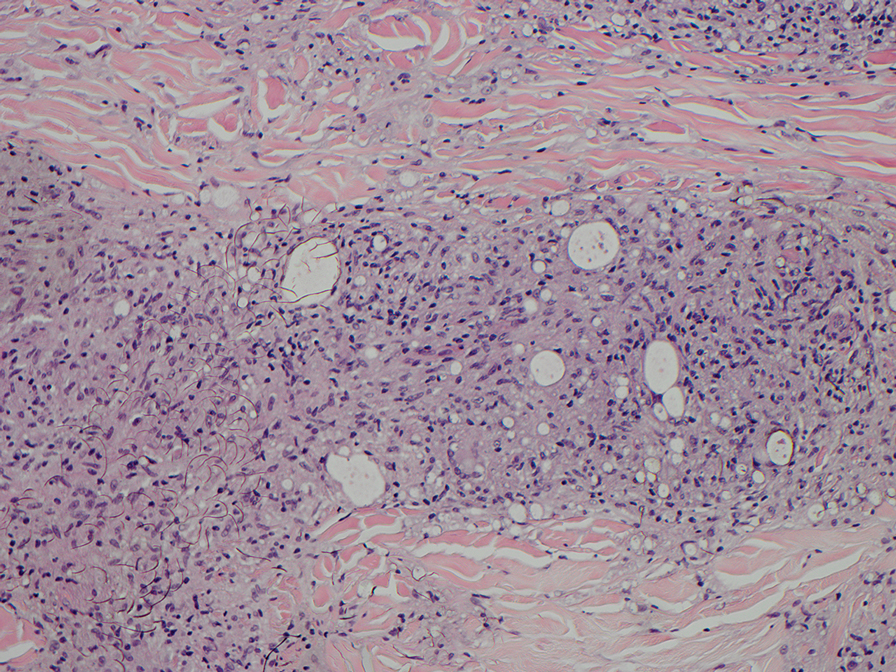
Mycosis fungoides (MF) is the most common cutaneous lymphoma. There are patch, plaque, and tumor stages of MF, each of which exhibits various histopathologic findings.9 In early patch-stage MF, lymphocytes have perinuclear clearing, and the degree of lymphocytic infiltrate is out of proportion to the spongiosis present. Epidermotropism and Pautrier microabscesses often are present in the epidermis (Figure 3). In the plaque stage, there is a denser lymphoid infiltrate in a lichenoid pattern with epidermotropism and Pautrier microabscesses. The tumor stage shows a dense dermal lymphoid infiltrate with more atypia and typically a lack of epidermotropism. Rarely, MF can exhibit a granulomatous variant in which epithelioid histiocytes collect to form granulomas along with atypical lymphocytes.10
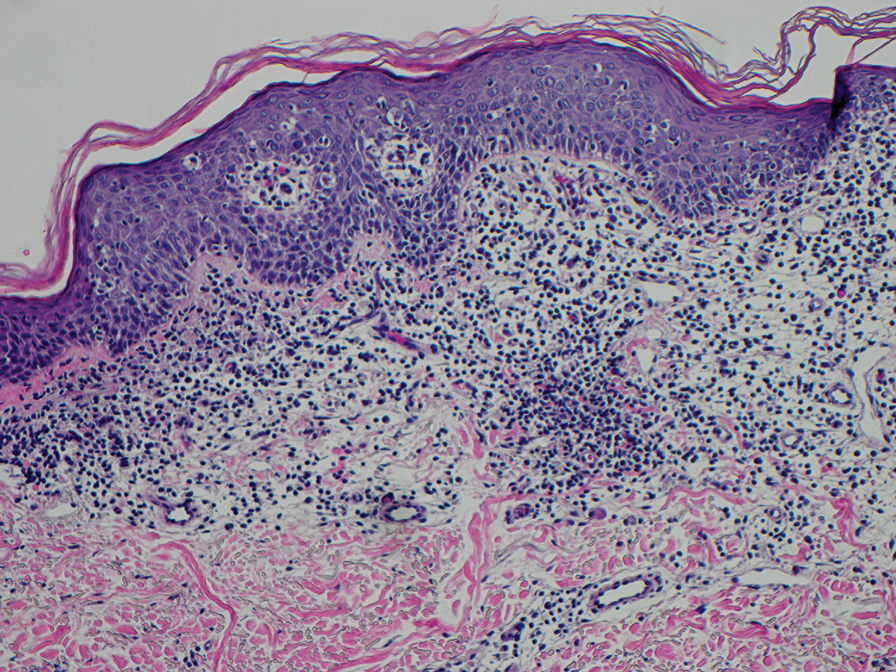
The diagnosis of cutaneous sarcoidosis requires clinicopathologic corroboration. Histopathology demonstrates epithelioid histiocytes forming noncaseating granulomas with little to no lymphocytic infiltrate (Figure 4). There typically is no necrosis or necrobiosis as there is in GA. The diagnosis of sarcoidosis can be challenging histopathologically, and stains should be used to rule out infectious processes.4 Asteroid bodies— star-shaped eosinophilic inclusions within giant cells—may be present but are nonspecific for sarcoidosis.11 Schaumann bodies—inclusions of calcifications within giant cells—also may be present and can aid in diagnosis.12
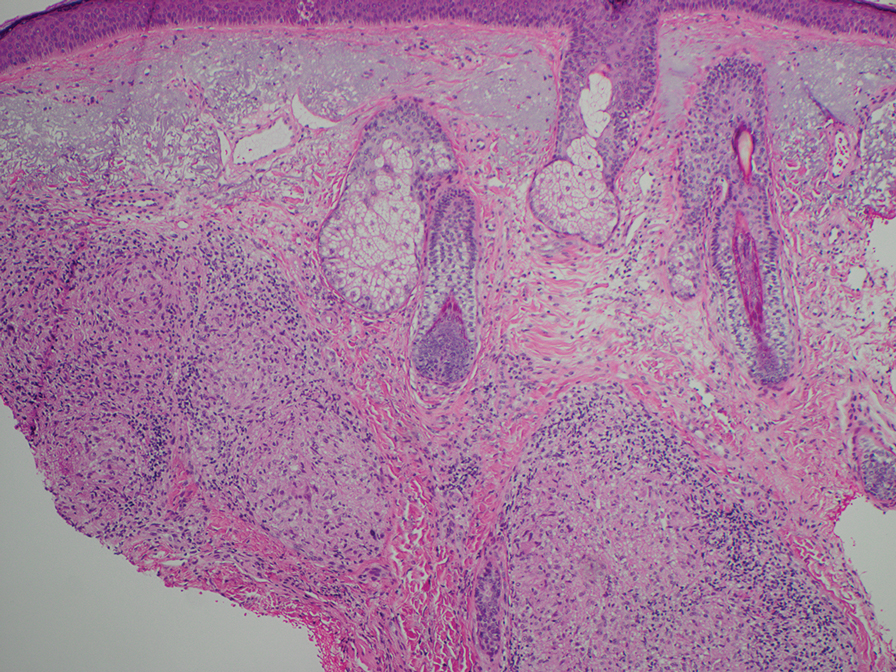
- Kovich O, Burgin S. Generalized granuloma annulare [published online December 30, 2005]. Dermatol Online J. 2005;11:23.
- Al Ameer MA, Al-Natour SH, Alsahaf HAA, et al. Eruptive granuloma annulare in an elderly man with diabetes [published online January 14, 2022]. Cureus. 2022;14:E21242. doi:10.7759/cureus.21242
- Howard A, White CR Jr. Non-infectious granulomas. In: Bolognia JL, et al, eds. Dermatology. Mosby; 2003:1455.
- Elston DM, Ferringer T, Ko CJ, et al. Dermatopathology. 3rd ed. Elsevier; 2018.
- Gore M, Winters ME. Erythema gyratum repens: a rare paraneoplastic rash. West J Emerg Med. 2011;12:556-558. doi:10.5811/westjem.2010.11.2090
- Maymone MBC, Laughter M, Venkatesh S, et al. Leprosy: clinical aspects and diagnostic techniques. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:1-14. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2019.12.080
- Pedley JC, Harman DJ, Waudby H, et al. Leprosy in peripheral nerves: histopathological findings in 119 untreated patients in Nepal. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1980;43:198-204. doi:10.1136/jnnp.43.3.198
- Booth AV, Kovich OI. Lepromatous leprosy [published online January 27, 2007]. Dermatol Online J. 2007;13:9.
- Robson A. The pathology of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Oncology (Williston Park). 2007;21(2 suppl 1):9-12.
- Kempf W, Ostheeren-Michaelis S, Paulli M, et al. Granulomatous mycosis fungoides and granulomatous slack skin: a multicenter study of the Cutaneous Lymphoma Histopathology Task Force Group of the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC). Arch Dermatol. 2008;144:1609-1617. doi:10.1001/archdermatol.2008.46
- Azar HA, Lunardelli C. Collagen nature of asteroid bodies of giant cells in sarcoidosis. Am J Pathol. 1969;57:81-92.
- Sreeja C, Priyadarshini A, Premika, et al. Sarcoidosis—a review article. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. 2022;26:242-253. doi:10.4103 /jomfp.jomfp_373_21
The Diagnosis: Granuloma Annulare
The biopsies revealed palisading granulomatous dermatitis consistent with granuloma annulare (GA). This diagnosis was supported by the clinical presentation and histopathologic findings. Although the pathogenesis of GA is unclear, it is a benign, self-limiting condition. Primarily affected sites include the trunk and forearms. Generalized GA (or GA with ≥10 lesions) may warrant workup for malignancy, as it may represent a paraneoplastic process.1 Histopathology reveals granulomas comprising a dermal lymphohistiocytic infiltrate as well as central mucin and nuclear debris. There are a few histologic subtypes of GA, including palisading and interstitial, which refer to the distribution of the histiocytic infiltrate.2,3 This case—with palisading histiocytes lining the collection of necrobiosis and mucin (bottom quiz image)—features palisading GA. Notably, GA exhibits central rather than diffuse mucin.4
Erythema gyratum repens is a paraneoplastic arcuate erythema that manifests as erythematous figurate, gyrate, or annular plaques exhibiting a trailing scale. Clinically, erythema gyratum repens spreads rapidly—as quickly as 1 cm/d—and can be extensive (as in this case). Histopathology ruled out this diagnosis in our patient. Nonspecific findings of acanthosis, parakeratosis, and superficial spongiosis can be found in erythema gyratum repens. A superficial and deep perivascular lymphohistiocytic infiltrate may be seen in figurate erythemas (Figure 1).5 Unlike GA, this infiltrate does not form granulomas, is more superficial, and does not contain mucin.

Histopathology also can help establish the diagnosis of leprosy and its specific subtype, as leprosy exists on a spectrum from tuberculoid to lepromatous, with a great deal of overlap in between.6 Lepromatous leprosy has many cutaneous clinical presentations but typically manifests as erythematous papules or nodules. It is multibacillary, and these mycobacteria form clumps known as globi that can be seen on Fite stain.7 In lepromatous leprosy, there is a characteristic dense lymphohistiocytic infiltrate (Figure 2) above which a Grenz zone can be seen.4,8 There are no well-formed granulomas in lepromatous leprosy, unlike in tuberculoid leprosy, which is paucibacillary and creates a granulomatous response surrounding nerves and adnexal structures.6

Mycosis fungoides (MF) is the most common cutaneous lymphoma. There are patch, plaque, and tumor stages of MF, each of which exhibits various histopathologic findings.9 In early patch-stage MF, lymphocytes have perinuclear clearing, and the degree of lymphocytic infiltrate is out of proportion to the spongiosis present. Epidermotropism and Pautrier microabscesses often are present in the epidermis (Figure 3). In the plaque stage, there is a denser lymphoid infiltrate in a lichenoid pattern with epidermotropism and Pautrier microabscesses. The tumor stage shows a dense dermal lymphoid infiltrate with more atypia and typically a lack of epidermotropism. Rarely, MF can exhibit a granulomatous variant in which epithelioid histiocytes collect to form granulomas along with atypical lymphocytes.10

The diagnosis of cutaneous sarcoidosis requires clinicopathologic corroboration. Histopathology demonstrates epithelioid histiocytes forming noncaseating granulomas with little to no lymphocytic infiltrate (Figure 4). There typically is no necrosis or necrobiosis as there is in GA. The diagnosis of sarcoidosis can be challenging histopathologically, and stains should be used to rule out infectious processes.4 Asteroid bodies— star-shaped eosinophilic inclusions within giant cells—may be present but are nonspecific for sarcoidosis.11 Schaumann bodies—inclusions of calcifications within giant cells—also may be present and can aid in diagnosis.12

The Diagnosis: Granuloma Annulare
The biopsies revealed palisading granulomatous dermatitis consistent with granuloma annulare (GA). This diagnosis was supported by the clinical presentation and histopathologic findings. Although the pathogenesis of GA is unclear, it is a benign, self-limiting condition. Primarily affected sites include the trunk and forearms. Generalized GA (or GA with ≥10 lesions) may warrant workup for malignancy, as it may represent a paraneoplastic process.1 Histopathology reveals granulomas comprising a dermal lymphohistiocytic infiltrate as well as central mucin and nuclear debris. There are a few histologic subtypes of GA, including palisading and interstitial, which refer to the distribution of the histiocytic infiltrate.2,3 This case—with palisading histiocytes lining the collection of necrobiosis and mucin (bottom quiz image)—features palisading GA. Notably, GA exhibits central rather than diffuse mucin.4
Erythema gyratum repens is a paraneoplastic arcuate erythema that manifests as erythematous figurate, gyrate, or annular plaques exhibiting a trailing scale. Clinically, erythema gyratum repens spreads rapidly—as quickly as 1 cm/d—and can be extensive (as in this case). Histopathology ruled out this diagnosis in our patient. Nonspecific findings of acanthosis, parakeratosis, and superficial spongiosis can be found in erythema gyratum repens. A superficial and deep perivascular lymphohistiocytic infiltrate may be seen in figurate erythemas (Figure 1).5 Unlike GA, this infiltrate does not form granulomas, is more superficial, and does not contain mucin.

Histopathology also can help establish the diagnosis of leprosy and its specific subtype, as leprosy exists on a spectrum from tuberculoid to lepromatous, with a great deal of overlap in between.6 Lepromatous leprosy has many cutaneous clinical presentations but typically manifests as erythematous papules or nodules. It is multibacillary, and these mycobacteria form clumps known as globi that can be seen on Fite stain.7 In lepromatous leprosy, there is a characteristic dense lymphohistiocytic infiltrate (Figure 2) above which a Grenz zone can be seen.4,8 There are no well-formed granulomas in lepromatous leprosy, unlike in tuberculoid leprosy, which is paucibacillary and creates a granulomatous response surrounding nerves and adnexal structures.6

Mycosis fungoides (MF) is the most common cutaneous lymphoma. There are patch, plaque, and tumor stages of MF, each of which exhibits various histopathologic findings.9 In early patch-stage MF, lymphocytes have perinuclear clearing, and the degree of lymphocytic infiltrate is out of proportion to the spongiosis present. Epidermotropism and Pautrier microabscesses often are present in the epidermis (Figure 3). In the plaque stage, there is a denser lymphoid infiltrate in a lichenoid pattern with epidermotropism and Pautrier microabscesses. The tumor stage shows a dense dermal lymphoid infiltrate with more atypia and typically a lack of epidermotropism. Rarely, MF can exhibit a granulomatous variant in which epithelioid histiocytes collect to form granulomas along with atypical lymphocytes.10

The diagnosis of cutaneous sarcoidosis requires clinicopathologic corroboration. Histopathology demonstrates epithelioid histiocytes forming noncaseating granulomas with little to no lymphocytic infiltrate (Figure 4). There typically is no necrosis or necrobiosis as there is in GA. The diagnosis of sarcoidosis can be challenging histopathologically, and stains should be used to rule out infectious processes.4 Asteroid bodies— star-shaped eosinophilic inclusions within giant cells—may be present but are nonspecific for sarcoidosis.11 Schaumann bodies—inclusions of calcifications within giant cells—also may be present and can aid in diagnosis.12

- Kovich O, Burgin S. Generalized granuloma annulare [published online December 30, 2005]. Dermatol Online J. 2005;11:23.
- Al Ameer MA, Al-Natour SH, Alsahaf HAA, et al. Eruptive granuloma annulare in an elderly man with diabetes [published online January 14, 2022]. Cureus. 2022;14:E21242. doi:10.7759/cureus.21242
- Howard A, White CR Jr. Non-infectious granulomas. In: Bolognia JL, et al, eds. Dermatology. Mosby; 2003:1455.
- Elston DM, Ferringer T, Ko CJ, et al. Dermatopathology. 3rd ed. Elsevier; 2018.
- Gore M, Winters ME. Erythema gyratum repens: a rare paraneoplastic rash. West J Emerg Med. 2011;12:556-558. doi:10.5811/westjem.2010.11.2090
- Maymone MBC, Laughter M, Venkatesh S, et al. Leprosy: clinical aspects and diagnostic techniques. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:1-14. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2019.12.080
- Pedley JC, Harman DJ, Waudby H, et al. Leprosy in peripheral nerves: histopathological findings in 119 untreated patients in Nepal. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1980;43:198-204. doi:10.1136/jnnp.43.3.198
- Booth AV, Kovich OI. Lepromatous leprosy [published online January 27, 2007]. Dermatol Online J. 2007;13:9.
- Robson A. The pathology of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Oncology (Williston Park). 2007;21(2 suppl 1):9-12.
- Kempf W, Ostheeren-Michaelis S, Paulli M, et al. Granulomatous mycosis fungoides and granulomatous slack skin: a multicenter study of the Cutaneous Lymphoma Histopathology Task Force Group of the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC). Arch Dermatol. 2008;144:1609-1617. doi:10.1001/archdermatol.2008.46
- Azar HA, Lunardelli C. Collagen nature of asteroid bodies of giant cells in sarcoidosis. Am J Pathol. 1969;57:81-92.
- Sreeja C, Priyadarshini A, Premika, et al. Sarcoidosis—a review article. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. 2022;26:242-253. doi:10.4103 /jomfp.jomfp_373_21
- Kovich O, Burgin S. Generalized granuloma annulare [published online December 30, 2005]. Dermatol Online J. 2005;11:23.
- Al Ameer MA, Al-Natour SH, Alsahaf HAA, et al. Eruptive granuloma annulare in an elderly man with diabetes [published online January 14, 2022]. Cureus. 2022;14:E21242. doi:10.7759/cureus.21242
- Howard A, White CR Jr. Non-infectious granulomas. In: Bolognia JL, et al, eds. Dermatology. Mosby; 2003:1455.
- Elston DM, Ferringer T, Ko CJ, et al. Dermatopathology. 3rd ed. Elsevier; 2018.
- Gore M, Winters ME. Erythema gyratum repens: a rare paraneoplastic rash. West J Emerg Med. 2011;12:556-558. doi:10.5811/westjem.2010.11.2090
- Maymone MBC, Laughter M, Venkatesh S, et al. Leprosy: clinical aspects and diagnostic techniques. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:1-14. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2019.12.080
- Pedley JC, Harman DJ, Waudby H, et al. Leprosy in peripheral nerves: histopathological findings in 119 untreated patients in Nepal. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1980;43:198-204. doi:10.1136/jnnp.43.3.198
- Booth AV, Kovich OI. Lepromatous leprosy [published online January 27, 2007]. Dermatol Online J. 2007;13:9.
- Robson A. The pathology of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Oncology (Williston Park). 2007;21(2 suppl 1):9-12.
- Kempf W, Ostheeren-Michaelis S, Paulli M, et al. Granulomatous mycosis fungoides and granulomatous slack skin: a multicenter study of the Cutaneous Lymphoma Histopathology Task Force Group of the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC). Arch Dermatol. 2008;144:1609-1617. doi:10.1001/archdermatol.2008.46
- Azar HA, Lunardelli C. Collagen nature of asteroid bodies of giant cells in sarcoidosis. Am J Pathol. 1969;57:81-92.
- Sreeja C, Priyadarshini A, Premika, et al. Sarcoidosis—a review article. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. 2022;26:242-253. doi:10.4103 /jomfp.jomfp_373_21
An 84-year-old man presented to the clinic for evaluation of a pruritic rash on the back of 6 months’ duration that spread to the neck and chest over the past 2 months and then to the abdomen and thighs more recently. His primary care provider prescribed a 1-week course of oral steroids and steroid cream. The oral medication did not help, but the cream alleviated the pruritus. He had a medical history of coronary artery disease, hypertension, and diabetes mellitus. He also had a rash on the forearms that had waxed and waned for many years but was not associated with pruritus. He had not sought medical care for the rash and had never treated it. Physical examination revealed pink to violaceous annular plaques with central clearing and raised borders that coalesced into larger plaques on the trunk (top). Dusky, scaly, pink plaques were present on the dorsal forearms. Three punch biopsies—2 from the upper back (bottom) and 1 from the left forearm—all demonstrated consistent findings.
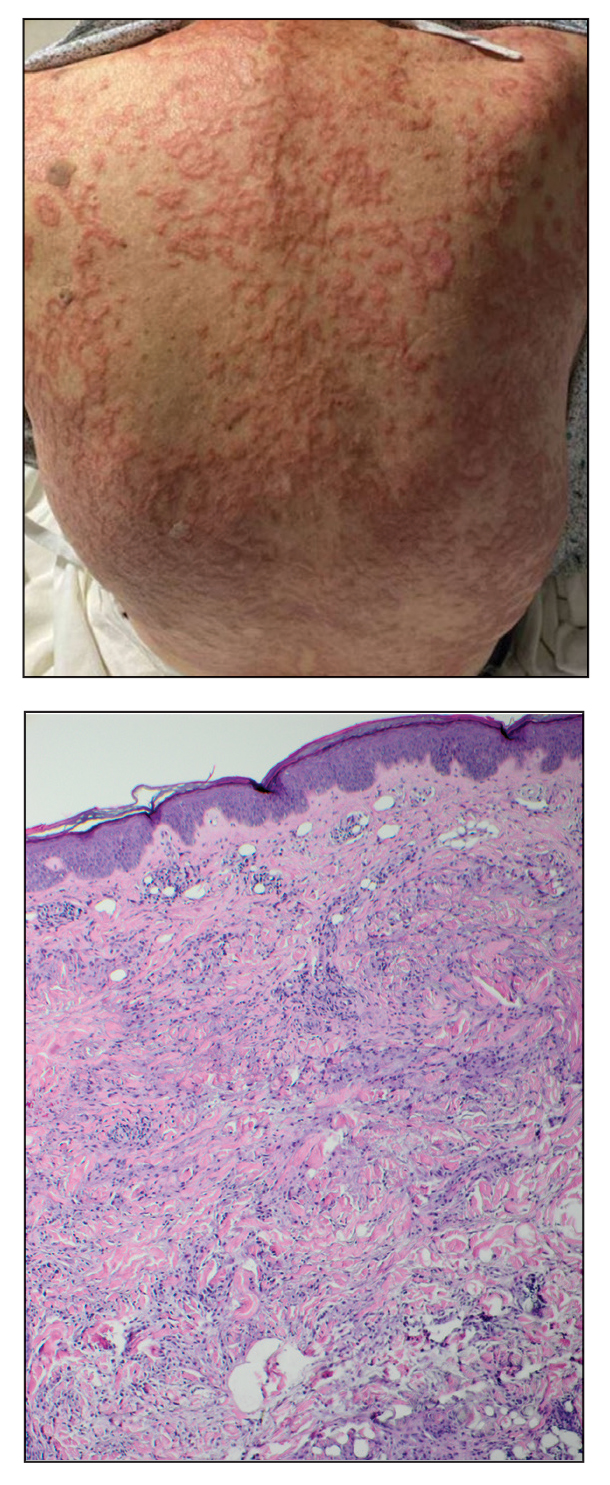
The Potential Benefits of Dietary Changes in Psoriasis Patients
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory skin disease for which several lifestyle factors—smoking, alcohol use, and psychological stress—are associated with higher incidence and more severe disease.1-3 Diet also has been implicated as a factor that can affect psoriasis,4 and many patients have shown interest in possible dietary interventions to help their disease.5
In 2018, the National Psoriasis Foundation (NPF) presented dietary recommendations for patients based on results from a systematic review. From the available literature, only dietary weight reduction with hypocaloric diets in overweight or obese patients could be strongly recommended, and it has been proven that obesity is associated with worse psoriasis severity.6 Other more recent studies have shown that dietary modifications such as intermittent fasting and the ketogenic diet also led to weight loss and improved psoriasis severity in overweight patients; however, it is difficult to discern if the improvement was due to weight loss alone or if the dietary patterns themselves played a role.7,8 The paucity of well-designed studies evaluating the effects of other dietary changes has prevented further guidelines from being written. We propose that dietary patterns such as the Mediterranean diet (MeD) and vegan/vegetarian diets—even without strong data showing benefits in skin disease—may help to decrease systemic inflammation, improve gut dysbiosis, and help decrease the risk for cardiometabolic comorbidities that are associated with psoriasis.
Mediterranean Diet
The MeD is based on the dietary tendencies of inhabitants from the regions surrounding the Mediterranean Sea and is centered around nutrient-rich foods such as vegetables, olive oil, and legumes while limiting meat and dairy.9 The NPF recommended considering a trial of the MeD based on low-quality evidence.6 Observational studies have indicated that psoriasis patients are less likely to adhere to the MeD, but those who do have less severe disease.8 However, a search of PubMed articles indexed for MEDLINE using the terms Mediterranean diet and psoriasis yielded no prospective interventional studies. Given the association of the MeD with less severe disease, it is important to understand which specific foods in the MeD could be beneficial. Intake of omega-3 fatty acids, such as those found in fatty fish, are important for modulation of systemic inflammation.7 High intake of polyphenols—found in fruits and vegetables, extra-virgin olive oil, and wine—also have been implicated in improving inflammatory diseases due to potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Individually, fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and sea fish have been associated with lowering C-reactive protein levels, which also is indicative of the benefits of these foods on systemic inflammation.7
Vegan/Vegetarian Diets
Although fruits, vegetables, legumes, and whole grains are a substantial component of the MeD, there are limited data on vegetarian or purely vegan plant-based diets. An observational study from the NPF found that only 48.4% (15/31) of patients on the MeD vs 69.0% (20/29) on a vegan diet reported a favorable skin response.5 Two case reports also have shown beneficial results of a strict vegan diet for psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis, where whole-food plant-based diets also improved joint symptoms.10-12 As with any diet, those who pursue a plant-based diet should strive to consume a variety of foods to avoid nutrient deficiencies. A recent systematic meta-analysis of 141 studies evaluated nutrient status of vegan and vegetarian diets compared to pescovegetarians and those who consume meat. All dietary patterns showed varying degrees of low levels of different nutrients.13 Of note, the researchers found that vitamin B12, vitamin D, iron, zinc, iodine, calcium, and docosahexaenoic acid were lower in plant-based diets. In contrast, folate; vitamins B1, B6, C, and E; polyunsaturated fatty acids; α-linolenic acid; and magnesium intake were higher. Those who consumed meat were at risk for inadequate intake of fiber, polyunsaturated fatty acids, α-linolenic acid, folate, vitamin E, calcium, magnesium, and vitamin D, though vitamin D intake was higher than in vegans/vegetarians.13 The results of this meta-analysis indicated the importance of educating patients on what constitutes a well-rounded, micronutrient-rich diet or appropriate supplementation for any diet.
Effects on Gut Microbiome
Any changes in diet can lead to alterations in the gut microbiome, which may impact skin disease, as evidence indicates a bidirectional relationship between gut and skin health.10 A metagenomic analysis of the gut microbiota in patients with untreated plaque psoriasis revealed a signature dysbiosis for which the researchers developed a psoriasis microbiota index, suggesting the gut microbiota may play a role in psoriasis pathophysiology.14 Research shows that both the MeD and vegan/vegetarian diets, which are relatively rich in fiber and omega-3 fatty acids and low in saturated fat and animal protein compared to many diets, cause increases in dietary fiber–metabolizing bacteria that produce short-chain fatty acids. These short-chain fatty acids improve gut epithelial integrity and alleviate both gut and systemic inflammation.10
The changes to the gut microbiome induced by a high-fat diet also are concerning. In contrast to the MeD or vegan/vegetarian diets, consumption of a high-fat diet induces alterations in the composition of the gut microbiota that in turn increase the release of proinflammatory cytokines and promote higher intestinal permeability.10 Similarly, high sugar consumption promotes increased intestinal permeability and shifts the gut microbiota to organisms that can rapidly utilize simple carbohydrates at the expense of other beneficial organisms, reducing bacterial diversity.15 The Western diet, which is notable for both high fat and high sugar content, is sometimes referred to as a proinflammatory diet and has been shown to worsen psoriasiformlike lesions in mice.16 Importantly, most research indicates that high fat and high sugar consumption appear to be more prevalent in psoriasis patients,8 but the type of fat consumed in the diet matters. The Western diet includes abundant saturated fat found in meat, dairy products, palm and coconut oils, and processed foods, as well as omega-6 fatty acids that are found in meat, poultry, and eggs. Saturated fat has been shown to promote helper T cell (TH17) accumulation in the skin, and omega-6 fatty acids serve as precursors to various inflammatory lipid mediators.4 This distinction of sources of fat between the Western diet and MeD is important in understanding the diets’ different effects on psoriasis and overall health. As previously discussed, the high intake of omega-3 acids in the MeD is one of the ways it may exert its anti-inflammatory benefits.7
Next Steps in Advising Psoriasis Patients
A major limitation of the data for MeD and vegan/vegetarian diets is limited randomized controlled trials evaluating the impact of these diets on psoriasis. Thus, dietary recommendations for psoriasis are not as strong as for other diseases for which more conclusive data exist.8 Although the data on diet and psoriasis are not definitive, perhaps dermatologists should shift the question from “Does this diet definitely improve psoriasis?” to “Does this diet definitely improve my patient’s health as a whole and maybe also their psoriasis?” For instance, the MeD has been shown to reduce the risk for type 2 diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular disease as well as to slow cognitive decline.17 Vegan/vegetarian diets focusing on whole vs processed foods have been shown to be highly effective in combatting obesity, type 2 diabetes mellitus, coronary artery disease including severe atherosclerosis, and hypertension.18 Psoriasis patients are at increased risk for many of the ailments that the MeD and plant-based diets protect against, making these diets potentially even more impactful than for someone without psoriasis.19 Dietary recommendations should still be made in conjunction with continuing traditional therapies for psoriasis and in consultation with the patient’s primary care physician and/or dietitian; however, rather than waiting for more randomized controlled trials before making health-promoting recommendations, what would be the downside of starting now? At worst, the dietary change decreases their risk for several metabolic conditions, and at best they may even see an improvement in their psoriasis.
- Naldi L, Chatenoud L, Linder D, et al. Cigarette smoking, body mass index, and stressful life events as risk factors for psoriasis: results from an Italian case–control study. J Invest Dermatol. 2005;125:61-67. doi:10.1111/j.0022-202X.2005.23681.x
- Armstrong AW, Harskamp CT, Dhillon JS, et al. Psoriasis and smoking: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Br J Dermatol. 2014;170:304-314. doi:10.1111/bjd.12670
- Zhu K, Zhu C, Fan Y. Alcohol consumption and psoriatic risk: a meta‐analysis of case–control studies. J Dermatol. 2012;39:770-773. doi:10.1111/j.1346-8138.2012.01577.x
- Kanda N, Hoashi T, Saeki H. Nutrition and psoriasis. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21:5405. doi:10.3390/ijms21155405
- Afifi L, Danesh MJ, Lee KM, et al. Dietary behaviors in psoriasis: patient-reported outcomes from a U.S. national survey. Dermatol Ther. 2017;7:227-242. doi:10.1007/s13555-017-0183-4
- Ford AR, Siegel M, Bagel J, et al. Dietary recommendations for adults with psoriasis or psoriatic arthritis from the medical board of the National Psoriasis Foundation: a systematic review. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:934. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2018.1412
- Duchnik E, Kruk J, Tuchowska A, et al. The impact of diet and physical activity on psoriasis: a narrative review of the current evidence. Nutrients. 2023;15:840. doi:10.3390/nu15040840
- Chung M, Bartholomew E, Yeroushalmi S, et al. Dietary intervention and supplements in the management of psoriasis: current perspectives. Psoriasis Targets Ther. 2022;12:151-176. doi:10.2147/PTT.S328581
- Mazza E, Ferro Y, Pujia R, et al. Mediterranean diet in healthy aging. J Nutr Health Aging. 2021;25:1076-1083. doi:10.1007/s12603-021-1675-6
- Flores-Balderas X, Peña-Peña M, Rada KM, et al. Beneficial effects of plant-based diets on skin health and inflammatory skin diseases. Nutrients. 2023;15:2842. doi:10.3390/nu15132842
- Bonjour M, Gabriel S, Valencia A, et al. Challenging case in clinical practice: prolonged water-only fasting followed by an exclusively whole-plant-food diet in the management of severe plaque psoriasis. Integr Complement Ther. 2022;28:85-87. doi:10.1089/ict.2022.29010.mbo
- Lewandowska M, Dunbar K, Kassam S. Managing psoriatic arthritis with a whole food plant-based diet: a case study. Am J Lifestyle Med. 2021;15:402-406. doi:10.1177/1559827621993435
- Neufingerl N, Eilander A. Nutrient intake and status in adults consuming plant-based diets compared to meat-eaters: a systematic review. Nutrients. 2021;14:29. doi:10.3390/nu14010029
- Dei-Cas I, Giliberto F, Luce L, et al. Metagenomic analysis of gut microbiota in non-treated plaque psoriasis patients stratified by disease severity: development of a new psoriasis-microbiome index. Sci Rep. 2020;10:12754. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-69537-3
- Satokari R. High intake of sugar and the balance between pro- and anti-inflammatory gut bacteria. Nutrients. 2020;12:1348. doi:10.3390/nu12051348
- Shi Z, Wu X, Santos Rocha C, et al. Short-term Western diet intake promotes IL-23–mediated skin and joint inflammation accompanied by changes to the gut microbiota in mice. J Invest Dermatol. 2021;141:1780-1791. doi:10.1016/j.jid.2020.11.032
- Romagnolo DF, Selmin OI. Mediterranean diet and prevention of chronic diseases. Nutr Today. 2017;52:208-222. doi:10.1097/NT.0000000000000228
- Tuso PJ, Ismail MH, Ha BP, et al. Nutritional update for physicians: plant-based diets. Perm J. 2013;17:61-66. doi:10.7812/TPP/12-085
- Parisi R, Symmons DPM, Griffiths CEM, et al. Global epidemiology of psoriasis: a systematic review of incidence and prevalence. J Invest Dermatol. 2013;133:377-385. doi:10.1038/jid.2012.339
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory skin disease for which several lifestyle factors—smoking, alcohol use, and psychological stress—are associated with higher incidence and more severe disease.1-3 Diet also has been implicated as a factor that can affect psoriasis,4 and many patients have shown interest in possible dietary interventions to help their disease.5
In 2018, the National Psoriasis Foundation (NPF) presented dietary recommendations for patients based on results from a systematic review. From the available literature, only dietary weight reduction with hypocaloric diets in overweight or obese patients could be strongly recommended, and it has been proven that obesity is associated with worse psoriasis severity.6 Other more recent studies have shown that dietary modifications such as intermittent fasting and the ketogenic diet also led to weight loss and improved psoriasis severity in overweight patients; however, it is difficult to discern if the improvement was due to weight loss alone or if the dietary patterns themselves played a role.7,8 The paucity of well-designed studies evaluating the effects of other dietary changes has prevented further guidelines from being written. We propose that dietary patterns such as the Mediterranean diet (MeD) and vegan/vegetarian diets—even without strong data showing benefits in skin disease—may help to decrease systemic inflammation, improve gut dysbiosis, and help decrease the risk for cardiometabolic comorbidities that are associated with psoriasis.
Mediterranean Diet
The MeD is based on the dietary tendencies of inhabitants from the regions surrounding the Mediterranean Sea and is centered around nutrient-rich foods such as vegetables, olive oil, and legumes while limiting meat and dairy.9 The NPF recommended considering a trial of the MeD based on low-quality evidence.6 Observational studies have indicated that psoriasis patients are less likely to adhere to the MeD, but those who do have less severe disease.8 However, a search of PubMed articles indexed for MEDLINE using the terms Mediterranean diet and psoriasis yielded no prospective interventional studies. Given the association of the MeD with less severe disease, it is important to understand which specific foods in the MeD could be beneficial. Intake of omega-3 fatty acids, such as those found in fatty fish, are important for modulation of systemic inflammation.7 High intake of polyphenols—found in fruits and vegetables, extra-virgin olive oil, and wine—also have been implicated in improving inflammatory diseases due to potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Individually, fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and sea fish have been associated with lowering C-reactive protein levels, which also is indicative of the benefits of these foods on systemic inflammation.7
Vegan/Vegetarian Diets
Although fruits, vegetables, legumes, and whole grains are a substantial component of the MeD, there are limited data on vegetarian or purely vegan plant-based diets. An observational study from the NPF found that only 48.4% (15/31) of patients on the MeD vs 69.0% (20/29) on a vegan diet reported a favorable skin response.5 Two case reports also have shown beneficial results of a strict vegan diet for psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis, where whole-food plant-based diets also improved joint symptoms.10-12 As with any diet, those who pursue a plant-based diet should strive to consume a variety of foods to avoid nutrient deficiencies. A recent systematic meta-analysis of 141 studies evaluated nutrient status of vegan and vegetarian diets compared to pescovegetarians and those who consume meat. All dietary patterns showed varying degrees of low levels of different nutrients.13 Of note, the researchers found that vitamin B12, vitamin D, iron, zinc, iodine, calcium, and docosahexaenoic acid were lower in plant-based diets. In contrast, folate; vitamins B1, B6, C, and E; polyunsaturated fatty acids; α-linolenic acid; and magnesium intake were higher. Those who consumed meat were at risk for inadequate intake of fiber, polyunsaturated fatty acids, α-linolenic acid, folate, vitamin E, calcium, magnesium, and vitamin D, though vitamin D intake was higher than in vegans/vegetarians.13 The results of this meta-analysis indicated the importance of educating patients on what constitutes a well-rounded, micronutrient-rich diet or appropriate supplementation for any diet.
Effects on Gut Microbiome
Any changes in diet can lead to alterations in the gut microbiome, which may impact skin disease, as evidence indicates a bidirectional relationship between gut and skin health.10 A metagenomic analysis of the gut microbiota in patients with untreated plaque psoriasis revealed a signature dysbiosis for which the researchers developed a psoriasis microbiota index, suggesting the gut microbiota may play a role in psoriasis pathophysiology.14 Research shows that both the MeD and vegan/vegetarian diets, which are relatively rich in fiber and omega-3 fatty acids and low in saturated fat and animal protein compared to many diets, cause increases in dietary fiber–metabolizing bacteria that produce short-chain fatty acids. These short-chain fatty acids improve gut epithelial integrity and alleviate both gut and systemic inflammation.10
The changes to the gut microbiome induced by a high-fat diet also are concerning. In contrast to the MeD or vegan/vegetarian diets, consumption of a high-fat diet induces alterations in the composition of the gut microbiota that in turn increase the release of proinflammatory cytokines and promote higher intestinal permeability.10 Similarly, high sugar consumption promotes increased intestinal permeability and shifts the gut microbiota to organisms that can rapidly utilize simple carbohydrates at the expense of other beneficial organisms, reducing bacterial diversity.15 The Western diet, which is notable for both high fat and high sugar content, is sometimes referred to as a proinflammatory diet and has been shown to worsen psoriasiformlike lesions in mice.16 Importantly, most research indicates that high fat and high sugar consumption appear to be more prevalent in psoriasis patients,8 but the type of fat consumed in the diet matters. The Western diet includes abundant saturated fat found in meat, dairy products, palm and coconut oils, and processed foods, as well as omega-6 fatty acids that are found in meat, poultry, and eggs. Saturated fat has been shown to promote helper T cell (TH17) accumulation in the skin, and omega-6 fatty acids serve as precursors to various inflammatory lipid mediators.4 This distinction of sources of fat between the Western diet and MeD is important in understanding the diets’ different effects on psoriasis and overall health. As previously discussed, the high intake of omega-3 acids in the MeD is one of the ways it may exert its anti-inflammatory benefits.7
Next Steps in Advising Psoriasis Patients
A major limitation of the data for MeD and vegan/vegetarian diets is limited randomized controlled trials evaluating the impact of these diets on psoriasis. Thus, dietary recommendations for psoriasis are not as strong as for other diseases for which more conclusive data exist.8 Although the data on diet and psoriasis are not definitive, perhaps dermatologists should shift the question from “Does this diet definitely improve psoriasis?” to “Does this diet definitely improve my patient’s health as a whole and maybe also their psoriasis?” For instance, the MeD has been shown to reduce the risk for type 2 diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular disease as well as to slow cognitive decline.17 Vegan/vegetarian diets focusing on whole vs processed foods have been shown to be highly effective in combatting obesity, type 2 diabetes mellitus, coronary artery disease including severe atherosclerosis, and hypertension.18 Psoriasis patients are at increased risk for many of the ailments that the MeD and plant-based diets protect against, making these diets potentially even more impactful than for someone without psoriasis.19 Dietary recommendations should still be made in conjunction with continuing traditional therapies for psoriasis and in consultation with the patient’s primary care physician and/or dietitian; however, rather than waiting for more randomized controlled trials before making health-promoting recommendations, what would be the downside of starting now? At worst, the dietary change decreases their risk for several metabolic conditions, and at best they may even see an improvement in their psoriasis.
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory skin disease for which several lifestyle factors—smoking, alcohol use, and psychological stress—are associated with higher incidence and more severe disease.1-3 Diet also has been implicated as a factor that can affect psoriasis,4 and many patients have shown interest in possible dietary interventions to help their disease.5
In 2018, the National Psoriasis Foundation (NPF) presented dietary recommendations for patients based on results from a systematic review. From the available literature, only dietary weight reduction with hypocaloric diets in overweight or obese patients could be strongly recommended, and it has been proven that obesity is associated with worse psoriasis severity.6 Other more recent studies have shown that dietary modifications such as intermittent fasting and the ketogenic diet also led to weight loss and improved psoriasis severity in overweight patients; however, it is difficult to discern if the improvement was due to weight loss alone or if the dietary patterns themselves played a role.7,8 The paucity of well-designed studies evaluating the effects of other dietary changes has prevented further guidelines from being written. We propose that dietary patterns such as the Mediterranean diet (MeD) and vegan/vegetarian diets—even without strong data showing benefits in skin disease—may help to decrease systemic inflammation, improve gut dysbiosis, and help decrease the risk for cardiometabolic comorbidities that are associated with psoriasis.
Mediterranean Diet
The MeD is based on the dietary tendencies of inhabitants from the regions surrounding the Mediterranean Sea and is centered around nutrient-rich foods such as vegetables, olive oil, and legumes while limiting meat and dairy.9 The NPF recommended considering a trial of the MeD based on low-quality evidence.6 Observational studies have indicated that psoriasis patients are less likely to adhere to the MeD, but those who do have less severe disease.8 However, a search of PubMed articles indexed for MEDLINE using the terms Mediterranean diet and psoriasis yielded no prospective interventional studies. Given the association of the MeD with less severe disease, it is important to understand which specific foods in the MeD could be beneficial. Intake of omega-3 fatty acids, such as those found in fatty fish, are important for modulation of systemic inflammation.7 High intake of polyphenols—found in fruits and vegetables, extra-virgin olive oil, and wine—also have been implicated in improving inflammatory diseases due to potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Individually, fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and sea fish have been associated with lowering C-reactive protein levels, which also is indicative of the benefits of these foods on systemic inflammation.7
Vegan/Vegetarian Diets
Although fruits, vegetables, legumes, and whole grains are a substantial component of the MeD, there are limited data on vegetarian or purely vegan plant-based diets. An observational study from the NPF found that only 48.4% (15/31) of patients on the MeD vs 69.0% (20/29) on a vegan diet reported a favorable skin response.5 Two case reports also have shown beneficial results of a strict vegan diet for psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis, where whole-food plant-based diets also improved joint symptoms.10-12 As with any diet, those who pursue a plant-based diet should strive to consume a variety of foods to avoid nutrient deficiencies. A recent systematic meta-analysis of 141 studies evaluated nutrient status of vegan and vegetarian diets compared to pescovegetarians and those who consume meat. All dietary patterns showed varying degrees of low levels of different nutrients.13 Of note, the researchers found that vitamin B12, vitamin D, iron, zinc, iodine, calcium, and docosahexaenoic acid were lower in plant-based diets. In contrast, folate; vitamins B1, B6, C, and E; polyunsaturated fatty acids; α-linolenic acid; and magnesium intake were higher. Those who consumed meat were at risk for inadequate intake of fiber, polyunsaturated fatty acids, α-linolenic acid, folate, vitamin E, calcium, magnesium, and vitamin D, though vitamin D intake was higher than in vegans/vegetarians.13 The results of this meta-analysis indicated the importance of educating patients on what constitutes a well-rounded, micronutrient-rich diet or appropriate supplementation for any diet.
Effects on Gut Microbiome
Any changes in diet can lead to alterations in the gut microbiome, which may impact skin disease, as evidence indicates a bidirectional relationship between gut and skin health.10 A metagenomic analysis of the gut microbiota in patients with untreated plaque psoriasis revealed a signature dysbiosis for which the researchers developed a psoriasis microbiota index, suggesting the gut microbiota may play a role in psoriasis pathophysiology.14 Research shows that both the MeD and vegan/vegetarian diets, which are relatively rich in fiber and omega-3 fatty acids and low in saturated fat and animal protein compared to many diets, cause increases in dietary fiber–metabolizing bacteria that produce short-chain fatty acids. These short-chain fatty acids improve gut epithelial integrity and alleviate both gut and systemic inflammation.10
The changes to the gut microbiome induced by a high-fat diet also are concerning. In contrast to the MeD or vegan/vegetarian diets, consumption of a high-fat diet induces alterations in the composition of the gut microbiota that in turn increase the release of proinflammatory cytokines and promote higher intestinal permeability.10 Similarly, high sugar consumption promotes increased intestinal permeability and shifts the gut microbiota to organisms that can rapidly utilize simple carbohydrates at the expense of other beneficial organisms, reducing bacterial diversity.15 The Western diet, which is notable for both high fat and high sugar content, is sometimes referred to as a proinflammatory diet and has been shown to worsen psoriasiformlike lesions in mice.16 Importantly, most research indicates that high fat and high sugar consumption appear to be more prevalent in psoriasis patients,8 but the type of fat consumed in the diet matters. The Western diet includes abundant saturated fat found in meat, dairy products, palm and coconut oils, and processed foods, as well as omega-6 fatty acids that are found in meat, poultry, and eggs. Saturated fat has been shown to promote helper T cell (TH17) accumulation in the skin, and omega-6 fatty acids serve as precursors to various inflammatory lipid mediators.4 This distinction of sources of fat between the Western diet and MeD is important in understanding the diets’ different effects on psoriasis and overall health. As previously discussed, the high intake of omega-3 acids in the MeD is one of the ways it may exert its anti-inflammatory benefits.7
Next Steps in Advising Psoriasis Patients
A major limitation of the data for MeD and vegan/vegetarian diets is limited randomized controlled trials evaluating the impact of these diets on psoriasis. Thus, dietary recommendations for psoriasis are not as strong as for other diseases for which more conclusive data exist.8 Although the data on diet and psoriasis are not definitive, perhaps dermatologists should shift the question from “Does this diet definitely improve psoriasis?” to “Does this diet definitely improve my patient’s health as a whole and maybe also their psoriasis?” For instance, the MeD has been shown to reduce the risk for type 2 diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular disease as well as to slow cognitive decline.17 Vegan/vegetarian diets focusing on whole vs processed foods have been shown to be highly effective in combatting obesity, type 2 diabetes mellitus, coronary artery disease including severe atherosclerosis, and hypertension.18 Psoriasis patients are at increased risk for many of the ailments that the MeD and plant-based diets protect against, making these diets potentially even more impactful than for someone without psoriasis.19 Dietary recommendations should still be made in conjunction with continuing traditional therapies for psoriasis and in consultation with the patient’s primary care physician and/or dietitian; however, rather than waiting for more randomized controlled trials before making health-promoting recommendations, what would be the downside of starting now? At worst, the dietary change decreases their risk for several metabolic conditions, and at best they may even see an improvement in their psoriasis.
- Naldi L, Chatenoud L, Linder D, et al. Cigarette smoking, body mass index, and stressful life events as risk factors for psoriasis: results from an Italian case–control study. J Invest Dermatol. 2005;125:61-67. doi:10.1111/j.0022-202X.2005.23681.x
- Armstrong AW, Harskamp CT, Dhillon JS, et al. Psoriasis and smoking: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Br J Dermatol. 2014;170:304-314. doi:10.1111/bjd.12670
- Zhu K, Zhu C, Fan Y. Alcohol consumption and psoriatic risk: a meta‐analysis of case–control studies. J Dermatol. 2012;39:770-773. doi:10.1111/j.1346-8138.2012.01577.x
- Kanda N, Hoashi T, Saeki H. Nutrition and psoriasis. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21:5405. doi:10.3390/ijms21155405
- Afifi L, Danesh MJ, Lee KM, et al. Dietary behaviors in psoriasis: patient-reported outcomes from a U.S. national survey. Dermatol Ther. 2017;7:227-242. doi:10.1007/s13555-017-0183-4
- Ford AR, Siegel M, Bagel J, et al. Dietary recommendations for adults with psoriasis or psoriatic arthritis from the medical board of the National Psoriasis Foundation: a systematic review. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:934. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2018.1412
- Duchnik E, Kruk J, Tuchowska A, et al. The impact of diet and physical activity on psoriasis: a narrative review of the current evidence. Nutrients. 2023;15:840. doi:10.3390/nu15040840
- Chung M, Bartholomew E, Yeroushalmi S, et al. Dietary intervention and supplements in the management of psoriasis: current perspectives. Psoriasis Targets Ther. 2022;12:151-176. doi:10.2147/PTT.S328581
- Mazza E, Ferro Y, Pujia R, et al. Mediterranean diet in healthy aging. J Nutr Health Aging. 2021;25:1076-1083. doi:10.1007/s12603-021-1675-6
- Flores-Balderas X, Peña-Peña M, Rada KM, et al. Beneficial effects of plant-based diets on skin health and inflammatory skin diseases. Nutrients. 2023;15:2842. doi:10.3390/nu15132842
- Bonjour M, Gabriel S, Valencia A, et al. Challenging case in clinical practice: prolonged water-only fasting followed by an exclusively whole-plant-food diet in the management of severe plaque psoriasis. Integr Complement Ther. 2022;28:85-87. doi:10.1089/ict.2022.29010.mbo
- Lewandowska M, Dunbar K, Kassam S. Managing psoriatic arthritis with a whole food plant-based diet: a case study. Am J Lifestyle Med. 2021;15:402-406. doi:10.1177/1559827621993435
- Neufingerl N, Eilander A. Nutrient intake and status in adults consuming plant-based diets compared to meat-eaters: a systematic review. Nutrients. 2021;14:29. doi:10.3390/nu14010029
- Dei-Cas I, Giliberto F, Luce L, et al. Metagenomic analysis of gut microbiota in non-treated plaque psoriasis patients stratified by disease severity: development of a new psoriasis-microbiome index. Sci Rep. 2020;10:12754. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-69537-3
- Satokari R. High intake of sugar and the balance between pro- and anti-inflammatory gut bacteria. Nutrients. 2020;12:1348. doi:10.3390/nu12051348
- Shi Z, Wu X, Santos Rocha C, et al. Short-term Western diet intake promotes IL-23–mediated skin and joint inflammation accompanied by changes to the gut microbiota in mice. J Invest Dermatol. 2021;141:1780-1791. doi:10.1016/j.jid.2020.11.032
- Romagnolo DF, Selmin OI. Mediterranean diet and prevention of chronic diseases. Nutr Today. 2017;52:208-222. doi:10.1097/NT.0000000000000228
- Tuso PJ, Ismail MH, Ha BP, et al. Nutritional update for physicians: plant-based diets. Perm J. 2013;17:61-66. doi:10.7812/TPP/12-085
- Parisi R, Symmons DPM, Griffiths CEM, et al. Global epidemiology of psoriasis: a systematic review of incidence and prevalence. J Invest Dermatol. 2013;133:377-385. doi:10.1038/jid.2012.339
- Naldi L, Chatenoud L, Linder D, et al. Cigarette smoking, body mass index, and stressful life events as risk factors for psoriasis: results from an Italian case–control study. J Invest Dermatol. 2005;125:61-67. doi:10.1111/j.0022-202X.2005.23681.x
- Armstrong AW, Harskamp CT, Dhillon JS, et al. Psoriasis and smoking: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Br J Dermatol. 2014;170:304-314. doi:10.1111/bjd.12670
- Zhu K, Zhu C, Fan Y. Alcohol consumption and psoriatic risk: a meta‐analysis of case–control studies. J Dermatol. 2012;39:770-773. doi:10.1111/j.1346-8138.2012.01577.x
- Kanda N, Hoashi T, Saeki H. Nutrition and psoriasis. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21:5405. doi:10.3390/ijms21155405
- Afifi L, Danesh MJ, Lee KM, et al. Dietary behaviors in psoriasis: patient-reported outcomes from a U.S. national survey. Dermatol Ther. 2017;7:227-242. doi:10.1007/s13555-017-0183-4
- Ford AR, Siegel M, Bagel J, et al. Dietary recommendations for adults with psoriasis or psoriatic arthritis from the medical board of the National Psoriasis Foundation: a systematic review. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:934. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2018.1412
- Duchnik E, Kruk J, Tuchowska A, et al. The impact of diet and physical activity on psoriasis: a narrative review of the current evidence. Nutrients. 2023;15:840. doi:10.3390/nu15040840
- Chung M, Bartholomew E, Yeroushalmi S, et al. Dietary intervention and supplements in the management of psoriasis: current perspectives. Psoriasis Targets Ther. 2022;12:151-176. doi:10.2147/PTT.S328581
- Mazza E, Ferro Y, Pujia R, et al. Mediterranean diet in healthy aging. J Nutr Health Aging. 2021;25:1076-1083. doi:10.1007/s12603-021-1675-6
- Flores-Balderas X, Peña-Peña M, Rada KM, et al. Beneficial effects of plant-based diets on skin health and inflammatory skin diseases. Nutrients. 2023;15:2842. doi:10.3390/nu15132842
- Bonjour M, Gabriel S, Valencia A, et al. Challenging case in clinical practice: prolonged water-only fasting followed by an exclusively whole-plant-food diet in the management of severe plaque psoriasis. Integr Complement Ther. 2022;28:85-87. doi:10.1089/ict.2022.29010.mbo
- Lewandowska M, Dunbar K, Kassam S. Managing psoriatic arthritis with a whole food plant-based diet: a case study. Am J Lifestyle Med. 2021;15:402-406. doi:10.1177/1559827621993435
- Neufingerl N, Eilander A. Nutrient intake and status in adults consuming plant-based diets compared to meat-eaters: a systematic review. Nutrients. 2021;14:29. doi:10.3390/nu14010029
- Dei-Cas I, Giliberto F, Luce L, et al. Metagenomic analysis of gut microbiota in non-treated plaque psoriasis patients stratified by disease severity: development of a new psoriasis-microbiome index. Sci Rep. 2020;10:12754. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-69537-3
- Satokari R. High intake of sugar and the balance between pro- and anti-inflammatory gut bacteria. Nutrients. 2020;12:1348. doi:10.3390/nu12051348
- Shi Z, Wu X, Santos Rocha C, et al. Short-term Western diet intake promotes IL-23–mediated skin and joint inflammation accompanied by changes to the gut microbiota in mice. J Invest Dermatol. 2021;141:1780-1791. doi:10.1016/j.jid.2020.11.032
- Romagnolo DF, Selmin OI. Mediterranean diet and prevention of chronic diseases. Nutr Today. 2017;52:208-222. doi:10.1097/NT.0000000000000228
- Tuso PJ, Ismail MH, Ha BP, et al. Nutritional update for physicians: plant-based diets. Perm J. 2013;17:61-66. doi:10.7812/TPP/12-085
- Parisi R, Symmons DPM, Griffiths CEM, et al. Global epidemiology of psoriasis: a systematic review of incidence and prevalence. J Invest Dermatol. 2013;133:377-385. doi:10.1038/jid.2012.339
Practice Points
- Psoriasis is affected by lifestyle factors such as diet, which is an area of interest for many patients.
- Low-calorie diets are strongly recommended for overweight/obese patients with psoriasis to improve their disease.
- Changes in dietary patterns, such as adopting a Mediterranean diet or a plant-based diet, also have shown promise.