User login
A suicide attempt, or something else?
CASE Unexplained hypoglycemia
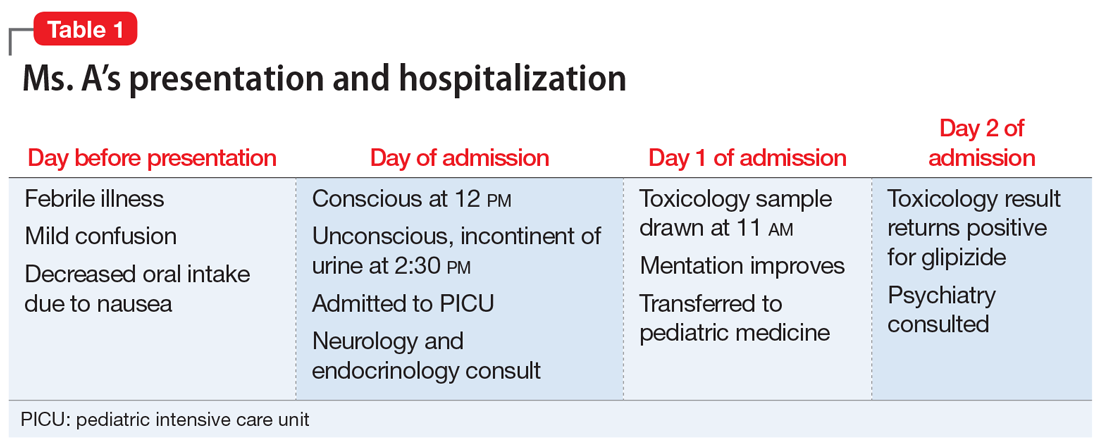
Ms. A, age 12, is brought to the emergency department (ED) via ambulance with altered mentation and life-threatening hypoglycemia for management of a hypoglycemic seizure. Earlier that day, Ms. A’s parents had found her unresponsive and incontinent of urine. In the ED, Ms. A is minimally responsive. Her blood glucose level measurements are in the range of 30 to 39 mg/dL (reference range: 70 to 99 mg/dL), despite having received IV dextrose first from paramedics, and then in the ED. Ms. A has no history of hypoglycemia or diabetes. Her parents say that the night before coming to the ED, Ms. A had experienced flu-like symptoms, including nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea, that continued overnight and resulted in minimal food intake for 24 hours (Table 1).
A physical exam demonstrates left-sided weakness of face, arm, and leg, rightward gaze, and left-sided neglect. However, the results of CT angiography and an MRI of the brain rule out a stroke. An EEG shows right hemispheric slowing consistent with postictal paralysis, but no ongoing seizure activity. Ms. A is transferred to the pediatric intensive care unit (PICU).
Although Ms. A has no psychiatric diagnoses, she has a history of depressive symptoms, self-harm by cutting, and a suicide attempt by ingestion of an over-the-counter (OTC) medication 1 year ago. She had reported the suicide attempt to her parents several months after the fact, and asked them to find her a therapist, which her parents arranged. She also has a history of asthma, which is well-controlled with montelukast, 5 mg/d.
EVALUATION Elevated insulin levels
Subsequent investigations for organic causes of hypoglycemia are negative for adrenal insufficiency, fatty acid oxidation defect, and sepsis. Blood results demonstrate significantly elevated insulin levels of 92.4 mcIU/mL (reference range: 2.6 to 24.9 mcIU/mL) and a C-peptide level of 9.5 ng/mL (reference range: 1.1 to 4.4 ng/mL).
On Day 1 of admission to the PICU, Ms. A’s blood glucose level normalizes, and her mentation improves. Her parents report that one of them has diabetes and takes oral hypoglycemic agents at home, including glipizide immediate release (IR) tablets, 10 mg, and long-acting insulin glargine. The treatment team suspects that Ms. A may have ingested one or both of these agents, and orders a toxicologic screening for oral hypoglycemic agents.
On Day 2, the toxicology results are returned and are positive for glipizide, which Ms. A had not been prescribed. Ms. A states that she had taken only her montelukast tablet on the day of admission and adamantly denies deliberately ingesting her parent’s diabetes medications. Her parents check the home medications and state there are no missing glipizide IR tablets or insulin vials. They also report that Ms. A had no access to extended-release glipizide.
The treatment team discuss Ms. A’s clinical condition and toxicology results with the pediatric endocrinology team. The endocrinology team states that with no history of hypoglycemic episodes, it is unlikely that Ms. A had an endogenous etiology that would present so catastrophically. In their experience, inexplicable hypoglycemia in a healthy individual who lives in a household with someone who has diabetes is due to ingestion of a hypoglycemic agent until proven otherwise.
[polldaddy:10252689]
Continue to: The authors' observations
The authors’ observations
In the context of Ms. A’s prior suicide attempt and history of self-harm, the pediatric team was concerned that her presentation was consistent with a suicide attempt and consulted the psychiatry service.
Glipizide is a second-generation sulfonylurea used to treat type 2 diabetes. It lowers blood glucose by stimulating pancreatic insulin secretion. It is a rare drug of overdose.1 Although pediatric glipizide overdoses have been documented, there are currently no pediatric or adolescent glipizide pharmacokinetic studies in the literature.1-4 In adults, the immediate-release formulation has 100% oral bioavailability, with a maximum plasma concentration (Tmax) of approximately 2 hours.5 The half-life typically ranges from 4 to 6 hours in adults.6 Patients who do not have diabetes are much more susceptible to the hypoglycemic effects of glipizide because the medication simulates their fully functional pancreas to produce a vigorous insulin response.
Ms. A’s significantly elevated insulin was consistent with normal glipizide effects in a healthy child, while the elevated C-peptide was consistent with insulin being endogenously produced, which ruled out ingestion of her parent’s insulin. Importantly, the pediatric endocrinology team noted that, in their experience, a single 5- to 10-mg dose of glipizide IR was sufficient to lower blood glucose levels to the low 30s mg/dL in the context of a functional pancreas, which suggested that Ms. A might have accidentally ingested a single glipizide IR tablet, and might be telling the truth when she denies deliberately ingesting it to hurt herself.
The clinical value of pharmacokinetics
The screen of Ms. A’s toxicology sample detected glipizide. The laboratory used a semi-quantitative serum screen of several hypoglycemic agents. A positive result for each agent is based on a quantitative cut-off value, which is 3 ng/mL for glipizide. The clinical chemist on call was asked to assist in interpreting the results. The serum specimen collected on Day 1 had a significantly positive glipizide result of 86 to 130 ng/mL. The maximum effective glipizide concentration for adult patients with diabetes is 100 ng/mL.7 Thus, the glipizide level of 86 to 130 ng/mL (20.5 hours after initial symptoms) is consistent with the clinical presentation of persistent hypoglycemia requiring ongoing glucose replacement therapy.
Due to the lack of pediatric pharmacokinetic data for glipizide and only a single serum measurement, it is not possible to estimate the glipizide concentration at the time of maximal symptoms (loss of consciousness at 2:30
Continue to: Clinicians need to be aware that...
Clinicians need to be aware that although hypoglycemia usually presents rapidly, in children glipizide IR can rarely cause delayed hypoglycemia up to 16 hours after ingestion,2 and a delay of 45 hours was reported in a case of ingestion of extended-release glipizide.8 Hypoglycemia can last up to nearly 24 hours and is exacerbated if the patient has not eaten.1,2 Importantly, Ms. A’s parents reported that she had no access to extended-release glipizide. When detailed pharmacokinetic data are not available, the information provided by the patient and parents becomes extremely important, especially in distinguishing between single and multiple overdoses prior to presentation, or co-ingestions, or decreased food intake that could exacerbate hypoglycemia.
EVALUATION Safety assessment
On Day 2, Ms. A and her parents are interviewed separately, and they all are consistent in their recollection that Ms. A had been feverish with flu-like symptoms throughout the night before coming to the ED, and had still seemed mildly confused on the morning of admission.
During the interview, her parents wonder when Ms. A took her daily dose of a single montelukast tablet for asthma, and whether she had accidentally confused it with their glipizide. They report that on the morning of admission, both the glipizide and montelukast medication vials were in the same room. The vials are the same color, the same size, and labeled from the same pharmacy, and contain white, scored, round tablets that look very similar.
During the interview, Ms. A consistently denies having thoughts of hurting or killing herself on the day of admission or before that.
[polldaddy:10252690]
Continue to: The authors' observations
The authors’ observations
This case was ultimately an accidental ingestion of glipizide, rather than a suicide attempt. The initial suspicion for a suicide attempt had been reasonable in the context of Ms. A’s depressive symptoms, remote history of a prior suicide attempt by ingesting an OTC medication, and toxicologic evidence of ingesting a drug not prescribed to her. Additionally, because of the life-threatening presentation, it was easy to make the erroneous assumption that the ingestion of glipizide must have involved many tablets, and thus must have been deliberate. However, through multidisciplinary teamwork, we were able to demonstrate that this was likely an accidental ingestion by a patient who had an acute febrile illness. Her illness had caused confusion, which contributed to the accidental ingestion, and also caused reduced food intake, which enhanced the hypoglycemic effects of glipizide. Additionally, a lack of awareness of medication safety in the home had facilitated the confusion between the two medication vials.
A single tablet of glipizide IR is sufficient to produce profound clinical effects that could be mistaken by medical and psychiatric teams for a much larger and/or deliberate overdose, especially in patients with a psychiatric history. The inappropriate psychiatric hospitalization of a patient, especially a child, who has been mistakenly diagnosed as having attempted suicide, can have negative therapeutic consequences (Table 2). A psychiatric admission would have been misguided if it attempted to address safety and reduce suicidality when no such concerns were present. Additionally, it could have damaged relationships with the patient and the family, especially in a child who had historically not sought psychiatric care despite depressive symptoms and a previous suicide attempt. When assessing for suicidality, consider accidental ingestion in the differential and use specialty expertise and confirmatory testing in the evaluation, taking the pharmacokinetics of the suspected agent into account.
OUTCOME Outpatient treatment
Ms. A’s neurologic symptoms resolve within 24 hours of admission. She is offered psychiatric inpatient hospitalization to address her depressive symptoms; however, her parents prefer that she receive outpatient care. Ms. A’s parents also state that after Ms. A’s admission, they locked up all household medications and will be more mindful with medication in the home. Because her parents are arranging appropriate outpatient treatment for Ms. A’s depression and maintenance of her safety, an involuntary hospitalization is not deemed necessary.
On Day 2, Ms. A is eating normally, her blood glucose levels remain stable, and she is discharged home.
Bottom Line
Oral hypoglycemic agents can cause life-threatening syndromes in healthy patients and can clinically mimic large, intentional overdoses. Clinicians must be aware of the differential of accidental ingestion when assessing for suicidality, and can use toxicology results in their assessment.
Related Resources
- Kidemergencies.com. Emergencies: One pill can kill. http://kidemergencies.com/onepill1.html.
- Safe Kids Worldwide. Medication safety. https://www.safekids.org/medicinesafety.
- American Association of Poison Control Centers. http://www.aapcc.org/.
Drug Brand Names
Glipizide • Glucotrol
Insulin glargine • Lantus
Montelukast • Singulair
1. Spiller HA, Villalobos D, Krenzelok EP, et al. Prospective multicenter study of sulfonylurea ingestion in children. J Pediatr. 1997;131(1):141-146.
2. Quadrani DA, Spiller HA, Widder P. Five year retrospective evaluation of sulfonylurea ingestion in children. J Toxicol Clin Toxicol. 1996;34(3):267-270.
3. Borowski H, Caraccio T, Mofenson H. Sulfonylurea ingestion in children: is an 8-hour observation period sufficient? J Pediatr. 1998;133(4):584-585.
4. Little GL, Boniface KS. Are one or two dangerous? Sulfony-lurea exposure in toddlers. J Emerg Med. 2005;28(3):305-310.
5. Huupponen R, Seppala P, Iisalo E. Glipizide pharma-cokinetics and response in diabetics. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther Toxicol. 1982;20(9):417-422.
6. Baselt RC. Disposition of toxic drugs and chemicals in man. 10th ed. Seal Beach, California: Biomedical Publications; 2014.
7. Simonson DC, Kourides IA, Feinglos M, et al; the Glipizide Gastrointestinal Therapeutic System Study Group. Efficacy, safety, and dose-response characteristics of glipizide gastrointestinal therapeutic system on glycemic control and insulin secretion in NIDDM. Results of two multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trials. Diabetes Care. 1997;20(4):597-606.
8. Pelavin PI, Abramson E, Pon S, et al. Extended-release glipizide overdose presenting with delayed hypoglycemia and treated with subcutaneous octreotide. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2009;22(2):171-175.
CASE Unexplained hypoglycemia
Ms. A, age 12, is brought to the emergency department (ED) via ambulance with altered mentation and life-threatening hypoglycemia for management of a hypoglycemic seizure. Earlier that day, Ms. A’s parents had found her unresponsive and incontinent of urine. In the ED, Ms. A is minimally responsive. Her blood glucose level measurements are in the range of 30 to 39 mg/dL (reference range: 70 to 99 mg/dL), despite having received IV dextrose first from paramedics, and then in the ED. Ms. A has no history of hypoglycemia or diabetes. Her parents say that the night before coming to the ED, Ms. A had experienced flu-like symptoms, including nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea, that continued overnight and resulted in minimal food intake for 24 hours (Table 1).

A physical exam demonstrates left-sided weakness of face, arm, and leg, rightward gaze, and left-sided neglect. However, the results of CT angiography and an MRI of the brain rule out a stroke. An EEG shows right hemispheric slowing consistent with postictal paralysis, but no ongoing seizure activity. Ms. A is transferred to the pediatric intensive care unit (PICU).
Although Ms. A has no psychiatric diagnoses, she has a history of depressive symptoms, self-harm by cutting, and a suicide attempt by ingestion of an over-the-counter (OTC) medication 1 year ago. She had reported the suicide attempt to her parents several months after the fact, and asked them to find her a therapist, which her parents arranged. She also has a history of asthma, which is well-controlled with montelukast, 5 mg/d.
EVALUATION Elevated insulin levels
Subsequent investigations for organic causes of hypoglycemia are negative for adrenal insufficiency, fatty acid oxidation defect, and sepsis. Blood results demonstrate significantly elevated insulin levels of 92.4 mcIU/mL (reference range: 2.6 to 24.9 mcIU/mL) and a C-peptide level of 9.5 ng/mL (reference range: 1.1 to 4.4 ng/mL).
On Day 1 of admission to the PICU, Ms. A’s blood glucose level normalizes, and her mentation improves. Her parents report that one of them has diabetes and takes oral hypoglycemic agents at home, including glipizide immediate release (IR) tablets, 10 mg, and long-acting insulin glargine. The treatment team suspects that Ms. A may have ingested one or both of these agents, and orders a toxicologic screening for oral hypoglycemic agents.
On Day 2, the toxicology results are returned and are positive for glipizide, which Ms. A had not been prescribed. Ms. A states that she had taken only her montelukast tablet on the day of admission and adamantly denies deliberately ingesting her parent’s diabetes medications. Her parents check the home medications and state there are no missing glipizide IR tablets or insulin vials. They also report that Ms. A had no access to extended-release glipizide.
The treatment team discuss Ms. A’s clinical condition and toxicology results with the pediatric endocrinology team. The endocrinology team states that with no history of hypoglycemic episodes, it is unlikely that Ms. A had an endogenous etiology that would present so catastrophically. In their experience, inexplicable hypoglycemia in a healthy individual who lives in a household with someone who has diabetes is due to ingestion of a hypoglycemic agent until proven otherwise.
[polldaddy:10252689]
Continue to: The authors' observations
The authors’ observations
In the context of Ms. A’s prior suicide attempt and history of self-harm, the pediatric team was concerned that her presentation was consistent with a suicide attempt and consulted the psychiatry service.
Glipizide is a second-generation sulfonylurea used to treat type 2 diabetes. It lowers blood glucose by stimulating pancreatic insulin secretion. It is a rare drug of overdose.1 Although pediatric glipizide overdoses have been documented, there are currently no pediatric or adolescent glipizide pharmacokinetic studies in the literature.1-4 In adults, the immediate-release formulation has 100% oral bioavailability, with a maximum plasma concentration (Tmax) of approximately 2 hours.5 The half-life typically ranges from 4 to 6 hours in adults.6 Patients who do not have diabetes are much more susceptible to the hypoglycemic effects of glipizide because the medication simulates their fully functional pancreas to produce a vigorous insulin response.
Ms. A’s significantly elevated insulin was consistent with normal glipizide effects in a healthy child, while the elevated C-peptide was consistent with insulin being endogenously produced, which ruled out ingestion of her parent’s insulin. Importantly, the pediatric endocrinology team noted that, in their experience, a single 5- to 10-mg dose of glipizide IR was sufficient to lower blood glucose levels to the low 30s mg/dL in the context of a functional pancreas, which suggested that Ms. A might have accidentally ingested a single glipizide IR tablet, and might be telling the truth when she denies deliberately ingesting it to hurt herself.
The clinical value of pharmacokinetics
The screen of Ms. A’s toxicology sample detected glipizide. The laboratory used a semi-quantitative serum screen of several hypoglycemic agents. A positive result for each agent is based on a quantitative cut-off value, which is 3 ng/mL for glipizide. The clinical chemist on call was asked to assist in interpreting the results. The serum specimen collected on Day 1 had a significantly positive glipizide result of 86 to 130 ng/mL. The maximum effective glipizide concentration for adult patients with diabetes is 100 ng/mL.7 Thus, the glipizide level of 86 to 130 ng/mL (20.5 hours after initial symptoms) is consistent with the clinical presentation of persistent hypoglycemia requiring ongoing glucose replacement therapy.
Due to the lack of pediatric pharmacokinetic data for glipizide and only a single serum measurement, it is not possible to estimate the glipizide concentration at the time of maximal symptoms (loss of consciousness at 2:30
Continue to: Clinicians need to be aware that...
Clinicians need to be aware that although hypoglycemia usually presents rapidly, in children glipizide IR can rarely cause delayed hypoglycemia up to 16 hours after ingestion,2 and a delay of 45 hours was reported in a case of ingestion of extended-release glipizide.8 Hypoglycemia can last up to nearly 24 hours and is exacerbated if the patient has not eaten.1,2 Importantly, Ms. A’s parents reported that she had no access to extended-release glipizide. When detailed pharmacokinetic data are not available, the information provided by the patient and parents becomes extremely important, especially in distinguishing between single and multiple overdoses prior to presentation, or co-ingestions, or decreased food intake that could exacerbate hypoglycemia.
EVALUATION Safety assessment
On Day 2, Ms. A and her parents are interviewed separately, and they all are consistent in their recollection that Ms. A had been feverish with flu-like symptoms throughout the night before coming to the ED, and had still seemed mildly confused on the morning of admission.
During the interview, her parents wonder when Ms. A took her daily dose of a single montelukast tablet for asthma, and whether she had accidentally confused it with their glipizide. They report that on the morning of admission, both the glipizide and montelukast medication vials were in the same room. The vials are the same color, the same size, and labeled from the same pharmacy, and contain white, scored, round tablets that look very similar.
During the interview, Ms. A consistently denies having thoughts of hurting or killing herself on the day of admission or before that.
[polldaddy:10252690]
Continue to: The authors' observations
The authors’ observations
This case was ultimately an accidental ingestion of glipizide, rather than a suicide attempt. The initial suspicion for a suicide attempt had been reasonable in the context of Ms. A’s depressive symptoms, remote history of a prior suicide attempt by ingesting an OTC medication, and toxicologic evidence of ingesting a drug not prescribed to her. Additionally, because of the life-threatening presentation, it was easy to make the erroneous assumption that the ingestion of glipizide must have involved many tablets, and thus must have been deliberate. However, through multidisciplinary teamwork, we were able to demonstrate that this was likely an accidental ingestion by a patient who had an acute febrile illness. Her illness had caused confusion, which contributed to the accidental ingestion, and also caused reduced food intake, which enhanced the hypoglycemic effects of glipizide. Additionally, a lack of awareness of medication safety in the home had facilitated the confusion between the two medication vials.
A single tablet of glipizide IR is sufficient to produce profound clinical effects that could be mistaken by medical and psychiatric teams for a much larger and/or deliberate overdose, especially in patients with a psychiatric history. The inappropriate psychiatric hospitalization of a patient, especially a child, who has been mistakenly diagnosed as having attempted suicide, can have negative therapeutic consequences (Table 2). A psychiatric admission would have been misguided if it attempted to address safety and reduce suicidality when no such concerns were present. Additionally, it could have damaged relationships with the patient and the family, especially in a child who had historically not sought psychiatric care despite depressive symptoms and a previous suicide attempt. When assessing for suicidality, consider accidental ingestion in the differential and use specialty expertise and confirmatory testing in the evaluation, taking the pharmacokinetics of the suspected agent into account.
OUTCOME Outpatient treatment
Ms. A’s neurologic symptoms resolve within 24 hours of admission. She is offered psychiatric inpatient hospitalization to address her depressive symptoms; however, her parents prefer that she receive outpatient care. Ms. A’s parents also state that after Ms. A’s admission, they locked up all household medications and will be more mindful with medication in the home. Because her parents are arranging appropriate outpatient treatment for Ms. A’s depression and maintenance of her safety, an involuntary hospitalization is not deemed necessary.
On Day 2, Ms. A is eating normally, her blood glucose levels remain stable, and she is discharged home.
Bottom Line
Oral hypoglycemic agents can cause life-threatening syndromes in healthy patients and can clinically mimic large, intentional overdoses. Clinicians must be aware of the differential of accidental ingestion when assessing for suicidality, and can use toxicology results in their assessment.
Related Resources
- Kidemergencies.com. Emergencies: One pill can kill. http://kidemergencies.com/onepill1.html.
- Safe Kids Worldwide. Medication safety. https://www.safekids.org/medicinesafety.
- American Association of Poison Control Centers. http://www.aapcc.org/.
Drug Brand Names
Glipizide • Glucotrol
Insulin glargine • Lantus
Montelukast • Singulair
CASE Unexplained hypoglycemia
Ms. A, age 12, is brought to the emergency department (ED) via ambulance with altered mentation and life-threatening hypoglycemia for management of a hypoglycemic seizure. Earlier that day, Ms. A’s parents had found her unresponsive and incontinent of urine. In the ED, Ms. A is minimally responsive. Her blood glucose level measurements are in the range of 30 to 39 mg/dL (reference range: 70 to 99 mg/dL), despite having received IV dextrose first from paramedics, and then in the ED. Ms. A has no history of hypoglycemia or diabetes. Her parents say that the night before coming to the ED, Ms. A had experienced flu-like symptoms, including nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea, that continued overnight and resulted in minimal food intake for 24 hours (Table 1).

A physical exam demonstrates left-sided weakness of face, arm, and leg, rightward gaze, and left-sided neglect. However, the results of CT angiography and an MRI of the brain rule out a stroke. An EEG shows right hemispheric slowing consistent with postictal paralysis, but no ongoing seizure activity. Ms. A is transferred to the pediatric intensive care unit (PICU).
Although Ms. A has no psychiatric diagnoses, she has a history of depressive symptoms, self-harm by cutting, and a suicide attempt by ingestion of an over-the-counter (OTC) medication 1 year ago. She had reported the suicide attempt to her parents several months after the fact, and asked them to find her a therapist, which her parents arranged. She also has a history of asthma, which is well-controlled with montelukast, 5 mg/d.
EVALUATION Elevated insulin levels
Subsequent investigations for organic causes of hypoglycemia are negative for adrenal insufficiency, fatty acid oxidation defect, and sepsis. Blood results demonstrate significantly elevated insulin levels of 92.4 mcIU/mL (reference range: 2.6 to 24.9 mcIU/mL) and a C-peptide level of 9.5 ng/mL (reference range: 1.1 to 4.4 ng/mL).
On Day 1 of admission to the PICU, Ms. A’s blood glucose level normalizes, and her mentation improves. Her parents report that one of them has diabetes and takes oral hypoglycemic agents at home, including glipizide immediate release (IR) tablets, 10 mg, and long-acting insulin glargine. The treatment team suspects that Ms. A may have ingested one or both of these agents, and orders a toxicologic screening for oral hypoglycemic agents.
On Day 2, the toxicology results are returned and are positive for glipizide, which Ms. A had not been prescribed. Ms. A states that she had taken only her montelukast tablet on the day of admission and adamantly denies deliberately ingesting her parent’s diabetes medications. Her parents check the home medications and state there are no missing glipizide IR tablets or insulin vials. They also report that Ms. A had no access to extended-release glipizide.
The treatment team discuss Ms. A’s clinical condition and toxicology results with the pediatric endocrinology team. The endocrinology team states that with no history of hypoglycemic episodes, it is unlikely that Ms. A had an endogenous etiology that would present so catastrophically. In their experience, inexplicable hypoglycemia in a healthy individual who lives in a household with someone who has diabetes is due to ingestion of a hypoglycemic agent until proven otherwise.
[polldaddy:10252689]
Continue to: The authors' observations
The authors’ observations
In the context of Ms. A’s prior suicide attempt and history of self-harm, the pediatric team was concerned that her presentation was consistent with a suicide attempt and consulted the psychiatry service.
Glipizide is a second-generation sulfonylurea used to treat type 2 diabetes. It lowers blood glucose by stimulating pancreatic insulin secretion. It is a rare drug of overdose.1 Although pediatric glipizide overdoses have been documented, there are currently no pediatric or adolescent glipizide pharmacokinetic studies in the literature.1-4 In adults, the immediate-release formulation has 100% oral bioavailability, with a maximum plasma concentration (Tmax) of approximately 2 hours.5 The half-life typically ranges from 4 to 6 hours in adults.6 Patients who do not have diabetes are much more susceptible to the hypoglycemic effects of glipizide because the medication simulates their fully functional pancreas to produce a vigorous insulin response.
Ms. A’s significantly elevated insulin was consistent with normal glipizide effects in a healthy child, while the elevated C-peptide was consistent with insulin being endogenously produced, which ruled out ingestion of her parent’s insulin. Importantly, the pediatric endocrinology team noted that, in their experience, a single 5- to 10-mg dose of glipizide IR was sufficient to lower blood glucose levels to the low 30s mg/dL in the context of a functional pancreas, which suggested that Ms. A might have accidentally ingested a single glipizide IR tablet, and might be telling the truth when she denies deliberately ingesting it to hurt herself.
The clinical value of pharmacokinetics
The screen of Ms. A’s toxicology sample detected glipizide. The laboratory used a semi-quantitative serum screen of several hypoglycemic agents. A positive result for each agent is based on a quantitative cut-off value, which is 3 ng/mL for glipizide. The clinical chemist on call was asked to assist in interpreting the results. The serum specimen collected on Day 1 had a significantly positive glipizide result of 86 to 130 ng/mL. The maximum effective glipizide concentration for adult patients with diabetes is 100 ng/mL.7 Thus, the glipizide level of 86 to 130 ng/mL (20.5 hours after initial symptoms) is consistent with the clinical presentation of persistent hypoglycemia requiring ongoing glucose replacement therapy.
Due to the lack of pediatric pharmacokinetic data for glipizide and only a single serum measurement, it is not possible to estimate the glipizide concentration at the time of maximal symptoms (loss of consciousness at 2:30
Continue to: Clinicians need to be aware that...
Clinicians need to be aware that although hypoglycemia usually presents rapidly, in children glipizide IR can rarely cause delayed hypoglycemia up to 16 hours after ingestion,2 and a delay of 45 hours was reported in a case of ingestion of extended-release glipizide.8 Hypoglycemia can last up to nearly 24 hours and is exacerbated if the patient has not eaten.1,2 Importantly, Ms. A’s parents reported that she had no access to extended-release glipizide. When detailed pharmacokinetic data are not available, the information provided by the patient and parents becomes extremely important, especially in distinguishing between single and multiple overdoses prior to presentation, or co-ingestions, or decreased food intake that could exacerbate hypoglycemia.
EVALUATION Safety assessment
On Day 2, Ms. A and her parents are interviewed separately, and they all are consistent in their recollection that Ms. A had been feverish with flu-like symptoms throughout the night before coming to the ED, and had still seemed mildly confused on the morning of admission.
During the interview, her parents wonder when Ms. A took her daily dose of a single montelukast tablet for asthma, and whether she had accidentally confused it with their glipizide. They report that on the morning of admission, both the glipizide and montelukast medication vials were in the same room. The vials are the same color, the same size, and labeled from the same pharmacy, and contain white, scored, round tablets that look very similar.
During the interview, Ms. A consistently denies having thoughts of hurting or killing herself on the day of admission or before that.
[polldaddy:10252690]
Continue to: The authors' observations
The authors’ observations
This case was ultimately an accidental ingestion of glipizide, rather than a suicide attempt. The initial suspicion for a suicide attempt had been reasonable in the context of Ms. A’s depressive symptoms, remote history of a prior suicide attempt by ingesting an OTC medication, and toxicologic evidence of ingesting a drug not prescribed to her. Additionally, because of the life-threatening presentation, it was easy to make the erroneous assumption that the ingestion of glipizide must have involved many tablets, and thus must have been deliberate. However, through multidisciplinary teamwork, we were able to demonstrate that this was likely an accidental ingestion by a patient who had an acute febrile illness. Her illness had caused confusion, which contributed to the accidental ingestion, and also caused reduced food intake, which enhanced the hypoglycemic effects of glipizide. Additionally, a lack of awareness of medication safety in the home had facilitated the confusion between the two medication vials.
A single tablet of glipizide IR is sufficient to produce profound clinical effects that could be mistaken by medical and psychiatric teams for a much larger and/or deliberate overdose, especially in patients with a psychiatric history. The inappropriate psychiatric hospitalization of a patient, especially a child, who has been mistakenly diagnosed as having attempted suicide, can have negative therapeutic consequences (Table 2). A psychiatric admission would have been misguided if it attempted to address safety and reduce suicidality when no such concerns were present. Additionally, it could have damaged relationships with the patient and the family, especially in a child who had historically not sought psychiatric care despite depressive symptoms and a previous suicide attempt. When assessing for suicidality, consider accidental ingestion in the differential and use specialty expertise and confirmatory testing in the evaluation, taking the pharmacokinetics of the suspected agent into account.
OUTCOME Outpatient treatment
Ms. A’s neurologic symptoms resolve within 24 hours of admission. She is offered psychiatric inpatient hospitalization to address her depressive symptoms; however, her parents prefer that she receive outpatient care. Ms. A’s parents also state that after Ms. A’s admission, they locked up all household medications and will be more mindful with medication in the home. Because her parents are arranging appropriate outpatient treatment for Ms. A’s depression and maintenance of her safety, an involuntary hospitalization is not deemed necessary.
On Day 2, Ms. A is eating normally, her blood glucose levels remain stable, and she is discharged home.
Bottom Line
Oral hypoglycemic agents can cause life-threatening syndromes in healthy patients and can clinically mimic large, intentional overdoses. Clinicians must be aware of the differential of accidental ingestion when assessing for suicidality, and can use toxicology results in their assessment.
Related Resources
- Kidemergencies.com. Emergencies: One pill can kill. http://kidemergencies.com/onepill1.html.
- Safe Kids Worldwide. Medication safety. https://www.safekids.org/medicinesafety.
- American Association of Poison Control Centers. http://www.aapcc.org/.
Drug Brand Names
Glipizide • Glucotrol
Insulin glargine • Lantus
Montelukast • Singulair
1. Spiller HA, Villalobos D, Krenzelok EP, et al. Prospective multicenter study of sulfonylurea ingestion in children. J Pediatr. 1997;131(1):141-146.
2. Quadrani DA, Spiller HA, Widder P. Five year retrospective evaluation of sulfonylurea ingestion in children. J Toxicol Clin Toxicol. 1996;34(3):267-270.
3. Borowski H, Caraccio T, Mofenson H. Sulfonylurea ingestion in children: is an 8-hour observation period sufficient? J Pediatr. 1998;133(4):584-585.
4. Little GL, Boniface KS. Are one or two dangerous? Sulfony-lurea exposure in toddlers. J Emerg Med. 2005;28(3):305-310.
5. Huupponen R, Seppala P, Iisalo E. Glipizide pharma-cokinetics and response in diabetics. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther Toxicol. 1982;20(9):417-422.
6. Baselt RC. Disposition of toxic drugs and chemicals in man. 10th ed. Seal Beach, California: Biomedical Publications; 2014.
7. Simonson DC, Kourides IA, Feinglos M, et al; the Glipizide Gastrointestinal Therapeutic System Study Group. Efficacy, safety, and dose-response characteristics of glipizide gastrointestinal therapeutic system on glycemic control and insulin secretion in NIDDM. Results of two multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trials. Diabetes Care. 1997;20(4):597-606.
8. Pelavin PI, Abramson E, Pon S, et al. Extended-release glipizide overdose presenting with delayed hypoglycemia and treated with subcutaneous octreotide. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2009;22(2):171-175.
1. Spiller HA, Villalobos D, Krenzelok EP, et al. Prospective multicenter study of sulfonylurea ingestion in children. J Pediatr. 1997;131(1):141-146.
2. Quadrani DA, Spiller HA, Widder P. Five year retrospective evaluation of sulfonylurea ingestion in children. J Toxicol Clin Toxicol. 1996;34(3):267-270.
3. Borowski H, Caraccio T, Mofenson H. Sulfonylurea ingestion in children: is an 8-hour observation period sufficient? J Pediatr. 1998;133(4):584-585.
4. Little GL, Boniface KS. Are one or two dangerous? Sulfony-lurea exposure in toddlers. J Emerg Med. 2005;28(3):305-310.
5. Huupponen R, Seppala P, Iisalo E. Glipizide pharma-cokinetics and response in diabetics. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther Toxicol. 1982;20(9):417-422.
6. Baselt RC. Disposition of toxic drugs and chemicals in man. 10th ed. Seal Beach, California: Biomedical Publications; 2014.
7. Simonson DC, Kourides IA, Feinglos M, et al; the Glipizide Gastrointestinal Therapeutic System Study Group. Efficacy, safety, and dose-response characteristics of glipizide gastrointestinal therapeutic system on glycemic control and insulin secretion in NIDDM. Results of two multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trials. Diabetes Care. 1997;20(4):597-606.
8. Pelavin PI, Abramson E, Pon S, et al. Extended-release glipizide overdose presenting with delayed hypoglycemia and treated with subcutaneous octreotide. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2009;22(2):171-175.
