User login
A Unique Presentation of Lupus Erythematosus Tumidus in an Adolescent Boy
To the Editor:
Lupus erythematosus tumidus (LET) is a rarely diagnosed condition that was first described in 1909 by Hoffmann.1 Limited cases have been reported in the literature, with few documenting the disease in children.2 We report a unique clinical case of LET in a 14-year-old adolescent boy that was distributed solely on the hands. With slight heterogeneity in regards to clinical presentation and histopathology, there is a need for further exploration with regard to LET.
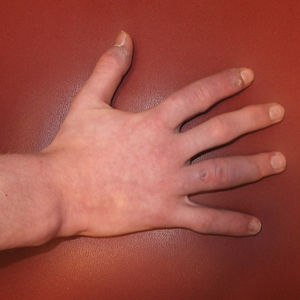
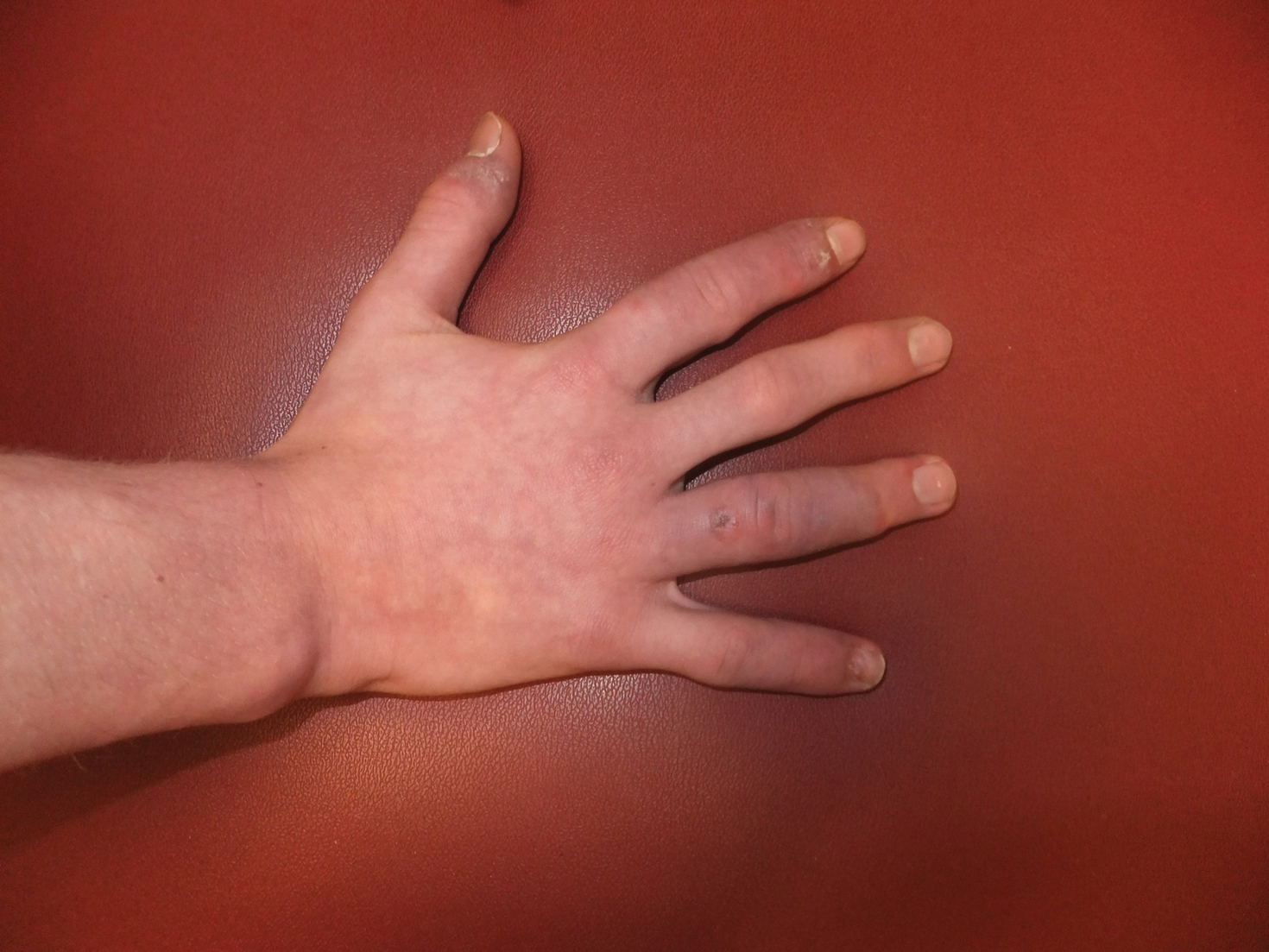
A 14-year-old adolescent boy presented to the dermatology clinic with progressive bilateral edema of 1 year’s duration with plaques and some scaling on the dorsal aspects of the digits and the nail bases predominantly on the right hand (Figure 1) and to a lesser extent on the left hand. The edema, erythema, and tenderness started in the right fifth digit; soon after the edema appeared, plaques began to form at the base of each nail bed, and the edema and erythema progressively spread to the other digits. He denied worsening of symptoms when exposed to cold temperatures. A complete review of systems was negative. The differential diagnoses included chilblain lupus erythematosus, perniosis, dermatomyositis, and polymorphous light eruption. A punch biopsy from the right fourth digit was performed.
The biopsy showed superficial and deep perivascular and periadnexal mononuclear inflammation with large amounts of interstitial mucin deposition (Figure 2). The epidermis exhibited a loose orthokeratotic scale with no signs of interface damage. A diagnosis of perniosis was entertained but was ruled out due to the lack of papillary dermal edema and large amounts of mucin. With the lack of interface change and large amounts of mucin, a diagnosis of LET was favored over chilblain lupus erythematosus, as the latter diagnosis typically demonstrates interface change. The patient was started on hydroxychloroquine 200 mg twice daily and a short course of prednisone, and improvement of the lesions/plaques was noted at follow-up 6 weeks later. Continued improvement was noted 2 years after the initial presentation. His condition recurred when the hydroxychloroquine dosage was reduced to 200 mg once daily after 1 year. The patient did not report any adverse sequelae to treatment.
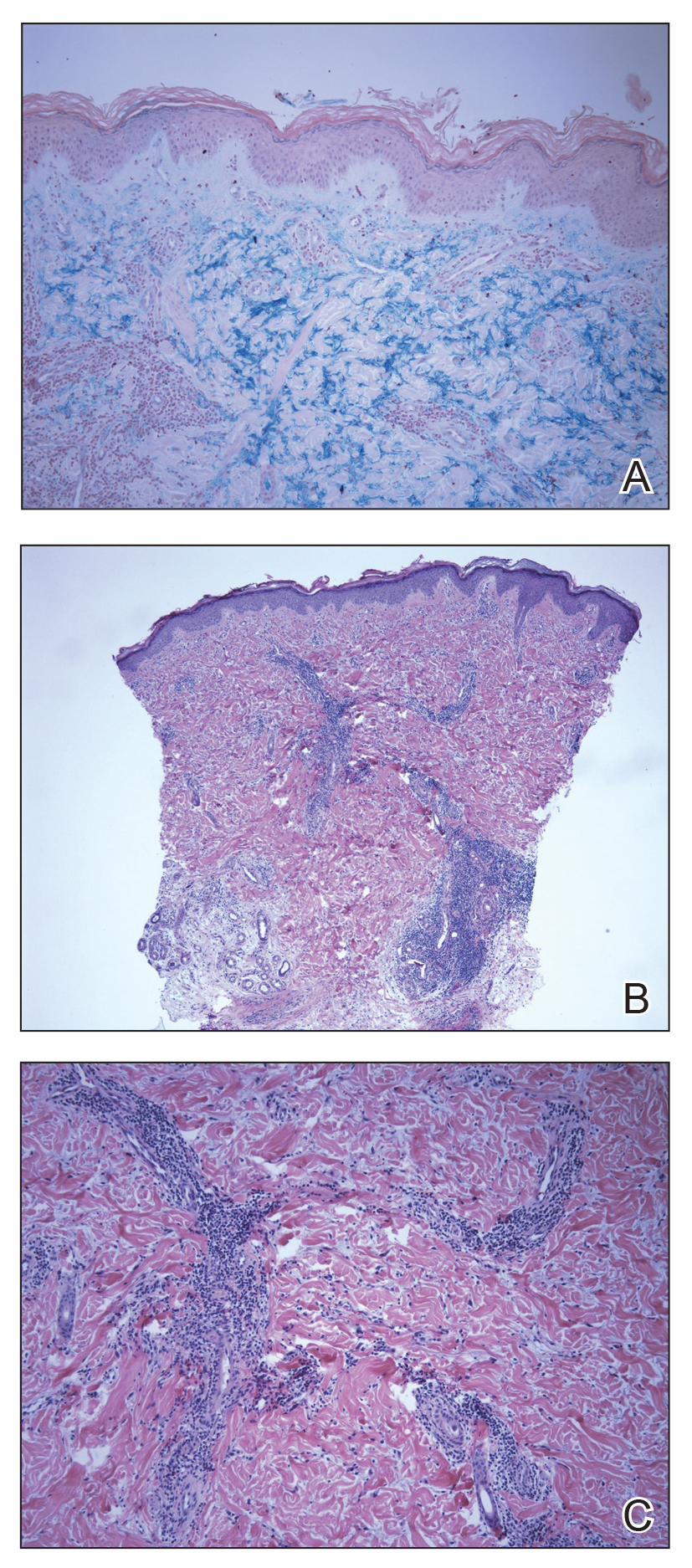
Histopathologic findings of superficial and deep perivascular and periadnexal lymphocytic infiltrates and interstitial dermal deposition of mucin in LET have remained consistent in the literature. Direct immunofluorescence has not revealed any complement or immunoglobulin deposition on the basement membrane.3,4 The epidermal characteristics are not as uniform, with the majority of cases in one review showing no epidermal changes and a minority showing minimal epidermal changes (eg, epidermal atrophy, hyperkeratosis, parakeratosis, acanthosis, spongiosis).5 When working up patients for LET, blood work usually is unremarkable, as LET rarely is associated with antinuclear antibodies or anti-Ro, anti-La, and anti-DNA antibodies.3,4 Lupus erythematosus tumidus generally is an independent process, but it has been reported to coexist with discoid lupus erythematosus and systemic lupus erythematosus in rare cases.6
The lesions of LET have been consistently described in the literature as photosensitive, erythematous, non-scarring, annular plaques and papules commonly occurring on the head/neck and other sun-exposed areas that do not cause hypopigmentation.3 Treatment of LET consists of systemic treatment with antimalarial drugs, sunscreens, and topical steroids for flares.
Lupus erythematosus tumidus is rare in children, with few case reports noted in the literature. Sonntag et al2 documented the disease in 3 children ranging from 3 to 8 years of age. Furthermore, Ruiz and Sanchez7 reported a case of LET in a 16-year-old adolescent girl. Our case is unique in that the lesions only occurred on the hands, whereas most case reports document distribution of the lesions on the head, neck, face, arms, back, and chest. Our patient’s age and the location of the lesions make it a unique clinical presentation of LET.
Reports in the literature show evidence of heterogeneity in the presentation, classification, and some of the histopathologic features of LET; however, there are minimal data on childhood LET. Further research and investigations are needed to more precisely define this condition.
Acknowledgment
The authors acknowledge Richard Schwartz, MD (Akron, Ohio), for reading the biopsy reports and assisting with photomicrographs.
- Hoffmann E. Demonstrationen: lupus erythematosus tumidus. Derm Zeitschr. 1909;16:159-160.
- Sonntag M, Lehmann P, Megahed M, et al. Lupus erythematosus tumidus in childhood. Dermatology. 2003;207:188-192.
- Schmitt V, Meuth AM, Amler S, et al. Lupus erythematosus tumidus is a separate subtype of cutaneous lupus erythematosus. Br J Dermatol. 2010;162:64-73.
- Vieira V, Del Pozo J, Yebra-Pimentel MT, et al. Lupus erythematosus tumidus: a series of 26 cases. Int J Dermatol. 2006;45:512-517.
- Kuhn A, Richter-Hintz D, Oslislo C, et al. Lupus erythematosus tumidus—a neglected subset of cutaneous lupus erythematosus: report of 40 cases. Arch Dermatol. 2000;136:1033-1041.
- Chen X, Wang S, Li L. A case report of lupus erythematosus tumidus converted from discoid lupus erythematosus. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018;97:e0375.
- Ruiz H, Sanchez J. Tumid lupus erythematosus. Am J Dermatopathol. 1999;21:356-360.
To the Editor:
Lupus erythematosus tumidus (LET) is a rarely diagnosed condition that was first described in 1909 by Hoffmann.1 Limited cases have been reported in the literature, with few documenting the disease in children.2 We report a unique clinical case of LET in a 14-year-old adolescent boy that was distributed solely on the hands. With slight heterogeneity in regards to clinical presentation and histopathology, there is a need for further exploration with regard to LET.
A 14-year-old adolescent boy presented to the dermatology clinic with progressive bilateral edema of 1 year’s duration with plaques and some scaling on the dorsal aspects of the digits and the nail bases predominantly on the right hand (Figure 1) and to a lesser extent on the left hand. The edema, erythema, and tenderness started in the right fifth digit; soon after the edema appeared, plaques began to form at the base of each nail bed, and the edema and erythema progressively spread to the other digits. He denied worsening of symptoms when exposed to cold temperatures. A complete review of systems was negative. The differential diagnoses included chilblain lupus erythematosus, perniosis, dermatomyositis, and polymorphous light eruption. A punch biopsy from the right fourth digit was performed.

The biopsy showed superficial and deep perivascular and periadnexal mononuclear inflammation with large amounts of interstitial mucin deposition (Figure 2). The epidermis exhibited a loose orthokeratotic scale with no signs of interface damage. A diagnosis of perniosis was entertained but was ruled out due to the lack of papillary dermal edema and large amounts of mucin. With the lack of interface change and large amounts of mucin, a diagnosis of LET was favored over chilblain lupus erythematosus, as the latter diagnosis typically demonstrates interface change. The patient was started on hydroxychloroquine 200 mg twice daily and a short course of prednisone, and improvement of the lesions/plaques was noted at follow-up 6 weeks later. Continued improvement was noted 2 years after the initial presentation. His condition recurred when the hydroxychloroquine dosage was reduced to 200 mg once daily after 1 year. The patient did not report any adverse sequelae to treatment.

Histopathologic findings of superficial and deep perivascular and periadnexal lymphocytic infiltrates and interstitial dermal deposition of mucin in LET have remained consistent in the literature. Direct immunofluorescence has not revealed any complement or immunoglobulin deposition on the basement membrane.3,4 The epidermal characteristics are not as uniform, with the majority of cases in one review showing no epidermal changes and a minority showing minimal epidermal changes (eg, epidermal atrophy, hyperkeratosis, parakeratosis, acanthosis, spongiosis).5 When working up patients for LET, blood work usually is unremarkable, as LET rarely is associated with antinuclear antibodies or anti-Ro, anti-La, and anti-DNA antibodies.3,4 Lupus erythematosus tumidus generally is an independent process, but it has been reported to coexist with discoid lupus erythematosus and systemic lupus erythematosus in rare cases.6
The lesions of LET have been consistently described in the literature as photosensitive, erythematous, non-scarring, annular plaques and papules commonly occurring on the head/neck and other sun-exposed areas that do not cause hypopigmentation.3 Treatment of LET consists of systemic treatment with antimalarial drugs, sunscreens, and topical steroids for flares.
Lupus erythematosus tumidus is rare in children, with few case reports noted in the literature. Sonntag et al2 documented the disease in 3 children ranging from 3 to 8 years of age. Furthermore, Ruiz and Sanchez7 reported a case of LET in a 16-year-old adolescent girl. Our case is unique in that the lesions only occurred on the hands, whereas most case reports document distribution of the lesions on the head, neck, face, arms, back, and chest. Our patient’s age and the location of the lesions make it a unique clinical presentation of LET.
Reports in the literature show evidence of heterogeneity in the presentation, classification, and some of the histopathologic features of LET; however, there are minimal data on childhood LET. Further research and investigations are needed to more precisely define this condition.
Acknowledgment
The authors acknowledge Richard Schwartz, MD (Akron, Ohio), for reading the biopsy reports and assisting with photomicrographs.
To the Editor:
Lupus erythematosus tumidus (LET) is a rarely diagnosed condition that was first described in 1909 by Hoffmann.1 Limited cases have been reported in the literature, with few documenting the disease in children.2 We report a unique clinical case of LET in a 14-year-old adolescent boy that was distributed solely on the hands. With slight heterogeneity in regards to clinical presentation and histopathology, there is a need for further exploration with regard to LET.
A 14-year-old adolescent boy presented to the dermatology clinic with progressive bilateral edema of 1 year’s duration with plaques and some scaling on the dorsal aspects of the digits and the nail bases predominantly on the right hand (Figure 1) and to a lesser extent on the left hand. The edema, erythema, and tenderness started in the right fifth digit; soon after the edema appeared, plaques began to form at the base of each nail bed, and the edema and erythema progressively spread to the other digits. He denied worsening of symptoms when exposed to cold temperatures. A complete review of systems was negative. The differential diagnoses included chilblain lupus erythematosus, perniosis, dermatomyositis, and polymorphous light eruption. A punch biopsy from the right fourth digit was performed.

The biopsy showed superficial and deep perivascular and periadnexal mononuclear inflammation with large amounts of interstitial mucin deposition (Figure 2). The epidermis exhibited a loose orthokeratotic scale with no signs of interface damage. A diagnosis of perniosis was entertained but was ruled out due to the lack of papillary dermal edema and large amounts of mucin. With the lack of interface change and large amounts of mucin, a diagnosis of LET was favored over chilblain lupus erythematosus, as the latter diagnosis typically demonstrates interface change. The patient was started on hydroxychloroquine 200 mg twice daily and a short course of prednisone, and improvement of the lesions/plaques was noted at follow-up 6 weeks later. Continued improvement was noted 2 years after the initial presentation. His condition recurred when the hydroxychloroquine dosage was reduced to 200 mg once daily after 1 year. The patient did not report any adverse sequelae to treatment.

Histopathologic findings of superficial and deep perivascular and periadnexal lymphocytic infiltrates and interstitial dermal deposition of mucin in LET have remained consistent in the literature. Direct immunofluorescence has not revealed any complement or immunoglobulin deposition on the basement membrane.3,4 The epidermal characteristics are not as uniform, with the majority of cases in one review showing no epidermal changes and a minority showing minimal epidermal changes (eg, epidermal atrophy, hyperkeratosis, parakeratosis, acanthosis, spongiosis).5 When working up patients for LET, blood work usually is unremarkable, as LET rarely is associated with antinuclear antibodies or anti-Ro, anti-La, and anti-DNA antibodies.3,4 Lupus erythematosus tumidus generally is an independent process, but it has been reported to coexist with discoid lupus erythematosus and systemic lupus erythematosus in rare cases.6
The lesions of LET have been consistently described in the literature as photosensitive, erythematous, non-scarring, annular plaques and papules commonly occurring on the head/neck and other sun-exposed areas that do not cause hypopigmentation.3 Treatment of LET consists of systemic treatment with antimalarial drugs, sunscreens, and topical steroids for flares.
Lupus erythematosus tumidus is rare in children, with few case reports noted in the literature. Sonntag et al2 documented the disease in 3 children ranging from 3 to 8 years of age. Furthermore, Ruiz and Sanchez7 reported a case of LET in a 16-year-old adolescent girl. Our case is unique in that the lesions only occurred on the hands, whereas most case reports document distribution of the lesions on the head, neck, face, arms, back, and chest. Our patient’s age and the location of the lesions make it a unique clinical presentation of LET.
Reports in the literature show evidence of heterogeneity in the presentation, classification, and some of the histopathologic features of LET; however, there are minimal data on childhood LET. Further research and investigations are needed to more precisely define this condition.
Acknowledgment
The authors acknowledge Richard Schwartz, MD (Akron, Ohio), for reading the biopsy reports and assisting with photomicrographs.
- Hoffmann E. Demonstrationen: lupus erythematosus tumidus. Derm Zeitschr. 1909;16:159-160.
- Sonntag M, Lehmann P, Megahed M, et al. Lupus erythematosus tumidus in childhood. Dermatology. 2003;207:188-192.
- Schmitt V, Meuth AM, Amler S, et al. Lupus erythematosus tumidus is a separate subtype of cutaneous lupus erythematosus. Br J Dermatol. 2010;162:64-73.
- Vieira V, Del Pozo J, Yebra-Pimentel MT, et al. Lupus erythematosus tumidus: a series of 26 cases. Int J Dermatol. 2006;45:512-517.
- Kuhn A, Richter-Hintz D, Oslislo C, et al. Lupus erythematosus tumidus—a neglected subset of cutaneous lupus erythematosus: report of 40 cases. Arch Dermatol. 2000;136:1033-1041.
- Chen X, Wang S, Li L. A case report of lupus erythematosus tumidus converted from discoid lupus erythematosus. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018;97:e0375.
- Ruiz H, Sanchez J. Tumid lupus erythematosus. Am J Dermatopathol. 1999;21:356-360.
- Hoffmann E. Demonstrationen: lupus erythematosus tumidus. Derm Zeitschr. 1909;16:159-160.
- Sonntag M, Lehmann P, Megahed M, et al. Lupus erythematosus tumidus in childhood. Dermatology. 2003;207:188-192.
- Schmitt V, Meuth AM, Amler S, et al. Lupus erythematosus tumidus is a separate subtype of cutaneous lupus erythematosus. Br J Dermatol. 2010;162:64-73.
- Vieira V, Del Pozo J, Yebra-Pimentel MT, et al. Lupus erythematosus tumidus: a series of 26 cases. Int J Dermatol. 2006;45:512-517.
- Kuhn A, Richter-Hintz D, Oslislo C, et al. Lupus erythematosus tumidus—a neglected subset of cutaneous lupus erythematosus: report of 40 cases. Arch Dermatol. 2000;136:1033-1041.
- Chen X, Wang S, Li L. A case report of lupus erythematosus tumidus converted from discoid lupus erythematosus. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018;97:e0375.
- Ruiz H, Sanchez J. Tumid lupus erythematosus. Am J Dermatopathol. 1999;21:356-360.
Practice Points
- Lupus erythematosus tumidus rarely occurs in the pediatric population.
- Lupus erythematosus tumidus is a unique subset of lupus associated with lack of interface change on histology and large amounts of mucin.
- Lesions typically present on the face and trunk but can very rarely present on the extremities and hands.
Idiopathic Livedo Racemosa Presenting With Splenomegaly and Diffuse Lymphadenopathy
Sneddon syndrome (SS) was first described in 1965 in patients with persistent livedo racemosa and neurological events.1 Because the other manifestations of SS are nonspecific (eg, hypertension, cardiac valvulopathy, arterial and venous occlusion), the diagnosis often is delayed. Many patients who experience prodromal neurologic symptoms such as headaches, depression, anxiety, dizziness, and neuropathy often present to a physician prior to developing ischemic brain manifestations2 but seldom receive the correct diagnosis. Onset of cerebral occlusive events typically occurs in patients younger than 45 years and may present as a transient ischemic attack, stroke, or intracranial hemorrhage.3 The disease is more prevalent in females than males (2:1 ratio). The exact pathogenesis of SS is still unknown, and although it has been thought of as a separate entity from systemic lupus erythematosus and other antiphospholipid disorders, it has been postulated that an immunological dysfunction damages vessel walls leading to thrombosis.
Cutaneous findings associated with SS involve small- to medium-sized dermal-subdermal arteries. Histopathology in some patients demonstrates proliferation of the endothelium and fibrin deposits with subsequent obliteration of involved arteries.4 In many patients including our patient, histopathologic examination of involved skin fails to show specific abnormalities.1 Zelger et al5 reported the sequence of histopathologic skin events in a series of antiphospholipid-negative SS patients. The authors reported that only small arteries at the dermis-subcutis junction were involved and a progression of endothelial dysfunction was observed. The authors believed there were several nonspecific stages prior to fibrin occlusion of involved arteries.5 Stage I involved loosening of endothelial cells with nonspecific perivascular lymphocytic infiltration with perivascular inflammation and lymphocytic infiltration representing the prime mover of the disease.5,6 This stage is thought to be short lived, thus the reason why it has gone undetected for many years in SS patients. Stages II to IV progress through fibrin deposition and occlusion.5 Histological features of stages I to II have not been reported because of late diagnosis of SS. Stage I patients typically present with an average duration of symptoms of 6 months with few neurologic symptoms, the most common being paresthesia of the legs.5
Case Report
A 37-year-old woman with epigastric tenderness on the left side and splenomegaly seen on computed tomography was referred by a hematologist for evaluation of a reticular rash on the left side of the flank of 9 months’ duration with a presumed diagnosis of focal melanoderma. Her medical history was remarkable for a congenital ventricular septal defect and coarctation of the aorta, as well as endometriosis, myalgia, and joint stiffness that had all developed over the last year. Her medical history also was remarkable for nephrolithiasis, irritable bowel syndrome, and chronic sinusitis, as well as psychiatric depression and anxiety disorders. She recently had been diagnosed with moderate hypertension and had experienced difficulty getting pregnant for the last several years with 3 consecutive miscarriages in the first trimester. Neurologic symptoms included neuropathy involving the feet, intermittent paresthesia of the legs, and a history of chronic migraine headaches for several months.
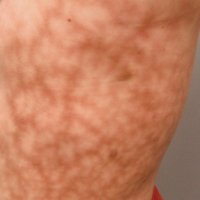
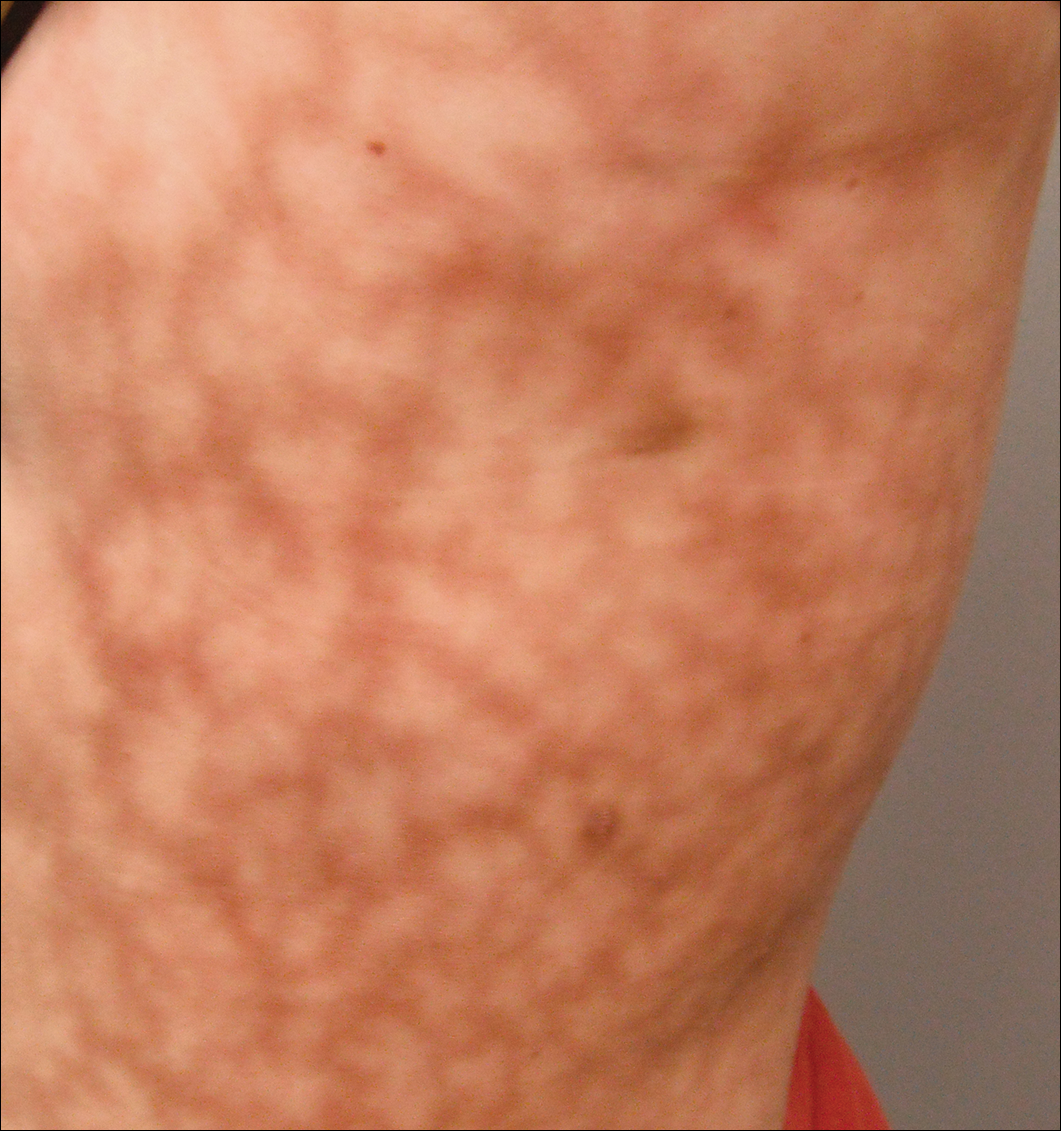
Dermatologic examination revealed a slightly overweight woman with a 25×30-cm dusky, erythematous, irregular, netlike pattern on the left side of the upper and lower trunk (Figure 1). Extensive livedo racemosa was not altered by changes in temperature and had been unchanged for more than 9 months. There were no signs of pruritus or ulcerations, and areas of livedo racemosa were slightly tender to palpation.
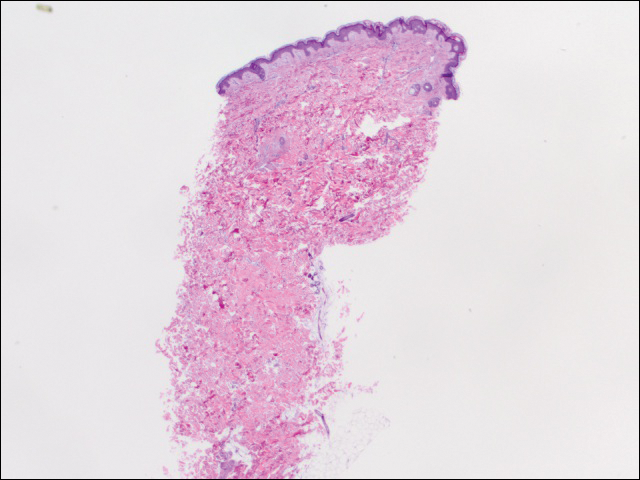
We performed 2 sets of three 4-mm biopsies. The first set targeted areas within the violaceous pattern, while the second set targeted areas of normal tissue between the mottled areas. All 6 specimens demonstrated superficial perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate with no evidence of vasculitis or connective tissue disease. The vessels showed no microthrombi or surrounding fibrosis. No eosinophils were identified within the epidermis. There was no evidence of increased dermal mucin. Both the superficial and deep vascular plexuses were unremarkable and showed no evidence of damage to the walls (Figure 2).
To rule out other possible causes of livedo racemosa, complete blood cell count, comprehensive metabolic panel, coagulation profile, lipase test, urinalysis, serologic testing, and immunologic workup were performed. Lipase was within reference range. The complete blood cell count revealed mild anemia, while the rest of the values were within reference range. An immunologic workup included Sjögren syndrome antigen A, Sjögren syndrome antigen B, anticardiolipin antibodies, and antinuclear antibody, which were all negative. Family history was remarkable for first-degree relatives with systemic lupus erythematosus and Crohn disease.
Computed tomography revealed enlargement of the spleen, as well as periaortic, portacaval, and porta hepatis lymphadenopathy. Based on the laboratory findings and clinical presentation as well as the patient’s medical history, the diagnosis of exclusion was idiopathic livedo racemosa with unknown progression to full-blown SS. The patient did not meet the current diagnostic criteria for SS, and her immunologic studies failed to confirm any present antibodies, but involvement of the reticuloendothelial system pointed to production of antibodies that were not yet detectable on laboratory testing.
Comment
More than 50 years after the first case of SS was diagnosed, better laboratory workup is available and more information is known about the pathophysiology. Sneddon syndrome is a rare disorder, affecting only approximately 4 patients per million each year worldwide. Seronegative antiphospholipid antibody syndrome (SNAPS) describes patients with clinical presentations of antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) without detectable serological markers.7 Antiphospholipid-negative SS, which was seen in our patient, would be categorized under SNAPS. A PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the terms livedo racemosa, Sneddon syndrome, and SNAPS and splenomegaly revealed there currently are no known cases of SNAPS that have been reported with splenomegaly and lymphadenopathy. Our patient presented with the following clinical features of SS: livedo racemosa, history of miscarriage, psychiatric disturbances, and hypertension. Surprisingly, biopsies from affected skin did not show any fibrin deposition or microthrombi but did reveal perivascular lymphocytic infiltrations. Magnetic resonance imaging did not show any pathological lesions or vascular changes.
Sneddon syndrome and APS share a common pathway to occlusive arteriolopathy for which 4 stages have been described by Zelger et al.5 Stage I involves a nonspecific Langerhans cell infiltrate with polymorphonuclear leukocytes. The tunica media and elastic lamina usually are unaltered at this early stage, while the surrounding connective tissue may appear edematous.5 This early stage of histopathology has not been evaluated in SS patients, primarily because of delay of diagnosis. Late stages III and IV will show fibrin deposition and shrinkage of affected vessels.7
A PubMed search using the terms Sneddon syndrome, lymphadenopathy and livedo racemosa, and Sneddon syndrome and lymphadenopathy revealed that splenomegaly and lymphadenopathy have not been reported in patients with SS. In patients with antiphospholipid-negative SS, one can assume that antibodies to other phospholipids not tested must exist because of striking similarities between APS and antiphospholipid-negative SS.8 Although our patient did not test positive for any of these antibodies, she did present with lymphadenopathy and splenic enlargement, leading us to believe that involvement of the reticuloendothelial system may be a feature of SS that has not been previously reported. Further studies are required to name specific antigens responsible for clinical manifestations in SS.
Currently, no single diagnostic test for SS exists, thus delaying both diagnosis and initiation of treatment. Histopathologic examination may be helpful, but in many cases it is nonspecific, as are serologic markers. Neuroradiological confirmation of involvement usually is the confirmatory feature in many patients with late-stage diagnosis.2 A diagnostic schematic for SS, which was first described by Daoud et al,2 illustrates classification of symptoms and aids in diagnosis. A working diagnosis of idiopathic livedo racemosa is made after ruling out other causes of SS in a patient with nonspecific biopsy findings and negative magnetic resonance imaging results with prodromal symptoms. The prognosis for such patients progressing to full SS is unknown with or without management using anticoagulant therapy.
Conclusion
Early diagnosis of livedo racemosa and SS is essential, as prevention of cerebrovascular accidents, myocardial infarction, and other thromboembolic diseases can be minimized by attacking risk factors such as smoking, taking oral contraceptive pills, becoming pregnant,9 and by initiating either antiplatelet or anticoagulation treatments. These treatments have been shown to delay the development of neurovascular damage and early-onset dementia. We present this case to demonstrate the variability of early-presenting symptoms in idiopathic livedo racemosa. Recognizing some of the early manifestations can lead to early diagnosis and initiation of treatment.
- Sneddon IB. Cerebro-vascular lesions and livedo reticularis. Br J Dermatol. 1965;77:180-185.
- Daoud MS, Wilmoth GJ, Su WP, et al. Sneddon syndrome. Semin Dermatol. 1995;14:166-172.
- Besnier R, Francès C, Ankri A, et al. Factor V Leiden mutation in Sneddon syndrome. Lupus. 2003;12:406-408.
- K aragülle AT, Karadağ D, Erden A, et al. Sneddon’s syndrome: MR imaging findings. Eur Radiol. 2002;12:144-146.
- Zelg er B, Sepp N, Schmid KW, et al. Life-history of cutaneous vascular-lesions in Sneddon’s syndrome. Hum Pathol. 1992;23:668-675.
- Ayoub N, Esposito G, Barete S, et al. Protein Z deficiency in antiphospholipid-negative Sneddon’s syndrome. Stroke. 2004;35:1329-1332.
- Duva l A, Darnige L, Glowacki F, et al. Livedo, dementia, thrombocytopenia, and endotheliitis without antiphospholipid antibodies: seronegative antiphospholipid-like syndrome. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;61:1076-1078.
- Kala shnikova LA, Nasonov EL, Kushekbaeva AE, et al. Anticardiolipin antibodies in Sneddon’s syndrome. Neurology. 1990;40:464-467.
- Wohl rab J, Fischer M, Wolter M, et al. Diagnostic impact and sensitivity of skin biopsies in Sneddon’s syndrome. a report of 15 cases. Br J Dermatol. 2001;145:285-288.
Sneddon syndrome (SS) was first described in 1965 in patients with persistent livedo racemosa and neurological events.1 Because the other manifestations of SS are nonspecific (eg, hypertension, cardiac valvulopathy, arterial and venous occlusion), the diagnosis often is delayed. Many patients who experience prodromal neurologic symptoms such as headaches, depression, anxiety, dizziness, and neuropathy often present to a physician prior to developing ischemic brain manifestations2 but seldom receive the correct diagnosis. Onset of cerebral occlusive events typically occurs in patients younger than 45 years and may present as a transient ischemic attack, stroke, or intracranial hemorrhage.3 The disease is more prevalent in females than males (2:1 ratio). The exact pathogenesis of SS is still unknown, and although it has been thought of as a separate entity from systemic lupus erythematosus and other antiphospholipid disorders, it has been postulated that an immunological dysfunction damages vessel walls leading to thrombosis.
Cutaneous findings associated with SS involve small- to medium-sized dermal-subdermal arteries. Histopathology in some patients demonstrates proliferation of the endothelium and fibrin deposits with subsequent obliteration of involved arteries.4 In many patients including our patient, histopathologic examination of involved skin fails to show specific abnormalities.1 Zelger et al5 reported the sequence of histopathologic skin events in a series of antiphospholipid-negative SS patients. The authors reported that only small arteries at the dermis-subcutis junction were involved and a progression of endothelial dysfunction was observed. The authors believed there were several nonspecific stages prior to fibrin occlusion of involved arteries.5 Stage I involved loosening of endothelial cells with nonspecific perivascular lymphocytic infiltration with perivascular inflammation and lymphocytic infiltration representing the prime mover of the disease.5,6 This stage is thought to be short lived, thus the reason why it has gone undetected for many years in SS patients. Stages II to IV progress through fibrin deposition and occlusion.5 Histological features of stages I to II have not been reported because of late diagnosis of SS. Stage I patients typically present with an average duration of symptoms of 6 months with few neurologic symptoms, the most common being paresthesia of the legs.5
Case Report
A 37-year-old woman with epigastric tenderness on the left side and splenomegaly seen on computed tomography was referred by a hematologist for evaluation of a reticular rash on the left side of the flank of 9 months’ duration with a presumed diagnosis of focal melanoderma. Her medical history was remarkable for a congenital ventricular septal defect and coarctation of the aorta, as well as endometriosis, myalgia, and joint stiffness that had all developed over the last year. Her medical history also was remarkable for nephrolithiasis, irritable bowel syndrome, and chronic sinusitis, as well as psychiatric depression and anxiety disorders. She recently had been diagnosed with moderate hypertension and had experienced difficulty getting pregnant for the last several years with 3 consecutive miscarriages in the first trimester. Neurologic symptoms included neuropathy involving the feet, intermittent paresthesia of the legs, and a history of chronic migraine headaches for several months.
Dermatologic examination revealed a slightly overweight woman with a 25×30-cm dusky, erythematous, irregular, netlike pattern on the left side of the upper and lower trunk (Figure 1). Extensive livedo racemosa was not altered by changes in temperature and had been unchanged for more than 9 months. There were no signs of pruritus or ulcerations, and areas of livedo racemosa were slightly tender to palpation.

We performed 2 sets of three 4-mm biopsies. The first set targeted areas within the violaceous pattern, while the second set targeted areas of normal tissue between the mottled areas. All 6 specimens demonstrated superficial perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate with no evidence of vasculitis or connective tissue disease. The vessels showed no microthrombi or surrounding fibrosis. No eosinophils were identified within the epidermis. There was no evidence of increased dermal mucin. Both the superficial and deep vascular plexuses were unremarkable and showed no evidence of damage to the walls (Figure 2).

To rule out other possible causes of livedo racemosa, complete blood cell count, comprehensive metabolic panel, coagulation profile, lipase test, urinalysis, serologic testing, and immunologic workup were performed. Lipase was within reference range. The complete blood cell count revealed mild anemia, while the rest of the values were within reference range. An immunologic workup included Sjögren syndrome antigen A, Sjögren syndrome antigen B, anticardiolipin antibodies, and antinuclear antibody, which were all negative. Family history was remarkable for first-degree relatives with systemic lupus erythematosus and Crohn disease.
Computed tomography revealed enlargement of the spleen, as well as periaortic, portacaval, and porta hepatis lymphadenopathy. Based on the laboratory findings and clinical presentation as well as the patient’s medical history, the diagnosis of exclusion was idiopathic livedo racemosa with unknown progression to full-blown SS. The patient did not meet the current diagnostic criteria for SS, and her immunologic studies failed to confirm any present antibodies, but involvement of the reticuloendothelial system pointed to production of antibodies that were not yet detectable on laboratory testing.
Comment
More than 50 years after the first case of SS was diagnosed, better laboratory workup is available and more information is known about the pathophysiology. Sneddon syndrome is a rare disorder, affecting only approximately 4 patients per million each year worldwide. Seronegative antiphospholipid antibody syndrome (SNAPS) describes patients with clinical presentations of antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) without detectable serological markers.7 Antiphospholipid-negative SS, which was seen in our patient, would be categorized under SNAPS. A PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the terms livedo racemosa, Sneddon syndrome, and SNAPS and splenomegaly revealed there currently are no known cases of SNAPS that have been reported with splenomegaly and lymphadenopathy. Our patient presented with the following clinical features of SS: livedo racemosa, history of miscarriage, psychiatric disturbances, and hypertension. Surprisingly, biopsies from affected skin did not show any fibrin deposition or microthrombi but did reveal perivascular lymphocytic infiltrations. Magnetic resonance imaging did not show any pathological lesions or vascular changes.
Sneddon syndrome and APS share a common pathway to occlusive arteriolopathy for which 4 stages have been described by Zelger et al.5 Stage I involves a nonspecific Langerhans cell infiltrate with polymorphonuclear leukocytes. The tunica media and elastic lamina usually are unaltered at this early stage, while the surrounding connective tissue may appear edematous.5 This early stage of histopathology has not been evaluated in SS patients, primarily because of delay of diagnosis. Late stages III and IV will show fibrin deposition and shrinkage of affected vessels.7
A PubMed search using the terms Sneddon syndrome, lymphadenopathy and livedo racemosa, and Sneddon syndrome and lymphadenopathy revealed that splenomegaly and lymphadenopathy have not been reported in patients with SS. In patients with antiphospholipid-negative SS, one can assume that antibodies to other phospholipids not tested must exist because of striking similarities between APS and antiphospholipid-negative SS.8 Although our patient did not test positive for any of these antibodies, she did present with lymphadenopathy and splenic enlargement, leading us to believe that involvement of the reticuloendothelial system may be a feature of SS that has not been previously reported. Further studies are required to name specific antigens responsible for clinical manifestations in SS.
Currently, no single diagnostic test for SS exists, thus delaying both diagnosis and initiation of treatment. Histopathologic examination may be helpful, but in many cases it is nonspecific, as are serologic markers. Neuroradiological confirmation of involvement usually is the confirmatory feature in many patients with late-stage diagnosis.2 A diagnostic schematic for SS, which was first described by Daoud et al,2 illustrates classification of symptoms and aids in diagnosis. A working diagnosis of idiopathic livedo racemosa is made after ruling out other causes of SS in a patient with nonspecific biopsy findings and negative magnetic resonance imaging results with prodromal symptoms. The prognosis for such patients progressing to full SS is unknown with or without management using anticoagulant therapy.
Conclusion
Early diagnosis of livedo racemosa and SS is essential, as prevention of cerebrovascular accidents, myocardial infarction, and other thromboembolic diseases can be minimized by attacking risk factors such as smoking, taking oral contraceptive pills, becoming pregnant,9 and by initiating either antiplatelet or anticoagulation treatments. These treatments have been shown to delay the development of neurovascular damage and early-onset dementia. We present this case to demonstrate the variability of early-presenting symptoms in idiopathic livedo racemosa. Recognizing some of the early manifestations can lead to early diagnosis and initiation of treatment.
Sneddon syndrome (SS) was first described in 1965 in patients with persistent livedo racemosa and neurological events.1 Because the other manifestations of SS are nonspecific (eg, hypertension, cardiac valvulopathy, arterial and venous occlusion), the diagnosis often is delayed. Many patients who experience prodromal neurologic symptoms such as headaches, depression, anxiety, dizziness, and neuropathy often present to a physician prior to developing ischemic brain manifestations2 but seldom receive the correct diagnosis. Onset of cerebral occlusive events typically occurs in patients younger than 45 years and may present as a transient ischemic attack, stroke, or intracranial hemorrhage.3 The disease is more prevalent in females than males (2:1 ratio). The exact pathogenesis of SS is still unknown, and although it has been thought of as a separate entity from systemic lupus erythematosus and other antiphospholipid disorders, it has been postulated that an immunological dysfunction damages vessel walls leading to thrombosis.
Cutaneous findings associated with SS involve small- to medium-sized dermal-subdermal arteries. Histopathology in some patients demonstrates proliferation of the endothelium and fibrin deposits with subsequent obliteration of involved arteries.4 In many patients including our patient, histopathologic examination of involved skin fails to show specific abnormalities.1 Zelger et al5 reported the sequence of histopathologic skin events in a series of antiphospholipid-negative SS patients. The authors reported that only small arteries at the dermis-subcutis junction were involved and a progression of endothelial dysfunction was observed. The authors believed there were several nonspecific stages prior to fibrin occlusion of involved arteries.5 Stage I involved loosening of endothelial cells with nonspecific perivascular lymphocytic infiltration with perivascular inflammation and lymphocytic infiltration representing the prime mover of the disease.5,6 This stage is thought to be short lived, thus the reason why it has gone undetected for many years in SS patients. Stages II to IV progress through fibrin deposition and occlusion.5 Histological features of stages I to II have not been reported because of late diagnosis of SS. Stage I patients typically present with an average duration of symptoms of 6 months with few neurologic symptoms, the most common being paresthesia of the legs.5
Case Report
A 37-year-old woman with epigastric tenderness on the left side and splenomegaly seen on computed tomography was referred by a hematologist for evaluation of a reticular rash on the left side of the flank of 9 months’ duration with a presumed diagnosis of focal melanoderma. Her medical history was remarkable for a congenital ventricular septal defect and coarctation of the aorta, as well as endometriosis, myalgia, and joint stiffness that had all developed over the last year. Her medical history also was remarkable for nephrolithiasis, irritable bowel syndrome, and chronic sinusitis, as well as psychiatric depression and anxiety disorders. She recently had been diagnosed with moderate hypertension and had experienced difficulty getting pregnant for the last several years with 3 consecutive miscarriages in the first trimester. Neurologic symptoms included neuropathy involving the feet, intermittent paresthesia of the legs, and a history of chronic migraine headaches for several months.
Dermatologic examination revealed a slightly overweight woman with a 25×30-cm dusky, erythematous, irregular, netlike pattern on the left side of the upper and lower trunk (Figure 1). Extensive livedo racemosa was not altered by changes in temperature and had been unchanged for more than 9 months. There were no signs of pruritus or ulcerations, and areas of livedo racemosa were slightly tender to palpation.

We performed 2 sets of three 4-mm biopsies. The first set targeted areas within the violaceous pattern, while the second set targeted areas of normal tissue between the mottled areas. All 6 specimens demonstrated superficial perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate with no evidence of vasculitis or connective tissue disease. The vessels showed no microthrombi or surrounding fibrosis. No eosinophils were identified within the epidermis. There was no evidence of increased dermal mucin. Both the superficial and deep vascular plexuses were unremarkable and showed no evidence of damage to the walls (Figure 2).

To rule out other possible causes of livedo racemosa, complete blood cell count, comprehensive metabolic panel, coagulation profile, lipase test, urinalysis, serologic testing, and immunologic workup were performed. Lipase was within reference range. The complete blood cell count revealed mild anemia, while the rest of the values were within reference range. An immunologic workup included Sjögren syndrome antigen A, Sjögren syndrome antigen B, anticardiolipin antibodies, and antinuclear antibody, which were all negative. Family history was remarkable for first-degree relatives with systemic lupus erythematosus and Crohn disease.
Computed tomography revealed enlargement of the spleen, as well as periaortic, portacaval, and porta hepatis lymphadenopathy. Based on the laboratory findings and clinical presentation as well as the patient’s medical history, the diagnosis of exclusion was idiopathic livedo racemosa with unknown progression to full-blown SS. The patient did not meet the current diagnostic criteria for SS, and her immunologic studies failed to confirm any present antibodies, but involvement of the reticuloendothelial system pointed to production of antibodies that were not yet detectable on laboratory testing.
Comment
More than 50 years after the first case of SS was diagnosed, better laboratory workup is available and more information is known about the pathophysiology. Sneddon syndrome is a rare disorder, affecting only approximately 4 patients per million each year worldwide. Seronegative antiphospholipid antibody syndrome (SNAPS) describes patients with clinical presentations of antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) without detectable serological markers.7 Antiphospholipid-negative SS, which was seen in our patient, would be categorized under SNAPS. A PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the terms livedo racemosa, Sneddon syndrome, and SNAPS and splenomegaly revealed there currently are no known cases of SNAPS that have been reported with splenomegaly and lymphadenopathy. Our patient presented with the following clinical features of SS: livedo racemosa, history of miscarriage, psychiatric disturbances, and hypertension. Surprisingly, biopsies from affected skin did not show any fibrin deposition or microthrombi but did reveal perivascular lymphocytic infiltrations. Magnetic resonance imaging did not show any pathological lesions or vascular changes.
Sneddon syndrome and APS share a common pathway to occlusive arteriolopathy for which 4 stages have been described by Zelger et al.5 Stage I involves a nonspecific Langerhans cell infiltrate with polymorphonuclear leukocytes. The tunica media and elastic lamina usually are unaltered at this early stage, while the surrounding connective tissue may appear edematous.5 This early stage of histopathology has not been evaluated in SS patients, primarily because of delay of diagnosis. Late stages III and IV will show fibrin deposition and shrinkage of affected vessels.7
A PubMed search using the terms Sneddon syndrome, lymphadenopathy and livedo racemosa, and Sneddon syndrome and lymphadenopathy revealed that splenomegaly and lymphadenopathy have not been reported in patients with SS. In patients with antiphospholipid-negative SS, one can assume that antibodies to other phospholipids not tested must exist because of striking similarities between APS and antiphospholipid-negative SS.8 Although our patient did not test positive for any of these antibodies, she did present with lymphadenopathy and splenic enlargement, leading us to believe that involvement of the reticuloendothelial system may be a feature of SS that has not been previously reported. Further studies are required to name specific antigens responsible for clinical manifestations in SS.
Currently, no single diagnostic test for SS exists, thus delaying both diagnosis and initiation of treatment. Histopathologic examination may be helpful, but in many cases it is nonspecific, as are serologic markers. Neuroradiological confirmation of involvement usually is the confirmatory feature in many patients with late-stage diagnosis.2 A diagnostic schematic for SS, which was first described by Daoud et al,2 illustrates classification of symptoms and aids in diagnosis. A working diagnosis of idiopathic livedo racemosa is made after ruling out other causes of SS in a patient with nonspecific biopsy findings and negative magnetic resonance imaging results with prodromal symptoms. The prognosis for such patients progressing to full SS is unknown with or without management using anticoagulant therapy.
Conclusion
Early diagnosis of livedo racemosa and SS is essential, as prevention of cerebrovascular accidents, myocardial infarction, and other thromboembolic diseases can be minimized by attacking risk factors such as smoking, taking oral contraceptive pills, becoming pregnant,9 and by initiating either antiplatelet or anticoagulation treatments. These treatments have been shown to delay the development of neurovascular damage and early-onset dementia. We present this case to demonstrate the variability of early-presenting symptoms in idiopathic livedo racemosa. Recognizing some of the early manifestations can lead to early diagnosis and initiation of treatment.
- Sneddon IB. Cerebro-vascular lesions and livedo reticularis. Br J Dermatol. 1965;77:180-185.
- Daoud MS, Wilmoth GJ, Su WP, et al. Sneddon syndrome. Semin Dermatol. 1995;14:166-172.
- Besnier R, Francès C, Ankri A, et al. Factor V Leiden mutation in Sneddon syndrome. Lupus. 2003;12:406-408.
- K aragülle AT, Karadağ D, Erden A, et al. Sneddon’s syndrome: MR imaging findings. Eur Radiol. 2002;12:144-146.
- Zelg er B, Sepp N, Schmid KW, et al. Life-history of cutaneous vascular-lesions in Sneddon’s syndrome. Hum Pathol. 1992;23:668-675.
- Ayoub N, Esposito G, Barete S, et al. Protein Z deficiency in antiphospholipid-negative Sneddon’s syndrome. Stroke. 2004;35:1329-1332.
- Duva l A, Darnige L, Glowacki F, et al. Livedo, dementia, thrombocytopenia, and endotheliitis without antiphospholipid antibodies: seronegative antiphospholipid-like syndrome. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;61:1076-1078.
- Kala shnikova LA, Nasonov EL, Kushekbaeva AE, et al. Anticardiolipin antibodies in Sneddon’s syndrome. Neurology. 1990;40:464-467.
- Wohl rab J, Fischer M, Wolter M, et al. Diagnostic impact and sensitivity of skin biopsies in Sneddon’s syndrome. a report of 15 cases. Br J Dermatol. 2001;145:285-288.
- Sneddon IB. Cerebro-vascular lesions and livedo reticularis. Br J Dermatol. 1965;77:180-185.
- Daoud MS, Wilmoth GJ, Su WP, et al. Sneddon syndrome. Semin Dermatol. 1995;14:166-172.
- Besnier R, Francès C, Ankri A, et al. Factor V Leiden mutation in Sneddon syndrome. Lupus. 2003;12:406-408.
- K aragülle AT, Karadağ D, Erden A, et al. Sneddon’s syndrome: MR imaging findings. Eur Radiol. 2002;12:144-146.
- Zelg er B, Sepp N, Schmid KW, et al. Life-history of cutaneous vascular-lesions in Sneddon’s syndrome. Hum Pathol. 1992;23:668-675.
- Ayoub N, Esposito G, Barete S, et al. Protein Z deficiency in antiphospholipid-negative Sneddon’s syndrome. Stroke. 2004;35:1329-1332.
- Duva l A, Darnige L, Glowacki F, et al. Livedo, dementia, thrombocytopenia, and endotheliitis without antiphospholipid antibodies: seronegative antiphospholipid-like syndrome. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;61:1076-1078.
- Kala shnikova LA, Nasonov EL, Kushekbaeva AE, et al. Anticardiolipin antibodies in Sneddon’s syndrome. Neurology. 1990;40:464-467.
- Wohl rab J, Fischer M, Wolter M, et al. Diagnostic impact and sensitivity of skin biopsies in Sneddon’s syndrome. a report of 15 cases. Br J Dermatol. 2001;145:285-288.
Practice Points
- The classic physical diagnostic finding of Sneddon syndrome (SS) is livedo racemosa.
- Early identification and treatment of SS can prevent serious morbidity due to stroke, myocardial infarction, and other thrombotic events.
- Preventive care in SS should include antiplatelet therapy or anticoagulants and smoking cessation along with avoidance of birth control pills.