User login
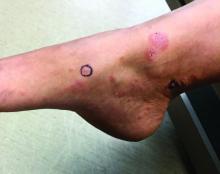
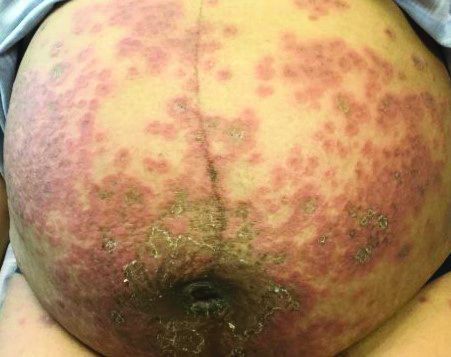
Itchy, vesicular rash
Pemphigoid gestationis
It typically presents with the abrupt onset of very pruritic urticarial plaques and papules, which start around the umbilicus and then spread to involve the trunk and extremities. The papules and plaques evolve to generalized tense blisters, which typically spare the face, palms, soles, and mucous membranes. Half of affected patients may present in an atypical distribution involving the extremities, palms, or soles. Patients may be at an increased risk for the development of Graves disease.
The cause of pemphigoid gestationis is a factor known as “herpes gestationis factor” that induces C3 deposition along the dermal-epidermal junction. As in bullous pemphigoid, patients with pemphigoid gestationis have antibodies to a transmembrane hemidesmosomal protein called BPAG2/BP180/collagen XVII.
Three-quarters of patients worsen at the time of delivery and up to 10% of newborns will have bullous lesions secondary to placental transfer of antibodies. In most cases, lesions will spontaneously resolve over a few weeks following delivery. Recurrence with future pregnancies is common, with severity increasing with each pregnancy. Recurrence with menstruation and with the use of oral contraceptives can also occur. Although there is no increase in maternal mortality, onset in the first or second trimester and presence of blisters is associated with decreased gestational age of baby at delivery and lower-birth-weight infants. There is no increase in fetal mortality.
Histopathology reveals a subepidermal vesicle and perivascular infiltrate consisting of lymphocytes and eosinophils. Diagnosis can be confirmed with direct immunofluorescence showing C3 in a linear band along the basement membrane zone. IgG may be present as well. Complement added indirect immunofluorescence reveals circulating anti–basement zone IgG, which allows differentiation from pruritic urticarial papules and plaques of pregnancy.
Treatment for localized disease includes class I topical steroids and oral antihistamines. More severe cases require systemic corticosteroid treatment. Systemic steroids may cause lower-birth-weight infants.
This case and the photos were submitted by Dr. Hanson of Associated Skin Care Specialists in Eden Prairie, Minn. The case was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
Pemphigoid gestationis
It typically presents with the abrupt onset of very pruritic urticarial plaques and papules, which start around the umbilicus and then spread to involve the trunk and extremities. The papules and plaques evolve to generalized tense blisters, which typically spare the face, palms, soles, and mucous membranes. Half of affected patients may present in an atypical distribution involving the extremities, palms, or soles. Patients may be at an increased risk for the development of Graves disease.
The cause of pemphigoid gestationis is a factor known as “herpes gestationis factor” that induces C3 deposition along the dermal-epidermal junction. As in bullous pemphigoid, patients with pemphigoid gestationis have antibodies to a transmembrane hemidesmosomal protein called BPAG2/BP180/collagen XVII.
Three-quarters of patients worsen at the time of delivery and up to 10% of newborns will have bullous lesions secondary to placental transfer of antibodies. In most cases, lesions will spontaneously resolve over a few weeks following delivery. Recurrence with future pregnancies is common, with severity increasing with each pregnancy. Recurrence with menstruation and with the use of oral contraceptives can also occur. Although there is no increase in maternal mortality, onset in the first or second trimester and presence of blisters is associated with decreased gestational age of baby at delivery and lower-birth-weight infants. There is no increase in fetal mortality.
Histopathology reveals a subepidermal vesicle and perivascular infiltrate consisting of lymphocytes and eosinophils. Diagnosis can be confirmed with direct immunofluorescence showing C3 in a linear band along the basement membrane zone. IgG may be present as well. Complement added indirect immunofluorescence reveals circulating anti–basement zone IgG, which allows differentiation from pruritic urticarial papules and plaques of pregnancy.
Treatment for localized disease includes class I topical steroids and oral antihistamines. More severe cases require systemic corticosteroid treatment. Systemic steroids may cause lower-birth-weight infants.
This case and the photos were submitted by Dr. Hanson of Associated Skin Care Specialists in Eden Prairie, Minn. The case was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
Pemphigoid gestationis
It typically presents with the abrupt onset of very pruritic urticarial plaques and papules, which start around the umbilicus and then spread to involve the trunk and extremities. The papules and plaques evolve to generalized tense blisters, which typically spare the face, palms, soles, and mucous membranes. Half of affected patients may present in an atypical distribution involving the extremities, palms, or soles. Patients may be at an increased risk for the development of Graves disease.
The cause of pemphigoid gestationis is a factor known as “herpes gestationis factor” that induces C3 deposition along the dermal-epidermal junction. As in bullous pemphigoid, patients with pemphigoid gestationis have antibodies to a transmembrane hemidesmosomal protein called BPAG2/BP180/collagen XVII.
Three-quarters of patients worsen at the time of delivery and up to 10% of newborns will have bullous lesions secondary to placental transfer of antibodies. In most cases, lesions will spontaneously resolve over a few weeks following delivery. Recurrence with future pregnancies is common, with severity increasing with each pregnancy. Recurrence with menstruation and with the use of oral contraceptives can also occur. Although there is no increase in maternal mortality, onset in the first or second trimester and presence of blisters is associated with decreased gestational age of baby at delivery and lower-birth-weight infants. There is no increase in fetal mortality.
Histopathology reveals a subepidermal vesicle and perivascular infiltrate consisting of lymphocytes and eosinophils. Diagnosis can be confirmed with direct immunofluorescence showing C3 in a linear band along the basement membrane zone. IgG may be present as well. Complement added indirect immunofluorescence reveals circulating anti–basement zone IgG, which allows differentiation from pruritic urticarial papules and plaques of pregnancy.
Treatment for localized disease includes class I topical steroids and oral antihistamines. More severe cases require systemic corticosteroid treatment. Systemic steroids may cause lower-birth-weight infants.
This case and the photos were submitted by Dr. Hanson of Associated Skin Care Specialists in Eden Prairie, Minn. The case was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].