User login
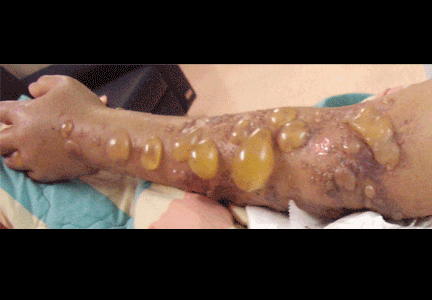
Multiple huge bullae after renal transplant
Q: What is the most likely diagnosis?
- Contact dermatitis
- Herpes zoster
- Herpes simplex
- Pemphigus
- Bullous pemphigoid
- Graft-vs-host disease
A: The correct answer is herpes zoster (shingles), which represents reactivation of varicella-zoster virus.
The diagnosis of herpes zoster is usually based solely on the clinical presentation. It is typically characterized in immunocompetent patients by a unilateral vesicular eruption with a well-defined dermatomal distribution. But occasionally, as in this patient on immunosuppressant drugs, it presents with atypical skin lesions such as multiple huge bullae involving multiple dermatomes.1,2
Patients treated with immunosuppressive agents after organ transplantation are at high risk of herpes zoster. A recent published retrospective study of adult kidney transplant recipients showed an average incidence of approximately 28 per 1,000 person-years.3
Treatment involves analgesics and sometimes antiviral drugs, and the decisions should take into account the patient’s age and immune status.1
- Nagel MA, Gilden DH. The protean neurologic manifestations of varicella-zoster virus infection. Cleve Clin J Med 2007; 74:489–504.
- Albrecht MA. Clinical manifestations of varicella-zoster virus infection: Herpes zoster. InRose BD, editor: UpToDate. Waltham, MA: UpToDate, 2008.
- Arness T, Pedersen R, Dierkhising R, Kremers W, Patel R. Varicella zoster virus-associated disease in adult kidney transplant recipients: incidence and risk-factor analysis. Transpl Infect Dis 2008; 10:260–268.
Q: What is the most likely diagnosis?
- Contact dermatitis
- Herpes zoster
- Herpes simplex
- Pemphigus
- Bullous pemphigoid
- Graft-vs-host disease
A: The correct answer is herpes zoster (shingles), which represents reactivation of varicella-zoster virus.
The diagnosis of herpes zoster is usually based solely on the clinical presentation. It is typically characterized in immunocompetent patients by a unilateral vesicular eruption with a well-defined dermatomal distribution. But occasionally, as in this patient on immunosuppressant drugs, it presents with atypical skin lesions such as multiple huge bullae involving multiple dermatomes.1,2
Patients treated with immunosuppressive agents after organ transplantation are at high risk of herpes zoster. A recent published retrospective study of adult kidney transplant recipients showed an average incidence of approximately 28 per 1,000 person-years.3
Treatment involves analgesics and sometimes antiviral drugs, and the decisions should take into account the patient’s age and immune status.1
Q: What is the most likely diagnosis?
- Contact dermatitis
- Herpes zoster
- Herpes simplex
- Pemphigus
- Bullous pemphigoid
- Graft-vs-host disease
A: The correct answer is herpes zoster (shingles), which represents reactivation of varicella-zoster virus.
The diagnosis of herpes zoster is usually based solely on the clinical presentation. It is typically characterized in immunocompetent patients by a unilateral vesicular eruption with a well-defined dermatomal distribution. But occasionally, as in this patient on immunosuppressant drugs, it presents with atypical skin lesions such as multiple huge bullae involving multiple dermatomes.1,2
Patients treated with immunosuppressive agents after organ transplantation are at high risk of herpes zoster. A recent published retrospective study of adult kidney transplant recipients showed an average incidence of approximately 28 per 1,000 person-years.3
Treatment involves analgesics and sometimes antiviral drugs, and the decisions should take into account the patient’s age and immune status.1
- Nagel MA, Gilden DH. The protean neurologic manifestations of varicella-zoster virus infection. Cleve Clin J Med 2007; 74:489–504.
- Albrecht MA. Clinical manifestations of varicella-zoster virus infection: Herpes zoster. InRose BD, editor: UpToDate. Waltham, MA: UpToDate, 2008.
- Arness T, Pedersen R, Dierkhising R, Kremers W, Patel R. Varicella zoster virus-associated disease in adult kidney transplant recipients: incidence and risk-factor analysis. Transpl Infect Dis 2008; 10:260–268.
- Nagel MA, Gilden DH. The protean neurologic manifestations of varicella-zoster virus infection. Cleve Clin J Med 2007; 74:489–504.
- Albrecht MA. Clinical manifestations of varicella-zoster virus infection: Herpes zoster. InRose BD, editor: UpToDate. Waltham, MA: UpToDate, 2008.
- Arness T, Pedersen R, Dierkhising R, Kremers W, Patel R. Varicella zoster virus-associated disease in adult kidney transplant recipients: incidence and risk-factor analysis. Transpl Infect Dis 2008; 10:260–268.