User login
Analysis of Education on Nail Conditions at the American Academy of Dermatology Annual Meetings
To the Editor:
The diagnosis and treatment of nail conditions are necessary competencies for board-certified dermatologists, but appropriate education often is lacking.1 The American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) annual meeting is one of the largest and most highly attended dermatology educational conferences worldwide. We sought to determine the number of hours dedicated to nail-related topics at the AAD annual meetings from 2013 to 2019.
We accessed programs from the AAD annual meetings archive online (https://www.aad.org/meetings/previous-meetings-archive), and we used hair and psoriasis content for comparison. Event titles and descriptions were searched for nail-related content (using search terms nail, onychia, and onycho), hair-related content (hair, alopecia, trichosis, hirsutism), and psoriasis content (psoriasis). Data acquired for each event included the date, hours, title, and event type (eg, forum, course, focus session, symposium, discussion group, workshop, plenary session).
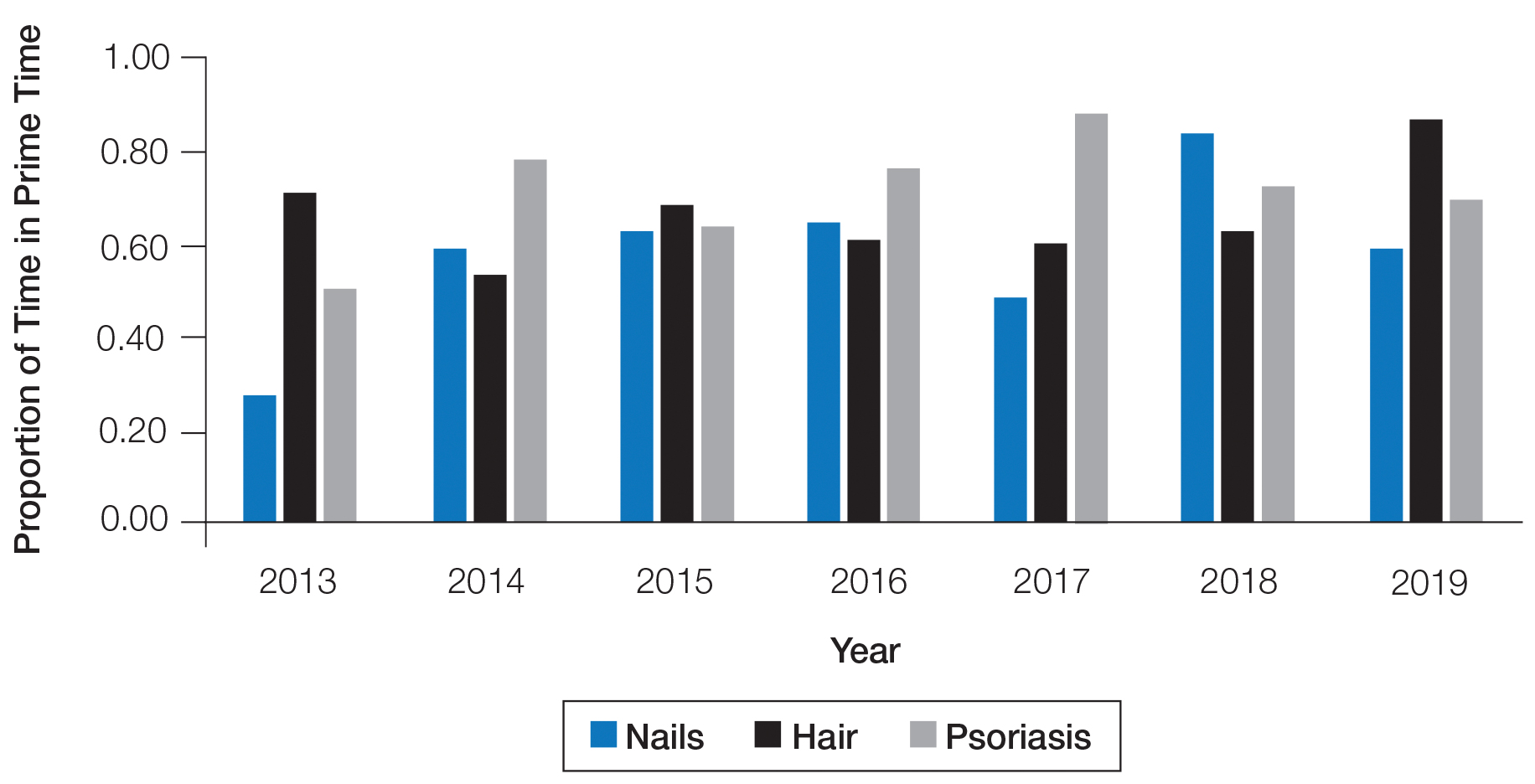
The number of hours dedicated to nail education consistently lagged behind those related to hair and psoriasis content during the study period (Figure 1). According to the AAD, the conference runs Friday to Tuesday with higher attendance Friday to Sunday (Tim Moses, personal communication, July 9, 2019). Lectures during the weekend are likely to have a broader reach than lectures on Monday and Tuesday. The proportion of nail content during weekend prime time slots was similar to that of hair and psoriasis (Figure 2). Plenary sessions often are presented by renowned experts on hot topics in dermatology. Notably, hair (2014-2015) and psoriasis (2015-2017) content were represented in the plenary sessions during the study period, while nail content was not featured.

Our study shows that nail-related education was underrepresented at the AAD annual meetings from 2013 to 2019 compared to hair- and psoriasis-related content. Educational gaps in the diagnosis of fignail conditions previously have been delineated, and prioritization of instruction on nail disease pathology and diagnostic procedures has been recommended to improve patient care.1 The majority of nail unit melanomas are diagnosed at late stages, which has been attributed to deficiencies in clinical knowledge and failure to perform or inadequate biopsy techniques.2 Notably, a survey of third-year dermatology residents (N=240) assessing experience in procedural dermatology showed that 58% performed 10 or fewer nail procedures and 30% did not feel competent in performing nail surgery.3 Furthermore, a survey examining the management of longitudinal melanonychia among attending and resident dermatologists (N=402) found that 62% of residents and 28% of total respondents were not confident in managing melanonychia.4
A limitation of this study was the lack of online data available for AAD annual meetings before 2013, so we were unable to characterize any long-term trends. Furthermore, we were unable to assess the educational reach of these sessions, as data on attendance are lacking.
This study demonstrates a paucity of nail-related content at the AAD annual meetings. The introduction of the “Hands-on: Nail Surgery” in 2015 is an important step forward to diminish the knowledge gap in the diagnosis of various nail diseases and malignancies. We recommend increasing the number of hours and overall content of didactic nail sessions at the AAD annual meeting to further the knowledge and procedural skills of dermatologists in caring for patients with nail disorders.
- Hare AQ, R ich P. Clinical and educational gaps in diagnosis of nail disorders. Dermatol Clin. 2016;34:269-273.
- Tan KB, Moncrieff M, Thompson JF, et al. Subungual melanoma: a study of 124 cases highlighting features of early lesions, potential pitfalls in diagnosis, and guidelines for histologic reporting. Am J Surg Pathol. 2007;31:1902-1912.
- Lee EH, Nehal KS, Dusza SW, et al. Procedural dermatology training during dermatology residency: a survey of third-year dermatology residents. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;64:475-483.
- Halteh P, Scher R, Artis A, et al. A survey-based study of management of longitudinal melanonychia amongst attending and resident dermatologists. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76:994-996.
To the Editor:
The diagnosis and treatment of nail conditions are necessary competencies for board-certified dermatologists, but appropriate education often is lacking.1 The American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) annual meeting is one of the largest and most highly attended dermatology educational conferences worldwide. We sought to determine the number of hours dedicated to nail-related topics at the AAD annual meetings from 2013 to 2019.
We accessed programs from the AAD annual meetings archive online (https://www.aad.org/meetings/previous-meetings-archive), and we used hair and psoriasis content for comparison. Event titles and descriptions were searched for nail-related content (using search terms nail, onychia, and onycho), hair-related content (hair, alopecia, trichosis, hirsutism), and psoriasis content (psoriasis). Data acquired for each event included the date, hours, title, and event type (eg, forum, course, focus session, symposium, discussion group, workshop, plenary session).
The number of hours dedicated to nail education consistently lagged behind those related to hair and psoriasis content during the study period (Figure 1). According to the AAD, the conference runs Friday to Tuesday with higher attendance Friday to Sunday (Tim Moses, personal communication, July 9, 2019). Lectures during the weekend are likely to have a broader reach than lectures on Monday and Tuesday. The proportion of nail content during weekend prime time slots was similar to that of hair and psoriasis (Figure 2). Plenary sessions often are presented by renowned experts on hot topics in dermatology. Notably, hair (2014-2015) and psoriasis (2015-2017) content were represented in the plenary sessions during the study period, while nail content was not featured.


Our study shows that nail-related education was underrepresented at the AAD annual meetings from 2013 to 2019 compared to hair- and psoriasis-related content. Educational gaps in the diagnosis of fignail conditions previously have been delineated, and prioritization of instruction on nail disease pathology and diagnostic procedures has been recommended to improve patient care.1 The majority of nail unit melanomas are diagnosed at late stages, which has been attributed to deficiencies in clinical knowledge and failure to perform or inadequate biopsy techniques.2 Notably, a survey of third-year dermatology residents (N=240) assessing experience in procedural dermatology showed that 58% performed 10 or fewer nail procedures and 30% did not feel competent in performing nail surgery.3 Furthermore, a survey examining the management of longitudinal melanonychia among attending and resident dermatologists (N=402) found that 62% of residents and 28% of total respondents were not confident in managing melanonychia.4
A limitation of this study was the lack of online data available for AAD annual meetings before 2013, so we were unable to characterize any long-term trends. Furthermore, we were unable to assess the educational reach of these sessions, as data on attendance are lacking.
This study demonstrates a paucity of nail-related content at the AAD annual meetings. The introduction of the “Hands-on: Nail Surgery” in 2015 is an important step forward to diminish the knowledge gap in the diagnosis of various nail diseases and malignancies. We recommend increasing the number of hours and overall content of didactic nail sessions at the AAD annual meeting to further the knowledge and procedural skills of dermatologists in caring for patients with nail disorders.
To the Editor:
The diagnosis and treatment of nail conditions are necessary competencies for board-certified dermatologists, but appropriate education often is lacking.1 The American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) annual meeting is one of the largest and most highly attended dermatology educational conferences worldwide. We sought to determine the number of hours dedicated to nail-related topics at the AAD annual meetings from 2013 to 2019.
We accessed programs from the AAD annual meetings archive online (https://www.aad.org/meetings/previous-meetings-archive), and we used hair and psoriasis content for comparison. Event titles and descriptions were searched for nail-related content (using search terms nail, onychia, and onycho), hair-related content (hair, alopecia, trichosis, hirsutism), and psoriasis content (psoriasis). Data acquired for each event included the date, hours, title, and event type (eg, forum, course, focus session, symposium, discussion group, workshop, plenary session).
The number of hours dedicated to nail education consistently lagged behind those related to hair and psoriasis content during the study period (Figure 1). According to the AAD, the conference runs Friday to Tuesday with higher attendance Friday to Sunday (Tim Moses, personal communication, July 9, 2019). Lectures during the weekend are likely to have a broader reach than lectures on Monday and Tuesday. The proportion of nail content during weekend prime time slots was similar to that of hair and psoriasis (Figure 2). Plenary sessions often are presented by renowned experts on hot topics in dermatology. Notably, hair (2014-2015) and psoriasis (2015-2017) content were represented in the plenary sessions during the study period, while nail content was not featured.


Our study shows that nail-related education was underrepresented at the AAD annual meetings from 2013 to 2019 compared to hair- and psoriasis-related content. Educational gaps in the diagnosis of fignail conditions previously have been delineated, and prioritization of instruction on nail disease pathology and diagnostic procedures has been recommended to improve patient care.1 The majority of nail unit melanomas are diagnosed at late stages, which has been attributed to deficiencies in clinical knowledge and failure to perform or inadequate biopsy techniques.2 Notably, a survey of third-year dermatology residents (N=240) assessing experience in procedural dermatology showed that 58% performed 10 or fewer nail procedures and 30% did not feel competent in performing nail surgery.3 Furthermore, a survey examining the management of longitudinal melanonychia among attending and resident dermatologists (N=402) found that 62% of residents and 28% of total respondents were not confident in managing melanonychia.4
A limitation of this study was the lack of online data available for AAD annual meetings before 2013, so we were unable to characterize any long-term trends. Furthermore, we were unable to assess the educational reach of these sessions, as data on attendance are lacking.
This study demonstrates a paucity of nail-related content at the AAD annual meetings. The introduction of the “Hands-on: Nail Surgery” in 2015 is an important step forward to diminish the knowledge gap in the diagnosis of various nail diseases and malignancies. We recommend increasing the number of hours and overall content of didactic nail sessions at the AAD annual meeting to further the knowledge and procedural skills of dermatologists in caring for patients with nail disorders.
- Hare AQ, R ich P. Clinical and educational gaps in diagnosis of nail disorders. Dermatol Clin. 2016;34:269-273.
- Tan KB, Moncrieff M, Thompson JF, et al. Subungual melanoma: a study of 124 cases highlighting features of early lesions, potential pitfalls in diagnosis, and guidelines for histologic reporting. Am J Surg Pathol. 2007;31:1902-1912.
- Lee EH, Nehal KS, Dusza SW, et al. Procedural dermatology training during dermatology residency: a survey of third-year dermatology residents. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;64:475-483.
- Halteh P, Scher R, Artis A, et al. A survey-based study of management of longitudinal melanonychia amongst attending and resident dermatologists. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76:994-996.
- Hare AQ, R ich P. Clinical and educational gaps in diagnosis of nail disorders. Dermatol Clin. 2016;34:269-273.
- Tan KB, Moncrieff M, Thompson JF, et al. Subungual melanoma: a study of 124 cases highlighting features of early lesions, potential pitfalls in diagnosis, and guidelines for histologic reporting. Am J Surg Pathol. 2007;31:1902-1912.
- Lee EH, Nehal KS, Dusza SW, et al. Procedural dermatology training during dermatology residency: a survey of third-year dermatology residents. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;64:475-483.
- Halteh P, Scher R, Artis A, et al. A survey-based study of management of longitudinal melanonychia amongst attending and resident dermatologists. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76:994-996.
Practice Points
- Diagnosis and treatment of nail conditions are necessary competencies for board-certified dermatologists, but appropriate education often is lacking.
- We recommend increasing the number of hours and overall content of didactic nail sessions at the American Academy of Dermatology annual meeting to further the knowledge and procedural skills of dermatologists caring for patients with nail disorders.
