User login
An Imposter Twice Over: A Case of IgG4-Related Disease
Immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is an immune-mediated fibroinflammatory condition that involves multiple organs and appears as syndromes that were once thought to be unrelated. This disease leads to mass lesions, fibrosis, and subsequent organ failure if allowed to progress untreated.1 Involvement of gastrointestinal (GI) organs, salivary glands, lacrimal glands, lymph, prostate, pulmonary, and vascular system have all been reported.2 Elevated IgG4 serum levels are common, but about one-third of patients with biopsy-proven IgG4-RD do not manifest this characteristic.3,4
Diagnostic confirmation is with biopsy, and all patients with symptomatic, active IgG4-RD require treatment. Glucocorticoids are first-line treatment and are utilized for relapse of symptoms. In addition to glucocorticoids, steroid-sparing medications, including rituximab, azathioprine, mycophenolate mofetil, tacrolimus, and cyclophosphamide have all been used with successful remission.5,6 Here, the authors discuss a case of IgG4-RD that presented with intrahepatic biliary obstruction (mimicking cholangiocarcinoma) and subsequent development of coronary arteritis despite treatment.
Case Presentation
In June 2015, a 57-year-old Air Force veteran presented to Eglin AFB Hospital with pruritic jaundice and acute abdominal pain. He was found to have elevated bilirubin levels (total bilirubin 10 mg/dL [normal range 0.2-1.3 mg/dL], direct bilirubin 6.6 mg/dL [normal range 0.1-0.4 mg/dL]). Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) also were moderately elevated (147 U/L and 337 U/L, respectively).
Prior to this presentation, the patient had been in his usual state of health. His past medical history was notable only for minimal change kidney disease (MCD). MCD is defined as effacement of the podocyte seen on electron microscopy, which allows the passage of large amounts of protein.
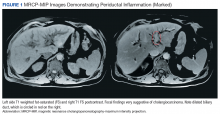
A cholangiogram showed abnormal filling into the left main intrahepatic duct and obvious obstruction at the bifurcation of the bile duct. A biliary drainage catheter was placed, and a repeat cholangiogram 2 days later showed involvement of both right and left intrahepatic ducts. The distal common bile duct appeared uninvolved as did the pancreas. Lymphadenopathy was noted at the liver hilum. Klatskin cholangiocarcinoma (type IIIB) was the presumed diagnosis. Based on these findings, tumor resection was performed 3 weeks later, including left hepatectomy, caudate lobe resection, complete bile duct resection, cholecystectomy, with reconstruction by Roux-en-Y intrahepaticojejunostomy. In addition, portal and hepatic artery lymph node dissection was completed.
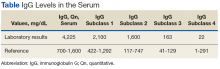
Surgical specimens were sent for pathologic evaluation and were found negative for malignancy. Patchy areas of storiform fibrosis, obliterative phlebitis, and lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate were noted. IgG4 immunostain highlighted the presence of IgG4 positive plasma cells with a peak count of 145 IgG4 positive plasma cells/hpf. About 80% of the plasma cells were positive for IgG4. Unusually dense eosinophilic infiltrate with plasma cells and regions of dense fibrosis that strongly contributed to the masslike appearance on CT imaging also were noted. Final histology confirmed the diagnosis of IgG4-RD. Elevated levels of total IgG in the serum were observed without elevation in serum IgG4 (Table).
The patient was started on prednisone 40 mg and azathioprine 150 mg daily, with subsequent taper of prednisone over the next 6 months. After prednisone was discontinued, the patient reported new symptoms of lower extremity pain, neuropathy, and swelling of his face. Laboratory results were notable for elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate. The patient was restarted on prednisone 40 mg daily. Azathioprine was replaced with a regimen of 4 doses every 6 months of IV rituximab 700 mg q week and mycophenolate mofetil (1,000 mg bid). After remission was induced, the patient was slowly weaned off prednisone again.
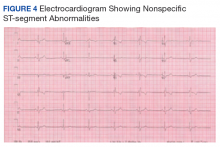
Following 6 months of successful discontinuation of prednisone and continued rituximab and mycophenolate mofetil therapy, the patient presented to the emergency department with new onset chest pain and shortness of breath. A CT angiography of the chest showed right upper and middle lobe infiltrate, and he was treated for community acquired pneumonia. Additionally, he was noted to have elevated troponin levels suggestive of myocardial infarction (MI). Initial troponin was 1.23 ng/mL (normal range < 0.015 ng/mL), which trended down over the next 18 hours. A bedside echocardiogram showed a normal left ventricular ejection fraction without wall motion abnormalities. Etiology for his acute MI was presumed to be demand ischemia from fixed atherosclerotic plaque. Further inpatient cardiac risk stratification was changed to the outpatient setting, and he was started on medical management for coronary artery disease with a beta blocker, a statin, and aspirin. He was discharged home on 10 mg prednisone daily, which was subsequently tapered over several weeks.
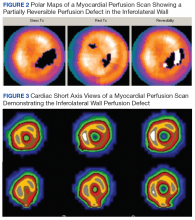
In follow-up, a Lexiscan myocardial perfusion imaging was conducted that demonstrated an inferolateral defect and associated wall motion abnormalities (Figures 2 and 3).
Discussion
IgG4-related disease has been found to be a systemic disorder. Typical characteristics include predominance in men aged > 50 years, elevated IgG4 levels, and findings on histology.1 It has been reported to involve many organs, including pancreas, liver, gallbladder, salivary glands, thyroid, and pleura of the lung.2,5
This case report begins with a presumptive diagnosis of cholangiocarcinoma, which was treated aggressively with extensive surgery. Several case reports of complex tumefactive lesions in the GI area (mostly pancreatic and biliary) have detailed IgG4-RD as both a risk factor for subsequent development of cholangiocarcinoma and as a separate entity of IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis.7-9 It is hypothesized that the induction of IgG4- positive plasma cells has been intertwined with the development of cholangiocarcinoma. Differentiation between IgG4 reaction that is scattered around cancerous nests and IgG4 sclerosing cholangitis without malignancy is challenging. It has been documented that both elevated IgG4 levels and hilar hepatic lesions that resemble cholangiocarcinoma frequently accompany those cases of IgG4 sclerosing chlolangitis without pancreatic involvement.9 The histologic features of IgG4-RD need to be identified with multiple biopsies and cytology, and superficial biopsy from biliary mucosa cannot reliably exclude cholangiocarcinoma.
Lymphoplasmacytic aortitis and arteritis have been documented in IgG4-RD. In 2017, Barbu and colleagues described how one such case of coronary arteritis presented with typical angina and coronary catheterization revealing coronary artery stenosis.10 However, during coronary artery bypass surgery, the aorta and coronary vessels were noted to be abnormally stiff. A diffuse fibrotic tissue was identified to be causing the significant stenosis without evidence of atherosclerosis. Pathology showed typical findings of IgG4-RD, and there was a rapid response to immunosuppressive therapy. Involvement of coronary arteries has been described in a small number of cases at this time and is associated with progressive fibrotic changes resulting in an MI, aneurysms, and sudden cardiac death.2,10,11
IgG4-RD can be an extensively systemic disease. All presentations of fibrosis or vasculitis should be viewed with heightened suspicion in the future as being a facet of his IgG4-RD. Pleural involvement has been reported in 12% of cases presenting with systemic presentation, kidney involvement in 13%.2,12
Unfortunately, there is no standard laboratory parameter to date that is diagnostic for IgG4-RD. The gold standard remains confirmation of histologic findings with biopsy. According to an international consensus from 2015, 2 out of the 3 major findings need to be present: (1) dense lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate; (2) storiform fibrosis; and (3) obliterative phlebitis in veins and arteries.1,5 Most patients present with symptoms related to either tumefaction or fibrosis of an organ system.1 Peripheral eosinophilia and elevated serum IgE are often present in IgG4-RD.13 Although IgG4 values are elevated in 51% of biopsy-proven cases, flow cytometry of CD19lowCD38+CD20-CD27+ plasmablasts has been explored recently as a correlation with disease flare.3,14 These particular plasmablasts mark a stage between B cells and plasma cells and have been reported to have a sensitivity of 95% and a specificity of 82% in association with actual IgG4-RD.14 Furthermore, blood plasmablast concentrations decrease in response to glucocorticoid treatment, thereby providing a possible quantifiable value by which to measure success of IgG4 treatment.5,12
Treatment for this disease consists of immunosuppressive therapy. There is documentation of successful remission with rituximab and azathioprine, as well as methotrexate.1,5 Both 2015 consensus guidelines and a recent small single-center retrospective study support addition of second-line steroid sparing agents such as mycophenolate mofetil.5,6 For acute flairs, however, glucocorticoids with slow taper are usually utilized. In these cases, they should be tapered as soon as clinically feasible to avoid long-term adverse effects. Untreated IgG4-RD, even asymptomatic, has been shown to progress to fibrosis.5
Conclusion
IgG4-RD is a complicated disease process that requires a high index of suspicion to diagnose. In addition, for patients who are diagnosed with this condition, its ability to mimic other pathologic conditions should be taken into account with manifestation of any new illness. This case emphasizes the ability of this disease to localize in multiple organs over time and the need for lifetime surveillance in patients with IgG4-RD disease.
1. Lang D, Zwerina J, Pieringer H. IgG4-related disease: current challenges and future prospects. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2016;12:189-199.
2. Brito-Zerón P, Ramos-Casals M, Bosch X, Stone JH. The clinical spectrum of IgG4-related disease. Autoimmun Rev. 2014;13(12):1203-1210.
3. Wallace ZS, Deshpande V, Mattoo H, et al. IgG4-related disease: clinical and laboratory features in one hundred twenty-five patients. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015;67(9):2466-2475.
4. Carruthers MN, Khosroshahi A, Augustin T, Deshpande V, Stone JH. The diagnostic utility of serum IgG4 concentrations in IgG4-RD. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015;74(1):14-18.
5. Khosroshahi A, Wallace ZS, Crowe JL, et al; Second International Symposium on IgG4-Related Disease. International consensus guidance statement on the management and treatment of IgG4-Related disease. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015;67(7):1688-1699.
6. Gupta N, Mathew J, Mohan H, et al. Addition of second-line steroid sparing immunosuppressants like mycophenolate mofetil improves outcome of immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4-RD): a series from a tertiary care teaching hospital in South India. Rheumatol Int. 2017;38(2):203-209.
7. Lin HP, Lin KT, Ho WC, Chen CB, Kuo, CY, Lin YC. IgG4-associated cholangitis mimicking cholangiocarcinoma-report of a case. J Intern Med Taiwan. 2013;24:137-141.
8. Douhara A, Mitoro A, Otani E, et al. Cholangiocarcinoma developed in a patient with IgG4-related disease. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2013;5(8):181-185.
9. Harada K, Nakanuma Y. Cholangiocarcinoma with respect to IgG4 reaction. Int J Hepatol. 2014;2014:803876.
10. Barbu M, Lindström U, Nordborg C, Martinsson A, Dworeck C, Jeppsson A. Sclerosing aortic and coronary arteritis due to IgG4-related disease. Ann Thorac Surg. 2017;103(6):e487-e489.
11. Kim YJ, Park YS, Koo BS, et al. Immunoglobulin G4-related disease with lymphoplasmacytic aortitis mimicking Takayasu arteritis. J Clin Rheumatol. 2011;17(8):451-452.
12. Khosroshahi A, Digumarthy SR, Gibbons FK, Deshpande V. Case 34-2015: A 36-year-old woman with a lung mass, pleural effusion and hip pain. N Engl J Med. 2015;373(18):1762-1772.
13. Della Torre E, Mattoo H, Mahajan VS, Carruthers M, Pillai S, Stone JH. Prevalence of atopy, eosinophilia and IgE elevation in IgG4-related disease. Allergy. 2014;69(2):191-206.
14. Wallace ZS, Mattoo H, Carruthers M, et al. Plasmablasts as a biomarker for IgG4-related disease, independent of serum IgG4 concentrations. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015;74(1):190-195.
Immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is an immune-mediated fibroinflammatory condition that involves multiple organs and appears as syndromes that were once thought to be unrelated. This disease leads to mass lesions, fibrosis, and subsequent organ failure if allowed to progress untreated.1 Involvement of gastrointestinal (GI) organs, salivary glands, lacrimal glands, lymph, prostate, pulmonary, and vascular system have all been reported.2 Elevated IgG4 serum levels are common, but about one-third of patients with biopsy-proven IgG4-RD do not manifest this characteristic.3,4
Diagnostic confirmation is with biopsy, and all patients with symptomatic, active IgG4-RD require treatment. Glucocorticoids are first-line treatment and are utilized for relapse of symptoms. In addition to glucocorticoids, steroid-sparing medications, including rituximab, azathioprine, mycophenolate mofetil, tacrolimus, and cyclophosphamide have all been used with successful remission.5,6 Here, the authors discuss a case of IgG4-RD that presented with intrahepatic biliary obstruction (mimicking cholangiocarcinoma) and subsequent development of coronary arteritis despite treatment.
Case Presentation
In June 2015, a 57-year-old Air Force veteran presented to Eglin AFB Hospital with pruritic jaundice and acute abdominal pain. He was found to have elevated bilirubin levels (total bilirubin 10 mg/dL [normal range 0.2-1.3 mg/dL], direct bilirubin 6.6 mg/dL [normal range 0.1-0.4 mg/dL]). Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) also were moderately elevated (147 U/L and 337 U/L, respectively).
Prior to this presentation, the patient had been in his usual state of health. His past medical history was notable only for minimal change kidney disease (MCD). MCD is defined as effacement of the podocyte seen on electron microscopy, which allows the passage of large amounts of protein.
A cholangiogram showed abnormal filling into the left main intrahepatic duct and obvious obstruction at the bifurcation of the bile duct. A biliary drainage catheter was placed, and a repeat cholangiogram 2 days later showed involvement of both right and left intrahepatic ducts. The distal common bile duct appeared uninvolved as did the pancreas. Lymphadenopathy was noted at the liver hilum. Klatskin cholangiocarcinoma (type IIIB) was the presumed diagnosis. Based on these findings, tumor resection was performed 3 weeks later, including left hepatectomy, caudate lobe resection, complete bile duct resection, cholecystectomy, with reconstruction by Roux-en-Y intrahepaticojejunostomy. In addition, portal and hepatic artery lymph node dissection was completed.
Surgical specimens were sent for pathologic evaluation and were found negative for malignancy. Patchy areas of storiform fibrosis, obliterative phlebitis, and lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate were noted. IgG4 immunostain highlighted the presence of IgG4 positive plasma cells with a peak count of 145 IgG4 positive plasma cells/hpf. About 80% of the plasma cells were positive for IgG4. Unusually dense eosinophilic infiltrate with plasma cells and regions of dense fibrosis that strongly contributed to the masslike appearance on CT imaging also were noted. Final histology confirmed the diagnosis of IgG4-RD. Elevated levels of total IgG in the serum were observed without elevation in serum IgG4 (Table).
The patient was started on prednisone 40 mg and azathioprine 150 mg daily, with subsequent taper of prednisone over the next 6 months. After prednisone was discontinued, the patient reported new symptoms of lower extremity pain, neuropathy, and swelling of his face. Laboratory results were notable for elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate. The patient was restarted on prednisone 40 mg daily. Azathioprine was replaced with a regimen of 4 doses every 6 months of IV rituximab 700 mg q week and mycophenolate mofetil (1,000 mg bid). After remission was induced, the patient was slowly weaned off prednisone again.
Following 6 months of successful discontinuation of prednisone and continued rituximab and mycophenolate mofetil therapy, the patient presented to the emergency department with new onset chest pain and shortness of breath. A CT angiography of the chest showed right upper and middle lobe infiltrate, and he was treated for community acquired pneumonia. Additionally, he was noted to have elevated troponin levels suggestive of myocardial infarction (MI). Initial troponin was 1.23 ng/mL (normal range < 0.015 ng/mL), which trended down over the next 18 hours. A bedside echocardiogram showed a normal left ventricular ejection fraction without wall motion abnormalities. Etiology for his acute MI was presumed to be demand ischemia from fixed atherosclerotic plaque. Further inpatient cardiac risk stratification was changed to the outpatient setting, and he was started on medical management for coronary artery disease with a beta blocker, a statin, and aspirin. He was discharged home on 10 mg prednisone daily, which was subsequently tapered over several weeks.
In follow-up, a Lexiscan myocardial perfusion imaging was conducted that demonstrated an inferolateral defect and associated wall motion abnormalities (Figures 2 and 3).
Discussion
IgG4-related disease has been found to be a systemic disorder. Typical characteristics include predominance in men aged > 50 years, elevated IgG4 levels, and findings on histology.1 It has been reported to involve many organs, including pancreas, liver, gallbladder, salivary glands, thyroid, and pleura of the lung.2,5
This case report begins with a presumptive diagnosis of cholangiocarcinoma, which was treated aggressively with extensive surgery. Several case reports of complex tumefactive lesions in the GI area (mostly pancreatic and biliary) have detailed IgG4-RD as both a risk factor for subsequent development of cholangiocarcinoma and as a separate entity of IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis.7-9 It is hypothesized that the induction of IgG4- positive plasma cells has been intertwined with the development of cholangiocarcinoma. Differentiation between IgG4 reaction that is scattered around cancerous nests and IgG4 sclerosing cholangitis without malignancy is challenging. It has been documented that both elevated IgG4 levels and hilar hepatic lesions that resemble cholangiocarcinoma frequently accompany those cases of IgG4 sclerosing chlolangitis without pancreatic involvement.9 The histologic features of IgG4-RD need to be identified with multiple biopsies and cytology, and superficial biopsy from biliary mucosa cannot reliably exclude cholangiocarcinoma.
Lymphoplasmacytic aortitis and arteritis have been documented in IgG4-RD. In 2017, Barbu and colleagues described how one such case of coronary arteritis presented with typical angina and coronary catheterization revealing coronary artery stenosis.10 However, during coronary artery bypass surgery, the aorta and coronary vessels were noted to be abnormally stiff. A diffuse fibrotic tissue was identified to be causing the significant stenosis without evidence of atherosclerosis. Pathology showed typical findings of IgG4-RD, and there was a rapid response to immunosuppressive therapy. Involvement of coronary arteries has been described in a small number of cases at this time and is associated with progressive fibrotic changes resulting in an MI, aneurysms, and sudden cardiac death.2,10,11
IgG4-RD can be an extensively systemic disease. All presentations of fibrosis or vasculitis should be viewed with heightened suspicion in the future as being a facet of his IgG4-RD. Pleural involvement has been reported in 12% of cases presenting with systemic presentation, kidney involvement in 13%.2,12
Unfortunately, there is no standard laboratory parameter to date that is diagnostic for IgG4-RD. The gold standard remains confirmation of histologic findings with biopsy. According to an international consensus from 2015, 2 out of the 3 major findings need to be present: (1) dense lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate; (2) storiform fibrosis; and (3) obliterative phlebitis in veins and arteries.1,5 Most patients present with symptoms related to either tumefaction or fibrosis of an organ system.1 Peripheral eosinophilia and elevated serum IgE are often present in IgG4-RD.13 Although IgG4 values are elevated in 51% of biopsy-proven cases, flow cytometry of CD19lowCD38+CD20-CD27+ plasmablasts has been explored recently as a correlation with disease flare.3,14 These particular plasmablasts mark a stage between B cells and plasma cells and have been reported to have a sensitivity of 95% and a specificity of 82% in association with actual IgG4-RD.14 Furthermore, blood plasmablast concentrations decrease in response to glucocorticoid treatment, thereby providing a possible quantifiable value by which to measure success of IgG4 treatment.5,12
Treatment for this disease consists of immunosuppressive therapy. There is documentation of successful remission with rituximab and azathioprine, as well as methotrexate.1,5 Both 2015 consensus guidelines and a recent small single-center retrospective study support addition of second-line steroid sparing agents such as mycophenolate mofetil.5,6 For acute flairs, however, glucocorticoids with slow taper are usually utilized. In these cases, they should be tapered as soon as clinically feasible to avoid long-term adverse effects. Untreated IgG4-RD, even asymptomatic, has been shown to progress to fibrosis.5
Conclusion
IgG4-RD is a complicated disease process that requires a high index of suspicion to diagnose. In addition, for patients who are diagnosed with this condition, its ability to mimic other pathologic conditions should be taken into account with manifestation of any new illness. This case emphasizes the ability of this disease to localize in multiple organs over time and the need for lifetime surveillance in patients with IgG4-RD disease.
Immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is an immune-mediated fibroinflammatory condition that involves multiple organs and appears as syndromes that were once thought to be unrelated. This disease leads to mass lesions, fibrosis, and subsequent organ failure if allowed to progress untreated.1 Involvement of gastrointestinal (GI) organs, salivary glands, lacrimal glands, lymph, prostate, pulmonary, and vascular system have all been reported.2 Elevated IgG4 serum levels are common, but about one-third of patients with biopsy-proven IgG4-RD do not manifest this characteristic.3,4
Diagnostic confirmation is with biopsy, and all patients with symptomatic, active IgG4-RD require treatment. Glucocorticoids are first-line treatment and are utilized for relapse of symptoms. In addition to glucocorticoids, steroid-sparing medications, including rituximab, azathioprine, mycophenolate mofetil, tacrolimus, and cyclophosphamide have all been used with successful remission.5,6 Here, the authors discuss a case of IgG4-RD that presented with intrahepatic biliary obstruction (mimicking cholangiocarcinoma) and subsequent development of coronary arteritis despite treatment.
Case Presentation
In June 2015, a 57-year-old Air Force veteran presented to Eglin AFB Hospital with pruritic jaundice and acute abdominal pain. He was found to have elevated bilirubin levels (total bilirubin 10 mg/dL [normal range 0.2-1.3 mg/dL], direct bilirubin 6.6 mg/dL [normal range 0.1-0.4 mg/dL]). Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) also were moderately elevated (147 U/L and 337 U/L, respectively).
Prior to this presentation, the patient had been in his usual state of health. His past medical history was notable only for minimal change kidney disease (MCD). MCD is defined as effacement of the podocyte seen on electron microscopy, which allows the passage of large amounts of protein.
A cholangiogram showed abnormal filling into the left main intrahepatic duct and obvious obstruction at the bifurcation of the bile duct. A biliary drainage catheter was placed, and a repeat cholangiogram 2 days later showed involvement of both right and left intrahepatic ducts. The distal common bile duct appeared uninvolved as did the pancreas. Lymphadenopathy was noted at the liver hilum. Klatskin cholangiocarcinoma (type IIIB) was the presumed diagnosis. Based on these findings, tumor resection was performed 3 weeks later, including left hepatectomy, caudate lobe resection, complete bile duct resection, cholecystectomy, with reconstruction by Roux-en-Y intrahepaticojejunostomy. In addition, portal and hepatic artery lymph node dissection was completed.
Surgical specimens were sent for pathologic evaluation and were found negative for malignancy. Patchy areas of storiform fibrosis, obliterative phlebitis, and lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate were noted. IgG4 immunostain highlighted the presence of IgG4 positive plasma cells with a peak count of 145 IgG4 positive plasma cells/hpf. About 80% of the plasma cells were positive for IgG4. Unusually dense eosinophilic infiltrate with plasma cells and regions of dense fibrosis that strongly contributed to the masslike appearance on CT imaging also were noted. Final histology confirmed the diagnosis of IgG4-RD. Elevated levels of total IgG in the serum were observed without elevation in serum IgG4 (Table).
The patient was started on prednisone 40 mg and azathioprine 150 mg daily, with subsequent taper of prednisone over the next 6 months. After prednisone was discontinued, the patient reported new symptoms of lower extremity pain, neuropathy, and swelling of his face. Laboratory results were notable for elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate. The patient was restarted on prednisone 40 mg daily. Azathioprine was replaced with a regimen of 4 doses every 6 months of IV rituximab 700 mg q week and mycophenolate mofetil (1,000 mg bid). After remission was induced, the patient was slowly weaned off prednisone again.
Following 6 months of successful discontinuation of prednisone and continued rituximab and mycophenolate mofetil therapy, the patient presented to the emergency department with new onset chest pain and shortness of breath. A CT angiography of the chest showed right upper and middle lobe infiltrate, and he was treated for community acquired pneumonia. Additionally, he was noted to have elevated troponin levels suggestive of myocardial infarction (MI). Initial troponin was 1.23 ng/mL (normal range < 0.015 ng/mL), which trended down over the next 18 hours. A bedside echocardiogram showed a normal left ventricular ejection fraction without wall motion abnormalities. Etiology for his acute MI was presumed to be demand ischemia from fixed atherosclerotic plaque. Further inpatient cardiac risk stratification was changed to the outpatient setting, and he was started on medical management for coronary artery disease with a beta blocker, a statin, and aspirin. He was discharged home on 10 mg prednisone daily, which was subsequently tapered over several weeks.
In follow-up, a Lexiscan myocardial perfusion imaging was conducted that demonstrated an inferolateral defect and associated wall motion abnormalities (Figures 2 and 3).
Discussion
IgG4-related disease has been found to be a systemic disorder. Typical characteristics include predominance in men aged > 50 years, elevated IgG4 levels, and findings on histology.1 It has been reported to involve many organs, including pancreas, liver, gallbladder, salivary glands, thyroid, and pleura of the lung.2,5
This case report begins with a presumptive diagnosis of cholangiocarcinoma, which was treated aggressively with extensive surgery. Several case reports of complex tumefactive lesions in the GI area (mostly pancreatic and biliary) have detailed IgG4-RD as both a risk factor for subsequent development of cholangiocarcinoma and as a separate entity of IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis.7-9 It is hypothesized that the induction of IgG4- positive plasma cells has been intertwined with the development of cholangiocarcinoma. Differentiation between IgG4 reaction that is scattered around cancerous nests and IgG4 sclerosing cholangitis without malignancy is challenging. It has been documented that both elevated IgG4 levels and hilar hepatic lesions that resemble cholangiocarcinoma frequently accompany those cases of IgG4 sclerosing chlolangitis without pancreatic involvement.9 The histologic features of IgG4-RD need to be identified with multiple biopsies and cytology, and superficial biopsy from biliary mucosa cannot reliably exclude cholangiocarcinoma.
Lymphoplasmacytic aortitis and arteritis have been documented in IgG4-RD. In 2017, Barbu and colleagues described how one such case of coronary arteritis presented with typical angina and coronary catheterization revealing coronary artery stenosis.10 However, during coronary artery bypass surgery, the aorta and coronary vessels were noted to be abnormally stiff. A diffuse fibrotic tissue was identified to be causing the significant stenosis without evidence of atherosclerosis. Pathology showed typical findings of IgG4-RD, and there was a rapid response to immunosuppressive therapy. Involvement of coronary arteries has been described in a small number of cases at this time and is associated with progressive fibrotic changes resulting in an MI, aneurysms, and sudden cardiac death.2,10,11
IgG4-RD can be an extensively systemic disease. All presentations of fibrosis or vasculitis should be viewed with heightened suspicion in the future as being a facet of his IgG4-RD. Pleural involvement has been reported in 12% of cases presenting with systemic presentation, kidney involvement in 13%.2,12
Unfortunately, there is no standard laboratory parameter to date that is diagnostic for IgG4-RD. The gold standard remains confirmation of histologic findings with biopsy. According to an international consensus from 2015, 2 out of the 3 major findings need to be present: (1) dense lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate; (2) storiform fibrosis; and (3) obliterative phlebitis in veins and arteries.1,5 Most patients present with symptoms related to either tumefaction or fibrosis of an organ system.1 Peripheral eosinophilia and elevated serum IgE are often present in IgG4-RD.13 Although IgG4 values are elevated in 51% of biopsy-proven cases, flow cytometry of CD19lowCD38+CD20-CD27+ plasmablasts has been explored recently as a correlation with disease flare.3,14 These particular plasmablasts mark a stage between B cells and plasma cells and have been reported to have a sensitivity of 95% and a specificity of 82% in association with actual IgG4-RD.14 Furthermore, blood plasmablast concentrations decrease in response to glucocorticoid treatment, thereby providing a possible quantifiable value by which to measure success of IgG4 treatment.5,12
Treatment for this disease consists of immunosuppressive therapy. There is documentation of successful remission with rituximab and azathioprine, as well as methotrexate.1,5 Both 2015 consensus guidelines and a recent small single-center retrospective study support addition of second-line steroid sparing agents such as mycophenolate mofetil.5,6 For acute flairs, however, glucocorticoids with slow taper are usually utilized. In these cases, they should be tapered as soon as clinically feasible to avoid long-term adverse effects. Untreated IgG4-RD, even asymptomatic, has been shown to progress to fibrosis.5
Conclusion
IgG4-RD is a complicated disease process that requires a high index of suspicion to diagnose. In addition, for patients who are diagnosed with this condition, its ability to mimic other pathologic conditions should be taken into account with manifestation of any new illness. This case emphasizes the ability of this disease to localize in multiple organs over time and the need for lifetime surveillance in patients with IgG4-RD disease.
1. Lang D, Zwerina J, Pieringer H. IgG4-related disease: current challenges and future prospects. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2016;12:189-199.
2. Brito-Zerón P, Ramos-Casals M, Bosch X, Stone JH. The clinical spectrum of IgG4-related disease. Autoimmun Rev. 2014;13(12):1203-1210.
3. Wallace ZS, Deshpande V, Mattoo H, et al. IgG4-related disease: clinical and laboratory features in one hundred twenty-five patients. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015;67(9):2466-2475.
4. Carruthers MN, Khosroshahi A, Augustin T, Deshpande V, Stone JH. The diagnostic utility of serum IgG4 concentrations in IgG4-RD. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015;74(1):14-18.
5. Khosroshahi A, Wallace ZS, Crowe JL, et al; Second International Symposium on IgG4-Related Disease. International consensus guidance statement on the management and treatment of IgG4-Related disease. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015;67(7):1688-1699.
6. Gupta N, Mathew J, Mohan H, et al. Addition of second-line steroid sparing immunosuppressants like mycophenolate mofetil improves outcome of immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4-RD): a series from a tertiary care teaching hospital in South India. Rheumatol Int. 2017;38(2):203-209.
7. Lin HP, Lin KT, Ho WC, Chen CB, Kuo, CY, Lin YC. IgG4-associated cholangitis mimicking cholangiocarcinoma-report of a case. J Intern Med Taiwan. 2013;24:137-141.
8. Douhara A, Mitoro A, Otani E, et al. Cholangiocarcinoma developed in a patient with IgG4-related disease. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2013;5(8):181-185.
9. Harada K, Nakanuma Y. Cholangiocarcinoma with respect to IgG4 reaction. Int J Hepatol. 2014;2014:803876.
10. Barbu M, Lindström U, Nordborg C, Martinsson A, Dworeck C, Jeppsson A. Sclerosing aortic and coronary arteritis due to IgG4-related disease. Ann Thorac Surg. 2017;103(6):e487-e489.
11. Kim YJ, Park YS, Koo BS, et al. Immunoglobulin G4-related disease with lymphoplasmacytic aortitis mimicking Takayasu arteritis. J Clin Rheumatol. 2011;17(8):451-452.
12. Khosroshahi A, Digumarthy SR, Gibbons FK, Deshpande V. Case 34-2015: A 36-year-old woman with a lung mass, pleural effusion and hip pain. N Engl J Med. 2015;373(18):1762-1772.
13. Della Torre E, Mattoo H, Mahajan VS, Carruthers M, Pillai S, Stone JH. Prevalence of atopy, eosinophilia and IgE elevation in IgG4-related disease. Allergy. 2014;69(2):191-206.
14. Wallace ZS, Mattoo H, Carruthers M, et al. Plasmablasts as a biomarker for IgG4-related disease, independent of serum IgG4 concentrations. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015;74(1):190-195.
1. Lang D, Zwerina J, Pieringer H. IgG4-related disease: current challenges and future prospects. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2016;12:189-199.
2. Brito-Zerón P, Ramos-Casals M, Bosch X, Stone JH. The clinical spectrum of IgG4-related disease. Autoimmun Rev. 2014;13(12):1203-1210.
3. Wallace ZS, Deshpande V, Mattoo H, et al. IgG4-related disease: clinical and laboratory features in one hundred twenty-five patients. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015;67(9):2466-2475.
4. Carruthers MN, Khosroshahi A, Augustin T, Deshpande V, Stone JH. The diagnostic utility of serum IgG4 concentrations in IgG4-RD. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015;74(1):14-18.
5. Khosroshahi A, Wallace ZS, Crowe JL, et al; Second International Symposium on IgG4-Related Disease. International consensus guidance statement on the management and treatment of IgG4-Related disease. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015;67(7):1688-1699.
6. Gupta N, Mathew J, Mohan H, et al. Addition of second-line steroid sparing immunosuppressants like mycophenolate mofetil improves outcome of immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4-RD): a series from a tertiary care teaching hospital in South India. Rheumatol Int. 2017;38(2):203-209.
7. Lin HP, Lin KT, Ho WC, Chen CB, Kuo, CY, Lin YC. IgG4-associated cholangitis mimicking cholangiocarcinoma-report of a case. J Intern Med Taiwan. 2013;24:137-141.
8. Douhara A, Mitoro A, Otani E, et al. Cholangiocarcinoma developed in a patient with IgG4-related disease. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2013;5(8):181-185.
9. Harada K, Nakanuma Y. Cholangiocarcinoma with respect to IgG4 reaction. Int J Hepatol. 2014;2014:803876.
10. Barbu M, Lindström U, Nordborg C, Martinsson A, Dworeck C, Jeppsson A. Sclerosing aortic and coronary arteritis due to IgG4-related disease. Ann Thorac Surg. 2017;103(6):e487-e489.
11. Kim YJ, Park YS, Koo BS, et al. Immunoglobulin G4-related disease with lymphoplasmacytic aortitis mimicking Takayasu arteritis. J Clin Rheumatol. 2011;17(8):451-452.
12. Khosroshahi A, Digumarthy SR, Gibbons FK, Deshpande V. Case 34-2015: A 36-year-old woman with a lung mass, pleural effusion and hip pain. N Engl J Med. 2015;373(18):1762-1772.
13. Della Torre E, Mattoo H, Mahajan VS, Carruthers M, Pillai S, Stone JH. Prevalence of atopy, eosinophilia and IgE elevation in IgG4-related disease. Allergy. 2014;69(2):191-206.
14. Wallace ZS, Mattoo H, Carruthers M, et al. Plasmablasts as a biomarker for IgG4-related disease, independent of serum IgG4 concentrations. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015;74(1):190-195.