User login
TP53 mutations could help stratify MCL patients
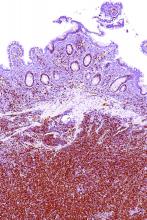
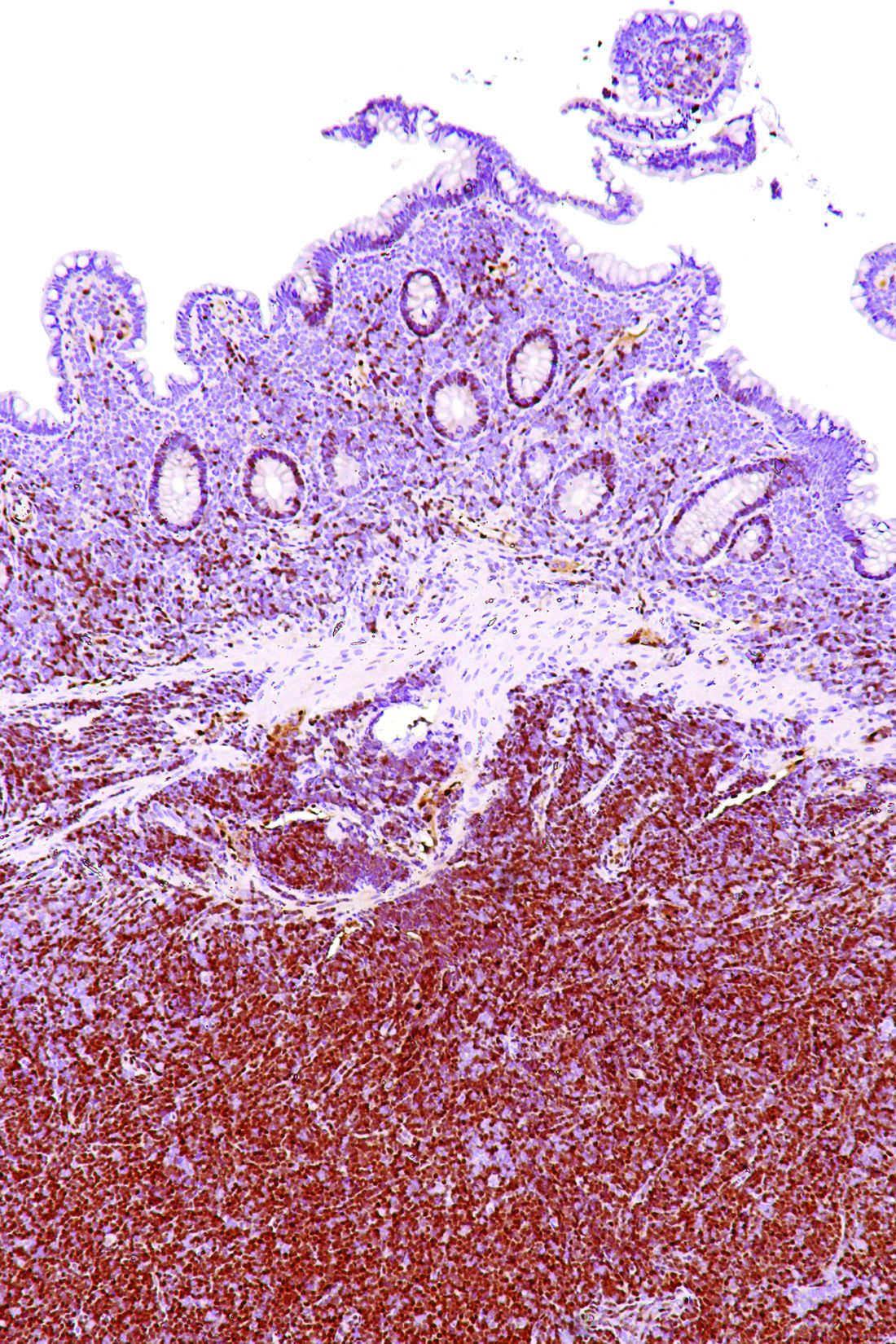
TP53 mutations identified a phenotypically distinct and aggressive form of mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) that did not respond to standard-of-care treatments, according to results from 183 patients younger than 66 years from the Nordic MCL2 and MCL3 trials.
, and that patients with the mutations should be considered for experimental trials of novel agents, wrote Christian W. Eskelund of the department of hematology at Rigshospitalet, Copenhagen, and colleagues.
The researchers collected DNA from the Nordic MCL2 and MCL3 trials and 183 samples were of sufficient quality for genetic analyses. They examined the prognostic value of eight recurrently mutated and two recurrently deleted genes. Only TP53 mutations showed an independent prognostic effect for overall survival (hazard ratio 6.2; P less than .0001) in multivariate Cox regression analyses.
“Our data show that TP53 mutations identify a unique MCL subtype associated with high-risk baseline characteristics, dismal response to standard treatment, and poor clinical outcome,” the researchers wrote.
Read the full study in Blood (2017 Oct 26;130[17]:1903-10).
[email protected]
On Twitter @maryellenny
TP53 mutations identified a phenotypically distinct and aggressive form of mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) that did not respond to standard-of-care treatments, according to results from 183 patients younger than 66 years from the Nordic MCL2 and MCL3 trials.
, and that patients with the mutations should be considered for experimental trials of novel agents, wrote Christian W. Eskelund of the department of hematology at Rigshospitalet, Copenhagen, and colleagues.
The researchers collected DNA from the Nordic MCL2 and MCL3 trials and 183 samples were of sufficient quality for genetic analyses. They examined the prognostic value of eight recurrently mutated and two recurrently deleted genes. Only TP53 mutations showed an independent prognostic effect for overall survival (hazard ratio 6.2; P less than .0001) in multivariate Cox regression analyses.
“Our data show that TP53 mutations identify a unique MCL subtype associated with high-risk baseline characteristics, dismal response to standard treatment, and poor clinical outcome,” the researchers wrote.
Read the full study in Blood (2017 Oct 26;130[17]:1903-10).
[email protected]
On Twitter @maryellenny
TP53 mutations identified a phenotypically distinct and aggressive form of mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) that did not respond to standard-of-care treatments, according to results from 183 patients younger than 66 years from the Nordic MCL2 and MCL3 trials.
, and that patients with the mutations should be considered for experimental trials of novel agents, wrote Christian W. Eskelund of the department of hematology at Rigshospitalet, Copenhagen, and colleagues.
The researchers collected DNA from the Nordic MCL2 and MCL3 trials and 183 samples were of sufficient quality for genetic analyses. They examined the prognostic value of eight recurrently mutated and two recurrently deleted genes. Only TP53 mutations showed an independent prognostic effect for overall survival (hazard ratio 6.2; P less than .0001) in multivariate Cox regression analyses.
“Our data show that TP53 mutations identify a unique MCL subtype associated with high-risk baseline characteristics, dismal response to standard treatment, and poor clinical outcome,” the researchers wrote.
Read the full study in Blood (2017 Oct 26;130[17]:1903-10).
[email protected]
On Twitter @maryellenny
FROM BLOOD
Lenalidomide shows clinical activity in relapsed/refractory MCL
Lenalidomide alone and in combination showed “clinically significant activity” and no new safety signals in patients with mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) who had previously failed on ibrutinib, according to findings from a retrospective, observational study.
Michael Wang, MD, of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, and his colleagues enrolled 58 MCL patients across 11 study sites. The patients had a median age of 71 years and 88% of patients had received three or more prior therapies. Most had received ibrutinib as monotherapy and used a lenalidomide-containing therapy next.
The overall response rate was 29% (95% confidence interval, 18%-43%). The rate was similar between patients with MCL refractory to ibrutinib and patients who relapsed/progressed on or following ibrutinib use (32% versus 30%, respectively). There was a 14% complete response, though it varied by subgroup with 8% among MCL patients refractory to ibrutinib and 22% among relapsed/progressed patients. There was a 20-week median duration of response, but 82% of responders were censored so the researchers urged caution in interpreting that finding.
Among the 58 patients, more than 80% reported one or more treatment-emergent adverse events during lenalidomide treatment and 20 patients (34%) had serious events. Nine patients (16%) discontinued the drug because of adverse events.
“Lenalidomide addresses an unmet medical need and widens the therapeutic options in a difficult-to-treat patient population,” the researchers wrote.
Read the full study in the Journal of Hematology Oncology (2017 Nov 2;10[1]:171).
[email protected]
On Twitter @maryellenny
Lenalidomide alone and in combination showed “clinically significant activity” and no new safety signals in patients with mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) who had previously failed on ibrutinib, according to findings from a retrospective, observational study.
Michael Wang, MD, of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, and his colleagues enrolled 58 MCL patients across 11 study sites. The patients had a median age of 71 years and 88% of patients had received three or more prior therapies. Most had received ibrutinib as monotherapy and used a lenalidomide-containing therapy next.
The overall response rate was 29% (95% confidence interval, 18%-43%). The rate was similar between patients with MCL refractory to ibrutinib and patients who relapsed/progressed on or following ibrutinib use (32% versus 30%, respectively). There was a 14% complete response, though it varied by subgroup with 8% among MCL patients refractory to ibrutinib and 22% among relapsed/progressed patients. There was a 20-week median duration of response, but 82% of responders were censored so the researchers urged caution in interpreting that finding.
Among the 58 patients, more than 80% reported one or more treatment-emergent adverse events during lenalidomide treatment and 20 patients (34%) had serious events. Nine patients (16%) discontinued the drug because of adverse events.
“Lenalidomide addresses an unmet medical need and widens the therapeutic options in a difficult-to-treat patient population,” the researchers wrote.
Read the full study in the Journal of Hematology Oncology (2017 Nov 2;10[1]:171).
[email protected]
On Twitter @maryellenny
Lenalidomide alone and in combination showed “clinically significant activity” and no new safety signals in patients with mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) who had previously failed on ibrutinib, according to findings from a retrospective, observational study.
Michael Wang, MD, of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, and his colleagues enrolled 58 MCL patients across 11 study sites. The patients had a median age of 71 years and 88% of patients had received three or more prior therapies. Most had received ibrutinib as monotherapy and used a lenalidomide-containing therapy next.
The overall response rate was 29% (95% confidence interval, 18%-43%). The rate was similar between patients with MCL refractory to ibrutinib and patients who relapsed/progressed on or following ibrutinib use (32% versus 30%, respectively). There was a 14% complete response, though it varied by subgroup with 8% among MCL patients refractory to ibrutinib and 22% among relapsed/progressed patients. There was a 20-week median duration of response, but 82% of responders were censored so the researchers urged caution in interpreting that finding.
Among the 58 patients, more than 80% reported one or more treatment-emergent adverse events during lenalidomide treatment and 20 patients (34%) had serious events. Nine patients (16%) discontinued the drug because of adverse events.
“Lenalidomide addresses an unmet medical need and widens the therapeutic options in a difficult-to-treat patient population,” the researchers wrote.
Read the full study in the Journal of Hematology Oncology (2017 Nov 2;10[1]:171).
[email protected]
On Twitter @maryellenny
FROM THE JOURNAL OF HEMATOLOGY & ONCOLOGY
AML candidate drug back in the pipeline
The Food and Drug Administration has given the biopharmaceutical company Cellectis permission to resume phase 1 trials of UCART123, a gene-edited T-cell investigational drug that targets CD123, as a potential treatment for acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm (BPDCN), according to a press release from the company.
UCART123 is the first allogeneic, “off-the-shelf” gene-edited chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell product candidate that the FDA has approved for clinical trials. The agency had placed a clinical hold on phase 1 trials of the gene-edited CAR T-cell drug on Sept. 4, following a patient death in the BPDCN clinical study. In order to proceed with the trials, Cellectis agreed to several changes in the study protocols.
The changes include decreasing the dose of the UCART123 therapy to 6.25x104 cells/kg and lowering the dose of the lympho-depleting regimen of cyclophosphamide to 750 mg/m2 per day over 3 days with a maximum daily dose of 1.33 g. Additionally, there can be no uncontrolled infection after receipt of the lympho-depleting preconditioning regimen. Patients must be afebrile at the start of treatment, off all but a replacement dose of corticosteroids, and have no organ dysfunction. Plus, the next three patients treated in each study must be under age 65.
There’s also a condition that patient enrollments be staggered by at least 28 days.
The drug sponsor is working with investigators and each clinical site to obtain the Institutional Review Board’s approval of the revised protocols.
The hold followed the death of a 78-year-old man with relapsed/refractory BPDCN with 30% blasts in his bone marrow and cutaneous lesions. The first dose of UCART123 at 6.25x105 cells/kg was administered without complication, but at day 5 the patient began experiencing side effects, including cytokine release syndrome and a lung infection. At day 8, the cytokine release syndrome had worsened and the patient had also developed capillary leak syndrome. He died on day 9 of the study.
In the AML phase 1 study, a 58-year-old woman with AML and 84% blasts in her bone marrow received the same dose of UCART123. She also developed cytokine release syndrome and capillary leak syndrome but both resolved with treatment.
Both patients also received the same preconditioning treatment: 30 mg/m2 per day fludarabine for 4 days and 1g/m2 per day cyclophosphamide for 3 days.
[email protected]
On Twitter @maryellenny
The Food and Drug Administration has given the biopharmaceutical company Cellectis permission to resume phase 1 trials of UCART123, a gene-edited T-cell investigational drug that targets CD123, as a potential treatment for acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm (BPDCN), according to a press release from the company.
UCART123 is the first allogeneic, “off-the-shelf” gene-edited chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell product candidate that the FDA has approved for clinical trials. The agency had placed a clinical hold on phase 1 trials of the gene-edited CAR T-cell drug on Sept. 4, following a patient death in the BPDCN clinical study. In order to proceed with the trials, Cellectis agreed to several changes in the study protocols.
The changes include decreasing the dose of the UCART123 therapy to 6.25x104 cells/kg and lowering the dose of the lympho-depleting regimen of cyclophosphamide to 750 mg/m2 per day over 3 days with a maximum daily dose of 1.33 g. Additionally, there can be no uncontrolled infection after receipt of the lympho-depleting preconditioning regimen. Patients must be afebrile at the start of treatment, off all but a replacement dose of corticosteroids, and have no organ dysfunction. Plus, the next three patients treated in each study must be under age 65.
There’s also a condition that patient enrollments be staggered by at least 28 days.
The drug sponsor is working with investigators and each clinical site to obtain the Institutional Review Board’s approval of the revised protocols.
The hold followed the death of a 78-year-old man with relapsed/refractory BPDCN with 30% blasts in his bone marrow and cutaneous lesions. The first dose of UCART123 at 6.25x105 cells/kg was administered without complication, but at day 5 the patient began experiencing side effects, including cytokine release syndrome and a lung infection. At day 8, the cytokine release syndrome had worsened and the patient had also developed capillary leak syndrome. He died on day 9 of the study.
In the AML phase 1 study, a 58-year-old woman with AML and 84% blasts in her bone marrow received the same dose of UCART123. She also developed cytokine release syndrome and capillary leak syndrome but both resolved with treatment.
Both patients also received the same preconditioning treatment: 30 mg/m2 per day fludarabine for 4 days and 1g/m2 per day cyclophosphamide for 3 days.
[email protected]
On Twitter @maryellenny
The Food and Drug Administration has given the biopharmaceutical company Cellectis permission to resume phase 1 trials of UCART123, a gene-edited T-cell investigational drug that targets CD123, as a potential treatment for acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm (BPDCN), according to a press release from the company.
UCART123 is the first allogeneic, “off-the-shelf” gene-edited chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell product candidate that the FDA has approved for clinical trials. The agency had placed a clinical hold on phase 1 trials of the gene-edited CAR T-cell drug on Sept. 4, following a patient death in the BPDCN clinical study. In order to proceed with the trials, Cellectis agreed to several changes in the study protocols.
The changes include decreasing the dose of the UCART123 therapy to 6.25x104 cells/kg and lowering the dose of the lympho-depleting regimen of cyclophosphamide to 750 mg/m2 per day over 3 days with a maximum daily dose of 1.33 g. Additionally, there can be no uncontrolled infection after receipt of the lympho-depleting preconditioning regimen. Patients must be afebrile at the start of treatment, off all but a replacement dose of corticosteroids, and have no organ dysfunction. Plus, the next three patients treated in each study must be under age 65.
There’s also a condition that patient enrollments be staggered by at least 28 days.
The drug sponsor is working with investigators and each clinical site to obtain the Institutional Review Board’s approval of the revised protocols.
The hold followed the death of a 78-year-old man with relapsed/refractory BPDCN with 30% blasts in his bone marrow and cutaneous lesions. The first dose of UCART123 at 6.25x105 cells/kg was administered without complication, but at day 5 the patient began experiencing side effects, including cytokine release syndrome and a lung infection. At day 8, the cytokine release syndrome had worsened and the patient had also developed capillary leak syndrome. He died on day 9 of the study.
In the AML phase 1 study, a 58-year-old woman with AML and 84% blasts in her bone marrow received the same dose of UCART123. She also developed cytokine release syndrome and capillary leak syndrome but both resolved with treatment.
Both patients also received the same preconditioning treatment: 30 mg/m2 per day fludarabine for 4 days and 1g/m2 per day cyclophosphamide for 3 days.
[email protected]
On Twitter @maryellenny
Top research to be presented at AAGL
The 46th AAGL Global Congress on Minimally Invasive Gynecologic Surgery starts Nov. 12, 2017, in National Harbor, Md., and attendees will have a chance to hear presentations on more than 300 studies, plus numerous virtual posters.
Dr. Charles E. Miller, a minimally invasive gynecologic surgeon in Naperville, Ill., and a past president of the AAGL, offered his top picks for not-to-be-missed research at this year’s meeting.
Cesarean-induced isthmoceles
On Wednesday, Nov. 15, at 12:17 p.m., researchers from West Virginia University in Morgantown and Universidad Autónoma de Nuevo León in Mexico will present data from a prospective study on the anatomy of cesarean-induced isthmoceles. The paper won the Golden Hysteroscope Award for best paper on hysteroscopy. It is being presented during the Open Communications 13 session on reproductive medicine.
“Isthmocele has become such a hot topic,” Dr. Miller said. “Besides the implications in terms of pelvic pain and abnormal bleeding, it can be a cause of infertility as fluid goes into the endometrial cavity and impacts implantation.”
Dr. Miller will be performing a telesurgery featuring robotic-assisted excision and repair of a cesarean section isthmocele on Thursday, Nov. 16, as part of General Session V from 8:30 a.m. to 12:30 p.m.
Rectosigmoid endometriosis
On Wednesday, Nov. 15, at 12:50 p.m., researchers from the University of Pittsburgh will show a surgical video on anterior discoid resection for rectosigmoid endometriosis. They use various laparoscopic instruments and techniques to assess and resect the nodule, including a “squeeze” technique, barbed suture, and a V-shaped closure. The video, which won the Golden Laparoscope Award for best surgical video, is being presented during the Plenary 6 session on endometriosis and adenomyosis.
“There is great debate in just how aggressively patients should be treated when a woman has deep infiltrative endometriosis involving the rectosigmoid area,” Dr. Miller said.
Most of the research in this area is from single-institution studies that do not always completely describe the procedure, leaving surgeons “unsure of which way to go,” Dr. Miller said. In addition, because many patients with endometriosis are young, surgeons need to consider how the procedure will impact them in 20 or even 50 years. While more aggressive than shaving, discoid resection is less aggressive than standard bowel resection.
Postsurgical pain control
On Tuesday, Nov. 14, at 3:46 p.m., researchers from the University of Pittsburgh, Oregon Health & Science University, Southern California Permanente Medical Group, and the University of Wisconsin, Madison, will present results from a prospective, double-blind, randomized study comparing intravenous acetaminophen with placebo for postsurgical pain control and patient satisfaction after laparoscopic hysterectomy. Their findings indicate no difference in either pain or satisfaction, casting doubt on routine use during hysterectomy. The study, which won the Jay M. Cooper Award for best paper on minimally invasive gynecology by a fellow, will be presented during the Open Communications 9 session on laparoscopy.
On Tuesday, Nov. 14, at 1:21 p.m., researchers from the University of Maryland, Baltimore; Mercy Medical Center, Baltimore; and Yoyodyne General Services, New York, will present a single-center, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial to assess the use of a single belladonna and opium suppository placed after laparoscopic or robotic hysterectomy to control postoperative pain. As with acetaminophen, they also found that the suppositories did not significantly lower pain or narcotic use. However, the belladonna/opium suppository reduced time to discharge from the postanesthesia care unit in phase I. The research, which won the Jerome J. Hoffman Award for best abstract by a resident or fellow, will be presented during Session 2 of the Virtual Posters.
“Here again are two treatments that really have minimal basis,” Dr. Miller said. “In the days of cost containment, is there really any reason for either?”
Cervical ripening
Dr. Miller also recommended that attendees take note of a randomized controlled trial evaluating whether misoprostol oral is as effective as vaginal tablets for cervical ripening. Researchers at Cairo University in Egypt considered this question among more than 350 women who were undergoing operative hysterectomy for various indications. They found no statistically significant difference in efficacy and similar adverse effects.
“There has been some concern raised about, is there a better way?” Dr. Miller said. “This is especially important as we move hysteroscopy to the office.”
The cervical priming study, which won the Robert B. Hunt Award for best paper published in the Journal of Minimally Invasive Gynecology between September 2016 and August 2017, will be presented on Tuesday, Nov. 14, at 7:10 a.m. during the journal’s editorial/advisory board breakfast. You can read the full article online (J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2016 Nov - Dec;23[7]:1107-12).
[email protected]
On Twitter @maryellenny
The 46th AAGL Global Congress on Minimally Invasive Gynecologic Surgery starts Nov. 12, 2017, in National Harbor, Md., and attendees will have a chance to hear presentations on more than 300 studies, plus numerous virtual posters.
Dr. Charles E. Miller, a minimally invasive gynecologic surgeon in Naperville, Ill., and a past president of the AAGL, offered his top picks for not-to-be-missed research at this year’s meeting.
Cesarean-induced isthmoceles
On Wednesday, Nov. 15, at 12:17 p.m., researchers from West Virginia University in Morgantown and Universidad Autónoma de Nuevo León in Mexico will present data from a prospective study on the anatomy of cesarean-induced isthmoceles. The paper won the Golden Hysteroscope Award for best paper on hysteroscopy. It is being presented during the Open Communications 13 session on reproductive medicine.
“Isthmocele has become such a hot topic,” Dr. Miller said. “Besides the implications in terms of pelvic pain and abnormal bleeding, it can be a cause of infertility as fluid goes into the endometrial cavity and impacts implantation.”
Dr. Miller will be performing a telesurgery featuring robotic-assisted excision and repair of a cesarean section isthmocele on Thursday, Nov. 16, as part of General Session V from 8:30 a.m. to 12:30 p.m.
Rectosigmoid endometriosis
On Wednesday, Nov. 15, at 12:50 p.m., researchers from the University of Pittsburgh will show a surgical video on anterior discoid resection for rectosigmoid endometriosis. They use various laparoscopic instruments and techniques to assess and resect the nodule, including a “squeeze” technique, barbed suture, and a V-shaped closure. The video, which won the Golden Laparoscope Award for best surgical video, is being presented during the Plenary 6 session on endometriosis and adenomyosis.
“There is great debate in just how aggressively patients should be treated when a woman has deep infiltrative endometriosis involving the rectosigmoid area,” Dr. Miller said.
Most of the research in this area is from single-institution studies that do not always completely describe the procedure, leaving surgeons “unsure of which way to go,” Dr. Miller said. In addition, because many patients with endometriosis are young, surgeons need to consider how the procedure will impact them in 20 or even 50 years. While more aggressive than shaving, discoid resection is less aggressive than standard bowel resection.
Postsurgical pain control
On Tuesday, Nov. 14, at 3:46 p.m., researchers from the University of Pittsburgh, Oregon Health & Science University, Southern California Permanente Medical Group, and the University of Wisconsin, Madison, will present results from a prospective, double-blind, randomized study comparing intravenous acetaminophen with placebo for postsurgical pain control and patient satisfaction after laparoscopic hysterectomy. Their findings indicate no difference in either pain or satisfaction, casting doubt on routine use during hysterectomy. The study, which won the Jay M. Cooper Award for best paper on minimally invasive gynecology by a fellow, will be presented during the Open Communications 9 session on laparoscopy.
On Tuesday, Nov. 14, at 1:21 p.m., researchers from the University of Maryland, Baltimore; Mercy Medical Center, Baltimore; and Yoyodyne General Services, New York, will present a single-center, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial to assess the use of a single belladonna and opium suppository placed after laparoscopic or robotic hysterectomy to control postoperative pain. As with acetaminophen, they also found that the suppositories did not significantly lower pain or narcotic use. However, the belladonna/opium suppository reduced time to discharge from the postanesthesia care unit in phase I. The research, which won the Jerome J. Hoffman Award for best abstract by a resident or fellow, will be presented during Session 2 of the Virtual Posters.
“Here again are two treatments that really have minimal basis,” Dr. Miller said. “In the days of cost containment, is there really any reason for either?”
Cervical ripening
Dr. Miller also recommended that attendees take note of a randomized controlled trial evaluating whether misoprostol oral is as effective as vaginal tablets for cervical ripening. Researchers at Cairo University in Egypt considered this question among more than 350 women who were undergoing operative hysterectomy for various indications. They found no statistically significant difference in efficacy and similar adverse effects.
“There has been some concern raised about, is there a better way?” Dr. Miller said. “This is especially important as we move hysteroscopy to the office.”
The cervical priming study, which won the Robert B. Hunt Award for best paper published in the Journal of Minimally Invasive Gynecology between September 2016 and August 2017, will be presented on Tuesday, Nov. 14, at 7:10 a.m. during the journal’s editorial/advisory board breakfast. You can read the full article online (J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2016 Nov - Dec;23[7]:1107-12).
[email protected]
On Twitter @maryellenny
The 46th AAGL Global Congress on Minimally Invasive Gynecologic Surgery starts Nov. 12, 2017, in National Harbor, Md., and attendees will have a chance to hear presentations on more than 300 studies, plus numerous virtual posters.
Dr. Charles E. Miller, a minimally invasive gynecologic surgeon in Naperville, Ill., and a past president of the AAGL, offered his top picks for not-to-be-missed research at this year’s meeting.
Cesarean-induced isthmoceles
On Wednesday, Nov. 15, at 12:17 p.m., researchers from West Virginia University in Morgantown and Universidad Autónoma de Nuevo León in Mexico will present data from a prospective study on the anatomy of cesarean-induced isthmoceles. The paper won the Golden Hysteroscope Award for best paper on hysteroscopy. It is being presented during the Open Communications 13 session on reproductive medicine.
“Isthmocele has become such a hot topic,” Dr. Miller said. “Besides the implications in terms of pelvic pain and abnormal bleeding, it can be a cause of infertility as fluid goes into the endometrial cavity and impacts implantation.”
Dr. Miller will be performing a telesurgery featuring robotic-assisted excision and repair of a cesarean section isthmocele on Thursday, Nov. 16, as part of General Session V from 8:30 a.m. to 12:30 p.m.
Rectosigmoid endometriosis
On Wednesday, Nov. 15, at 12:50 p.m., researchers from the University of Pittsburgh will show a surgical video on anterior discoid resection for rectosigmoid endometriosis. They use various laparoscopic instruments and techniques to assess and resect the nodule, including a “squeeze” technique, barbed suture, and a V-shaped closure. The video, which won the Golden Laparoscope Award for best surgical video, is being presented during the Plenary 6 session on endometriosis and adenomyosis.
“There is great debate in just how aggressively patients should be treated when a woman has deep infiltrative endometriosis involving the rectosigmoid area,” Dr. Miller said.
Most of the research in this area is from single-institution studies that do not always completely describe the procedure, leaving surgeons “unsure of which way to go,” Dr. Miller said. In addition, because many patients with endometriosis are young, surgeons need to consider how the procedure will impact them in 20 or even 50 years. While more aggressive than shaving, discoid resection is less aggressive than standard bowel resection.
Postsurgical pain control
On Tuesday, Nov. 14, at 3:46 p.m., researchers from the University of Pittsburgh, Oregon Health & Science University, Southern California Permanente Medical Group, and the University of Wisconsin, Madison, will present results from a prospective, double-blind, randomized study comparing intravenous acetaminophen with placebo for postsurgical pain control and patient satisfaction after laparoscopic hysterectomy. Their findings indicate no difference in either pain or satisfaction, casting doubt on routine use during hysterectomy. The study, which won the Jay M. Cooper Award for best paper on minimally invasive gynecology by a fellow, will be presented during the Open Communications 9 session on laparoscopy.
On Tuesday, Nov. 14, at 1:21 p.m., researchers from the University of Maryland, Baltimore; Mercy Medical Center, Baltimore; and Yoyodyne General Services, New York, will present a single-center, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial to assess the use of a single belladonna and opium suppository placed after laparoscopic or robotic hysterectomy to control postoperative pain. As with acetaminophen, they also found that the suppositories did not significantly lower pain or narcotic use. However, the belladonna/opium suppository reduced time to discharge from the postanesthesia care unit in phase I. The research, which won the Jerome J. Hoffman Award for best abstract by a resident or fellow, will be presented during Session 2 of the Virtual Posters.
“Here again are two treatments that really have minimal basis,” Dr. Miller said. “In the days of cost containment, is there really any reason for either?”
Cervical ripening
Dr. Miller also recommended that attendees take note of a randomized controlled trial evaluating whether misoprostol oral is as effective as vaginal tablets for cervical ripening. Researchers at Cairo University in Egypt considered this question among more than 350 women who were undergoing operative hysterectomy for various indications. They found no statistically significant difference in efficacy and similar adverse effects.
“There has been some concern raised about, is there a better way?” Dr. Miller said. “This is especially important as we move hysteroscopy to the office.”
The cervical priming study, which won the Robert B. Hunt Award for best paper published in the Journal of Minimally Invasive Gynecology between September 2016 and August 2017, will be presented on Tuesday, Nov. 14, at 7:10 a.m. during the journal’s editorial/advisory board breakfast. You can read the full article online (J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2016 Nov - Dec;23[7]:1107-12).
[email protected]
On Twitter @maryellenny
FDA approves first Erdheim-Chester disease treatment
The kinase inhibitor – marketed as Zelboraf – was approved on Nov. 6. It is the first approved treatment for ECD and is already on the market as a treatment for patients with unresectable or metastatic melanoma with BRAF V600E mutation.
The FDA expedited approval of the drug under the Priority Review and Breakthrough Therapy programs. The drug also received an orphan status designation, which makes the sponsor eligible for incentives such as tax credits for clinical testing.
The agency based its approval on results from 22 patients with BRAF-V600-mutation positive ECD. Half of the patients (11) experienced a partial reduction in tumor size and 1 patient experienced a complete response, according to the FDA. Initial results from the phase 2, open-label VE-BASKET study were published in 2015 (N Engl J Med. 2015 Aug 20;373[8]:726-36).
Common side effects of vemurafenib include arthralgias, maculopapular rash, alopecia, fatigue, prolonged QT interval, and papilloma. Severe side effects include development of new cancers, growth of tumors in patients with BRAF wild-type melanoma, anaphylaxis and DRESS syndrome, severe skin reactions, heart abnormalities, hepatotoxicity, photosensitivity, uveitis, radiation sensitization and radiation recall, and Dupuytren’s contracture and plantar fascial fibromatosis. The drug is also considered teratogenic and women should be advised to use contraception while taking it, according to the FDA.
The full prescribing information is available at zelboraf.com.
[email protected]
On Twitter @maryellenny
The kinase inhibitor – marketed as Zelboraf – was approved on Nov. 6. It is the first approved treatment for ECD and is already on the market as a treatment for patients with unresectable or metastatic melanoma with BRAF V600E mutation.
The FDA expedited approval of the drug under the Priority Review and Breakthrough Therapy programs. The drug also received an orphan status designation, which makes the sponsor eligible for incentives such as tax credits for clinical testing.
The agency based its approval on results from 22 patients with BRAF-V600-mutation positive ECD. Half of the patients (11) experienced a partial reduction in tumor size and 1 patient experienced a complete response, according to the FDA. Initial results from the phase 2, open-label VE-BASKET study were published in 2015 (N Engl J Med. 2015 Aug 20;373[8]:726-36).
Common side effects of vemurafenib include arthralgias, maculopapular rash, alopecia, fatigue, prolonged QT interval, and papilloma. Severe side effects include development of new cancers, growth of tumors in patients with BRAF wild-type melanoma, anaphylaxis and DRESS syndrome, severe skin reactions, heart abnormalities, hepatotoxicity, photosensitivity, uveitis, radiation sensitization and radiation recall, and Dupuytren’s contracture and plantar fascial fibromatosis. The drug is also considered teratogenic and women should be advised to use contraception while taking it, according to the FDA.
The full prescribing information is available at zelboraf.com.
[email protected]
On Twitter @maryellenny
The kinase inhibitor – marketed as Zelboraf – was approved on Nov. 6. It is the first approved treatment for ECD and is already on the market as a treatment for patients with unresectable or metastatic melanoma with BRAF V600E mutation.
The FDA expedited approval of the drug under the Priority Review and Breakthrough Therapy programs. The drug also received an orphan status designation, which makes the sponsor eligible for incentives such as tax credits for clinical testing.
The agency based its approval on results from 22 patients with BRAF-V600-mutation positive ECD. Half of the patients (11) experienced a partial reduction in tumor size and 1 patient experienced a complete response, according to the FDA. Initial results from the phase 2, open-label VE-BASKET study were published in 2015 (N Engl J Med. 2015 Aug 20;373[8]:726-36).
Common side effects of vemurafenib include arthralgias, maculopapular rash, alopecia, fatigue, prolonged QT interval, and papilloma. Severe side effects include development of new cancers, growth of tumors in patients with BRAF wild-type melanoma, anaphylaxis and DRESS syndrome, severe skin reactions, heart abnormalities, hepatotoxicity, photosensitivity, uveitis, radiation sensitization and radiation recall, and Dupuytren’s contracture and plantar fascial fibromatosis. The drug is also considered teratogenic and women should be advised to use contraception while taking it, according to the FDA.
The full prescribing information is available at zelboraf.com.
[email protected]
On Twitter @maryellenny
VIDEO: Expert roundtable on hormone therapy
PHILADELPHIA – The updated hormone therapy position statement from the North American Menopause Society tells clinicians to move away from “lowest dose for the shortest time” and toward prescribing the appropriate dose, formulation, and route of administration to meet treatment goals.
At the group’s annual meeting, some of the authors of the position statement outlined the latest evidence for the safety of hormone therapy and special clinical considerations based on age or time of menopause and unique health risks like breast cancer. Additionally, the authors said there should not be an arbitrary “stop date” for hormone therapy.
The authors also discussed the risks of using compounded bioidentical hormones to treat menopausal symptoms.
This roundtable discussion includes JoAnn V. Pinkerton, MD, NAMS executive director and professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Virginia, Charlottesville; Andrew Kaunitz, MD, associate chairman of the department of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Florida, Jacksonville; and Cynthia A. Stuenkel, MD, clinical professor of medicine at the University of California, San Diego.
Dr. Pinkerton reported institutional research support from TherapeuticsMD. Dr. Kaunitz reported consultant/advisory board work for Allergan, Amag Pharmaceuticals, Bayer, Mithra Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, and Shionogi. He has also received grant/research support from Bayer, Radius Health, TherapeuticsMD, and Millendo Therapeutics. Dr. Stuenkel reported having no financial disclosures.
[email protected]
On Twitter @maryellenny
PHILADELPHIA – The updated hormone therapy position statement from the North American Menopause Society tells clinicians to move away from “lowest dose for the shortest time” and toward prescribing the appropriate dose, formulation, and route of administration to meet treatment goals.
At the group’s annual meeting, some of the authors of the position statement outlined the latest evidence for the safety of hormone therapy and special clinical considerations based on age or time of menopause and unique health risks like breast cancer. Additionally, the authors said there should not be an arbitrary “stop date” for hormone therapy.
The authors also discussed the risks of using compounded bioidentical hormones to treat menopausal symptoms.
This roundtable discussion includes JoAnn V. Pinkerton, MD, NAMS executive director and professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Virginia, Charlottesville; Andrew Kaunitz, MD, associate chairman of the department of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Florida, Jacksonville; and Cynthia A. Stuenkel, MD, clinical professor of medicine at the University of California, San Diego.
Dr. Pinkerton reported institutional research support from TherapeuticsMD. Dr. Kaunitz reported consultant/advisory board work for Allergan, Amag Pharmaceuticals, Bayer, Mithra Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, and Shionogi. He has also received grant/research support from Bayer, Radius Health, TherapeuticsMD, and Millendo Therapeutics. Dr. Stuenkel reported having no financial disclosures.
[email protected]
On Twitter @maryellenny
PHILADELPHIA – The updated hormone therapy position statement from the North American Menopause Society tells clinicians to move away from “lowest dose for the shortest time” and toward prescribing the appropriate dose, formulation, and route of administration to meet treatment goals.
At the group’s annual meeting, some of the authors of the position statement outlined the latest evidence for the safety of hormone therapy and special clinical considerations based on age or time of menopause and unique health risks like breast cancer. Additionally, the authors said there should not be an arbitrary “stop date” for hormone therapy.
The authors also discussed the risks of using compounded bioidentical hormones to treat menopausal symptoms.
This roundtable discussion includes JoAnn V. Pinkerton, MD, NAMS executive director and professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Virginia, Charlottesville; Andrew Kaunitz, MD, associate chairman of the department of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Florida, Jacksonville; and Cynthia A. Stuenkel, MD, clinical professor of medicine at the University of California, San Diego.
Dr. Pinkerton reported institutional research support from TherapeuticsMD. Dr. Kaunitz reported consultant/advisory board work for Allergan, Amag Pharmaceuticals, Bayer, Mithra Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, and Shionogi. He has also received grant/research support from Bayer, Radius Health, TherapeuticsMD, and Millendo Therapeutics. Dr. Stuenkel reported having no financial disclosures.
[email protected]
On Twitter @maryellenny
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM NAMS 2017
VIDEO: New sexual desire drugs coming for women
PHILADELPHIA – Despite the slow start that flibanserin had since being approved to treat hypoactive sexual desire disorder (HSDD) in premenopausal women in 2015, more drugs are in the pipeline to help women address low desire.
One drug – bremelanotide – has completed phase 3 trials and could be considered by the Food and Drug Administration as early as 2018, Sheryl A. Kingsberg, PhD, said during an interview at the annual meeting of the North American Menopause Society.
Bremelanotide is a first-in-class melanocortin receptor 4 agonist being developed for premenopausal women to use on an as-needed basis and is delivered using a single-dose, auto injector.
Another drug, prasterone, is also being studied to treat HSDD. The intravaginal DHEA treatment is already approved to treat dyspareunia due to vulvovaginal atrophy in menopause. The manufacturer is beginning phase 3 trials for HSDD in postmenopausal women, said Dr. Kingsberg, who is chief of the division of behavioral medicine at MacDonald Women’s Hospital/University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center and the president of NAMS.
Additional drugs are in earlier stages of development for HSDD. While flibanserin hasn’t been a blockbuster drug, its approval by the FDA paved the way for additional drug development in this area, Dr. Kingsberg said.
Dr. Kingsberg reported consultant/advisory board work for Amag Pharmaceuticals, Duchesnay, Emotional Brain, EndoCeutics, Materna Medical, Palatin Technologies, Pfizer, Shionogi, TherapeuticsMD, Valeant Pharmaceuticals, and Viveve. She is on the speakers bureau for Valeant Pharmaceuticals and owns stock in Viveve.
[email protected]
On Twitter @maryellenny
PHILADELPHIA – Despite the slow start that flibanserin had since being approved to treat hypoactive sexual desire disorder (HSDD) in premenopausal women in 2015, more drugs are in the pipeline to help women address low desire.
One drug – bremelanotide – has completed phase 3 trials and could be considered by the Food and Drug Administration as early as 2018, Sheryl A. Kingsberg, PhD, said during an interview at the annual meeting of the North American Menopause Society.
Bremelanotide is a first-in-class melanocortin receptor 4 agonist being developed for premenopausal women to use on an as-needed basis and is delivered using a single-dose, auto injector.
Another drug, prasterone, is also being studied to treat HSDD. The intravaginal DHEA treatment is already approved to treat dyspareunia due to vulvovaginal atrophy in menopause. The manufacturer is beginning phase 3 trials for HSDD in postmenopausal women, said Dr. Kingsberg, who is chief of the division of behavioral medicine at MacDonald Women’s Hospital/University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center and the president of NAMS.
Additional drugs are in earlier stages of development for HSDD. While flibanserin hasn’t been a blockbuster drug, its approval by the FDA paved the way for additional drug development in this area, Dr. Kingsberg said.
Dr. Kingsberg reported consultant/advisory board work for Amag Pharmaceuticals, Duchesnay, Emotional Brain, EndoCeutics, Materna Medical, Palatin Technologies, Pfizer, Shionogi, TherapeuticsMD, Valeant Pharmaceuticals, and Viveve. She is on the speakers bureau for Valeant Pharmaceuticals and owns stock in Viveve.
[email protected]
On Twitter @maryellenny
PHILADELPHIA – Despite the slow start that flibanserin had since being approved to treat hypoactive sexual desire disorder (HSDD) in premenopausal women in 2015, more drugs are in the pipeline to help women address low desire.
One drug – bremelanotide – has completed phase 3 trials and could be considered by the Food and Drug Administration as early as 2018, Sheryl A. Kingsberg, PhD, said during an interview at the annual meeting of the North American Menopause Society.
Bremelanotide is a first-in-class melanocortin receptor 4 agonist being developed for premenopausal women to use on an as-needed basis and is delivered using a single-dose, auto injector.
Another drug, prasterone, is also being studied to treat HSDD. The intravaginal DHEA treatment is already approved to treat dyspareunia due to vulvovaginal atrophy in menopause. The manufacturer is beginning phase 3 trials for HSDD in postmenopausal women, said Dr. Kingsberg, who is chief of the division of behavioral medicine at MacDonald Women’s Hospital/University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center and the president of NAMS.
Additional drugs are in earlier stages of development for HSDD. While flibanserin hasn’t been a blockbuster drug, its approval by the FDA paved the way for additional drug development in this area, Dr. Kingsberg said.
Dr. Kingsberg reported consultant/advisory board work for Amag Pharmaceuticals, Duchesnay, Emotional Brain, EndoCeutics, Materna Medical, Palatin Technologies, Pfizer, Shionogi, TherapeuticsMD, Valeant Pharmaceuticals, and Viveve. She is on the speakers bureau for Valeant Pharmaceuticals and owns stock in Viveve.
[email protected]
On Twitter @maryellenny
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM NAMS 2017
VIDEO: Dr. Andrew Kaunitz’s top lessons from NAMS 2017
PHILADELPHIA – Andrew Kaunitz, MD, the chair of the 2017 scientific program committee for the annual meeting of the North American Menopause Society, shared his top take-home messages from the meeting.
New anabolic medications that increase bone mineral density and dramatically reduce fracture risk are in the pipeline, Dr. Kaunitz, a professor in the department of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Florida, Jacksonville, said in a video interview.
Another finding from the meeting is that type 2 diabetes, despite being associated with an increased body mass index, actually elevates a woman’s risk for fracture. “That was something new for me, and I think it was something new for a lot of the practitioners attending the NAMS meeting,” Dr. Kaunitz said.
The meeting also offered tips for managing polycystic ovarian syndrome in women who are in midlife, including the importance of screening for diabetes and assessing for lipid disorders. Additionally, attendees learned about the management of migraines in menopausal women and older reproductive-age women.
A well-attended session on breast imaging explored how breast tomosynthesis can reduce false positives and recalls, as well as how new technology can reduce the radiation exposure associated with tomosynthesis. The session also featured evidence that screening mammography has lower-than-reported sensitivity, but offered a hopeful note on the promise of improved sensitivity through molecular breast imaging.
Dr. Kaunitz reported consultant/advisory board work for Allergan, Amag Pharmaceuticals, Bayer, Mithra Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, and Shionogi. He has received grant/research support from Bayer, Radius Health, TherapeuticsMD, and Millendo Therapeutics.
[email protected]
On Twitter @maryellenny
PHILADELPHIA – Andrew Kaunitz, MD, the chair of the 2017 scientific program committee for the annual meeting of the North American Menopause Society, shared his top take-home messages from the meeting.
New anabolic medications that increase bone mineral density and dramatically reduce fracture risk are in the pipeline, Dr. Kaunitz, a professor in the department of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Florida, Jacksonville, said in a video interview.
Another finding from the meeting is that type 2 diabetes, despite being associated with an increased body mass index, actually elevates a woman’s risk for fracture. “That was something new for me, and I think it was something new for a lot of the practitioners attending the NAMS meeting,” Dr. Kaunitz said.
The meeting also offered tips for managing polycystic ovarian syndrome in women who are in midlife, including the importance of screening for diabetes and assessing for lipid disorders. Additionally, attendees learned about the management of migraines in menopausal women and older reproductive-age women.
A well-attended session on breast imaging explored how breast tomosynthesis can reduce false positives and recalls, as well as how new technology can reduce the radiation exposure associated with tomosynthesis. The session also featured evidence that screening mammography has lower-than-reported sensitivity, but offered a hopeful note on the promise of improved sensitivity through molecular breast imaging.
Dr. Kaunitz reported consultant/advisory board work for Allergan, Amag Pharmaceuticals, Bayer, Mithra Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, and Shionogi. He has received grant/research support from Bayer, Radius Health, TherapeuticsMD, and Millendo Therapeutics.
[email protected]
On Twitter @maryellenny
PHILADELPHIA – Andrew Kaunitz, MD, the chair of the 2017 scientific program committee for the annual meeting of the North American Menopause Society, shared his top take-home messages from the meeting.
New anabolic medications that increase bone mineral density and dramatically reduce fracture risk are in the pipeline, Dr. Kaunitz, a professor in the department of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Florida, Jacksonville, said in a video interview.
Another finding from the meeting is that type 2 diabetes, despite being associated with an increased body mass index, actually elevates a woman’s risk for fracture. “That was something new for me, and I think it was something new for a lot of the practitioners attending the NAMS meeting,” Dr. Kaunitz said.
The meeting also offered tips for managing polycystic ovarian syndrome in women who are in midlife, including the importance of screening for diabetes and assessing for lipid disorders. Additionally, attendees learned about the management of migraines in menopausal women and older reproductive-age women.
A well-attended session on breast imaging explored how breast tomosynthesis can reduce false positives and recalls, as well as how new technology can reduce the radiation exposure associated with tomosynthesis. The session also featured evidence that screening mammography has lower-than-reported sensitivity, but offered a hopeful note on the promise of improved sensitivity through molecular breast imaging.
Dr. Kaunitz reported consultant/advisory board work for Allergan, Amag Pharmaceuticals, Bayer, Mithra Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, and Shionogi. He has received grant/research support from Bayer, Radius Health, TherapeuticsMD, and Millendo Therapeutics.
[email protected]
On Twitter @maryellenny
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM NAMS 2017
VIDEO: Does genitourinary syndrome of menopause capture all the symptoms?
PHILADELPHIA – Genitourinary syndrome of menopause (GSM) replaced vulvovaginal atrophy in 2014 as a way to describe the changes to the genital and urinary tracts after menopause, but preliminary research shows it may be missing some symptoms.
In 2015, Amanda Clark, MD, a urogynecologist at the Kaiser Center for Health Research in Portland, Ore., and her colleagues surveyed women aged 55 years and older about their vulvar, vaginal, urinary, and sexual symptoms within 2 weeks of a well-woman visit to their primary care physician or gynecologist in the Kaiser system. In total, 1,533 provided valid data.
The researchers then used factor analysis to see if the symptoms matched up with GSM. If GSM is a true syndrome and only a single syndrome, then all of the factors would fit together in a one-factor model, Dr. Clark explained at the annual meeting of the North American Menopause Society. Instead, the researchers found that a three-factor model – with vulvovaginal symptoms of irritation and pain in one group, urinary symptoms in another group, and vaginal discharge and odor in a third group – fit best with the symptoms reported in their survey.
“This work is very preliminary and needs to be replicated in many other samples and looked at carefully,” Dr. Clark said in an interview. “But what we think is that genitourinary syndrome of menopause is a starting point.”
The study was funded by a Pfizer Independent Grant for Learning & Change and the North American Menopause Society. Dr. Clark reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
The video associated with this article is no longer available on this site. Please view all of our videos on the MDedge YouTube channel
[email protected]
On Twitter @maryellenny
PHILADELPHIA – Genitourinary syndrome of menopause (GSM) replaced vulvovaginal atrophy in 2014 as a way to describe the changes to the genital and urinary tracts after menopause, but preliminary research shows it may be missing some symptoms.
In 2015, Amanda Clark, MD, a urogynecologist at the Kaiser Center for Health Research in Portland, Ore., and her colleagues surveyed women aged 55 years and older about their vulvar, vaginal, urinary, and sexual symptoms within 2 weeks of a well-woman visit to their primary care physician or gynecologist in the Kaiser system. In total, 1,533 provided valid data.
The researchers then used factor analysis to see if the symptoms matched up with GSM. If GSM is a true syndrome and only a single syndrome, then all of the factors would fit together in a one-factor model, Dr. Clark explained at the annual meeting of the North American Menopause Society. Instead, the researchers found that a three-factor model – with vulvovaginal symptoms of irritation and pain in one group, urinary symptoms in another group, and vaginal discharge and odor in a third group – fit best with the symptoms reported in their survey.
“This work is very preliminary and needs to be replicated in many other samples and looked at carefully,” Dr. Clark said in an interview. “But what we think is that genitourinary syndrome of menopause is a starting point.”
The study was funded by a Pfizer Independent Grant for Learning & Change and the North American Menopause Society. Dr. Clark reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
The video associated with this article is no longer available on this site. Please view all of our videos on the MDedge YouTube channel
[email protected]
On Twitter @maryellenny
PHILADELPHIA – Genitourinary syndrome of menopause (GSM) replaced vulvovaginal atrophy in 2014 as a way to describe the changes to the genital and urinary tracts after menopause, but preliminary research shows it may be missing some symptoms.
In 2015, Amanda Clark, MD, a urogynecologist at the Kaiser Center for Health Research in Portland, Ore., and her colleagues surveyed women aged 55 years and older about their vulvar, vaginal, urinary, and sexual symptoms within 2 weeks of a well-woman visit to their primary care physician or gynecologist in the Kaiser system. In total, 1,533 provided valid data.
The researchers then used factor analysis to see if the symptoms matched up with GSM. If GSM is a true syndrome and only a single syndrome, then all of the factors would fit together in a one-factor model, Dr. Clark explained at the annual meeting of the North American Menopause Society. Instead, the researchers found that a three-factor model – with vulvovaginal symptoms of irritation and pain in one group, urinary symptoms in another group, and vaginal discharge and odor in a third group – fit best with the symptoms reported in their survey.
“This work is very preliminary and needs to be replicated in many other samples and looked at carefully,” Dr. Clark said in an interview. “But what we think is that genitourinary syndrome of menopause is a starting point.”
The study was funded by a Pfizer Independent Grant for Learning & Change and the North American Menopause Society. Dr. Clark reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
The video associated with this article is no longer available on this site. Please view all of our videos on the MDedge YouTube channel
[email protected]
On Twitter @maryellenny
AT NAMS 2017
VIDEO: What’s next in women’s health policy?
PHILADELPHIA – The Affordable Care Act (ACA) largely has delivered on its promises to expand access to care for women, but those benefits are in jeopardy because of actions by the Trump administration, one health policy expert said.
President Trump’s announcement that he plans to end the ACA’s cost-sharing reduction payments, which help subsidize the cost of insurance for low-income Americans, combined with new federal regulations expanding religious exemptions to the health law’s contraception mandate, would make it harder for women to obtain health care, said Michael Policar, MD, MPH, a clinical professor of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive sciences at the University of California, San Francisco.
In an interview at the annual meeting of the North American Menopause Society, Dr. Policar said it’s unclear whether these executive actions actually will go into effect because they are being challenged in court. But Dr. Policar said his concern is that this is just the “leading edge of more proposals and more changes” to come from the administration, which could target family planning funding.
Dr. Policar reported that he is a litigation consultant for Bayer.

[email protected]
On Twitter @maryellenny
PHILADELPHIA – The Affordable Care Act (ACA) largely has delivered on its promises to expand access to care for women, but those benefits are in jeopardy because of actions by the Trump administration, one health policy expert said.
President Trump’s announcement that he plans to end the ACA’s cost-sharing reduction payments, which help subsidize the cost of insurance for low-income Americans, combined with new federal regulations expanding religious exemptions to the health law’s contraception mandate, would make it harder for women to obtain health care, said Michael Policar, MD, MPH, a clinical professor of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive sciences at the University of California, San Francisco.
In an interview at the annual meeting of the North American Menopause Society, Dr. Policar said it’s unclear whether these executive actions actually will go into effect because they are being challenged in court. But Dr. Policar said his concern is that this is just the “leading edge of more proposals and more changes” to come from the administration, which could target family planning funding.
Dr. Policar reported that he is a litigation consultant for Bayer.

[email protected]
On Twitter @maryellenny
PHILADELPHIA – The Affordable Care Act (ACA) largely has delivered on its promises to expand access to care for women, but those benefits are in jeopardy because of actions by the Trump administration, one health policy expert said.
President Trump’s announcement that he plans to end the ACA’s cost-sharing reduction payments, which help subsidize the cost of insurance for low-income Americans, combined with new federal regulations expanding religious exemptions to the health law’s contraception mandate, would make it harder for women to obtain health care, said Michael Policar, MD, MPH, a clinical professor of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive sciences at the University of California, San Francisco.
In an interview at the annual meeting of the North American Menopause Society, Dr. Policar said it’s unclear whether these executive actions actually will go into effect because they are being challenged in court. But Dr. Policar said his concern is that this is just the “leading edge of more proposals and more changes” to come from the administration, which could target family planning funding.
Dr. Policar reported that he is a litigation consultant for Bayer.

[email protected]
On Twitter @maryellenny
AT NAMS 2017