User login
Blood disorders researcher is finalist for Trailblazer Prize
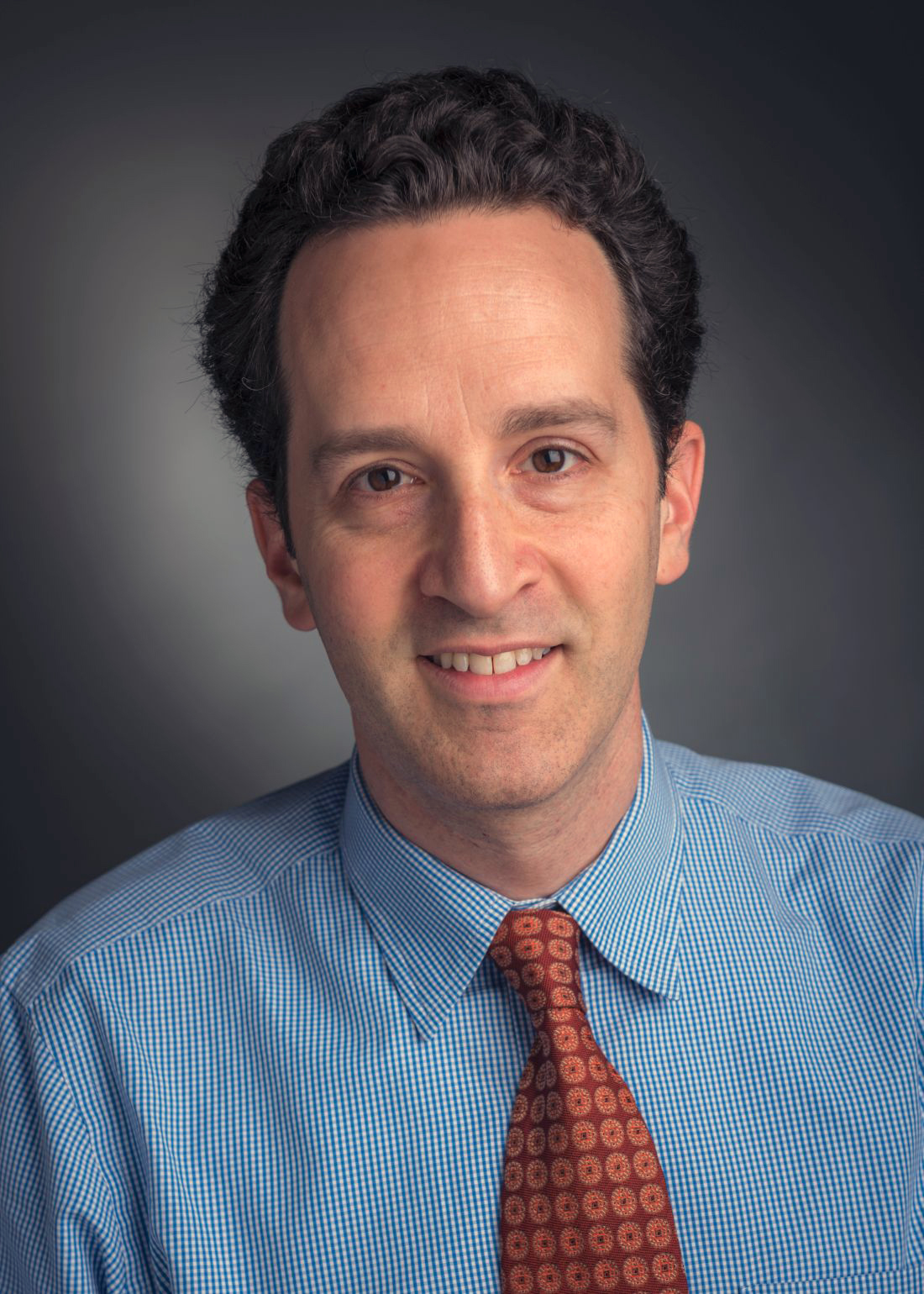
Daniel Bauer, MD, PhD, a pediatric hematologist and blood disorders researcher in Boston, is one of three finalists for the inaugural Trailblazer Prize for Clinician-Scientists, which is awarded by the Foundation for the National Institutes of Health.
Dr. Bauer, of Dana-Farber/Boston Children’s Cancer and Blood Disorders Center and Harvard Medical School, was selected based on his research using genome editing to tease out the causes of blood disorders, such as sickle cell disease and beta-thalassemia.
All three finalists for the Trailblazer Prize are early career clinician-scientists whose work has the potential to or has led to innovations in patient care, according to the Foundation for the National Institutes of Health.
The other two finalists are Jaehyuk Choi, MD, PhD, of Northwestern University in Chicago and Michael Fox, MD, PhD, of Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Boston.
Dr. Choi was selected for using genomics to identify mutations in skin cells that can lead to autoinflammatory diseases and cancer. Dr. Fox was selected for the development of innovative techniques to map human brain connectivity that can be used in novel treatments for Parkinson’s disease and depression.
The winner will be announced during a ceremony in Washington on Oct. 24, 2018, and will receive a $10,000 honorarium.
Daniel Bauer, MD, PhD, a pediatric hematologist and blood disorders researcher in Boston, is one of three finalists for the inaugural Trailblazer Prize for Clinician-Scientists, which is awarded by the Foundation for the National Institutes of Health.
Dr. Bauer, of Dana-Farber/Boston Children’s Cancer and Blood Disorders Center and Harvard Medical School, was selected based on his research using genome editing to tease out the causes of blood disorders, such as sickle cell disease and beta-thalassemia.
All three finalists for the Trailblazer Prize are early career clinician-scientists whose work has the potential to or has led to innovations in patient care, according to the Foundation for the National Institutes of Health.
The other two finalists are Jaehyuk Choi, MD, PhD, of Northwestern University in Chicago and Michael Fox, MD, PhD, of Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Boston.
Dr. Choi was selected for using genomics to identify mutations in skin cells that can lead to autoinflammatory diseases and cancer. Dr. Fox was selected for the development of innovative techniques to map human brain connectivity that can be used in novel treatments for Parkinson’s disease and depression.
The winner will be announced during a ceremony in Washington on Oct. 24, 2018, and will receive a $10,000 honorarium.
Daniel Bauer, MD, PhD, a pediatric hematologist and blood disorders researcher in Boston, is one of three finalists for the inaugural Trailblazer Prize for Clinician-Scientists, which is awarded by the Foundation for the National Institutes of Health.
Dr. Bauer, of Dana-Farber/Boston Children’s Cancer and Blood Disorders Center and Harvard Medical School, was selected based on his research using genome editing to tease out the causes of blood disorders, such as sickle cell disease and beta-thalassemia.
All three finalists for the Trailblazer Prize are early career clinician-scientists whose work has the potential to or has led to innovations in patient care, according to the Foundation for the National Institutes of Health.
The other two finalists are Jaehyuk Choi, MD, PhD, of Northwestern University in Chicago and Michael Fox, MD, PhD, of Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Boston.
Dr. Choi was selected for using genomics to identify mutations in skin cells that can lead to autoinflammatory diseases and cancer. Dr. Fox was selected for the development of innovative techniques to map human brain connectivity that can be used in novel treatments for Parkinson’s disease and depression.
The winner will be announced during a ceremony in Washington on Oct. 24, 2018, and will receive a $10,000 honorarium.
PET/CT accurately predicts MCL stage
Bone marrow involvement in mantle cell lymphoma could be assessed using just 18fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG)–PET/CT, according to findings from a small, retrospective study published in Clinical Lymphoma, Myeloma & Leukemia.
Rustain Morgan, MD, of the University of Colorado, Aurora, and his colleagues found that, at a certain threshold of bone marrow voxels in standard uptake value (SUV), there was 100% sensitivity and 80% specificity in determining bone marrow involvement in mantle cell lymphoma (MCL).
Currently, National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines call for bone marrow biopsy and whole body FDG PET/CT scan to complete an initial diagnosis of MCL.
“One of the most important factors for correct staging is the identification of bone marrow involvement, occurring in approximately 55% of patients with MCL, which classifies patients as advanced stage. However, accurate analysis of bone marrow involvement can be challenging due to sampling error,” the researchers wrote. “While bone marrow biopsy remains the gold standard, it is not a perfect standard given unilateral variability.”
In previous studies, FDG PET/CT was not considered sensitive enough to detect gastrointestinal or bone marrow involvement. However, these earlier studies used SUV maximum or mean or a visual assessment of the bone marrow activity, compared with hepatic uptake. To address this issue, the researchers developed a new method of examining SUV distribution throughout the pelvic bones by analyzing thousands of bone marrow voxels within the bilateral iliacs.
During the developmental phase, an institutional dataset of 11 patients with MCL was used to define the voxel-based analysis. These patients had undergone both unilateral iliac bone marrow biopsy and FDG PET/CT at the initial diagnosis. Then, FDG PET/CT scans from another 12 patients with MCL from a different institution were used to validate the developmental phase findings. Finally, a control group of 5 people with no known malignancy were referred for FDG PET/CT pulmonary nodule evaluation.
“The hypothesis of the study was that, if the bone marrow was involved by lymphoma, then there would be a small increase in the SUV of each voxel, reflecting involvement by the lymphoma. In order to capture such changes, we analyzed the percent of total voxels in SUV ranging from 0.75 to 1.20, in increments of 0.05, as this is where the greatest divergence was visually identified,” the researchers wrote. “The goal was to identify if a percentage of voxels at a set SUV could detect lymphomatous involvement.”
The researchers identified 10 candidate thresholds in the developmental phase; 4 of these performed better than the others in the validation phase. Using those thresholds, 10 of the 12 patients in the validation cohort could be correctly staged using FDG PET/CT.
Further analysis identified a single threshold that performed best: If greater than 38% of the voxels (averaging 1,734 voxels) demonstrated an SUV of less than 0.95, the sensitivity was 100% and the specificity was 80%.
The researchers acknowledged that the findings are limited because of the study’s small sample size and said the results should be validated in a larger trial.
There was no external funding for the study and the researchers reported having no financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Morgan R et al. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2018 Jul 4. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2018.06.024.
Bone marrow involvement in mantle cell lymphoma could be assessed using just 18fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG)–PET/CT, according to findings from a small, retrospective study published in Clinical Lymphoma, Myeloma & Leukemia.
Rustain Morgan, MD, of the University of Colorado, Aurora, and his colleagues found that, at a certain threshold of bone marrow voxels in standard uptake value (SUV), there was 100% sensitivity and 80% specificity in determining bone marrow involvement in mantle cell lymphoma (MCL).
Currently, National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines call for bone marrow biopsy and whole body FDG PET/CT scan to complete an initial diagnosis of MCL.
“One of the most important factors for correct staging is the identification of bone marrow involvement, occurring in approximately 55% of patients with MCL, which classifies patients as advanced stage. However, accurate analysis of bone marrow involvement can be challenging due to sampling error,” the researchers wrote. “While bone marrow biopsy remains the gold standard, it is not a perfect standard given unilateral variability.”
In previous studies, FDG PET/CT was not considered sensitive enough to detect gastrointestinal or bone marrow involvement. However, these earlier studies used SUV maximum or mean or a visual assessment of the bone marrow activity, compared with hepatic uptake. To address this issue, the researchers developed a new method of examining SUV distribution throughout the pelvic bones by analyzing thousands of bone marrow voxels within the bilateral iliacs.
During the developmental phase, an institutional dataset of 11 patients with MCL was used to define the voxel-based analysis. These patients had undergone both unilateral iliac bone marrow biopsy and FDG PET/CT at the initial diagnosis. Then, FDG PET/CT scans from another 12 patients with MCL from a different institution were used to validate the developmental phase findings. Finally, a control group of 5 people with no known malignancy were referred for FDG PET/CT pulmonary nodule evaluation.
“The hypothesis of the study was that, if the bone marrow was involved by lymphoma, then there would be a small increase in the SUV of each voxel, reflecting involvement by the lymphoma. In order to capture such changes, we analyzed the percent of total voxels in SUV ranging from 0.75 to 1.20, in increments of 0.05, as this is where the greatest divergence was visually identified,” the researchers wrote. “The goal was to identify if a percentage of voxels at a set SUV could detect lymphomatous involvement.”
The researchers identified 10 candidate thresholds in the developmental phase; 4 of these performed better than the others in the validation phase. Using those thresholds, 10 of the 12 patients in the validation cohort could be correctly staged using FDG PET/CT.
Further analysis identified a single threshold that performed best: If greater than 38% of the voxels (averaging 1,734 voxels) demonstrated an SUV of less than 0.95, the sensitivity was 100% and the specificity was 80%.
The researchers acknowledged that the findings are limited because of the study’s small sample size and said the results should be validated in a larger trial.
There was no external funding for the study and the researchers reported having no financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Morgan R et al. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2018 Jul 4. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2018.06.024.
Bone marrow involvement in mantle cell lymphoma could be assessed using just 18fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG)–PET/CT, according to findings from a small, retrospective study published in Clinical Lymphoma, Myeloma & Leukemia.
Rustain Morgan, MD, of the University of Colorado, Aurora, and his colleagues found that, at a certain threshold of bone marrow voxels in standard uptake value (SUV), there was 100% sensitivity and 80% specificity in determining bone marrow involvement in mantle cell lymphoma (MCL).
Currently, National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines call for bone marrow biopsy and whole body FDG PET/CT scan to complete an initial diagnosis of MCL.
“One of the most important factors for correct staging is the identification of bone marrow involvement, occurring in approximately 55% of patients with MCL, which classifies patients as advanced stage. However, accurate analysis of bone marrow involvement can be challenging due to sampling error,” the researchers wrote. “While bone marrow biopsy remains the gold standard, it is not a perfect standard given unilateral variability.”
In previous studies, FDG PET/CT was not considered sensitive enough to detect gastrointestinal or bone marrow involvement. However, these earlier studies used SUV maximum or mean or a visual assessment of the bone marrow activity, compared with hepatic uptake. To address this issue, the researchers developed a new method of examining SUV distribution throughout the pelvic bones by analyzing thousands of bone marrow voxels within the bilateral iliacs.
During the developmental phase, an institutional dataset of 11 patients with MCL was used to define the voxel-based analysis. These patients had undergone both unilateral iliac bone marrow biopsy and FDG PET/CT at the initial diagnosis. Then, FDG PET/CT scans from another 12 patients with MCL from a different institution were used to validate the developmental phase findings. Finally, a control group of 5 people with no known malignancy were referred for FDG PET/CT pulmonary nodule evaluation.
“The hypothesis of the study was that, if the bone marrow was involved by lymphoma, then there would be a small increase in the SUV of each voxel, reflecting involvement by the lymphoma. In order to capture such changes, we analyzed the percent of total voxels in SUV ranging from 0.75 to 1.20, in increments of 0.05, as this is where the greatest divergence was visually identified,” the researchers wrote. “The goal was to identify if a percentage of voxels at a set SUV could detect lymphomatous involvement.”
The researchers identified 10 candidate thresholds in the developmental phase; 4 of these performed better than the others in the validation phase. Using those thresholds, 10 of the 12 patients in the validation cohort could be correctly staged using FDG PET/CT.
Further analysis identified a single threshold that performed best: If greater than 38% of the voxels (averaging 1,734 voxels) demonstrated an SUV of less than 0.95, the sensitivity was 100% and the specificity was 80%.
The researchers acknowledged that the findings are limited because of the study’s small sample size and said the results should be validated in a larger trial.
There was no external funding for the study and the researchers reported having no financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Morgan R et al. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2018 Jul 4. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2018.06.024.
REPORTING FROM CLINICAL LYMPHOMA, MYELOMA & LEUKEMIA
Key clinical point:
Major finding: If greater than 38% of the voxels demonstrated an standard uptake value of less than 0.95, there was a sensitivity of 100% and a specificity of 80%.
Study details: A retrospective cohort study of 23 patients with mantle cell leukemia and 5 controls.
Disclosures: There was no external funding for the study and the researchers reported having no financial disclosures.
Source: Morgan R et al. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2018 Jul 4. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2018.06.024.
Ibrutinib stacks up well on safety in pooled analysis
in the treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma (CLL/SLL) and mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), according to findings from a pooled analysis.
Susan M. O’Brien, MD, of the University of California, Irvine, and her colleagues reported pooled data from four randomized, controlled trials that included a 756 patients treated with ibrutinib and 749 patients who received a comparator drug. Patients were treated for either CLL/SLL or MCL, and safety was assessed by comparing crude and exposure-adjusted incidence rates of reported adverse events (AEs).
The comparator drugs included intravenous ofatumumab, oral chlorambucil, intravenous bendamustine plus rituximab, and intravenous temsirolimus.
While adverse event data have been published for each study analyzed, the researchers noted that the pooled analysis allows for an “in-depth assessment of the frequency and severity of both common AEs as well as additional AEs of clinical interest.”
Ibrutinib-treated patients had low rates of treatment discontinuation, compared with comparator-treatment patients (27% vs. 85%), the researchers reported in Clinical Lymphoma, Myeloma & Leukemia. Most discontinuations were caused by disease progression.
In terms of AEs, the types of events reported were similar among the drugs, with the three most common being infections, gastrointestinal disorders, and general disorders/administration-site conditions.
Diarrhea, muscle spasms, and arthralgia were reported more often among ibrutinib-treated patients. The prevalence of the most common all-grade AEs generally decreased over time with ibrutinib, peaking in the first 3 months of treatment. For serious AEs, only atrial fibrillation was higher with ibrutinib than comparator drugs when adjusted for exposure.
SOURCE: O’Brien SM et al. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2018 Jun 27. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2018.06.016.
in the treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma (CLL/SLL) and mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), according to findings from a pooled analysis.
Susan M. O’Brien, MD, of the University of California, Irvine, and her colleagues reported pooled data from four randomized, controlled trials that included a 756 patients treated with ibrutinib and 749 patients who received a comparator drug. Patients were treated for either CLL/SLL or MCL, and safety was assessed by comparing crude and exposure-adjusted incidence rates of reported adverse events (AEs).
The comparator drugs included intravenous ofatumumab, oral chlorambucil, intravenous bendamustine plus rituximab, and intravenous temsirolimus.
While adverse event data have been published for each study analyzed, the researchers noted that the pooled analysis allows for an “in-depth assessment of the frequency and severity of both common AEs as well as additional AEs of clinical interest.”
Ibrutinib-treated patients had low rates of treatment discontinuation, compared with comparator-treatment patients (27% vs. 85%), the researchers reported in Clinical Lymphoma, Myeloma & Leukemia. Most discontinuations were caused by disease progression.
In terms of AEs, the types of events reported were similar among the drugs, with the three most common being infections, gastrointestinal disorders, and general disorders/administration-site conditions.
Diarrhea, muscle spasms, and arthralgia were reported more often among ibrutinib-treated patients. The prevalence of the most common all-grade AEs generally decreased over time with ibrutinib, peaking in the first 3 months of treatment. For serious AEs, only atrial fibrillation was higher with ibrutinib than comparator drugs when adjusted for exposure.
SOURCE: O’Brien SM et al. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2018 Jun 27. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2018.06.016.
in the treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma (CLL/SLL) and mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), according to findings from a pooled analysis.
Susan M. O’Brien, MD, of the University of California, Irvine, and her colleagues reported pooled data from four randomized, controlled trials that included a 756 patients treated with ibrutinib and 749 patients who received a comparator drug. Patients were treated for either CLL/SLL or MCL, and safety was assessed by comparing crude and exposure-adjusted incidence rates of reported adverse events (AEs).
The comparator drugs included intravenous ofatumumab, oral chlorambucil, intravenous bendamustine plus rituximab, and intravenous temsirolimus.
While adverse event data have been published for each study analyzed, the researchers noted that the pooled analysis allows for an “in-depth assessment of the frequency and severity of both common AEs as well as additional AEs of clinical interest.”
Ibrutinib-treated patients had low rates of treatment discontinuation, compared with comparator-treatment patients (27% vs. 85%), the researchers reported in Clinical Lymphoma, Myeloma & Leukemia. Most discontinuations were caused by disease progression.
In terms of AEs, the types of events reported were similar among the drugs, with the three most common being infections, gastrointestinal disorders, and general disorders/administration-site conditions.
Diarrhea, muscle spasms, and arthralgia were reported more often among ibrutinib-treated patients. The prevalence of the most common all-grade AEs generally decreased over time with ibrutinib, peaking in the first 3 months of treatment. For serious AEs, only atrial fibrillation was higher with ibrutinib than comparator drugs when adjusted for exposure.
SOURCE: O’Brien SM et al. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2018 Jun 27. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2018.06.016.
FROM CLINICAL LYMPHOMA, MYELOMA & LEUKEMIA
FDA issues guidance for hemophilia gene therapy development
The Food and Drug Administration issued its first-ever guidance on the development of human gene therapy for hemophilia.
The draft document provides a glimpse at the agency’s current thinking on clinical trial design and preclinical considerations in developing gene therapies. Specifically, it provides information to help companies set surrogate endpoints when seeking accelerated approval for hemophilia gene therapy products.
The hemophilia guidance is one of three disease-specific guidance documents. The other two clinical areas are retinal disorders and rare diseases.
FDA officials also issued updates to three more technical documents that deal with manufacturing of gene therapies.
The overall framework is similar to what FDA officials issued in 2017 for regenerative medicine. In a statement, FDA Commissioner Scott Gottlieb, MD, said the agency was responding to an increasing number of gene therapy approvals and anticipated development.
“Once just a theory, gene therapies are now a therapeutic reality for some patients,” Dr. Gottlieb said. “These platforms may have the potential to treat and cure some of our most intractable and vexing diseases. The policy framework we construct for how these products should be developed, reviewed by regulators, and reimbursed, will help set the stage for the continued advancement of this new market.”
The Food and Drug Administration issued its first-ever guidance on the development of human gene therapy for hemophilia.
The draft document provides a glimpse at the agency’s current thinking on clinical trial design and preclinical considerations in developing gene therapies. Specifically, it provides information to help companies set surrogate endpoints when seeking accelerated approval for hemophilia gene therapy products.
The hemophilia guidance is one of three disease-specific guidance documents. The other two clinical areas are retinal disorders and rare diseases.
FDA officials also issued updates to three more technical documents that deal with manufacturing of gene therapies.
The overall framework is similar to what FDA officials issued in 2017 for regenerative medicine. In a statement, FDA Commissioner Scott Gottlieb, MD, said the agency was responding to an increasing number of gene therapy approvals and anticipated development.
“Once just a theory, gene therapies are now a therapeutic reality for some patients,” Dr. Gottlieb said. “These platforms may have the potential to treat and cure some of our most intractable and vexing diseases. The policy framework we construct for how these products should be developed, reviewed by regulators, and reimbursed, will help set the stage for the continued advancement of this new market.”
The Food and Drug Administration issued its first-ever guidance on the development of human gene therapy for hemophilia.
The draft document provides a glimpse at the agency’s current thinking on clinical trial design and preclinical considerations in developing gene therapies. Specifically, it provides information to help companies set surrogate endpoints when seeking accelerated approval for hemophilia gene therapy products.
The hemophilia guidance is one of three disease-specific guidance documents. The other two clinical areas are retinal disorders and rare diseases.
FDA officials also issued updates to three more technical documents that deal with manufacturing of gene therapies.
The overall framework is similar to what FDA officials issued in 2017 for regenerative medicine. In a statement, FDA Commissioner Scott Gottlieb, MD, said the agency was responding to an increasing number of gene therapy approvals and anticipated development.
“Once just a theory, gene therapies are now a therapeutic reality for some patients,” Dr. Gottlieb said. “These platforms may have the potential to treat and cure some of our most intractable and vexing diseases. The policy framework we construct for how these products should be developed, reviewed by regulators, and reimbursed, will help set the stage for the continued advancement of this new market.”
Pfizer launches phase 3 gene therapy study in hemophilia B
Pfizer has begun early work on a phase 3 study of an investigational gene therapy to treat hemophilia B.
Pfizer, along with Spark Therapeutics, launched a phase 3 lead-in study at multiple centers to evaluate the efficacy and safety of current factor IX prophylaxis replacement therapy in the usual care setting. The efficacy data from the lead-in study will become the within-subject control group for patients who enroll in the next part of the
Fidanacogene elaparvovec is a vector containing a bioengineered adeno-associated virus capsid and a high-activity human coagulation factor IX gene. In an ongoing phase 1/2 trial of fidanacogene elaparvovec, all 15 participants with hemophilia B were able to discontinue routine infusion of factor IX concentrates without serious adverse events, according to data released by Pfizer and Spark Therapeutics in May 2018.
Pfizer has begun early work on a phase 3 study of an investigational gene therapy to treat hemophilia B.
Pfizer, along with Spark Therapeutics, launched a phase 3 lead-in study at multiple centers to evaluate the efficacy and safety of current factor IX prophylaxis replacement therapy in the usual care setting. The efficacy data from the lead-in study will become the within-subject control group for patients who enroll in the next part of the
Fidanacogene elaparvovec is a vector containing a bioengineered adeno-associated virus capsid and a high-activity human coagulation factor IX gene. In an ongoing phase 1/2 trial of fidanacogene elaparvovec, all 15 participants with hemophilia B were able to discontinue routine infusion of factor IX concentrates without serious adverse events, according to data released by Pfizer and Spark Therapeutics in May 2018.
Pfizer has begun early work on a phase 3 study of an investigational gene therapy to treat hemophilia B.
Pfizer, along with Spark Therapeutics, launched a phase 3 lead-in study at multiple centers to evaluate the efficacy and safety of current factor IX prophylaxis replacement therapy in the usual care setting. The efficacy data from the lead-in study will become the within-subject control group for patients who enroll in the next part of the
Fidanacogene elaparvovec is a vector containing a bioengineered adeno-associated virus capsid and a high-activity human coagulation factor IX gene. In an ongoing phase 1/2 trial of fidanacogene elaparvovec, all 15 participants with hemophilia B were able to discontinue routine infusion of factor IX concentrates without serious adverse events, according to data released by Pfizer and Spark Therapeutics in May 2018.
Lab results may help predict complications in ALL treatment
(ALL) who were treated with four-drug induction therapy.
Kasper Warrick, MD, and his colleagues at Indiana University in Indianapolis reported findings from a retrospective study of 73 ALL patients at their hospital. They performed chart reviews comparing a cohort of 42 patients who were discharged on day 4 of their induction treatment with 31 similar patients who had a longer hospital stay or admission to the intensive care unit. The report was published in Leukemia Research.
Univariate analysis found that patients with a longer length of stay were more likely to have a fever, pretransfusion hemoglobin of less than 8 g/dL, lower serum bicarbonate values, abnormal serum calcium, and abnormal serum phosphate. Multivariate stepwise logistic regression found that low serum bicarbonate and a lower platelet count on day 4 of admission was predictive of a prolonged hospital stay. About a third of patients from each group had an unplanned readmission within 30 days.
The researchers concluded that early discharge is safe in only a subgroup of high-risk ALL patients undergoing induction chemotherapy. “Treating physicians could opt for a discharge only after normalization of electrolyte abnormalities and renal functions, and when no transfusion support is needed (stable hematocrit and platelet count),” they wrote. Even in those cases, they recommended “aggressive and close outpatient follow” since patients are vulnerable to complications and readmissions.
SOURCE: Warrick K et al. Leuk Res. 2018 Jun 30:71:36-42.
(ALL) who were treated with four-drug induction therapy.
Kasper Warrick, MD, and his colleagues at Indiana University in Indianapolis reported findings from a retrospective study of 73 ALL patients at their hospital. They performed chart reviews comparing a cohort of 42 patients who were discharged on day 4 of their induction treatment with 31 similar patients who had a longer hospital stay or admission to the intensive care unit. The report was published in Leukemia Research.
Univariate analysis found that patients with a longer length of stay were more likely to have a fever, pretransfusion hemoglobin of less than 8 g/dL, lower serum bicarbonate values, abnormal serum calcium, and abnormal serum phosphate. Multivariate stepwise logistic regression found that low serum bicarbonate and a lower platelet count on day 4 of admission was predictive of a prolonged hospital stay. About a third of patients from each group had an unplanned readmission within 30 days.
The researchers concluded that early discharge is safe in only a subgroup of high-risk ALL patients undergoing induction chemotherapy. “Treating physicians could opt for a discharge only after normalization of electrolyte abnormalities and renal functions, and when no transfusion support is needed (stable hematocrit and platelet count),” they wrote. Even in those cases, they recommended “aggressive and close outpatient follow” since patients are vulnerable to complications and readmissions.
SOURCE: Warrick K et al. Leuk Res. 2018 Jun 30:71:36-42.
(ALL) who were treated with four-drug induction therapy.
Kasper Warrick, MD, and his colleagues at Indiana University in Indianapolis reported findings from a retrospective study of 73 ALL patients at their hospital. They performed chart reviews comparing a cohort of 42 patients who were discharged on day 4 of their induction treatment with 31 similar patients who had a longer hospital stay or admission to the intensive care unit. The report was published in Leukemia Research.
Univariate analysis found that patients with a longer length of stay were more likely to have a fever, pretransfusion hemoglobin of less than 8 g/dL, lower serum bicarbonate values, abnormal serum calcium, and abnormal serum phosphate. Multivariate stepwise logistic regression found that low serum bicarbonate and a lower platelet count on day 4 of admission was predictive of a prolonged hospital stay. About a third of patients from each group had an unplanned readmission within 30 days.
The researchers concluded that early discharge is safe in only a subgroup of high-risk ALL patients undergoing induction chemotherapy. “Treating physicians could opt for a discharge only after normalization of electrolyte abnormalities and renal functions, and when no transfusion support is needed (stable hematocrit and platelet count),” they wrote. Even in those cases, they recommended “aggressive and close outpatient follow” since patients are vulnerable to complications and readmissions.
SOURCE: Warrick K et al. Leuk Res. 2018 Jun 30:71:36-42.
FROM LEUKEMIA RESEARCH
New guideline for managing MCL
Rituximab should be included in first-line chemotherapy when treating mantle cell lymphoma, according to a new management guideline from the British Society for Haematology.
The best outcome data is for the R-CHOP regimen (rituximab plus cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisolone) followed by maintenance treatment with rituximab, wrote Pamela McKay, MD, of Beatson West of Scotland Cancer Centre in Glasgow, and her colleagues. The report was published in the British Journal of Haematology. But the combination of rituximab and bendamustine is also effective and a more favorable safety profile, according to the guideline. Single agent rituximab is not recommended.
At relapse, the guideline calls on physicians to take an individualized approach based on age, comorbidities, performance status, and response to prior therapy. Some options to consider include ibrutinib as a single agent or rituximab plus chemotherapy. The authors cautioned that there is little evidence to support maintenance rituximab after relapse treatment.
The guideline also explores the role of autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT) and allogeneic SCT (alloSCT). The authors recommend that ASCT be considered as consolidation of first-line therapy for patients who are fit for intensive therapy. AlloSCT is a viable option in second remission among fit patients who have an appropriate donor and it may also be effective as a rescue therapy for patients who relapse after ASCT. But alloSCT is appropriate only as a first-line therapy for high-risk patients and is best used as part of a clinical trial, according to the recommendations.
The British Society of Haematology previously issued guidance on mantle cell lymphoma in 2012, but the updated document includes new drug therapeutic options and transplant data. The guideline includes a therapeutic algorithm to assist physicians in choosing first-line therapy, options after first relapse, and management in the case of higher relapse.
The guideline authors reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: McKay P et al. Br J Haematol. 2018 Jul;182(1):46-62.
Rituximab should be included in first-line chemotherapy when treating mantle cell lymphoma, according to a new management guideline from the British Society for Haematology.
The best outcome data is for the R-CHOP regimen (rituximab plus cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisolone) followed by maintenance treatment with rituximab, wrote Pamela McKay, MD, of Beatson West of Scotland Cancer Centre in Glasgow, and her colleagues. The report was published in the British Journal of Haematology. But the combination of rituximab and bendamustine is also effective and a more favorable safety profile, according to the guideline. Single agent rituximab is not recommended.
At relapse, the guideline calls on physicians to take an individualized approach based on age, comorbidities, performance status, and response to prior therapy. Some options to consider include ibrutinib as a single agent or rituximab plus chemotherapy. The authors cautioned that there is little evidence to support maintenance rituximab after relapse treatment.
The guideline also explores the role of autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT) and allogeneic SCT (alloSCT). The authors recommend that ASCT be considered as consolidation of first-line therapy for patients who are fit for intensive therapy. AlloSCT is a viable option in second remission among fit patients who have an appropriate donor and it may also be effective as a rescue therapy for patients who relapse after ASCT. But alloSCT is appropriate only as a first-line therapy for high-risk patients and is best used as part of a clinical trial, according to the recommendations.
The British Society of Haematology previously issued guidance on mantle cell lymphoma in 2012, but the updated document includes new drug therapeutic options and transplant data. The guideline includes a therapeutic algorithm to assist physicians in choosing first-line therapy, options after first relapse, and management in the case of higher relapse.
The guideline authors reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: McKay P et al. Br J Haematol. 2018 Jul;182(1):46-62.
Rituximab should be included in first-line chemotherapy when treating mantle cell lymphoma, according to a new management guideline from the British Society for Haematology.
The best outcome data is for the R-CHOP regimen (rituximab plus cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisolone) followed by maintenance treatment with rituximab, wrote Pamela McKay, MD, of Beatson West of Scotland Cancer Centre in Glasgow, and her colleagues. The report was published in the British Journal of Haematology. But the combination of rituximab and bendamustine is also effective and a more favorable safety profile, according to the guideline. Single agent rituximab is not recommended.
At relapse, the guideline calls on physicians to take an individualized approach based on age, comorbidities, performance status, and response to prior therapy. Some options to consider include ibrutinib as a single agent or rituximab plus chemotherapy. The authors cautioned that there is little evidence to support maintenance rituximab after relapse treatment.
The guideline also explores the role of autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT) and allogeneic SCT (alloSCT). The authors recommend that ASCT be considered as consolidation of first-line therapy for patients who are fit for intensive therapy. AlloSCT is a viable option in second remission among fit patients who have an appropriate donor and it may also be effective as a rescue therapy for patients who relapse after ASCT. But alloSCT is appropriate only as a first-line therapy for high-risk patients and is best used as part of a clinical trial, according to the recommendations.
The British Society of Haematology previously issued guidance on mantle cell lymphoma in 2012, but the updated document includes new drug therapeutic options and transplant data. The guideline includes a therapeutic algorithm to assist physicians in choosing first-line therapy, options after first relapse, and management in the case of higher relapse.
The guideline authors reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: McKay P et al. Br J Haematol. 2018 Jul;182(1):46-62.
FROM THE BRITISH JOURNAL OF HAEMATOLOGY
Promising phase 3 results for ixazomib in multiple myeloma
who had responded to high-dose therapy and autologous stem cell transplant.
The drug’s sponsor, Takeda, announced that the oral proteasome inhibitor had met the primary endpoint – progression-free survival versus placebo – in the randomized, phase 3 TOURMALINE-MM3 study. They also reported that adverse events were consistent with previously reported results for single-agent use of ixazomib and that there were no new safety signals.
Full study results will be presented at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology. Company officials plan to submit the trial data to the Food and Drug Administration and regulatory agencies around the world to gain approval of ixazomib as a single-agent maintenance therapy, according to a Takeda announcement.
The TOURMALINE-MM3 study is a double-blind study of 656 patients with multiple myeloma who have had complete response, very good partial response, or partial response to induction therapy followed by high-dose therapy and autologous stem cell transplant. In addition to progression-free survival, the trial assessed overall survival.
who had responded to high-dose therapy and autologous stem cell transplant.
The drug’s sponsor, Takeda, announced that the oral proteasome inhibitor had met the primary endpoint – progression-free survival versus placebo – in the randomized, phase 3 TOURMALINE-MM3 study. They also reported that adverse events were consistent with previously reported results for single-agent use of ixazomib and that there were no new safety signals.
Full study results will be presented at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology. Company officials plan to submit the trial data to the Food and Drug Administration and regulatory agencies around the world to gain approval of ixazomib as a single-agent maintenance therapy, according to a Takeda announcement.
The TOURMALINE-MM3 study is a double-blind study of 656 patients with multiple myeloma who have had complete response, very good partial response, or partial response to induction therapy followed by high-dose therapy and autologous stem cell transplant. In addition to progression-free survival, the trial assessed overall survival.
who had responded to high-dose therapy and autologous stem cell transplant.
The drug’s sponsor, Takeda, announced that the oral proteasome inhibitor had met the primary endpoint – progression-free survival versus placebo – in the randomized, phase 3 TOURMALINE-MM3 study. They also reported that adverse events were consistent with previously reported results for single-agent use of ixazomib and that there were no new safety signals.
Full study results will be presented at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology. Company officials plan to submit the trial data to the Food and Drug Administration and regulatory agencies around the world to gain approval of ixazomib as a single-agent maintenance therapy, according to a Takeda announcement.
The TOURMALINE-MM3 study is a double-blind study of 656 patients with multiple myeloma who have had complete response, very good partial response, or partial response to induction therapy followed by high-dose therapy and autologous stem cell transplant. In addition to progression-free survival, the trial assessed overall survival.
European Medicines Agency recommends CAR T-cell approvals
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) has recommended a handful of hematology medications for approval, including two chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapies.
All of the drugs must next be approved by the European Commission in order to be marketed to patients throughout Europe.
At the end of June, the EMA’s Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use tisagenlecleucel (Kymriah) and axicabtagene ciloleucel (Yescarta).
The EMA approval recommendations come with risk management measures to address the potential for cytokine release syndrome with both of these treatments. Drug makers must use a patient registry to monitor the long-term safety and efficacy of the therapies.
The EMA is also recommending approval of caplacizumab for acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura, vonicog alfa for the treatment of von Willebrand disease, and daunorubicin/cytarabine for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia.
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) has recommended a handful of hematology medications for approval, including two chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapies.
All of the drugs must next be approved by the European Commission in order to be marketed to patients throughout Europe.
At the end of June, the EMA’s Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use tisagenlecleucel (Kymriah) and axicabtagene ciloleucel (Yescarta).
The EMA approval recommendations come with risk management measures to address the potential for cytokine release syndrome with both of these treatments. Drug makers must use a patient registry to monitor the long-term safety and efficacy of the therapies.
The EMA is also recommending approval of caplacizumab for acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura, vonicog alfa for the treatment of von Willebrand disease, and daunorubicin/cytarabine for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia.
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) has recommended a handful of hematology medications for approval, including two chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapies.
All of the drugs must next be approved by the European Commission in order to be marketed to patients throughout Europe.
At the end of June, the EMA’s Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use tisagenlecleucel (Kymriah) and axicabtagene ciloleucel (Yescarta).
The EMA approval recommendations come with risk management measures to address the potential for cytokine release syndrome with both of these treatments. Drug makers must use a patient registry to monitor the long-term safety and efficacy of the therapies.
The EMA is also recommending approval of caplacizumab for acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura, vonicog alfa for the treatment of von Willebrand disease, and daunorubicin/cytarabine for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia.
Bortezomib plus vorinostat shows modest response in MCL
but was less impressive among patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
Victor Yazbeck, MD, of the Massey Cancer Center at Virginia Commonwealth University in Richmond, and his colleagues reported the findings from the multicenter, nonrandomized, phase 2 trial with 65 treated patients. The trial included three cohorts: 22 patients with MCL and no prior treatment with bortezomib; 4 patients with MCL and prior treatment with bortezomib; and 39 patients with relapsed or refractory DLBCL and no prior bortezomib.
The best results were seen among MCL patients with no prior bortezomib treatment, with an overall response rate of 31.8% and a median progression-free survival (PFS) of 7.6 months. Responses were limited among the DLBCL cohort, which had an overall response rate of 7.7% and a median PFS of just 1.8 months. Among MCL patients who had received prior bortezomib treatment, there were no responses.
From a safety perspective, the combination treatment was well tolerated. The most common grade 3 and 4 hematologic toxicities were thrombocytopenia, lymphopenia, and neutropenia. There was one death among the DLBCL patients and it was unclear if it was related to treatment or progression of disease.
“Patients with MCL had a higher [overall response rate] compared to those with DLBCL, most likely due to the single-agent activity of bortezomib in MCL,” the researchers wrote. “Overall, the synergism previously demonstrated in preclinical models could not be confirmed.”
The study was supported by the Southeast Phase 2 Consortium and by a grant from the National Cancer Institute. Dr. Yazbeck reported having no financial disclosures. One of his coauthors is an employee of Amgen and owns Amgen stock. Another coauthor receives research support from Takeda, Celgene, Karyopharm Therapeutics, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Merck, and Signal Genetics.
SOURCE: Yazbeck V et al. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2018 Jun 6. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2018.05.023.
but was less impressive among patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
Victor Yazbeck, MD, of the Massey Cancer Center at Virginia Commonwealth University in Richmond, and his colleagues reported the findings from the multicenter, nonrandomized, phase 2 trial with 65 treated patients. The trial included three cohorts: 22 patients with MCL and no prior treatment with bortezomib; 4 patients with MCL and prior treatment with bortezomib; and 39 patients with relapsed or refractory DLBCL and no prior bortezomib.
The best results were seen among MCL patients with no prior bortezomib treatment, with an overall response rate of 31.8% and a median progression-free survival (PFS) of 7.6 months. Responses were limited among the DLBCL cohort, which had an overall response rate of 7.7% and a median PFS of just 1.8 months. Among MCL patients who had received prior bortezomib treatment, there were no responses.
From a safety perspective, the combination treatment was well tolerated. The most common grade 3 and 4 hematologic toxicities were thrombocytopenia, lymphopenia, and neutropenia. There was one death among the DLBCL patients and it was unclear if it was related to treatment or progression of disease.
“Patients with MCL had a higher [overall response rate] compared to those with DLBCL, most likely due to the single-agent activity of bortezomib in MCL,” the researchers wrote. “Overall, the synergism previously demonstrated in preclinical models could not be confirmed.”
The study was supported by the Southeast Phase 2 Consortium and by a grant from the National Cancer Institute. Dr. Yazbeck reported having no financial disclosures. One of his coauthors is an employee of Amgen and owns Amgen stock. Another coauthor receives research support from Takeda, Celgene, Karyopharm Therapeutics, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Merck, and Signal Genetics.
SOURCE: Yazbeck V et al. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2018 Jun 6. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2018.05.023.
but was less impressive among patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
Victor Yazbeck, MD, of the Massey Cancer Center at Virginia Commonwealth University in Richmond, and his colleagues reported the findings from the multicenter, nonrandomized, phase 2 trial with 65 treated patients. The trial included three cohorts: 22 patients with MCL and no prior treatment with bortezomib; 4 patients with MCL and prior treatment with bortezomib; and 39 patients with relapsed or refractory DLBCL and no prior bortezomib.
The best results were seen among MCL patients with no prior bortezomib treatment, with an overall response rate of 31.8% and a median progression-free survival (PFS) of 7.6 months. Responses were limited among the DLBCL cohort, which had an overall response rate of 7.7% and a median PFS of just 1.8 months. Among MCL patients who had received prior bortezomib treatment, there were no responses.
From a safety perspective, the combination treatment was well tolerated. The most common grade 3 and 4 hematologic toxicities were thrombocytopenia, lymphopenia, and neutropenia. There was one death among the DLBCL patients and it was unclear if it was related to treatment or progression of disease.
“Patients with MCL had a higher [overall response rate] compared to those with DLBCL, most likely due to the single-agent activity of bortezomib in MCL,” the researchers wrote. “Overall, the synergism previously demonstrated in preclinical models could not be confirmed.”
The study was supported by the Southeast Phase 2 Consortium and by a grant from the National Cancer Institute. Dr. Yazbeck reported having no financial disclosures. One of his coauthors is an employee of Amgen and owns Amgen stock. Another coauthor receives research support from Takeda, Celgene, Karyopharm Therapeutics, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Merck, and Signal Genetics.
SOURCE: Yazbeck V et al. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2018 Jun 6. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2018.05.023.
FROM CLINICAL LYMPHOMA, MYELOMA AND LEUKEMIA