User login
Emergency Ultrasound: Ultrasound-Guided Femoral Nerve Block
Case Scenario
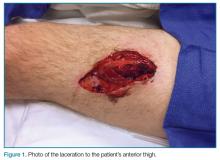
A young man presented to the ED for evaluation of a large laceration to the anterior thigh that resulted from an industrial accident (Figure 1).
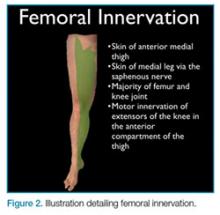
Femoral nerve blocks are useful in a variety of clinical scenarios, including fractures of the femur or hip1 and laceration repairs (Figure 2).
Identifying the Femoral Nerve on Ultrasound
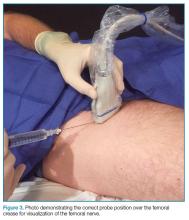
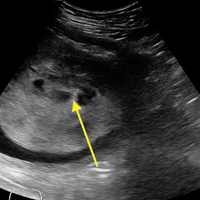
To perform this nerve block, one must recall the anatomy of femoral central-line placement. The femoral nerve lies lateral to the femoral artery and vein. The high-frequency probe should be placed over the femoral crease (Figure 3).
Performing the Block
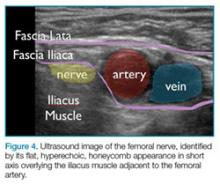
An ultrasound-guided femoral nerve block can be performed using a 22-gauge blunt tip spinal needle, and an in-plane or out-of-plane technique can be employed. We prefer using an in-plane technique because the entire shaft of the needle can be visualized as it approaches the nerve. Anatomically, the femoral nerve lies in a separate fascial plane from the artery and vein, beneath the fascia iliaca (Figure 4). You can use this anatomic location of the femoral nerve to your advantage when performing the block. The needle can be advanced to a target slightly lateral to the nerve until it pops beneath the fascia iliaca. On the ultrasound, you can monitor the spread of anesthetic as it is injected. If the needle is in the right location, the hypoechoic fluid will spread medially toward the nerve, but will not track around the artery or vein. At least 15 cc to 20 cc of local anesthetic is typically required.2,3 If you prefer, the anesthetic can be diluted in normal saline, in a 1:1 ratio, to achieve adequate volume.
If you do not see the anesthetic spread during the injection, you should stop and check the needle placement, as it may be intravascular. Using a more lateral approach, targeting the injection at the fascial plane, rather than the nerve, helps to avoid direct intraneural injection or contact with the nerve—and it keeps the needle far away from the femoral vascular bundle.
Safety Considerations
As with any technique, prior to the procedure, aseptic measures should be taken, including the use of a sterile probe cover and sterile gloves. All patients undergoing ultrasound-guided nerve blocks proximal to the wrist or ankle should be placed on a cardiac monitor. In addition, intralipid emulsion should be readily available for administration in the unlikely event there is inadvertent intravascular injection of local anesthetic and cardiovascular collapse occurs.
Summary
With practice, ultrasound guidance can improve the procedural success of femoral nerve blocks and decrease the risk of nerve injury compared to blind nerve blocks
1. Dickman E, Pushkar I, Likourezos A, et al. Ultrasound-guided nerve blocks for intracapsular and extracapsular hip fractures. Am J Emerg Med. 2016;34(3):586-589.
2. Femoral nerve block. In: Hadzic A, Carrera A, Clark T, et al, eds. Hadzic’s Peripheral Nerve Blocks: An Anatomy for Ultrasound-Guided Regional Anesthesia. 2nd ed. New York, NY: The McGraw Hill Companies, Inc; 2012:267-279.
3. Ultrasound-guided femoral nerve block. In: Hadzic A, Carrera A, Clark T, et al, eds. Hadzic’s Peripheral Nerve Blocks: An Anatomy for Ultrasound-Guided Regional Anesthesia. 2nd ed. New York, NY: The McGraw Hill Companies, Inc; 2012:397-404.
Case Scenario
A young man presented to the ED for evaluation of a large laceration to the anterior thigh that resulted from an industrial accident (Figure 1).
Femoral nerve blocks are useful in a variety of clinical scenarios, including fractures of the femur or hip1 and laceration repairs (Figure 2).
Identifying the Femoral Nerve on Ultrasound
To perform this nerve block, one must recall the anatomy of femoral central-line placement. The femoral nerve lies lateral to the femoral artery and vein. The high-frequency probe should be placed over the femoral crease (Figure 3).
Performing the Block
An ultrasound-guided femoral nerve block can be performed using a 22-gauge blunt tip spinal needle, and an in-plane or out-of-plane technique can be employed. We prefer using an in-plane technique because the entire shaft of the needle can be visualized as it approaches the nerve. Anatomically, the femoral nerve lies in a separate fascial plane from the artery and vein, beneath the fascia iliaca (Figure 4). You can use this anatomic location of the femoral nerve to your advantage when performing the block. The needle can be advanced to a target slightly lateral to the nerve until it pops beneath the fascia iliaca. On the ultrasound, you can monitor the spread of anesthetic as it is injected. If the needle is in the right location, the hypoechoic fluid will spread medially toward the nerve, but will not track around the artery or vein. At least 15 cc to 20 cc of local anesthetic is typically required.2,3 If you prefer, the anesthetic can be diluted in normal saline, in a 1:1 ratio, to achieve adequate volume.
If you do not see the anesthetic spread during the injection, you should stop and check the needle placement, as it may be intravascular. Using a more lateral approach, targeting the injection at the fascial plane, rather than the nerve, helps to avoid direct intraneural injection or contact with the nerve—and it keeps the needle far away from the femoral vascular bundle.
Safety Considerations
As with any technique, prior to the procedure, aseptic measures should be taken, including the use of a sterile probe cover and sterile gloves. All patients undergoing ultrasound-guided nerve blocks proximal to the wrist or ankle should be placed on a cardiac monitor. In addition, intralipid emulsion should be readily available for administration in the unlikely event there is inadvertent intravascular injection of local anesthetic and cardiovascular collapse occurs.
Summary
With practice, ultrasound guidance can improve the procedural success of femoral nerve blocks and decrease the risk of nerve injury compared to blind nerve blocks
Case Scenario
A young man presented to the ED for evaluation of a large laceration to the anterior thigh that resulted from an industrial accident (Figure 1).
Femoral nerve blocks are useful in a variety of clinical scenarios, including fractures of the femur or hip1 and laceration repairs (Figure 2).
Identifying the Femoral Nerve on Ultrasound
To perform this nerve block, one must recall the anatomy of femoral central-line placement. The femoral nerve lies lateral to the femoral artery and vein. The high-frequency probe should be placed over the femoral crease (Figure 3).
Performing the Block
An ultrasound-guided femoral nerve block can be performed using a 22-gauge blunt tip spinal needle, and an in-plane or out-of-plane technique can be employed. We prefer using an in-plane technique because the entire shaft of the needle can be visualized as it approaches the nerve. Anatomically, the femoral nerve lies in a separate fascial plane from the artery and vein, beneath the fascia iliaca (Figure 4). You can use this anatomic location of the femoral nerve to your advantage when performing the block. The needle can be advanced to a target slightly lateral to the nerve until it pops beneath the fascia iliaca. On the ultrasound, you can monitor the spread of anesthetic as it is injected. If the needle is in the right location, the hypoechoic fluid will spread medially toward the nerve, but will not track around the artery or vein. At least 15 cc to 20 cc of local anesthetic is typically required.2,3 If you prefer, the anesthetic can be diluted in normal saline, in a 1:1 ratio, to achieve adequate volume.
If you do not see the anesthetic spread during the injection, you should stop and check the needle placement, as it may be intravascular. Using a more lateral approach, targeting the injection at the fascial plane, rather than the nerve, helps to avoid direct intraneural injection or contact with the nerve—and it keeps the needle far away from the femoral vascular bundle.
Safety Considerations
As with any technique, prior to the procedure, aseptic measures should be taken, including the use of a sterile probe cover and sterile gloves. All patients undergoing ultrasound-guided nerve blocks proximal to the wrist or ankle should be placed on a cardiac monitor. In addition, intralipid emulsion should be readily available for administration in the unlikely event there is inadvertent intravascular injection of local anesthetic and cardiovascular collapse occurs.
Summary
With practice, ultrasound guidance can improve the procedural success of femoral nerve blocks and decrease the risk of nerve injury compared to blind nerve blocks
1. Dickman E, Pushkar I, Likourezos A, et al. Ultrasound-guided nerve blocks for intracapsular and extracapsular hip fractures. Am J Emerg Med. 2016;34(3):586-589.
2. Femoral nerve block. In: Hadzic A, Carrera A, Clark T, et al, eds. Hadzic’s Peripheral Nerve Blocks: An Anatomy for Ultrasound-Guided Regional Anesthesia. 2nd ed. New York, NY: The McGraw Hill Companies, Inc; 2012:267-279.
3. Ultrasound-guided femoral nerve block. In: Hadzic A, Carrera A, Clark T, et al, eds. Hadzic’s Peripheral Nerve Blocks: An Anatomy for Ultrasound-Guided Regional Anesthesia. 2nd ed. New York, NY: The McGraw Hill Companies, Inc; 2012:397-404.
1. Dickman E, Pushkar I, Likourezos A, et al. Ultrasound-guided nerve blocks for intracapsular and extracapsular hip fractures. Am J Emerg Med. 2016;34(3):586-589.
2. Femoral nerve block. In: Hadzic A, Carrera A, Clark T, et al, eds. Hadzic’s Peripheral Nerve Blocks: An Anatomy for Ultrasound-Guided Regional Anesthesia. 2nd ed. New York, NY: The McGraw Hill Companies, Inc; 2012:267-279.
3. Ultrasound-guided femoral nerve block. In: Hadzic A, Carrera A, Clark T, et al, eds. Hadzic’s Peripheral Nerve Blocks: An Anatomy for Ultrasound-Guided Regional Anesthesia. 2nd ed. New York, NY: The McGraw Hill Companies, Inc; 2012:397-404.