User login
The Signs That Can’t Be Ignored
ANSWER
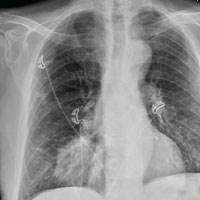
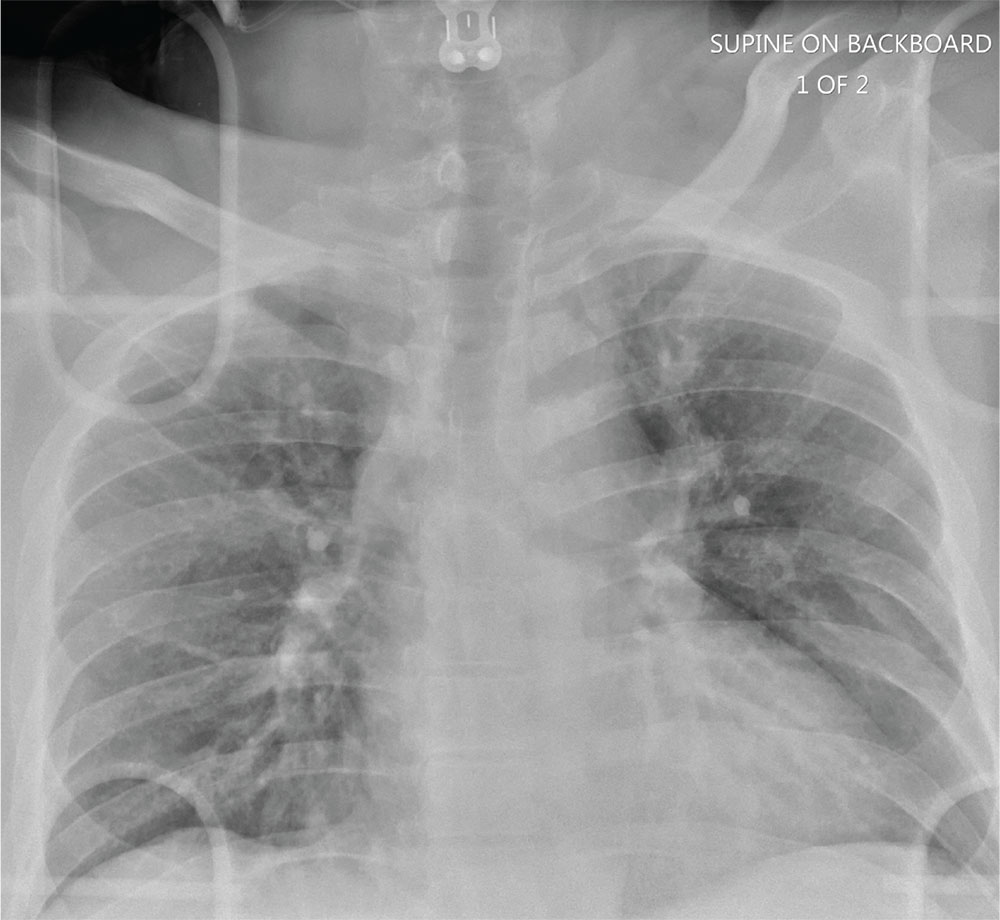
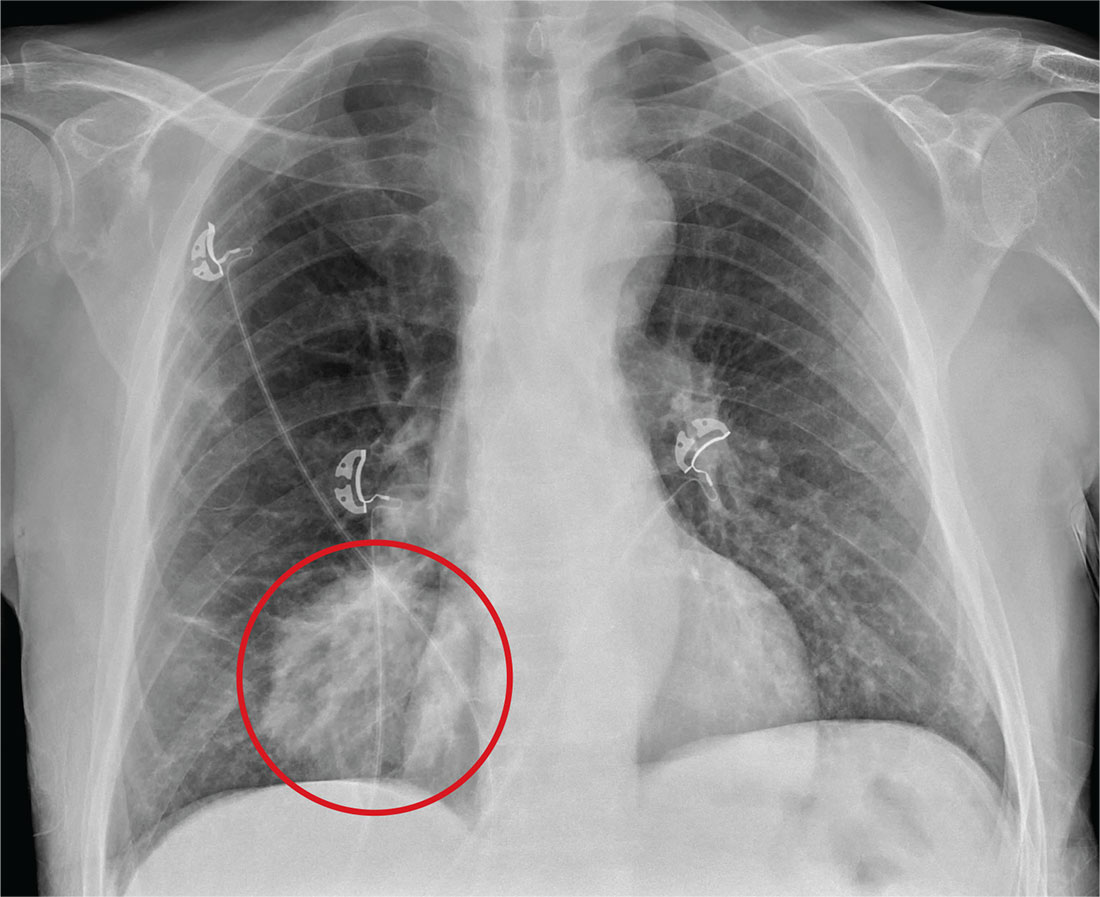
The radiograph shows a large, round hyperdensity within the right lower lobe. This lesion is highly concerning for malignancy and warrants further work-up.
With his gastrointestinal bleed and hypercoagulability from warfarin toxicity, the patient required admission anyway. Subsequent biopsy confirmed the presence of a primary lung carcinoma.

ANSWER
The radiograph shows a large, round hyperdensity within the right lower lobe. This lesion is highly concerning for malignancy and warrants further work-up.
With his gastrointestinal bleed and hypercoagulability from warfarin toxicity, the patient required admission anyway. Subsequent biopsy confirmed the presence of a primary lung carcinoma.

ANSWER
The radiograph shows a large, round hyperdensity within the right lower lobe. This lesion is highly concerning for malignancy and warrants further work-up.
With his gastrointestinal bleed and hypercoagulability from warfarin toxicity, the patient required admission anyway. Subsequent biopsy confirmed the presence of a primary lung carcinoma.
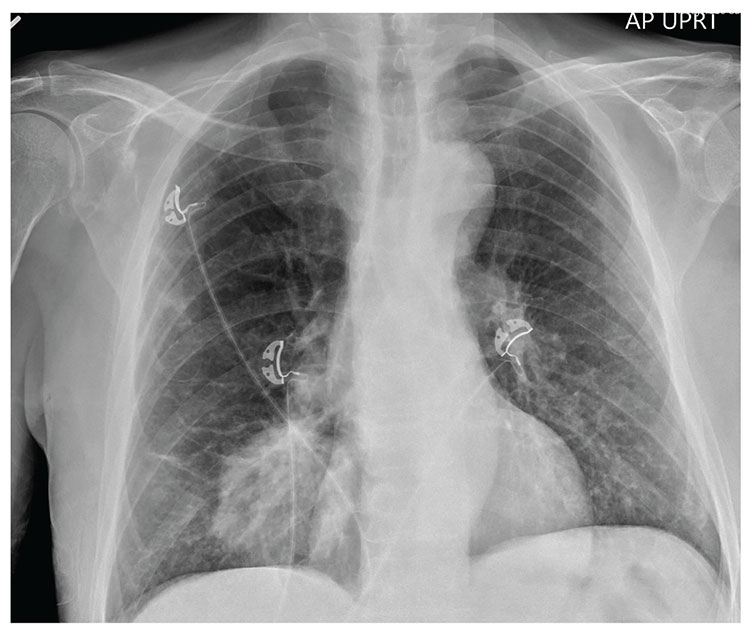
For several days, a 60-year-old man has been feeling weak. He has also noticed that he bruises easily, and he’s experienced black, tarry stools and episodic hemoptysis. He presents to the emergency department, where the triage team sends him for further evaluation.
The patient’s history is significant for a remote diagnosis of a deep venous thrombosis in one of his lower extremities, for which he takes warfarin. He does not recall his most recent INR level. He reports smoking up to one pack of cigarettes per day and consuming alcohol regularly.
Examination reveals an older appearing male in no obvious distress. His blood pressure is 90/60 mm Hg, and his heart rate is 110 beats/min. You note bruises on both arms. The rest of his physical exam is normal. Lung sounds are clear.
Labwork ordered by the triage team indicates a hemoglobin level of 8 g/dL and an INR of 9. In addition, his stool guaiac test came back positive.
You obtain a portable chest radiograph (shown). What is your impression?
When the Diagnosis Hurts
ANSWER
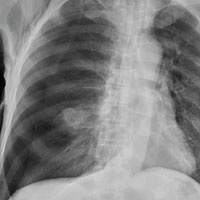
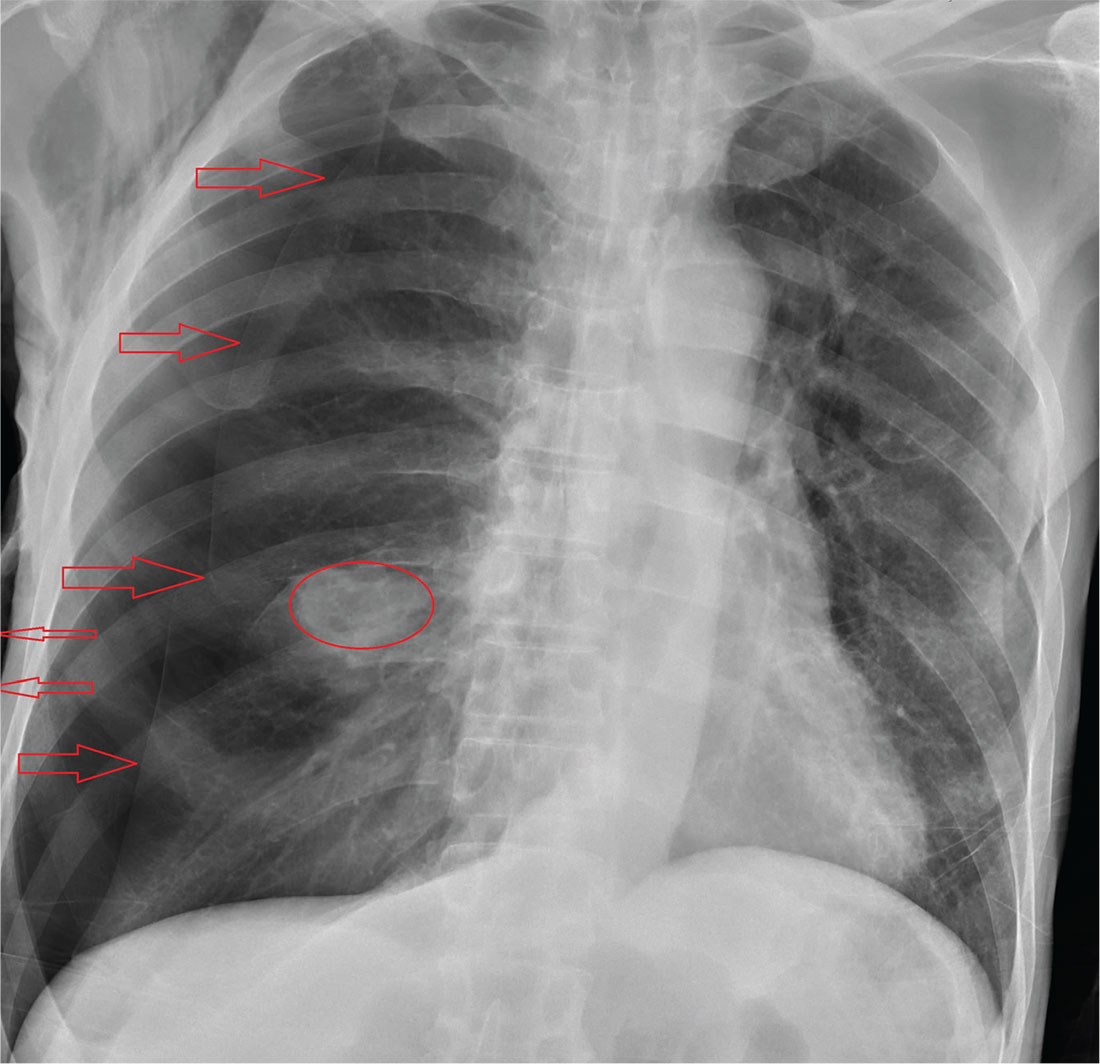
The radiograph shows an oval hyperdensity within the right mid lung, presumably the known lung mass. Of note, however, is an approximate 50% pneumothorax of the right lung. It is creating mild tension, indicated by the slightly displaced trachea. There is also evidence of subcutaneous air in the right lateral chest.
These findings likely result from a complication of the aforementioned biopsy. The patient underwent chest tube placement and was admitted for further treatment.

ANSWER
The radiograph shows an oval hyperdensity within the right mid lung, presumably the known lung mass. Of note, however, is an approximate 50% pneumothorax of the right lung. It is creating mild tension, indicated by the slightly displaced trachea. There is also evidence of subcutaneous air in the right lateral chest.
These findings likely result from a complication of the aforementioned biopsy. The patient underwent chest tube placement and was admitted for further treatment.

ANSWER
The radiograph shows an oval hyperdensity within the right mid lung, presumably the known lung mass. Of note, however, is an approximate 50% pneumothorax of the right lung. It is creating mild tension, indicated by the slightly displaced trachea. There is also evidence of subcutaneous air in the right lateral chest.
These findings likely result from a complication of the aforementioned biopsy. The patient underwent chest tube placement and was admitted for further treatment.
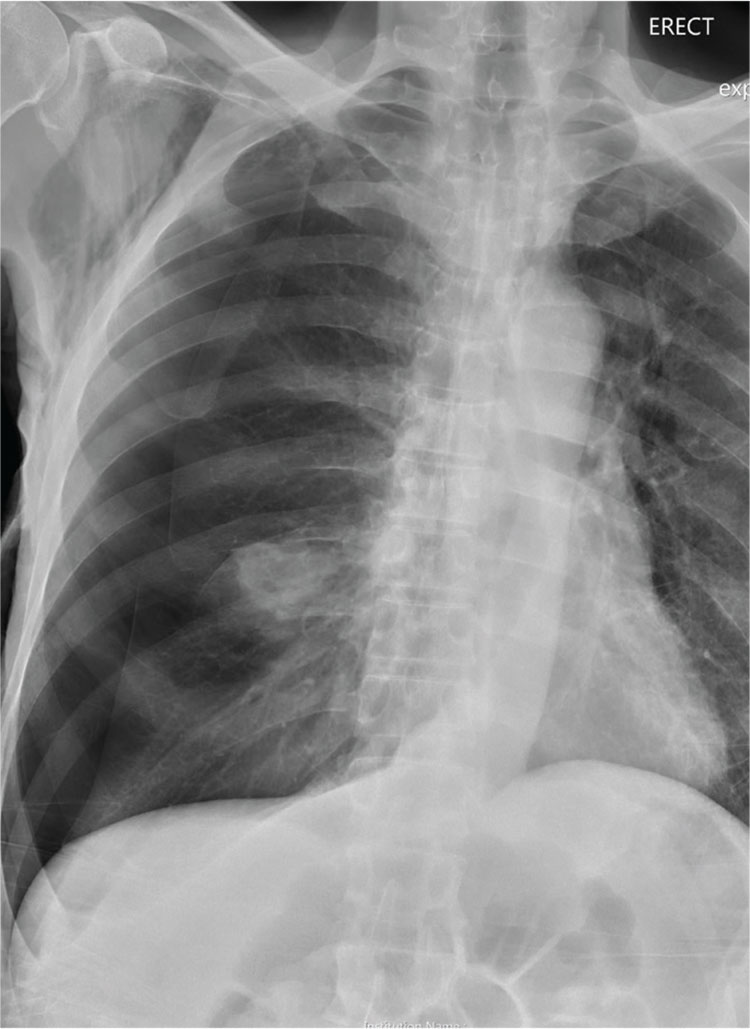
A 60-year-old man presents to the emergency department for evaluation of chest pain that began a few hours ago. He denies injury and has no associated nausea or shortness of breath. Earlier today, he underwent biopsy of a recently discovered mass in his right lung. Otherwise, his medical history is only significant for hypertension. He is a former pack-a-day smoker but quit three months ago.
On physical exam, you note an uncomfortable male in no obvious distress. He is afebrile, with normal vital signs. His O2 saturation is 96% on room air. Breath sounds appear to be clear bilaterally, although the patient expresses some discomfort with inhalation. Heart sounds are normal as well.
While the nurse and tech place an IV, a portable chest radiograph is obtained. What is your impression?
From Hydroplane to Ankle Pain
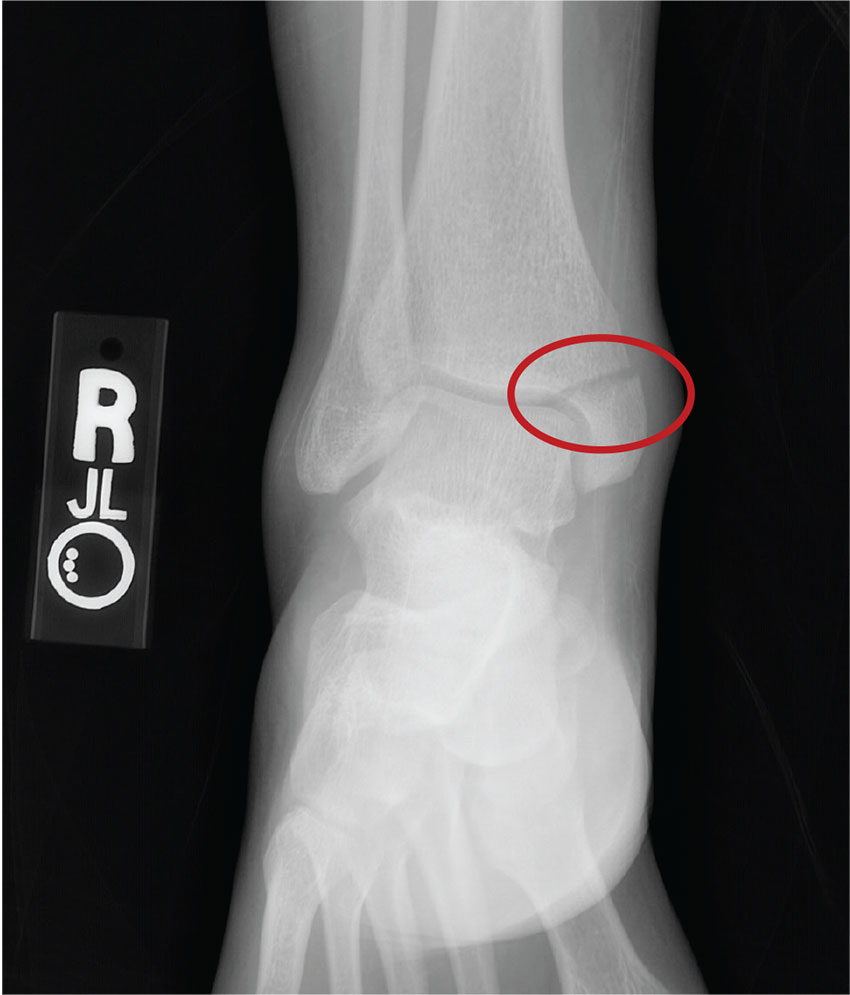
ANSWER
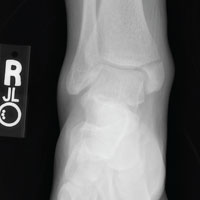
The radiograph shows an acute fracture of the medial malleolus. It is minimally displaced. The mortise joint appears intact. The patient was placed in a short leg splint for immobilization, and prompt orthopedic follow-up was arranged.

ANSWER
The radiograph shows an acute fracture of the medial malleolus. It is minimally displaced. The mortise joint appears intact. The patient was placed in a short leg splint for immobilization, and prompt orthopedic follow-up was arranged.

ANSWER
The radiograph shows an acute fracture of the medial malleolus. It is minimally displaced. The mortise joint appears intact. The patient was placed in a short leg splint for immobilization, and prompt orthopedic follow-up was arranged.

A 40-year-old woman presents to urgent care for evaluation of ankle pain following a car accident. She was a restrained driver who lost control of her vehicle while driving on wet roads. Her vehicle hit a telephone pole head on. There was no air bag deployment. Initially, she thought she was fine and declined EMS transport to a local hospital. But when she experienced severe pain bearing weight on her right foot, she opted to have it evaluated.
She denies any other complaints. Her medical history is otherwise unremarkable, and vital signs are normal. Physical examination of her right ankle demonstrates general soft-tissue swelling but no obvious deformity. She has moderate tenderness on both the medial and lateral aspects of her ankle. She has limited dorsiflexion and plantar flexion secondary to pain. Good distal pulses are palpable, and good capillary refill is noted in all of the toes.
A radiograph of the ankle is shown. What is your impression?
Does Chronic Complaining Mask Acute Problem?
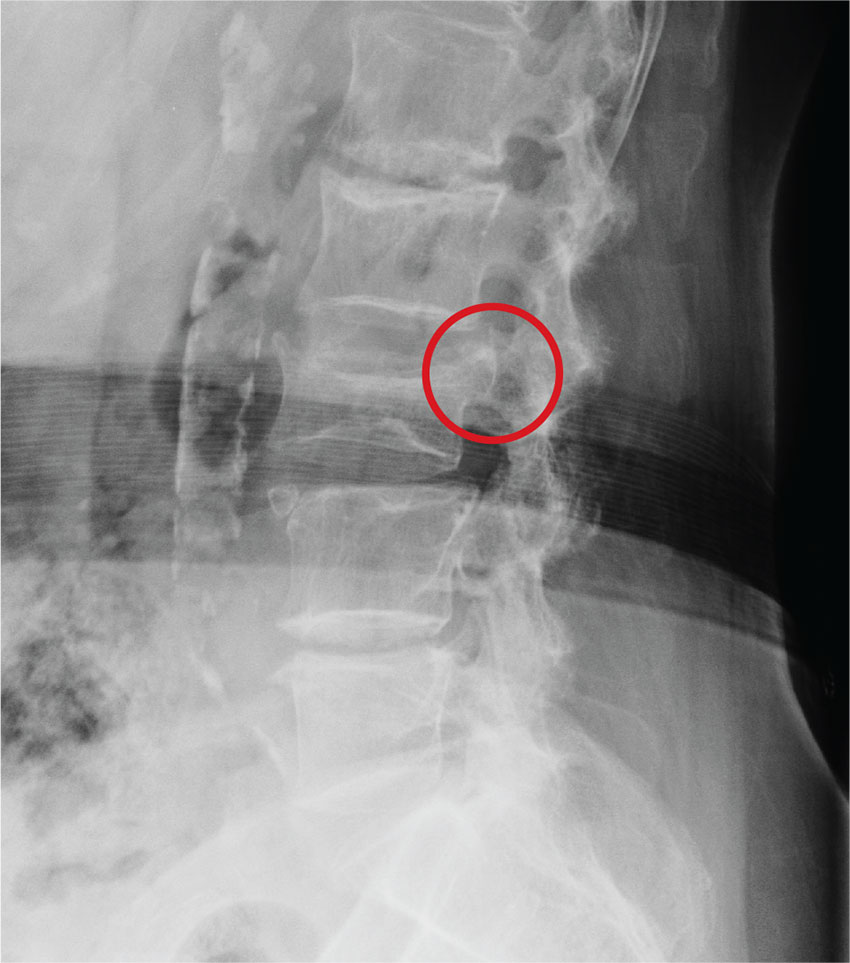
ANSWER
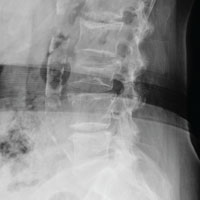
The radiograph demonstrates age-related degenerative changes. Of note is a moderate compression fracture of L3 with close to 50% loss of height. It is difficult to say for sure the fracture is acute; by plain film alone, it would be deemed age indeterminate.
Of concern, though, is the posterior portion of the superior endplate of L3, which appears to be posteriorly displaced into the spinal canal. This finding suggests possible retropulsion and, if this fracture was in fact acute, would suggest a possible unstable fracture. Further imaging is warranted.
The patient underwent noncontrast CT of the lumbar spine, which demonstrated that the fracture was acute. It also indicated that there was dorsal retropulsion causing close to 50% canal compromise. The patient was subsequently admitted for further workup and evaluation.

ANSWER
The radiograph demonstrates age-related degenerative changes. Of note is a moderate compression fracture of L3 with close to 50% loss of height. It is difficult to say for sure the fracture is acute; by plain film alone, it would be deemed age indeterminate.
Of concern, though, is the posterior portion of the superior endplate of L3, which appears to be posteriorly displaced into the spinal canal. This finding suggests possible retropulsion and, if this fracture was in fact acute, would suggest a possible unstable fracture. Further imaging is warranted.
The patient underwent noncontrast CT of the lumbar spine, which demonstrated that the fracture was acute. It also indicated that there was dorsal retropulsion causing close to 50% canal compromise. The patient was subsequently admitted for further workup and evaluation.

ANSWER
The radiograph demonstrates age-related degenerative changes. Of note is a moderate compression fracture of L3 with close to 50% loss of height. It is difficult to say for sure the fracture is acute; by plain film alone, it would be deemed age indeterminate.
Of concern, though, is the posterior portion of the superior endplate of L3, which appears to be posteriorly displaced into the spinal canal. This finding suggests possible retropulsion and, if this fracture was in fact acute, would suggest a possible unstable fracture. Further imaging is warranted.
The patient underwent noncontrast CT of the lumbar spine, which demonstrated that the fracture was acute. It also indicated that there was dorsal retropulsion causing close to 50% canal compromise. The patient was subsequently admitted for further workup and evaluation.
An 80-year-old woman who resides in a nursing home is sent to urgent care for evaluation of back pain. There have been no witnessed injuries or falls. The notes from the nursing home staff indicate that the patient, who has severe dementia, tends to chronically complain about one ailment or another. However, the patient’s family seems to feel she is complaining more than usual.
Her only other medical history is controlled hypertension. Her vital signs are stable. On physical exam, you note an elderly female who is pleasant but very confused. She is able to follow simple commands and appears to be able to move all her extremities well, with no obvious neurologic compromise. Inspection of her back does not demonstrate any obvious wounds, bruising, or step-offs. She does have generalized tenderness as you palpate her lumbar region.
The triage nurse already ordered lumbar spine radiographs, which have been completed. The lateral view is shown. What is your impression?
Man Thrown From Balky Bike

ANSWER
The radiograph does not demonstrate any evidence of acute chest or intrathoracic injury. Of note, it appears that the left humerus is dislocated anteriorly and inferiorly.
Dedicated shoulder radiographs were obtained, which confirmed the dislocation with no evidence of fracture. Orthopedics was consulted for evaluation and subsequent reduction.

ANSWER
The radiograph does not demonstrate any evidence of acute chest or intrathoracic injury. Of note, it appears that the left humerus is dislocated anteriorly and inferiorly.
Dedicated shoulder radiographs were obtained, which confirmed the dislocation with no evidence of fracture. Orthopedics was consulted for evaluation and subsequent reduction.

ANSWER
The radiograph does not demonstrate any evidence of acute chest or intrathoracic injury. Of note, it appears that the left humerus is dislocated anteriorly and inferiorly.
Dedicated shoulder radiographs were obtained, which confirmed the dislocation with no evidence of fracture. Orthopedics was consulted for evaluation and subsequent reduction.
A 55-year-old man is brought to your facility following a motorcycle accident. He was a helmeted rider who was inadvertently thrown from the motorcycle when the accelerator got stuck. Bystanders reported he had brief loss of consciousness, but upon arrival to your facility, he is awake.
History is limited as the patient is confused and repetitive in his speech, indicating he is post concussive. He is complaining of head, face, and chest wall pain. His vital signs are all within normal limits; he is hemodynamically stable. His O2 saturation is 98% on room air. Breath sounds are clear.
As you are completing your primary survey, portable chest and pelvic radiographs are obtained. The chest radiograph is shown. What is your impression?
Fast Track to Abdominal Pain
ANSWER
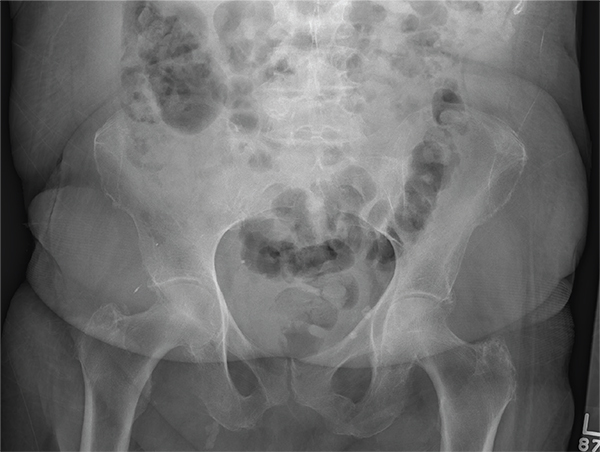
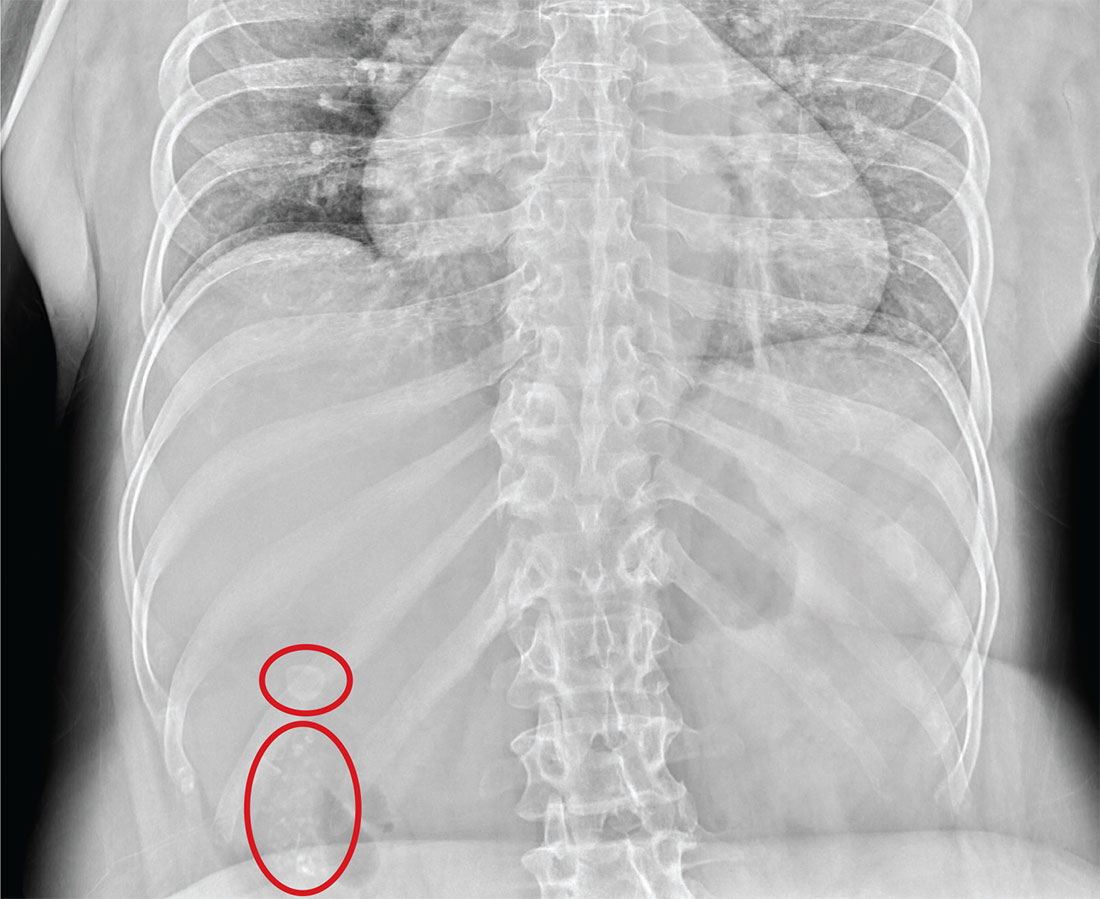
The radiograph illustrates a large calcification within the right upper quadrant—most likely a gallstone. Several smaller calcifications are clustered together in the same area, making the diagnosis cholelithiasis. The patient was referred to the general surgery clinic for further
evaluation.
For recent findings on gallstone disease and heart risk, see here.

ANSWER
The radiograph illustrates a large calcification within the right upper quadrant—most likely a gallstone. Several smaller calcifications are clustered together in the same area, making the diagnosis cholelithiasis. The patient was referred to the general surgery clinic for further
evaluation.
For recent findings on gallstone disease and heart risk, see here.

ANSWER
The radiograph illustrates a large calcification within the right upper quadrant—most likely a gallstone. Several smaller calcifications are clustered together in the same area, making the diagnosis cholelithiasis. The patient was referred to the general surgery clinic for further
evaluation.
For recent findings on gallstone disease and heart risk, see here.
An NP student you are precepting in the emergency department fast track area presents her patient to you: a 60-year-old woman with abdominal pain. The pain is chronic but has worsened slightly, prompting the patient, who does not have a primary care provider, to present today. She experiences occasional nausea but no fever, and she denies any bowel or bladder complaints other than constipation. Her medical history is significant for mild hypertension.
On exam, your student notes an obese female who is in no obvious distress. The patient’s vital signs are all within normal limits. The abdominal exam is unimpressive, revealing a soft abdomen with good bowel sounds. Although she does have mild diffuse tenderness, she has no rebound or guarding.
Although your student suspects the patient is just constipated, she orders blood work and urinalysis. An abdominal survey is obtained as well. What is your impression?
When Man’s Legs “Give Out,” His Buttocks Takes the Brunt
ANSWER

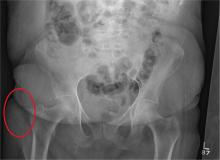
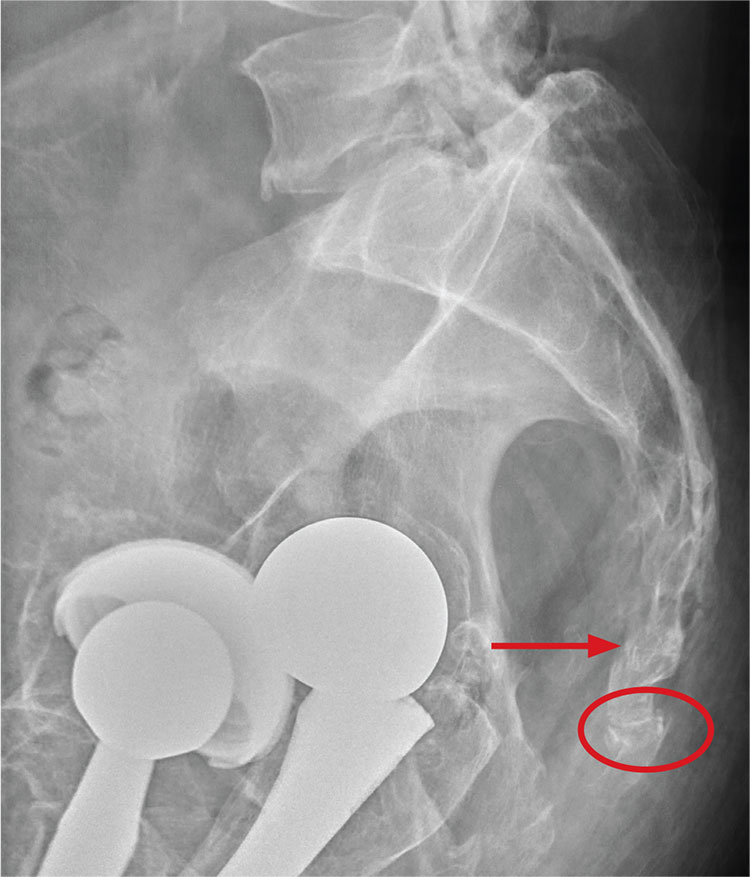
There are degenerative changes present. Bilateral hip prostheses are noted. Within the coccyx, there is bone remodeling and angulation that are likely chronic and related to remote trauma or injury (arrow). Below this, some cortical lucency (circled) is noted, most likely consistent with an acute fracture. The patient was prescribed a nonsteroidal medication and a mild narcotic pain medication.

ANSWER

There are degenerative changes present. Bilateral hip prostheses are noted. Within the coccyx, there is bone remodeling and angulation that are likely chronic and related to remote trauma or injury (arrow). Below this, some cortical lucency (circled) is noted, most likely consistent with an acute fracture. The patient was prescribed a nonsteroidal medication and a mild narcotic pain medication.

ANSWER

There are degenerative changes present. Bilateral hip prostheses are noted. Within the coccyx, there is bone remodeling and angulation that are likely chronic and related to remote trauma or injury (arrow). Below this, some cortical lucency (circled) is noted, most likely consistent with an acute fracture. The patient was prescribed a nonsteroidal medication and a mild narcotic pain medication.
A 75-year-old man presents to the urgent care center for evaluation of pain in his buttocks after a fall. He states he was walking when his “legs gave out” and he hit the ground. He landed squarely on his buttocks, causing immediate pain. He was eventually able to get up with some assistance. He denies current weakness or any bowel or bladder complaints.
His medical/surgical history is significant for coronary artery disease, hypertension, and bilateral hip replacements. Physical exam reveals an elderly male who is uncomfortable but in no obvious distress. His vital signs are stable. He has moderate point tenderness over his sacrum but is able to move all his extremities well, with normal strength.
Radiograph of his sacrum/coccyx is shown. What is your impression?
An Alarming Slip of the Hip
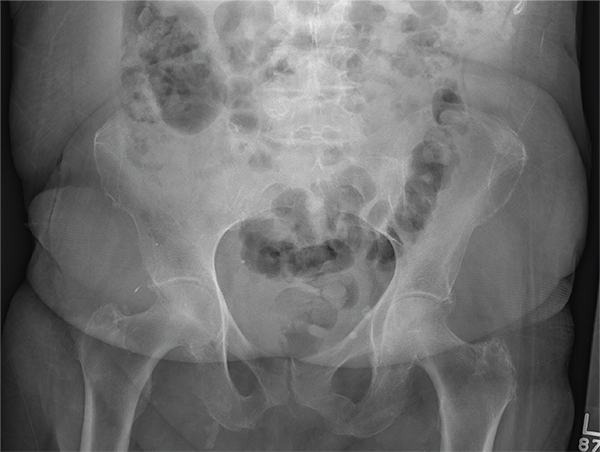
After a fall, an 80-year-old woman is brought to the emergency department for evaluation of hip pain. She was getting out of bed when she slipped, fell, and landed on her right hip; bearing weight now is painful. She denies hitting her head. The patient’s vital signs are normal. Her medical history is significant for hypertension and diabetes. Inspection of the hip reveals no obvious deformity or shortening. The right lateral aspect of the hip exhibits mild swelling and decreased range of motion secondary to the pain. You order a pelvic radiograph, which is shown. What is your impression?
Altered Mental Status Demands Closer Look
Answer
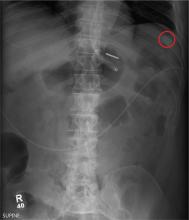
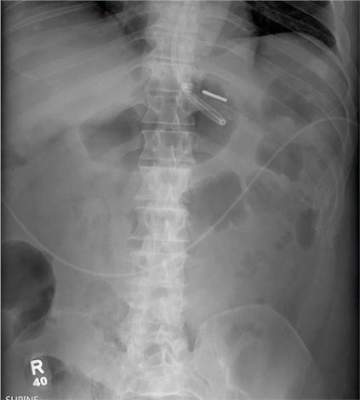
The radiograph demonstrates a normal gas pattern with a properly placed enteric feeding tube, which appears to be within the stomach. Of note is a sclerotic-appearing lesion on the posterior aspect of the left eighth rib. In a patient with a possible tumor, this lesion poses concern for potential metastasis and warrants appropriate work-up.
Answer
The radiograph demonstrates a normal gas pattern with a properly placed enteric feeding tube, which appears to be within the stomach. Of note is a sclerotic-appearing lesion on the posterior aspect of the left eighth rib. In a patient with a possible tumor, this lesion poses concern for potential metastasis and warrants appropriate work-up.
Answer
The radiograph demonstrates a normal gas pattern with a properly placed enteric feeding tube, which appears to be within the stomach. Of note is a sclerotic-appearing lesion on the posterior aspect of the left eighth rib. In a patient with a possible tumor, this lesion poses concern for potential metastasis and warrants appropriate work-up.
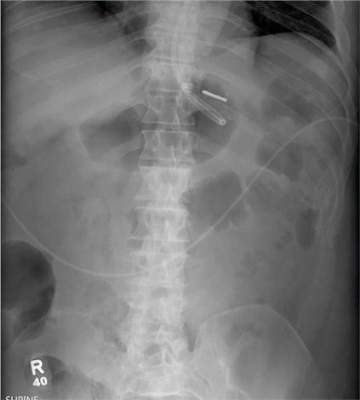
You receive a call from an ICU nurse regarding a patient your service is following—a 60-year-old man who was admitted for altered mental status and is being worked up for a possible brain mass. He has no other significant medical history. The nurse has placed a nasogastric feeding tube to facilitate nutrition and medication administration and has ordered a portable abdominal radiograph to confirm its placement. The completed radiograph is shown. What is your impression?
In Middle of Trip, Woman Falls
Answer
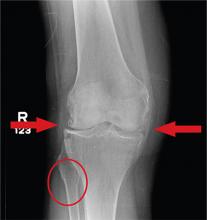
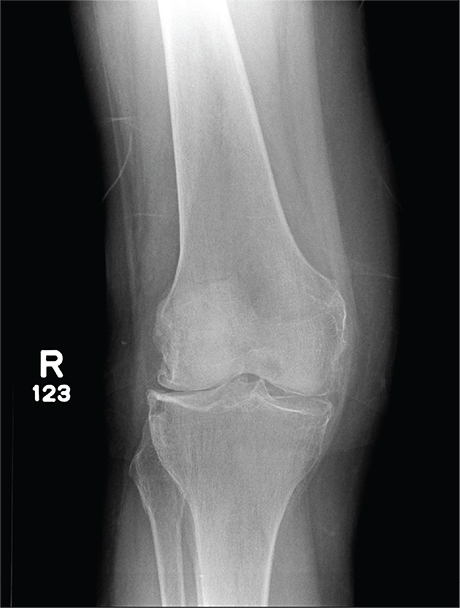
The radiograph has several findings, one of which is a nondisplaced proximal fibula fracture. In addition, there is a moderate suprapatellar joint effusion. The patient also has fairly advanced tricompartment degenerative arthrosis. (To review, the tricompartment comprises all three anatomic areas of the knee: the patellofemoral, lateral tibiofemoral, and medial tibiofemoral joints.)
Answer
The radiograph has several findings, one of which is a nondisplaced proximal fibula fracture. In addition, there is a moderate suprapatellar joint effusion. The patient also has fairly advanced tricompartment degenerative arthrosis. (To review, the tricompartment comprises all three anatomic areas of the knee: the patellofemoral, lateral tibiofemoral, and medial tibiofemoral joints.)
Answer
The radiograph has several findings, one of which is a nondisplaced proximal fibula fracture. In addition, there is a moderate suprapatellar joint effusion. The patient also has fairly advanced tricompartment degenerative arthrosis. (To review, the tricompartment comprises all three anatomic areas of the knee: the patellofemoral, lateral tibiofemoral, and medial tibiofemoral joints.)
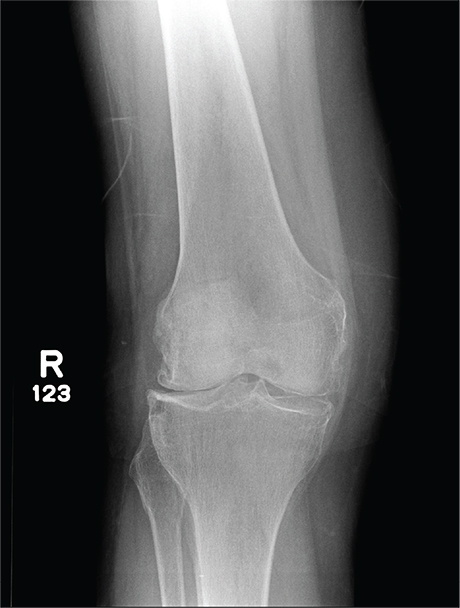
A 70-year-old woman presents to your emergency department for evaluation of right knee pain secondary to a fall. She and her husband, in the process of driving from Florida to their home in California, stopped for the night in your town. The patient states that shortly after getting up this morning, she tripped, lost her balance, and fell. All her weight landed on her right knee; she says it is now “extremely painful” to bear weight on that leg. She also twisted her right ankle, causing additional discomfort. Her medical history is significant for hypertension, which is controlled by medication. On physical exam, you note an elderly female who is uncomfortable but in no obvious distress. Inspection of her right knee shows no obvious deformity but a moderate amount of swelling. The patient has limited range of motion secondary to the swelling. She also has moderate tenderness circumferentially around the knee. There is additional swelling and mild bruising on both the medial and lateral aspects of the right ankle. You obtain a radiograph of the right knee. What is your impression?