User login
Short Interval Repeat Colonoscopy After Inadequate Bowel Preparation Is Low Among Veterans
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the third-most diagnosed cancer after breast and lung cancer, and is the second leading cause of global cancer related deaths.1 In 2023 in the United States, > 150,000 individuals were diagnosed with CRC and 52,000 died.2
Colonoscopy is an effective CRC screening method and the lone method recommended for polyp surveillance. Inadequate bowel preparation (IBP) has been estimated to occur in about 6% to 26% of colonoscopies. 3,4 The prevalence varies based on a variety of comorbidities, including immobility, diabetes mellitus, neurologic disorders, and use of opioids, with more occurrences of IBP noted in older adult, non-English speaking, and male individuals.4-6
The quality of bowel preparation is integral to the effectiveness of screening and surveillance colonoscopies. IBP has been associated with missed adenomas and significantly lower adenoma detection rates.7-9 In particular, IBP is independently associated with an increased risk of CRC in the future.3 Accordingly, the US Multisociety Task Force recommends repeat colonoscopies for individuals with IBP within 1 year.10 Ensuring that these individuals receive repeat colonoscopies is an essential part of CRC prevention. The benefit of repeat colonoscopy after IBP is highlighted by a retrospective analysis from Fung and colleagues that showed 81% of repeat colonoscopies had adequate bowel preparation, with higher numbers of adenomas detected on repeat compared to initial colonoscopies.11
Given the impact of bowel preparation quality on the diagnostic capability of the colonoscopy, adherence to guidelines for repeat colonoscopies in cases of IBP is paramount for effective CRC prevention. This study aims to measure the frequency of repeat colonoscopy after IBP and the factors associated with adherence to recommendations.
METHODS
Individuals who underwent colonoscopy at the Minneapolis Veterans Affairs Medical Center (MVAMC) from January 1, 2016, to October 19, 2021, were identified to allow for 400 days of follow-up from the index colonoscopy to the data collection date. During the COVID-19 pandemic, the colonoscopy procedure capacity was reduced by 50% from June 1, 2020, to December 1, 2020, delaying nonurgent procedures, including screening and surveillance colonoscopies.
Individuals who underwent colonoscopy for CRC screening or polyp surveillance, or following a positive fecal immunohistochemistry test (FIT) or virtual computed tomography colonoscopy were included. Patients with colonoscopy indications for iron deficiency anemia, gastrointestinal bleeding, disease activity assessment of inflammatory bowel disease, abdominal pain, or changes in bowel movement pattern were excluded. IBP was defined as recording a Boston Bowel Preparation Scale (BBPS) score of < 6, or < 2 in any segment, or described as poor or inadequate using the Aronchick scale.
Age, sex, race, marital status, distance to MVAMC, smoking status, comorbidities, and concurrent medication use, including antiplatelet, anticoagulation, and prescription opiates at the time of index colonoscopy were obtained from the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) Corporate Data Warehouse (CDW) using structured query language processing of colonoscopy procedure notes to extract preparation scores and other procedure information. The CDW contains extracts from VHA clinical and administrative systems that contain complete clinical data from October 1999.12 Current smoking status was defined as any smoking activity at the time the questionnaire was administered during a routine clinic visit within 400 days from the index colonoscopy.
Only individuals who were recommended to have repeat colonoscopy within 1 year were included. The intervals of 365 days and 400 days (1 year + about 1 additional month) were used in the event that the individual had a delay in scheduling their 1-year repeat colonoscopy. For individuals who did not undergo a colonoscopy at MVAMC within 400 days, a manual chart review of all available records was performed to determine whether a colonoscopy was performed at a non-VA facility.
Patients received written instructions for bowel preparation 2 weeks prior to the procedure. The preparation included magnesium citrate and a split dose of 4 liters of polyethylene glycol. Patients were also advised to start a low-fiber diet 3 days prior to the procedure and a clear liquid diet the day before the procedure. Patients with a history of IBP or those undergoing procedures with anesthesia received an additional 2 liters for a total of 6 liters of polyethylene glycol.
Statistical analysis
Baseline characteristics were reported as mean (SD) or median and IQR for continuous variables and percentage for categorical variables. Individuals who returned for colonoscopy within 400 days were compared to those who did not identify factors associated with adherence to recommendations. The data on individuals who returned for colonoscopy within 400 days were also analyzed for additional minor delays in the timing of the repeat colonoscopy. Continuous data were compared using Mann-Whitney U tests. Categorical data were compared using X2 or Fisher exact tests. Missing data were imputed from the analyses. All analyses were performed using SAS JMP Pro version 16. P < .05 was considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
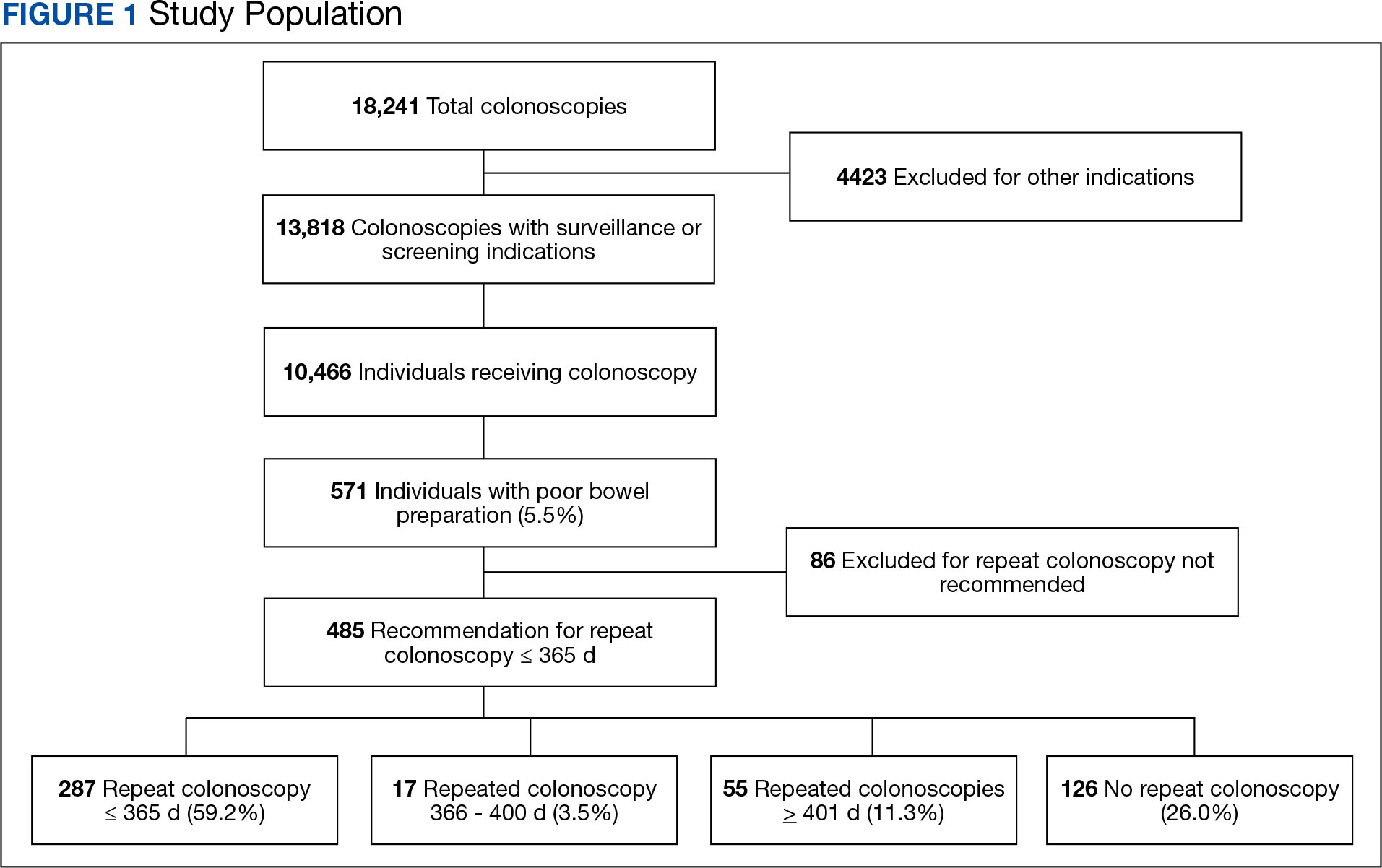
There were 18,241 total colonoscopies performed between January 1, 2016, to October 19, 2021, and 13,818 colonoscopies had indications for screening for colon cancer, positive FIT, virtual colonoscopy, or surveillance. Of the 10,466 unique patients there were 5369 patients for polyp surveillance, 4054 patients for CRC screening, and 1043 patients for positive FIT or virtual colonoscopy. Of these, 571 individuals (5.5%) had IBP. Repeat colonoscopy within 1 year was recommended for 485 individuals (84.9%) who were included in this study (153 CRC screenings and 46 positive FITs) but not for 86 individuals (15.1%) (Figure 1). Among included patients, the mean (SD) age was 66.6 (7.2) years, and the majority were male (460 [94.8%]) and White (435 [89.7%]) (Table). Two hundred and forty-three (50.1%) were married.
Adherence to Recommended Interval Colonoscopy
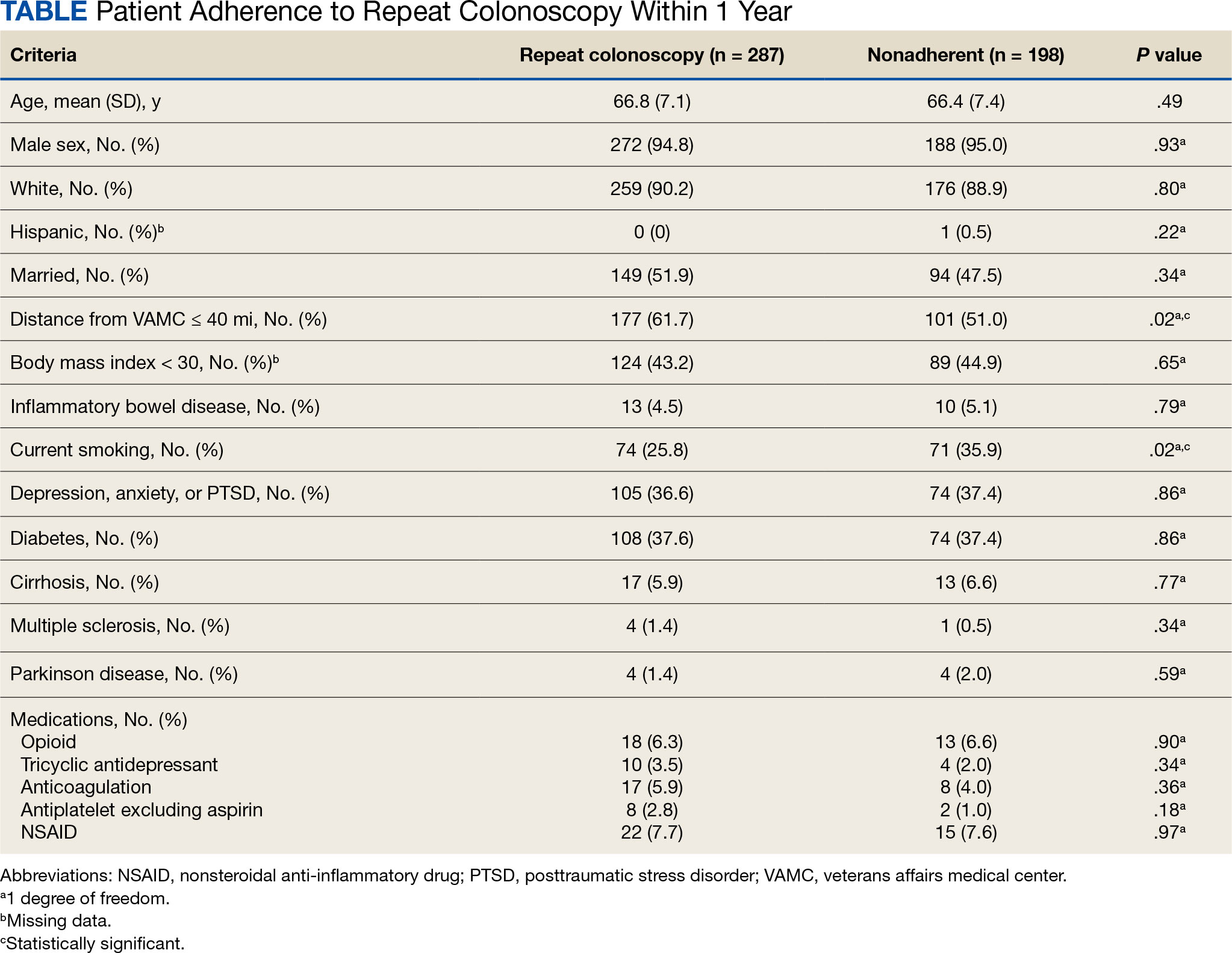
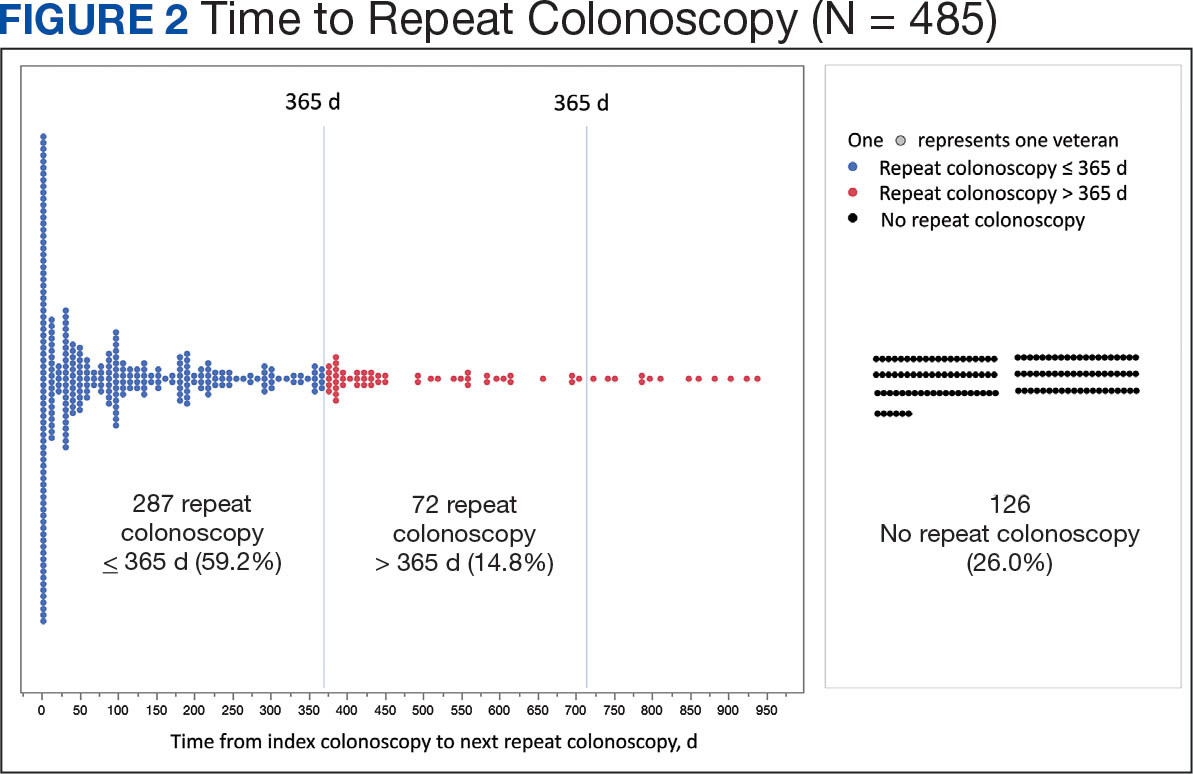
Of the 485 patients with IBP who were recommended for follow-up colonoscopy, 287 (59.2%) had a colonoscopy within 1 year, and 198 (40.8%) did not; 17 patients (13.5%) had repeat colonoscopy within 366 to 400 days. Five (1.0%) individuals had a repeat colonoscopy the next day, and 77 (15.9%) had a repeat colonoscopy within 7 days. One hundred and twentysix (26.0%) individuals underwent no repeat colonoscopy during the study period (Figure 2).
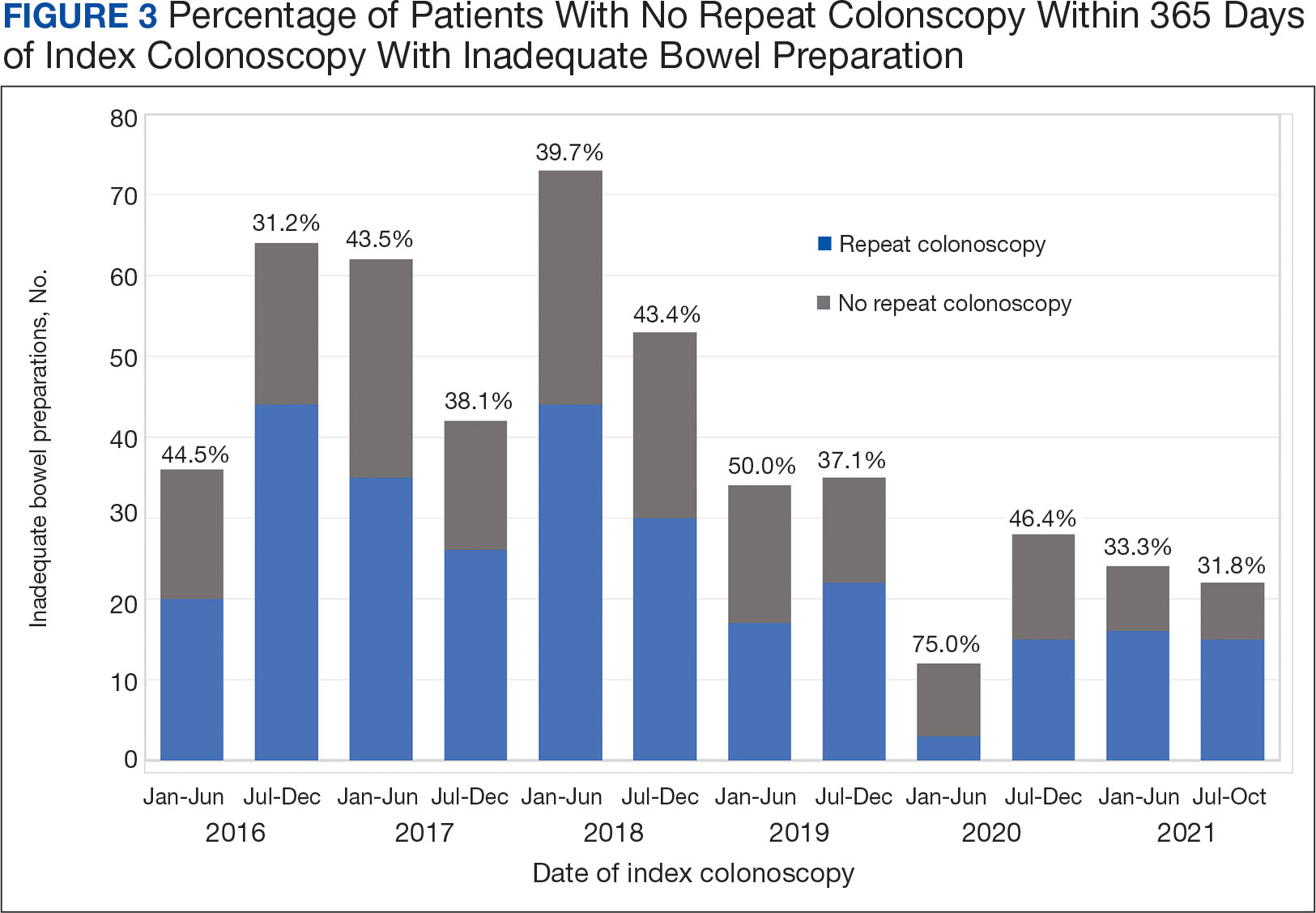
To account for the COVID-19 pandemic, the adherence rate of repeat colonoscopy within 1 year prepandemic (January 1, 2016, to December 1, 2018) was calculated along with the adherence rate postpandemic (January 1, 2019 to the end of the study). The rates were similar: 199 of 330 (60.3%) individuals prepandemic vs 88 of 155 (56.8%) individuals postpandemic (Figure 3).
Significant Associations
Age, sex, and race were not associated with adherence to repeat colonoscopy within 1 year. Individuals living ≤ 40 miles from the endoscopy center were more likely to undergo a repeat colonoscopy within 1 year compared with those who lived > 40 miles away (61.7% vs 51.0%, P = .02). Current smoking status was associated with a lower rate of repeat colonoscopy within 1 year (25.8% vs 35.9%; P = .02). There were no differences with respect to inflammatory bowel disease diagnosis, mental health diagnosis, diabetes mellitus, cirrhosis, or medications used, including opioids, anticoagulation, and antiplatelet therapy.
Outcomes
Among individuals who had a repeat colonoscopy the day after the index colonoscopy, 53 of 56 individuals (94.6%) had adequate bowel preparation. Among individuals who had a repeat colonoscopy within 7 days, 70 of 77 (90.9%) had adequate bowel preparation. Of 287 individuals with a repeat colonoscopy within 1 year, 251 (87.5%) had adequate bowel preparation on the repeat colonoscopy. By 400 days after the index colonoscopy, 268 of 304 individuals (88.2%) had adequate bowel preparation.
In this study conducted at a large VA medical center, we found that 5.6% of individuals undergoing colonoscopies had IBP, a rate comparable to prior studies (6% to 26%).3,4 Only 59.2% of individuals underwent repeat colonoscopies within 1 year, as recommended after an index colonoscopy with IBP. Smoking and living longer distances (> 40 miles) from the endoscopy center were associated with a decreased adherence to the repeat colonoscopy recommendation.
Current guidelines recommend repeat colonoscopy for individuals with IBP within 1 year.10 In cases of IBP, the advanced adenoma miss rate is 36% upon repeat colonoscopy within 1 year.13 Despite the importance of a follow-up colonoscopy, clinician adherence with this recommendation remains low.10,14,15 However, in this study cohort, 485 of 571 individuals with IBP (84.9%) received recommendations for a repeat colonoscopy within 1 year. In the US, only 31.9% of 260,314 colonoscopies with IBP included recommendations for a follow-up colonoscopy within 1 year.14 This could be related to variations in endoscopist practice as well as patient risk factors for developing polyps, including family history of cancer and personal history of prior polyps. The findings of multiple polyps, high-risk adenomas, and cancer on the index colonoscopy also influences the endoscopist for repeat colonoscopy within 1 year.14
The timing for repeat colonoscopies within 1 year will be determined by the patients, clinicians, and available scheduling. In this study, the earlier repeat colonoscopies, especially those occurring the day after the index colonoscopy, had the highest success rate of adequate bowel preparation. In a prior study, repeating colonoscopies within the same day or the next day was also found to have a higher rate of adequate bowel preparation than repeat colonoscopies within 1 year (88.9% vs 83.5%).16
Ensuring the return of individuals with IBP for repeat colonoscopy is a challenging task. We identified that individuals who live further away from MVAMC and current smokers had a decreased probability of returning for a repeat colonoscopy. Toro and colleagues found a 68.7% return rate for a repeat colonoscopy within 1 year with individuals age ≥ 60 years, and patients who were White were less likely to proceed with a repeat colonoscopy within 1 year.17 The study did not provide data regarding smoking status or distance to the endoscopy center.17 In a prior study of veterans, the dual diagnosis of psychiatric disorders and substance abuse was associated with missed and canceled colonoscopy appointments.18 The distance to the endoscopy center has also been previously identified as a barrier to a colonoscopy following an abnormal FIT.19 Although not identified in this study due to the homogenous demographic profile, social determinants of health such as socioeconomic status, education, and insurance coverage are known barriers to cancer screening but were not evaluated in this study.20
Based on the identified risk factors, we have created a model for utilizing those risk factors to identify individuals at higher risk for noncompliance (ie, those who live further away from the endoscopy center or currently smoke). These individuals are proactively offered to use an intraprocedural bowel cleansing device to achieve adequate bowel preparation or priority rescheduling for a next-day colonoscopy.
Limitations
This study was a single-center study of the veteran population, which is predominantly White and male, thus limiting generalizability. The study is also limited by minimal available data on adenoma detection and colon cancer incidence on subsequent colonoscopies.
CONCLUSIONS
The rate of IBP was 5.5% in individuals undergoing colonoscopy for colon cancer screening, surveillance, positive FIT, or computed tomography colonography. Only 59.2% of those with IBP underwent the recommended repeat colonoscopy within 1 year. Smoking and distance to the endoscopy center were associated with a decreased adherence to the repeat colonoscopy recommendation. Additional efforts are needed to ensure that individuals with IBP return for timely repeat colonoscopy.
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209-249. doi:10.3322/caac.21660
- Siegel RL, Wagle NS, Cercek A, Smith RA, Jemal A. Colorectal cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin. 2023;73(3):233-254. doi:10.3322/caac.21772
- Atkin W, Wooldrage K, Brenner A, et al. Adenoma surveillance and colorectal cancer incidence: a retrospective, multicentre, cohort study. Lancet Oncol. 2017;18(6):823- 834. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30187-0
- Froehlich F, Wietlisbach V, Gonvers JJ, Burnand B, Vader JP. Impact of colonic cleansing on quality and diagnostic yield of colonoscopy: the European Panel of Appropriateness of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy European multicenter study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2005;61(3):378- 384. doi:10.1016/s0016-5107(04)02776-2
- Mahmood S, Farooqui SM, Madhoun MF. Predictors of inadequate bowel preparation for colonoscopy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;30(8):819-826. doi:10.1097/MEG.0000000000001175
- ASGE Standards of Practice Committee, Saltzman JR, Cash BD, et al. Bowel preparation before colonoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015;81(4):781-794. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2014.09.048
- Clark BT, Protiva P, Nagar A, et al. Quantification of Adequate Bowel Preparation for Screening or Surveillance Colonoscopy in Men. Gastroenterology. 2016;150(2):396- e15. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2015.09.041
- Sulz MC, Kröger A, Prakash M, Manser CN, Heinrich H, Misselwitz B. Meta-Analysis of the Effect of Bowel Preparation on Adenoma Detection: Early Adenomas Affected Stronger than Advanced Adenomas. PLoS One. 2016;11(6):e0154149. Published 2016 Jun 3. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0154149
- Chokshi RV, Hovis CE, Hollander T, Early DS, Wang JS. Prevalence of missed adenomas in patients with inadequate bowel preparation on screening colonoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2012;75(6):1197-1203. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2012.01.005
- Lieberman DA, Rex DK, Winawer SJ, Giardiello FM, Johnson DA, Levin TR. Guidelines for colonoscopy surveillance after screening and polypectomy: a consensus update by the US Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer. Gastroenterology. 2012;143(3):844-857. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2012.06.001
- Fung P, Syed A, Cole R, Farah K. Poor bowel prep: are you really going to come back within a year? Abstract presented at American Gastroenterological Association DDW 2021, May 21-23, 2021. doi:10.1016/S0016-5085(21)01204-X
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, VA Health Systems Research. Corporate data warehouse (CDW). Updated January 11, 2023. Accessed August 6, 2024. https://www.hsrd.research.va.gov/for_researchers/cdw.cfm
- Lebwohl B, Kastrinos F, Glick M, Rosenbaum AJ, Wang T, Neugut AI. The impact of suboptimal bowel preparation on adenoma miss rates and the factors associated with early repeat colonoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2011;73(6):1207-1214. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2011.01.051
- Calderwood AH, Holub JL, Greenwald DA. Recommendations for follow-up interval after colonoscopy with inadequate bowel preparation in a national colonoscopy quality registry. Gastrointest Endosc. 2022;95(2):360-367. e2. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2021.09.027
- Latorre M, Roy A, Spyrou E, Garcia-Carrasquillo R, Rosenberg R, Lebwohl B. Adherence to guidelines after poor colonoscopy preparation: experience from a patient navigator program. Gastroenterology. 2016;151(1):P196. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2016.05.027
- Bouquet E, Tomal J, Choksi Y. Next-day screening colonoscopy following inadequate bowel preparation may improve quality of preparation and adenoma detection in a veteran population. Am J Gastroenterol. 2020;115:S259. doi:10.14309/ajg.0000000000000853
- Toro B, Dawkins G, Friedenberg FK, Ehrlich AC. Risk factors for failure to return after a poor preparation colonoscopy: experience in a safety-net hospital, 255. Abstract presented at ACG October 2016. https://journals.lww.com/ajg/fulltext/2016/10001/risk_factors_for_failure_to_return_after_a_poor.255.aspx
- Partin MR, Gravely A, Gellad ZF, et al. Factors Associated With Missed and Cancelled Colonoscopy Appointments at Veterans Health Administration Facilities. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;14(2):259-267. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2015.07.051
- Idos GE, Bonner JD, Haghighat S, et al. Bridging the Gap: Patient Navigation Increases Colonoscopy Follow-up After Abnormal FIT. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2021;12(2):e00307. doi:10.14309/ctg.0000000000000307
- Islami F, Baeker Bispo J, Lee H, et al. American Cancer Society’s report on the status of cancer disparities in the United States, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin. 2024;74(2):136- 166. doi:10.3322/caac.21812
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the third-most diagnosed cancer after breast and lung cancer, and is the second leading cause of global cancer related deaths.1 In 2023 in the United States, > 150,000 individuals were diagnosed with CRC and 52,000 died.2
Colonoscopy is an effective CRC screening method and the lone method recommended for polyp surveillance. Inadequate bowel preparation (IBP) has been estimated to occur in about 6% to 26% of colonoscopies. 3,4 The prevalence varies based on a variety of comorbidities, including immobility, diabetes mellitus, neurologic disorders, and use of opioids, with more occurrences of IBP noted in older adult, non-English speaking, and male individuals.4-6
The quality of bowel preparation is integral to the effectiveness of screening and surveillance colonoscopies. IBP has been associated with missed adenomas and significantly lower adenoma detection rates.7-9 In particular, IBP is independently associated with an increased risk of CRC in the future.3 Accordingly, the US Multisociety Task Force recommends repeat colonoscopies for individuals with IBP within 1 year.10 Ensuring that these individuals receive repeat colonoscopies is an essential part of CRC prevention. The benefit of repeat colonoscopy after IBP is highlighted by a retrospective analysis from Fung and colleagues that showed 81% of repeat colonoscopies had adequate bowel preparation, with higher numbers of adenomas detected on repeat compared to initial colonoscopies.11
Given the impact of bowel preparation quality on the diagnostic capability of the colonoscopy, adherence to guidelines for repeat colonoscopies in cases of IBP is paramount for effective CRC prevention. This study aims to measure the frequency of repeat colonoscopy after IBP and the factors associated with adherence to recommendations.
METHODS
Individuals who underwent colonoscopy at the Minneapolis Veterans Affairs Medical Center (MVAMC) from January 1, 2016, to October 19, 2021, were identified to allow for 400 days of follow-up from the index colonoscopy to the data collection date. During the COVID-19 pandemic, the colonoscopy procedure capacity was reduced by 50% from June 1, 2020, to December 1, 2020, delaying nonurgent procedures, including screening and surveillance colonoscopies.
Individuals who underwent colonoscopy for CRC screening or polyp surveillance, or following a positive fecal immunohistochemistry test (FIT) or virtual computed tomography colonoscopy were included. Patients with colonoscopy indications for iron deficiency anemia, gastrointestinal bleeding, disease activity assessment of inflammatory bowel disease, abdominal pain, or changes in bowel movement pattern were excluded. IBP was defined as recording a Boston Bowel Preparation Scale (BBPS) score of < 6, or < 2 in any segment, or described as poor or inadequate using the Aronchick scale.
Age, sex, race, marital status, distance to MVAMC, smoking status, comorbidities, and concurrent medication use, including antiplatelet, anticoagulation, and prescription opiates at the time of index colonoscopy were obtained from the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) Corporate Data Warehouse (CDW) using structured query language processing of colonoscopy procedure notes to extract preparation scores and other procedure information. The CDW contains extracts from VHA clinical and administrative systems that contain complete clinical data from October 1999.12 Current smoking status was defined as any smoking activity at the time the questionnaire was administered during a routine clinic visit within 400 days from the index colonoscopy.
Only individuals who were recommended to have repeat colonoscopy within 1 year were included. The intervals of 365 days and 400 days (1 year + about 1 additional month) were used in the event that the individual had a delay in scheduling their 1-year repeat colonoscopy. For individuals who did not undergo a colonoscopy at MVAMC within 400 days, a manual chart review of all available records was performed to determine whether a colonoscopy was performed at a non-VA facility.
Patients received written instructions for bowel preparation 2 weeks prior to the procedure. The preparation included magnesium citrate and a split dose of 4 liters of polyethylene glycol. Patients were also advised to start a low-fiber diet 3 days prior to the procedure and a clear liquid diet the day before the procedure. Patients with a history of IBP or those undergoing procedures with anesthesia received an additional 2 liters for a total of 6 liters of polyethylene glycol.
Statistical analysis
Baseline characteristics were reported as mean (SD) or median and IQR for continuous variables and percentage for categorical variables. Individuals who returned for colonoscopy within 400 days were compared to those who did not identify factors associated with adherence to recommendations. The data on individuals who returned for colonoscopy within 400 days were also analyzed for additional minor delays in the timing of the repeat colonoscopy. Continuous data were compared using Mann-Whitney U tests. Categorical data were compared using X2 or Fisher exact tests. Missing data were imputed from the analyses. All analyses were performed using SAS JMP Pro version 16. P < .05 was considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
There were 18,241 total colonoscopies performed between January 1, 2016, to October 19, 2021, and 13,818 colonoscopies had indications for screening for colon cancer, positive FIT, virtual colonoscopy, or surveillance. Of the 10,466 unique patients there were 5369 patients for polyp surveillance, 4054 patients for CRC screening, and 1043 patients for positive FIT or virtual colonoscopy. Of these, 571 individuals (5.5%) had IBP. Repeat colonoscopy within 1 year was recommended for 485 individuals (84.9%) who were included in this study (153 CRC screenings and 46 positive FITs) but not for 86 individuals (15.1%) (Figure 1). Among included patients, the mean (SD) age was 66.6 (7.2) years, and the majority were male (460 [94.8%]) and White (435 [89.7%]) (Table). Two hundred and forty-three (50.1%) were married.


Adherence to Recommended Interval Colonoscopy
Of the 485 patients with IBP who were recommended for follow-up colonoscopy, 287 (59.2%) had a colonoscopy within 1 year, and 198 (40.8%) did not; 17 patients (13.5%) had repeat colonoscopy within 366 to 400 days. Five (1.0%) individuals had a repeat colonoscopy the next day, and 77 (15.9%) had a repeat colonoscopy within 7 days. One hundred and twentysix (26.0%) individuals underwent no repeat colonoscopy during the study period (Figure 2).

To account for the COVID-19 pandemic, the adherence rate of repeat colonoscopy within 1 year prepandemic (January 1, 2016, to December 1, 2018) was calculated along with the adherence rate postpandemic (January 1, 2019 to the end of the study). The rates were similar: 199 of 330 (60.3%) individuals prepandemic vs 88 of 155 (56.8%) individuals postpandemic (Figure 3).

Significant Associations
Age, sex, and race were not associated with adherence to repeat colonoscopy within 1 year. Individuals living ≤ 40 miles from the endoscopy center were more likely to undergo a repeat colonoscopy within 1 year compared with those who lived > 40 miles away (61.7% vs 51.0%, P = .02). Current smoking status was associated with a lower rate of repeat colonoscopy within 1 year (25.8% vs 35.9%; P = .02). There were no differences with respect to inflammatory bowel disease diagnosis, mental health diagnosis, diabetes mellitus, cirrhosis, or medications used, including opioids, anticoagulation, and antiplatelet therapy.
Outcomes
Among individuals who had a repeat colonoscopy the day after the index colonoscopy, 53 of 56 individuals (94.6%) had adequate bowel preparation. Among individuals who had a repeat colonoscopy within 7 days, 70 of 77 (90.9%) had adequate bowel preparation. Of 287 individuals with a repeat colonoscopy within 1 year, 251 (87.5%) had adequate bowel preparation on the repeat colonoscopy. By 400 days after the index colonoscopy, 268 of 304 individuals (88.2%) had adequate bowel preparation.
In this study conducted at a large VA medical center, we found that 5.6% of individuals undergoing colonoscopies had IBP, a rate comparable to prior studies (6% to 26%).3,4 Only 59.2% of individuals underwent repeat colonoscopies within 1 year, as recommended after an index colonoscopy with IBP. Smoking and living longer distances (> 40 miles) from the endoscopy center were associated with a decreased adherence to the repeat colonoscopy recommendation.
Current guidelines recommend repeat colonoscopy for individuals with IBP within 1 year.10 In cases of IBP, the advanced adenoma miss rate is 36% upon repeat colonoscopy within 1 year.13 Despite the importance of a follow-up colonoscopy, clinician adherence with this recommendation remains low.10,14,15 However, in this study cohort, 485 of 571 individuals with IBP (84.9%) received recommendations for a repeat colonoscopy within 1 year. In the US, only 31.9% of 260,314 colonoscopies with IBP included recommendations for a follow-up colonoscopy within 1 year.14 This could be related to variations in endoscopist practice as well as patient risk factors for developing polyps, including family history of cancer and personal history of prior polyps. The findings of multiple polyps, high-risk adenomas, and cancer on the index colonoscopy also influences the endoscopist for repeat colonoscopy within 1 year.14
The timing for repeat colonoscopies within 1 year will be determined by the patients, clinicians, and available scheduling. In this study, the earlier repeat colonoscopies, especially those occurring the day after the index colonoscopy, had the highest success rate of adequate bowel preparation. In a prior study, repeating colonoscopies within the same day or the next day was also found to have a higher rate of adequate bowel preparation than repeat colonoscopies within 1 year (88.9% vs 83.5%).16
Ensuring the return of individuals with IBP for repeat colonoscopy is a challenging task. We identified that individuals who live further away from MVAMC and current smokers had a decreased probability of returning for a repeat colonoscopy. Toro and colleagues found a 68.7% return rate for a repeat colonoscopy within 1 year with individuals age ≥ 60 years, and patients who were White were less likely to proceed with a repeat colonoscopy within 1 year.17 The study did not provide data regarding smoking status or distance to the endoscopy center.17 In a prior study of veterans, the dual diagnosis of psychiatric disorders and substance abuse was associated with missed and canceled colonoscopy appointments.18 The distance to the endoscopy center has also been previously identified as a barrier to a colonoscopy following an abnormal FIT.19 Although not identified in this study due to the homogenous demographic profile, social determinants of health such as socioeconomic status, education, and insurance coverage are known barriers to cancer screening but were not evaluated in this study.20
Based on the identified risk factors, we have created a model for utilizing those risk factors to identify individuals at higher risk for noncompliance (ie, those who live further away from the endoscopy center or currently smoke). These individuals are proactively offered to use an intraprocedural bowel cleansing device to achieve adequate bowel preparation or priority rescheduling for a next-day colonoscopy.
Limitations
This study was a single-center study of the veteran population, which is predominantly White and male, thus limiting generalizability. The study is also limited by minimal available data on adenoma detection and colon cancer incidence on subsequent colonoscopies.
CONCLUSIONS
The rate of IBP was 5.5% in individuals undergoing colonoscopy for colon cancer screening, surveillance, positive FIT, or computed tomography colonography. Only 59.2% of those with IBP underwent the recommended repeat colonoscopy within 1 year. Smoking and distance to the endoscopy center were associated with a decreased adherence to the repeat colonoscopy recommendation. Additional efforts are needed to ensure that individuals with IBP return for timely repeat colonoscopy.
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the third-most diagnosed cancer after breast and lung cancer, and is the second leading cause of global cancer related deaths.1 In 2023 in the United States, > 150,000 individuals were diagnosed with CRC and 52,000 died.2
Colonoscopy is an effective CRC screening method and the lone method recommended for polyp surveillance. Inadequate bowel preparation (IBP) has been estimated to occur in about 6% to 26% of colonoscopies. 3,4 The prevalence varies based on a variety of comorbidities, including immobility, diabetes mellitus, neurologic disorders, and use of opioids, with more occurrences of IBP noted in older adult, non-English speaking, and male individuals.4-6
The quality of bowel preparation is integral to the effectiveness of screening and surveillance colonoscopies. IBP has been associated with missed adenomas and significantly lower adenoma detection rates.7-9 In particular, IBP is independently associated with an increased risk of CRC in the future.3 Accordingly, the US Multisociety Task Force recommends repeat colonoscopies for individuals with IBP within 1 year.10 Ensuring that these individuals receive repeat colonoscopies is an essential part of CRC prevention. The benefit of repeat colonoscopy after IBP is highlighted by a retrospective analysis from Fung and colleagues that showed 81% of repeat colonoscopies had adequate bowel preparation, with higher numbers of adenomas detected on repeat compared to initial colonoscopies.11
Given the impact of bowel preparation quality on the diagnostic capability of the colonoscopy, adherence to guidelines for repeat colonoscopies in cases of IBP is paramount for effective CRC prevention. This study aims to measure the frequency of repeat colonoscopy after IBP and the factors associated with adherence to recommendations.
METHODS
Individuals who underwent colonoscopy at the Minneapolis Veterans Affairs Medical Center (MVAMC) from January 1, 2016, to October 19, 2021, were identified to allow for 400 days of follow-up from the index colonoscopy to the data collection date. During the COVID-19 pandemic, the colonoscopy procedure capacity was reduced by 50% from June 1, 2020, to December 1, 2020, delaying nonurgent procedures, including screening and surveillance colonoscopies.
Individuals who underwent colonoscopy for CRC screening or polyp surveillance, or following a positive fecal immunohistochemistry test (FIT) or virtual computed tomography colonoscopy were included. Patients with colonoscopy indications for iron deficiency anemia, gastrointestinal bleeding, disease activity assessment of inflammatory bowel disease, abdominal pain, or changes in bowel movement pattern were excluded. IBP was defined as recording a Boston Bowel Preparation Scale (BBPS) score of < 6, or < 2 in any segment, or described as poor or inadequate using the Aronchick scale.
Age, sex, race, marital status, distance to MVAMC, smoking status, comorbidities, and concurrent medication use, including antiplatelet, anticoagulation, and prescription opiates at the time of index colonoscopy were obtained from the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) Corporate Data Warehouse (CDW) using structured query language processing of colonoscopy procedure notes to extract preparation scores and other procedure information. The CDW contains extracts from VHA clinical and administrative systems that contain complete clinical data from October 1999.12 Current smoking status was defined as any smoking activity at the time the questionnaire was administered during a routine clinic visit within 400 days from the index colonoscopy.
Only individuals who were recommended to have repeat colonoscopy within 1 year were included. The intervals of 365 days and 400 days (1 year + about 1 additional month) were used in the event that the individual had a delay in scheduling their 1-year repeat colonoscopy. For individuals who did not undergo a colonoscopy at MVAMC within 400 days, a manual chart review of all available records was performed to determine whether a colonoscopy was performed at a non-VA facility.
Patients received written instructions for bowel preparation 2 weeks prior to the procedure. The preparation included magnesium citrate and a split dose of 4 liters of polyethylene glycol. Patients were also advised to start a low-fiber diet 3 days prior to the procedure and a clear liquid diet the day before the procedure. Patients with a history of IBP or those undergoing procedures with anesthesia received an additional 2 liters for a total of 6 liters of polyethylene glycol.
Statistical analysis
Baseline characteristics were reported as mean (SD) or median and IQR for continuous variables and percentage for categorical variables. Individuals who returned for colonoscopy within 400 days were compared to those who did not identify factors associated with adherence to recommendations. The data on individuals who returned for colonoscopy within 400 days were also analyzed for additional minor delays in the timing of the repeat colonoscopy. Continuous data were compared using Mann-Whitney U tests. Categorical data were compared using X2 or Fisher exact tests. Missing data were imputed from the analyses. All analyses were performed using SAS JMP Pro version 16. P < .05 was considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
There were 18,241 total colonoscopies performed between January 1, 2016, to October 19, 2021, and 13,818 colonoscopies had indications for screening for colon cancer, positive FIT, virtual colonoscopy, or surveillance. Of the 10,466 unique patients there were 5369 patients for polyp surveillance, 4054 patients for CRC screening, and 1043 patients for positive FIT or virtual colonoscopy. Of these, 571 individuals (5.5%) had IBP. Repeat colonoscopy within 1 year was recommended for 485 individuals (84.9%) who were included in this study (153 CRC screenings and 46 positive FITs) but not for 86 individuals (15.1%) (Figure 1). Among included patients, the mean (SD) age was 66.6 (7.2) years, and the majority were male (460 [94.8%]) and White (435 [89.7%]) (Table). Two hundred and forty-three (50.1%) were married.


Adherence to Recommended Interval Colonoscopy
Of the 485 patients with IBP who were recommended for follow-up colonoscopy, 287 (59.2%) had a colonoscopy within 1 year, and 198 (40.8%) did not; 17 patients (13.5%) had repeat colonoscopy within 366 to 400 days. Five (1.0%) individuals had a repeat colonoscopy the next day, and 77 (15.9%) had a repeat colonoscopy within 7 days. One hundred and twentysix (26.0%) individuals underwent no repeat colonoscopy during the study period (Figure 2).

To account for the COVID-19 pandemic, the adherence rate of repeat colonoscopy within 1 year prepandemic (January 1, 2016, to December 1, 2018) was calculated along with the adherence rate postpandemic (January 1, 2019 to the end of the study). The rates were similar: 199 of 330 (60.3%) individuals prepandemic vs 88 of 155 (56.8%) individuals postpandemic (Figure 3).

Significant Associations
Age, sex, and race were not associated with adherence to repeat colonoscopy within 1 year. Individuals living ≤ 40 miles from the endoscopy center were more likely to undergo a repeat colonoscopy within 1 year compared with those who lived > 40 miles away (61.7% vs 51.0%, P = .02). Current smoking status was associated with a lower rate of repeat colonoscopy within 1 year (25.8% vs 35.9%; P = .02). There were no differences with respect to inflammatory bowel disease diagnosis, mental health diagnosis, diabetes mellitus, cirrhosis, or medications used, including opioids, anticoagulation, and antiplatelet therapy.
Outcomes
Among individuals who had a repeat colonoscopy the day after the index colonoscopy, 53 of 56 individuals (94.6%) had adequate bowel preparation. Among individuals who had a repeat colonoscopy within 7 days, 70 of 77 (90.9%) had adequate bowel preparation. Of 287 individuals with a repeat colonoscopy within 1 year, 251 (87.5%) had adequate bowel preparation on the repeat colonoscopy. By 400 days after the index colonoscopy, 268 of 304 individuals (88.2%) had adequate bowel preparation.
In this study conducted at a large VA medical center, we found that 5.6% of individuals undergoing colonoscopies had IBP, a rate comparable to prior studies (6% to 26%).3,4 Only 59.2% of individuals underwent repeat colonoscopies within 1 year, as recommended after an index colonoscopy with IBP. Smoking and living longer distances (> 40 miles) from the endoscopy center were associated with a decreased adherence to the repeat colonoscopy recommendation.
Current guidelines recommend repeat colonoscopy for individuals with IBP within 1 year.10 In cases of IBP, the advanced adenoma miss rate is 36% upon repeat colonoscopy within 1 year.13 Despite the importance of a follow-up colonoscopy, clinician adherence with this recommendation remains low.10,14,15 However, in this study cohort, 485 of 571 individuals with IBP (84.9%) received recommendations for a repeat colonoscopy within 1 year. In the US, only 31.9% of 260,314 colonoscopies with IBP included recommendations for a follow-up colonoscopy within 1 year.14 This could be related to variations in endoscopist practice as well as patient risk factors for developing polyps, including family history of cancer and personal history of prior polyps. The findings of multiple polyps, high-risk adenomas, and cancer on the index colonoscopy also influences the endoscopist for repeat colonoscopy within 1 year.14
The timing for repeat colonoscopies within 1 year will be determined by the patients, clinicians, and available scheduling. In this study, the earlier repeat colonoscopies, especially those occurring the day after the index colonoscopy, had the highest success rate of adequate bowel preparation. In a prior study, repeating colonoscopies within the same day or the next day was also found to have a higher rate of adequate bowel preparation than repeat colonoscopies within 1 year (88.9% vs 83.5%).16
Ensuring the return of individuals with IBP for repeat colonoscopy is a challenging task. We identified that individuals who live further away from MVAMC and current smokers had a decreased probability of returning for a repeat colonoscopy. Toro and colleagues found a 68.7% return rate for a repeat colonoscopy within 1 year with individuals age ≥ 60 years, and patients who were White were less likely to proceed with a repeat colonoscopy within 1 year.17 The study did not provide data regarding smoking status or distance to the endoscopy center.17 In a prior study of veterans, the dual diagnosis of psychiatric disorders and substance abuse was associated with missed and canceled colonoscopy appointments.18 The distance to the endoscopy center has also been previously identified as a barrier to a colonoscopy following an abnormal FIT.19 Although not identified in this study due to the homogenous demographic profile, social determinants of health such as socioeconomic status, education, and insurance coverage are known barriers to cancer screening but were not evaluated in this study.20
Based on the identified risk factors, we have created a model for utilizing those risk factors to identify individuals at higher risk for noncompliance (ie, those who live further away from the endoscopy center or currently smoke). These individuals are proactively offered to use an intraprocedural bowel cleansing device to achieve adequate bowel preparation or priority rescheduling for a next-day colonoscopy.
Limitations
This study was a single-center study of the veteran population, which is predominantly White and male, thus limiting generalizability. The study is also limited by minimal available data on adenoma detection and colon cancer incidence on subsequent colonoscopies.
CONCLUSIONS
The rate of IBP was 5.5% in individuals undergoing colonoscopy for colon cancer screening, surveillance, positive FIT, or computed tomography colonography. Only 59.2% of those with IBP underwent the recommended repeat colonoscopy within 1 year. Smoking and distance to the endoscopy center were associated with a decreased adherence to the repeat colonoscopy recommendation. Additional efforts are needed to ensure that individuals with IBP return for timely repeat colonoscopy.
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209-249. doi:10.3322/caac.21660
- Siegel RL, Wagle NS, Cercek A, Smith RA, Jemal A. Colorectal cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin. 2023;73(3):233-254. doi:10.3322/caac.21772
- Atkin W, Wooldrage K, Brenner A, et al. Adenoma surveillance and colorectal cancer incidence: a retrospective, multicentre, cohort study. Lancet Oncol. 2017;18(6):823- 834. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30187-0
- Froehlich F, Wietlisbach V, Gonvers JJ, Burnand B, Vader JP. Impact of colonic cleansing on quality and diagnostic yield of colonoscopy: the European Panel of Appropriateness of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy European multicenter study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2005;61(3):378- 384. doi:10.1016/s0016-5107(04)02776-2
- Mahmood S, Farooqui SM, Madhoun MF. Predictors of inadequate bowel preparation for colonoscopy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;30(8):819-826. doi:10.1097/MEG.0000000000001175
- ASGE Standards of Practice Committee, Saltzman JR, Cash BD, et al. Bowel preparation before colonoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015;81(4):781-794. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2014.09.048
- Clark BT, Protiva P, Nagar A, et al. Quantification of Adequate Bowel Preparation for Screening or Surveillance Colonoscopy in Men. Gastroenterology. 2016;150(2):396- e15. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2015.09.041
- Sulz MC, Kröger A, Prakash M, Manser CN, Heinrich H, Misselwitz B. Meta-Analysis of the Effect of Bowel Preparation on Adenoma Detection: Early Adenomas Affected Stronger than Advanced Adenomas. PLoS One. 2016;11(6):e0154149. Published 2016 Jun 3. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0154149
- Chokshi RV, Hovis CE, Hollander T, Early DS, Wang JS. Prevalence of missed adenomas in patients with inadequate bowel preparation on screening colonoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2012;75(6):1197-1203. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2012.01.005
- Lieberman DA, Rex DK, Winawer SJ, Giardiello FM, Johnson DA, Levin TR. Guidelines for colonoscopy surveillance after screening and polypectomy: a consensus update by the US Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer. Gastroenterology. 2012;143(3):844-857. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2012.06.001
- Fung P, Syed A, Cole R, Farah K. Poor bowel prep: are you really going to come back within a year? Abstract presented at American Gastroenterological Association DDW 2021, May 21-23, 2021. doi:10.1016/S0016-5085(21)01204-X
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, VA Health Systems Research. Corporate data warehouse (CDW). Updated January 11, 2023. Accessed August 6, 2024. https://www.hsrd.research.va.gov/for_researchers/cdw.cfm
- Lebwohl B, Kastrinos F, Glick M, Rosenbaum AJ, Wang T, Neugut AI. The impact of suboptimal bowel preparation on adenoma miss rates and the factors associated with early repeat colonoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2011;73(6):1207-1214. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2011.01.051
- Calderwood AH, Holub JL, Greenwald DA. Recommendations for follow-up interval after colonoscopy with inadequate bowel preparation in a national colonoscopy quality registry. Gastrointest Endosc. 2022;95(2):360-367. e2. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2021.09.027
- Latorre M, Roy A, Spyrou E, Garcia-Carrasquillo R, Rosenberg R, Lebwohl B. Adherence to guidelines after poor colonoscopy preparation: experience from a patient navigator program. Gastroenterology. 2016;151(1):P196. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2016.05.027
- Bouquet E, Tomal J, Choksi Y. Next-day screening colonoscopy following inadequate bowel preparation may improve quality of preparation and adenoma detection in a veteran population. Am J Gastroenterol. 2020;115:S259. doi:10.14309/ajg.0000000000000853
- Toro B, Dawkins G, Friedenberg FK, Ehrlich AC. Risk factors for failure to return after a poor preparation colonoscopy: experience in a safety-net hospital, 255. Abstract presented at ACG October 2016. https://journals.lww.com/ajg/fulltext/2016/10001/risk_factors_for_failure_to_return_after_a_poor.255.aspx
- Partin MR, Gravely A, Gellad ZF, et al. Factors Associated With Missed and Cancelled Colonoscopy Appointments at Veterans Health Administration Facilities. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;14(2):259-267. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2015.07.051
- Idos GE, Bonner JD, Haghighat S, et al. Bridging the Gap: Patient Navigation Increases Colonoscopy Follow-up After Abnormal FIT. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2021;12(2):e00307. doi:10.14309/ctg.0000000000000307
- Islami F, Baeker Bispo J, Lee H, et al. American Cancer Society’s report on the status of cancer disparities in the United States, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin. 2024;74(2):136- 166. doi:10.3322/caac.21812
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209-249. doi:10.3322/caac.21660
- Siegel RL, Wagle NS, Cercek A, Smith RA, Jemal A. Colorectal cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin. 2023;73(3):233-254. doi:10.3322/caac.21772
- Atkin W, Wooldrage K, Brenner A, et al. Adenoma surveillance and colorectal cancer incidence: a retrospective, multicentre, cohort study. Lancet Oncol. 2017;18(6):823- 834. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30187-0
- Froehlich F, Wietlisbach V, Gonvers JJ, Burnand B, Vader JP. Impact of colonic cleansing on quality and diagnostic yield of colonoscopy: the European Panel of Appropriateness of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy European multicenter study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2005;61(3):378- 384. doi:10.1016/s0016-5107(04)02776-2
- Mahmood S, Farooqui SM, Madhoun MF. Predictors of inadequate bowel preparation for colonoscopy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;30(8):819-826. doi:10.1097/MEG.0000000000001175
- ASGE Standards of Practice Committee, Saltzman JR, Cash BD, et al. Bowel preparation before colonoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015;81(4):781-794. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2014.09.048
- Clark BT, Protiva P, Nagar A, et al. Quantification of Adequate Bowel Preparation for Screening or Surveillance Colonoscopy in Men. Gastroenterology. 2016;150(2):396- e15. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2015.09.041
- Sulz MC, Kröger A, Prakash M, Manser CN, Heinrich H, Misselwitz B. Meta-Analysis of the Effect of Bowel Preparation on Adenoma Detection: Early Adenomas Affected Stronger than Advanced Adenomas. PLoS One. 2016;11(6):e0154149. Published 2016 Jun 3. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0154149
- Chokshi RV, Hovis CE, Hollander T, Early DS, Wang JS. Prevalence of missed adenomas in patients with inadequate bowel preparation on screening colonoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2012;75(6):1197-1203. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2012.01.005
- Lieberman DA, Rex DK, Winawer SJ, Giardiello FM, Johnson DA, Levin TR. Guidelines for colonoscopy surveillance after screening and polypectomy: a consensus update by the US Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer. Gastroenterology. 2012;143(3):844-857. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2012.06.001
- Fung P, Syed A, Cole R, Farah K. Poor bowel prep: are you really going to come back within a year? Abstract presented at American Gastroenterological Association DDW 2021, May 21-23, 2021. doi:10.1016/S0016-5085(21)01204-X
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, VA Health Systems Research. Corporate data warehouse (CDW). Updated January 11, 2023. Accessed August 6, 2024. https://www.hsrd.research.va.gov/for_researchers/cdw.cfm
- Lebwohl B, Kastrinos F, Glick M, Rosenbaum AJ, Wang T, Neugut AI. The impact of suboptimal bowel preparation on adenoma miss rates and the factors associated with early repeat colonoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2011;73(6):1207-1214. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2011.01.051
- Calderwood AH, Holub JL, Greenwald DA. Recommendations for follow-up interval after colonoscopy with inadequate bowel preparation in a national colonoscopy quality registry. Gastrointest Endosc. 2022;95(2):360-367. e2. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2021.09.027
- Latorre M, Roy A, Spyrou E, Garcia-Carrasquillo R, Rosenberg R, Lebwohl B. Adherence to guidelines after poor colonoscopy preparation: experience from a patient navigator program. Gastroenterology. 2016;151(1):P196. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2016.05.027
- Bouquet E, Tomal J, Choksi Y. Next-day screening colonoscopy following inadequate bowel preparation may improve quality of preparation and adenoma detection in a veteran population. Am J Gastroenterol. 2020;115:S259. doi:10.14309/ajg.0000000000000853
- Toro B, Dawkins G, Friedenberg FK, Ehrlich AC. Risk factors for failure to return after a poor preparation colonoscopy: experience in a safety-net hospital, 255. Abstract presented at ACG October 2016. https://journals.lww.com/ajg/fulltext/2016/10001/risk_factors_for_failure_to_return_after_a_poor.255.aspx
- Partin MR, Gravely A, Gellad ZF, et al. Factors Associated With Missed and Cancelled Colonoscopy Appointments at Veterans Health Administration Facilities. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;14(2):259-267. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2015.07.051
- Idos GE, Bonner JD, Haghighat S, et al. Bridging the Gap: Patient Navigation Increases Colonoscopy Follow-up After Abnormal FIT. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2021;12(2):e00307. doi:10.14309/ctg.0000000000000307
- Islami F, Baeker Bispo J, Lee H, et al. American Cancer Society’s report on the status of cancer disparities in the United States, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin. 2024;74(2):136- 166. doi:10.3322/caac.21812
A Novel Text Message Protocol to Improve Bowel Preparation for Outpatient Colonoscopies in Veterans
Colorectal cancer is the third leading cause of cancer-related death in both men and women.1 Colonoscopy is the current gold standard for screening due to the ability to remove precancerous lesions but remains highly dependent on the quality of bowel preparation.2 Poor bowel preparation has been associated with impaired adenoma detection as well as increased health care utilization due to the need for a repeat colonoscopy.3
Multiple patient factors are associated with increased risk of poor bowel preparation, including age > 60 years, male sex, diabetes mellitus, and presence of a mental health diagnosis, factors that are prevalent among the veteran population.3-5 Text messages have been shown to improve the quality of bowel preparation by increasing patients' understanding and adherence with the preparation process. Improved adherence with bowel preparation directions is associated with a cleaner colon prior to colonoscopy, leading to a thorough examination. Studies using text messaging instructions prior to colonoscopies have also shown measurable improvement in adenoma detection rate, patient preparation-associated discomfort, and completion of colonoscopy.6-10
In 2016, the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) introduced Annie, one of the first automated text messaging services, named after Army Lieutenant Annie Fox, the first woman to receive the Purple Heart for combat. The Annie platform allows for notifications, instructions, and simple data collection. The development of this platform allows VHA practitioners to engage and educate veterans in a similar way to other health care systems using text messaging protocols. Annie text messages have been piloted for the use of hepatitis C treatment, demonstrating promise of improved medication adherence and patient satisfaction.11 We aimed to develop and pilot the Annie bowel preparation protocol to improve the quality of colonoscopy bowel preparation for outpatients at the Minneapolis Veterans Affairs Medical Center (MVAMC) in Minnesota. A secondary goal included measuring patient satisfaction with the text messaging instructions for outpatient colonoscopy preparation.
Methods
We conducted a single center, prospective, endoscopist-blinded, study with two 3-month long Plan-Do-Study-Act (PDSA) cycles to improve the text messaging bowel preparation protocol at MVAMC between January 2019 and April 2020. The MVAMC Institutional Review Board determined the quality improvement project was exempt. Veterans who had outpatient colonoscopies scheduled were included. Veterans undergoing inpatient colonoscopies or outpatients who could not be reached to obtain informed consent, lacked text message capability, declined participation, or required extended colonoscopy preparation were excluded. Per MVAMC procedures, extended colonoscopy preparation was provided to patients receiving general or monitored anesthesia care, with a history of poor bowel preparation, or with risk factors for poor preparation as determined by the ordering health care professional (HCP). Standard bowel preparation involves ingestion of 4 L of polyethylene glycol 3350 with electrolytes; extended bowel preparation requires ingestion of an additional 2 L to total 6 L and uses a different set of instructions. Additionally, the patient population requiring extended bowel preparation also includes patients with spinal cord injuries, who often are admitted for assistance with extended preparation. Patients who consented to receiving text messages were placed in the Annie intervention group, and all others were placed in the control group.
The control group received standardized patient education, including a mailed copy of bowel preparation instructions and a phone call from a gastroenterology service nurse about 1 to 2 weeks before the procedure. Current MVAMC standard of care involves a phone call from a nurse to confirm that patients have received the polyethylene glycol preparation solution, the mailed instructions, have an escort and transportation, and to answer any questions. Both the usual care and intervention group received the phone call. During this call, the Annie text messaging bowel preparation protocol was introduced; if the veteran chose to participate, consent and enrollment were completed.
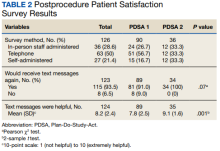
On the day of the colonoscopy, veterans in the intervention group were surveyed in the waiting room about their experience receiving the text messages and soliciting feedback for improvement or surveyed via telephone call within 3 days of their procedure. Patient satisfaction was quantified with a scale from 1 (low) to 10 (high), including questions about how helpful the texts were in relation to total number, timing, and content of messages as well as whether veterans would like to receive the text messages again for future procedures.
We reviewed individual charts and collected Boston Bowel Preparation Scale (BBPS) scores to determine adequate preparation. BBPS assigns a score of 0 to 3 for the right, transverse, and left colon applied upon withdrawal after flushing and suctioning have been completed.12 Adequate preparation is considered a total score of ≥ 6 with no segment scoring < 2. This method of preparation assessment is preferred due to its ability to account for difference in preparation quality among colonic segments, well-defined scoring characteristics, and several studies validating its use showing inter- and intraobserver reliability.12 Follow-up studies have shown validity of the BBPS when compared with relevant outcomes such as polyp detection rate and recommended timing for repeat procedure.13 Variables associated with poor bowel preparation (ie, gender, prior abdominal surgery, impaired mobility, high body mass index, diabetes mellitus, stroke, dementia, any neurologic diagnosis, cirrhosis, smoking, polypharmacy [> 8 active medications], and narcotic or tricyclic antidepressant medication use) were also collected through chart review.3-5 We note that immobility was defined by International Classification of Diseases (ICD)-9 and ICD-10 codes and prescriptions for assistive devices (ie, canes, wheelchairs, 4-wheeled walkers).
Veterans assent to be enrolled in Annie. After enrollment, veterans must text back a specific word response to an initial text message to receive the protocolized messages from the Annie program. A contact phone number to the gastrointestinal nurse line was provided for questions during business hours. The start date for the text message protocol is 6 days prior to the procedure date. If a patient rescheduled their colonoscopy, the Annie database was updated manually.
Statistical Analysis
We used both Pearson χ2 test and 2-sample t test analyses to compare demographic information and patient satisfaction scores between the control and intervention groups. We compared continuous BBPS scores between Annie intervention vs control group using parametric and nonparametric independent t tests using the Mann-Whitney U test. We repeated this analysis controlling for both mental health diagnoses and age using linear regression. We were unable to survey 61 of the 187 veterans who received Annie text messages.
RESULTS
During PDSA cycles 1 and 2, 640 veterans were scheduled for outpatient colonoscopy: 453 veterans were in the control group; 187 veterans were in the intervention group, of which 126 were surveyed. A significant percentage of veterans declined participation because they felt like they did not need reinforced education; others were not eligible for Annie due to requirement for extended bowel preparation, cancelled colonoscopy, inability to physically read text messages, or lack of cell phone.
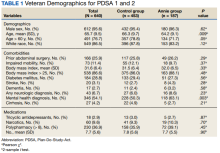
The mean (SD) age was 65 (8) years; 184 (28.8%) had a diabetes mellitus diagnosis, and the mean (SD) body mass index was 31.6 (6.4). The Annie group was slightly more likely to have mental health diagnoses and lower age compared with the control group (Table 1).
Patient Feedback
We collected feedback from veterans after each PDSA cycle to identify areas for improvement by both in-person and telephone surveys. Based on feedback from PDSA cycle 1, we decreased the total number of text messages to create a more succinct set of instructions. The most frequently requested change involved timing the text messages to align with the exact morning a specific instruction should take place.
Patient satisfaction with the Annie text messaging service was high.
DISCUSSION
To our knowledge, this is the first report of using Annie at a VAMC for colonoscopy bowel preparation improvement. We found a statistically significant improvement in the average BBPS in those receiving Annie text messages compared with the routine care control group. We also found high levels of patient satisfaction with most patients requesting to receive them again for future procedures.
The clinical significance of a BBPS of 7.8 vs 8.2 is unclear, although any score > 6 is considered to be adequate. However, subjectively speaking, the higher the BBPS the cleaner the colon, and theoretically the easier it is to see small or flat polyps. Future steps could include calculating adenoma detection rates for those enrolled in the Annie program vs the control group.
We have received inquiries regarding potential program implementation at other facilities. Success and sustainability of the program will require long-term commitment and ideally protected time for staff. It is helpful to remember that for each person who chooses to enroll in the intervention, the program currently requires that a brief consent note is placed in the patient’s chart. Thus, depending on the facilities’ resources, it is ideal for one staff member to be the designated lead to help oversee, troubleshoot, and train additional personnel. Surveys can be intermittently used to obtain feedback for improvement but are not required for sustainability. Automated text messaging is a promising addition to medicine for clinical education and communication. Future studies should examine the clinical significance (ie, adenoma detection rates) of text messaging bowel preparation protocols.
Limitations
Our study has several limitations. First, this was a single center study, thus generalizability is limited. MVAMC represents a predominantly White, male, and rural population. Second, data are likely an underestimation of the true impact of intervention, because results do not account for patients who were turned away on day of procedure (typically still reporting brown stools at time of check-in for procedure) due to poor preparation or aborted procedures secondary to poor preparation. Only about one-third of the 640 veterans opted to receive Annie text messages.
Studies have shown veterans are willing to use technology for health care; however, access to technology and lack of training remain barriers to use.14 This has been most robustly studied at the VA in veterans experiencing mental illness and homelessness. Targeted strategies to improve veteran adoption of technology within their health care include supplying veterans with cell phones and paid data plans and providing training on specific technology-based resources.15-17 Future improvement for the Annie platform should include improved integration with CPRS. Integration will facilitate automatic import of key information such as mobile phone number or colonoscopy procedure date. Unfortunately, this is not currently an automated process, and the manual workload of staff limits sustainability. Since our study ended, the Annie database now allows an “event date” to be programmed in to center the text message series around. This will be entered at the time of Annie enrollment and eliminate manual activation of the protocol. The issue of updating information for rescheduled procedures remains.
Conclusions
There is increasing evidence that automated text messaging is a promising addition to medicine for clinical education and communication. It continues to gain traction as a readily available and acceptable option, and many patients are willing to incorporate the technology platform into their care plan. We found high patient satisfaction with our protocol, and Annie patients had cleaner bowel preparations compared with control patients. Our study supports the use of text message reminders as an effective intervention for improving patient adherence with bowel preparation instructions. We suspect that creation of a text messaging protocol designed for patients requiring outpatient extended bowel preparation will yield great benefit. As technology continues to improve, future implementation of Annie text messaging will become increasingly seamless within the field of gastroenterology and beyond.
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Colorectal cancer statistics. Updated June 6, 2022. Accessed September 8, 2022. https://www.cdc.gov/cancer/colorectal/statistics
2. Lieberman D, Ladabaum U, Cruz-Correa M, et al. Screening for colorectal cancer and evolving issues for physicians and patients: a review. JAMA. 2016;316(20):2135-2145. doi:10.1001/jama.2016.17418
3. Nguyen DL, Wieland M. Risk factors predictive of poor quality preparation during average risk colonoscopy screening: the importance of health literacy. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 2010;19(4):369-372.
4. Mahmood S, Farooqui SM, Madhoun MF. Predictors of inadequate bowel preparation for colonoscopy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;30(8):819-826. doi:10.1097/MEG.0000000000001175
5. Harrington KM, Nguyen XT, Song RJ, et al. Gender differences in demographic and health characteristics of the Million Veteran Program cohort. Womens Health Issues. 2019;29(suppl 1):S56-S66. doi:10.1016/j.whi.2019.04.012
6. Zhang QX, Li J, Zhang Q, et al. Effect of education by messaging software on the quality of bowel preparation for colonoscopy. Chin Med J (Engl). 2018;131(14):1750-1752. doi:10.4103/0366-6999.235881
7. Walter B, Klare P, Strehle K, et al. Improving the quality and acceptance of colonoscopy preparation by reinforced patient education with short message service: results from a randomized, multicenter study (PERICLES-II). Gastrointest Endosc. 2019;89(3):506-513.e4. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2018.08.014
8. Nadim MM, Doshi S, Coniglio M, et al. Automated text message navigation to improve preparation quality and show rate for colonoscopy. Am J Gastroenterol. 2018;113:S64-S66.
9. Walter B, Frank R, Ludwig L, et al. Smartphone application to reinforce education increases high-quality preparation for colorectal cancer screening colonoscopies in a randomized trial. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;19(2):331-338.e5. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2020.03.051
10. Guo B, Zuo X, Li Z, et al. Improving the quality of bowel preparation through an app for inpatients undergoing colonoscopy: a randomized controlled trial. J Adv Nurs. 2020;76(4):1037-1045. doi:10.1111/jan.14295
11. Yakovchenko V, Hogan TP, Houston TK, et al. Automated text messaging with patients in department of veterans affairs specialty clinics: cluster randomized trial. J Med Internet Res. 2019;21(8):e14750. doi:10.2196/14750
12. Lai EJ, Calderwood AH, Doros G, Fix OK, Jacobson BC. The Boston bowel preparation scale: a valid and reliable instrument for colonoscopy-oriented research. Gastrointest Endosc. 2009;69(3 Pt 2):620-625. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2008.05.057
13. Calderwood AH, Jacobson BC. Comprehensive validation of the Boston Bowel Preparation Scale. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010;72(4):686-692. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2010.06.068
14. Duan-Porter W, Van Houtven CH, Mahanna EP, et al. Internet use and technology-related attitudes of veterans and informal caregivers of veterans. Telemed J E Health. 2018;24(7):471-480. doi:10.1089/tmj.2017.0015
15. Boston University School of Public Health. how mobile technology can increase veteran healthcare and wellbeing. November 10, 2021. Accessed November 1, 2022. https://www.ideahub.org/research-data/how-mobile-technology-increases-veteran-healthcare-and-wellbeing/
16. Klee A, Stacy M, Rosenheck R, Harkness L, Tsai J. Interest in technology-based therapies hampered by access: A survey of veterans with serious mental illnesses. Psychiatr Rehabil J. 2016;39(2):173-179. doi:10.1037/prj0000180
17. Berrouiguet S, Baca-García E, Brandt S, Walter M, Courtet P. Fundamentals for future mobile-health (mHealth): a systematic review of mobile phone and web-based text messaging in mental health. J Med Internet Res. 2016;18(6):e135. Published 2016 Jun 10. doi:10.2196/jmir.5066
Colorectal cancer is the third leading cause of cancer-related death in both men and women.1 Colonoscopy is the current gold standard for screening due to the ability to remove precancerous lesions but remains highly dependent on the quality of bowel preparation.2 Poor bowel preparation has been associated with impaired adenoma detection as well as increased health care utilization due to the need for a repeat colonoscopy.3
Multiple patient factors are associated with increased risk of poor bowel preparation, including age > 60 years, male sex, diabetes mellitus, and presence of a mental health diagnosis, factors that are prevalent among the veteran population.3-5 Text messages have been shown to improve the quality of bowel preparation by increasing patients' understanding and adherence with the preparation process. Improved adherence with bowel preparation directions is associated with a cleaner colon prior to colonoscopy, leading to a thorough examination. Studies using text messaging instructions prior to colonoscopies have also shown measurable improvement in adenoma detection rate, patient preparation-associated discomfort, and completion of colonoscopy.6-10
In 2016, the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) introduced Annie, one of the first automated text messaging services, named after Army Lieutenant Annie Fox, the first woman to receive the Purple Heart for combat. The Annie platform allows for notifications, instructions, and simple data collection. The development of this platform allows VHA practitioners to engage and educate veterans in a similar way to other health care systems using text messaging protocols. Annie text messages have been piloted for the use of hepatitis C treatment, demonstrating promise of improved medication adherence and patient satisfaction.11 We aimed to develop and pilot the Annie bowel preparation protocol to improve the quality of colonoscopy bowel preparation for outpatients at the Minneapolis Veterans Affairs Medical Center (MVAMC) in Minnesota. A secondary goal included measuring patient satisfaction with the text messaging instructions for outpatient colonoscopy preparation.
Methods
We conducted a single center, prospective, endoscopist-blinded, study with two 3-month long Plan-Do-Study-Act (PDSA) cycles to improve the text messaging bowel preparation protocol at MVAMC between January 2019 and April 2020. The MVAMC Institutional Review Board determined the quality improvement project was exempt. Veterans who had outpatient colonoscopies scheduled were included. Veterans undergoing inpatient colonoscopies or outpatients who could not be reached to obtain informed consent, lacked text message capability, declined participation, or required extended colonoscopy preparation were excluded. Per MVAMC procedures, extended colonoscopy preparation was provided to patients receiving general or monitored anesthesia care, with a history of poor bowel preparation, or with risk factors for poor preparation as determined by the ordering health care professional (HCP). Standard bowel preparation involves ingestion of 4 L of polyethylene glycol 3350 with electrolytes; extended bowel preparation requires ingestion of an additional 2 L to total 6 L and uses a different set of instructions. Additionally, the patient population requiring extended bowel preparation also includes patients with spinal cord injuries, who often are admitted for assistance with extended preparation. Patients who consented to receiving text messages were placed in the Annie intervention group, and all others were placed in the control group.
The control group received standardized patient education, including a mailed copy of bowel preparation instructions and a phone call from a gastroenterology service nurse about 1 to 2 weeks before the procedure. Current MVAMC standard of care involves a phone call from a nurse to confirm that patients have received the polyethylene glycol preparation solution, the mailed instructions, have an escort and transportation, and to answer any questions. Both the usual care and intervention group received the phone call. During this call, the Annie text messaging bowel preparation protocol was introduced; if the veteran chose to participate, consent and enrollment were completed.
On the day of the colonoscopy, veterans in the intervention group were surveyed in the waiting room about their experience receiving the text messages and soliciting feedback for improvement or surveyed via telephone call within 3 days of their procedure. Patient satisfaction was quantified with a scale from 1 (low) to 10 (high), including questions about how helpful the texts were in relation to total number, timing, and content of messages as well as whether veterans would like to receive the text messages again for future procedures.
We reviewed individual charts and collected Boston Bowel Preparation Scale (BBPS) scores to determine adequate preparation. BBPS assigns a score of 0 to 3 for the right, transverse, and left colon applied upon withdrawal after flushing and suctioning have been completed.12 Adequate preparation is considered a total score of ≥ 6 with no segment scoring < 2. This method of preparation assessment is preferred due to its ability to account for difference in preparation quality among colonic segments, well-defined scoring characteristics, and several studies validating its use showing inter- and intraobserver reliability.12 Follow-up studies have shown validity of the BBPS when compared with relevant outcomes such as polyp detection rate and recommended timing for repeat procedure.13 Variables associated with poor bowel preparation (ie, gender, prior abdominal surgery, impaired mobility, high body mass index, diabetes mellitus, stroke, dementia, any neurologic diagnosis, cirrhosis, smoking, polypharmacy [> 8 active medications], and narcotic or tricyclic antidepressant medication use) were also collected through chart review.3-5 We note that immobility was defined by International Classification of Diseases (ICD)-9 and ICD-10 codes and prescriptions for assistive devices (ie, canes, wheelchairs, 4-wheeled walkers).
Veterans assent to be enrolled in Annie. After enrollment, veterans must text back a specific word response to an initial text message to receive the protocolized messages from the Annie program. A contact phone number to the gastrointestinal nurse line was provided for questions during business hours. The start date for the text message protocol is 6 days prior to the procedure date. If a patient rescheduled their colonoscopy, the Annie database was updated manually.
Statistical Analysis
We used both Pearson χ2 test and 2-sample t test analyses to compare demographic information and patient satisfaction scores between the control and intervention groups. We compared continuous BBPS scores between Annie intervention vs control group using parametric and nonparametric independent t tests using the Mann-Whitney U test. We repeated this analysis controlling for both mental health diagnoses and age using linear regression. We were unable to survey 61 of the 187 veterans who received Annie text messages.
RESULTS
During PDSA cycles 1 and 2, 640 veterans were scheduled for outpatient colonoscopy: 453 veterans were in the control group; 187 veterans were in the intervention group, of which 126 were surveyed. A significant percentage of veterans declined participation because they felt like they did not need reinforced education; others were not eligible for Annie due to requirement for extended bowel preparation, cancelled colonoscopy, inability to physically read text messages, or lack of cell phone.
The mean (SD) age was 65 (8) years; 184 (28.8%) had a diabetes mellitus diagnosis, and the mean (SD) body mass index was 31.6 (6.4). The Annie group was slightly more likely to have mental health diagnoses and lower age compared with the control group (Table 1).
Patient Feedback
We collected feedback from veterans after each PDSA cycle to identify areas for improvement by both in-person and telephone surveys. Based on feedback from PDSA cycle 1, we decreased the total number of text messages to create a more succinct set of instructions. The most frequently requested change involved timing the text messages to align with the exact morning a specific instruction should take place.
Patient satisfaction with the Annie text messaging service was high.
DISCUSSION
To our knowledge, this is the first report of using Annie at a VAMC for colonoscopy bowel preparation improvement. We found a statistically significant improvement in the average BBPS in those receiving Annie text messages compared with the routine care control group. We also found high levels of patient satisfaction with most patients requesting to receive them again for future procedures.
The clinical significance of a BBPS of 7.8 vs 8.2 is unclear, although any score > 6 is considered to be adequate. However, subjectively speaking, the higher the BBPS the cleaner the colon, and theoretically the easier it is to see small or flat polyps. Future steps could include calculating adenoma detection rates for those enrolled in the Annie program vs the control group.
We have received inquiries regarding potential program implementation at other facilities. Success and sustainability of the program will require long-term commitment and ideally protected time for staff. It is helpful to remember that for each person who chooses to enroll in the intervention, the program currently requires that a brief consent note is placed in the patient’s chart. Thus, depending on the facilities’ resources, it is ideal for one staff member to be the designated lead to help oversee, troubleshoot, and train additional personnel. Surveys can be intermittently used to obtain feedback for improvement but are not required for sustainability. Automated text messaging is a promising addition to medicine for clinical education and communication. Future studies should examine the clinical significance (ie, adenoma detection rates) of text messaging bowel preparation protocols.
Limitations
Our study has several limitations. First, this was a single center study, thus generalizability is limited. MVAMC represents a predominantly White, male, and rural population. Second, data are likely an underestimation of the true impact of intervention, because results do not account for patients who were turned away on day of procedure (typically still reporting brown stools at time of check-in for procedure) due to poor preparation or aborted procedures secondary to poor preparation. Only about one-third of the 640 veterans opted to receive Annie text messages.
Studies have shown veterans are willing to use technology for health care; however, access to technology and lack of training remain barriers to use.14 This has been most robustly studied at the VA in veterans experiencing mental illness and homelessness. Targeted strategies to improve veteran adoption of technology within their health care include supplying veterans with cell phones and paid data plans and providing training on specific technology-based resources.15-17 Future improvement for the Annie platform should include improved integration with CPRS. Integration will facilitate automatic import of key information such as mobile phone number or colonoscopy procedure date. Unfortunately, this is not currently an automated process, and the manual workload of staff limits sustainability. Since our study ended, the Annie database now allows an “event date” to be programmed in to center the text message series around. This will be entered at the time of Annie enrollment and eliminate manual activation of the protocol. The issue of updating information for rescheduled procedures remains.
Conclusions
There is increasing evidence that automated text messaging is a promising addition to medicine for clinical education and communication. It continues to gain traction as a readily available and acceptable option, and many patients are willing to incorporate the technology platform into their care plan. We found high patient satisfaction with our protocol, and Annie patients had cleaner bowel preparations compared with control patients. Our study supports the use of text message reminders as an effective intervention for improving patient adherence with bowel preparation instructions. We suspect that creation of a text messaging protocol designed for patients requiring outpatient extended bowel preparation will yield great benefit. As technology continues to improve, future implementation of Annie text messaging will become increasingly seamless within the field of gastroenterology and beyond.
Colorectal cancer is the third leading cause of cancer-related death in both men and women.1 Colonoscopy is the current gold standard for screening due to the ability to remove precancerous lesions but remains highly dependent on the quality of bowel preparation.2 Poor bowel preparation has been associated with impaired adenoma detection as well as increased health care utilization due to the need for a repeat colonoscopy.3
Multiple patient factors are associated with increased risk of poor bowel preparation, including age > 60 years, male sex, diabetes mellitus, and presence of a mental health diagnosis, factors that are prevalent among the veteran population.3-5 Text messages have been shown to improve the quality of bowel preparation by increasing patients' understanding and adherence with the preparation process. Improved adherence with bowel preparation directions is associated with a cleaner colon prior to colonoscopy, leading to a thorough examination. Studies using text messaging instructions prior to colonoscopies have also shown measurable improvement in adenoma detection rate, patient preparation-associated discomfort, and completion of colonoscopy.6-10
In 2016, the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) introduced Annie, one of the first automated text messaging services, named after Army Lieutenant Annie Fox, the first woman to receive the Purple Heart for combat. The Annie platform allows for notifications, instructions, and simple data collection. The development of this platform allows VHA practitioners to engage and educate veterans in a similar way to other health care systems using text messaging protocols. Annie text messages have been piloted for the use of hepatitis C treatment, demonstrating promise of improved medication adherence and patient satisfaction.11 We aimed to develop and pilot the Annie bowel preparation protocol to improve the quality of colonoscopy bowel preparation for outpatients at the Minneapolis Veterans Affairs Medical Center (MVAMC) in Minnesota. A secondary goal included measuring patient satisfaction with the text messaging instructions for outpatient colonoscopy preparation.
Methods
We conducted a single center, prospective, endoscopist-blinded, study with two 3-month long Plan-Do-Study-Act (PDSA) cycles to improve the text messaging bowel preparation protocol at MVAMC between January 2019 and April 2020. The MVAMC Institutional Review Board determined the quality improvement project was exempt. Veterans who had outpatient colonoscopies scheduled were included. Veterans undergoing inpatient colonoscopies or outpatients who could not be reached to obtain informed consent, lacked text message capability, declined participation, or required extended colonoscopy preparation were excluded. Per MVAMC procedures, extended colonoscopy preparation was provided to patients receiving general or monitored anesthesia care, with a history of poor bowel preparation, or with risk factors for poor preparation as determined by the ordering health care professional (HCP). Standard bowel preparation involves ingestion of 4 L of polyethylene glycol 3350 with electrolytes; extended bowel preparation requires ingestion of an additional 2 L to total 6 L and uses a different set of instructions. Additionally, the patient population requiring extended bowel preparation also includes patients with spinal cord injuries, who often are admitted for assistance with extended preparation. Patients who consented to receiving text messages were placed in the Annie intervention group, and all others were placed in the control group.
The control group received standardized patient education, including a mailed copy of bowel preparation instructions and a phone call from a gastroenterology service nurse about 1 to 2 weeks before the procedure. Current MVAMC standard of care involves a phone call from a nurse to confirm that patients have received the polyethylene glycol preparation solution, the mailed instructions, have an escort and transportation, and to answer any questions. Both the usual care and intervention group received the phone call. During this call, the Annie text messaging bowel preparation protocol was introduced; if the veteran chose to participate, consent and enrollment were completed.
On the day of the colonoscopy, veterans in the intervention group were surveyed in the waiting room about their experience receiving the text messages and soliciting feedback for improvement or surveyed via telephone call within 3 days of their procedure. Patient satisfaction was quantified with a scale from 1 (low) to 10 (high), including questions about how helpful the texts were in relation to total number, timing, and content of messages as well as whether veterans would like to receive the text messages again for future procedures.
We reviewed individual charts and collected Boston Bowel Preparation Scale (BBPS) scores to determine adequate preparation. BBPS assigns a score of 0 to 3 for the right, transverse, and left colon applied upon withdrawal after flushing and suctioning have been completed.12 Adequate preparation is considered a total score of ≥ 6 with no segment scoring < 2. This method of preparation assessment is preferred due to its ability to account for difference in preparation quality among colonic segments, well-defined scoring characteristics, and several studies validating its use showing inter- and intraobserver reliability.12 Follow-up studies have shown validity of the BBPS when compared with relevant outcomes such as polyp detection rate and recommended timing for repeat procedure.13 Variables associated with poor bowel preparation (ie, gender, prior abdominal surgery, impaired mobility, high body mass index, diabetes mellitus, stroke, dementia, any neurologic diagnosis, cirrhosis, smoking, polypharmacy [> 8 active medications], and narcotic or tricyclic antidepressant medication use) were also collected through chart review.3-5 We note that immobility was defined by International Classification of Diseases (ICD)-9 and ICD-10 codes and prescriptions for assistive devices (ie, canes, wheelchairs, 4-wheeled walkers).
Veterans assent to be enrolled in Annie. After enrollment, veterans must text back a specific word response to an initial text message to receive the protocolized messages from the Annie program. A contact phone number to the gastrointestinal nurse line was provided for questions during business hours. The start date for the text message protocol is 6 days prior to the procedure date. If a patient rescheduled their colonoscopy, the Annie database was updated manually.
Statistical Analysis
We used both Pearson χ2 test and 2-sample t test analyses to compare demographic information and patient satisfaction scores between the control and intervention groups. We compared continuous BBPS scores between Annie intervention vs control group using parametric and nonparametric independent t tests using the Mann-Whitney U test. We repeated this analysis controlling for both mental health diagnoses and age using linear regression. We were unable to survey 61 of the 187 veterans who received Annie text messages.
RESULTS
During PDSA cycles 1 and 2, 640 veterans were scheduled for outpatient colonoscopy: 453 veterans were in the control group; 187 veterans were in the intervention group, of which 126 were surveyed. A significant percentage of veterans declined participation because they felt like they did not need reinforced education; others were not eligible for Annie due to requirement for extended bowel preparation, cancelled colonoscopy, inability to physically read text messages, or lack of cell phone.
The mean (SD) age was 65 (8) years; 184 (28.8%) had a diabetes mellitus diagnosis, and the mean (SD) body mass index was 31.6 (6.4). The Annie group was slightly more likely to have mental health diagnoses and lower age compared with the control group (Table 1).
Patient Feedback
We collected feedback from veterans after each PDSA cycle to identify areas for improvement by both in-person and telephone surveys. Based on feedback from PDSA cycle 1, we decreased the total number of text messages to create a more succinct set of instructions. The most frequently requested change involved timing the text messages to align with the exact morning a specific instruction should take place.
Patient satisfaction with the Annie text messaging service was high.
DISCUSSION
To our knowledge, this is the first report of using Annie at a VAMC for colonoscopy bowel preparation improvement. We found a statistically significant improvement in the average BBPS in those receiving Annie text messages compared with the routine care control group. We also found high levels of patient satisfaction with most patients requesting to receive them again for future procedures.
The clinical significance of a BBPS of 7.8 vs 8.2 is unclear, although any score > 6 is considered to be adequate. However, subjectively speaking, the higher the BBPS the cleaner the colon, and theoretically the easier it is to see small or flat polyps. Future steps could include calculating adenoma detection rates for those enrolled in the Annie program vs the control group.
We have received inquiries regarding potential program implementation at other facilities. Success and sustainability of the program will require long-term commitment and ideally protected time for staff. It is helpful to remember that for each person who chooses to enroll in the intervention, the program currently requires that a brief consent note is placed in the patient’s chart. Thus, depending on the facilities’ resources, it is ideal for one staff member to be the designated lead to help oversee, troubleshoot, and train additional personnel. Surveys can be intermittently used to obtain feedback for improvement but are not required for sustainability. Automated text messaging is a promising addition to medicine for clinical education and communication. Future studies should examine the clinical significance (ie, adenoma detection rates) of text messaging bowel preparation protocols.
Limitations
Our study has several limitations. First, this was a single center study, thus generalizability is limited. MVAMC represents a predominantly White, male, and rural population. Second, data are likely an underestimation of the true impact of intervention, because results do not account for patients who were turned away on day of procedure (typically still reporting brown stools at time of check-in for procedure) due to poor preparation or aborted procedures secondary to poor preparation. Only about one-third of the 640 veterans opted to receive Annie text messages.
Studies have shown veterans are willing to use technology for health care; however, access to technology and lack of training remain barriers to use.14 This has been most robustly studied at the VA in veterans experiencing mental illness and homelessness. Targeted strategies to improve veteran adoption of technology within their health care include supplying veterans with cell phones and paid data plans and providing training on specific technology-based resources.15-17 Future improvement for the Annie platform should include improved integration with CPRS. Integration will facilitate automatic import of key information such as mobile phone number or colonoscopy procedure date. Unfortunately, this is not currently an automated process, and the manual workload of staff limits sustainability. Since our study ended, the Annie database now allows an “event date” to be programmed in to center the text message series around. This will be entered at the time of Annie enrollment and eliminate manual activation of the protocol. The issue of updating information for rescheduled procedures remains.
Conclusions
There is increasing evidence that automated text messaging is a promising addition to medicine for clinical education and communication. It continues to gain traction as a readily available and acceptable option, and many patients are willing to incorporate the technology platform into their care plan. We found high patient satisfaction with our protocol, and Annie patients had cleaner bowel preparations compared with control patients. Our study supports the use of text message reminders as an effective intervention for improving patient adherence with bowel preparation instructions. We suspect that creation of a text messaging protocol designed for patients requiring outpatient extended bowel preparation will yield great benefit. As technology continues to improve, future implementation of Annie text messaging will become increasingly seamless within the field of gastroenterology and beyond.
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Colorectal cancer statistics. Updated June 6, 2022. Accessed September 8, 2022. https://www.cdc.gov/cancer/colorectal/statistics
2. Lieberman D, Ladabaum U, Cruz-Correa M, et al. Screening for colorectal cancer and evolving issues for physicians and patients: a review. JAMA. 2016;316(20):2135-2145. doi:10.1001/jama.2016.17418
3. Nguyen DL, Wieland M. Risk factors predictive of poor quality preparation during average risk colonoscopy screening: the importance of health literacy. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 2010;19(4):369-372.
4. Mahmood S, Farooqui SM, Madhoun MF. Predictors of inadequate bowel preparation for colonoscopy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;30(8):819-826. doi:10.1097/MEG.0000000000001175
5. Harrington KM, Nguyen XT, Song RJ, et al. Gender differences in demographic and health characteristics of the Million Veteran Program cohort. Womens Health Issues. 2019;29(suppl 1):S56-S66. doi:10.1016/j.whi.2019.04.012
6. Zhang QX, Li J, Zhang Q, et al. Effect of education by messaging software on the quality of bowel preparation for colonoscopy. Chin Med J (Engl). 2018;131(14):1750-1752. doi:10.4103/0366-6999.235881
7. Walter B, Klare P, Strehle K, et al. Improving the quality and acceptance of colonoscopy preparation by reinforced patient education with short message service: results from a randomized, multicenter study (PERICLES-II). Gastrointest Endosc. 2019;89(3):506-513.e4. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2018.08.014
8. Nadim MM, Doshi S, Coniglio M, et al. Automated text message navigation to improve preparation quality and show rate for colonoscopy. Am J Gastroenterol. 2018;113:S64-S66.
9. Walter B, Frank R, Ludwig L, et al. Smartphone application to reinforce education increases high-quality preparation for colorectal cancer screening colonoscopies in a randomized trial. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;19(2):331-338.e5. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2020.03.051
10. Guo B, Zuo X, Li Z, et al. Improving the quality of bowel preparation through an app for inpatients undergoing colonoscopy: a randomized controlled trial. J Adv Nurs. 2020;76(4):1037-1045. doi:10.1111/jan.14295
11. Yakovchenko V, Hogan TP, Houston TK, et al. Automated text messaging with patients in department of veterans affairs specialty clinics: cluster randomized trial. J Med Internet Res. 2019;21(8):e14750. doi:10.2196/14750
12. Lai EJ, Calderwood AH, Doros G, Fix OK, Jacobson BC. The Boston bowel preparation scale: a valid and reliable instrument for colonoscopy-oriented research. Gastrointest Endosc. 2009;69(3 Pt 2):620-625. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2008.05.057
13. Calderwood AH, Jacobson BC. Comprehensive validation of the Boston Bowel Preparation Scale. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010;72(4):686-692. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2010.06.068
14. Duan-Porter W, Van Houtven CH, Mahanna EP, et al. Internet use and technology-related attitudes of veterans and informal caregivers of veterans. Telemed J E Health. 2018;24(7):471-480. doi:10.1089/tmj.2017.0015
15. Boston University School of Public Health. how mobile technology can increase veteran healthcare and wellbeing. November 10, 2021. Accessed November 1, 2022. https://www.ideahub.org/research-data/how-mobile-technology-increases-veteran-healthcare-and-wellbeing/
16. Klee A, Stacy M, Rosenheck R, Harkness L, Tsai J. Interest in technology-based therapies hampered by access: A survey of veterans with serious mental illnesses. Psychiatr Rehabil J. 2016;39(2):173-179. doi:10.1037/prj0000180
17. Berrouiguet S, Baca-García E, Brandt S, Walter M, Courtet P. Fundamentals for future mobile-health (mHealth): a systematic review of mobile phone and web-based text messaging in mental health. J Med Internet Res. 2016;18(6):e135. Published 2016 Jun 10. doi:10.2196/jmir.5066
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Colorectal cancer statistics. Updated June 6, 2022. Accessed September 8, 2022. https://www.cdc.gov/cancer/colorectal/statistics
2. Lieberman D, Ladabaum U, Cruz-Correa M, et al. Screening for colorectal cancer and evolving issues for physicians and patients: a review. JAMA. 2016;316(20):2135-2145. doi:10.1001/jama.2016.17418
3. Nguyen DL, Wieland M. Risk factors predictive of poor quality preparation during average risk colonoscopy screening: the importance of health literacy. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 2010;19(4):369-372.
4. Mahmood S, Farooqui SM, Madhoun MF. Predictors of inadequate bowel preparation for colonoscopy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;30(8):819-826. doi:10.1097/MEG.0000000000001175
5. Harrington KM, Nguyen XT, Song RJ, et al. Gender differences in demographic and health characteristics of the Million Veteran Program cohort. Womens Health Issues. 2019;29(suppl 1):S56-S66. doi:10.1016/j.whi.2019.04.012
6. Zhang QX, Li J, Zhang Q, et al. Effect of education by messaging software on the quality of bowel preparation for colonoscopy. Chin Med J (Engl). 2018;131(14):1750-1752. doi:10.4103/0366-6999.235881
7. Walter B, Klare P, Strehle K, et al. Improving the quality and acceptance of colonoscopy preparation by reinforced patient education with short message service: results from a randomized, multicenter study (PERICLES-II). Gastrointest Endosc. 2019;89(3):506-513.e4. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2018.08.014
8. Nadim MM, Doshi S, Coniglio M, et al. Automated text message navigation to improve preparation quality and show rate for colonoscopy. Am J Gastroenterol. 2018;113:S64-S66.
9. Walter B, Frank R, Ludwig L, et al. Smartphone application to reinforce education increases high-quality preparation for colorectal cancer screening colonoscopies in a randomized trial. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;19(2):331-338.e5. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2020.03.051
10. Guo B, Zuo X, Li Z, et al. Improving the quality of bowel preparation through an app for inpatients undergoing colonoscopy: a randomized controlled trial. J Adv Nurs. 2020;76(4):1037-1045. doi:10.1111/jan.14295
11. Yakovchenko V, Hogan TP, Houston TK, et al. Automated text messaging with patients in department of veterans affairs specialty clinics: cluster randomized trial. J Med Internet Res. 2019;21(8):e14750. doi:10.2196/14750
12. Lai EJ, Calderwood AH, Doros G, Fix OK, Jacobson BC. The Boston bowel preparation scale: a valid and reliable instrument for colonoscopy-oriented research. Gastrointest Endosc. 2009;69(3 Pt 2):620-625. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2008.05.057
13. Calderwood AH, Jacobson BC. Comprehensive validation of the Boston Bowel Preparation Scale. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010;72(4):686-692. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2010.06.068
14. Duan-Porter W, Van Houtven CH, Mahanna EP, et al. Internet use and technology-related attitudes of veterans and informal caregivers of veterans. Telemed J E Health. 2018;24(7):471-480. doi:10.1089/tmj.2017.0015
15. Boston University School of Public Health. how mobile technology can increase veteran healthcare and wellbeing. November 10, 2021. Accessed November 1, 2022. https://www.ideahub.org/research-data/how-mobile-technology-increases-veteran-healthcare-and-wellbeing/
16. Klee A, Stacy M, Rosenheck R, Harkness L, Tsai J. Interest in technology-based therapies hampered by access: A survey of veterans with serious mental illnesses. Psychiatr Rehabil J. 2016;39(2):173-179. doi:10.1037/prj0000180
17. Berrouiguet S, Baca-García E, Brandt S, Walter M, Courtet P. Fundamentals for future mobile-health (mHealth): a systematic review of mobile phone and web-based text messaging in mental health. J Med Internet Res. 2016;18(6):e135. Published 2016 Jun 10. doi:10.2196/jmir.5066