User login
Multiple Painless Whitish Papules on the Vulva and Perianal Region
THE DIAGNOSIS: Papular Acantholytic Dyskeratosis
Histopathology of the lesion in our patient revealed hyperkeratosis, parakeratosis, dyskeratosis, and acantholysis of keratinocytes. The dermis showed variable chronic inflammatory cells. Corps ronds and grains in the acantholytic layer of the epidermis were identified. Hair follicles were not affected by acantholysis. Anti–desmoglein 1 and anti–desmoglein 3 serum antibodies were negative. Based on the combined clinical and histologic findings, the patient was diagnosed with papular acantholytic dyskeratosis (PAD) of the genitocrural area.
Although its typical histopathologic pattern mimics both Hailey-Hailey disease and Darier disease, PAD is a rare unique clinicopathologic entity recognized by dermatopathologists. It usually occurs in middle-aged women with no family history of similar conditions. The multiple localized, flesh-colored to whitish papules of PAD tend to coalesce into plaques in the anogenital and genitocrural regions. Plaques usually are asymptomatic but may be pruritic. Histopathologically, PAD will demonstrate hyperkeratosis, dyskeratosis, and acantholysis. Corps ronds and grains will be present in the acantholytic layer of the epidermis.1,2
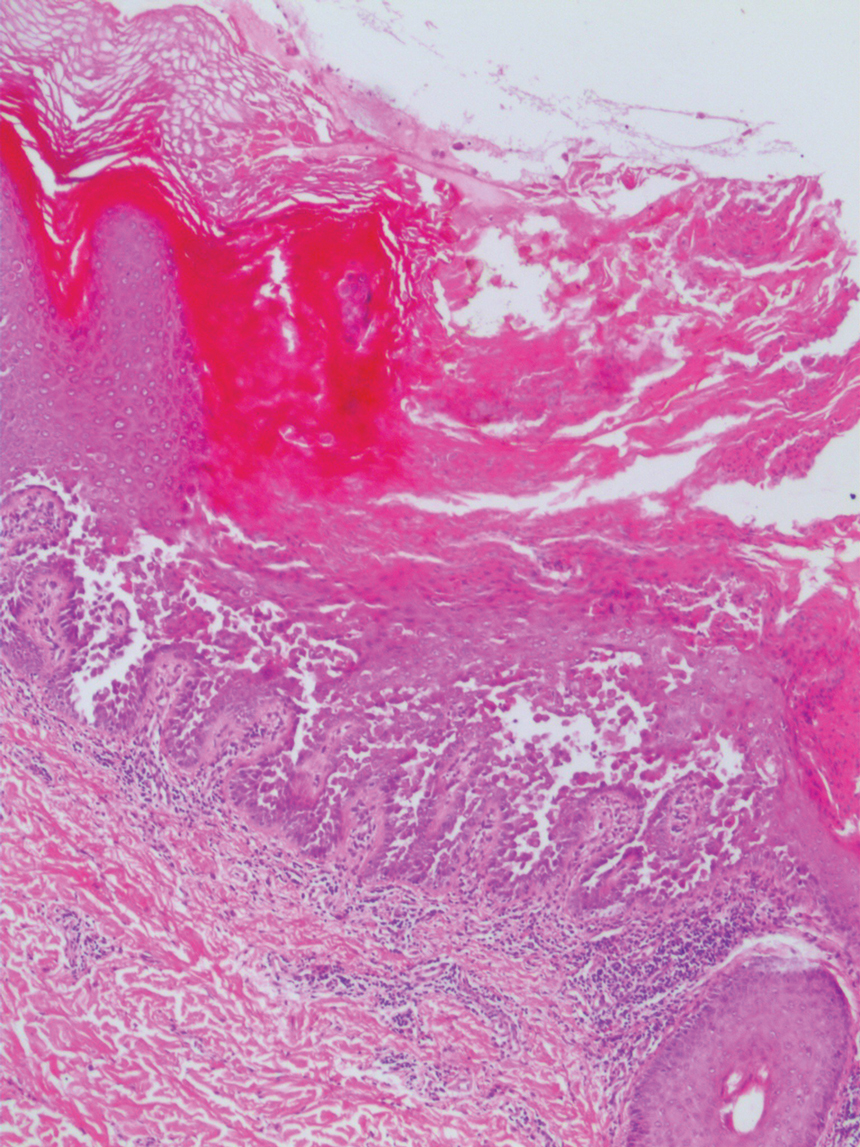
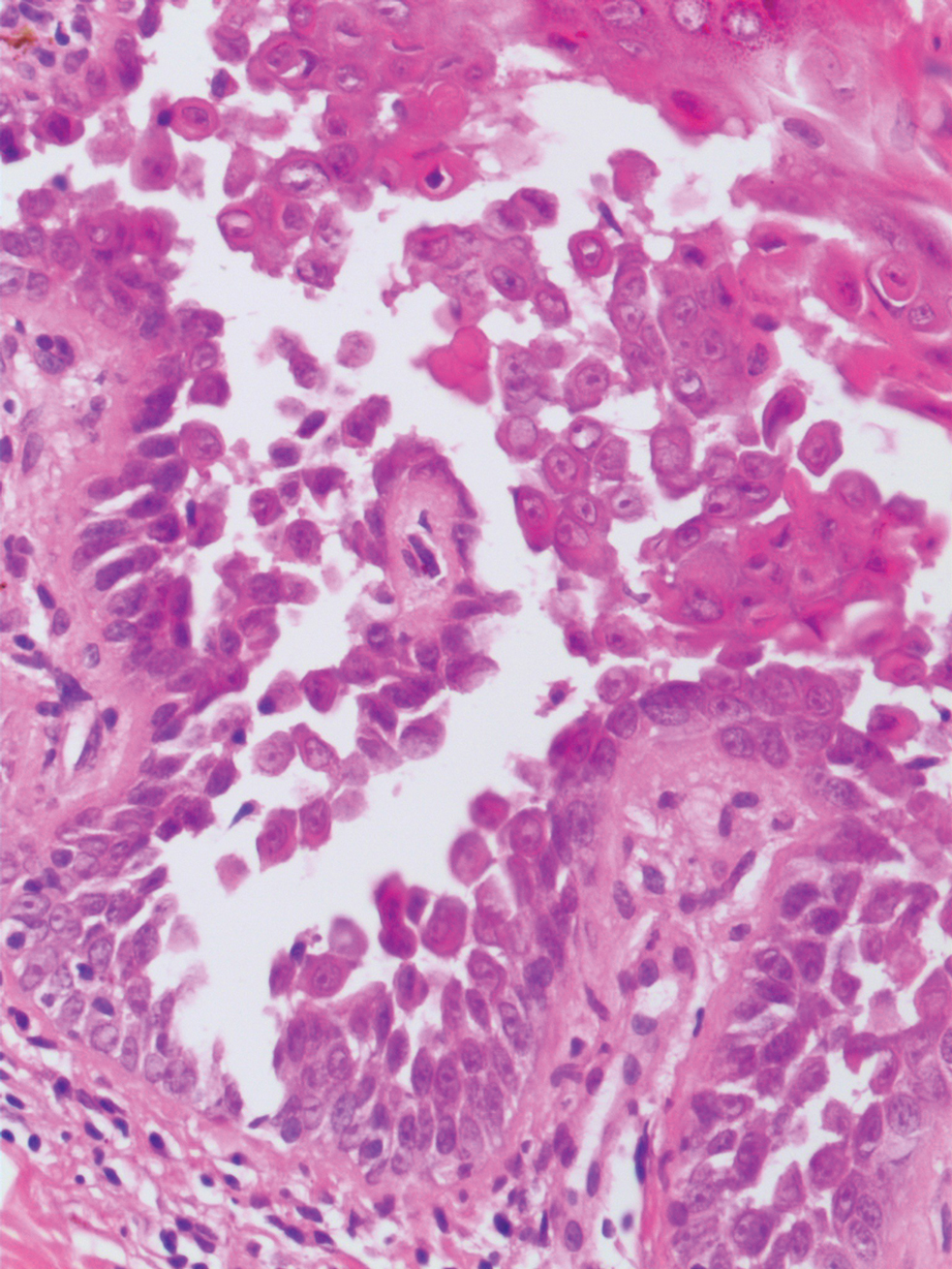
The differential diagnosis for PAD includes pemphigus vegetans, Hailey-Hailey disease, Darier disease, and Grover disease. Patients usually develop pemphigus vegetans at an older age (typically 50–70 years).3 Histopathologically, it is characterized by pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia with an eosinophilic microabscess as well as acantholysis that involves the follicular epithelium (Figure 1),4 which were not seen in our patient. Direct immunofluorescence will show the intercellular pattern of the pemphigus group, and antidesmoglein antibodies can be detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.4,5
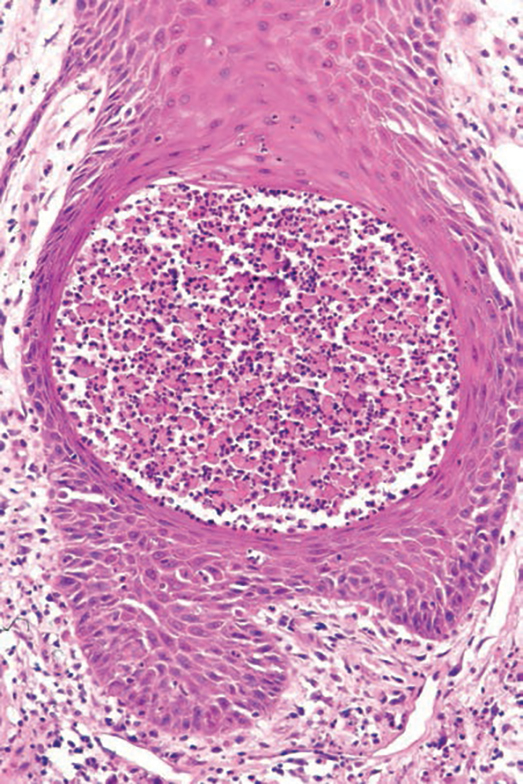
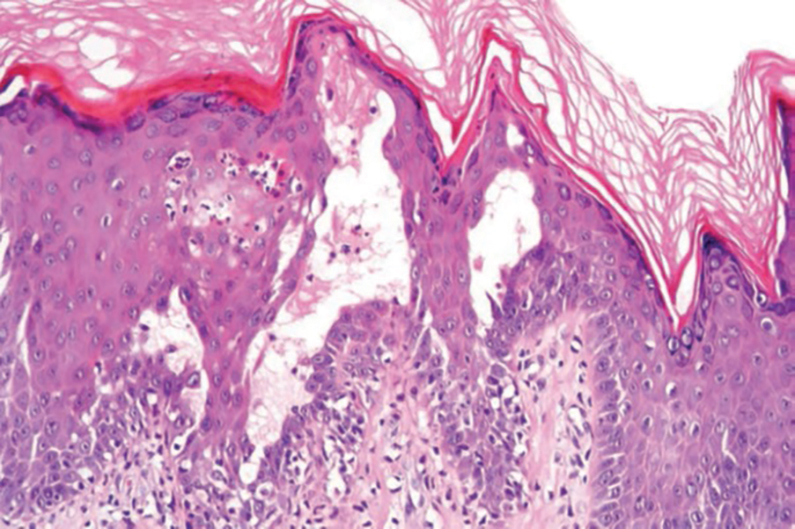
Hailey-Hailey disease (also known as benign familial pemphigus) typically manifests as itchy malodorous vesicles and erosions, especially in intertriginous areas. The most commonly affected sites are the groin, neck, under the breasts, and between the buttocks. In one study, two-thirds of affected patients reported a relevant family history.4 Histopathology will show minimal dyskeratosis and suprabasilar acantholysis with loss of intercellular bridges, classically described as resembling a dilapidated brick wall (Figure 2).4,5 There is no notable follicular involvement with acantholysis.4
characteristic dilapidated brick wall appearance (H&E, original
magnification ×40).
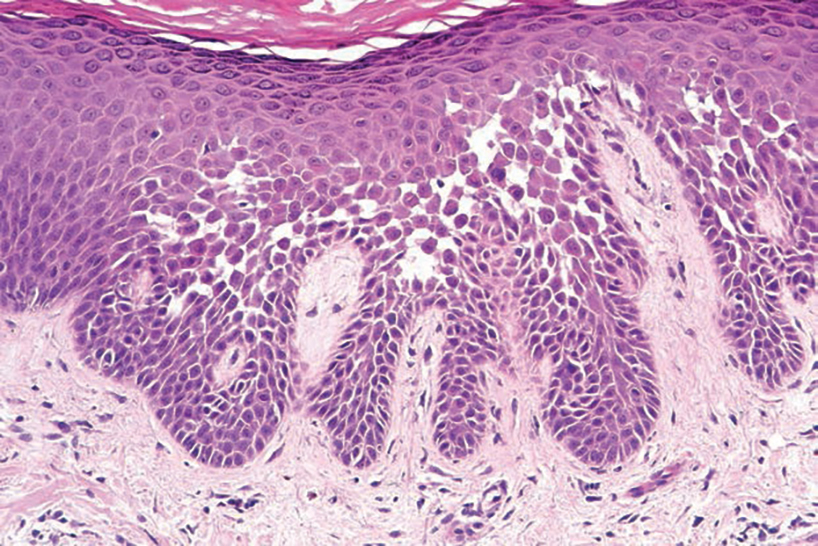
Darier disease (also known as keratosis follicularis) typically is inherited in an autosomal-dominant pattern.4 It is found on the seborrheic areas such as the scalp, forehead, nasolabial folds, and upper chest. Characteristic features include distal notching of the nails, mucosal lesions, and palmoplantar papules. Histopathology will reveal acantholysis, dyskeratosis, suprabasilar acantholysis, and corps ronds and grains.4 Acantholysis in Darier disease can be in discrete foci and/or widespread (Figure 3).4 Darier disease demonstrates more dyskeratosis than Hailey-Hailey disease.4,5

Grover disease (also referred to as transient acantholytic dermatosis) is observed predominantly in individuals who are middle-aged or older, though occurrence in children has been rarely reported.4 It affects the trunk, neck, and proximal limbs but spares the genital area. Histopathology may reveal acantholysis (similar to Hailey-Hailey disease or pemphigus vulgaris), dyskeratosis (resembling Darier disease), spongiosis, parakeratosis, and a superficial perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate with eosinophils.4 A histologic clue to the diagnosis is small lesion size (1–3 mm). Usually, only 1 or 2 small discrete lesions that span a few rete ridges are noted (Figure 4).4 Grover disease can cause follicular or acrosyringeal involvement.4
- Al-Muriesh M, Abdul-Fattah B, Wang X, et al. Papular acantholytic dyskeratosis of the anogenital and genitocrural area: case series and review of the literature. J Cutan Pathol. 2016;43:749-758. doi:10.1111/cup.12736
- Harrell J, Nielson C, Beers P, et al. Eruption on the vulva and groin. JAAD Case Reports. 2019;6:6-8. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2019.11.003
- Messersmith L, Krauland K. Pemphigus vegetans. StatPearls [Internet]. Updated June 26, 2023. Accessed September 18, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK545229
- Acantholytic disorders. In: Calonje E, Brenn T, Lazar A, et al, eds. McKee’s Pathology of the Skin: With Clinical Correlations. Elsevier/ Saunders; 2012:171-200.
- Mohr MR, Erdag G, Shada AL, et al. Two patients with Hailey- Hailey disease, multiple primary melanomas, and other cancers. Arch Dermatol. 2011;147:211215. doi:10.1001/archdermatol.2010.445
THE DIAGNOSIS: Papular Acantholytic Dyskeratosis
Histopathology of the lesion in our patient revealed hyperkeratosis, parakeratosis, dyskeratosis, and acantholysis of keratinocytes. The dermis showed variable chronic inflammatory cells. Corps ronds and grains in the acantholytic layer of the epidermis were identified. Hair follicles were not affected by acantholysis. Anti–desmoglein 1 and anti–desmoglein 3 serum antibodies were negative. Based on the combined clinical and histologic findings, the patient was diagnosed with papular acantholytic dyskeratosis (PAD) of the genitocrural area.
Although its typical histopathologic pattern mimics both Hailey-Hailey disease and Darier disease, PAD is a rare unique clinicopathologic entity recognized by dermatopathologists. It usually occurs in middle-aged women with no family history of similar conditions. The multiple localized, flesh-colored to whitish papules of PAD tend to coalesce into plaques in the anogenital and genitocrural regions. Plaques usually are asymptomatic but may be pruritic. Histopathologically, PAD will demonstrate hyperkeratosis, dyskeratosis, and acantholysis. Corps ronds and grains will be present in the acantholytic layer of the epidermis.1,2
The differential diagnosis for PAD includes pemphigus vegetans, Hailey-Hailey disease, Darier disease, and Grover disease. Patients usually develop pemphigus vegetans at an older age (typically 50–70 years).3 Histopathologically, it is characterized by pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia with an eosinophilic microabscess as well as acantholysis that involves the follicular epithelium (Figure 1),4 which were not seen in our patient. Direct immunofluorescence will show the intercellular pattern of the pemphigus group, and antidesmoglein antibodies can be detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.4,5

Hailey-Hailey disease (also known as benign familial pemphigus) typically manifests as itchy malodorous vesicles and erosions, especially in intertriginous areas. The most commonly affected sites are the groin, neck, under the breasts, and between the buttocks. In one study, two-thirds of affected patients reported a relevant family history.4 Histopathology will show minimal dyskeratosis and suprabasilar acantholysis with loss of intercellular bridges, classically described as resembling a dilapidated brick wall (Figure 2).4,5 There is no notable follicular involvement with acantholysis.4

characteristic dilapidated brick wall appearance (H&E, original
magnification ×40).
Darier disease (also known as keratosis follicularis) typically is inherited in an autosomal-dominant pattern.4 It is found on the seborrheic areas such as the scalp, forehead, nasolabial folds, and upper chest. Characteristic features include distal notching of the nails, mucosal lesions, and palmoplantar papules. Histopathology will reveal acantholysis, dyskeratosis, suprabasilar acantholysis, and corps ronds and grains.4 Acantholysis in Darier disease can be in discrete foci and/or widespread (Figure 3).4 Darier disease demonstrates more dyskeratosis than Hailey-Hailey disease.4,5

Grover disease (also referred to as transient acantholytic dermatosis) is observed predominantly in individuals who are middle-aged or older, though occurrence in children has been rarely reported.4 It affects the trunk, neck, and proximal limbs but spares the genital area. Histopathology may reveal acantholysis (similar to Hailey-Hailey disease or pemphigus vulgaris), dyskeratosis (resembling Darier disease), spongiosis, parakeratosis, and a superficial perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate with eosinophils.4 A histologic clue to the diagnosis is small lesion size (1–3 mm). Usually, only 1 or 2 small discrete lesions that span a few rete ridges are noted (Figure 4).4 Grover disease can cause follicular or acrosyringeal involvement.4

THE DIAGNOSIS: Papular Acantholytic Dyskeratosis
Histopathology of the lesion in our patient revealed hyperkeratosis, parakeratosis, dyskeratosis, and acantholysis of keratinocytes. The dermis showed variable chronic inflammatory cells. Corps ronds and grains in the acantholytic layer of the epidermis were identified. Hair follicles were not affected by acantholysis. Anti–desmoglein 1 and anti–desmoglein 3 serum antibodies were negative. Based on the combined clinical and histologic findings, the patient was diagnosed with papular acantholytic dyskeratosis (PAD) of the genitocrural area.
Although its typical histopathologic pattern mimics both Hailey-Hailey disease and Darier disease, PAD is a rare unique clinicopathologic entity recognized by dermatopathologists. It usually occurs in middle-aged women with no family history of similar conditions. The multiple localized, flesh-colored to whitish papules of PAD tend to coalesce into plaques in the anogenital and genitocrural regions. Plaques usually are asymptomatic but may be pruritic. Histopathologically, PAD will demonstrate hyperkeratosis, dyskeratosis, and acantholysis. Corps ronds and grains will be present in the acantholytic layer of the epidermis.1,2
The differential diagnosis for PAD includes pemphigus vegetans, Hailey-Hailey disease, Darier disease, and Grover disease. Patients usually develop pemphigus vegetans at an older age (typically 50–70 years).3 Histopathologically, it is characterized by pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia with an eosinophilic microabscess as well as acantholysis that involves the follicular epithelium (Figure 1),4 which were not seen in our patient. Direct immunofluorescence will show the intercellular pattern of the pemphigus group, and antidesmoglein antibodies can be detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.4,5

Hailey-Hailey disease (also known as benign familial pemphigus) typically manifests as itchy malodorous vesicles and erosions, especially in intertriginous areas. The most commonly affected sites are the groin, neck, under the breasts, and between the buttocks. In one study, two-thirds of affected patients reported a relevant family history.4 Histopathology will show minimal dyskeratosis and suprabasilar acantholysis with loss of intercellular bridges, classically described as resembling a dilapidated brick wall (Figure 2).4,5 There is no notable follicular involvement with acantholysis.4

characteristic dilapidated brick wall appearance (H&E, original
magnification ×40).
Darier disease (also known as keratosis follicularis) typically is inherited in an autosomal-dominant pattern.4 It is found on the seborrheic areas such as the scalp, forehead, nasolabial folds, and upper chest. Characteristic features include distal notching of the nails, mucosal lesions, and palmoplantar papules. Histopathology will reveal acantholysis, dyskeratosis, suprabasilar acantholysis, and corps ronds and grains.4 Acantholysis in Darier disease can be in discrete foci and/or widespread (Figure 3).4 Darier disease demonstrates more dyskeratosis than Hailey-Hailey disease.4,5

Grover disease (also referred to as transient acantholytic dermatosis) is observed predominantly in individuals who are middle-aged or older, though occurrence in children has been rarely reported.4 It affects the trunk, neck, and proximal limbs but spares the genital area. Histopathology may reveal acantholysis (similar to Hailey-Hailey disease or pemphigus vulgaris), dyskeratosis (resembling Darier disease), spongiosis, parakeratosis, and a superficial perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate with eosinophils.4 A histologic clue to the diagnosis is small lesion size (1–3 mm). Usually, only 1 or 2 small discrete lesions that span a few rete ridges are noted (Figure 4).4 Grover disease can cause follicular or acrosyringeal involvement.4

- Al-Muriesh M, Abdul-Fattah B, Wang X, et al. Papular acantholytic dyskeratosis of the anogenital and genitocrural area: case series and review of the literature. J Cutan Pathol. 2016;43:749-758. doi:10.1111/cup.12736
- Harrell J, Nielson C, Beers P, et al. Eruption on the vulva and groin. JAAD Case Reports. 2019;6:6-8. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2019.11.003
- Messersmith L, Krauland K. Pemphigus vegetans. StatPearls [Internet]. Updated June 26, 2023. Accessed September 18, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK545229
- Acantholytic disorders. In: Calonje E, Brenn T, Lazar A, et al, eds. McKee’s Pathology of the Skin: With Clinical Correlations. Elsevier/ Saunders; 2012:171-200.
- Mohr MR, Erdag G, Shada AL, et al. Two patients with Hailey- Hailey disease, multiple primary melanomas, and other cancers. Arch Dermatol. 2011;147:211215. doi:10.1001/archdermatol.2010.445
- Al-Muriesh M, Abdul-Fattah B, Wang X, et al. Papular acantholytic dyskeratosis of the anogenital and genitocrural area: case series and review of the literature. J Cutan Pathol. 2016;43:749-758. doi:10.1111/cup.12736
- Harrell J, Nielson C, Beers P, et al. Eruption on the vulva and groin. JAAD Case Reports. 2019;6:6-8. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2019.11.003
- Messersmith L, Krauland K. Pemphigus vegetans. StatPearls [Internet]. Updated June 26, 2023. Accessed September 18, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK545229
- Acantholytic disorders. In: Calonje E, Brenn T, Lazar A, et al, eds. McKee’s Pathology of the Skin: With Clinical Correlations. Elsevier/ Saunders; 2012:171-200.
- Mohr MR, Erdag G, Shada AL, et al. Two patients with Hailey- Hailey disease, multiple primary melanomas, and other cancers. Arch Dermatol. 2011;147:211215. doi:10.1001/archdermatol.2010.445
A 21-year-old woman presented with a chronic eruption in the anogenital region of 4 years’ duration. Clinical examination revealed numerous painless, mildly itchy, malodorous, whitish papules on an erythematous base that were distributed on the vulva and perianal region. There were no erosions, and no other areas were involved. Routine laboratory tests were within reference range. The patient had no sexual partner and no family history of similar lesions. A skin biopsy was performed.