User login
2022 Update: Beyond prenatal exome sequencing
Last year, our Update focused on the expansion of sequencing in prenatal diagnosis. This year, we are taking a step sideways to remember the many diagnoses we may miss if we rely on exome sequencing alone. A recent case report in Prenatal Diagnosis describes a pregnancy affected by fetal akinesia sequence and polyhydramnios in which sequencing did not reveal a diagnosis. Expansion of the differential to include congenital myotonic dystrophy and subsequent triplet repeat testing led the clinicians to the diagnosis and identification of a triplet repeat expansion in the DMPK gene. This case serves as our first example of how complementary testing and technologies should continue to help us make critical diagnoses.
What is the yield of exome sequencing vs panels in nonimmune hydrops?
Rogers R, Moyer K, Moise KJ Jr. Congenital myotonic dystrophy: an overlooked diagnosis not amenable to detection by sequencing. Prenat Diagn. 2022;42:233-235. doi:10.1002/pd.6105.
Norton ME, Ziffle JV, Lianoglou BR, et al. Exome sequencing vs targeted gene panels for the evaluation of nonimmune hydrops fetalis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2021;28:S0002-9378(21)00828-0. doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2021.07.014.
We have had several illuminating discussions with our colleagues about the merits of exome sequencing (ES) versus panels and other modalities for fetal diagnosis. Many obstetricians practicing at the leading edge may feel like ES should be utilized uniformly for fetal anomalies with nondiagnostic karyotype or microarray. However, for well-defined phenotypes with clear and narrow lists of implicated genes (eg, skeletal dysplasias) or patients without insurance coverage, panel sequencing still has utility in prenatal diagnosis. The question of which phenotypes most benefit from ES versus panel sequencing is an area of interesting, ongoing research for several investigators.
Secondary analysis of nonimmune hydrops cohort
Norton and colleagues tackled one such cohort in a study presented in the American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology. They compared the proportion of diagnoses that would have been identified in commercial lab panels with their research of phenotype-driven ES in a cohort of 127 fetuses with features of nonimmune hydrops fetalis (NIHF). NIHF can be caused by a variety of single-gene disorders in addition to chromosomal disorders and copy number variants on chromosomal microarray. Patients were eligible for inclusion in the cohort if they had a nondiagnostic karyotype or microarray and any of the following features: nuchal translucency of 3.5 mm or greater, cystic hygroma, pleural effusion, pericardial effusion, ascites, or skin edema. Standard sequencing methods and variant analysis were performed. They assumed 100% analytical sensitivity and specificity of the panels for variant detection and collected cost information on the targeted gene panels.
Study outcomes
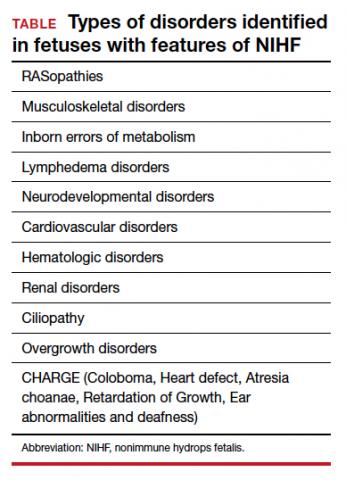
In the ES analysis of cases, 37 of 127 cases (29%) had a pathogenic or likely pathogenic variant in 1 of 29 genes, and another 12 of 127 cases (9%) had variants of uncertain significance that were strongly suspected to be the etiology during clinical analysis. The types of disorders that were identified are listed in the TABLE. In addition to a feature of NIHF, 50% of the cases had a structural anomaly.
There were 10 identified clinical panels from 7 clinical laboratories. These panels ranged in size from 11 to 128 genes. The highest simulated yield of any commercial panel was only 62% of the pathogenic variants identified by ES. The other commercial laboratory panels detection yield ranged from 11% to 62% of pathogenic variants detected by ES. For overall yield, the largest panel would have a diagnostic yield of 18% of diagnoses relative to the 29% diagnostic yield from ES.
The largest panel included 128 genes prior to the publication of the original cohort and was updated after publication to include 148 genes. The larger updated panel would have identified all of the patients in the ES cohort. However, many of the other panels listed would have identified a smaller fraction of the variants identified by ES (range, 11%-62%). At the time of publication, the cost of the panels ranged from $640 to $3,500, and the cost of prenatal ES ranged from $2,458 to $7,500.
Continue to: Strengths and limitations...
Strengths and limitations
Twenty-three percent of the patients who were sequenced had an increased fetal nuchal translucency or cystic hygroma, and another 17% had a single fetal effusion. This inclusivity makes this study more applicable to broader fetal anomaly populations. However, it is worth noting that only 61% of patients had NIHF by the definition of 2 or more fluid collections or skin thickening.
The authors assumed 100% sensitivity and specificity for the panel tests relative to diagnostic ES results, but this may not reflect real-life analysis. There is inherent subjectivity and subsequent differences in variant calling (deciding which genetic changes are pathogenic) between institutions and companies despite efforts to standardize this process. Due to the simulated nature of this study, these differences are not captured. Additionally, although the authors note that the research ES had at least 30 times the coverage (an adequate number of sequence reads for accurate testing) than did the commercial lab panels, some gene panels have additional sequencing of intronic regions, copy number analysis, and up to 10 times more coverage than ES, which could lead to more diagnoses.
This study illustrates that there is nuance involved in selecting which type of gene sequencing and which clinical laboratory to use for prenatal diagnosis. Labs with more updated literature searches and more inclusive gene panels may be excellent options for patients in whom ES is not covered by insurance or with phenotypes with a narrow range of suspected causative genes. However, there is a lag time in updating the genes offered on each panel, and new genedisease associations will not be captured by existing panels.
From a cost, speed-of-analysis, and depth-of-sequencing perspective, panel sequencing can have advantages that should be considered in some patients, particularly if the panels are large and regularly updated. However, the authors summarize our sentiments and their findings with the following:
“For disorders, such as NIHF with marked genetic heterogeneity and less clear in utero phenotypes of underlying genetic diseases, the broader coverage of exome sequencing makes it a superior option to targeted panel testing.”
We look forward to the publication of further anomaly-specific cohorts and secondary analyses of the utility of current panels and ES that may follow.
Frequency of Beckwith-Widemann syndrome in prenatally diagnosed omphaloceles
Abbasi N, Moore A, Chiu P, et al. Prenatally diagnosed omphaloceles: report of 92 cases and association with Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome. Prenat Diagn. 2021;41:798-816. doi:10.1002/pd.5930.
An omphalocele is diagnosed prenatally on ultrasound when an anterior midline mass, often containing abdominal contents, is seen herniating into the base of the umbilical cord. Omphaloceles are often associated with additional structural abnormalities and underlying genetic syndromes, thus a thorough fetal assessment is required for accurate prenatal counseling and neonatal care.
Identification of Beckwith-Widemann syndrome (BWS) in the setting of a prenatally diagnosed omphalocele is difficult because of its wide range of clinical features and its unique genetic basis. Unlike many genetic disorders that are caused by specific genetic variants, or spelling changes in the genes, BWS results from a change in the expression of one or more of the genes in a specific region of chromosome 11. A high index of clinical suspicion as well as an understanding of the various genetic and epigenetics alterations that cause BWS is required for prenatal diagnosis.
Retrospective cohort at a single center
The authors in this study reviewed all pregnancies in which an omphalocele was diagnosed prenatally at a single center between 2010 and 2015. They describe a standard prenatal evaluation following identification of an omphalocele including echocardiogram, detailed anatomic survey, and availability of an amniocentesis to facilitate aneuploidy screening and testing for BWS. This review also includes an overview of perinatal and long-term outcomes for cases of BWS diagnosed at their center between 2000 and 2015.
Study outcomes
Results of prenatal genetic testing in this cohort were divided between cases of an isolated omphalocele (without other structural changes) and cases of nonisolated omphaloceles. In the group of pregnancies with an isolated omphalocele, 2 of 27 pregnancies (7.4%) were found to have an abnormal karyotype, and 6 of 16 of the remaining pregnancies (37.5%) were diagnosed with BWS. Among the group of pregnancies with a nonisolated omphalocele, 23 of 59 pregnancies (39%) were found to have an abnormal karyotype, and 1 of 20 pregnancies (5%) were diagnosed with BWS.
Prenatal sonographic features associated with cases of BWS included polyhydramnios in 12 of 19 cases (63%) and macrosomia in 8 of 19 cases (42%). Macroglossia is another characteristic feature of the disorder, which was identified in 4 of 19 cases (21%) prenatally and in an additional 10 of 19 cases (52.6%) postnatally. Interestingly, only 1 of the cases of BWS was caused by a microdeletion at 11p15.4—a change that was identified on microarray. The additional 6 cases of BWS were caused by imprinting changes in the region, which are only detectable with a specific methylation-analysis technique.
Among the 19 cases of BWS identified over a 15-year period, there was 1 intrauterine demise. Preterm birth occurred in 10 of 19 cases (52.6%), including 8 of 19 cases (42.1%) of spontaneous preterm labor. Respiratory distress (27.8%), hypoglycemia (61%), and gastrointestinal reflux (59%) were common neonatal complications. Embryonal tumors were diagnosed in 2 of 16 patients (12.5%). Although neurodevelopmental outcomes were incomplete, their data suggested normal development in 75% of children. There were 2 neonatal deaths in this cohort and 1 childhood death at age 2 years.
Study strengths and limitations
As with many studies investigating a rare disorder, this study is limited by its retrospective nature and small sample size. Nevertheless, it adds an important cohort of patients with a prenatally diagnosed omphalocele to the literature and illuminates the utility of a standardized approach to testing for BWS in this population.
In this cohort with prenatally diagnosed omphaloceles with standardized testing for BWS, the prevalence of the disorder was approximately 8% and more common in cases of an isolated omphalocele. The most common supporting sonographic features of BWS may not be detected until later in gestation, including polyhydramnios and macrosomia. This demonstrates the importance of both sonographic follow-up as well as universal testing for BWS in euploid cases of a prenatally diagnosed omphalocele. Almost all cases of BWS in this cohort required specialized molecular techniques for diagnosis, and the diagnosis would have been missed on karyotype, microarray, and ES.
Continue to: Genetic diagnoses that could have been identified by expanded carrier screening...
Genetic diagnoses that could have been identified by expanded carrier screening
Stevens BK, Nunley PB, Wagner C, et al. Utility of expanded carrier screening in pregnancies with ultrasound abnormalities. Prenat Diagn. 2022;42:60-78. doi:10.1002/pd.6069.
This series is a thorough retrospective review of patients evaluated in a pediatric genetics clinic from 2014 through 2017. Patients were included if they were evaluated in the first 6 months of life and had a structural abnormality that might be detected on prenatal ultrasonography. The genetic testing results were analyzed and categorized according to types of genetic disorders, with the goal of identifying how many patients might have been identified by expanded carrier screening (ECS) panels.
Study outcomes
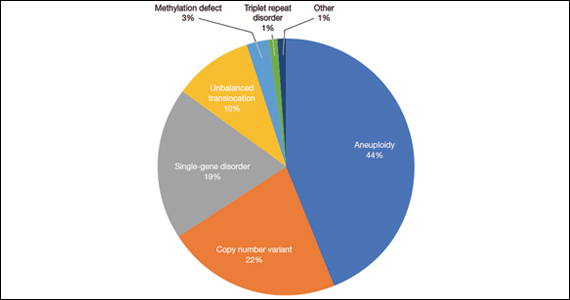
A total of 931 charts were reviewed, and 85% (791 of 931) of patients evaluated in the first 6 months of life were determined to have a structural anomaly that might be detected on prenatal ultrasonography. Of those patients, 691 went on to have genetic testing and 32.1% (222 of 691) of them had a diagnostic (pathogenic) genetic testing result related to the phenotype. The types of diagnostic testing results are shown in the FIGURE. Notably, 42 single-gene disorders were detected.
FIGURE Diagnostic test result in pediatric patients evaluated under age 6 months
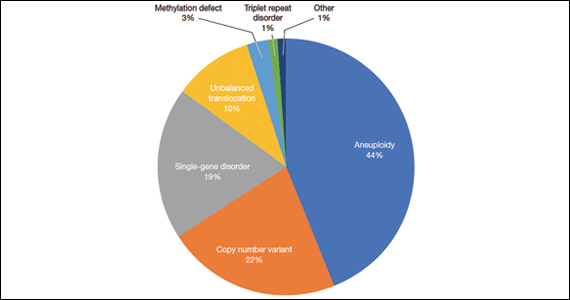
Of those 222 patients with diagnostic results, there were 8 patients with autosomal recessive and X-linked conditions that could be detected using a 500-gene ECS panel. Five patients could be detected with a 271-gene panel. After nondiagnostic microarray, 11.3% of patients had a condition that could be detected by using a 500-gene ECS panel. The identified conditions included cystic fibrosis, CYP21‐related congenital adrenal hyperplasia, autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease, Antley‐Bixler syndrome, and Morquio syndrome type A.
Furthermore, the authors conducted a literature review of 271 conditions and found that 32% (88 of 271) of conditions may be associated with ultrasound findings.
Study strengths and limitations
When applying these data to prenatal populations, the authors acknowledge several notable limitations. There is a selection bias toward less-severe phenotypes for many patients choosing to continue rather than to interrupt a pregnancy. Additionally, only 23% of the patients in the study had a microarray and ES, which may lead to an underrepresentation of single-gene disorders and an underestimation of the utility of ECS. Finally, a retrospective classification of structural abnormalities that may be detectable by ultrasonography may not always reflect what is actually reported in prenatal imaging.
However, the work that the authors put forth to evaluate and categorize 931 participants by the results of genetic testing and structural anomalies is appreciated, and the level of detail is impressive for this retrospective chart review. Additionally, the tables itemizing the authors’ review of 271 ECS disorders that may have ultrasonography findings categorized by disorder and system are helpful and quick diagnostic references for clinicians providing prenatal care. ●
This study of potentially detectable prenatal findings from the lens of a pediatric genetics clinic lends an interesting perspective: Exome sequencing is not the primary route to establish a diagnosis; karyotype, microarray, methylation disorders, and triplet repeat disorders all have an established role in the diagnostic toolkit. Keeping in mind the contribution of these modalities to pediatric testing may shorten the diagnostic odyssey to continue pregnancies or help to fully counsel patients on expectations and decision-making after birth.
Carrier screening is not a substitute for diagnostic testing in pregnancy. However, in appropriately selected patients, a broad carrier screening panel may have added utility. ECS can be conducted while awaiting microarray results to help target testing and may be particularly useful for patients who decline diagnostic testing until the postnatal period. It is important to counsel patients that carrier screening is not a diagnostic test, and results will only report likely pathogenic or pathogenic variants, not variants of uncertain significance that may be of clinical relevance. However, our practice has had several insightful diagnoses reached through ECS, in conjunction with microarray testing that allowed for faster and more targeted sequencing and precise fetal diagnosis. This readily available molecular tool (often covered by insurance) deserves a spot in your fetal diagnosis tool belt based on available evidence.
Last year, our Update focused on the expansion of sequencing in prenatal diagnosis. This year, we are taking a step sideways to remember the many diagnoses we may miss if we rely on exome sequencing alone. A recent case report in Prenatal Diagnosis describes a pregnancy affected by fetal akinesia sequence and polyhydramnios in which sequencing did not reveal a diagnosis. Expansion of the differential to include congenital myotonic dystrophy and subsequent triplet repeat testing led the clinicians to the diagnosis and identification of a triplet repeat expansion in the DMPK gene. This case serves as our first example of how complementary testing and technologies should continue to help us make critical diagnoses.
What is the yield of exome sequencing vs panels in nonimmune hydrops?
Rogers R, Moyer K, Moise KJ Jr. Congenital myotonic dystrophy: an overlooked diagnosis not amenable to detection by sequencing. Prenat Diagn. 2022;42:233-235. doi:10.1002/pd.6105.
Norton ME, Ziffle JV, Lianoglou BR, et al. Exome sequencing vs targeted gene panels for the evaluation of nonimmune hydrops fetalis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2021;28:S0002-9378(21)00828-0. doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2021.07.014.
We have had several illuminating discussions with our colleagues about the merits of exome sequencing (ES) versus panels and other modalities for fetal diagnosis. Many obstetricians practicing at the leading edge may feel like ES should be utilized uniformly for fetal anomalies with nondiagnostic karyotype or microarray. However, for well-defined phenotypes with clear and narrow lists of implicated genes (eg, skeletal dysplasias) or patients without insurance coverage, panel sequencing still has utility in prenatal diagnosis. The question of which phenotypes most benefit from ES versus panel sequencing is an area of interesting, ongoing research for several investigators.
Secondary analysis of nonimmune hydrops cohort
Norton and colleagues tackled one such cohort in a study presented in the American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology. They compared the proportion of diagnoses that would have been identified in commercial lab panels with their research of phenotype-driven ES in a cohort of 127 fetuses with features of nonimmune hydrops fetalis (NIHF). NIHF can be caused by a variety of single-gene disorders in addition to chromosomal disorders and copy number variants on chromosomal microarray. Patients were eligible for inclusion in the cohort if they had a nondiagnostic karyotype or microarray and any of the following features: nuchal translucency of 3.5 mm or greater, cystic hygroma, pleural effusion, pericardial effusion, ascites, or skin edema. Standard sequencing methods and variant analysis were performed. They assumed 100% analytical sensitivity and specificity of the panels for variant detection and collected cost information on the targeted gene panels.
Study outcomes
In the ES analysis of cases, 37 of 127 cases (29%) had a pathogenic or likely pathogenic variant in 1 of 29 genes, and another 12 of 127 cases (9%) had variants of uncertain significance that were strongly suspected to be the etiology during clinical analysis. The types of disorders that were identified are listed in the TABLE. In addition to a feature of NIHF, 50% of the cases had a structural anomaly.
There were 10 identified clinical panels from 7 clinical laboratories. These panels ranged in size from 11 to 128 genes. The highest simulated yield of any commercial panel was only 62% of the pathogenic variants identified by ES. The other commercial laboratory panels detection yield ranged from 11% to 62% of pathogenic variants detected by ES. For overall yield, the largest panel would have a diagnostic yield of 18% of diagnoses relative to the 29% diagnostic yield from ES.
The largest panel included 128 genes prior to the publication of the original cohort and was updated after publication to include 148 genes. The larger updated panel would have identified all of the patients in the ES cohort. However, many of the other panels listed would have identified a smaller fraction of the variants identified by ES (range, 11%-62%). At the time of publication, the cost of the panels ranged from $640 to $3,500, and the cost of prenatal ES ranged from $2,458 to $7,500.
Continue to: Strengths and limitations...
Strengths and limitations
Twenty-three percent of the patients who were sequenced had an increased fetal nuchal translucency or cystic hygroma, and another 17% had a single fetal effusion. This inclusivity makes this study more applicable to broader fetal anomaly populations. However, it is worth noting that only 61% of patients had NIHF by the definition of 2 or more fluid collections or skin thickening.
The authors assumed 100% sensitivity and specificity for the panel tests relative to diagnostic ES results, but this may not reflect real-life analysis. There is inherent subjectivity and subsequent differences in variant calling (deciding which genetic changes are pathogenic) between institutions and companies despite efforts to standardize this process. Due to the simulated nature of this study, these differences are not captured. Additionally, although the authors note that the research ES had at least 30 times the coverage (an adequate number of sequence reads for accurate testing) than did the commercial lab panels, some gene panels have additional sequencing of intronic regions, copy number analysis, and up to 10 times more coverage than ES, which could lead to more diagnoses.
This study illustrates that there is nuance involved in selecting which type of gene sequencing and which clinical laboratory to use for prenatal diagnosis. Labs with more updated literature searches and more inclusive gene panels may be excellent options for patients in whom ES is not covered by insurance or with phenotypes with a narrow range of suspected causative genes. However, there is a lag time in updating the genes offered on each panel, and new genedisease associations will not be captured by existing panels.
From a cost, speed-of-analysis, and depth-of-sequencing perspective, panel sequencing can have advantages that should be considered in some patients, particularly if the panels are large and regularly updated. However, the authors summarize our sentiments and their findings with the following:
“For disorders, such as NIHF with marked genetic heterogeneity and less clear in utero phenotypes of underlying genetic diseases, the broader coverage of exome sequencing makes it a superior option to targeted panel testing.”
We look forward to the publication of further anomaly-specific cohorts and secondary analyses of the utility of current panels and ES that may follow.
Frequency of Beckwith-Widemann syndrome in prenatally diagnosed omphaloceles
Abbasi N, Moore A, Chiu P, et al. Prenatally diagnosed omphaloceles: report of 92 cases and association with Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome. Prenat Diagn. 2021;41:798-816. doi:10.1002/pd.5930.
An omphalocele is diagnosed prenatally on ultrasound when an anterior midline mass, often containing abdominal contents, is seen herniating into the base of the umbilical cord. Omphaloceles are often associated with additional structural abnormalities and underlying genetic syndromes, thus a thorough fetal assessment is required for accurate prenatal counseling and neonatal care.
Identification of Beckwith-Widemann syndrome (BWS) in the setting of a prenatally diagnosed omphalocele is difficult because of its wide range of clinical features and its unique genetic basis. Unlike many genetic disorders that are caused by specific genetic variants, or spelling changes in the genes, BWS results from a change in the expression of one or more of the genes in a specific region of chromosome 11. A high index of clinical suspicion as well as an understanding of the various genetic and epigenetics alterations that cause BWS is required for prenatal diagnosis.
Retrospective cohort at a single center
The authors in this study reviewed all pregnancies in which an omphalocele was diagnosed prenatally at a single center between 2010 and 2015. They describe a standard prenatal evaluation following identification of an omphalocele including echocardiogram, detailed anatomic survey, and availability of an amniocentesis to facilitate aneuploidy screening and testing for BWS. This review also includes an overview of perinatal and long-term outcomes for cases of BWS diagnosed at their center between 2000 and 2015.
Study outcomes
Results of prenatal genetic testing in this cohort were divided between cases of an isolated omphalocele (without other structural changes) and cases of nonisolated omphaloceles. In the group of pregnancies with an isolated omphalocele, 2 of 27 pregnancies (7.4%) were found to have an abnormal karyotype, and 6 of 16 of the remaining pregnancies (37.5%) were diagnosed with BWS. Among the group of pregnancies with a nonisolated omphalocele, 23 of 59 pregnancies (39%) were found to have an abnormal karyotype, and 1 of 20 pregnancies (5%) were diagnosed with BWS.
Prenatal sonographic features associated with cases of BWS included polyhydramnios in 12 of 19 cases (63%) and macrosomia in 8 of 19 cases (42%). Macroglossia is another characteristic feature of the disorder, which was identified in 4 of 19 cases (21%) prenatally and in an additional 10 of 19 cases (52.6%) postnatally. Interestingly, only 1 of the cases of BWS was caused by a microdeletion at 11p15.4—a change that was identified on microarray. The additional 6 cases of BWS were caused by imprinting changes in the region, which are only detectable with a specific methylation-analysis technique.
Among the 19 cases of BWS identified over a 15-year period, there was 1 intrauterine demise. Preterm birth occurred in 10 of 19 cases (52.6%), including 8 of 19 cases (42.1%) of spontaneous preterm labor. Respiratory distress (27.8%), hypoglycemia (61%), and gastrointestinal reflux (59%) were common neonatal complications. Embryonal tumors were diagnosed in 2 of 16 patients (12.5%). Although neurodevelopmental outcomes were incomplete, their data suggested normal development in 75% of children. There were 2 neonatal deaths in this cohort and 1 childhood death at age 2 years.
Study strengths and limitations
As with many studies investigating a rare disorder, this study is limited by its retrospective nature and small sample size. Nevertheless, it adds an important cohort of patients with a prenatally diagnosed omphalocele to the literature and illuminates the utility of a standardized approach to testing for BWS in this population.
In this cohort with prenatally diagnosed omphaloceles with standardized testing for BWS, the prevalence of the disorder was approximately 8% and more common in cases of an isolated omphalocele. The most common supporting sonographic features of BWS may not be detected until later in gestation, including polyhydramnios and macrosomia. This demonstrates the importance of both sonographic follow-up as well as universal testing for BWS in euploid cases of a prenatally diagnosed omphalocele. Almost all cases of BWS in this cohort required specialized molecular techniques for diagnosis, and the diagnosis would have been missed on karyotype, microarray, and ES.
Continue to: Genetic diagnoses that could have been identified by expanded carrier screening...
Genetic diagnoses that could have been identified by expanded carrier screening
Stevens BK, Nunley PB, Wagner C, et al. Utility of expanded carrier screening in pregnancies with ultrasound abnormalities. Prenat Diagn. 2022;42:60-78. doi:10.1002/pd.6069.
This series is a thorough retrospective review of patients evaluated in a pediatric genetics clinic from 2014 through 2017. Patients were included if they were evaluated in the first 6 months of life and had a structural abnormality that might be detected on prenatal ultrasonography. The genetic testing results were analyzed and categorized according to types of genetic disorders, with the goal of identifying how many patients might have been identified by expanded carrier screening (ECS) panels.
Study outcomes
A total of 931 charts were reviewed, and 85% (791 of 931) of patients evaluated in the first 6 months of life were determined to have a structural anomaly that might be detected on prenatal ultrasonography. Of those patients, 691 went on to have genetic testing and 32.1% (222 of 691) of them had a diagnostic (pathogenic) genetic testing result related to the phenotype. The types of diagnostic testing results are shown in the FIGURE. Notably, 42 single-gene disorders were detected.
FIGURE Diagnostic test result in pediatric patients evaluated under age 6 months

Of those 222 patients with diagnostic results, there were 8 patients with autosomal recessive and X-linked conditions that could be detected using a 500-gene ECS panel. Five patients could be detected with a 271-gene panel. After nondiagnostic microarray, 11.3% of patients had a condition that could be detected by using a 500-gene ECS panel. The identified conditions included cystic fibrosis, CYP21‐related congenital adrenal hyperplasia, autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease, Antley‐Bixler syndrome, and Morquio syndrome type A.
Furthermore, the authors conducted a literature review of 271 conditions and found that 32% (88 of 271) of conditions may be associated with ultrasound findings.
Study strengths and limitations
When applying these data to prenatal populations, the authors acknowledge several notable limitations. There is a selection bias toward less-severe phenotypes for many patients choosing to continue rather than to interrupt a pregnancy. Additionally, only 23% of the patients in the study had a microarray and ES, which may lead to an underrepresentation of single-gene disorders and an underestimation of the utility of ECS. Finally, a retrospective classification of structural abnormalities that may be detectable by ultrasonography may not always reflect what is actually reported in prenatal imaging.
However, the work that the authors put forth to evaluate and categorize 931 participants by the results of genetic testing and structural anomalies is appreciated, and the level of detail is impressive for this retrospective chart review. Additionally, the tables itemizing the authors’ review of 271 ECS disorders that may have ultrasonography findings categorized by disorder and system are helpful and quick diagnostic references for clinicians providing prenatal care. ●
This study of potentially detectable prenatal findings from the lens of a pediatric genetics clinic lends an interesting perspective: Exome sequencing is not the primary route to establish a diagnosis; karyotype, microarray, methylation disorders, and triplet repeat disorders all have an established role in the diagnostic toolkit. Keeping in mind the contribution of these modalities to pediatric testing may shorten the diagnostic odyssey to continue pregnancies or help to fully counsel patients on expectations and decision-making after birth.
Carrier screening is not a substitute for diagnostic testing in pregnancy. However, in appropriately selected patients, a broad carrier screening panel may have added utility. ECS can be conducted while awaiting microarray results to help target testing and may be particularly useful for patients who decline diagnostic testing until the postnatal period. It is important to counsel patients that carrier screening is not a diagnostic test, and results will only report likely pathogenic or pathogenic variants, not variants of uncertain significance that may be of clinical relevance. However, our practice has had several insightful diagnoses reached through ECS, in conjunction with microarray testing that allowed for faster and more targeted sequencing and precise fetal diagnosis. This readily available molecular tool (often covered by insurance) deserves a spot in your fetal diagnosis tool belt based on available evidence.
Last year, our Update focused on the expansion of sequencing in prenatal diagnosis. This year, we are taking a step sideways to remember the many diagnoses we may miss if we rely on exome sequencing alone. A recent case report in Prenatal Diagnosis describes a pregnancy affected by fetal akinesia sequence and polyhydramnios in which sequencing did not reveal a diagnosis. Expansion of the differential to include congenital myotonic dystrophy and subsequent triplet repeat testing led the clinicians to the diagnosis and identification of a triplet repeat expansion in the DMPK gene. This case serves as our first example of how complementary testing and technologies should continue to help us make critical diagnoses.
What is the yield of exome sequencing vs panels in nonimmune hydrops?
Rogers R, Moyer K, Moise KJ Jr. Congenital myotonic dystrophy: an overlooked diagnosis not amenable to detection by sequencing. Prenat Diagn. 2022;42:233-235. doi:10.1002/pd.6105.
Norton ME, Ziffle JV, Lianoglou BR, et al. Exome sequencing vs targeted gene panels for the evaluation of nonimmune hydrops fetalis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2021;28:S0002-9378(21)00828-0. doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2021.07.014.
We have had several illuminating discussions with our colleagues about the merits of exome sequencing (ES) versus panels and other modalities for fetal diagnosis. Many obstetricians practicing at the leading edge may feel like ES should be utilized uniformly for fetal anomalies with nondiagnostic karyotype or microarray. However, for well-defined phenotypes with clear and narrow lists of implicated genes (eg, skeletal dysplasias) or patients without insurance coverage, panel sequencing still has utility in prenatal diagnosis. The question of which phenotypes most benefit from ES versus panel sequencing is an area of interesting, ongoing research for several investigators.
Secondary analysis of nonimmune hydrops cohort
Norton and colleagues tackled one such cohort in a study presented in the American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology. They compared the proportion of diagnoses that would have been identified in commercial lab panels with their research of phenotype-driven ES in a cohort of 127 fetuses with features of nonimmune hydrops fetalis (NIHF). NIHF can be caused by a variety of single-gene disorders in addition to chromosomal disorders and copy number variants on chromosomal microarray. Patients were eligible for inclusion in the cohort if they had a nondiagnostic karyotype or microarray and any of the following features: nuchal translucency of 3.5 mm or greater, cystic hygroma, pleural effusion, pericardial effusion, ascites, or skin edema. Standard sequencing methods and variant analysis were performed. They assumed 100% analytical sensitivity and specificity of the panels for variant detection and collected cost information on the targeted gene panels.
Study outcomes
In the ES analysis of cases, 37 of 127 cases (29%) had a pathogenic or likely pathogenic variant in 1 of 29 genes, and another 12 of 127 cases (9%) had variants of uncertain significance that were strongly suspected to be the etiology during clinical analysis. The types of disorders that were identified are listed in the TABLE. In addition to a feature of NIHF, 50% of the cases had a structural anomaly.
There were 10 identified clinical panels from 7 clinical laboratories. These panels ranged in size from 11 to 128 genes. The highest simulated yield of any commercial panel was only 62% of the pathogenic variants identified by ES. The other commercial laboratory panels detection yield ranged from 11% to 62% of pathogenic variants detected by ES. For overall yield, the largest panel would have a diagnostic yield of 18% of diagnoses relative to the 29% diagnostic yield from ES.
The largest panel included 128 genes prior to the publication of the original cohort and was updated after publication to include 148 genes. The larger updated panel would have identified all of the patients in the ES cohort. However, many of the other panels listed would have identified a smaller fraction of the variants identified by ES (range, 11%-62%). At the time of publication, the cost of the panels ranged from $640 to $3,500, and the cost of prenatal ES ranged from $2,458 to $7,500.
Continue to: Strengths and limitations...
Strengths and limitations
Twenty-three percent of the patients who were sequenced had an increased fetal nuchal translucency or cystic hygroma, and another 17% had a single fetal effusion. This inclusivity makes this study more applicable to broader fetal anomaly populations. However, it is worth noting that only 61% of patients had NIHF by the definition of 2 or more fluid collections or skin thickening.
The authors assumed 100% sensitivity and specificity for the panel tests relative to diagnostic ES results, but this may not reflect real-life analysis. There is inherent subjectivity and subsequent differences in variant calling (deciding which genetic changes are pathogenic) between institutions and companies despite efforts to standardize this process. Due to the simulated nature of this study, these differences are not captured. Additionally, although the authors note that the research ES had at least 30 times the coverage (an adequate number of sequence reads for accurate testing) than did the commercial lab panels, some gene panels have additional sequencing of intronic regions, copy number analysis, and up to 10 times more coverage than ES, which could lead to more diagnoses.
This study illustrates that there is nuance involved in selecting which type of gene sequencing and which clinical laboratory to use for prenatal diagnosis. Labs with more updated literature searches and more inclusive gene panels may be excellent options for patients in whom ES is not covered by insurance or with phenotypes with a narrow range of suspected causative genes. However, there is a lag time in updating the genes offered on each panel, and new genedisease associations will not be captured by existing panels.
From a cost, speed-of-analysis, and depth-of-sequencing perspective, panel sequencing can have advantages that should be considered in some patients, particularly if the panels are large and regularly updated. However, the authors summarize our sentiments and their findings with the following:
“For disorders, such as NIHF with marked genetic heterogeneity and less clear in utero phenotypes of underlying genetic diseases, the broader coverage of exome sequencing makes it a superior option to targeted panel testing.”
We look forward to the publication of further anomaly-specific cohorts and secondary analyses of the utility of current panels and ES that may follow.
Frequency of Beckwith-Widemann syndrome in prenatally diagnosed omphaloceles
Abbasi N, Moore A, Chiu P, et al. Prenatally diagnosed omphaloceles: report of 92 cases and association with Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome. Prenat Diagn. 2021;41:798-816. doi:10.1002/pd.5930.
An omphalocele is diagnosed prenatally on ultrasound when an anterior midline mass, often containing abdominal contents, is seen herniating into the base of the umbilical cord. Omphaloceles are often associated with additional structural abnormalities and underlying genetic syndromes, thus a thorough fetal assessment is required for accurate prenatal counseling and neonatal care.
Identification of Beckwith-Widemann syndrome (BWS) in the setting of a prenatally diagnosed omphalocele is difficult because of its wide range of clinical features and its unique genetic basis. Unlike many genetic disorders that are caused by specific genetic variants, or spelling changes in the genes, BWS results from a change in the expression of one or more of the genes in a specific region of chromosome 11. A high index of clinical suspicion as well as an understanding of the various genetic and epigenetics alterations that cause BWS is required for prenatal diagnosis.
Retrospective cohort at a single center
The authors in this study reviewed all pregnancies in which an omphalocele was diagnosed prenatally at a single center between 2010 and 2015. They describe a standard prenatal evaluation following identification of an omphalocele including echocardiogram, detailed anatomic survey, and availability of an amniocentesis to facilitate aneuploidy screening and testing for BWS. This review also includes an overview of perinatal and long-term outcomes for cases of BWS diagnosed at their center between 2000 and 2015.
Study outcomes
Results of prenatal genetic testing in this cohort were divided between cases of an isolated omphalocele (without other structural changes) and cases of nonisolated omphaloceles. In the group of pregnancies with an isolated omphalocele, 2 of 27 pregnancies (7.4%) were found to have an abnormal karyotype, and 6 of 16 of the remaining pregnancies (37.5%) were diagnosed with BWS. Among the group of pregnancies with a nonisolated omphalocele, 23 of 59 pregnancies (39%) were found to have an abnormal karyotype, and 1 of 20 pregnancies (5%) were diagnosed with BWS.
Prenatal sonographic features associated with cases of BWS included polyhydramnios in 12 of 19 cases (63%) and macrosomia in 8 of 19 cases (42%). Macroglossia is another characteristic feature of the disorder, which was identified in 4 of 19 cases (21%) prenatally and in an additional 10 of 19 cases (52.6%) postnatally. Interestingly, only 1 of the cases of BWS was caused by a microdeletion at 11p15.4—a change that was identified on microarray. The additional 6 cases of BWS were caused by imprinting changes in the region, which are only detectable with a specific methylation-analysis technique.
Among the 19 cases of BWS identified over a 15-year period, there was 1 intrauterine demise. Preterm birth occurred in 10 of 19 cases (52.6%), including 8 of 19 cases (42.1%) of spontaneous preterm labor. Respiratory distress (27.8%), hypoglycemia (61%), and gastrointestinal reflux (59%) were common neonatal complications. Embryonal tumors were diagnosed in 2 of 16 patients (12.5%). Although neurodevelopmental outcomes were incomplete, their data suggested normal development in 75% of children. There were 2 neonatal deaths in this cohort and 1 childhood death at age 2 years.
Study strengths and limitations
As with many studies investigating a rare disorder, this study is limited by its retrospective nature and small sample size. Nevertheless, it adds an important cohort of patients with a prenatally diagnosed omphalocele to the literature and illuminates the utility of a standardized approach to testing for BWS in this population.
In this cohort with prenatally diagnosed omphaloceles with standardized testing for BWS, the prevalence of the disorder was approximately 8% and more common in cases of an isolated omphalocele. The most common supporting sonographic features of BWS may not be detected until later in gestation, including polyhydramnios and macrosomia. This demonstrates the importance of both sonographic follow-up as well as universal testing for BWS in euploid cases of a prenatally diagnosed omphalocele. Almost all cases of BWS in this cohort required specialized molecular techniques for diagnosis, and the diagnosis would have been missed on karyotype, microarray, and ES.
Continue to: Genetic diagnoses that could have been identified by expanded carrier screening...
Genetic diagnoses that could have been identified by expanded carrier screening
Stevens BK, Nunley PB, Wagner C, et al. Utility of expanded carrier screening in pregnancies with ultrasound abnormalities. Prenat Diagn. 2022;42:60-78. doi:10.1002/pd.6069.
This series is a thorough retrospective review of patients evaluated in a pediatric genetics clinic from 2014 through 2017. Patients were included if they were evaluated in the first 6 months of life and had a structural abnormality that might be detected on prenatal ultrasonography. The genetic testing results were analyzed and categorized according to types of genetic disorders, with the goal of identifying how many patients might have been identified by expanded carrier screening (ECS) panels.
Study outcomes
A total of 931 charts were reviewed, and 85% (791 of 931) of patients evaluated in the first 6 months of life were determined to have a structural anomaly that might be detected on prenatal ultrasonography. Of those patients, 691 went on to have genetic testing and 32.1% (222 of 691) of them had a diagnostic (pathogenic) genetic testing result related to the phenotype. The types of diagnostic testing results are shown in the FIGURE. Notably, 42 single-gene disorders were detected.
FIGURE Diagnostic test result in pediatric patients evaluated under age 6 months

Of those 222 patients with diagnostic results, there were 8 patients with autosomal recessive and X-linked conditions that could be detected using a 500-gene ECS panel. Five patients could be detected with a 271-gene panel. After nondiagnostic microarray, 11.3% of patients had a condition that could be detected by using a 500-gene ECS panel. The identified conditions included cystic fibrosis, CYP21‐related congenital adrenal hyperplasia, autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease, Antley‐Bixler syndrome, and Morquio syndrome type A.
Furthermore, the authors conducted a literature review of 271 conditions and found that 32% (88 of 271) of conditions may be associated with ultrasound findings.
Study strengths and limitations
When applying these data to prenatal populations, the authors acknowledge several notable limitations. There is a selection bias toward less-severe phenotypes for many patients choosing to continue rather than to interrupt a pregnancy. Additionally, only 23% of the patients in the study had a microarray and ES, which may lead to an underrepresentation of single-gene disorders and an underestimation of the utility of ECS. Finally, a retrospective classification of structural abnormalities that may be detectable by ultrasonography may not always reflect what is actually reported in prenatal imaging.
However, the work that the authors put forth to evaluate and categorize 931 participants by the results of genetic testing and structural anomalies is appreciated, and the level of detail is impressive for this retrospective chart review. Additionally, the tables itemizing the authors’ review of 271 ECS disorders that may have ultrasonography findings categorized by disorder and system are helpful and quick diagnostic references for clinicians providing prenatal care. ●
This study of potentially detectable prenatal findings from the lens of a pediatric genetics clinic lends an interesting perspective: Exome sequencing is not the primary route to establish a diagnosis; karyotype, microarray, methylation disorders, and triplet repeat disorders all have an established role in the diagnostic toolkit. Keeping in mind the contribution of these modalities to pediatric testing may shorten the diagnostic odyssey to continue pregnancies or help to fully counsel patients on expectations and decision-making after birth.
Carrier screening is not a substitute for diagnostic testing in pregnancy. However, in appropriately selected patients, a broad carrier screening panel may have added utility. ECS can be conducted while awaiting microarray results to help target testing and may be particularly useful for patients who decline diagnostic testing until the postnatal period. It is important to counsel patients that carrier screening is not a diagnostic test, and results will only report likely pathogenic or pathogenic variants, not variants of uncertain significance that may be of clinical relevance. However, our practice has had several insightful diagnoses reached through ECS, in conjunction with microarray testing that allowed for faster and more targeted sequencing and precise fetal diagnosis. This readily available molecular tool (often covered by insurance) deserves a spot in your fetal diagnosis tool belt based on available evidence.
2021 Update on sequencing in prenatal genetics
Prenatal diagnosis has expanded from identification of aneuploidy to include copy number variants detected on microarray (such as 22q11 deletion syndrome) and now single-gene disorders identified by targeted or exome and genome sequencing. How and when different sequencing tests should be used clinically are questions faced by every provider engaged in modern prenatal diagnosis.
In this Update, we highlight new clinical insights into prenatal sequencing and explore how information gained from sequencing may help us understand some of the unanswered questions in obstetrics.
What is the yield of a RASopathy gene panel with specific prenatal findings?
Scott A, Di Giosaffatte N, Pinna V, et al. When to test fetuses for RASopathies? Proposition from a systematic analysis of 352 multicenter cases and a postnatal cohort. Genet Med. Published online February 10, 2021. doi:10.1038/s41436-020-01093-7.
RASopathies, a group of genetic conditions caused by mutations in the RAS/mitogen-activated protein kinase (RAS-MAPK) pathway, are common, occurring in 1:1,000 to 1:2,500 live births. RASopathies are much more common than 22q11 deletion syndrome, or DiGeorge syndrome, which occurs in 1.4:10,000 live births.1
RASopathy disorders include Noonan syndrome, Noonan syndrome with multiple lentigines, Costello syndrome, cardiofaciocutaneous syndrome, and Noonan-like syndrome with loose anagen hair. These are autosomal dominant disorders caused by a pathogenic variant (or mutation) in 1 of more than 20 genes in the RAS-MAPK signaling pathway in the body. Clinical features include congenital anomalies of the kidney and urinary tract, lymphatic anomalies, congenital heart disease (CHD), hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM), postnatal growth disorders, neurodevelopmental disorders, and more rarely hematologic malignancies. Prenatal clues include an increased nuchal translucency (NT), CHD, cystic hygroma, lymphatic anomalies, anomalies of the kidney and urinary tract, hydrops, and HCM.
Cohort of pregnancies that received a RASopathy panel
Scott and colleagues sought to clarify the utility of testing for RASopathies with a prenatal gene panel. They conducted a multicenter retrospective cohort study with cases from 2 hospitals in Italy and Canada; data were collected between 2012 and 2019.
Eligible fetuses were those referred to the prenatal genetics clinic because of an increased NT, increased nuchal fold (NF), hydrops, ascites, thoracic effusions, chylothorax, other lymphatic anomalies, CHD, or HCM with a nondiagnostic (negative) microarray or karyotype. All eligible cases had RASopathy molecular testing in the prenatal or neonatal period.
Among the 352 referrals to clinic, 50 cases of a RASopathy disorder were diagnosed. Additionally, to complement this cohort over the same time period, 25 postnatal diagnoses were made after retrospective review performed to ascertain additional prenatal findings. The size of the testing panel ranged from 9 to 20 genes, which were sent to clinical laboratories that performed sequencing based on standard protocols.
Study outcomes
Overall, 14% of fetuses with an indication for testing had a pathogenic or likely pathogenic variant (diagnostic) on panel testing among 11 genes (notably, all presented results are after excluding copy number variants and aneuploidy). Fetuses with only 1 ultrasonography finding were much less likely to have a positive result than those with more than 1 ultrasonography finding, 3% versus 18%. The highest diagnostic yields were for HCM at 69%; thoracic effusions and ascites, 41%; persistent hydrops, 39%; cystic hygroma combined with another suggestive ultrasonography finding, 28%; CHD, 23%; and persistent cystic hygroma, 21%. Five fetuses were affected with CHD and HCM, and 44% had an intrauterine fetal demise.
Importance of NT size. An isolated increased NT had a diagnostic yield of 1% overall (1/90); however, the size of the NT mattered. Seventeen fetuses had an NT between 3 and 3.5 mm and none of these had diagnostic sequencing, whereas 26% with an NT greater than 6 mm had a diagnostic result (11/43). An increased NF had a diagnostic yield of 25%.
Other findings. Of fetuses with a cystic hygroma, 16% had a pathogenic or likely pathogenic variant, and when these persisted into the second trimester or were associated with other anomalies, the percentages increased to 21% and 28%, respectively. Of prenatal patients, 20.6% had variants of uncertain significance, and 12% of the pathogenic and likely pathogenic variants were inherited, which is less than previously reported series. Additionally, 48% of the postnatal RASopathy diagnosis group did not have an ultrasonography finding on record review.
Continue to: Study strengths and limitations...
Study strengths and limitations
This study presents a large cohort of prenatal and neonatal patients tested for RASopathies at 2 international centers with very granular and clinically useful data about ultrasonography findings and yield of panel testing. Prenatal care providers, geneticists, and computational biologists may find this study of great interest and take away useful information and ideas due to the authors’ presentation and details.
The number of genes tested changed over the inclusion time period, but this is an inescapable reality of retrospective clinical research in an advancing field. The authors presented the prenatal and postnatal diagnoses ultrasonography findings separately and together. Given the different nature of cohort ascertainment, we prefer to consider these groups separately and have presented the data for the prenatal group.
Prenatal sequencing panels and exome sequencing are detecting disorders with important implications for prenatal care. If your practice is not testing for RASopathies in prenatal patients with concerning ultrasonography features, you are missing cases. In this study, the most concerning ultrasonography features (more than 20% diagnosis) were HCM, thoracic effusions and ascites, persistent hydrops, cystic hygroma combined with another suggestive ultrasonography finding, CHD, and persistent cystic hygroma. Isolated ultrasonography findings or findings that resolved had a lower diagnostic yield, and an isolated enlarged NT had a 1% diagnostic yield, with most cases having an NT larger than 6 mm.
For pretest counseling, in this study 20% of patients had a variant of uncertain significance, and preparing patients for this possibility is crucial. Most variants of uncertain significance are reclassified to benign when more information is available. Providers can consider sending parental samples concurrently with the fetal sample to help obtain useful information quickly, although the possibility of an inherited pathogenic variant still exists (12% in this study).
Prenatal diagnosis gives your patients the opportunity to learn about the disorder, plan for treatment and delivery location, and establish their care team before birth or consider pregnancy termination.
Sequencing provides insights into twin pregnancies
Jonsson H, Magnusdottir E, Eggertsson HP, et al. Differences between germline genomes of monozygotic twins. Nat Genet. 2021;53:27-34. doi:10.1038/s41588 -020-00755-1.
You have a monozygotic twin pair with an anomaly and intend to do diagnostic testing for prenatal diagnosis. The question always arises: Do you sample both twins or just one? Surely, they are genetically identical? A wise mentor once instilled a valuable lesson: Monozygotic twins are more likely to have an anomaly. Their existence is already out of the realm of normal. Finally, we now have an engaging and interesting answer to this and other fascinating embryology questions through the work of Jonsson and colleagues.
Study eligibility criteria and treatment protocol
The authors enrolled 381 twin pairs and 2 monozygotic triplets and compared genome sequencing of different tissues (cheek cells and blood). They went further to assess what other tissues might share the genetic change. To do this, they sequenced the children and the partners of 181 of the pairs. Presumably, if a twin and their offspring shared a genetic change that was not present in the spouse or twin, this genetic change must be present in the oocytes or sperm of the parent twin. The goal of sequencing multiple tissue sources in each twin was to help determine when the genetic change occurred in embryonic development.
Study outcomes
The authors found that 15% of twins had mutations that were absent in the other twin. Because of the extent of tissues that had the genetic change, the authors asserted that these changes must have occurred very early in embryonic development (even from one cell after twinning) for the changes to be near-constitutional (among sampled tissues).
An average of 14 genetic differences were found between twin pairs that developed after twinning. However, the number of differences varied. For example, 39 pairs of twins differed by more than 100 changes, and 38 did not differ at all. Differences between twins were more likely in blood samples than in cheek swabs, suggesting that some differences were due to acquired genetic changes in hematologic cell lines, or clonal hematopoiesis.
The authors also looked at what percentage of sequenced DNA contained the variants (or mutations) and found that many of these DNA differences were present at high amounts in sequencing reads. This suggests that the DNA changes happened very early after twinning in about one-third of pairs. Additionally, if one twin had a near-constitutional change, in 42% of pairs the other twin had a different near-constitutional change. Among the triplets, 2 of a triplet pair shared more genetic similarity and were likely descendent from a single split cell and the third likely was formed from a different set of cells.
By examining the offspring of twins, Jonsson and colleagues found that there were 2.6 early embryonic mutations, and this did not differ when blood or buccal DNA was compared. The rate of transmission of a variant to offspring was proportional to the variant allele frequency (proportion of alternate alleles) in the blood or buccal cells. This is an important counseling point when considering patients with mosaic genetic disorders and counseling about the likelihood of inheritance or transmission to future offspring. If the rate of mosaicism was higher in blood or buccal cells, the likelihood of transmission was higher. Additionally, the mutations did not differ by sex, and there was no relationship to whether the chromosome was maternally or paternally inherited.
Continue to: Study strengths and limitations...
Study strengths and limitations
The authors did not have access to information about chorionicity of the monozygotic twin pairs. Consequently, they were unable to correlate chorionicity with the degree of noted genetic difference between the monozygotic twin pairs. Additionally, although the authors were thoughtful in their utilization of offspring and spouses to infer germline genomic content, the study had a limited number of tissues sampled, which could reduce the applicability. However, the sample size, clinically accessible tissue sampling, and thoughtful analysis used in this study make it an interesting and relevant contribution to reproductive medicine and evolutionary biology.
We all accumulate changes to our DNA throughout life. The study by Jonsson and colleagues illustrates that for many, this accumulation of genetic changes starts very early in gestation. In the early zygote, the authors observed roughly 1 mutation per cell division prior to the point of twinning. In the realm of prenatal diagnosis, one should consider that monochorionic twins with different phenotypes (that is, an ultrasonography anomaly in 1 of the twin pair) could represent a genetic change rather than an environmental difference. This genetic change may not be shared by the other twin despite originating from the same primordial cell line. The genetic changes that the authors investigated were detected on genome sequencing, which is much more comprehensive than the exome sequencing that is increasingly utilized in rare disease diagnosis. The clinical utility of this observation in prenatal diagnosis has yet to be proven, but this study provides preliminary data that 15% of monozygotic twins have genetic differences and may warrant individualized testing.
The genetic landscape of the placenta
Coorens TH, Oliver TR, Sanghvi R, et al. Inherent mosaicism and extensive mutation of human placentas. Nature. Published online March 10, 2021. doi:10.1038/ s41586-021-03345-1.
Confined placental mosaicism (CPM) is a phenomenon in which the genetics of the placenta are different from those of the fetus. Historically, this phenomenon has been described in 1% to 2% of pregnancies based on karyotype data obtained from chorionic villus sampling. Some studies have demonstrated adverse pregnancy outcomes in the setting of CPM, thought to be secondary to aneuploid cells in the placenta leading to insufficiency or dysfunction.
Although our sophistication and level of detail in prenatal genetic testing has rapidly expanded to include information about copy number variants and singlenucleotide changes, their contribution to CPM has been understudied. Coorens and colleagues recently published a landmark study that describes a surprisingly high rate of mosaicism for these smaller genetic changes.
A cohort study of placentas
The authors performed whole genome sequencing on placental samples obtained from 37 term pregnancies. Umbilical cord tissue and maternal blood also were collected and served as controls for fetal and maternal genetic profiles, respectively.
In a subgroup of 5 placentas, lasercapture microscopy was used to separate placental cells of different origins, including trophoblastic cells, mesenchymal core cells, and cells originating from the inner cell mass. To investigate variation within different geographic regions of a single placenta, these cell lines were derived multiple times from each quadrant of the 5 placentas.
Placental biopsies revealed “bottlenecks” of genetic differentiation
Genome sequencing was used uniquely in this study to help delineate the phylogeny of placental cells by tracking somatic mutations both in different geographic locations of each placenta and between different cells of origin within 1 placenta.
The authors concluded that bottlenecks of differentiation in placental development led to unique genetic signatures in every bulk placental sample studied. Their findings led them to describe the placenta as a “patchwork” of independent genetic units resulting from clonal expansion at different stages of embryonic development.
Early insights into human placental cells
This study provides fascinating insight into the surprisingly high rates of copy number variants and single-gene changes that exist, in mosaic form, within human placentas. The authors distinguish the placenta from other human organs (such as the colon, endometrium, liver, and skin) in which many fewer genetic changes exist. In fact, they suggest parallels between the “mutational signature” of the placenta with rapidly dividing neoplastic cells.
As one of the first investigations into the variation and complexity of genetic changes within the placenta, this study was not designed to draw conclusions regarding the clinical impact of the numerous genetic changes described. Further studies will elucidate the potential contribution of genetically mosaic placentas to common adverse obstetric outcomes. ●
With a new appreciation for the smaller genetic alterations that exist within placental tissue, it appears that the rate of CPM has been vastly underestimated. We know that aneuploid placental cells increase the risk of adverse pregnancy outcomes and we may learn more about the contribution of copy number variants and single-nucleotide changes to preeclampsia, growth restriction, and pregnancy loss. Furthermore, as the applications of cell-free fetal DNA (cffDNA) in genetic screening continue to expand, we must exercise caution in assuming that copy number variants or single-nucleotide changes detected by cffDNA reflect those of the developing fetus.
- Roberts AE, Allanson JE, Tartaglia M, et al. Noonan syndrome. Lancet. 2013;381:333-342. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61023-X.
Prenatal diagnosis has expanded from identification of aneuploidy to include copy number variants detected on microarray (such as 22q11 deletion syndrome) and now single-gene disorders identified by targeted or exome and genome sequencing. How and when different sequencing tests should be used clinically are questions faced by every provider engaged in modern prenatal diagnosis.
In this Update, we highlight new clinical insights into prenatal sequencing and explore how information gained from sequencing may help us understand some of the unanswered questions in obstetrics.
What is the yield of a RASopathy gene panel with specific prenatal findings?
Scott A, Di Giosaffatte N, Pinna V, et al. When to test fetuses for RASopathies? Proposition from a systematic analysis of 352 multicenter cases and a postnatal cohort. Genet Med. Published online February 10, 2021. doi:10.1038/s41436-020-01093-7.
RASopathies, a group of genetic conditions caused by mutations in the RAS/mitogen-activated protein kinase (RAS-MAPK) pathway, are common, occurring in 1:1,000 to 1:2,500 live births. RASopathies are much more common than 22q11 deletion syndrome, or DiGeorge syndrome, which occurs in 1.4:10,000 live births.1
RASopathy disorders include Noonan syndrome, Noonan syndrome with multiple lentigines, Costello syndrome, cardiofaciocutaneous syndrome, and Noonan-like syndrome with loose anagen hair. These are autosomal dominant disorders caused by a pathogenic variant (or mutation) in 1 of more than 20 genes in the RAS-MAPK signaling pathway in the body. Clinical features include congenital anomalies of the kidney and urinary tract, lymphatic anomalies, congenital heart disease (CHD), hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM), postnatal growth disorders, neurodevelopmental disorders, and more rarely hematologic malignancies. Prenatal clues include an increased nuchal translucency (NT), CHD, cystic hygroma, lymphatic anomalies, anomalies of the kidney and urinary tract, hydrops, and HCM.
Cohort of pregnancies that received a RASopathy panel
Scott and colleagues sought to clarify the utility of testing for RASopathies with a prenatal gene panel. They conducted a multicenter retrospective cohort study with cases from 2 hospitals in Italy and Canada; data were collected between 2012 and 2019.
Eligible fetuses were those referred to the prenatal genetics clinic because of an increased NT, increased nuchal fold (NF), hydrops, ascites, thoracic effusions, chylothorax, other lymphatic anomalies, CHD, or HCM with a nondiagnostic (negative) microarray or karyotype. All eligible cases had RASopathy molecular testing in the prenatal or neonatal period.
Among the 352 referrals to clinic, 50 cases of a RASopathy disorder were diagnosed. Additionally, to complement this cohort over the same time period, 25 postnatal diagnoses were made after retrospective review performed to ascertain additional prenatal findings. The size of the testing panel ranged from 9 to 20 genes, which were sent to clinical laboratories that performed sequencing based on standard protocols.
Study outcomes
Overall, 14% of fetuses with an indication for testing had a pathogenic or likely pathogenic variant (diagnostic) on panel testing among 11 genes (notably, all presented results are after excluding copy number variants and aneuploidy). Fetuses with only 1 ultrasonography finding were much less likely to have a positive result than those with more than 1 ultrasonography finding, 3% versus 18%. The highest diagnostic yields were for HCM at 69%; thoracic effusions and ascites, 41%; persistent hydrops, 39%; cystic hygroma combined with another suggestive ultrasonography finding, 28%; CHD, 23%; and persistent cystic hygroma, 21%. Five fetuses were affected with CHD and HCM, and 44% had an intrauterine fetal demise.
Importance of NT size. An isolated increased NT had a diagnostic yield of 1% overall (1/90); however, the size of the NT mattered. Seventeen fetuses had an NT between 3 and 3.5 mm and none of these had diagnostic sequencing, whereas 26% with an NT greater than 6 mm had a diagnostic result (11/43). An increased NF had a diagnostic yield of 25%.
Other findings. Of fetuses with a cystic hygroma, 16% had a pathogenic or likely pathogenic variant, and when these persisted into the second trimester or were associated with other anomalies, the percentages increased to 21% and 28%, respectively. Of prenatal patients, 20.6% had variants of uncertain significance, and 12% of the pathogenic and likely pathogenic variants were inherited, which is less than previously reported series. Additionally, 48% of the postnatal RASopathy diagnosis group did not have an ultrasonography finding on record review.
Continue to: Study strengths and limitations...
Study strengths and limitations
This study presents a large cohort of prenatal and neonatal patients tested for RASopathies at 2 international centers with very granular and clinically useful data about ultrasonography findings and yield of panel testing. Prenatal care providers, geneticists, and computational biologists may find this study of great interest and take away useful information and ideas due to the authors’ presentation and details.
The number of genes tested changed over the inclusion time period, but this is an inescapable reality of retrospective clinical research in an advancing field. The authors presented the prenatal and postnatal diagnoses ultrasonography findings separately and together. Given the different nature of cohort ascertainment, we prefer to consider these groups separately and have presented the data for the prenatal group.
Prenatal sequencing panels and exome sequencing are detecting disorders with important implications for prenatal care. If your practice is not testing for RASopathies in prenatal patients with concerning ultrasonography features, you are missing cases. In this study, the most concerning ultrasonography features (more than 20% diagnosis) were HCM, thoracic effusions and ascites, persistent hydrops, cystic hygroma combined with another suggestive ultrasonography finding, CHD, and persistent cystic hygroma. Isolated ultrasonography findings or findings that resolved had a lower diagnostic yield, and an isolated enlarged NT had a 1% diagnostic yield, with most cases having an NT larger than 6 mm.
For pretest counseling, in this study 20% of patients had a variant of uncertain significance, and preparing patients for this possibility is crucial. Most variants of uncertain significance are reclassified to benign when more information is available. Providers can consider sending parental samples concurrently with the fetal sample to help obtain useful information quickly, although the possibility of an inherited pathogenic variant still exists (12% in this study).
Prenatal diagnosis gives your patients the opportunity to learn about the disorder, plan for treatment and delivery location, and establish their care team before birth or consider pregnancy termination.
Sequencing provides insights into twin pregnancies
Jonsson H, Magnusdottir E, Eggertsson HP, et al. Differences between germline genomes of monozygotic twins. Nat Genet. 2021;53:27-34. doi:10.1038/s41588 -020-00755-1.
You have a monozygotic twin pair with an anomaly and intend to do diagnostic testing for prenatal diagnosis. The question always arises: Do you sample both twins or just one? Surely, they are genetically identical? A wise mentor once instilled a valuable lesson: Monozygotic twins are more likely to have an anomaly. Their existence is already out of the realm of normal. Finally, we now have an engaging and interesting answer to this and other fascinating embryology questions through the work of Jonsson and colleagues.
Study eligibility criteria and treatment protocol
The authors enrolled 381 twin pairs and 2 monozygotic triplets and compared genome sequencing of different tissues (cheek cells and blood). They went further to assess what other tissues might share the genetic change. To do this, they sequenced the children and the partners of 181 of the pairs. Presumably, if a twin and their offspring shared a genetic change that was not present in the spouse or twin, this genetic change must be present in the oocytes or sperm of the parent twin. The goal of sequencing multiple tissue sources in each twin was to help determine when the genetic change occurred in embryonic development.
Study outcomes
The authors found that 15% of twins had mutations that were absent in the other twin. Because of the extent of tissues that had the genetic change, the authors asserted that these changes must have occurred very early in embryonic development (even from one cell after twinning) for the changes to be near-constitutional (among sampled tissues).
An average of 14 genetic differences were found between twin pairs that developed after twinning. However, the number of differences varied. For example, 39 pairs of twins differed by more than 100 changes, and 38 did not differ at all. Differences between twins were more likely in blood samples than in cheek swabs, suggesting that some differences were due to acquired genetic changes in hematologic cell lines, or clonal hematopoiesis.
The authors also looked at what percentage of sequenced DNA contained the variants (or mutations) and found that many of these DNA differences were present at high amounts in sequencing reads. This suggests that the DNA changes happened very early after twinning in about one-third of pairs. Additionally, if one twin had a near-constitutional change, in 42% of pairs the other twin had a different near-constitutional change. Among the triplets, 2 of a triplet pair shared more genetic similarity and were likely descendent from a single split cell and the third likely was formed from a different set of cells.
By examining the offspring of twins, Jonsson and colleagues found that there were 2.6 early embryonic mutations, and this did not differ when blood or buccal DNA was compared. The rate of transmission of a variant to offspring was proportional to the variant allele frequency (proportion of alternate alleles) in the blood or buccal cells. This is an important counseling point when considering patients with mosaic genetic disorders and counseling about the likelihood of inheritance or transmission to future offspring. If the rate of mosaicism was higher in blood or buccal cells, the likelihood of transmission was higher. Additionally, the mutations did not differ by sex, and there was no relationship to whether the chromosome was maternally or paternally inherited.
Continue to: Study strengths and limitations...
Study strengths and limitations
The authors did not have access to information about chorionicity of the monozygotic twin pairs. Consequently, they were unable to correlate chorionicity with the degree of noted genetic difference between the monozygotic twin pairs. Additionally, although the authors were thoughtful in their utilization of offspring and spouses to infer germline genomic content, the study had a limited number of tissues sampled, which could reduce the applicability. However, the sample size, clinically accessible tissue sampling, and thoughtful analysis used in this study make it an interesting and relevant contribution to reproductive medicine and evolutionary biology.
We all accumulate changes to our DNA throughout life. The study by Jonsson and colleagues illustrates that for many, this accumulation of genetic changes starts very early in gestation. In the early zygote, the authors observed roughly 1 mutation per cell division prior to the point of twinning. In the realm of prenatal diagnosis, one should consider that monochorionic twins with different phenotypes (that is, an ultrasonography anomaly in 1 of the twin pair) could represent a genetic change rather than an environmental difference. This genetic change may not be shared by the other twin despite originating from the same primordial cell line. The genetic changes that the authors investigated were detected on genome sequencing, which is much more comprehensive than the exome sequencing that is increasingly utilized in rare disease diagnosis. The clinical utility of this observation in prenatal diagnosis has yet to be proven, but this study provides preliminary data that 15% of monozygotic twins have genetic differences and may warrant individualized testing.
The genetic landscape of the placenta
Coorens TH, Oliver TR, Sanghvi R, et al. Inherent mosaicism and extensive mutation of human placentas. Nature. Published online March 10, 2021. doi:10.1038/ s41586-021-03345-1.
Confined placental mosaicism (CPM) is a phenomenon in which the genetics of the placenta are different from those of the fetus. Historically, this phenomenon has been described in 1% to 2% of pregnancies based on karyotype data obtained from chorionic villus sampling. Some studies have demonstrated adverse pregnancy outcomes in the setting of CPM, thought to be secondary to aneuploid cells in the placenta leading to insufficiency or dysfunction.
Although our sophistication and level of detail in prenatal genetic testing has rapidly expanded to include information about copy number variants and singlenucleotide changes, their contribution to CPM has been understudied. Coorens and colleagues recently published a landmark study that describes a surprisingly high rate of mosaicism for these smaller genetic changes.
A cohort study of placentas
The authors performed whole genome sequencing on placental samples obtained from 37 term pregnancies. Umbilical cord tissue and maternal blood also were collected and served as controls for fetal and maternal genetic profiles, respectively.
In a subgroup of 5 placentas, lasercapture microscopy was used to separate placental cells of different origins, including trophoblastic cells, mesenchymal core cells, and cells originating from the inner cell mass. To investigate variation within different geographic regions of a single placenta, these cell lines were derived multiple times from each quadrant of the 5 placentas.
Placental biopsies revealed “bottlenecks” of genetic differentiation
Genome sequencing was used uniquely in this study to help delineate the phylogeny of placental cells by tracking somatic mutations both in different geographic locations of each placenta and between different cells of origin within 1 placenta.
The authors concluded that bottlenecks of differentiation in placental development led to unique genetic signatures in every bulk placental sample studied. Their findings led them to describe the placenta as a “patchwork” of independent genetic units resulting from clonal expansion at different stages of embryonic development.
Early insights into human placental cells
This study provides fascinating insight into the surprisingly high rates of copy number variants and single-gene changes that exist, in mosaic form, within human placentas. The authors distinguish the placenta from other human organs (such as the colon, endometrium, liver, and skin) in which many fewer genetic changes exist. In fact, they suggest parallels between the “mutational signature” of the placenta with rapidly dividing neoplastic cells.
As one of the first investigations into the variation and complexity of genetic changes within the placenta, this study was not designed to draw conclusions regarding the clinical impact of the numerous genetic changes described. Further studies will elucidate the potential contribution of genetically mosaic placentas to common adverse obstetric outcomes. ●
With a new appreciation for the smaller genetic alterations that exist within placental tissue, it appears that the rate of CPM has been vastly underestimated. We know that aneuploid placental cells increase the risk of adverse pregnancy outcomes and we may learn more about the contribution of copy number variants and single-nucleotide changes to preeclampsia, growth restriction, and pregnancy loss. Furthermore, as the applications of cell-free fetal DNA (cffDNA) in genetic screening continue to expand, we must exercise caution in assuming that copy number variants or single-nucleotide changes detected by cffDNA reflect those of the developing fetus.
Prenatal diagnosis has expanded from identification of aneuploidy to include copy number variants detected on microarray (such as 22q11 deletion syndrome) and now single-gene disorders identified by targeted or exome and genome sequencing. How and when different sequencing tests should be used clinically are questions faced by every provider engaged in modern prenatal diagnosis.
In this Update, we highlight new clinical insights into prenatal sequencing and explore how information gained from sequencing may help us understand some of the unanswered questions in obstetrics.
What is the yield of a RASopathy gene panel with specific prenatal findings?
Scott A, Di Giosaffatte N, Pinna V, et al. When to test fetuses for RASopathies? Proposition from a systematic analysis of 352 multicenter cases and a postnatal cohort. Genet Med. Published online February 10, 2021. doi:10.1038/s41436-020-01093-7.
RASopathies, a group of genetic conditions caused by mutations in the RAS/mitogen-activated protein kinase (RAS-MAPK) pathway, are common, occurring in 1:1,000 to 1:2,500 live births. RASopathies are much more common than 22q11 deletion syndrome, or DiGeorge syndrome, which occurs in 1.4:10,000 live births.1
RASopathy disorders include Noonan syndrome, Noonan syndrome with multiple lentigines, Costello syndrome, cardiofaciocutaneous syndrome, and Noonan-like syndrome with loose anagen hair. These are autosomal dominant disorders caused by a pathogenic variant (or mutation) in 1 of more than 20 genes in the RAS-MAPK signaling pathway in the body. Clinical features include congenital anomalies of the kidney and urinary tract, lymphatic anomalies, congenital heart disease (CHD), hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM), postnatal growth disorders, neurodevelopmental disorders, and more rarely hematologic malignancies. Prenatal clues include an increased nuchal translucency (NT), CHD, cystic hygroma, lymphatic anomalies, anomalies of the kidney and urinary tract, hydrops, and HCM.
Cohort of pregnancies that received a RASopathy panel
Scott and colleagues sought to clarify the utility of testing for RASopathies with a prenatal gene panel. They conducted a multicenter retrospective cohort study with cases from 2 hospitals in Italy and Canada; data were collected between 2012 and 2019.
Eligible fetuses were those referred to the prenatal genetics clinic because of an increased NT, increased nuchal fold (NF), hydrops, ascites, thoracic effusions, chylothorax, other lymphatic anomalies, CHD, or HCM with a nondiagnostic (negative) microarray or karyotype. All eligible cases had RASopathy molecular testing in the prenatal or neonatal period.
Among the 352 referrals to clinic, 50 cases of a RASopathy disorder were diagnosed. Additionally, to complement this cohort over the same time period, 25 postnatal diagnoses were made after retrospective review performed to ascertain additional prenatal findings. The size of the testing panel ranged from 9 to 20 genes, which were sent to clinical laboratories that performed sequencing based on standard protocols.
Study outcomes
Overall, 14% of fetuses with an indication for testing had a pathogenic or likely pathogenic variant (diagnostic) on panel testing among 11 genes (notably, all presented results are after excluding copy number variants and aneuploidy). Fetuses with only 1 ultrasonography finding were much less likely to have a positive result than those with more than 1 ultrasonography finding, 3% versus 18%. The highest diagnostic yields were for HCM at 69%; thoracic effusions and ascites, 41%; persistent hydrops, 39%; cystic hygroma combined with another suggestive ultrasonography finding, 28%; CHD, 23%; and persistent cystic hygroma, 21%. Five fetuses were affected with CHD and HCM, and 44% had an intrauterine fetal demise.
Importance of NT size. An isolated increased NT had a diagnostic yield of 1% overall (1/90); however, the size of the NT mattered. Seventeen fetuses had an NT between 3 and 3.5 mm and none of these had diagnostic sequencing, whereas 26% with an NT greater than 6 mm had a diagnostic result (11/43). An increased NF had a diagnostic yield of 25%.
Other findings. Of fetuses with a cystic hygroma, 16% had a pathogenic or likely pathogenic variant, and when these persisted into the second trimester or were associated with other anomalies, the percentages increased to 21% and 28%, respectively. Of prenatal patients, 20.6% had variants of uncertain significance, and 12% of the pathogenic and likely pathogenic variants were inherited, which is less than previously reported series. Additionally, 48% of the postnatal RASopathy diagnosis group did not have an ultrasonography finding on record review.
Continue to: Study strengths and limitations...
Study strengths and limitations
This study presents a large cohort of prenatal and neonatal patients tested for RASopathies at 2 international centers with very granular and clinically useful data about ultrasonography findings and yield of panel testing. Prenatal care providers, geneticists, and computational biologists may find this study of great interest and take away useful information and ideas due to the authors’ presentation and details.
The number of genes tested changed over the inclusion time period, but this is an inescapable reality of retrospective clinical research in an advancing field. The authors presented the prenatal and postnatal diagnoses ultrasonography findings separately and together. Given the different nature of cohort ascertainment, we prefer to consider these groups separately and have presented the data for the prenatal group.
Prenatal sequencing panels and exome sequencing are detecting disorders with important implications for prenatal care. If your practice is not testing for RASopathies in prenatal patients with concerning ultrasonography features, you are missing cases. In this study, the most concerning ultrasonography features (more than 20% diagnosis) were HCM, thoracic effusions and ascites, persistent hydrops, cystic hygroma combined with another suggestive ultrasonography finding, CHD, and persistent cystic hygroma. Isolated ultrasonography findings or findings that resolved had a lower diagnostic yield, and an isolated enlarged NT had a 1% diagnostic yield, with most cases having an NT larger than 6 mm.
For pretest counseling, in this study 20% of patients had a variant of uncertain significance, and preparing patients for this possibility is crucial. Most variants of uncertain significance are reclassified to benign when more information is available. Providers can consider sending parental samples concurrently with the fetal sample to help obtain useful information quickly, although the possibility of an inherited pathogenic variant still exists (12% in this study).
Prenatal diagnosis gives your patients the opportunity to learn about the disorder, plan for treatment and delivery location, and establish their care team before birth or consider pregnancy termination.
Sequencing provides insights into twin pregnancies
Jonsson H, Magnusdottir E, Eggertsson HP, et al. Differences between germline genomes of monozygotic twins. Nat Genet. 2021;53:27-34. doi:10.1038/s41588 -020-00755-1.
You have a monozygotic twin pair with an anomaly and intend to do diagnostic testing for prenatal diagnosis. The question always arises: Do you sample both twins or just one? Surely, they are genetically identical? A wise mentor once instilled a valuable lesson: Monozygotic twins are more likely to have an anomaly. Their existence is already out of the realm of normal. Finally, we now have an engaging and interesting answer to this and other fascinating embryology questions through the work of Jonsson and colleagues.
Study eligibility criteria and treatment protocol
The authors enrolled 381 twin pairs and 2 monozygotic triplets and compared genome sequencing of different tissues (cheek cells and blood). They went further to assess what other tissues might share the genetic change. To do this, they sequenced the children and the partners of 181 of the pairs. Presumably, if a twin and their offspring shared a genetic change that was not present in the spouse or twin, this genetic change must be present in the oocytes or sperm of the parent twin. The goal of sequencing multiple tissue sources in each twin was to help determine when the genetic change occurred in embryonic development.
Study outcomes
The authors found that 15% of twins had mutations that were absent in the other twin. Because of the extent of tissues that had the genetic change, the authors asserted that these changes must have occurred very early in embryonic development (even from one cell after twinning) for the changes to be near-constitutional (among sampled tissues).
An average of 14 genetic differences were found between twin pairs that developed after twinning. However, the number of differences varied. For example, 39 pairs of twins differed by more than 100 changes, and 38 did not differ at all. Differences between twins were more likely in blood samples than in cheek swabs, suggesting that some differences were due to acquired genetic changes in hematologic cell lines, or clonal hematopoiesis.
The authors also looked at what percentage of sequenced DNA contained the variants (or mutations) and found that many of these DNA differences were present at high amounts in sequencing reads. This suggests that the DNA changes happened very early after twinning in about one-third of pairs. Additionally, if one twin had a near-constitutional change, in 42% of pairs the other twin had a different near-constitutional change. Among the triplets, 2 of a triplet pair shared more genetic similarity and were likely descendent from a single split cell and the third likely was formed from a different set of cells.
By examining the offspring of twins, Jonsson and colleagues found that there were 2.6 early embryonic mutations, and this did not differ when blood or buccal DNA was compared. The rate of transmission of a variant to offspring was proportional to the variant allele frequency (proportion of alternate alleles) in the blood or buccal cells. This is an important counseling point when considering patients with mosaic genetic disorders and counseling about the likelihood of inheritance or transmission to future offspring. If the rate of mosaicism was higher in blood or buccal cells, the likelihood of transmission was higher. Additionally, the mutations did not differ by sex, and there was no relationship to whether the chromosome was maternally or paternally inherited.
Continue to: Study strengths and limitations...
Study strengths and limitations
The authors did not have access to information about chorionicity of the monozygotic twin pairs. Consequently, they were unable to correlate chorionicity with the degree of noted genetic difference between the monozygotic twin pairs. Additionally, although the authors were thoughtful in their utilization of offspring and spouses to infer germline genomic content, the study had a limited number of tissues sampled, which could reduce the applicability. However, the sample size, clinically accessible tissue sampling, and thoughtful analysis used in this study make it an interesting and relevant contribution to reproductive medicine and evolutionary biology.
We all accumulate changes to our DNA throughout life. The study by Jonsson and colleagues illustrates that for many, this accumulation of genetic changes starts very early in gestation. In the early zygote, the authors observed roughly 1 mutation per cell division prior to the point of twinning. In the realm of prenatal diagnosis, one should consider that monochorionic twins with different phenotypes (that is, an ultrasonography anomaly in 1 of the twin pair) could represent a genetic change rather than an environmental difference. This genetic change may not be shared by the other twin despite originating from the same primordial cell line. The genetic changes that the authors investigated were detected on genome sequencing, which is much more comprehensive than the exome sequencing that is increasingly utilized in rare disease diagnosis. The clinical utility of this observation in prenatal diagnosis has yet to be proven, but this study provides preliminary data that 15% of monozygotic twins have genetic differences and may warrant individualized testing.
The genetic landscape of the placenta
Coorens TH, Oliver TR, Sanghvi R, et al. Inherent mosaicism and extensive mutation of human placentas. Nature. Published online March 10, 2021. doi:10.1038/ s41586-021-03345-1.
Confined placental mosaicism (CPM) is a phenomenon in which the genetics of the placenta are different from those of the fetus. Historically, this phenomenon has been described in 1% to 2% of pregnancies based on karyotype data obtained from chorionic villus sampling. Some studies have demonstrated adverse pregnancy outcomes in the setting of CPM, thought to be secondary to aneuploid cells in the placenta leading to insufficiency or dysfunction.
Although our sophistication and level of detail in prenatal genetic testing has rapidly expanded to include information about copy number variants and singlenucleotide changes, their contribution to CPM has been understudied. Coorens and colleagues recently published a landmark study that describes a surprisingly high rate of mosaicism for these smaller genetic changes.
A cohort study of placentas
The authors performed whole genome sequencing on placental samples obtained from 37 term pregnancies. Umbilical cord tissue and maternal blood also were collected and served as controls for fetal and maternal genetic profiles, respectively.
In a subgroup of 5 placentas, lasercapture microscopy was used to separate placental cells of different origins, including trophoblastic cells, mesenchymal core cells, and cells originating from the inner cell mass. To investigate variation within different geographic regions of a single placenta, these cell lines were derived multiple times from each quadrant of the 5 placentas.
Placental biopsies revealed “bottlenecks” of genetic differentiation
Genome sequencing was used uniquely in this study to help delineate the phylogeny of placental cells by tracking somatic mutations both in different geographic locations of each placenta and between different cells of origin within 1 placenta.
The authors concluded that bottlenecks of differentiation in placental development led to unique genetic signatures in every bulk placental sample studied. Their findings led them to describe the placenta as a “patchwork” of independent genetic units resulting from clonal expansion at different stages of embryonic development.
Early insights into human placental cells
This study provides fascinating insight into the surprisingly high rates of copy number variants and single-gene changes that exist, in mosaic form, within human placentas. The authors distinguish the placenta from other human organs (such as the colon, endometrium, liver, and skin) in which many fewer genetic changes exist. In fact, they suggest parallels between the “mutational signature” of the placenta with rapidly dividing neoplastic cells.
As one of the first investigations into the variation and complexity of genetic changes within the placenta, this study was not designed to draw conclusions regarding the clinical impact of the numerous genetic changes described. Further studies will elucidate the potential contribution of genetically mosaic placentas to common adverse obstetric outcomes. ●
With a new appreciation for the smaller genetic alterations that exist within placental tissue, it appears that the rate of CPM has been vastly underestimated. We know that aneuploid placental cells increase the risk of adverse pregnancy outcomes and we may learn more about the contribution of copy number variants and single-nucleotide changes to preeclampsia, growth restriction, and pregnancy loss. Furthermore, as the applications of cell-free fetal DNA (cffDNA) in genetic screening continue to expand, we must exercise caution in assuming that copy number variants or single-nucleotide changes detected by cffDNA reflect those of the developing fetus.
- Roberts AE, Allanson JE, Tartaglia M, et al. Noonan syndrome. Lancet. 2013;381:333-342. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61023-X.
- Roberts AE, Allanson JE, Tartaglia M, et al. Noonan syndrome. Lancet. 2013;381:333-342. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61023-X.