User login
Tool May Help Prioritize High-Risk Patients for Hysteroscopy
Hysteroscopy is a crucial examination for the diagnosis of endometrial cancer. In Brazil, women with postmenopausal bleeding who need to undergo this procedure in the public health system wait in line alongside patients with less severe complaints. Until now, there has been no system to prioritize patients at high risk for cancer. But this situation may change, thanks to a Brazilian study published in February in the Journal of Clinical Medicine.
Researchers from the Municipal Hospital of Vila Santa Catarina in São Paulo, a public unit managed by Hospital Israelita Albert Einstein, have developed the Endometrial Malignancy Prediction System (EMPS), a nomogram to identify patients at high risk for endometrial cancer and prioritize them in the hysteroscopy waiting list.
Bruna Bottura, MD, a gynecologist and obstetrician at Hospital Israelita Albert Einstein and the study’s lead author, told this news organization that the idea to create the nomogram arose during the COVID-19 pandemic. “We noticed that ... when outpatient clinics resumed, we were seeing many patients for intrauterine device (IUD) removal. We thought it was unfair for a patient with postmenopausal bleeding, who has a chance of having cancer, to have to wait in the same line as a patient needing IUD removal,” she said. This realization motivated the development of the tool, which was overseen by Renato Moretti-Marques, MD, PhD.
The EMPS Score
The team conducted a retrospective case-control study involving 1945 patients with suspected endometrial cancer who had undergone diagnostic hysteroscopy at Hospital Israelita Albert Einstein between March 2019 and March 2022. Among these patients, 107 were diagnosed with precursor lesions or endometrial cancer on the basis of biopsy. The other 1838 participants, who had had cancer ruled out by biopsy, formed the control group.
Through bivariate and multivariate linear regression analysis, the authors determined that the presence or absence of hypertension, diabetes, postmenopausal bleeding, endometrial polyps, uterine volume, number of pregnancies, body mass index, age, and endometrial thickness were the main risk factors for endometrial cancer diagnosis.
On the basis of these data, the group developed the EMPS nomogram. Physicians can use it to classify the patient’s risk according to the sum of the scores assigned to each of these factors.
The Table shows the classification system. The scoring tables available in the supplemental materials of the article can be accessed here.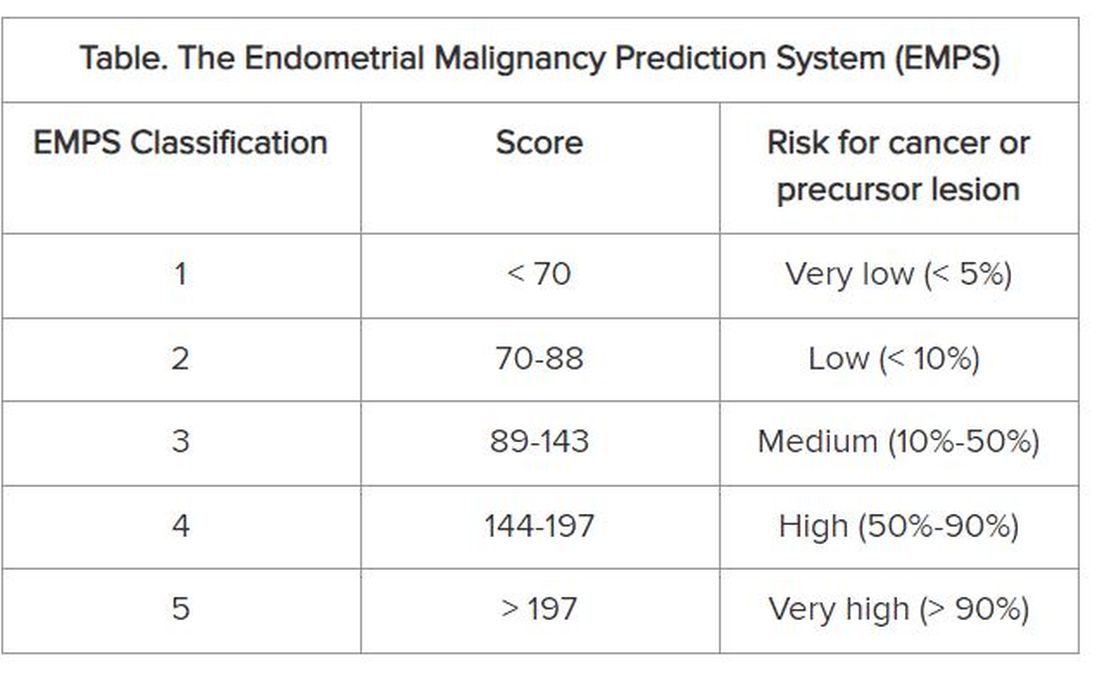
Focus on Primary Care
The goal is not to remove patients classified as low risk from the hysteroscopy waiting list, but rather to prioritize those classified as high risk to get the examination, according to Dr. Bottura.
At the Municipal Hospital of Vila Santa Catarina, the average wait time for hysteroscopy was 120 days. But because the unit is focused on oncologic patients and has a high level of organization, this time is much shorter than observed in other parts of Brazil’s National Health Service, said Dr. Bottura. “Many patients are on the hysteroscopy waiting list for 2 years. Considering patients in more advanced stages [of endometrial cancer], it makes a difference,” she said.
Although the nomogram was developed in tertiary care, it is aimed at professionals working in primary care. The reason is that physicians from primary care health units refer women with clinical indications for hysteroscopy to specialized national health services, such as the Municipal Hospital of Vila Santa Catarina. “Our goal is the primary sector, to enable the clinic to refer this high-risk patient sooner. By the time you reach the tertiary sector, where hysteroscopies are performed, all patients will undergo the procedure. Usually, it is not the hospitals that predetermine the line, but rather the health clinics,” she explained.
The researchers hope to continue the research, starting with a prospective study. “We intend to apply and evaluate the tool within our own service to observe whether any patient with a high [EMPS] score patient ended up waiting too long to be referred. In fact, this will be a system validation step,” said Dr. Bottura.
In parallel, the team has a proposal to take the tool to health clinics in the same region as the study hospital. “We know this involves changing the protocol at a national level, so it’s more challenging,” said Dr. Bottura. She added that the final goal is to create a calculator, possibly an app, that allows primary care doctors to calculate the risk score in the office. This calculator could enable risk classification to be linked to patient referrals.
This story was translated from the Medscape Portuguese edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Hysteroscopy is a crucial examination for the diagnosis of endometrial cancer. In Brazil, women with postmenopausal bleeding who need to undergo this procedure in the public health system wait in line alongside patients with less severe complaints. Until now, there has been no system to prioritize patients at high risk for cancer. But this situation may change, thanks to a Brazilian study published in February in the Journal of Clinical Medicine.
Researchers from the Municipal Hospital of Vila Santa Catarina in São Paulo, a public unit managed by Hospital Israelita Albert Einstein, have developed the Endometrial Malignancy Prediction System (EMPS), a nomogram to identify patients at high risk for endometrial cancer and prioritize them in the hysteroscopy waiting list.
Bruna Bottura, MD, a gynecologist and obstetrician at Hospital Israelita Albert Einstein and the study’s lead author, told this news organization that the idea to create the nomogram arose during the COVID-19 pandemic. “We noticed that ... when outpatient clinics resumed, we were seeing many patients for intrauterine device (IUD) removal. We thought it was unfair for a patient with postmenopausal bleeding, who has a chance of having cancer, to have to wait in the same line as a patient needing IUD removal,” she said. This realization motivated the development of the tool, which was overseen by Renato Moretti-Marques, MD, PhD.
The EMPS Score
The team conducted a retrospective case-control study involving 1945 patients with suspected endometrial cancer who had undergone diagnostic hysteroscopy at Hospital Israelita Albert Einstein between March 2019 and March 2022. Among these patients, 107 were diagnosed with precursor lesions or endometrial cancer on the basis of biopsy. The other 1838 participants, who had had cancer ruled out by biopsy, formed the control group.
Through bivariate and multivariate linear regression analysis, the authors determined that the presence or absence of hypertension, diabetes, postmenopausal bleeding, endometrial polyps, uterine volume, number of pregnancies, body mass index, age, and endometrial thickness were the main risk factors for endometrial cancer diagnosis.
On the basis of these data, the group developed the EMPS nomogram. Physicians can use it to classify the patient’s risk according to the sum of the scores assigned to each of these factors.
The Table shows the classification system. The scoring tables available in the supplemental materials of the article can be accessed here.
Focus on Primary Care
The goal is not to remove patients classified as low risk from the hysteroscopy waiting list, but rather to prioritize those classified as high risk to get the examination, according to Dr. Bottura.
At the Municipal Hospital of Vila Santa Catarina, the average wait time for hysteroscopy was 120 days. But because the unit is focused on oncologic patients and has a high level of organization, this time is much shorter than observed in other parts of Brazil’s National Health Service, said Dr. Bottura. “Many patients are on the hysteroscopy waiting list for 2 years. Considering patients in more advanced stages [of endometrial cancer], it makes a difference,” she said.
Although the nomogram was developed in tertiary care, it is aimed at professionals working in primary care. The reason is that physicians from primary care health units refer women with clinical indications for hysteroscopy to specialized national health services, such as the Municipal Hospital of Vila Santa Catarina. “Our goal is the primary sector, to enable the clinic to refer this high-risk patient sooner. By the time you reach the tertiary sector, where hysteroscopies are performed, all patients will undergo the procedure. Usually, it is not the hospitals that predetermine the line, but rather the health clinics,” she explained.
The researchers hope to continue the research, starting with a prospective study. “We intend to apply and evaluate the tool within our own service to observe whether any patient with a high [EMPS] score patient ended up waiting too long to be referred. In fact, this will be a system validation step,” said Dr. Bottura.
In parallel, the team has a proposal to take the tool to health clinics in the same region as the study hospital. “We know this involves changing the protocol at a national level, so it’s more challenging,” said Dr. Bottura. She added that the final goal is to create a calculator, possibly an app, that allows primary care doctors to calculate the risk score in the office. This calculator could enable risk classification to be linked to patient referrals.
This story was translated from the Medscape Portuguese edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Hysteroscopy is a crucial examination for the diagnosis of endometrial cancer. In Brazil, women with postmenopausal bleeding who need to undergo this procedure in the public health system wait in line alongside patients with less severe complaints. Until now, there has been no system to prioritize patients at high risk for cancer. But this situation may change, thanks to a Brazilian study published in February in the Journal of Clinical Medicine.
Researchers from the Municipal Hospital of Vila Santa Catarina in São Paulo, a public unit managed by Hospital Israelita Albert Einstein, have developed the Endometrial Malignancy Prediction System (EMPS), a nomogram to identify patients at high risk for endometrial cancer and prioritize them in the hysteroscopy waiting list.
Bruna Bottura, MD, a gynecologist and obstetrician at Hospital Israelita Albert Einstein and the study’s lead author, told this news organization that the idea to create the nomogram arose during the COVID-19 pandemic. “We noticed that ... when outpatient clinics resumed, we were seeing many patients for intrauterine device (IUD) removal. We thought it was unfair for a patient with postmenopausal bleeding, who has a chance of having cancer, to have to wait in the same line as a patient needing IUD removal,” she said. This realization motivated the development of the tool, which was overseen by Renato Moretti-Marques, MD, PhD.
The EMPS Score
The team conducted a retrospective case-control study involving 1945 patients with suspected endometrial cancer who had undergone diagnostic hysteroscopy at Hospital Israelita Albert Einstein between March 2019 and March 2022. Among these patients, 107 were diagnosed with precursor lesions or endometrial cancer on the basis of biopsy. The other 1838 participants, who had had cancer ruled out by biopsy, formed the control group.
Through bivariate and multivariate linear regression analysis, the authors determined that the presence or absence of hypertension, diabetes, postmenopausal bleeding, endometrial polyps, uterine volume, number of pregnancies, body mass index, age, and endometrial thickness were the main risk factors for endometrial cancer diagnosis.
On the basis of these data, the group developed the EMPS nomogram. Physicians can use it to classify the patient’s risk according to the sum of the scores assigned to each of these factors.
The Table shows the classification system. The scoring tables available in the supplemental materials of the article can be accessed here.
Focus on Primary Care
The goal is not to remove patients classified as low risk from the hysteroscopy waiting list, but rather to prioritize those classified as high risk to get the examination, according to Dr. Bottura.
At the Municipal Hospital of Vila Santa Catarina, the average wait time for hysteroscopy was 120 days. But because the unit is focused on oncologic patients and has a high level of organization, this time is much shorter than observed in other parts of Brazil’s National Health Service, said Dr. Bottura. “Many patients are on the hysteroscopy waiting list for 2 years. Considering patients in more advanced stages [of endometrial cancer], it makes a difference,” she said.
Although the nomogram was developed in tertiary care, it is aimed at professionals working in primary care. The reason is that physicians from primary care health units refer women with clinical indications for hysteroscopy to specialized national health services, such as the Municipal Hospital of Vila Santa Catarina. “Our goal is the primary sector, to enable the clinic to refer this high-risk patient sooner. By the time you reach the tertiary sector, where hysteroscopies are performed, all patients will undergo the procedure. Usually, it is not the hospitals that predetermine the line, but rather the health clinics,” she explained.
The researchers hope to continue the research, starting with a prospective study. “We intend to apply and evaluate the tool within our own service to observe whether any patient with a high [EMPS] score patient ended up waiting too long to be referred. In fact, this will be a system validation step,” said Dr. Bottura.
In parallel, the team has a proposal to take the tool to health clinics in the same region as the study hospital. “We know this involves changing the protocol at a national level, so it’s more challenging,” said Dr. Bottura. She added that the final goal is to create a calculator, possibly an app, that allows primary care doctors to calculate the risk score in the office. This calculator could enable risk classification to be linked to patient referrals.
This story was translated from the Medscape Portuguese edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
How Long Should a Woman Wait Before Becoming Pregnant Again?
How long should a woman wait before becoming pregnant again? According to the World Health Organization (WHO), it is advisable to wait at least 24 months between childbirth and a new pregnancy. But a study published in February of this year in The Lancet Regional Health — Americas, using data from more than 4.7 million live births in Brazil, suggests that this recommendation should be individualized, considering factors such as maternal obstetric history.
Researchers from the Federal University of Grande Dourados (UFGD), Oswaldo Cruz Foundation, São José do Rio Preto Medical School, Federal University of Bahia, and the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine in the United Kingdom, used a birth cohort from the Center for Data Integration and Knowledge for Health, which combines data from the Ministry of Health’s Information System on Live Births (SINASC) and from a cohort of 100 million Brazilians.
In total, the analysis included information on 3,804,152 women and 4,788,279 births. All participants had at least two consecutive live births.
Most interpregnancy intervals, ie, the difference between the previous childbirth and the subsequent conception, ranged from 23 to 58 months (39.1%). Extreme intervals of < 6 months and > 120 months occurred in 5.6% and 1.6% of cases, respectively.
Regarding adverse outcomes, the research indicated that, in the general population, small-for-gestational-age (SGA) babies were observed in 8.4% of subsequent births, while low birth weight (LBW) occurred in 5.9% and preterm birth in 7.5%.
Interpregnancy Interval and SGA Risk
The authors noted that the risk for subsequent adverse outcomes increased with extreme interpregnancy intervals, with SGA being the only exception. In this case, women who had an interval between the previous childbirth and the subsequent conception > 120 months had a lower risk for SGA.
According to João Guilherme Tedde, a medical student at UFGD and the first author of the study, similar patterns (extremely long interpregnancy intervals associated with a lower risk for subsequent SGA) have been described in the literature. In an interview with this news organization, he explained some hypotheses that could explain this phenomenon.
According to the researcher, the finding may reflect the distinct risk profile of mothers who wait a very long time to conceive again. “This group, composed of older women, likely has a higher prevalence of health problems, such as diabetes and obesity, which are known risk factors for having large-for-gestational-age (LGA) babies,” he said. He also highlighted the fact that the study showed that the risk for LGA also increased as the interval between pregnancies grew.
Another hypothesis suggested by the author is the possible occurrence of events between pregnancies, such as miscarriages or stillbirths. According to him, women who have experienced these events between two consecutive pregnancies may have falsely increased interpregnancy intervals, since miscarriages and stillbirths (which are considered conceptions) are not counted in SINASC.
“Thus, the lower occurrence of SGA in the group with very long intervals may reflect a competition of events between stillbirths or miscarriages and live SGAs,” he said.
Previous and Subsequent Adverse Events
The research also showed that the risks for subsequent SGA, LBW, and preterm birth were higher among women with a history of adverse events in previous pregnancies.
Furthermore, the authors noted that the previous occurrence of adverse outcomes seems to “have a more significant impact on the outcome of the current pregnancy than the interpregnancy interval.”
“We found that, for women with the same interpregnancy interval (say < 6 months), but with different obstetric history (zero previous events vs one event), the absolute risk for subsequent adverse outcomes increased much more than when we change only the duration of the interval in a group with the same number of previous adverse events,” said Dr. Tedde.
There is still no convincing explanation for this fact, he said, since the cause-and-effect relationship between interpregnancy intervals and perinatal events is not clear. But the obstetrics literature generally shows that among the main risk factors for an adverse event is the previous occurrence of the same event. This effect could be related to living conditions and maternal habits, genetics, epigenetics, among others.
The researcher observed that this study is one of the largest in terms of sampling to investigate how maternal obstetric history can modulate the effect of interpregnancy interval on the risk for adverse outcomes in subsequent pregnancies.
The findings of the research published this year reinforce the importance of individualizing recommendations regarding interpregnancy intervals, considering factors such as maternal obstetric history. However, the author warns that it is still too early to point out the “best” interval for each situation.
“We need more studies that reproduce our findings and that expand the analyzed outcomes to also include those of interest to the mother, such as maternal mortality,” he concluded.
This story was translated from the Medscape Portuguese edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
How long should a woman wait before becoming pregnant again? According to the World Health Organization (WHO), it is advisable to wait at least 24 months between childbirth and a new pregnancy. But a study published in February of this year in The Lancet Regional Health — Americas, using data from more than 4.7 million live births in Brazil, suggests that this recommendation should be individualized, considering factors such as maternal obstetric history.
Researchers from the Federal University of Grande Dourados (UFGD), Oswaldo Cruz Foundation, São José do Rio Preto Medical School, Federal University of Bahia, and the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine in the United Kingdom, used a birth cohort from the Center for Data Integration and Knowledge for Health, which combines data from the Ministry of Health’s Information System on Live Births (SINASC) and from a cohort of 100 million Brazilians.
In total, the analysis included information on 3,804,152 women and 4,788,279 births. All participants had at least two consecutive live births.
Most interpregnancy intervals, ie, the difference between the previous childbirth and the subsequent conception, ranged from 23 to 58 months (39.1%). Extreme intervals of < 6 months and > 120 months occurred in 5.6% and 1.6% of cases, respectively.
Regarding adverse outcomes, the research indicated that, in the general population, small-for-gestational-age (SGA) babies were observed in 8.4% of subsequent births, while low birth weight (LBW) occurred in 5.9% and preterm birth in 7.5%.
Interpregnancy Interval and SGA Risk
The authors noted that the risk for subsequent adverse outcomes increased with extreme interpregnancy intervals, with SGA being the only exception. In this case, women who had an interval between the previous childbirth and the subsequent conception > 120 months had a lower risk for SGA.
According to João Guilherme Tedde, a medical student at UFGD and the first author of the study, similar patterns (extremely long interpregnancy intervals associated with a lower risk for subsequent SGA) have been described in the literature. In an interview with this news organization, he explained some hypotheses that could explain this phenomenon.
According to the researcher, the finding may reflect the distinct risk profile of mothers who wait a very long time to conceive again. “This group, composed of older women, likely has a higher prevalence of health problems, such as diabetes and obesity, which are known risk factors for having large-for-gestational-age (LGA) babies,” he said. He also highlighted the fact that the study showed that the risk for LGA also increased as the interval between pregnancies grew.
Another hypothesis suggested by the author is the possible occurrence of events between pregnancies, such as miscarriages or stillbirths. According to him, women who have experienced these events between two consecutive pregnancies may have falsely increased interpregnancy intervals, since miscarriages and stillbirths (which are considered conceptions) are not counted in SINASC.
“Thus, the lower occurrence of SGA in the group with very long intervals may reflect a competition of events between stillbirths or miscarriages and live SGAs,” he said.
Previous and Subsequent Adverse Events
The research also showed that the risks for subsequent SGA, LBW, and preterm birth were higher among women with a history of adverse events in previous pregnancies.
Furthermore, the authors noted that the previous occurrence of adverse outcomes seems to “have a more significant impact on the outcome of the current pregnancy than the interpregnancy interval.”
“We found that, for women with the same interpregnancy interval (say < 6 months), but with different obstetric history (zero previous events vs one event), the absolute risk for subsequent adverse outcomes increased much more than when we change only the duration of the interval in a group with the same number of previous adverse events,” said Dr. Tedde.
There is still no convincing explanation for this fact, he said, since the cause-and-effect relationship between interpregnancy intervals and perinatal events is not clear. But the obstetrics literature generally shows that among the main risk factors for an adverse event is the previous occurrence of the same event. This effect could be related to living conditions and maternal habits, genetics, epigenetics, among others.
The researcher observed that this study is one of the largest in terms of sampling to investigate how maternal obstetric history can modulate the effect of interpregnancy interval on the risk for adverse outcomes in subsequent pregnancies.
The findings of the research published this year reinforce the importance of individualizing recommendations regarding interpregnancy intervals, considering factors such as maternal obstetric history. However, the author warns that it is still too early to point out the “best” interval for each situation.
“We need more studies that reproduce our findings and that expand the analyzed outcomes to also include those of interest to the mother, such as maternal mortality,” he concluded.
This story was translated from the Medscape Portuguese edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
How long should a woman wait before becoming pregnant again? According to the World Health Organization (WHO), it is advisable to wait at least 24 months between childbirth and a new pregnancy. But a study published in February of this year in The Lancet Regional Health — Americas, using data from more than 4.7 million live births in Brazil, suggests that this recommendation should be individualized, considering factors such as maternal obstetric history.
Researchers from the Federal University of Grande Dourados (UFGD), Oswaldo Cruz Foundation, São José do Rio Preto Medical School, Federal University of Bahia, and the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine in the United Kingdom, used a birth cohort from the Center for Data Integration and Knowledge for Health, which combines data from the Ministry of Health’s Information System on Live Births (SINASC) and from a cohort of 100 million Brazilians.
In total, the analysis included information on 3,804,152 women and 4,788,279 births. All participants had at least two consecutive live births.
Most interpregnancy intervals, ie, the difference between the previous childbirth and the subsequent conception, ranged from 23 to 58 months (39.1%). Extreme intervals of < 6 months and > 120 months occurred in 5.6% and 1.6% of cases, respectively.
Regarding adverse outcomes, the research indicated that, in the general population, small-for-gestational-age (SGA) babies were observed in 8.4% of subsequent births, while low birth weight (LBW) occurred in 5.9% and preterm birth in 7.5%.
Interpregnancy Interval and SGA Risk
The authors noted that the risk for subsequent adverse outcomes increased with extreme interpregnancy intervals, with SGA being the only exception. In this case, women who had an interval between the previous childbirth and the subsequent conception > 120 months had a lower risk for SGA.
According to João Guilherme Tedde, a medical student at UFGD and the first author of the study, similar patterns (extremely long interpregnancy intervals associated with a lower risk for subsequent SGA) have been described in the literature. In an interview with this news organization, he explained some hypotheses that could explain this phenomenon.
According to the researcher, the finding may reflect the distinct risk profile of mothers who wait a very long time to conceive again. “This group, composed of older women, likely has a higher prevalence of health problems, such as diabetes and obesity, which are known risk factors for having large-for-gestational-age (LGA) babies,” he said. He also highlighted the fact that the study showed that the risk for LGA also increased as the interval between pregnancies grew.
Another hypothesis suggested by the author is the possible occurrence of events between pregnancies, such as miscarriages or stillbirths. According to him, women who have experienced these events between two consecutive pregnancies may have falsely increased interpregnancy intervals, since miscarriages and stillbirths (which are considered conceptions) are not counted in SINASC.
“Thus, the lower occurrence of SGA in the group with very long intervals may reflect a competition of events between stillbirths or miscarriages and live SGAs,” he said.
Previous and Subsequent Adverse Events
The research also showed that the risks for subsequent SGA, LBW, and preterm birth were higher among women with a history of adverse events in previous pregnancies.
Furthermore, the authors noted that the previous occurrence of adverse outcomes seems to “have a more significant impact on the outcome of the current pregnancy than the interpregnancy interval.”
“We found that, for women with the same interpregnancy interval (say < 6 months), but with different obstetric history (zero previous events vs one event), the absolute risk for subsequent adverse outcomes increased much more than when we change only the duration of the interval in a group with the same number of previous adverse events,” said Dr. Tedde.
There is still no convincing explanation for this fact, he said, since the cause-and-effect relationship between interpregnancy intervals and perinatal events is not clear. But the obstetrics literature generally shows that among the main risk factors for an adverse event is the previous occurrence of the same event. This effect could be related to living conditions and maternal habits, genetics, epigenetics, among others.
The researcher observed that this study is one of the largest in terms of sampling to investigate how maternal obstetric history can modulate the effect of interpregnancy interval on the risk for adverse outcomes in subsequent pregnancies.
The findings of the research published this year reinforce the importance of individualizing recommendations regarding interpregnancy intervals, considering factors such as maternal obstetric history. However, the author warns that it is still too early to point out the “best” interval for each situation.
“We need more studies that reproduce our findings and that expand the analyzed outcomes to also include those of interest to the mother, such as maternal mortality,” he concluded.
This story was translated from the Medscape Portuguese edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.