User login
, although women are more often affected than men. GA most commonly appears in the first 3 decades of life. Although the etiology is not known, GA may represent a delayed hypersensitivity reaction. A link between GA and diabetes mellitus, autoimmune thyroiditis, dyslipidemia, and rarely, malignancy may exist.
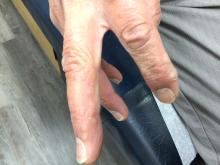
GA is most commonly localized, presenting as an asymptomatic, erythematous, annular plaque with a firm border and central clearing localized to the wrists, ankles, and dorsal hands or feet. This form is the type most often seen in children. Generalized GA is far less common and presents later in life as multiple asymptomatic or pruritic papules and plaques on the trunk and extremities. Less common variants include subcutaneous GA, patch GA, atypical GA, and perforating GA. Perforating GA occurs on the dorsal hands and presents as (umbilicated) papules, and seems consistent with this patient’s clinical presentation. Histologically, transepidermal elimination of collagen is typically seen in perforating GA.1
Histology in this patient’s biopsy revealed a granulomatous dermatitis consistent with granuloma annulare. A palisaded arrangement of histiocytic cells surrounding altered collagen with increased dermal mucin was seen. There was associated perivascular mononuclear inflammatory infiltrates. The overlying epidermis was unremarkable.
Granuloma annulare often spontaneously resolves without sequelae. In some cases, atrophy may result. Lesions may also recur. Localized GA is often treated with high-potency topical corticosteroids or intralesional corticosteroids. For generalized GA, topical or intralesional corticosteroids may be used for select lesions. Topical calcineurin inhibitors, light therapy, cryotherapy, imiquimod, hydroxychloroquine, isotretinoin, and dapsone have also been reported in the literature as possible treatments.
This case and photo were provided by Dr. Berke, of Three Rivers Dermatology, Pittsburgh, and Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1 Alves J, Barreiros H, Bartolo E. Healthcare (Basel). 2014 Sep 4;2(3):338-45.
2. Bolognia J et al. Dermatology (St. Louis: Mosby/Elsevier, 2008).
3. “Andrews’ Diseases of the Skin,” 13th ed. James W et al. Philadelphia: Saunders Elsevier, 2006.
, although women are more often affected than men. GA most commonly appears in the first 3 decades of life. Although the etiology is not known, GA may represent a delayed hypersensitivity reaction. A link between GA and diabetes mellitus, autoimmune thyroiditis, dyslipidemia, and rarely, malignancy may exist.
GA is most commonly localized, presenting as an asymptomatic, erythematous, annular plaque with a firm border and central clearing localized to the wrists, ankles, and dorsal hands or feet. This form is the type most often seen in children. Generalized GA is far less common and presents later in life as multiple asymptomatic or pruritic papules and plaques on the trunk and extremities. Less common variants include subcutaneous GA, patch GA, atypical GA, and perforating GA. Perforating GA occurs on the dorsal hands and presents as (umbilicated) papules, and seems consistent with this patient’s clinical presentation. Histologically, transepidermal elimination of collagen is typically seen in perforating GA.1
Histology in this patient’s biopsy revealed a granulomatous dermatitis consistent with granuloma annulare. A palisaded arrangement of histiocytic cells surrounding altered collagen with increased dermal mucin was seen. There was associated perivascular mononuclear inflammatory infiltrates. The overlying epidermis was unremarkable.
Granuloma annulare often spontaneously resolves without sequelae. In some cases, atrophy may result. Lesions may also recur. Localized GA is often treated with high-potency topical corticosteroids or intralesional corticosteroids. For generalized GA, topical or intralesional corticosteroids may be used for select lesions. Topical calcineurin inhibitors, light therapy, cryotherapy, imiquimod, hydroxychloroquine, isotretinoin, and dapsone have also been reported in the literature as possible treatments.
This case and photo were provided by Dr. Berke, of Three Rivers Dermatology, Pittsburgh, and Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1 Alves J, Barreiros H, Bartolo E. Healthcare (Basel). 2014 Sep 4;2(3):338-45.
2. Bolognia J et al. Dermatology (St. Louis: Mosby/Elsevier, 2008).
3. “Andrews’ Diseases of the Skin,” 13th ed. James W et al. Philadelphia: Saunders Elsevier, 2006.
, although women are more often affected than men. GA most commonly appears in the first 3 decades of life. Although the etiology is not known, GA may represent a delayed hypersensitivity reaction. A link between GA and diabetes mellitus, autoimmune thyroiditis, dyslipidemia, and rarely, malignancy may exist.
GA is most commonly localized, presenting as an asymptomatic, erythematous, annular plaque with a firm border and central clearing localized to the wrists, ankles, and dorsal hands or feet. This form is the type most often seen in children. Generalized GA is far less common and presents later in life as multiple asymptomatic or pruritic papules and plaques on the trunk and extremities. Less common variants include subcutaneous GA, patch GA, atypical GA, and perforating GA. Perforating GA occurs on the dorsal hands and presents as (umbilicated) papules, and seems consistent with this patient’s clinical presentation. Histologically, transepidermal elimination of collagen is typically seen in perforating GA.1
Histology in this patient’s biopsy revealed a granulomatous dermatitis consistent with granuloma annulare. A palisaded arrangement of histiocytic cells surrounding altered collagen with increased dermal mucin was seen. There was associated perivascular mononuclear inflammatory infiltrates. The overlying epidermis was unremarkable.
Granuloma annulare often spontaneously resolves without sequelae. In some cases, atrophy may result. Lesions may also recur. Localized GA is often treated with high-potency topical corticosteroids or intralesional corticosteroids. For generalized GA, topical or intralesional corticosteroids may be used for select lesions. Topical calcineurin inhibitors, light therapy, cryotherapy, imiquimod, hydroxychloroquine, isotretinoin, and dapsone have also been reported in the literature as possible treatments.
This case and photo were provided by Dr. Berke, of Three Rivers Dermatology, Pittsburgh, and Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1 Alves J, Barreiros H, Bartolo E. Healthcare (Basel). 2014 Sep 4;2(3):338-45.
2. Bolognia J et al. Dermatology (St. Louis: Mosby/Elsevier, 2008).
3. “Andrews’ Diseases of the Skin,” 13th ed. James W et al. Philadelphia: Saunders Elsevier, 2006.