User login
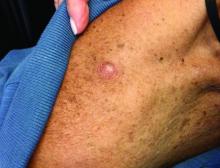
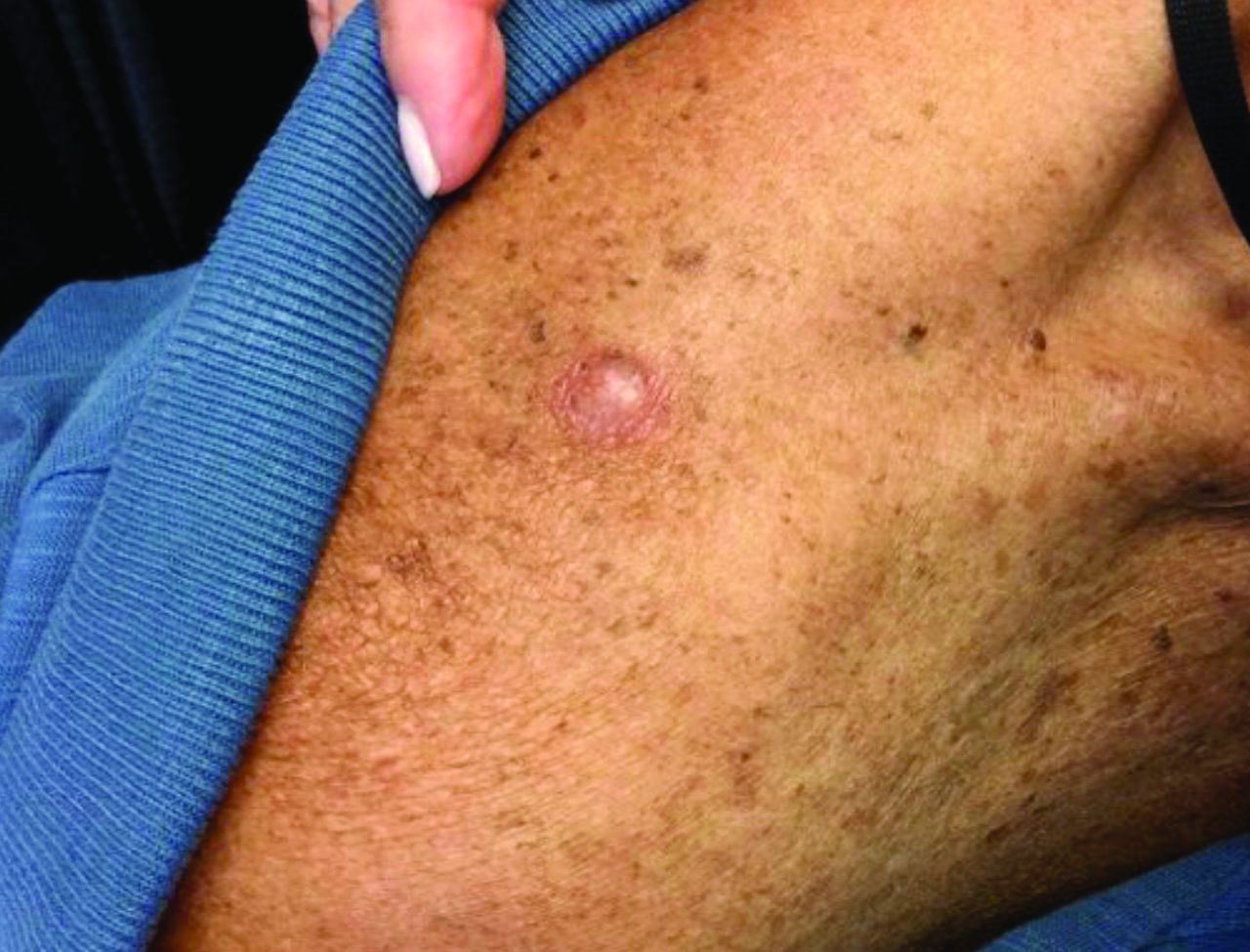
Melanoma is a type of skin cancer that arises from melanocytes. According to the American Cancer Society, about 106,110 new melanomas will be diagnosed in the United States in 2021.The risk for developing melanoma increases with age. There are multiple clinical forms of cutaneous melanoma. The four main types are superficial spreading melanoma, nodular melanoma, melanoma in situ (lentigo maligna), and acral lentiginous melanoma. Rare variants include amelanotic melanoma, nevoid melanoma, spitzoid melanoma, and desmoplastic melanoma (DM). Melanoma can also rarely affect parts of the eye and mucosa.
, according to the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center. It typically presents as a subtle pigmented, pink, red, or skin colored patch, papule or plaque on sun-exposed skin (head and neck most frequently). Chronic UV exposure has been linked to DM. It may be mistaken for a scar or dermatofibroma. DM tends to grow locally and has less risk for nodal metastasis.1
Histologic diagnosis may be challenging. Two histologic variants in desmoplastic melanoma have been described: pure and mixed, depending on the degree of desmoplasia and cellularity present in the tumor.1 Pure DM tends to have a less aggressive course. Melanocytes can appear spindled in a fibrotic stroma. Patchy lymphocyte aggregates may be seen. Perineural invasion is more common in desmoplastic melanoma. Histologically, the differential includes spindle cell carcinoma and sarcoma. Immunostaining is helpful in differentiation.
Our patient had no lymphadenopathy on physical examination. Biopsy revealed a desmoplastic melanoma, 3.6 mm in depth, no ulceration, no regression, mitotic rate 1/mm2. He was referred to surgical oncology. The patient underwent wide excision. Sentinel lymph node biopsy was deferred.
It is imperative for dermatologists to be cognizant of this challenging subtype of melanoma when evaluating patients.
This case and photo were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. Chen L et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013 May;68(5):825-33.
Melanoma is a type of skin cancer that arises from melanocytes. According to the American Cancer Society, about 106,110 new melanomas will be diagnosed in the United States in 2021.The risk for developing melanoma increases with age. There are multiple clinical forms of cutaneous melanoma. The four main types are superficial spreading melanoma, nodular melanoma, melanoma in situ (lentigo maligna), and acral lentiginous melanoma. Rare variants include amelanotic melanoma, nevoid melanoma, spitzoid melanoma, and desmoplastic melanoma (DM). Melanoma can also rarely affect parts of the eye and mucosa.
, according to the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center. It typically presents as a subtle pigmented, pink, red, or skin colored patch, papule or plaque on sun-exposed skin (head and neck most frequently). Chronic UV exposure has been linked to DM. It may be mistaken for a scar or dermatofibroma. DM tends to grow locally and has less risk for nodal metastasis.1
Histologic diagnosis may be challenging. Two histologic variants in desmoplastic melanoma have been described: pure and mixed, depending on the degree of desmoplasia and cellularity present in the tumor.1 Pure DM tends to have a less aggressive course. Melanocytes can appear spindled in a fibrotic stroma. Patchy lymphocyte aggregates may be seen. Perineural invasion is more common in desmoplastic melanoma. Histologically, the differential includes spindle cell carcinoma and sarcoma. Immunostaining is helpful in differentiation.
Our patient had no lymphadenopathy on physical examination. Biopsy revealed a desmoplastic melanoma, 3.6 mm in depth, no ulceration, no regression, mitotic rate 1/mm2. He was referred to surgical oncology. The patient underwent wide excision. Sentinel lymph node biopsy was deferred.
It is imperative for dermatologists to be cognizant of this challenging subtype of melanoma when evaluating patients.
This case and photo were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. Chen L et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013 May;68(5):825-33.
Melanoma is a type of skin cancer that arises from melanocytes. According to the American Cancer Society, about 106,110 new melanomas will be diagnosed in the United States in 2021.The risk for developing melanoma increases with age. There are multiple clinical forms of cutaneous melanoma. The four main types are superficial spreading melanoma, nodular melanoma, melanoma in situ (lentigo maligna), and acral lentiginous melanoma. Rare variants include amelanotic melanoma, nevoid melanoma, spitzoid melanoma, and desmoplastic melanoma (DM). Melanoma can also rarely affect parts of the eye and mucosa.
, according to the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center. It typically presents as a subtle pigmented, pink, red, or skin colored patch, papule or plaque on sun-exposed skin (head and neck most frequently). Chronic UV exposure has been linked to DM. It may be mistaken for a scar or dermatofibroma. DM tends to grow locally and has less risk for nodal metastasis.1
Histologic diagnosis may be challenging. Two histologic variants in desmoplastic melanoma have been described: pure and mixed, depending on the degree of desmoplasia and cellularity present in the tumor.1 Pure DM tends to have a less aggressive course. Melanocytes can appear spindled in a fibrotic stroma. Patchy lymphocyte aggregates may be seen. Perineural invasion is more common in desmoplastic melanoma. Histologically, the differential includes spindle cell carcinoma and sarcoma. Immunostaining is helpful in differentiation.
Our patient had no lymphadenopathy on physical examination. Biopsy revealed a desmoplastic melanoma, 3.6 mm in depth, no ulceration, no regression, mitotic rate 1/mm2. He was referred to surgical oncology. The patient underwent wide excision. Sentinel lymph node biopsy was deferred.
It is imperative for dermatologists to be cognizant of this challenging subtype of melanoma when evaluating patients.
This case and photo were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. Chen L et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013 May;68(5):825-33.