User login
Practice Gap
OnabotulinumtoxinA is a US Food and Drug Administration–approved second-line treatment of axillary hyperhidrosis, with a long-term success rate greater than 80% and minimal adverse effects.1 The recommended depth and angle of injection of onabotulinumtoxinA for most cases of primary hyperhidrosis is 2 to 3 mm at a 45° angle to the skin surface.2 This small depth is difficult to accurately estimate once the needle tip is in the skin.
Injection Technique
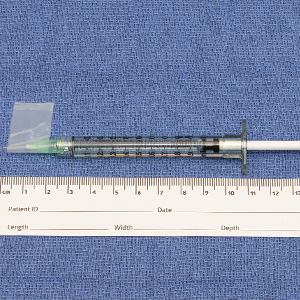
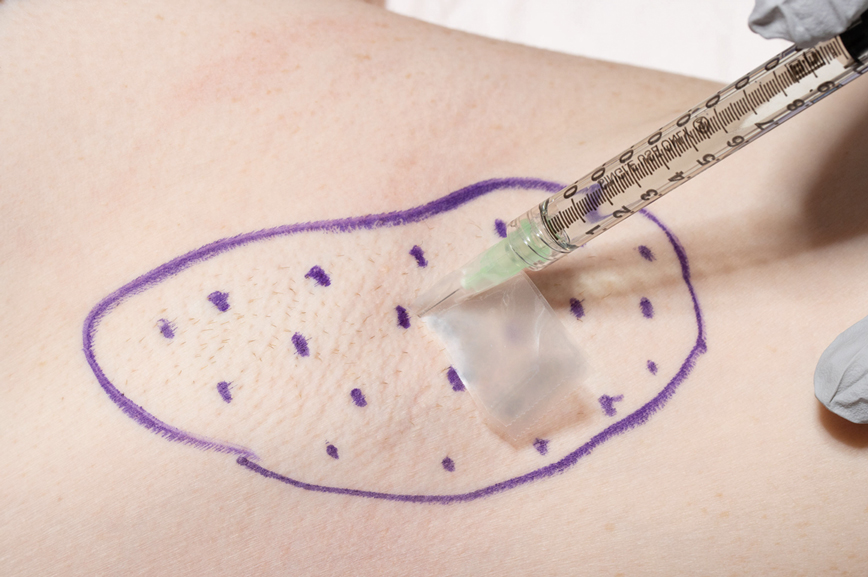
We have found that measuring 2 to 3 mm on the needle tip and then wrapping a piece of adhesive tape at that point acts as a depth guide (Figure 1). The flag shape of the tape acts as a physical barrier to prevent the needle tip from penetrating too deeply (Figure 2). This barrier also allows the injector to inject quickly to reduce the amount of pain that the patient experiences.

Practice Implications
Applying adhesive tape to a needle tip at a premeasured distance is a fast, inexpensive, and effective tool to aid accurate depth of injection for both experienced clinicians and clinicians in-training. The tape is a common office supply and the amount of tape used for a patient costs a fraction of a cent. Additionally, applying the tape takes less than 1 minute. This technique is useful for axillary hyperhidrosis injection (Figures 1 and 2) but could be used in palmar and plantar hyperhidrosis injections as well as injections other than onabotulinumtoxinA that require a specific fixed depth.
- Naumann M, Lowe NJ, Kumar CR, et al; Hyperhidrosis Clinical Investigators Group. Botulinum toxin type A is a safe and effective treatment for axillary hyperhidrosis over 16 months: a prospective study. Arch Dermatol. 2003;139:731-736. doi:10.1001/archderm.139.6.731
- Botox. Prescribing information. Allergan Pharmaceuticals Ireland;2011. Accessed May 12, 2022. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2011/103000s5236lbl.pdf
Practice Gap
OnabotulinumtoxinA is a US Food and Drug Administration–approved second-line treatment of axillary hyperhidrosis, with a long-term success rate greater than 80% and minimal adverse effects.1 The recommended depth and angle of injection of onabotulinumtoxinA for most cases of primary hyperhidrosis is 2 to 3 mm at a 45° angle to the skin surface.2 This small depth is difficult to accurately estimate once the needle tip is in the skin.
Injection Technique
We have found that measuring 2 to 3 mm on the needle tip and then wrapping a piece of adhesive tape at that point acts as a depth guide (Figure 1). The flag shape of the tape acts as a physical barrier to prevent the needle tip from penetrating too deeply (Figure 2). This barrier also allows the injector to inject quickly to reduce the amount of pain that the patient experiences.

Practice Implications
Applying adhesive tape to a needle tip at a premeasured distance is a fast, inexpensive, and effective tool to aid accurate depth of injection for both experienced clinicians and clinicians in-training. The tape is a common office supply and the amount of tape used for a patient costs a fraction of a cent. Additionally, applying the tape takes less than 1 minute. This technique is useful for axillary hyperhidrosis injection (Figures 1 and 2) but could be used in palmar and plantar hyperhidrosis injections as well as injections other than onabotulinumtoxinA that require a specific fixed depth.

Practice Gap
OnabotulinumtoxinA is a US Food and Drug Administration–approved second-line treatment of axillary hyperhidrosis, with a long-term success rate greater than 80% and minimal adverse effects.1 The recommended depth and angle of injection of onabotulinumtoxinA for most cases of primary hyperhidrosis is 2 to 3 mm at a 45° angle to the skin surface.2 This small depth is difficult to accurately estimate once the needle tip is in the skin.
Injection Technique
We have found that measuring 2 to 3 mm on the needle tip and then wrapping a piece of adhesive tape at that point acts as a depth guide (Figure 1). The flag shape of the tape acts as a physical barrier to prevent the needle tip from penetrating too deeply (Figure 2). This barrier also allows the injector to inject quickly to reduce the amount of pain that the patient experiences.

Practice Implications
Applying adhesive tape to a needle tip at a premeasured distance is a fast, inexpensive, and effective tool to aid accurate depth of injection for both experienced clinicians and clinicians in-training. The tape is a common office supply and the amount of tape used for a patient costs a fraction of a cent. Additionally, applying the tape takes less than 1 minute. This technique is useful for axillary hyperhidrosis injection (Figures 1 and 2) but could be used in palmar and plantar hyperhidrosis injections as well as injections other than onabotulinumtoxinA that require a specific fixed depth.

- Naumann M, Lowe NJ, Kumar CR, et al; Hyperhidrosis Clinical Investigators Group. Botulinum toxin type A is a safe and effective treatment for axillary hyperhidrosis over 16 months: a prospective study. Arch Dermatol. 2003;139:731-736. doi:10.1001/archderm.139.6.731
- Botox. Prescribing information. Allergan Pharmaceuticals Ireland;2011. Accessed May 12, 2022. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2011/103000s5236lbl.pdf
- Naumann M, Lowe NJ, Kumar CR, et al; Hyperhidrosis Clinical Investigators Group. Botulinum toxin type A is a safe and effective treatment for axillary hyperhidrosis over 16 months: a prospective study. Arch Dermatol. 2003;139:731-736. doi:10.1001/archderm.139.6.731
- Botox. Prescribing information. Allergan Pharmaceuticals Ireland;2011. Accessed May 12, 2022. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2011/103000s5236lbl.pdf