User login
I began thinking of a topic for this column weeks ago determined to discuss anything except COVID-19. Yet, news reports from all sources blasted daily reminders of rising COVID-19 cases overall and specifically in children.
In August, school resumed for many of our patients and the battle over mandating masks for school attendance was in full swing. The fact that it is a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommendation supported by both the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Pediatric Infectious Disease Society fell on deaf ears. One day, I heard a report that over 25,000 students attending Texas public schools were diagnosed with COVID-19 between Aug. 23 and Aug. 29. This peak in activity occurred just 2 weeks after the start of school and led to the closure of 45 school districts. Texas does not have a monopoly on these rising cases. Delta, a more contagious variant, began circulating in June 2021 and by July it was the most predominant. Emergency department visits and hospitalizations have increased nationwide. During the latter 2 weeks of August 2021, COVID-19–related ED visits and hospitalizations for persons aged 0-17 years were 3.4 and 3.7 times higher in states with the lowest vaccination coverage, compared with states with high vaccination coverage (MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021;70:1249-54). Specifically, the rates of hospitalization the week ending Aug. 14, 2021, were nearly 5 times the rates for the week ending June 26, 2021, for 0- to 17-year-olds and nearly 10 times the rates for children 0-4 years of age. Hospitalization rates were 10.1 times higher for unimmunized adolescents than for fully vaccinated ones (MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021;70:1255-60).
Multiple elected state leaders have opposed interventions such as mandating masks in school, and our children are paying for it. These leaders have relinquished their responsibility to local school boards. Several have reinforced the no-mask mandate while others have had the courage and insight to ignore state government leaders and have established mask mandates.
How is this lack of enforcement of national recommendations affecting our patients? Let’s look at two neighboring school districts in Texas. School districts have COVID-19 dashboards that are updated daily and accessible to the general public. School District A requires masks for school entry. It serves 196,171 students and has 27,195 teachers and staff. Since school opened in August, 1,606 cumulative cases of COVID-19 in students (0.8%) and 282 in staff (1%) have been reported. Fifty-five percent of the student cases occurred in elementary schools. In contrast, School District B located in the adjacent county serves 64,517 students and has 3,906 teachers and staff with no mask mandate. Since August, there have been 4,506 cumulative COVID-19 cases in students (6.9%) and 578 (14.7%) in staff. Information regarding the specific school type was not provided; however, the dashboard indicates that 2,924 cases (64.8%) occurred in children younger than 11 years of age. County data indicate 62% of those older than 12 years of age were fully vaccinated in District A, compared with 54% of persons older than 12 years in District B. The county COVID-19 positivity rate in District A is 17.6% and in District B it is 20%. Both counties are experiencing increased COVID-19 activity yet have had strikingly different outcomes in the student/staff population. While supporting the case for wearing masks to prevent disease transmission, one can’t ignore the adolescents who were infected and vaccine eligible (District A: 706; District B: 1,582). Their vaccination status could not be determined.
As pediatricians we have played an integral part in the elimination of diseases through educating and administering vaccinations. Adolescents are relatively healthy, thus limiting the number of encounters with them. The majority complete the 11-year visit; however, many fail to return for the 16- to 18-year visit.
So how are we doing? CDC data from 10 U.S. jurisdictions demonstrated a substantial decrease in vaccine administration between March and May of 2020, compared with the same period in 2018 and 2019. A decline was anticipated because of the nationwide lockdown. Doses of HPV administered declined almost 64% and 71% for 9- to 12-year-olds and 13- to 17-year-olds, respectively. Tdap administration declined 66% and 61% for the same respective age groups. Although administered doses increased between June and September of 2020, it was not sufficient to achieve catch-up coverage. Compared to the same period in 2018-2019, administration of the HPV vaccine declined 12.8% and 28% (ages 9-12 and ages 13-17) and for Tdap it was 21% and 30% lower (ages 9-12 and ages 13-17) (MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021;70:840-5).
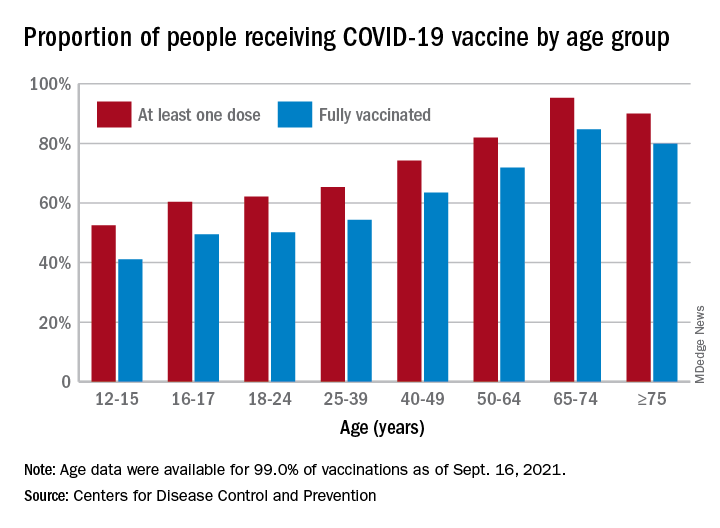
Now, we have another adolescent vaccine to discuss and encourage our patients to receive. We also need to address their concerns and/or to at least direct them to a reliable source to obtain accurate information. For the first time, a recommended vaccine may not be available at their medical home. Many don’t know where to go to receive it (http://www.vaccines.gov). Results of a Kaiser Family Foundation COVID-19 survey (August 2021) indicated that parents trusted their pediatricians most often (78%) for vaccine advice. The respondents voiced concern about trusting the location where the child would be immunized and long-term effects especially related to fertility. Parents who received communications regarding the benefits of vaccination were twice as likely to have their adolescents immunized. Finally, remember: Like parent, like child. An immunized parent is more likely to immunize the adolescent. (See Fig. 1.)
It is beyond the scope of this column to discuss the psychosocial aspects of this disease: children experiencing the death of teachers, classmates, family members, and those viewing the vitriol between pro- and antimask proponents often exhibited on school premises. And let’s not forget the child who wants to wear a mask but may be ostracized or bullied for doing so.
Our job is to do our very best to advocate for and to protect our patients by promoting mandatory masks at schools and encouraging vaccination of adolescents as we patiently wait for vaccines to become available for all of our children.
Dr. Word is a pediatric infectious disease specialist and director of the Houston Travel Medicine Clinic. She said she had no relevant financial disclosures.
I began thinking of a topic for this column weeks ago determined to discuss anything except COVID-19. Yet, news reports from all sources blasted daily reminders of rising COVID-19 cases overall and specifically in children.
In August, school resumed for many of our patients and the battle over mandating masks for school attendance was in full swing. The fact that it is a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommendation supported by both the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Pediatric Infectious Disease Society fell on deaf ears. One day, I heard a report that over 25,000 students attending Texas public schools were diagnosed with COVID-19 between Aug. 23 and Aug. 29. This peak in activity occurred just 2 weeks after the start of school and led to the closure of 45 school districts. Texas does not have a monopoly on these rising cases. Delta, a more contagious variant, began circulating in June 2021 and by July it was the most predominant. Emergency department visits and hospitalizations have increased nationwide. During the latter 2 weeks of August 2021, COVID-19–related ED visits and hospitalizations for persons aged 0-17 years were 3.4 and 3.7 times higher in states with the lowest vaccination coverage, compared with states with high vaccination coverage (MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021;70:1249-54). Specifically, the rates of hospitalization the week ending Aug. 14, 2021, were nearly 5 times the rates for the week ending June 26, 2021, for 0- to 17-year-olds and nearly 10 times the rates for children 0-4 years of age. Hospitalization rates were 10.1 times higher for unimmunized adolescents than for fully vaccinated ones (MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021;70:1255-60).
Multiple elected state leaders have opposed interventions such as mandating masks in school, and our children are paying for it. These leaders have relinquished their responsibility to local school boards. Several have reinforced the no-mask mandate while others have had the courage and insight to ignore state government leaders and have established mask mandates.
How is this lack of enforcement of national recommendations affecting our patients? Let’s look at two neighboring school districts in Texas. School districts have COVID-19 dashboards that are updated daily and accessible to the general public. School District A requires masks for school entry. It serves 196,171 students and has 27,195 teachers and staff. Since school opened in August, 1,606 cumulative cases of COVID-19 in students (0.8%) and 282 in staff (1%) have been reported. Fifty-five percent of the student cases occurred in elementary schools. In contrast, School District B located in the adjacent county serves 64,517 students and has 3,906 teachers and staff with no mask mandate. Since August, there have been 4,506 cumulative COVID-19 cases in students (6.9%) and 578 (14.7%) in staff. Information regarding the specific school type was not provided; however, the dashboard indicates that 2,924 cases (64.8%) occurred in children younger than 11 years of age. County data indicate 62% of those older than 12 years of age were fully vaccinated in District A, compared with 54% of persons older than 12 years in District B. The county COVID-19 positivity rate in District A is 17.6% and in District B it is 20%. Both counties are experiencing increased COVID-19 activity yet have had strikingly different outcomes in the student/staff population. While supporting the case for wearing masks to prevent disease transmission, one can’t ignore the adolescents who were infected and vaccine eligible (District A: 706; District B: 1,582). Their vaccination status could not be determined.
As pediatricians we have played an integral part in the elimination of diseases through educating and administering vaccinations. Adolescents are relatively healthy, thus limiting the number of encounters with them. The majority complete the 11-year visit; however, many fail to return for the 16- to 18-year visit.
So how are we doing? CDC data from 10 U.S. jurisdictions demonstrated a substantial decrease in vaccine administration between March and May of 2020, compared with the same period in 2018 and 2019. A decline was anticipated because of the nationwide lockdown. Doses of HPV administered declined almost 64% and 71% for 9- to 12-year-olds and 13- to 17-year-olds, respectively. Tdap administration declined 66% and 61% for the same respective age groups. Although administered doses increased between June and September of 2020, it was not sufficient to achieve catch-up coverage. Compared to the same period in 2018-2019, administration of the HPV vaccine declined 12.8% and 28% (ages 9-12 and ages 13-17) and for Tdap it was 21% and 30% lower (ages 9-12 and ages 13-17) (MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021;70:840-5).
Now, we have another adolescent vaccine to discuss and encourage our patients to receive. We also need to address their concerns and/or to at least direct them to a reliable source to obtain accurate information. For the first time, a recommended vaccine may not be available at their medical home. Many don’t know where to go to receive it (http://www.vaccines.gov). Results of a Kaiser Family Foundation COVID-19 survey (August 2021) indicated that parents trusted their pediatricians most often (78%) for vaccine advice. The respondents voiced concern about trusting the location where the child would be immunized and long-term effects especially related to fertility. Parents who received communications regarding the benefits of vaccination were twice as likely to have their adolescents immunized. Finally, remember: Like parent, like child. An immunized parent is more likely to immunize the adolescent. (See Fig. 1.)

It is beyond the scope of this column to discuss the psychosocial aspects of this disease: children experiencing the death of teachers, classmates, family members, and those viewing the vitriol between pro- and antimask proponents often exhibited on school premises. And let’s not forget the child who wants to wear a mask but may be ostracized or bullied for doing so.
Our job is to do our very best to advocate for and to protect our patients by promoting mandatory masks at schools and encouraging vaccination of adolescents as we patiently wait for vaccines to become available for all of our children.
Dr. Word is a pediatric infectious disease specialist and director of the Houston Travel Medicine Clinic. She said she had no relevant financial disclosures.
I began thinking of a topic for this column weeks ago determined to discuss anything except COVID-19. Yet, news reports from all sources blasted daily reminders of rising COVID-19 cases overall and specifically in children.
In August, school resumed for many of our patients and the battle over mandating masks for school attendance was in full swing. The fact that it is a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommendation supported by both the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Pediatric Infectious Disease Society fell on deaf ears. One day, I heard a report that over 25,000 students attending Texas public schools were diagnosed with COVID-19 between Aug. 23 and Aug. 29. This peak in activity occurred just 2 weeks after the start of school and led to the closure of 45 school districts. Texas does not have a monopoly on these rising cases. Delta, a more contagious variant, began circulating in June 2021 and by July it was the most predominant. Emergency department visits and hospitalizations have increased nationwide. During the latter 2 weeks of August 2021, COVID-19–related ED visits and hospitalizations for persons aged 0-17 years were 3.4 and 3.7 times higher in states with the lowest vaccination coverage, compared with states with high vaccination coverage (MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021;70:1249-54). Specifically, the rates of hospitalization the week ending Aug. 14, 2021, were nearly 5 times the rates for the week ending June 26, 2021, for 0- to 17-year-olds and nearly 10 times the rates for children 0-4 years of age. Hospitalization rates were 10.1 times higher for unimmunized adolescents than for fully vaccinated ones (MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021;70:1255-60).
Multiple elected state leaders have opposed interventions such as mandating masks in school, and our children are paying for it. These leaders have relinquished their responsibility to local school boards. Several have reinforced the no-mask mandate while others have had the courage and insight to ignore state government leaders and have established mask mandates.
How is this lack of enforcement of national recommendations affecting our patients? Let’s look at two neighboring school districts in Texas. School districts have COVID-19 dashboards that are updated daily and accessible to the general public. School District A requires masks for school entry. It serves 196,171 students and has 27,195 teachers and staff. Since school opened in August, 1,606 cumulative cases of COVID-19 in students (0.8%) and 282 in staff (1%) have been reported. Fifty-five percent of the student cases occurred in elementary schools. In contrast, School District B located in the adjacent county serves 64,517 students and has 3,906 teachers and staff with no mask mandate. Since August, there have been 4,506 cumulative COVID-19 cases in students (6.9%) and 578 (14.7%) in staff. Information regarding the specific school type was not provided; however, the dashboard indicates that 2,924 cases (64.8%) occurred in children younger than 11 years of age. County data indicate 62% of those older than 12 years of age were fully vaccinated in District A, compared with 54% of persons older than 12 years in District B. The county COVID-19 positivity rate in District A is 17.6% and in District B it is 20%. Both counties are experiencing increased COVID-19 activity yet have had strikingly different outcomes in the student/staff population. While supporting the case for wearing masks to prevent disease transmission, one can’t ignore the adolescents who were infected and vaccine eligible (District A: 706; District B: 1,582). Their vaccination status could not be determined.
As pediatricians we have played an integral part in the elimination of diseases through educating and administering vaccinations. Adolescents are relatively healthy, thus limiting the number of encounters with them. The majority complete the 11-year visit; however, many fail to return for the 16- to 18-year visit.
So how are we doing? CDC data from 10 U.S. jurisdictions demonstrated a substantial decrease in vaccine administration between March and May of 2020, compared with the same period in 2018 and 2019. A decline was anticipated because of the nationwide lockdown. Doses of HPV administered declined almost 64% and 71% for 9- to 12-year-olds and 13- to 17-year-olds, respectively. Tdap administration declined 66% and 61% for the same respective age groups. Although administered doses increased between June and September of 2020, it was not sufficient to achieve catch-up coverage. Compared to the same period in 2018-2019, administration of the HPV vaccine declined 12.8% and 28% (ages 9-12 and ages 13-17) and for Tdap it was 21% and 30% lower (ages 9-12 and ages 13-17) (MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021;70:840-5).
Now, we have another adolescent vaccine to discuss and encourage our patients to receive. We also need to address their concerns and/or to at least direct them to a reliable source to obtain accurate information. For the first time, a recommended vaccine may not be available at their medical home. Many don’t know where to go to receive it (http://www.vaccines.gov). Results of a Kaiser Family Foundation COVID-19 survey (August 2021) indicated that parents trusted their pediatricians most often (78%) for vaccine advice. The respondents voiced concern about trusting the location where the child would be immunized and long-term effects especially related to fertility. Parents who received communications regarding the benefits of vaccination were twice as likely to have their adolescents immunized. Finally, remember: Like parent, like child. An immunized parent is more likely to immunize the adolescent. (See Fig. 1.)

It is beyond the scope of this column to discuss the psychosocial aspects of this disease: children experiencing the death of teachers, classmates, family members, and those viewing the vitriol between pro- and antimask proponents often exhibited on school premises. And let’s not forget the child who wants to wear a mask but may be ostracized or bullied for doing so.
Our job is to do our very best to advocate for and to protect our patients by promoting mandatory masks at schools and encouraging vaccination of adolescents as we patiently wait for vaccines to become available for all of our children.
Dr. Word is a pediatric infectious disease specialist and director of the Houston Travel Medicine Clinic. She said she had no relevant financial disclosures.

