User login
AI in Gastroenterology and Endoscopy
Dear colleagues,
Since our last Perspectives feature on artificial intelligence (AI) in gastroenterology and hepatology, the field has experienced remarkable growth in both innovation and clinical adoption. AI tools that were once conceptual are now entering everyday practice, with many more on the horizon poised to transform how we diagnose, treat, and manage patients.
Dr. Yuvaraj Singh, Dr. Alessandro Colletta, and Dr. Neil Marya discuss how purpose-built AI models can reduce diagnostic uncertainty in advanced endoscopy. From cholangioscopy systems that outperform standard ERCP sampling in distinguishing malignant biliary strictures to EUS-based platforms that differentiate autoimmune pancreatitis from pancreatic cancer, they envision a near-term future in which machine intelligence enhances accuracy, accelerates decision-making, and refines interpretation—without replacing the clinician’s expertise.
Complementing this, Dr. Dennis Shung takes a broader view across the endoscopy unit and outpatient clinic. He highlights the promise of AI for polyp detection, digital biopsy, and automated reporting, while underscoring the importance of human oversight, workflow integration, and safeguards against misinformation. Dr. Shung also emphasizes the pivotal role professional societies can play in establishing clear standards, ethical boundaries, and trusted frameworks for AI deployment in GI practice.
We hope these perspectives spark practical conversations about when—and how—to integrate AI in your own practice. As always, we welcome your feedback and real-world experience. Join the conversation on X at @AGA_GIHN.
Gyanprakash A. Ketwaroo, MD, MSc, is associate professor of medicine, Yale University, New Haven, and chief of endoscopy at West Haven VA Medical Center, both in Connecticut. He is an associate editor for GI & Hepatology News.
AI Models in Advanced Endoscopy
BY YUVARAJ SINGH, MD; ALESSANDRO COLLETTA, MD; NEIL MARYA, MD
As the adage goes, “if tumor is the rumor, then tissue is the issue, because cancer may be the answer.”
Establishing an accurate diagnosis is the essential first step toward curing or palliating malignancy. From detecting an early neoplastic lesion, to distinguishing between malignant and benign pathology, or to determining when and where to obtain tissue, endoscopists are frequently faced with the challenge of transforming diagnostic suspicion into certainty.
Artificial intelligence (AI), designed to replicate human cognition such as pattern recognition and decision-making, has emerged as a technology to assist gastroenterologists in addressing a variety of different tasks during endoscopy. AI research in gastrointestinal endoscopy has initially focused on computer-aided detection (CADe) of colorectal polyps. More recently, however, there has been increased emphasis on developing AI to assist advanced endoscopists.
For instance, in biliary endoscopy, AI is being explored to improve the notoriously challenging diagnosis of cholangiocarcinoma, where conventional tissue sampling often falls short of providing a definitive diagnosis. Similarly, in the pancreas, AI models are showing potential to differentiate autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP) from pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), a distinction with profound therapeutic implications. Even pancreatic cysts are beginning to benefit from AI models that refine risk stratification and guide management. Together, these advances underscore how AI is not merely an adjunct but a potentially massive catalyst for reimagining the diagnostic role of advanced endoscopists.
Classifying biliary strictures (MBS) accurately remains a challenge. Standard ERCP-based sampling techniques (forceps biopsy and brush cytology) are suboptimal diagnostic tools with false negative rates for detecting MBS of less than 50%. The diagnostic uncertainty related to biliary stricture classification carries significant consequences for patients. For example, patients with biliary cancer without positive cytology have treatments delayed until a malignant diagnosis is established.
Ancillary technologies to enhance ERCP-based tissue acquisition are still weighed down by low sensitivity and accuracy; even with ancillary use of fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH), diagnostic yield remains limited. EUS-FNA can help with distal biliary strictures, but this technique risks needle-tract seeding in cases of perihilar disease. Cholangioscopy allows for direct visualization and targeted sampling; however, cholangioscopy-guided forceps biopsies are burdened by low sensitivities.1 Additionally, physician interpretation of visual findings during cholangioscopy often suffers from poor interobserver agreement and poor accuracy.2
To improve the classification of biliary strictures, several groups have studied the application of AI for cholangioscopy footage of biliary pathology. In our lab, we trained an AI incorporating over 2.3 million cholangioscopy still images and nearly 20,000 expert-annotated frames to enhance its development. The AI closely mirrored expert labeling of cholangioscopy images of malignant pathology and, when tested on full cholangioscopy videos of indeterminate biliary strictures, the AI achieved a diagnostic accuracy of 91%—outperforming both brush cytology (63%) and forceps biopsy (61%).3
The results from this initial study were later validated across multiple centers. AI-assisted cholangioscopy could thus offer a reproducible, real-world solution to one of the most persistent diagnostic dilemmas advanced endoscopists face—helping clinicians act earlier and with greater confidence when evaluating indeterminate strictures.
Moving from the biliary tree to the pancreas, autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP) is a benign fibro-inflammatory disease that often frustrates advanced endoscopists as it closely mimics the appearance of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC). The stakes are high: despite modern diagnostic techniques, including advanced imaging, some patients with pancreatic resections for “suspected PDAC” are still found to have AIP on final pathology. Conventional tools to distinguish AIP from PDAC have gaps: serum IgG4 and EUS-guided biopsies are both specific but insensitive.
Using EUS videos and images of various pancreas pathologies at Mayo Clinic, we developed an AI to tackle this dilemma. After intensive training, the EUS AI achieved a greater accuracy for distinguishing AIP from PDAC than a group of expert Mayo clinic endosonographers.5 In practice, an EUS-AI can identify AIP patterns in real-time, guiding clinicians toward steroid trials or biopsies and reducing the need for unnecessary surgeries.
Looking ahead, there are multiple opportunities for integration of AI into advanced endoscopy practices. Ongoing research suggests that AI could soon assist with identification of pancreas cysts most at risk for malignant transformation, classification of high risk Barrett’s esophagus, and even help with rapid on-site assessment of cytologic specimens obtained during EUS. Beyond diagnosis, AI could likely play an important role in guiding therapeutic interventions. For example, an ERCP AI in the future may be able to provide cannulation assistance or an AI assistant could help endosonographers during deployments of lumen apposing metal stents.
By enhancing image interpretation and procedural consistency, AI has the potential to uphold the fundamental principle of primum non nocere, enabling us to intervene with precision while minimizing harm. AI can also bridge grey zones in clinical practice and narrow diagnostic uncertainty in real time. Importantly, these systems can help clinicians achieve expertise in a fraction of the time it traditionally takes to acquire comparable human proficiency, while offering wider availability across practice settings and reducing interobserver variability that has long challenged endoscopic interpretation.
Currently, adoption is limited by high bias risk, lack of external validation, and interpretability Still, the trajectory of AI suggests a future where these computer technologies will not only support but also elevate human expertise, reshaping the standards of care of diseases managed by advanced endoscopists.
Dr. Singh, Dr. Colletta, and Dr. Marya are based at the Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, UMass Chan Medical School, Worcester, Massachusetts. Dr. Marya is a consultant for Boston Scientific, and has no other disclosures. Dr. Singh and Dr. Colletta have no disclosures.
References
1. Navaneethan U, et al. Comparative effectiveness of biliary brush cytology and intraductal biopsy for detection of malignant biliary strictures: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015 Jan. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2014.09.017.
2. Stassen PMC, et al. Diagnostic accuracy and interobserver agreement of digital single-operator cholangioscopy for indeterminate biliary strictures. Gastrointest Endosc 2021 Dec. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2021.06.027.
3. Marya NB, et al. Identification of patients with malignant biliary strictures using a cholangioscopy-based deep learning artificial intelligence (with video). Gastrointest Endosc. 2023 Feb. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2022.08.021.
4. Marya NB, et al. Multicenter validation of a cholangioscopy artificial intelligence system for the evaluation of biliary tract disease. Endoscopy. 2025 Aug. doi: 10.1055/a-2650-0789.
5. Marya NB, et al. Utilisation of artificial intelligence for the development of an EUS-convolutional neural network model trained to enhance the diagnosis of autoimmune pancreatitis. Gut. 2021 Jul. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2020-322821.
AI in General GI and Endoscopy
BY DENNIS L. SHUNG, MD, MHS, PHD
The practice of gastroenterology is changing, but much of it will be rooted in the same – careful, focused attention on endoscopic procedures, and compassionate, attentive care in clinic. Artificial intelligence (AI), like the Industrial Revolution before, is going to transform our practice. This comes with upsides and downsides, and highlights the need for strong leadership from our societies to safeguard the technology for practitioners and patients.
What are the upsides?
AI has the potential to serve as a second set of eyes in detecting colon polyps, increasing the adenoma detection rate (ADR).1 AI can be applied to all areas of the gastrointestinal tract, providing digital biopsies, guiding resection, and ensuring quality, which are all now possible with powerful new endoscopy foundation models, such as GastroNet-5M.2
Additionally. the advent of automating the collection of data into reports may herald the end of our days as data entry clerks. Generative AI also has the potential to give us all the best information at our fingertips, suggesting guideline-based care, providing the most up to date evidence, and guiding the differential diagnosis. The potential for patient-facing AI systems could lead to better health literacy, more meaningful engagement, and improved patient satisfaction.3
What are the downsides?
For endoscopy, AI cannot make up for poor technique to ensure adequate mucosal exposure by the endoscopist, and an increase in AI-supported ADR does not yet convincingly translate into concrete gains in colorectal cancer-related mortality. For the foreseeable future, AI cannot make a connection with the patient in front of us, which is critical in diagnosing and treating patients.
Currently, AI appears to worsen loneliness4, and does not necessarily deepen the bonds or provide the positive touch that can heal, and which for many of us, was the reason we became physicians. Finally, as information proliferates, the information risk to patients and providers is growing – in the future, trusted sources to monitor, curate, and guide AI will be ever more important.
Black Swans
As AI begins to mature, there are risks that lurk beneath the surface. When regulatory bodies begin to look at AI-assisted diagnostics or therapeutics as the new standard of care, reimbursement models may adjust, and providers may be left behind. The rapid proliferation and haphazard adoption of AI could lead to overdependence and deskilling or result in weird and as yet unknown errors that are difficult to troubleshoot.
What is the role of the GI societies?
Specialty societies like AGA are taking leadership roles in determining the bounds of where AIs may tread, not just in providing information to their membership but also in digesting evidence and synthesizing recommendations. Societies must balance the real promise of AI in endoscopy with the practice realities for members, and provide living guidelines that reflect the consensus of members regarding scope of practice with the ability to update as new data become available.5
Societies also have a role as advocates for safety, taking ownership of high-quality content to prevent misinformation. AGA recently announced the development of a chat interface that will be focused on providing its members the highest quality information, and serve as a portal to identify and respond to its members’ information needs. By staying united rather than fragmenting, societies can maintain bounds to protect its members and their patients and advance areas where there is clinical need, together.
Dr. Shung is senior associate consultant, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, and director of clinical generative artificial intelligence and informatics, Department of Medicine, at Mayo Clinic Rochester, Minnesota. He has no disclosures in regard to this article.
References
1. Soleymanjahi S, et al. Artificial Intelligence-Assisted Colonoscopy for Polyp Detection : A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med. 2024 Dec. doi:10.7326/annals-24-00981.
2. Jong MR, et al. GastroNet-5M: A Multicenter Dataset for Developing Foundation Models in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. Gastroenterology. 2025 Jul. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2025.07.030.
3. Soroush A, et al. Generative Artificial Intelligence in Clinical Medicine and Impact on Gastroenterology. Gastroenterology. 2025 Aug. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2025.03.038.
4. Mengying Fang C, et al. How AI and Human Behaviors Shape Psychosocial Effects of Extended Chatbot Use: A Longitudinal Randomized Controlled Study. arXiv e-prints. 2025 Mar. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2503.17473.
5. Sultan S, et al. AGA Living Clinical Practice Guideline on Computer-Aided Detection-Assisted Colonoscopy. Gastroenterology. 2025 Apr. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2025.01.002.
Dear colleagues,
Since our last Perspectives feature on artificial intelligence (AI) in gastroenterology and hepatology, the field has experienced remarkable growth in both innovation and clinical adoption. AI tools that were once conceptual are now entering everyday practice, with many more on the horizon poised to transform how we diagnose, treat, and manage patients.
Dr. Yuvaraj Singh, Dr. Alessandro Colletta, and Dr. Neil Marya discuss how purpose-built AI models can reduce diagnostic uncertainty in advanced endoscopy. From cholangioscopy systems that outperform standard ERCP sampling in distinguishing malignant biliary strictures to EUS-based platforms that differentiate autoimmune pancreatitis from pancreatic cancer, they envision a near-term future in which machine intelligence enhances accuracy, accelerates decision-making, and refines interpretation—without replacing the clinician’s expertise.
Complementing this, Dr. Dennis Shung takes a broader view across the endoscopy unit and outpatient clinic. He highlights the promise of AI for polyp detection, digital biopsy, and automated reporting, while underscoring the importance of human oversight, workflow integration, and safeguards against misinformation. Dr. Shung also emphasizes the pivotal role professional societies can play in establishing clear standards, ethical boundaries, and trusted frameworks for AI deployment in GI practice.
We hope these perspectives spark practical conversations about when—and how—to integrate AI in your own practice. As always, we welcome your feedback and real-world experience. Join the conversation on X at @AGA_GIHN.
Gyanprakash A. Ketwaroo, MD, MSc, is associate professor of medicine, Yale University, New Haven, and chief of endoscopy at West Haven VA Medical Center, both in Connecticut. He is an associate editor for GI & Hepatology News.
AI Models in Advanced Endoscopy
BY YUVARAJ SINGH, MD; ALESSANDRO COLLETTA, MD; NEIL MARYA, MD
As the adage goes, “if tumor is the rumor, then tissue is the issue, because cancer may be the answer.”
Establishing an accurate diagnosis is the essential first step toward curing or palliating malignancy. From detecting an early neoplastic lesion, to distinguishing between malignant and benign pathology, or to determining when and where to obtain tissue, endoscopists are frequently faced with the challenge of transforming diagnostic suspicion into certainty.
Artificial intelligence (AI), designed to replicate human cognition such as pattern recognition and decision-making, has emerged as a technology to assist gastroenterologists in addressing a variety of different tasks during endoscopy. AI research in gastrointestinal endoscopy has initially focused on computer-aided detection (CADe) of colorectal polyps. More recently, however, there has been increased emphasis on developing AI to assist advanced endoscopists.
For instance, in biliary endoscopy, AI is being explored to improve the notoriously challenging diagnosis of cholangiocarcinoma, where conventional tissue sampling often falls short of providing a definitive diagnosis. Similarly, in the pancreas, AI models are showing potential to differentiate autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP) from pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), a distinction with profound therapeutic implications. Even pancreatic cysts are beginning to benefit from AI models that refine risk stratification and guide management. Together, these advances underscore how AI is not merely an adjunct but a potentially massive catalyst for reimagining the diagnostic role of advanced endoscopists.
Classifying biliary strictures (MBS) accurately remains a challenge. Standard ERCP-based sampling techniques (forceps biopsy and brush cytology) are suboptimal diagnostic tools with false negative rates for detecting MBS of less than 50%. The diagnostic uncertainty related to biliary stricture classification carries significant consequences for patients. For example, patients with biliary cancer without positive cytology have treatments delayed until a malignant diagnosis is established.
Ancillary technologies to enhance ERCP-based tissue acquisition are still weighed down by low sensitivity and accuracy; even with ancillary use of fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH), diagnostic yield remains limited. EUS-FNA can help with distal biliary strictures, but this technique risks needle-tract seeding in cases of perihilar disease. Cholangioscopy allows for direct visualization and targeted sampling; however, cholangioscopy-guided forceps biopsies are burdened by low sensitivities.1 Additionally, physician interpretation of visual findings during cholangioscopy often suffers from poor interobserver agreement and poor accuracy.2
To improve the classification of biliary strictures, several groups have studied the application of AI for cholangioscopy footage of biliary pathology. In our lab, we trained an AI incorporating over 2.3 million cholangioscopy still images and nearly 20,000 expert-annotated frames to enhance its development. The AI closely mirrored expert labeling of cholangioscopy images of malignant pathology and, when tested on full cholangioscopy videos of indeterminate biliary strictures, the AI achieved a diagnostic accuracy of 91%—outperforming both brush cytology (63%) and forceps biopsy (61%).3
The results from this initial study were later validated across multiple centers. AI-assisted cholangioscopy could thus offer a reproducible, real-world solution to one of the most persistent diagnostic dilemmas advanced endoscopists face—helping clinicians act earlier and with greater confidence when evaluating indeterminate strictures.
Moving from the biliary tree to the pancreas, autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP) is a benign fibro-inflammatory disease that often frustrates advanced endoscopists as it closely mimics the appearance of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC). The stakes are high: despite modern diagnostic techniques, including advanced imaging, some patients with pancreatic resections for “suspected PDAC” are still found to have AIP on final pathology. Conventional tools to distinguish AIP from PDAC have gaps: serum IgG4 and EUS-guided biopsies are both specific but insensitive.
Using EUS videos and images of various pancreas pathologies at Mayo Clinic, we developed an AI to tackle this dilemma. After intensive training, the EUS AI achieved a greater accuracy for distinguishing AIP from PDAC than a group of expert Mayo clinic endosonographers.5 In practice, an EUS-AI can identify AIP patterns in real-time, guiding clinicians toward steroid trials or biopsies and reducing the need for unnecessary surgeries.
Looking ahead, there are multiple opportunities for integration of AI into advanced endoscopy practices. Ongoing research suggests that AI could soon assist with identification of pancreas cysts most at risk for malignant transformation, classification of high risk Barrett’s esophagus, and even help with rapid on-site assessment of cytologic specimens obtained during EUS. Beyond diagnosis, AI could likely play an important role in guiding therapeutic interventions. For example, an ERCP AI in the future may be able to provide cannulation assistance or an AI assistant could help endosonographers during deployments of lumen apposing metal stents.
By enhancing image interpretation and procedural consistency, AI has the potential to uphold the fundamental principle of primum non nocere, enabling us to intervene with precision while minimizing harm. AI can also bridge grey zones in clinical practice and narrow diagnostic uncertainty in real time. Importantly, these systems can help clinicians achieve expertise in a fraction of the time it traditionally takes to acquire comparable human proficiency, while offering wider availability across practice settings and reducing interobserver variability that has long challenged endoscopic interpretation.
Currently, adoption is limited by high bias risk, lack of external validation, and interpretability Still, the trajectory of AI suggests a future where these computer technologies will not only support but also elevate human expertise, reshaping the standards of care of diseases managed by advanced endoscopists.
Dr. Singh, Dr. Colletta, and Dr. Marya are based at the Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, UMass Chan Medical School, Worcester, Massachusetts. Dr. Marya is a consultant for Boston Scientific, and has no other disclosures. Dr. Singh and Dr. Colletta have no disclosures.
References
1. Navaneethan U, et al. Comparative effectiveness of biliary brush cytology and intraductal biopsy for detection of malignant biliary strictures: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015 Jan. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2014.09.017.
2. Stassen PMC, et al. Diagnostic accuracy and interobserver agreement of digital single-operator cholangioscopy for indeterminate biliary strictures. Gastrointest Endosc 2021 Dec. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2021.06.027.
3. Marya NB, et al. Identification of patients with malignant biliary strictures using a cholangioscopy-based deep learning artificial intelligence (with video). Gastrointest Endosc. 2023 Feb. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2022.08.021.
4. Marya NB, et al. Multicenter validation of a cholangioscopy artificial intelligence system for the evaluation of biliary tract disease. Endoscopy. 2025 Aug. doi: 10.1055/a-2650-0789.
5. Marya NB, et al. Utilisation of artificial intelligence for the development of an EUS-convolutional neural network model trained to enhance the diagnosis of autoimmune pancreatitis. Gut. 2021 Jul. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2020-322821.
AI in General GI and Endoscopy
BY DENNIS L. SHUNG, MD, MHS, PHD
The practice of gastroenterology is changing, but much of it will be rooted in the same – careful, focused attention on endoscopic procedures, and compassionate, attentive care in clinic. Artificial intelligence (AI), like the Industrial Revolution before, is going to transform our practice. This comes with upsides and downsides, and highlights the need for strong leadership from our societies to safeguard the technology for practitioners and patients.
What are the upsides?
AI has the potential to serve as a second set of eyes in detecting colon polyps, increasing the adenoma detection rate (ADR).1 AI can be applied to all areas of the gastrointestinal tract, providing digital biopsies, guiding resection, and ensuring quality, which are all now possible with powerful new endoscopy foundation models, such as GastroNet-5M.2
Additionally. the advent of automating the collection of data into reports may herald the end of our days as data entry clerks. Generative AI also has the potential to give us all the best information at our fingertips, suggesting guideline-based care, providing the most up to date evidence, and guiding the differential diagnosis. The potential for patient-facing AI systems could lead to better health literacy, more meaningful engagement, and improved patient satisfaction.3
What are the downsides?
For endoscopy, AI cannot make up for poor technique to ensure adequate mucosal exposure by the endoscopist, and an increase in AI-supported ADR does not yet convincingly translate into concrete gains in colorectal cancer-related mortality. For the foreseeable future, AI cannot make a connection with the patient in front of us, which is critical in diagnosing and treating patients.
Currently, AI appears to worsen loneliness4, and does not necessarily deepen the bonds or provide the positive touch that can heal, and which for many of us, was the reason we became physicians. Finally, as information proliferates, the information risk to patients and providers is growing – in the future, trusted sources to monitor, curate, and guide AI will be ever more important.
Black Swans
As AI begins to mature, there are risks that lurk beneath the surface. When regulatory bodies begin to look at AI-assisted diagnostics or therapeutics as the new standard of care, reimbursement models may adjust, and providers may be left behind. The rapid proliferation and haphazard adoption of AI could lead to overdependence and deskilling or result in weird and as yet unknown errors that are difficult to troubleshoot.
What is the role of the GI societies?
Specialty societies like AGA are taking leadership roles in determining the bounds of where AIs may tread, not just in providing information to their membership but also in digesting evidence and synthesizing recommendations. Societies must balance the real promise of AI in endoscopy with the practice realities for members, and provide living guidelines that reflect the consensus of members regarding scope of practice with the ability to update as new data become available.5
Societies also have a role as advocates for safety, taking ownership of high-quality content to prevent misinformation. AGA recently announced the development of a chat interface that will be focused on providing its members the highest quality information, and serve as a portal to identify and respond to its members’ information needs. By staying united rather than fragmenting, societies can maintain bounds to protect its members and their patients and advance areas where there is clinical need, together.
Dr. Shung is senior associate consultant, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, and director of clinical generative artificial intelligence and informatics, Department of Medicine, at Mayo Clinic Rochester, Minnesota. He has no disclosures in regard to this article.
References
1. Soleymanjahi S, et al. Artificial Intelligence-Assisted Colonoscopy for Polyp Detection : A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med. 2024 Dec. doi:10.7326/annals-24-00981.
2. Jong MR, et al. GastroNet-5M: A Multicenter Dataset for Developing Foundation Models in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. Gastroenterology. 2025 Jul. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2025.07.030.
3. Soroush A, et al. Generative Artificial Intelligence in Clinical Medicine and Impact on Gastroenterology. Gastroenterology. 2025 Aug. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2025.03.038.
4. Mengying Fang C, et al. How AI and Human Behaviors Shape Psychosocial Effects of Extended Chatbot Use: A Longitudinal Randomized Controlled Study. arXiv e-prints. 2025 Mar. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2503.17473.
5. Sultan S, et al. AGA Living Clinical Practice Guideline on Computer-Aided Detection-Assisted Colonoscopy. Gastroenterology. 2025 Apr. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2025.01.002.
Dear colleagues,
Since our last Perspectives feature on artificial intelligence (AI) in gastroenterology and hepatology, the field has experienced remarkable growth in both innovation and clinical adoption. AI tools that were once conceptual are now entering everyday practice, with many more on the horizon poised to transform how we diagnose, treat, and manage patients.
Dr. Yuvaraj Singh, Dr. Alessandro Colletta, and Dr. Neil Marya discuss how purpose-built AI models can reduce diagnostic uncertainty in advanced endoscopy. From cholangioscopy systems that outperform standard ERCP sampling in distinguishing malignant biliary strictures to EUS-based platforms that differentiate autoimmune pancreatitis from pancreatic cancer, they envision a near-term future in which machine intelligence enhances accuracy, accelerates decision-making, and refines interpretation—without replacing the clinician’s expertise.
Complementing this, Dr. Dennis Shung takes a broader view across the endoscopy unit and outpatient clinic. He highlights the promise of AI for polyp detection, digital biopsy, and automated reporting, while underscoring the importance of human oversight, workflow integration, and safeguards against misinformation. Dr. Shung also emphasizes the pivotal role professional societies can play in establishing clear standards, ethical boundaries, and trusted frameworks for AI deployment in GI practice.
We hope these perspectives spark practical conversations about when—and how—to integrate AI in your own practice. As always, we welcome your feedback and real-world experience. Join the conversation on X at @AGA_GIHN.
Gyanprakash A. Ketwaroo, MD, MSc, is associate professor of medicine, Yale University, New Haven, and chief of endoscopy at West Haven VA Medical Center, both in Connecticut. He is an associate editor for GI & Hepatology News.
AI Models in Advanced Endoscopy
BY YUVARAJ SINGH, MD; ALESSANDRO COLLETTA, MD; NEIL MARYA, MD
As the adage goes, “if tumor is the rumor, then tissue is the issue, because cancer may be the answer.”
Establishing an accurate diagnosis is the essential first step toward curing or palliating malignancy. From detecting an early neoplastic lesion, to distinguishing between malignant and benign pathology, or to determining when and where to obtain tissue, endoscopists are frequently faced with the challenge of transforming diagnostic suspicion into certainty.
Artificial intelligence (AI), designed to replicate human cognition such as pattern recognition and decision-making, has emerged as a technology to assist gastroenterologists in addressing a variety of different tasks during endoscopy. AI research in gastrointestinal endoscopy has initially focused on computer-aided detection (CADe) of colorectal polyps. More recently, however, there has been increased emphasis on developing AI to assist advanced endoscopists.
For instance, in biliary endoscopy, AI is being explored to improve the notoriously challenging diagnosis of cholangiocarcinoma, where conventional tissue sampling often falls short of providing a definitive diagnosis. Similarly, in the pancreas, AI models are showing potential to differentiate autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP) from pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), a distinction with profound therapeutic implications. Even pancreatic cysts are beginning to benefit from AI models that refine risk stratification and guide management. Together, these advances underscore how AI is not merely an adjunct but a potentially massive catalyst for reimagining the diagnostic role of advanced endoscopists.
Classifying biliary strictures (MBS) accurately remains a challenge. Standard ERCP-based sampling techniques (forceps biopsy and brush cytology) are suboptimal diagnostic tools with false negative rates for detecting MBS of less than 50%. The diagnostic uncertainty related to biliary stricture classification carries significant consequences for patients. For example, patients with biliary cancer without positive cytology have treatments delayed until a malignant diagnosis is established.
Ancillary technologies to enhance ERCP-based tissue acquisition are still weighed down by low sensitivity and accuracy; even with ancillary use of fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH), diagnostic yield remains limited. EUS-FNA can help with distal biliary strictures, but this technique risks needle-tract seeding in cases of perihilar disease. Cholangioscopy allows for direct visualization and targeted sampling; however, cholangioscopy-guided forceps biopsies are burdened by low sensitivities.1 Additionally, physician interpretation of visual findings during cholangioscopy often suffers from poor interobserver agreement and poor accuracy.2
To improve the classification of biliary strictures, several groups have studied the application of AI for cholangioscopy footage of biliary pathology. In our lab, we trained an AI incorporating over 2.3 million cholangioscopy still images and nearly 20,000 expert-annotated frames to enhance its development. The AI closely mirrored expert labeling of cholangioscopy images of malignant pathology and, when tested on full cholangioscopy videos of indeterminate biliary strictures, the AI achieved a diagnostic accuracy of 91%—outperforming both brush cytology (63%) and forceps biopsy (61%).3
The results from this initial study were later validated across multiple centers. AI-assisted cholangioscopy could thus offer a reproducible, real-world solution to one of the most persistent diagnostic dilemmas advanced endoscopists face—helping clinicians act earlier and with greater confidence when evaluating indeterminate strictures.
Moving from the biliary tree to the pancreas, autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP) is a benign fibro-inflammatory disease that often frustrates advanced endoscopists as it closely mimics the appearance of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC). The stakes are high: despite modern diagnostic techniques, including advanced imaging, some patients with pancreatic resections for “suspected PDAC” are still found to have AIP on final pathology. Conventional tools to distinguish AIP from PDAC have gaps: serum IgG4 and EUS-guided biopsies are both specific but insensitive.
Using EUS videos and images of various pancreas pathologies at Mayo Clinic, we developed an AI to tackle this dilemma. After intensive training, the EUS AI achieved a greater accuracy for distinguishing AIP from PDAC than a group of expert Mayo clinic endosonographers.5 In practice, an EUS-AI can identify AIP patterns in real-time, guiding clinicians toward steroid trials or biopsies and reducing the need for unnecessary surgeries.
Looking ahead, there are multiple opportunities for integration of AI into advanced endoscopy practices. Ongoing research suggests that AI could soon assist with identification of pancreas cysts most at risk for malignant transformation, classification of high risk Barrett’s esophagus, and even help with rapid on-site assessment of cytologic specimens obtained during EUS. Beyond diagnosis, AI could likely play an important role in guiding therapeutic interventions. For example, an ERCP AI in the future may be able to provide cannulation assistance or an AI assistant could help endosonographers during deployments of lumen apposing metal stents.
By enhancing image interpretation and procedural consistency, AI has the potential to uphold the fundamental principle of primum non nocere, enabling us to intervene with precision while minimizing harm. AI can also bridge grey zones in clinical practice and narrow diagnostic uncertainty in real time. Importantly, these systems can help clinicians achieve expertise in a fraction of the time it traditionally takes to acquire comparable human proficiency, while offering wider availability across practice settings and reducing interobserver variability that has long challenged endoscopic interpretation.
Currently, adoption is limited by high bias risk, lack of external validation, and interpretability Still, the trajectory of AI suggests a future where these computer technologies will not only support but also elevate human expertise, reshaping the standards of care of diseases managed by advanced endoscopists.
Dr. Singh, Dr. Colletta, and Dr. Marya are based at the Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, UMass Chan Medical School, Worcester, Massachusetts. Dr. Marya is a consultant for Boston Scientific, and has no other disclosures. Dr. Singh and Dr. Colletta have no disclosures.
References
1. Navaneethan U, et al. Comparative effectiveness of biliary brush cytology and intraductal biopsy for detection of malignant biliary strictures: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015 Jan. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2014.09.017.
2. Stassen PMC, et al. Diagnostic accuracy and interobserver agreement of digital single-operator cholangioscopy for indeterminate biliary strictures. Gastrointest Endosc 2021 Dec. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2021.06.027.
3. Marya NB, et al. Identification of patients with malignant biliary strictures using a cholangioscopy-based deep learning artificial intelligence (with video). Gastrointest Endosc. 2023 Feb. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2022.08.021.
4. Marya NB, et al. Multicenter validation of a cholangioscopy artificial intelligence system for the evaluation of biliary tract disease. Endoscopy. 2025 Aug. doi: 10.1055/a-2650-0789.
5. Marya NB, et al. Utilisation of artificial intelligence for the development of an EUS-convolutional neural network model trained to enhance the diagnosis of autoimmune pancreatitis. Gut. 2021 Jul. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2020-322821.
AI in General GI and Endoscopy
BY DENNIS L. SHUNG, MD, MHS, PHD
The practice of gastroenterology is changing, but much of it will be rooted in the same – careful, focused attention on endoscopic procedures, and compassionate, attentive care in clinic. Artificial intelligence (AI), like the Industrial Revolution before, is going to transform our practice. This comes with upsides and downsides, and highlights the need for strong leadership from our societies to safeguard the technology for practitioners and patients.
What are the upsides?
AI has the potential to serve as a second set of eyes in detecting colon polyps, increasing the adenoma detection rate (ADR).1 AI can be applied to all areas of the gastrointestinal tract, providing digital biopsies, guiding resection, and ensuring quality, which are all now possible with powerful new endoscopy foundation models, such as GastroNet-5M.2
Additionally. the advent of automating the collection of data into reports may herald the end of our days as data entry clerks. Generative AI also has the potential to give us all the best information at our fingertips, suggesting guideline-based care, providing the most up to date evidence, and guiding the differential diagnosis. The potential for patient-facing AI systems could lead to better health literacy, more meaningful engagement, and improved patient satisfaction.3
What are the downsides?
For endoscopy, AI cannot make up for poor technique to ensure adequate mucosal exposure by the endoscopist, and an increase in AI-supported ADR does not yet convincingly translate into concrete gains in colorectal cancer-related mortality. For the foreseeable future, AI cannot make a connection with the patient in front of us, which is critical in diagnosing and treating patients.
Currently, AI appears to worsen loneliness4, and does not necessarily deepen the bonds or provide the positive touch that can heal, and which for many of us, was the reason we became physicians. Finally, as information proliferates, the information risk to patients and providers is growing – in the future, trusted sources to monitor, curate, and guide AI will be ever more important.
Black Swans
As AI begins to mature, there are risks that lurk beneath the surface. When regulatory bodies begin to look at AI-assisted diagnostics or therapeutics as the new standard of care, reimbursement models may adjust, and providers may be left behind. The rapid proliferation and haphazard adoption of AI could lead to overdependence and deskilling or result in weird and as yet unknown errors that are difficult to troubleshoot.
What is the role of the GI societies?
Specialty societies like AGA are taking leadership roles in determining the bounds of where AIs may tread, not just in providing information to their membership but also in digesting evidence and synthesizing recommendations. Societies must balance the real promise of AI in endoscopy with the practice realities for members, and provide living guidelines that reflect the consensus of members regarding scope of practice with the ability to update as new data become available.5
Societies also have a role as advocates for safety, taking ownership of high-quality content to prevent misinformation. AGA recently announced the development of a chat interface that will be focused on providing its members the highest quality information, and serve as a portal to identify and respond to its members’ information needs. By staying united rather than fragmenting, societies can maintain bounds to protect its members and their patients and advance areas where there is clinical need, together.
Dr. Shung is senior associate consultant, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, and director of clinical generative artificial intelligence and informatics, Department of Medicine, at Mayo Clinic Rochester, Minnesota. He has no disclosures in regard to this article.
References
1. Soleymanjahi S, et al. Artificial Intelligence-Assisted Colonoscopy for Polyp Detection : A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med. 2024 Dec. doi:10.7326/annals-24-00981.
2. Jong MR, et al. GastroNet-5M: A Multicenter Dataset for Developing Foundation Models in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. Gastroenterology. 2025 Jul. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2025.07.030.
3. Soroush A, et al. Generative Artificial Intelligence in Clinical Medicine and Impact on Gastroenterology. Gastroenterology. 2025 Aug. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2025.03.038.
4. Mengying Fang C, et al. How AI and Human Behaviors Shape Psychosocial Effects of Extended Chatbot Use: A Longitudinal Randomized Controlled Study. arXiv e-prints. 2025 Mar. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2503.17473.
5. Sultan S, et al. AGA Living Clinical Practice Guideline on Computer-Aided Detection-Assisted Colonoscopy. Gastroenterology. 2025 Apr. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2025.01.002.
Evolving Standards of Practice: Esophageal Varices and Barrett’s Esophagus
Dear colleagues,
In the dynamic field of medicine, long-held practices are being reevaluated in light of new evidence and evolving standards of practice.
Dr. Anahita Rabiee discusses the importance of prioritizing non-selective beta blockers (NSBB) over endoscopic variceal ligation (EVL) in the primary prophylaxis of variceal bleeding in patients with compensated cirrhosis. Drawing on data from the PREDESCI trial and real-world experience, she argues that NSBB address the upstream driver—portal hypertension—more broadly and effectively than EVL. In a complementary piece, Dr. Tarek Sawas explores the nuanced landscape of screening and surveillance in Barrett’s esophagus. From how to manage irregular Z-lines, to rethinking the need for 1-year follow-up endoscopies and interpreting the implications of the BOSS trial, Dr. Sawas advocates for a more personalized, risk-based approach.
We hope these perspectives spark dialogue and reflection in your own practice. Join the conversation on X at @AGA_GIHN.
Gyanprakash A. Ketwaroo, MD, MSc, is associate professor of medicine, Yale University, New Haven, and chief of endoscopy at West Haven VA Medical Center, both in Connecticut. He is an associate editor for GI & Hepatology News.
Choose NSBBs, Not EVL, in Patients with Compensated Cirrhosis
BY ANAHITA RABIEE, MD, MHS
I strongly favor the use of non selective beta blockers (NSBBs) in patients with compensated cirrhosis, rather than endoscopy and esophageal variceal ligation (EVL) for primary prophylaxis.
Since the results of PREDESCI trial (β blockers to prevent decompensation of cirrhosis in patients with clinically significant portal hypertension (CSPH)) were published in 2019, there has been much debate on the role of screening endoscopy and EVL for primary prophylaxis. While many argue that a single randomized trial should not overturn long standing practice, several compelling reasons convince me to choose NSBBs, when possible.
Recent guidance from major liver societies now recommends NSBBs as first line therapy for CSPH. Yet, adoption in clinical practice remains inconsistent.
Here is why I believe NSBB represent a better solution:
Treating Upstream, Not Just a Local Treatment
NSBBs such as propranolol and nadolol decrease portal pressure by decreasing portal venous inflow through β1 and β2 adrenergic blockade. Carvedilol is often preferred given its additional α1 adrenergic blocking activity making it the most effective one in decreasing the portal pressure. Therefore, NSBBs address the upstream driver of decompensation by decreasing portal pressures.
EVL, in contrast, is a local fix that only prevents variceal bleeding. Ascites, not variceal bleeding, is the most common initial decompensating event and is associated with high mortality. Preventing all forms of decompensation is clearly preferable to preventing just one.
Broader Eligibility, More Patients Benefit
CSPH is defined as hepatic venous pressure gradient (HVPG)>10 mmHg, the threshold where increased portal venous inflow secondary to splanchnic vasodilation and hyperdynamic circulation drives the increase in portal hypertension. This threshold has been shown to strongly predict decompensation in patients with compensated disease.
While all patients with varices have CSPH, not all patients with CSPH have varices. They can be identified by other non invasive criteria such as cross sectional imaging showing collaterals, or liver stiffness and platelet thresholds that have been previously validated. By restricting intervention to those with large varices and offering only EVL, we miss the opportunity to intervene earlier and to a broader group that would benefit from this treatment.
Comprehensive Protection Without Repeated Endoscopies
Once on an appropriate NSBB dose, patients are protected against variceal bleeding (at least as effectively as EVL). This eliminates the need for repeated surveillance endoscopies to identify and treat large varices in otherwise compensated patients.
Better Tolerated and – In Many Cases – Overlaps With Existing Medication List!
While overtreatment is a concern, regular endoscopies every two years are also burdensome. Many patients already need beta blockers for cardiac conditions such as atrial fibrillation, ischemic heart disease or hypertension. Carvedilol, in particular, offers dual benefit for both hepatologists and cardiologists.
It is important to emphasize that these arguments apply to compensated cirrhosis. In decompensated disease, the approach changes. After a variceal bleed, both NSBBs and EVL are required for secondary prophylaxis. In patients with prior ascites but no variceal bleed, the benefit of NSBBs is less pronounced since decompensation has already occurred. In this setting, NSBBs can still be used selectively, but only if systolic blood pressure remains above 90 mmHg.
The evidence supporting NSBBs over EVL in compensated cirrhosis is not perfect, but few things in medicine are. Given current data, NSBBs should be the first line therapy in compensated cirrhosis with CSPH. Once a patient is on an appropriate and tolerated NSBB dose, routine endoscopic surveillance is unnecessary. Endoscopy should be reserved for those who cannot tolerate NSBBs, in whom EVL is then indicated if large varices are present.
Dr. Rabiee is based at the Yale School of Medicine, New Haven, Connecticut, and the Veterans Affairs Connecticut Healthcare System, West Haven, Connecticut. She has no disclosures in regard to this article.
Rethinking Screening and Surveillance in Barrett’s Esophagus: Navigating Controversies and Nuances
BY TAREK SAWAS, MD, MPH
Barrett’s esophagus (BE) is a precursor to esophageal adenocarcinoma (EAC). Despite our comprehensive guidelines, many of the day-to-day decisions still rely on clinical judgment and honest conversations with patients. This article explores common scenarios in which management decisions are nuanced and the right answer remains debatable.
Irregular Z-Line/Ultrashort Segment BE: Leave Or Watch It?
Few findings provoke more confusion than irregular Z-line or intestinal metaplasia (IM) < 1 cm at the gastroesophageal junction (GEJ). For years, we have debated whether these subtle changes represent a precursor to EAC or simply a benign variant. We have wrestled with how to handle these cases from whether we should take biopsies to how to perform surveillance.
The American College of Gastroenterology (ACG) guideline suggests that irregular Z-lines should not be routinely biopsied or surveyed. Similarly, the upcoming American Gastroenterology Association (AGA) surveillance guideline suggests against surveillance of IM<1 cm citing the low individual annual risk of progression to high-grade dysplasia (HGD) and EAC of 0.23% per year which is lower than that of non-dysplastic Barrett’s esophagus (NDBE). However, this is not the entire picture.
Despite the low per-patient risk, IM<1cm is highly prevalent with columnar mucosa observed in approximately 15% of patients undergoing upper endoscopy. This paradox is unsettling. While any one patient with IM<1 cm is unlikely to progress to EAC, the group accounts for a meaningful share of the EAC burden. Some experts have argued that this justifies routine biopsy and surveillance in all patients with visible columnar mucosa regardless of length. However, this approach risks overwhelming our surveillance infrastructure.
A recent decision modeling analysis suggested that at the lowest progression rates, either no surveillance or one-time endoscopy can be considered. Based on these data, I do not regularly biopsy ultrashort segments unless the mucosa appears suspicious. In those with IM<1 cm detected during a high-quality endoscopic exam, no follow-up is needed. However, if the exam is suboptimal, I perform a 1-time high-quality repeat exam. If there is no evidence of dysplasia then I do not pursue any further surveillance.
The One-Year Follow-Up Endoscopy: Is It Necessary?
Another controversy is the one-year follow-up endoscopy after an initial diagnosis of NDBE. Proponents of this approach cite the high proportion of post endoscopy esophageal neoplasia and cancer (PEEN/PEEC) detected in the first year after diagnosis (missed HGD/EAC). In fact, PEEN account for about a quarter of all HGD/EAC cases diagnosed during surveillance.
While this approach might mitigate PEEN/PEEC risk, it may not be necessary if the index endoscopy is high quality. To ensure high quality exams, several best practices have been proposed including:
- Use of high-definition white light endoscopy (HD-WLE) with chromoendoscopy (virtual or dye based)
- Appropriate inspection time (1 minute per cm of circumferential BE)
- Accurate documentation using the Prague criteria
- Adherence to the Seattle protocol with additional targeted biopsies
If the index endoscopy meets these quality metrics, I typically do not bring the patient back at one year. However, if the exam quality is in question, then I repeat it at one year to establish a reliable baseline and rule out prevalent neoplasia.
Surveillance In NDBE: After BOSS, Do We Rethink Everything?
The recently published BOSS trial (Barrett’s Oesophagus Surveillance Study) has reignited the debate over the value of endoscopic surveillance in NDBE. In this study, 3,453 patients with NDBE across the UK were randomized to either surveillance endoscopy every two years or endoscopy only as clinically indicated. After a median follow-up of 12.8 years, the trial found no significant difference in all-cause mortality between the two groups.
While these findings are important, they should be interpreted with caution. First, the primary endpoint, all-cause mortality, is not optimal for evaluating surveillance for EAC. Surveillance is not intended to reduce all-cause mortality but rather to reduce EAC–related mortality. Second, a substantial number of patients in the no surveillance group still underwent endoscopy at intervals that were not meaningfully different from those in the surveillance group. If both groups receive similar exposure to endoscopy, the comparison loses power. Lastly, the trial was underpowered due to overestimation of progression risk during its initial design. As we have since learned, the risk of progression of NDBE is lower than originally assumed.
So where do we stand now? For me, the BOSS trial does not negate the value of surveillance. it reminds us that a one-size-fits-all approach is inefficient, and our strategy must be risk based. For low-risk individuals, particularly older adults with short-segment NDBE, surveillance may offer little benefit. But in healthier, younger patients with longer segments or additional risk factors, surveillance remains an essential tool for early neoplasia detection.
When to Stop Surveillance
Perhaps the most under-discussed point is when to stop surveillance. Existing guidelines do not account for competing mortality risks unrelated to EAC or provide specific recommendations regarding cessation of surveillance. The desired benefits of surveillance likely diminish with advanced age and greater comorbidity because of lower life expectancy and ineligibility for definitive therapy for EAC.
A recent modeling study found that the optimal ages for last surveillance were 81, 80, 77, and 73 years for men with no, mild, moderate, and severe comorbidity respectively and 75, 73, 73, and 69 years for women. In my practice, I discuss surveillance cessation in patients older than 75 based on their comorbidities. If the risk of progression is outweighed by the risk of the procedure or by the reality of limited life expectancy, we should not hesitate to consider surveillance cessation.
In summary, high-quality endoscopic exam in appropriately selected patients remains the cornerstone of BE surveillance. A more personalized, risk-based approach is needed taking into account competing comorbidities. Emerging technology through risk stratification tools such as biomarkers and artificial intelligence may refine our approach and help address the current limitations.
Dr. Sawas is based at the University of Texas Southwestern, Dallas, Texas. He has no disclosures in regard to this article.
Dear colleagues,
In the dynamic field of medicine, long-held practices are being reevaluated in light of new evidence and evolving standards of practice.
Dr. Anahita Rabiee discusses the importance of prioritizing non-selective beta blockers (NSBB) over endoscopic variceal ligation (EVL) in the primary prophylaxis of variceal bleeding in patients with compensated cirrhosis. Drawing on data from the PREDESCI trial and real-world experience, she argues that NSBB address the upstream driver—portal hypertension—more broadly and effectively than EVL. In a complementary piece, Dr. Tarek Sawas explores the nuanced landscape of screening and surveillance in Barrett’s esophagus. From how to manage irregular Z-lines, to rethinking the need for 1-year follow-up endoscopies and interpreting the implications of the BOSS trial, Dr. Sawas advocates for a more personalized, risk-based approach.
We hope these perspectives spark dialogue and reflection in your own practice. Join the conversation on X at @AGA_GIHN.
Gyanprakash A. Ketwaroo, MD, MSc, is associate professor of medicine, Yale University, New Haven, and chief of endoscopy at West Haven VA Medical Center, both in Connecticut. He is an associate editor for GI & Hepatology News.
Choose NSBBs, Not EVL, in Patients with Compensated Cirrhosis
BY ANAHITA RABIEE, MD, MHS
I strongly favor the use of non selective beta blockers (NSBBs) in patients with compensated cirrhosis, rather than endoscopy and esophageal variceal ligation (EVL) for primary prophylaxis.
Since the results of PREDESCI trial (β blockers to prevent decompensation of cirrhosis in patients with clinically significant portal hypertension (CSPH)) were published in 2019, there has been much debate on the role of screening endoscopy and EVL for primary prophylaxis. While many argue that a single randomized trial should not overturn long standing practice, several compelling reasons convince me to choose NSBBs, when possible.
Recent guidance from major liver societies now recommends NSBBs as first line therapy for CSPH. Yet, adoption in clinical practice remains inconsistent.
Here is why I believe NSBB represent a better solution:
Treating Upstream, Not Just a Local Treatment
NSBBs such as propranolol and nadolol decrease portal pressure by decreasing portal venous inflow through β1 and β2 adrenergic blockade. Carvedilol is often preferred given its additional α1 adrenergic blocking activity making it the most effective one in decreasing the portal pressure. Therefore, NSBBs address the upstream driver of decompensation by decreasing portal pressures.
EVL, in contrast, is a local fix that only prevents variceal bleeding. Ascites, not variceal bleeding, is the most common initial decompensating event and is associated with high mortality. Preventing all forms of decompensation is clearly preferable to preventing just one.
Broader Eligibility, More Patients Benefit
CSPH is defined as hepatic venous pressure gradient (HVPG)>10 mmHg, the threshold where increased portal venous inflow secondary to splanchnic vasodilation and hyperdynamic circulation drives the increase in portal hypertension. This threshold has been shown to strongly predict decompensation in patients with compensated disease.
While all patients with varices have CSPH, not all patients with CSPH have varices. They can be identified by other non invasive criteria such as cross sectional imaging showing collaterals, or liver stiffness and platelet thresholds that have been previously validated. By restricting intervention to those with large varices and offering only EVL, we miss the opportunity to intervene earlier and to a broader group that would benefit from this treatment.
Comprehensive Protection Without Repeated Endoscopies
Once on an appropriate NSBB dose, patients are protected against variceal bleeding (at least as effectively as EVL). This eliminates the need for repeated surveillance endoscopies to identify and treat large varices in otherwise compensated patients.
Better Tolerated and – In Many Cases – Overlaps With Existing Medication List!
While overtreatment is a concern, regular endoscopies every two years are also burdensome. Many patients already need beta blockers for cardiac conditions such as atrial fibrillation, ischemic heart disease or hypertension. Carvedilol, in particular, offers dual benefit for both hepatologists and cardiologists.
It is important to emphasize that these arguments apply to compensated cirrhosis. In decompensated disease, the approach changes. After a variceal bleed, both NSBBs and EVL are required for secondary prophylaxis. In patients with prior ascites but no variceal bleed, the benefit of NSBBs is less pronounced since decompensation has already occurred. In this setting, NSBBs can still be used selectively, but only if systolic blood pressure remains above 90 mmHg.
The evidence supporting NSBBs over EVL in compensated cirrhosis is not perfect, but few things in medicine are. Given current data, NSBBs should be the first line therapy in compensated cirrhosis with CSPH. Once a patient is on an appropriate and tolerated NSBB dose, routine endoscopic surveillance is unnecessary. Endoscopy should be reserved for those who cannot tolerate NSBBs, in whom EVL is then indicated if large varices are present.
Dr. Rabiee is based at the Yale School of Medicine, New Haven, Connecticut, and the Veterans Affairs Connecticut Healthcare System, West Haven, Connecticut. She has no disclosures in regard to this article.
Rethinking Screening and Surveillance in Barrett’s Esophagus: Navigating Controversies and Nuances
BY TAREK SAWAS, MD, MPH
Barrett’s esophagus (BE) is a precursor to esophageal adenocarcinoma (EAC). Despite our comprehensive guidelines, many of the day-to-day decisions still rely on clinical judgment and honest conversations with patients. This article explores common scenarios in which management decisions are nuanced and the right answer remains debatable.
Irregular Z-Line/Ultrashort Segment BE: Leave Or Watch It?
Few findings provoke more confusion than irregular Z-line or intestinal metaplasia (IM) < 1 cm at the gastroesophageal junction (GEJ). For years, we have debated whether these subtle changes represent a precursor to EAC or simply a benign variant. We have wrestled with how to handle these cases from whether we should take biopsies to how to perform surveillance.
The American College of Gastroenterology (ACG) guideline suggests that irregular Z-lines should not be routinely biopsied or surveyed. Similarly, the upcoming American Gastroenterology Association (AGA) surveillance guideline suggests against surveillance of IM<1 cm citing the low individual annual risk of progression to high-grade dysplasia (HGD) and EAC of 0.23% per year which is lower than that of non-dysplastic Barrett’s esophagus (NDBE). However, this is not the entire picture.
Despite the low per-patient risk, IM<1cm is highly prevalent with columnar mucosa observed in approximately 15% of patients undergoing upper endoscopy. This paradox is unsettling. While any one patient with IM<1 cm is unlikely to progress to EAC, the group accounts for a meaningful share of the EAC burden. Some experts have argued that this justifies routine biopsy and surveillance in all patients with visible columnar mucosa regardless of length. However, this approach risks overwhelming our surveillance infrastructure.
A recent decision modeling analysis suggested that at the lowest progression rates, either no surveillance or one-time endoscopy can be considered. Based on these data, I do not regularly biopsy ultrashort segments unless the mucosa appears suspicious. In those with IM<1 cm detected during a high-quality endoscopic exam, no follow-up is needed. However, if the exam is suboptimal, I perform a 1-time high-quality repeat exam. If there is no evidence of dysplasia then I do not pursue any further surveillance.
The One-Year Follow-Up Endoscopy: Is It Necessary?
Another controversy is the one-year follow-up endoscopy after an initial diagnosis of NDBE. Proponents of this approach cite the high proportion of post endoscopy esophageal neoplasia and cancer (PEEN/PEEC) detected in the first year after diagnosis (missed HGD/EAC). In fact, PEEN account for about a quarter of all HGD/EAC cases diagnosed during surveillance.
While this approach might mitigate PEEN/PEEC risk, it may not be necessary if the index endoscopy is high quality. To ensure high quality exams, several best practices have been proposed including:
- Use of high-definition white light endoscopy (HD-WLE) with chromoendoscopy (virtual or dye based)
- Appropriate inspection time (1 minute per cm of circumferential BE)
- Accurate documentation using the Prague criteria
- Adherence to the Seattle protocol with additional targeted biopsies
If the index endoscopy meets these quality metrics, I typically do not bring the patient back at one year. However, if the exam quality is in question, then I repeat it at one year to establish a reliable baseline and rule out prevalent neoplasia.
Surveillance In NDBE: After BOSS, Do We Rethink Everything?
The recently published BOSS trial (Barrett’s Oesophagus Surveillance Study) has reignited the debate over the value of endoscopic surveillance in NDBE. In this study, 3,453 patients with NDBE across the UK were randomized to either surveillance endoscopy every two years or endoscopy only as clinically indicated. After a median follow-up of 12.8 years, the trial found no significant difference in all-cause mortality between the two groups.
While these findings are important, they should be interpreted with caution. First, the primary endpoint, all-cause mortality, is not optimal for evaluating surveillance for EAC. Surveillance is not intended to reduce all-cause mortality but rather to reduce EAC–related mortality. Second, a substantial number of patients in the no surveillance group still underwent endoscopy at intervals that were not meaningfully different from those in the surveillance group. If both groups receive similar exposure to endoscopy, the comparison loses power. Lastly, the trial was underpowered due to overestimation of progression risk during its initial design. As we have since learned, the risk of progression of NDBE is lower than originally assumed.
So where do we stand now? For me, the BOSS trial does not negate the value of surveillance. it reminds us that a one-size-fits-all approach is inefficient, and our strategy must be risk based. For low-risk individuals, particularly older adults with short-segment NDBE, surveillance may offer little benefit. But in healthier, younger patients with longer segments or additional risk factors, surveillance remains an essential tool for early neoplasia detection.
When to Stop Surveillance
Perhaps the most under-discussed point is when to stop surveillance. Existing guidelines do not account for competing mortality risks unrelated to EAC or provide specific recommendations regarding cessation of surveillance. The desired benefits of surveillance likely diminish with advanced age and greater comorbidity because of lower life expectancy and ineligibility for definitive therapy for EAC.
A recent modeling study found that the optimal ages for last surveillance were 81, 80, 77, and 73 years for men with no, mild, moderate, and severe comorbidity respectively and 75, 73, 73, and 69 years for women. In my practice, I discuss surveillance cessation in patients older than 75 based on their comorbidities. If the risk of progression is outweighed by the risk of the procedure or by the reality of limited life expectancy, we should not hesitate to consider surveillance cessation.
In summary, high-quality endoscopic exam in appropriately selected patients remains the cornerstone of BE surveillance. A more personalized, risk-based approach is needed taking into account competing comorbidities. Emerging technology through risk stratification tools such as biomarkers and artificial intelligence may refine our approach and help address the current limitations.
Dr. Sawas is based at the University of Texas Southwestern, Dallas, Texas. He has no disclosures in regard to this article.
Dear colleagues,
In the dynamic field of medicine, long-held practices are being reevaluated in light of new evidence and evolving standards of practice.
Dr. Anahita Rabiee discusses the importance of prioritizing non-selective beta blockers (NSBB) over endoscopic variceal ligation (EVL) in the primary prophylaxis of variceal bleeding in patients with compensated cirrhosis. Drawing on data from the PREDESCI trial and real-world experience, she argues that NSBB address the upstream driver—portal hypertension—more broadly and effectively than EVL. In a complementary piece, Dr. Tarek Sawas explores the nuanced landscape of screening and surveillance in Barrett’s esophagus. From how to manage irregular Z-lines, to rethinking the need for 1-year follow-up endoscopies and interpreting the implications of the BOSS trial, Dr. Sawas advocates for a more personalized, risk-based approach.
We hope these perspectives spark dialogue and reflection in your own practice. Join the conversation on X at @AGA_GIHN.
Gyanprakash A. Ketwaroo, MD, MSc, is associate professor of medicine, Yale University, New Haven, and chief of endoscopy at West Haven VA Medical Center, both in Connecticut. He is an associate editor for GI & Hepatology News.
Choose NSBBs, Not EVL, in Patients with Compensated Cirrhosis
BY ANAHITA RABIEE, MD, MHS
I strongly favor the use of non selective beta blockers (NSBBs) in patients with compensated cirrhosis, rather than endoscopy and esophageal variceal ligation (EVL) for primary prophylaxis.
Since the results of PREDESCI trial (β blockers to prevent decompensation of cirrhosis in patients with clinically significant portal hypertension (CSPH)) were published in 2019, there has been much debate on the role of screening endoscopy and EVL for primary prophylaxis. While many argue that a single randomized trial should not overturn long standing practice, several compelling reasons convince me to choose NSBBs, when possible.
Recent guidance from major liver societies now recommends NSBBs as first line therapy for CSPH. Yet, adoption in clinical practice remains inconsistent.
Here is why I believe NSBB represent a better solution:
Treating Upstream, Not Just a Local Treatment
NSBBs such as propranolol and nadolol decrease portal pressure by decreasing portal venous inflow through β1 and β2 adrenergic blockade. Carvedilol is often preferred given its additional α1 adrenergic blocking activity making it the most effective one in decreasing the portal pressure. Therefore, NSBBs address the upstream driver of decompensation by decreasing portal pressures.
EVL, in contrast, is a local fix that only prevents variceal bleeding. Ascites, not variceal bleeding, is the most common initial decompensating event and is associated with high mortality. Preventing all forms of decompensation is clearly preferable to preventing just one.
Broader Eligibility, More Patients Benefit
CSPH is defined as hepatic venous pressure gradient (HVPG)>10 mmHg, the threshold where increased portal venous inflow secondary to splanchnic vasodilation and hyperdynamic circulation drives the increase in portal hypertension. This threshold has been shown to strongly predict decompensation in patients with compensated disease.
While all patients with varices have CSPH, not all patients with CSPH have varices. They can be identified by other non invasive criteria such as cross sectional imaging showing collaterals, or liver stiffness and platelet thresholds that have been previously validated. By restricting intervention to those with large varices and offering only EVL, we miss the opportunity to intervene earlier and to a broader group that would benefit from this treatment.
Comprehensive Protection Without Repeated Endoscopies
Once on an appropriate NSBB dose, patients are protected against variceal bleeding (at least as effectively as EVL). This eliminates the need for repeated surveillance endoscopies to identify and treat large varices in otherwise compensated patients.
Better Tolerated and – In Many Cases – Overlaps With Existing Medication List!
While overtreatment is a concern, regular endoscopies every two years are also burdensome. Many patients already need beta blockers for cardiac conditions such as atrial fibrillation, ischemic heart disease or hypertension. Carvedilol, in particular, offers dual benefit for both hepatologists and cardiologists.
It is important to emphasize that these arguments apply to compensated cirrhosis. In decompensated disease, the approach changes. After a variceal bleed, both NSBBs and EVL are required for secondary prophylaxis. In patients with prior ascites but no variceal bleed, the benefit of NSBBs is less pronounced since decompensation has already occurred. In this setting, NSBBs can still be used selectively, but only if systolic blood pressure remains above 90 mmHg.
The evidence supporting NSBBs over EVL in compensated cirrhosis is not perfect, but few things in medicine are. Given current data, NSBBs should be the first line therapy in compensated cirrhosis with CSPH. Once a patient is on an appropriate and tolerated NSBB dose, routine endoscopic surveillance is unnecessary. Endoscopy should be reserved for those who cannot tolerate NSBBs, in whom EVL is then indicated if large varices are present.
Dr. Rabiee is based at the Yale School of Medicine, New Haven, Connecticut, and the Veterans Affairs Connecticut Healthcare System, West Haven, Connecticut. She has no disclosures in regard to this article.
Rethinking Screening and Surveillance in Barrett’s Esophagus: Navigating Controversies and Nuances
BY TAREK SAWAS, MD, MPH
Barrett’s esophagus (BE) is a precursor to esophageal adenocarcinoma (EAC). Despite our comprehensive guidelines, many of the day-to-day decisions still rely on clinical judgment and honest conversations with patients. This article explores common scenarios in which management decisions are nuanced and the right answer remains debatable.
Irregular Z-Line/Ultrashort Segment BE: Leave Or Watch It?
Few findings provoke more confusion than irregular Z-line or intestinal metaplasia (IM) < 1 cm at the gastroesophageal junction (GEJ). For years, we have debated whether these subtle changes represent a precursor to EAC or simply a benign variant. We have wrestled with how to handle these cases from whether we should take biopsies to how to perform surveillance.
The American College of Gastroenterology (ACG) guideline suggests that irregular Z-lines should not be routinely biopsied or surveyed. Similarly, the upcoming American Gastroenterology Association (AGA) surveillance guideline suggests against surveillance of IM<1 cm citing the low individual annual risk of progression to high-grade dysplasia (HGD) and EAC of 0.23% per year which is lower than that of non-dysplastic Barrett’s esophagus (NDBE). However, this is not the entire picture.
Despite the low per-patient risk, IM<1cm is highly prevalent with columnar mucosa observed in approximately 15% of patients undergoing upper endoscopy. This paradox is unsettling. While any one patient with IM<1 cm is unlikely to progress to EAC, the group accounts for a meaningful share of the EAC burden. Some experts have argued that this justifies routine biopsy and surveillance in all patients with visible columnar mucosa regardless of length. However, this approach risks overwhelming our surveillance infrastructure.
A recent decision modeling analysis suggested that at the lowest progression rates, either no surveillance or one-time endoscopy can be considered. Based on these data, I do not regularly biopsy ultrashort segments unless the mucosa appears suspicious. In those with IM<1 cm detected during a high-quality endoscopic exam, no follow-up is needed. However, if the exam is suboptimal, I perform a 1-time high-quality repeat exam. If there is no evidence of dysplasia then I do not pursue any further surveillance.
The One-Year Follow-Up Endoscopy: Is It Necessary?
Another controversy is the one-year follow-up endoscopy after an initial diagnosis of NDBE. Proponents of this approach cite the high proportion of post endoscopy esophageal neoplasia and cancer (PEEN/PEEC) detected in the first year after diagnosis (missed HGD/EAC). In fact, PEEN account for about a quarter of all HGD/EAC cases diagnosed during surveillance.
While this approach might mitigate PEEN/PEEC risk, it may not be necessary if the index endoscopy is high quality. To ensure high quality exams, several best practices have been proposed including:
- Use of high-definition white light endoscopy (HD-WLE) with chromoendoscopy (virtual or dye based)
- Appropriate inspection time (1 minute per cm of circumferential BE)
- Accurate documentation using the Prague criteria
- Adherence to the Seattle protocol with additional targeted biopsies
If the index endoscopy meets these quality metrics, I typically do not bring the patient back at one year. However, if the exam quality is in question, then I repeat it at one year to establish a reliable baseline and rule out prevalent neoplasia.
Surveillance In NDBE: After BOSS, Do We Rethink Everything?
The recently published BOSS trial (Barrett’s Oesophagus Surveillance Study) has reignited the debate over the value of endoscopic surveillance in NDBE. In this study, 3,453 patients with NDBE across the UK were randomized to either surveillance endoscopy every two years or endoscopy only as clinically indicated. After a median follow-up of 12.8 years, the trial found no significant difference in all-cause mortality between the two groups.
While these findings are important, they should be interpreted with caution. First, the primary endpoint, all-cause mortality, is not optimal for evaluating surveillance for EAC. Surveillance is not intended to reduce all-cause mortality but rather to reduce EAC–related mortality. Second, a substantial number of patients in the no surveillance group still underwent endoscopy at intervals that were not meaningfully different from those in the surveillance group. If both groups receive similar exposure to endoscopy, the comparison loses power. Lastly, the trial was underpowered due to overestimation of progression risk during its initial design. As we have since learned, the risk of progression of NDBE is lower than originally assumed.
So where do we stand now? For me, the BOSS trial does not negate the value of surveillance. it reminds us that a one-size-fits-all approach is inefficient, and our strategy must be risk based. For low-risk individuals, particularly older adults with short-segment NDBE, surveillance may offer little benefit. But in healthier, younger patients with longer segments or additional risk factors, surveillance remains an essential tool for early neoplasia detection.
When to Stop Surveillance
Perhaps the most under-discussed point is when to stop surveillance. Existing guidelines do not account for competing mortality risks unrelated to EAC or provide specific recommendations regarding cessation of surveillance. The desired benefits of surveillance likely diminish with advanced age and greater comorbidity because of lower life expectancy and ineligibility for definitive therapy for EAC.
A recent modeling study found that the optimal ages for last surveillance were 81, 80, 77, and 73 years for men with no, mild, moderate, and severe comorbidity respectively and 75, 73, 73, and 69 years for women. In my practice, I discuss surveillance cessation in patients older than 75 based on their comorbidities. If the risk of progression is outweighed by the risk of the procedure or by the reality of limited life expectancy, we should not hesitate to consider surveillance cessation.
In summary, high-quality endoscopic exam in appropriately selected patients remains the cornerstone of BE surveillance. A more personalized, risk-based approach is needed taking into account competing comorbidities. Emerging technology through risk stratification tools such as biomarkers and artificial intelligence may refine our approach and help address the current limitations.
Dr. Sawas is based at the University of Texas Southwestern, Dallas, Texas. He has no disclosures in regard to this article.
Lower Gastrointestinal Bleeding: Two Perspectives
Dear colleagues,
: What is the role and optimal timing of colonoscopy? How can we best utilize radiologic studies like CTA or tagged RBC scans? How should we manage patients with recurrent or intermittent bleeding that defies localization?
In this issue of Perspectives, Dr. David Wan, Dr. Fredella Lee, and Dr. Zeyad Metwalli offer their expert insights on these difficult questions. Dr. Wan, drawing on over 15 years of experience as a GI hospitalist, shares – along with his coauthor Dr. Lee – a pragmatic approach to LGIB based on clinical patterns, evolving data, and multidisciplinary collaboration. Dr. Metwalli provides the interventional radiologist’s perspective, highlighting how angiographic techniques can complement GI management and introducing novel IR strategies for patients with recurrent or elusive bleeding.
We hope their perspectives will offer valuable guidance for your practice. Join the conversation on X at @AGA_GIHN.
Gyanprakash A. Ketwaroo, MD, MSc, is associate professor of medicine, Yale University, New Haven, and chief of endoscopy at West Haven VA Medical Center, both in Connecticut. He is an associate editor for GI & Hepatology News.
Management of Lower Gastrointestinal Bleeds: GI Perspective
BY FREDELLA LEE, MD; DAVID WAN, MD
Acute lower gastrointestinal bleeding (LGIB) presents unique challenges. Much of this stems from the natural history of diverticular bleeding, the most common etiology of LGIB.
First, while bleeding can be severe, most will spontaneously stop. Second, despite our best efforts with imaging or colonoscopy, finding an intervenable lesion is rare. Third, LGIB has significant rates of rebleeding that are unpredictable.
While serving as a GI hospitalist for 15 years and after managing over 300 cases of LGIB, I often find myself frustrated and colonoscopy feels futile. So how can we rationally approach these patients? We will focus on three clinical questions to develop a framework for LGIB management.
- What is the role and timing for a colonoscopy?
- How do we best utilize radiologic tests?
- How can we prevent recurrent LGIB?
The Role of Colonoscopy
Traditionally, colonoscopy within 24 hours of presentation was recommended. This was based on retrospective cohort data showing higher endoscopic intervention rates and better clinical outcomes. However, this protocol requires patients to drink a significant volume of bowel preparation over a few hours (often requiring an NGT) to achieve clear rectal effluent. Moreover, one needs to mobilize a team (i.e., nurse, technician, anesthesiologist, and gastroenterologist), and find an appropriate location to scope (i.e., ED, ICU, or OR), Understandably, this is challenging, especially overnight. When the therapeutic yield is relatively low, this approach quickly loses enthusiasm.
Importantly, meta-analyses of the randomized controlled trials, have shown that urgent colonoscopies (<24 hours upon presentation), compared to elective colonoscopies (>24 hours upon presentation), do not improve clinical outcomes such as re-bleeding rates, transfusion requirements, mortality, or length of stay. In these studies, the endoscopic intervention rates were 17-34%, however, observational data shows rates of only 8%. In our practice, we will use a clear cap attachment device and water jet irrigation to increase the odds of detecting an active source of bleeding. Colonoscopy has a diagnostic yield of 95% – despite its low therapeutic yield; and while diverticular bleeds constitute up to 64% of cases, one does not want to miss colorectal cancer or other diagnoses. Regardless, there is generally no urgency to perform a colonoscopy. To quote a colleague, Dr. Elizabeth Ross, “there is no such thing as door-to-butt time.”
The Role of Radiology
Given the limits of colonoscopy, can radiographic tests such as computed tomography angiography (CTA) or tagged red blood cell (RBC) scan be helpful? Multiple studies have suggested using CTA as the initial diagnostic test. The advantages of CTAs are:
- Fast, readily available, and does not require a bowel preparation
- If negative, CTAs portend a good prognosis and make it highly unlikely to detect active extravasation on visceral angiography
- If positive, can localize the source of bleed and increase the success of intervention
Whether a positive CTA should be followed with a colonoscopy or visceral angiography remains unclear. Studies show that positive CTAs increase the detection rate of stigmata of recent hemorrhage on colonoscopy. Positive CTAs can also identify a target for embolization by interventional radiology (IR). Though an important caveat is that the success rate of embolization is highest when performed within 90 minutes of a positive CTA. This highlights that if you have IR availability, it is critical to have clear communication, a well-defined protocol, and collaboration among disciplines (i.e., ED, medical team, GI, and IR).
At our institution, we have implemented a CTA-guided protocol for severe LGIB. Those with positive CTAs are referred immediately to IR for embolization. If the embolization is unsuccessful or CTA is negative, the patient will be planned for a non-urgent inpatient colonoscopy. However, our unpublished data and other studies have shown that the overall CTA positivity rates are only between 16-22%. Moreover, one randomized controlled trial comparing CTA versus colonoscopy as an initial test did not show any meaningful difference in clinical outcomes. Thus, the benefit of CTA and the best approach to positive CTAs remains in question.
Lastly, people often ask about the utility of RBC nuclear scans. While they can detect bleeds at a slower rate (as low as 0.1 mL/min) compared to CTA (at least 0.4 mL/min), there are many limitations. RBC scans take time, are not available 24-7, and cannot precisely localize the site of bleeding. Therefore, we rarely recommend them for LGIB.
Approach to Recurrent Diverticular Bleeding
Unfortunately, diverticular bleeding recurs in the hospital 14% of the time and up to 25% at 5 years. When this occurs, is it worthwhile to repeat another colonoscopy or CTA?
Given the lack of clear data, we have adopted a shared decision-making framework with patients. Oftentimes, these patients are older and have significant co-morbidities, and undergoing bowel preparation, anesthesia, and colonoscopy is not trivial. If the patient is stable and prior work-up has excluded pertinent alternative diagnoses other than diverticular bleeding, then we tell patients the chance of finding an intervenable lesion is low and opt for conservative management. Meanwhile, if the patient has persistent, hemodynamically significant bleeding, we recommend a CTA based on the rationale discussed previously.
The most important clinical decision may not be about scoping or obtaining a CTA – it is medication management. If they are taking NSAIDs, they should be discontinued. If antiplatelet or anticoagulation agents were held, they should be restarted promptly in individuals with significant thrombotic risk given studies showing that while rebleeding rates may increase, overall mortality decreases.
In summary, managing LGIB and altering its natural history with either endoscopic or radiographic means is challenging. More studies are needed to guide the optimal approach. Reassuringly, most bleeding self-resolves and patients have good clinical outcomes.
Dr. Lee is a resident physician at New York Presbyterian Weill Cornell Medical Center, New York, NY. Dr. Wan is associate professor of clinical medicine at Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, N.Y. They declare no conflicts of interest.
Lower Gastrointestinal Bleeding: An Interventional Radiologist’s Perspective
BY ZEYAD METWALLI, MD, FSIR
When colonoscopy fails to localize and/or stop lower gastrointestinal bleeding (LGIB), catheter angiography has been commonly employed as a tool for both diagnosis and treatment of bleeding with embolization. Nuclear medicine or CT imaging studies can serve as useful adjuncts for confirming active bleeding and localizing the site of bleeding prior to angiography, particularly if this information is not provided by colonoscopy. Provocative mesenteric angiography has also become increasingly popular as a troubleshooting technique in patients with initially negative angiography.
Localization of Lower Gastrointestinal Bleeding
Radionuclide technetium-99m-lableled red blood cell scintigraphy (RBCS), also known as tagged RBC scintigraphy, has been in use since the early 1980s for investigation of acute gastrointestinal bleeding. RBCS has a high sensitivity for detection of active bleeding with a theoretical ability to detect bleeding at rates as low as 0.04-0.2 mL/minute.
Imaging protocols vary but should include dynamic images, which may aid in localization of bleeding. The relatively long half-life of the tracer used for imaging allows for delayed imaging 12 to 24 hours after injection. This can be useful to confirm active bleeding, particularly when bleeding is intermittent and is not visible on initial images.
With the advent of computed tomography angiography (CTA), which continues to increase in speed, imaging quality and availability, the use of RBCS for evaluation of LGIB has declined. CTA is quicker to perform than RBCS and allows for detection of bleeding as well as accurate anatomic localization, which can guide interventions.
CTA provides a more comprehensive anatomic evaluation, which can aid in the diagnosis of a wide variety of intra-abdominal issues. Conversely, CTA may be less sensitive than RBCS for detection of slower acute bleeding, detecting bleeding at rates of 0.1-1 mL/min. In addition, intermittent bleeding which has temporarily stopped at the time of CTA may evade detection.
Lastly, CTA may not be appropriate in patients with impaired renal function due to risk of contrast-induced nephropathy, particularly in patients with acute kidney injury, which commonly afflicts hospitalized patients with LGIB. Prophylaxis with normal saline hydration should be employed aggressively in patients with impaired renal function, particularly when eGFR is less than 30 mL/minute. Iodinated contrast should be used judiciously in these patients.
In clinical practice, CTA and RBCS have a similar ability to confirm the presence or absence of clinically significant active gastrointestinal bleeding. Given the greater ability to rapidly localize the bleeding site with CTA, this is generally preferred over RBCS unless there is a contraindication to performing CTA, such as severe contrast allergy or high risk for development of contrast-induced nephropathy.
Role of Catheter Angiography and Embolization
Mesenteric angiography is a well-established technique for both detection and treatment of LGIB. Hemodynamic instability and need for packed RBC transfusion increases the likelihood of positive angiography. Limitations include reduced sensitivity for detection of bleeding slower than 0.5-1 mL/minute as well as the intermittent nature of LGIB, which will often resolve spontaneously. Angiography is variably successful in the literature with a diagnostic yield between 40-80%, which encompasses the rate of success in my own practice.
Once bleeding is identified, microcatheter placement within the feeding vessel as close as possible to the site of bleeding is important to ensure treatment efficacy and to limit risk of complications such as non-target embolization and bowel ischemia. Once the feeding vessel is selected with a microcatheter, embolization can be accomplished with a wide variety of tools including metallic coils, liquid embolic agents, and particles. In the treatment of LGIB, liquid embolic agents (e.g., n-butyl cyanoacrylate or NBCA, ethylene vinyl alcohol copolymer, etc.) and particles should be used judiciously as distal penetration increases the risk of bowel ischemia and procedure-related morbidity. For this reason, metallic coils are often preferred in the treatment of LGIB.
Although the source of bleeding is variable and may include diverticulosis, recent polypectomy, ulcer, tumor or angiodysplasia, the techniques employed are similar. Accurate and distal microcatheter selection is a key driver for successful embolization and minimizing the risk of bowel ischemia. Small intestinal bleeds can be challenging to treat due to the redundant supply of the arterial arcades supplying small bowel and may require occlusion of several branches to achieve hemostasis. This approach must be balanced with the risk of developing ischemia after embolization. Angiodysplasia, a less frequently encountered culprit of LGIB, may also be managed with selective embolization with many reports of successful treatment with liquid embolic agents such as NBCA mixed with ethiodized oil.
Provocative Mesenteric Angiography for Occult Bleeding
When initial angiography in a patient with suspected active LGIB is negative, provocative angiography can be considered to uncover an intermittent bleed. This may be particularly helpful in a patient where active bleeding is confirmed on a prior diagnostic test.
The approach to provocative mesenteric angiography varies by center, and a variety of agents have been used to provoke bleeding including heparin, vasodilators (i.e., nitroglycerin, verapamil, etc.) and thrombolytics (i.e., tPA), often in combination. Thrombolytics can be administered directly into the territory of interest (i.e., superior mesenteric or inferior mesenteric artery) while heparin may be administered systemically or directly into the catheterized artery. Reported success rates for provoking angiographically visible bleeding vary, but most larger series report a 40-50% success rate. The newly detected bleeding can then be treated with either embolization or surgery. A surgeon should be involved and available when provocative angiography is planned should bleeding fail to be controlled by embolization.
In summary, when colonoscopy fails to identify or control lower gastrointestinal bleeding (LGIB), imaging techniques such as RBCS and CTA play a crucial role in localizing active bleeding. While RBCS is highly sensitive, especially for intermittent or slow bleeding, CTA offers faster, more detailed anatomical information and is typically preferred unless contraindicated by renal issues or contrast allergies. Catheter-based mesenteric angiography is a well-established method for both diagnosing and treating LGIB, often using metallic coils to minimize complications like bowel ischemia. In cases where initial angiography is negative, provocative angiography – using agents like heparin or thrombolytics – may help unmask intermittent bleeding, allowing for targeted embolization or surgical intervention.
Dr. Metwalli is associate professor in the Department of Interventional Radiology, Division of Diagnostic Imaging, at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, Texas. He declares no conflicts of interest.
Dear colleagues,
: What is the role and optimal timing of colonoscopy? How can we best utilize radiologic studies like CTA or tagged RBC scans? How should we manage patients with recurrent or intermittent bleeding that defies localization?
In this issue of Perspectives, Dr. David Wan, Dr. Fredella Lee, and Dr. Zeyad Metwalli offer their expert insights on these difficult questions. Dr. Wan, drawing on over 15 years of experience as a GI hospitalist, shares – along with his coauthor Dr. Lee – a pragmatic approach to LGIB based on clinical patterns, evolving data, and multidisciplinary collaboration. Dr. Metwalli provides the interventional radiologist’s perspective, highlighting how angiographic techniques can complement GI management and introducing novel IR strategies for patients with recurrent or elusive bleeding.
We hope their perspectives will offer valuable guidance for your practice. Join the conversation on X at @AGA_GIHN.
Gyanprakash A. Ketwaroo, MD, MSc, is associate professor of medicine, Yale University, New Haven, and chief of endoscopy at West Haven VA Medical Center, both in Connecticut. He is an associate editor for GI & Hepatology News.
Management of Lower Gastrointestinal Bleeds: GI Perspective
BY FREDELLA LEE, MD; DAVID WAN, MD
Acute lower gastrointestinal bleeding (LGIB) presents unique challenges. Much of this stems from the natural history of diverticular bleeding, the most common etiology of LGIB.
First, while bleeding can be severe, most will spontaneously stop. Second, despite our best efforts with imaging or colonoscopy, finding an intervenable lesion is rare. Third, LGIB has significant rates of rebleeding that are unpredictable.
While serving as a GI hospitalist for 15 years and after managing over 300 cases of LGIB, I often find myself frustrated and colonoscopy feels futile. So how can we rationally approach these patients? We will focus on three clinical questions to develop a framework for LGIB management.
- What is the role and timing for a colonoscopy?
- How do we best utilize radiologic tests?
- How can we prevent recurrent LGIB?
The Role of Colonoscopy
Traditionally, colonoscopy within 24 hours of presentation was recommended. This was based on retrospective cohort data showing higher endoscopic intervention rates and better clinical outcomes. However, this protocol requires patients to drink a significant volume of bowel preparation over a few hours (often requiring an NGT) to achieve clear rectal effluent. Moreover, one needs to mobilize a team (i.e., nurse, technician, anesthesiologist, and gastroenterologist), and find an appropriate location to scope (i.e., ED, ICU, or OR), Understandably, this is challenging, especially overnight. When the therapeutic yield is relatively low, this approach quickly loses enthusiasm.
Importantly, meta-analyses of the randomized controlled trials, have shown that urgent colonoscopies (<24 hours upon presentation), compared to elective colonoscopies (>24 hours upon presentation), do not improve clinical outcomes such as re-bleeding rates, transfusion requirements, mortality, or length of stay. In these studies, the endoscopic intervention rates were 17-34%, however, observational data shows rates of only 8%. In our practice, we will use a clear cap attachment device and water jet irrigation to increase the odds of detecting an active source of bleeding. Colonoscopy has a diagnostic yield of 95% – despite its low therapeutic yield; and while diverticular bleeds constitute up to 64% of cases, one does not want to miss colorectal cancer or other diagnoses. Regardless, there is generally no urgency to perform a colonoscopy. To quote a colleague, Dr. Elizabeth Ross, “there is no such thing as door-to-butt time.”
The Role of Radiology
Given the limits of colonoscopy, can radiographic tests such as computed tomography angiography (CTA) or tagged red blood cell (RBC) scan be helpful? Multiple studies have suggested using CTA as the initial diagnostic test. The advantages of CTAs are:
- Fast, readily available, and does not require a bowel preparation
- If negative, CTAs portend a good prognosis and make it highly unlikely to detect active extravasation on visceral angiography
- If positive, can localize the source of bleed and increase the success of intervention
Whether a positive CTA should be followed with a colonoscopy or visceral angiography remains unclear. Studies show that positive CTAs increase the detection rate of stigmata of recent hemorrhage on colonoscopy. Positive CTAs can also identify a target for embolization by interventional radiology (IR). Though an important caveat is that the success rate of embolization is highest when performed within 90 minutes of a positive CTA. This highlights that if you have IR availability, it is critical to have clear communication, a well-defined protocol, and collaboration among disciplines (i.e., ED, medical team, GI, and IR).
At our institution, we have implemented a CTA-guided protocol for severe LGIB. Those with positive CTAs are referred immediately to IR for embolization. If the embolization is unsuccessful or CTA is negative, the patient will be planned for a non-urgent inpatient colonoscopy. However, our unpublished data and other studies have shown that the overall CTA positivity rates are only between 16-22%. Moreover, one randomized controlled trial comparing CTA versus colonoscopy as an initial test did not show any meaningful difference in clinical outcomes. Thus, the benefit of CTA and the best approach to positive CTAs remains in question.
Lastly, people often ask about the utility of RBC nuclear scans. While they can detect bleeds at a slower rate (as low as 0.1 mL/min) compared to CTA (at least 0.4 mL/min), there are many limitations. RBC scans take time, are not available 24-7, and cannot precisely localize the site of bleeding. Therefore, we rarely recommend them for LGIB.
Approach to Recurrent Diverticular Bleeding
Unfortunately, diverticular bleeding recurs in the hospital 14% of the time and up to 25% at 5 years. When this occurs, is it worthwhile to repeat another colonoscopy or CTA?
Given the lack of clear data, we have adopted a shared decision-making framework with patients. Oftentimes, these patients are older and have significant co-morbidities, and undergoing bowel preparation, anesthesia, and colonoscopy is not trivial. If the patient is stable and prior work-up has excluded pertinent alternative diagnoses other than diverticular bleeding, then we tell patients the chance of finding an intervenable lesion is low and opt for conservative management. Meanwhile, if the patient has persistent, hemodynamically significant bleeding, we recommend a CTA based on the rationale discussed previously.
The most important clinical decision may not be about scoping or obtaining a CTA – it is medication management. If they are taking NSAIDs, they should be discontinued. If antiplatelet or anticoagulation agents were held, they should be restarted promptly in individuals with significant thrombotic risk given studies showing that while rebleeding rates may increase, overall mortality decreases.
In summary, managing LGIB and altering its natural history with either endoscopic or radiographic means is challenging. More studies are needed to guide the optimal approach. Reassuringly, most bleeding self-resolves and patients have good clinical outcomes.
Dr. Lee is a resident physician at New York Presbyterian Weill Cornell Medical Center, New York, NY. Dr. Wan is associate professor of clinical medicine at Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, N.Y. They declare no conflicts of interest.
Lower Gastrointestinal Bleeding: An Interventional Radiologist’s Perspective
BY ZEYAD METWALLI, MD, FSIR
When colonoscopy fails to localize and/or stop lower gastrointestinal bleeding (LGIB), catheter angiography has been commonly employed as a tool for both diagnosis and treatment of bleeding with embolization. Nuclear medicine or CT imaging studies can serve as useful adjuncts for confirming active bleeding and localizing the site of bleeding prior to angiography, particularly if this information is not provided by colonoscopy. Provocative mesenteric angiography has also become increasingly popular as a troubleshooting technique in patients with initially negative angiography.
Localization of Lower Gastrointestinal Bleeding
Radionuclide technetium-99m-lableled red blood cell scintigraphy (RBCS), also known as tagged RBC scintigraphy, has been in use since the early 1980s for investigation of acute gastrointestinal bleeding. RBCS has a high sensitivity for detection of active bleeding with a theoretical ability to detect bleeding at rates as low as 0.04-0.2 mL/minute.
Imaging protocols vary but should include dynamic images, which may aid in localization of bleeding. The relatively long half-life of the tracer used for imaging allows for delayed imaging 12 to 24 hours after injection. This can be useful to confirm active bleeding, particularly when bleeding is intermittent and is not visible on initial images.
With the advent of computed tomography angiography (CTA), which continues to increase in speed, imaging quality and availability, the use of RBCS for evaluation of LGIB has declined. CTA is quicker to perform than RBCS and allows for detection of bleeding as well as accurate anatomic localization, which can guide interventions.
CTA provides a more comprehensive anatomic evaluation, which can aid in the diagnosis of a wide variety of intra-abdominal issues. Conversely, CTA may be less sensitive than RBCS for detection of slower acute bleeding, detecting bleeding at rates of 0.1-1 mL/min. In addition, intermittent bleeding which has temporarily stopped at the time of CTA may evade detection.
Lastly, CTA may not be appropriate in patients with impaired renal function due to risk of contrast-induced nephropathy, particularly in patients with acute kidney injury, which commonly afflicts hospitalized patients with LGIB. Prophylaxis with normal saline hydration should be employed aggressively in patients with impaired renal function, particularly when eGFR is less than 30 mL/minute. Iodinated contrast should be used judiciously in these patients.
In clinical practice, CTA and RBCS have a similar ability to confirm the presence or absence of clinically significant active gastrointestinal bleeding. Given the greater ability to rapidly localize the bleeding site with CTA, this is generally preferred over RBCS unless there is a contraindication to performing CTA, such as severe contrast allergy or high risk for development of contrast-induced nephropathy.
Role of Catheter Angiography and Embolization
Mesenteric angiography is a well-established technique for both detection and treatment of LGIB. Hemodynamic instability and need for packed RBC transfusion increases the likelihood of positive angiography. Limitations include reduced sensitivity for detection of bleeding slower than 0.5-1 mL/minute as well as the intermittent nature of LGIB, which will often resolve spontaneously. Angiography is variably successful in the literature with a diagnostic yield between 40-80%, which encompasses the rate of success in my own practice.
Once bleeding is identified, microcatheter placement within the feeding vessel as close as possible to the site of bleeding is important to ensure treatment efficacy and to limit risk of complications such as non-target embolization and bowel ischemia. Once the feeding vessel is selected with a microcatheter, embolization can be accomplished with a wide variety of tools including metallic coils, liquid embolic agents, and particles. In the treatment of LGIB, liquid embolic agents (e.g., n-butyl cyanoacrylate or NBCA, ethylene vinyl alcohol copolymer, etc.) and particles should be used judiciously as distal penetration increases the risk of bowel ischemia and procedure-related morbidity. For this reason, metallic coils are often preferred in the treatment of LGIB.
Although the source of bleeding is variable and may include diverticulosis, recent polypectomy, ulcer, tumor or angiodysplasia, the techniques employed are similar. Accurate and distal microcatheter selection is a key driver for successful embolization and minimizing the risk of bowel ischemia. Small intestinal bleeds can be challenging to treat due to the redundant supply of the arterial arcades supplying small bowel and may require occlusion of several branches to achieve hemostasis. This approach must be balanced with the risk of developing ischemia after embolization. Angiodysplasia, a less frequently encountered culprit of LGIB, may also be managed with selective embolization with many reports of successful treatment with liquid embolic agents such as NBCA mixed with ethiodized oil.
Provocative Mesenteric Angiography for Occult Bleeding
When initial angiography in a patient with suspected active LGIB is negative, provocative angiography can be considered to uncover an intermittent bleed. This may be particularly helpful in a patient where active bleeding is confirmed on a prior diagnostic test.
The approach to provocative mesenteric angiography varies by center, and a variety of agents have been used to provoke bleeding including heparin, vasodilators (i.e., nitroglycerin, verapamil, etc.) and thrombolytics (i.e., tPA), often in combination. Thrombolytics can be administered directly into the territory of interest (i.e., superior mesenteric or inferior mesenteric artery) while heparin may be administered systemically or directly into the catheterized artery. Reported success rates for provoking angiographically visible bleeding vary, but most larger series report a 40-50% success rate. The newly detected bleeding can then be treated with either embolization or surgery. A surgeon should be involved and available when provocative angiography is planned should bleeding fail to be controlled by embolization.
In summary, when colonoscopy fails to identify or control lower gastrointestinal bleeding (LGIB), imaging techniques such as RBCS and CTA play a crucial role in localizing active bleeding. While RBCS is highly sensitive, especially for intermittent or slow bleeding, CTA offers faster, more detailed anatomical information and is typically preferred unless contraindicated by renal issues or contrast allergies. Catheter-based mesenteric angiography is a well-established method for both diagnosing and treating LGIB, often using metallic coils to minimize complications like bowel ischemia. In cases where initial angiography is negative, provocative angiography – using agents like heparin or thrombolytics – may help unmask intermittent bleeding, allowing for targeted embolization or surgical intervention.
Dr. Metwalli is associate professor in the Department of Interventional Radiology, Division of Diagnostic Imaging, at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, Texas. He declares no conflicts of interest.
Dear colleagues,
: What is the role and optimal timing of colonoscopy? How can we best utilize radiologic studies like CTA or tagged RBC scans? How should we manage patients with recurrent or intermittent bleeding that defies localization?
In this issue of Perspectives, Dr. David Wan, Dr. Fredella Lee, and Dr. Zeyad Metwalli offer their expert insights on these difficult questions. Dr. Wan, drawing on over 15 years of experience as a GI hospitalist, shares – along with his coauthor Dr. Lee – a pragmatic approach to LGIB based on clinical patterns, evolving data, and multidisciplinary collaboration. Dr. Metwalli provides the interventional radiologist’s perspective, highlighting how angiographic techniques can complement GI management and introducing novel IR strategies for patients with recurrent or elusive bleeding.
We hope their perspectives will offer valuable guidance for your practice. Join the conversation on X at @AGA_GIHN.
Gyanprakash A. Ketwaroo, MD, MSc, is associate professor of medicine, Yale University, New Haven, and chief of endoscopy at West Haven VA Medical Center, both in Connecticut. He is an associate editor for GI & Hepatology News.
Management of Lower Gastrointestinal Bleeds: GI Perspective
BY FREDELLA LEE, MD; DAVID WAN, MD
Acute lower gastrointestinal bleeding (LGIB) presents unique challenges. Much of this stems from the natural history of diverticular bleeding, the most common etiology of LGIB.
First, while bleeding can be severe, most will spontaneously stop. Second, despite our best efforts with imaging or colonoscopy, finding an intervenable lesion is rare. Third, LGIB has significant rates of rebleeding that are unpredictable.
While serving as a GI hospitalist for 15 years and after managing over 300 cases of LGIB, I often find myself frustrated and colonoscopy feels futile. So how can we rationally approach these patients? We will focus on three clinical questions to develop a framework for LGIB management.
- What is the role and timing for a colonoscopy?
- How do we best utilize radiologic tests?
- How can we prevent recurrent LGIB?
The Role of Colonoscopy
Traditionally, colonoscopy within 24 hours of presentation was recommended. This was based on retrospective cohort data showing higher endoscopic intervention rates and better clinical outcomes. However, this protocol requires patients to drink a significant volume of bowel preparation over a few hours (often requiring an NGT) to achieve clear rectal effluent. Moreover, one needs to mobilize a team (i.e., nurse, technician, anesthesiologist, and gastroenterologist), and find an appropriate location to scope (i.e., ED, ICU, or OR), Understandably, this is challenging, especially overnight. When the therapeutic yield is relatively low, this approach quickly loses enthusiasm.
Importantly, meta-analyses of the randomized controlled trials, have shown that urgent colonoscopies (<24 hours upon presentation), compared to elective colonoscopies (>24 hours upon presentation), do not improve clinical outcomes such as re-bleeding rates, transfusion requirements, mortality, or length of stay. In these studies, the endoscopic intervention rates were 17-34%, however, observational data shows rates of only 8%. In our practice, we will use a clear cap attachment device and water jet irrigation to increase the odds of detecting an active source of bleeding. Colonoscopy has a diagnostic yield of 95% – despite its low therapeutic yield; and while diverticular bleeds constitute up to 64% of cases, one does not want to miss colorectal cancer or other diagnoses. Regardless, there is generally no urgency to perform a colonoscopy. To quote a colleague, Dr. Elizabeth Ross, “there is no such thing as door-to-butt time.”
The Role of Radiology
Given the limits of colonoscopy, can radiographic tests such as computed tomography angiography (CTA) or tagged red blood cell (RBC) scan be helpful? Multiple studies have suggested using CTA as the initial diagnostic test. The advantages of CTAs are:
- Fast, readily available, and does not require a bowel preparation
- If negative, CTAs portend a good prognosis and make it highly unlikely to detect active extravasation on visceral angiography
- If positive, can localize the source of bleed and increase the success of intervention
Whether a positive CTA should be followed with a colonoscopy or visceral angiography remains unclear. Studies show that positive CTAs increase the detection rate of stigmata of recent hemorrhage on colonoscopy. Positive CTAs can also identify a target for embolization by interventional radiology (IR). Though an important caveat is that the success rate of embolization is highest when performed within 90 minutes of a positive CTA. This highlights that if you have IR availability, it is critical to have clear communication, a well-defined protocol, and collaboration among disciplines (i.e., ED, medical team, GI, and IR).
At our institution, we have implemented a CTA-guided protocol for severe LGIB. Those with positive CTAs are referred immediately to IR for embolization. If the embolization is unsuccessful or CTA is negative, the patient will be planned for a non-urgent inpatient colonoscopy. However, our unpublished data and other studies have shown that the overall CTA positivity rates are only between 16-22%. Moreover, one randomized controlled trial comparing CTA versus colonoscopy as an initial test did not show any meaningful difference in clinical outcomes. Thus, the benefit of CTA and the best approach to positive CTAs remains in question.
Lastly, people often ask about the utility of RBC nuclear scans. While they can detect bleeds at a slower rate (as low as 0.1 mL/min) compared to CTA (at least 0.4 mL/min), there are many limitations. RBC scans take time, are not available 24-7, and cannot precisely localize the site of bleeding. Therefore, we rarely recommend them for LGIB.
Approach to Recurrent Diverticular Bleeding
Unfortunately, diverticular bleeding recurs in the hospital 14% of the time and up to 25% at 5 years. When this occurs, is it worthwhile to repeat another colonoscopy or CTA?
Given the lack of clear data, we have adopted a shared decision-making framework with patients. Oftentimes, these patients are older and have significant co-morbidities, and undergoing bowel preparation, anesthesia, and colonoscopy is not trivial. If the patient is stable and prior work-up has excluded pertinent alternative diagnoses other than diverticular bleeding, then we tell patients the chance of finding an intervenable lesion is low and opt for conservative management. Meanwhile, if the patient has persistent, hemodynamically significant bleeding, we recommend a CTA based on the rationale discussed previously.
The most important clinical decision may not be about scoping or obtaining a CTA – it is medication management. If they are taking NSAIDs, they should be discontinued. If antiplatelet or anticoagulation agents were held, they should be restarted promptly in individuals with significant thrombotic risk given studies showing that while rebleeding rates may increase, overall mortality decreases.
In summary, managing LGIB and altering its natural history with either endoscopic or radiographic means is challenging. More studies are needed to guide the optimal approach. Reassuringly, most bleeding self-resolves and patients have good clinical outcomes.
Dr. Lee is a resident physician at New York Presbyterian Weill Cornell Medical Center, New York, NY. Dr. Wan is associate professor of clinical medicine at Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, N.Y. They declare no conflicts of interest.
Lower Gastrointestinal Bleeding: An Interventional Radiologist’s Perspective
BY ZEYAD METWALLI, MD, FSIR
When colonoscopy fails to localize and/or stop lower gastrointestinal bleeding (LGIB), catheter angiography has been commonly employed as a tool for both diagnosis and treatment of bleeding with embolization. Nuclear medicine or CT imaging studies can serve as useful adjuncts for confirming active bleeding and localizing the site of bleeding prior to angiography, particularly if this information is not provided by colonoscopy. Provocative mesenteric angiography has also become increasingly popular as a troubleshooting technique in patients with initially negative angiography.
Localization of Lower Gastrointestinal Bleeding
Radionuclide technetium-99m-lableled red blood cell scintigraphy (RBCS), also known as tagged RBC scintigraphy, has been in use since the early 1980s for investigation of acute gastrointestinal bleeding. RBCS has a high sensitivity for detection of active bleeding with a theoretical ability to detect bleeding at rates as low as 0.04-0.2 mL/minute.
Imaging protocols vary but should include dynamic images, which may aid in localization of bleeding. The relatively long half-life of the tracer used for imaging allows for delayed imaging 12 to 24 hours after injection. This can be useful to confirm active bleeding, particularly when bleeding is intermittent and is not visible on initial images.
With the advent of computed tomography angiography (CTA), which continues to increase in speed, imaging quality and availability, the use of RBCS for evaluation of LGIB has declined. CTA is quicker to perform than RBCS and allows for detection of bleeding as well as accurate anatomic localization, which can guide interventions.
CTA provides a more comprehensive anatomic evaluation, which can aid in the diagnosis of a wide variety of intra-abdominal issues. Conversely, CTA may be less sensitive than RBCS for detection of slower acute bleeding, detecting bleeding at rates of 0.1-1 mL/min. In addition, intermittent bleeding which has temporarily stopped at the time of CTA may evade detection.
Lastly, CTA may not be appropriate in patients with impaired renal function due to risk of contrast-induced nephropathy, particularly in patients with acute kidney injury, which commonly afflicts hospitalized patients with LGIB. Prophylaxis with normal saline hydration should be employed aggressively in patients with impaired renal function, particularly when eGFR is less than 30 mL/minute. Iodinated contrast should be used judiciously in these patients.
In clinical practice, CTA and RBCS have a similar ability to confirm the presence or absence of clinically significant active gastrointestinal bleeding. Given the greater ability to rapidly localize the bleeding site with CTA, this is generally preferred over RBCS unless there is a contraindication to performing CTA, such as severe contrast allergy or high risk for development of contrast-induced nephropathy.
Role of Catheter Angiography and Embolization
Mesenteric angiography is a well-established technique for both detection and treatment of LGIB. Hemodynamic instability and need for packed RBC transfusion increases the likelihood of positive angiography. Limitations include reduced sensitivity for detection of bleeding slower than 0.5-1 mL/minute as well as the intermittent nature of LGIB, which will often resolve spontaneously. Angiography is variably successful in the literature with a diagnostic yield between 40-80%, which encompasses the rate of success in my own practice.
Once bleeding is identified, microcatheter placement within the feeding vessel as close as possible to the site of bleeding is important to ensure treatment efficacy and to limit risk of complications such as non-target embolization and bowel ischemia. Once the feeding vessel is selected with a microcatheter, embolization can be accomplished with a wide variety of tools including metallic coils, liquid embolic agents, and particles. In the treatment of LGIB, liquid embolic agents (e.g., n-butyl cyanoacrylate or NBCA, ethylene vinyl alcohol copolymer, etc.) and particles should be used judiciously as distal penetration increases the risk of bowel ischemia and procedure-related morbidity. For this reason, metallic coils are often preferred in the treatment of LGIB.
Although the source of bleeding is variable and may include diverticulosis, recent polypectomy, ulcer, tumor or angiodysplasia, the techniques employed are similar. Accurate and distal microcatheter selection is a key driver for successful embolization and minimizing the risk of bowel ischemia. Small intestinal bleeds can be challenging to treat due to the redundant supply of the arterial arcades supplying small bowel and may require occlusion of several branches to achieve hemostasis. This approach must be balanced with the risk of developing ischemia after embolization. Angiodysplasia, a less frequently encountered culprit of LGIB, may also be managed with selective embolization with many reports of successful treatment with liquid embolic agents such as NBCA mixed with ethiodized oil.
Provocative Mesenteric Angiography for Occult Bleeding
When initial angiography in a patient with suspected active LGIB is negative, provocative angiography can be considered to uncover an intermittent bleed. This may be particularly helpful in a patient where active bleeding is confirmed on a prior diagnostic test.
The approach to provocative mesenteric angiography varies by center, and a variety of agents have been used to provoke bleeding including heparin, vasodilators (i.e., nitroglycerin, verapamil, etc.) and thrombolytics (i.e., tPA), often in combination. Thrombolytics can be administered directly into the territory of interest (i.e., superior mesenteric or inferior mesenteric artery) while heparin may be administered systemically or directly into the catheterized artery. Reported success rates for provoking angiographically visible bleeding vary, but most larger series report a 40-50% success rate. The newly detected bleeding can then be treated with either embolization or surgery. A surgeon should be involved and available when provocative angiography is planned should bleeding fail to be controlled by embolization.
In summary, when colonoscopy fails to identify or control lower gastrointestinal bleeding (LGIB), imaging techniques such as RBCS and CTA play a crucial role in localizing active bleeding. While RBCS is highly sensitive, especially for intermittent or slow bleeding, CTA offers faster, more detailed anatomical information and is typically preferred unless contraindicated by renal issues or contrast allergies. Catheter-based mesenteric angiography is a well-established method for both diagnosing and treating LGIB, often using metallic coils to minimize complications like bowel ischemia. In cases where initial angiography is negative, provocative angiography – using agents like heparin or thrombolytics – may help unmask intermittent bleeding, allowing for targeted embolization or surgical intervention.
Dr. Metwalli is associate professor in the Department of Interventional Radiology, Division of Diagnostic Imaging, at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, Texas. He declares no conflicts of interest.
Treating Barrett’s Esophagus: Comparing EMR and ESD
Dear colleagues,
Many of us diagnose and treat patients with Barrett’s esophagus, estimated to affect up to 5.6% of the US adult population. There has been an expanding array of tools to help diagnose and effectively treat Barrett’s esophagus with dysplasia and malignancy. In particular, endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) has emerged as an important method for treating early cancer in the gastrointestinal tract.
But how do we incorporate ESD into our algorithm for management, especially with the popularity and effectiveness of endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR)? In this issue of Perspectives we aim to provide context for the use of ESD, as compared with EMR. Dr. Silvio de Melo discusses his preferred EMR technique and its many advantages in the management of BE, including for residual or refractory areas. In contrast, Dr. Mohamed Othman reviews the power of ESD and when we should consider this approach over EMR. We hope these discussions will facilitate your care for patients with Barrett’s esophagus.
We also welcome your thoughts on this topic — join the conversation on X at @AGA_GIHN.
Gyanprakash A. Ketwaroo, MD, MSc, is associate professor of medicine, Yale University, New Haven, and chief of endoscopy at West Haven VA Medical Center, both in Connecticut. He is an associate editor for GI & Hepatology News.
Endoscopic Mucosal Resection: The ‘Workhorse’ for Patient Care
BY SILVIO W. DE MELO JR, MD, AGAF
Barrett’s esophagus (BE) remains an important clinical problem, being one of the modifiable risk factors for esophageal adenocarcinoma. The care for BE is complex and requires several steps to correctly formulate a therapeutic plan. It starts with a proper endoscopic examination. It is recommended to spend at least 1 minute inspecting and evaluating every centimeter of the salmon-colored epithelium, looking for change in vascular pattern, erosions/ulcers, nodules, and/or masses. After the inspection, random biopsies every 1-2 cm plus targeted biopsies will guide you. It is still controversial if the addition of other sampling strategies, such as brushings or confocal endomicroscopy, is needed.
The introduction of radiofrequency ablation (RFA) was paramount in popularizing the treatment options for BE and sunsetting the previous dominant modality, photodynamic therapy (PDT). RFA proved to have a superior clinical efficacy in replacing the intestinal metaplasia/BE with neosquamous epithelium while boosting a much better safety profile, compared with PDT. However, RFA is most efficacious for “flat BE” and it is not an effective, nor recommended, method to treat nodular BE or early cancer, such as carcinoma in situ or nodular high-grade dysplasia. Endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) is utilized to overcome those limitations.
There are several techniques utilized for EMR:
- The lift and snare technique.
- The snare-in-cap technique.
- The Band-snare technique.
The free-hand submucosal lift and snare is not frequently used in the esophagus. It is difficult to maintain visualization while being confident that one has the whole lesion inside the snare and that the distal (anal side) part of the lesion is free of any unwanted tissue (to minimize complications such as perforations or unwelcomed gastric resections). It is difficult after the first resection to lift an adjacent area, as the fluid easily leaks from the first resected spot, thus removing larger lesions in piece-meal fashion is challenging. This technique can be used in small (in my personal experience, less than 5 mm) lesions, but, given that there are better and safer alternatives, I almost never use this technique for my esophageal EMR cases. I prefer to use the band-snare technique even for lesions under 5 mm.
The snare-in-cap technique has been utilized in the esophagus. In this technique, a cap is attached to the distal end of the scope and the size of the resection is determined by the size of the cap, usually under 1.5 cm. Because of the risk of perforation without previous lifting, it is required that the lesion is lifted with a submucosal fluid, saline or any Food and Drug Administration–approved EMR solution. The lesion is then suctioned inside the cap where the snare had been previously opened inside the cap, the snare is closed, and the tissue is resected. The same limitations regarding the inability to remove larger lesions (greater than 1.5 cm) because of the challenge in lifting the adjacent area applies here. However, the perforation risk for this technique is higher than the traditional lift and the band and snare techniques. Thus, this technique has fallen out of favor for most endoscopists.
The third technique (band-snare EMR) is the one that most endoscopists use for endoscopic mucosal resection. It is a small variation of the already time-tested and very familiar procedure of esophageal variceal band ligation (EVL). There are multiple commercially available kits for esophageal EMR. The kit contains the chamber with the bands and a proprietary hexagonal snare used to resect the specimen.
The advantages of this technique are:
- It is widely commercially available.
- It builds on a familiar procedure, EVL, therefore the learning curve is short.
- The set-up is quick and the procedure can be completed safely and effectively.
- There is no need for injecting the submucosal with a lifting solution.
- Despite the band having a size limitation of 1 cm, one can remove larger lesions by repeating the band and resect process, using the rosette technique.
Band-snare EMR also has limitations:
- There are only six bands on each chamber. Depending on the size of the lesion, one may need to use multiple kits.
- It is not suitable for en bloc resection of lesions greater than 1 cm.
My experience with band EMR is that we can complete the procedure in under 1 hour. The dreaded complication of perforation occurs in under 1% of cases, most bleeding episodes can easily be controlled endoscopically, and the risk of post-EMR stricture is minimal. Therefore, band EMR is the most used technique for esophageal endoscopic resections.
Esophageal EMR is also effective for other indications in BE therapy, such as residual and recurrent BE. Band-snare EMR can be used for an en bloc resection or rosette technique for the areas resistant to ablation therapies with great success and safety.
From a financial standpoint, comparing EMR with endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD), EMR is the superior strategy given that EMR is widely available, has a much shorter learning curve, has a greater safety profile, is applicable to a wider variety of indications, and has a more favorable return on investment. EMR should be the workhorse for the care of patients with BE, reserving ESD for specific indications.
In summary, there is no “one-size-fits-all” endoscopic therapy in the care of BE. Most Barrett’s patients can be successfully treated with a combination of ablation plus EMR, reserving ESD for select cases.
Dr. de Melo is section chief of gastroenterology at the Orlando VA Healthcare System, Orlando, Florida. He declares no conflicts of interest.
ESD Over EMR for Resecting Esophageal Lesions
BY MOHAMED O. OTHMAN, MD, AGAF
Although endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) is the preferred endoscopic resection method in the East, the adoption of this technique in the West, particularly in the United States, has faced many hurdles. Many endoscopists who routinely perform piecemeal endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) question the utility of ESD, arguing that EMR is just as effective. While this may hold true in certain situations, the global trend in the endoscopic treatment of early esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, nodular Barrett’s esophagus (BE), and early esophageal adenocarcinoma (EAC) has clearly shifted toward ESD. In this perspective, I will summarize why ESD is preferred over EMR for these indications and explore why ESD has yet to gain widespread adoption in the United States.
The superiority of ESD over EMR has been well established in multiple publications from both Eastern and Western literature. Mejia-Perez et al, in a multicenter cohort study from eight centers in North America, compared outcomes of ESD vs EMR for BE with high-grade dysplasia (HGD) or T1a adenocarcinoma in 243 patients. ESD achieved significantly higher en bloc resection rates (89% vs 43%) and R0 resection rates (73% vs 56%), compared with EMR, along with a substantially lower recurrence/residual disease rate on follow-up (3.5% in the ESD group vs 31.4% in EMR group). Additionally, more patients required repeat endoscopic resection after EMR to treat residual or recurrent disease (EMR, 24.2% vs ESD, 3.5%; P < .001).
Han et al conducted a meta-analysis of 22 studies comparing ESD and EMR for early esophageal neoplasia, including both squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) and BE-associated lesions. ESD was associated with significantly higher curative resection rates than EMR (OR, 9.74; 95% CI, 4.83-19.62; P < .0001). Of note, lesion size was a critical factor in determining the advantage of ESD. For lesions ≤ 10 mm, curative resection rates were comparable between ESD and EMR. However, for lesions > 10 mm, ESD achieved significantly higher curative resection rates. This size-based recommendation has been adopted by the American Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ASGE) in their recent guidelines on ESD indications for esophageal lesions. ASGE guidelines favors ESD over EMR for SCC lesions > 15 mm and for nodular BE with dysplasia or early EAC > 20 mm.
ESD is particularly beneficial in patients who develop early adenocarcinoma after RFA or EMR. Mesureur et al evaluated the efficacy of salvage ESD for Barrett’s recurrence or residual BE following RFA. In their multicenter retrospective study of 56 patients, salvage ESD achieved an en bloc resection rate of 89.3%, despite significant fibrosis, with an R0 resection rate of 66%. At a median follow-up of 14 months, most patients remained in endoscopic remission without the need for esophagectomy.
Combining ESD with RFA has also been shown to accelerate the eradication of BE with dysplasia while reducing the number of required sessions. Our group demonstrated the high efficacy of ESD followed by RFA in 18 patients, most of whom had long-segment BE with HGD or EAC. On average, patients required only one to two RFA sessions after ESD to achieve complete eradication of intestinal metaplasia (CE-IM). Over a median follow-up of 42.5 months (IQR, 28-59.25), complete eradication of early esophageal cancer was achieved in 13 patients (100%), eradication of dysplasia in 15 patients (100%), and CE-IM in 14 patients (77.8%).
Despite the overwhelming evidence supporting ESD and the strong endorsement from professional societies, adoption in the West continues to lag. Several factors contribute to this gap. First, ESD has a steep learning curve. Our data showed that, on average, an untutored practitioner achieved competency after 150-250 procedures, a finding corroborated by other US groups.
Second, there is no specific CPT code for ESD in the United States. Physicians are forced to bill the procedure as EMR or use an unlisted code, resulting in reimbursement that does not reflect the time and complexity of the procedure. Our group showed that physician reimbursement for ESD is highly variable, ranging from $50 to $800 per case, depending on insurance type.
Third, the increasing emphasis on productivity and RVU generation in academic settings has hindered the growth of ESD training in many institutions. Still, the outlook for ESD in the United States remains encouraging. Multiple industry-sponsored training courses are held annually, and professional societies are investing heavily in expanding access to structured education in ESD. Industry is also innovating devices that improve procedural efficiency and safety. Adopting novel approaches, such as traction-assisted ESD, has made the technique more appealing to endoscopists concerned about long procedure times. For example, our group proposed a standardized esophageal ESD technique that incorporates specimen self-retraction. This method improves both safety and speed and has helped address several procedural challenges. We’ve demonstrated that consistency in technique can substantially expedite esophageal ESD.
Fast forward 5 years: We anticipate a dedicated CPT code for ESD, broader access to advanced resection tools, and an expanding number of fellowships offering structured ESD training. These developments are poised to eliminate many of the current barriers. In summary, with robust data supporting the efficacy of ESD in early esophageal cancer, the focus in the United States should shift toward mastering and integrating the technique, rather than dismissing it in favor of piecemeal EMR.
Dr. Othman is chief of the gastroenterology and hepatology section at Baylor College of Medicine and Medicine Subspecialities Service Line Chief at Baylor St Luke’s Medical Center, both in Houston. He declares no conflicts of interest.
Dear colleagues,
Many of us diagnose and treat patients with Barrett’s esophagus, estimated to affect up to 5.6% of the US adult population. There has been an expanding array of tools to help diagnose and effectively treat Barrett’s esophagus with dysplasia and malignancy. In particular, endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) has emerged as an important method for treating early cancer in the gastrointestinal tract.
But how do we incorporate ESD into our algorithm for management, especially with the popularity and effectiveness of endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR)? In this issue of Perspectives we aim to provide context for the use of ESD, as compared with EMR. Dr. Silvio de Melo discusses his preferred EMR technique and its many advantages in the management of BE, including for residual or refractory areas. In contrast, Dr. Mohamed Othman reviews the power of ESD and when we should consider this approach over EMR. We hope these discussions will facilitate your care for patients with Barrett’s esophagus.
We also welcome your thoughts on this topic — join the conversation on X at @AGA_GIHN.
Gyanprakash A. Ketwaroo, MD, MSc, is associate professor of medicine, Yale University, New Haven, and chief of endoscopy at West Haven VA Medical Center, both in Connecticut. He is an associate editor for GI & Hepatology News.
Endoscopic Mucosal Resection: The ‘Workhorse’ for Patient Care
BY SILVIO W. DE MELO JR, MD, AGAF
Barrett’s esophagus (BE) remains an important clinical problem, being one of the modifiable risk factors for esophageal adenocarcinoma. The care for BE is complex and requires several steps to correctly formulate a therapeutic plan. It starts with a proper endoscopic examination. It is recommended to spend at least 1 minute inspecting and evaluating every centimeter of the salmon-colored epithelium, looking for change in vascular pattern, erosions/ulcers, nodules, and/or masses. After the inspection, random biopsies every 1-2 cm plus targeted biopsies will guide you. It is still controversial if the addition of other sampling strategies, such as brushings or confocal endomicroscopy, is needed.
The introduction of radiofrequency ablation (RFA) was paramount in popularizing the treatment options for BE and sunsetting the previous dominant modality, photodynamic therapy (PDT). RFA proved to have a superior clinical efficacy in replacing the intestinal metaplasia/BE with neosquamous epithelium while boosting a much better safety profile, compared with PDT. However, RFA is most efficacious for “flat BE” and it is not an effective, nor recommended, method to treat nodular BE or early cancer, such as carcinoma in situ or nodular high-grade dysplasia. Endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) is utilized to overcome those limitations.
There are several techniques utilized for EMR:
- The lift and snare technique.
- The snare-in-cap technique.
- The Band-snare technique.
The free-hand submucosal lift and snare is not frequently used in the esophagus. It is difficult to maintain visualization while being confident that one has the whole lesion inside the snare and that the distal (anal side) part of the lesion is free of any unwanted tissue (to minimize complications such as perforations or unwelcomed gastric resections). It is difficult after the first resection to lift an adjacent area, as the fluid easily leaks from the first resected spot, thus removing larger lesions in piece-meal fashion is challenging. This technique can be used in small (in my personal experience, less than 5 mm) lesions, but, given that there are better and safer alternatives, I almost never use this technique for my esophageal EMR cases. I prefer to use the band-snare technique even for lesions under 5 mm.
The snare-in-cap technique has been utilized in the esophagus. In this technique, a cap is attached to the distal end of the scope and the size of the resection is determined by the size of the cap, usually under 1.5 cm. Because of the risk of perforation without previous lifting, it is required that the lesion is lifted with a submucosal fluid, saline or any Food and Drug Administration–approved EMR solution. The lesion is then suctioned inside the cap where the snare had been previously opened inside the cap, the snare is closed, and the tissue is resected. The same limitations regarding the inability to remove larger lesions (greater than 1.5 cm) because of the challenge in lifting the adjacent area applies here. However, the perforation risk for this technique is higher than the traditional lift and the band and snare techniques. Thus, this technique has fallen out of favor for most endoscopists.
The third technique (band-snare EMR) is the one that most endoscopists use for endoscopic mucosal resection. It is a small variation of the already time-tested and very familiar procedure of esophageal variceal band ligation (EVL). There are multiple commercially available kits for esophageal EMR. The kit contains the chamber with the bands and a proprietary hexagonal snare used to resect the specimen.
The advantages of this technique are:
- It is widely commercially available.
- It builds on a familiar procedure, EVL, therefore the learning curve is short.
- The set-up is quick and the procedure can be completed safely and effectively.
- There is no need for injecting the submucosal with a lifting solution.
- Despite the band having a size limitation of 1 cm, one can remove larger lesions by repeating the band and resect process, using the rosette technique.
Band-snare EMR also has limitations:
- There are only six bands on each chamber. Depending on the size of the lesion, one may need to use multiple kits.
- It is not suitable for en bloc resection of lesions greater than 1 cm.
My experience with band EMR is that we can complete the procedure in under 1 hour. The dreaded complication of perforation occurs in under 1% of cases, most bleeding episodes can easily be controlled endoscopically, and the risk of post-EMR stricture is minimal. Therefore, band EMR is the most used technique for esophageal endoscopic resections.
Esophageal EMR is also effective for other indications in BE therapy, such as residual and recurrent BE. Band-snare EMR can be used for an en bloc resection or rosette technique for the areas resistant to ablation therapies with great success and safety.
From a financial standpoint, comparing EMR with endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD), EMR is the superior strategy given that EMR is widely available, has a much shorter learning curve, has a greater safety profile, is applicable to a wider variety of indications, and has a more favorable return on investment. EMR should be the workhorse for the care of patients with BE, reserving ESD for specific indications.
In summary, there is no “one-size-fits-all” endoscopic therapy in the care of BE. Most Barrett’s patients can be successfully treated with a combination of ablation plus EMR, reserving ESD for select cases.
Dr. de Melo is section chief of gastroenterology at the Orlando VA Healthcare System, Orlando, Florida. He declares no conflicts of interest.
ESD Over EMR for Resecting Esophageal Lesions
BY MOHAMED O. OTHMAN, MD, AGAF
Although endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) is the preferred endoscopic resection method in the East, the adoption of this technique in the West, particularly in the United States, has faced many hurdles. Many endoscopists who routinely perform piecemeal endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) question the utility of ESD, arguing that EMR is just as effective. While this may hold true in certain situations, the global trend in the endoscopic treatment of early esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, nodular Barrett’s esophagus (BE), and early esophageal adenocarcinoma (EAC) has clearly shifted toward ESD. In this perspective, I will summarize why ESD is preferred over EMR for these indications and explore why ESD has yet to gain widespread adoption in the United States.
The superiority of ESD over EMR has been well established in multiple publications from both Eastern and Western literature. Mejia-Perez et al, in a multicenter cohort study from eight centers in North America, compared outcomes of ESD vs EMR for BE with high-grade dysplasia (HGD) or T1a adenocarcinoma in 243 patients. ESD achieved significantly higher en bloc resection rates (89% vs 43%) and R0 resection rates (73% vs 56%), compared with EMR, along with a substantially lower recurrence/residual disease rate on follow-up (3.5% in the ESD group vs 31.4% in EMR group). Additionally, more patients required repeat endoscopic resection after EMR to treat residual or recurrent disease (EMR, 24.2% vs ESD, 3.5%; P < .001).
Han et al conducted a meta-analysis of 22 studies comparing ESD and EMR for early esophageal neoplasia, including both squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) and BE-associated lesions. ESD was associated with significantly higher curative resection rates than EMR (OR, 9.74; 95% CI, 4.83-19.62; P < .0001). Of note, lesion size was a critical factor in determining the advantage of ESD. For lesions ≤ 10 mm, curative resection rates were comparable between ESD and EMR. However, for lesions > 10 mm, ESD achieved significantly higher curative resection rates. This size-based recommendation has been adopted by the American Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ASGE) in their recent guidelines on ESD indications for esophageal lesions. ASGE guidelines favors ESD over EMR for SCC lesions > 15 mm and for nodular BE with dysplasia or early EAC > 20 mm.
ESD is particularly beneficial in patients who develop early adenocarcinoma after RFA or EMR. Mesureur et al evaluated the efficacy of salvage ESD for Barrett’s recurrence or residual BE following RFA. In their multicenter retrospective study of 56 patients, salvage ESD achieved an en bloc resection rate of 89.3%, despite significant fibrosis, with an R0 resection rate of 66%. At a median follow-up of 14 months, most patients remained in endoscopic remission without the need for esophagectomy.
Combining ESD with RFA has also been shown to accelerate the eradication of BE with dysplasia while reducing the number of required sessions. Our group demonstrated the high efficacy of ESD followed by RFA in 18 patients, most of whom had long-segment BE with HGD or EAC. On average, patients required only one to two RFA sessions after ESD to achieve complete eradication of intestinal metaplasia (CE-IM). Over a median follow-up of 42.5 months (IQR, 28-59.25), complete eradication of early esophageal cancer was achieved in 13 patients (100%), eradication of dysplasia in 15 patients (100%), and CE-IM in 14 patients (77.8%).
Despite the overwhelming evidence supporting ESD and the strong endorsement from professional societies, adoption in the West continues to lag. Several factors contribute to this gap. First, ESD has a steep learning curve. Our data showed that, on average, an untutored practitioner achieved competency after 150-250 procedures, a finding corroborated by other US groups.
Second, there is no specific CPT code for ESD in the United States. Physicians are forced to bill the procedure as EMR or use an unlisted code, resulting in reimbursement that does not reflect the time and complexity of the procedure. Our group showed that physician reimbursement for ESD is highly variable, ranging from $50 to $800 per case, depending on insurance type.
Third, the increasing emphasis on productivity and RVU generation in academic settings has hindered the growth of ESD training in many institutions. Still, the outlook for ESD in the United States remains encouraging. Multiple industry-sponsored training courses are held annually, and professional societies are investing heavily in expanding access to structured education in ESD. Industry is also innovating devices that improve procedural efficiency and safety. Adopting novel approaches, such as traction-assisted ESD, has made the technique more appealing to endoscopists concerned about long procedure times. For example, our group proposed a standardized esophageal ESD technique that incorporates specimen self-retraction. This method improves both safety and speed and has helped address several procedural challenges. We’ve demonstrated that consistency in technique can substantially expedite esophageal ESD.
Fast forward 5 years: We anticipate a dedicated CPT code for ESD, broader access to advanced resection tools, and an expanding number of fellowships offering structured ESD training. These developments are poised to eliminate many of the current barriers. In summary, with robust data supporting the efficacy of ESD in early esophageal cancer, the focus in the United States should shift toward mastering and integrating the technique, rather than dismissing it in favor of piecemeal EMR.
Dr. Othman is chief of the gastroenterology and hepatology section at Baylor College of Medicine and Medicine Subspecialities Service Line Chief at Baylor St Luke’s Medical Center, both in Houston. He declares no conflicts of interest.
Dear colleagues,
Many of us diagnose and treat patients with Barrett’s esophagus, estimated to affect up to 5.6% of the US adult population. There has been an expanding array of tools to help diagnose and effectively treat Barrett’s esophagus with dysplasia and malignancy. In particular, endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) has emerged as an important method for treating early cancer in the gastrointestinal tract.
But how do we incorporate ESD into our algorithm for management, especially with the popularity and effectiveness of endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR)? In this issue of Perspectives we aim to provide context for the use of ESD, as compared with EMR. Dr. Silvio de Melo discusses his preferred EMR technique and its many advantages in the management of BE, including for residual or refractory areas. In contrast, Dr. Mohamed Othman reviews the power of ESD and when we should consider this approach over EMR. We hope these discussions will facilitate your care for patients with Barrett’s esophagus.
We also welcome your thoughts on this topic — join the conversation on X at @AGA_GIHN.
Gyanprakash A. Ketwaroo, MD, MSc, is associate professor of medicine, Yale University, New Haven, and chief of endoscopy at West Haven VA Medical Center, both in Connecticut. He is an associate editor for GI & Hepatology News.
Endoscopic Mucosal Resection: The ‘Workhorse’ for Patient Care
BY SILVIO W. DE MELO JR, MD, AGAF
Barrett’s esophagus (BE) remains an important clinical problem, being one of the modifiable risk factors for esophageal adenocarcinoma. The care for BE is complex and requires several steps to correctly formulate a therapeutic plan. It starts with a proper endoscopic examination. It is recommended to spend at least 1 minute inspecting and evaluating every centimeter of the salmon-colored epithelium, looking for change in vascular pattern, erosions/ulcers, nodules, and/or masses. After the inspection, random biopsies every 1-2 cm plus targeted biopsies will guide you. It is still controversial if the addition of other sampling strategies, such as brushings or confocal endomicroscopy, is needed.
The introduction of radiofrequency ablation (RFA) was paramount in popularizing the treatment options for BE and sunsetting the previous dominant modality, photodynamic therapy (PDT). RFA proved to have a superior clinical efficacy in replacing the intestinal metaplasia/BE with neosquamous epithelium while boosting a much better safety profile, compared with PDT. However, RFA is most efficacious for “flat BE” and it is not an effective, nor recommended, method to treat nodular BE or early cancer, such as carcinoma in situ or nodular high-grade dysplasia. Endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) is utilized to overcome those limitations.
There are several techniques utilized for EMR:
- The lift and snare technique.
- The snare-in-cap technique.
- The Band-snare technique.
The free-hand submucosal lift and snare is not frequently used in the esophagus. It is difficult to maintain visualization while being confident that one has the whole lesion inside the snare and that the distal (anal side) part of the lesion is free of any unwanted tissue (to minimize complications such as perforations or unwelcomed gastric resections). It is difficult after the first resection to lift an adjacent area, as the fluid easily leaks from the first resected spot, thus removing larger lesions in piece-meal fashion is challenging. This technique can be used in small (in my personal experience, less than 5 mm) lesions, but, given that there are better and safer alternatives, I almost never use this technique for my esophageal EMR cases. I prefer to use the band-snare technique even for lesions under 5 mm.
The snare-in-cap technique has been utilized in the esophagus. In this technique, a cap is attached to the distal end of the scope and the size of the resection is determined by the size of the cap, usually under 1.5 cm. Because of the risk of perforation without previous lifting, it is required that the lesion is lifted with a submucosal fluid, saline or any Food and Drug Administration–approved EMR solution. The lesion is then suctioned inside the cap where the snare had been previously opened inside the cap, the snare is closed, and the tissue is resected. The same limitations regarding the inability to remove larger lesions (greater than 1.5 cm) because of the challenge in lifting the adjacent area applies here. However, the perforation risk for this technique is higher than the traditional lift and the band and snare techniques. Thus, this technique has fallen out of favor for most endoscopists.
The third technique (band-snare EMR) is the one that most endoscopists use for endoscopic mucosal resection. It is a small variation of the already time-tested and very familiar procedure of esophageal variceal band ligation (EVL). There are multiple commercially available kits for esophageal EMR. The kit contains the chamber with the bands and a proprietary hexagonal snare used to resect the specimen.
The advantages of this technique are:
- It is widely commercially available.
- It builds on a familiar procedure, EVL, therefore the learning curve is short.
- The set-up is quick and the procedure can be completed safely and effectively.
- There is no need for injecting the submucosal with a lifting solution.
- Despite the band having a size limitation of 1 cm, one can remove larger lesions by repeating the band and resect process, using the rosette technique.
Band-snare EMR also has limitations:
- There are only six bands on each chamber. Depending on the size of the lesion, one may need to use multiple kits.
- It is not suitable for en bloc resection of lesions greater than 1 cm.
My experience with band EMR is that we can complete the procedure in under 1 hour. The dreaded complication of perforation occurs in under 1% of cases, most bleeding episodes can easily be controlled endoscopically, and the risk of post-EMR stricture is minimal. Therefore, band EMR is the most used technique for esophageal endoscopic resections.
Esophageal EMR is also effective for other indications in BE therapy, such as residual and recurrent BE. Band-snare EMR can be used for an en bloc resection or rosette technique for the areas resistant to ablation therapies with great success and safety.
From a financial standpoint, comparing EMR with endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD), EMR is the superior strategy given that EMR is widely available, has a much shorter learning curve, has a greater safety profile, is applicable to a wider variety of indications, and has a more favorable return on investment. EMR should be the workhorse for the care of patients with BE, reserving ESD for specific indications.
In summary, there is no “one-size-fits-all” endoscopic therapy in the care of BE. Most Barrett’s patients can be successfully treated with a combination of ablation plus EMR, reserving ESD for select cases.
Dr. de Melo is section chief of gastroenterology at the Orlando VA Healthcare System, Orlando, Florida. He declares no conflicts of interest.
ESD Over EMR for Resecting Esophageal Lesions
BY MOHAMED O. OTHMAN, MD, AGAF
Although endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) is the preferred endoscopic resection method in the East, the adoption of this technique in the West, particularly in the United States, has faced many hurdles. Many endoscopists who routinely perform piecemeal endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) question the utility of ESD, arguing that EMR is just as effective. While this may hold true in certain situations, the global trend in the endoscopic treatment of early esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, nodular Barrett’s esophagus (BE), and early esophageal adenocarcinoma (EAC) has clearly shifted toward ESD. In this perspective, I will summarize why ESD is preferred over EMR for these indications and explore why ESD has yet to gain widespread adoption in the United States.
The superiority of ESD over EMR has been well established in multiple publications from both Eastern and Western literature. Mejia-Perez et al, in a multicenter cohort study from eight centers in North America, compared outcomes of ESD vs EMR for BE with high-grade dysplasia (HGD) or T1a adenocarcinoma in 243 patients. ESD achieved significantly higher en bloc resection rates (89% vs 43%) and R0 resection rates (73% vs 56%), compared with EMR, along with a substantially lower recurrence/residual disease rate on follow-up (3.5% in the ESD group vs 31.4% in EMR group). Additionally, more patients required repeat endoscopic resection after EMR to treat residual or recurrent disease (EMR, 24.2% vs ESD, 3.5%; P < .001).
Han et al conducted a meta-analysis of 22 studies comparing ESD and EMR for early esophageal neoplasia, including both squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) and BE-associated lesions. ESD was associated with significantly higher curative resection rates than EMR (OR, 9.74; 95% CI, 4.83-19.62; P < .0001). Of note, lesion size was a critical factor in determining the advantage of ESD. For lesions ≤ 10 mm, curative resection rates were comparable between ESD and EMR. However, for lesions > 10 mm, ESD achieved significantly higher curative resection rates. This size-based recommendation has been adopted by the American Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ASGE) in their recent guidelines on ESD indications for esophageal lesions. ASGE guidelines favors ESD over EMR for SCC lesions > 15 mm and for nodular BE with dysplasia or early EAC > 20 mm.
ESD is particularly beneficial in patients who develop early adenocarcinoma after RFA or EMR. Mesureur et al evaluated the efficacy of salvage ESD for Barrett’s recurrence or residual BE following RFA. In their multicenter retrospective study of 56 patients, salvage ESD achieved an en bloc resection rate of 89.3%, despite significant fibrosis, with an R0 resection rate of 66%. At a median follow-up of 14 months, most patients remained in endoscopic remission without the need for esophagectomy.
Combining ESD with RFA has also been shown to accelerate the eradication of BE with dysplasia while reducing the number of required sessions. Our group demonstrated the high efficacy of ESD followed by RFA in 18 patients, most of whom had long-segment BE with HGD or EAC. On average, patients required only one to two RFA sessions after ESD to achieve complete eradication of intestinal metaplasia (CE-IM). Over a median follow-up of 42.5 months (IQR, 28-59.25), complete eradication of early esophageal cancer was achieved in 13 patients (100%), eradication of dysplasia in 15 patients (100%), and CE-IM in 14 patients (77.8%).
Despite the overwhelming evidence supporting ESD and the strong endorsement from professional societies, adoption in the West continues to lag. Several factors contribute to this gap. First, ESD has a steep learning curve. Our data showed that, on average, an untutored practitioner achieved competency after 150-250 procedures, a finding corroborated by other US groups.
Second, there is no specific CPT code for ESD in the United States. Physicians are forced to bill the procedure as EMR or use an unlisted code, resulting in reimbursement that does not reflect the time and complexity of the procedure. Our group showed that physician reimbursement for ESD is highly variable, ranging from $50 to $800 per case, depending on insurance type.
Third, the increasing emphasis on productivity and RVU generation in academic settings has hindered the growth of ESD training in many institutions. Still, the outlook for ESD in the United States remains encouraging. Multiple industry-sponsored training courses are held annually, and professional societies are investing heavily in expanding access to structured education in ESD. Industry is also innovating devices that improve procedural efficiency and safety. Adopting novel approaches, such as traction-assisted ESD, has made the technique more appealing to endoscopists concerned about long procedure times. For example, our group proposed a standardized esophageal ESD technique that incorporates specimen self-retraction. This method improves both safety and speed and has helped address several procedural challenges. We’ve demonstrated that consistency in technique can substantially expedite esophageal ESD.
Fast forward 5 years: We anticipate a dedicated CPT code for ESD, broader access to advanced resection tools, and an expanding number of fellowships offering structured ESD training. These developments are poised to eliminate many of the current barriers. In summary, with robust data supporting the efficacy of ESD in early esophageal cancer, the focus in the United States should shift toward mastering and integrating the technique, rather than dismissing it in favor of piecemeal EMR.
Dr. Othman is chief of the gastroenterology and hepatology section at Baylor College of Medicine and Medicine Subspecialities Service Line Chief at Baylor St Luke’s Medical Center, both in Houston. He declares no conflicts of interest.
Surgical vs Endoscopic Excision of Large Colon Polyps
Dear colleagues,
We now have the ability to remove almost any large colon polyp endoscopically using a variety of techniques — from the widely used endoscopic mucosal resection to the increasingly prevalent endoscopic submucosal dissection. Yet, in this new era,
In this issue of Perspectives, Dr. Jeffrey Mosko and Dr. Moamen Gabr discuss the importance of careful polyp selection and argue that almost all polyps can be safely removed endoscopically, with low recurrence rates. In contrast, Dr. Ira Leeds from colorectal surgery offers a counterpoint, urging caution when managing polyps in the cecum and rectum while highlighting the role of minimally invasive surgical approaches. We hope these discussions provide valuable insights to support your approach to managing large colorectal polyps, especially in an era of increasing colon cancer screening.
We also welcome your thoughts on this topic — join the conversation on X at @AGA_GIHN.
Gyanprakash A. Ketwaroo, MD, MSc, is associate professor of medicine, Yale University, New Haven, and chief of endoscopy at West Haven VA Medical Center, both in Connecticut. He is an associate editor for GI & Hepatology News.
Advantages of Endoscopic Resection for Large Colon Polyps
BY MOAMEN GABR, MD, MSC, AND JEFFREY D. MOSKO MD, MSC
General Advantages
Endoscopy has revolutionized the management of large colorectal polyps, offering a minimally invasive alternative to surgical resection. The dawn of endoscopic resection in the late 20th century, particularly the evolution of endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) in Japan, marked a paradigm shift in the treatment of colonic lesions by enabling the removal of lesions that would otherwise necessitate surgery.
Endoscopic resection of colorectal polyps is generally performed in an outpatient setting, allowing patients to recover at home the same day. This not only minimizes disruption to daily life but also significantly enhances patient satisfaction.
Most procedures are performed under moderate or deep sedation eliminating the need for general anesthesia. This represents a critical benefit, particularly for older or medically frail patients who are at higher risk of anesthesia-related complications.
From an economic perspective, endoscopic resection reduces healthcare costs by eliminating prolonged hospital stays and complex perioperative care. Additionally, preserving the colon’s structure and function avoids long-term consequences such as altered bowel habits or ostomy dependence, common with surgical interventions.
The advantages of endoscopic intervention are clear: safety, cost-effectiveness, organ preservation, and convenience for patients.
Lesion Selection
The superiority of endoscopic resection relies on selecting lesions appropriately, specifically those with a low risk of lymph node metastases. This meticulous process should include assessing a lesion’s size, location, morphology, granularity, microvascular and surface pit pattern using a combination of high-definition white light endoscopy, virtual chromoendoscopy and image magnification (when available).
Gross morphologic assessment utilizes the Paris and LST classifications. Combining the Paris classification, lesion granularity and location is both straightforward and revealing. Ulcerated/excavated lesions (0-III) are concerning for deep invasion. Depressed (0-IIc) morphologies are strongly associated with T1 CRC. Nodular lesions (0-Is or IIa + Is) have a higher risk of T1 colorectal cancer (CRC), compared with flat lesions (0-IIa or 0-IIb). Non-granular lesions (0-Is and 0-IIa + Is) have a higher risk of covert cancer. Finally, the rectosigmoid location is associated with an increased risk of T1 CRC (vs. proximal locations).
Endoscopic surface pattern assessment increases one’s diagnostic accuracy. There are three primary endoscopic surface pattern classifications: NBI International Colorectal Endoscopic (NICE), Japanese NBI expert team (JNET), and Kudo pit pattern classifications. Colonic lesions that have a NICE Type 3, JNET 3, or Kudo type Vn pattern should be referred promptly for surgical resection. Lesions with a JNET 2B or Kudo type VI carry a higher risk of superficial T1 CRC but can still be removed endoscopically (see below) in expert centers. All other lesions should undergo endoscopic resection.
Endoscopic Resection Techniques
Endoscopic resection of large colorectal polyps encompasses two primary techniques: EMR and endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD), each tailored to specific lesion characteristics and operator expertise.
EMR, the technique of choice for the vast majority of lesions, relies on injecting a submucosal cushion to lift the lesion before excision. Recent advances, including enhanced snare designs and underwater EMR, have improved en-bloc resection rates, significantly reducing recurrence and enhancing the efficacy of this technique.
ESD offers unparalleled precision for en-bloc resection of complex lesions, particularly those with fibrosis or high-risk features. Cutting-edge innovations, such as traction devices, have streamlined the procedure, addressing the traditional challenges of ESD. Despite being more time intensive, ESD minimizes recurrence and provides complete histopathological evaluation, critical for the management of malignant or pre-malignant lesions.
For non-lifting polyps, newer techniques such as endoscopic full-thickness resection (eFTR), using tools like the Full-Thickness Resection Device (FTRD), enable resection of up to 2-3 cm of the colonic or rectal wall. This ensures complete removal of any lesion and its underlying tissue, effectively preventing recurrence.
These advancements demonstrate how endoscopy can tackle even the most challenging colorectal polyps, reinforcing its position as the preferred treatment modality.
Perceived Limitations
With ongoing refinement over the last 2 decades, many of the perceived limitations (below) of endoscopic resection have now been overcome.
- Difficult locations/access: Historically lesions at the anorectal junction, ileocecal valve, appendiceal orifice and anastomoses were preferentially sent for surgery. In spite of unique technical challenges at each of these locations, there is now compelling data supporting EMR for these scenarios. We now also have techniques aimed at enabling the resection of lesions with poor access including patient repositioning, distal attachments, variable endoscope diameter/flexibility, traction and overtube devices.
- Recurrence: In the past, recurrence after endoscopic resection of lesions > 20 mm has been reported to be as high as 20%. With our current systematic approach to complete resection, meticulous examination of the post-resection defect for residual polyp tissue, adjunctive techniques to address submucosal fibrosis (hot avulsion, CAST, submucosal release) and thermal ablation to the resection margin (EMR-T), the risk of recurrence for piecemeal resections can be decreased to < 5%. In fact, some groups argue for the en-bloc resection of all large colorectal lesions based on the extremely low (< 1%) recurrence rates and potential for decreased follow-up.
- Post-resection bleeding: Post-resection bleeding is no longer a major limitation of any endoscopic approach because of the combination of improved intra-procedural hemostatic and resection techniques, optimized electrosurgical technology, and enhanced defect closure capabilities and devices (with prophylactic defect closure now supported by randomized control trial level data).
- Perforation: Deep mural injury, once an endoscopists’ worst fear during resection, is no longer a surgical emergency. It can now be predicted, identified (Sydney classification) and successfully managed. In spite of more widespread aggressive resection strategies, the risk of emergency surgery in patients undergoing EMR and even ESD (where the risk of DMI is significantly higher) is extremely low.
Endoscopic resection for large colorectal polyps is effective, available, minimally invasive and organ sparing making it the standard of care for the management of colonic polyps. With ongoing iteration in techniques, more invasive surgical approaches can be avoided in almost all patients with benign and low-risk T1 colorectal cancers.
Dr. Gabr is associate GI division director at the University of Cincinnati, Ohio. Dr. Mosko is based in the division of gastroenterology at St. Michael’s Hospital, Toronto, Ontario, Canada. The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Blurred Lines: Polyp Needing Surgical versus Endoscopic Excision
BY IRA LEEDS, MD
I am grateful for the invitation to join in discussion with Dr. Gabr and Dr. Mosko on the ever-increasing role of endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) and endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD). However, as a surgeon, I do carry at least mild trepidation entering one of the literary “safe spaces” of my gastroenterology colleagues.
With the increasing evidentiary support of EMR approaches and the increasing experience of those performing ESD, these two techniques are quickly becoming the options of choice. As these practices become ubiquitous, it is important to recognize both their advantages and limitations, compared with available surgical options. The decision to proceed with EMR and ESD is essentially a turning point away from early surgical referral for a complex lesion. In this discussion, I intend to highlight when EMR and ESD have a clear advantage to early surgical referral, why I believe that early surgical referral is still superior to advanced endoscopic techniques in the rectum, and why the approach for right-sided lesions should hinge on careful shared decision-making.
Endoscopic approaches nearly always beat surgical approaches when considering short-term risks. Even in the best surgical series, colorectal surgery typically leads to complications in 10%-15% of patients, 1%-5% being serious. Moreover, transabdominal surgical interventions (ie, colectomy) require considerable recovery involving at least a few days in the inpatient setting and over a month of activity restrictions. Finally, there is a minority of chronically unwell patients who cannot tolerate surgical intervention but may be fortunate enough to have a lesion that with enhanced attention can be endoscopically resectioned. While EMR and ESD also contribute a disproportionate burden of complications to endoscopy practice, overall complication rates are still favorable when compared with surgical resection.
Moreover, the most feared short-term complication of EMR and ESD, perforation, has the added benefit of a “controlled failure” to colectomy. Advanced endoscopic approaches already require a prepared colon, and patients are given strict return instructions. Hence, the yearly handful of postprocedural perforations that I get called upon to assist with typically tolerate a routine surgical exploration, repair or resection, and recover at rates equal to or better than elective colon resections. For these reasons, lesions that can be endoscopically removed within appropriate risk tolerances, can and should be considered for EMR or ESD at time of diagnosis.
There are two clinical scenarios where this consideration for up-front EMR or ESD requires further caution. First, any rectal lesion considered for advanced endoscopic techniques really needs to be done in multidisciplinary conference with a colorectal surgeon. In the modern era of colorectal surgery, surgeons now have numerous approaches to reach the rectum that bridge the gap between traditional endoscopy and transabdominal resection. For many rectal lesions, transanal laparoscopic and robotic approaches offer the opportunity for local excision. The most commonly practiced approach, transanal minimally invasive microsurgery (TAMIS), provides many of the benefits of endoscopy (eg, same-day discharge, no activity restrictions, limited periprocedural physiologic stress, low complication rates) while providing the surgical precision, repair strategies, and specimen orientation of conventional surgery. Anecdotally, the time it takes to do a high-quality TAMIS excision in the rectum can be substantially less than that required for a comparable ESD.
For rectal lesions in particular, specimen quality is paramount for oncologic prognosis. Regardless of any intrinsic favorable histopathology or deft hand of the endoscopist, a TAMIS approach will typically provide for a deeper partial thickness or even full thickness excision. More times each year than I would like, I find myself at a multidisciplinary tumor board discussing an endoscopically removed rectal lesion done in a piecemeal fashion or insufficient deep ESD where appropriate risk stratification is impossible and we end up offering patients a likely overly aggressive proctectomy or a potentially oncologically unsound re-excision. Consideration of EMR/ESD vs TAMIS up front would allow better sorting of which technique is most suited to which lesion and avoid these diagnostic dilemmas that only seem to be more common as EMR and ESD practices proliferate.
For a different set of reasons, an advanced cecal adenoma may also be more suited to upfront surgical considerations. Right colon lesions can be more challenging for surveillance for a host of reasons. Procedurally, right colon lesions are undeniably more difficult. The thin-walled cecum can be unforgiving for repeated polypectomies. Despite it being an uncomfortable subject for colonoscopists, the evidence suggests that getting to the cecum is not consistent or 100% expected. Finally, patients can be unwilling to undergo serial bowel preparation and endoscopic examination. In contrast, a laparoscopic right colectomy avoids these issues while also attributing little additional risk. Laparoscopic right-colon operations have overall complication rates of less than 10% and major complications of less than 1%. Hospital stays for laparoscopic right colectomy are typically 3 days or less. Finally, surgery reduces both the frequency of surveillance, and a shortened colon makes surveillance easier.
Advanced polypectomy techniques broaden our ability to address even difficult lesions under the ideally aligned degree of invasive procedure. However, like any procedure, these techniques have their own advantages and limitations. There will always be a minority of premalignant colon lesions that are best suited to surgery-first approaches to treatment. In my practice, maintaining open lines of communication and regular interaction with my endoscopy colleagues naturally leads to polyps being addressed in their most suitable fashion.
Dr. Leeds is assistant professor of surgery at the Yale School of Medicine and a staff surgeon at the VA Connecticut Healthcare System. He declares no conflicts of interest.
Dear colleagues,
We now have the ability to remove almost any large colon polyp endoscopically using a variety of techniques — from the widely used endoscopic mucosal resection to the increasingly prevalent endoscopic submucosal dissection. Yet, in this new era,
In this issue of Perspectives, Dr. Jeffrey Mosko and Dr. Moamen Gabr discuss the importance of careful polyp selection and argue that almost all polyps can be safely removed endoscopically, with low recurrence rates. In contrast, Dr. Ira Leeds from colorectal surgery offers a counterpoint, urging caution when managing polyps in the cecum and rectum while highlighting the role of minimally invasive surgical approaches. We hope these discussions provide valuable insights to support your approach to managing large colorectal polyps, especially in an era of increasing colon cancer screening.
We also welcome your thoughts on this topic — join the conversation on X at @AGA_GIHN.
Gyanprakash A. Ketwaroo, MD, MSc, is associate professor of medicine, Yale University, New Haven, and chief of endoscopy at West Haven VA Medical Center, both in Connecticut. He is an associate editor for GI & Hepatology News.
Advantages of Endoscopic Resection for Large Colon Polyps
BY MOAMEN GABR, MD, MSC, AND JEFFREY D. MOSKO MD, MSC
General Advantages
Endoscopy has revolutionized the management of large colorectal polyps, offering a minimally invasive alternative to surgical resection. The dawn of endoscopic resection in the late 20th century, particularly the evolution of endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) in Japan, marked a paradigm shift in the treatment of colonic lesions by enabling the removal of lesions that would otherwise necessitate surgery.
Endoscopic resection of colorectal polyps is generally performed in an outpatient setting, allowing patients to recover at home the same day. This not only minimizes disruption to daily life but also significantly enhances patient satisfaction.
Most procedures are performed under moderate or deep sedation eliminating the need for general anesthesia. This represents a critical benefit, particularly for older or medically frail patients who are at higher risk of anesthesia-related complications.
From an economic perspective, endoscopic resection reduces healthcare costs by eliminating prolonged hospital stays and complex perioperative care. Additionally, preserving the colon’s structure and function avoids long-term consequences such as altered bowel habits or ostomy dependence, common with surgical interventions.
The advantages of endoscopic intervention are clear: safety, cost-effectiveness, organ preservation, and convenience for patients.
Lesion Selection
The superiority of endoscopic resection relies on selecting lesions appropriately, specifically those with a low risk of lymph node metastases. This meticulous process should include assessing a lesion’s size, location, morphology, granularity, microvascular and surface pit pattern using a combination of high-definition white light endoscopy, virtual chromoendoscopy and image magnification (when available).
Gross morphologic assessment utilizes the Paris and LST classifications. Combining the Paris classification, lesion granularity and location is both straightforward and revealing. Ulcerated/excavated lesions (0-III) are concerning for deep invasion. Depressed (0-IIc) morphologies are strongly associated with T1 CRC. Nodular lesions (0-Is or IIa + Is) have a higher risk of T1 colorectal cancer (CRC), compared with flat lesions (0-IIa or 0-IIb). Non-granular lesions (0-Is and 0-IIa + Is) have a higher risk of covert cancer. Finally, the rectosigmoid location is associated with an increased risk of T1 CRC (vs. proximal locations).
Endoscopic surface pattern assessment increases one’s diagnostic accuracy. There are three primary endoscopic surface pattern classifications: NBI International Colorectal Endoscopic (NICE), Japanese NBI expert team (JNET), and Kudo pit pattern classifications. Colonic lesions that have a NICE Type 3, JNET 3, or Kudo type Vn pattern should be referred promptly for surgical resection. Lesions with a JNET 2B or Kudo type VI carry a higher risk of superficial T1 CRC but can still be removed endoscopically (see below) in expert centers. All other lesions should undergo endoscopic resection.
Endoscopic Resection Techniques
Endoscopic resection of large colorectal polyps encompasses two primary techniques: EMR and endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD), each tailored to specific lesion characteristics and operator expertise.
EMR, the technique of choice for the vast majority of lesions, relies on injecting a submucosal cushion to lift the lesion before excision. Recent advances, including enhanced snare designs and underwater EMR, have improved en-bloc resection rates, significantly reducing recurrence and enhancing the efficacy of this technique.
ESD offers unparalleled precision for en-bloc resection of complex lesions, particularly those with fibrosis or high-risk features. Cutting-edge innovations, such as traction devices, have streamlined the procedure, addressing the traditional challenges of ESD. Despite being more time intensive, ESD minimizes recurrence and provides complete histopathological evaluation, critical for the management of malignant or pre-malignant lesions.
For non-lifting polyps, newer techniques such as endoscopic full-thickness resection (eFTR), using tools like the Full-Thickness Resection Device (FTRD), enable resection of up to 2-3 cm of the colonic or rectal wall. This ensures complete removal of any lesion and its underlying tissue, effectively preventing recurrence.
These advancements demonstrate how endoscopy can tackle even the most challenging colorectal polyps, reinforcing its position as the preferred treatment modality.
Perceived Limitations
With ongoing refinement over the last 2 decades, many of the perceived limitations (below) of endoscopic resection have now been overcome.
- Difficult locations/access: Historically lesions at the anorectal junction, ileocecal valve, appendiceal orifice and anastomoses were preferentially sent for surgery. In spite of unique technical challenges at each of these locations, there is now compelling data supporting EMR for these scenarios. We now also have techniques aimed at enabling the resection of lesions with poor access including patient repositioning, distal attachments, variable endoscope diameter/flexibility, traction and overtube devices.
- Recurrence: In the past, recurrence after endoscopic resection of lesions > 20 mm has been reported to be as high as 20%. With our current systematic approach to complete resection, meticulous examination of the post-resection defect for residual polyp tissue, adjunctive techniques to address submucosal fibrosis (hot avulsion, CAST, submucosal release) and thermal ablation to the resection margin (EMR-T), the risk of recurrence for piecemeal resections can be decreased to < 5%. In fact, some groups argue for the en-bloc resection of all large colorectal lesions based on the extremely low (< 1%) recurrence rates and potential for decreased follow-up.
- Post-resection bleeding: Post-resection bleeding is no longer a major limitation of any endoscopic approach because of the combination of improved intra-procedural hemostatic and resection techniques, optimized electrosurgical technology, and enhanced defect closure capabilities and devices (with prophylactic defect closure now supported by randomized control trial level data).
- Perforation: Deep mural injury, once an endoscopists’ worst fear during resection, is no longer a surgical emergency. It can now be predicted, identified (Sydney classification) and successfully managed. In spite of more widespread aggressive resection strategies, the risk of emergency surgery in patients undergoing EMR and even ESD (where the risk of DMI is significantly higher) is extremely low.
Endoscopic resection for large colorectal polyps is effective, available, minimally invasive and organ sparing making it the standard of care for the management of colonic polyps. With ongoing iteration in techniques, more invasive surgical approaches can be avoided in almost all patients with benign and low-risk T1 colorectal cancers.
Dr. Gabr is associate GI division director at the University of Cincinnati, Ohio. Dr. Mosko is based in the division of gastroenterology at St. Michael’s Hospital, Toronto, Ontario, Canada. The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Blurred Lines: Polyp Needing Surgical versus Endoscopic Excision
BY IRA LEEDS, MD
I am grateful for the invitation to join in discussion with Dr. Gabr and Dr. Mosko on the ever-increasing role of endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) and endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD). However, as a surgeon, I do carry at least mild trepidation entering one of the literary “safe spaces” of my gastroenterology colleagues.
With the increasing evidentiary support of EMR approaches and the increasing experience of those performing ESD, these two techniques are quickly becoming the options of choice. As these practices become ubiquitous, it is important to recognize both their advantages and limitations, compared with available surgical options. The decision to proceed with EMR and ESD is essentially a turning point away from early surgical referral for a complex lesion. In this discussion, I intend to highlight when EMR and ESD have a clear advantage to early surgical referral, why I believe that early surgical referral is still superior to advanced endoscopic techniques in the rectum, and why the approach for right-sided lesions should hinge on careful shared decision-making.
Endoscopic approaches nearly always beat surgical approaches when considering short-term risks. Even in the best surgical series, colorectal surgery typically leads to complications in 10%-15% of patients, 1%-5% being serious. Moreover, transabdominal surgical interventions (ie, colectomy) require considerable recovery involving at least a few days in the inpatient setting and over a month of activity restrictions. Finally, there is a minority of chronically unwell patients who cannot tolerate surgical intervention but may be fortunate enough to have a lesion that with enhanced attention can be endoscopically resectioned. While EMR and ESD also contribute a disproportionate burden of complications to endoscopy practice, overall complication rates are still favorable when compared with surgical resection.
Moreover, the most feared short-term complication of EMR and ESD, perforation, has the added benefit of a “controlled failure” to colectomy. Advanced endoscopic approaches already require a prepared colon, and patients are given strict return instructions. Hence, the yearly handful of postprocedural perforations that I get called upon to assist with typically tolerate a routine surgical exploration, repair or resection, and recover at rates equal to or better than elective colon resections. For these reasons, lesions that can be endoscopically removed within appropriate risk tolerances, can and should be considered for EMR or ESD at time of diagnosis.
There are two clinical scenarios where this consideration for up-front EMR or ESD requires further caution. First, any rectal lesion considered for advanced endoscopic techniques really needs to be done in multidisciplinary conference with a colorectal surgeon. In the modern era of colorectal surgery, surgeons now have numerous approaches to reach the rectum that bridge the gap between traditional endoscopy and transabdominal resection. For many rectal lesions, transanal laparoscopic and robotic approaches offer the opportunity for local excision. The most commonly practiced approach, transanal minimally invasive microsurgery (TAMIS), provides many of the benefits of endoscopy (eg, same-day discharge, no activity restrictions, limited periprocedural physiologic stress, low complication rates) while providing the surgical precision, repair strategies, and specimen orientation of conventional surgery. Anecdotally, the time it takes to do a high-quality TAMIS excision in the rectum can be substantially less than that required for a comparable ESD.
For rectal lesions in particular, specimen quality is paramount for oncologic prognosis. Regardless of any intrinsic favorable histopathology or deft hand of the endoscopist, a TAMIS approach will typically provide for a deeper partial thickness or even full thickness excision. More times each year than I would like, I find myself at a multidisciplinary tumor board discussing an endoscopically removed rectal lesion done in a piecemeal fashion or insufficient deep ESD where appropriate risk stratification is impossible and we end up offering patients a likely overly aggressive proctectomy or a potentially oncologically unsound re-excision. Consideration of EMR/ESD vs TAMIS up front would allow better sorting of which technique is most suited to which lesion and avoid these diagnostic dilemmas that only seem to be more common as EMR and ESD practices proliferate.
For a different set of reasons, an advanced cecal adenoma may also be more suited to upfront surgical considerations. Right colon lesions can be more challenging for surveillance for a host of reasons. Procedurally, right colon lesions are undeniably more difficult. The thin-walled cecum can be unforgiving for repeated polypectomies. Despite it being an uncomfortable subject for colonoscopists, the evidence suggests that getting to the cecum is not consistent or 100% expected. Finally, patients can be unwilling to undergo serial bowel preparation and endoscopic examination. In contrast, a laparoscopic right colectomy avoids these issues while also attributing little additional risk. Laparoscopic right-colon operations have overall complication rates of less than 10% and major complications of less than 1%. Hospital stays for laparoscopic right colectomy are typically 3 days or less. Finally, surgery reduces both the frequency of surveillance, and a shortened colon makes surveillance easier.
Advanced polypectomy techniques broaden our ability to address even difficult lesions under the ideally aligned degree of invasive procedure. However, like any procedure, these techniques have their own advantages and limitations. There will always be a minority of premalignant colon lesions that are best suited to surgery-first approaches to treatment. In my practice, maintaining open lines of communication and regular interaction with my endoscopy colleagues naturally leads to polyps being addressed in their most suitable fashion.
Dr. Leeds is assistant professor of surgery at the Yale School of Medicine and a staff surgeon at the VA Connecticut Healthcare System. He declares no conflicts of interest.
Dear colleagues,
We now have the ability to remove almost any large colon polyp endoscopically using a variety of techniques — from the widely used endoscopic mucosal resection to the increasingly prevalent endoscopic submucosal dissection. Yet, in this new era,
In this issue of Perspectives, Dr. Jeffrey Mosko and Dr. Moamen Gabr discuss the importance of careful polyp selection and argue that almost all polyps can be safely removed endoscopically, with low recurrence rates. In contrast, Dr. Ira Leeds from colorectal surgery offers a counterpoint, urging caution when managing polyps in the cecum and rectum while highlighting the role of minimally invasive surgical approaches. We hope these discussions provide valuable insights to support your approach to managing large colorectal polyps, especially in an era of increasing colon cancer screening.
We also welcome your thoughts on this topic — join the conversation on X at @AGA_GIHN.
Gyanprakash A. Ketwaroo, MD, MSc, is associate professor of medicine, Yale University, New Haven, and chief of endoscopy at West Haven VA Medical Center, both in Connecticut. He is an associate editor for GI & Hepatology News.
Advantages of Endoscopic Resection for Large Colon Polyps
BY MOAMEN GABR, MD, MSC, AND JEFFREY D. MOSKO MD, MSC
General Advantages
Endoscopy has revolutionized the management of large colorectal polyps, offering a minimally invasive alternative to surgical resection. The dawn of endoscopic resection in the late 20th century, particularly the evolution of endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) in Japan, marked a paradigm shift in the treatment of colonic lesions by enabling the removal of lesions that would otherwise necessitate surgery.
Endoscopic resection of colorectal polyps is generally performed in an outpatient setting, allowing patients to recover at home the same day. This not only minimizes disruption to daily life but also significantly enhances patient satisfaction.
Most procedures are performed under moderate or deep sedation eliminating the need for general anesthesia. This represents a critical benefit, particularly for older or medically frail patients who are at higher risk of anesthesia-related complications.
From an economic perspective, endoscopic resection reduces healthcare costs by eliminating prolonged hospital stays and complex perioperative care. Additionally, preserving the colon’s structure and function avoids long-term consequences such as altered bowel habits or ostomy dependence, common with surgical interventions.
The advantages of endoscopic intervention are clear: safety, cost-effectiveness, organ preservation, and convenience for patients.
Lesion Selection
The superiority of endoscopic resection relies on selecting lesions appropriately, specifically those with a low risk of lymph node metastases. This meticulous process should include assessing a lesion’s size, location, morphology, granularity, microvascular and surface pit pattern using a combination of high-definition white light endoscopy, virtual chromoendoscopy and image magnification (when available).
Gross morphologic assessment utilizes the Paris and LST classifications. Combining the Paris classification, lesion granularity and location is both straightforward and revealing. Ulcerated/excavated lesions (0-III) are concerning for deep invasion. Depressed (0-IIc) morphologies are strongly associated with T1 CRC. Nodular lesions (0-Is or IIa + Is) have a higher risk of T1 colorectal cancer (CRC), compared with flat lesions (0-IIa or 0-IIb). Non-granular lesions (0-Is and 0-IIa + Is) have a higher risk of covert cancer. Finally, the rectosigmoid location is associated with an increased risk of T1 CRC (vs. proximal locations).
Endoscopic surface pattern assessment increases one’s diagnostic accuracy. There are three primary endoscopic surface pattern classifications: NBI International Colorectal Endoscopic (NICE), Japanese NBI expert team (JNET), and Kudo pit pattern classifications. Colonic lesions that have a NICE Type 3, JNET 3, or Kudo type Vn pattern should be referred promptly for surgical resection. Lesions with a JNET 2B or Kudo type VI carry a higher risk of superficial T1 CRC but can still be removed endoscopically (see below) in expert centers. All other lesions should undergo endoscopic resection.
Endoscopic Resection Techniques
Endoscopic resection of large colorectal polyps encompasses two primary techniques: EMR and endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD), each tailored to specific lesion characteristics and operator expertise.
EMR, the technique of choice for the vast majority of lesions, relies on injecting a submucosal cushion to lift the lesion before excision. Recent advances, including enhanced snare designs and underwater EMR, have improved en-bloc resection rates, significantly reducing recurrence and enhancing the efficacy of this technique.
ESD offers unparalleled precision for en-bloc resection of complex lesions, particularly those with fibrosis or high-risk features. Cutting-edge innovations, such as traction devices, have streamlined the procedure, addressing the traditional challenges of ESD. Despite being more time intensive, ESD minimizes recurrence and provides complete histopathological evaluation, critical for the management of malignant or pre-malignant lesions.
For non-lifting polyps, newer techniques such as endoscopic full-thickness resection (eFTR), using tools like the Full-Thickness Resection Device (FTRD), enable resection of up to 2-3 cm of the colonic or rectal wall. This ensures complete removal of any lesion and its underlying tissue, effectively preventing recurrence.
These advancements demonstrate how endoscopy can tackle even the most challenging colorectal polyps, reinforcing its position as the preferred treatment modality.
Perceived Limitations
With ongoing refinement over the last 2 decades, many of the perceived limitations (below) of endoscopic resection have now been overcome.
- Difficult locations/access: Historically lesions at the anorectal junction, ileocecal valve, appendiceal orifice and anastomoses were preferentially sent for surgery. In spite of unique technical challenges at each of these locations, there is now compelling data supporting EMR for these scenarios. We now also have techniques aimed at enabling the resection of lesions with poor access including patient repositioning, distal attachments, variable endoscope diameter/flexibility, traction and overtube devices.
- Recurrence: In the past, recurrence after endoscopic resection of lesions > 20 mm has been reported to be as high as 20%. With our current systematic approach to complete resection, meticulous examination of the post-resection defect for residual polyp tissue, adjunctive techniques to address submucosal fibrosis (hot avulsion, CAST, submucosal release) and thermal ablation to the resection margin (EMR-T), the risk of recurrence for piecemeal resections can be decreased to < 5%. In fact, some groups argue for the en-bloc resection of all large colorectal lesions based on the extremely low (< 1%) recurrence rates and potential for decreased follow-up.
- Post-resection bleeding: Post-resection bleeding is no longer a major limitation of any endoscopic approach because of the combination of improved intra-procedural hemostatic and resection techniques, optimized electrosurgical technology, and enhanced defect closure capabilities and devices (with prophylactic defect closure now supported by randomized control trial level data).
- Perforation: Deep mural injury, once an endoscopists’ worst fear during resection, is no longer a surgical emergency. It can now be predicted, identified (Sydney classification) and successfully managed. In spite of more widespread aggressive resection strategies, the risk of emergency surgery in patients undergoing EMR and even ESD (where the risk of DMI is significantly higher) is extremely low.
Endoscopic resection for large colorectal polyps is effective, available, minimally invasive and organ sparing making it the standard of care for the management of colonic polyps. With ongoing iteration in techniques, more invasive surgical approaches can be avoided in almost all patients with benign and low-risk T1 colorectal cancers.
Dr. Gabr is associate GI division director at the University of Cincinnati, Ohio. Dr. Mosko is based in the division of gastroenterology at St. Michael’s Hospital, Toronto, Ontario, Canada. The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Blurred Lines: Polyp Needing Surgical versus Endoscopic Excision
BY IRA LEEDS, MD
I am grateful for the invitation to join in discussion with Dr. Gabr and Dr. Mosko on the ever-increasing role of endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) and endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD). However, as a surgeon, I do carry at least mild trepidation entering one of the literary “safe spaces” of my gastroenterology colleagues.
With the increasing evidentiary support of EMR approaches and the increasing experience of those performing ESD, these two techniques are quickly becoming the options of choice. As these practices become ubiquitous, it is important to recognize both their advantages and limitations, compared with available surgical options. The decision to proceed with EMR and ESD is essentially a turning point away from early surgical referral for a complex lesion. In this discussion, I intend to highlight when EMR and ESD have a clear advantage to early surgical referral, why I believe that early surgical referral is still superior to advanced endoscopic techniques in the rectum, and why the approach for right-sided lesions should hinge on careful shared decision-making.
Endoscopic approaches nearly always beat surgical approaches when considering short-term risks. Even in the best surgical series, colorectal surgery typically leads to complications in 10%-15% of patients, 1%-5% being serious. Moreover, transabdominal surgical interventions (ie, colectomy) require considerable recovery involving at least a few days in the inpatient setting and over a month of activity restrictions. Finally, there is a minority of chronically unwell patients who cannot tolerate surgical intervention but may be fortunate enough to have a lesion that with enhanced attention can be endoscopically resectioned. While EMR and ESD also contribute a disproportionate burden of complications to endoscopy practice, overall complication rates are still favorable when compared with surgical resection.
Moreover, the most feared short-term complication of EMR and ESD, perforation, has the added benefit of a “controlled failure” to colectomy. Advanced endoscopic approaches already require a prepared colon, and patients are given strict return instructions. Hence, the yearly handful of postprocedural perforations that I get called upon to assist with typically tolerate a routine surgical exploration, repair or resection, and recover at rates equal to or better than elective colon resections. For these reasons, lesions that can be endoscopically removed within appropriate risk tolerances, can and should be considered for EMR or ESD at time of diagnosis.
There are two clinical scenarios where this consideration for up-front EMR or ESD requires further caution. First, any rectal lesion considered for advanced endoscopic techniques really needs to be done in multidisciplinary conference with a colorectal surgeon. In the modern era of colorectal surgery, surgeons now have numerous approaches to reach the rectum that bridge the gap between traditional endoscopy and transabdominal resection. For many rectal lesions, transanal laparoscopic and robotic approaches offer the opportunity for local excision. The most commonly practiced approach, transanal minimally invasive microsurgery (TAMIS), provides many of the benefits of endoscopy (eg, same-day discharge, no activity restrictions, limited periprocedural physiologic stress, low complication rates) while providing the surgical precision, repair strategies, and specimen orientation of conventional surgery. Anecdotally, the time it takes to do a high-quality TAMIS excision in the rectum can be substantially less than that required for a comparable ESD.
For rectal lesions in particular, specimen quality is paramount for oncologic prognosis. Regardless of any intrinsic favorable histopathology or deft hand of the endoscopist, a TAMIS approach will typically provide for a deeper partial thickness or even full thickness excision. More times each year than I would like, I find myself at a multidisciplinary tumor board discussing an endoscopically removed rectal lesion done in a piecemeal fashion or insufficient deep ESD where appropriate risk stratification is impossible and we end up offering patients a likely overly aggressive proctectomy or a potentially oncologically unsound re-excision. Consideration of EMR/ESD vs TAMIS up front would allow better sorting of which technique is most suited to which lesion and avoid these diagnostic dilemmas that only seem to be more common as EMR and ESD practices proliferate.
For a different set of reasons, an advanced cecal adenoma may also be more suited to upfront surgical considerations. Right colon lesions can be more challenging for surveillance for a host of reasons. Procedurally, right colon lesions are undeniably more difficult. The thin-walled cecum can be unforgiving for repeated polypectomies. Despite it being an uncomfortable subject for colonoscopists, the evidence suggests that getting to the cecum is not consistent or 100% expected. Finally, patients can be unwilling to undergo serial bowel preparation and endoscopic examination. In contrast, a laparoscopic right colectomy avoids these issues while also attributing little additional risk. Laparoscopic right-colon operations have overall complication rates of less than 10% and major complications of less than 1%. Hospital stays for laparoscopic right colectomy are typically 3 days or less. Finally, surgery reduces both the frequency of surveillance, and a shortened colon makes surveillance easier.
Advanced polypectomy techniques broaden our ability to address even difficult lesions under the ideally aligned degree of invasive procedure. However, like any procedure, these techniques have their own advantages and limitations. There will always be a minority of premalignant colon lesions that are best suited to surgery-first approaches to treatment. In my practice, maintaining open lines of communication and regular interaction with my endoscopy colleagues naturally leads to polyps being addressed in their most suitable fashion.
Dr. Leeds is assistant professor of surgery at the Yale School of Medicine and a staff surgeon at the VA Connecticut Healthcare System. He declares no conflicts of interest.
Daycare Providers’ Little Helper
It is no secret that we have a daycare problem in this country. Twenty percent of families spend more than $36,000 for child care annually. Three quarters of a single parent’s income is spent on infant care. The result is that more than $122 billion is syphoned out of our economy in lost productivity and income.
How we got into this situation is less clear. Women who once were stay-at-home moms have moved into the workplace. Families are more mobile and grandparents who had been a source of childcare may live hours away. And, when they are nearby grandparents may themselves been forced to remain employed for economic reasons.
Despite the increase demand the market has failed to respond with more daycare providers because with a median hourly wage of less than $15.00 it is difficult to attract applicants from a pool of potential employees that is already in great demand.
And, let’s be honest, long hours cooped up inside with infants and toddlers isn’t the right job for everyone. For the most successful, although maybe not financially, providing daycare is truly a labor of love. There are high school and community college courses taught on child development and day care management. Experienced providers can be a source of tips-of-the trade to those just starting out. But, when there are three infants crying, two diapers to be changed, and a toddler heading toward a tantrum, two experienced providers may not be enough to calm the turbulent waters.
A recent article in my local newspaper provided stark evidence of how serious our daycare situation has become. Although the daycare owner denies the allegation, the Department of Health and Human Service told the parents that the investigation currently supports their complaints that the children had been given melatonin gummies without their permission. Final action is pending but it is likely the daycare will lose its license. Not surprisingly the parents have already removed their children.
Curious about whether this situation was an isolated event, it didn’t take Google too long to find evidence of other daycares in which children had been given sleep-related medications without their parents’ permission. In May 2024 a daycare provider and three of her employees in Manchester, New Hampshire, were arrested and charged with endangering the welfare of a child after allegedly spiking their charges food with melatonin. Lest you think drugging infants in daycare is just a New England thing, my research found a news story dating back to 2003 that reported on several cases in which daycare providers had been administering diphenhydramine without parents permission. In one instance there was a fatal outcome. While melatonin does not pose a health risk on a par with diphenhydramine, the issue is the fact that the parents were not consulted.
I suspect that these two incidents in Maine and New Hampshire are not isolated events and melatonin has replaced diphenhydramine as the daycare provider’s “little helper” nationwide. It’s not clear how we as pediatricians can help police this practice, other than suggesting to parents that they initiate dialogues about napping strategies with their daycare providers. Not with an accusatory tone but more of a sharing about what tricks each party uses to make napping happen. It may be that the daycare provider has some valuable and sound advice that the parents can adapt to their home situation. However, if the daycare provider’s explanation for why the child naps well doesn’t sound right or the child is unusually drowsy after daycare visits they should share their concerns with us a pediatric health care advisors.
Dr Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
It is no secret that we have a daycare problem in this country. Twenty percent of families spend more than $36,000 for child care annually. Three quarters of a single parent’s income is spent on infant care. The result is that more than $122 billion is syphoned out of our economy in lost productivity and income.
How we got into this situation is less clear. Women who once were stay-at-home moms have moved into the workplace. Families are more mobile and grandparents who had been a source of childcare may live hours away. And, when they are nearby grandparents may themselves been forced to remain employed for economic reasons.
Despite the increase demand the market has failed to respond with more daycare providers because with a median hourly wage of less than $15.00 it is difficult to attract applicants from a pool of potential employees that is already in great demand.
And, let’s be honest, long hours cooped up inside with infants and toddlers isn’t the right job for everyone. For the most successful, although maybe not financially, providing daycare is truly a labor of love. There are high school and community college courses taught on child development and day care management. Experienced providers can be a source of tips-of-the trade to those just starting out. But, when there are three infants crying, two diapers to be changed, and a toddler heading toward a tantrum, two experienced providers may not be enough to calm the turbulent waters.
A recent article in my local newspaper provided stark evidence of how serious our daycare situation has become. Although the daycare owner denies the allegation, the Department of Health and Human Service told the parents that the investigation currently supports their complaints that the children had been given melatonin gummies without their permission. Final action is pending but it is likely the daycare will lose its license. Not surprisingly the parents have already removed their children.
Curious about whether this situation was an isolated event, it didn’t take Google too long to find evidence of other daycares in which children had been given sleep-related medications without their parents’ permission. In May 2024 a daycare provider and three of her employees in Manchester, New Hampshire, were arrested and charged with endangering the welfare of a child after allegedly spiking their charges food with melatonin. Lest you think drugging infants in daycare is just a New England thing, my research found a news story dating back to 2003 that reported on several cases in which daycare providers had been administering diphenhydramine without parents permission. In one instance there was a fatal outcome. While melatonin does not pose a health risk on a par with diphenhydramine, the issue is the fact that the parents were not consulted.
I suspect that these two incidents in Maine and New Hampshire are not isolated events and melatonin has replaced diphenhydramine as the daycare provider’s “little helper” nationwide. It’s not clear how we as pediatricians can help police this practice, other than suggesting to parents that they initiate dialogues about napping strategies with their daycare providers. Not with an accusatory tone but more of a sharing about what tricks each party uses to make napping happen. It may be that the daycare provider has some valuable and sound advice that the parents can adapt to their home situation. However, if the daycare provider’s explanation for why the child naps well doesn’t sound right or the child is unusually drowsy after daycare visits they should share their concerns with us a pediatric health care advisors.
Dr Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
It is no secret that we have a daycare problem in this country. Twenty percent of families spend more than $36,000 for child care annually. Three quarters of a single parent’s income is spent on infant care. The result is that more than $122 billion is syphoned out of our economy in lost productivity and income.
How we got into this situation is less clear. Women who once were stay-at-home moms have moved into the workplace. Families are more mobile and grandparents who had been a source of childcare may live hours away. And, when they are nearby grandparents may themselves been forced to remain employed for economic reasons.
Despite the increase demand the market has failed to respond with more daycare providers because with a median hourly wage of less than $15.00 it is difficult to attract applicants from a pool of potential employees that is already in great demand.
And, let’s be honest, long hours cooped up inside with infants and toddlers isn’t the right job for everyone. For the most successful, although maybe not financially, providing daycare is truly a labor of love. There are high school and community college courses taught on child development and day care management. Experienced providers can be a source of tips-of-the trade to those just starting out. But, when there are three infants crying, two diapers to be changed, and a toddler heading toward a tantrum, two experienced providers may not be enough to calm the turbulent waters.
A recent article in my local newspaper provided stark evidence of how serious our daycare situation has become. Although the daycare owner denies the allegation, the Department of Health and Human Service told the parents that the investigation currently supports their complaints that the children had been given melatonin gummies without their permission. Final action is pending but it is likely the daycare will lose its license. Not surprisingly the parents have already removed their children.
Curious about whether this situation was an isolated event, it didn’t take Google too long to find evidence of other daycares in which children had been given sleep-related medications without their parents’ permission. In May 2024 a daycare provider and three of her employees in Manchester, New Hampshire, were arrested and charged with endangering the welfare of a child after allegedly spiking their charges food with melatonin. Lest you think drugging infants in daycare is just a New England thing, my research found a news story dating back to 2003 that reported on several cases in which daycare providers had been administering diphenhydramine without parents permission. In one instance there was a fatal outcome. While melatonin does not pose a health risk on a par with diphenhydramine, the issue is the fact that the parents were not consulted.
I suspect that these two incidents in Maine and New Hampshire are not isolated events and melatonin has replaced diphenhydramine as the daycare provider’s “little helper” nationwide. It’s not clear how we as pediatricians can help police this practice, other than suggesting to parents that they initiate dialogues about napping strategies with their daycare providers. Not with an accusatory tone but more of a sharing about what tricks each party uses to make napping happen. It may be that the daycare provider has some valuable and sound advice that the parents can adapt to their home situation. However, if the daycare provider’s explanation for why the child naps well doesn’t sound right or the child is unusually drowsy after daycare visits they should share their concerns with us a pediatric health care advisors.
Dr Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
ADHD Myths
In the second half of the school year, you may find that there is a surge of families coming to appointments with concerns about school performance, wondering if their child has ADHD. We expect you are very familiar with this condition, both diagnosing and treating it. So this month we will offer “mythbusters” for ADHD: Responding to common misperceptions about ADHD with a summary of what the research has demonstrated as emerging facts, what is clearly fiction and what falls into the gray space between.
Demographics
A CDC survey of parents from 2022 indicates that 11.4% of children aged 3-17 have ever been diagnosed with ADHD in the United States. This is more than double the ADHD global prevalence of 5%, suggesting that there is overdiagnosis of this condition in this country. Boys are almost twice as likely to be diagnosed (14.5%) as girls (8%), and White children were more likely to be diagnosed than were Black and Hispanic children. The prevalence of ADHD diagnosis decreases as family income increases, and the condition is more frequently diagnosed in 12- to 17-year-olds than in children 11 and younger. The great majority of youth with an ADHD diagnosis (78%) have at least one co-occurring psychiatric condition. Of the children diagnosed with ADHD, slightly over half receive medication treatment (53.6%) whereas nearly a third (30.1%) receive no ADHD-specific treatment.
The Multimodal Treatment of ADHD Study (MTA), a large (600 children, aged 7-9 years), multicenter, longitudinal study of treatment outcomes for medication as well as behavioral and combination therapies demonstrated in every site that medication alone and combination therapy were significantly superior to intensive behavioral treatment alone and to routine community care in the reduction of ADHD symptoms. Of note, problems commonly associated with ADHD (parent-child conflict, anxiety symptoms, poor academic performance, and limited social skills) improved only with the combination treatment. This suggests that while core ADHD symptoms require medication, associated problems will also require behavioral treatment.
The American Academy of Pediatrics has a useful resource guide (healthychildren.org) highlighting the possible symptoms of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity that should be investigated when considering this diagnosis. It is a clinical diagnosis, but screening instruments (such as the Vanderbilt) can be very helpful to identifying symptoms that should be present in more than one setting (home and school). While a child with ADHD can appear calm and focused when receiving direct one-to-one attention (as during a pediatrician’s appointment), symptoms may flourish in less structured or supervised settings. Sometimes parents are keen reporters of a child’s behaviors, but some loving (and exhausted) parents may overreact to a normal degree of inattention or disobedience. This can be especially true when a parent has a more detail-oriented temperament than the child, or with younger children and first-time parents. It is important to consider ADHD when you hear about social difficulties as well as academic ones, where there is a family history of ADHD or when a child is more impulsive, hyperactive, or inattentive than you would expect given their age and developmental stage. Confirm your clinical exam with teacher and parent reports. If the reports don’t line up or there are persistent learning problems in school, consider neuropsychological testing to root out a learning disability.
Myth 1: “ADHD never starts in adolescence; you can’t diagnose it after elementary school.”
Diagnostic criteria used to require that symptoms were present before the age of 7 (DSM 3). But current criteria allow for diagnosis before 12 years of age or after. While the consensus is that ADHD is present in childhood, its symptoms are often not apparent. This is because normal development in much younger children is marked by higher levels of activity, distractibility, and impulsivity. Also, children with inattentive-type ADHD may not be apparent to adults if they are performing adequately in school. These youth often do not present for assessment until the challenges of a busy course load make their inattention and consequent inefficiency apparent, in high school or even college. Certainly, when a teenager presents complaining of trouble performing at school, it is critical to rule out an overburdened schedule, anxiety or mood disorder, poor sleep habits or sleep disorder, and substance use disorders, all of which are more common in adolescence. But inattentive-type ADHD that was previously missed is also a possibility worth investigating.
Myth 2: “Most children outgrow ADHD; it’s best to find natural solutions and wait it out.”
Early epidemiological studies suggested that as many as 30% of ADHD cases remitted by adulthood, but more recent data has adjusted that number down substantially, closer to 9%. Interestingly, it appears that 10% of patients will experience sustained symptoms, 9% will experience recovery (sustained remission without treatment), and a large majority will have a remitting and relapsing course into adulthood.1
This emerging evidence suggests that ADHD is almost always a lifelong condition. Untreated, it can threaten healthy development (including social skills and self-esteem) and day-to-day function (academic, social and athletic performance and even vulnerability to accidents) in ways that can be profound. The MTA Study has powerfully demonstrated the efficacy of pharmacological treatment and of specific behavioral treatments for ADHD and associated problems.
Myth 3: “You should exhaust natural cures first before trying medications.”
There has been a large amount of research into a variety of “natural” treatments for ADHD: special diets, supplements, increased exercise, and interventions like neurofeedback. While high-dose omega 3 fatty acid supplementation has demonstrated mild improvement in ADHD symptoms, no “natural” treatment has come close to the efficacy of stimulant medications. Interventions such as neurofeedback are expensive and time-consuming without any demonstrated efficacy. That said, improving a child’s routines around sleep, nutrition, and regular exercise are broadly useful strategies to improve any child’s (or adult’s) energy, impulse control, attention, motivation, and capacity to manage adversity and stress. Start any treatment by addressing sleep and exercise, including moderating time spent on screens, to support healthy function. But only medication will achieve symptom remission if your patient has underlying ADHD.
Myth 4: “All medications are equally effective in ADHD.”
It is well-established that stimulants are more effective than non-stimulants in the treatment of ADHD symptoms, with an effect size that is almost double that of non-stimulants.2
Amphetamine-based medications are slightly more effective than methylphenidate-based medications, but they are also generally less well-tolerated. Individual patients commonly have a better response to one class than the other, but you will need a trial to determine which one. It is reasonable to start a patient with an extended formulation of one class, based on your assessment of their vulnerability to side effects or a family history of medication response. Non-stimulants are of use when stimulants are not tolerated (ie, use of atomoxetine with patients who have comorbid anxiety), or to target specific symptoms, such as guanfacine or clonidine for hyperactivity.
Myth 5: “You can’t treat ADHD in substance abusing teens, stimulant medications are addictive.”
ADHD itself (not medications) increases the risk for addiction; those with ADHD are almost twice as likely to develop a substance use disorder, with highest risk for marijuana, alcohol, and nicotine abuse.3
This may be a function of limited impulse control or increased sensitivity in the ADHD brain to a drug’s addictive potential. Importantly, there is growing evidence that youth whose ADHD is treated pharmacologically are at lower risk for addiction than their peers with untreated ADHD.4
Those youth who have both ADHD and addiction are more likely to stay engaged in treatment for addiction when their ADHD is effectively treated, and there are medication formulations (lisdexamfetamine) that are safe in addiction (cannot be absorbed nasally or intravenously). It is important for you to talk about the heightened vulnerability to addiction with your ADHD patients and their parents, and the value of effective treatment in preventing this complication.
Myth 6: “ADHD is usually behavioral. Help parents to set rules, expectations, and limits instead of medicating the problem.”
Bad parenting does not cause ADHD. ADHD is marked by difficulties with impulse control, hyperactivity, and sustaining attention with matters that are not intrinsically engaging. “Behavioral issues” are patterns of behavior children learn to seek rewards or avoid negative consequences. Youth with ADHD can develop behavioral problems, but these are usually driven by negative feedback about their activity level, forgetfulness, or impulse control, which they are not able to change. This can lead to frustration and irritability, poor self-esteem, and even hopelessness — in parents and children both!
While parents are not the source of ADHD symptoms, there is a great deal of parent education and support that can be powerfully effective for these families. Parents benefit from learning strategies that can help their children to shift their attention, plan ahead, and manage frustration, especially for times when their children are unmedicated (vacations and bedtime). It is worth noting that ADHD is among the most heritable of youth psychiatric illnesses, so it is not uncommon for a parent of a child with ADHD to have similar symptoms. If the parents’ ADHD is untreated, they may be more impulsive themselves. They may also be extra sensitive to the qualities they dislike in themselves, inadvertently adding to their children’s sense of shame. ADHD is very treatable, and those with it can learn executive function skills and organizational strategies that can equip them to manage residual symptoms. Parents will benefit from strategies to understand their children and to help them learn adaptive skills in a realistic way. Your discussions with parents could help the families in your practice make adjustments that can translate into big differences in their child’s healthiest development.
Swick is physician in chief at Ohana, Center for Child and Adolescent Behavioral Health, Community Hospital of the Monterey (Calif.) Peninsula. Jellinek is professor emeritus of psychiatry and pediatrics, Harvard Medical School, Boston. Email them at [email protected].
References
1. Sibley MH et al. MTA Cooperative Group. Variable Patterns of Remission From ADHD in the Multimodal Treatment Study of ADHD. Am J Psychiatry. 2022 Feb;179(2):142-151. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2021.21010032.
2. Cortese S et al. Comparative Efficacy and Tolerability of Medications for Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder in Children, Adolescents, and Adults: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Lancet Psychiatry. 2018 Sep;5(9):727-738. doi: 10.1016/S2215-0366(18)30269-4.
3. Lee SS et al. Prospective Association of Childhood Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) and Substance Use and Abuse/Dependence: A Meta-Analytic Review. Clin Psychol Rev. 2011 Apr;31(3):328-41. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2011.01.006.
4. Chorniy A, Kitashima L. Sex, Drugs, and ADHD: The Effects of ADHD Pharmacological Treatment on Teens’ Risky Behaviors. Labour Economics. 2016;43:87-105. doi.org/10.1016/j.labeco.2016.06.014.
In the second half of the school year, you may find that there is a surge of families coming to appointments with concerns about school performance, wondering if their child has ADHD. We expect you are very familiar with this condition, both diagnosing and treating it. So this month we will offer “mythbusters” for ADHD: Responding to common misperceptions about ADHD with a summary of what the research has demonstrated as emerging facts, what is clearly fiction and what falls into the gray space between.
Demographics
A CDC survey of parents from 2022 indicates that 11.4% of children aged 3-17 have ever been diagnosed with ADHD in the United States. This is more than double the ADHD global prevalence of 5%, suggesting that there is overdiagnosis of this condition in this country. Boys are almost twice as likely to be diagnosed (14.5%) as girls (8%), and White children were more likely to be diagnosed than were Black and Hispanic children. The prevalence of ADHD diagnosis decreases as family income increases, and the condition is more frequently diagnosed in 12- to 17-year-olds than in children 11 and younger. The great majority of youth with an ADHD diagnosis (78%) have at least one co-occurring psychiatric condition. Of the children diagnosed with ADHD, slightly over half receive medication treatment (53.6%) whereas nearly a third (30.1%) receive no ADHD-specific treatment.
The Multimodal Treatment of ADHD Study (MTA), a large (600 children, aged 7-9 years), multicenter, longitudinal study of treatment outcomes for medication as well as behavioral and combination therapies demonstrated in every site that medication alone and combination therapy were significantly superior to intensive behavioral treatment alone and to routine community care in the reduction of ADHD symptoms. Of note, problems commonly associated with ADHD (parent-child conflict, anxiety symptoms, poor academic performance, and limited social skills) improved only with the combination treatment. This suggests that while core ADHD symptoms require medication, associated problems will also require behavioral treatment.
The American Academy of Pediatrics has a useful resource guide (healthychildren.org) highlighting the possible symptoms of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity that should be investigated when considering this diagnosis. It is a clinical diagnosis, but screening instruments (such as the Vanderbilt) can be very helpful to identifying symptoms that should be present in more than one setting (home and school). While a child with ADHD can appear calm and focused when receiving direct one-to-one attention (as during a pediatrician’s appointment), symptoms may flourish in less structured or supervised settings. Sometimes parents are keen reporters of a child’s behaviors, but some loving (and exhausted) parents may overreact to a normal degree of inattention or disobedience. This can be especially true when a parent has a more detail-oriented temperament than the child, or with younger children and first-time parents. It is important to consider ADHD when you hear about social difficulties as well as academic ones, where there is a family history of ADHD or when a child is more impulsive, hyperactive, or inattentive than you would expect given their age and developmental stage. Confirm your clinical exam with teacher and parent reports. If the reports don’t line up or there are persistent learning problems in school, consider neuropsychological testing to root out a learning disability.
Myth 1: “ADHD never starts in adolescence; you can’t diagnose it after elementary school.”
Diagnostic criteria used to require that symptoms were present before the age of 7 (DSM 3). But current criteria allow for diagnosis before 12 years of age or after. While the consensus is that ADHD is present in childhood, its symptoms are often not apparent. This is because normal development in much younger children is marked by higher levels of activity, distractibility, and impulsivity. Also, children with inattentive-type ADHD may not be apparent to adults if they are performing adequately in school. These youth often do not present for assessment until the challenges of a busy course load make their inattention and consequent inefficiency apparent, in high school or even college. Certainly, when a teenager presents complaining of trouble performing at school, it is critical to rule out an overburdened schedule, anxiety or mood disorder, poor sleep habits or sleep disorder, and substance use disorders, all of which are more common in adolescence. But inattentive-type ADHD that was previously missed is also a possibility worth investigating.
Myth 2: “Most children outgrow ADHD; it’s best to find natural solutions and wait it out.”
Early epidemiological studies suggested that as many as 30% of ADHD cases remitted by adulthood, but more recent data has adjusted that number down substantially, closer to 9%. Interestingly, it appears that 10% of patients will experience sustained symptoms, 9% will experience recovery (sustained remission without treatment), and a large majority will have a remitting and relapsing course into adulthood.1
This emerging evidence suggests that ADHD is almost always a lifelong condition. Untreated, it can threaten healthy development (including social skills and self-esteem) and day-to-day function (academic, social and athletic performance and even vulnerability to accidents) in ways that can be profound. The MTA Study has powerfully demonstrated the efficacy of pharmacological treatment and of specific behavioral treatments for ADHD and associated problems.
Myth 3: “You should exhaust natural cures first before trying medications.”
There has been a large amount of research into a variety of “natural” treatments for ADHD: special diets, supplements, increased exercise, and interventions like neurofeedback. While high-dose omega 3 fatty acid supplementation has demonstrated mild improvement in ADHD symptoms, no “natural” treatment has come close to the efficacy of stimulant medications. Interventions such as neurofeedback are expensive and time-consuming without any demonstrated efficacy. That said, improving a child’s routines around sleep, nutrition, and regular exercise are broadly useful strategies to improve any child’s (or adult’s) energy, impulse control, attention, motivation, and capacity to manage adversity and stress. Start any treatment by addressing sleep and exercise, including moderating time spent on screens, to support healthy function. But only medication will achieve symptom remission if your patient has underlying ADHD.
Myth 4: “All medications are equally effective in ADHD.”
It is well-established that stimulants are more effective than non-stimulants in the treatment of ADHD symptoms, with an effect size that is almost double that of non-stimulants.2
Amphetamine-based medications are slightly more effective than methylphenidate-based medications, but they are also generally less well-tolerated. Individual patients commonly have a better response to one class than the other, but you will need a trial to determine which one. It is reasonable to start a patient with an extended formulation of one class, based on your assessment of their vulnerability to side effects or a family history of medication response. Non-stimulants are of use when stimulants are not tolerated (ie, use of atomoxetine with patients who have comorbid anxiety), or to target specific symptoms, such as guanfacine or clonidine for hyperactivity.
Myth 5: “You can’t treat ADHD in substance abusing teens, stimulant medications are addictive.”
ADHD itself (not medications) increases the risk for addiction; those with ADHD are almost twice as likely to develop a substance use disorder, with highest risk for marijuana, alcohol, and nicotine abuse.3
This may be a function of limited impulse control or increased sensitivity in the ADHD brain to a drug’s addictive potential. Importantly, there is growing evidence that youth whose ADHD is treated pharmacologically are at lower risk for addiction than their peers with untreated ADHD.4
Those youth who have both ADHD and addiction are more likely to stay engaged in treatment for addiction when their ADHD is effectively treated, and there are medication formulations (lisdexamfetamine) that are safe in addiction (cannot be absorbed nasally or intravenously). It is important for you to talk about the heightened vulnerability to addiction with your ADHD patients and their parents, and the value of effective treatment in preventing this complication.
Myth 6: “ADHD is usually behavioral. Help parents to set rules, expectations, and limits instead of medicating the problem.”
Bad parenting does not cause ADHD. ADHD is marked by difficulties with impulse control, hyperactivity, and sustaining attention with matters that are not intrinsically engaging. “Behavioral issues” are patterns of behavior children learn to seek rewards or avoid negative consequences. Youth with ADHD can develop behavioral problems, but these are usually driven by negative feedback about their activity level, forgetfulness, or impulse control, which they are not able to change. This can lead to frustration and irritability, poor self-esteem, and even hopelessness — in parents and children both!
While parents are not the source of ADHD symptoms, there is a great deal of parent education and support that can be powerfully effective for these families. Parents benefit from learning strategies that can help their children to shift their attention, plan ahead, and manage frustration, especially for times when their children are unmedicated (vacations and bedtime). It is worth noting that ADHD is among the most heritable of youth psychiatric illnesses, so it is not uncommon for a parent of a child with ADHD to have similar symptoms. If the parents’ ADHD is untreated, they may be more impulsive themselves. They may also be extra sensitive to the qualities they dislike in themselves, inadvertently adding to their children’s sense of shame. ADHD is very treatable, and those with it can learn executive function skills and organizational strategies that can equip them to manage residual symptoms. Parents will benefit from strategies to understand their children and to help them learn adaptive skills in a realistic way. Your discussions with parents could help the families in your practice make adjustments that can translate into big differences in their child’s healthiest development.
Swick is physician in chief at Ohana, Center for Child and Adolescent Behavioral Health, Community Hospital of the Monterey (Calif.) Peninsula. Jellinek is professor emeritus of psychiatry and pediatrics, Harvard Medical School, Boston. Email them at [email protected].
References
1. Sibley MH et al. MTA Cooperative Group. Variable Patterns of Remission From ADHD in the Multimodal Treatment Study of ADHD. Am J Psychiatry. 2022 Feb;179(2):142-151. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2021.21010032.
2. Cortese S et al. Comparative Efficacy and Tolerability of Medications for Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder in Children, Adolescents, and Adults: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Lancet Psychiatry. 2018 Sep;5(9):727-738. doi: 10.1016/S2215-0366(18)30269-4.
3. Lee SS et al. Prospective Association of Childhood Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) and Substance Use and Abuse/Dependence: A Meta-Analytic Review. Clin Psychol Rev. 2011 Apr;31(3):328-41. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2011.01.006.
4. Chorniy A, Kitashima L. Sex, Drugs, and ADHD: The Effects of ADHD Pharmacological Treatment on Teens’ Risky Behaviors. Labour Economics. 2016;43:87-105. doi.org/10.1016/j.labeco.2016.06.014.
In the second half of the school year, you may find that there is a surge of families coming to appointments with concerns about school performance, wondering if their child has ADHD. We expect you are very familiar with this condition, both diagnosing and treating it. So this month we will offer “mythbusters” for ADHD: Responding to common misperceptions about ADHD with a summary of what the research has demonstrated as emerging facts, what is clearly fiction and what falls into the gray space between.
Demographics
A CDC survey of parents from 2022 indicates that 11.4% of children aged 3-17 have ever been diagnosed with ADHD in the United States. This is more than double the ADHD global prevalence of 5%, suggesting that there is overdiagnosis of this condition in this country. Boys are almost twice as likely to be diagnosed (14.5%) as girls (8%), and White children were more likely to be diagnosed than were Black and Hispanic children. The prevalence of ADHD diagnosis decreases as family income increases, and the condition is more frequently diagnosed in 12- to 17-year-olds than in children 11 and younger. The great majority of youth with an ADHD diagnosis (78%) have at least one co-occurring psychiatric condition. Of the children diagnosed with ADHD, slightly over half receive medication treatment (53.6%) whereas nearly a third (30.1%) receive no ADHD-specific treatment.
The Multimodal Treatment of ADHD Study (MTA), a large (600 children, aged 7-9 years), multicenter, longitudinal study of treatment outcomes for medication as well as behavioral and combination therapies demonstrated in every site that medication alone and combination therapy were significantly superior to intensive behavioral treatment alone and to routine community care in the reduction of ADHD symptoms. Of note, problems commonly associated with ADHD (parent-child conflict, anxiety symptoms, poor academic performance, and limited social skills) improved only with the combination treatment. This suggests that while core ADHD symptoms require medication, associated problems will also require behavioral treatment.
The American Academy of Pediatrics has a useful resource guide (healthychildren.org) highlighting the possible symptoms of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity that should be investigated when considering this diagnosis. It is a clinical diagnosis, but screening instruments (such as the Vanderbilt) can be very helpful to identifying symptoms that should be present in more than one setting (home and school). While a child with ADHD can appear calm and focused when receiving direct one-to-one attention (as during a pediatrician’s appointment), symptoms may flourish in less structured or supervised settings. Sometimes parents are keen reporters of a child’s behaviors, but some loving (and exhausted) parents may overreact to a normal degree of inattention or disobedience. This can be especially true when a parent has a more detail-oriented temperament than the child, or with younger children and first-time parents. It is important to consider ADHD when you hear about social difficulties as well as academic ones, where there is a family history of ADHD or when a child is more impulsive, hyperactive, or inattentive than you would expect given their age and developmental stage. Confirm your clinical exam with teacher and parent reports. If the reports don’t line up or there are persistent learning problems in school, consider neuropsychological testing to root out a learning disability.
Myth 1: “ADHD never starts in adolescence; you can’t diagnose it after elementary school.”
Diagnostic criteria used to require that symptoms were present before the age of 7 (DSM 3). But current criteria allow for diagnosis before 12 years of age or after. While the consensus is that ADHD is present in childhood, its symptoms are often not apparent. This is because normal development in much younger children is marked by higher levels of activity, distractibility, and impulsivity. Also, children with inattentive-type ADHD may not be apparent to adults if they are performing adequately in school. These youth often do not present for assessment until the challenges of a busy course load make their inattention and consequent inefficiency apparent, in high school or even college. Certainly, when a teenager presents complaining of trouble performing at school, it is critical to rule out an overburdened schedule, anxiety or mood disorder, poor sleep habits or sleep disorder, and substance use disorders, all of which are more common in adolescence. But inattentive-type ADHD that was previously missed is also a possibility worth investigating.
Myth 2: “Most children outgrow ADHD; it’s best to find natural solutions and wait it out.”
Early epidemiological studies suggested that as many as 30% of ADHD cases remitted by adulthood, but more recent data has adjusted that number down substantially, closer to 9%. Interestingly, it appears that 10% of patients will experience sustained symptoms, 9% will experience recovery (sustained remission without treatment), and a large majority will have a remitting and relapsing course into adulthood.1
This emerging evidence suggests that ADHD is almost always a lifelong condition. Untreated, it can threaten healthy development (including social skills and self-esteem) and day-to-day function (academic, social and athletic performance and even vulnerability to accidents) in ways that can be profound. The MTA Study has powerfully demonstrated the efficacy of pharmacological treatment and of specific behavioral treatments for ADHD and associated problems.
Myth 3: “You should exhaust natural cures first before trying medications.”
There has been a large amount of research into a variety of “natural” treatments for ADHD: special diets, supplements, increased exercise, and interventions like neurofeedback. While high-dose omega 3 fatty acid supplementation has demonstrated mild improvement in ADHD symptoms, no “natural” treatment has come close to the efficacy of stimulant medications. Interventions such as neurofeedback are expensive and time-consuming without any demonstrated efficacy. That said, improving a child’s routines around sleep, nutrition, and regular exercise are broadly useful strategies to improve any child’s (or adult’s) energy, impulse control, attention, motivation, and capacity to manage adversity and stress. Start any treatment by addressing sleep and exercise, including moderating time spent on screens, to support healthy function. But only medication will achieve symptom remission if your patient has underlying ADHD.
Myth 4: “All medications are equally effective in ADHD.”
It is well-established that stimulants are more effective than non-stimulants in the treatment of ADHD symptoms, with an effect size that is almost double that of non-stimulants.2
Amphetamine-based medications are slightly more effective than methylphenidate-based medications, but they are also generally less well-tolerated. Individual patients commonly have a better response to one class than the other, but you will need a trial to determine which one. It is reasonable to start a patient with an extended formulation of one class, based on your assessment of their vulnerability to side effects or a family history of medication response. Non-stimulants are of use when stimulants are not tolerated (ie, use of atomoxetine with patients who have comorbid anxiety), or to target specific symptoms, such as guanfacine or clonidine for hyperactivity.
Myth 5: “You can’t treat ADHD in substance abusing teens, stimulant medications are addictive.”
ADHD itself (not medications) increases the risk for addiction; those with ADHD are almost twice as likely to develop a substance use disorder, with highest risk for marijuana, alcohol, and nicotine abuse.3
This may be a function of limited impulse control or increased sensitivity in the ADHD brain to a drug’s addictive potential. Importantly, there is growing evidence that youth whose ADHD is treated pharmacologically are at lower risk for addiction than their peers with untreated ADHD.4
Those youth who have both ADHD and addiction are more likely to stay engaged in treatment for addiction when their ADHD is effectively treated, and there are medication formulations (lisdexamfetamine) that are safe in addiction (cannot be absorbed nasally or intravenously). It is important for you to talk about the heightened vulnerability to addiction with your ADHD patients and their parents, and the value of effective treatment in preventing this complication.
Myth 6: “ADHD is usually behavioral. Help parents to set rules, expectations, and limits instead of medicating the problem.”
Bad parenting does not cause ADHD. ADHD is marked by difficulties with impulse control, hyperactivity, and sustaining attention with matters that are not intrinsically engaging. “Behavioral issues” are patterns of behavior children learn to seek rewards or avoid negative consequences. Youth with ADHD can develop behavioral problems, but these are usually driven by negative feedback about their activity level, forgetfulness, or impulse control, which they are not able to change. This can lead to frustration and irritability, poor self-esteem, and even hopelessness — in parents and children both!
While parents are not the source of ADHD symptoms, there is a great deal of parent education and support that can be powerfully effective for these families. Parents benefit from learning strategies that can help their children to shift their attention, plan ahead, and manage frustration, especially for times when their children are unmedicated (vacations and bedtime). It is worth noting that ADHD is among the most heritable of youth psychiatric illnesses, so it is not uncommon for a parent of a child with ADHD to have similar symptoms. If the parents’ ADHD is untreated, they may be more impulsive themselves. They may also be extra sensitive to the qualities they dislike in themselves, inadvertently adding to their children’s sense of shame. ADHD is very treatable, and those with it can learn executive function skills and organizational strategies that can equip them to manage residual symptoms. Parents will benefit from strategies to understand their children and to help them learn adaptive skills in a realistic way. Your discussions with parents could help the families in your practice make adjustments that can translate into big differences in their child’s healthiest development.
Swick is physician in chief at Ohana, Center for Child and Adolescent Behavioral Health, Community Hospital of the Monterey (Calif.) Peninsula. Jellinek is professor emeritus of psychiatry and pediatrics, Harvard Medical School, Boston. Email them at [email protected].
References
1. Sibley MH et al. MTA Cooperative Group. Variable Patterns of Remission From ADHD in the Multimodal Treatment Study of ADHD. Am J Psychiatry. 2022 Feb;179(2):142-151. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2021.21010032.
2. Cortese S et al. Comparative Efficacy and Tolerability of Medications for Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder in Children, Adolescents, and Adults: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Lancet Psychiatry. 2018 Sep;5(9):727-738. doi: 10.1016/S2215-0366(18)30269-4.
3. Lee SS et al. Prospective Association of Childhood Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) and Substance Use and Abuse/Dependence: A Meta-Analytic Review. Clin Psychol Rev. 2011 Apr;31(3):328-41. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2011.01.006.
4. Chorniy A, Kitashima L. Sex, Drugs, and ADHD: The Effects of ADHD Pharmacological Treatment on Teens’ Risky Behaviors. Labour Economics. 2016;43:87-105. doi.org/10.1016/j.labeco.2016.06.014.
Group A Streptococcal Pharyngitis Diagnosis
It’s wintertime, peak season for GAS pharyngitis, and you’d think that this far into the 21st century we would have a foolproof process for diagnosing which among the many patients with pharyngitis have true GAS pharyngitis. Thinking back to the 1980s, we have come a long way from simple throat cultures for detecting GAS, e.g., numerous point of care (POC) Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (CLIA), waved rapid antigen detection tests (RADT), and numerous highly sensitive molecular assays, e.g. nucleic acid amplification tests (NAAT). But if you think the issues surrounding management of GAS pharyngitis have been solved by these newer tests, think again.
Several good reviews1-3 are excellent resources for those wishing a refresher on GAS diagnosis/management issues. They present nitty gritty details on comparative advantages/disadvantages of the many testing options while reminding us of the nuts and bolts of GAS pharyngitis. The following are a few nuggets from these articles.
Properly collected throat specimen. A quality throat specimen involves swabbing both tonsillar pillars plus posterior pharynx without touching tongue or inner cheeks. Two swab collections increase sensitivity by almost 10% compared with a single swab. Transport media is preferred if samples will not be cultured within 24 hours. Caveat: RADT testing of a transport media-diluted sample lowers sensitivity compared with direct swab use.
Reliable GAS detection. Commercially available tests in 2025 are well studied. Culture is considered a gold standard for detecting clinically relevant GAS by CDC.4 Culture has good sensitivity (estimated 80%-90% varying among studies and by quality of specimens) and 99% specificity but requires 16-24 hours for results. RADT solves the time-delay issues and has near 100% specificity but sensitivity used to be as low as 65%, hence the 2012 Infectious Diseases Society of America guideline recommendation for backup throat culture for negative tests.5 However, current RADT have sensitivities in the 85%-90% range.3,4 So a positive RADT reliably and quickly indicates GAS antigens are present. NAAT have the highest combined sensitivity and specificity, near 100% for each, and a positive reliably indicates GAS nucleic acids are present.
So why not simply always use NAAT? First, it’s a “be careful what you wish for” scenario. NAAT can, and do, detect dead remnants and colonizing GAS way more than culture.2,3 So NAAT are overly sensitive, adding an extra layer of interpretation difficulty, ie, as many as 20% of positive NAAT detections may be carriers or dead GAS. Second, NAAT often requires special instrumentation and kits are more expensive. That said, reimbursement is often higher for NAAT.
Choice based on accuracy in detecting GAS. If time delays were not a problem, culture would still seem the answer. If more rapid detection is needed, either RADT with culture back up or NAAT could be the answer. That said, consider that in the real world, throat cultures are less sensitive and RADT are less specific than indicated by some published data.6 So, the ideal answer, it seems, would be NAAT GAS detection coupled with a confirmatory biomarker of GAS infection. Such innate immune biomarkers may be on the horizon.3
But first, pretest screening. In 2025 what do we do with a positive result? Do we prescribe antibiotics? Do we think the detected GAS bacteria/antigens/nucleic acids represent the cause of the pharyngitis? Or did we just detect dead GAS or even a carrier, while a virus is the true cause? Challenges for this decision include most pharyngitis (up to 70%) being due to viruses, not GAS, plus up to 20% of GAS detections even by less sensitive culture or RADT can be carriers, plus an added 10%-20% of RADT and NAAT detections are dead GAS. Thus, with indiscriminate testing of all pharyngitis patients, the number of truly positive GAS detections that are actually “false positives” (GAS in some form is present but not causing pharyngitis) may be almost as high as for those representing true GAS pharyngitis.
Some tool is needed to minimize testing patients who are likely to have viral pharyngitis to reduce test-positive/GAS-pharyngitis-negative scenarios. Pretest patient screening therefore is critical to increase the positive predictive value of positive GAS testing results. The history and physical can be helpful. In the simplest form of pretest screening, eliminate those younger than 3 years old* or those with viral type sign/symptoms, eg conjunctivitis, cough, coryza.7 This could cut “false” positives by as much as a half. More complete validated scoring systems are also available but remain imperfect. The most published is the McIsaac score (modified Centor score).3-5,8 (See Table and Figure.)
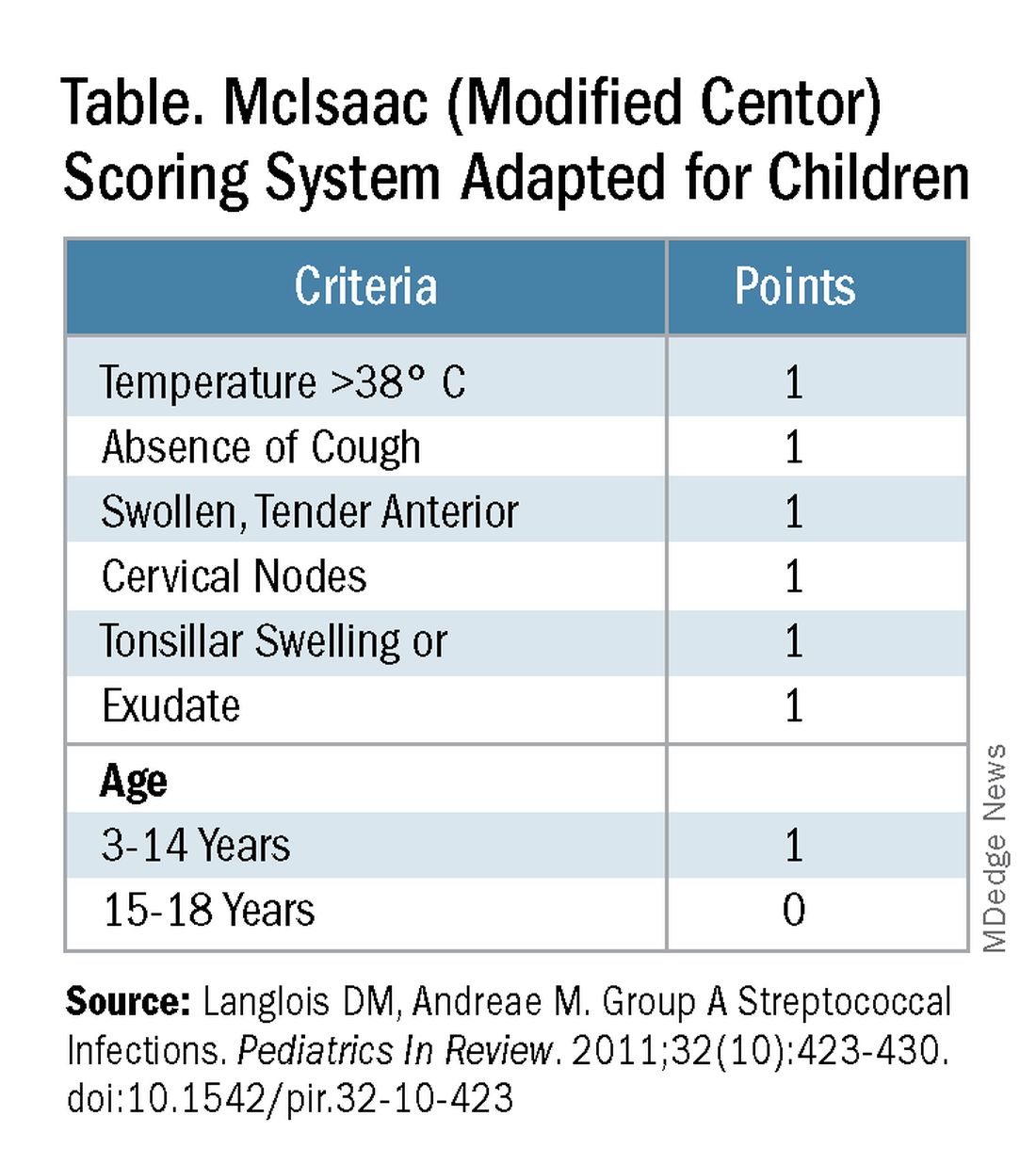
However, even with this validated scoring system, misdiagnoses and some antibiotic misuse will likely occur, particularly if the controversial option to treat a patient with a score above 4 without testing is used. For example, a 2004 study in patients older than 3 years old revealed that 45% with a score above 4 points did not have GAS pharyngitis. (McIsaac et al.) A 2012 study showed similar potential overdiagnosis from using the score without testing (45% with > 4 points did not have GAS pharyngitis). Of note, clinical scores of below 2 comprised up to 10% and would be neither tested nor treated. (Figure.)
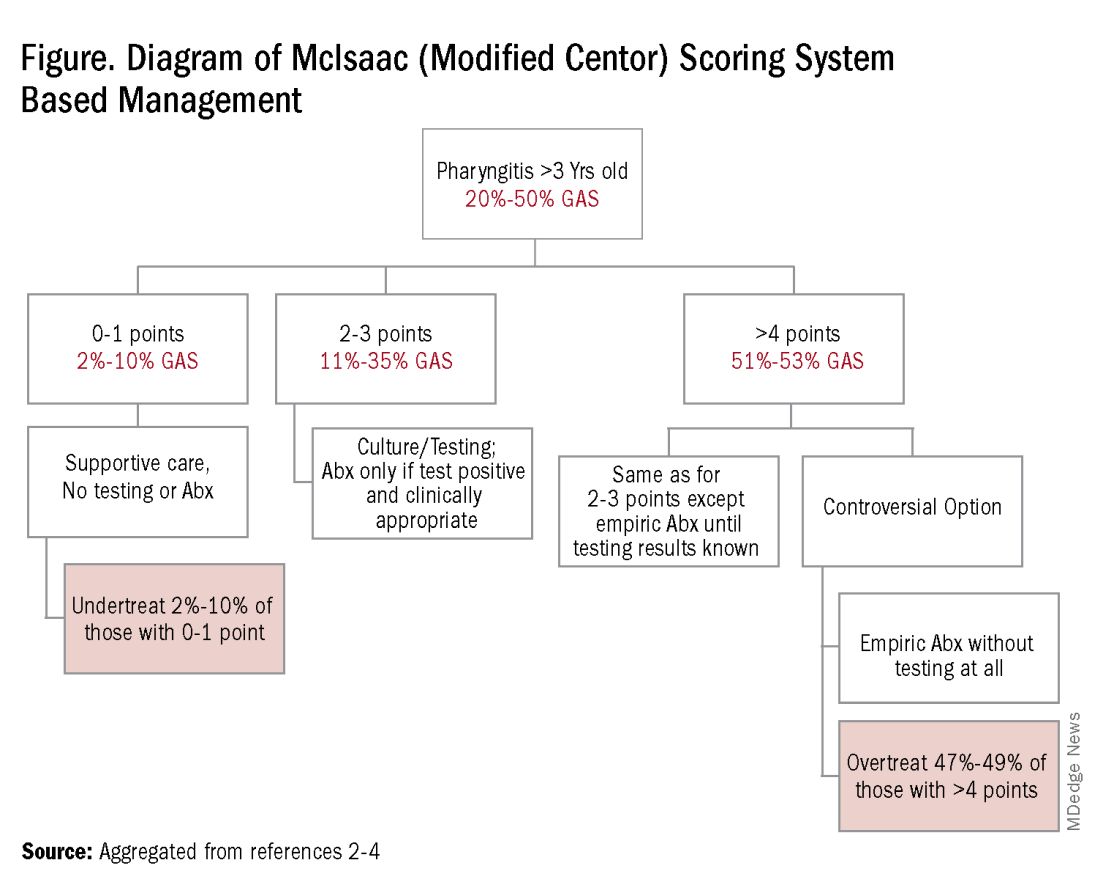
Best clinical judgment. Regardless of the chosen test, we still need to interpret positive results, ie, use best clinical judgment. We know that even with pretest screening some positives tests will represent carriers or nonviable GAS. Yet true GAS pharyngitis needs antibiotic treatment to minimize nonpyogenic and pyogenic complications, plus reduce contagion/transmission risk and days of illness. Thus, we are forced to use best clinical judgment when considering if what could be GAS pharyngitis, particularly exudative pharyngitis, could actually be due to EBV, adenovirus, or gonococcus, each of which can mimic GAS findings. Differentiating these requires discussion beyond the scope of this article, but clues are often found in the history, the patient’s age, associated symptoms and distribution of tonsillopharyngeal exudate. Likewise Group C and G streptococcal pharyngitis can mimic GAS. Note: A comprehensive throat culture can identify these streptococci but requires a special order and likely a call to the laboratory.
Summary: The age-old problem persists, ie, differentiating the minority (~30%) of pharyngitis cases needing antibiotics from the majority that do not. We all wish to promptly treat true GAS pharyngitis; however our current tools remain imperfect. That said, we should strive to correctly diagnose/manage as many patients with pharyngitis as possible. I, for one, can’t wait until we get a validated biomarker that confirms GAS as the culprit in pharyngitis episodes. In the meantime, most providers likely have clinic or hospital approved pathways for managing GAS pharyngitis, many of which are at least in part based on data from sources for this discussion. If not, a firm foundation for creating one can be found in sources among the reference list below. Finally, if you think such pathways somehow interfere with patient flow, consider that a busy multi-provider private practice successfully integrated pretest screening and a pathway while maintaining patient flow and improving antibiotic stewardship.7
*Focal pharyngotonsillar GAS infection is rare in children younger than 3 years old, when GAS nasal passage infection may manifest as streptococcosis.9
Dr Harrison is professor of pediatrics and pediatric infectious diseases at Children’s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics, Kansas City, Missouri. He has no relevant financial disclosures. Email him at [email protected].
References
1. Bannerjee D, Selvarangan RS. The Evolution of Group A Streptococcus Pharyngitis Testing. Association for Diagnostics and Laboratory Medicine, 2018, Sep 1.
2. Cohen JF et al. Group A Streptococcus Pharyngitis in Children: New Perspectives on Rapid Diagnostic Testing and Antimicrobial Stewardship. J Pediatric Infect Dis Soc. 2024 Apr 24;13(4):250-256. doi: 10.1093/jpids/piae0223.
3. Boyanton Jr BL et al. Current Laboratory and Point-of-Care Pharyngitis Diagnostic Testing and Knowledge Gaps. J Infect Dis. 2024 Oct 23;230(Suppl 3):S182–S189. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiae415.
4. Group A Strep Infection. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2024, Mar 1.
5. Shulman ST et al. Clinical Practice Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Group A Streptococcal Pharyngitis: 2012 Update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2012 Nov 15;55(10):e86-102. doi: 10.1093/cid/cis629.
6. Rao A et al. Diagnosis and Antibiotic Treatment of Group A Streptococcal Pharyngitis in Children in a Primary Care Setting: Impact of Point-of-Care Polymerase Chain Reaction. BMC Pediatr. 2019 Jan 16;19(1):24. doi: 10.1186/s12887-019-1393-y.
7. Norton LE et al. Improving Guideline-Based Streptococcal Pharyngitis Testing: A Quality Improvement Initiative. Pediatrics. 2018 Jul;142(1):e20172033. doi: 10.1542/peds.2017-2033.
8. MD+ Calc website. Centor Score (Modified/McIsaac) for Strep Pharyngitis.
9. Langlois DM, Andreae M. Group A Streptococcal Infections. Pediatr Rev. 2011 Oct;32(10):423-9; quiz 430. doi: 10.1542/pir.32-10-423.
It’s wintertime, peak season for GAS pharyngitis, and you’d think that this far into the 21st century we would have a foolproof process for diagnosing which among the many patients with pharyngitis have true GAS pharyngitis. Thinking back to the 1980s, we have come a long way from simple throat cultures for detecting GAS, e.g., numerous point of care (POC) Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (CLIA), waved rapid antigen detection tests (RADT), and numerous highly sensitive molecular assays, e.g. nucleic acid amplification tests (NAAT). But if you think the issues surrounding management of GAS pharyngitis have been solved by these newer tests, think again.
Several good reviews1-3 are excellent resources for those wishing a refresher on GAS diagnosis/management issues. They present nitty gritty details on comparative advantages/disadvantages of the many testing options while reminding us of the nuts and bolts of GAS pharyngitis. The following are a few nuggets from these articles.
Properly collected throat specimen. A quality throat specimen involves swabbing both tonsillar pillars plus posterior pharynx without touching tongue or inner cheeks. Two swab collections increase sensitivity by almost 10% compared with a single swab. Transport media is preferred if samples will not be cultured within 24 hours. Caveat: RADT testing of a transport media-diluted sample lowers sensitivity compared with direct swab use.
Reliable GAS detection. Commercially available tests in 2025 are well studied. Culture is considered a gold standard for detecting clinically relevant GAS by CDC.4 Culture has good sensitivity (estimated 80%-90% varying among studies and by quality of specimens) and 99% specificity but requires 16-24 hours for results. RADT solves the time-delay issues and has near 100% specificity but sensitivity used to be as low as 65%, hence the 2012 Infectious Diseases Society of America guideline recommendation for backup throat culture for negative tests.5 However, current RADT have sensitivities in the 85%-90% range.3,4 So a positive RADT reliably and quickly indicates GAS antigens are present. NAAT have the highest combined sensitivity and specificity, near 100% for each, and a positive reliably indicates GAS nucleic acids are present.
So why not simply always use NAAT? First, it’s a “be careful what you wish for” scenario. NAAT can, and do, detect dead remnants and colonizing GAS way more than culture.2,3 So NAAT are overly sensitive, adding an extra layer of interpretation difficulty, ie, as many as 20% of positive NAAT detections may be carriers or dead GAS. Second, NAAT often requires special instrumentation and kits are more expensive. That said, reimbursement is often higher for NAAT.
Choice based on accuracy in detecting GAS. If time delays were not a problem, culture would still seem the answer. If more rapid detection is needed, either RADT with culture back up or NAAT could be the answer. That said, consider that in the real world, throat cultures are less sensitive and RADT are less specific than indicated by some published data.6 So, the ideal answer, it seems, would be NAAT GAS detection coupled with a confirmatory biomarker of GAS infection. Such innate immune biomarkers may be on the horizon.3
But first, pretest screening. In 2025 what do we do with a positive result? Do we prescribe antibiotics? Do we think the detected GAS bacteria/antigens/nucleic acids represent the cause of the pharyngitis? Or did we just detect dead GAS or even a carrier, while a virus is the true cause? Challenges for this decision include most pharyngitis (up to 70%) being due to viruses, not GAS, plus up to 20% of GAS detections even by less sensitive culture or RADT can be carriers, plus an added 10%-20% of RADT and NAAT detections are dead GAS. Thus, with indiscriminate testing of all pharyngitis patients, the number of truly positive GAS detections that are actually “false positives” (GAS in some form is present but not causing pharyngitis) may be almost as high as for those representing true GAS pharyngitis.
Some tool is needed to minimize testing patients who are likely to have viral pharyngitis to reduce test-positive/GAS-pharyngitis-negative scenarios. Pretest patient screening therefore is critical to increase the positive predictive value of positive GAS testing results. The history and physical can be helpful. In the simplest form of pretest screening, eliminate those younger than 3 years old* or those with viral type sign/symptoms, eg conjunctivitis, cough, coryza.7 This could cut “false” positives by as much as a half. More complete validated scoring systems are also available but remain imperfect. The most published is the McIsaac score (modified Centor score).3-5,8 (See Table and Figure.)

However, even with this validated scoring system, misdiagnoses and some antibiotic misuse will likely occur, particularly if the controversial option to treat a patient with a score above 4 without testing is used. For example, a 2004 study in patients older than 3 years old revealed that 45% with a score above 4 points did not have GAS pharyngitis. (McIsaac et al.) A 2012 study showed similar potential overdiagnosis from using the score without testing (45% with > 4 points did not have GAS pharyngitis). Of note, clinical scores of below 2 comprised up to 10% and would be neither tested nor treated. (Figure.)

Best clinical judgment. Regardless of the chosen test, we still need to interpret positive results, ie, use best clinical judgment. We know that even with pretest screening some positives tests will represent carriers or nonviable GAS. Yet true GAS pharyngitis needs antibiotic treatment to minimize nonpyogenic and pyogenic complications, plus reduce contagion/transmission risk and days of illness. Thus, we are forced to use best clinical judgment when considering if what could be GAS pharyngitis, particularly exudative pharyngitis, could actually be due to EBV, adenovirus, or gonococcus, each of which can mimic GAS findings. Differentiating these requires discussion beyond the scope of this article, but clues are often found in the history, the patient’s age, associated symptoms and distribution of tonsillopharyngeal exudate. Likewise Group C and G streptococcal pharyngitis can mimic GAS. Note: A comprehensive throat culture can identify these streptococci but requires a special order and likely a call to the laboratory.
Summary: The age-old problem persists, ie, differentiating the minority (~30%) of pharyngitis cases needing antibiotics from the majority that do not. We all wish to promptly treat true GAS pharyngitis; however our current tools remain imperfect. That said, we should strive to correctly diagnose/manage as many patients with pharyngitis as possible. I, for one, can’t wait until we get a validated biomarker that confirms GAS as the culprit in pharyngitis episodes. In the meantime, most providers likely have clinic or hospital approved pathways for managing GAS pharyngitis, many of which are at least in part based on data from sources for this discussion. If not, a firm foundation for creating one can be found in sources among the reference list below. Finally, if you think such pathways somehow interfere with patient flow, consider that a busy multi-provider private practice successfully integrated pretest screening and a pathway while maintaining patient flow and improving antibiotic stewardship.7
*Focal pharyngotonsillar GAS infection is rare in children younger than 3 years old, when GAS nasal passage infection may manifest as streptococcosis.9
Dr Harrison is professor of pediatrics and pediatric infectious diseases at Children’s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics, Kansas City, Missouri. He has no relevant financial disclosures. Email him at [email protected].
References
1. Bannerjee D, Selvarangan RS. The Evolution of Group A Streptococcus Pharyngitis Testing. Association for Diagnostics and Laboratory Medicine, 2018, Sep 1.
2. Cohen JF et al. Group A Streptococcus Pharyngitis in Children: New Perspectives on Rapid Diagnostic Testing and Antimicrobial Stewardship. J Pediatric Infect Dis Soc. 2024 Apr 24;13(4):250-256. doi: 10.1093/jpids/piae0223.
3. Boyanton Jr BL et al. Current Laboratory and Point-of-Care Pharyngitis Diagnostic Testing and Knowledge Gaps. J Infect Dis. 2024 Oct 23;230(Suppl 3):S182–S189. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiae415.
4. Group A Strep Infection. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2024, Mar 1.
5. Shulman ST et al. Clinical Practice Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Group A Streptococcal Pharyngitis: 2012 Update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2012 Nov 15;55(10):e86-102. doi: 10.1093/cid/cis629.
6. Rao A et al. Diagnosis and Antibiotic Treatment of Group A Streptococcal Pharyngitis in Children in a Primary Care Setting: Impact of Point-of-Care Polymerase Chain Reaction. BMC Pediatr. 2019 Jan 16;19(1):24. doi: 10.1186/s12887-019-1393-y.
7. Norton LE et al. Improving Guideline-Based Streptococcal Pharyngitis Testing: A Quality Improvement Initiative. Pediatrics. 2018 Jul;142(1):e20172033. doi: 10.1542/peds.2017-2033.
8. MD+ Calc website. Centor Score (Modified/McIsaac) for Strep Pharyngitis.
9. Langlois DM, Andreae M. Group A Streptococcal Infections. Pediatr Rev. 2011 Oct;32(10):423-9; quiz 430. doi: 10.1542/pir.32-10-423.
It’s wintertime, peak season for GAS pharyngitis, and you’d think that this far into the 21st century we would have a foolproof process for diagnosing which among the many patients with pharyngitis have true GAS pharyngitis. Thinking back to the 1980s, we have come a long way from simple throat cultures for detecting GAS, e.g., numerous point of care (POC) Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (CLIA), waved rapid antigen detection tests (RADT), and numerous highly sensitive molecular assays, e.g. nucleic acid amplification tests (NAAT). But if you think the issues surrounding management of GAS pharyngitis have been solved by these newer tests, think again.
Several good reviews1-3 are excellent resources for those wishing a refresher on GAS diagnosis/management issues. They present nitty gritty details on comparative advantages/disadvantages of the many testing options while reminding us of the nuts and bolts of GAS pharyngitis. The following are a few nuggets from these articles.
Properly collected throat specimen. A quality throat specimen involves swabbing both tonsillar pillars plus posterior pharynx without touching tongue or inner cheeks. Two swab collections increase sensitivity by almost 10% compared with a single swab. Transport media is preferred if samples will not be cultured within 24 hours. Caveat: RADT testing of a transport media-diluted sample lowers sensitivity compared with direct swab use.
Reliable GAS detection. Commercially available tests in 2025 are well studied. Culture is considered a gold standard for detecting clinically relevant GAS by CDC.4 Culture has good sensitivity (estimated 80%-90% varying among studies and by quality of specimens) and 99% specificity but requires 16-24 hours for results. RADT solves the time-delay issues and has near 100% specificity but sensitivity used to be as low as 65%, hence the 2012 Infectious Diseases Society of America guideline recommendation for backup throat culture for negative tests.5 However, current RADT have sensitivities in the 85%-90% range.3,4 So a positive RADT reliably and quickly indicates GAS antigens are present. NAAT have the highest combined sensitivity and specificity, near 100% for each, and a positive reliably indicates GAS nucleic acids are present.
So why not simply always use NAAT? First, it’s a “be careful what you wish for” scenario. NAAT can, and do, detect dead remnants and colonizing GAS way more than culture.2,3 So NAAT are overly sensitive, adding an extra layer of interpretation difficulty, ie, as many as 20% of positive NAAT detections may be carriers or dead GAS. Second, NAAT often requires special instrumentation and kits are more expensive. That said, reimbursement is often higher for NAAT.
Choice based on accuracy in detecting GAS. If time delays were not a problem, culture would still seem the answer. If more rapid detection is needed, either RADT with culture back up or NAAT could be the answer. That said, consider that in the real world, throat cultures are less sensitive and RADT are less specific than indicated by some published data.6 So, the ideal answer, it seems, would be NAAT GAS detection coupled with a confirmatory biomarker of GAS infection. Such innate immune biomarkers may be on the horizon.3
But first, pretest screening. In 2025 what do we do with a positive result? Do we prescribe antibiotics? Do we think the detected GAS bacteria/antigens/nucleic acids represent the cause of the pharyngitis? Or did we just detect dead GAS or even a carrier, while a virus is the true cause? Challenges for this decision include most pharyngitis (up to 70%) being due to viruses, not GAS, plus up to 20% of GAS detections even by less sensitive culture or RADT can be carriers, plus an added 10%-20% of RADT and NAAT detections are dead GAS. Thus, with indiscriminate testing of all pharyngitis patients, the number of truly positive GAS detections that are actually “false positives” (GAS in some form is present but not causing pharyngitis) may be almost as high as for those representing true GAS pharyngitis.
Some tool is needed to minimize testing patients who are likely to have viral pharyngitis to reduce test-positive/GAS-pharyngitis-negative scenarios. Pretest patient screening therefore is critical to increase the positive predictive value of positive GAS testing results. The history and physical can be helpful. In the simplest form of pretest screening, eliminate those younger than 3 years old* or those with viral type sign/symptoms, eg conjunctivitis, cough, coryza.7 This could cut “false” positives by as much as a half. More complete validated scoring systems are also available but remain imperfect. The most published is the McIsaac score (modified Centor score).3-5,8 (See Table and Figure.)

However, even with this validated scoring system, misdiagnoses and some antibiotic misuse will likely occur, particularly if the controversial option to treat a patient with a score above 4 without testing is used. For example, a 2004 study in patients older than 3 years old revealed that 45% with a score above 4 points did not have GAS pharyngitis. (McIsaac et al.) A 2012 study showed similar potential overdiagnosis from using the score without testing (45% with > 4 points did not have GAS pharyngitis). Of note, clinical scores of below 2 comprised up to 10% and would be neither tested nor treated. (Figure.)

Best clinical judgment. Regardless of the chosen test, we still need to interpret positive results, ie, use best clinical judgment. We know that even with pretest screening some positives tests will represent carriers or nonviable GAS. Yet true GAS pharyngitis needs antibiotic treatment to minimize nonpyogenic and pyogenic complications, plus reduce contagion/transmission risk and days of illness. Thus, we are forced to use best clinical judgment when considering if what could be GAS pharyngitis, particularly exudative pharyngitis, could actually be due to EBV, adenovirus, or gonococcus, each of which can mimic GAS findings. Differentiating these requires discussion beyond the scope of this article, but clues are often found in the history, the patient’s age, associated symptoms and distribution of tonsillopharyngeal exudate. Likewise Group C and G streptococcal pharyngitis can mimic GAS. Note: A comprehensive throat culture can identify these streptococci but requires a special order and likely a call to the laboratory.
Summary: The age-old problem persists, ie, differentiating the minority (~30%) of pharyngitis cases needing antibiotics from the majority that do not. We all wish to promptly treat true GAS pharyngitis; however our current tools remain imperfect. That said, we should strive to correctly diagnose/manage as many patients with pharyngitis as possible. I, for one, can’t wait until we get a validated biomarker that confirms GAS as the culprit in pharyngitis episodes. In the meantime, most providers likely have clinic or hospital approved pathways for managing GAS pharyngitis, many of which are at least in part based on data from sources for this discussion. If not, a firm foundation for creating one can be found in sources among the reference list below. Finally, if you think such pathways somehow interfere with patient flow, consider that a busy multi-provider private practice successfully integrated pretest screening and a pathway while maintaining patient flow and improving antibiotic stewardship.7
*Focal pharyngotonsillar GAS infection is rare in children younger than 3 years old, when GAS nasal passage infection may manifest as streptococcosis.9
Dr Harrison is professor of pediatrics and pediatric infectious diseases at Children’s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics, Kansas City, Missouri. He has no relevant financial disclosures. Email him at [email protected].
References
1. Bannerjee D, Selvarangan RS. The Evolution of Group A Streptococcus Pharyngitis Testing. Association for Diagnostics and Laboratory Medicine, 2018, Sep 1.
2. Cohen JF et al. Group A Streptococcus Pharyngitis in Children: New Perspectives on Rapid Diagnostic Testing and Antimicrobial Stewardship. J Pediatric Infect Dis Soc. 2024 Apr 24;13(4):250-256. doi: 10.1093/jpids/piae0223.
3. Boyanton Jr BL et al. Current Laboratory and Point-of-Care Pharyngitis Diagnostic Testing and Knowledge Gaps. J Infect Dis. 2024 Oct 23;230(Suppl 3):S182–S189. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiae415.
4. Group A Strep Infection. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2024, Mar 1.
5. Shulman ST et al. Clinical Practice Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Group A Streptococcal Pharyngitis: 2012 Update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2012 Nov 15;55(10):e86-102. doi: 10.1093/cid/cis629.
6. Rao A et al. Diagnosis and Antibiotic Treatment of Group A Streptococcal Pharyngitis in Children in a Primary Care Setting: Impact of Point-of-Care Polymerase Chain Reaction. BMC Pediatr. 2019 Jan 16;19(1):24. doi: 10.1186/s12887-019-1393-y.
7. Norton LE et al. Improving Guideline-Based Streptococcal Pharyngitis Testing: A Quality Improvement Initiative. Pediatrics. 2018 Jul;142(1):e20172033. doi: 10.1542/peds.2017-2033.
8. MD+ Calc website. Centor Score (Modified/McIsaac) for Strep Pharyngitis.
9. Langlois DM, Andreae M. Group A Streptococcal Infections. Pediatr Rev. 2011 Oct;32(10):423-9; quiz 430. doi: 10.1542/pir.32-10-423.
Crying Tolerance
Most of the papers I review merely validate a relationship that most of us, including the investigators, have already assumed based on common sense. However, every now and then I encounter a study whose findings clearly don’t support the researchers’ initial thesis. The most recent example of this unexpected finding is a paper designed to determine whether the sound of a crying infant would have an effect on a parent’s ability to accurately mix formula.
After a cursory reading of the investigators’ plan, most of us would have assumed from our own difficulties trying to accomplish something while our infant is crying that the crying would have a negative effect on our accuracy. Especially if it was a task that required careful measurement. However, when I skipped ahead to read the paper’s conclusion I was surprised that the investigators could found no significant negative relationship.
The explanation for this counterintuitive finding became readily apparent when I read the details of the study’s design more carefully. The investigators had chosen to use a generic recording of an infant crying, not the parent’s child nor even a live generic child on site.
No one enjoys listening to a child cry. It is certainly not a pleasant sound to the human ear. We seem to be hardwired to find it irritating. But, listening to our own child cry raises an entirely different suite of emotions, particularly if the child is close enough for us to intervene.
I’m not sure exactly what made the investigators choose a generic recording, but I suspect it was less expensive. Otherwise it would have required that the parents agree to subjecting their child to some stimulus that would have predictably induced the child to cry. Fortunately, the investigators were able to regroup in the wake of this lack of common sense in their experimental design and realized that, while their data failed to show a negative association with crying, it did provide an important message. Formula mixing errors, some with potentially harmful consequences, are far too common. In a commentary accompanying this paper, a pediatrician not involved in the study observes that, in our efforts to promote breastfeeding, we have given short shrift to teaching parents about accurate and safe formula preparation.
But, let’s return to the crying piece. Why is it so difficult for parents to tolerate their own crying infant? Common sense should tell us that we know our infant is helpless. The little child is totally reliant on us to for nutrition and protection from the ever-present environmental threats to its health and safety in the environment. In short, whether we are parents, daycare providers, or the mother’s boyfriend who has been left in charge, we are totally responsible for the life of that infant, at times a heavy burden.
That example of biologic variability is just one of the reasons why so many families find it difficult to set limits and follow through with consequences. When I have written about and spoken to parents in the office about discipline, I am happy if I can convince both parents to be on the same page (literally sometimes) in how they respond to their crying child.
Helping an infant learn to put itself to sleep is usually the first challenge that requires some agreement between parents on how long they can tolerate crying. Although allowing the infant to cry itself to sleep may be the best and most efficient strategy, it isn’t going to work when two parents and/or caregivers have widely different cry tolerances. In some situations these discrepancies can be managed by having the less tolerant parent temporarily move himself/herself to a location out of earshot. Something often easier said than accomplished.
At the heart of the solution is an acceptance by both parents that differing cry intolerances are not unusual and don’t imply that one partner is a better parent. As advisors we also must accept this reality and help the family find some other solution. Nothing is gained by allowing a disagreement between parents to make an already uncomfortable situation any worse.
While we don’t give out merit badges for it, being able to tolerate one’s own child crying for brief periods of time is a gift that can be helpful in certain situations. It is not a skill listed in the curriculum of most parenting classes, but learning more about what prompts babies to cry can be very helpful. This educational approach is exemplified by a Pediatrics Patient Page in a recent issue of JAMA Pediatrics. It’s rarely hunger and most often is sleep deprivation. It’s rarely the result of an undiscovered injury or medical condition, but may be a response to an overstimulating environment.
For those of us who are advisers, one of our responsibilities is to be alert to those few individuals whose intolerance to crying is so great that they are likely to injure the child or its mother to stop the crying. The simple question at an early well-child visit should be something like “How is everyone in the house when the child starts crying” might save a life. The stereotypic example is the young boyfriend of the mother, who may suspect that he is not the biologic father. However, any parent who is feeling insecure because of a financial situation, poor physical or mental health, or fatigue may lash out to achieve quiet. Crying is one of the realities of infancy. It is our job to help parents cope with it safely.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
Most of the papers I review merely validate a relationship that most of us, including the investigators, have already assumed based on common sense. However, every now and then I encounter a study whose findings clearly don’t support the researchers’ initial thesis. The most recent example of this unexpected finding is a paper designed to determine whether the sound of a crying infant would have an effect on a parent’s ability to accurately mix formula.
After a cursory reading of the investigators’ plan, most of us would have assumed from our own difficulties trying to accomplish something while our infant is crying that the crying would have a negative effect on our accuracy. Especially if it was a task that required careful measurement. However, when I skipped ahead to read the paper’s conclusion I was surprised that the investigators could found no significant negative relationship.
The explanation for this counterintuitive finding became readily apparent when I read the details of the study’s design more carefully. The investigators had chosen to use a generic recording of an infant crying, not the parent’s child nor even a live generic child on site.
No one enjoys listening to a child cry. It is certainly not a pleasant sound to the human ear. We seem to be hardwired to find it irritating. But, listening to our own child cry raises an entirely different suite of emotions, particularly if the child is close enough for us to intervene.
I’m not sure exactly what made the investigators choose a generic recording, but I suspect it was less expensive. Otherwise it would have required that the parents agree to subjecting their child to some stimulus that would have predictably induced the child to cry. Fortunately, the investigators were able to regroup in the wake of this lack of common sense in their experimental design and realized that, while their data failed to show a negative association with crying, it did provide an important message. Formula mixing errors, some with potentially harmful consequences, are far too common. In a commentary accompanying this paper, a pediatrician not involved in the study observes that, in our efforts to promote breastfeeding, we have given short shrift to teaching parents about accurate and safe formula preparation.
But, let’s return to the crying piece. Why is it so difficult for parents to tolerate their own crying infant? Common sense should tell us that we know our infant is helpless. The little child is totally reliant on us to for nutrition and protection from the ever-present environmental threats to its health and safety in the environment. In short, whether we are parents, daycare providers, or the mother’s boyfriend who has been left in charge, we are totally responsible for the life of that infant, at times a heavy burden.
That example of biologic variability is just one of the reasons why so many families find it difficult to set limits and follow through with consequences. When I have written about and spoken to parents in the office about discipline, I am happy if I can convince both parents to be on the same page (literally sometimes) in how they respond to their crying child.
Helping an infant learn to put itself to sleep is usually the first challenge that requires some agreement between parents on how long they can tolerate crying. Although allowing the infant to cry itself to sleep may be the best and most efficient strategy, it isn’t going to work when two parents and/or caregivers have widely different cry tolerances. In some situations these discrepancies can be managed by having the less tolerant parent temporarily move himself/herself to a location out of earshot. Something often easier said than accomplished.
At the heart of the solution is an acceptance by both parents that differing cry intolerances are not unusual and don’t imply that one partner is a better parent. As advisors we also must accept this reality and help the family find some other solution. Nothing is gained by allowing a disagreement between parents to make an already uncomfortable situation any worse.
While we don’t give out merit badges for it, being able to tolerate one’s own child crying for brief periods of time is a gift that can be helpful in certain situations. It is not a skill listed in the curriculum of most parenting classes, but learning more about what prompts babies to cry can be very helpful. This educational approach is exemplified by a Pediatrics Patient Page in a recent issue of JAMA Pediatrics. It’s rarely hunger and most often is sleep deprivation. It’s rarely the result of an undiscovered injury or medical condition, but may be a response to an overstimulating environment.
For those of us who are advisers, one of our responsibilities is to be alert to those few individuals whose intolerance to crying is so great that they are likely to injure the child or its mother to stop the crying. The simple question at an early well-child visit should be something like “How is everyone in the house when the child starts crying” might save a life. The stereotypic example is the young boyfriend of the mother, who may suspect that he is not the biologic father. However, any parent who is feeling insecure because of a financial situation, poor physical or mental health, or fatigue may lash out to achieve quiet. Crying is one of the realities of infancy. It is our job to help parents cope with it safely.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
Most of the papers I review merely validate a relationship that most of us, including the investigators, have already assumed based on common sense. However, every now and then I encounter a study whose findings clearly don’t support the researchers’ initial thesis. The most recent example of this unexpected finding is a paper designed to determine whether the sound of a crying infant would have an effect on a parent’s ability to accurately mix formula.
After a cursory reading of the investigators’ plan, most of us would have assumed from our own difficulties trying to accomplish something while our infant is crying that the crying would have a negative effect on our accuracy. Especially if it was a task that required careful measurement. However, when I skipped ahead to read the paper’s conclusion I was surprised that the investigators could found no significant negative relationship.
The explanation for this counterintuitive finding became readily apparent when I read the details of the study’s design more carefully. The investigators had chosen to use a generic recording of an infant crying, not the parent’s child nor even a live generic child on site.
No one enjoys listening to a child cry. It is certainly not a pleasant sound to the human ear. We seem to be hardwired to find it irritating. But, listening to our own child cry raises an entirely different suite of emotions, particularly if the child is close enough for us to intervene.
I’m not sure exactly what made the investigators choose a generic recording, but I suspect it was less expensive. Otherwise it would have required that the parents agree to subjecting their child to some stimulus that would have predictably induced the child to cry. Fortunately, the investigators were able to regroup in the wake of this lack of common sense in their experimental design and realized that, while their data failed to show a negative association with crying, it did provide an important message. Formula mixing errors, some with potentially harmful consequences, are far too common. In a commentary accompanying this paper, a pediatrician not involved in the study observes that, in our efforts to promote breastfeeding, we have given short shrift to teaching parents about accurate and safe formula preparation.
But, let’s return to the crying piece. Why is it so difficult for parents to tolerate their own crying infant? Common sense should tell us that we know our infant is helpless. The little child is totally reliant on us to for nutrition and protection from the ever-present environmental threats to its health and safety in the environment. In short, whether we are parents, daycare providers, or the mother’s boyfriend who has been left in charge, we are totally responsible for the life of that infant, at times a heavy burden.
That example of biologic variability is just one of the reasons why so many families find it difficult to set limits and follow through with consequences. When I have written about and spoken to parents in the office about discipline, I am happy if I can convince both parents to be on the same page (literally sometimes) in how they respond to their crying child.
Helping an infant learn to put itself to sleep is usually the first challenge that requires some agreement between parents on how long they can tolerate crying. Although allowing the infant to cry itself to sleep may be the best and most efficient strategy, it isn’t going to work when two parents and/or caregivers have widely different cry tolerances. In some situations these discrepancies can be managed by having the less tolerant parent temporarily move himself/herself to a location out of earshot. Something often easier said than accomplished.
At the heart of the solution is an acceptance by both parents that differing cry intolerances are not unusual and don’t imply that one partner is a better parent. As advisors we also must accept this reality and help the family find some other solution. Nothing is gained by allowing a disagreement between parents to make an already uncomfortable situation any worse.
While we don’t give out merit badges for it, being able to tolerate one’s own child crying for brief periods of time is a gift that can be helpful in certain situations. It is not a skill listed in the curriculum of most parenting classes, but learning more about what prompts babies to cry can be very helpful. This educational approach is exemplified by a Pediatrics Patient Page in a recent issue of JAMA Pediatrics. It’s rarely hunger and most often is sleep deprivation. It’s rarely the result of an undiscovered injury or medical condition, but may be a response to an overstimulating environment.
For those of us who are advisers, one of our responsibilities is to be alert to those few individuals whose intolerance to crying is so great that they are likely to injure the child or its mother to stop the crying. The simple question at an early well-child visit should be something like “How is everyone in the house when the child starts crying” might save a life. The stereotypic example is the young boyfriend of the mother, who may suspect that he is not the biologic father. However, any parent who is feeling insecure because of a financial situation, poor physical or mental health, or fatigue may lash out to achieve quiet. Crying is one of the realities of infancy. It is our job to help parents cope with it safely.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
Simufilam: Just Another Placebo
An Alzheimer’s drug trial failing is, unfortunately, nothing new. This one, however, had more baggage behind it than most.
Like all of these things, it was worth a try. It’s an interesting molecule with a reasonable mechanism of action.
But the trials have been raising questions for a few years, with allegations of misconduct against the drug’s co-discoverer Hoau-Yan Wang. He’s been indicted for defrauding the National Institutes of Health of $16 million in grants related to the drug. There have been concerns over doctored images and other not-so-minor issues in trying to move simufilam forward. Cassava itself agreed to pay the Securities and Exchange Commission $40 million in 2024 to settle charges about misleading investors.
Yet, like an innocent child with criminal parents, many of us hoped that the drug would work, regardless of the ethical shenanigans behind it. On the front lines we deal with a tragic disease that robs people of what makes them human and robs the families who have to live with it.
As the wheels started to come off the bus I told a friend, “it would be really sad if this drug is THE ONE and it never gets to finish trials because of everything else.”
Now we know it isn’t. Regardless of the controversy, the final data show that simufilam is just another placebo, joining the ranks of many others in the Alzheimer’s development graveyard.
Yes, there is a vague sense of jubilation behind it. I believe in fair play, and it’s good to know that those who misled investors and falsified data were wrong and will never have their day in the sun.
At the same time, however, I’m disappointed. I’m happy that the drug at least got a chance to prove itself, but when it’s all said and done, it doesn’t do anything.
I feel bad for the innocent people in the company, who had nothing to do with the scheming and were just hoping the drug would go somewhere. The majority, if not all, of them will likely lose their jobs. Like me, they have families, bills, and mortgages.
But I’m even more disappointed for the patients and families who only wanted an effective treatment for Alzheimer’s disease, and were hoping that, regardless of its dirty laundry, simufilam would work.
They’re the ones that I, and many other neurologists, have to face every day when they ask “is there anything new out?” and we sadly shake our heads.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Arizona.
An Alzheimer’s drug trial failing is, unfortunately, nothing new. This one, however, had more baggage behind it than most.
Like all of these things, it was worth a try. It’s an interesting molecule with a reasonable mechanism of action.
But the trials have been raising questions for a few years, with allegations of misconduct against the drug’s co-discoverer Hoau-Yan Wang. He’s been indicted for defrauding the National Institutes of Health of $16 million in grants related to the drug. There have been concerns over doctored images and other not-so-minor issues in trying to move simufilam forward. Cassava itself agreed to pay the Securities and Exchange Commission $40 million in 2024 to settle charges about misleading investors.
Yet, like an innocent child with criminal parents, many of us hoped that the drug would work, regardless of the ethical shenanigans behind it. On the front lines we deal with a tragic disease that robs people of what makes them human and robs the families who have to live with it.
As the wheels started to come off the bus I told a friend, “it would be really sad if this drug is THE ONE and it never gets to finish trials because of everything else.”
Now we know it isn’t. Regardless of the controversy, the final data show that simufilam is just another placebo, joining the ranks of many others in the Alzheimer’s development graveyard.
Yes, there is a vague sense of jubilation behind it. I believe in fair play, and it’s good to know that those who misled investors and falsified data were wrong and will never have their day in the sun.
At the same time, however, I’m disappointed. I’m happy that the drug at least got a chance to prove itself, but when it’s all said and done, it doesn’t do anything.
I feel bad for the innocent people in the company, who had nothing to do with the scheming and were just hoping the drug would go somewhere. The majority, if not all, of them will likely lose their jobs. Like me, they have families, bills, and mortgages.
But I’m even more disappointed for the patients and families who only wanted an effective treatment for Alzheimer’s disease, and were hoping that, regardless of its dirty laundry, simufilam would work.
They’re the ones that I, and many other neurologists, have to face every day when they ask “is there anything new out?” and we sadly shake our heads.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Arizona.
An Alzheimer’s drug trial failing is, unfortunately, nothing new. This one, however, had more baggage behind it than most.
Like all of these things, it was worth a try. It’s an interesting molecule with a reasonable mechanism of action.
But the trials have been raising questions for a few years, with allegations of misconduct against the drug’s co-discoverer Hoau-Yan Wang. He’s been indicted for defrauding the National Institutes of Health of $16 million in grants related to the drug. There have been concerns over doctored images and other not-so-minor issues in trying to move simufilam forward. Cassava itself agreed to pay the Securities and Exchange Commission $40 million in 2024 to settle charges about misleading investors.
Yet, like an innocent child with criminal parents, many of us hoped that the drug would work, regardless of the ethical shenanigans behind it. On the front lines we deal with a tragic disease that robs people of what makes them human and robs the families who have to live with it.
As the wheels started to come off the bus I told a friend, “it would be really sad if this drug is THE ONE and it never gets to finish trials because of everything else.”
Now we know it isn’t. Regardless of the controversy, the final data show that simufilam is just another placebo, joining the ranks of many others in the Alzheimer’s development graveyard.
Yes, there is a vague sense of jubilation behind it. I believe in fair play, and it’s good to know that those who misled investors and falsified data were wrong and will never have their day in the sun.
At the same time, however, I’m disappointed. I’m happy that the drug at least got a chance to prove itself, but when it’s all said and done, it doesn’t do anything.
I feel bad for the innocent people in the company, who had nothing to do with the scheming and were just hoping the drug would go somewhere. The majority, if not all, of them will likely lose their jobs. Like me, they have families, bills, and mortgages.
But I’m even more disappointed for the patients and families who only wanted an effective treatment for Alzheimer’s disease, and were hoping that, regardless of its dirty laundry, simufilam would work.
They’re the ones that I, and many other neurologists, have to face every day when they ask “is there anything new out?” and we sadly shake our heads.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Arizona.


















