User login
Beauty has been a topic of interest for centuries. Treatments and technologies have advanced, and more women are utilizing cosmetic procedures than ever before, especially neuromodulators, minimally invasive procedures, and topical treatments.1 Over the last decade, there was a 99% increase in minimally invasive cosmetic procedures in the United States.2 There also has been an observable increase in the utilization of cosmetic procedures by Black patients in recent years; the American Society of Plastic Surgeons reported that the number of cosmetic plastic surgery procedures performed on “ethnic patients” (referring to Asian, Black, or Hispanic patients) increased 243% from 2000 to 2013,3 possibly attributed to increased accessibility, awareness of procedures due to social media, cultural acceptance, and affordability. Minimally invasive procedures are considerably less expensive than major surgical procedures and are becoming progressively more affordable, with numerous financing options available.2 Additionally, neuromodulators and fillers are now commonly administered by nonaesthetic health professionals including dentists and nurses, which has increased accessibility of these procedures among patients who typically may not seek out a consultation with a plastic surgeon or dermatologist.4
When examining the most common cosmetic procedures collectively sought out by patients with skin of color (SOC), it has been found that an even skin tone is a highly desirable feature that impacts the selection of products and procedures in this particular patient population.5 Black, Hispanic, and Asian women report fewer signs of facial aging compared to White women in the glabellar lines, crow’s-feet, oral commissures, perioral lines, and lips.6 Increased melanocytes in darker skin types help prevent photoaging but also increase susceptibility to dyschromia. Prior studies have reported the most common concerns by patients with SOC are dyschromic disorders such as postinflammatory hyperpigmentation, postinflammatory hypopigmentation, and melasma.7 Common minimally invasive cosmetic procedures utilized by the SOC population include chemical peels, laser treatments, and injectables. Fillers are utilized more for volume loss in SOC patients rather than for the deep furrows and rhytides commonly seen in the lower face of White patients.8
We conducted a survey among Black women currently residing in the United States to better understand attitudes toward beauty and aging as well as the utilization of minimally invasive cosmetic procedures in this patient population.
Methods
An in-depth questionnaire comprised of 17 questions was created for this cross-sectional observational study. The study was submitted to and deemed exempt by the institutional review board at the University of Miami (Miami, Florida)(IRB #20211184). Survey participants primarily were recruited via social media posts on personal profiles of Black dermatologists, medical residents, and medicalstudents, including the authors, targeting Black women in the United States. Utilizing a method called snowball sampling, whereby study participants are used to recruit future participants, individuals were instructed to share the survey with their social network to assist with survey distribution. After participants provided informed consent, data were captured using the REDCap secure online data collection software. The questionnaire was structured to include a sociodemographic profile of respondents, attitudes toward beauty and aging, current usage of beauty products, prior utilization of cosmetic procedures, and intentions to use cosmetic procedures in the future. Surveys with incomplete consent forms, incomplete responses, and duplicate responses, as well as surveys from participants who were not residing in the United States at the time of survey completion, were excluded.
Data characteristics were summarized by frequency and percentage. A χ2 test was performed to compare participants’ age demographics with their attitudes toward beauty and aging, utilization of cosmetic procedures, and intention to try cosmetic procedures in the future. The Fisher exact test was used instead of the χ2 test when the expected cell count was less than 5. For all tests, P<.05 was considered statistically significant. All statistical analyses were performed using SPSS software version 28.
Results
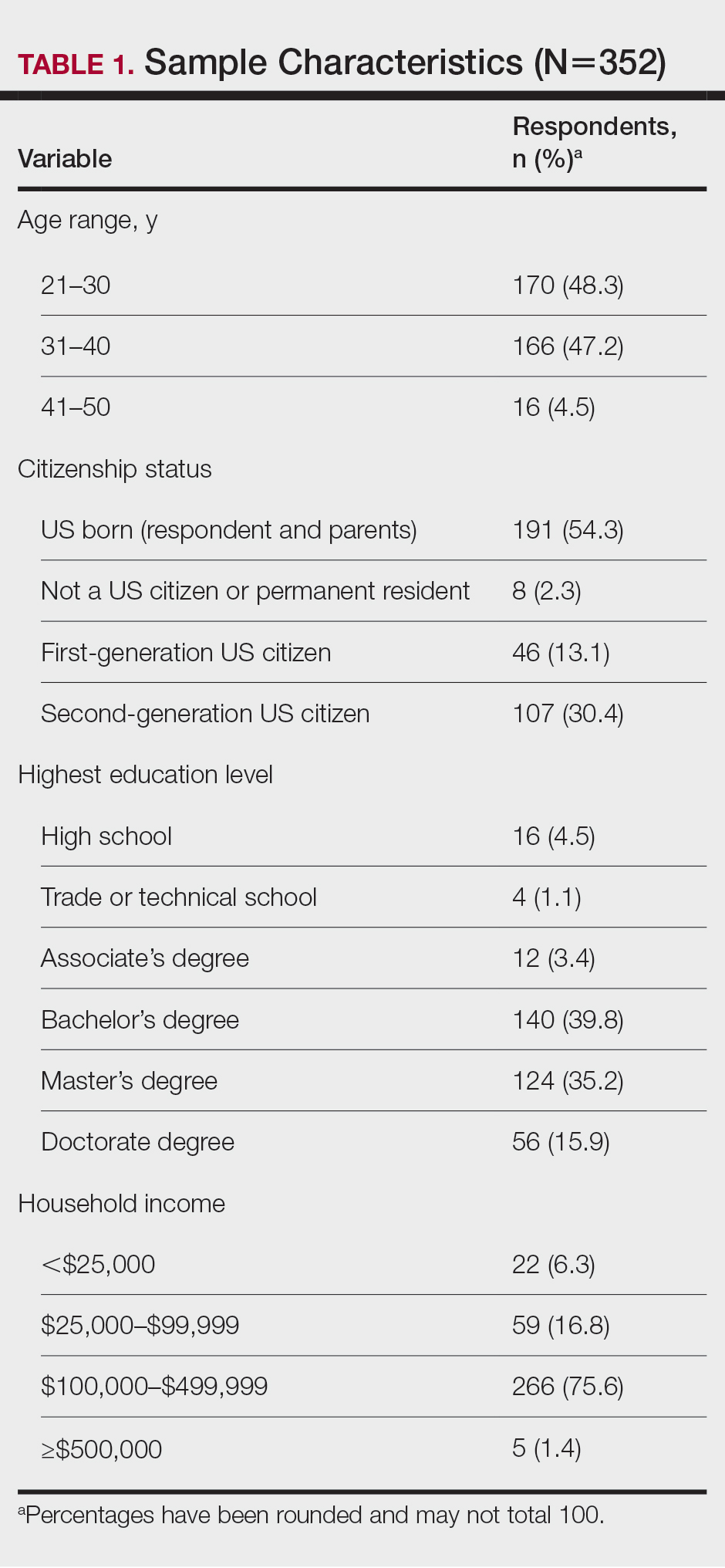
General Characteristics of Participants—A sample of 475 self-identified Black women aged 21 to 70 years participated in the study, and 352 eligible participants were included in the final analysis. Of the 352 eligible participants, 48.3% were aged 21 to 30 years, 47.2% were aged 31 to 40 years, and 4.5% were aged 41 to 50 years. All survey participants identified their race as Black; among them, 4% specified Hispanic or Latino ethnicity, and 9% indicated that they held multiracial identities including White/Caucasian, Asian, and Native American backgrounds. Regarding the participants’ citizenship status, 54.3% reported that both they and their parents were born in the United States; 2.3% were not US citizens or permanent residents, 13.1% identified as first-generation Americans (born outside of the United States), and 30.4% identified as second-generation Americans (one or both parents born outside of the United States). Participant education levels (based on highest level) varied greatly: 4.5% were high school graduates, 1.1% attended trade or technical schools, 3.4% had associate’s degrees, 39.8% had bachelor’s degrees, 35.2% had master’s degrees, and 15.9% had doctorate degrees. Regarding household income, 6.3% earned less than $25,000 per year, 16.8% earned from $25,000 to $99,999, 75.6% earned from $100,000 to $499,999, and 1.4% earned $500,000 or more. Patient demographics are provided in Table 1.
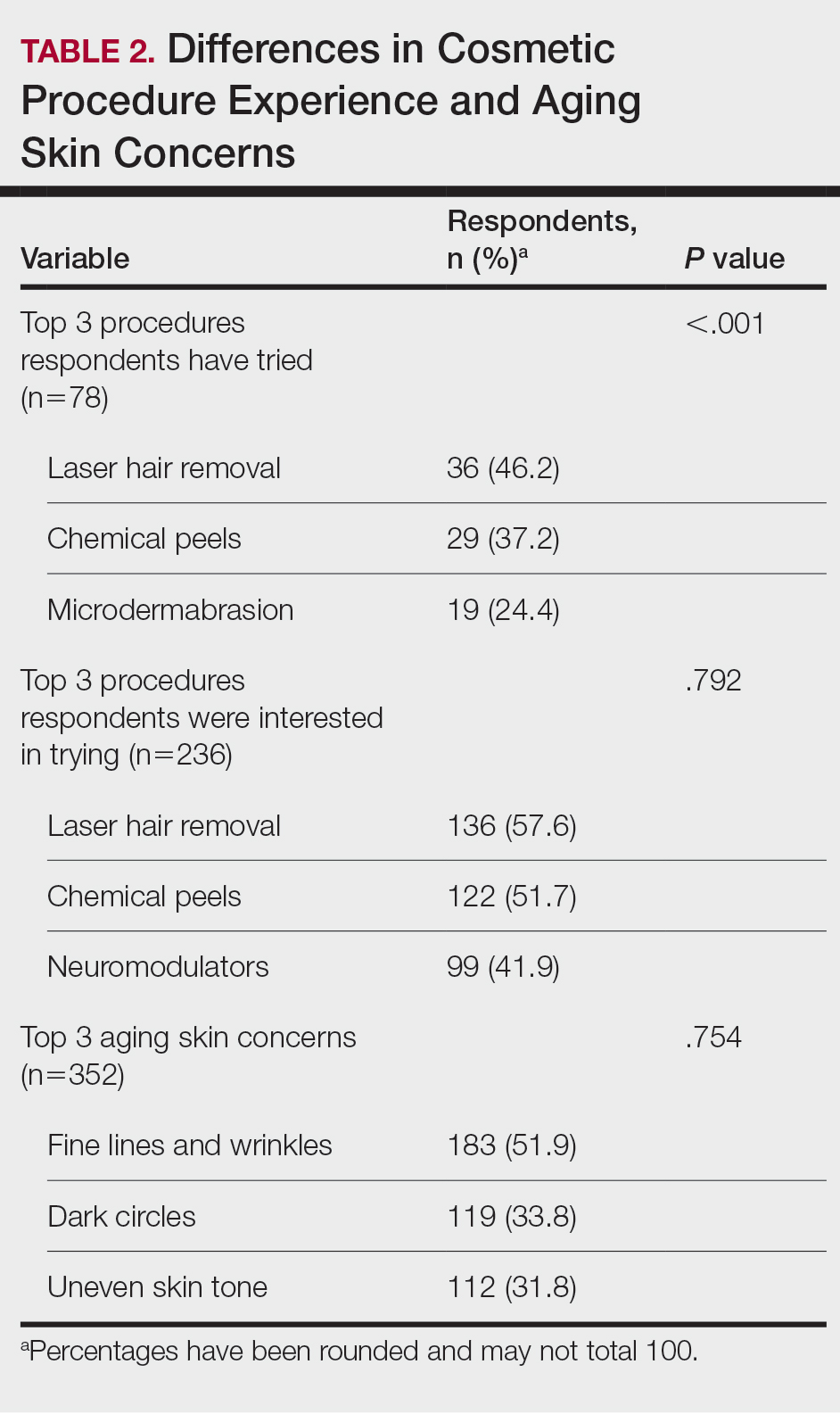
Cosmetic Skin Concerns—The top 3 aging skin concerns among participants were fine lines and wrinkles (51.9%), dark circles (33.8%), and uneven skin tone (31.8%) (Table 2). Approximately 5.4% of participants reported no desire to avoid the natural aging process. Among age groups, fine lines and wrinkles were a major concern for 51.7% of 21- to 30-year-olds, 47.6% of 31- to 40-year-olds, and 43.5% of 41- to 50-year-olds. Dark circles were a major concern for 61.3% of 21- to 30-year-olds, 44.4% of 31- to 40-year-olds, and 46.8% of 41- to 50-year-olds. Uneven skin tone was a major concern for 56.2% of 21- to 30-year-olds, 46.5% of 31- to 40-year-olds, and 31.2% of 41- to 50-year-olds. There was no statistically significant association between participants’ age and their concern with aging skin concerns.
Differences in Experience and Acceptance of Cosmetic Procedures—Regarding participants’ prior experience with cosmetic procedures, 22.3% had tried 1 or more procedures. Additionally, 67.0% reported having intentions of trying cosmetic procedures in the future, while 10.8% reported no intentions. Of those who were uninterested in trying cosmetic procedures, 78.9% (30/38) believed it unnecessary while 47.3% (18/38) reported a fear of looking unnatural. Other perceived deterrents to cosmetic procedures among this subset of participants were the need to repeat treatment for lasting results (28.9% [11/38]), too expensive (31.6% [12/38]), and fear of side effects (39.5% [15/38]). A significant difference was found between participants’ age and their experience with cosmetic procedures (P=.020). Participants aged 21 to 30 years reported they were more likely to want to try cosmetic procedures in the future. Participants aged 31 to 40 years were more likely to have already tried a cosmetic procedure. Participants aged 41 to 50 years were more likely to report no desire to try cosmetic procedures in the future. There was no significant difference in cosmetic procedure acceptance according to citizenship status, education level, or household income.
Differences in Cosmetic Procedure Experience—Study participants indicated awareness of typically practiced cosmetic procedures. Of the 78 participants who have tried cosmetic procedures (Figure 1), the most common were laser hair removal (46.2% [36/78]), chemical peels (37.2% [29/78]), and microdermabrasion (24.4% [19/78])(Table 2). Age significantly influenced the type of cosmetic procedures utilized by participants (P<.001). Laser hair removal was the most common cosmetic procedure utilized by participants aged 21 to 30 years (64.7%) and chemical peels in participants aged 31 to 40 years (47.8%); participants aged 41 to 50 years reported equal use of chemical peels (50.0%) and microdermabrasion (50.0%).
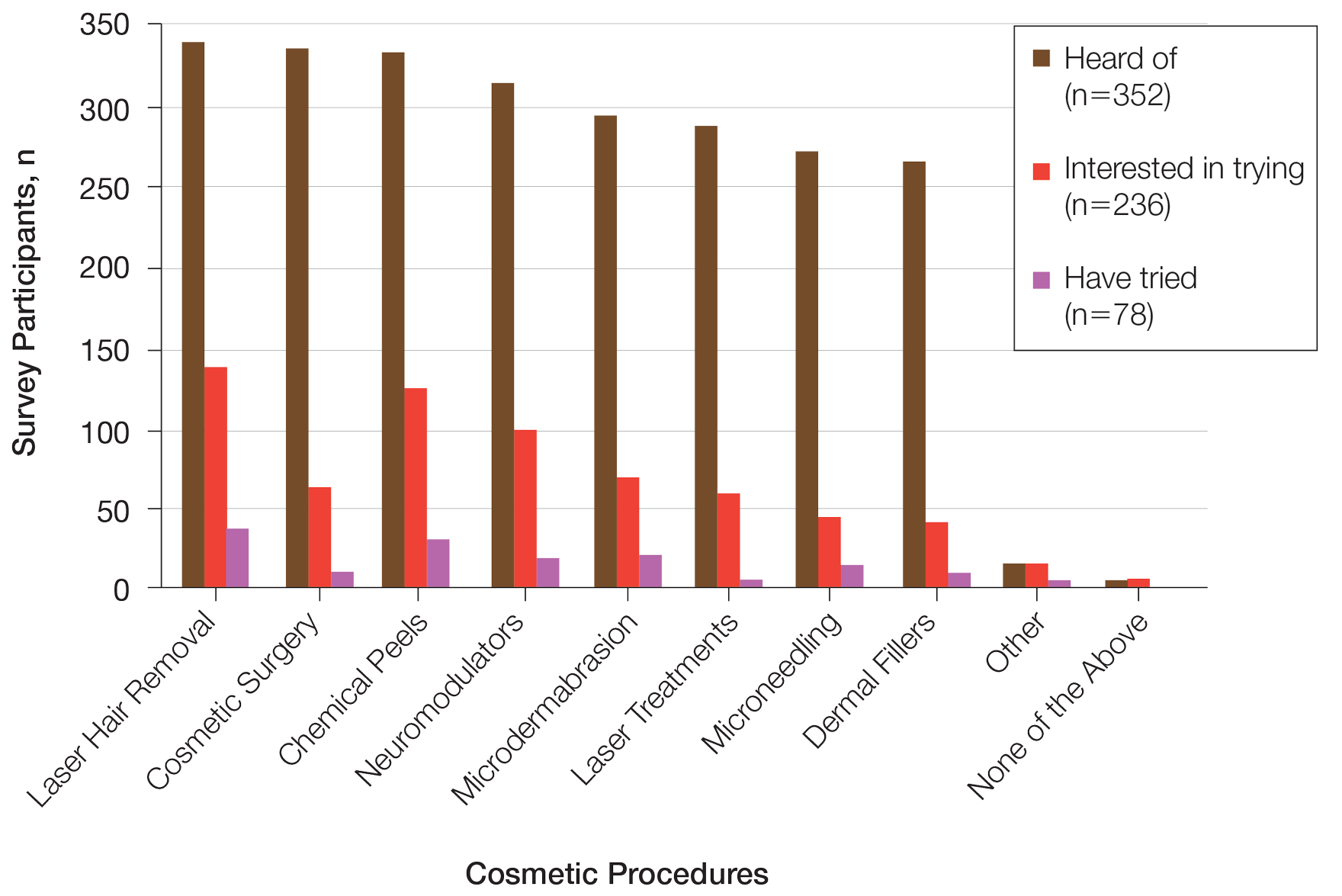
Two hundred thirty-six participants reported interest in trying cosmetic procedures, specifically laser hair removal (57.6%), chemical peels (51.7%), and neuromodulators (41.9%)(Table 2). Although not statistically significant, age appeared to influence interest levels in cosmetic procedures. Participants aged 21 to 30 years and 31 to 40 years were most interested in trying laser hair removal (60.7% and 58.3%, respectively). Participants aged 41 to 50 years were most interested in trying neuromodulators (36.4%). There was no significant association between age and intention to try neuromodulators, chemical peels, or laser hair removal.
Attitudes Toward Beauty—Approximately 40.6% of participants believed that peak beauty occurs when women reach their 20s, and 38.6% believed that peak beauty occurs when women reach their 30s. Participants’ strategies for maintaining beauty were assessed through their regular use of certain skin care products. The most frequently used skin care products were face wash or cleanser (92.6%), moisturizer (90.1%), lip balm (76.1%), and facial sunscreen (62.2%). Other commonly used items were serum (34.7%), toner (34.9%), topical vitamin C (33.2%), and retinol/retinoid products (33.0%). Only 2.3% of participants reported not using any skin care products regularly.
Perceptions of Aging—Concerning perceived external age, most respondents believed they looked younger than their true age (69.9%); 24.4% believed they looked their true age, and 5.7% believed they looked older. Perception of age also varied considerably by age group, though most believed they looked younger than their true age.
Comment
This survey helped to identify trends in cosmetic procedure acceptance and utilization in Black women. As expected, younger Black women were more receptive to cosmetic procedures, which was consistent with a recent finding that cosmetic procedures tend to be more widely accepted among younger generations overall.8 Participants aged 21 to 30 years had greater intentions to try a cosmetic procedure, while those aged 31 to 40 years were more likely to have tried 1 or more cosmetic procedures already, which may be because they are just beginning to see the signs of aging and are motivated to address these concerns. Additionally, women in this age group may be more likely to have a stable source of income and be able to afford these procedures. It is important to note that the population surveyed had a much higher reported household income than the average Black household income, with most respondents reporting an average annual income of $100,000 to $499,000. Our data also showed a trend toward greater acceptance and utilization of cosmetic procedures in those with higher levels of income, though the results were not statistically significant.
Respondents were most concerned about fine lines and wrinkles, followed by dark circles and uneven skin tone. One report in the literature (N=2000) indicated that the most common cosmetic concerns in women with SOC were hyperpigmentation/dark spots (86%) and blotchy or uneven skin (80%).9 Interestingly, sunscreen was one of the more commonly used products in our survey, which historically has not been the case among individuals with SOC10 and suggests that the attitudes and perceptions of SOC patients are changing to favor more frequent sunscreen use, at least among the younger generations. Because we did not specify moisturizer vs moisturizer with sun protection factor, the use of facial sunscreen may even be underestimated in our survey.
Compared to cosmetic surgery or dermal fillers, the procedures found to be most frequently utilized in our study population—microdermabrasion, chemical peels, and laser hair removal—are less invasive and fairly accessible with minimal downtime. An interesting topic for further research would be to investigate how the willingness of women to openly share their cosmetic procedure usage has changed over time. The rise of social media and influencer culture has undoubtedly had an impact on the sharing of such information. It also would have been interesting to ask participants where they receive the majority of their health/beauty information.
All skin types are susceptible to photoaging; however, melanin is known to have a natural photoprotective effect, resulting in a lesser degree and later onset of photoaging in patients with darker vs lighter skin.11 It has been reported that individuals with SOC show signs of facial aging on average a decade later than those with lighter skin tones,12 which may be why the majority of participants believed they look younger than they truly are. As expected, dyspigmentation was among the top skin concerns in our study population. Although melanin does offer some degree of protection against UVA and UVB, melanocyte lability with inflammation may make darker skin types more susceptible to pigmentary issues.13
Study Limitations—The income levels of our study population were not representative of typical Black American households, which is a limitation. Seventy-seven percent of our study population earned more than $100,000 annually, while only 18% of Black American households earned more than $100,000 in 2019.14 Another major limitation of our study was the lack of representation from older generations, as most participants were aged 21 to 40 years, which was expected, as it is the younger generation who typically is targeted by a snowball sampling method primarily shared through social media. Additionally, because participants were recruited from the social media profiles of medical professionals, followers of these accounts may be more interested in cosmetic procedures, skewing the study results. Finally, because geographic location was not captured in our initial data collection, we were unable to determine if results from a particular location within the United States were overrepresented in the data set.
Conclusion
Although the discourse around beauty and antiaging is constantly evolving, data about Black women frequently are underrepresented in the literature. The results of this study highlight the changing attitudes and perceptions of Black women regarding beauty, aging, and minimally invasive cosmetic procedures. Dermatologists should stay abreast of current trends in this population to be able to make appropriate, culturally sensitive recommendations to their Black patients—for example, pointing them to sunscreen brands that are best suited for darker skin.
- Ahn CS, Suchonwanit P, Foy CG, et al. Hair and scalp care in African American women who exercise. JAMA Dermatol. 2016;152:579-580.
- Prendergast TI, Ong’uti SK, Ortega G, et al. Differential trends in racial preferences for cosmetic surgery procedures. Am Surg. 2011;77:1081-1085.
- American Society of Plastic Surgeons. Briefing paper: plastic surgeryfor ethnic patients. Accessed October 20, 2023. https://www.plasticsurgery.org/news/briefing-papers/briefing-paper-plastic-surgery-for-ethnic-patients
- Small K, Kelly KM, Spinelli HM. Are nurse injectors the new norm? Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2014;38:946-955.
- Quiñonez RL, Agbai ON, Burgess CM, et al. An update on cosmetic procedures in people of color. part 1: scientific background, assessment, preprocedure preparation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;86:715-725.
- Alexis AF, Grimes P, Boyd C, et al. Racial and ethnic differences in self-assessed facial aging in women: results from a multinational study. Dermatol Surg. 2019;45:1635-1648.
- Talakoub L, Wesley NO. Differences in perceptions of beauty and cosmetic procedures performed in ethnic patients. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2009;28:115-129.
- Alotaibi AS. Demographic and cultural differences in the acceptance and pursuit of cosmetic surgery: a systematic literature review. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2021;9:E3501.
- Grimes PE. Skin and hair cosmetic issues in women of color. Dermatol Clin. 2000;18:659-665.
- Buchanan Lunsford N, Berktold J, Holman DM, et al. Skin cancer knowledge, awareness, beliefs and preventive behaviors among black and Hispanic men and women. Prev Med Rep. 2018;12:203-209.
- Alexis AF, Rossi, A. Photoaging in skin of color. Cosmet Dermatol. 2011;24:367-370.
- Vashi NA, de Castro Maymone MB, Kundu RV. Aging differences in ethnic skin. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2016;9:31-38.
- Alexis AF, Sergay AB, Taylor SC. Common dermatologic disorders in skin of color: a comparative practice survey. Cutis. 2007;80:387-394.
- Tamir C, Budiman A, Noe-Bustamante L, et al. Facts about the U.S. Black population. Pew Research Center website. Published March 2, 2023. Accessed October 20, 2023. https://www.pewresearch.org/social-trends/fact-sheet/facts-about-the-us-black-population/
Beauty has been a topic of interest for centuries. Treatments and technologies have advanced, and more women are utilizing cosmetic procedures than ever before, especially neuromodulators, minimally invasive procedures, and topical treatments.1 Over the last decade, there was a 99% increase in minimally invasive cosmetic procedures in the United States.2 There also has been an observable increase in the utilization of cosmetic procedures by Black patients in recent years; the American Society of Plastic Surgeons reported that the number of cosmetic plastic surgery procedures performed on “ethnic patients” (referring to Asian, Black, or Hispanic patients) increased 243% from 2000 to 2013,3 possibly attributed to increased accessibility, awareness of procedures due to social media, cultural acceptance, and affordability. Minimally invasive procedures are considerably less expensive than major surgical procedures and are becoming progressively more affordable, with numerous financing options available.2 Additionally, neuromodulators and fillers are now commonly administered by nonaesthetic health professionals including dentists and nurses, which has increased accessibility of these procedures among patients who typically may not seek out a consultation with a plastic surgeon or dermatologist.4
When examining the most common cosmetic procedures collectively sought out by patients with skin of color (SOC), it has been found that an even skin tone is a highly desirable feature that impacts the selection of products and procedures in this particular patient population.5 Black, Hispanic, and Asian women report fewer signs of facial aging compared to White women in the glabellar lines, crow’s-feet, oral commissures, perioral lines, and lips.6 Increased melanocytes in darker skin types help prevent photoaging but also increase susceptibility to dyschromia. Prior studies have reported the most common concerns by patients with SOC are dyschromic disorders such as postinflammatory hyperpigmentation, postinflammatory hypopigmentation, and melasma.7 Common minimally invasive cosmetic procedures utilized by the SOC population include chemical peels, laser treatments, and injectables. Fillers are utilized more for volume loss in SOC patients rather than for the deep furrows and rhytides commonly seen in the lower face of White patients.8
We conducted a survey among Black women currently residing in the United States to better understand attitudes toward beauty and aging as well as the utilization of minimally invasive cosmetic procedures in this patient population.
Methods
An in-depth questionnaire comprised of 17 questions was created for this cross-sectional observational study. The study was submitted to and deemed exempt by the institutional review board at the University of Miami (Miami, Florida)(IRB #20211184). Survey participants primarily were recruited via social media posts on personal profiles of Black dermatologists, medical residents, and medicalstudents, including the authors, targeting Black women in the United States. Utilizing a method called snowball sampling, whereby study participants are used to recruit future participants, individuals were instructed to share the survey with their social network to assist with survey distribution. After participants provided informed consent, data were captured using the REDCap secure online data collection software. The questionnaire was structured to include a sociodemographic profile of respondents, attitudes toward beauty and aging, current usage of beauty products, prior utilization of cosmetic procedures, and intentions to use cosmetic procedures in the future. Surveys with incomplete consent forms, incomplete responses, and duplicate responses, as well as surveys from participants who were not residing in the United States at the time of survey completion, were excluded.
Data characteristics were summarized by frequency and percentage. A χ2 test was performed to compare participants’ age demographics with their attitudes toward beauty and aging, utilization of cosmetic procedures, and intention to try cosmetic procedures in the future. The Fisher exact test was used instead of the χ2 test when the expected cell count was less than 5. For all tests, P<.05 was considered statistically significant. All statistical analyses were performed using SPSS software version 28.
Results
General Characteristics of Participants—A sample of 475 self-identified Black women aged 21 to 70 years participated in the study, and 352 eligible participants were included in the final analysis. Of the 352 eligible participants, 48.3% were aged 21 to 30 years, 47.2% were aged 31 to 40 years, and 4.5% were aged 41 to 50 years. All survey participants identified their race as Black; among them, 4% specified Hispanic or Latino ethnicity, and 9% indicated that they held multiracial identities including White/Caucasian, Asian, and Native American backgrounds. Regarding the participants’ citizenship status, 54.3% reported that both they and their parents were born in the United States; 2.3% were not US citizens or permanent residents, 13.1% identified as first-generation Americans (born outside of the United States), and 30.4% identified as second-generation Americans (one or both parents born outside of the United States). Participant education levels (based on highest level) varied greatly: 4.5% were high school graduates, 1.1% attended trade or technical schools, 3.4% had associate’s degrees, 39.8% had bachelor’s degrees, 35.2% had master’s degrees, and 15.9% had doctorate degrees. Regarding household income, 6.3% earned less than $25,000 per year, 16.8% earned from $25,000 to $99,999, 75.6% earned from $100,000 to $499,999, and 1.4% earned $500,000 or more. Patient demographics are provided in Table 1.

Cosmetic Skin Concerns—The top 3 aging skin concerns among participants were fine lines and wrinkles (51.9%), dark circles (33.8%), and uneven skin tone (31.8%) (Table 2). Approximately 5.4% of participants reported no desire to avoid the natural aging process. Among age groups, fine lines and wrinkles were a major concern for 51.7% of 21- to 30-year-olds, 47.6% of 31- to 40-year-olds, and 43.5% of 41- to 50-year-olds. Dark circles were a major concern for 61.3% of 21- to 30-year-olds, 44.4% of 31- to 40-year-olds, and 46.8% of 41- to 50-year-olds. Uneven skin tone was a major concern for 56.2% of 21- to 30-year-olds, 46.5% of 31- to 40-year-olds, and 31.2% of 41- to 50-year-olds. There was no statistically significant association between participants’ age and their concern with aging skin concerns.

Differences in Experience and Acceptance of Cosmetic Procedures—Regarding participants’ prior experience with cosmetic procedures, 22.3% had tried 1 or more procedures. Additionally, 67.0% reported having intentions of trying cosmetic procedures in the future, while 10.8% reported no intentions. Of those who were uninterested in trying cosmetic procedures, 78.9% (30/38) believed it unnecessary while 47.3% (18/38) reported a fear of looking unnatural. Other perceived deterrents to cosmetic procedures among this subset of participants were the need to repeat treatment for lasting results (28.9% [11/38]), too expensive (31.6% [12/38]), and fear of side effects (39.5% [15/38]). A significant difference was found between participants’ age and their experience with cosmetic procedures (P=.020). Participants aged 21 to 30 years reported they were more likely to want to try cosmetic procedures in the future. Participants aged 31 to 40 years were more likely to have already tried a cosmetic procedure. Participants aged 41 to 50 years were more likely to report no desire to try cosmetic procedures in the future. There was no significant difference in cosmetic procedure acceptance according to citizenship status, education level, or household income.
Differences in Cosmetic Procedure Experience—Study participants indicated awareness of typically practiced cosmetic procedures. Of the 78 participants who have tried cosmetic procedures (Figure 1), the most common were laser hair removal (46.2% [36/78]), chemical peels (37.2% [29/78]), and microdermabrasion (24.4% [19/78])(Table 2). Age significantly influenced the type of cosmetic procedures utilized by participants (P<.001). Laser hair removal was the most common cosmetic procedure utilized by participants aged 21 to 30 years (64.7%) and chemical peels in participants aged 31 to 40 years (47.8%); participants aged 41 to 50 years reported equal use of chemical peels (50.0%) and microdermabrasion (50.0%).

Two hundred thirty-six participants reported interest in trying cosmetic procedures, specifically laser hair removal (57.6%), chemical peels (51.7%), and neuromodulators (41.9%)(Table 2). Although not statistically significant, age appeared to influence interest levels in cosmetic procedures. Participants aged 21 to 30 years and 31 to 40 years were most interested in trying laser hair removal (60.7% and 58.3%, respectively). Participants aged 41 to 50 years were most interested in trying neuromodulators (36.4%). There was no significant association between age and intention to try neuromodulators, chemical peels, or laser hair removal.
Attitudes Toward Beauty—Approximately 40.6% of participants believed that peak beauty occurs when women reach their 20s, and 38.6% believed that peak beauty occurs when women reach their 30s. Participants’ strategies for maintaining beauty were assessed through their regular use of certain skin care products. The most frequently used skin care products were face wash or cleanser (92.6%), moisturizer (90.1%), lip balm (76.1%), and facial sunscreen (62.2%). Other commonly used items were serum (34.7%), toner (34.9%), topical vitamin C (33.2%), and retinol/retinoid products (33.0%). Only 2.3% of participants reported not using any skin care products regularly.
Perceptions of Aging—Concerning perceived external age, most respondents believed they looked younger than their true age (69.9%); 24.4% believed they looked their true age, and 5.7% believed they looked older. Perception of age also varied considerably by age group, though most believed they looked younger than their true age.
Comment
This survey helped to identify trends in cosmetic procedure acceptance and utilization in Black women. As expected, younger Black women were more receptive to cosmetic procedures, which was consistent with a recent finding that cosmetic procedures tend to be more widely accepted among younger generations overall.8 Participants aged 21 to 30 years had greater intentions to try a cosmetic procedure, while those aged 31 to 40 years were more likely to have tried 1 or more cosmetic procedures already, which may be because they are just beginning to see the signs of aging and are motivated to address these concerns. Additionally, women in this age group may be more likely to have a stable source of income and be able to afford these procedures. It is important to note that the population surveyed had a much higher reported household income than the average Black household income, with most respondents reporting an average annual income of $100,000 to $499,000. Our data also showed a trend toward greater acceptance and utilization of cosmetic procedures in those with higher levels of income, though the results were not statistically significant.
Respondents were most concerned about fine lines and wrinkles, followed by dark circles and uneven skin tone. One report in the literature (N=2000) indicated that the most common cosmetic concerns in women with SOC were hyperpigmentation/dark spots (86%) and blotchy or uneven skin (80%).9 Interestingly, sunscreen was one of the more commonly used products in our survey, which historically has not been the case among individuals with SOC10 and suggests that the attitudes and perceptions of SOC patients are changing to favor more frequent sunscreen use, at least among the younger generations. Because we did not specify moisturizer vs moisturizer with sun protection factor, the use of facial sunscreen may even be underestimated in our survey.
Compared to cosmetic surgery or dermal fillers, the procedures found to be most frequently utilized in our study population—microdermabrasion, chemical peels, and laser hair removal—are less invasive and fairly accessible with minimal downtime. An interesting topic for further research would be to investigate how the willingness of women to openly share their cosmetic procedure usage has changed over time. The rise of social media and influencer culture has undoubtedly had an impact on the sharing of such information. It also would have been interesting to ask participants where they receive the majority of their health/beauty information.
All skin types are susceptible to photoaging; however, melanin is known to have a natural photoprotective effect, resulting in a lesser degree and later onset of photoaging in patients with darker vs lighter skin.11 It has been reported that individuals with SOC show signs of facial aging on average a decade later than those with lighter skin tones,12 which may be why the majority of participants believed they look younger than they truly are. As expected, dyspigmentation was among the top skin concerns in our study population. Although melanin does offer some degree of protection against UVA and UVB, melanocyte lability with inflammation may make darker skin types more susceptible to pigmentary issues.13
Study Limitations—The income levels of our study population were not representative of typical Black American households, which is a limitation. Seventy-seven percent of our study population earned more than $100,000 annually, while only 18% of Black American households earned more than $100,000 in 2019.14 Another major limitation of our study was the lack of representation from older generations, as most participants were aged 21 to 40 years, which was expected, as it is the younger generation who typically is targeted by a snowball sampling method primarily shared through social media. Additionally, because participants were recruited from the social media profiles of medical professionals, followers of these accounts may be more interested in cosmetic procedures, skewing the study results. Finally, because geographic location was not captured in our initial data collection, we were unable to determine if results from a particular location within the United States were overrepresented in the data set.
Conclusion
Although the discourse around beauty and antiaging is constantly evolving, data about Black women frequently are underrepresented in the literature. The results of this study highlight the changing attitudes and perceptions of Black women regarding beauty, aging, and minimally invasive cosmetic procedures. Dermatologists should stay abreast of current trends in this population to be able to make appropriate, culturally sensitive recommendations to their Black patients—for example, pointing them to sunscreen brands that are best suited for darker skin.
Beauty has been a topic of interest for centuries. Treatments and technologies have advanced, and more women are utilizing cosmetic procedures than ever before, especially neuromodulators, minimally invasive procedures, and topical treatments.1 Over the last decade, there was a 99% increase in minimally invasive cosmetic procedures in the United States.2 There also has been an observable increase in the utilization of cosmetic procedures by Black patients in recent years; the American Society of Plastic Surgeons reported that the number of cosmetic plastic surgery procedures performed on “ethnic patients” (referring to Asian, Black, or Hispanic patients) increased 243% from 2000 to 2013,3 possibly attributed to increased accessibility, awareness of procedures due to social media, cultural acceptance, and affordability. Minimally invasive procedures are considerably less expensive than major surgical procedures and are becoming progressively more affordable, with numerous financing options available.2 Additionally, neuromodulators and fillers are now commonly administered by nonaesthetic health professionals including dentists and nurses, which has increased accessibility of these procedures among patients who typically may not seek out a consultation with a plastic surgeon or dermatologist.4
When examining the most common cosmetic procedures collectively sought out by patients with skin of color (SOC), it has been found that an even skin tone is a highly desirable feature that impacts the selection of products and procedures in this particular patient population.5 Black, Hispanic, and Asian women report fewer signs of facial aging compared to White women in the glabellar lines, crow’s-feet, oral commissures, perioral lines, and lips.6 Increased melanocytes in darker skin types help prevent photoaging but also increase susceptibility to dyschromia. Prior studies have reported the most common concerns by patients with SOC are dyschromic disorders such as postinflammatory hyperpigmentation, postinflammatory hypopigmentation, and melasma.7 Common minimally invasive cosmetic procedures utilized by the SOC population include chemical peels, laser treatments, and injectables. Fillers are utilized more for volume loss in SOC patients rather than for the deep furrows and rhytides commonly seen in the lower face of White patients.8
We conducted a survey among Black women currently residing in the United States to better understand attitudes toward beauty and aging as well as the utilization of minimally invasive cosmetic procedures in this patient population.
Methods
An in-depth questionnaire comprised of 17 questions was created for this cross-sectional observational study. The study was submitted to and deemed exempt by the institutional review board at the University of Miami (Miami, Florida)(IRB #20211184). Survey participants primarily were recruited via social media posts on personal profiles of Black dermatologists, medical residents, and medicalstudents, including the authors, targeting Black women in the United States. Utilizing a method called snowball sampling, whereby study participants are used to recruit future participants, individuals were instructed to share the survey with their social network to assist with survey distribution. After participants provided informed consent, data were captured using the REDCap secure online data collection software. The questionnaire was structured to include a sociodemographic profile of respondents, attitudes toward beauty and aging, current usage of beauty products, prior utilization of cosmetic procedures, and intentions to use cosmetic procedures in the future. Surveys with incomplete consent forms, incomplete responses, and duplicate responses, as well as surveys from participants who were not residing in the United States at the time of survey completion, were excluded.
Data characteristics were summarized by frequency and percentage. A χ2 test was performed to compare participants’ age demographics with their attitudes toward beauty and aging, utilization of cosmetic procedures, and intention to try cosmetic procedures in the future. The Fisher exact test was used instead of the χ2 test when the expected cell count was less than 5. For all tests, P<.05 was considered statistically significant. All statistical analyses were performed using SPSS software version 28.
Results
General Characteristics of Participants—A sample of 475 self-identified Black women aged 21 to 70 years participated in the study, and 352 eligible participants were included in the final analysis. Of the 352 eligible participants, 48.3% were aged 21 to 30 years, 47.2% were aged 31 to 40 years, and 4.5% were aged 41 to 50 years. All survey participants identified their race as Black; among them, 4% specified Hispanic or Latino ethnicity, and 9% indicated that they held multiracial identities including White/Caucasian, Asian, and Native American backgrounds. Regarding the participants’ citizenship status, 54.3% reported that both they and their parents were born in the United States; 2.3% were not US citizens or permanent residents, 13.1% identified as first-generation Americans (born outside of the United States), and 30.4% identified as second-generation Americans (one or both parents born outside of the United States). Participant education levels (based on highest level) varied greatly: 4.5% were high school graduates, 1.1% attended trade or technical schools, 3.4% had associate’s degrees, 39.8% had bachelor’s degrees, 35.2% had master’s degrees, and 15.9% had doctorate degrees. Regarding household income, 6.3% earned less than $25,000 per year, 16.8% earned from $25,000 to $99,999, 75.6% earned from $100,000 to $499,999, and 1.4% earned $500,000 or more. Patient demographics are provided in Table 1.

Cosmetic Skin Concerns—The top 3 aging skin concerns among participants were fine lines and wrinkles (51.9%), dark circles (33.8%), and uneven skin tone (31.8%) (Table 2). Approximately 5.4% of participants reported no desire to avoid the natural aging process. Among age groups, fine lines and wrinkles were a major concern for 51.7% of 21- to 30-year-olds, 47.6% of 31- to 40-year-olds, and 43.5% of 41- to 50-year-olds. Dark circles were a major concern for 61.3% of 21- to 30-year-olds, 44.4% of 31- to 40-year-olds, and 46.8% of 41- to 50-year-olds. Uneven skin tone was a major concern for 56.2% of 21- to 30-year-olds, 46.5% of 31- to 40-year-olds, and 31.2% of 41- to 50-year-olds. There was no statistically significant association between participants’ age and their concern with aging skin concerns.

Differences in Experience and Acceptance of Cosmetic Procedures—Regarding participants’ prior experience with cosmetic procedures, 22.3% had tried 1 or more procedures. Additionally, 67.0% reported having intentions of trying cosmetic procedures in the future, while 10.8% reported no intentions. Of those who were uninterested in trying cosmetic procedures, 78.9% (30/38) believed it unnecessary while 47.3% (18/38) reported a fear of looking unnatural. Other perceived deterrents to cosmetic procedures among this subset of participants were the need to repeat treatment for lasting results (28.9% [11/38]), too expensive (31.6% [12/38]), and fear of side effects (39.5% [15/38]). A significant difference was found between participants’ age and their experience with cosmetic procedures (P=.020). Participants aged 21 to 30 years reported they were more likely to want to try cosmetic procedures in the future. Participants aged 31 to 40 years were more likely to have already tried a cosmetic procedure. Participants aged 41 to 50 years were more likely to report no desire to try cosmetic procedures in the future. There was no significant difference in cosmetic procedure acceptance according to citizenship status, education level, or household income.
Differences in Cosmetic Procedure Experience—Study participants indicated awareness of typically practiced cosmetic procedures. Of the 78 participants who have tried cosmetic procedures (Figure 1), the most common were laser hair removal (46.2% [36/78]), chemical peels (37.2% [29/78]), and microdermabrasion (24.4% [19/78])(Table 2). Age significantly influenced the type of cosmetic procedures utilized by participants (P<.001). Laser hair removal was the most common cosmetic procedure utilized by participants aged 21 to 30 years (64.7%) and chemical peels in participants aged 31 to 40 years (47.8%); participants aged 41 to 50 years reported equal use of chemical peels (50.0%) and microdermabrasion (50.0%).

Two hundred thirty-six participants reported interest in trying cosmetic procedures, specifically laser hair removal (57.6%), chemical peels (51.7%), and neuromodulators (41.9%)(Table 2). Although not statistically significant, age appeared to influence interest levels in cosmetic procedures. Participants aged 21 to 30 years and 31 to 40 years were most interested in trying laser hair removal (60.7% and 58.3%, respectively). Participants aged 41 to 50 years were most interested in trying neuromodulators (36.4%). There was no significant association between age and intention to try neuromodulators, chemical peels, or laser hair removal.
Attitudes Toward Beauty—Approximately 40.6% of participants believed that peak beauty occurs when women reach their 20s, and 38.6% believed that peak beauty occurs when women reach their 30s. Participants’ strategies for maintaining beauty were assessed through their regular use of certain skin care products. The most frequently used skin care products were face wash or cleanser (92.6%), moisturizer (90.1%), lip balm (76.1%), and facial sunscreen (62.2%). Other commonly used items were serum (34.7%), toner (34.9%), topical vitamin C (33.2%), and retinol/retinoid products (33.0%). Only 2.3% of participants reported not using any skin care products regularly.
Perceptions of Aging—Concerning perceived external age, most respondents believed they looked younger than their true age (69.9%); 24.4% believed they looked their true age, and 5.7% believed they looked older. Perception of age also varied considerably by age group, though most believed they looked younger than their true age.
Comment
This survey helped to identify trends in cosmetic procedure acceptance and utilization in Black women. As expected, younger Black women were more receptive to cosmetic procedures, which was consistent with a recent finding that cosmetic procedures tend to be more widely accepted among younger generations overall.8 Participants aged 21 to 30 years had greater intentions to try a cosmetic procedure, while those aged 31 to 40 years were more likely to have tried 1 or more cosmetic procedures already, which may be because they are just beginning to see the signs of aging and are motivated to address these concerns. Additionally, women in this age group may be more likely to have a stable source of income and be able to afford these procedures. It is important to note that the population surveyed had a much higher reported household income than the average Black household income, with most respondents reporting an average annual income of $100,000 to $499,000. Our data also showed a trend toward greater acceptance and utilization of cosmetic procedures in those with higher levels of income, though the results were not statistically significant.
Respondents were most concerned about fine lines and wrinkles, followed by dark circles and uneven skin tone. One report in the literature (N=2000) indicated that the most common cosmetic concerns in women with SOC were hyperpigmentation/dark spots (86%) and blotchy or uneven skin (80%).9 Interestingly, sunscreen was one of the more commonly used products in our survey, which historically has not been the case among individuals with SOC10 and suggests that the attitudes and perceptions of SOC patients are changing to favor more frequent sunscreen use, at least among the younger generations. Because we did not specify moisturizer vs moisturizer with sun protection factor, the use of facial sunscreen may even be underestimated in our survey.
Compared to cosmetic surgery or dermal fillers, the procedures found to be most frequently utilized in our study population—microdermabrasion, chemical peels, and laser hair removal—are less invasive and fairly accessible with minimal downtime. An interesting topic for further research would be to investigate how the willingness of women to openly share their cosmetic procedure usage has changed over time. The rise of social media and influencer culture has undoubtedly had an impact on the sharing of such information. It also would have been interesting to ask participants where they receive the majority of their health/beauty information.
All skin types are susceptible to photoaging; however, melanin is known to have a natural photoprotective effect, resulting in a lesser degree and later onset of photoaging in patients with darker vs lighter skin.11 It has been reported that individuals with SOC show signs of facial aging on average a decade later than those with lighter skin tones,12 which may be why the majority of participants believed they look younger than they truly are. As expected, dyspigmentation was among the top skin concerns in our study population. Although melanin does offer some degree of protection against UVA and UVB, melanocyte lability with inflammation may make darker skin types more susceptible to pigmentary issues.13
Study Limitations—The income levels of our study population were not representative of typical Black American households, which is a limitation. Seventy-seven percent of our study population earned more than $100,000 annually, while only 18% of Black American households earned more than $100,000 in 2019.14 Another major limitation of our study was the lack of representation from older generations, as most participants were aged 21 to 40 years, which was expected, as it is the younger generation who typically is targeted by a snowball sampling method primarily shared through social media. Additionally, because participants were recruited from the social media profiles of medical professionals, followers of these accounts may be more interested in cosmetic procedures, skewing the study results. Finally, because geographic location was not captured in our initial data collection, we were unable to determine if results from a particular location within the United States were overrepresented in the data set.
Conclusion
Although the discourse around beauty and antiaging is constantly evolving, data about Black women frequently are underrepresented in the literature. The results of this study highlight the changing attitudes and perceptions of Black women regarding beauty, aging, and minimally invasive cosmetic procedures. Dermatologists should stay abreast of current trends in this population to be able to make appropriate, culturally sensitive recommendations to their Black patients—for example, pointing them to sunscreen brands that are best suited for darker skin.
- Ahn CS, Suchonwanit P, Foy CG, et al. Hair and scalp care in African American women who exercise. JAMA Dermatol. 2016;152:579-580.
- Prendergast TI, Ong’uti SK, Ortega G, et al. Differential trends in racial preferences for cosmetic surgery procedures. Am Surg. 2011;77:1081-1085.
- American Society of Plastic Surgeons. Briefing paper: plastic surgeryfor ethnic patients. Accessed October 20, 2023. https://www.plasticsurgery.org/news/briefing-papers/briefing-paper-plastic-surgery-for-ethnic-patients
- Small K, Kelly KM, Spinelli HM. Are nurse injectors the new norm? Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2014;38:946-955.
- Quiñonez RL, Agbai ON, Burgess CM, et al. An update on cosmetic procedures in people of color. part 1: scientific background, assessment, preprocedure preparation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;86:715-725.
- Alexis AF, Grimes P, Boyd C, et al. Racial and ethnic differences in self-assessed facial aging in women: results from a multinational study. Dermatol Surg. 2019;45:1635-1648.
- Talakoub L, Wesley NO. Differences in perceptions of beauty and cosmetic procedures performed in ethnic patients. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2009;28:115-129.
- Alotaibi AS. Demographic and cultural differences in the acceptance and pursuit of cosmetic surgery: a systematic literature review. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2021;9:E3501.
- Grimes PE. Skin and hair cosmetic issues in women of color. Dermatol Clin. 2000;18:659-665.
- Buchanan Lunsford N, Berktold J, Holman DM, et al. Skin cancer knowledge, awareness, beliefs and preventive behaviors among black and Hispanic men and women. Prev Med Rep. 2018;12:203-209.
- Alexis AF, Rossi, A. Photoaging in skin of color. Cosmet Dermatol. 2011;24:367-370.
- Vashi NA, de Castro Maymone MB, Kundu RV. Aging differences in ethnic skin. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2016;9:31-38.
- Alexis AF, Sergay AB, Taylor SC. Common dermatologic disorders in skin of color: a comparative practice survey. Cutis. 2007;80:387-394.
- Tamir C, Budiman A, Noe-Bustamante L, et al. Facts about the U.S. Black population. Pew Research Center website. Published March 2, 2023. Accessed October 20, 2023. https://www.pewresearch.org/social-trends/fact-sheet/facts-about-the-us-black-population/
- Ahn CS, Suchonwanit P, Foy CG, et al. Hair and scalp care in African American women who exercise. JAMA Dermatol. 2016;152:579-580.
- Prendergast TI, Ong’uti SK, Ortega G, et al. Differential trends in racial preferences for cosmetic surgery procedures. Am Surg. 2011;77:1081-1085.
- American Society of Plastic Surgeons. Briefing paper: plastic surgeryfor ethnic patients. Accessed October 20, 2023. https://www.plasticsurgery.org/news/briefing-papers/briefing-paper-plastic-surgery-for-ethnic-patients
- Small K, Kelly KM, Spinelli HM. Are nurse injectors the new norm? Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2014;38:946-955.
- Quiñonez RL, Agbai ON, Burgess CM, et al. An update on cosmetic procedures in people of color. part 1: scientific background, assessment, preprocedure preparation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;86:715-725.
- Alexis AF, Grimes P, Boyd C, et al. Racial and ethnic differences in self-assessed facial aging in women: results from a multinational study. Dermatol Surg. 2019;45:1635-1648.
- Talakoub L, Wesley NO. Differences in perceptions of beauty and cosmetic procedures performed in ethnic patients. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2009;28:115-129.
- Alotaibi AS. Demographic and cultural differences in the acceptance and pursuit of cosmetic surgery: a systematic literature review. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2021;9:E3501.
- Grimes PE. Skin and hair cosmetic issues in women of color. Dermatol Clin. 2000;18:659-665.
- Buchanan Lunsford N, Berktold J, Holman DM, et al. Skin cancer knowledge, awareness, beliefs and preventive behaviors among black and Hispanic men and women. Prev Med Rep. 2018;12:203-209.
- Alexis AF, Rossi, A. Photoaging in skin of color. Cosmet Dermatol. 2011;24:367-370.
- Vashi NA, de Castro Maymone MB, Kundu RV. Aging differences in ethnic skin. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2016;9:31-38.
- Alexis AF, Sergay AB, Taylor SC. Common dermatologic disorders in skin of color: a comparative practice survey. Cutis. 2007;80:387-394.
- Tamir C, Budiman A, Noe-Bustamante L, et al. Facts about the U.S. Black population. Pew Research Center website. Published March 2, 2023. Accessed October 20, 2023. https://www.pewresearch.org/social-trends/fact-sheet/facts-about-the-us-black-population/
Practice Points
- Cosmetic procedures may be more widely accepted among younger Black women than older Black women.
- Age has a considerable influence on the types of cosmetic procedures that Black women are interested in trying.
- Microdermabrasion, chemical peels, and laser hair removal were the most frequently utilized procedures in this study population.
- As attitudes and perceptions of young Black women are changing and favoring more frequent sunscreen use, dermatologists should remain on top of current trends to provide culturally sensitive and relevant recommendations to patients with darker skin tones.