User login
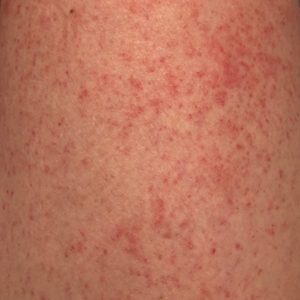
Autoeczematization (AE), or id reaction, is a disseminated eczematous reaction that occurs days or weeks after exposure to a primary stimulus, resulting from a release of antigen(s). Whitfield1 first described AE in 1921, when he postulated that the id reaction was due to sensitization of the skin after a primary stimulus. He called it “a form of auto-intoxication derived from changes in the patient’s own tissues.”1 The exact prevalence of id reactions is unknown; one study showed that 17% of patients with dermatophyte infections developed an id reaction, typically tinea pedis linked with vesicles on the palms.2 Tinea capitis is one of the most common causes of AE in children, which is frequently misdiagnosed as a drug reaction. Approximately 37% of patients diagnosed with stasis dermatitis develop an id reaction (Figure 1). A history of contact dermatitis is common in patients presenting with AE.2-6

Pathophysiology of Id Reactions
An abnormal immune response against autologous skin antigens may be responsible for the development of AE. Shelley5 postulated that hair follicles play an important role in id reactions, as Sharquie et al6 recently emphasized for many skin disorders. The pathogenesis of AE is uncertain, but circulating T lymphocytes play a role in this reaction. Normally, T cells are activated by a release of antigens after a primary exposure to a stimulus. However, overactivation of these T cells induces autoimmune reactions such as AE.7 Activated T lymphocytes express HLA-DR and IL-2 receptor, markers elevated in the peripheral blood of patients undergoing id reactions. After treatment, the levels of activated T lymphocytes decline. An increase in the number of CD25+ T cells and a decrease in the number of suppressor T cells in the blood may occur during an id reaction.7-9 Keratinocytes produce proinflammatory cytokines, such as thymic stromal erythropoietin, IL-25, and IL-33, that activate T cells.10-12 Therefore, the most likely pathogenesis of an id reaction is that T lymphocytes are activated at the primary reaction site due to proinflammatory cytokines released by keratinocytes. These activated T cells then travel systemically via hematogenous dissemination. The spread of activated T lymphocytes produces an eczematous reaction at secondary locations distant to the primary site.9
Clinical and Histopathological Features of Id Reactions
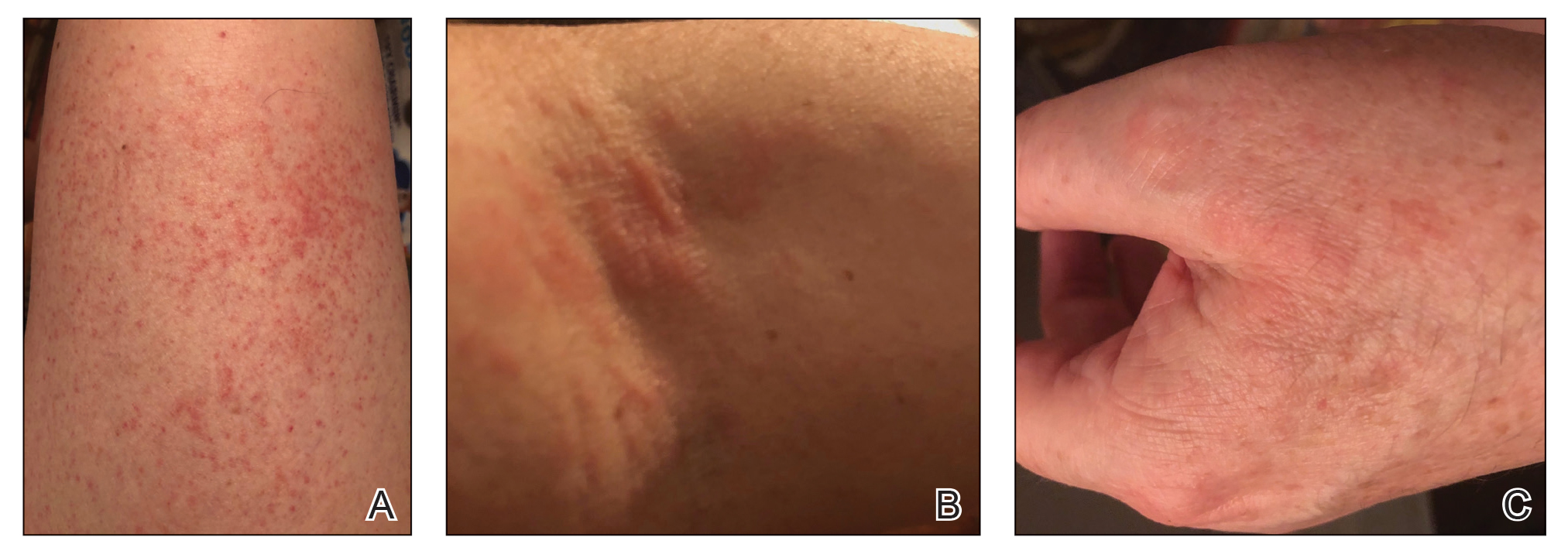
Clinically, AE is first evident as a vesicular dissemination that groups to form papules or nummular patches and usually is present on the legs, feet, arms, and/or trunk (Figure 2). The primary dermatitis is localized to the area that was the site of contact to the offending stimuli. This localized eczematous eruption begins with an acute or subacute onset. It has the appearance of small crusted vesicles with erythema (Figure 1). The first sign of AE is vesicles presenting near the primary site on flexural surfaces or on the hands and feet. A classic example is tinea pedis linked with vesicles on the palms and sides of the fingers, resembling dyshidrotic eczema. Sites of prior cutaneous trauma, such as dermatoses, scars, and burns, are common locations for early AE. In later stages, vesicles disseminate to the legs, arms, and trunk, where they group to form papules and nummular patches in a symmetrical pattern.5,13-15 These lesions may be extremely pruritic. The pruritus may be so intense that it interrupts daily activities and disrupts the ability to fall or stay asleep.16
Histologically, biopsy specimens show psoriasiform spongiotic dermatitis with mononuclear cells contained in the vesicles. Interstitial edema and perivascular lymphohistiocytic infiltrates are evident. Eosinophils also may be present. This pattern is not unique toid reactions.17-19 Although AE is a reaction pattern that may be due to a fungal or bacterial infection, the etiologic agent is not evident microscopically within the eczema itself.
Etiology of Id Reactions
Id reactions most commonly occur from either stasis dermatitis or tinea pedis, although a wide variety of other causes should be considered. Evaluation of the primary site rather than the id reaction may identify an infectious or parasitic agent. Sometimes the AE reaction is specifically named: dermatophytid with dermatophytosis, bacterid with a bacterial infectious process, and tuberculid with tuberculosis. Similarly, there may be reactions to underlying candidiasis, sporotrichosis, histoplasmosis, and other fungal infections that can cause a cutaneous id reaction.18,20-22Mycobacterium species, Pseudomonas, Staphylococcus, and Streptococcus are bacterial causes of AE.15,23-26 Viral infections that can cause an id reaction are herpes simplex virus and molluscum contagiosum.27-29 Scabies, leishmaniasis, and pediculosis capitis are parasitic infections that may be etiologic.14,30,31 In addition, noninfectious stimuli besides stasis dermatitis that can produce id reactions include medications, topical creams, tattoo ink, sutures, radiotherapy, and dyshidrotic eczema. The primary reaction to these agents is a localized dermatitis followed by the immunological response that induces a secondary reaction distant from the primary site.17,18,32-38
Differential Diagnoses
Differential diagnoses include other types of eczema and some vesicular eruptions. Irritant contact dermatitis is another dermatosis that presents as a widespread vesicular eruption due to repetitive exposure to toxic irritants. The rash is erythematous with pustules, blisters, and crusts. It is only found in areas directly exposed to irritants, as opposed to AE, which spreads to areas distant to the primary reaction site. Irritant contact dermatitis presents with more of a burning sensation, whereas AE is more pruritic.39,40 Allergic contact dermatitis presents with erythematous vesicles and papules and sometimes with bullae. There is edema and crust formation, which often can spread past the point of contact in later stages. Similar to AE, there is intense pruritus. However, allergic contact dermatitis most commonly is caused by exposure to metals, cosmetics, and fragrances, whereas infectious agents and stasis dermatitis are the most common causes of AE.40,41 It may be challenging to distinguish AE from other causes of widespread eczematous dissemination. Vesicular eruptions sometimes require distinction from AE, including herpetic infections, insect bite reactions, and drug eruptions.18,42
Treatment
The underlying condition should be treated to mitigate the inflammatory response causing the id reaction. If not skillfully orchestrated, the id reaction can reoccur. For infectious causes of AE, an antifungal, antibacterial, antiviral, or antiparasitic should be given. If stasis dermatitis is responsible for the id reaction, compression stockings and leg elevation are indicated. The id reaction itself is treated with systemic or topical corticosteroids and wet compresses if acute. The goal of these treatments is to reduce patient discomfort caused by the inflammation and pruritus.18,43
Conclusion
Id reactions are an unusual phenomenon that commonly occurs after fungal skin infections and stasis dermatitis. T lymphocytes and keratinocytes may play a key role in this reaction, with newer research further delineating the process and possibly providing enhanced treatment options. Therapy focuses on treating the underlying condition, supplemented with corticosteroids for the autoeczema.
- Whitfield A. Lumleian Lectures on Some Points in the Aetiology of Skin Diseases. Delivered before the Royal College of Physicians of London on March 10th, 15th, and 17th, 1921. Lecture II. Lancet. 1921;2:122-127.
- Cheng N, Rucker Wright D, Cohen BA. Dermatophytid in tinea capitis: rarely reported common phenomenon with clinical implications. Pediatrics. 2011;128:E453-E457.
- Schrom KP, Kobs A, Nedorost S. Clinical psoriasiform dermatitis following dupilumab use for autoeczematization secondary to chronic stasis dermatitis. Cureus. 2020;12:e7831. doi:10.7759/cureus.7831
- Templeton HJ, Lunsford CJ, Allington HV. Autosensitization dermatitis; report of five cases and protocol of an experiment. Arch Derm Syphilol. 1949;59:68-77.
- Shelley WB. Id reaction. In: Consultations in Dermatology. Saunders; 1972:262-267.
- Sharquie KE, Noaimi AA, Flayih RA. Clinical and histopathological findings in patients with follicular dermatoses: all skin diseases starts in the hair follicles as new hypothesis. Am J Clin Res Rev. 2020;4:17.
- Kasteler JS, Petersen MJ, Vance JE, et al. Circulating activated T lymphocytes in autoeczematization. Arch Dermatol. 1992;128:795-798.
- González-Amaro R, Baranda L, Abud-Mendoza C, et al. Autoeczematization is associated with abnormal immune recognition of autologous skin antigens. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1993;28:56-60.
- Cunningham MJ, Zone JJ, Petersen MJ, et al. Circulating activated (DR-positive) T lymphocytes in a patient with autoeczematization. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1986;14:1039-1041.
- Furue M, Ulzii D, Vu YH, et al. Pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis: current paradigm. Iran J Immunol. 2019;16:97-107.
- Uchi H, Terao H, Koga T, et al. Cytokines and chemokines in the epidermis. J Dermatol Sci. 2000;24(suppl 1):S29-S38.
- Bos JD, Kapsenberg ML. The skin immune system: progress in cutaneous biology. Immunol Today. 1993;14:75-78.
- Young AW Jr. Dynamics of autosensitization dermatitis; a clinical and microscopic concept of autoeczematization. AMA Arch Derm. 1958;77:495-502.
- Brenner S, Wolf R, Landau M. Scabid: an unusual id reaction to scabies. Int J Dermatol. 1993;32:128-129.
- Yamany T, Schwartz RA. Infectious eczematoid dermatitis: a comprehensive review. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2015;29:203-208.
- Wang X, Li L, Shi X, et al. Itching and its related factors in subtypes of eczema: a cross-sectional multicenter study in tertiary hospitals of China. Sci Rep. 2018;8:10754.
- Price A, Tavazoie M, Meehan SA, et al. Id reaction associated with red tattoo ink. Cutis. 2018;102:E32-E34.
- Ilkit M, Durdu M, Karaks¸ M. Cutaneous id reactions: a comprehensive review of clinical manifestations, epidemiology, etiology, and management. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2012;38:191-202.
- Kaner SR. Dermatitis venenata of the feet with a generalized “id” reaction. J Am Podiatry Assoc. 1970;60:199-204.
- Jordan L, Jackson NA, Carter-Snell B, et al. Pustular tinea id reaction. Cutis. 2019;103:E3-E4.
- Crum N, Hardaway C, Graham B. Development of an idlike reaction during treatment for acute pulmonary histoplasmosis: a new cutaneous manifestation in histoplasmosis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003;48(2 suppl):S5-S6.
- Chirac A, Brzezinski P, Chiriac AE, et al. Autosensitisation (autoeczematisation) reactions in a case of diaper dermatitis candidiasis. Niger Med J. 2014;55:274-275.
- Singh PY, Sinha P, Baveja S, et al. Immune-mediated tuberculous uveitis—a rare association with papulonecrotic tuberculid. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2019;67:1207-1209.
- Urso B, Georgesen C, Harp J. Papulonecrotic tuberculid secondary to Mycobacterium avium complex. Cutis. 2019;104:E11-E13.
- Choudhri SH, Magro CM, Crowson AN, et al. An id reaction to Mycobacterium leprae: first documented case. Cutis. 1994;54:282-286.
- Park JW, Jeong GJ, Seo SJ, et al. Pseudomonas toe web infection and autosensitisation dermatitis: diagnostic and therapeutic challenge. Int Wound J. 2020;17:1543-1544. doi:10.1111/iwj.13386
- Netchiporouk E, Cohen BA. Recognizing and managing eczematous id reactions to molluscum contagiosum virus in children. Pediatrics. 2012;129:E1072-E1075.
- Aurelian L, Ono F, Burnett J. Herpes simplex virus (HSV)-associated erythema multiforme (HAEM): a viral disease with an autoimmune component. Dermatol Online J. 2003;9:1.
- Rocamora V, Romaní J, Puig L, et al. Id reaction to molluscum contagiosum. Pediatr Dermatol. 1996;13:349-350.
- Yes¸ilova Y, Özbilgin A, Turan E, et al. Clinical exacerbation developing during treatment of cutaneous leishmaniasis: an id reaction? Turkiye Parazitol Derg. 2014;38:281-282.
- Connor CJ, Selby JC, Wanat KA. Severe pediculosis capitus: a case of “crusted lice” with autoeczematization. Dermatol Online J. 2016;22:13030/qt7c91z913.
- Shelley WB. The autoimmune mechanism in clinical dermatology. Arch Dermatol. 1962;86:27-34.
- Bosworth A, Hull PR. Disseminated eczema following radiotherapy: a case report. J Cutan Med Surg. 2018;22:353-355.
- Lowther C, Miedler JD, Cockerell CJ. Id-like reaction to BCG therapy for bladder cancer. Cutis. 2013;91:145-151.
- Huerth KA, Glick PL, Glick ZR. Cutaneous id reaction after using cyanoacrylate for wound closure. Cutis. 2020;105:E11-E13.
- Amini S, Burdick AE, Janniger CK. Dyshidrotic eczema (pompholyx). Updated April 22, 2020. Accessed August 23, 2021. https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1122527-overview
- Sundaresan S, Migden MR, Silapunt S. Stasis dermatitis: pathophysiology, evaluation, and management. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2017;18:383-390.
- Hughes JDM, Pratt MD. Allergic contact dermatitis and autoeczematization to proctosedyl® cream and proctomyxin® cream. Case Rep Dermatol. 2018;10:238-246.
- Bains SN, Nash P, Fonacier L. Irritant contact dermatitis. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2019;56:99-109.
- Novak-Bilic´ G, Vucˇic´ M, Japundžic´ I, et al. Irritant and allergic contact dermatitis—skin lesion characteristics. Acta Clin Croat. 2018;57:713-720.
- Nassau S, Fonacier L. Allergic contact dermatitis. Med Clin North Am. 2020;104:61-76.
- Lewis DJ, Schlichte MJ, Dao H Jr. Atypical disseminated herpes zoster: management guidelines in immunocompromised patients. Cutis. 2017;100:321-330.
- Nedorost S, White S, Rowland DY, et al. Development and implementation of an order set to improve value of care for patients with severe stasis dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:815-817.
Autoeczematization (AE), or id reaction, is a disseminated eczematous reaction that occurs days or weeks after exposure to a primary stimulus, resulting from a release of antigen(s). Whitfield1 first described AE in 1921, when he postulated that the id reaction was due to sensitization of the skin after a primary stimulus. He called it “a form of auto-intoxication derived from changes in the patient’s own tissues.”1 The exact prevalence of id reactions is unknown; one study showed that 17% of patients with dermatophyte infections developed an id reaction, typically tinea pedis linked with vesicles on the palms.2 Tinea capitis is one of the most common causes of AE in children, which is frequently misdiagnosed as a drug reaction. Approximately 37% of patients diagnosed with stasis dermatitis develop an id reaction (Figure 1). A history of contact dermatitis is common in patients presenting with AE.2-6

Pathophysiology of Id Reactions
An abnormal immune response against autologous skin antigens may be responsible for the development of AE. Shelley5 postulated that hair follicles play an important role in id reactions, as Sharquie et al6 recently emphasized for many skin disorders. The pathogenesis of AE is uncertain, but circulating T lymphocytes play a role in this reaction. Normally, T cells are activated by a release of antigens after a primary exposure to a stimulus. However, overactivation of these T cells induces autoimmune reactions such as AE.7 Activated T lymphocytes express HLA-DR and IL-2 receptor, markers elevated in the peripheral blood of patients undergoing id reactions. After treatment, the levels of activated T lymphocytes decline. An increase in the number of CD25+ T cells and a decrease in the number of suppressor T cells in the blood may occur during an id reaction.7-9 Keratinocytes produce proinflammatory cytokines, such as thymic stromal erythropoietin, IL-25, and IL-33, that activate T cells.10-12 Therefore, the most likely pathogenesis of an id reaction is that T lymphocytes are activated at the primary reaction site due to proinflammatory cytokines released by keratinocytes. These activated T cells then travel systemically via hematogenous dissemination. The spread of activated T lymphocytes produces an eczematous reaction at secondary locations distant to the primary site.9
Clinical and Histopathological Features of Id Reactions
Clinically, AE is first evident as a vesicular dissemination that groups to form papules or nummular patches and usually is present on the legs, feet, arms, and/or trunk (Figure 2). The primary dermatitis is localized to the area that was the site of contact to the offending stimuli. This localized eczematous eruption begins with an acute or subacute onset. It has the appearance of small crusted vesicles with erythema (Figure 1). The first sign of AE is vesicles presenting near the primary site on flexural surfaces or on the hands and feet. A classic example is tinea pedis linked with vesicles on the palms and sides of the fingers, resembling dyshidrotic eczema. Sites of prior cutaneous trauma, such as dermatoses, scars, and burns, are common locations for early AE. In later stages, vesicles disseminate to the legs, arms, and trunk, where they group to form papules and nummular patches in a symmetrical pattern.5,13-15 These lesions may be extremely pruritic. The pruritus may be so intense that it interrupts daily activities and disrupts the ability to fall or stay asleep.16

Histologically, biopsy specimens show psoriasiform spongiotic dermatitis with mononuclear cells contained in the vesicles. Interstitial edema and perivascular lymphohistiocytic infiltrates are evident. Eosinophils also may be present. This pattern is not unique toid reactions.17-19 Although AE is a reaction pattern that may be due to a fungal or bacterial infection, the etiologic agent is not evident microscopically within the eczema itself.
Etiology of Id Reactions
Id reactions most commonly occur from either stasis dermatitis or tinea pedis, although a wide variety of other causes should be considered. Evaluation of the primary site rather than the id reaction may identify an infectious or parasitic agent. Sometimes the AE reaction is specifically named: dermatophytid with dermatophytosis, bacterid with a bacterial infectious process, and tuberculid with tuberculosis. Similarly, there may be reactions to underlying candidiasis, sporotrichosis, histoplasmosis, and other fungal infections that can cause a cutaneous id reaction.18,20-22Mycobacterium species, Pseudomonas, Staphylococcus, and Streptococcus are bacterial causes of AE.15,23-26 Viral infections that can cause an id reaction are herpes simplex virus and molluscum contagiosum.27-29 Scabies, leishmaniasis, and pediculosis capitis are parasitic infections that may be etiologic.14,30,31 In addition, noninfectious stimuli besides stasis dermatitis that can produce id reactions include medications, topical creams, tattoo ink, sutures, radiotherapy, and dyshidrotic eczema. The primary reaction to these agents is a localized dermatitis followed by the immunological response that induces a secondary reaction distant from the primary site.17,18,32-38
Differential Diagnoses
Differential diagnoses include other types of eczema and some vesicular eruptions. Irritant contact dermatitis is another dermatosis that presents as a widespread vesicular eruption due to repetitive exposure to toxic irritants. The rash is erythematous with pustules, blisters, and crusts. It is only found in areas directly exposed to irritants, as opposed to AE, which spreads to areas distant to the primary reaction site. Irritant contact dermatitis presents with more of a burning sensation, whereas AE is more pruritic.39,40 Allergic contact dermatitis presents with erythematous vesicles and papules and sometimes with bullae. There is edema and crust formation, which often can spread past the point of contact in later stages. Similar to AE, there is intense pruritus. However, allergic contact dermatitis most commonly is caused by exposure to metals, cosmetics, and fragrances, whereas infectious agents and stasis dermatitis are the most common causes of AE.40,41 It may be challenging to distinguish AE from other causes of widespread eczematous dissemination. Vesicular eruptions sometimes require distinction from AE, including herpetic infections, insect bite reactions, and drug eruptions.18,42
Treatment
The underlying condition should be treated to mitigate the inflammatory response causing the id reaction. If not skillfully orchestrated, the id reaction can reoccur. For infectious causes of AE, an antifungal, antibacterial, antiviral, or antiparasitic should be given. If stasis dermatitis is responsible for the id reaction, compression stockings and leg elevation are indicated. The id reaction itself is treated with systemic or topical corticosteroids and wet compresses if acute. The goal of these treatments is to reduce patient discomfort caused by the inflammation and pruritus.18,43
Conclusion
Id reactions are an unusual phenomenon that commonly occurs after fungal skin infections and stasis dermatitis. T lymphocytes and keratinocytes may play a key role in this reaction, with newer research further delineating the process and possibly providing enhanced treatment options. Therapy focuses on treating the underlying condition, supplemented with corticosteroids for the autoeczema.
Autoeczematization (AE), or id reaction, is a disseminated eczematous reaction that occurs days or weeks after exposure to a primary stimulus, resulting from a release of antigen(s). Whitfield1 first described AE in 1921, when he postulated that the id reaction was due to sensitization of the skin after a primary stimulus. He called it “a form of auto-intoxication derived from changes in the patient’s own tissues.”1 The exact prevalence of id reactions is unknown; one study showed that 17% of patients with dermatophyte infections developed an id reaction, typically tinea pedis linked with vesicles on the palms.2 Tinea capitis is one of the most common causes of AE in children, which is frequently misdiagnosed as a drug reaction. Approximately 37% of patients diagnosed with stasis dermatitis develop an id reaction (Figure 1). A history of contact dermatitis is common in patients presenting with AE.2-6

Pathophysiology of Id Reactions
An abnormal immune response against autologous skin antigens may be responsible for the development of AE. Shelley5 postulated that hair follicles play an important role in id reactions, as Sharquie et al6 recently emphasized for many skin disorders. The pathogenesis of AE is uncertain, but circulating T lymphocytes play a role in this reaction. Normally, T cells are activated by a release of antigens after a primary exposure to a stimulus. However, overactivation of these T cells induces autoimmune reactions such as AE.7 Activated T lymphocytes express HLA-DR and IL-2 receptor, markers elevated in the peripheral blood of patients undergoing id reactions. After treatment, the levels of activated T lymphocytes decline. An increase in the number of CD25+ T cells and a decrease in the number of suppressor T cells in the blood may occur during an id reaction.7-9 Keratinocytes produce proinflammatory cytokines, such as thymic stromal erythropoietin, IL-25, and IL-33, that activate T cells.10-12 Therefore, the most likely pathogenesis of an id reaction is that T lymphocytes are activated at the primary reaction site due to proinflammatory cytokines released by keratinocytes. These activated T cells then travel systemically via hematogenous dissemination. The spread of activated T lymphocytes produces an eczematous reaction at secondary locations distant to the primary site.9
Clinical and Histopathological Features of Id Reactions
Clinically, AE is first evident as a vesicular dissemination that groups to form papules or nummular patches and usually is present on the legs, feet, arms, and/or trunk (Figure 2). The primary dermatitis is localized to the area that was the site of contact to the offending stimuli. This localized eczematous eruption begins with an acute or subacute onset. It has the appearance of small crusted vesicles with erythema (Figure 1). The first sign of AE is vesicles presenting near the primary site on flexural surfaces or on the hands and feet. A classic example is tinea pedis linked with vesicles on the palms and sides of the fingers, resembling dyshidrotic eczema. Sites of prior cutaneous trauma, such as dermatoses, scars, and burns, are common locations for early AE. In later stages, vesicles disseminate to the legs, arms, and trunk, where they group to form papules and nummular patches in a symmetrical pattern.5,13-15 These lesions may be extremely pruritic. The pruritus may be so intense that it interrupts daily activities and disrupts the ability to fall or stay asleep.16

Histologically, biopsy specimens show psoriasiform spongiotic dermatitis with mononuclear cells contained in the vesicles. Interstitial edema and perivascular lymphohistiocytic infiltrates are evident. Eosinophils also may be present. This pattern is not unique toid reactions.17-19 Although AE is a reaction pattern that may be due to a fungal or bacterial infection, the etiologic agent is not evident microscopically within the eczema itself.
Etiology of Id Reactions
Id reactions most commonly occur from either stasis dermatitis or tinea pedis, although a wide variety of other causes should be considered. Evaluation of the primary site rather than the id reaction may identify an infectious or parasitic agent. Sometimes the AE reaction is specifically named: dermatophytid with dermatophytosis, bacterid with a bacterial infectious process, and tuberculid with tuberculosis. Similarly, there may be reactions to underlying candidiasis, sporotrichosis, histoplasmosis, and other fungal infections that can cause a cutaneous id reaction.18,20-22Mycobacterium species, Pseudomonas, Staphylococcus, and Streptococcus are bacterial causes of AE.15,23-26 Viral infections that can cause an id reaction are herpes simplex virus and molluscum contagiosum.27-29 Scabies, leishmaniasis, and pediculosis capitis are parasitic infections that may be etiologic.14,30,31 In addition, noninfectious stimuli besides stasis dermatitis that can produce id reactions include medications, topical creams, tattoo ink, sutures, radiotherapy, and dyshidrotic eczema. The primary reaction to these agents is a localized dermatitis followed by the immunological response that induces a secondary reaction distant from the primary site.17,18,32-38
Differential Diagnoses
Differential diagnoses include other types of eczema and some vesicular eruptions. Irritant contact dermatitis is another dermatosis that presents as a widespread vesicular eruption due to repetitive exposure to toxic irritants. The rash is erythematous with pustules, blisters, and crusts. It is only found in areas directly exposed to irritants, as opposed to AE, which spreads to areas distant to the primary reaction site. Irritant contact dermatitis presents with more of a burning sensation, whereas AE is more pruritic.39,40 Allergic contact dermatitis presents with erythematous vesicles and papules and sometimes with bullae. There is edema and crust formation, which often can spread past the point of contact in later stages. Similar to AE, there is intense pruritus. However, allergic contact dermatitis most commonly is caused by exposure to metals, cosmetics, and fragrances, whereas infectious agents and stasis dermatitis are the most common causes of AE.40,41 It may be challenging to distinguish AE from other causes of widespread eczematous dissemination. Vesicular eruptions sometimes require distinction from AE, including herpetic infections, insect bite reactions, and drug eruptions.18,42
Treatment
The underlying condition should be treated to mitigate the inflammatory response causing the id reaction. If not skillfully orchestrated, the id reaction can reoccur. For infectious causes of AE, an antifungal, antibacterial, antiviral, or antiparasitic should be given. If stasis dermatitis is responsible for the id reaction, compression stockings and leg elevation are indicated. The id reaction itself is treated with systemic or topical corticosteroids and wet compresses if acute. The goal of these treatments is to reduce patient discomfort caused by the inflammation and pruritus.18,43
Conclusion
Id reactions are an unusual phenomenon that commonly occurs after fungal skin infections and stasis dermatitis. T lymphocytes and keratinocytes may play a key role in this reaction, with newer research further delineating the process and possibly providing enhanced treatment options. Therapy focuses on treating the underlying condition, supplemented with corticosteroids for the autoeczema.
- Whitfield A. Lumleian Lectures on Some Points in the Aetiology of Skin Diseases. Delivered before the Royal College of Physicians of London on March 10th, 15th, and 17th, 1921. Lecture II. Lancet. 1921;2:122-127.
- Cheng N, Rucker Wright D, Cohen BA. Dermatophytid in tinea capitis: rarely reported common phenomenon with clinical implications. Pediatrics. 2011;128:E453-E457.
- Schrom KP, Kobs A, Nedorost S. Clinical psoriasiform dermatitis following dupilumab use for autoeczematization secondary to chronic stasis dermatitis. Cureus. 2020;12:e7831. doi:10.7759/cureus.7831
- Templeton HJ, Lunsford CJ, Allington HV. Autosensitization dermatitis; report of five cases and protocol of an experiment. Arch Derm Syphilol. 1949;59:68-77.
- Shelley WB. Id reaction. In: Consultations in Dermatology. Saunders; 1972:262-267.
- Sharquie KE, Noaimi AA, Flayih RA. Clinical and histopathological findings in patients with follicular dermatoses: all skin diseases starts in the hair follicles as new hypothesis. Am J Clin Res Rev. 2020;4:17.
- Kasteler JS, Petersen MJ, Vance JE, et al. Circulating activated T lymphocytes in autoeczematization. Arch Dermatol. 1992;128:795-798.
- González-Amaro R, Baranda L, Abud-Mendoza C, et al. Autoeczematization is associated with abnormal immune recognition of autologous skin antigens. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1993;28:56-60.
- Cunningham MJ, Zone JJ, Petersen MJ, et al. Circulating activated (DR-positive) T lymphocytes in a patient with autoeczematization. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1986;14:1039-1041.
- Furue M, Ulzii D, Vu YH, et al. Pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis: current paradigm. Iran J Immunol. 2019;16:97-107.
- Uchi H, Terao H, Koga T, et al. Cytokines and chemokines in the epidermis. J Dermatol Sci. 2000;24(suppl 1):S29-S38.
- Bos JD, Kapsenberg ML. The skin immune system: progress in cutaneous biology. Immunol Today. 1993;14:75-78.
- Young AW Jr. Dynamics of autosensitization dermatitis; a clinical and microscopic concept of autoeczematization. AMA Arch Derm. 1958;77:495-502.
- Brenner S, Wolf R, Landau M. Scabid: an unusual id reaction to scabies. Int J Dermatol. 1993;32:128-129.
- Yamany T, Schwartz RA. Infectious eczematoid dermatitis: a comprehensive review. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2015;29:203-208.
- Wang X, Li L, Shi X, et al. Itching and its related factors in subtypes of eczema: a cross-sectional multicenter study in tertiary hospitals of China. Sci Rep. 2018;8:10754.
- Price A, Tavazoie M, Meehan SA, et al. Id reaction associated with red tattoo ink. Cutis. 2018;102:E32-E34.
- Ilkit M, Durdu M, Karaks¸ M. Cutaneous id reactions: a comprehensive review of clinical manifestations, epidemiology, etiology, and management. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2012;38:191-202.
- Kaner SR. Dermatitis venenata of the feet with a generalized “id” reaction. J Am Podiatry Assoc. 1970;60:199-204.
- Jordan L, Jackson NA, Carter-Snell B, et al. Pustular tinea id reaction. Cutis. 2019;103:E3-E4.
- Crum N, Hardaway C, Graham B. Development of an idlike reaction during treatment for acute pulmonary histoplasmosis: a new cutaneous manifestation in histoplasmosis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003;48(2 suppl):S5-S6.
- Chirac A, Brzezinski P, Chiriac AE, et al. Autosensitisation (autoeczematisation) reactions in a case of diaper dermatitis candidiasis. Niger Med J. 2014;55:274-275.
- Singh PY, Sinha P, Baveja S, et al. Immune-mediated tuberculous uveitis—a rare association with papulonecrotic tuberculid. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2019;67:1207-1209.
- Urso B, Georgesen C, Harp J. Papulonecrotic tuberculid secondary to Mycobacterium avium complex. Cutis. 2019;104:E11-E13.
- Choudhri SH, Magro CM, Crowson AN, et al. An id reaction to Mycobacterium leprae: first documented case. Cutis. 1994;54:282-286.
- Park JW, Jeong GJ, Seo SJ, et al. Pseudomonas toe web infection and autosensitisation dermatitis: diagnostic and therapeutic challenge. Int Wound J. 2020;17:1543-1544. doi:10.1111/iwj.13386
- Netchiporouk E, Cohen BA. Recognizing and managing eczematous id reactions to molluscum contagiosum virus in children. Pediatrics. 2012;129:E1072-E1075.
- Aurelian L, Ono F, Burnett J. Herpes simplex virus (HSV)-associated erythema multiforme (HAEM): a viral disease with an autoimmune component. Dermatol Online J. 2003;9:1.
- Rocamora V, Romaní J, Puig L, et al. Id reaction to molluscum contagiosum. Pediatr Dermatol. 1996;13:349-350.
- Yes¸ilova Y, Özbilgin A, Turan E, et al. Clinical exacerbation developing during treatment of cutaneous leishmaniasis: an id reaction? Turkiye Parazitol Derg. 2014;38:281-282.
- Connor CJ, Selby JC, Wanat KA. Severe pediculosis capitus: a case of “crusted lice” with autoeczematization. Dermatol Online J. 2016;22:13030/qt7c91z913.
- Shelley WB. The autoimmune mechanism in clinical dermatology. Arch Dermatol. 1962;86:27-34.
- Bosworth A, Hull PR. Disseminated eczema following radiotherapy: a case report. J Cutan Med Surg. 2018;22:353-355.
- Lowther C, Miedler JD, Cockerell CJ. Id-like reaction to BCG therapy for bladder cancer. Cutis. 2013;91:145-151.
- Huerth KA, Glick PL, Glick ZR. Cutaneous id reaction after using cyanoacrylate for wound closure. Cutis. 2020;105:E11-E13.
- Amini S, Burdick AE, Janniger CK. Dyshidrotic eczema (pompholyx). Updated April 22, 2020. Accessed August 23, 2021. https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1122527-overview
- Sundaresan S, Migden MR, Silapunt S. Stasis dermatitis: pathophysiology, evaluation, and management. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2017;18:383-390.
- Hughes JDM, Pratt MD. Allergic contact dermatitis and autoeczematization to proctosedyl® cream and proctomyxin® cream. Case Rep Dermatol. 2018;10:238-246.
- Bains SN, Nash P, Fonacier L. Irritant contact dermatitis. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2019;56:99-109.
- Novak-Bilic´ G, Vucˇic´ M, Japundžic´ I, et al. Irritant and allergic contact dermatitis—skin lesion characteristics. Acta Clin Croat. 2018;57:713-720.
- Nassau S, Fonacier L. Allergic contact dermatitis. Med Clin North Am. 2020;104:61-76.
- Lewis DJ, Schlichte MJ, Dao H Jr. Atypical disseminated herpes zoster: management guidelines in immunocompromised patients. Cutis. 2017;100:321-330.
- Nedorost S, White S, Rowland DY, et al. Development and implementation of an order set to improve value of care for patients with severe stasis dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:815-817.
- Whitfield A. Lumleian Lectures on Some Points in the Aetiology of Skin Diseases. Delivered before the Royal College of Physicians of London on March 10th, 15th, and 17th, 1921. Lecture II. Lancet. 1921;2:122-127.
- Cheng N, Rucker Wright D, Cohen BA. Dermatophytid in tinea capitis: rarely reported common phenomenon with clinical implications. Pediatrics. 2011;128:E453-E457.
- Schrom KP, Kobs A, Nedorost S. Clinical psoriasiform dermatitis following dupilumab use for autoeczematization secondary to chronic stasis dermatitis. Cureus. 2020;12:e7831. doi:10.7759/cureus.7831
- Templeton HJ, Lunsford CJ, Allington HV. Autosensitization dermatitis; report of five cases and protocol of an experiment. Arch Derm Syphilol. 1949;59:68-77.
- Shelley WB. Id reaction. In: Consultations in Dermatology. Saunders; 1972:262-267.
- Sharquie KE, Noaimi AA, Flayih RA. Clinical and histopathological findings in patients with follicular dermatoses: all skin diseases starts in the hair follicles as new hypothesis. Am J Clin Res Rev. 2020;4:17.
- Kasteler JS, Petersen MJ, Vance JE, et al. Circulating activated T lymphocytes in autoeczematization. Arch Dermatol. 1992;128:795-798.
- González-Amaro R, Baranda L, Abud-Mendoza C, et al. Autoeczematization is associated with abnormal immune recognition of autologous skin antigens. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1993;28:56-60.
- Cunningham MJ, Zone JJ, Petersen MJ, et al. Circulating activated (DR-positive) T lymphocytes in a patient with autoeczematization. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1986;14:1039-1041.
- Furue M, Ulzii D, Vu YH, et al. Pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis: current paradigm. Iran J Immunol. 2019;16:97-107.
- Uchi H, Terao H, Koga T, et al. Cytokines and chemokines in the epidermis. J Dermatol Sci. 2000;24(suppl 1):S29-S38.
- Bos JD, Kapsenberg ML. The skin immune system: progress in cutaneous biology. Immunol Today. 1993;14:75-78.
- Young AW Jr. Dynamics of autosensitization dermatitis; a clinical and microscopic concept of autoeczematization. AMA Arch Derm. 1958;77:495-502.
- Brenner S, Wolf R, Landau M. Scabid: an unusual id reaction to scabies. Int J Dermatol. 1993;32:128-129.
- Yamany T, Schwartz RA. Infectious eczematoid dermatitis: a comprehensive review. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2015;29:203-208.
- Wang X, Li L, Shi X, et al. Itching and its related factors in subtypes of eczema: a cross-sectional multicenter study in tertiary hospitals of China. Sci Rep. 2018;8:10754.
- Price A, Tavazoie M, Meehan SA, et al. Id reaction associated with red tattoo ink. Cutis. 2018;102:E32-E34.
- Ilkit M, Durdu M, Karaks¸ M. Cutaneous id reactions: a comprehensive review of clinical manifestations, epidemiology, etiology, and management. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2012;38:191-202.
- Kaner SR. Dermatitis venenata of the feet with a generalized “id” reaction. J Am Podiatry Assoc. 1970;60:199-204.
- Jordan L, Jackson NA, Carter-Snell B, et al. Pustular tinea id reaction. Cutis. 2019;103:E3-E4.
- Crum N, Hardaway C, Graham B. Development of an idlike reaction during treatment for acute pulmonary histoplasmosis: a new cutaneous manifestation in histoplasmosis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003;48(2 suppl):S5-S6.
- Chirac A, Brzezinski P, Chiriac AE, et al. Autosensitisation (autoeczematisation) reactions in a case of diaper dermatitis candidiasis. Niger Med J. 2014;55:274-275.
- Singh PY, Sinha P, Baveja S, et al. Immune-mediated tuberculous uveitis—a rare association with papulonecrotic tuberculid. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2019;67:1207-1209.
- Urso B, Georgesen C, Harp J. Papulonecrotic tuberculid secondary to Mycobacterium avium complex. Cutis. 2019;104:E11-E13.
- Choudhri SH, Magro CM, Crowson AN, et al. An id reaction to Mycobacterium leprae: first documented case. Cutis. 1994;54:282-286.
- Park JW, Jeong GJ, Seo SJ, et al. Pseudomonas toe web infection and autosensitisation dermatitis: diagnostic and therapeutic challenge. Int Wound J. 2020;17:1543-1544. doi:10.1111/iwj.13386
- Netchiporouk E, Cohen BA. Recognizing and managing eczematous id reactions to molluscum contagiosum virus in children. Pediatrics. 2012;129:E1072-E1075.
- Aurelian L, Ono F, Burnett J. Herpes simplex virus (HSV)-associated erythema multiforme (HAEM): a viral disease with an autoimmune component. Dermatol Online J. 2003;9:1.
- Rocamora V, Romaní J, Puig L, et al. Id reaction to molluscum contagiosum. Pediatr Dermatol. 1996;13:349-350.
- Yes¸ilova Y, Özbilgin A, Turan E, et al. Clinical exacerbation developing during treatment of cutaneous leishmaniasis: an id reaction? Turkiye Parazitol Derg. 2014;38:281-282.
- Connor CJ, Selby JC, Wanat KA. Severe pediculosis capitus: a case of “crusted lice” with autoeczematization. Dermatol Online J. 2016;22:13030/qt7c91z913.
- Shelley WB. The autoimmune mechanism in clinical dermatology. Arch Dermatol. 1962;86:27-34.
- Bosworth A, Hull PR. Disseminated eczema following radiotherapy: a case report. J Cutan Med Surg. 2018;22:353-355.
- Lowther C, Miedler JD, Cockerell CJ. Id-like reaction to BCG therapy for bladder cancer. Cutis. 2013;91:145-151.
- Huerth KA, Glick PL, Glick ZR. Cutaneous id reaction after using cyanoacrylate for wound closure. Cutis. 2020;105:E11-E13.
- Amini S, Burdick AE, Janniger CK. Dyshidrotic eczema (pompholyx). Updated April 22, 2020. Accessed August 23, 2021. https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1122527-overview
- Sundaresan S, Migden MR, Silapunt S. Stasis dermatitis: pathophysiology, evaluation, and management. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2017;18:383-390.
- Hughes JDM, Pratt MD. Allergic contact dermatitis and autoeczematization to proctosedyl® cream and proctomyxin® cream. Case Rep Dermatol. 2018;10:238-246.
- Bains SN, Nash P, Fonacier L. Irritant contact dermatitis. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2019;56:99-109.
- Novak-Bilic´ G, Vucˇic´ M, Japundžic´ I, et al. Irritant and allergic contact dermatitis—skin lesion characteristics. Acta Clin Croat. 2018;57:713-720.
- Nassau S, Fonacier L. Allergic contact dermatitis. Med Clin North Am. 2020;104:61-76.
- Lewis DJ, Schlichte MJ, Dao H Jr. Atypical disseminated herpes zoster: management guidelines in immunocompromised patients. Cutis. 2017;100:321-330.
- Nedorost S, White S, Rowland DY, et al. Development and implementation of an order set to improve value of care for patients with severe stasis dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:815-817.
Practice Points
- Autoeczematization, or id reaction, is a disseminated reaction of the skin occurring at a site distant to a primary cutaneous infection or stimulus.
- T lymphocytes and keratinocytes are postulated to be involved in the pathogenesis of id reactions.
- Therapy includes treating the underlying pathology while providing topical corticosteroids for the autoeczematous lesions.