User login
Overall cancer mortality in females continues to decrease in the United States, but “previous declining trends in death rates slowed” for breast cancer in recent years, according to an annual report by several national organizations.
The analysis of long-term trends in cancer death rates shows that a decline of 1.4% per year from 2001 to 2016 accelerated to 2.1% per year in 2016-2018, the American Cancer Society, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Cancer Institute, and the North American Association of Central Cancer Registries said.
Decreases in overall cancer mortality were seen in females of all races and ethnic groups over the most recent 5-year period included in the report, 2014-2018, varying from –1.6% per year in both non-Hispanic Blacks and Whites to –0.9% for non-Hispanic American Indians/Alaska Natives (AI/ANs), Farhad Islami, MD, PhD, of the American Cancer Society, Atlanta, and associates said in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute.
Over those 5 years, death rates fell for 14 of the 20 most common cancers in females; increased for liver, uterus, brain, pancreas, and soft tissue including heart; and remained stable for cancers of the oral cavity/pharynx, they reported.
Breast cancer was among those that declined, but the rate of that decline has been slowing. Mortality declined by an average of 2.3% per year in 2003-2007, by 1.6% a year in 2007-2014, and by just 1.0% annually during 2014-2018, based on data from the National Center for Health Statistics’ National Vital Statistics System.
Mortality from all cancers in 2014-2018 was 133.5 deaths per 100,000 standard population, with the racial/ethnic gap ranging from 85.4 per 100,000 (non-Hispanic Asian/Pacific Islander) to 154.9 (non-Hispanic Black), Dr. Islami and associates said.
Melanoma had the largest decline in mortality over that period among the 20 most common cancers in females, falling by an average of 4.4% per year, with lung cancer next at 4.3%. Among those with increased death rates, uterine cancer saw the largest rise at 2.0% a year, the research team said.
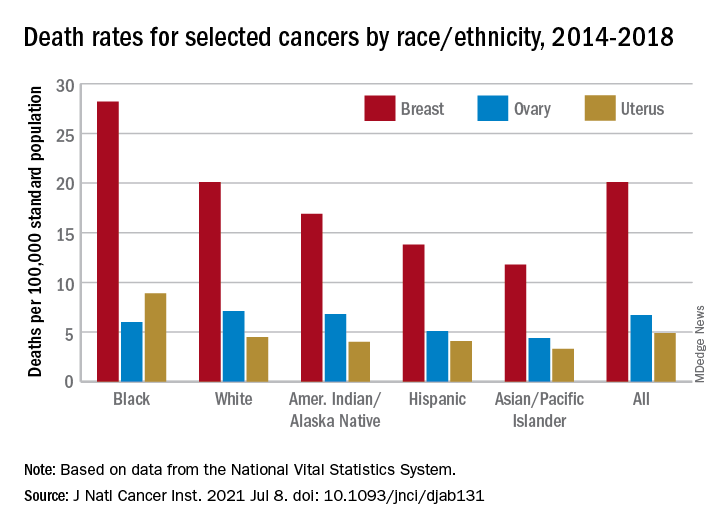
The deaths caused by cancer of the uterus were most common in non-Hispanic Black females, 8.9 per 100,000 population, followed by non-Hispanic White (4.5), Hispanic (4.1), non-Hispanic AI/AN (4.0), and non-Hispanic Asian/Pacific Islander (3.3), they reported.
“Long-term increasing trends in uterine cancer death rates parallel trends in incidence, although death rates are increasing at a somewhat faster rate. Increasing uterine cancer incidence has been attributed to increasing obesity prevalence and decreased use of combined hormone replacement therapy,” Dr. Islami and associates pointed out.
Breast cancer deaths also were most common among Blacks in 2014-2018, occurring at a rate of 28.2 per 100,000, as were deaths from cancer of the cervix (3.4 per 100,000), while ovarian cancers deaths were highest in White females (7.1 per 100,000), the researchers noted.
The continuing racial and ethnic disparity “largely reflects a combination of multiple intertwined factors” of tumor biology, diagnosis, treatment, and systemic discrimination, they wrote, adding that Black persons “are more likely to have a higher exposure to some cancer risk factors and limited access to healthy food, safe places for physical activity, and evidence-based cancer preventive services.”
The report was funded by the four participating groups. Six of the 12 investigators are employees of the American Cancer Society whose salaries are solely paid by the society; the other authors had no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Overall cancer mortality in females continues to decrease in the United States, but “previous declining trends in death rates slowed” for breast cancer in recent years, according to an annual report by several national organizations.

The analysis of long-term trends in cancer death rates shows that a decline of 1.4% per year from 2001 to 2016 accelerated to 2.1% per year in 2016-2018, the American Cancer Society, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Cancer Institute, and the North American Association of Central Cancer Registries said.
Decreases in overall cancer mortality were seen in females of all races and ethnic groups over the most recent 5-year period included in the report, 2014-2018, varying from –1.6% per year in both non-Hispanic Blacks and Whites to –0.9% for non-Hispanic American Indians/Alaska Natives (AI/ANs), Farhad Islami, MD, PhD, of the American Cancer Society, Atlanta, and associates said in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute.
Over those 5 years, death rates fell for 14 of the 20 most common cancers in females; increased for liver, uterus, brain, pancreas, and soft tissue including heart; and remained stable for cancers of the oral cavity/pharynx, they reported.
Breast cancer was among those that declined, but the rate of that decline has been slowing. Mortality declined by an average of 2.3% per year in 2003-2007, by 1.6% a year in 2007-2014, and by just 1.0% annually during 2014-2018, based on data from the National Center for Health Statistics’ National Vital Statistics System.
Mortality from all cancers in 2014-2018 was 133.5 deaths per 100,000 standard population, with the racial/ethnic gap ranging from 85.4 per 100,000 (non-Hispanic Asian/Pacific Islander) to 154.9 (non-Hispanic Black), Dr. Islami and associates said.
Melanoma had the largest decline in mortality over that period among the 20 most common cancers in females, falling by an average of 4.4% per year, with lung cancer next at 4.3%. Among those with increased death rates, uterine cancer saw the largest rise at 2.0% a year, the research team said.
The deaths caused by cancer of the uterus were most common in non-Hispanic Black females, 8.9 per 100,000 population, followed by non-Hispanic White (4.5), Hispanic (4.1), non-Hispanic AI/AN (4.0), and non-Hispanic Asian/Pacific Islander (3.3), they reported.
“Long-term increasing trends in uterine cancer death rates parallel trends in incidence, although death rates are increasing at a somewhat faster rate. Increasing uterine cancer incidence has been attributed to increasing obesity prevalence and decreased use of combined hormone replacement therapy,” Dr. Islami and associates pointed out.
Breast cancer deaths also were most common among Blacks in 2014-2018, occurring at a rate of 28.2 per 100,000, as were deaths from cancer of the cervix (3.4 per 100,000), while ovarian cancers deaths were highest in White females (7.1 per 100,000), the researchers noted.
The continuing racial and ethnic disparity “largely reflects a combination of multiple intertwined factors” of tumor biology, diagnosis, treatment, and systemic discrimination, they wrote, adding that Black persons “are more likely to have a higher exposure to some cancer risk factors and limited access to healthy food, safe places for physical activity, and evidence-based cancer preventive services.”
The report was funded by the four participating groups. Six of the 12 investigators are employees of the American Cancer Society whose salaries are solely paid by the society; the other authors had no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Overall cancer mortality in females continues to decrease in the United States, but “previous declining trends in death rates slowed” for breast cancer in recent years, according to an annual report by several national organizations.

The analysis of long-term trends in cancer death rates shows that a decline of 1.4% per year from 2001 to 2016 accelerated to 2.1% per year in 2016-2018, the American Cancer Society, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Cancer Institute, and the North American Association of Central Cancer Registries said.
Decreases in overall cancer mortality were seen in females of all races and ethnic groups over the most recent 5-year period included in the report, 2014-2018, varying from –1.6% per year in both non-Hispanic Blacks and Whites to –0.9% for non-Hispanic American Indians/Alaska Natives (AI/ANs), Farhad Islami, MD, PhD, of the American Cancer Society, Atlanta, and associates said in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute.
Over those 5 years, death rates fell for 14 of the 20 most common cancers in females; increased for liver, uterus, brain, pancreas, and soft tissue including heart; and remained stable for cancers of the oral cavity/pharynx, they reported.
Breast cancer was among those that declined, but the rate of that decline has been slowing. Mortality declined by an average of 2.3% per year in 2003-2007, by 1.6% a year in 2007-2014, and by just 1.0% annually during 2014-2018, based on data from the National Center for Health Statistics’ National Vital Statistics System.
Mortality from all cancers in 2014-2018 was 133.5 deaths per 100,000 standard population, with the racial/ethnic gap ranging from 85.4 per 100,000 (non-Hispanic Asian/Pacific Islander) to 154.9 (non-Hispanic Black), Dr. Islami and associates said.
Melanoma had the largest decline in mortality over that period among the 20 most common cancers in females, falling by an average of 4.4% per year, with lung cancer next at 4.3%. Among those with increased death rates, uterine cancer saw the largest rise at 2.0% a year, the research team said.
The deaths caused by cancer of the uterus were most common in non-Hispanic Black females, 8.9 per 100,000 population, followed by non-Hispanic White (4.5), Hispanic (4.1), non-Hispanic AI/AN (4.0), and non-Hispanic Asian/Pacific Islander (3.3), they reported.
“Long-term increasing trends in uterine cancer death rates parallel trends in incidence, although death rates are increasing at a somewhat faster rate. Increasing uterine cancer incidence has been attributed to increasing obesity prevalence and decreased use of combined hormone replacement therapy,” Dr. Islami and associates pointed out.
Breast cancer deaths also were most common among Blacks in 2014-2018, occurring at a rate of 28.2 per 100,000, as were deaths from cancer of the cervix (3.4 per 100,000), while ovarian cancers deaths were highest in White females (7.1 per 100,000), the researchers noted.
The continuing racial and ethnic disparity “largely reflects a combination of multiple intertwined factors” of tumor biology, diagnosis, treatment, and systemic discrimination, they wrote, adding that Black persons “are more likely to have a higher exposure to some cancer risk factors and limited access to healthy food, safe places for physical activity, and evidence-based cancer preventive services.”
The report was funded by the four participating groups. Six of the 12 investigators are employees of the American Cancer Society whose salaries are solely paid by the society; the other authors had no conflicts of interest to disclose.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE NATIONAL CANCER INSTITUTE