User login
ANSWER
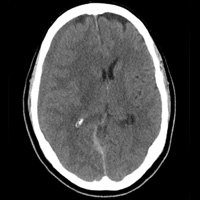
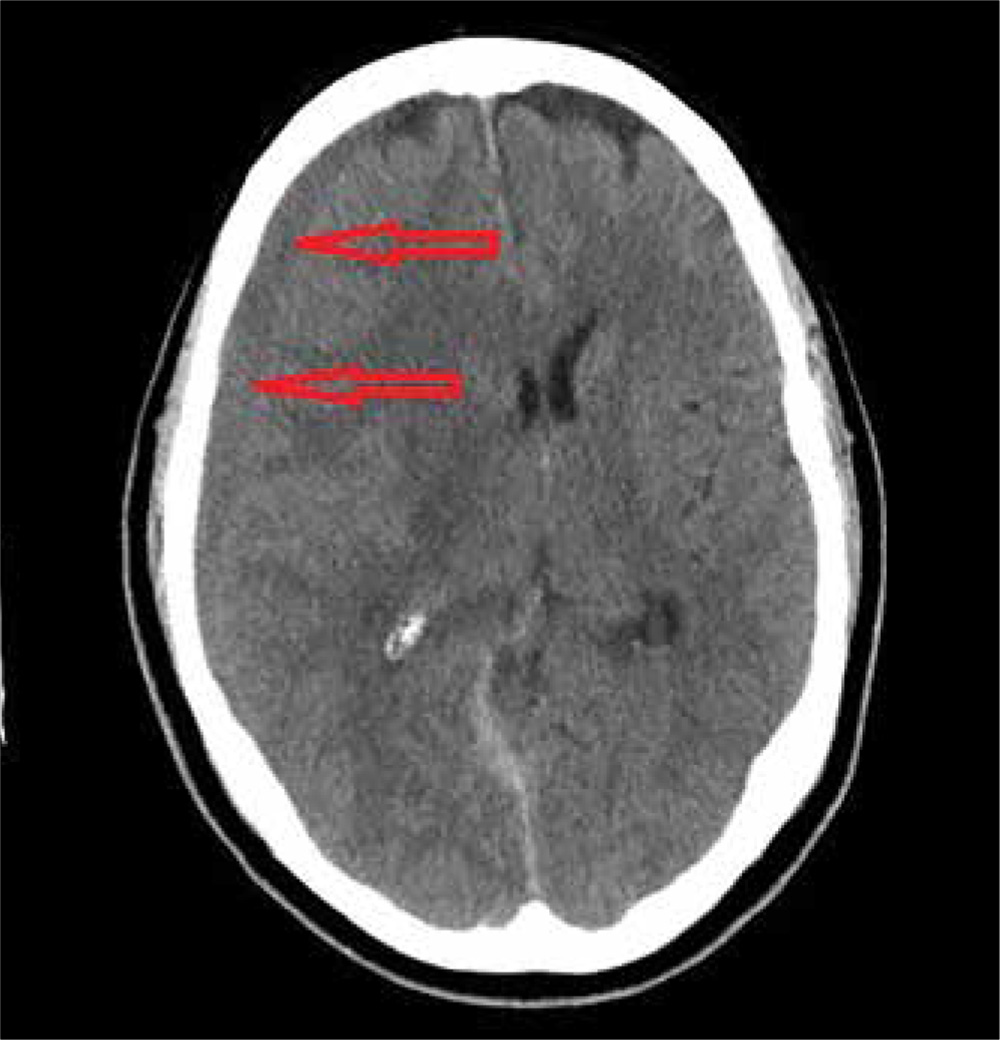
The image reveals a hypodense extra-axial fluid collection in the right frontoparietal region, measuring 8 to 10 mm in diameter. There is some mass effect and evidence of right-to-left shift. These findings are consistent with a subacute subdural hematoma, possibly secondary to the patient’s anticoagulant use. (The patient later recalled bumping his head a couple of months prior—but that may have been incidental.)
Arrangements were made for him at a local hospital where neurosurgical services were available. He underwent successful evacuation and was subsequently symptom free.

ANSWER
The image reveals a hypodense extra-axial fluid collection in the right frontoparietal region, measuring 8 to 10 mm in diameter. There is some mass effect and evidence of right-to-left shift. These findings are consistent with a subacute subdural hematoma, possibly secondary to the patient’s anticoagulant use. (The patient later recalled bumping his head a couple of months prior—but that may have been incidental.)
Arrangements were made for him at a local hospital where neurosurgical services were available. He underwent successful evacuation and was subsequently symptom free.

ANSWER
The image reveals a hypodense extra-axial fluid collection in the right frontoparietal region, measuring 8 to 10 mm in diameter. There is some mass effect and evidence of right-to-left shift. These findings are consistent with a subacute subdural hematoma, possibly secondary to the patient’s anticoagulant use. (The patient later recalled bumping his head a couple of months prior—but that may have been incidental.)
Arrangements were made for him at a local hospital where neurosurgical services were available. He underwent successful evacuation and was subsequently symptom free.
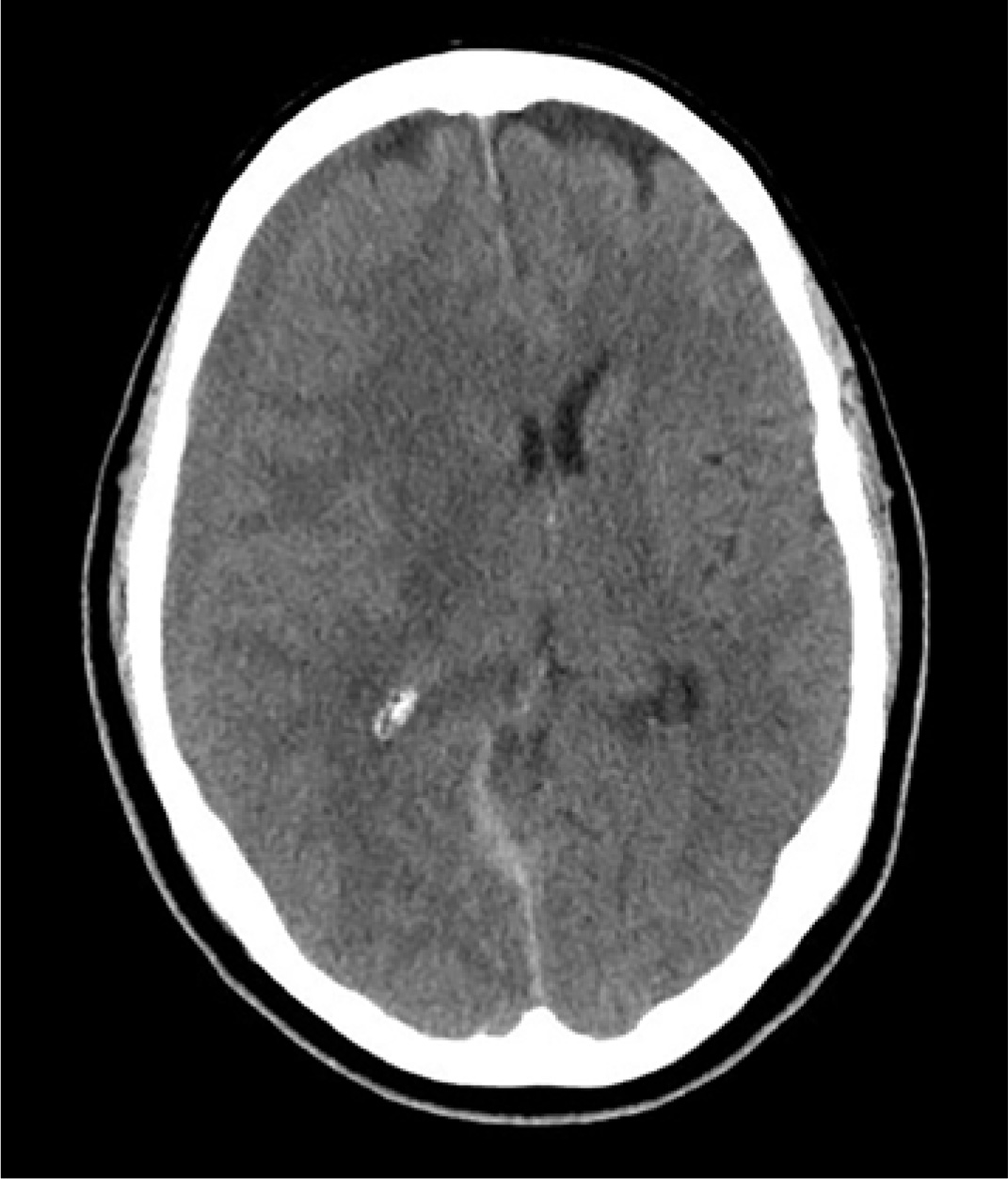
An 80-year-old man presents to urgent care for intermittent severe headaches. The pain is reportedly bifrontal, slightly worse on the right side than the left. He denies any recent injury or trauma, as well as symptoms including fever, chills, nausea, vomiting, and visual disturbance.
His medical history is significant for hypertension and hyperlipidemia. His current medications include prasugrel and aspirin.
On examination, you note an elderly male who is awake, alert, and oriented x 3. His vital signs are normal. His physical exam is overall normal, with no focal findings or neurologic deficits.
Noncontrast CT of the head is obtained at a local hospital. As you review the images, you see the following cut (shown). What is your impression?