User login
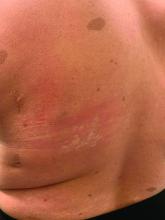
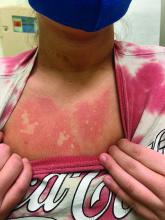
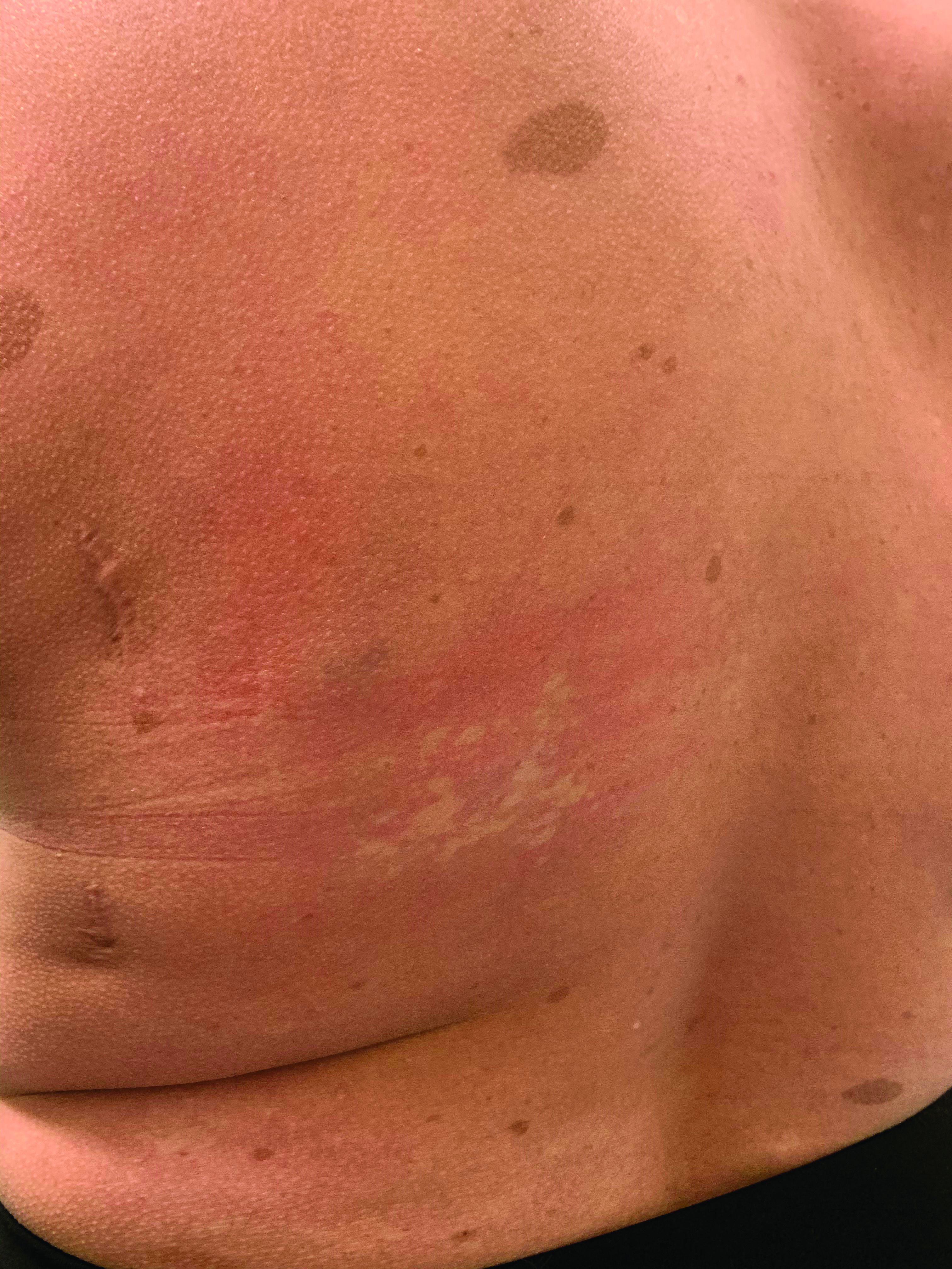
On close evaluation of the picture on her chest, she has pale macules and patches surrounded by erythematous ill-defined patches consistent with nevus anemicus. The findings of the picture raise the suspicion for neurofibromatosis, and it was recommended for her to be evaluated in person.
She comes several days later to the clinic. The caretaker, who is her aunt, reports she does not know much of the girl’s medical history as she recently moved from South America to live with her. The girl is a very nice and pleasant 8-year-old. She reports noticing the spots on her chest for about a year and that they seem to get a little itchier and more noticeable when she is hot or when she is running. She also reports increasing headaches for several months. She is being home schooled, and according to her aunt she is at par with her cousins who are about the same age. There is no history of seizures. She has had back surgery in the past. There is no history of hypertension. There is no family history of any genetic disorder or similar lesions.
On physical exam, her vital signs are normal, but her head circumference is over the 90th percentile. She is pleasant and interactive. On skin examination, she has slightly noticeable pale macules and patches on the chest and back that become more apparent after rubbing her skin. She has multiple light brown macules and oval patches on the chest, back, and neck. She has no axillary or inguinal freckling. She has scars on the back from her prior surgery.
As she was having worsening headaches, an MRI of the brain was ordered, which showed a left optic glioma. She was then referred to ophthalmology, neurology, and genetics.
Neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) is a common genetic autosomal dominant disorder cause by mutations on the NF1 gene on chromosome 17, which encodes for the protein neurofibromin. This protein works in the Ras-mitogen–activated protein kinase pathway as a negative regulator. Based on the National Institute of Health criteria, children need two or more of the following to be diagnosed with NF1: more than six café au lait macules larger than 5 mm in prepubescent children and 2.5 cm after puberty; axillary or inguinal freckling; two or more Lisch nodules; optic gliomas; two or more neurofibromas or one plexiform neurofibroma; or a first degree relative with a diagnosis of NF1. With these criteria, about 70% of the children can be diagnosed before the age of 1 year.1
Nevus anemicus is an uncommon birthmark, sometimes overlooked, that is characterized by pale, hypopigmented, well-defined macules and patches that do not turn red after trauma or changes in temperature. Nevus anemicus is usually localized on the torso but can be seen on the face, neck, and extremities. These lesions are present in 1%-2% of the general population. They are thought to occur because of increased sensitivity of the affected blood vessels to catecholamines, which causes permanent vasoconstriction, which leads to hypopigmentation on the area.2 These lesions are usually present at birth and have been described in patients with tuberous sclerosis, neurofibromatosis, and phakomatosis pigmentovascularis.
Recent studies of patients with neurofibromatosis and other RASopathies have noticed that nevus anemicus is present in about 8.8%-51% of the patients studied with a diagnosis NF1, compared with only 2% of the controls.3,4 The studies failed to report any cases of nevus anemicus in patients with other RASopathies associated with café au lait macules. Bulteel and colleagues recently reported two cases of non-NF1 RASopathies also associated with nevus anemicus in a patient with Legius syndrome and a patient with Noonan syndrome with multiple lentigines.5 The nevus anemicus was reported to occur most commonly on the anterior chest and be multiple, as seen in our patient.
The authors of the published studies advocate for the introduction of nevus anemicus as part of the diagnostic criteria for NF1, especially because it can be an early finding seen in babies, which can aid in early diagnosis of NF1.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego. She has no relevant financial disclosures. Email Dr. Matiz at [email protected].
References
1. Pediatrics. 2000 Mar. doi: 10.1542/peds.105.3.608.
2. Nevus Anemicus. StatPearls [Internet] (Treasure Island, Fla.: StatPearls Publishing; 2020 Jan).
3. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013 Nov. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2013.06.039.
4. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015 May-Jun. doi: 10.1111/pde.12525.
5. JAAD Case Rep. 2018 Apr 5. doi: 10.1016/j.jdcr.2017.09.037.
On close evaluation of the picture on her chest, she has pale macules and patches surrounded by erythematous ill-defined patches consistent with nevus anemicus. The findings of the picture raise the suspicion for neurofibromatosis, and it was recommended for her to be evaluated in person.
She comes several days later to the clinic. The caretaker, who is her aunt, reports she does not know much of the girl’s medical history as she recently moved from South America to live with her. The girl is a very nice and pleasant 8-year-old. She reports noticing the spots on her chest for about a year and that they seem to get a little itchier and more noticeable when she is hot or when she is running. She also reports increasing headaches for several months. She is being home schooled, and according to her aunt she is at par with her cousins who are about the same age. There is no history of seizures. She has had back surgery in the past. There is no history of hypertension. There is no family history of any genetic disorder or similar lesions.
On physical exam, her vital signs are normal, but her head circumference is over the 90th percentile. She is pleasant and interactive. On skin examination, she has slightly noticeable pale macules and patches on the chest and back that become more apparent after rubbing her skin. She has multiple light brown macules and oval patches on the chest, back, and neck. She has no axillary or inguinal freckling. She has scars on the back from her prior surgery.
As she was having worsening headaches, an MRI of the brain was ordered, which showed a left optic glioma. She was then referred to ophthalmology, neurology, and genetics.
Neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) is a common genetic autosomal dominant disorder cause by mutations on the NF1 gene on chromosome 17, which encodes for the protein neurofibromin. This protein works in the Ras-mitogen–activated protein kinase pathway as a negative regulator. Based on the National Institute of Health criteria, children need two or more of the following to be diagnosed with NF1: more than six café au lait macules larger than 5 mm in prepubescent children and 2.5 cm after puberty; axillary or inguinal freckling; two or more Lisch nodules; optic gliomas; two or more neurofibromas or one plexiform neurofibroma; or a first degree relative with a diagnosis of NF1. With these criteria, about 70% of the children can be diagnosed before the age of 1 year.1
Nevus anemicus is an uncommon birthmark, sometimes overlooked, that is characterized by pale, hypopigmented, well-defined macules and patches that do not turn red after trauma or changes in temperature. Nevus anemicus is usually localized on the torso but can be seen on the face, neck, and extremities. These lesions are present in 1%-2% of the general population. They are thought to occur because of increased sensitivity of the affected blood vessels to catecholamines, which causes permanent vasoconstriction, which leads to hypopigmentation on the area.2 These lesions are usually present at birth and have been described in patients with tuberous sclerosis, neurofibromatosis, and phakomatosis pigmentovascularis.
Recent studies of patients with neurofibromatosis and other RASopathies have noticed that nevus anemicus is present in about 8.8%-51% of the patients studied with a diagnosis NF1, compared with only 2% of the controls.3,4 The studies failed to report any cases of nevus anemicus in patients with other RASopathies associated with café au lait macules. Bulteel and colleagues recently reported two cases of non-NF1 RASopathies also associated with nevus anemicus in a patient with Legius syndrome and a patient with Noonan syndrome with multiple lentigines.5 The nevus anemicus was reported to occur most commonly on the anterior chest and be multiple, as seen in our patient.
The authors of the published studies advocate for the introduction of nevus anemicus as part of the diagnostic criteria for NF1, especially because it can be an early finding seen in babies, which can aid in early diagnosis of NF1.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego. She has no relevant financial disclosures. Email Dr. Matiz at [email protected].
References
1. Pediatrics. 2000 Mar. doi: 10.1542/peds.105.3.608.
2. Nevus Anemicus. StatPearls [Internet] (Treasure Island, Fla.: StatPearls Publishing; 2020 Jan).
3. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013 Nov. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2013.06.039.
4. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015 May-Jun. doi: 10.1111/pde.12525.
5. JAAD Case Rep. 2018 Apr 5. doi: 10.1016/j.jdcr.2017.09.037.
On close evaluation of the picture on her chest, she has pale macules and patches surrounded by erythematous ill-defined patches consistent with nevus anemicus. The findings of the picture raise the suspicion for neurofibromatosis, and it was recommended for her to be evaluated in person.
She comes several days later to the clinic. The caretaker, who is her aunt, reports she does not know much of the girl’s medical history as she recently moved from South America to live with her. The girl is a very nice and pleasant 8-year-old. She reports noticing the spots on her chest for about a year and that they seem to get a little itchier and more noticeable when she is hot or when she is running. She also reports increasing headaches for several months. She is being home schooled, and according to her aunt she is at par with her cousins who are about the same age. There is no history of seizures. She has had back surgery in the past. There is no history of hypertension. There is no family history of any genetic disorder or similar lesions.
On physical exam, her vital signs are normal, but her head circumference is over the 90th percentile. She is pleasant and interactive. On skin examination, she has slightly noticeable pale macules and patches on the chest and back that become more apparent after rubbing her skin. She has multiple light brown macules and oval patches on the chest, back, and neck. She has no axillary or inguinal freckling. She has scars on the back from her prior surgery.
As she was having worsening headaches, an MRI of the brain was ordered, which showed a left optic glioma. She was then referred to ophthalmology, neurology, and genetics.
Neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) is a common genetic autosomal dominant disorder cause by mutations on the NF1 gene on chromosome 17, which encodes for the protein neurofibromin. This protein works in the Ras-mitogen–activated protein kinase pathway as a negative regulator. Based on the National Institute of Health criteria, children need two or more of the following to be diagnosed with NF1: more than six café au lait macules larger than 5 mm in prepubescent children and 2.5 cm after puberty; axillary or inguinal freckling; two or more Lisch nodules; optic gliomas; two or more neurofibromas or one plexiform neurofibroma; or a first degree relative with a diagnosis of NF1. With these criteria, about 70% of the children can be diagnosed before the age of 1 year.1
Nevus anemicus is an uncommon birthmark, sometimes overlooked, that is characterized by pale, hypopigmented, well-defined macules and patches that do not turn red after trauma or changes in temperature. Nevus anemicus is usually localized on the torso but can be seen on the face, neck, and extremities. These lesions are present in 1%-2% of the general population. They are thought to occur because of increased sensitivity of the affected blood vessels to catecholamines, which causes permanent vasoconstriction, which leads to hypopigmentation on the area.2 These lesions are usually present at birth and have been described in patients with tuberous sclerosis, neurofibromatosis, and phakomatosis pigmentovascularis.
Recent studies of patients with neurofibromatosis and other RASopathies have noticed that nevus anemicus is present in about 8.8%-51% of the patients studied with a diagnosis NF1, compared with only 2% of the controls.3,4 The studies failed to report any cases of nevus anemicus in patients with other RASopathies associated with café au lait macules. Bulteel and colleagues recently reported two cases of non-NF1 RASopathies also associated with nevus anemicus in a patient with Legius syndrome and a patient with Noonan syndrome with multiple lentigines.5 The nevus anemicus was reported to occur most commonly on the anterior chest and be multiple, as seen in our patient.
The authors of the published studies advocate for the introduction of nevus anemicus as part of the diagnostic criteria for NF1, especially because it can be an early finding seen in babies, which can aid in early diagnosis of NF1.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego. She has no relevant financial disclosures. Email Dr. Matiz at [email protected].
References
1. Pediatrics. 2000 Mar. doi: 10.1542/peds.105.3.608.
2. Nevus Anemicus. StatPearls [Internet] (Treasure Island, Fla.: StatPearls Publishing; 2020 Jan).
3. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013 Nov. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2013.06.039.
4. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015 May-Jun. doi: 10.1111/pde.12525.
5. JAAD Case Rep. 2018 Apr 5. doi: 10.1016/j.jdcr.2017.09.037.