User login
The United States has never achieved a single high standard of medical care equity for all of its people, and the trend line does not appear favorable. The closest we have reached is basic Medicare (Parts A and B), military medicine, the Veterans Health Administration, and large nonprofit groups like Kaiser Permanente. It seems that the nature of we individualistic Americans is to always try to seek an advantage.
But even achieving equity in medical care would not ensure equity in health. The social determinants of health (income level, education, politics, government, geography, neighborhood, country of origin, language spoken, literacy, gender, and yes – race and ethnicity) have far more influence on health equity than does medical care.
Narratives can both reflect and influence culture. Considering the harmful effects of the current political divisiveness in the United States, the timing is ideal for our three leading medical and health education organizations – the American Medical Association, the Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC), and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention – to publish a definitive position paper called “Advancing Health Equity: A Guide to Language, Narrative and Concepts.”
What’s in a word?
According to William Shakespeare, “A rose by any other name would smell as sweet” (Romeo and Juliet). Maybe. But if the word used were “thorn” or “thistle,” it just would not be the same.
Words comprise language and wield enormous power with human beings. Wars are fought over geographic boundaries often defined by the language spoken by the people: think 2022, Russian-speaking Ukrainians. Think Winston Churchill’s massive 1,500-page “A History of the English-Speaking Peoples.” Think about the political power of French in Quebec, Canada.
Thus, it should be no surprise that words, acronyms, and abbreviations become rallying cries for political activists of all stripes: PC, January 6, Woke, 1619, BLM, Critical Race Theory, 1776, Remember Pearl Harbor, Remember the Alamo, the Civil War or the War Between the States, the War for Southern Independence, the War of Northern Aggression, the War of the Rebellion, or simply “The Lost Cause.” How about Realpolitik?
Is “medical language” the language of the people or of the profession? Physicians must understand each other, and physicians also must communicate clearly with patients using words that convey neutral meanings and don’t interfere with objective understanding. Medical editors prefer the brevity of one or a few words to clearly convey meaning.
I consider this document from the AMA and AAMC to be both profound and profoundly important for the healing professions. The contributors frequently use words like “humility” as they describe their efforts and products, knowing full well that they (and their organizations) stand to be figuratively torn limb from limb by a host of critics – or worse, ignored and marginalized.
Part 1 of the Health Equity Guide is titled “Language for promoting health equity.”(the reader is referred to the Health Equity Guide for the reasoning and explanations for all).
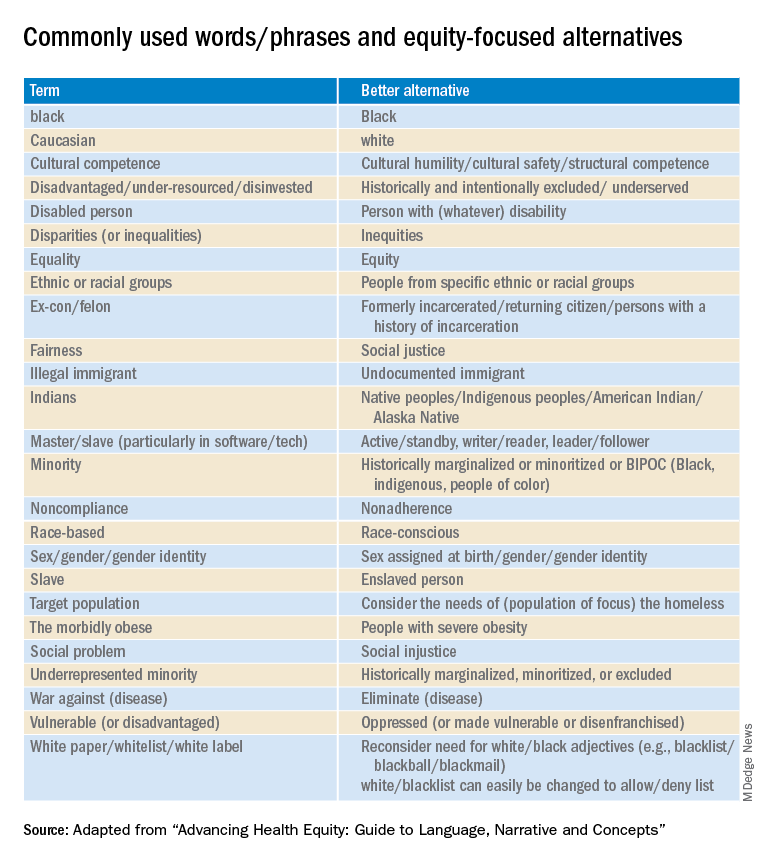
Part 2 of the Health Equity Guide is called “Why narratives matter.” It includes features of dominant narratives; a substantial section on the narrative of race and the narrative of individualism; the purpose of a health equity–based narrative; how to change the narrative; and how to see and think critically through dialogue.
Part 3 of the Health Equity Guide is a glossary of 138 key terms such as “class,” “discrimination,” “gender dysphoria,” “non-White,” “racial capitalism,” and “structural competency.”
The CDC also has a toolkit for inclusive communication, the “Health Equity Guiding Principles for Inclusive Communication.”
The substantive message of the Health Equity Guide could affect what you say, write, and do (even how you think) every day as well as how those with whom you interact view you. It can affect the entire communication milieu in which you live, whether or not you like it. Read it seriously, as though your professional life depended on it. It may.
Dr. Lundberg is consulting professor of health research policy and pathology at Stanford (Calif.) University. He reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The United States has never achieved a single high standard of medical care equity for all of its people, and the trend line does not appear favorable. The closest we have reached is basic Medicare (Parts A and B), military medicine, the Veterans Health Administration, and large nonprofit groups like Kaiser Permanente. It seems that the nature of we individualistic Americans is to always try to seek an advantage.
But even achieving equity in medical care would not ensure equity in health. The social determinants of health (income level, education, politics, government, geography, neighborhood, country of origin, language spoken, literacy, gender, and yes – race and ethnicity) have far more influence on health equity than does medical care.
Narratives can both reflect and influence culture. Considering the harmful effects of the current political divisiveness in the United States, the timing is ideal for our three leading medical and health education organizations – the American Medical Association, the Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC), and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention – to publish a definitive position paper called “Advancing Health Equity: A Guide to Language, Narrative and Concepts.”
What’s in a word?
According to William Shakespeare, “A rose by any other name would smell as sweet” (Romeo and Juliet). Maybe. But if the word used were “thorn” or “thistle,” it just would not be the same.
Words comprise language and wield enormous power with human beings. Wars are fought over geographic boundaries often defined by the language spoken by the people: think 2022, Russian-speaking Ukrainians. Think Winston Churchill’s massive 1,500-page “A History of the English-Speaking Peoples.” Think about the political power of French in Quebec, Canada.
Thus, it should be no surprise that words, acronyms, and abbreviations become rallying cries for political activists of all stripes: PC, January 6, Woke, 1619, BLM, Critical Race Theory, 1776, Remember Pearl Harbor, Remember the Alamo, the Civil War or the War Between the States, the War for Southern Independence, the War of Northern Aggression, the War of the Rebellion, or simply “The Lost Cause.” How about Realpolitik?
Is “medical language” the language of the people or of the profession? Physicians must understand each other, and physicians also must communicate clearly with patients using words that convey neutral meanings and don’t interfere with objective understanding. Medical editors prefer the brevity of one or a few words to clearly convey meaning.
I consider this document from the AMA and AAMC to be both profound and profoundly important for the healing professions. The contributors frequently use words like “humility” as they describe their efforts and products, knowing full well that they (and their organizations) stand to be figuratively torn limb from limb by a host of critics – or worse, ignored and marginalized.
Part 1 of the Health Equity Guide is titled “Language for promoting health equity.”(the reader is referred to the Health Equity Guide for the reasoning and explanations for all).

Part 2 of the Health Equity Guide is called “Why narratives matter.” It includes features of dominant narratives; a substantial section on the narrative of race and the narrative of individualism; the purpose of a health equity–based narrative; how to change the narrative; and how to see and think critically through dialogue.
Part 3 of the Health Equity Guide is a glossary of 138 key terms such as “class,” “discrimination,” “gender dysphoria,” “non-White,” “racial capitalism,” and “structural competency.”
The CDC also has a toolkit for inclusive communication, the “Health Equity Guiding Principles for Inclusive Communication.”
The substantive message of the Health Equity Guide could affect what you say, write, and do (even how you think) every day as well as how those with whom you interact view you. It can affect the entire communication milieu in which you live, whether or not you like it. Read it seriously, as though your professional life depended on it. It may.
Dr. Lundberg is consulting professor of health research policy and pathology at Stanford (Calif.) University. He reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The United States has never achieved a single high standard of medical care equity for all of its people, and the trend line does not appear favorable. The closest we have reached is basic Medicare (Parts A and B), military medicine, the Veterans Health Administration, and large nonprofit groups like Kaiser Permanente. It seems that the nature of we individualistic Americans is to always try to seek an advantage.
But even achieving equity in medical care would not ensure equity in health. The social determinants of health (income level, education, politics, government, geography, neighborhood, country of origin, language spoken, literacy, gender, and yes – race and ethnicity) have far more influence on health equity than does medical care.
Narratives can both reflect and influence culture. Considering the harmful effects of the current political divisiveness in the United States, the timing is ideal for our three leading medical and health education organizations – the American Medical Association, the Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC), and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention – to publish a definitive position paper called “Advancing Health Equity: A Guide to Language, Narrative and Concepts.”
What’s in a word?
According to William Shakespeare, “A rose by any other name would smell as sweet” (Romeo and Juliet). Maybe. But if the word used were “thorn” or “thistle,” it just would not be the same.
Words comprise language and wield enormous power with human beings. Wars are fought over geographic boundaries often defined by the language spoken by the people: think 2022, Russian-speaking Ukrainians. Think Winston Churchill’s massive 1,500-page “A History of the English-Speaking Peoples.” Think about the political power of French in Quebec, Canada.
Thus, it should be no surprise that words, acronyms, and abbreviations become rallying cries for political activists of all stripes: PC, January 6, Woke, 1619, BLM, Critical Race Theory, 1776, Remember Pearl Harbor, Remember the Alamo, the Civil War or the War Between the States, the War for Southern Independence, the War of Northern Aggression, the War of the Rebellion, or simply “The Lost Cause.” How about Realpolitik?
Is “medical language” the language of the people or of the profession? Physicians must understand each other, and physicians also must communicate clearly with patients using words that convey neutral meanings and don’t interfere with objective understanding. Medical editors prefer the brevity of one or a few words to clearly convey meaning.
I consider this document from the AMA and AAMC to be both profound and profoundly important for the healing professions. The contributors frequently use words like “humility” as they describe their efforts and products, knowing full well that they (and their organizations) stand to be figuratively torn limb from limb by a host of critics – or worse, ignored and marginalized.
Part 1 of the Health Equity Guide is titled “Language for promoting health equity.”(the reader is referred to the Health Equity Guide for the reasoning and explanations for all).

Part 2 of the Health Equity Guide is called “Why narratives matter.” It includes features of dominant narratives; a substantial section on the narrative of race and the narrative of individualism; the purpose of a health equity–based narrative; how to change the narrative; and how to see and think critically through dialogue.
Part 3 of the Health Equity Guide is a glossary of 138 key terms such as “class,” “discrimination,” “gender dysphoria,” “non-White,” “racial capitalism,” and “structural competency.”
The CDC also has a toolkit for inclusive communication, the “Health Equity Guiding Principles for Inclusive Communication.”
The substantive message of the Health Equity Guide could affect what you say, write, and do (even how you think) every day as well as how those with whom you interact view you. It can affect the entire communication milieu in which you live, whether or not you like it. Read it seriously, as though your professional life depended on it. It may.
Dr. Lundberg is consulting professor of health research policy and pathology at Stanford (Calif.) University. He reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.