User login
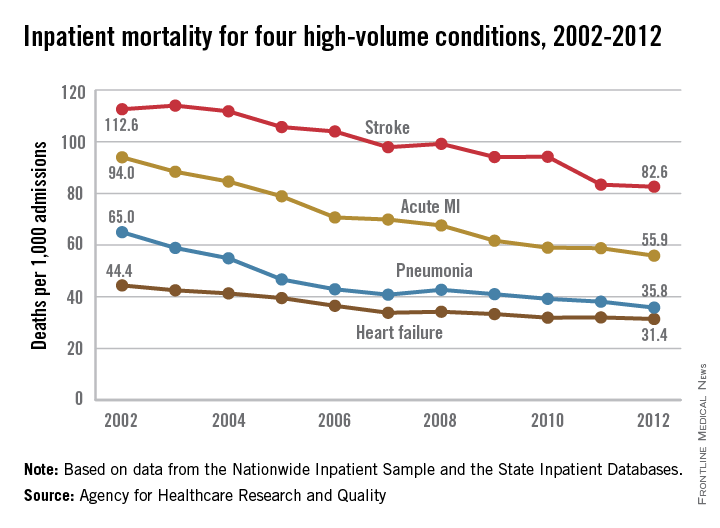
Inpatient mortality for pneumonia, acute MI, heart failure, and stroke each fell significantly from 2002 to 2012, the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality reported.
Over that period, mortality among adults hospitalized with pneumonia went from 65 per 1,000 admissions to 35.8 per 1,000 for a drop of 45% – largest of the four high-volume conditions. Corresponding declines for the others were 41% for acute MI, 29% for heart failure, and 27% for stroke, the AHRQ noted.

Since “death following discharge from a hospital is not reflected in these data,” the report said, measures of inpatient mortality “can reflect both improvements in health care and shifts in where end-of-life care takes place over time.”
The estimates in the report are based on data from the Nationwide Inpatient Sample (2002-2011) and State Inpatient Databases (2012).
Inpatient mortality for pneumonia, acute MI, heart failure, and stroke each fell significantly from 2002 to 2012, the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality reported.
Over that period, mortality among adults hospitalized with pneumonia went from 65 per 1,000 admissions to 35.8 per 1,000 for a drop of 45% – largest of the four high-volume conditions. Corresponding declines for the others were 41% for acute MI, 29% for heart failure, and 27% for stroke, the AHRQ noted.

Since “death following discharge from a hospital is not reflected in these data,” the report said, measures of inpatient mortality “can reflect both improvements in health care and shifts in where end-of-life care takes place over time.”
The estimates in the report are based on data from the Nationwide Inpatient Sample (2002-2011) and State Inpatient Databases (2012).
Inpatient mortality for pneumonia, acute MI, heart failure, and stroke each fell significantly from 2002 to 2012, the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality reported.
Over that period, mortality among adults hospitalized with pneumonia went from 65 per 1,000 admissions to 35.8 per 1,000 for a drop of 45% – largest of the four high-volume conditions. Corresponding declines for the others were 41% for acute MI, 29% for heart failure, and 27% for stroke, the AHRQ noted.

Since “death following discharge from a hospital is not reflected in these data,” the report said, measures of inpatient mortality “can reflect both improvements in health care and shifts in where end-of-life care takes place over time.”
The estimates in the report are based on data from the Nationwide Inpatient Sample (2002-2011) and State Inpatient Databases (2012).