User login
Endometriosis is a common condition, occurring in this country in 1 of 10 women of reproductive age. An association between endometriosis and subsequent ovarian carcinoma has been reported for decades, yet it is only recently that our knowledge has deepened enough to support more rational methods for preventing the malignancy.
Each year, approximately 22,000 new cases of ovarian cancer are diagnosed. The lifetime risk of developing this malignancy is low, but it is the deadliest of the gynecologic malignancies, with diagnosis usually made in advanced stages when prognosis is poor.
Endometriosis shows some characteristics of malignancy, such as the development of local and distant foci, and attachment to and invasion of other tissues with subsequent damage to these tissues. Endometriosis also is characterized by recurrent, unregulated cell proliferation and estrogen-dependent growth.
Our attempts during the past 2 decades to detect ovarian carcinoma at the early stages through a combined screening modality involving transvaginal ultrasound and a test for the serum level of cancer antigen 125 have failed to provide any survival benefit or even any measurable reduction in morbidity. Today, early-stage ovarian carcinoma, which has a 5-year survival rate of more than 90%, is diagnosed in only a minority of women.
There is good news, however. In recent years our insight into the pathophysiology of ovarian cancer has deepened, providing us with a new paradigm for ovarian cancer pathogenesis that divides ovarian epithelial carcinoma into two distinct types with distinct molecular profiles – one which originates largely in the distal portion of the fallopian tube and the other which traces back to endometriosis.
This new paradigm strengthens and helps to explain the reported association between endometriosis and ovarian cancer. It also has important clinical implications for current practice. While we have much more to learn about the etiology of endometriosis and the causes of malignant transformation, our current knowledge provides a strong rationale for identification and close monitoring of some patients with endometriosis deemed at risk for ovarian cancer, risk-reducing medical management, earlier and more meticulous surgical treatment, and close monitoring.
By combining this new approach to endometriosis with consideration of salpingectomy after completion of childbearing, we have an unprecedented opportunity to reduce the incidence of epithelial ovarian cancer.
Dual pathogenesis
The majority of ovarian cancers are of epithelial origin and fall into four histologic categories: serous, endometrioid, clear cell, and mucinous. In recent years, we have gained a deeper understanding of the pathogenesis of ovarian carcinoma, with an array of epidemiologic, histologic, and molecular data showing us that epithelial ovarian cancers are also of two distinct types (Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2015 Sep;213[3]:262-7).
One of these types, a high-grade serous carcinoma, appears to arise in many cases in the epithelium of the fallopian tube. The other type of tumor is a low-grade carcinoma – particularly of the endometrioid and clear cell histologic subtypes – that originates largely from ovarian endometriotic lesions or from borderline serous tumors in the case of serous histology.
The majority of diagnosed stage 1 ovarian cancers are carcinomas of this low-grade type and not high-grade serous carcinomas. In a study of 76 consecutive stage 1 carcinomas, investigators found that ovarian endometriosis was present in 40 of the 76 cases. More than two-thirds of the 76 cases (71%) were nonserous cancers, and almost all of these cases were associated with endometriosis based on histologic examination (Fertil Steril. 2007 Oct;88[4]:906-10).
This study was among the first to show that the majority of stage 1 ovarian carcinomas are not high-grade serous carcinomas, but rather nonserous, primarily endometrioid and clear cell, cancers. The research demonstrated that endometriosis should be viewed as a potential precursor lesion to specific subtypes of ovarian cancer.
The malignant transformation of endometriosis was first suggested by Dr. J. A. Sampson in 1925, and a number of studies – in addition to the 2007 landmark study – have since described ovarian cancer arising from endometriosis, based on the frequent co-occurrence in surgical specimens.
Most recently, a study from the Ovarian Cancer Association Consortium (OCAC) found that women who reported a history of endometriosis had a significantly higher risk of developing ovarian cancer than the general population (odds ratio, 1.46).
Investigators of this critical study pooled data from 13 ovarian cancer case-control studies involving more than 13,226 controls and 7,911 women with invasive epithelial ovarian cancer – 818 (6.2%) and 738 (9.3%) of whom, respectively, reported a history of endometriosis. Specifically, they determined that self-reported endometriosis was associated with a 3.05-fold increased risk for clear cell invasive ovarian cancer and a 2.04-fold increased risk of endometrioid ovarian cancer.
Moreover, a significant association between preexisting endometriosis and low-grade serous invasive ovarian cancer (OR, 2.11) was demonstrated, while no association was found between endometriosis and the risk of high-grade serous invasive ovarian cancer (Lancet Oncol. 2012 Apr;13[4]:385-94).
A second recently published report – a meta-analysis of 20 case-control and 15 cohort studies published between 1990 and 2012 and involving more than 444,000 patients – found that endometriosis increased cancer risk in case-control or two-arm cohort studies by 27% (relative risk, 1.265) and by approximately 80% in single-arm cohort studies (standard incidence ratio, 1.797). Endometrioid and clear cell carcinomas were more common in endometriosis-associated ovarian cancer, while serous carcinoma was less frequent (Br J Cancer. 2014 Apr 2;110[7]:1878-90).
Findings of both of these large studies have served to clarify the association between endometriosis and specific histologic subtypes and suggested that there are important differences in the pathogenesis of low-grade and high-grade serous ovarian carcinomas.
Clinical implications
It is not clear what causes malignant transformation or what predisposes some patients with endometriosis to develop ovarian cancer, but the risk likely involves genetic and epigenetic influences as well as immunologic, inflammatory, and hormonal factors.
The molecular profiles of the main two types of ovarian cancer are different: While the majority of high-grade serous ovarian tumors are characterized by TP53 mutations, the low-grade carcinomas are characterized by a variety of mutations, including KRAS, BRAF, ERBB2, CTNNB1, and BCL2 mutations.
There currently are not enough data to recommend genetic screening tests in patients with endometriosis, but our hope is that we eventually will be able to screen for “high-risk” endometriotic lesions by testing for genes specific to various histologic subtypes of low-grade ovarian cancer, or by finding and utilizing other biomarkers.
In the meantime, we believe it is important to more thoroughly treat endometriosis and to identify and follow women with a history of the condition, especially those with a long-standing history, those with a history of endometriosis associated with infertility, and those with ovarian endometrioma. Each of these factors predisposes patients to a higher risk of malignant transformation.
Complete surgical resection of all visible endometriosis is the most effective treatment and will afford the best cancer prevention, even in women who are asymptomatic. In a recent Swedish national registry case-control study, women who underwent radical surgical excision of all visible endometriosis were significantly less likely (OR, 0.30) to develop ovarian cancer (Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2013 May;92[5]:546-54).
Suppressive hormonal therapy is another treatment option for patients with no interest in conceiving. Most large endometriomas are functional ovarian cysts that have been invaded by cortical ovarian endometriosis or by small primary endometriomas (J Reprod Med. 1992 Sep;37[9]:771-6).
While hormonal therapy will not always result in complete regression of endometriotic lesions, it will decrease the recurrence rate of endometriomas and can be considered for long-term prevention of potentially premalignant lesions. It is most effective when it follows surgical excision of endometriomas and associated endometriosis.
A patient who has completed childbearing at the time of surgical resection may be offered bilateral salpingectomy, regardless of menopausal status. Salpingectomy in both average and high-risk populations (e.g., BRCA 1/2 carriers) not only prevents high-grade serous carcinoma by eliminating the site of origin, but also may decrease the risk of endometrioid and clear cell carcinoma by blocking the passageway that enables the flow of endometrium and factors that induce inflammation. It is estimated that the procedure reduces the risk of ovarian cancer by 40%.
Interestingly, tubal ligation has historically been shown to decrease the risk of ovarian cancer, and recent data have shown that the risk of endometrioid and clear cell carcinoma is cut even more than the risk of high-grade serous carcinoma (Int J Epidemiol. 2013 Apr;42[2]:579-89).
The Society of Gynecologic Oncology recommends that risk-reducing salpingectomy be considered at the time of hysterectomy or other abdominal or pelvic surgery, and in lieu of tubal ligation. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists similarly has stated that prophylactic salpingectomy may offer clinicians the opportunity to prevent ovarian cancer in their patients. Salpingectomy is an important option for all patients, but is especially important when the fallopian tubes are found to be damaged by endometriosis and/or pelvic inflammatory disease. When imaging studies show that endometriomas are present and resection is not performed, pelvic ultrasound should become part of the patient’s routine examination.
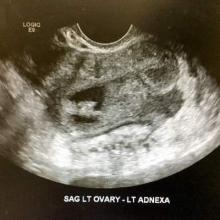
Most endometriomas have a homogeneous appearance; any significant increase in size or a change in the homogeneous cystic characteristics to a more heterogeneous appearance with mural components should raise suspicion about malignant change.
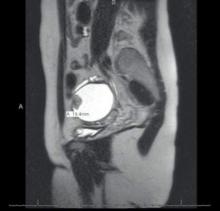
It can be difficult to detect relatively small endocystic components with ultrasound, so if there is any doubt about whether there is some heterogeneous consistency, an MRI should be performed. MRI is showing more promise in detecting malignant change. Hyperdense mural nodules within the ovary and rapid growth of an endometrioma have both been associated with malignant transformation and can be seen on these images.
In a cohort study comparing MRI findings of 10 patients with ovarian adenocarcinoma to 10 patients with benign endometriomas, investigators found mural nodules in all 10 malignancies but in only three of the benign cases (AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2000 Nov;175[5]:1423-30).
Long-term follow-up is necessary to understand the timeline of transformation in patients with mural nodules. This together with increasing knowledge of molecular events underpinning evolution of endometriosis will lead to better screening and preventive strategies.
Dr. Nezhat is the director of minimally invasive gynecologic surgery and robotics at Winthrop University Hospital in Mineola, N.Y., and an adjunct professor of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive medicine at the State University of New York at Stony Brook. He reported having no financial disclosures.
Endometriosis is a common condition, occurring in this country in 1 of 10 women of reproductive age. An association between endometriosis and subsequent ovarian carcinoma has been reported for decades, yet it is only recently that our knowledge has deepened enough to support more rational methods for preventing the malignancy.
Each year, approximately 22,000 new cases of ovarian cancer are diagnosed. The lifetime risk of developing this malignancy is low, but it is the deadliest of the gynecologic malignancies, with diagnosis usually made in advanced stages when prognosis is poor.
Endometriosis shows some characteristics of malignancy, such as the development of local and distant foci, and attachment to and invasion of other tissues with subsequent damage to these tissues. Endometriosis also is characterized by recurrent, unregulated cell proliferation and estrogen-dependent growth.
Our attempts during the past 2 decades to detect ovarian carcinoma at the early stages through a combined screening modality involving transvaginal ultrasound and a test for the serum level of cancer antigen 125 have failed to provide any survival benefit or even any measurable reduction in morbidity. Today, early-stage ovarian carcinoma, which has a 5-year survival rate of more than 90%, is diagnosed in only a minority of women.
There is good news, however. In recent years our insight into the pathophysiology of ovarian cancer has deepened, providing us with a new paradigm for ovarian cancer pathogenesis that divides ovarian epithelial carcinoma into two distinct types with distinct molecular profiles – one which originates largely in the distal portion of the fallopian tube and the other which traces back to endometriosis.
This new paradigm strengthens and helps to explain the reported association between endometriosis and ovarian cancer. It also has important clinical implications for current practice. While we have much more to learn about the etiology of endometriosis and the causes of malignant transformation, our current knowledge provides a strong rationale for identification and close monitoring of some patients with endometriosis deemed at risk for ovarian cancer, risk-reducing medical management, earlier and more meticulous surgical treatment, and close monitoring.
By combining this new approach to endometriosis with consideration of salpingectomy after completion of childbearing, we have an unprecedented opportunity to reduce the incidence of epithelial ovarian cancer.
Dual pathogenesis
The majority of ovarian cancers are of epithelial origin and fall into four histologic categories: serous, endometrioid, clear cell, and mucinous. In recent years, we have gained a deeper understanding of the pathogenesis of ovarian carcinoma, with an array of epidemiologic, histologic, and molecular data showing us that epithelial ovarian cancers are also of two distinct types (Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2015 Sep;213[3]:262-7).
One of these types, a high-grade serous carcinoma, appears to arise in many cases in the epithelium of the fallopian tube. The other type of tumor is a low-grade carcinoma – particularly of the endometrioid and clear cell histologic subtypes – that originates largely from ovarian endometriotic lesions or from borderline serous tumors in the case of serous histology.
The majority of diagnosed stage 1 ovarian cancers are carcinomas of this low-grade type and not high-grade serous carcinomas. In a study of 76 consecutive stage 1 carcinomas, investigators found that ovarian endometriosis was present in 40 of the 76 cases. More than two-thirds of the 76 cases (71%) were nonserous cancers, and almost all of these cases were associated with endometriosis based on histologic examination (Fertil Steril. 2007 Oct;88[4]:906-10).
This study was among the first to show that the majority of stage 1 ovarian carcinomas are not high-grade serous carcinomas, but rather nonserous, primarily endometrioid and clear cell, cancers. The research demonstrated that endometriosis should be viewed as a potential precursor lesion to specific subtypes of ovarian cancer.
The malignant transformation of endometriosis was first suggested by Dr. J. A. Sampson in 1925, and a number of studies – in addition to the 2007 landmark study – have since described ovarian cancer arising from endometriosis, based on the frequent co-occurrence in surgical specimens.
Most recently, a study from the Ovarian Cancer Association Consortium (OCAC) found that women who reported a history of endometriosis had a significantly higher risk of developing ovarian cancer than the general population (odds ratio, 1.46).
Investigators of this critical study pooled data from 13 ovarian cancer case-control studies involving more than 13,226 controls and 7,911 women with invasive epithelial ovarian cancer – 818 (6.2%) and 738 (9.3%) of whom, respectively, reported a history of endometriosis. Specifically, they determined that self-reported endometriosis was associated with a 3.05-fold increased risk for clear cell invasive ovarian cancer and a 2.04-fold increased risk of endometrioid ovarian cancer.
Moreover, a significant association between preexisting endometriosis and low-grade serous invasive ovarian cancer (OR, 2.11) was demonstrated, while no association was found between endometriosis and the risk of high-grade serous invasive ovarian cancer (Lancet Oncol. 2012 Apr;13[4]:385-94).
A second recently published report – a meta-analysis of 20 case-control and 15 cohort studies published between 1990 and 2012 and involving more than 444,000 patients – found that endometriosis increased cancer risk in case-control or two-arm cohort studies by 27% (relative risk, 1.265) and by approximately 80% in single-arm cohort studies (standard incidence ratio, 1.797). Endometrioid and clear cell carcinomas were more common in endometriosis-associated ovarian cancer, while serous carcinoma was less frequent (Br J Cancer. 2014 Apr 2;110[7]:1878-90).
Findings of both of these large studies have served to clarify the association between endometriosis and specific histologic subtypes and suggested that there are important differences in the pathogenesis of low-grade and high-grade serous ovarian carcinomas.
Clinical implications
It is not clear what causes malignant transformation or what predisposes some patients with endometriosis to develop ovarian cancer, but the risk likely involves genetic and epigenetic influences as well as immunologic, inflammatory, and hormonal factors.
The molecular profiles of the main two types of ovarian cancer are different: While the majority of high-grade serous ovarian tumors are characterized by TP53 mutations, the low-grade carcinomas are characterized by a variety of mutations, including KRAS, BRAF, ERBB2, CTNNB1, and BCL2 mutations.
There currently are not enough data to recommend genetic screening tests in patients with endometriosis, but our hope is that we eventually will be able to screen for “high-risk” endometriotic lesions by testing for genes specific to various histologic subtypes of low-grade ovarian cancer, or by finding and utilizing other biomarkers.
In the meantime, we believe it is important to more thoroughly treat endometriosis and to identify and follow women with a history of the condition, especially those with a long-standing history, those with a history of endometriosis associated with infertility, and those with ovarian endometrioma. Each of these factors predisposes patients to a higher risk of malignant transformation.
Complete surgical resection of all visible endometriosis is the most effective treatment and will afford the best cancer prevention, even in women who are asymptomatic. In a recent Swedish national registry case-control study, women who underwent radical surgical excision of all visible endometriosis were significantly less likely (OR, 0.30) to develop ovarian cancer (Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2013 May;92[5]:546-54).
Suppressive hormonal therapy is another treatment option for patients with no interest in conceiving. Most large endometriomas are functional ovarian cysts that have been invaded by cortical ovarian endometriosis or by small primary endometriomas (J Reprod Med. 1992 Sep;37[9]:771-6).
While hormonal therapy will not always result in complete regression of endometriotic lesions, it will decrease the recurrence rate of endometriomas and can be considered for long-term prevention of potentially premalignant lesions. It is most effective when it follows surgical excision of endometriomas and associated endometriosis.
A patient who has completed childbearing at the time of surgical resection may be offered bilateral salpingectomy, regardless of menopausal status. Salpingectomy in both average and high-risk populations (e.g., BRCA 1/2 carriers) not only prevents high-grade serous carcinoma by eliminating the site of origin, but also may decrease the risk of endometrioid and clear cell carcinoma by blocking the passageway that enables the flow of endometrium and factors that induce inflammation. It is estimated that the procedure reduces the risk of ovarian cancer by 40%.
Interestingly, tubal ligation has historically been shown to decrease the risk of ovarian cancer, and recent data have shown that the risk of endometrioid and clear cell carcinoma is cut even more than the risk of high-grade serous carcinoma (Int J Epidemiol. 2013 Apr;42[2]:579-89).
The Society of Gynecologic Oncology recommends that risk-reducing salpingectomy be considered at the time of hysterectomy or other abdominal or pelvic surgery, and in lieu of tubal ligation. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists similarly has stated that prophylactic salpingectomy may offer clinicians the opportunity to prevent ovarian cancer in their patients. Salpingectomy is an important option for all patients, but is especially important when the fallopian tubes are found to be damaged by endometriosis and/or pelvic inflammatory disease. When imaging studies show that endometriomas are present and resection is not performed, pelvic ultrasound should become part of the patient’s routine examination.
Most endometriomas have a homogeneous appearance; any significant increase in size or a change in the homogeneous cystic characteristics to a more heterogeneous appearance with mural components should raise suspicion about malignant change.
It can be difficult to detect relatively small endocystic components with ultrasound, so if there is any doubt about whether there is some heterogeneous consistency, an MRI should be performed. MRI is showing more promise in detecting malignant change. Hyperdense mural nodules within the ovary and rapid growth of an endometrioma have both been associated with malignant transformation and can be seen on these images.
In a cohort study comparing MRI findings of 10 patients with ovarian adenocarcinoma to 10 patients with benign endometriomas, investigators found mural nodules in all 10 malignancies but in only three of the benign cases (AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2000 Nov;175[5]:1423-30).
Long-term follow-up is necessary to understand the timeline of transformation in patients with mural nodules. This together with increasing knowledge of molecular events underpinning evolution of endometriosis will lead to better screening and preventive strategies.
Dr. Nezhat is the director of minimally invasive gynecologic surgery and robotics at Winthrop University Hospital in Mineola, N.Y., and an adjunct professor of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive medicine at the State University of New York at Stony Brook. He reported having no financial disclosures.
Endometriosis is a common condition, occurring in this country in 1 of 10 women of reproductive age. An association between endometriosis and subsequent ovarian carcinoma has been reported for decades, yet it is only recently that our knowledge has deepened enough to support more rational methods for preventing the malignancy.
Each year, approximately 22,000 new cases of ovarian cancer are diagnosed. The lifetime risk of developing this malignancy is low, but it is the deadliest of the gynecologic malignancies, with diagnosis usually made in advanced stages when prognosis is poor.
Endometriosis shows some characteristics of malignancy, such as the development of local and distant foci, and attachment to and invasion of other tissues with subsequent damage to these tissues. Endometriosis also is characterized by recurrent, unregulated cell proliferation and estrogen-dependent growth.
Our attempts during the past 2 decades to detect ovarian carcinoma at the early stages through a combined screening modality involving transvaginal ultrasound and a test for the serum level of cancer antigen 125 have failed to provide any survival benefit or even any measurable reduction in morbidity. Today, early-stage ovarian carcinoma, which has a 5-year survival rate of more than 90%, is diagnosed in only a minority of women.
There is good news, however. In recent years our insight into the pathophysiology of ovarian cancer has deepened, providing us with a new paradigm for ovarian cancer pathogenesis that divides ovarian epithelial carcinoma into two distinct types with distinct molecular profiles – one which originates largely in the distal portion of the fallopian tube and the other which traces back to endometriosis.
This new paradigm strengthens and helps to explain the reported association between endometriosis and ovarian cancer. It also has important clinical implications for current practice. While we have much more to learn about the etiology of endometriosis and the causes of malignant transformation, our current knowledge provides a strong rationale for identification and close monitoring of some patients with endometriosis deemed at risk for ovarian cancer, risk-reducing medical management, earlier and more meticulous surgical treatment, and close monitoring.
By combining this new approach to endometriosis with consideration of salpingectomy after completion of childbearing, we have an unprecedented opportunity to reduce the incidence of epithelial ovarian cancer.
Dual pathogenesis
The majority of ovarian cancers are of epithelial origin and fall into four histologic categories: serous, endometrioid, clear cell, and mucinous. In recent years, we have gained a deeper understanding of the pathogenesis of ovarian carcinoma, with an array of epidemiologic, histologic, and molecular data showing us that epithelial ovarian cancers are also of two distinct types (Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2015 Sep;213[3]:262-7).
One of these types, a high-grade serous carcinoma, appears to arise in many cases in the epithelium of the fallopian tube. The other type of tumor is a low-grade carcinoma – particularly of the endometrioid and clear cell histologic subtypes – that originates largely from ovarian endometriotic lesions or from borderline serous tumors in the case of serous histology.
The majority of diagnosed stage 1 ovarian cancers are carcinomas of this low-grade type and not high-grade serous carcinomas. In a study of 76 consecutive stage 1 carcinomas, investigators found that ovarian endometriosis was present in 40 of the 76 cases. More than two-thirds of the 76 cases (71%) were nonserous cancers, and almost all of these cases were associated with endometriosis based on histologic examination (Fertil Steril. 2007 Oct;88[4]:906-10).
This study was among the first to show that the majority of stage 1 ovarian carcinomas are not high-grade serous carcinomas, but rather nonserous, primarily endometrioid and clear cell, cancers. The research demonstrated that endometriosis should be viewed as a potential precursor lesion to specific subtypes of ovarian cancer.
The malignant transformation of endometriosis was first suggested by Dr. J. A. Sampson in 1925, and a number of studies – in addition to the 2007 landmark study – have since described ovarian cancer arising from endometriosis, based on the frequent co-occurrence in surgical specimens.
Most recently, a study from the Ovarian Cancer Association Consortium (OCAC) found that women who reported a history of endometriosis had a significantly higher risk of developing ovarian cancer than the general population (odds ratio, 1.46).
Investigators of this critical study pooled data from 13 ovarian cancer case-control studies involving more than 13,226 controls and 7,911 women with invasive epithelial ovarian cancer – 818 (6.2%) and 738 (9.3%) of whom, respectively, reported a history of endometriosis. Specifically, they determined that self-reported endometriosis was associated with a 3.05-fold increased risk for clear cell invasive ovarian cancer and a 2.04-fold increased risk of endometrioid ovarian cancer.
Moreover, a significant association between preexisting endometriosis and low-grade serous invasive ovarian cancer (OR, 2.11) was demonstrated, while no association was found between endometriosis and the risk of high-grade serous invasive ovarian cancer (Lancet Oncol. 2012 Apr;13[4]:385-94).
A second recently published report – a meta-analysis of 20 case-control and 15 cohort studies published between 1990 and 2012 and involving more than 444,000 patients – found that endometriosis increased cancer risk in case-control or two-arm cohort studies by 27% (relative risk, 1.265) and by approximately 80% in single-arm cohort studies (standard incidence ratio, 1.797). Endometrioid and clear cell carcinomas were more common in endometriosis-associated ovarian cancer, while serous carcinoma was less frequent (Br J Cancer. 2014 Apr 2;110[7]:1878-90).
Findings of both of these large studies have served to clarify the association between endometriosis and specific histologic subtypes and suggested that there are important differences in the pathogenesis of low-grade and high-grade serous ovarian carcinomas.
Clinical implications
It is not clear what causes malignant transformation or what predisposes some patients with endometriosis to develop ovarian cancer, but the risk likely involves genetic and epigenetic influences as well as immunologic, inflammatory, and hormonal factors.
The molecular profiles of the main two types of ovarian cancer are different: While the majority of high-grade serous ovarian tumors are characterized by TP53 mutations, the low-grade carcinomas are characterized by a variety of mutations, including KRAS, BRAF, ERBB2, CTNNB1, and BCL2 mutations.
There currently are not enough data to recommend genetic screening tests in patients with endometriosis, but our hope is that we eventually will be able to screen for “high-risk” endometriotic lesions by testing for genes specific to various histologic subtypes of low-grade ovarian cancer, or by finding and utilizing other biomarkers.
In the meantime, we believe it is important to more thoroughly treat endometriosis and to identify and follow women with a history of the condition, especially those with a long-standing history, those with a history of endometriosis associated with infertility, and those with ovarian endometrioma. Each of these factors predisposes patients to a higher risk of malignant transformation.
Complete surgical resection of all visible endometriosis is the most effective treatment and will afford the best cancer prevention, even in women who are asymptomatic. In a recent Swedish national registry case-control study, women who underwent radical surgical excision of all visible endometriosis were significantly less likely (OR, 0.30) to develop ovarian cancer (Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2013 May;92[5]:546-54).
Suppressive hormonal therapy is another treatment option for patients with no interest in conceiving. Most large endometriomas are functional ovarian cysts that have been invaded by cortical ovarian endometriosis or by small primary endometriomas (J Reprod Med. 1992 Sep;37[9]:771-6).
While hormonal therapy will not always result in complete regression of endometriotic lesions, it will decrease the recurrence rate of endometriomas and can be considered for long-term prevention of potentially premalignant lesions. It is most effective when it follows surgical excision of endometriomas and associated endometriosis.
A patient who has completed childbearing at the time of surgical resection may be offered bilateral salpingectomy, regardless of menopausal status. Salpingectomy in both average and high-risk populations (e.g., BRCA 1/2 carriers) not only prevents high-grade serous carcinoma by eliminating the site of origin, but also may decrease the risk of endometrioid and clear cell carcinoma by blocking the passageway that enables the flow of endometrium and factors that induce inflammation. It is estimated that the procedure reduces the risk of ovarian cancer by 40%.
Interestingly, tubal ligation has historically been shown to decrease the risk of ovarian cancer, and recent data have shown that the risk of endometrioid and clear cell carcinoma is cut even more than the risk of high-grade serous carcinoma (Int J Epidemiol. 2013 Apr;42[2]:579-89).
The Society of Gynecologic Oncology recommends that risk-reducing salpingectomy be considered at the time of hysterectomy or other abdominal or pelvic surgery, and in lieu of tubal ligation. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists similarly has stated that prophylactic salpingectomy may offer clinicians the opportunity to prevent ovarian cancer in their patients. Salpingectomy is an important option for all patients, but is especially important when the fallopian tubes are found to be damaged by endometriosis and/or pelvic inflammatory disease. When imaging studies show that endometriomas are present and resection is not performed, pelvic ultrasound should become part of the patient’s routine examination.
Most endometriomas have a homogeneous appearance; any significant increase in size or a change in the homogeneous cystic characteristics to a more heterogeneous appearance with mural components should raise suspicion about malignant change.
It can be difficult to detect relatively small endocystic components with ultrasound, so if there is any doubt about whether there is some heterogeneous consistency, an MRI should be performed. MRI is showing more promise in detecting malignant change. Hyperdense mural nodules within the ovary and rapid growth of an endometrioma have both been associated with malignant transformation and can be seen on these images.
In a cohort study comparing MRI findings of 10 patients with ovarian adenocarcinoma to 10 patients with benign endometriomas, investigators found mural nodules in all 10 malignancies but in only three of the benign cases (AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2000 Nov;175[5]:1423-30).
Long-term follow-up is necessary to understand the timeline of transformation in patients with mural nodules. This together with increasing knowledge of molecular events underpinning evolution of endometriosis will lead to better screening and preventive strategies.
Dr. Nezhat is the director of minimally invasive gynecologic surgery and robotics at Winthrop University Hospital in Mineola, N.Y., and an adjunct professor of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive medicine at the State University of New York at Stony Brook. He reported having no financial disclosures.