User login
, results from a single-center retrospective study found.
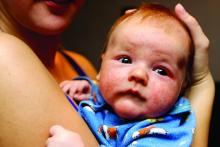
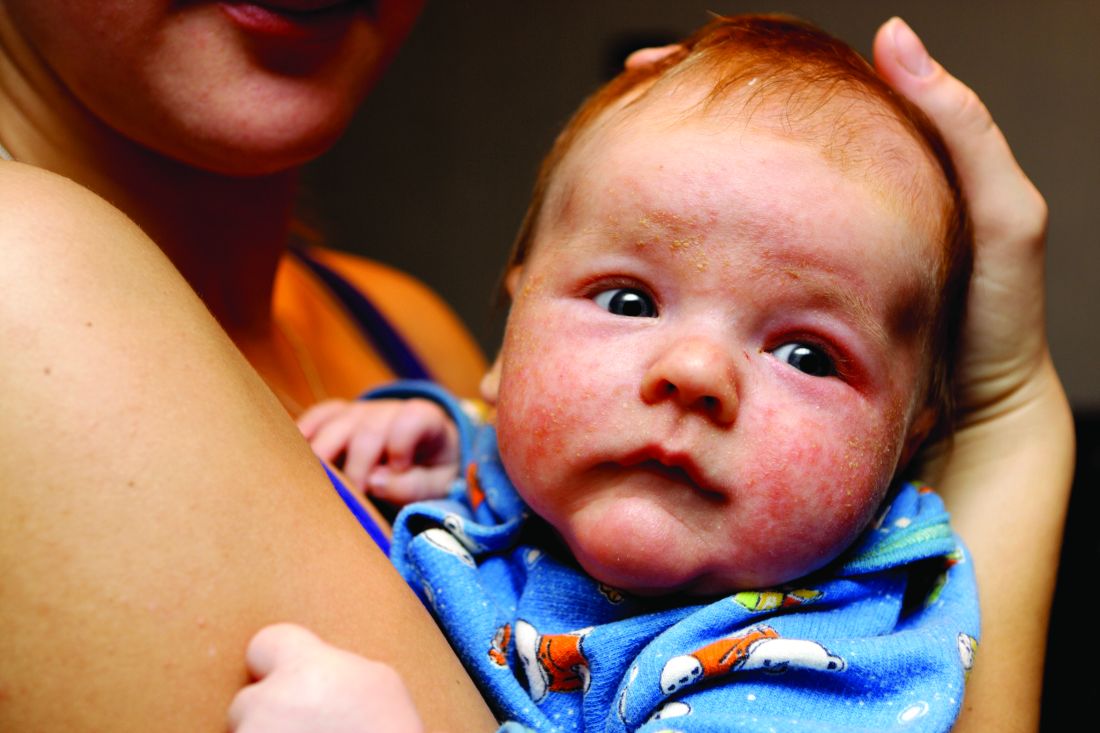
“Atopic dermatitis is a very common pediatric skin condition with significant morbidity for patients and their families,” lead study author Reesa L. Monir, MD, said during the virtual annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology. “Existing studies show increased disease prevalence in Black and Asian children relative to White children, with conflicting data for Hispanic children. The methodology behind many of these existing studies, however, is somewhat questionable. Many were survey-based studies asking parents to remember a diagnosis of eczema or even asking parents to just report an itchy rash and using that as a diagnosis.”
For the current study, Dr. Monir and colleagues reviewed the records of 4,016 infants born between June 1, 2011, and April 30, 2017, who were followed in the University of Florida’s health care system. The researchers defined this as having two or more well-child visits after birth and at least one visit at 300 days of life or later, and the used documentation of specific ICD-9 or ICD-10 codes to capture an objective diagnosis of atopic dermatitis (AD). Of the 4,016 patients, 39.2% were Black, 38.5% were White, 7.1% were Hispanic, 5.3% were Asian, 6.5% were from other racial backgrounds, and 3.4% were multiracial.
Dr. Monir, who is a resident in the department of dermatology at the University of Florida, Gainesville, reported that Black infants had the highest prevalence of AD at 37%, followed by Asian infants (25.8%), Hispanic infants (24.1%), multiracial infants (23%), infants from other racial backgrounds (19.1%), and non-Hispanic White infants (17.9%). Compared with White infants, the odds ratio estimates for AD was highest for Black infants (OR, 2.62), followed by Asian infants (OR, 1.55), multiracial infants (OR, 1.42), Hispanic infants (OR, 1.41), and infants from other racial backgrounds (OR, .97).
On unadjusted analysis, the following factors were significantly associated with race: delivery mode (P = .006), insurance type (P less than .001), NICU stay (P less than .001), and gestational age (P less than .0001). However, on multivariate logistic regression, only two factors were significantly associated with the diagnosis of AD: race (P less than .0001) and NICU stay (P = .0385).
“When we looked at the early childhood period specifically, we found striking racial differences in the rates of AD arising early in life,” Dr. Monir concluded. “The diagnosis was independently associated with race and NICU stay. We suggest that further investigation into these disparities and ways we can mitigate them should focus on this early childhood period.”
The researchers reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
, results from a single-center retrospective study found.
“Atopic dermatitis is a very common pediatric skin condition with significant morbidity for patients and their families,” lead study author Reesa L. Monir, MD, said during the virtual annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology. “Existing studies show increased disease prevalence in Black and Asian children relative to White children, with conflicting data for Hispanic children. The methodology behind many of these existing studies, however, is somewhat questionable. Many were survey-based studies asking parents to remember a diagnosis of eczema or even asking parents to just report an itchy rash and using that as a diagnosis.”
For the current study, Dr. Monir and colleagues reviewed the records of 4,016 infants born between June 1, 2011, and April 30, 2017, who were followed in the University of Florida’s health care system. The researchers defined this as having two or more well-child visits after birth and at least one visit at 300 days of life or later, and the used documentation of specific ICD-9 or ICD-10 codes to capture an objective diagnosis of atopic dermatitis (AD). Of the 4,016 patients, 39.2% were Black, 38.5% were White, 7.1% were Hispanic, 5.3% were Asian, 6.5% were from other racial backgrounds, and 3.4% were multiracial.
Dr. Monir, who is a resident in the department of dermatology at the University of Florida, Gainesville, reported that Black infants had the highest prevalence of AD at 37%, followed by Asian infants (25.8%), Hispanic infants (24.1%), multiracial infants (23%), infants from other racial backgrounds (19.1%), and non-Hispanic White infants (17.9%). Compared with White infants, the odds ratio estimates for AD was highest for Black infants (OR, 2.62), followed by Asian infants (OR, 1.55), multiracial infants (OR, 1.42), Hispanic infants (OR, 1.41), and infants from other racial backgrounds (OR, .97).
On unadjusted analysis, the following factors were significantly associated with race: delivery mode (P = .006), insurance type (P less than .001), NICU stay (P less than .001), and gestational age (P less than .0001). However, on multivariate logistic regression, only two factors were significantly associated with the diagnosis of AD: race (P less than .0001) and NICU stay (P = .0385).
“When we looked at the early childhood period specifically, we found striking racial differences in the rates of AD arising early in life,” Dr. Monir concluded. “The diagnosis was independently associated with race and NICU stay. We suggest that further investigation into these disparities and ways we can mitigate them should focus on this early childhood period.”
The researchers reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
, results from a single-center retrospective study found.
“Atopic dermatitis is a very common pediatric skin condition with significant morbidity for patients and their families,” lead study author Reesa L. Monir, MD, said during the virtual annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology. “Existing studies show increased disease prevalence in Black and Asian children relative to White children, with conflicting data for Hispanic children. The methodology behind many of these existing studies, however, is somewhat questionable. Many were survey-based studies asking parents to remember a diagnosis of eczema or even asking parents to just report an itchy rash and using that as a diagnosis.”
For the current study, Dr. Monir and colleagues reviewed the records of 4,016 infants born between June 1, 2011, and April 30, 2017, who were followed in the University of Florida’s health care system. The researchers defined this as having two or more well-child visits after birth and at least one visit at 300 days of life or later, and the used documentation of specific ICD-9 or ICD-10 codes to capture an objective diagnosis of atopic dermatitis (AD). Of the 4,016 patients, 39.2% were Black, 38.5% were White, 7.1% were Hispanic, 5.3% were Asian, 6.5% were from other racial backgrounds, and 3.4% were multiracial.
Dr. Monir, who is a resident in the department of dermatology at the University of Florida, Gainesville, reported that Black infants had the highest prevalence of AD at 37%, followed by Asian infants (25.8%), Hispanic infants (24.1%), multiracial infants (23%), infants from other racial backgrounds (19.1%), and non-Hispanic White infants (17.9%). Compared with White infants, the odds ratio estimates for AD was highest for Black infants (OR, 2.62), followed by Asian infants (OR, 1.55), multiracial infants (OR, 1.42), Hispanic infants (OR, 1.41), and infants from other racial backgrounds (OR, .97).
On unadjusted analysis, the following factors were significantly associated with race: delivery mode (P = .006), insurance type (P less than .001), NICU stay (P less than .001), and gestational age (P less than .0001). However, on multivariate logistic regression, only two factors were significantly associated with the diagnosis of AD: race (P less than .0001) and NICU stay (P = .0385).
“When we looked at the early childhood period specifically, we found striking racial differences in the rates of AD arising early in life,” Dr. Monir concluded. “The diagnosis was independently associated with race and NICU stay. We suggest that further investigation into these disparities and ways we can mitigate them should focus on this early childhood period.”
The researchers reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
FROM SPD 2020