User login
1. A 23-year-old man is brought in after being hit by a car. There is a moderate amount of soft tissue swelling around the knee, with limited flexion and extension due to pain. He can wiggle his toes, and there appears to be no neurovascular compromise.
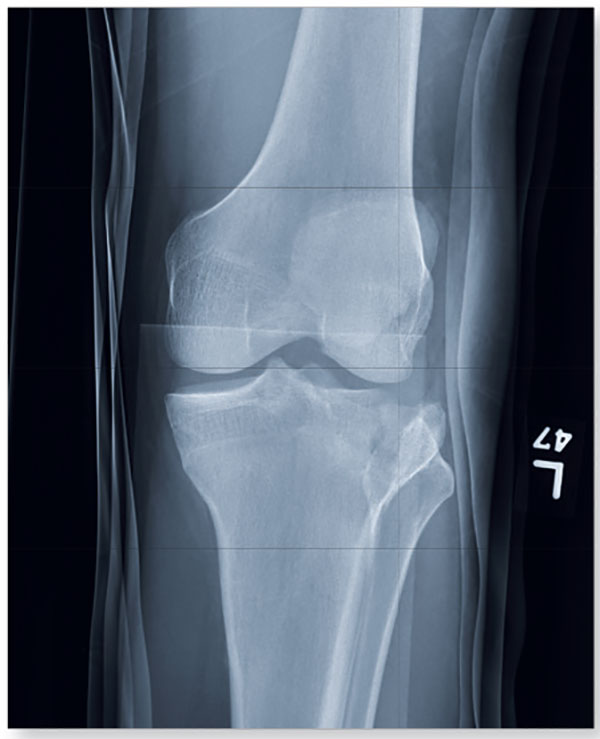
Diagnosis: The image shows a comminuted and depressed fracture of the lateral tibial plateau. It is depressed approximately 6 to 7 mm. The patient was admitted, and orthopedic consultation was obtained. The patient subsequently underwent an open reduction and internal fixation of the fracture.
For more information, see “Clipped by an Oncoming Car.” Clinician Reviews. 2014;24(6):23,36.
2. A 20-year-old man presents after his car was broadsided by another vehicle. His air bag deployed, and the patient now complains of right-sided chest wall pain and right knee pain. Inspection of his right knee shows some joint deformity, with mild swelling and moderate tenderness. The patient is unable to perform flexion with his right knee. Good distal pulses are present, and sensation is intact.
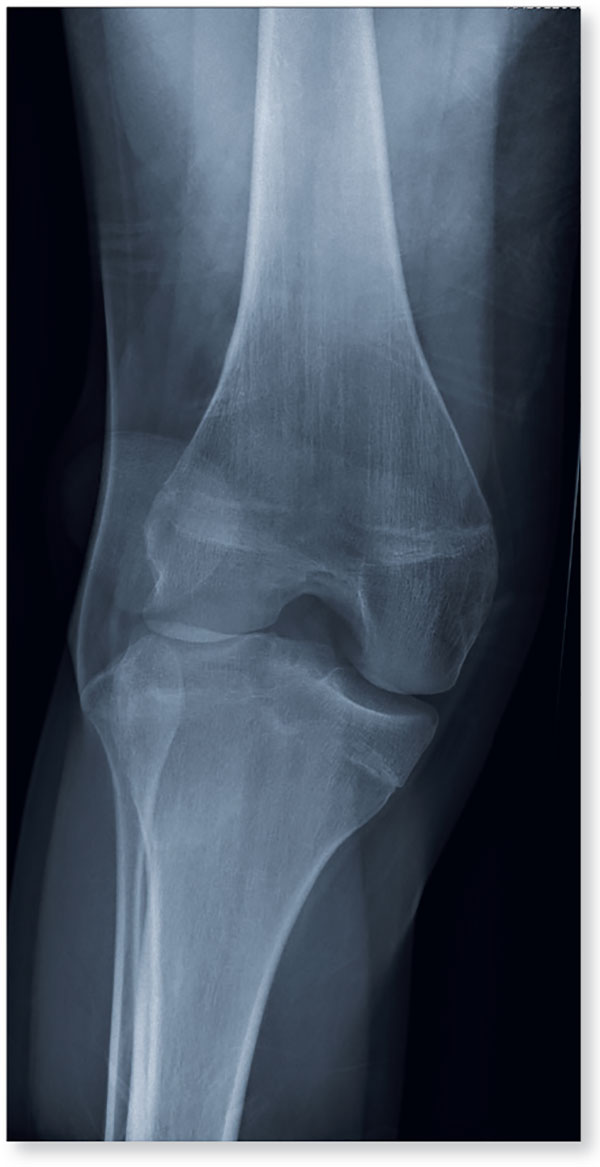
Diagnosis: The radiograph demonstrates lateral dislocation of the patella, with no evidence of an acute fracture in any surrounding bones. The patella was easily reduced in the emergency department, and the patient was placed in a knee immobilizer. Orthopedic consultation was obtained.
For more information, see “Chest Wall and Knee Pain Following Motor Vehicle Collision.” Clinician Reviews. 2013;23(1):8.
3. A 70-year-old woman presents for evaluation of right knee pain secondary to a fall. When she tripped and fell, all her weight landed on her right knee; she says it is now “extremely painful” to bear weight on that leg. Inspection of her right knee shows no obvious deformity, but a moderate amount of swelling and limited range of motion. She also has moderate tenderness circumferentially around the knee. There is additional swelling and mild bruising on both the medial and lateral aspects of the right ankle.

Diagnosis: The radiograph has several findings, one of which is a nondisplaced proximal fibula fracture. In addition, there is a moderate suprapatellar joint effusion. The patient also has fairly advanced tricompartment degenerative arthrosis. (To review, the tricompartment comprises all three anatomic areas of the knee: the patellofemoral, lateral tibiofemoral, and medial tibiofemoral joints.) The patient was placed in a knee immobilizer, and orthopedic evaluation was coordinated.
For more information, see “In Middle of Trip, Woman Falls.” Clinician Reviews. 2016;26(6):20,53.
4. A 28-year-old man is brought to you by EMS for evaluation after a motor vehicle accident. The patient was an unrestrained driver in a truck that went off the road into a ditch. The paramedics state that he was partially ejected, with his left leg caught in the window. He complains of back and left leg pain. Primary survey shows no obvious injury. Secondary survey reveals moderate swelling and decreased range of motion in the left knee. Good distal pulses are present.
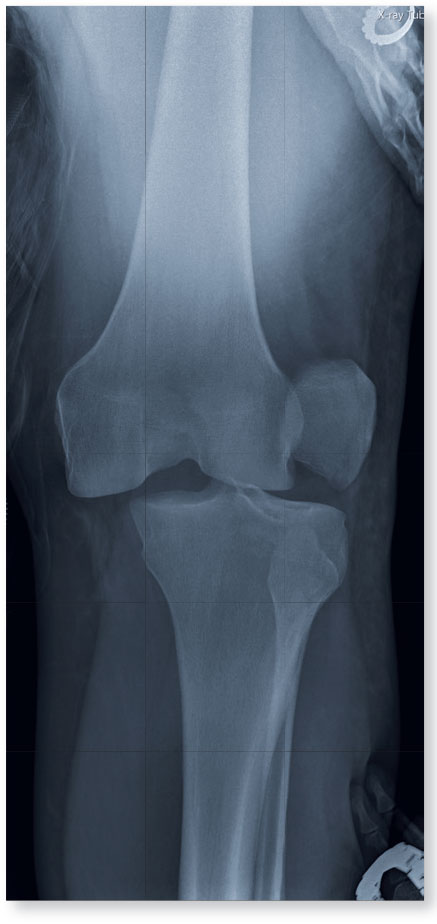
Diagnosis: The radiograph shows that the distal femur is medially dislocated relative to the tibial plateau. In addition, the patella is laterally dislocated. No obvious fractures are evident. Such injuries are typically associated with significant ligament injuries, especially of the medial collateral ligament (MCL), lateral collateral ligament (LCL), and anterior cruciate ligament (ACL). Orthopedics was consulted for reduction of the dislocation and further workup (including MRI of the knee).
For more information, see “Driver Partially Ejected From Vehicle.” Clinician Reviews. 2015;25(7):20,27.
1. A 23-year-old man is brought in after being hit by a car. There is a moderate amount of soft tissue swelling around the knee, with limited flexion and extension due to pain. He can wiggle his toes, and there appears to be no neurovascular compromise.

Diagnosis: The image shows a comminuted and depressed fracture of the lateral tibial plateau. It is depressed approximately 6 to 7 mm. The patient was admitted, and orthopedic consultation was obtained. The patient subsequently underwent an open reduction and internal fixation of the fracture.
For more information, see “Clipped by an Oncoming Car.” Clinician Reviews. 2014;24(6):23,36.
2. A 20-year-old man presents after his car was broadsided by another vehicle. His air bag deployed, and the patient now complains of right-sided chest wall pain and right knee pain. Inspection of his right knee shows some joint deformity, with mild swelling and moderate tenderness. The patient is unable to perform flexion with his right knee. Good distal pulses are present, and sensation is intact.

Diagnosis: The radiograph demonstrates lateral dislocation of the patella, with no evidence of an acute fracture in any surrounding bones. The patella was easily reduced in the emergency department, and the patient was placed in a knee immobilizer. Orthopedic consultation was obtained.
For more information, see “Chest Wall and Knee Pain Following Motor Vehicle Collision.” Clinician Reviews. 2013;23(1):8.
3. A 70-year-old woman presents for evaluation of right knee pain secondary to a fall. When she tripped and fell, all her weight landed on her right knee; she says it is now “extremely painful” to bear weight on that leg. Inspection of her right knee shows no obvious deformity, but a moderate amount of swelling and limited range of motion. She also has moderate tenderness circumferentially around the knee. There is additional swelling and mild bruising on both the medial and lateral aspects of the right ankle.

Diagnosis: The radiograph has several findings, one of which is a nondisplaced proximal fibula fracture. In addition, there is a moderate suprapatellar joint effusion. The patient also has fairly advanced tricompartment degenerative arthrosis. (To review, the tricompartment comprises all three anatomic areas of the knee: the patellofemoral, lateral tibiofemoral, and medial tibiofemoral joints.) The patient was placed in a knee immobilizer, and orthopedic evaluation was coordinated.
For more information, see “In Middle of Trip, Woman Falls.” Clinician Reviews. 2016;26(6):20,53.
4. A 28-year-old man is brought to you by EMS for evaluation after a motor vehicle accident. The patient was an unrestrained driver in a truck that went off the road into a ditch. The paramedics state that he was partially ejected, with his left leg caught in the window. He complains of back and left leg pain. Primary survey shows no obvious injury. Secondary survey reveals moderate swelling and decreased range of motion in the left knee. Good distal pulses are present.

Diagnosis: The radiograph shows that the distal femur is medially dislocated relative to the tibial plateau. In addition, the patella is laterally dislocated. No obvious fractures are evident. Such injuries are typically associated with significant ligament injuries, especially of the medial collateral ligament (MCL), lateral collateral ligament (LCL), and anterior cruciate ligament (ACL). Orthopedics was consulted for reduction of the dislocation and further workup (including MRI of the knee).
For more information, see “Driver Partially Ejected From Vehicle.” Clinician Reviews. 2015;25(7):20,27.
1. A 23-year-old man is brought in after being hit by a car. There is a moderate amount of soft tissue swelling around the knee, with limited flexion and extension due to pain. He can wiggle his toes, and there appears to be no neurovascular compromise.

Diagnosis: The image shows a comminuted and depressed fracture of the lateral tibial plateau. It is depressed approximately 6 to 7 mm. The patient was admitted, and orthopedic consultation was obtained. The patient subsequently underwent an open reduction and internal fixation of the fracture.
For more information, see “Clipped by an Oncoming Car.” Clinician Reviews. 2014;24(6):23,36.
2. A 20-year-old man presents after his car was broadsided by another vehicle. His air bag deployed, and the patient now complains of right-sided chest wall pain and right knee pain. Inspection of his right knee shows some joint deformity, with mild swelling and moderate tenderness. The patient is unable to perform flexion with his right knee. Good distal pulses are present, and sensation is intact.

Diagnosis: The radiograph demonstrates lateral dislocation of the patella, with no evidence of an acute fracture in any surrounding bones. The patella was easily reduced in the emergency department, and the patient was placed in a knee immobilizer. Orthopedic consultation was obtained.
For more information, see “Chest Wall and Knee Pain Following Motor Vehicle Collision.” Clinician Reviews. 2013;23(1):8.
3. A 70-year-old woman presents for evaluation of right knee pain secondary to a fall. When she tripped and fell, all her weight landed on her right knee; she says it is now “extremely painful” to bear weight on that leg. Inspection of her right knee shows no obvious deformity, but a moderate amount of swelling and limited range of motion. She also has moderate tenderness circumferentially around the knee. There is additional swelling and mild bruising on both the medial and lateral aspects of the right ankle.

Diagnosis: The radiograph has several findings, one of which is a nondisplaced proximal fibula fracture. In addition, there is a moderate suprapatellar joint effusion. The patient also has fairly advanced tricompartment degenerative arthrosis. (To review, the tricompartment comprises all three anatomic areas of the knee: the patellofemoral, lateral tibiofemoral, and medial tibiofemoral joints.) The patient was placed in a knee immobilizer, and orthopedic evaluation was coordinated.
For more information, see “In Middle of Trip, Woman Falls.” Clinician Reviews. 2016;26(6):20,53.
4. A 28-year-old man is brought to you by EMS for evaluation after a motor vehicle accident. The patient was an unrestrained driver in a truck that went off the road into a ditch. The paramedics state that he was partially ejected, with his left leg caught in the window. He complains of back and left leg pain. Primary survey shows no obvious injury. Secondary survey reveals moderate swelling and decreased range of motion in the left knee. Good distal pulses are present.

Diagnosis: The radiograph shows that the distal femur is medially dislocated relative to the tibial plateau. In addition, the patella is laterally dislocated. No obvious fractures are evident. Such injuries are typically associated with significant ligament injuries, especially of the medial collateral ligament (MCL), lateral collateral ligament (LCL), and anterior cruciate ligament (ACL). Orthopedics was consulted for reduction of the dislocation and further workup (including MRI of the knee).
For more information, see “Driver Partially Ejected From Vehicle.” Clinician Reviews. 2015;25(7):20,27.