User login
Three beta-blockers—carvedilol, metoprolol, and bisoprolol—reduce mortality in chronic heart failure caused by left ventricular systolic dysfunction, when used in addition to diuretics and angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors (strength of recommendation [SOR]: A, based on large randomized placebo-controlled trials). No differences in mortality or patient tolerance have been demonstrated in studies comparing carvedilol and metoprolol (SOR: B, based on small head-to-head trials).
Evidence summary
The Table shows the 5 largest trials of beta-blockers in systolic dysfunction, including patients with both ischemic and nonischemic heart disease. In all trials, the majority of subjects were taking diuretics and either an ACE inhibitor or angiotensin receptor blocker.
The Carvedilol Prospective Randomized Cumulative Survival2 (COPERNICUS) trial, Metoprolol CR/XL Randomized Intervention Trial in Heart Failure3 (MERIT-HF), and Cardiac Insufficiency Bisoprolol Study II4 (CIBIS-II) all showed similar reductions in mortality in moderately ill patients with heart failure.
In contrast, the Beta-Blocker Evaluation of Survival Trial5 (BEST) demonstrated no effect with bucindolol. This suggests there may be differences in effectiveness among beta-blockers in reducing mortality in heart failure, and that it would be unwise to assume that protection is a class effect. We found no meta-analysis that pooled data on individual drugs for comparison purposes.
The US Carvedilol trial1 demonstrated a larger reduction in mortality than that seen in other beta-blocker trials. However, it had several methodologic problems: it was a composite of 4 smaller studies that used exercise tolerance as the primary endpoint; median duration of data collection on subjects was only 6 months; it included many minimally symptomatic patients; the actual number of deaths was small (producing a wide confidence interval); and subjects who did not survive the run-in phase were excluded from analysis.6
Three randomized controlled trials have compared carvedilol and metoprolol head-to-head. The largest7 included 150 subjects with ejection fractions below 35% who were randomized to 1 of the 2 drugs and followed for more than 3 years. Symptom scores and quality of life assessments were similar in the 2 groups. A trend toward lower mortality in the carvedilol group did not reach statistical significance. Peak oxygen uptake during exercise was greater in the metoprolol group. The carvedilol group had a statistically greater improvement in ejection fraction (+10.9 ± 11.0 vs +7.2 ± 7.7 at rest). The Carvedilol or Metoprolol European Trial (COMET), a larger head-to-head trial of carvedilol and metoprolol (N=3029), is ongoing.8
No large studies of older beta-blockers adequately assess mortality in heart failure. One study of propranolol (N=158) showed a 27% reduction in mortality in mild heart failure in the setting of ischemic heart disease.9 A study of atenolol versus placebo in subjects with ejection fraction ≤25% from various causes (N=100) was halted early when atenolol produced a 50% reduction in worsening heart failure and a 71% reduction in cardiac hospitalizations.10 A trend toward improved survival was noted but did not reach statistical significance.
TABLE
Selected trials of beta-blockers for systolic dysfunction
| Study | Drug | N | Mortality reduction (%) | 95% CI (%) | Statistically significant? | NNT | Mean duration of follow-up (months) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| US Carvedilol1 | Carvedilol | 1094 | (65) | 39–80 | Yes | 22 | 6.5 |
| COPERNICUS2 | Carvedilol | 2289 | (35) | 19–48 | Yes | 14 | 10.4 |
| MERIT-HF3 | Metoprolol | 3991 | (34) | 19–46 | Yes | 26 | 12 |
| CIBIS II4 | Bisoprolol | 2647 | (34) | 19–47 | Yes | 18 | 15.6 |
| BEST5 | Bucindolol | 2708 | (9) | –0.2–22 | No | — | 24 |
| CI, confidence interval; NNT, number needed to treat | |||||||
Recommendations from others
We found no guidelines that specifically endorsed one beta-blocker over another for heart failure.
Fred Grover, Jr, MD
University of Colorado Health Sciences Center, Denver
To provide the best care, we must go beyond the conventional ACE inhibitor and diuretic therapy for congestive heart failure patients. Adding 1 of the 3 beta-blockers (carvedilol, metoprolol, or bisoprolol), as recommended above, will further improve the survival rates and decrease hospitalization rates.
Remember these pearls when using beta-blockers in congestive heart failure:
- Do not start therapy until the patient’s fluid status has been stable for at least 1 month
- Avoid using in patients with bronchospastic disease, symptomatic bradycardia, or advanced heart blockage
- Start with low doses and titrate up slowly as tolerated every 2 weeks to the recommended target range of the beta-blocker chosen
- Decrease the dose if significant bradycardia or atrioventricular block occurs
- Let your patients know that it may take several months of beta-blocker therapy to obtain the protective benefits.
If you encounter difficulties with titration or don’t feel comfortable initiating beta-blocker therapy, consult your cardiologist for help.
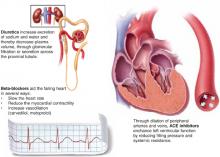
Chronic heart failure
Complementary actions of diuretics, ACE inhibitors, and beta blockers
Evidence shows that the combination of diuretics, ACE inhibitors, and 1 of 3 beta-blockers—carvedilol, metoprolol, bisoprolol—is more effective than just diuretics plus ACE inhibitors. The clinical effect of their combined actions is reduced workload on the failing heart.
1. Packer M, Bristow MR, Cohn JN, et al. The effect of carvedilol on morbidity and mortality in patients with chronic heart failure. U.S. Carvedilol Heart Failure Study Group. N Engl J Med 1996;334:1349-1355.
2. Packer M, Coats AJS, Fowler MB, et al. Effect of carvedilol on survival in severe chronic heart failure. N Engl J Med 2001;344:1651-1658.
3. Effect of metoprolol CR/XL in chronic heart failure: Metotprolol CR/XL Randomized Intervention Trial in Congestive Heart Failure (MERIT-HF). Lancet 1999;353:2001-2007.
4. The Cardiac Insufficiency Bisoprolol Study II (CIBIS-II): a randomised trial. Lancet 1999;353:9-13.
5. A trial of the beta-blocker bucindolol in patients with advanced chronic heart failure. N Engl J Med 2001;344:1659-1667.
6. Hart SM. Influence of beta-blockers on mortality in chronic heart failure. Ann Pharmacother 2000;34:1440-1451.
7. Metra M, Giubbini Raffaele, Nodari E, Boldi E, Modena MG, Dei Cas L. Differential effects of beta-blockers in patients with heart failure: A prospective, randomized, double-blind comparison of the long-term effects of metoprolol versus carvedilol. Circulation 2000;102:546-551.
8. Poole-Wilson PA, Cleland JG, Di Lenarda A, et al. Rationale and design of the carvedilol or metoprolol European trail in patients with chronic heart failure: COMET. Eur J Heart Fail 2002;4:321-329.
9. Aronow WS, Ahn C, Kronzon AI. Effect of propranolol versus no propanolol on total mortality plus nonfatal myocardial infarction in older patients with prior myocardial infarction, congestive heart failure, and left ventricular ejection fraction ≥40% treated with diuretics plus angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors. Am J Cardiol 1997;80:207-209.
10. Sturm B, Pacher R, Strametz-Juranek J, et al. Effect of beta 1 blockade with atenolol on progression of heart failure in patients pretreated with high-dose enalapril. Eur J Heart Fail 2000;2:407-412.
Three beta-blockers—carvedilol, metoprolol, and bisoprolol—reduce mortality in chronic heart failure caused by left ventricular systolic dysfunction, when used in addition to diuretics and angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors (strength of recommendation [SOR]: A, based on large randomized placebo-controlled trials). No differences in mortality or patient tolerance have been demonstrated in studies comparing carvedilol and metoprolol (SOR: B, based on small head-to-head trials).
Evidence summary
The Table shows the 5 largest trials of beta-blockers in systolic dysfunction, including patients with both ischemic and nonischemic heart disease. In all trials, the majority of subjects were taking diuretics and either an ACE inhibitor or angiotensin receptor blocker.
The Carvedilol Prospective Randomized Cumulative Survival2 (COPERNICUS) trial, Metoprolol CR/XL Randomized Intervention Trial in Heart Failure3 (MERIT-HF), and Cardiac Insufficiency Bisoprolol Study II4 (CIBIS-II) all showed similar reductions in mortality in moderately ill patients with heart failure.
In contrast, the Beta-Blocker Evaluation of Survival Trial5 (BEST) demonstrated no effect with bucindolol. This suggests there may be differences in effectiveness among beta-blockers in reducing mortality in heart failure, and that it would be unwise to assume that protection is a class effect. We found no meta-analysis that pooled data on individual drugs for comparison purposes.
The US Carvedilol trial1 demonstrated a larger reduction in mortality than that seen in other beta-blocker trials. However, it had several methodologic problems: it was a composite of 4 smaller studies that used exercise tolerance as the primary endpoint; median duration of data collection on subjects was only 6 months; it included many minimally symptomatic patients; the actual number of deaths was small (producing a wide confidence interval); and subjects who did not survive the run-in phase were excluded from analysis.6
Three randomized controlled trials have compared carvedilol and metoprolol head-to-head. The largest7 included 150 subjects with ejection fractions below 35% who were randomized to 1 of the 2 drugs and followed for more than 3 years. Symptom scores and quality of life assessments were similar in the 2 groups. A trend toward lower mortality in the carvedilol group did not reach statistical significance. Peak oxygen uptake during exercise was greater in the metoprolol group. The carvedilol group had a statistically greater improvement in ejection fraction (+10.9 ± 11.0 vs +7.2 ± 7.7 at rest). The Carvedilol or Metoprolol European Trial (COMET), a larger head-to-head trial of carvedilol and metoprolol (N=3029), is ongoing.8
No large studies of older beta-blockers adequately assess mortality in heart failure. One study of propranolol (N=158) showed a 27% reduction in mortality in mild heart failure in the setting of ischemic heart disease.9 A study of atenolol versus placebo in subjects with ejection fraction ≤25% from various causes (N=100) was halted early when atenolol produced a 50% reduction in worsening heart failure and a 71% reduction in cardiac hospitalizations.10 A trend toward improved survival was noted but did not reach statistical significance.
TABLE
Selected trials of beta-blockers for systolic dysfunction
| Study | Drug | N | Mortality reduction (%) | 95% CI (%) | Statistically significant? | NNT | Mean duration of follow-up (months) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| US Carvedilol1 | Carvedilol | 1094 | (65) | 39–80 | Yes | 22 | 6.5 |
| COPERNICUS2 | Carvedilol | 2289 | (35) | 19–48 | Yes | 14 | 10.4 |
| MERIT-HF3 | Metoprolol | 3991 | (34) | 19–46 | Yes | 26 | 12 |
| CIBIS II4 | Bisoprolol | 2647 | (34) | 19–47 | Yes | 18 | 15.6 |
| BEST5 | Bucindolol | 2708 | (9) | –0.2–22 | No | — | 24 |
| CI, confidence interval; NNT, number needed to treat | |||||||
Recommendations from others
We found no guidelines that specifically endorsed one beta-blocker over another for heart failure.
Fred Grover, Jr, MD
University of Colorado Health Sciences Center, Denver
To provide the best care, we must go beyond the conventional ACE inhibitor and diuretic therapy for congestive heart failure patients. Adding 1 of the 3 beta-blockers (carvedilol, metoprolol, or bisoprolol), as recommended above, will further improve the survival rates and decrease hospitalization rates.
Remember these pearls when using beta-blockers in congestive heart failure:
- Do not start therapy until the patient’s fluid status has been stable for at least 1 month
- Avoid using in patients with bronchospastic disease, symptomatic bradycardia, or advanced heart blockage
- Start with low doses and titrate up slowly as tolerated every 2 weeks to the recommended target range of the beta-blocker chosen
- Decrease the dose if significant bradycardia or atrioventricular block occurs
- Let your patients know that it may take several months of beta-blocker therapy to obtain the protective benefits.
If you encounter difficulties with titration or don’t feel comfortable initiating beta-blocker therapy, consult your cardiologist for help.
Chronic heart failure
Complementary actions of diuretics, ACE inhibitors, and beta blockers
Evidence shows that the combination of diuretics, ACE inhibitors, and 1 of 3 beta-blockers—carvedilol, metoprolol, bisoprolol—is more effective than just diuretics plus ACE inhibitors. The clinical effect of their combined actions is reduced workload on the failing heart.
Three beta-blockers—carvedilol, metoprolol, and bisoprolol—reduce mortality in chronic heart failure caused by left ventricular systolic dysfunction, when used in addition to diuretics and angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors (strength of recommendation [SOR]: A, based on large randomized placebo-controlled trials). No differences in mortality or patient tolerance have been demonstrated in studies comparing carvedilol and metoprolol (SOR: B, based on small head-to-head trials).
Evidence summary
The Table shows the 5 largest trials of beta-blockers in systolic dysfunction, including patients with both ischemic and nonischemic heart disease. In all trials, the majority of subjects were taking diuretics and either an ACE inhibitor or angiotensin receptor blocker.
The Carvedilol Prospective Randomized Cumulative Survival2 (COPERNICUS) trial, Metoprolol CR/XL Randomized Intervention Trial in Heart Failure3 (MERIT-HF), and Cardiac Insufficiency Bisoprolol Study II4 (CIBIS-II) all showed similar reductions in mortality in moderately ill patients with heart failure.
In contrast, the Beta-Blocker Evaluation of Survival Trial5 (BEST) demonstrated no effect with bucindolol. This suggests there may be differences in effectiveness among beta-blockers in reducing mortality in heart failure, and that it would be unwise to assume that protection is a class effect. We found no meta-analysis that pooled data on individual drugs for comparison purposes.
The US Carvedilol trial1 demonstrated a larger reduction in mortality than that seen in other beta-blocker trials. However, it had several methodologic problems: it was a composite of 4 smaller studies that used exercise tolerance as the primary endpoint; median duration of data collection on subjects was only 6 months; it included many minimally symptomatic patients; the actual number of deaths was small (producing a wide confidence interval); and subjects who did not survive the run-in phase were excluded from analysis.6
Three randomized controlled trials have compared carvedilol and metoprolol head-to-head. The largest7 included 150 subjects with ejection fractions below 35% who were randomized to 1 of the 2 drugs and followed for more than 3 years. Symptom scores and quality of life assessments were similar in the 2 groups. A trend toward lower mortality in the carvedilol group did not reach statistical significance. Peak oxygen uptake during exercise was greater in the metoprolol group. The carvedilol group had a statistically greater improvement in ejection fraction (+10.9 ± 11.0 vs +7.2 ± 7.7 at rest). The Carvedilol or Metoprolol European Trial (COMET), a larger head-to-head trial of carvedilol and metoprolol (N=3029), is ongoing.8
No large studies of older beta-blockers adequately assess mortality in heart failure. One study of propranolol (N=158) showed a 27% reduction in mortality in mild heart failure in the setting of ischemic heart disease.9 A study of atenolol versus placebo in subjects with ejection fraction ≤25% from various causes (N=100) was halted early when atenolol produced a 50% reduction in worsening heart failure and a 71% reduction in cardiac hospitalizations.10 A trend toward improved survival was noted but did not reach statistical significance.
TABLE
Selected trials of beta-blockers for systolic dysfunction
| Study | Drug | N | Mortality reduction (%) | 95% CI (%) | Statistically significant? | NNT | Mean duration of follow-up (months) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| US Carvedilol1 | Carvedilol | 1094 | (65) | 39–80 | Yes | 22 | 6.5 |
| COPERNICUS2 | Carvedilol | 2289 | (35) | 19–48 | Yes | 14 | 10.4 |
| MERIT-HF3 | Metoprolol | 3991 | (34) | 19–46 | Yes | 26 | 12 |
| CIBIS II4 | Bisoprolol | 2647 | (34) | 19–47 | Yes | 18 | 15.6 |
| BEST5 | Bucindolol | 2708 | (9) | –0.2–22 | No | — | 24 |
| CI, confidence interval; NNT, number needed to treat | |||||||
Recommendations from others
We found no guidelines that specifically endorsed one beta-blocker over another for heart failure.
Fred Grover, Jr, MD
University of Colorado Health Sciences Center, Denver
To provide the best care, we must go beyond the conventional ACE inhibitor and diuretic therapy for congestive heart failure patients. Adding 1 of the 3 beta-blockers (carvedilol, metoprolol, or bisoprolol), as recommended above, will further improve the survival rates and decrease hospitalization rates.
Remember these pearls when using beta-blockers in congestive heart failure:
- Do not start therapy until the patient’s fluid status has been stable for at least 1 month
- Avoid using in patients with bronchospastic disease, symptomatic bradycardia, or advanced heart blockage
- Start with low doses and titrate up slowly as tolerated every 2 weeks to the recommended target range of the beta-blocker chosen
- Decrease the dose if significant bradycardia or atrioventricular block occurs
- Let your patients know that it may take several months of beta-blocker therapy to obtain the protective benefits.
If you encounter difficulties with titration or don’t feel comfortable initiating beta-blocker therapy, consult your cardiologist for help.
Chronic heart failure
Complementary actions of diuretics, ACE inhibitors, and beta blockers
Evidence shows that the combination of diuretics, ACE inhibitors, and 1 of 3 beta-blockers—carvedilol, metoprolol, bisoprolol—is more effective than just diuretics plus ACE inhibitors. The clinical effect of their combined actions is reduced workload on the failing heart.
1. Packer M, Bristow MR, Cohn JN, et al. The effect of carvedilol on morbidity and mortality in patients with chronic heart failure. U.S. Carvedilol Heart Failure Study Group. N Engl J Med 1996;334:1349-1355.
2. Packer M, Coats AJS, Fowler MB, et al. Effect of carvedilol on survival in severe chronic heart failure. N Engl J Med 2001;344:1651-1658.
3. Effect of metoprolol CR/XL in chronic heart failure: Metotprolol CR/XL Randomized Intervention Trial in Congestive Heart Failure (MERIT-HF). Lancet 1999;353:2001-2007.
4. The Cardiac Insufficiency Bisoprolol Study II (CIBIS-II): a randomised trial. Lancet 1999;353:9-13.
5. A trial of the beta-blocker bucindolol in patients with advanced chronic heart failure. N Engl J Med 2001;344:1659-1667.
6. Hart SM. Influence of beta-blockers on mortality in chronic heart failure. Ann Pharmacother 2000;34:1440-1451.
7. Metra M, Giubbini Raffaele, Nodari E, Boldi E, Modena MG, Dei Cas L. Differential effects of beta-blockers in patients with heart failure: A prospective, randomized, double-blind comparison of the long-term effects of metoprolol versus carvedilol. Circulation 2000;102:546-551.
8. Poole-Wilson PA, Cleland JG, Di Lenarda A, et al. Rationale and design of the carvedilol or metoprolol European trail in patients with chronic heart failure: COMET. Eur J Heart Fail 2002;4:321-329.
9. Aronow WS, Ahn C, Kronzon AI. Effect of propranolol versus no propanolol on total mortality plus nonfatal myocardial infarction in older patients with prior myocardial infarction, congestive heart failure, and left ventricular ejection fraction ≥40% treated with diuretics plus angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors. Am J Cardiol 1997;80:207-209.
10. Sturm B, Pacher R, Strametz-Juranek J, et al. Effect of beta 1 blockade with atenolol on progression of heart failure in patients pretreated with high-dose enalapril. Eur J Heart Fail 2000;2:407-412.
1. Packer M, Bristow MR, Cohn JN, et al. The effect of carvedilol on morbidity and mortality in patients with chronic heart failure. U.S. Carvedilol Heart Failure Study Group. N Engl J Med 1996;334:1349-1355.
2. Packer M, Coats AJS, Fowler MB, et al. Effect of carvedilol on survival in severe chronic heart failure. N Engl J Med 2001;344:1651-1658.
3. Effect of metoprolol CR/XL in chronic heart failure: Metotprolol CR/XL Randomized Intervention Trial in Congestive Heart Failure (MERIT-HF). Lancet 1999;353:2001-2007.
4. The Cardiac Insufficiency Bisoprolol Study II (CIBIS-II): a randomised trial. Lancet 1999;353:9-13.
5. A trial of the beta-blocker bucindolol in patients with advanced chronic heart failure. N Engl J Med 2001;344:1659-1667.
6. Hart SM. Influence of beta-blockers on mortality in chronic heart failure. Ann Pharmacother 2000;34:1440-1451.
7. Metra M, Giubbini Raffaele, Nodari E, Boldi E, Modena MG, Dei Cas L. Differential effects of beta-blockers in patients with heart failure: A prospective, randomized, double-blind comparison of the long-term effects of metoprolol versus carvedilol. Circulation 2000;102:546-551.
8. Poole-Wilson PA, Cleland JG, Di Lenarda A, et al. Rationale and design of the carvedilol or metoprolol European trail in patients with chronic heart failure: COMET. Eur J Heart Fail 2002;4:321-329.
9. Aronow WS, Ahn C, Kronzon AI. Effect of propranolol versus no propanolol on total mortality plus nonfatal myocardial infarction in older patients with prior myocardial infarction, congestive heart failure, and left ventricular ejection fraction ≥40% treated with diuretics plus angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors. Am J Cardiol 1997;80:207-209.
10. Sturm B, Pacher R, Strametz-Juranek J, et al. Effect of beta 1 blockade with atenolol on progression of heart failure in patients pretreated with high-dose enalapril. Eur J Heart Fail 2000;2:407-412.
Evidence-based answers from the Family Physicians Inquiries Network