User login
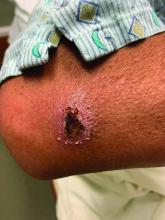
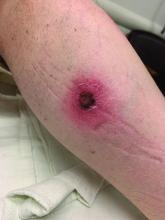
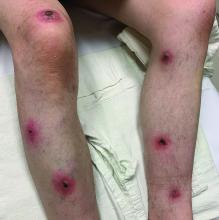
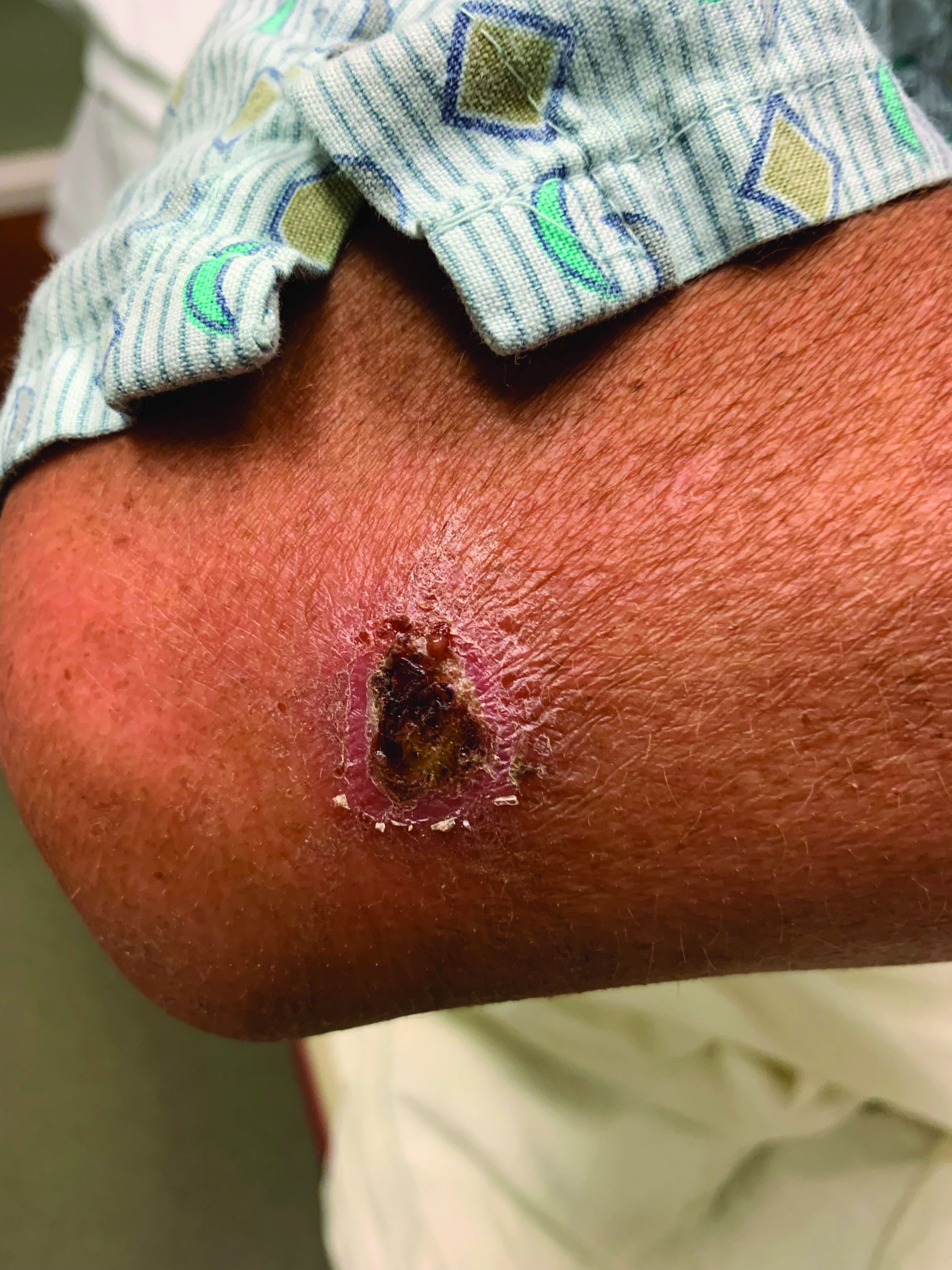
Coinfection of staphylococci and streptococci can make it more challenging to treat. Lesions typically begin as a vesicle that enlarges and forms an ulcer with a hemorrhagic crust. Even with treatment, the depth of the lesions may result in scarring. Shins and dorsal feet are nearly always involved. Systemic involvement is rare.
Open wounds, bites, or dermatoses are risk factors for the development of ecthyma. Additionally, poor hygiene and malnutrition play a major role in inoculation and severity of the disease. Poor hygiene may serve as the initiating factor for infection, but malnutrition permits further development because of the body’s inability to mount a sufficient immune response. Intravenous drug users and patients with HIV tend to be affected.
When diagnosing ecthyma, it is important to correlate clinical signs with a bacterial culture. This condition can be difficult to treat because of both coinfection and growing antibiotic resistance in staphylococcal and streptococcal species. Specifically, S. aureus has been found to be resistant to beta-lactam antibiotics for many years, with methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) being first detected in 1961. While a variety of antibiotics are indicated, the prescription should be tailored to cover the cultured organism.
Topical antibiotics are sufficient for more superficial lesions. Both topical and oral antibiotics may be recommended for ecthyma as the infection can spread more deeply into the skin, eventually causing a cellulitis. Treatment protocol for oral agents varies based on which drug is indicated. This patient was seen in the emergency room. His white blood cell count was elevated at 9 × 109/L. He was started empirically on amoxicillin/clavulanate (Augmentin) and ciprofloxacin. Bacterial cultures grew out Streptococcus pyogenes.
The case and photos were submitted by Lucas Shapiro, BS, Nova Southeastern University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Fort Lauderdale, Fla., and Susannah Berke, MD, Three Rivers Dermatology, Coraopolis, Pa. Dr. Bilu Martin edited the column. Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. Kwak Y et al. Infect Chemother. 2017 Dec;49(4):301-25.
2. Pereira LB. An Bras Dermatol. 2014 Mar-Apr;89(2):293-9.
3. Wasserzug O et al. Clin Infect Dis. 2009 May 1;48(9):1213-9.
Coinfection of staphylococci and streptococci can make it more challenging to treat. Lesions typically begin as a vesicle that enlarges and forms an ulcer with a hemorrhagic crust. Even with treatment, the depth of the lesions may result in scarring. Shins and dorsal feet are nearly always involved. Systemic involvement is rare.
Open wounds, bites, or dermatoses are risk factors for the development of ecthyma. Additionally, poor hygiene and malnutrition play a major role in inoculation and severity of the disease. Poor hygiene may serve as the initiating factor for infection, but malnutrition permits further development because of the body’s inability to mount a sufficient immune response. Intravenous drug users and patients with HIV tend to be affected.
When diagnosing ecthyma, it is important to correlate clinical signs with a bacterial culture. This condition can be difficult to treat because of both coinfection and growing antibiotic resistance in staphylococcal and streptococcal species. Specifically, S. aureus has been found to be resistant to beta-lactam antibiotics for many years, with methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) being first detected in 1961. While a variety of antibiotics are indicated, the prescription should be tailored to cover the cultured organism.
Topical antibiotics are sufficient for more superficial lesions. Both topical and oral antibiotics may be recommended for ecthyma as the infection can spread more deeply into the skin, eventually causing a cellulitis. Treatment protocol for oral agents varies based on which drug is indicated. This patient was seen in the emergency room. His white blood cell count was elevated at 9 × 109/L. He was started empirically on amoxicillin/clavulanate (Augmentin) and ciprofloxacin. Bacterial cultures grew out Streptococcus pyogenes.
The case and photos were submitted by Lucas Shapiro, BS, Nova Southeastern University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Fort Lauderdale, Fla., and Susannah Berke, MD, Three Rivers Dermatology, Coraopolis, Pa. Dr. Bilu Martin edited the column. Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. Kwak Y et al. Infect Chemother. 2017 Dec;49(4):301-25.
2. Pereira LB. An Bras Dermatol. 2014 Mar-Apr;89(2):293-9.
3. Wasserzug O et al. Clin Infect Dis. 2009 May 1;48(9):1213-9.
Coinfection of staphylococci and streptococci can make it more challenging to treat. Lesions typically begin as a vesicle that enlarges and forms an ulcer with a hemorrhagic crust. Even with treatment, the depth of the lesions may result in scarring. Shins and dorsal feet are nearly always involved. Systemic involvement is rare.
Open wounds, bites, or dermatoses are risk factors for the development of ecthyma. Additionally, poor hygiene and malnutrition play a major role in inoculation and severity of the disease. Poor hygiene may serve as the initiating factor for infection, but malnutrition permits further development because of the body’s inability to mount a sufficient immune response. Intravenous drug users and patients with HIV tend to be affected.
When diagnosing ecthyma, it is important to correlate clinical signs with a bacterial culture. This condition can be difficult to treat because of both coinfection and growing antibiotic resistance in staphylococcal and streptococcal species. Specifically, S. aureus has been found to be resistant to beta-lactam antibiotics for many years, with methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) being first detected in 1961. While a variety of antibiotics are indicated, the prescription should be tailored to cover the cultured organism.
Topical antibiotics are sufficient for more superficial lesions. Both topical and oral antibiotics may be recommended for ecthyma as the infection can spread more deeply into the skin, eventually causing a cellulitis. Treatment protocol for oral agents varies based on which drug is indicated. This patient was seen in the emergency room. His white blood cell count was elevated at 9 × 109/L. He was started empirically on amoxicillin/clavulanate (Augmentin) and ciprofloxacin. Bacterial cultures grew out Streptococcus pyogenes.
The case and photos were submitted by Lucas Shapiro, BS, Nova Southeastern University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Fort Lauderdale, Fla., and Susannah Berke, MD, Three Rivers Dermatology, Coraopolis, Pa. Dr. Bilu Martin edited the column. Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. Kwak Y et al. Infect Chemother. 2017 Dec;49(4):301-25.
2. Pereira LB. An Bras Dermatol. 2014 Mar-Apr;89(2):293-9.
3. Wasserzug O et al. Clin Infect Dis. 2009 May 1;48(9):1213-9.