User login
AVAHO
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]


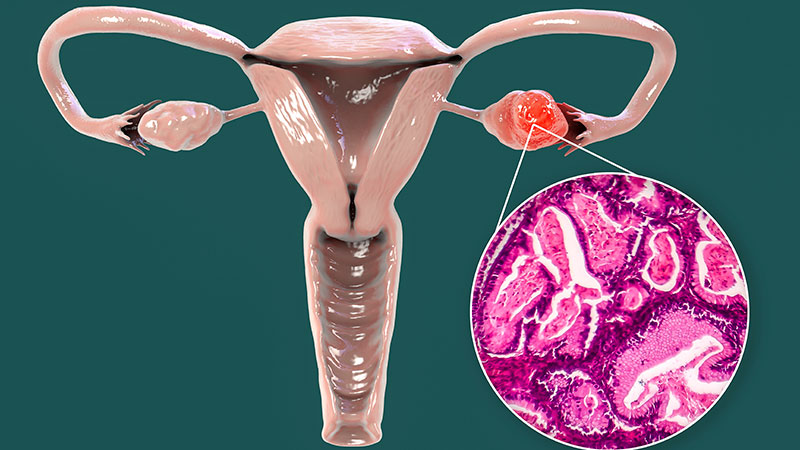
SBRT: A New Front-Runner in Treating Localized Renal Cell Carcinoma?
For patients with primary localized renal cell carcinoma (RCC), especially those who aren’t good candidates for surgery, noninvasive or minimally invasive ablative treatments have emerged as important options. These ablative treatments include radiofrequency ablation (RFA), microwave ablation, cryoablation, and the relative new-comer stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT).
But how do these approaches stack up against each other?
A recent meta-analysis published in Lancet Oncology found that SBRT appears to be equally safe and potentially more effective than other ablative treatment options for localized RCC.
“Our findings suggest that SBRT might offer a particularly advantageous option for treating larger renal cell carcinoma tumors, yielding the highest local control rates among ablative options with comparatively low rates of severe complications,” Srinivas Raman, MD, Department of Radiation Oncology, Princess Margaret Cancer Centre, Toronto, Ontario, Canada, and colleagues wrote.
Outside experts who spoke with Medscape Medical News said SBRT should likely play a larger role in the management of early-stage RCC.
“Given its noninvasive nature, favorable toxicity profile, and comparable renal outcomes, SBRT warrants broader adoption,” said Shankar Siva, PhD, MBBS, a radiation oncologist at the Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre and professor at the University of Melbourne, both in Melbourne, Australia.
This new analysis is “helpful as it provides reassurance and further strong quality data to present in multidisciplinary renal rounds and tumor boards to consider the use of SBRT as an alternative to other ablative technique,” said Joelle Helou, MD, MSc, radiation oncologist, Verspeeten Family Cancer Centre, and assistant professor, Department of Oncology, Western University, both in London, Ontario, Canada.
Filling a Knowledge Gap
RCC is the most common malignancy of the kidney, accounting for > 90% of all renal malignancies. Worldwide, the incidence of RCC has continued to rise, with a 2% annual rate of increase over the past two decades.
The conventional treatment of choice is radical or partial nephrectomy; however, not all patients are ideally suited for surgery, especially those who are older or have compromised kidney function or comorbid conditions.
Ablative therapies have been integrated into clinical guidelines as evidence-based interventions to treat primary RCC. These therapies include RFA and microwave ablation — two minimally invasive thermal ablation techniques that use heat to destroy the tumor tissue — and cryoablation, which uses extreme cold to destroy the tumor tissue.
Studies have generally found similar outcomes with RFA and microwave ablation, with the choice of treatment often guided by what’s available and operator expertise. The US and European guidelines recommend these treatments, particularly for smaller tumors (< 4 cm), citing their effectiveness and minimal invasiveness.
SBRT is a relatively new noninvasive option that delivers highly focused radiation doses to the tumor across multiple sessions and may be particularly suited to larger tumors (≥ 4 cm).
National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines state that SBRT may be considered for nonoptimal surgical candidates with stage I, II, or III kidney cancer.
However, comparative data on these four techniques has been limited until now.
What Did the Meta-Analysis Find?
Raman and colleagues performed a systematic review and meta-analysis pooled data from 133 studies involving 8910 patients (mean age, 68 years) with localized RCC treated with one of the four ablative therapies.
Overall, across the four ablative approaches, local control rates were very similar at 1 year, ranging from 95% for cryoablation to 99% for SBRT, and at 2 years, ranging from 94% for cryoablation to 97% for SBRT. At 5 years, however, there was a slightly greater separation in outcomes favoring SBRT (95%) and RFA (92%) compared with cryoablation (90%) and microwave ablation (86%).
Although all four techniques demonstrated similar local control for small tumors measuring < 4 cm, the approaches began to diverge for larger tumors measuring ≥ 4 cm at 1, 2, and 5 years. At 5 years, for instance, SBRT had the highest local control rate (93%), outperforming RFA (79%), microwave ablation (82%), and cryoablation (85%).
Looking at survival outcomes, cancer-specific survival was 100% at 1 year across all treatments. At 5 years, small differences in cancer-specific survival were observed. For smaller tumors, cancer-specific survival ranged from 100% for both SBRT and RFA to 97% for microwave ablation and 98% for cryoablation. For larger tumors, the cancer-specific survival rate was 100% for microwave ablation, 95% for SBRT, and 94% for cryoablation.
These small differences in cancer-specific survival likely reflect differences in patient and tumor characteristics across the treatment groups, the study authors said.
Notably, patients treated with SBRT were older than those treated with microwave ablation and RFA, while also having the largest tumors, which have consistently been shown to be associated with worse local control, greater propensity for regional and distant metastases, worse survival outcomes, and increased treatment-related toxicity, the authors explained.
There were no significant differences in the rate of grade 1-2 adverse events between the ablative methods, although grade 3-4 adverse events occurred in a significantly higher proportion of patients treated with cryoablation (3%) than in those who received RFA and SBRT (2%) or microwave ablation (1%). Baseline or change in renal function, as measured by estimated glomerular filtration rate, did not differ between the ablative techniques.
Overall, the findings reinforce that, although typically offered to older patients with worse baseline renal function and much larger tumors, “SBRT maintained high effectiveness at 1, 2, and 5 years compared to thermal ablation,” Siva told Medscape Medical News.
SBRT in Clinical Practice?
Despite the mounting evidence in favor of SBRT for primary localized RCC unsuitable for surgery, “there is still some reluctance from urologists, mainly, to refer patients for consideration of SBRT,” Helou told Medscape Medical News.
This hesitance is reflected in the meta-analysis, he noted, with SBRT being the least performed ablative therapy (612 patients). Cryoablation was the most common technique used in 3726 patients, followed by RFA (2503 patients) and microwave ablation (2069 patients).
The “compelling efficacy and safety data suggest SBRT should play a larger role in managing early-stage RCC in nonsurgical candidates, particularly for larger tumors where it offers excellent long-term local control,” said Siva, who led the phase 2 FASTTRACK II study evaluating SBRT in patients with inoperable or high-risk primary RCC.
Despite patients having larger than average tumors (4.6 cm) compared with those in many other trials, Siva and colleagues reported a 100% local control rate following SBRT and no patient deaths from cancer during the study period.
The FASTTRACK II study marked “an inflection point for SBRT, and [the approach] is now slowly getting traction,” Chad Tang, MD, radiation oncologist, MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, told Medscape Medical News.
Overall, Raman and colleagues said decisions about ablative therapy should be “precisely tailored to the individual patient’s clinical condition and treatment objectives.” Treatment selection should, for instance, depend on tumor size, location, patient comorbidities, availability of a technique, institutional and physician expertise, and patient preference.
Looking ahead, randomized controlled trials across larger patient populations are needed to further elucidate the long-term cancer and survival outcomes associated with these ablative treatments. Research comparing ablative methods with surgery and surveillance as well as exploring other relevant clinical outcomes, such as cost-effectiveness and quality of life, should be performed as well.
“Prospective randomized trials remain essential to further refine the position of SBRT in clinical practice in patients who are surgical candidates,” Siva told Medscape Medical News.
This research had no commercial funding. Raman reported receiving personal fees from AstraZeneca, Sanofi, Knight Pharmaceuticals, Verity Pharma, and Tersera, and grants from Knight Therapeutics, AstraZeneca, and Varian. Siva reported financial relationships with AstraZeneca and Telix Pharmaceuticals. Helou and Tang had no relevant disclosures.
For patients with primary localized renal cell carcinoma (RCC), especially those who aren’t good candidates for surgery, noninvasive or minimally invasive ablative treatments have emerged as important options. These ablative treatments include radiofrequency ablation (RFA), microwave ablation, cryoablation, and the relative new-comer stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT).
But how do these approaches stack up against each other?
A recent meta-analysis published in Lancet Oncology found that SBRT appears to be equally safe and potentially more effective than other ablative treatment options for localized RCC.
“Our findings suggest that SBRT might offer a particularly advantageous option for treating larger renal cell carcinoma tumors, yielding the highest local control rates among ablative options with comparatively low rates of severe complications,” Srinivas Raman, MD, Department of Radiation Oncology, Princess Margaret Cancer Centre, Toronto, Ontario, Canada, and colleagues wrote.
Outside experts who spoke with Medscape Medical News said SBRT should likely play a larger role in the management of early-stage RCC.
“Given its noninvasive nature, favorable toxicity profile, and comparable renal outcomes, SBRT warrants broader adoption,” said Shankar Siva, PhD, MBBS, a radiation oncologist at the Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre and professor at the University of Melbourne, both in Melbourne, Australia.
This new analysis is “helpful as it provides reassurance and further strong quality data to present in multidisciplinary renal rounds and tumor boards to consider the use of SBRT as an alternative to other ablative technique,” said Joelle Helou, MD, MSc, radiation oncologist, Verspeeten Family Cancer Centre, and assistant professor, Department of Oncology, Western University, both in London, Ontario, Canada.
Filling a Knowledge Gap
RCC is the most common malignancy of the kidney, accounting for > 90% of all renal malignancies. Worldwide, the incidence of RCC has continued to rise, with a 2% annual rate of increase over the past two decades.
The conventional treatment of choice is radical or partial nephrectomy; however, not all patients are ideally suited for surgery, especially those who are older or have compromised kidney function or comorbid conditions.
Ablative therapies have been integrated into clinical guidelines as evidence-based interventions to treat primary RCC. These therapies include RFA and microwave ablation — two minimally invasive thermal ablation techniques that use heat to destroy the tumor tissue — and cryoablation, which uses extreme cold to destroy the tumor tissue.
Studies have generally found similar outcomes with RFA and microwave ablation, with the choice of treatment often guided by what’s available and operator expertise. The US and European guidelines recommend these treatments, particularly for smaller tumors (< 4 cm), citing their effectiveness and minimal invasiveness.
SBRT is a relatively new noninvasive option that delivers highly focused radiation doses to the tumor across multiple sessions and may be particularly suited to larger tumors (≥ 4 cm).
National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines state that SBRT may be considered for nonoptimal surgical candidates with stage I, II, or III kidney cancer.
However, comparative data on these four techniques has been limited until now.
What Did the Meta-Analysis Find?
Raman and colleagues performed a systematic review and meta-analysis pooled data from 133 studies involving 8910 patients (mean age, 68 years) with localized RCC treated with one of the four ablative therapies.
Overall, across the four ablative approaches, local control rates were very similar at 1 year, ranging from 95% for cryoablation to 99% for SBRT, and at 2 years, ranging from 94% for cryoablation to 97% for SBRT. At 5 years, however, there was a slightly greater separation in outcomes favoring SBRT (95%) and RFA (92%) compared with cryoablation (90%) and microwave ablation (86%).
Although all four techniques demonstrated similar local control for small tumors measuring < 4 cm, the approaches began to diverge for larger tumors measuring ≥ 4 cm at 1, 2, and 5 years. At 5 years, for instance, SBRT had the highest local control rate (93%), outperforming RFA (79%), microwave ablation (82%), and cryoablation (85%).
Looking at survival outcomes, cancer-specific survival was 100% at 1 year across all treatments. At 5 years, small differences in cancer-specific survival were observed. For smaller tumors, cancer-specific survival ranged from 100% for both SBRT and RFA to 97% for microwave ablation and 98% for cryoablation. For larger tumors, the cancer-specific survival rate was 100% for microwave ablation, 95% for SBRT, and 94% for cryoablation.
These small differences in cancer-specific survival likely reflect differences in patient and tumor characteristics across the treatment groups, the study authors said.
Notably, patients treated with SBRT were older than those treated with microwave ablation and RFA, while also having the largest tumors, which have consistently been shown to be associated with worse local control, greater propensity for regional and distant metastases, worse survival outcomes, and increased treatment-related toxicity, the authors explained.
There were no significant differences in the rate of grade 1-2 adverse events between the ablative methods, although grade 3-4 adverse events occurred in a significantly higher proportion of patients treated with cryoablation (3%) than in those who received RFA and SBRT (2%) or microwave ablation (1%). Baseline or change in renal function, as measured by estimated glomerular filtration rate, did not differ between the ablative techniques.
Overall, the findings reinforce that, although typically offered to older patients with worse baseline renal function and much larger tumors, “SBRT maintained high effectiveness at 1, 2, and 5 years compared to thermal ablation,” Siva told Medscape Medical News.
SBRT in Clinical Practice?
Despite the mounting evidence in favor of SBRT for primary localized RCC unsuitable for surgery, “there is still some reluctance from urologists, mainly, to refer patients for consideration of SBRT,” Helou told Medscape Medical News.
This hesitance is reflected in the meta-analysis, he noted, with SBRT being the least performed ablative therapy (612 patients). Cryoablation was the most common technique used in 3726 patients, followed by RFA (2503 patients) and microwave ablation (2069 patients).
The “compelling efficacy and safety data suggest SBRT should play a larger role in managing early-stage RCC in nonsurgical candidates, particularly for larger tumors where it offers excellent long-term local control,” said Siva, who led the phase 2 FASTTRACK II study evaluating SBRT in patients with inoperable or high-risk primary RCC.
Despite patients having larger than average tumors (4.6 cm) compared with those in many other trials, Siva and colleagues reported a 100% local control rate following SBRT and no patient deaths from cancer during the study period.
The FASTTRACK II study marked “an inflection point for SBRT, and [the approach] is now slowly getting traction,” Chad Tang, MD, radiation oncologist, MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, told Medscape Medical News.
Overall, Raman and colleagues said decisions about ablative therapy should be “precisely tailored to the individual patient’s clinical condition and treatment objectives.” Treatment selection should, for instance, depend on tumor size, location, patient comorbidities, availability of a technique, institutional and physician expertise, and patient preference.
Looking ahead, randomized controlled trials across larger patient populations are needed to further elucidate the long-term cancer and survival outcomes associated with these ablative treatments. Research comparing ablative methods with surgery and surveillance as well as exploring other relevant clinical outcomes, such as cost-effectiveness and quality of life, should be performed as well.
“Prospective randomized trials remain essential to further refine the position of SBRT in clinical practice in patients who are surgical candidates,” Siva told Medscape Medical News.
This research had no commercial funding. Raman reported receiving personal fees from AstraZeneca, Sanofi, Knight Pharmaceuticals, Verity Pharma, and Tersera, and grants from Knight Therapeutics, AstraZeneca, and Varian. Siva reported financial relationships with AstraZeneca and Telix Pharmaceuticals. Helou and Tang had no relevant disclosures.
For patients with primary localized renal cell carcinoma (RCC), especially those who aren’t good candidates for surgery, noninvasive or minimally invasive ablative treatments have emerged as important options. These ablative treatments include radiofrequency ablation (RFA), microwave ablation, cryoablation, and the relative new-comer stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT).
But how do these approaches stack up against each other?
A recent meta-analysis published in Lancet Oncology found that SBRT appears to be equally safe and potentially more effective than other ablative treatment options for localized RCC.
“Our findings suggest that SBRT might offer a particularly advantageous option for treating larger renal cell carcinoma tumors, yielding the highest local control rates among ablative options with comparatively low rates of severe complications,” Srinivas Raman, MD, Department of Radiation Oncology, Princess Margaret Cancer Centre, Toronto, Ontario, Canada, and colleagues wrote.
Outside experts who spoke with Medscape Medical News said SBRT should likely play a larger role in the management of early-stage RCC.
“Given its noninvasive nature, favorable toxicity profile, and comparable renal outcomes, SBRT warrants broader adoption,” said Shankar Siva, PhD, MBBS, a radiation oncologist at the Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre and professor at the University of Melbourne, both in Melbourne, Australia.
This new analysis is “helpful as it provides reassurance and further strong quality data to present in multidisciplinary renal rounds and tumor boards to consider the use of SBRT as an alternative to other ablative technique,” said Joelle Helou, MD, MSc, radiation oncologist, Verspeeten Family Cancer Centre, and assistant professor, Department of Oncology, Western University, both in London, Ontario, Canada.
Filling a Knowledge Gap
RCC is the most common malignancy of the kidney, accounting for > 90% of all renal malignancies. Worldwide, the incidence of RCC has continued to rise, with a 2% annual rate of increase over the past two decades.
The conventional treatment of choice is radical or partial nephrectomy; however, not all patients are ideally suited for surgery, especially those who are older or have compromised kidney function or comorbid conditions.
Ablative therapies have been integrated into clinical guidelines as evidence-based interventions to treat primary RCC. These therapies include RFA and microwave ablation — two minimally invasive thermal ablation techniques that use heat to destroy the tumor tissue — and cryoablation, which uses extreme cold to destroy the tumor tissue.
Studies have generally found similar outcomes with RFA and microwave ablation, with the choice of treatment often guided by what’s available and operator expertise. The US and European guidelines recommend these treatments, particularly for smaller tumors (< 4 cm), citing their effectiveness and minimal invasiveness.
SBRT is a relatively new noninvasive option that delivers highly focused radiation doses to the tumor across multiple sessions and may be particularly suited to larger tumors (≥ 4 cm).
National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines state that SBRT may be considered for nonoptimal surgical candidates with stage I, II, or III kidney cancer.
However, comparative data on these four techniques has been limited until now.
What Did the Meta-Analysis Find?
Raman and colleagues performed a systematic review and meta-analysis pooled data from 133 studies involving 8910 patients (mean age, 68 years) with localized RCC treated with one of the four ablative therapies.
Overall, across the four ablative approaches, local control rates were very similar at 1 year, ranging from 95% for cryoablation to 99% for SBRT, and at 2 years, ranging from 94% for cryoablation to 97% for SBRT. At 5 years, however, there was a slightly greater separation in outcomes favoring SBRT (95%) and RFA (92%) compared with cryoablation (90%) and microwave ablation (86%).
Although all four techniques demonstrated similar local control for small tumors measuring < 4 cm, the approaches began to diverge for larger tumors measuring ≥ 4 cm at 1, 2, and 5 years. At 5 years, for instance, SBRT had the highest local control rate (93%), outperforming RFA (79%), microwave ablation (82%), and cryoablation (85%).
Looking at survival outcomes, cancer-specific survival was 100% at 1 year across all treatments. At 5 years, small differences in cancer-specific survival were observed. For smaller tumors, cancer-specific survival ranged from 100% for both SBRT and RFA to 97% for microwave ablation and 98% for cryoablation. For larger tumors, the cancer-specific survival rate was 100% for microwave ablation, 95% for SBRT, and 94% for cryoablation.
These small differences in cancer-specific survival likely reflect differences in patient and tumor characteristics across the treatment groups, the study authors said.
Notably, patients treated with SBRT were older than those treated with microwave ablation and RFA, while also having the largest tumors, which have consistently been shown to be associated with worse local control, greater propensity for regional and distant metastases, worse survival outcomes, and increased treatment-related toxicity, the authors explained.
There were no significant differences in the rate of grade 1-2 adverse events between the ablative methods, although grade 3-4 adverse events occurred in a significantly higher proportion of patients treated with cryoablation (3%) than in those who received RFA and SBRT (2%) or microwave ablation (1%). Baseline or change in renal function, as measured by estimated glomerular filtration rate, did not differ between the ablative techniques.
Overall, the findings reinforce that, although typically offered to older patients with worse baseline renal function and much larger tumors, “SBRT maintained high effectiveness at 1, 2, and 5 years compared to thermal ablation,” Siva told Medscape Medical News.
SBRT in Clinical Practice?
Despite the mounting evidence in favor of SBRT for primary localized RCC unsuitable for surgery, “there is still some reluctance from urologists, mainly, to refer patients for consideration of SBRT,” Helou told Medscape Medical News.
This hesitance is reflected in the meta-analysis, he noted, with SBRT being the least performed ablative therapy (612 patients). Cryoablation was the most common technique used in 3726 patients, followed by RFA (2503 patients) and microwave ablation (2069 patients).
The “compelling efficacy and safety data suggest SBRT should play a larger role in managing early-stage RCC in nonsurgical candidates, particularly for larger tumors where it offers excellent long-term local control,” said Siva, who led the phase 2 FASTTRACK II study evaluating SBRT in patients with inoperable or high-risk primary RCC.
Despite patients having larger than average tumors (4.6 cm) compared with those in many other trials, Siva and colleagues reported a 100% local control rate following SBRT and no patient deaths from cancer during the study period.
The FASTTRACK II study marked “an inflection point for SBRT, and [the approach] is now slowly getting traction,” Chad Tang, MD, radiation oncologist, MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, told Medscape Medical News.
Overall, Raman and colleagues said decisions about ablative therapy should be “precisely tailored to the individual patient’s clinical condition and treatment objectives.” Treatment selection should, for instance, depend on tumor size, location, patient comorbidities, availability of a technique, institutional and physician expertise, and patient preference.
Looking ahead, randomized controlled trials across larger patient populations are needed to further elucidate the long-term cancer and survival outcomes associated with these ablative treatments. Research comparing ablative methods with surgery and surveillance as well as exploring other relevant clinical outcomes, such as cost-effectiveness and quality of life, should be performed as well.
“Prospective randomized trials remain essential to further refine the position of SBRT in clinical practice in patients who are surgical candidates,” Siva told Medscape Medical News.
This research had no commercial funding. Raman reported receiving personal fees from AstraZeneca, Sanofi, Knight Pharmaceuticals, Verity Pharma, and Tersera, and grants from Knight Therapeutics, AstraZeneca, and Varian. Siva reported financial relationships with AstraZeneca and Telix Pharmaceuticals. Helou and Tang had no relevant disclosures.
PSA Screening in VA Patients After Age 70 Years
TOPLINE: Most men receiving care through the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) continue prostate-specific antigen (PSA) screening after aged 70 years despite low absolute risk for prostate cancer-specific mortality (PCSM), even among Black men in the healthiest quintile.
METHODOLOGY:
Researchers conducted a cohort study of 921,609 men aged 70 years receiving VHA care between 2008 and 2020, who had normal screening PSA values (< 4 ng/mL) between ages 65-69 years.
- Analysis included electronic health record data from VHA Corporate Data Warehouse, linked Medicare claims data, and VHA community care data.
- Investigators examined the value of PSA levels, race and ethnicity, and competing mortality in risk stratification for PCSM and mPCa using regression modeling.
TAKEAWAY:
The 10-year cumulative incidence of PCSM was 0.26% overall, with 95% of men having a 10-year risk < 0.73%, and higher baseline PSA levels associated with increased risk (0.79% for 3.00-3.99 ng/mL vs 0.10% for 0.20-0.99 ng/mL).
- Race and ethnicity showed modest association with PCSM risk: Black patients had a 0.79% risk of mPCa vs 0.38% for White patients. The risk of PCSM was 0.36% for Black patients vs 0.25% for White patients.
- Most patients (87%) continued PSA screening after age 70 years, with little variation by competing mortality risk or race and ethnicity.
- Low PSA (0.20-0.99 ng/mL) identified very low-risk populations with < 1% 10-year risk for prostate biopsy, clinically significant prostate cancer diagnosis, and treatment.
IN PRACTICE: "Our data suggest that a simple assessment of personal risk based on PSA values before age 70 years captures a large proportion of relevant prognostic information with respect to mPCa and PCSM risk ... Low PSA (0.20-0.99 ng/mL) was associated with very low PCSM and mPCa risk, even among the healthiest Black men," wrote the authors of the study.
SOURCE: The study was led by Alex K. Bryant,MD, MAS and the Veterans Affairs Center for Clinical Management Research in Ann Arbor. It was published online on February 14 in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS: According to the authors, any potential PCSM or mPCa reduction from continued PSA screening > age 70 years remains unproven due to lack of randomized trial data. The study relied on death certificates to define PCSM, which may have introduced misclassification error. Family history of prostate cancer was not included due to unreliable electronic medical record data availability. Additionally, veterans have higher comorbidity burdens than the general population and unique military-related environmental exposures, potentially limiting result generalizability.
DISCLOSURES: The study was supported by grants U01CA253915, PSOCA097186, R35CA274442, and R50CA221836 from the National Cancer Institute. Matthew J. Schipper, MD, reported receiving consulting fees from Innovative Analytics. Phoebe A. Tsao, MD, disclosed receiving grants from the Prostate Cancer Foundation outside the submitted work. Kristian D. Stensland, MD, reported receiving a grant from the National Institutes of Health during the conduct of the study.
TOPLINE: Most men receiving care through the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) continue prostate-specific antigen (PSA) screening after aged 70 years despite low absolute risk for prostate cancer-specific mortality (PCSM), even among Black men in the healthiest quintile.
METHODOLOGY:
Researchers conducted a cohort study of 921,609 men aged 70 years receiving VHA care between 2008 and 2020, who had normal screening PSA values (< 4 ng/mL) between ages 65-69 years.
- Analysis included electronic health record data from VHA Corporate Data Warehouse, linked Medicare claims data, and VHA community care data.
- Investigators examined the value of PSA levels, race and ethnicity, and competing mortality in risk stratification for PCSM and mPCa using regression modeling.
TAKEAWAY:
The 10-year cumulative incidence of PCSM was 0.26% overall, with 95% of men having a 10-year risk < 0.73%, and higher baseline PSA levels associated with increased risk (0.79% for 3.00-3.99 ng/mL vs 0.10% for 0.20-0.99 ng/mL).
- Race and ethnicity showed modest association with PCSM risk: Black patients had a 0.79% risk of mPCa vs 0.38% for White patients. The risk of PCSM was 0.36% for Black patients vs 0.25% for White patients.
- Most patients (87%) continued PSA screening after age 70 years, with little variation by competing mortality risk or race and ethnicity.
- Low PSA (0.20-0.99 ng/mL) identified very low-risk populations with < 1% 10-year risk for prostate biopsy, clinically significant prostate cancer diagnosis, and treatment.
IN PRACTICE: "Our data suggest that a simple assessment of personal risk based on PSA values before age 70 years captures a large proportion of relevant prognostic information with respect to mPCa and PCSM risk ... Low PSA (0.20-0.99 ng/mL) was associated with very low PCSM and mPCa risk, even among the healthiest Black men," wrote the authors of the study.
SOURCE: The study was led by Alex K. Bryant,MD, MAS and the Veterans Affairs Center for Clinical Management Research in Ann Arbor. It was published online on February 14 in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS: According to the authors, any potential PCSM or mPCa reduction from continued PSA screening > age 70 years remains unproven due to lack of randomized trial data. The study relied on death certificates to define PCSM, which may have introduced misclassification error. Family history of prostate cancer was not included due to unreliable electronic medical record data availability. Additionally, veterans have higher comorbidity burdens than the general population and unique military-related environmental exposures, potentially limiting result generalizability.
DISCLOSURES: The study was supported by grants U01CA253915, PSOCA097186, R35CA274442, and R50CA221836 from the National Cancer Institute. Matthew J. Schipper, MD, reported receiving consulting fees from Innovative Analytics. Phoebe A. Tsao, MD, disclosed receiving grants from the Prostate Cancer Foundation outside the submitted work. Kristian D. Stensland, MD, reported receiving a grant from the National Institutes of Health during the conduct of the study.
TOPLINE: Most men receiving care through the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) continue prostate-specific antigen (PSA) screening after aged 70 years despite low absolute risk for prostate cancer-specific mortality (PCSM), even among Black men in the healthiest quintile.
METHODOLOGY:
Researchers conducted a cohort study of 921,609 men aged 70 years receiving VHA care between 2008 and 2020, who had normal screening PSA values (< 4 ng/mL) between ages 65-69 years.
- Analysis included electronic health record data from VHA Corporate Data Warehouse, linked Medicare claims data, and VHA community care data.
- Investigators examined the value of PSA levels, race and ethnicity, and competing mortality in risk stratification for PCSM and mPCa using regression modeling.
TAKEAWAY:
The 10-year cumulative incidence of PCSM was 0.26% overall, with 95% of men having a 10-year risk < 0.73%, and higher baseline PSA levels associated with increased risk (0.79% for 3.00-3.99 ng/mL vs 0.10% for 0.20-0.99 ng/mL).
- Race and ethnicity showed modest association with PCSM risk: Black patients had a 0.79% risk of mPCa vs 0.38% for White patients. The risk of PCSM was 0.36% for Black patients vs 0.25% for White patients.
- Most patients (87%) continued PSA screening after age 70 years, with little variation by competing mortality risk or race and ethnicity.
- Low PSA (0.20-0.99 ng/mL) identified very low-risk populations with < 1% 10-year risk for prostate biopsy, clinically significant prostate cancer diagnosis, and treatment.
IN PRACTICE: "Our data suggest that a simple assessment of personal risk based on PSA values before age 70 years captures a large proportion of relevant prognostic information with respect to mPCa and PCSM risk ... Low PSA (0.20-0.99 ng/mL) was associated with very low PCSM and mPCa risk, even among the healthiest Black men," wrote the authors of the study.
SOURCE: The study was led by Alex K. Bryant,MD, MAS and the Veterans Affairs Center for Clinical Management Research in Ann Arbor. It was published online on February 14 in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS: According to the authors, any potential PCSM or mPCa reduction from continued PSA screening > age 70 years remains unproven due to lack of randomized trial data. The study relied on death certificates to define PCSM, which may have introduced misclassification error. Family history of prostate cancer was not included due to unreliable electronic medical record data availability. Additionally, veterans have higher comorbidity burdens than the general population and unique military-related environmental exposures, potentially limiting result generalizability.
DISCLOSURES: The study was supported by grants U01CA253915, PSOCA097186, R35CA274442, and R50CA221836 from the National Cancer Institute. Matthew J. Schipper, MD, reported receiving consulting fees from Innovative Analytics. Phoebe A. Tsao, MD, disclosed receiving grants from the Prostate Cancer Foundation outside the submitted work. Kristian D. Stensland, MD, reported receiving a grant from the National Institutes of Health during the conduct of the study.
No Racial Disparities in CVD Outcomes For VA Patients with Prostate Cancer Receiving ADT
TOPLINE: Veterans treated in the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) who had preexisting cardiometabolic disease and received androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) with radiation therapy developed major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) at 4 times the rate compared to those without cardiometabolic disease. Black and White veterans showed similar cardiovascular outcomes regardless of treatment type.
METHODOLOGY:
Researchers conducted a retrospective cohort study examining 39,580 veterans in the VHA system diagnosed with prostate cancer between 2000 and 2015, following them for a median of 9.6 years to assess time to MACE diagnosis.
- Analysis utilized a 1:1 propensity score matching process to compare outcomes between treatment types (ADT with radiation therapy vs radiation therapy alone) and racial groups (Black vs White men).
- Participants had a mean age of 65.9 years at diagnosis; 68% identified as White and 32% as Black, and 83% had stage 2 disease classified with 43.1% intermediate risk. Most lived in nonrural zip codes
- Primary outcome measure was time to MACE, defined as a composite of cardiovascular death, myocardial infarction, or ischemic stroke, with patients censored at non-cardiovascular death or study end.
TAKEAWAY:
Compared to those without CMD, the hazard ratio (HR) for MACE for men with preexisting CMD who received ADT was 4.2. Those receiving radiation alone had an HR of 2.5.
- Patients diagnosed between 2010 and 2015 showed significantly lower MACE rates compared to those diagnosed in 2000 to 2005: HR, 0.23; 95% CI, 0.08-0.71 for White patients; and HR, 0.23; 95% CI, 0.07-0.77 for Black patients.
- Multiple comorbidities were associated with doubled MACE risk (HR, 2.22; 95% CI, 1.08-4.59) compared to those without comorbidities.
- No significant differences in MACE rates were observed between Black and White veterans, regardless of treatment type.
IN PRACTICE: “Within the VHA, men treated with ADT + radiation therapy for prostate cancer do not appear to be at greater risk for MACE than those receiving radiation therapy alone. Black men have similar risk of MACE as White men, whether receiving radiation therapy alone or in combination with ADT," the authors wrote.
SOURCE: The study was led by Alexander R. Lucas, Virginia Commonwealth University School of Public Health in Richmond. It was published online on February 6 in Cardio-Oncology.
LIMITATIONS: According to the authors, the retrospective nature of the data may have limited their ability to detect MACE events occurring outside the VHA. Additionally, the study was limited to men who initiated ADT prior to radiation therapy, excluding those who had surgery or radiation before ADT. The researchers also note that the analysis did not compare outcomes between different types of ADT treatments, such as GnRH agonists vs antagonists, which may have different cardiovascular risk profiles.
DISCLOSURES: Alexander R. Lucas’s work was partly funded by grants 1KO1HL161419 and NRG FP00019789. Ashit K. Paul disclosed receiving honorarium for serving on scientific consultancy panels of SANOFI-Genzyme, Bayer, and Tempus & Cardinal Health. Additional disclosures are noted but not specified in the article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication
TOPLINE: Veterans treated in the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) who had preexisting cardiometabolic disease and received androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) with radiation therapy developed major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) at 4 times the rate compared to those without cardiometabolic disease. Black and White veterans showed similar cardiovascular outcomes regardless of treatment type.
METHODOLOGY:
Researchers conducted a retrospective cohort study examining 39,580 veterans in the VHA system diagnosed with prostate cancer between 2000 and 2015, following them for a median of 9.6 years to assess time to MACE diagnosis.
- Analysis utilized a 1:1 propensity score matching process to compare outcomes between treatment types (ADT with radiation therapy vs radiation therapy alone) and racial groups (Black vs White men).
- Participants had a mean age of 65.9 years at diagnosis; 68% identified as White and 32% as Black, and 83% had stage 2 disease classified with 43.1% intermediate risk. Most lived in nonrural zip codes
- Primary outcome measure was time to MACE, defined as a composite of cardiovascular death, myocardial infarction, or ischemic stroke, with patients censored at non-cardiovascular death or study end.
TAKEAWAY:
Compared to those without CMD, the hazard ratio (HR) for MACE for men with preexisting CMD who received ADT was 4.2. Those receiving radiation alone had an HR of 2.5.
- Patients diagnosed between 2010 and 2015 showed significantly lower MACE rates compared to those diagnosed in 2000 to 2005: HR, 0.23; 95% CI, 0.08-0.71 for White patients; and HR, 0.23; 95% CI, 0.07-0.77 for Black patients.
- Multiple comorbidities were associated with doubled MACE risk (HR, 2.22; 95% CI, 1.08-4.59) compared to those without comorbidities.
- No significant differences in MACE rates were observed between Black and White veterans, regardless of treatment type.
IN PRACTICE: “Within the VHA, men treated with ADT + radiation therapy for prostate cancer do not appear to be at greater risk for MACE than those receiving radiation therapy alone. Black men have similar risk of MACE as White men, whether receiving radiation therapy alone or in combination with ADT," the authors wrote.
SOURCE: The study was led by Alexander R. Lucas, Virginia Commonwealth University School of Public Health in Richmond. It was published online on February 6 in Cardio-Oncology.
LIMITATIONS: According to the authors, the retrospective nature of the data may have limited their ability to detect MACE events occurring outside the VHA. Additionally, the study was limited to men who initiated ADT prior to radiation therapy, excluding those who had surgery or radiation before ADT. The researchers also note that the analysis did not compare outcomes between different types of ADT treatments, such as GnRH agonists vs antagonists, which may have different cardiovascular risk profiles.
DISCLOSURES: Alexander R. Lucas’s work was partly funded by grants 1KO1HL161419 and NRG FP00019789. Ashit K. Paul disclosed receiving honorarium for serving on scientific consultancy panels of SANOFI-Genzyme, Bayer, and Tempus & Cardinal Health. Additional disclosures are noted but not specified in the article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication
TOPLINE: Veterans treated in the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) who had preexisting cardiometabolic disease and received androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) with radiation therapy developed major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) at 4 times the rate compared to those without cardiometabolic disease. Black and White veterans showed similar cardiovascular outcomes regardless of treatment type.
METHODOLOGY:
Researchers conducted a retrospective cohort study examining 39,580 veterans in the VHA system diagnosed with prostate cancer between 2000 and 2015, following them for a median of 9.6 years to assess time to MACE diagnosis.
- Analysis utilized a 1:1 propensity score matching process to compare outcomes between treatment types (ADT with radiation therapy vs radiation therapy alone) and racial groups (Black vs White men).
- Participants had a mean age of 65.9 years at diagnosis; 68% identified as White and 32% as Black, and 83% had stage 2 disease classified with 43.1% intermediate risk. Most lived in nonrural zip codes
- Primary outcome measure was time to MACE, defined as a composite of cardiovascular death, myocardial infarction, or ischemic stroke, with patients censored at non-cardiovascular death or study end.
TAKEAWAY:
Compared to those without CMD, the hazard ratio (HR) for MACE for men with preexisting CMD who received ADT was 4.2. Those receiving radiation alone had an HR of 2.5.
- Patients diagnosed between 2010 and 2015 showed significantly lower MACE rates compared to those diagnosed in 2000 to 2005: HR, 0.23; 95% CI, 0.08-0.71 for White patients; and HR, 0.23; 95% CI, 0.07-0.77 for Black patients.
- Multiple comorbidities were associated with doubled MACE risk (HR, 2.22; 95% CI, 1.08-4.59) compared to those without comorbidities.
- No significant differences in MACE rates were observed between Black and White veterans, regardless of treatment type.
IN PRACTICE: “Within the VHA, men treated with ADT + radiation therapy for prostate cancer do not appear to be at greater risk for MACE than those receiving radiation therapy alone. Black men have similar risk of MACE as White men, whether receiving radiation therapy alone or in combination with ADT," the authors wrote.
SOURCE: The study was led by Alexander R. Lucas, Virginia Commonwealth University School of Public Health in Richmond. It was published online on February 6 in Cardio-Oncology.
LIMITATIONS: According to the authors, the retrospective nature of the data may have limited their ability to detect MACE events occurring outside the VHA. Additionally, the study was limited to men who initiated ADT prior to radiation therapy, excluding those who had surgery or radiation before ADT. The researchers also note that the analysis did not compare outcomes between different types of ADT treatments, such as GnRH agonists vs antagonists, which may have different cardiovascular risk profiles.
DISCLOSURES: Alexander R. Lucas’s work was partly funded by grants 1KO1HL161419 and NRG FP00019789. Ashit K. Paul disclosed receiving honorarium for serving on scientific consultancy panels of SANOFI-Genzyme, Bayer, and Tempus & Cardinal Health. Additional disclosures are noted but not specified in the article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication
How Many Patients in Early Cancer Trials Get Drugs Ultimately Approved by FDA?
TOPLINE:
One in six patients in phase 2 cancer trials received treatments that were eventually approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), a new analysis found. This proportion increased to 1 in 5 when considering National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) off-label recommendations and decreased to about 1 in 11 for approved regimens considered to have a substantial clinical benefit.
METHODOLOGY:
- Patients enroll in phase 2 oncology trials seeking access to promising new treatments, but the risk-benefit assessments and the likelihood of receiving a therapy that ultimately gains FDA approval remain unclear. Previous research suggests that the odds are 1 in 83 patients for those enrolled in a phase 1 cancer trial.
- Researchers randomly selected 400 phase 2 cancer trials initiated between November 2012 and November 2015 (to give enough time for an approval to occur); these trials included more than 25,000 patients across 608 specific treatment cohorts testing 332 drugs.
- The primary endpoint was the proportion of patients enrolled in phase 2 trials who received a treatment regimen that later attained FDA approval — defined as the “therapeutic proportion.”
- A secondary endpoint was determining the therapeutic proportion based on the therapeutic value of drugs. The three benchmarks were FDA approval alone, FDA approval plus NCCN off-label recommendations, and FDA approval for drugs considered to have a substantial clinical benefit, based on the European Society for Medical Oncology-Magnitude of Clinical Benefit Scale (ESMO-MCBS).
TAKEAWAY:
- A total of 4045 patients received a treatment regimen that advanced to FDA approval, corresponding to a therapeutic proportion of 16.2%.
- The therapeutic proportion increased to 19.4% when considering NCCN off-label recommendations and decreased to 9.3% for FDA-approved regimens considered to have a substantial clinical benefit, based on the ESMO-MCBS.
- The proportion of patients who participated in a trial in which the drug-indication pairing went on to phase 3 testing was 32.5%.
- Enrollment in a trial featuring biomarker enrichment, an immunotherapy drug, a large phase 2 cohort, and a nonrandomized, industry-sponsored trial all showed a trend toward a higher therapeutic proportion.
IN PRACTICE:
“By entering a phase 2 trial, a patient has a one in six chance of receiving a treatment that will later be approved for their condition,” the authors wrote. “The proportions described here, when juxtaposed with those estimated previously for phase 1 trials, suggest a striking improvement for a patient’s therapeutic prospects. This suggests that phase 1 trials do a good job at protecting patients downstream from unsafe and ineffective cancer treatments.”
In an editorial accompanying the study, Howard S. Hochster, MD, of the Rutgers Cancer Institute in New Brunswick, New Jersey, suggested that the 16.2% therapeutic proportion reported may be understated. For instance, “if using the criterion of drugs that were FDA approved in any indication and dose, the proportion of patient benefit in these trials rises to 38%, with a 51% benefit rate considering inclusion in NCCN guidelines,” he wrote.
SOURCE:
This study, led by Charlotte Ouimet, MSc, Department of Equity, Ethics and Policy, McGill University School of Population and Global Health, Montréal, Québec, Canada, was published online in Journal of the National Cancer Institute.
LIMITATIONS:
The longitudinal design of this study required using a historical cohort of phase 2 clinical trials, which may not reflect current drug development patterns. This study was underpowered to determine trial characteristics that predicted higher therapeutic proportions. Furthermore, the exclusion of cytotoxic drugs from the analysis resulted in a somewhat restricted view of overall drug development.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. The authors reported having no relevant conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
One in six patients in phase 2 cancer trials received treatments that were eventually approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), a new analysis found. This proportion increased to 1 in 5 when considering National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) off-label recommendations and decreased to about 1 in 11 for approved regimens considered to have a substantial clinical benefit.
METHODOLOGY:
- Patients enroll in phase 2 oncology trials seeking access to promising new treatments, but the risk-benefit assessments and the likelihood of receiving a therapy that ultimately gains FDA approval remain unclear. Previous research suggests that the odds are 1 in 83 patients for those enrolled in a phase 1 cancer trial.
- Researchers randomly selected 400 phase 2 cancer trials initiated between November 2012 and November 2015 (to give enough time for an approval to occur); these trials included more than 25,000 patients across 608 specific treatment cohorts testing 332 drugs.
- The primary endpoint was the proportion of patients enrolled in phase 2 trials who received a treatment regimen that later attained FDA approval — defined as the “therapeutic proportion.”
- A secondary endpoint was determining the therapeutic proportion based on the therapeutic value of drugs. The three benchmarks were FDA approval alone, FDA approval plus NCCN off-label recommendations, and FDA approval for drugs considered to have a substantial clinical benefit, based on the European Society for Medical Oncology-Magnitude of Clinical Benefit Scale (ESMO-MCBS).
TAKEAWAY:
- A total of 4045 patients received a treatment regimen that advanced to FDA approval, corresponding to a therapeutic proportion of 16.2%.
- The therapeutic proportion increased to 19.4% when considering NCCN off-label recommendations and decreased to 9.3% for FDA-approved regimens considered to have a substantial clinical benefit, based on the ESMO-MCBS.
- The proportion of patients who participated in a trial in which the drug-indication pairing went on to phase 3 testing was 32.5%.
- Enrollment in a trial featuring biomarker enrichment, an immunotherapy drug, a large phase 2 cohort, and a nonrandomized, industry-sponsored trial all showed a trend toward a higher therapeutic proportion.
IN PRACTICE:
“By entering a phase 2 trial, a patient has a one in six chance of receiving a treatment that will later be approved for their condition,” the authors wrote. “The proportions described here, when juxtaposed with those estimated previously for phase 1 trials, suggest a striking improvement for a patient’s therapeutic prospects. This suggests that phase 1 trials do a good job at protecting patients downstream from unsafe and ineffective cancer treatments.”
In an editorial accompanying the study, Howard S. Hochster, MD, of the Rutgers Cancer Institute in New Brunswick, New Jersey, suggested that the 16.2% therapeutic proportion reported may be understated. For instance, “if using the criterion of drugs that were FDA approved in any indication and dose, the proportion of patient benefit in these trials rises to 38%, with a 51% benefit rate considering inclusion in NCCN guidelines,” he wrote.
SOURCE:
This study, led by Charlotte Ouimet, MSc, Department of Equity, Ethics and Policy, McGill University School of Population and Global Health, Montréal, Québec, Canada, was published online in Journal of the National Cancer Institute.
LIMITATIONS:
The longitudinal design of this study required using a historical cohort of phase 2 clinical trials, which may not reflect current drug development patterns. This study was underpowered to determine trial characteristics that predicted higher therapeutic proportions. Furthermore, the exclusion of cytotoxic drugs from the analysis resulted in a somewhat restricted view of overall drug development.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. The authors reported having no relevant conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
One in six patients in phase 2 cancer trials received treatments that were eventually approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), a new analysis found. This proportion increased to 1 in 5 when considering National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) off-label recommendations and decreased to about 1 in 11 for approved regimens considered to have a substantial clinical benefit.
METHODOLOGY:
- Patients enroll in phase 2 oncology trials seeking access to promising new treatments, but the risk-benefit assessments and the likelihood of receiving a therapy that ultimately gains FDA approval remain unclear. Previous research suggests that the odds are 1 in 83 patients for those enrolled in a phase 1 cancer trial.
- Researchers randomly selected 400 phase 2 cancer trials initiated between November 2012 and November 2015 (to give enough time for an approval to occur); these trials included more than 25,000 patients across 608 specific treatment cohorts testing 332 drugs.
- The primary endpoint was the proportion of patients enrolled in phase 2 trials who received a treatment regimen that later attained FDA approval — defined as the “therapeutic proportion.”
- A secondary endpoint was determining the therapeutic proportion based on the therapeutic value of drugs. The three benchmarks were FDA approval alone, FDA approval plus NCCN off-label recommendations, and FDA approval for drugs considered to have a substantial clinical benefit, based on the European Society for Medical Oncology-Magnitude of Clinical Benefit Scale (ESMO-MCBS).
TAKEAWAY:
- A total of 4045 patients received a treatment regimen that advanced to FDA approval, corresponding to a therapeutic proportion of 16.2%.
- The therapeutic proportion increased to 19.4% when considering NCCN off-label recommendations and decreased to 9.3% for FDA-approved regimens considered to have a substantial clinical benefit, based on the ESMO-MCBS.
- The proportion of patients who participated in a trial in which the drug-indication pairing went on to phase 3 testing was 32.5%.
- Enrollment in a trial featuring biomarker enrichment, an immunotherapy drug, a large phase 2 cohort, and a nonrandomized, industry-sponsored trial all showed a trend toward a higher therapeutic proportion.
IN PRACTICE:
“By entering a phase 2 trial, a patient has a one in six chance of receiving a treatment that will later be approved for their condition,” the authors wrote. “The proportions described here, when juxtaposed with those estimated previously for phase 1 trials, suggest a striking improvement for a patient’s therapeutic prospects. This suggests that phase 1 trials do a good job at protecting patients downstream from unsafe and ineffective cancer treatments.”
In an editorial accompanying the study, Howard S. Hochster, MD, of the Rutgers Cancer Institute in New Brunswick, New Jersey, suggested that the 16.2% therapeutic proportion reported may be understated. For instance, “if using the criterion of drugs that were FDA approved in any indication and dose, the proportion of patient benefit in these trials rises to 38%, with a 51% benefit rate considering inclusion in NCCN guidelines,” he wrote.
SOURCE:
This study, led by Charlotte Ouimet, MSc, Department of Equity, Ethics and Policy, McGill University School of Population and Global Health, Montréal, Québec, Canada, was published online in Journal of the National Cancer Institute.
LIMITATIONS:
The longitudinal design of this study required using a historical cohort of phase 2 clinical trials, which may not reflect current drug development patterns. This study was underpowered to determine trial characteristics that predicted higher therapeutic proportions. Furthermore, the exclusion of cytotoxic drugs from the analysis resulted in a somewhat restricted view of overall drug development.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. The authors reported having no relevant conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Open Clinical Trials for Patients With Prostate Cancer
The clinical trials listed below are open as of March 10, 2025; have ≥ 1 US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) medical center (VAMC) or US Department of Defense (DoD) military treatment facility location recruiting patients; and are focused on treatments for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). For additional information and full inclusion/exclusion criteria, please consult clinicaltrials.gov.
Actively Recruiting
Patient Decision-making About Precision Oncology in Veterans With Advanced Prostate Cancer
This clinical trial explores and implements methods to improve informed decision making (IDM) regarding precision oncology tests amongst veterans with prostate cancer that may have spread from where it first started to nearby tissue, lymph nodes, or distant parts of the body (advanced). Precision oncology, the use of germline genetic testing and tumor-based molecular assays to inform cancer care, has become an important aspect of evidence-based care for men with advanced prostate cancer. Veterans with metastatic castrate-resistant prostate cancer may not be carrying out IDM due to unmet decisional needs. An informed decision is a choice based on complete and accurate information. The information gained from this study will help researchers develop a decision support intervention (DSI) and implement the intervention. A DSI may serve as a valuable tool to reduce ongoing racial disparities in genetic testing and encourage enrollment to precision oncology trials.
ID: NCT05396872
Sponsor; Investigator; Collaborator: University of California, San Francisco; Daniel Kwon, MD; US Department of Defense VA Office of Research and Development; Madalina Macrea, MD, PhD
Location: San Francisco Veterans Affairs Medical Center, CA
Veterans Affairs Seamless Phase II/III Randomized Trial of STAndard Systemic theRapy With or Without PET-directed Local Therapy for Oligometastatic pRosTate Cancer (VA STARPORT)
This is a prospective, open-label, multi-center seamless phase II to phase III randomized clinical trial designed to compare SST with or without PET-directed local therapy in improving the castration-resistant prostate cancer-free survival (CRPC-free survival) for veterans with oligometastatic prostate cancer. Oligometastasis will be defined as 1-10 sites of metastatic disease based on the clinical determination of the LSI which incorporates all imaging, clinical, and pathologic data available.
ID: NCT04787744
Sponsor; Collaborator: VA Office of Research and Development; Abhishek Solanki, MD, MS VA Office of Research and Development; Madalina Macrea, MD, PhD
Location: 19 locations, including Edwards Hines Jr. VA Hospital, Hines, IL
The Prostate Cancer, Genetic Risk, and Equitable Screening Study (ProGRESS) (ProGRESS)
Prostate cancer is the most common non-skin cancer among veterans and the second leading cause of male cancer death. Current methods of screening men for prostate cancer are inaccurate and cannot identify which men do not have prostate cancer or have low-grade cases that will not cause harm and which men have significant prostate cancer needing treatment. False-positive screening tests can result in unnecessary prostate biopsies for men who do not need them. However, new genetic testing might help identify which men are at highest risk for prostate cancer. This study will examine whether a genetic test helps identify men at risk for significant prostate cancer while helping men who are at low risk for prostate cancer avoid unnecessary biopsies. If this genetic test proves beneficial, it will improve the way that health care providers screen male veterans for prostate cancer.
ID: NCT05926102
Sponsor; Collaborator: VA Office of Research and Development; Jason L. Vassy, MD, MPH VA Office of Research and Development; Madalina Macrea, MD, PhD
Location: VA Boston Healthcare System Jamaica Plain Campus, MA
A Single-Arm Phase II Study of Neoadjuvant Intensified Androgen Deprivation (Leuprolide and Abiraterone Acetate) in Combination With AKT Inhibition (Capivasertib) for High-Risk Localized Prostate Cancer With PTEN Loss (SNARE)
The purpose of this study is to learn about how an investigational drug intervention completed before doing prostate surgery (specifically, radical prostatectomy with lymph node dissection) may help in treatment of high risk localized prostate cancers that are most resistant to standard treatments. This is a phase II research study. For this study, capivasertib, the study drug, will be taken with intensified androgen deprivation drugs (iADT; abiraterone and leuprolide) prior to radical prostatectomy. This study drug treatment will be evaluated to see if it is effective in shrinking and destroying prostate cancer tumors prior to surgery and to further evaluate its safety prior to prostate cancer surgery.
ID: NCT05593497
Sponsor; Collaborator: VA Office of Research and Development; Ryan P. Kopp, MD VA Office of Research and Development; Madalina Macrea, MD, PhD
Location: 5 locations, including VA Portland Health Care System, OR
18F-Fluciclovine PET/CT Impact on Predicting Clinical Outcome of 177Lu-PSMA-617 Therapy in Patients With Prostate Cancer
This is a single-center, prospective, exploratory study. Patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) scheduled to undergo Lutetium labelled prostate-specific membrane antigen radioligand therapy (LuPSMA RLT) at the West Los Angeles VA (WLA-VA) will be imaged with a baseline F-18 fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography 18F-FDG PET/CT and a 18F-DCFPyL PET/CT (18F-DCFPyL (2-(3-{1-carboxy-5-[(6-18F-fluoro-pyridine-3-carbonyl)-amino]-pentyl}-ureido)-pentanedioic acid)positron emission tomography/computed tomography , as per standard of care in our institution. All patients further undergo eventual follow-up prostate-specific membrane antigen positron emission tomography (PSMA PET) after the 2nd, 4th, and 6th LuPSMA RLT cycle. In this prospective study, an18F-Fluciclovine positron emission tomography/computed tomography (Axumin PET/CT) will be additionally obtained at baseline (pre-LuPSMA RLT), and after the 2nd, 4th, 6th LuPSMA RLT cycles. Axumin PET/CT will be acquired within 7 days from the PSMA PET.
This study is open to veterans only.
ID: NCT06706921
Sponsor; Collaborator: VA Greater Los Angeles Healthcare System; Gholam Berenji, MD, Janake Wijesuriya, BS VA Office of Research and Development; Madalina Macrea, MD, PhD
Location: VA Greater Los Angeles Healthcare System, CA
High Dose Testosterone for ATM, CDK12 or CHEK2 Altered Prostate Cancers (VA-BAT)
This study will determine whether the presence of DNA repair deficiency in the form of alterations in the genes ATM, CDK12 or CHEK2 predicts for a high likelihood of responding to the use of intermittent high dose testosterone. This therapy may result in responses in tumors which are genetically unstable because of DNA repair deficiency and this is a prospective study to test that hypothesis.
ID: NCT05011383
Sponsor; Collaborator: VA Office of Research and Development; Robert B. Montgomery, MD VA Office of Research and Development; Madalina Macrea, MD, PhD
Location: 17 locations, including VA Puget Sound Health Care System, Seattle, WA
A Study of CHeckpoint Inhibitors in Men With prOgressive Metastatic Castrate Resistant Prostate Cancer Characterized by a Mismatch Repair Deficiency or Biallelic CDK12 Inactivation (CHOMP)
The primary objective is to assess the activity and efficacy of pembrolizumab, a checkpoint inhibitor, in veterans with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) characterized by either mismatch repair deficiency (dMMR) or biallelic inactivation of CDK12 (CDK12-/-). The secondary objectives involve determining the frequency with which dMMR and CDK12-/- occur in this patient population, as well as the effects of pembrolizumab on various clinical endpoints (time to PSA progression, maximal PSA response, time to initiation of alternative anti-neoplastic therapy, time to radiographic progression, overall survival, and safety and tolerability). Lastly, the study will compare the pre-treatment and at-progression metastatic tumor biopsies to investigate the molecular correlates of resistance and sensitivity to pembrolizumab via RNA-sequencing, exome-sequencing, selected protein analyses, and multiplexed immunofluorescence.
ID: NCT04104893
Sponsor; Investigator; Collaborator: VA Office of Research and Development; Matthew B. Rettig, MD; Merck Sharp & Dohme LLC VA Office of Research and Development; Madalina Macrea, MD, PhD
Location: 12 locations, including VA Greater Los Angeles Healthcare System, CA
Carboplatin or Olaparib for BRcA Deficient Prostate Cancer (COBRA)
This is an unblinded, randomized clinical study comparing the efficacy of DNA damaging chemotherapy using carboplatin, to standard of care therapy for patients who have metastatic castrate resistant prostate cancer. This trial will use olaparib or carboplatin as initial therapy with crossover to the alternate or second-line drug after first progression for patients with tumors containing BARD1, BRCA1, BRCA2, BRIP1, CHEK1, FANCL, PALB2, RAD51B, RAD51C, RAD51D, or RAD54L inactivating mutations.
Participants are randomized (1:1) and receive either carboplatin (AUC 5, IV) every 21 days, first or olaparib taken orally (300 mg), twice daily in 28-day cycles, until intolerance, complete response, or progression by Prostate Cancer Working Group 3 (PCWG3) criteria.
Participants then cross over from the first-line therapy to the second-line therapy with the opposite study medication and receive treatment to intolerance or progression (whichever is first). Enrolled participants will be allowed to crossover to second line therapy if they continue to meet initial eligibility criteria, and at least three weeks have elapsed since last administration of either carboplatin or olaparib. Throughout the study, safety and tolerability will be assessed. Progression will be evaluated with bone scan, CT of the abdomen/pelvis, or MRI and PSA as per PCWG3 criteria.
ID: NCT04038502
Sponsor; Collaborator: VA Office of Research and Development; Robert B. Montgomery, MD; Ryan Burri, MD; Phoebe Tsao, MD, MSc; Maneesh Jain, MD VA Office of Research and Development; Madalina Macrea, MD, PhD
Location: 17 locations, including VA Puget Sound Health Care System, Seattle, WA
The clinical trials listed below are open as of March 10, 2025; have ≥ 1 US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) medical center (VAMC) or US Department of Defense (DoD) military treatment facility location recruiting patients; and are focused on treatments for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). For additional information and full inclusion/exclusion criteria, please consult clinicaltrials.gov.
Actively Recruiting
Patient Decision-making About Precision Oncology in Veterans With Advanced Prostate Cancer
This clinical trial explores and implements methods to improve informed decision making (IDM) regarding precision oncology tests amongst veterans with prostate cancer that may have spread from where it first started to nearby tissue, lymph nodes, or distant parts of the body (advanced). Precision oncology, the use of germline genetic testing and tumor-based molecular assays to inform cancer care, has become an important aspect of evidence-based care for men with advanced prostate cancer. Veterans with metastatic castrate-resistant prostate cancer may not be carrying out IDM due to unmet decisional needs. An informed decision is a choice based on complete and accurate information. The information gained from this study will help researchers develop a decision support intervention (DSI) and implement the intervention. A DSI may serve as a valuable tool to reduce ongoing racial disparities in genetic testing and encourage enrollment to precision oncology trials.
ID: NCT05396872
Sponsor; Investigator; Collaborator: University of California, San Francisco; Daniel Kwon, MD; US Department of Defense VA Office of Research and Development; Madalina Macrea, MD, PhD
Location: San Francisco Veterans Affairs Medical Center, CA
Veterans Affairs Seamless Phase II/III Randomized Trial of STAndard Systemic theRapy With or Without PET-directed Local Therapy for Oligometastatic pRosTate Cancer (VA STARPORT)
This is a prospective, open-label, multi-center seamless phase II to phase III randomized clinical trial designed to compare SST with or without PET-directed local therapy in improving the castration-resistant prostate cancer-free survival (CRPC-free survival) for veterans with oligometastatic prostate cancer. Oligometastasis will be defined as 1-10 sites of metastatic disease based on the clinical determination of the LSI which incorporates all imaging, clinical, and pathologic data available.
ID: NCT04787744
Sponsor; Collaborator: VA Office of Research and Development; Abhishek Solanki, MD, MS VA Office of Research and Development; Madalina Macrea, MD, PhD
Location: 19 locations, including Edwards Hines Jr. VA Hospital, Hines, IL
The Prostate Cancer, Genetic Risk, and Equitable Screening Study (ProGRESS) (ProGRESS)
Prostate cancer is the most common non-skin cancer among veterans and the second leading cause of male cancer death. Current methods of screening men for prostate cancer are inaccurate and cannot identify which men do not have prostate cancer or have low-grade cases that will not cause harm and which men have significant prostate cancer needing treatment. False-positive screening tests can result in unnecessary prostate biopsies for men who do not need them. However, new genetic testing might help identify which men are at highest risk for prostate cancer. This study will examine whether a genetic test helps identify men at risk for significant prostate cancer while helping men who are at low risk for prostate cancer avoid unnecessary biopsies. If this genetic test proves beneficial, it will improve the way that health care providers screen male veterans for prostate cancer.
ID: NCT05926102
Sponsor; Collaborator: VA Office of Research and Development; Jason L. Vassy, MD, MPH VA Office of Research and Development; Madalina Macrea, MD, PhD
Location: VA Boston Healthcare System Jamaica Plain Campus, MA
A Single-Arm Phase II Study of Neoadjuvant Intensified Androgen Deprivation (Leuprolide and Abiraterone Acetate) in Combination With AKT Inhibition (Capivasertib) for High-Risk Localized Prostate Cancer With PTEN Loss (SNARE)
The purpose of this study is to learn about how an investigational drug intervention completed before doing prostate surgery (specifically, radical prostatectomy with lymph node dissection) may help in treatment of high risk localized prostate cancers that are most resistant to standard treatments. This is a phase II research study. For this study, capivasertib, the study drug, will be taken with intensified androgen deprivation drugs (iADT; abiraterone and leuprolide) prior to radical prostatectomy. This study drug treatment will be evaluated to see if it is effective in shrinking and destroying prostate cancer tumors prior to surgery and to further evaluate its safety prior to prostate cancer surgery.
ID: NCT05593497
Sponsor; Collaborator: VA Office of Research and Development; Ryan P. Kopp, MD VA Office of Research and Development; Madalina Macrea, MD, PhD
Location: 5 locations, including VA Portland Health Care System, OR
18F-Fluciclovine PET/CT Impact on Predicting Clinical Outcome of 177Lu-PSMA-617 Therapy in Patients With Prostate Cancer
This is a single-center, prospective, exploratory study. Patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) scheduled to undergo Lutetium labelled prostate-specific membrane antigen radioligand therapy (LuPSMA RLT) at the West Los Angeles VA (WLA-VA) will be imaged with a baseline F-18 fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography 18F-FDG PET/CT and a 18F-DCFPyL PET/CT (18F-DCFPyL (2-(3-{1-carboxy-5-[(6-18F-fluoro-pyridine-3-carbonyl)-amino]-pentyl}-ureido)-pentanedioic acid)positron emission tomography/computed tomography , as per standard of care in our institution. All patients further undergo eventual follow-up prostate-specific membrane antigen positron emission tomography (PSMA PET) after the 2nd, 4th, and 6th LuPSMA RLT cycle. In this prospective study, an18F-Fluciclovine positron emission tomography/computed tomography (Axumin PET/CT) will be additionally obtained at baseline (pre-LuPSMA RLT), and after the 2nd, 4th, 6th LuPSMA RLT cycles. Axumin PET/CT will be acquired within 7 days from the PSMA PET.
This study is open to veterans only.
ID: NCT06706921
Sponsor; Collaborator: VA Greater Los Angeles Healthcare System; Gholam Berenji, MD, Janake Wijesuriya, BS VA Office of Research and Development; Madalina Macrea, MD, PhD
Location: VA Greater Los Angeles Healthcare System, CA
High Dose Testosterone for ATM, CDK12 or CHEK2 Altered Prostate Cancers (VA-BAT)
This study will determine whether the presence of DNA repair deficiency in the form of alterations in the genes ATM, CDK12 or CHEK2 predicts for a high likelihood of responding to the use of intermittent high dose testosterone. This therapy may result in responses in tumors which are genetically unstable because of DNA repair deficiency and this is a prospective study to test that hypothesis.
ID: NCT05011383
Sponsor; Collaborator: VA Office of Research and Development; Robert B. Montgomery, MD VA Office of Research and Development; Madalina Macrea, MD, PhD
Location: 17 locations, including VA Puget Sound Health Care System, Seattle, WA
A Study of CHeckpoint Inhibitors in Men With prOgressive Metastatic Castrate Resistant Prostate Cancer Characterized by a Mismatch Repair Deficiency or Biallelic CDK12 Inactivation (CHOMP)
The primary objective is to assess the activity and efficacy of pembrolizumab, a checkpoint inhibitor, in veterans with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) characterized by either mismatch repair deficiency (dMMR) or biallelic inactivation of CDK12 (CDK12-/-). The secondary objectives involve determining the frequency with which dMMR and CDK12-/- occur in this patient population, as well as the effects of pembrolizumab on various clinical endpoints (time to PSA progression, maximal PSA response, time to initiation of alternative anti-neoplastic therapy, time to radiographic progression, overall survival, and safety and tolerability). Lastly, the study will compare the pre-treatment and at-progression metastatic tumor biopsies to investigate the molecular correlates of resistance and sensitivity to pembrolizumab via RNA-sequencing, exome-sequencing, selected protein analyses, and multiplexed immunofluorescence.
ID: NCT04104893
Sponsor; Investigator; Collaborator: VA Office of Research and Development; Matthew B. Rettig, MD; Merck Sharp & Dohme LLC VA Office of Research and Development; Madalina Macrea, MD, PhD
Location: 12 locations, including VA Greater Los Angeles Healthcare System, CA
Carboplatin or Olaparib for BRcA Deficient Prostate Cancer (COBRA)
This is an unblinded, randomized clinical study comparing the efficacy of DNA damaging chemotherapy using carboplatin, to standard of care therapy for patients who have metastatic castrate resistant prostate cancer. This trial will use olaparib or carboplatin as initial therapy with crossover to the alternate or second-line drug after first progression for patients with tumors containing BARD1, BRCA1, BRCA2, BRIP1, CHEK1, FANCL, PALB2, RAD51B, RAD51C, RAD51D, or RAD54L inactivating mutations.
Participants are randomized (1:1) and receive either carboplatin (AUC 5, IV) every 21 days, first or olaparib taken orally (300 mg), twice daily in 28-day cycles, until intolerance, complete response, or progression by Prostate Cancer Working Group 3 (PCWG3) criteria.
Participants then cross over from the first-line therapy to the second-line therapy with the opposite study medication and receive treatment to intolerance or progression (whichever is first). Enrolled participants will be allowed to crossover to second line therapy if they continue to meet initial eligibility criteria, and at least three weeks have elapsed since last administration of either carboplatin or olaparib. Throughout the study, safety and tolerability will be assessed. Progression will be evaluated with bone scan, CT of the abdomen/pelvis, or MRI and PSA as per PCWG3 criteria.
ID: NCT04038502
Sponsor; Collaborator: VA Office of Research and Development; Robert B. Montgomery, MD; Ryan Burri, MD; Phoebe Tsao, MD, MSc; Maneesh Jain, MD VA Office of Research and Development; Madalina Macrea, MD, PhD
Location: 17 locations, including VA Puget Sound Health Care System, Seattle, WA
The clinical trials listed below are open as of March 10, 2025; have ≥ 1 US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) medical center (VAMC) or US Department of Defense (DoD) military treatment facility location recruiting patients; and are focused on treatments for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). For additional information and full inclusion/exclusion criteria, please consult clinicaltrials.gov.
Actively Recruiting
Patient Decision-making About Precision Oncology in Veterans With Advanced Prostate Cancer
This clinical trial explores and implements methods to improve informed decision making (IDM) regarding precision oncology tests amongst veterans with prostate cancer that may have spread from where it first started to nearby tissue, lymph nodes, or distant parts of the body (advanced). Precision oncology, the use of germline genetic testing and tumor-based molecular assays to inform cancer care, has become an important aspect of evidence-based care for men with advanced prostate cancer. Veterans with metastatic castrate-resistant prostate cancer may not be carrying out IDM due to unmet decisional needs. An informed decision is a choice based on complete and accurate information. The information gained from this study will help researchers develop a decision support intervention (DSI) and implement the intervention. A DSI may serve as a valuable tool to reduce ongoing racial disparities in genetic testing and encourage enrollment to precision oncology trials.
ID: NCT05396872
Sponsor; Investigator; Collaborator: University of California, San Francisco; Daniel Kwon, MD; US Department of Defense VA Office of Research and Development; Madalina Macrea, MD, PhD
Location: San Francisco Veterans Affairs Medical Center, CA
Veterans Affairs Seamless Phase II/III Randomized Trial of STAndard Systemic theRapy With or Without PET-directed Local Therapy for Oligometastatic pRosTate Cancer (VA STARPORT)
This is a prospective, open-label, multi-center seamless phase II to phase III randomized clinical trial designed to compare SST with or without PET-directed local therapy in improving the castration-resistant prostate cancer-free survival (CRPC-free survival) for veterans with oligometastatic prostate cancer. Oligometastasis will be defined as 1-10 sites of metastatic disease based on the clinical determination of the LSI which incorporates all imaging, clinical, and pathologic data available.
ID: NCT04787744
Sponsor; Collaborator: VA Office of Research and Development; Abhishek Solanki, MD, MS VA Office of Research and Development; Madalina Macrea, MD, PhD
Location: 19 locations, including Edwards Hines Jr. VA Hospital, Hines, IL
The Prostate Cancer, Genetic Risk, and Equitable Screening Study (ProGRESS) (ProGRESS)
Prostate cancer is the most common non-skin cancer among veterans and the second leading cause of male cancer death. Current methods of screening men for prostate cancer are inaccurate and cannot identify which men do not have prostate cancer or have low-grade cases that will not cause harm and which men have significant prostate cancer needing treatment. False-positive screening tests can result in unnecessary prostate biopsies for men who do not need them. However, new genetic testing might help identify which men are at highest risk for prostate cancer. This study will examine whether a genetic test helps identify men at risk for significant prostate cancer while helping men who are at low risk for prostate cancer avoid unnecessary biopsies. If this genetic test proves beneficial, it will improve the way that health care providers screen male veterans for prostate cancer.
ID: NCT05926102
Sponsor; Collaborator: VA Office of Research and Development; Jason L. Vassy, MD, MPH VA Office of Research and Development; Madalina Macrea, MD, PhD
Location: VA Boston Healthcare System Jamaica Plain Campus, MA
A Single-Arm Phase II Study of Neoadjuvant Intensified Androgen Deprivation (Leuprolide and Abiraterone Acetate) in Combination With AKT Inhibition (Capivasertib) for High-Risk Localized Prostate Cancer With PTEN Loss (SNARE)
The purpose of this study is to learn about how an investigational drug intervention completed before doing prostate surgery (specifically, radical prostatectomy with lymph node dissection) may help in treatment of high risk localized prostate cancers that are most resistant to standard treatments. This is a phase II research study. For this study, capivasertib, the study drug, will be taken with intensified androgen deprivation drugs (iADT; abiraterone and leuprolide) prior to radical prostatectomy. This study drug treatment will be evaluated to see if it is effective in shrinking and destroying prostate cancer tumors prior to surgery and to further evaluate its safety prior to prostate cancer surgery.
ID: NCT05593497
Sponsor; Collaborator: VA Office of Research and Development; Ryan P. Kopp, MD VA Office of Research and Development; Madalina Macrea, MD, PhD
Location: 5 locations, including VA Portland Health Care System, OR
18F-Fluciclovine PET/CT Impact on Predicting Clinical Outcome of 177Lu-PSMA-617 Therapy in Patients With Prostate Cancer
This is a single-center, prospective, exploratory study. Patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) scheduled to undergo Lutetium labelled prostate-specific membrane antigen radioligand therapy (LuPSMA RLT) at the West Los Angeles VA (WLA-VA) will be imaged with a baseline F-18 fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography 18F-FDG PET/CT and a 18F-DCFPyL PET/CT (18F-DCFPyL (2-(3-{1-carboxy-5-[(6-18F-fluoro-pyridine-3-carbonyl)-amino]-pentyl}-ureido)-pentanedioic acid)positron emission tomography/computed tomography , as per standard of care in our institution. All patients further undergo eventual follow-up prostate-specific membrane antigen positron emission tomography (PSMA PET) after the 2nd, 4th, and 6th LuPSMA RLT cycle. In this prospective study, an18F-Fluciclovine positron emission tomography/computed tomography (Axumin PET/CT) will be additionally obtained at baseline (pre-LuPSMA RLT), and after the 2nd, 4th, 6th LuPSMA RLT cycles. Axumin PET/CT will be acquired within 7 days from the PSMA PET.
This study is open to veterans only.
ID: NCT06706921
Sponsor; Collaborator: VA Greater Los Angeles Healthcare System; Gholam Berenji, MD, Janake Wijesuriya, BS VA Office of Research and Development; Madalina Macrea, MD, PhD
Location: VA Greater Los Angeles Healthcare System, CA
High Dose Testosterone for ATM, CDK12 or CHEK2 Altered Prostate Cancers (VA-BAT)
This study will determine whether the presence of DNA repair deficiency in the form of alterations in the genes ATM, CDK12 or CHEK2 predicts for a high likelihood of responding to the use of intermittent high dose testosterone. This therapy may result in responses in tumors which are genetically unstable because of DNA repair deficiency and this is a prospective study to test that hypothesis.
ID: NCT05011383
Sponsor; Collaborator: VA Office of Research and Development; Robert B. Montgomery, MD VA Office of Research and Development; Madalina Macrea, MD, PhD
Location: 17 locations, including VA Puget Sound Health Care System, Seattle, WA
A Study of CHeckpoint Inhibitors in Men With prOgressive Metastatic Castrate Resistant Prostate Cancer Characterized by a Mismatch Repair Deficiency or Biallelic CDK12 Inactivation (CHOMP)
The primary objective is to assess the activity and efficacy of pembrolizumab, a checkpoint inhibitor, in veterans with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) characterized by either mismatch repair deficiency (dMMR) or biallelic inactivation of CDK12 (CDK12-/-). The secondary objectives involve determining the frequency with which dMMR and CDK12-/- occur in this patient population, as well as the effects of pembrolizumab on various clinical endpoints (time to PSA progression, maximal PSA response, time to initiation of alternative anti-neoplastic therapy, time to radiographic progression, overall survival, and safety and tolerability). Lastly, the study will compare the pre-treatment and at-progression metastatic tumor biopsies to investigate the molecular correlates of resistance and sensitivity to pembrolizumab via RNA-sequencing, exome-sequencing, selected protein analyses, and multiplexed immunofluorescence.
ID: NCT04104893
Sponsor; Investigator; Collaborator: VA Office of Research and Development; Matthew B. Rettig, MD; Merck Sharp & Dohme LLC VA Office of Research and Development; Madalina Macrea, MD, PhD
Location: 12 locations, including VA Greater Los Angeles Healthcare System, CA
Carboplatin or Olaparib for BRcA Deficient Prostate Cancer (COBRA)
This is an unblinded, randomized clinical study comparing the efficacy of DNA damaging chemotherapy using carboplatin, to standard of care therapy for patients who have metastatic castrate resistant prostate cancer. This trial will use olaparib or carboplatin as initial therapy with crossover to the alternate or second-line drug after first progression for patients with tumors containing BARD1, BRCA1, BRCA2, BRIP1, CHEK1, FANCL, PALB2, RAD51B, RAD51C, RAD51D, or RAD54L inactivating mutations.
Participants are randomized (1:1) and receive either carboplatin (AUC 5, IV) every 21 days, first or olaparib taken orally (300 mg), twice daily in 28-day cycles, until intolerance, complete response, or progression by Prostate Cancer Working Group 3 (PCWG3) criteria.
Participants then cross over from the first-line therapy to the second-line therapy with the opposite study medication and receive treatment to intolerance or progression (whichever is first). Enrolled participants will be allowed to crossover to second line therapy if they continue to meet initial eligibility criteria, and at least three weeks have elapsed since last administration of either carboplatin or olaparib. Throughout the study, safety and tolerability will be assessed. Progression will be evaluated with bone scan, CT of the abdomen/pelvis, or MRI and PSA as per PCWG3 criteria.
ID: NCT04038502
Sponsor; Collaborator: VA Office of Research and Development; Robert B. Montgomery, MD; Ryan Burri, MD; Phoebe Tsao, MD, MSc; Maneesh Jain, MD VA Office of Research and Development; Madalina Macrea, MD, PhD
Location: 17 locations, including VA Puget Sound Health Care System, Seattle, WA
AVAHO Implores VA Secretary Collins to Use Caution Amid Rapid Changes
The Association of VA Hematology/Oncology outlined its concerns over “unintended consequences” to recent changes at the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) in a March 3, 2025, letter to Secretary Doug A. Collins. “Indiscriminate cuts to contracts and personnel could have unforeseen consequences in many research areas within the VA, so we implore scrutiny,” the letter warns.
“We have already seen specific examples this past week of swift contract cuts impairing the VA’s ability to implement research protocols, process and report pharmacogenomic results, management of Electronic Health Record Modernization (EHRM) council workgroups, and execute new oncology services through the Close to Me initiative,” AVAHO Executive Director Julie Lawson said.
As Lawson noted, the return-to-office order for the staff of the Clinical Resource Hubs (CRHs) and the National Tele-Oncology programs could significantly impair their ability to function. Both departments have been fully remote since their start and are key elements of VA care for rural veterans. In fiscal year 2024, > 500,000 veterans received > 1.4 million CRH encounters. Nearly 20,000 veterans have utilized the National Tele-Oncology program in > 80,000 cancer-care encounters.
“We have significant concern that a blanket return to office of these fully remote programs, without an adequate plan for office space, teleworking equipment, and clinical and administrative support could have significant disruption and impairment in their delivery of care, negatively impacting veteran outcomes,” Lawson said.
AVAHO also strongly urged Collins to continue VA investment in clinical trials specifically and research in general: "To implement and execute research, there must be an adequte system in place to support these research programs."
The Association of VA Hematology/Oncology outlined its concerns over “unintended consequences” to recent changes at the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) in a March 3, 2025, letter to Secretary Doug A. Collins. “Indiscriminate cuts to contracts and personnel could have unforeseen consequences in many research areas within the VA, so we implore scrutiny,” the letter warns.
“We have already seen specific examples this past week of swift contract cuts impairing the VA’s ability to implement research protocols, process and report pharmacogenomic results, management of Electronic Health Record Modernization (EHRM) council workgroups, and execute new oncology services through the Close to Me initiative,” AVAHO Executive Director Julie Lawson said.
As Lawson noted, the return-to-office order for the staff of the Clinical Resource Hubs (CRHs) and the National Tele-Oncology programs could significantly impair their ability to function. Both departments have been fully remote since their start and are key elements of VA care for rural veterans. In fiscal year 2024, > 500,000 veterans received > 1.4 million CRH encounters. Nearly 20,000 veterans have utilized the National Tele-Oncology program in > 80,000 cancer-care encounters.
“We have significant concern that a blanket return to office of these fully remote programs, without an adequate plan for office space, teleworking equipment, and clinical and administrative support could have significant disruption and impairment in their delivery of care, negatively impacting veteran outcomes,” Lawson said.
AVAHO also strongly urged Collins to continue VA investment in clinical trials specifically and research in general: "To implement and execute research, there must be an adequte system in place to support these research programs."
The Association of VA Hematology/Oncology outlined its concerns over “unintended consequences” to recent changes at the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) in a March 3, 2025, letter to Secretary Doug A. Collins. “Indiscriminate cuts to contracts and personnel could have unforeseen consequences in many research areas within the VA, so we implore scrutiny,” the letter warns.
“We have already seen specific examples this past week of swift contract cuts impairing the VA’s ability to implement research protocols, process and report pharmacogenomic results, management of Electronic Health Record Modernization (EHRM) council workgroups, and execute new oncology services through the Close to Me initiative,” AVAHO Executive Director Julie Lawson said.
As Lawson noted, the return-to-office order for the staff of the Clinical Resource Hubs (CRHs) and the National Tele-Oncology programs could significantly impair their ability to function. Both departments have been fully remote since their start and are key elements of VA care for rural veterans. In fiscal year 2024, > 500,000 veterans received > 1.4 million CRH encounters. Nearly 20,000 veterans have utilized the National Tele-Oncology program in > 80,000 cancer-care encounters.
“We have significant concern that a blanket return to office of these fully remote programs, without an adequate plan for office space, teleworking equipment, and clinical and administrative support could have significant disruption and impairment in their delivery of care, negatively impacting veteran outcomes,” Lawson said.
AVAHO also strongly urged Collins to continue VA investment in clinical trials specifically and research in general: "To implement and execute research, there must be an adequte system in place to support these research programs."
PATINA Trial Shifts Paradigm in HER2+/ER+ Breast Cancer Treatment, Prolonging Survival With Targeted Combination Therapy
This is a transcript of a video essay, which can be found on Medscape.
I’m here with you today to talk about what I think was one of the most important trials reported at the December San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium meeting, the PATINA trial.
This is a trial that was not on our radar as we were looking forward to the meeting. In fact, it wasn’t on the agenda because the results didn’t become available until about a week and a half before the meeting kicked off. Kudos to the authors for getting these data out there, and to the organizers for recognizing the importance and finding a way to add this to the program.
The PATINA trial enrolled patients whose tumors were both HER2 positive and ER positive. That is about half of our patients with HER2-positive disease.
Almost all of our trials looking at HER2-targeted therapies did not allow patients to continue antiestrogen therapy. Patients could have had antiestrogen therapy before they came to those HER2-focused trials. Some did, some may not have. It was not a requirement, but they could not continue it.
The same is true for patients with ER-positive disease. If your disease was ER positive and HER2 positive, you were excluded from all of our recent trials focusing on ER-positive disease. That includes those looking at the benefit of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors.
It also includes those looking at PI3 kinase inhibitors, AKT inhibitors, and selective estrogen receptor downregulators in their oral formulations. We›ve had to pick: Do we want to focus on HER2 or do we want to focus on ER? The PATINA trial results are not only important for practice, but they also show us the problem in that dichotomy.
PATINA enrolled patients who were receiving their first chemotherapy and HER2-targeted therapy for metastatic disease. Once they had received at least four cycles of combined therapy, they could receive additional chemotherapy, but they could also move into a maintenance phase if their disease was responding or stable, continuing HER2-targeted therapy alone without chemotherapy.
At that point, hormone therapy was reintroduced. This is a common practice for many of us. Those patients were then randomized to either palbociclib or not. This was a large effort, with 518 patients in this randomized trial. The expectations of progression-free survival were based on the results of the CLEOPATRA trial.
The trial assumed about a 15-month progression-free survival in those randomized to the control arm. What was actually observed was a 29-month progression-free survival. Two things might have contributed to this difference.
First, the CLEOPATRA trial did not allow patients to receive concurrent hormone therapy, and that may have had a major impact on its own. Also, CLEOPATRA reported the PFS for all of the patients enrolled. To get into PATINA, you had to be responding or stable to your initial combined modality therapy. Those patients with really resistant disease who progressed early were excluded, and that may have had an impact as well.
With the addition of palbociclib, that 29-month progression-free survival became 44 months. Stop and think about this. There was almost a 4-year period of time where patients were on trastuzumab and pertuzumab, an aromatase inhibitor, and a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor. No chemotherapy, much less day-to-day toxicities — not no toxicity, but less of the day-to-day toxicities that patients are really troubled by.
We don’t yet have mature overall survival data. Those will be coming. You can imagine with progression-free survival nearing 4 years, overall survival data will be some months or years hence until there are enough events for us to look at that evaluation.
Realizing that there are going to be issues with insurance approval and regulatory approvals, I would like to take these results into account for my patients in that situation.
It also challenges those of us who are developing clinical trials and drugs to realize that studying targets in isolation is needed early in the development of new agents. To get the maximum benefit for our patients, you need to put those building blocks back together and stop this forced dichotomy.
That doesn’t serve our patients well and it’s not where we will need to be in the future.
Kathy D. Miller, Professor of Medicine, Indiana University School of Medicine; Co-Director, Breast Cancer Program, Indiana University Simon Cancer Center, Indianapolis, Indiana, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This is a transcript of a video essay, which can be found on Medscape.
I’m here with you today to talk about what I think was one of the most important trials reported at the December San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium meeting, the PATINA trial.
This is a trial that was not on our radar as we were looking forward to the meeting. In fact, it wasn’t on the agenda because the results didn’t become available until about a week and a half before the meeting kicked off. Kudos to the authors for getting these data out there, and to the organizers for recognizing the importance and finding a way to add this to the program.
The PATINA trial enrolled patients whose tumors were both HER2 positive and ER positive. That is about half of our patients with HER2-positive disease.
Almost all of our trials looking at HER2-targeted therapies did not allow patients to continue antiestrogen therapy. Patients could have had antiestrogen therapy before they came to those HER2-focused trials. Some did, some may not have. It was not a requirement, but they could not continue it.
The same is true for patients with ER-positive disease. If your disease was ER positive and HER2 positive, you were excluded from all of our recent trials focusing on ER-positive disease. That includes those looking at the benefit of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors.
It also includes those looking at PI3 kinase inhibitors, AKT inhibitors, and selective estrogen receptor downregulators in their oral formulations. We›ve had to pick: Do we want to focus on HER2 or do we want to focus on ER? The PATINA trial results are not only important for practice, but they also show us the problem in that dichotomy.
PATINA enrolled patients who were receiving their first chemotherapy and HER2-targeted therapy for metastatic disease. Once they had received at least four cycles of combined therapy, they could receive additional chemotherapy, but they could also move into a maintenance phase if their disease was responding or stable, continuing HER2-targeted therapy alone without chemotherapy.
At that point, hormone therapy was reintroduced. This is a common practice for many of us. Those patients were then randomized to either palbociclib or not. This was a large effort, with 518 patients in this randomized trial. The expectations of progression-free survival were based on the results of the CLEOPATRA trial.
The trial assumed about a 15-month progression-free survival in those randomized to the control arm. What was actually observed was a 29-month progression-free survival. Two things might have contributed to this difference.
First, the CLEOPATRA trial did not allow patients to receive concurrent hormone therapy, and that may have had a major impact on its own. Also, CLEOPATRA reported the PFS for all of the patients enrolled. To get into PATINA, you had to be responding or stable to your initial combined modality therapy. Those patients with really resistant disease who progressed early were excluded, and that may have had an impact as well.
With the addition of palbociclib, that 29-month progression-free survival became 44 months. Stop and think about this. There was almost a 4-year period of time where patients were on trastuzumab and pertuzumab, an aromatase inhibitor, and a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor. No chemotherapy, much less day-to-day toxicities — not no toxicity, but less of the day-to-day toxicities that patients are really troubled by.
We don’t yet have mature overall survival data. Those will be coming. You can imagine with progression-free survival nearing 4 years, overall survival data will be some months or years hence until there are enough events for us to look at that evaluation.
Realizing that there are going to be issues with insurance approval and regulatory approvals, I would like to take these results into account for my patients in that situation.
It also challenges those of us who are developing clinical trials and drugs to realize that studying targets in isolation is needed early in the development of new agents. To get the maximum benefit for our patients, you need to put those building blocks back together and stop this forced dichotomy.
That doesn’t serve our patients well and it’s not where we will need to be in the future.
Kathy D. Miller, Professor of Medicine, Indiana University School of Medicine; Co-Director, Breast Cancer Program, Indiana University Simon Cancer Center, Indianapolis, Indiana, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This is a transcript of a video essay, which can be found on Medscape.
I’m here with you today to talk about what I think was one of the most important trials reported at the December San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium meeting, the PATINA trial.
This is a trial that was not on our radar as we were looking forward to the meeting. In fact, it wasn’t on the agenda because the results didn’t become available until about a week and a half before the meeting kicked off. Kudos to the authors for getting these data out there, and to the organizers for recognizing the importance and finding a way to add this to the program.
The PATINA trial enrolled patients whose tumors were both HER2 positive and ER positive. That is about half of our patients with HER2-positive disease.
Almost all of our trials looking at HER2-targeted therapies did not allow patients to continue antiestrogen therapy. Patients could have had antiestrogen therapy before they came to those HER2-focused trials. Some did, some may not have. It was not a requirement, but they could not continue it.
The same is true for patients with ER-positive disease. If your disease was ER positive and HER2 positive, you were excluded from all of our recent trials focusing on ER-positive disease. That includes those looking at the benefit of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors.
It also includes those looking at PI3 kinase inhibitors, AKT inhibitors, and selective estrogen receptor downregulators in their oral formulations. We›ve had to pick: Do we want to focus on HER2 or do we want to focus on ER? The PATINA trial results are not only important for practice, but they also show us the problem in that dichotomy.
PATINA enrolled patients who were receiving their first chemotherapy and HER2-targeted therapy for metastatic disease. Once they had received at least four cycles of combined therapy, they could receive additional chemotherapy, but they could also move into a maintenance phase if their disease was responding or stable, continuing HER2-targeted therapy alone without chemotherapy.
At that point, hormone therapy was reintroduced. This is a common practice for many of us. Those patients were then randomized to either palbociclib or not. This was a large effort, with 518 patients in this randomized trial. The expectations of progression-free survival were based on the results of the CLEOPATRA trial.
The trial assumed about a 15-month progression-free survival in those randomized to the control arm. What was actually observed was a 29-month progression-free survival. Two things might have contributed to this difference.
First, the CLEOPATRA trial did not allow patients to receive concurrent hormone therapy, and that may have had a major impact on its own. Also, CLEOPATRA reported the PFS for all of the patients enrolled. To get into PATINA, you had to be responding or stable to your initial combined modality therapy. Those patients with really resistant disease who progressed early were excluded, and that may have had an impact as well.
With the addition of palbociclib, that 29-month progression-free survival became 44 months. Stop and think about this. There was almost a 4-year period of time where patients were on trastuzumab and pertuzumab, an aromatase inhibitor, and a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor. No chemotherapy, much less day-to-day toxicities — not no toxicity, but less of the day-to-day toxicities that patients are really troubled by.
We don’t yet have mature overall survival data. Those will be coming. You can imagine with progression-free survival nearing 4 years, overall survival data will be some months or years hence until there are enough events for us to look at that evaluation.
Realizing that there are going to be issues with insurance approval and regulatory approvals, I would like to take these results into account for my patients in that situation.
It also challenges those of us who are developing clinical trials and drugs to realize that studying targets in isolation is needed early in the development of new agents. To get the maximum benefit for our patients, you need to put those building blocks back together and stop this forced dichotomy.
That doesn’t serve our patients well and it’s not where we will need to be in the future.
Kathy D. Miller, Professor of Medicine, Indiana University School of Medicine; Co-Director, Breast Cancer Program, Indiana University Simon Cancer Center, Indianapolis, Indiana, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Last Month in Oncology: FDA Cancer News Roundup
Last month, the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved two new drugs and two biosimilars as well as halted commercialization for a hemophilia treatment.
Here’s a deeper look of what happened last month.
New Drugs
1. The FDA has approved mirdametinib (Gomekli, SpringWorks Therapeutics, Inc.) for adult and pediatric patients 2 years or older with neurofibromatosis type 1 and symptomatic plexiform neurofibromas that are not amenable to complete resection.
Approval for this agent was based on overall response rate findings from a multicenter, single-arm, phase 2b trial. The trial, which enrolled 58 adults and 56 pediatric patients with this rare disease, reported confirmed overall response rates of 41% among adults and 52% among children.
Adverse reactions occurring in at least 25% of adults included rash, diarrhea, nausea, musculoskeletal pain, vomiting, and fatigue. Mirdametinib can also cause ocular toxicity. Treatment should be withheld, discontinued, or the dosage reduced based on the severity of these adverse reactions, according to the FDA notice.
2. The FDA has approved vimseltinib (Romvimza, Deciphera Pharmaceuticals, LLC) to treat adult patients with symptomatic tenosynovial giant cell tumors who will not benefit from surgical resection.
Vimseltinib was approved based on findings from the MOTION trial, which included 123 patients randomly assigned 2:1 to vimseltinib 30 mg twice weekly or to placebo for 24 weeks. At 25 weeks, the objective response rate was 40% in the vimseltinib arm and 0% in the placebo arm. The median duration of response was not reached in the vimseltinib arm. Patients receiving vimseltinib also demonstrated significant improvements in active range of motion, physical functioning, and pain at this time. After another 6 months of follow-up, 58% of responders had a duration of response of 9 months or longer.
Treatment-emergent adverse events in MOTION were largely of grade 1 or 2. The most common adverse reactions, occurring in at least 20% of patients, included increased aspartate aminotransferase, periorbital edema, fatigue, rash, and cholesterol.
New or Expanded Indications
1. The FDA has approved a supplemental Biologics License Application for brentuximab vedotin (Adcetris, Seagen Inc.), in combination with lenalidomide and rituximab, for adults with relapsed or refractory large B-cell lymphoma, after at least two prior lines of therapy, who are ineligible for stem cell transplant or chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy. This includes patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) not otherwise specified, DLBCL arising from indolent lymphoma, or high-grade B-cell lymphoma.
Approval was based on the randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled ECHELON-3 trial, which randomly assigned patients 1:1 to receive lenalidomide and rituximab plus either brentuximab vedotin or placebo until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. Researchers reported a median overall survival of 13.8 months in the treatment group vs 8.5 months in the placebo group (hazard ratio, 0.63).
2. The FDA has approved the Biologics License Application for Ospomyv and Xbryk (Samsung Bioepis Co.) — biosimilars referencing denosumab (Prolia and Xgeva, respectively) — to treat osteoporosis and cancer-related bone loss.
Ospomyv and Xbryk have been approved for use in all indications of the approved reference drugs. Specifically, Xbryk is indicated for the prevention of skeletal-related events in patients with bone metastases from solid tumors or multiple myeloma, and Ospomyv is indicated in several populations of patients with osteoporosis at high risk for fracture.
“The FDA approval of Ospomyv and Xbryk marks a key step in improving patient access and alleviating treatment cost for patients with osteoporosis and cancer-related bone loss in the United States,” Byoungin Jung, vice president at Samsung Bioepis, said in the news release.
Drug Commercialization Halt
Pfizer announced last month that it will halt the global development and commercialization of its hemophilia gene therapy fidanacogene elaparvovec (Beqvez). The company cited several reasons for the discontinuation, including low demand from patients and doctors.
Beqvez is a one-time therapy approved in the United States last April to treat adults with moderate to severe hemophilia B, a rare bleeding disorder that affects almost 4 in 100,000 men in the United States.
The significant price tag is one reason hematologists have cited for the low uptake. Another barrier is that “we don’t know the long-term outcomes” associated with the drug, pediatric hematologist Ben Samelson-Jones, MD, PhD, of the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania and Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, Philadelphia, told this news organization earlier this year.
Other issues include the prospect of newer treatment advances in the hemophilia space and logistical challenges. “There’s just a lot of logistics to getting an institution ready to provide this type of therapy,” Samelson-Jones added.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Last month, the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved two new drugs and two biosimilars as well as halted commercialization for a hemophilia treatment.
Here’s a deeper look of what happened last month.
New Drugs
1. The FDA has approved mirdametinib (Gomekli, SpringWorks Therapeutics, Inc.) for adult and pediatric patients 2 years or older with neurofibromatosis type 1 and symptomatic plexiform neurofibromas that are not amenable to complete resection.
Approval for this agent was based on overall response rate findings from a multicenter, single-arm, phase 2b trial. The trial, which enrolled 58 adults and 56 pediatric patients with this rare disease, reported confirmed overall response rates of 41% among adults and 52% among children.
Adverse reactions occurring in at least 25% of adults included rash, diarrhea, nausea, musculoskeletal pain, vomiting, and fatigue. Mirdametinib can also cause ocular toxicity. Treatment should be withheld, discontinued, or the dosage reduced based on the severity of these adverse reactions, according to the FDA notice.
2. The FDA has approved vimseltinib (Romvimza, Deciphera Pharmaceuticals, LLC) to treat adult patients with symptomatic tenosynovial giant cell tumors who will not benefit from surgical resection.
Vimseltinib was approved based on findings from the MOTION trial, which included 123 patients randomly assigned 2:1 to vimseltinib 30 mg twice weekly or to placebo for 24 weeks. At 25 weeks, the objective response rate was 40% in the vimseltinib arm and 0% in the placebo arm. The median duration of response was not reached in the vimseltinib arm. Patients receiving vimseltinib also demonstrated significant improvements in active range of motion, physical functioning, and pain at this time. After another 6 months of follow-up, 58% of responders had a duration of response of 9 months or longer.
Treatment-emergent adverse events in MOTION were largely of grade 1 or 2. The most common adverse reactions, occurring in at least 20% of patients, included increased aspartate aminotransferase, periorbital edema, fatigue, rash, and cholesterol.
New or Expanded Indications
1. The FDA has approved a supplemental Biologics License Application for brentuximab vedotin (Adcetris, Seagen Inc.), in combination with lenalidomide and rituximab, for adults with relapsed or refractory large B-cell lymphoma, after at least two prior lines of therapy, who are ineligible for stem cell transplant or chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy. This includes patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) not otherwise specified, DLBCL arising from indolent lymphoma, or high-grade B-cell lymphoma.
Approval was based on the randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled ECHELON-3 trial, which randomly assigned patients 1:1 to receive lenalidomide and rituximab plus either brentuximab vedotin or placebo until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. Researchers reported a median overall survival of 13.8 months in the treatment group vs 8.5 months in the placebo group (hazard ratio, 0.63).
2. The FDA has approved the Biologics License Application for Ospomyv and Xbryk (Samsung Bioepis Co.) — biosimilars referencing denosumab (Prolia and Xgeva, respectively) — to treat osteoporosis and cancer-related bone loss.
Ospomyv and Xbryk have been approved for use in all indications of the approved reference drugs. Specifically, Xbryk is indicated for the prevention of skeletal-related events in patients with bone metastases from solid tumors or multiple myeloma, and Ospomyv is indicated in several populations of patients with osteoporosis at high risk for fracture.
“The FDA approval of Ospomyv and Xbryk marks a key step in improving patient access and alleviating treatment cost for patients with osteoporosis and cancer-related bone loss in the United States,” Byoungin Jung, vice president at Samsung Bioepis, said in the news release.
Drug Commercialization Halt
Pfizer announced last month that it will halt the global development and commercialization of its hemophilia gene therapy fidanacogene elaparvovec (Beqvez). The company cited several reasons for the discontinuation, including low demand from patients and doctors.
Beqvez is a one-time therapy approved in the United States last April to treat adults with moderate to severe hemophilia B, a rare bleeding disorder that affects almost 4 in 100,000 men in the United States.
The significant price tag is one reason hematologists have cited for the low uptake. Another barrier is that “we don’t know the long-term outcomes” associated with the drug, pediatric hematologist Ben Samelson-Jones, MD, PhD, of the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania and Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, Philadelphia, told this news organization earlier this year.
Other issues include the prospect of newer treatment advances in the hemophilia space and logistical challenges. “There’s just a lot of logistics to getting an institution ready to provide this type of therapy,” Samelson-Jones added.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Last month, the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved two new drugs and two biosimilars as well as halted commercialization for a hemophilia treatment.
Here’s a deeper look of what happened last month.
New Drugs
1. The FDA has approved mirdametinib (Gomekli, SpringWorks Therapeutics, Inc.) for adult and pediatric patients 2 years or older with neurofibromatosis type 1 and symptomatic plexiform neurofibromas that are not amenable to complete resection.
Approval for this agent was based on overall response rate findings from a multicenter, single-arm, phase 2b trial. The trial, which enrolled 58 adults and 56 pediatric patients with this rare disease, reported confirmed overall response rates of 41% among adults and 52% among children.
Adverse reactions occurring in at least 25% of adults included rash, diarrhea, nausea, musculoskeletal pain, vomiting, and fatigue. Mirdametinib can also cause ocular toxicity. Treatment should be withheld, discontinued, or the dosage reduced based on the severity of these adverse reactions, according to the FDA notice.
2. The FDA has approved vimseltinib (Romvimza, Deciphera Pharmaceuticals, LLC) to treat adult patients with symptomatic tenosynovial giant cell tumors who will not benefit from surgical resection.
Vimseltinib was approved based on findings from the MOTION trial, which included 123 patients randomly assigned 2:1 to vimseltinib 30 mg twice weekly or to placebo for 24 weeks. At 25 weeks, the objective response rate was 40% in the vimseltinib arm and 0% in the placebo arm. The median duration of response was not reached in the vimseltinib arm. Patients receiving vimseltinib also demonstrated significant improvements in active range of motion, physical functioning, and pain at this time. After another 6 months of follow-up, 58% of responders had a duration of response of 9 months or longer.
Treatment-emergent adverse events in MOTION were largely of grade 1 or 2. The most common adverse reactions, occurring in at least 20% of patients, included increased aspartate aminotransferase, periorbital edema, fatigue, rash, and cholesterol.
New or Expanded Indications
1. The FDA has approved a supplemental Biologics License Application for brentuximab vedotin (Adcetris, Seagen Inc.), in combination with lenalidomide and rituximab, for adults with relapsed or refractory large B-cell lymphoma, after at least two prior lines of therapy, who are ineligible for stem cell transplant or chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy. This includes patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) not otherwise specified, DLBCL arising from indolent lymphoma, or high-grade B-cell lymphoma.
Approval was based on the randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled ECHELON-3 trial, which randomly assigned patients 1:1 to receive lenalidomide and rituximab plus either brentuximab vedotin or placebo until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. Researchers reported a median overall survival of 13.8 months in the treatment group vs 8.5 months in the placebo group (hazard ratio, 0.63).
2. The FDA has approved the Biologics License Application for Ospomyv and Xbryk (Samsung Bioepis Co.) — biosimilars referencing denosumab (Prolia and Xgeva, respectively) — to treat osteoporosis and cancer-related bone loss.
Ospomyv and Xbryk have been approved for use in all indications of the approved reference drugs. Specifically, Xbryk is indicated for the prevention of skeletal-related events in patients with bone metastases from solid tumors or multiple myeloma, and Ospomyv is indicated in several populations of patients with osteoporosis at high risk for fracture.
“The FDA approval of Ospomyv and Xbryk marks a key step in improving patient access and alleviating treatment cost for patients with osteoporosis and cancer-related bone loss in the United States,” Byoungin Jung, vice president at Samsung Bioepis, said in the news release.
Drug Commercialization Halt
Pfizer announced last month that it will halt the global development and commercialization of its hemophilia gene therapy fidanacogene elaparvovec (Beqvez). The company cited several reasons for the discontinuation, including low demand from patients and doctors.
Beqvez is a one-time therapy approved in the United States last April to treat adults with moderate to severe hemophilia B, a rare bleeding disorder that affects almost 4 in 100,000 men in the United States.
The significant price tag is one reason hematologists have cited for the low uptake. Another barrier is that “we don’t know the long-term outcomes” associated with the drug, pediatric hematologist Ben Samelson-Jones, MD, PhD, of the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania and Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, Philadelphia, told this news organization earlier this year.
Other issues include the prospect of newer treatment advances in the hemophilia space and logistical challenges. “There’s just a lot of logistics to getting an institution ready to provide this type of therapy,” Samelson-Jones added.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
More Layoffs at VA and Other Health Agencies
The large-scale layoffs in the federal government that began in January continue, as the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) announced the dismissal of > 1400 employees in “non-mission critical roles,” including those “related to DEI” (diversity, equity, inclusion) on Feb. 24. According to VA, those fired are bargaining-unit probationary employees who have served > 1 year in a competitive service appointment or who have served > 2 years in an excepted service appointment.
The agency says the “personnel moves” will save > $83 million annually, which will be redirected back toward health care, benefits and services for VA beneficiaries.
Of the nearly 40,000 probationary employees in the department, the majority were exempt, the VA says, because they serve in mission-critical positions—primarily those supporting benefits and services for VA beneficiaries, such as Veterans Crisis Line responders. VA employees who elected to participate in the Office of Personnel Management’s (OPM) deferred resignation program are also exempt. As an “additional safeguard,” the VA says the first Senior Executive Service (SES) or SES-equivalent leader in a dismissed employee’s chain of command can request the employee be exempted from removal.
The latest cuts follow the dismissal of > 1000 employees announced Feb. 13. In that case, the VA expected to save > $98 million annually, also to be “redirected back” toward health care, benefits, and services. VA insists it continues to hire for mission-critical positions that are exempt from the federal hiring freeze.
Layoffs are also impacting other federal public health agencies. Although the White House has not released figures, a ProPublica investigation details the impact of the layoffs on organ transplant and maternal mortality programs. Other layoffs that have been reported include :
- About 750 workers at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
- More than 1000 staffers at the National Institutes of Health
- “Dozens” at the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services
- “Scores” at the US Food and Drug Administration
- Downsizing at the VA EHR Modernization Integration Office
“By gutting essential health staff, hiding vital public health data, and silencing health experts, these actions have left every American family more vulnerable to deadly disease outbreaks, unsafe food and water, and preventable deaths,” the American Public Health Association said in a press release. “This is also not just an attack on federal institutions – it's a direct attack on every parent trying to protect their child from disease, every worker relying on public health safeguards and every family depending on rapid responses to outbreaks and emergencies.” American Public Health Association also announced that is suing the Department of Government Efficiency for violating federal transparency laws. “It is unfathomable that anybody thinks these cuts have value and are doing anything other than being performative.”
In 2024, the VA had planned to trim its 458,000-member workforce by about 2%, or 10,000 employees, through attrition (with most of the reduction coming from VHA). VHA Chief Financial Officer Laura Duke told reporters in March 2024 that the reduction was needed because the agency had far exceeded its hiring goals last year, and was also seeing higher-than-expected retention rates.
“These and other recent personnel decisions are extraordinarily difficult, but VA is focused on allocating its resources to help as many veterans, families, caregivers, and survivors as possible,” VA Secretary Doug Collins said. “These moves will not hurt VA health care, benefits or beneficiaries. In fact, veterans are going to notice a change for the better. In the coming weeks and months, VA will be announcing plans to put these resources to work helping the department fulfill its core mission: providing the best possible care and benefits to veterans, their families, caregivers and survivors.”
Senate Veterans’ Affairs Committee Ranking Member Richard Blumenthal (D-CT) and a group of 35 Democratic senators signed a letter earlier in February calling for Sec. Collins to immediately reinstate the terminated VA employees. “[W]e were outraged,” the letter said, “by the Administration’s abrupt and indiscriminate termination of tens of thousands of workers across almost every government agency, including more than 1000 Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) employees. We were further disturbed by the manner in which you publicly celebrated this reprehensible announcement—a clear departure from the assurances provided throughout your confirmation process to never ‘balance budgets on the back of veterans’ benefits’ and to always ‘put the veteran first.’”
Blumenthal also notes that the “continued mass terminations” come at a time when the VA faces critical staffing shortages and increased demand for its services. The senators detailed the effects the cuts were having, including how openings for new clinics were delayed because the VA cannot hire the necessary staff to open their doors; service lines at VA hospitals and clinics halted; beds and operating rooms at VA facilities suspended; support lines for caregivers reduced; Veterans Crisis Line employees fired; and suicide prevention training sessions postponed or canceled.
The large-scale layoffs in the federal government that began in January continue, as the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) announced the dismissal of > 1400 employees in “non-mission critical roles,” including those “related to DEI” (diversity, equity, inclusion) on Feb. 24. According to VA, those fired are bargaining-unit probationary employees who have served > 1 year in a competitive service appointment or who have served > 2 years in an excepted service appointment.
The agency says the “personnel moves” will save > $83 million annually, which will be redirected back toward health care, benefits and services for VA beneficiaries.
Of the nearly 40,000 probationary employees in the department, the majority were exempt, the VA says, because they serve in mission-critical positions—primarily those supporting benefits and services for VA beneficiaries, such as Veterans Crisis Line responders. VA employees who elected to participate in the Office of Personnel Management’s (OPM) deferred resignation program are also exempt. As an “additional safeguard,” the VA says the first Senior Executive Service (SES) or SES-equivalent leader in a dismissed employee’s chain of command can request the employee be exempted from removal.
The latest cuts follow the dismissal of > 1000 employees announced Feb. 13. In that case, the VA expected to save > $98 million annually, also to be “redirected back” toward health care, benefits, and services. VA insists it continues to hire for mission-critical positions that are exempt from the federal hiring freeze.
Layoffs are also impacting other federal public health agencies. Although the White House has not released figures, a ProPublica investigation details the impact of the layoffs on organ transplant and maternal mortality programs. Other layoffs that have been reported include :
- About 750 workers at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
- More than 1000 staffers at the National Institutes of Health
- “Dozens” at the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services
- “Scores” at the US Food and Drug Administration
- Downsizing at the VA EHR Modernization Integration Office
“By gutting essential health staff, hiding vital public health data, and silencing health experts, these actions have left every American family more vulnerable to deadly disease outbreaks, unsafe food and water, and preventable deaths,” the American Public Health Association said in a press release. “This is also not just an attack on federal institutions – it's a direct attack on every parent trying to protect their child from disease, every worker relying on public health safeguards and every family depending on rapid responses to outbreaks and emergencies.” American Public Health Association also announced that is suing the Department of Government Efficiency for violating federal transparency laws. “It is unfathomable that anybody thinks these cuts have value and are doing anything other than being performative.”
In 2024, the VA had planned to trim its 458,000-member workforce by about 2%, or 10,000 employees, through attrition (with most of the reduction coming from VHA). VHA Chief Financial Officer Laura Duke told reporters in March 2024 that the reduction was needed because the agency had far exceeded its hiring goals last year, and was also seeing higher-than-expected retention rates.
“These and other recent personnel decisions are extraordinarily difficult, but VA is focused on allocating its resources to help as many veterans, families, caregivers, and survivors as possible,” VA Secretary Doug Collins said. “These moves will not hurt VA health care, benefits or beneficiaries. In fact, veterans are going to notice a change for the better. In the coming weeks and months, VA will be announcing plans to put these resources to work helping the department fulfill its core mission: providing the best possible care and benefits to veterans, their families, caregivers and survivors.”
Senate Veterans’ Affairs Committee Ranking Member Richard Blumenthal (D-CT) and a group of 35 Democratic senators signed a letter earlier in February calling for Sec. Collins to immediately reinstate the terminated VA employees. “[W]e were outraged,” the letter said, “by the Administration’s abrupt and indiscriminate termination of tens of thousands of workers across almost every government agency, including more than 1000 Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) employees. We were further disturbed by the manner in which you publicly celebrated this reprehensible announcement—a clear departure from the assurances provided throughout your confirmation process to never ‘balance budgets on the back of veterans’ benefits’ and to always ‘put the veteran first.’”
Blumenthal also notes that the “continued mass terminations” come at a time when the VA faces critical staffing shortages and increased demand for its services. The senators detailed the effects the cuts were having, including how openings for new clinics were delayed because the VA cannot hire the necessary staff to open their doors; service lines at VA hospitals and clinics halted; beds and operating rooms at VA facilities suspended; support lines for caregivers reduced; Veterans Crisis Line employees fired; and suicide prevention training sessions postponed or canceled.
The large-scale layoffs in the federal government that began in January continue, as the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) announced the dismissal of > 1400 employees in “non-mission critical roles,” including those “related to DEI” (diversity, equity, inclusion) on Feb. 24. According to VA, those fired are bargaining-unit probationary employees who have served > 1 year in a competitive service appointment or who have served > 2 years in an excepted service appointment.
The agency says the “personnel moves” will save > $83 million annually, which will be redirected back toward health care, benefits and services for VA beneficiaries.
Of the nearly 40,000 probationary employees in the department, the majority were exempt, the VA says, because they serve in mission-critical positions—primarily those supporting benefits and services for VA beneficiaries, such as Veterans Crisis Line responders. VA employees who elected to participate in the Office of Personnel Management’s (OPM) deferred resignation program are also exempt. As an “additional safeguard,” the VA says the first Senior Executive Service (SES) or SES-equivalent leader in a dismissed employee’s chain of command can request the employee be exempted from removal.
The latest cuts follow the dismissal of > 1000 employees announced Feb. 13. In that case, the VA expected to save > $98 million annually, also to be “redirected back” toward health care, benefits, and services. VA insists it continues to hire for mission-critical positions that are exempt from the federal hiring freeze.
Layoffs are also impacting other federal public health agencies. Although the White House has not released figures, a ProPublica investigation details the impact of the layoffs on organ transplant and maternal mortality programs. Other layoffs that have been reported include :
- About 750 workers at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
- More than 1000 staffers at the National Institutes of Health
- “Dozens” at the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services
- “Scores” at the US Food and Drug Administration
- Downsizing at the VA EHR Modernization Integration Office
“By gutting essential health staff, hiding vital public health data, and silencing health experts, these actions have left every American family more vulnerable to deadly disease outbreaks, unsafe food and water, and preventable deaths,” the American Public Health Association said in a press release. “This is also not just an attack on federal institutions – it's a direct attack on every parent trying to protect their child from disease, every worker relying on public health safeguards and every family depending on rapid responses to outbreaks and emergencies.” American Public Health Association also announced that is suing the Department of Government Efficiency for violating federal transparency laws. “It is unfathomable that anybody thinks these cuts have value and are doing anything other than being performative.”
In 2024, the VA had planned to trim its 458,000-member workforce by about 2%, or 10,000 employees, through attrition (with most of the reduction coming from VHA). VHA Chief Financial Officer Laura Duke told reporters in March 2024 that the reduction was needed because the agency had far exceeded its hiring goals last year, and was also seeing higher-than-expected retention rates.
“These and other recent personnel decisions are extraordinarily difficult, but VA is focused on allocating its resources to help as many veterans, families, caregivers, and survivors as possible,” VA Secretary Doug Collins said. “These moves will not hurt VA health care, benefits or beneficiaries. In fact, veterans are going to notice a change for the better. In the coming weeks and months, VA will be announcing plans to put these resources to work helping the department fulfill its core mission: providing the best possible care and benefits to veterans, their families, caregivers and survivors.”
Senate Veterans’ Affairs Committee Ranking Member Richard Blumenthal (D-CT) and a group of 35 Democratic senators signed a letter earlier in February calling for Sec. Collins to immediately reinstate the terminated VA employees. “[W]e were outraged,” the letter said, “by the Administration’s abrupt and indiscriminate termination of tens of thousands of workers across almost every government agency, including more than 1000 Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) employees. We were further disturbed by the manner in which you publicly celebrated this reprehensible announcement—a clear departure from the assurances provided throughout your confirmation process to never ‘balance budgets on the back of veterans’ benefits’ and to always ‘put the veteran first.’”
Blumenthal also notes that the “continued mass terminations” come at a time when the VA faces critical staffing shortages and increased demand for its services. The senators detailed the effects the cuts were having, including how openings for new clinics were delayed because the VA cannot hire the necessary staff to open their doors; service lines at VA hospitals and clinics halted; beds and operating rooms at VA facilities suspended; support lines for caregivers reduced; Veterans Crisis Line employees fired; and suicide prevention training sessions postponed or canceled.
ASCO Updates Treatment Guidance for Newly Diagnosed, Advanced Ovarian Cancer
The American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) has released updated guidelines for neoadjuvant chemotherapy in newly diagnosed advanced ovarian cancer, introducing changes in patient selection and treatment strategies. The changes reflect emerging evidence on racial disparities, treatment outcomes, and quality of life considerations.
The publication of the new guidance follows dramatic shifts in treatment patterns over the past decade.
“There had been a big shift in how we were treating patients in the United States,” explained Stephanie Gaillard, MD, PhD, one of the authors of the updated guidelines. “We saw a substantial drop in the number of patients undergoing primary cytoreductive surgery for ovarian cancer from about 70% of patients in 2010 to only about 37% in 2021.”
The new guidelines maintain the recommendation for platinum/taxane-based neoadjuvant chemotherapy but introduce modifications regarding timing and duration.
“It’s still a recommendation that gynecologic oncologists are involved in determining whether someone is eligible for primary cytoreductive surgery or should undergo neoadjuvant chemotherapy first,” Gaillard noted. “We emphasize that patients who are eligible for primary cytoreductive surgery should undergo surgery as opposed to receiving neoadjuvant chemotherapy.”
Alexander Melamed, MD, MPH, a gynecologic oncologist at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, who was not involved in authoring the updated guidelines, noted that additional evidence-based guidance is needed to individualize treatment plans. He pointed to four completed trials comparing neoadjuvant chemotherapy with cytoreductive surgery, noting: “When these trials have been pooled together in meta-analyses, there was a higher risk of mortality associated with primary cytoreductive surgery and a higher risk of severe complications.”
The updated guidelines take this higher risk for mortality with primary cytoreductive surgery into consideration, and patients who are not eligible for primary surgery would receive neoadjuvant chemotherapy, Gaillard noted.
Changes in Patient Selection
The 2025 guidelines describe a more nuanced approach for selecting patients for neoadjuvant chemotherapy vs primary cytoreductive surgery. While the 2016 ASCO guidelines primarily focused on disease burden and surgical resectability when selecting patients for neoadjuvant chemotherapy, the new recommendations incorporate additional factors.
The guidelines discuss recent findings showing that Black patients experience a 38% lower likelihood of undergoing cytoreductive surgery than non-Black patients. In addition, compared with non-Hispanic White women, Asian and Black women more frequently receive neoadjuvant chemotherapy with interval debulking surgery rather than primary cytoreductive surgery. According to the authors, these differences persist even after accounting for clinical factors, suggesting that structural barriers to healthcare access may play a role.
The guidelines discuss how affordability, availability, and accessibility mediate racial disparities in ovarian cancer care. According to the authors, structural inequities in healthcare access influence treatment quality for minority patients. Non-White patients face greater challenges in accessing gynecologic oncology consultations and standard-of-care combination therapy, leading to poorer survival outcomes, the guidelines say.
According to Melamed, the guidelines serve as an important tool for promoting healthcare equity. “Having recommendations and standards is incredibly important for achieving equity because once there is consensus on a best practice, it doesn’t matter if you’re rich, poor, or a patient of a particular racial or ethnic group — if you have the disease, you ought to have access to that standard,” he said.
The 2016 ASCO guidelines focused primarily on disease burden and surgical resectability, whereas the 2024 National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) Clinical Practice Guidelines for ovarian cancer focus more on oncologic outcomes and surgical considerations. Based on the NCCN guidelines, treatment selection for ovarian cancer is primarily determined by the histologic subtype, stage of disease, and whether the patient is a candidate for primary surgery. The 2025 ASCO guidelines, on the other hand, emphasize the importance of quality-of-life outcomes during treatment selection. The authors of the updated ASCO guidelines acknowledged that treatment decisions should consider both the duration and quality of life, particularly for elderly patients or those with multiple comorbidities.
Treatment Timing and Duration
The guidelines maintain the recommendations for platinum/taxane-based neoadjuvant chemotherapy described in the previous ASCO guidelines but introduce modifications regarding treatment timing and duration. The optimal window for interval cytoreductive surgery now falls after three to four chemotherapy cycles, allowing more individualized approaches based on patient response and tolerance.
In addition, postsurgical chemotherapy protocols have become more flexible. Rather than mandating a fixed number of cycles, the guidelines encourage tailoring treatment duration to individual patient factors including response assessment, performance status, and quality-of-life considerations.
The updated guidelines also emphasize the importance of genetic and molecular testing at diagnosis, which Melamed identifies as “absolutely central to treatment and deciding who receives maintenance therapy.” This is also recommended by the NCCN guidelines.
However, he highlighted the following practical challenge in molecular testing after neoadjuvant chemotherapy. “Probably 20% of patients have an exceptional response to neoadjuvant therapy, such that there is insufficient tissue at the time of their cytoreduction to do somatic testing,” he said.
Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy (HIPEC)
A notable difference between the 2016 and 2025 guidelines is the inclusion of HIPEC in the updated guidelines.
Commenting to this news organization, Gaillard explained the nuanced approach to HIPEC: “The committee discussed HIPEC extensively. We recognize that it may not be available at many centers and requires specially trained staff and dedicated resources. The reason for including HIPEC in the guidelines is to highlight that there have been studies that show a potential overall survival benefit.”
Melamed considers the recommendation of HIPEC to be one of the strongest aspects of the updated guidelines. “There have been two large trials and one smaller one that have shown that for patients treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy, the addition of HIPEC appears to improve overall survival,” he explained.
Implementation Strategies
The authors acknowledged that barriers to healthcare delivery present significant challenges to the implementation of the guidelines. Limited access to gynecologic oncologists in rural areas, insurance coverage gaps, and varying surgical expertise across institutions complicate the delivery of optimal care. The guidelines also emphasize the need for solutions to ensure equitable access to recommended treatments.
Melamed noted that the decentralized structure of the healthcare system in the United States complicates the uniform adoption of guidelines, particularly in resource-limited settings, adding that “geographic region and local resources and expertise influence both access to treatment and outcomes.”
Although both the updated ASCO guidelines and NCCN guidelines emphasize the importance of evaluation by a gynecologic oncologist for determining the most appropriate treatment strategy, the scarcity of gynecologic oncologists is one of the most significant barriers to accessing optimal care, according to Gaillard. She proposes telemedicine consultations and enhanced communication between medical oncologists and gynecologic oncologists to ensure equitable access.
Gaillard also commented on the challenges in implementing a multidisciplinary treatment approach, the importance of which is emphasized in the updated guidelines.
“There can be a limited availability of the multidisciplinary team to be involved in this decision-making,” she said. “Ideally, patient assessment by a gynecologic oncologist would happen in person, but recognizing that availability is limited, it doesn’t necessarily have to. Sometimes, it can just be a conversation between a medical oncologist and a gynecologic oncologist detailing a treatment plan together.”
Looking Ahead
Gaillard noted that ovarian cancer is a very active field of research and that the guidelines may need to be updated again in the near future to incorporate novel treatment approaches.
“Newer and more effective targeted therapies based on tumor profiling are being developed,” she said. “These will hopefully move earlier in the treatment course for patients. Maybe we will not use chemotherapy in the future because we will have more directed and targeted therapies.”
She also emphasized the importance of early diagnosis in shaping future treatment guidelines for ovarian cancer.
“Neoadjuvant chemotherapy is predominantly used in situations where patients have very advanced disease and may not benefit from primary cytoreductive surgery,” she noted. “If we develop better diagnostic tools that will allow us to diagnose patients earlier, then we may not need to use neoadjuvant chemotherapy.”
All funding for the administration of the guideline development project was provided by ASCO. Gaillard reported receiving consulting or advisory fees from Verastem, Merck, AstraZeneca, and Compugen; research funding from AstraZeneca, Tesaro, Compugen, Genentech/Roche, Clovis Oncology, Tempest Therapeutics, Blueprint Pharmaceutic, Immunogen, Volastra Therapeutics, and Beigene; and patents, royalties, or other intellectual property from US Patent Nos 10,258,604 and 10,905,659, licensed by Duke University to Sermonix. Melamed reported receiving research funding from the National Cancer Institute and the National Institutes of Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) has released updated guidelines for neoadjuvant chemotherapy in newly diagnosed advanced ovarian cancer, introducing changes in patient selection and treatment strategies. The changes reflect emerging evidence on racial disparities, treatment outcomes, and quality of life considerations.
The publication of the new guidance follows dramatic shifts in treatment patterns over the past decade.
“There had been a big shift in how we were treating patients in the United States,” explained Stephanie Gaillard, MD, PhD, one of the authors of the updated guidelines. “We saw a substantial drop in the number of patients undergoing primary cytoreductive surgery for ovarian cancer from about 70% of patients in 2010 to only about 37% in 2021.”
The new guidelines maintain the recommendation for platinum/taxane-based neoadjuvant chemotherapy but introduce modifications regarding timing and duration.
“It’s still a recommendation that gynecologic oncologists are involved in determining whether someone is eligible for primary cytoreductive surgery or should undergo neoadjuvant chemotherapy first,” Gaillard noted. “We emphasize that patients who are eligible for primary cytoreductive surgery should undergo surgery as opposed to receiving neoadjuvant chemotherapy.”
Alexander Melamed, MD, MPH, a gynecologic oncologist at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, who was not involved in authoring the updated guidelines, noted that additional evidence-based guidance is needed to individualize treatment plans. He pointed to four completed trials comparing neoadjuvant chemotherapy with cytoreductive surgery, noting: “When these trials have been pooled together in meta-analyses, there was a higher risk of mortality associated with primary cytoreductive surgery and a higher risk of severe complications.”
The updated guidelines take this higher risk for mortality with primary cytoreductive surgery into consideration, and patients who are not eligible for primary surgery would receive neoadjuvant chemotherapy, Gaillard noted.
Changes in Patient Selection
The 2025 guidelines describe a more nuanced approach for selecting patients for neoadjuvant chemotherapy vs primary cytoreductive surgery. While the 2016 ASCO guidelines primarily focused on disease burden and surgical resectability when selecting patients for neoadjuvant chemotherapy, the new recommendations incorporate additional factors.
The guidelines discuss recent findings showing that Black patients experience a 38% lower likelihood of undergoing cytoreductive surgery than non-Black patients. In addition, compared with non-Hispanic White women, Asian and Black women more frequently receive neoadjuvant chemotherapy with interval debulking surgery rather than primary cytoreductive surgery. According to the authors, these differences persist even after accounting for clinical factors, suggesting that structural barriers to healthcare access may play a role.
The guidelines discuss how affordability, availability, and accessibility mediate racial disparities in ovarian cancer care. According to the authors, structural inequities in healthcare access influence treatment quality for minority patients. Non-White patients face greater challenges in accessing gynecologic oncology consultations and standard-of-care combination therapy, leading to poorer survival outcomes, the guidelines say.
According to Melamed, the guidelines serve as an important tool for promoting healthcare equity. “Having recommendations and standards is incredibly important for achieving equity because once there is consensus on a best practice, it doesn’t matter if you’re rich, poor, or a patient of a particular racial or ethnic group — if you have the disease, you ought to have access to that standard,” he said.
The 2016 ASCO guidelines focused primarily on disease burden and surgical resectability, whereas the 2024 National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) Clinical Practice Guidelines for ovarian cancer focus more on oncologic outcomes and surgical considerations. Based on the NCCN guidelines, treatment selection for ovarian cancer is primarily determined by the histologic subtype, stage of disease, and whether the patient is a candidate for primary surgery. The 2025 ASCO guidelines, on the other hand, emphasize the importance of quality-of-life outcomes during treatment selection. The authors of the updated ASCO guidelines acknowledged that treatment decisions should consider both the duration and quality of life, particularly for elderly patients or those with multiple comorbidities.
Treatment Timing and Duration
The guidelines maintain the recommendations for platinum/taxane-based neoadjuvant chemotherapy described in the previous ASCO guidelines but introduce modifications regarding treatment timing and duration. The optimal window for interval cytoreductive surgery now falls after three to four chemotherapy cycles, allowing more individualized approaches based on patient response and tolerance.
In addition, postsurgical chemotherapy protocols have become more flexible. Rather than mandating a fixed number of cycles, the guidelines encourage tailoring treatment duration to individual patient factors including response assessment, performance status, and quality-of-life considerations.
The updated guidelines also emphasize the importance of genetic and molecular testing at diagnosis, which Melamed identifies as “absolutely central to treatment and deciding who receives maintenance therapy.” This is also recommended by the NCCN guidelines.
However, he highlighted the following practical challenge in molecular testing after neoadjuvant chemotherapy. “Probably 20% of patients have an exceptional response to neoadjuvant therapy, such that there is insufficient tissue at the time of their cytoreduction to do somatic testing,” he said.
Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy (HIPEC)
A notable difference between the 2016 and 2025 guidelines is the inclusion of HIPEC in the updated guidelines.
Commenting to this news organization, Gaillard explained the nuanced approach to HIPEC: “The committee discussed HIPEC extensively. We recognize that it may not be available at many centers and requires specially trained staff and dedicated resources. The reason for including HIPEC in the guidelines is to highlight that there have been studies that show a potential overall survival benefit.”
Melamed considers the recommendation of HIPEC to be one of the strongest aspects of the updated guidelines. “There have been two large trials and one smaller one that have shown that for patients treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy, the addition of HIPEC appears to improve overall survival,” he explained.
Implementation Strategies
The authors acknowledged that barriers to healthcare delivery present significant challenges to the implementation of the guidelines. Limited access to gynecologic oncologists in rural areas, insurance coverage gaps, and varying surgical expertise across institutions complicate the delivery of optimal care. The guidelines also emphasize the need for solutions to ensure equitable access to recommended treatments.
Melamed noted that the decentralized structure of the healthcare system in the United States complicates the uniform adoption of guidelines, particularly in resource-limited settings, adding that “geographic region and local resources and expertise influence both access to treatment and outcomes.”
Although both the updated ASCO guidelines and NCCN guidelines emphasize the importance of evaluation by a gynecologic oncologist for determining the most appropriate treatment strategy, the scarcity of gynecologic oncologists is one of the most significant barriers to accessing optimal care, according to Gaillard. She proposes telemedicine consultations and enhanced communication between medical oncologists and gynecologic oncologists to ensure equitable access.
Gaillard also commented on the challenges in implementing a multidisciplinary treatment approach, the importance of which is emphasized in the updated guidelines.
“There can be a limited availability of the multidisciplinary team to be involved in this decision-making,” she said. “Ideally, patient assessment by a gynecologic oncologist would happen in person, but recognizing that availability is limited, it doesn’t necessarily have to. Sometimes, it can just be a conversation between a medical oncologist and a gynecologic oncologist detailing a treatment plan together.”
Looking Ahead
Gaillard noted that ovarian cancer is a very active field of research and that the guidelines may need to be updated again in the near future to incorporate novel treatment approaches.
“Newer and more effective targeted therapies based on tumor profiling are being developed,” she said. “These will hopefully move earlier in the treatment course for patients. Maybe we will not use chemotherapy in the future because we will have more directed and targeted therapies.”
She also emphasized the importance of early diagnosis in shaping future treatment guidelines for ovarian cancer.
“Neoadjuvant chemotherapy is predominantly used in situations where patients have very advanced disease and may not benefit from primary cytoreductive surgery,” she noted. “If we develop better diagnostic tools that will allow us to diagnose patients earlier, then we may not need to use neoadjuvant chemotherapy.”
All funding for the administration of the guideline development project was provided by ASCO. Gaillard reported receiving consulting or advisory fees from Verastem, Merck, AstraZeneca, and Compugen; research funding from AstraZeneca, Tesaro, Compugen, Genentech/Roche, Clovis Oncology, Tempest Therapeutics, Blueprint Pharmaceutic, Immunogen, Volastra Therapeutics, and Beigene; and patents, royalties, or other intellectual property from US Patent Nos 10,258,604 and 10,905,659, licensed by Duke University to Sermonix. Melamed reported receiving research funding from the National Cancer Institute and the National Institutes of Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) has released updated guidelines for neoadjuvant chemotherapy in newly diagnosed advanced ovarian cancer, introducing changes in patient selection and treatment strategies. The changes reflect emerging evidence on racial disparities, treatment outcomes, and quality of life considerations.
The publication of the new guidance follows dramatic shifts in treatment patterns over the past decade.
“There had been a big shift in how we were treating patients in the United States,” explained Stephanie Gaillard, MD, PhD, one of the authors of the updated guidelines. “We saw a substantial drop in the number of patients undergoing primary cytoreductive surgery for ovarian cancer from about 70% of patients in 2010 to only about 37% in 2021.”
The new guidelines maintain the recommendation for platinum/taxane-based neoadjuvant chemotherapy but introduce modifications regarding timing and duration.
“It’s still a recommendation that gynecologic oncologists are involved in determining whether someone is eligible for primary cytoreductive surgery or should undergo neoadjuvant chemotherapy first,” Gaillard noted. “We emphasize that patients who are eligible for primary cytoreductive surgery should undergo surgery as opposed to receiving neoadjuvant chemotherapy.”
Alexander Melamed, MD, MPH, a gynecologic oncologist at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, who was not involved in authoring the updated guidelines, noted that additional evidence-based guidance is needed to individualize treatment plans. He pointed to four completed trials comparing neoadjuvant chemotherapy with cytoreductive surgery, noting: “When these trials have been pooled together in meta-analyses, there was a higher risk of mortality associated with primary cytoreductive surgery and a higher risk of severe complications.”
The updated guidelines take this higher risk for mortality with primary cytoreductive surgery into consideration, and patients who are not eligible for primary surgery would receive neoadjuvant chemotherapy, Gaillard noted.
Changes in Patient Selection
The 2025 guidelines describe a more nuanced approach for selecting patients for neoadjuvant chemotherapy vs primary cytoreductive surgery. While the 2016 ASCO guidelines primarily focused on disease burden and surgical resectability when selecting patients for neoadjuvant chemotherapy, the new recommendations incorporate additional factors.
The guidelines discuss recent findings showing that Black patients experience a 38% lower likelihood of undergoing cytoreductive surgery than non-Black patients. In addition, compared with non-Hispanic White women, Asian and Black women more frequently receive neoadjuvant chemotherapy with interval debulking surgery rather than primary cytoreductive surgery. According to the authors, these differences persist even after accounting for clinical factors, suggesting that structural barriers to healthcare access may play a role.
The guidelines discuss how affordability, availability, and accessibility mediate racial disparities in ovarian cancer care. According to the authors, structural inequities in healthcare access influence treatment quality for minority patients. Non-White patients face greater challenges in accessing gynecologic oncology consultations and standard-of-care combination therapy, leading to poorer survival outcomes, the guidelines say.
According to Melamed, the guidelines serve as an important tool for promoting healthcare equity. “Having recommendations and standards is incredibly important for achieving equity because once there is consensus on a best practice, it doesn’t matter if you’re rich, poor, or a patient of a particular racial or ethnic group — if you have the disease, you ought to have access to that standard,” he said.
The 2016 ASCO guidelines focused primarily on disease burden and surgical resectability, whereas the 2024 National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) Clinical Practice Guidelines for ovarian cancer focus more on oncologic outcomes and surgical considerations. Based on the NCCN guidelines, treatment selection for ovarian cancer is primarily determined by the histologic subtype, stage of disease, and whether the patient is a candidate for primary surgery. The 2025 ASCO guidelines, on the other hand, emphasize the importance of quality-of-life outcomes during treatment selection. The authors of the updated ASCO guidelines acknowledged that treatment decisions should consider both the duration and quality of life, particularly for elderly patients or those with multiple comorbidities.
Treatment Timing and Duration
The guidelines maintain the recommendations for platinum/taxane-based neoadjuvant chemotherapy described in the previous ASCO guidelines but introduce modifications regarding treatment timing and duration. The optimal window for interval cytoreductive surgery now falls after three to four chemotherapy cycles, allowing more individualized approaches based on patient response and tolerance.
In addition, postsurgical chemotherapy protocols have become more flexible. Rather than mandating a fixed number of cycles, the guidelines encourage tailoring treatment duration to individual patient factors including response assessment, performance status, and quality-of-life considerations.
The updated guidelines also emphasize the importance of genetic and molecular testing at diagnosis, which Melamed identifies as “absolutely central to treatment and deciding who receives maintenance therapy.” This is also recommended by the NCCN guidelines.
However, he highlighted the following practical challenge in molecular testing after neoadjuvant chemotherapy. “Probably 20% of patients have an exceptional response to neoadjuvant therapy, such that there is insufficient tissue at the time of their cytoreduction to do somatic testing,” he said.
Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy (HIPEC)
A notable difference between the 2016 and 2025 guidelines is the inclusion of HIPEC in the updated guidelines.
Commenting to this news organization, Gaillard explained the nuanced approach to HIPEC: “The committee discussed HIPEC extensively. We recognize that it may not be available at many centers and requires specially trained staff and dedicated resources. The reason for including HIPEC in the guidelines is to highlight that there have been studies that show a potential overall survival benefit.”
Melamed considers the recommendation of HIPEC to be one of the strongest aspects of the updated guidelines. “There have been two large trials and one smaller one that have shown that for patients treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy, the addition of HIPEC appears to improve overall survival,” he explained.
Implementation Strategies
The authors acknowledged that barriers to healthcare delivery present significant challenges to the implementation of the guidelines. Limited access to gynecologic oncologists in rural areas, insurance coverage gaps, and varying surgical expertise across institutions complicate the delivery of optimal care. The guidelines also emphasize the need for solutions to ensure equitable access to recommended treatments.
Melamed noted that the decentralized structure of the healthcare system in the United States complicates the uniform adoption of guidelines, particularly in resource-limited settings, adding that “geographic region and local resources and expertise influence both access to treatment and outcomes.”
Although both the updated ASCO guidelines and NCCN guidelines emphasize the importance of evaluation by a gynecologic oncologist for determining the most appropriate treatment strategy, the scarcity of gynecologic oncologists is one of the most significant barriers to accessing optimal care, according to Gaillard. She proposes telemedicine consultations and enhanced communication between medical oncologists and gynecologic oncologists to ensure equitable access.
Gaillard also commented on the challenges in implementing a multidisciplinary treatment approach, the importance of which is emphasized in the updated guidelines.
“There can be a limited availability of the multidisciplinary team to be involved in this decision-making,” she said. “Ideally, patient assessment by a gynecologic oncologist would happen in person, but recognizing that availability is limited, it doesn’t necessarily have to. Sometimes, it can just be a conversation between a medical oncologist and a gynecologic oncologist detailing a treatment plan together.”
Looking Ahead
Gaillard noted that ovarian cancer is a very active field of research and that the guidelines may need to be updated again in the near future to incorporate novel treatment approaches.
“Newer and more effective targeted therapies based on tumor profiling are being developed,” she said. “These will hopefully move earlier in the treatment course for patients. Maybe we will not use chemotherapy in the future because we will have more directed and targeted therapies.”
She also emphasized the importance of early diagnosis in shaping future treatment guidelines for ovarian cancer.
“Neoadjuvant chemotherapy is predominantly used in situations where patients have very advanced disease and may not benefit from primary cytoreductive surgery,” she noted. “If we develop better diagnostic tools that will allow us to diagnose patients earlier, then we may not need to use neoadjuvant chemotherapy.”
All funding for the administration of the guideline development project was provided by ASCO. Gaillard reported receiving consulting or advisory fees from Verastem, Merck, AstraZeneca, and Compugen; research funding from AstraZeneca, Tesaro, Compugen, Genentech/Roche, Clovis Oncology, Tempest Therapeutics, Blueprint Pharmaceutic, Immunogen, Volastra Therapeutics, and Beigene; and patents, royalties, or other intellectual property from US Patent Nos 10,258,604 and 10,905,659, licensed by Duke University to Sermonix. Melamed reported receiving research funding from the National Cancer Institute and the National Institutes of Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.