User login
AVAHO
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]


A New ADC for Lung Cancer: Datopotamab Deruxtecan Now Approved by FDA
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Hello. It’s Mark Kris, from Memorial Sloan Kettering, talking about a birthday gift I received on June 23 when the FDA approved the indication of datopotamab deruxtecan for people with lung cancers. We have another drug, our third ADC (antibody-drug conjugate) to fight lung cancer, so that’s a gift.
Let’s talk a little bit about that agent. It’s an interesting twist in our practice patterns. What can the drug do? It had a response rate of 45%, which is really important in patients that had EGFR mutations with progression on osimertinib. We really need drugs in that space. The duration of response was about 7 months, which is significant.
One interesting thing in the approval, [was] that the response rate of the blinded folks was greater than that in the investigator-assessed response by about 10%. It’s very interesting. Clearly, we have another drug, and we have it in a space where we need it.
Let’s talk a bit about the toxicity. I’m going to focus more on the paper by Bardia et al that compared datopotamab deruxtecan to various chemo drugs in breast cancer, not in lung cancer. You can take this a little bit with a grain of salt.
First, they saw a whole different array of side effects with datopotamab deruxtecan, things that we don’t normally deal with here. Nausea, stomatitis, alopecia, dry eye, and vomiting. All of those were more than 10% more common in patients that received datopotamab deruxtecan compared to the control. The only things that were more common with the control were neutropenia, leukopenia, and hand-foot syndrome in patients that had capecitabine.
One thing, though, is while you say, “Oh, these weren’t dangerous side effects,” they surely were lifestyle altering. Nobody wants to have these side effects on a daily basis. Again, there’s an increasing awareness about these kinds of lower-grade but still lifestyle-disrupting side effects. When it goes on day after day, you really have to balance that into the benefit you’re going to receive.
I think the second important point is how, when we use this drug, we’re going to have to go to another level to deal with the adverse effects that we are going to see. The first would be nausea and emesis. It is a highly emetogenic regimen based on the NCCN (National Comprehensive Cancer Network) guidelines, so you would need either 3 or 4 antiemetic drugs. That’s number one.
Number two, because of the potential eye problems, you need an eye exam before treatment — and the label says at least annually — with any symptoms. I think it’s very important that you give the patients eyedrops, and in general, the preservative-free eyedrops are the ones that are most effective.
Stomatitis is a very common side effect with that agent. It’s really not seen with the other drugs that even contain the same warhead. There, dexamethasone rinses are important. Now, this is a compounded medicine so you need to be very careful in making sure that you identify pharmacies that will prepare this and will have it available for the patients that need it.
Last, there is the risk of hypersensitivity reactions and there’s a recommendation for premedication for that. As you think about using datopotamab deruxtecan, you need to have all your ducks in a row to treat side effects. You need prophylaxis for hypersensitivity reactions, nausea, and emesis.
The patient will need an eye exam. You need to prepare the patient for possible dry eye and teach them which eyedrops are the best. You also need to ensure the availability of dexamethasone rinses and mouth washes. All that needs to be in place to make sure that the patient can safely use the drug.
I think it’s going to be a useful drug. We don’t yet have a uniformly available way to select patients for its use other than EGFR. I should note that the approval is for EGFR-mutated lung cancers. It doesn’t say which type of mutation, so that would give you some latitude in giving it for exon 20 atypicals as well as for the common sensitizing mutation.
We have another drug. It’s clearly going to be a useful one. It clearly comes with many adverse effects that we don’t normally treat on an everyday basis, we’re used to the diarrhea and skin changes that come on with the EGFR TKIs.
This pattern of side effects is different and requires some additional attention, but with it, the drug can be useful. I’m glad that we have yet another way to fight this disease.
Mark G. Kris, MD, Professor of Medicine, Weill Cornell Medical College; Attending Physician, Department of Medicine, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, New York , has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for: AstraZeneca; Bristol-Myers Squibb; Merck; Daiichi Sankyo; Received research grant from: National Institute of Health; Received income in an amount equal to or greater than $250 from: AstraZeneca; Bristol-Myers Squibb; Merck; Daiichi Sankyo Others: Editorial support from Genentech
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Hello. It’s Mark Kris, from Memorial Sloan Kettering, talking about a birthday gift I received on June 23 when the FDA approved the indication of datopotamab deruxtecan for people with lung cancers. We have another drug, our third ADC (antibody-drug conjugate) to fight lung cancer, so that’s a gift.
Let’s talk a little bit about that agent. It’s an interesting twist in our practice patterns. What can the drug do? It had a response rate of 45%, which is really important in patients that had EGFR mutations with progression on osimertinib. We really need drugs in that space. The duration of response was about 7 months, which is significant.
One interesting thing in the approval, [was] that the response rate of the blinded folks was greater than that in the investigator-assessed response by about 10%. It’s very interesting. Clearly, we have another drug, and we have it in a space where we need it.
Let’s talk a bit about the toxicity. I’m going to focus more on the paper by Bardia et al that compared datopotamab deruxtecan to various chemo drugs in breast cancer, not in lung cancer. You can take this a little bit with a grain of salt.
First, they saw a whole different array of side effects with datopotamab deruxtecan, things that we don’t normally deal with here. Nausea, stomatitis, alopecia, dry eye, and vomiting. All of those were more than 10% more common in patients that received datopotamab deruxtecan compared to the control. The only things that were more common with the control were neutropenia, leukopenia, and hand-foot syndrome in patients that had capecitabine.
One thing, though, is while you say, “Oh, these weren’t dangerous side effects,” they surely were lifestyle altering. Nobody wants to have these side effects on a daily basis. Again, there’s an increasing awareness about these kinds of lower-grade but still lifestyle-disrupting side effects. When it goes on day after day, you really have to balance that into the benefit you’re going to receive.
I think the second important point is how, when we use this drug, we’re going to have to go to another level to deal with the adverse effects that we are going to see. The first would be nausea and emesis. It is a highly emetogenic regimen based on the NCCN (National Comprehensive Cancer Network) guidelines, so you would need either 3 or 4 antiemetic drugs. That’s number one.
Number two, because of the potential eye problems, you need an eye exam before treatment — and the label says at least annually — with any symptoms. I think it’s very important that you give the patients eyedrops, and in general, the preservative-free eyedrops are the ones that are most effective.
Stomatitis is a very common side effect with that agent. It’s really not seen with the other drugs that even contain the same warhead. There, dexamethasone rinses are important. Now, this is a compounded medicine so you need to be very careful in making sure that you identify pharmacies that will prepare this and will have it available for the patients that need it.
Last, there is the risk of hypersensitivity reactions and there’s a recommendation for premedication for that. As you think about using datopotamab deruxtecan, you need to have all your ducks in a row to treat side effects. You need prophylaxis for hypersensitivity reactions, nausea, and emesis.
The patient will need an eye exam. You need to prepare the patient for possible dry eye and teach them which eyedrops are the best. You also need to ensure the availability of dexamethasone rinses and mouth washes. All that needs to be in place to make sure that the patient can safely use the drug.
I think it’s going to be a useful drug. We don’t yet have a uniformly available way to select patients for its use other than EGFR. I should note that the approval is for EGFR-mutated lung cancers. It doesn’t say which type of mutation, so that would give you some latitude in giving it for exon 20 atypicals as well as for the common sensitizing mutation.
We have another drug. It’s clearly going to be a useful one. It clearly comes with many adverse effects that we don’t normally treat on an everyday basis, we’re used to the diarrhea and skin changes that come on with the EGFR TKIs.
This pattern of side effects is different and requires some additional attention, but with it, the drug can be useful. I’m glad that we have yet another way to fight this disease.
Mark G. Kris, MD, Professor of Medicine, Weill Cornell Medical College; Attending Physician, Department of Medicine, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, New York , has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for: AstraZeneca; Bristol-Myers Squibb; Merck; Daiichi Sankyo; Received research grant from: National Institute of Health; Received income in an amount equal to or greater than $250 from: AstraZeneca; Bristol-Myers Squibb; Merck; Daiichi Sankyo Others: Editorial support from Genentech
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Hello. It’s Mark Kris, from Memorial Sloan Kettering, talking about a birthday gift I received on June 23 when the FDA approved the indication of datopotamab deruxtecan for people with lung cancers. We have another drug, our third ADC (antibody-drug conjugate) to fight lung cancer, so that’s a gift.
Let’s talk a little bit about that agent. It’s an interesting twist in our practice patterns. What can the drug do? It had a response rate of 45%, which is really important in patients that had EGFR mutations with progression on osimertinib. We really need drugs in that space. The duration of response was about 7 months, which is significant.
One interesting thing in the approval, [was] that the response rate of the blinded folks was greater than that in the investigator-assessed response by about 10%. It’s very interesting. Clearly, we have another drug, and we have it in a space where we need it.
Let’s talk a bit about the toxicity. I’m going to focus more on the paper by Bardia et al that compared datopotamab deruxtecan to various chemo drugs in breast cancer, not in lung cancer. You can take this a little bit with a grain of salt.
First, they saw a whole different array of side effects with datopotamab deruxtecan, things that we don’t normally deal with here. Nausea, stomatitis, alopecia, dry eye, and vomiting. All of those were more than 10% more common in patients that received datopotamab deruxtecan compared to the control. The only things that were more common with the control were neutropenia, leukopenia, and hand-foot syndrome in patients that had capecitabine.
One thing, though, is while you say, “Oh, these weren’t dangerous side effects,” they surely were lifestyle altering. Nobody wants to have these side effects on a daily basis. Again, there’s an increasing awareness about these kinds of lower-grade but still lifestyle-disrupting side effects. When it goes on day after day, you really have to balance that into the benefit you’re going to receive.
I think the second important point is how, when we use this drug, we’re going to have to go to another level to deal with the adverse effects that we are going to see. The first would be nausea and emesis. It is a highly emetogenic regimen based on the NCCN (National Comprehensive Cancer Network) guidelines, so you would need either 3 or 4 antiemetic drugs. That’s number one.
Number two, because of the potential eye problems, you need an eye exam before treatment — and the label says at least annually — with any symptoms. I think it’s very important that you give the patients eyedrops, and in general, the preservative-free eyedrops are the ones that are most effective.
Stomatitis is a very common side effect with that agent. It’s really not seen with the other drugs that even contain the same warhead. There, dexamethasone rinses are important. Now, this is a compounded medicine so you need to be very careful in making sure that you identify pharmacies that will prepare this and will have it available for the patients that need it.
Last, there is the risk of hypersensitivity reactions and there’s a recommendation for premedication for that. As you think about using datopotamab deruxtecan, you need to have all your ducks in a row to treat side effects. You need prophylaxis for hypersensitivity reactions, nausea, and emesis.
The patient will need an eye exam. You need to prepare the patient for possible dry eye and teach them which eyedrops are the best. You also need to ensure the availability of dexamethasone rinses and mouth washes. All that needs to be in place to make sure that the patient can safely use the drug.
I think it’s going to be a useful drug. We don’t yet have a uniformly available way to select patients for its use other than EGFR. I should note that the approval is for EGFR-mutated lung cancers. It doesn’t say which type of mutation, so that would give you some latitude in giving it for exon 20 atypicals as well as for the common sensitizing mutation.
We have another drug. It’s clearly going to be a useful one. It clearly comes with many adverse effects that we don’t normally treat on an everyday basis, we’re used to the diarrhea and skin changes that come on with the EGFR TKIs.
This pattern of side effects is different and requires some additional attention, but with it, the drug can be useful. I’m glad that we have yet another way to fight this disease.
Mark G. Kris, MD, Professor of Medicine, Weill Cornell Medical College; Attending Physician, Department of Medicine, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, New York , has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for: AstraZeneca; Bristol-Myers Squibb; Merck; Daiichi Sankyo; Received research grant from: National Institute of Health; Received income in an amount equal to or greater than $250 from: AstraZeneca; Bristol-Myers Squibb; Merck; Daiichi Sankyo Others: Editorial support from Genentech
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A Voice for Those Caring for Veterans With Cancer
A Voice for Those Caring for Veterans With Cancer
At some point, most Americans will experience the anxiety associated with an organizational restructure or a corporate budget cut that leads to job loss. Self-assurances may follow by telling ourselves we will be fine, and we could even start a new position that (if we're lucky) will be better than our previous one. It can be devastating, but is not a life-or-death scenario.
Unless you care for veterans with cancer.
The recent workforce reductions across the US Department of Veterans of Affairs (VA) health care system, whether through voluntary retirements or forced layoffs, is a life-threatening crisis. Every position lost has the potential to directly impact whether a veteran receives the necessary care in their battle with cancer.
Veterans deserve every opportunity, treatment plan, and resource available to ensure their comfort and survival. They are entitled to the specialized, comprehensive, and thorough care they receive through the VA—care that cannot be duplicated in community health care. Because many of the health challenges they face are a direct result of serving our country, we owe it to them to provide the best care available from the most highly-trained and competent clinicians. This level of excellence cannot be achieved in a gutted or chaotic system.
Reducing or eliminating VA health care positions is a decision that demands careful examination. Like any organization, the VA experiences some measure of waste or inefficiency that should be eliminated. But that cannot be done swiftly or in large-scale action.
Consider these examples: the reduction of force resulting in the removal of those deemed to hold unnecessary administrative positions—such as continuing education or physician oversight—has a direct impact on a clinician's ability to provide the most current and precise care. Reduced research funding limits the VA's contribution to health care innovation. The loss of contract positions that appear superfluous on paper represent the staff who schedule appointments, chemotherapy or radiation therapy, and wrap-around services for veterans. Even reducing auxiliary services like laundry may seem like a cost-saving measure—until the hospital can't admit new patients due to lack of sanitized linens.
VA employees know that veterans need specialized care for their complex and unique challenges. That individualized care has led to the VA nearly eliminating disparity gaps experienced in traditional health care. The removal of support positions and opportunities in professional development demands coordination with less-prepared community-based health care; overpopulated work environments will have a lasting impact. Limiting the workforce will make it impossible to provide coordinated and exceptional care.
The Association of VA Hematology/Oncology (AVAHO) is a leader in professional development opportunities for those who care for veterans with cancer. As a nonprofit organization, AVAHO is also a voice for those working with veterans with cancer to ensure they receive the care they deserve. AVAHO is calling on its colleagues, veterans, and those committed to supporting veterans to voice their opposition to reducing critical staff, research, and resources within the VA.
We ask veterans to share stories describing the difference VA care makes. We ask clinicians—including those within the federal system—to explain how a system that is well-staffed, supported, and with ample resources can impact patient care. Americans must stand for the care our veterans have earned.
Most importantly, we call on policymakers to carefully consider the impact each position has on the outcome of excellent, well-coordinated, and state-of-the-art care. The lives of our veterans depend on it.
AVAHO is a 501(c)3 nonprofit organization dedicated to supporting and educating health care providers who serve veterans with cancer and hematological disorders. You can find out more and support their advocacy initiatives at www.avaho.org.
At some point, most Americans will experience the anxiety associated with an organizational restructure or a corporate budget cut that leads to job loss. Self-assurances may follow by telling ourselves we will be fine, and we could even start a new position that (if we're lucky) will be better than our previous one. It can be devastating, but is not a life-or-death scenario.
Unless you care for veterans with cancer.
The recent workforce reductions across the US Department of Veterans of Affairs (VA) health care system, whether through voluntary retirements or forced layoffs, is a life-threatening crisis. Every position lost has the potential to directly impact whether a veteran receives the necessary care in their battle with cancer.
Veterans deserve every opportunity, treatment plan, and resource available to ensure their comfort and survival. They are entitled to the specialized, comprehensive, and thorough care they receive through the VA—care that cannot be duplicated in community health care. Because many of the health challenges they face are a direct result of serving our country, we owe it to them to provide the best care available from the most highly-trained and competent clinicians. This level of excellence cannot be achieved in a gutted or chaotic system.
Reducing or eliminating VA health care positions is a decision that demands careful examination. Like any organization, the VA experiences some measure of waste or inefficiency that should be eliminated. But that cannot be done swiftly or in large-scale action.
Consider these examples: the reduction of force resulting in the removal of those deemed to hold unnecessary administrative positions—such as continuing education or physician oversight—has a direct impact on a clinician's ability to provide the most current and precise care. Reduced research funding limits the VA's contribution to health care innovation. The loss of contract positions that appear superfluous on paper represent the staff who schedule appointments, chemotherapy or radiation therapy, and wrap-around services for veterans. Even reducing auxiliary services like laundry may seem like a cost-saving measure—until the hospital can't admit new patients due to lack of sanitized linens.
VA employees know that veterans need specialized care for their complex and unique challenges. That individualized care has led to the VA nearly eliminating disparity gaps experienced in traditional health care. The removal of support positions and opportunities in professional development demands coordination with less-prepared community-based health care; overpopulated work environments will have a lasting impact. Limiting the workforce will make it impossible to provide coordinated and exceptional care.
The Association of VA Hematology/Oncology (AVAHO) is a leader in professional development opportunities for those who care for veterans with cancer. As a nonprofit organization, AVAHO is also a voice for those working with veterans with cancer to ensure they receive the care they deserve. AVAHO is calling on its colleagues, veterans, and those committed to supporting veterans to voice their opposition to reducing critical staff, research, and resources within the VA.
We ask veterans to share stories describing the difference VA care makes. We ask clinicians—including those within the federal system—to explain how a system that is well-staffed, supported, and with ample resources can impact patient care. Americans must stand for the care our veterans have earned.
Most importantly, we call on policymakers to carefully consider the impact each position has on the outcome of excellent, well-coordinated, and state-of-the-art care. The lives of our veterans depend on it.
AVAHO is a 501(c)3 nonprofit organization dedicated to supporting and educating health care providers who serve veterans with cancer and hematological disorders. You can find out more and support their advocacy initiatives at www.avaho.org.
At some point, most Americans will experience the anxiety associated with an organizational restructure or a corporate budget cut that leads to job loss. Self-assurances may follow by telling ourselves we will be fine, and we could even start a new position that (if we're lucky) will be better than our previous one. It can be devastating, but is not a life-or-death scenario.
Unless you care for veterans with cancer.
The recent workforce reductions across the US Department of Veterans of Affairs (VA) health care system, whether through voluntary retirements or forced layoffs, is a life-threatening crisis. Every position lost has the potential to directly impact whether a veteran receives the necessary care in their battle with cancer.
Veterans deserve every opportunity, treatment plan, and resource available to ensure their comfort and survival. They are entitled to the specialized, comprehensive, and thorough care they receive through the VA—care that cannot be duplicated in community health care. Because many of the health challenges they face are a direct result of serving our country, we owe it to them to provide the best care available from the most highly-trained and competent clinicians. This level of excellence cannot be achieved in a gutted or chaotic system.
Reducing or eliminating VA health care positions is a decision that demands careful examination. Like any organization, the VA experiences some measure of waste or inefficiency that should be eliminated. But that cannot be done swiftly or in large-scale action.
Consider these examples: the reduction of force resulting in the removal of those deemed to hold unnecessary administrative positions—such as continuing education or physician oversight—has a direct impact on a clinician's ability to provide the most current and precise care. Reduced research funding limits the VA's contribution to health care innovation. The loss of contract positions that appear superfluous on paper represent the staff who schedule appointments, chemotherapy or radiation therapy, and wrap-around services for veterans. Even reducing auxiliary services like laundry may seem like a cost-saving measure—until the hospital can't admit new patients due to lack of sanitized linens.
VA employees know that veterans need specialized care for their complex and unique challenges. That individualized care has led to the VA nearly eliminating disparity gaps experienced in traditional health care. The removal of support positions and opportunities in professional development demands coordination with less-prepared community-based health care; overpopulated work environments will have a lasting impact. Limiting the workforce will make it impossible to provide coordinated and exceptional care.
The Association of VA Hematology/Oncology (AVAHO) is a leader in professional development opportunities for those who care for veterans with cancer. As a nonprofit organization, AVAHO is also a voice for those working with veterans with cancer to ensure they receive the care they deserve. AVAHO is calling on its colleagues, veterans, and those committed to supporting veterans to voice their opposition to reducing critical staff, research, and resources within the VA.
We ask veterans to share stories describing the difference VA care makes. We ask clinicians—including those within the federal system—to explain how a system that is well-staffed, supported, and with ample resources can impact patient care. Americans must stand for the care our veterans have earned.
Most importantly, we call on policymakers to carefully consider the impact each position has on the outcome of excellent, well-coordinated, and state-of-the-art care. The lives of our veterans depend on it.
AVAHO is a 501(c)3 nonprofit organization dedicated to supporting and educating health care providers who serve veterans with cancer and hematological disorders. You can find out more and support their advocacy initiatives at www.avaho.org.
A Voice for Those Caring for Veterans With Cancer
A Voice for Those Caring for Veterans With Cancer
Radiation and Medical Oncology Perspectives on Oligometastatic Disease Treatment
Radiation and Medical Oncology Perspectives on Oligometastatic Disease Treatment
The treatment of metastatic solid tumors has been based historically on systemic therapies, with the goal of delaying progression and extend life as long as possible, with tolerable treatment-related adverse events. Some exceptions were made for local treatment with surgery or radiotherapy (RT), often for patients with a single metastasis. A 1939 report describes a patient with renal adenocarcinoma and a solitary lung metastasis who underwent RT to the lung lesion after nephrectomy and subsequently partial lobectomy after the metastatic lesion progressed. The authors argued that if a metastasis appears solitary and accessible, it is plausible to remove it in addition to the primary growth.1
In 1995 Hellman and Weichselbaum proposed oligometastatic disease (OMD). They reasoned that malignancy exists along a spectrum from localized disease to widely disseminated disease, with OMD existing in between with a still-restricted tumor metastatic capacity. Appropriately selected patients with OMD may be candidates for prolonged disease-free survival or cure with the addition of local therapy to systemic therapy.2
The EORTC 4004 phase 2 randomized control trial (RCT) analyzed radiofrequency ablation (RFA) for colorectal liver metastases with systemic therapy vs systemic therapy alone for patients with ≤ 9 liver lesions.3 Systemic therapyconsisted of 5-FU/leucovorin/oxaliplatin, with bevacizumab added to the regimen 3.5 years into the study, per updated standard- of-care. This trial was the first to demonstrate the benefit of aggressive local treatment vs system treatment alone for OMD with a progression-free survival (PFS) benefit (16.8 vs 9.9 months; hazard ratio [HR], 0.63; P = .03) and overall survival (OS) benefit (45.3 vs 40.5 months; HR, 0.74; P = .02) with the addition of local treatment with RFA.
Since the presentations of the SABR-COMET phase 2 RCT and another study by Gomez et al at the American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO) 2018 annual meeting, the paradigm for offering local RT for OMD has rapidly evolved. Both studies found PFS and OS benefits of RT for patients with OMD.4,5 Additional RCTs have since demonstrated that for properly selected patients with OMD, aggressive local RT improved PFS and OS.6-9 These small studies have led to larger RCTs to better understand who benefits from local consolidative treatment, particularly RT.10,11
There is a large degree of heterogeneity in how oncologists define and approach OMD treatment. The 2020 European Society for Radiotherapy and Oncology (ESTRO) and ASTRO consensus guidelines defined the OMD state as 1 to 5 metastatic lesions for which all metastatic sites are safely treatable.12 The purpose of this study was to evaluate perceptions and practice patterns among radiation oncologists and medical oncologists regarding the use of local RT for OMD across the Veterans Health Administration (VHA).
Methods
A 12-question survey was developed by the VHA Palliative Radiotherapy Task Force using the ESTRO-ASTRO consensus guidelines to define OMD. The survey was emailed to the VHA radiation oncology and medical oncology listservs on August 1, 2023. These listservs consist of physicians in these specialties either directly employed by the VHA or serve in its facilities as contractors. The original response closure date was August 11, 2023, but it was extended to August 18, 2023, to increase responses. No incentives were offered to respondents. Two email reminders were sent to the medical oncology listserv and 3 to the radiation oncology listserv. Descriptive statistics and X2 tests were used for data analysis. The impact of specialty and presence of an on-site department of radiation oncology were reviewed. This project was approved by the VHA National Oncology Program and National Radiation Oncology Program.
Results
The survey was sent to 125 radiation oncologists and 515 medical oncologists and 106 were completed for a 16.6% response rate. There were 59 (55.7%) radiation oncologist responses and 47 (44.3%) medical oncologist responses. Most (96.2%) respondents were board-certified, and 84 (79.2%) were affiliated with an academic center. Not every respondent answered every question (Table).
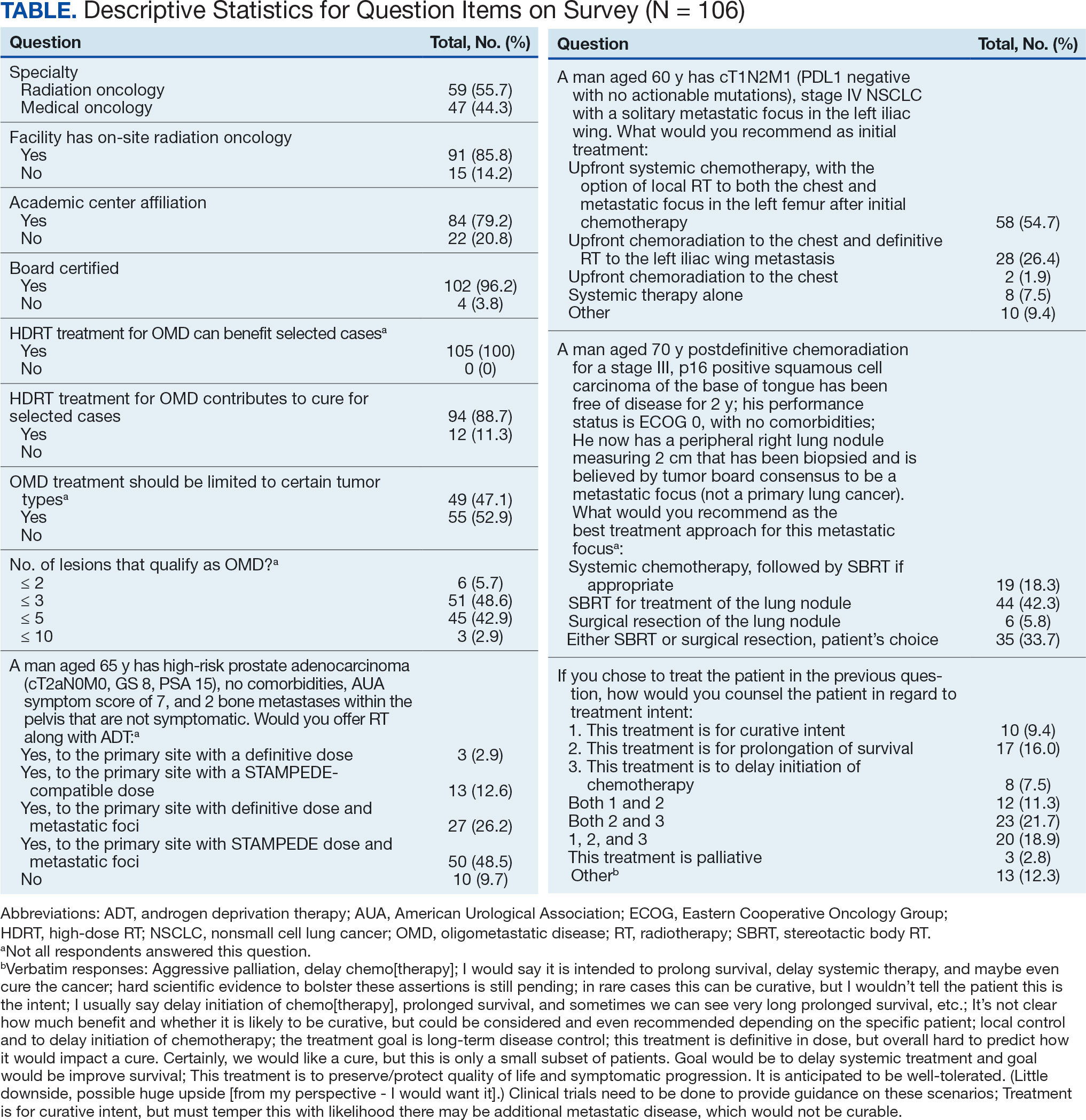
All respondents (n = 105) indicated there is a potential benefit of high-dose RT for appropriately selected cases. Ninety-four oncologists (88.7%) believed that RT for OMD contributes to cure (88.1% of radiation oncologists, 89.4% of medical oncologists; P = .84) for appropriately selected cases. Some respondents who did not believe RT for OMD contributes to cure added comments about other perceived benefits, such as local disease control for palliation, delaying systemic therapy with its associated toxicities, and prolongation of disease-free survival or OS. A higher percentage of respondents with academic affiliations believed high-dose RT contributes to cure, although this difference did not reach statistical significance (Figure 1).

Fifty-five respondents (51.9%; 55.2% radiation oncologists vs 50.0% medical oncologists; P = .60) responded that local RT for OMD treatment should not be limited by primary tumor type. Of respondents who responded that OMD treatment should be limited based on the type of primary tumor, many provided comments that argued there was a benefit for non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), prostate adenocarcinoma (PCa), and colorectal cancer.
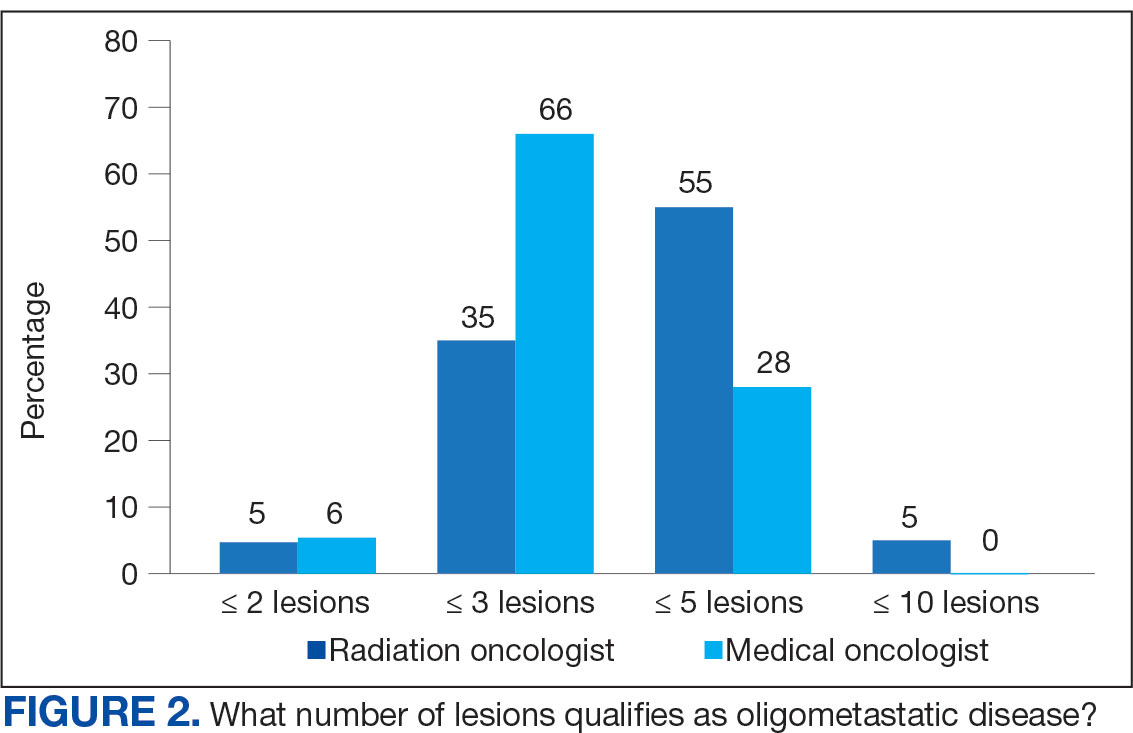
The definition of how many metastatic lesions qualify as OMD varied. A total of 48.6% of respondents defined OMD as ≤ 3 lesions and 42.9% answered ≤ 5 lesions. A majority of radiation oncologists (55.2%) classified ≤ 5 lesions as OMD, whereas a majority of medical oncologists (66.0%) considered ≤ 3 lesions as OMD (P = .006) (Figure 2).
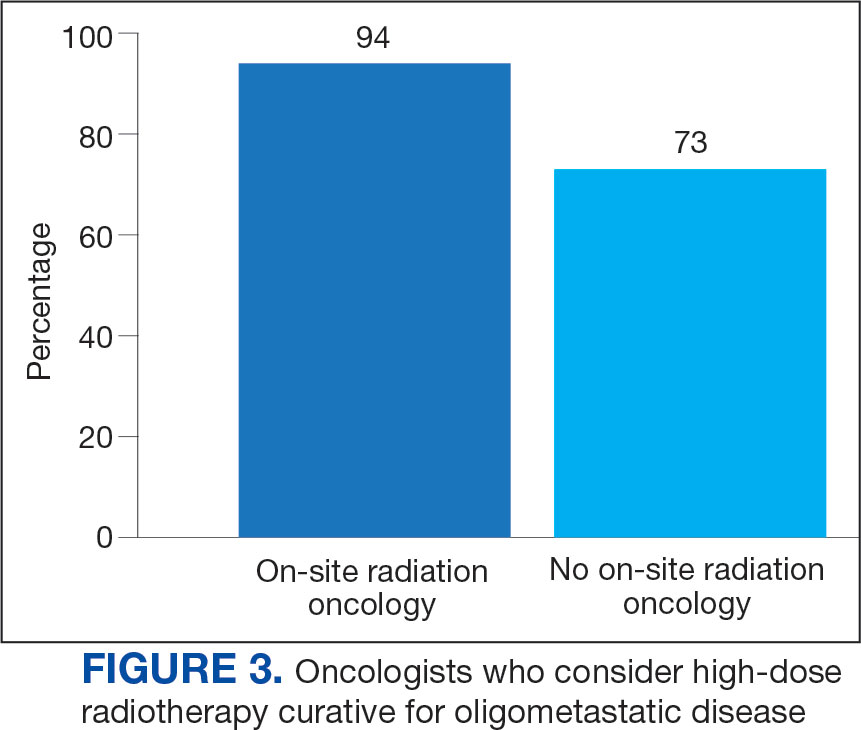
Thirty-six medical oncologists (76.6%) report having an on-site department of radiation oncology (Figure 3). This subgroup was more likely to consider local RT potentially curative compared with their medical oncology peers without on-site radiation oncology (94.4% vs 72.7%; P = .04).
Case Management
The 3 clinical cases demonstrated the heterogeneity of management approaches for OMD. The first described a man aged 65 years with PCa and 2 asymptomatic pelvic bone metastases. Ninety-three respondents (90.3%) recommended RT at the primary site and 74.8% recommended RT to both the primary site and metastatic foci. Sixty-three respondents (67.7%) recommended a STAMPEDE-compatible dose, and 30 (32.3%) recommended a definitive dose.
The second clinical case was a 60-year-old man with a cT1N2M1 NSCLC, with a solitary metastatic focus to the left iliac wing. Fifty-eight respondents (54.7%) recommended upfront systemic chemotherapy and the option of local therapy to the chest and metastatic focus after initial chemotherapy; 28 respondents (26.4%) recommended upfront chemoradiation to the chest and definitive radiation to the left iliac wing metastasis.
The third clinical case described a male aged 70 years with a history of a treated base of tongue squamous cell carcinoma, with a solitary metastatic focus within the right lung. Respondents could pick multiple treatment options and 85 (81.7%) favored upfront definitive local therapy with surgery or stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT), rather than upfront chemotherapy, with future consideration for local treatment. About half of respondents (51.8%) recommended SBRT and 41.2% would let the patient decide between surgery or SBRT. Additionally, 39.6% included in their patient counselling that the treatment may be for curative intent.
Discussion
The use of local treatment to increased PFS, OS, or even cure treatment for OMD has become more accepted since the 2018 ASTRO meeting.4,5 Palma et al analyzed a controlled primary malignancy of any histology and ≤ 5 metastatic lesions, with all lesions amenable to SBRT.4 With a median follow-up of 51 months when comparing the standard-of-care (SOC) arm and the SBRT arm, the 5-year PFS was not reached and the 5-year OS rates were 17.7% and 42.3% (P = .006), respectively. In the SBRT arm, about 1 in 5 patients survived > 5 years without a recurrence or disease progression, vs 0 patients in the control arm. There was a 29% rate of grade 2 or higher toxicity in the SBRT arm, including 3 deaths that were likely due to treatment. Subsequent trials, such as the phase 3 SABR-COMET-3 (1-3 metastases), phase 3 SABR-COMET-10 (4-10 metastases), and phase 1 ARREST (> 10 metastases) trials, have been specifically designed to minimize treatment-related toxicities.13-15
Gomez et al analyzed patients at 3 sites with a controlled NSCLC primary tumor and ≤ 3 metastases.5 At a follow-up of 38.8 months, the PFS was 4.4 months in the SOC arm vs 14.2 months in the RT and/or surgery local treatment arm (P = .02). There was also an OS benefit of 17.0 vs 41.2 months (P = .02), respectively.
Several RCTs soon followed that demonstrated improved PFS and OS with local radiotherapy for OMD; however, total metastatic ablation of the foci is necessary to attain these PFS and OS benefits.6-9 Still, an oncologic benefit has yet to be proven. The randomized NRGBR002 study phase 2/3 trial for oligometastatic breast cancer included patients with ≤ 4 extracranial metastases and controlled primary disease to metastasis-directed therapy (SBRT and/ or surgical resection) and systemic therapy vs systemic therapy alone.10 The study did not demonstrate improved PFS or OS at 3 years. However, for most breast cancers, especially with the rapid advancements in systemic therapy that have been achieved, longer follow-up may be necessary to detect a significant difference.
The prospective single-arm phase 2 SABR-5 trial retrospectively demonstrated important lessons about the timing of SBRT and systemic therapy.11 This study included patients with ≤ 5 metastases of any histology, and they received SBRT to all lesions. SABR-5 retrospectively compared patients who received upfront systemic therapy followed by SBRT vs another cohort that first received SBRT and did not receive systemic therapy until there was disease progression. Patients with oligo-progression were excluded, as it demonstrated systemic drug resistance. At a median follow-up time of 34 months, delayed systemic treatment was associated with shorter PFS (23 vs 34 months, respectively; P = .001), but not worse 3-year OS (80% vs 85%, respectively; P = .66). In addition, the delayed systemic treatment arm demonstrated a reduced risk of grade 2 or higher SBRT-related toxicity (odds ratio, 0.35; P < .001).
Similarly, the STOMP phase 2 trial analyzed the role of metastasis-directed therapy (MDT) in delaying initiation of androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) in a randomized phase 2 trial.16 This study included patients with asymptomatic PCa with a biochemical recurrence after primary treatment, 1 to 3 extracranial metastatic lesions, and serum testosterone levels > 50 ng/mL. Sixty-two patients were randomized 1:1 to either MDT (SBRT or surgery) of all lesions or surveillance. The 5-year ADT-free survival was 34% for MDT vs 8% for surveillance (P = .06).
VHA Radiation Oncology
The VHA has 138 departments of medical oncology, but only 41 departments of radiation oncology. Compared with medical oncologists without an on-site radiation oncology department, those with on-site departments were more likely to believe that local RT was potentially curative (94.4% vs 72.7%, respectively; P = .04). This finding suggests that a cancer center that includes both specialties has closer collaboration, which results in greater inclination to embrace local RT for OMD, as it has demonstrated PFS and OS benefits.
The radiation and medical oncologists surveyed had statistically significant differences in response by specialty regarding the maximal number of lesions still believed to constitute OMD. Most radiation oncologists classified ≤ 5 lesions as OMD, whereas most medical oncologists classified ≤ 3 lesions as OMD. This difference is not unexpected. There is no universally agreed-upon definition of OMD, and criteria differ across studies.
While the SABR-COMET trial did include ≤ 5 metastatic lesions, it was a phase 2 RCT, making subgroup analysis difficult. Ongoing phase 3 trials that are more specific in the number of metastases, comparing 1 to 3 vs 4 to 10 metastases (SABR-COMET-3 and SABR-COMET-10, respectively).13,14 There is even an ongoing phase 1 trial (ARREST) studying the potential benefits of treating (“restraining”) > 10 metastases, if dosimetrically feasible.15 Within the VHA, VA STARPORT is investigating MDT for recurrent or de novo hormone-sensitive metastatic PCa.17 The ongoing HALT phase 2/3 trial focuses on patients with actionable mutations to help determine management of oligo-progression in mutation-positive NSCLC.18
There was no significant difference by specialty in who responded that offering local RT for OMD treatment should not be limited by histology (55.2% of radiation oncologists and 50.0% of medical oncologists; P = .60). Oncologists could make the argument that some histologies (eg, pancreatic adenocarcinomas) have such poor prognoses that local RT would not meaningfully affect oncologic outcomes, while potentially adding toxicity, whereas others could point to improved systemic therapy regimens and the low toxicity rates with careful hypofractionation regimens. Of note, the 41-patient phase 2 EXTEND trial for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma suggested an oncologic benefit to MDT, with far better PFS and no grade ≥ 3 toxicities related to MDT.19 About half of respondents for each specialty believed the primary histology should affect the decision. Further clarification may emerge from phase 3 trials.
Of note, a 2023 study of 44 radiation and medical oncologists at 2 Harvard Medical School-affiliated hospitals found that for synchronous OMD, 50.0% of medical oncologists and 5.3% (P < .01) of radiation oncologists recommended systemic treatment, suggesting a greater divergence in approach than found in this study.20
Limitations
The response rate of 17.0% raised a potential for selection bias, but this rate is expected for a nonincentivized medical survey. A study by the American Board of Internal Medicine with 11 surveys and 6 weekly email contacts only generated a 23.7% response rate, while another study among physicians demonstrated a 4.5% response rate for email-based contact and 11.8% for mail-based contact.21,22 We could have asked participants questions regarding demographics and geography to ensure the survey represented a diverse sample of the medical community, although additional questions would likely suppress the response rate. Additional data collection about respondents may elucidate the rationale for differences in their responses, especially between the specialties. In a planned subsequent survey in several years, the question on the number of lesions that qualifies as OMD may be amended to reflect the context and dosimetry for the maximal number of metastases constituting OMD; the joint ESTRO-ASTRO consensus defined OMD as 1 to 5 metastatic lesions, but in which all metastatic sites must be safely treatable.12 Also, fewer example cases could be included to simplify the survey and boost response rates. A future survey may ask about the timing of SBRT and systemic therapy, and whether SBRT can safely delay systemic therapy.
Conclusions
Survey results demonstrated significant confidence among both radiation oncologists and medical oncologists that local RT for OMD improves outcomes, which is encouraging and a reflection of the recent evidence-based paradigm shift in viewing metastatic disease as a spectrum. However, there is a difference between radiation oncologists and medical oncologists in how they define OMD, and preferred treatment of the sample cases presented revealed nuanced differences by specialty. Close collaboration with radiation oncologists influences the belief of medical oncologists in the beneficial role of RT for OMD. As more phase 3 data for OMD local treatments emerge, additional investigation is needed on how beliefs and practice patterns evolve among radiation and medical oncologists.
- Barney JD, Churchill EJ. Adenocarcinoma of the kidney with metastasis to the lung. J Urology. 1939.
- Hellman S, Weichselbaum RR. Oligometastases. J Clin Oncol. 1995;13(1):8-10. doi:10.1200/JCO.1995.13.1.8
- Ruers T, Punt C, Van Coevorden F, et al. Radiofrequency ablation combined with systemic treatment versus systemic treatment alone in patients with non-resectable colorectal liver metastases: a randomized EORTC Intergroup phase II study (EORTC 4004). Ann Oncol. 2012;23(10):2619-2626. doi:10.1093/annonc/mds053
- Palma DA, Olson R, Harrow S, et al. Stereotactic ablative radiotherapy for the comprehensive treatment of oligometastatic cancers: long-term results of the SABR-COMET phase II randomized trial. J Clin Oncol. 2020;38(25):2830- 2838. doi:10.1200/JCO.20.00818
- Gomez DR, Tang C, Zhang J, et al. Local consolidative therapy vs. maintenance therapy or observation for patients with oligometastatic non-small-cell lung cancer: long-term results of a multi-institutional, phase II, randomized study. J Clin Oncol. 2019;37(18):1558-1565. doi:10.1200/JCO.19.00201
- Iyengar P, Wardak Z, Gerber DE, et al. Consolidative radiotherapy for limited metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer: a phase 2 randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 2018;4(1):e173501. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2017.3501
- Phillips R, Shi WY, Deek M, et al. Outcomes of observation vs stereotactic ablative radiation for oligometastatic prostate cancer: the ORIOLE phase 2 randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 2020;6(5):650-659. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2020.0147
- Wang XS, Bai YF, Verma V, et al. Randomized trial of first-line tyrosine kinase inhibitor with or without radiotherapy for synchronous oligometastatic EGFR-mutated NSCLC. J Natl Cancer Inst 2023;115(6):742-748. doi:10.1093/jnci/djac015
- Tang C, Sherry AD, Haymaker C, et al. Addition of metastasis- directed therapy to intermittent hormone therapy for oligometastatic prostate cancer (EXTEND): a multicenter, randomized phase II trial. Am Soc Radiat Oncol Annu Meet. 2023;9(6):825-834. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2023.0161
- Chmura SJ, Winter KA, Woodward WA, et al. NRG-BR002: a phase IIR/III trial of standard of care systemic therapy with or without stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) and/or surgical resection (SR) for newly oligometastatic breast cancer (NCT02364557). J Clin Oncol. 2022;40:1007. doi:10.1200/JCO.2022.40.16_suppl.1007
- Baker S, Lechner L, Liu M, et al. Upfront versus delayed systemic therapy in patients with oligometastatic cancer treated with SABR in the phase 2 SABR-5 trial. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2024;118(5):1497-1506. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2023.11.007
- Lievens Y, Guckenberger M, Gomez D, et al. Defining oligometastatic disease from a radiation oncology perspective: an ESTRO-ASTRO consensus document. Radiother Oncol. 2020;148:157-166. doi:10.1016/j.radonc.2020.04.003
- Olson R, Mathews L, Liu M, et al. Stereotactic ablative radiotherapy for the comprehensive treatment of 1-3 oligometastatic tumors (SABR-COMET-3): study protocol for a randomized phase III trial. BMC Cancer. 2020;20(1):380. doi:10.1186/s12885-020-06876-4
- Palma DA, Olson R, Harrow S, et al. Stereotactic ablative radiotherapy for the comprehensive treatment of 4-10 oligometastatic tumors (SABR-COMET-10): study protocol for a randomized phase III trial. BMC Cancer. 2019;19(1):816. doi:10.1186/s12885-019-5977-6
- Bauman GS, Corkum MT, Fakir H, et al. Ablative radiation therapy to restrain everything safely treatable (ARREST): study protocol for a phase I trial treating polymetastatic cancer with stereotactic radiotherapy. BMC Cancer. 2021;21(1):405. doi:10.1186/s12885-021-08136-5
- Ost P, Reynders D, Decaestecker K, et al. Surveillance or metastasis-directed therapy for oligometastatic prostate cancer recurrence (STOMP): five-year results of a randomized phase II trial. J Clin Oncol. 2020;38:suppl.
- Solanki AA, Campbell D, Carlson K, et al. Veterans Affairs seamless phase II/III randomized trial of standard systemic therapy with or without PET-directed local therapy for oligometastatic prostate cancer (VA STARPORT). J Clin Oncol. 2024;42:16.
- McDonald F, Guckenberger M, Popat S. EP08.03-005 HALT – Targeted therapy with or without dose-intensified radiotherapy in oligo-progressive disease in oncogene addicted lung tumours. J Thor Oncol. 2022;17:S492.
- Ludmir EB, Sherry AD, Fellman BM, et al. Addition of metastasis- directed therapy to systemic therapy for oligometastatic pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (EXTEND): a multicenter, randomized phase II trial. J Clin Oncol. 2024;42(32):3795-3805. doi:10.1200/JCO.24.00081
- Cho HL, Balboni T, Christ SB, et al. Is oligometastatic cancer curable? A survey of oncologist perspectives, decision making, and communication. Adv Radiat Oncol. 2023;8(5):101221. doi:10.1016/j.adro.2023.101221
- Barnhart BJ, Reddy SG, Arnold GK. Remind me again: physician response to web surveys: the effect of email reminders across 11 opinion survey efforts at the American Board of Internal Medicine from 2017 to 2019. Eval Health Prof. 2021;44(3):245-259. doi:10.1177/01632787211019445
- Murphy CC, Lee SJC, Geiger AM, et al. A randomized trial of mail and email recruitment strategies for a physician survey on clinical trial accrual. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2020;20(1):123. doi:10.1186/s12874-020-01014-x
The treatment of metastatic solid tumors has been based historically on systemic therapies, with the goal of delaying progression and extend life as long as possible, with tolerable treatment-related adverse events. Some exceptions were made for local treatment with surgery or radiotherapy (RT), often for patients with a single metastasis. A 1939 report describes a patient with renal adenocarcinoma and a solitary lung metastasis who underwent RT to the lung lesion after nephrectomy and subsequently partial lobectomy after the metastatic lesion progressed. The authors argued that if a metastasis appears solitary and accessible, it is plausible to remove it in addition to the primary growth.1
In 1995 Hellman and Weichselbaum proposed oligometastatic disease (OMD). They reasoned that malignancy exists along a spectrum from localized disease to widely disseminated disease, with OMD existing in between with a still-restricted tumor metastatic capacity. Appropriately selected patients with OMD may be candidates for prolonged disease-free survival or cure with the addition of local therapy to systemic therapy.2
The EORTC 4004 phase 2 randomized control trial (RCT) analyzed radiofrequency ablation (RFA) for colorectal liver metastases with systemic therapy vs systemic therapy alone for patients with ≤ 9 liver lesions.3 Systemic therapyconsisted of 5-FU/leucovorin/oxaliplatin, with bevacizumab added to the regimen 3.5 years into the study, per updated standard- of-care. This trial was the first to demonstrate the benefit of aggressive local treatment vs system treatment alone for OMD with a progression-free survival (PFS) benefit (16.8 vs 9.9 months; hazard ratio [HR], 0.63; P = .03) and overall survival (OS) benefit (45.3 vs 40.5 months; HR, 0.74; P = .02) with the addition of local treatment with RFA.
Since the presentations of the SABR-COMET phase 2 RCT and another study by Gomez et al at the American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO) 2018 annual meeting, the paradigm for offering local RT for OMD has rapidly evolved. Both studies found PFS and OS benefits of RT for patients with OMD.4,5 Additional RCTs have since demonstrated that for properly selected patients with OMD, aggressive local RT improved PFS and OS.6-9 These small studies have led to larger RCTs to better understand who benefits from local consolidative treatment, particularly RT.10,11
There is a large degree of heterogeneity in how oncologists define and approach OMD treatment. The 2020 European Society for Radiotherapy and Oncology (ESTRO) and ASTRO consensus guidelines defined the OMD state as 1 to 5 metastatic lesions for which all metastatic sites are safely treatable.12 The purpose of this study was to evaluate perceptions and practice patterns among radiation oncologists and medical oncologists regarding the use of local RT for OMD across the Veterans Health Administration (VHA).
Methods
A 12-question survey was developed by the VHA Palliative Radiotherapy Task Force using the ESTRO-ASTRO consensus guidelines to define OMD. The survey was emailed to the VHA radiation oncology and medical oncology listservs on August 1, 2023. These listservs consist of physicians in these specialties either directly employed by the VHA or serve in its facilities as contractors. The original response closure date was August 11, 2023, but it was extended to August 18, 2023, to increase responses. No incentives were offered to respondents. Two email reminders were sent to the medical oncology listserv and 3 to the radiation oncology listserv. Descriptive statistics and X2 tests were used for data analysis. The impact of specialty and presence of an on-site department of radiation oncology were reviewed. This project was approved by the VHA National Oncology Program and National Radiation Oncology Program.
Results
The survey was sent to 125 radiation oncologists and 515 medical oncologists and 106 were completed for a 16.6% response rate. There were 59 (55.7%) radiation oncologist responses and 47 (44.3%) medical oncologist responses. Most (96.2%) respondents were board-certified, and 84 (79.2%) were affiliated with an academic center. Not every respondent answered every question (Table).

All respondents (n = 105) indicated there is a potential benefit of high-dose RT for appropriately selected cases. Ninety-four oncologists (88.7%) believed that RT for OMD contributes to cure (88.1% of radiation oncologists, 89.4% of medical oncologists; P = .84) for appropriately selected cases. Some respondents who did not believe RT for OMD contributes to cure added comments about other perceived benefits, such as local disease control for palliation, delaying systemic therapy with its associated toxicities, and prolongation of disease-free survival or OS. A higher percentage of respondents with academic affiliations believed high-dose RT contributes to cure, although this difference did not reach statistical significance (Figure 1).

Fifty-five respondents (51.9%; 55.2% radiation oncologists vs 50.0% medical oncologists; P = .60) responded that local RT for OMD treatment should not be limited by primary tumor type. Of respondents who responded that OMD treatment should be limited based on the type of primary tumor, many provided comments that argued there was a benefit for non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), prostate adenocarcinoma (PCa), and colorectal cancer.
The definition of how many metastatic lesions qualify as OMD varied. A total of 48.6% of respondents defined OMD as ≤ 3 lesions and 42.9% answered ≤ 5 lesions. A majority of radiation oncologists (55.2%) classified ≤ 5 lesions as OMD, whereas a majority of medical oncologists (66.0%) considered ≤ 3 lesions as OMD (P = .006) (Figure 2).

Thirty-six medical oncologists (76.6%) report having an on-site department of radiation oncology (Figure 3). This subgroup was more likely to consider local RT potentially curative compared with their medical oncology peers without on-site radiation oncology (94.4% vs 72.7%; P = .04).

Case Management
The 3 clinical cases demonstrated the heterogeneity of management approaches for OMD. The first described a man aged 65 years with PCa and 2 asymptomatic pelvic bone metastases. Ninety-three respondents (90.3%) recommended RT at the primary site and 74.8% recommended RT to both the primary site and metastatic foci. Sixty-three respondents (67.7%) recommended a STAMPEDE-compatible dose, and 30 (32.3%) recommended a definitive dose.
The second clinical case was a 60-year-old man with a cT1N2M1 NSCLC, with a solitary metastatic focus to the left iliac wing. Fifty-eight respondents (54.7%) recommended upfront systemic chemotherapy and the option of local therapy to the chest and metastatic focus after initial chemotherapy; 28 respondents (26.4%) recommended upfront chemoradiation to the chest and definitive radiation to the left iliac wing metastasis.
The third clinical case described a male aged 70 years with a history of a treated base of tongue squamous cell carcinoma, with a solitary metastatic focus within the right lung. Respondents could pick multiple treatment options and 85 (81.7%) favored upfront definitive local therapy with surgery or stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT), rather than upfront chemotherapy, with future consideration for local treatment. About half of respondents (51.8%) recommended SBRT and 41.2% would let the patient decide between surgery or SBRT. Additionally, 39.6% included in their patient counselling that the treatment may be for curative intent.
Discussion
The use of local treatment to increased PFS, OS, or even cure treatment for OMD has become more accepted since the 2018 ASTRO meeting.4,5 Palma et al analyzed a controlled primary malignancy of any histology and ≤ 5 metastatic lesions, with all lesions amenable to SBRT.4 With a median follow-up of 51 months when comparing the standard-of-care (SOC) arm and the SBRT arm, the 5-year PFS was not reached and the 5-year OS rates were 17.7% and 42.3% (P = .006), respectively. In the SBRT arm, about 1 in 5 patients survived > 5 years without a recurrence or disease progression, vs 0 patients in the control arm. There was a 29% rate of grade 2 or higher toxicity in the SBRT arm, including 3 deaths that were likely due to treatment. Subsequent trials, such as the phase 3 SABR-COMET-3 (1-3 metastases), phase 3 SABR-COMET-10 (4-10 metastases), and phase 1 ARREST (> 10 metastases) trials, have been specifically designed to minimize treatment-related toxicities.13-15
Gomez et al analyzed patients at 3 sites with a controlled NSCLC primary tumor and ≤ 3 metastases.5 At a follow-up of 38.8 months, the PFS was 4.4 months in the SOC arm vs 14.2 months in the RT and/or surgery local treatment arm (P = .02). There was also an OS benefit of 17.0 vs 41.2 months (P = .02), respectively.
Several RCTs soon followed that demonstrated improved PFS and OS with local radiotherapy for OMD; however, total metastatic ablation of the foci is necessary to attain these PFS and OS benefits.6-9 Still, an oncologic benefit has yet to be proven. The randomized NRGBR002 study phase 2/3 trial for oligometastatic breast cancer included patients with ≤ 4 extracranial metastases and controlled primary disease to metastasis-directed therapy (SBRT and/ or surgical resection) and systemic therapy vs systemic therapy alone.10 The study did not demonstrate improved PFS or OS at 3 years. However, for most breast cancers, especially with the rapid advancements in systemic therapy that have been achieved, longer follow-up may be necessary to detect a significant difference.
The prospective single-arm phase 2 SABR-5 trial retrospectively demonstrated important lessons about the timing of SBRT and systemic therapy.11 This study included patients with ≤ 5 metastases of any histology, and they received SBRT to all lesions. SABR-5 retrospectively compared patients who received upfront systemic therapy followed by SBRT vs another cohort that first received SBRT and did not receive systemic therapy until there was disease progression. Patients with oligo-progression were excluded, as it demonstrated systemic drug resistance. At a median follow-up time of 34 months, delayed systemic treatment was associated with shorter PFS (23 vs 34 months, respectively; P = .001), but not worse 3-year OS (80% vs 85%, respectively; P = .66). In addition, the delayed systemic treatment arm demonstrated a reduced risk of grade 2 or higher SBRT-related toxicity (odds ratio, 0.35; P < .001).
Similarly, the STOMP phase 2 trial analyzed the role of metastasis-directed therapy (MDT) in delaying initiation of androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) in a randomized phase 2 trial.16 This study included patients with asymptomatic PCa with a biochemical recurrence after primary treatment, 1 to 3 extracranial metastatic lesions, and serum testosterone levels > 50 ng/mL. Sixty-two patients were randomized 1:1 to either MDT (SBRT or surgery) of all lesions or surveillance. The 5-year ADT-free survival was 34% for MDT vs 8% for surveillance (P = .06).
VHA Radiation Oncology
The VHA has 138 departments of medical oncology, but only 41 departments of radiation oncology. Compared with medical oncologists without an on-site radiation oncology department, those with on-site departments were more likely to believe that local RT was potentially curative (94.4% vs 72.7%, respectively; P = .04). This finding suggests that a cancer center that includes both specialties has closer collaboration, which results in greater inclination to embrace local RT for OMD, as it has demonstrated PFS and OS benefits.
The radiation and medical oncologists surveyed had statistically significant differences in response by specialty regarding the maximal number of lesions still believed to constitute OMD. Most radiation oncologists classified ≤ 5 lesions as OMD, whereas most medical oncologists classified ≤ 3 lesions as OMD. This difference is not unexpected. There is no universally agreed-upon definition of OMD, and criteria differ across studies.
While the SABR-COMET trial did include ≤ 5 metastatic lesions, it was a phase 2 RCT, making subgroup analysis difficult. Ongoing phase 3 trials that are more specific in the number of metastases, comparing 1 to 3 vs 4 to 10 metastases (SABR-COMET-3 and SABR-COMET-10, respectively).13,14 There is even an ongoing phase 1 trial (ARREST) studying the potential benefits of treating (“restraining”) > 10 metastases, if dosimetrically feasible.15 Within the VHA, VA STARPORT is investigating MDT for recurrent or de novo hormone-sensitive metastatic PCa.17 The ongoing HALT phase 2/3 trial focuses on patients with actionable mutations to help determine management of oligo-progression in mutation-positive NSCLC.18
There was no significant difference by specialty in who responded that offering local RT for OMD treatment should not be limited by histology (55.2% of radiation oncologists and 50.0% of medical oncologists; P = .60). Oncologists could make the argument that some histologies (eg, pancreatic adenocarcinomas) have such poor prognoses that local RT would not meaningfully affect oncologic outcomes, while potentially adding toxicity, whereas others could point to improved systemic therapy regimens and the low toxicity rates with careful hypofractionation regimens. Of note, the 41-patient phase 2 EXTEND trial for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma suggested an oncologic benefit to MDT, with far better PFS and no grade ≥ 3 toxicities related to MDT.19 About half of respondents for each specialty believed the primary histology should affect the decision. Further clarification may emerge from phase 3 trials.
Of note, a 2023 study of 44 radiation and medical oncologists at 2 Harvard Medical School-affiliated hospitals found that for synchronous OMD, 50.0% of medical oncologists and 5.3% (P < .01) of radiation oncologists recommended systemic treatment, suggesting a greater divergence in approach than found in this study.20
Limitations
The response rate of 17.0% raised a potential for selection bias, but this rate is expected for a nonincentivized medical survey. A study by the American Board of Internal Medicine with 11 surveys and 6 weekly email contacts only generated a 23.7% response rate, while another study among physicians demonstrated a 4.5% response rate for email-based contact and 11.8% for mail-based contact.21,22 We could have asked participants questions regarding demographics and geography to ensure the survey represented a diverse sample of the medical community, although additional questions would likely suppress the response rate. Additional data collection about respondents may elucidate the rationale for differences in their responses, especially between the specialties. In a planned subsequent survey in several years, the question on the number of lesions that qualifies as OMD may be amended to reflect the context and dosimetry for the maximal number of metastases constituting OMD; the joint ESTRO-ASTRO consensus defined OMD as 1 to 5 metastatic lesions, but in which all metastatic sites must be safely treatable.12 Also, fewer example cases could be included to simplify the survey and boost response rates. A future survey may ask about the timing of SBRT and systemic therapy, and whether SBRT can safely delay systemic therapy.
Conclusions
Survey results demonstrated significant confidence among both radiation oncologists and medical oncologists that local RT for OMD improves outcomes, which is encouraging and a reflection of the recent evidence-based paradigm shift in viewing metastatic disease as a spectrum. However, there is a difference between radiation oncologists and medical oncologists in how they define OMD, and preferred treatment of the sample cases presented revealed nuanced differences by specialty. Close collaboration with radiation oncologists influences the belief of medical oncologists in the beneficial role of RT for OMD. As more phase 3 data for OMD local treatments emerge, additional investigation is needed on how beliefs and practice patterns evolve among radiation and medical oncologists.
The treatment of metastatic solid tumors has been based historically on systemic therapies, with the goal of delaying progression and extend life as long as possible, with tolerable treatment-related adverse events. Some exceptions were made for local treatment with surgery or radiotherapy (RT), often for patients with a single metastasis. A 1939 report describes a patient with renal adenocarcinoma and a solitary lung metastasis who underwent RT to the lung lesion after nephrectomy and subsequently partial lobectomy after the metastatic lesion progressed. The authors argued that if a metastasis appears solitary and accessible, it is plausible to remove it in addition to the primary growth.1
In 1995 Hellman and Weichselbaum proposed oligometastatic disease (OMD). They reasoned that malignancy exists along a spectrum from localized disease to widely disseminated disease, with OMD existing in between with a still-restricted tumor metastatic capacity. Appropriately selected patients with OMD may be candidates for prolonged disease-free survival or cure with the addition of local therapy to systemic therapy.2
The EORTC 4004 phase 2 randomized control trial (RCT) analyzed radiofrequency ablation (RFA) for colorectal liver metastases with systemic therapy vs systemic therapy alone for patients with ≤ 9 liver lesions.3 Systemic therapyconsisted of 5-FU/leucovorin/oxaliplatin, with bevacizumab added to the regimen 3.5 years into the study, per updated standard- of-care. This trial was the first to demonstrate the benefit of aggressive local treatment vs system treatment alone for OMD with a progression-free survival (PFS) benefit (16.8 vs 9.9 months; hazard ratio [HR], 0.63; P = .03) and overall survival (OS) benefit (45.3 vs 40.5 months; HR, 0.74; P = .02) with the addition of local treatment with RFA.
Since the presentations of the SABR-COMET phase 2 RCT and another study by Gomez et al at the American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO) 2018 annual meeting, the paradigm for offering local RT for OMD has rapidly evolved. Both studies found PFS and OS benefits of RT for patients with OMD.4,5 Additional RCTs have since demonstrated that for properly selected patients with OMD, aggressive local RT improved PFS and OS.6-9 These small studies have led to larger RCTs to better understand who benefits from local consolidative treatment, particularly RT.10,11
There is a large degree of heterogeneity in how oncologists define and approach OMD treatment. The 2020 European Society for Radiotherapy and Oncology (ESTRO) and ASTRO consensus guidelines defined the OMD state as 1 to 5 metastatic lesions for which all metastatic sites are safely treatable.12 The purpose of this study was to evaluate perceptions and practice patterns among radiation oncologists and medical oncologists regarding the use of local RT for OMD across the Veterans Health Administration (VHA).
Methods
A 12-question survey was developed by the VHA Palliative Radiotherapy Task Force using the ESTRO-ASTRO consensus guidelines to define OMD. The survey was emailed to the VHA radiation oncology and medical oncology listservs on August 1, 2023. These listservs consist of physicians in these specialties either directly employed by the VHA or serve in its facilities as contractors. The original response closure date was August 11, 2023, but it was extended to August 18, 2023, to increase responses. No incentives were offered to respondents. Two email reminders were sent to the medical oncology listserv and 3 to the radiation oncology listserv. Descriptive statistics and X2 tests were used for data analysis. The impact of specialty and presence of an on-site department of radiation oncology were reviewed. This project was approved by the VHA National Oncology Program and National Radiation Oncology Program.
Results
The survey was sent to 125 radiation oncologists and 515 medical oncologists and 106 were completed for a 16.6% response rate. There were 59 (55.7%) radiation oncologist responses and 47 (44.3%) medical oncologist responses. Most (96.2%) respondents were board-certified, and 84 (79.2%) were affiliated with an academic center. Not every respondent answered every question (Table).

All respondents (n = 105) indicated there is a potential benefit of high-dose RT for appropriately selected cases. Ninety-four oncologists (88.7%) believed that RT for OMD contributes to cure (88.1% of radiation oncologists, 89.4% of medical oncologists; P = .84) for appropriately selected cases. Some respondents who did not believe RT for OMD contributes to cure added comments about other perceived benefits, such as local disease control for palliation, delaying systemic therapy with its associated toxicities, and prolongation of disease-free survival or OS. A higher percentage of respondents with academic affiliations believed high-dose RT contributes to cure, although this difference did not reach statistical significance (Figure 1).

Fifty-five respondents (51.9%; 55.2% radiation oncologists vs 50.0% medical oncologists; P = .60) responded that local RT for OMD treatment should not be limited by primary tumor type. Of respondents who responded that OMD treatment should be limited based on the type of primary tumor, many provided comments that argued there was a benefit for non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), prostate adenocarcinoma (PCa), and colorectal cancer.
The definition of how many metastatic lesions qualify as OMD varied. A total of 48.6% of respondents defined OMD as ≤ 3 lesions and 42.9% answered ≤ 5 lesions. A majority of radiation oncologists (55.2%) classified ≤ 5 lesions as OMD, whereas a majority of medical oncologists (66.0%) considered ≤ 3 lesions as OMD (P = .006) (Figure 2).

Thirty-six medical oncologists (76.6%) report having an on-site department of radiation oncology (Figure 3). This subgroup was more likely to consider local RT potentially curative compared with their medical oncology peers without on-site radiation oncology (94.4% vs 72.7%; P = .04).

Case Management
The 3 clinical cases demonstrated the heterogeneity of management approaches for OMD. The first described a man aged 65 years with PCa and 2 asymptomatic pelvic bone metastases. Ninety-three respondents (90.3%) recommended RT at the primary site and 74.8% recommended RT to both the primary site and metastatic foci. Sixty-three respondents (67.7%) recommended a STAMPEDE-compatible dose, and 30 (32.3%) recommended a definitive dose.
The second clinical case was a 60-year-old man with a cT1N2M1 NSCLC, with a solitary metastatic focus to the left iliac wing. Fifty-eight respondents (54.7%) recommended upfront systemic chemotherapy and the option of local therapy to the chest and metastatic focus after initial chemotherapy; 28 respondents (26.4%) recommended upfront chemoradiation to the chest and definitive radiation to the left iliac wing metastasis.
The third clinical case described a male aged 70 years with a history of a treated base of tongue squamous cell carcinoma, with a solitary metastatic focus within the right lung. Respondents could pick multiple treatment options and 85 (81.7%) favored upfront definitive local therapy with surgery or stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT), rather than upfront chemotherapy, with future consideration for local treatment. About half of respondents (51.8%) recommended SBRT and 41.2% would let the patient decide between surgery or SBRT. Additionally, 39.6% included in their patient counselling that the treatment may be for curative intent.
Discussion
The use of local treatment to increased PFS, OS, or even cure treatment for OMD has become more accepted since the 2018 ASTRO meeting.4,5 Palma et al analyzed a controlled primary malignancy of any histology and ≤ 5 metastatic lesions, with all lesions amenable to SBRT.4 With a median follow-up of 51 months when comparing the standard-of-care (SOC) arm and the SBRT arm, the 5-year PFS was not reached and the 5-year OS rates were 17.7% and 42.3% (P = .006), respectively. In the SBRT arm, about 1 in 5 patients survived > 5 years without a recurrence or disease progression, vs 0 patients in the control arm. There was a 29% rate of grade 2 or higher toxicity in the SBRT arm, including 3 deaths that were likely due to treatment. Subsequent trials, such as the phase 3 SABR-COMET-3 (1-3 metastases), phase 3 SABR-COMET-10 (4-10 metastases), and phase 1 ARREST (> 10 metastases) trials, have been specifically designed to minimize treatment-related toxicities.13-15
Gomez et al analyzed patients at 3 sites with a controlled NSCLC primary tumor and ≤ 3 metastases.5 At a follow-up of 38.8 months, the PFS was 4.4 months in the SOC arm vs 14.2 months in the RT and/or surgery local treatment arm (P = .02). There was also an OS benefit of 17.0 vs 41.2 months (P = .02), respectively.
Several RCTs soon followed that demonstrated improved PFS and OS with local radiotherapy for OMD; however, total metastatic ablation of the foci is necessary to attain these PFS and OS benefits.6-9 Still, an oncologic benefit has yet to be proven. The randomized NRGBR002 study phase 2/3 trial for oligometastatic breast cancer included patients with ≤ 4 extracranial metastases and controlled primary disease to metastasis-directed therapy (SBRT and/ or surgical resection) and systemic therapy vs systemic therapy alone.10 The study did not demonstrate improved PFS or OS at 3 years. However, for most breast cancers, especially with the rapid advancements in systemic therapy that have been achieved, longer follow-up may be necessary to detect a significant difference.
The prospective single-arm phase 2 SABR-5 trial retrospectively demonstrated important lessons about the timing of SBRT and systemic therapy.11 This study included patients with ≤ 5 metastases of any histology, and they received SBRT to all lesions. SABR-5 retrospectively compared patients who received upfront systemic therapy followed by SBRT vs another cohort that first received SBRT and did not receive systemic therapy until there was disease progression. Patients with oligo-progression were excluded, as it demonstrated systemic drug resistance. At a median follow-up time of 34 months, delayed systemic treatment was associated with shorter PFS (23 vs 34 months, respectively; P = .001), but not worse 3-year OS (80% vs 85%, respectively; P = .66). In addition, the delayed systemic treatment arm demonstrated a reduced risk of grade 2 or higher SBRT-related toxicity (odds ratio, 0.35; P < .001).
Similarly, the STOMP phase 2 trial analyzed the role of metastasis-directed therapy (MDT) in delaying initiation of androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) in a randomized phase 2 trial.16 This study included patients with asymptomatic PCa with a biochemical recurrence after primary treatment, 1 to 3 extracranial metastatic lesions, and serum testosterone levels > 50 ng/mL. Sixty-two patients were randomized 1:1 to either MDT (SBRT or surgery) of all lesions or surveillance. The 5-year ADT-free survival was 34% for MDT vs 8% for surveillance (P = .06).
VHA Radiation Oncology
The VHA has 138 departments of medical oncology, but only 41 departments of radiation oncology. Compared with medical oncologists without an on-site radiation oncology department, those with on-site departments were more likely to believe that local RT was potentially curative (94.4% vs 72.7%, respectively; P = .04). This finding suggests that a cancer center that includes both specialties has closer collaboration, which results in greater inclination to embrace local RT for OMD, as it has demonstrated PFS and OS benefits.
The radiation and medical oncologists surveyed had statistically significant differences in response by specialty regarding the maximal number of lesions still believed to constitute OMD. Most radiation oncologists classified ≤ 5 lesions as OMD, whereas most medical oncologists classified ≤ 3 lesions as OMD. This difference is not unexpected. There is no universally agreed-upon definition of OMD, and criteria differ across studies.
While the SABR-COMET trial did include ≤ 5 metastatic lesions, it was a phase 2 RCT, making subgroup analysis difficult. Ongoing phase 3 trials that are more specific in the number of metastases, comparing 1 to 3 vs 4 to 10 metastases (SABR-COMET-3 and SABR-COMET-10, respectively).13,14 There is even an ongoing phase 1 trial (ARREST) studying the potential benefits of treating (“restraining”) > 10 metastases, if dosimetrically feasible.15 Within the VHA, VA STARPORT is investigating MDT for recurrent or de novo hormone-sensitive metastatic PCa.17 The ongoing HALT phase 2/3 trial focuses on patients with actionable mutations to help determine management of oligo-progression in mutation-positive NSCLC.18
There was no significant difference by specialty in who responded that offering local RT for OMD treatment should not be limited by histology (55.2% of radiation oncologists and 50.0% of medical oncologists; P = .60). Oncologists could make the argument that some histologies (eg, pancreatic adenocarcinomas) have such poor prognoses that local RT would not meaningfully affect oncologic outcomes, while potentially adding toxicity, whereas others could point to improved systemic therapy regimens and the low toxicity rates with careful hypofractionation regimens. Of note, the 41-patient phase 2 EXTEND trial for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma suggested an oncologic benefit to MDT, with far better PFS and no grade ≥ 3 toxicities related to MDT.19 About half of respondents for each specialty believed the primary histology should affect the decision. Further clarification may emerge from phase 3 trials.
Of note, a 2023 study of 44 radiation and medical oncologists at 2 Harvard Medical School-affiliated hospitals found that for synchronous OMD, 50.0% of medical oncologists and 5.3% (P < .01) of radiation oncologists recommended systemic treatment, suggesting a greater divergence in approach than found in this study.20
Limitations
The response rate of 17.0% raised a potential for selection bias, but this rate is expected for a nonincentivized medical survey. A study by the American Board of Internal Medicine with 11 surveys and 6 weekly email contacts only generated a 23.7% response rate, while another study among physicians demonstrated a 4.5% response rate for email-based contact and 11.8% for mail-based contact.21,22 We could have asked participants questions regarding demographics and geography to ensure the survey represented a diverse sample of the medical community, although additional questions would likely suppress the response rate. Additional data collection about respondents may elucidate the rationale for differences in their responses, especially between the specialties. In a planned subsequent survey in several years, the question on the number of lesions that qualifies as OMD may be amended to reflect the context and dosimetry for the maximal number of metastases constituting OMD; the joint ESTRO-ASTRO consensus defined OMD as 1 to 5 metastatic lesions, but in which all metastatic sites must be safely treatable.12 Also, fewer example cases could be included to simplify the survey and boost response rates. A future survey may ask about the timing of SBRT and systemic therapy, and whether SBRT can safely delay systemic therapy.
Conclusions
Survey results demonstrated significant confidence among both radiation oncologists and medical oncologists that local RT for OMD improves outcomes, which is encouraging and a reflection of the recent evidence-based paradigm shift in viewing metastatic disease as a spectrum. However, there is a difference between radiation oncologists and medical oncologists in how they define OMD, and preferred treatment of the sample cases presented revealed nuanced differences by specialty. Close collaboration with radiation oncologists influences the belief of medical oncologists in the beneficial role of RT for OMD. As more phase 3 data for OMD local treatments emerge, additional investigation is needed on how beliefs and practice patterns evolve among radiation and medical oncologists.
- Barney JD, Churchill EJ. Adenocarcinoma of the kidney with metastasis to the lung. J Urology. 1939.
- Hellman S, Weichselbaum RR. Oligometastases. J Clin Oncol. 1995;13(1):8-10. doi:10.1200/JCO.1995.13.1.8
- Ruers T, Punt C, Van Coevorden F, et al. Radiofrequency ablation combined with systemic treatment versus systemic treatment alone in patients with non-resectable colorectal liver metastases: a randomized EORTC Intergroup phase II study (EORTC 4004). Ann Oncol. 2012;23(10):2619-2626. doi:10.1093/annonc/mds053
- Palma DA, Olson R, Harrow S, et al. Stereotactic ablative radiotherapy for the comprehensive treatment of oligometastatic cancers: long-term results of the SABR-COMET phase II randomized trial. J Clin Oncol. 2020;38(25):2830- 2838. doi:10.1200/JCO.20.00818
- Gomez DR, Tang C, Zhang J, et al. Local consolidative therapy vs. maintenance therapy or observation for patients with oligometastatic non-small-cell lung cancer: long-term results of a multi-institutional, phase II, randomized study. J Clin Oncol. 2019;37(18):1558-1565. doi:10.1200/JCO.19.00201
- Iyengar P, Wardak Z, Gerber DE, et al. Consolidative radiotherapy for limited metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer: a phase 2 randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 2018;4(1):e173501. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2017.3501
- Phillips R, Shi WY, Deek M, et al. Outcomes of observation vs stereotactic ablative radiation for oligometastatic prostate cancer: the ORIOLE phase 2 randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 2020;6(5):650-659. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2020.0147
- Wang XS, Bai YF, Verma V, et al. Randomized trial of first-line tyrosine kinase inhibitor with or without radiotherapy for synchronous oligometastatic EGFR-mutated NSCLC. J Natl Cancer Inst 2023;115(6):742-748. doi:10.1093/jnci/djac015
- Tang C, Sherry AD, Haymaker C, et al. Addition of metastasis- directed therapy to intermittent hormone therapy for oligometastatic prostate cancer (EXTEND): a multicenter, randomized phase II trial. Am Soc Radiat Oncol Annu Meet. 2023;9(6):825-834. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2023.0161
- Chmura SJ, Winter KA, Woodward WA, et al. NRG-BR002: a phase IIR/III trial of standard of care systemic therapy with or without stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) and/or surgical resection (SR) for newly oligometastatic breast cancer (NCT02364557). J Clin Oncol. 2022;40:1007. doi:10.1200/JCO.2022.40.16_suppl.1007
- Baker S, Lechner L, Liu M, et al. Upfront versus delayed systemic therapy in patients with oligometastatic cancer treated with SABR in the phase 2 SABR-5 trial. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2024;118(5):1497-1506. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2023.11.007
- Lievens Y, Guckenberger M, Gomez D, et al. Defining oligometastatic disease from a radiation oncology perspective: an ESTRO-ASTRO consensus document. Radiother Oncol. 2020;148:157-166. doi:10.1016/j.radonc.2020.04.003
- Olson R, Mathews L, Liu M, et al. Stereotactic ablative radiotherapy for the comprehensive treatment of 1-3 oligometastatic tumors (SABR-COMET-3): study protocol for a randomized phase III trial. BMC Cancer. 2020;20(1):380. doi:10.1186/s12885-020-06876-4
- Palma DA, Olson R, Harrow S, et al. Stereotactic ablative radiotherapy for the comprehensive treatment of 4-10 oligometastatic tumors (SABR-COMET-10): study protocol for a randomized phase III trial. BMC Cancer. 2019;19(1):816. doi:10.1186/s12885-019-5977-6
- Bauman GS, Corkum MT, Fakir H, et al. Ablative radiation therapy to restrain everything safely treatable (ARREST): study protocol for a phase I trial treating polymetastatic cancer with stereotactic radiotherapy. BMC Cancer. 2021;21(1):405. doi:10.1186/s12885-021-08136-5
- Ost P, Reynders D, Decaestecker K, et al. Surveillance or metastasis-directed therapy for oligometastatic prostate cancer recurrence (STOMP): five-year results of a randomized phase II trial. J Clin Oncol. 2020;38:suppl.
- Solanki AA, Campbell D, Carlson K, et al. Veterans Affairs seamless phase II/III randomized trial of standard systemic therapy with or without PET-directed local therapy for oligometastatic prostate cancer (VA STARPORT). J Clin Oncol. 2024;42:16.
- McDonald F, Guckenberger M, Popat S. EP08.03-005 HALT – Targeted therapy with or without dose-intensified radiotherapy in oligo-progressive disease in oncogene addicted lung tumours. J Thor Oncol. 2022;17:S492.
- Ludmir EB, Sherry AD, Fellman BM, et al. Addition of metastasis- directed therapy to systemic therapy for oligometastatic pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (EXTEND): a multicenter, randomized phase II trial. J Clin Oncol. 2024;42(32):3795-3805. doi:10.1200/JCO.24.00081
- Cho HL, Balboni T, Christ SB, et al. Is oligometastatic cancer curable? A survey of oncologist perspectives, decision making, and communication. Adv Radiat Oncol. 2023;8(5):101221. doi:10.1016/j.adro.2023.101221
- Barnhart BJ, Reddy SG, Arnold GK. Remind me again: physician response to web surveys: the effect of email reminders across 11 opinion survey efforts at the American Board of Internal Medicine from 2017 to 2019. Eval Health Prof. 2021;44(3):245-259. doi:10.1177/01632787211019445
- Murphy CC, Lee SJC, Geiger AM, et al. A randomized trial of mail and email recruitment strategies for a physician survey on clinical trial accrual. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2020;20(1):123. doi:10.1186/s12874-020-01014-x
- Barney JD, Churchill EJ. Adenocarcinoma of the kidney with metastasis to the lung. J Urology. 1939.
- Hellman S, Weichselbaum RR. Oligometastases. J Clin Oncol. 1995;13(1):8-10. doi:10.1200/JCO.1995.13.1.8
- Ruers T, Punt C, Van Coevorden F, et al. Radiofrequency ablation combined with systemic treatment versus systemic treatment alone in patients with non-resectable colorectal liver metastases: a randomized EORTC Intergroup phase II study (EORTC 4004). Ann Oncol. 2012;23(10):2619-2626. doi:10.1093/annonc/mds053
- Palma DA, Olson R, Harrow S, et al. Stereotactic ablative radiotherapy for the comprehensive treatment of oligometastatic cancers: long-term results of the SABR-COMET phase II randomized trial. J Clin Oncol. 2020;38(25):2830- 2838. doi:10.1200/JCO.20.00818
- Gomez DR, Tang C, Zhang J, et al. Local consolidative therapy vs. maintenance therapy or observation for patients with oligometastatic non-small-cell lung cancer: long-term results of a multi-institutional, phase II, randomized study. J Clin Oncol. 2019;37(18):1558-1565. doi:10.1200/JCO.19.00201
- Iyengar P, Wardak Z, Gerber DE, et al. Consolidative radiotherapy for limited metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer: a phase 2 randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 2018;4(1):e173501. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2017.3501
- Phillips R, Shi WY, Deek M, et al. Outcomes of observation vs stereotactic ablative radiation for oligometastatic prostate cancer: the ORIOLE phase 2 randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 2020;6(5):650-659. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2020.0147
- Wang XS, Bai YF, Verma V, et al. Randomized trial of first-line tyrosine kinase inhibitor with or without radiotherapy for synchronous oligometastatic EGFR-mutated NSCLC. J Natl Cancer Inst 2023;115(6):742-748. doi:10.1093/jnci/djac015
- Tang C, Sherry AD, Haymaker C, et al. Addition of metastasis- directed therapy to intermittent hormone therapy for oligometastatic prostate cancer (EXTEND): a multicenter, randomized phase II trial. Am Soc Radiat Oncol Annu Meet. 2023;9(6):825-834. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2023.0161
- Chmura SJ, Winter KA, Woodward WA, et al. NRG-BR002: a phase IIR/III trial of standard of care systemic therapy with or without stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) and/or surgical resection (SR) for newly oligometastatic breast cancer (NCT02364557). J Clin Oncol. 2022;40:1007. doi:10.1200/JCO.2022.40.16_suppl.1007
- Baker S, Lechner L, Liu M, et al. Upfront versus delayed systemic therapy in patients with oligometastatic cancer treated with SABR in the phase 2 SABR-5 trial. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2024;118(5):1497-1506. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2023.11.007
- Lievens Y, Guckenberger M, Gomez D, et al. Defining oligometastatic disease from a radiation oncology perspective: an ESTRO-ASTRO consensus document. Radiother Oncol. 2020;148:157-166. doi:10.1016/j.radonc.2020.04.003
- Olson R, Mathews L, Liu M, et al. Stereotactic ablative radiotherapy for the comprehensive treatment of 1-3 oligometastatic tumors (SABR-COMET-3): study protocol for a randomized phase III trial. BMC Cancer. 2020;20(1):380. doi:10.1186/s12885-020-06876-4
- Palma DA, Olson R, Harrow S, et al. Stereotactic ablative radiotherapy for the comprehensive treatment of 4-10 oligometastatic tumors (SABR-COMET-10): study protocol for a randomized phase III trial. BMC Cancer. 2019;19(1):816. doi:10.1186/s12885-019-5977-6
- Bauman GS, Corkum MT, Fakir H, et al. Ablative radiation therapy to restrain everything safely treatable (ARREST): study protocol for a phase I trial treating polymetastatic cancer with stereotactic radiotherapy. BMC Cancer. 2021;21(1):405. doi:10.1186/s12885-021-08136-5
- Ost P, Reynders D, Decaestecker K, et al. Surveillance or metastasis-directed therapy for oligometastatic prostate cancer recurrence (STOMP): five-year results of a randomized phase II trial. J Clin Oncol. 2020;38:suppl.
- Solanki AA, Campbell D, Carlson K, et al. Veterans Affairs seamless phase II/III randomized trial of standard systemic therapy with or without PET-directed local therapy for oligometastatic prostate cancer (VA STARPORT). J Clin Oncol. 2024;42:16.
- McDonald F, Guckenberger M, Popat S. EP08.03-005 HALT – Targeted therapy with or without dose-intensified radiotherapy in oligo-progressive disease in oncogene addicted lung tumours. J Thor Oncol. 2022;17:S492.
- Ludmir EB, Sherry AD, Fellman BM, et al. Addition of metastasis- directed therapy to systemic therapy for oligometastatic pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (EXTEND): a multicenter, randomized phase II trial. J Clin Oncol. 2024;42(32):3795-3805. doi:10.1200/JCO.24.00081
- Cho HL, Balboni T, Christ SB, et al. Is oligometastatic cancer curable? A survey of oncologist perspectives, decision making, and communication. Adv Radiat Oncol. 2023;8(5):101221. doi:10.1016/j.adro.2023.101221
- Barnhart BJ, Reddy SG, Arnold GK. Remind me again: physician response to web surveys: the effect of email reminders across 11 opinion survey efforts at the American Board of Internal Medicine from 2017 to 2019. Eval Health Prof. 2021;44(3):245-259. doi:10.1177/01632787211019445
- Murphy CC, Lee SJC, Geiger AM, et al. A randomized trial of mail and email recruitment strategies for a physician survey on clinical trial accrual. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2020;20(1):123. doi:10.1186/s12874-020-01014-x
Radiation and Medical Oncology Perspectives on Oligometastatic Disease Treatment
Radiation and Medical Oncology Perspectives on Oligometastatic Disease Treatment
Assessing the Impact of Antidepressants on Cancer Treatment: A Retrospective Analysis of 14 Antineoplastic Agents
Assessing the Impact of Antidepressants on Cancer Treatment: A Retrospective Analysis of 14 Antineoplastic Agents
Cancer patients experience depression at rates > 5 times that of the general population.1-11 Despite an increase in palliative care use, depression rates continued to rise.2-4 Between 5% to 16% of outpatients, 4% to 14% of inpatients, and up to 49% of patients receiving palliative care experience depression.5 This issue also impacts families and caregivers.1 A 2021 meta-analysis found that 23% of active military personnel and 20% of veterans experience depression.11
Antidepressants approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) target the serotonin, norepinephrine, or dopamine systems and include boxed warnings about an increased risk of suicidal thoughts in adults aged 18 to 24 years.12,13 These medications are categorized into several classes: monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs), tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs), tetracyclic antidepressants (TeCAs), norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitors (NDRIs), selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), serotonin receptor modulators (SRMs), serotonin-melatonin receptor antagonists (SMRAs), and N—methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonists (NMDARAs).14,15 The first FDA-approved antidepressants, iproniazid (an MAOI) and imipramine (a TCA) laid the foundation for the development of newer classes like SSRIs and SNRIs.15-17
Older antidepressants such as MAOIs and TCAs are used less due to their adverse effects (AEs) and drug interactions. MAOIs, such as iproniazid, selegiline, moclobemide, tranylcypromine, isocarboxazid, and phenelzine, have numerous AEs and drug interactions, making them unsuitable for first- or second-line treatment of depression.14,18-21 TCAs such as doxepin, amitriptyline, nortriptyline, imipramine, desipramine, clomipramine, trimipramine, protriptyline, maprotiline, and amoxapine have a narrow therapeutic index requiring careful monitoring for signs of toxicity such as QRS widening, tremors, or confusion. Despite the issues, TCAs are generally classified as second-line agents for major depressive disorder (MDD). TCAs have off-label uses for migraine prophylaxis, treatment of obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), insomnia, and chronic pain management first-line.14,22-29
Newer antidepressants, including TeCAs and NDRIs, are typically more effective, but also come with safety concerns. TeCAs like mirtazapine interact with several medications, including MAOIs, serotonin-increasing drugs, alcohol, cannabidiol, and marijuana. Mirtazapine is FDA-approved for the treatment of moderate to severe depression in adults. It is also used off-label to treat insomnia, panic disorder, posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), social anxiety disorder (SAD), headaches, and migraines. Compared to other antidepressants, mirtazapine is effective for all stages of depression and addresses a broad range of related symptoms.14,30-34 NDRIs, such as bupropion, also interact with various medications, including MAOIs, other antidepressants, stimulants, and alcohol. Bupropion is FDA-approved for smoking cessation and to treat depression and SAD. It is also used off-label for depression- related bipolar disorder or sexual dysfunction, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), and obesity.14,35-42
SSRIs, SNRIs, and SRMs should be used with caution. SSRIs such as sertraline, citalopram, escitalopram, fluoxetine, paroxetine, and fluvoxamine are first-line treatments for depression and various psychiatric disorders due to their safety and efficacy. Common AEs of SSRIs include sexual dysfunction, sleep disturbances, weight changes, and gastrointestinal (GI) issues. SSRIs can prolong the QT interval, posing a risk of life-threatening arrhythmia, and may interact with other medications, necessitating treatment adjustments. The FDA approved SSRIs for MDD, GAD, bulimia nervosa, bipolar depression, OCD, panic disorder, premenstrual dysphoric disorder, treatment-resistant depression, PTSD, and SAD. Off-label uses include binge eating disorder, body dysmorphic disorder, fibromyalgia, premature ejaculation, paraphilias, autism, Raynaud phenomenon, and vasomotor symptoms associated with menopause. Among SSRIs, sertraline and escitalopram are noted for their effectiveness and tolerability.14,43-53
SNRIs, including duloxetine, venlafaxine, desvenlafaxine, milnacipran, and levomilnacipran, may increase bleeding risk, especially when taken with blood thinners. They can also elevate blood pressure, which may worsen if combined with stimulants. SNRIs may interact with other medications that affect serotonin levels, increasing the risk of serotonin syndrome when taken with triptans, pain medications, or other antidepressants.14 Desvenlafaxine has been approved by the FDA (but not by the European Medicines Agency).54-56 Duloxetine is FDA-approved for the treatment of depression, neuropathic pain, anxiety disorders, fibromyalgia, and musculoskeletal disorders. It is used off-label to treat chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy and stress urinary incontinence.57-61 Venlafaxine is FDA-approved for depression, SAD, and panic disorder, and is prescribed off-label to treat ADHD, neuropathy, fibromyalgia, cataplexy, and PTSD, either alone or in combination with other medications.62,63 Milnacipran is not approved for MDD; levomilnacipran received approval in 2013.64
SRMs such as trazodone, nefazodone, vilazodone, and vortioxetine also function as serotonin reuptake inhibitors.14,15 Trazodone is FDA-approved for MDD. It has been used off-label to treat anxiety, Alzheimer disease, substance misuse, bulimia nervosa, insomnia, fibromyalgia, and PTSD when first-line SSRIs are ineffective. A notable AE of trazodone is orthostatic hypotension, which can lead to dizziness and increase the risk of falls, especially in geriatric patients.65-70 Nefazodone was discontinued in Europe in 2003 due to rare cases of liver toxicity but remains available in the US.71-74 Vilazodone and vortioxetine are FDA-approved.
The latest classes of antidepressants include SMRAs and NMDARAs.14 Agomelatine, an SMRA, was approved in Europe in 2009 but rejected by the FDA in 2011 due to liver toxicity.75 NMDARAs like esketamine and a combination of dextromethorphan and bupropion received FDA approval in 2019 and 2022, respectively.76,77
This retrospective study analyzes noncancer drugs used during systemic chemotherapy based on a dataset of 14 antineoplastic agents. It sought to identify the most dispensed noncancer drug groups, discuss findings, compare patients with and without antidepressant prescriptions, and examine trends in antidepressant use from 2002 to 2023. This analysis expands on prior research.78-81
Methods
The Walter Reed National Military Medical Center Institutional Review Board approved the study protocol and ensured compliance with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act as an exempt protocol. The Joint Pathology Center (JPC) of the US Department of Defense (DoD) Cancer Registry Program and Military Health System (MHS) data experts from the Comprehensive Ambulatory/Professional Encounter Record (CAPER) and Pharmacy Data Transaction Service (PDTS) provided data for the analysis.
Data Sources
The JPC DoD Cancer Registry Program contains data from 1998 to 2024. CAPER and PDTS are part of the MHS Data Repository/Management Analysis and Reporting Tool database. Each observation in CAPER represents an ambulatory encounter at a military treatment facility (MTF). CAPER records are available from 2003 to 2024. PDTS records are available from 2002 to 2004. Each observation in PDTS represents a prescription filled for an MHS beneficiary, excluding those filled at international civilian pharmacies and inpatient pharmacy prescriptions.
This cross-sectional analysis requested data extraction for specific cancer drugs from the DoD Cancer Registry, focusing on treatment details, diagnosis dates, patient demographics, and physicians’ comments on AEs. After identifying patients, CAPER was used to identify additional health conditions. PDTS was used to compile a list of prescription medications filled during systemic cancer treatment or < 2 years postdiagnosis.
The 2016 Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program Coding and Staging Manual and International Classification of Diseases for Oncology, 3rd edition, 1st revision, were used to decode disease and cancer types.82,83 Data sorting and analysis were performed using Microsoft Excel. The percentage for the total was calculated by using the number of patients or data available within the subgroup divided by the total number of patients or data variables. To compare the mean number of dispensed antidepressants to those without antidepressants, a 2-tailed, 2-sample z test was used to calculate the P value and determine statistical significance (P < .05) using socscistatistics.com.
Data were extracted 3 times between 2021 and 2023. The initial 2021 protocol focused on erlotinib and gefitinib. A modified protocol in 2022 added paclitaxel, cisplatin, docetaxel, pemetrexed, and crizotinib; further modification in 2023 included 8 new antineoplastic agents and 2 anticoagulants. Sotorasib has not been prescribed in the MHS, and JPC lacks records for noncancer drugs. The 2023 dataset comprised 2210 patients with cancer treated with 14 antineoplastic agents; 2104 had documented diagnoses and 2113 had recorded prescriptions. Data for erlotinib, gefitinib, and paclitaxel have been published previously.78,79
Results
Of 2113 patients with recorded prescriptions, 1297 patients (61.4%) received 109 cancer drugs, including 96 antineoplastics, 7 disease-modifying antirheumatic agents, 4 biologic response modifiers, and 2 calcitonin gene-related peptides. Fourteen antineoplastic agents had complete data from JPC, while others were noted for combination therapies or treatment switches from the PDTS (Table 1). Seventy-six cancer drugs were prescribed with antidepressants in 489 patients (eAppendix).
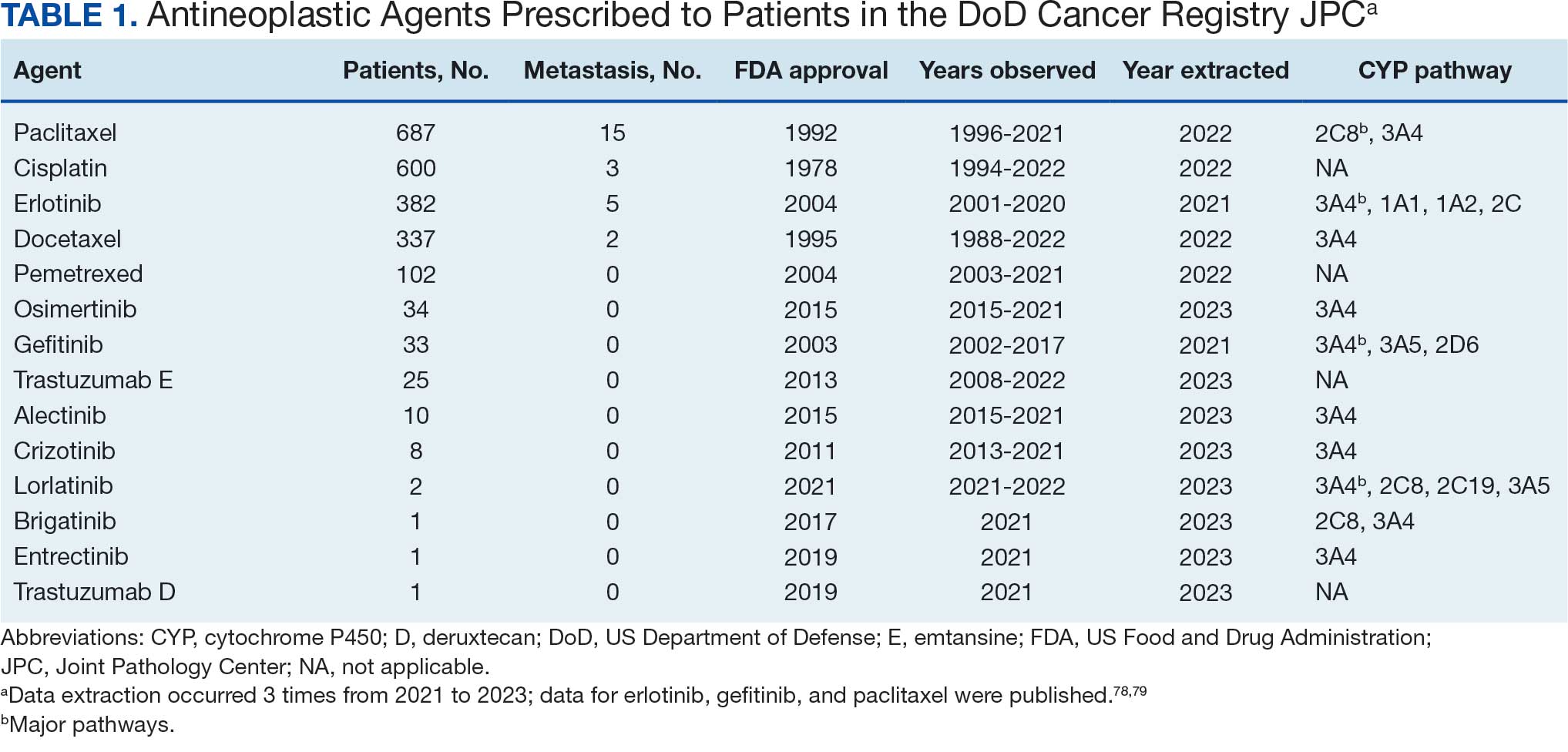
The JPC provided 2242 entries for 2210 patients, ranging in age from 2 months to 88 years (mean, 56 years), documenting treatment from September 1988 to January 2023. Thirty-two patients had duplicate entries due to multiple cancer locations or occurrences. Of the 2242 patients, 1541 (68.7%) were aged > 50 years, 975 patients (43.5%) had cancers that were stage III or IV, and 1267 (56.5%) had cancers that were stage 0, I, II, or not applicable/unknown. There were 51 different types of cancer: breast, lung, testicular, endometrial, and ovarian were most common (n ≥ 100 patients). Forty-two cancer types were documented among 750 patients prescribed antidepressants (Table 2).
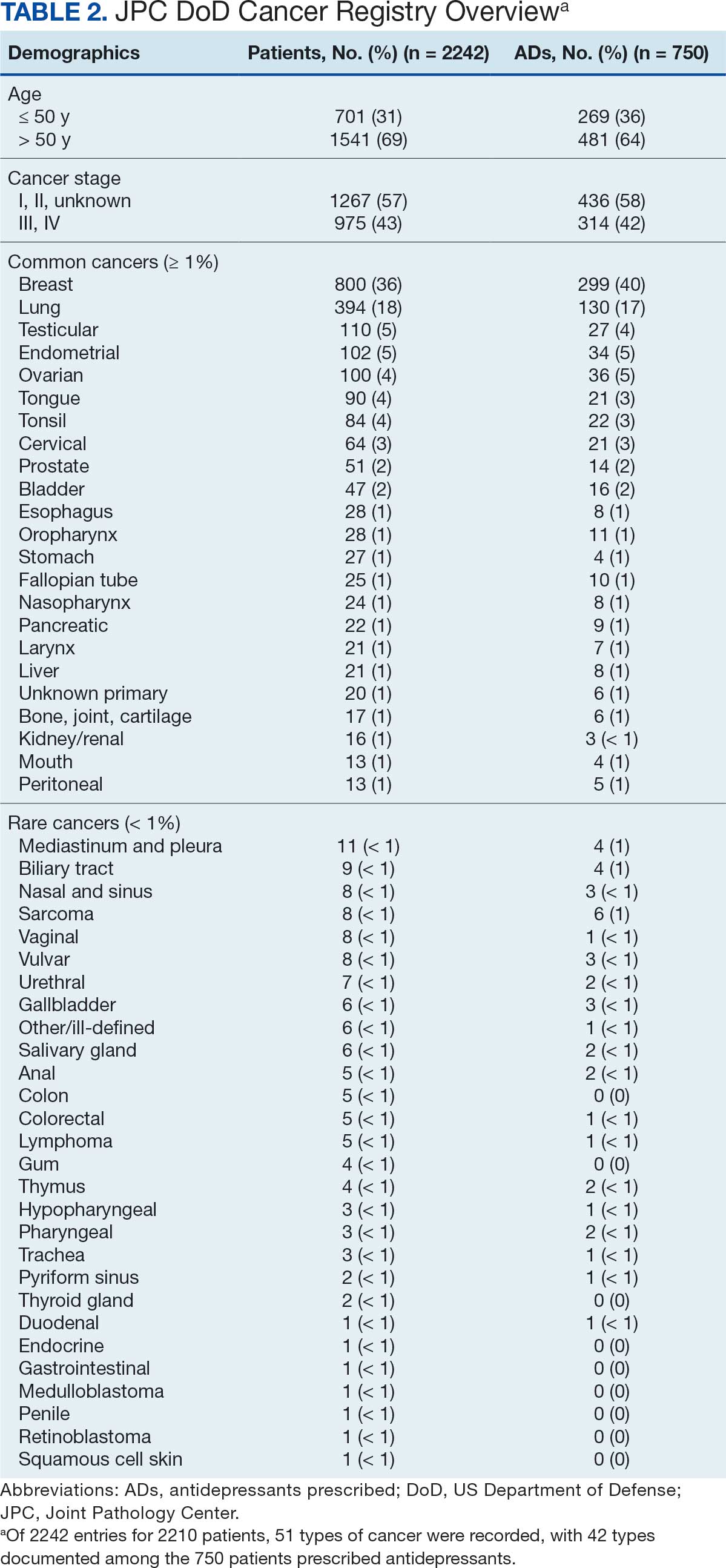
The CAPER database recorded 8882 unique diagnoses for 2104 patients, while PDTS noted 1089 unique prescriptions within 273 therapeutic codes for 2113 patients. Nine therapeutic codes (opiate agonists, adrenals, cathartics-laxatives, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents, antihistamines for GI conditions, 5-HT3 receptor antagonists, analgesics and antipyretic miscellanea, antineoplastic agents, and proton-pump inhibitors) and 8 drugs (dexamethasone, prochlorperazine, ondansetron, docusate, acetaminophen, ibuprofen, oxycodone, and polyethylene glycol 3350) were associated with > 1000 patients (≥ 50%). Patients had between 1 and 275 unique health conditions and filled 1 to 108 prescriptions. The mean (SD) number of diagnoses and prescriptions was 50 (28) and 29 (12), respectively. Of the 273 therapeutic codes, 30 groups were analyzed, with others categorized into miscellaneous groups such as lotions, vaccines, and devices. Significant differences in mean number of prescriptions were found for patients taking antidepressants compared to those not (P < .05), except for anticonvulsants and antipsychotics (P = .12 and .09, respectively) (Table 3).
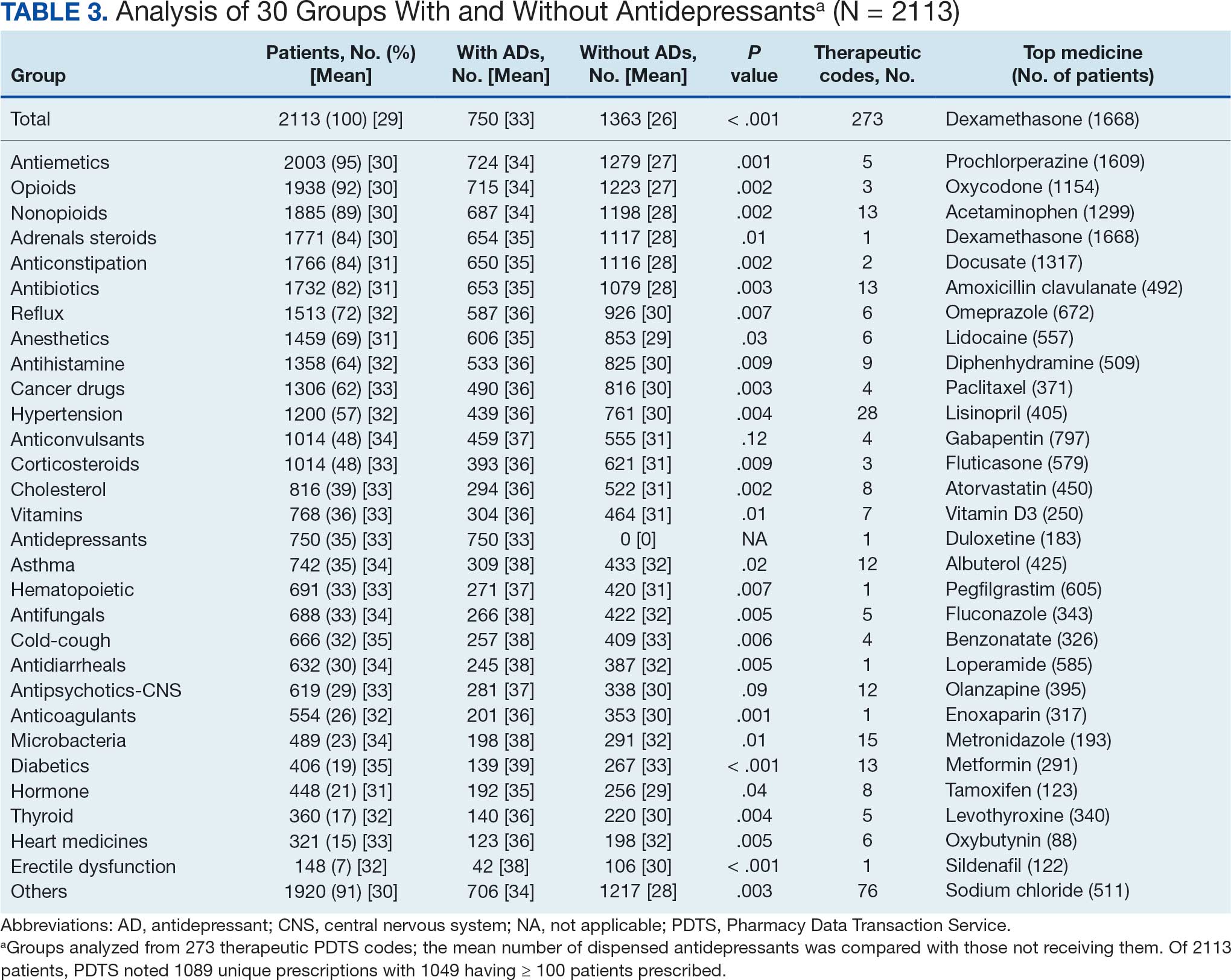
Antidepressants
Of the 2113 patients with recorded prescriptions, 750 (35.5%) were dispensed 17 different antidepressants. Among these 17 antidepressants, 183 (8.7%) patients received duloxetine, 158 (7.5%) received venlafaxine, 118 (5.6%) received trazodone, and 107 (5.1%) received sertraline (Figure 1, Table 4). Of the 750 patients, 509 (67.9%) received 1 antidepressant, 168 (22.4%) received 2, 60 (8.0%) received 3, and 13 (1.7%) received > 3. Combinations varied, but only duloxetine and trazodone were prescribed to > 10 patients.
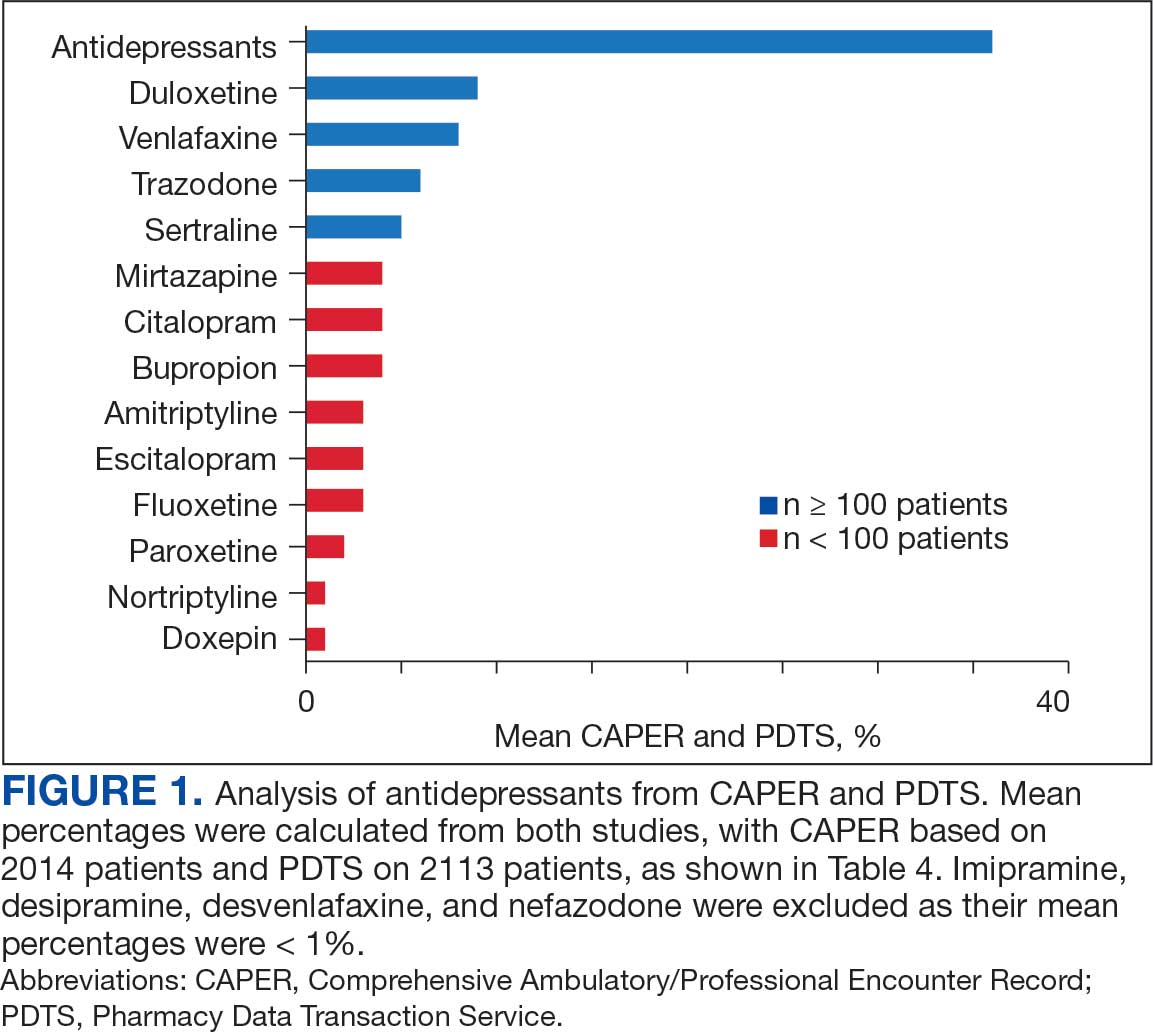
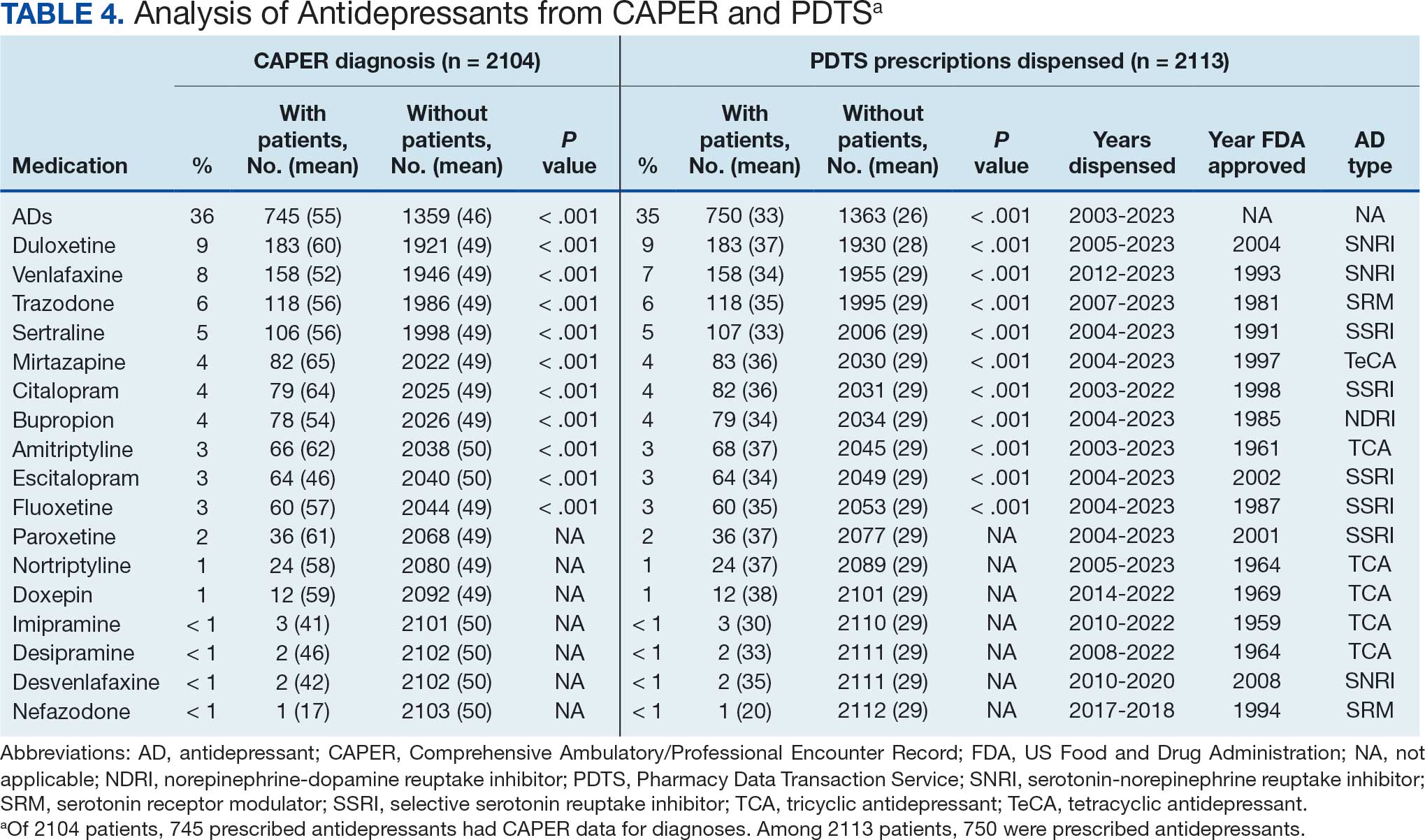
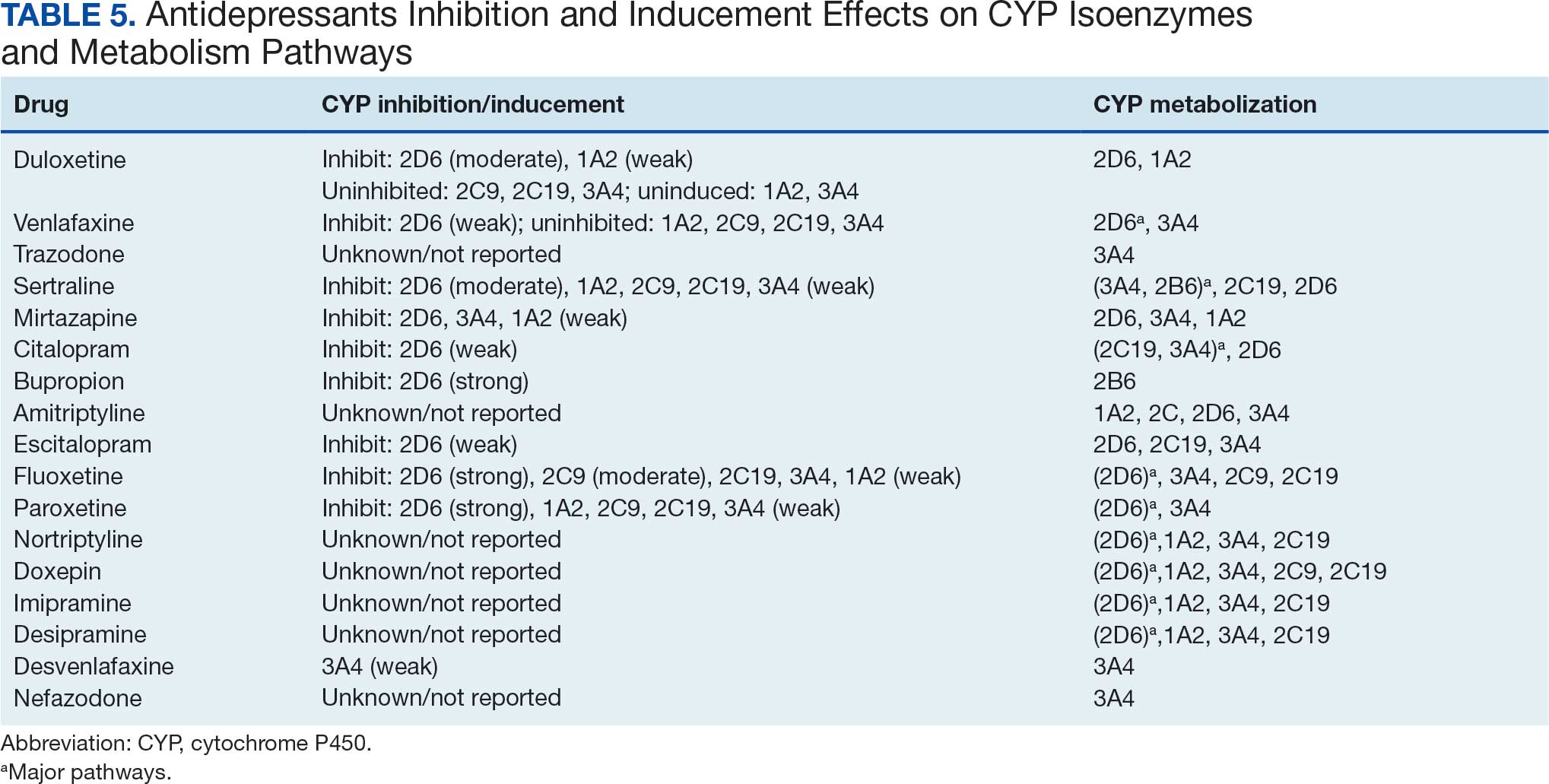
Antidepressants were prescribed annually at an overall mean (SD) rate of 23% (5%) from 2003 to 2022 (Figure 2). Patients on antidepressants during systemic therapy had a greater number of diagnosed medical conditions and received more prescription medications compared to those not taking antidepressants (P < .001) (Figure 3). The 745 patients taking antidepressants in CAPER data had between 1 and 275 diagnosed medical issues, with a mean (SD) of 55 (31) vs a range of 1 to 209 and a mean (SD) of 46 (26) for the 1359 patients not taking antidepressants. The 750 patients on antidepressants in PDTS data had between 8 and 108 prescriptions dispensed, with a mean (SD) of 32 (12), vs a range of 1 to 65 prescriptions and a mean (SD) of 29 (12) for 1363 patients not taking antidepressants.
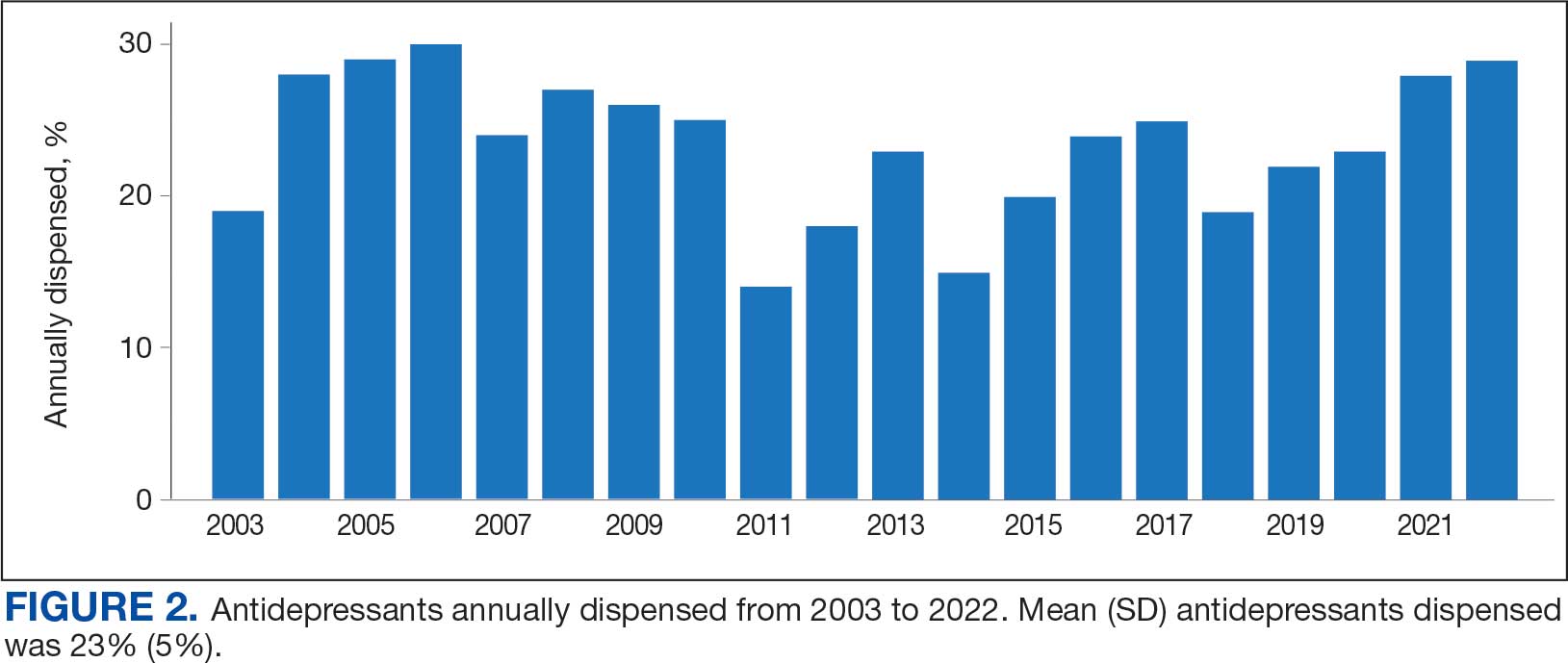
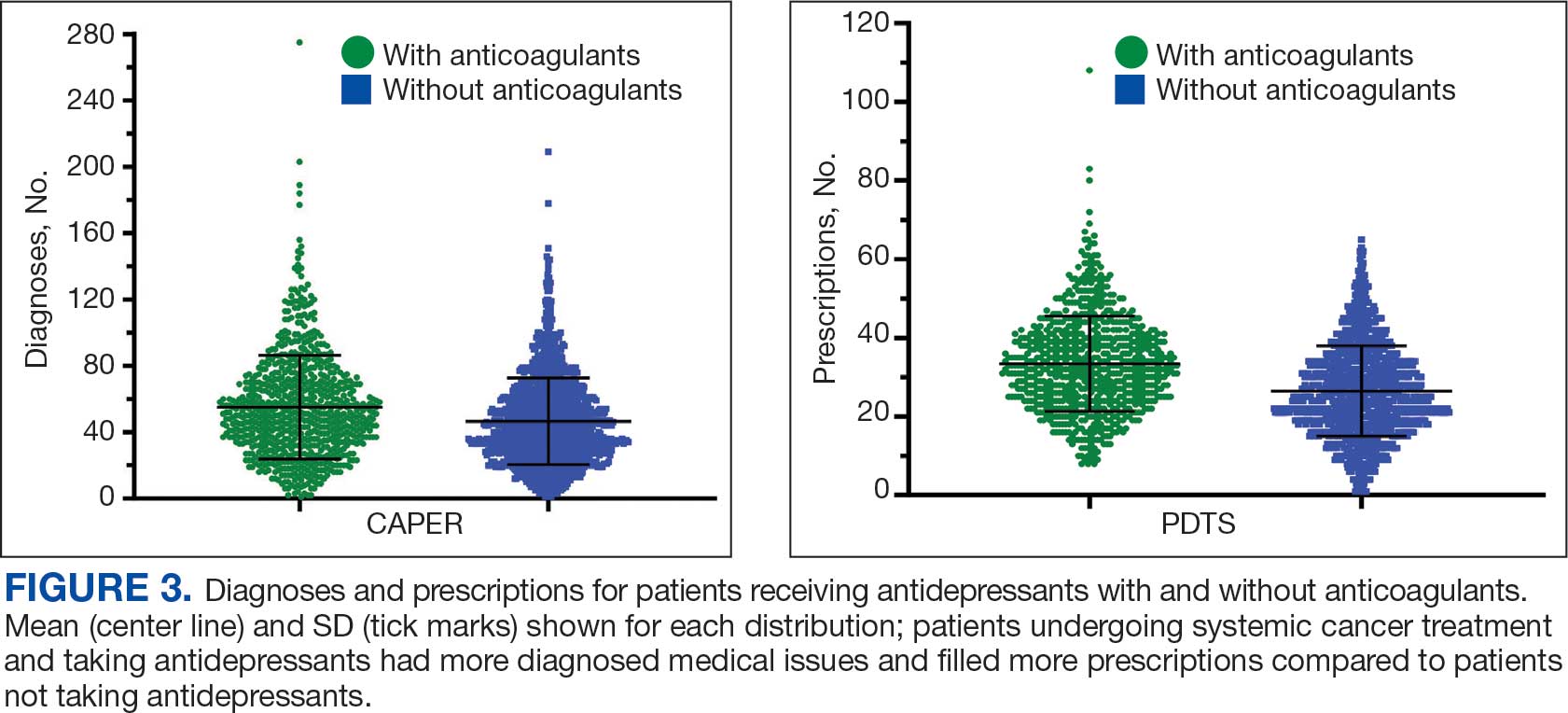
Discussion
The JPC DoD Cancer Registry includes information on cancer types, stages, treatment regimens, and physicians’ notes, while noncancer drugs are sourced from the PDTS database. The pharmacy uses a different documentation system, leading to varied classifications.
Database reliance has its drawbacks. For example, megestrol is coded as a cancer drug, although it’s primarily used for endometrial or gynecologic cancers. Many drugs have multiple therapeutic codes assigned to them, including 10 antineoplastic agents: diclofenac, Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG), megestrol acetate, tamoxifen, anastrozole, letrozole, leuprolide, goserelin, degarelix, and fluorouracil. Diclofenac, BCG, and mitomycin have been repurposed for cancer treatment.84-87 From 2003 to 2023, diclofenac was prescribed to 350 patients for mild-to-moderate pain, with only 2 patients receiving it for cancer in 2018. FDA-approved for bladder cancer in 1990, BCG was prescribed for cancer treatment for 1 patient in 2021 after being used for vaccines between 2003 and 2018. Tamoxifen, used for hormone receptor-positive breast cancer from 2004 to 2017 with 53 patients, switched to estrogen agonist-antagonists from 2017 to 2023 with 123 patients. Only a few of the 168 patients were prescribed tamoxifen using both codes.88-91 Anastrozole and letrozole were coded as antiestrogens for 7 and 18 patients, respectively, while leuprolide and goserelin were coded as gonadotropins for 59 and 18 patients. Degarelix was coded as antigonadotropins, fluorouracil as skin and mucous membrane agents miscellaneous, and megestrol acetate as progestins for 7, 6, and 3 patients, respectively. Duloxetine was given to 186 patients, primarily for depression from 2005 to 2023, with 7 patients treated for fibromyalgia from 2022 to 2023.
Antidepressants Observed
Tables 1 and 5 provide insight into the FDA approval of 14 antineoplastics and antidepressants and their CYP metabolic pathways.92-122 In Table 4, the most prescribed antidepressant classes are SNRIs, SRMs, SSRIs, TeCAs, NDRIs, and TCAs. This trend highlights a preference for newer medications with weak CYP inhibition. A total of 349 patients were prescribed SSRIs, 343 SNRIs, 119 SRMs, 109 TCAs, 83 TeCAs, and 79 NDRIs. MAOIs, SMRAs, and NMDARAs were not observed in this dataset. While there are instances of dextromethorphan-bupropion and sertraline-escitalopram being dispensed together, it remains unclear whether these were NMDARA combinations.
Among the 14 specific antineoplastic agents, 10 are metabolized by CYP isoenzymes, primarily CYP3A4. Duloxetine neither inhibits nor is metabolized by CYP3A4, a reason it is often recommended, following venlafaxine.
Both duloxetine and venlafaxine are used off-label for chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy related to paclitaxel and docetaxel. According to the CYP metabolized pathway, duloxetine tends to have more favorable DDIs than venlafaxine. In PDTS data, 371 patients were treated with paclitaxel and 180 with docetaxel, with respective antidepressant prescriptions of 156 and 70. Of the 156 patients dispensed paclitaxel, 62 (40%) were dispensed with duloxetine compared to 43 (28%) with venlafaxine. Of the 70 patients dispensed docetaxel, 23 (33%) received duloxetine vs 24 (34%) with venlafaxine.
Of 85 patients prescribed duloxetine, 75 received it with either paclitaxel or docetaxel (5 received both). Five patients had documented AEs (1 neuropathy related). Of 67 patients prescribed venlafaxine, 66 received it with either paclitaxel or docetaxel. Two patients had documented AEs (1 was neuropathy related, the same patient who received duloxetine). Of the 687 patients treated with paclitaxel and 337 with docetaxel in all databases, 4 experienced neuropathic AEs from both medications.79
Antidepressants can increase the risk of bleeding, especially when combined with blood thinners, and may elevate blood pressure, particularly alongside stimulants. Of the 554 patients prescribed 9 different anticoagulants, enoxaparin, apixaban, and rivaroxaban were the most common (each > 100 patients). Among these, 201 patients (36%) received both anticoagulants and antidepressants: duloxetine for 64 patients, venlafaxine for 30, trazodone for 35, and sertraline for 26. There were no data available to assess bleeding rates related to the evaluation of DDIs between these medication classes.
Antidepressants can be prescribed for erectile dysfunction. Of the 148 patients prescribed an antidepressant for erectile dysfunction, duloxetine, trazodone, and mirtazapine were the most common. Antidepressant preferences varied by cancer type. Duloxetine was the only antidepressant used for all types of cancer. Venlafaxine, duloxetine, trazodone, sertraline, and escitalopram were the most prescribed antidepressants for breast cancer, while duloxetine, mirtazapine, citalopram, sertraline, and trazodone were the most prescribed for lung cancer. Sertraline, duloxetine, trazodone, amitriptyline, and escitalopram were most common for testicular cancer. Duloxetine, venlafaxine, trazodone, amitriptyline, and sertraline were the most prescribed for endometrial cancer, while duloxetine, venlafaxine, amitriptyline, citalopram, and sertraline were most prescribed for ovarian cancer.
The broadness of International Statistical Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision codes made it challenging to identify nondepression diagnoses in the analyzed population. However, if all antidepressants were prescribed to treat depression, service members with cancer exhibited a higher depression rate (35%) than the general population (25%). Of 2104 patients, 191 (9.1%) had mood disorders, and 706 (33.6%) had mental disorders: 346 (49.0%) had 1 diagnosis, and 360 (51.0%) had multiple diagnoses. The percentage of diagnoses varied yearly, with notable drops in 2003, 2007, 2011, 2014, and 2018, and peaks in 2006, 2008, 2013, 2017, and 2022. This fluctuation was influenced by events like the establishment of PDTS in 2002, the 2008 economic recession, a hospital relocation in 2011, the 2014 Ebola outbreak, and the COVID-19 pandemic. Although the number of patients receiving antidepressants increased from 2019 to 2022, the overall percentage of patients receiving them did not significantly change from 2003 to 2022, aligning with previous research.5,125
Many medications have potential uses beyond what is detailed in the prescribing information. Antidepressants can relieve pain, while pain medications may help with depression. Opioids were once thought to effectively treat depression, but this perspective has changed with a greater understanding of their risks, including misuse.126-131 Pain is a severe and often unbearable AE of cancer. Of 2113 patients, 92% received opioids; 34% received both opioids and antidepressants; 2% received only antidepressants; and 7% received neither. This study didn’t clarify whether those on opioids alone recognized their depression or if those on both were aware of their dependence. While SSRIs are generally not addictive, they can lead to physical dependence, and any medication can be abused if not managed properly.132-134
Conclusions
This retrospective study analyzes data from antineoplastic agents used in systemic cancer treatment between 1988 and 2023, with a particular focus on the use of antidepressants. Data on antidepressant prescriptions are incomplete and specific to these agents, which means the findings cannot be generalized to all antidepressants. Hence, the results indicate that patients taking antidepressants had more diagnosed health issues and received more medications compared to patients who were not on these drugs.
This study underscores the need for further research into the effects of antidepressants on cancer treatment, utilizing all data from the DoD Cancer Registry. Future research should explore DDIs between antidepressants and other cancer and noncancer medications, as this study did not assess AE documentation, unlike in studies involving erlotinib, gefitinib, and paclitaxel.78,79 Further investigation is needed to evaluate the impact of discontinuing antidepressant use during cancer treatment. This comprehensive overview provides insights for clinicians to help them make informed decisions regarding the prescription of antidepressants in the context of cancer treatment.
- National Cancer Institute. Depression (PDQ)-Health Professional Version. Updated July 25, 2024. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/coping/feelings/depression-hp-pdq
- Krebber AM, Buffart LM, Kleijn G, et al. Prevalence of depression in cancer patients: a meta-analysis of diagnostic interviews and self-report instruments. Psychooncology. 2014;23(2):121-130. doi:10.1002/pon.3409
- Xiang X, An R, Gehlert S. Trends in antidepressant use among U.S. cancer survivors, 1999-2012. Psychiatr Serv. 2015;66(6):564. doi:10.1176/appi.ps.201500007
- Hartung TJ, Brähler E, Faller H, et al. The risk of being depressed is significantly higher in cancer patients than in the general population: Prevalence and severity of depressive symptoms across major cancer types. Eur J Cancer. 2017;72:46-53. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2016.11.017
- Walker J, Holm Hansen C, Martin P, et al. Prevalence of depression in adults with cancer: a systematic review. Ann Oncol. 2013;24(4):895-900. doi:10.1093/annonc/mds575
- Pitman A, Suleman S, Hyde N, Hodgkiss A. Depression and anxiety in patients with cancer. BMJ. 2018;361:k1415. doi:10.1136/bmj.k1415
- Kisely S, Alotiby MKN, Protani MM, Soole R, Arnautovska U, Siskind D. Breast cancer treatment disparities in patients with severe mental illness: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychooncology. 2023;32(5):651-662. doi:10.1002/pon.6120
- Massie MJ. Prevalence of depression in patients with cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 2004;(32):57-71. doi:10.1093/jncimonographs/lgh014
- Rodin G, Katz M, Lloyd N, Green E, Mackay JA, Wong RK. Treatment of depression in cancer patients. Curr Oncol. 2007;14(5):180-188. doi:10.3747/co.2007.146
- Wilson KG, Chochinov HM, Skirko MG, et al. Depression and anxiety disorders in palliative cancer care. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2007;33(2):118-129. doi:10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2006.07.016
- Moradi Y, Dowran B, Sepandi M. The global prevalence of depression, suicide ideation, and attempts in the military forces: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cross sectional studies. BMC Psychiatry. 2021;21(1):510. doi:10.1186/s12888-021-03526-2
- Lu CY, Zhang F, Lakoma MD, et al. Changes in antidepressant use by young people and suicidal behavior after FDA warnings and media coverage: quasi-experimental study. BMJ. 2014;348:g3596. doi:10.1136/bmj.g3596
- Friedman RA. Antidepressants’ black-box warning--10 years later. N Engl J Med. 2014;371(18):1666-1668. doi:10.1056/NEJMp1408480
- Sheffler ZM, Patel P, Abdijadid S. Antidepressants. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated May 26, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK538182/
- Miller JJ. Antidepressants, Part 1: 100 Years and Counting. Accessed April 4, 2025. Psychiatric Times. https:// www.psychiatrictimes.com/view/antidepressants-part-1-100-years-and-counting
- Hillhouse TM, Porter JH. A brief history of the development of antidepressant drugs: from monoamines to glutamate. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol. 2015;23(1):1-21. doi:10.1037/a0038550
- Mitchell PB, Mitchell MS. The management of depression. Part 2. The place of the new antidepressants. Aust Fam Physician. 1994;23(9):1771-1781.
- Sabri MA, Saber-Ayad MM. MAO Inhibitors. In: Stat- Pearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated June 5, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557395/
- Sub Laban T, Saadabadi A. Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOI). In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated July 17, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK539848/
- Fiedorowicz JG, Swartz KL. The role of monoamine oxidase inhibitors in current psychiatric practice. J Psychiatr Pract. 2004;10(4):239-248. doi:10.1097/00131746-200407000-00005
- Flockhart DA. Dietary restrictions and drug interactions with monoamine oxidase inhibitors: an update. J Clin Psychiatry. 2012;73 Suppl 1:17-24. doi:10.4088/JCP.11096su1c.03
- Moraczewski J, Awosika AO, Aedma KK. Tricyclic Antidepressants. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated August 17, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557791/
- Almasi A, Patel P, Meza CE. Doxepin. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated February 14, 2024. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK542306/
- Thour A, Marwaha R. Amitriptyline. In: StatPearls. Stat- Pearls Publishing. Updated July 18, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537225/
- Radley DC, Finkelstein SN, Stafford RS. Off-label prescribing among office-based physicians. Arch Intern Med. 2006;166(9):1021-1026. doi:10.1001/archinte.166.9.1021
- Tesfaye S, Sloan G, Petrie J, et al. Comparison of amitriptyline supplemented with pregabalin, pregabalin supplemented with amitriptyline, and duloxetine supplemented with pregabalin for the treatment of diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain (OPTION-DM): a multicentre, double-blind, randomised crossover trial. Lancet. 2022;400(10353):680- 690. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(22)01472-6
- Farag HM, Yunusa I, Goswami H, Sultan I, Doucette JA, Eguale T. Comparison of amitriptyline and US Food and Drug Administration-approved treatments for fibromyalgia: a systematic review and network metaanalysis. JAMA Netw Open. 2022;5(5):e2212939. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.12939
- Merwar G, Gibbons JR, Hosseini SA, Saadabadi A. Nortriptyline. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated June 5, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482214/
- Fayez R, Gupta V. Imipramine. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated May 22, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557656/
- Jilani TN, Gibbons JR, Faizy RM, Saadabadi A. Mirtazapine. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated August 28, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK519059/
- Nutt DJ. Tolerability and safety aspects of mirtazapine. Hum Psychopharmacol. 2002;17 Suppl 1:S37-S41. doi:10.1002/hup.388
- Gandotra K, Chen P, Jaskiw GE, Konicki PE, Strohl KP. Effective treatment of insomnia with mirtazapine attenuates concomitant suicidal ideation. J Clin Sleep Med. 2018;14(5):901-902. doi:10.5664/jcsm.7142
- Anttila SA, Leinonen EV. A review of the pharmacological and clinical profile of mirtazapine. CNS Drug Rev. 2001;7(3):249-264. doi:10.1111/j.1527-3458.2001.tb00198.x
- Wang SM, Han C, Bahk WM, et al. Addressing the side effects of contemporary antidepressant drugs: a comprehensive review. Chonnam Med J. 2018;54(2):101-112. doi:10.4068/cmj.2018.54.2.101
- Huecker MR, Smiley A, Saadabadi A. Bupropion. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated April 9, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470212/
- Hsieh MT, Tseng PT, Wu YC, et al. Effects of different pharmacologic smoking cessation treatments on body weight changes and success rates in patients with nicotine dependence: a network meta-analysis. Obes Rev. 2019;20(6):895- 905. doi:10.1111/obr.12835
- Hankosky ER, Bush HM, Dwoskin LP, et al. Retrospective analysis of health claims to evaluate pharmacotherapies with potential for repurposing: association of bupropion and stimulant use disorder remission. AMIA Annu Symp Proc. 2018;2018:1292-1299.
- Livingstone-Banks J, Norris E, Hartmann-Boyce J, West R, Jarvis M, Hajek P. Relapse prevention interventions for smoking cessation. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019; 2(2):CD003999. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003999.pub5
- Clayton AH, Kingsberg SA, Goldstein I. Evaluation and management of hypoactive sexual desire disorder. Sex Med. 2018;6(2):59-74. doi:10.1016/j.esxm.2018.01.004
- Verbeeck W, Bekkering GE, Van den Noortgate W, Kramers C. Bupropion for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017;10(10):CD009504. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD009504.pub2
- Ng QX. A systematic review of the use of bupropion for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents. J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol. 2017;27(2):112-116. doi:10.1089/cap.2016.0124
- Fava M, Rush AJ, Thase ME, et al. 15 years of clinical experience with bupropion HCl: from bupropion to bupropion SR to bupropion XL. Prim Care Companion J Clin Psychiatry. 2005;7(3):106-113. doi:10.4088/pcc.v07n0305
- Chu A, Wadhwa R. Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated May 1, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK554406/
- Singh HK, Saadabadi A. Sertraline. In: StatPearls. Stat- Pearls Publishing. Updated February 13, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK547689/
- MacQueen G, Born L, Steiner M. The selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor sertraline: its profile and use in psychiatric disorders. CNS Drug Rev. 2001;7(1):1-24. doi:10.1111/j.1527-3458.2001.tb00188.x
- Cipriani A, Furukawa TA, Salanti G, et al. Comparative efficacy and acceptability of 12 new-generation antidepressants: a multiple-treatments meta-analysis. Lancet. 2009;373(9665):746-758. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60046-5
- Nelson JC. The STAR*D study: a four-course meal that leaves us wanting more. Am J Psychiatry. 2006;163(11):1864-1866. doi:10.1176/ajp.2006.163.11.1864
- Sharbaf Shoar N, Fariba KA, Padhy RK. Citalopram. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated November 7, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482222/
- Landy K, Rosani A, Estevez R. Escitalopram. In: Stat- Pearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated November 10, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557734/
- Cavanah LR, Ray P, Goldhirsh JL, Huey LY, Piper BJ. Rise of escitalopram and the fall of citalopram. medRxiv. Preprint published online May 8, 2023. doi:10.1101/2023.05.07.23289632
- Sohel AJ, Shutter MC, Patel P, Molla M. Fluoxetine. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated July 4, 2022. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459223/
- Wong DT, Perry KW, Bymaster FP. Case history: the discovery of fluoxetine hydrochloride (Prozac). Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2005;4(9):764-774. doi:10.1038/nrd1821
- Shrestha P, Fariba KA, Abdijadid S. Paroxetine. In: Stat- Pearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated July 17, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK526022/
- Naseeruddin R, Rosani A, Marwaha R. Desvenlafaxine. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated July 10, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK534829
- Lieberman DZ, Massey SH. Desvenlafaxine in major depressive disorder: an evidence-based review of its place in therapy. Core Evid. 2010;4:67-82. doi:10.2147/ce.s5998
- Withdrawal assessment report for Ellefore (desvenlafaxine). European Medicine Agency. 2009. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/withdrawal-report/withdrawal-assessment-report-ellefore_en.pdf
- Dhaliwal JS, Spurling BC, Molla M. Duloxetine. In: Stat- Pearls. Statpearls Publishing. Updated May 29, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK549806/
- Hershman DL, Lacchetti C, Dworkin RH, et al. Prevention and management of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in survivors of adult cancers: American Society of Clinical Oncology clinical practice guideline. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32(18):1941-1967. doi:10.1200/JCO.2013.54.0914
- Sommer C, Häuser W, Alten R, et al. Medikamentöse Therapie des Fibromyalgiesyndroms. Systematische Übersicht und Metaanalyse [Drug therapy of fibromyalgia syndrome. Systematic review, meta-analysis and guideline]. Schmerz. 2012;26(3):297-310. doi:10.1007/s00482-012-1172-2
- Bril V, England J, Franklin GM, et al. Evidence-based guideline: treatment of painful diabetic neuropathy: report of the American Academy of Neurology, the American Association of Neuromuscular and Electrodiagnostic Medicine, and the American Academy of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. Neurology. 2011;76(20):1758-1765. doi:10.1212/WNL.0b013e3182166ebe
- Attal N, Cruccu G, Baron R, et al. EFNS guidelines on the pharmacological treatment of neuropathic pain: 2010 revision. Eur J Neurol. 2010;17(9):1113-e88. doi:10.1111/j.1468-1331.2010.02999.x
- Singh D, Saadabadi A. Venlafaxine. In: StatPearls. StatePearls Publishing. Updated February 26, 2024. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK535363/
- Sertraline and venlafaxine: new indication. Prevention of recurrent depression: no advance. Prescrire Int. 2005;14(75):19-20.
- Bruno A, Morabito P, S p i n a E , M u s c a t ello MRl. The role of levomilnacipran in the management of major depressive disorder: a comprehensive review. Curr Neuro pharmacol. 2016;14(2):191-199. doi:10.2174/1570159x14666151117122458
- Shin JJ, Saadabadi A. Trazodone. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated February 29, 2024. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470560/
- Khouzam HR. A review of trazodone use in psychiatric and medical conditions. Postgrad Med. 2017;129(1):140-148. doi:10.1080/00325481.2017.1249265
- Smales ET, Edwards BA, Deyoung PN, et al. Trazodone effects on obstructive sleep apnea and non-REM arousal threshold. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2015;12(5):758-764. doi:10.1513/AnnalsATS.201408-399OC
- Eckert DJ, Malhotra A, Wellman A, White DP. Trazodone increases the respiratory arousal threshold in patients with obstructive sleep apnea and a low arousal threshold. Sleep. 2014;37(4):811-819. doi:10.5665/sleep.3596
- Schatzberg AF, Nemeroff CB, eds. The American Psychiat ric Association Publishing Textbook of Psychopharmacology. 4th ed. American Psychiatric Publishing; 2009.
- Ruxton K, Woodman RJ, Mangoni AA. Drugs with anticholinergic effects and cognitive impairment, falls and allcause mortality in older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2015;80(2):209-220. doi:10.1111/bcp.12617
- Nefazodone. In: LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Updated March 6, 2020. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK548179/
- Drugs of Current Interest: Nefazodone. WHO Pharmaceuticals Newsletter:(1). 2003(1):7. https://web.archive.org/web/20150403165029/http:/apps.who.int/medicinedocs/en/d/Js4944e/3.html
- Choi S. Nefazodone (serzone) withdrawn because of hepatotoxicity. CMAJ. 2003;169(11):1187.
- Teva Nefazodone Statement. News release. Teva USA. December 20, 2021. Accessed April 4, 2025. https:// www.tevausa.com/news-and-media/press-releases/teva-nefazodone-statement/
- Levitan MN, Papelbaum M, Nardi AE. Profile of agomelatine and its potential in the treatment of generalized anxiety disorder. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2015;11:1149- 1155. doi:10.2147/NDT.S67470
- Fu DJ, Ionescu DF, Li X, et al. Esketamine nasal spray for rapid reduction of major depressive disorder symptoms in patients who have active suicidal ideation with intent: double-blind, randomized study (ASPIRE I). J Clin Psychiatry. 2020;81(3):19m13191. doi:10.4088/JCP.19m13191
- Iosifescu DV, Jones A, O’Gorman C, et al. Efficacy and safety of AXS-05 (dextromethorphan-bupropion) in patients with major depressive disorder: a phase 3 randomized clinical trial (GEMINI). J Clin Psychiatry. 2022;83(4): 21m14345. doi:10.4088/JCP.21m14345
- Luong TT, Powers CN, Reinhardt BJ, et al. Retrospective evaluation of drug-drug interactions with erlotinib and gefitinib use in the Military Health System. Fed Pract. 2023;40(Suppl 3):S24-S34. doi:10.12788/fp.0401
- Luong TT, Shou KJ, Reinhard BJ, Kigelman OF, Greenfield KM. Paclitaxel drug-drug interactions in the Military Health System. Fed Pract. 2024;41(Suppl 3):S70-S82. doi:10.12788/fp.0499
- Luong TT, Powers CN, Reinhardt BJ, Weina PJ. Preclinical drug-drug interactions (DDIs) of gefitinib with/without losartan and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs): citalopram, fluoxetine, fluvoxamine, paroxetine, sertraline, and venlafaxine. Curr Res Pharmacol Drug Discov. 2022;3:100112. doi:10.1016/j.crphar.2022.100112
- Luong TT, McAnulty MJ, Evers DL, Reinhardt BJ, Weina PJ. Pre-clinical drug-drug interaction (DDI) of gefitinib or erlotinib with cytochrome P450 (CYP) inhibiting drugs, fluoxetine and/or losartan. Curr Res Toxicol. 2021;2:217- 224. doi:10.1016/j.crtox.2021.05.006,
- Adamo M, Dickie L, Ruhl J. SEER program coding and staging manual 2016. National Cancer Institute; 2016. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://seer.cancer.gov/archive/manuals/2016/SPCSM_2016_maindoc.pdf
- World Health Organization. International classification of diseases for oncology (ICD-O). 3rd ed, 1st revision. World Health Organization; 2013. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/96612
- Simon S. FDA approves Jelmyto (mitomycin gel) for urothelial cancer. American Cancer Society. April 20, 2020. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/latest-news/fda-approves-jelmyto-mitomycin-gel-for-urothelial-cancer.html
- Pantziarka P, Sukhatme V, Bouche G, Meheus L, Sukhatme VP. Repurposing drugs in oncology (ReDO)- diclofenac as an anti-cancer agent. Ecancermedicalscience. 2016;10:610. doi:10.3332/ecancer.2016.610
- Choi S, Kim S, Park J, Lee SE, Kim C, Kang D. Diclofenac: a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug inducing cancer cell death by inhibiting microtubule polymerization and autophagy flux. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022;11(5):1009. doi:10.3390/antiox11051009
- Tontonoz M. The ABCs of BCG: oldest approved immunotherapy gets new explanation. Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center. July 17, 2020. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.mskcc.org/news/oldest-approved-immunotherapy-gets-new-explanation
- Jordan VC. Tamoxifen as the first targeted long-term adjuvant therapy for breast cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2014;21(3):R235-R246. doi:10.1530/ERC-14-0092
- Cole MP, Jones CT, Todd ID. A new anti-oestrogenic agent in late breast cancer. An early clinical appraisal of ICI46474. Br J Cancer. 1971;25(2):270-275. doi:10.1038/bjc.1971.33
- Jordan VC. Tamoxifen: a most unlikely pioneering medicine. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2003;2(3):205-213. doi:10.1038/nrd1031
- Maximov PY, McDaniel RE, Jordan VC. Tamoxifen: Pioneering Medicine in Breast Cancer. Springer Basel; 2013. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://link.springer.com/book/10.1007/978-3-0348-0664-0
- Taxol (paclitaxel). Prescribing information. Bristol-Myers Squibb Company; 2011. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2011/020262s049lbl.pdf
- Abraxane (paclitaxel). Prescribing information. Celgene Corporation; 2020. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/021660s047lbl.pdf
- Tarceva (erlotinib). Prescribing information. OSI Pharmaceuticals, LLC; 2016. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2016/021743s025lbl.pdf
- Docetaxel. Prescribing information. Sichuan Hyiyu Pharmaceutical Co.; 2022. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/215813s000lbl.pdf
- Alimta (pemetrexed). Prescribing information. Teva Pharmaceuticals; 2022. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/208419s004lbl.pdf
- Tagrisso (osimertinib). Prescribing information. Astra- Zeneca Pharmaceuticals; 2020. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/208065s021lbl.pdf
- Iressa (gefitinib). Prescribing information. AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals; 2018. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2018/206995s003lbl.pdf
- Kadcyla (ado-trastuzumab emtansine). Prescribing information. Genentech, Inc.; 2013. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2013/125427lbl.pdf
- Alecensa (alectinib). Prescribing information. Genetech, Inc.; 2017. Accessed April 4, 2025. https:// www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2017/208434s003lbl.pdf
- Xalkori (crizotinib). Prescribing information. Pfizer Laboratories; 2022. Accessed April 4, 2025. https:// www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/202570s033lbl.pdf
- Lorbrena (lorlatinib). Prescribing information. Pfizer Laboratories; 2018. Accessed April 14, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2018/210868s000lbl.pdf
- Alunbrig (brigatinib). Prescribing information. Takeda Pharmaceutical Company; 2020. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/208772s008lbl.pdf
- Rozlytrek (entrectinib). Prescribing information. Genentech, Inc.; 2019. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2019/212725s000lbl.pdf
- Herceptin (trastuzumab). Prescribing information. Genentech, Inc.; 2010. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2010/103792s5250lbl.pdf
- Cybalta (duloxetine). Prescribing information. Eli Lilly and Company; 2017. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2017/021427s049lbl.pdf
- Effexor XR (venlafaxine). Prescribing information. Pfizer Wyeth Pharmaceuticals Inc; 2022. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/020699s112lbl.pdf
- Desyrel (trazodone hydrochloride). Prescribing information. Pragma Pharmaceuticals; 2017. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2017/018207s032lbl.pdf
- Sertraline hydrochloride. Prescribing information. Almatica Pharma LLC; 2021. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2021/215133s000lbl.pdf
- Remeron (mirtazapine). Prescribing information. Merck & Co. Inc; 2020. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/020415s029,%20021208s019lbl.pdf
- Celexa (citalopram). Prescribing information. Allergan USA Inc; 2022. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/020822s041lbl.pdf
- information. GlaxoSmithKline; 2019. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/020358s066lbl.pdf
- Amitriptyline hydrochloride tablet. Prescribing information. Quality Care Products LLC; 2022. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/spl/data/0f12f50f-7087-46e7-a2e6-356b4c566c9f/0f12f50f-7087-46e7-a2e6-356b4c566c9f.xml
- Lexapro (escitalopram). Prescribing information. AbbVie Inc; 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2023/021323s055,021365s039lbl.pdf
- Fluoxetine. Prescribing information. Edgemont Pharmaceutical, LLC; 2017. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2017/202133s004s005lbl.pdf
- Paxil (paroxetine). Prescribing Information. Apotex Inc; 2021. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2021/020031s077lbl.pdf
- Pamelor (nortriptyline HCl). Prescribing information. Mallinckrodt, Inc; 2012. Accessed April 4, 2025. https:// www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2012/018012s029,018013s061lbl.pdf
- Silenor (doxepin). Prescribing information. Currax Pharmaceuticals; 2020. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/022036s006lbl.pdf
- Tofranil-PM (imipramine pamote). Prescribing information. Mallinckrodt, Inc; 2014. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2014/017090s078lbl.pdf
- Norpramin (desipramine hydrochloride). Prescribing information. Sanofi-aventis U.S. LLC; 2014. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2014/014399s069lbl.pdf
- Khedezla (desvenlafaxine). Prescribing information. Osmotical Pharmaceutical US LLC; 2019. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2019/204683s006lbl.pdf
- Nefazodone hydrochloride. Prescribing information. Bryant Ranch Prepack; 2022. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/spl/data/0bd4c34a-4f43-4c84-8b98-1d074cba97d5/0bd4c34a-4f43-4c84-8b98-1d074cba97d5.xml
- Grassi L, Nanni MG, Rodin G, Li M, Caruso R. The use of antidepressants in oncology: a review and practical tips for oncologists. Ann Oncol. 2018;29(1):101-111. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdx526
- Lee E, Park Y, Li D, Rodriguez-Fuguet A, Wang X, Zhang WC. Antidepressant use and lung cancer risk and survival: a meta-analysis of observational studies. Cancer Res Commun. 2023;3(6):1013-1025. doi:10.1158/2767-9764.CRC-23-0003
- Olfson M, Marcus SC. National patterns in antidepressant medication treatment. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2009;66(8):848 -856. doi:10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2009.81
- Grattan A, Sullivan MD, Saunders KW, Campbell CI, Von Korff MR. Depression and prescription opioid misuse among chronic opioid therapy recipients with no history of substance abuse. Ann Fam Med. 2012;10(4):304-311. doi:10.1370/afm.1371
- Cowan DT, Wilson-Barnett J, Griffiths P, Allan LG. A survey of chronic noncancer pain patients prescribed opioid analgesics. Pain Med. 2003;4(4):340-351. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4637.2003.03038.x
- Breckenridge J, Clark JD. Patient characteristics associated with opioid versus nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug management of chronic low back pain. J Pain. 2003;4(6):344-350. doi:10.1016/s1526-5900(03)00638-2
- Edlund MJ, Martin BC, Devries A, Fan MY, Braden JB, Sullivan MD. Trends in use of opioids for chronic noncancer pain among individuals with mental health and substance use disorders: the TROUP study. Clin J Pain. 2010;26(1):1-8. doi:10.1097/AJP.0b013e3181b99f35
- Sullivan MD, Edlund MJ, Fan MY, DeVries A, Braden JB, Martin BC. Risks for possible and probable opioid misuse among recipients of chronic opioid therapy in commercial and medicaid insurance plans: the TROUP study. Pain. 2010;150(2):332-339. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2010.05.020
- Dunn KM, Saunders KW, Rutter CM, et al. Opioid prescriptions for chronic pain and overdose: a cohort study. Ann Intern Med. 2010;152(2):85-92. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-152-2-201001190-00006
- Haddad P. Do antidepressants have any potential to cause addiction? J Psychopharmacol. 1999;13(3):300- 307. doi:10.1177/026988119901300321
- Lakeview Health Staff. America’s most abused antidepressants. Lakeview Health. January 24, 2004. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.lakeviewhealth.com/blog/us-most-abused-antidepressants/
- Greenhouse Treatment Center Editorial Staff. Addiction to antidepressants: is it possible? America Addiction Centers: Greenhouse Treatment Center. Updated April 23, 2024. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://greenhousetreatment.com/prescription-medication/antidepressants/
Cancer patients experience depression at rates > 5 times that of the general population.1-11 Despite an increase in palliative care use, depression rates continued to rise.2-4 Between 5% to 16% of outpatients, 4% to 14% of inpatients, and up to 49% of patients receiving palliative care experience depression.5 This issue also impacts families and caregivers.1 A 2021 meta-analysis found that 23% of active military personnel and 20% of veterans experience depression.11
Antidepressants approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) target the serotonin, norepinephrine, or dopamine systems and include boxed warnings about an increased risk of suicidal thoughts in adults aged 18 to 24 years.12,13 These medications are categorized into several classes: monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs), tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs), tetracyclic antidepressants (TeCAs), norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitors (NDRIs), selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), serotonin receptor modulators (SRMs), serotonin-melatonin receptor antagonists (SMRAs), and N—methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonists (NMDARAs).14,15 The first FDA-approved antidepressants, iproniazid (an MAOI) and imipramine (a TCA) laid the foundation for the development of newer classes like SSRIs and SNRIs.15-17
Older antidepressants such as MAOIs and TCAs are used less due to their adverse effects (AEs) and drug interactions. MAOIs, such as iproniazid, selegiline, moclobemide, tranylcypromine, isocarboxazid, and phenelzine, have numerous AEs and drug interactions, making them unsuitable for first- or second-line treatment of depression.14,18-21 TCAs such as doxepin, amitriptyline, nortriptyline, imipramine, desipramine, clomipramine, trimipramine, protriptyline, maprotiline, and amoxapine have a narrow therapeutic index requiring careful monitoring for signs of toxicity such as QRS widening, tremors, or confusion. Despite the issues, TCAs are generally classified as second-line agents for major depressive disorder (MDD). TCAs have off-label uses for migraine prophylaxis, treatment of obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), insomnia, and chronic pain management first-line.14,22-29
Newer antidepressants, including TeCAs and NDRIs, are typically more effective, but also come with safety concerns. TeCAs like mirtazapine interact with several medications, including MAOIs, serotonin-increasing drugs, alcohol, cannabidiol, and marijuana. Mirtazapine is FDA-approved for the treatment of moderate to severe depression in adults. It is also used off-label to treat insomnia, panic disorder, posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), social anxiety disorder (SAD), headaches, and migraines. Compared to other antidepressants, mirtazapine is effective for all stages of depression and addresses a broad range of related symptoms.14,30-34 NDRIs, such as bupropion, also interact with various medications, including MAOIs, other antidepressants, stimulants, and alcohol. Bupropion is FDA-approved for smoking cessation and to treat depression and SAD. It is also used off-label for depression- related bipolar disorder or sexual dysfunction, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), and obesity.14,35-42
SSRIs, SNRIs, and SRMs should be used with caution. SSRIs such as sertraline, citalopram, escitalopram, fluoxetine, paroxetine, and fluvoxamine are first-line treatments for depression and various psychiatric disorders due to their safety and efficacy. Common AEs of SSRIs include sexual dysfunction, sleep disturbances, weight changes, and gastrointestinal (GI) issues. SSRIs can prolong the QT interval, posing a risk of life-threatening arrhythmia, and may interact with other medications, necessitating treatment adjustments. The FDA approved SSRIs for MDD, GAD, bulimia nervosa, bipolar depression, OCD, panic disorder, premenstrual dysphoric disorder, treatment-resistant depression, PTSD, and SAD. Off-label uses include binge eating disorder, body dysmorphic disorder, fibromyalgia, premature ejaculation, paraphilias, autism, Raynaud phenomenon, and vasomotor symptoms associated with menopause. Among SSRIs, sertraline and escitalopram are noted for their effectiveness and tolerability.14,43-53
SNRIs, including duloxetine, venlafaxine, desvenlafaxine, milnacipran, and levomilnacipran, may increase bleeding risk, especially when taken with blood thinners. They can also elevate blood pressure, which may worsen if combined with stimulants. SNRIs may interact with other medications that affect serotonin levels, increasing the risk of serotonin syndrome when taken with triptans, pain medications, or other antidepressants.14 Desvenlafaxine has been approved by the FDA (but not by the European Medicines Agency).54-56 Duloxetine is FDA-approved for the treatment of depression, neuropathic pain, anxiety disorders, fibromyalgia, and musculoskeletal disorders. It is used off-label to treat chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy and stress urinary incontinence.57-61 Venlafaxine is FDA-approved for depression, SAD, and panic disorder, and is prescribed off-label to treat ADHD, neuropathy, fibromyalgia, cataplexy, and PTSD, either alone or in combination with other medications.62,63 Milnacipran is not approved for MDD; levomilnacipran received approval in 2013.64
SRMs such as trazodone, nefazodone, vilazodone, and vortioxetine also function as serotonin reuptake inhibitors.14,15 Trazodone is FDA-approved for MDD. It has been used off-label to treat anxiety, Alzheimer disease, substance misuse, bulimia nervosa, insomnia, fibromyalgia, and PTSD when first-line SSRIs are ineffective. A notable AE of trazodone is orthostatic hypotension, which can lead to dizziness and increase the risk of falls, especially in geriatric patients.65-70 Nefazodone was discontinued in Europe in 2003 due to rare cases of liver toxicity but remains available in the US.71-74 Vilazodone and vortioxetine are FDA-approved.
The latest classes of antidepressants include SMRAs and NMDARAs.14 Agomelatine, an SMRA, was approved in Europe in 2009 but rejected by the FDA in 2011 due to liver toxicity.75 NMDARAs like esketamine and a combination of dextromethorphan and bupropion received FDA approval in 2019 and 2022, respectively.76,77
This retrospective study analyzes noncancer drugs used during systemic chemotherapy based on a dataset of 14 antineoplastic agents. It sought to identify the most dispensed noncancer drug groups, discuss findings, compare patients with and without antidepressant prescriptions, and examine trends in antidepressant use from 2002 to 2023. This analysis expands on prior research.78-81
Methods
The Walter Reed National Military Medical Center Institutional Review Board approved the study protocol and ensured compliance with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act as an exempt protocol. The Joint Pathology Center (JPC) of the US Department of Defense (DoD) Cancer Registry Program and Military Health System (MHS) data experts from the Comprehensive Ambulatory/Professional Encounter Record (CAPER) and Pharmacy Data Transaction Service (PDTS) provided data for the analysis.
Data Sources
The JPC DoD Cancer Registry Program contains data from 1998 to 2024. CAPER and PDTS are part of the MHS Data Repository/Management Analysis and Reporting Tool database. Each observation in CAPER represents an ambulatory encounter at a military treatment facility (MTF). CAPER records are available from 2003 to 2024. PDTS records are available from 2002 to 2004. Each observation in PDTS represents a prescription filled for an MHS beneficiary, excluding those filled at international civilian pharmacies and inpatient pharmacy prescriptions.
This cross-sectional analysis requested data extraction for specific cancer drugs from the DoD Cancer Registry, focusing on treatment details, diagnosis dates, patient demographics, and physicians’ comments on AEs. After identifying patients, CAPER was used to identify additional health conditions. PDTS was used to compile a list of prescription medications filled during systemic cancer treatment or < 2 years postdiagnosis.
The 2016 Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program Coding and Staging Manual and International Classification of Diseases for Oncology, 3rd edition, 1st revision, were used to decode disease and cancer types.82,83 Data sorting and analysis were performed using Microsoft Excel. The percentage for the total was calculated by using the number of patients or data available within the subgroup divided by the total number of patients or data variables. To compare the mean number of dispensed antidepressants to those without antidepressants, a 2-tailed, 2-sample z test was used to calculate the P value and determine statistical significance (P < .05) using socscistatistics.com.
Data were extracted 3 times between 2021 and 2023. The initial 2021 protocol focused on erlotinib and gefitinib. A modified protocol in 2022 added paclitaxel, cisplatin, docetaxel, pemetrexed, and crizotinib; further modification in 2023 included 8 new antineoplastic agents and 2 anticoagulants. Sotorasib has not been prescribed in the MHS, and JPC lacks records for noncancer drugs. The 2023 dataset comprised 2210 patients with cancer treated with 14 antineoplastic agents; 2104 had documented diagnoses and 2113 had recorded prescriptions. Data for erlotinib, gefitinib, and paclitaxel have been published previously.78,79
Results
Of 2113 patients with recorded prescriptions, 1297 patients (61.4%) received 109 cancer drugs, including 96 antineoplastics, 7 disease-modifying antirheumatic agents, 4 biologic response modifiers, and 2 calcitonin gene-related peptides. Fourteen antineoplastic agents had complete data from JPC, while others were noted for combination therapies or treatment switches from the PDTS (Table 1). Seventy-six cancer drugs were prescribed with antidepressants in 489 patients (eAppendix).

The JPC provided 2242 entries for 2210 patients, ranging in age from 2 months to 88 years (mean, 56 years), documenting treatment from September 1988 to January 2023. Thirty-two patients had duplicate entries due to multiple cancer locations or occurrences. Of the 2242 patients, 1541 (68.7%) were aged > 50 years, 975 patients (43.5%) had cancers that were stage III or IV, and 1267 (56.5%) had cancers that were stage 0, I, II, or not applicable/unknown. There were 51 different types of cancer: breast, lung, testicular, endometrial, and ovarian were most common (n ≥ 100 patients). Forty-two cancer types were documented among 750 patients prescribed antidepressants (Table 2).

The CAPER database recorded 8882 unique diagnoses for 2104 patients, while PDTS noted 1089 unique prescriptions within 273 therapeutic codes for 2113 patients. Nine therapeutic codes (opiate agonists, adrenals, cathartics-laxatives, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents, antihistamines for GI conditions, 5-HT3 receptor antagonists, analgesics and antipyretic miscellanea, antineoplastic agents, and proton-pump inhibitors) and 8 drugs (dexamethasone, prochlorperazine, ondansetron, docusate, acetaminophen, ibuprofen, oxycodone, and polyethylene glycol 3350) were associated with > 1000 patients (≥ 50%). Patients had between 1 and 275 unique health conditions and filled 1 to 108 prescriptions. The mean (SD) number of diagnoses and prescriptions was 50 (28) and 29 (12), respectively. Of the 273 therapeutic codes, 30 groups were analyzed, with others categorized into miscellaneous groups such as lotions, vaccines, and devices. Significant differences in mean number of prescriptions were found for patients taking antidepressants compared to those not (P < .05), except for anticonvulsants and antipsychotics (P = .12 and .09, respectively) (Table 3).

Antidepressants
Of the 2113 patients with recorded prescriptions, 750 (35.5%) were dispensed 17 different antidepressants. Among these 17 antidepressants, 183 (8.7%) patients received duloxetine, 158 (7.5%) received venlafaxine, 118 (5.6%) received trazodone, and 107 (5.1%) received sertraline (Figure 1, Table 4). Of the 750 patients, 509 (67.9%) received 1 antidepressant, 168 (22.4%) received 2, 60 (8.0%) received 3, and 13 (1.7%) received > 3. Combinations varied, but only duloxetine and trazodone were prescribed to > 10 patients.



Antidepressants were prescribed annually at an overall mean (SD) rate of 23% (5%) from 2003 to 2022 (Figure 2). Patients on antidepressants during systemic therapy had a greater number of diagnosed medical conditions and received more prescription medications compared to those not taking antidepressants (P < .001) (Figure 3). The 745 patients taking antidepressants in CAPER data had between 1 and 275 diagnosed medical issues, with a mean (SD) of 55 (31) vs a range of 1 to 209 and a mean (SD) of 46 (26) for the 1359 patients not taking antidepressants. The 750 patients on antidepressants in PDTS data had between 8 and 108 prescriptions dispensed, with a mean (SD) of 32 (12), vs a range of 1 to 65 prescriptions and a mean (SD) of 29 (12) for 1363 patients not taking antidepressants.


Discussion
The JPC DoD Cancer Registry includes information on cancer types, stages, treatment regimens, and physicians’ notes, while noncancer drugs are sourced from the PDTS database. The pharmacy uses a different documentation system, leading to varied classifications.
Database reliance has its drawbacks. For example, megestrol is coded as a cancer drug, although it’s primarily used for endometrial or gynecologic cancers. Many drugs have multiple therapeutic codes assigned to them, including 10 antineoplastic agents: diclofenac, Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG), megestrol acetate, tamoxifen, anastrozole, letrozole, leuprolide, goserelin, degarelix, and fluorouracil. Diclofenac, BCG, and mitomycin have been repurposed for cancer treatment.84-87 From 2003 to 2023, diclofenac was prescribed to 350 patients for mild-to-moderate pain, with only 2 patients receiving it for cancer in 2018. FDA-approved for bladder cancer in 1990, BCG was prescribed for cancer treatment for 1 patient in 2021 after being used for vaccines between 2003 and 2018. Tamoxifen, used for hormone receptor-positive breast cancer from 2004 to 2017 with 53 patients, switched to estrogen agonist-antagonists from 2017 to 2023 with 123 patients. Only a few of the 168 patients were prescribed tamoxifen using both codes.88-91 Anastrozole and letrozole were coded as antiestrogens for 7 and 18 patients, respectively, while leuprolide and goserelin were coded as gonadotropins for 59 and 18 patients. Degarelix was coded as antigonadotropins, fluorouracil as skin and mucous membrane agents miscellaneous, and megestrol acetate as progestins for 7, 6, and 3 patients, respectively. Duloxetine was given to 186 patients, primarily for depression from 2005 to 2023, with 7 patients treated for fibromyalgia from 2022 to 2023.
Antidepressants Observed
Tables 1 and 5 provide insight into the FDA approval of 14 antineoplastics and antidepressants and their CYP metabolic pathways.92-122 In Table 4, the most prescribed antidepressant classes are SNRIs, SRMs, SSRIs, TeCAs, NDRIs, and TCAs. This trend highlights a preference for newer medications with weak CYP inhibition. A total of 349 patients were prescribed SSRIs, 343 SNRIs, 119 SRMs, 109 TCAs, 83 TeCAs, and 79 NDRIs. MAOIs, SMRAs, and NMDARAs were not observed in this dataset. While there are instances of dextromethorphan-bupropion and sertraline-escitalopram being dispensed together, it remains unclear whether these were NMDARA combinations.
Among the 14 specific antineoplastic agents, 10 are metabolized by CYP isoenzymes, primarily CYP3A4. Duloxetine neither inhibits nor is metabolized by CYP3A4, a reason it is often recommended, following venlafaxine.
Both duloxetine and venlafaxine are used off-label for chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy related to paclitaxel and docetaxel. According to the CYP metabolized pathway, duloxetine tends to have more favorable DDIs than venlafaxine. In PDTS data, 371 patients were treated with paclitaxel and 180 with docetaxel, with respective antidepressant prescriptions of 156 and 70. Of the 156 patients dispensed paclitaxel, 62 (40%) were dispensed with duloxetine compared to 43 (28%) with venlafaxine. Of the 70 patients dispensed docetaxel, 23 (33%) received duloxetine vs 24 (34%) with venlafaxine.
Of 85 patients prescribed duloxetine, 75 received it with either paclitaxel or docetaxel (5 received both). Five patients had documented AEs (1 neuropathy related). Of 67 patients prescribed venlafaxine, 66 received it with either paclitaxel or docetaxel. Two patients had documented AEs (1 was neuropathy related, the same patient who received duloxetine). Of the 687 patients treated with paclitaxel and 337 with docetaxel in all databases, 4 experienced neuropathic AEs from both medications.79
Antidepressants can increase the risk of bleeding, especially when combined with blood thinners, and may elevate blood pressure, particularly alongside stimulants. Of the 554 patients prescribed 9 different anticoagulants, enoxaparin, apixaban, and rivaroxaban were the most common (each > 100 patients). Among these, 201 patients (36%) received both anticoagulants and antidepressants: duloxetine for 64 patients, venlafaxine for 30, trazodone for 35, and sertraline for 26. There were no data available to assess bleeding rates related to the evaluation of DDIs between these medication classes.
Antidepressants can be prescribed for erectile dysfunction. Of the 148 patients prescribed an antidepressant for erectile dysfunction, duloxetine, trazodone, and mirtazapine were the most common. Antidepressant preferences varied by cancer type. Duloxetine was the only antidepressant used for all types of cancer. Venlafaxine, duloxetine, trazodone, sertraline, and escitalopram were the most prescribed antidepressants for breast cancer, while duloxetine, mirtazapine, citalopram, sertraline, and trazodone were the most prescribed for lung cancer. Sertraline, duloxetine, trazodone, amitriptyline, and escitalopram were most common for testicular cancer. Duloxetine, venlafaxine, trazodone, amitriptyline, and sertraline were the most prescribed for endometrial cancer, while duloxetine, venlafaxine, amitriptyline, citalopram, and sertraline were most prescribed for ovarian cancer.
The broadness of International Statistical Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision codes made it challenging to identify nondepression diagnoses in the analyzed population. However, if all antidepressants were prescribed to treat depression, service members with cancer exhibited a higher depression rate (35%) than the general population (25%). Of 2104 patients, 191 (9.1%) had mood disorders, and 706 (33.6%) had mental disorders: 346 (49.0%) had 1 diagnosis, and 360 (51.0%) had multiple diagnoses. The percentage of diagnoses varied yearly, with notable drops in 2003, 2007, 2011, 2014, and 2018, and peaks in 2006, 2008, 2013, 2017, and 2022. This fluctuation was influenced by events like the establishment of PDTS in 2002, the 2008 economic recession, a hospital relocation in 2011, the 2014 Ebola outbreak, and the COVID-19 pandemic. Although the number of patients receiving antidepressants increased from 2019 to 2022, the overall percentage of patients receiving them did not significantly change from 2003 to 2022, aligning with previous research.5,125
Many medications have potential uses beyond what is detailed in the prescribing information. Antidepressants can relieve pain, while pain medications may help with depression. Opioids were once thought to effectively treat depression, but this perspective has changed with a greater understanding of their risks, including misuse.126-131 Pain is a severe and often unbearable AE of cancer. Of 2113 patients, 92% received opioids; 34% received both opioids and antidepressants; 2% received only antidepressants; and 7% received neither. This study didn’t clarify whether those on opioids alone recognized their depression or if those on both were aware of their dependence. While SSRIs are generally not addictive, they can lead to physical dependence, and any medication can be abused if not managed properly.132-134
Conclusions
This retrospective study analyzes data from antineoplastic agents used in systemic cancer treatment between 1988 and 2023, with a particular focus on the use of antidepressants. Data on antidepressant prescriptions are incomplete and specific to these agents, which means the findings cannot be generalized to all antidepressants. Hence, the results indicate that patients taking antidepressants had more diagnosed health issues and received more medications compared to patients who were not on these drugs.
This study underscores the need for further research into the effects of antidepressants on cancer treatment, utilizing all data from the DoD Cancer Registry. Future research should explore DDIs between antidepressants and other cancer and noncancer medications, as this study did not assess AE documentation, unlike in studies involving erlotinib, gefitinib, and paclitaxel.78,79 Further investigation is needed to evaluate the impact of discontinuing antidepressant use during cancer treatment. This comprehensive overview provides insights for clinicians to help them make informed decisions regarding the prescription of antidepressants in the context of cancer treatment.
Cancer patients experience depression at rates > 5 times that of the general population.1-11 Despite an increase in palliative care use, depression rates continued to rise.2-4 Between 5% to 16% of outpatients, 4% to 14% of inpatients, and up to 49% of patients receiving palliative care experience depression.5 This issue also impacts families and caregivers.1 A 2021 meta-analysis found that 23% of active military personnel and 20% of veterans experience depression.11
Antidepressants approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) target the serotonin, norepinephrine, or dopamine systems and include boxed warnings about an increased risk of suicidal thoughts in adults aged 18 to 24 years.12,13 These medications are categorized into several classes: monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs), tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs), tetracyclic antidepressants (TeCAs), norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitors (NDRIs), selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), serotonin receptor modulators (SRMs), serotonin-melatonin receptor antagonists (SMRAs), and N—methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonists (NMDARAs).14,15 The first FDA-approved antidepressants, iproniazid (an MAOI) and imipramine (a TCA) laid the foundation for the development of newer classes like SSRIs and SNRIs.15-17
Older antidepressants such as MAOIs and TCAs are used less due to their adverse effects (AEs) and drug interactions. MAOIs, such as iproniazid, selegiline, moclobemide, tranylcypromine, isocarboxazid, and phenelzine, have numerous AEs and drug interactions, making them unsuitable for first- or second-line treatment of depression.14,18-21 TCAs such as doxepin, amitriptyline, nortriptyline, imipramine, desipramine, clomipramine, trimipramine, protriptyline, maprotiline, and amoxapine have a narrow therapeutic index requiring careful monitoring for signs of toxicity such as QRS widening, tremors, or confusion. Despite the issues, TCAs are generally classified as second-line agents for major depressive disorder (MDD). TCAs have off-label uses for migraine prophylaxis, treatment of obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), insomnia, and chronic pain management first-line.14,22-29
Newer antidepressants, including TeCAs and NDRIs, are typically more effective, but also come with safety concerns. TeCAs like mirtazapine interact with several medications, including MAOIs, serotonin-increasing drugs, alcohol, cannabidiol, and marijuana. Mirtazapine is FDA-approved for the treatment of moderate to severe depression in adults. It is also used off-label to treat insomnia, panic disorder, posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), social anxiety disorder (SAD), headaches, and migraines. Compared to other antidepressants, mirtazapine is effective for all stages of depression and addresses a broad range of related symptoms.14,30-34 NDRIs, such as bupropion, also interact with various medications, including MAOIs, other antidepressants, stimulants, and alcohol. Bupropion is FDA-approved for smoking cessation and to treat depression and SAD. It is also used off-label for depression- related bipolar disorder or sexual dysfunction, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), and obesity.14,35-42
SSRIs, SNRIs, and SRMs should be used with caution. SSRIs such as sertraline, citalopram, escitalopram, fluoxetine, paroxetine, and fluvoxamine are first-line treatments for depression and various psychiatric disorders due to their safety and efficacy. Common AEs of SSRIs include sexual dysfunction, sleep disturbances, weight changes, and gastrointestinal (GI) issues. SSRIs can prolong the QT interval, posing a risk of life-threatening arrhythmia, and may interact with other medications, necessitating treatment adjustments. The FDA approved SSRIs for MDD, GAD, bulimia nervosa, bipolar depression, OCD, panic disorder, premenstrual dysphoric disorder, treatment-resistant depression, PTSD, and SAD. Off-label uses include binge eating disorder, body dysmorphic disorder, fibromyalgia, premature ejaculation, paraphilias, autism, Raynaud phenomenon, and vasomotor symptoms associated with menopause. Among SSRIs, sertraline and escitalopram are noted for their effectiveness and tolerability.14,43-53
SNRIs, including duloxetine, venlafaxine, desvenlafaxine, milnacipran, and levomilnacipran, may increase bleeding risk, especially when taken with blood thinners. They can also elevate blood pressure, which may worsen if combined with stimulants. SNRIs may interact with other medications that affect serotonin levels, increasing the risk of serotonin syndrome when taken with triptans, pain medications, or other antidepressants.14 Desvenlafaxine has been approved by the FDA (but not by the European Medicines Agency).54-56 Duloxetine is FDA-approved for the treatment of depression, neuropathic pain, anxiety disorders, fibromyalgia, and musculoskeletal disorders. It is used off-label to treat chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy and stress urinary incontinence.57-61 Venlafaxine is FDA-approved for depression, SAD, and panic disorder, and is prescribed off-label to treat ADHD, neuropathy, fibromyalgia, cataplexy, and PTSD, either alone or in combination with other medications.62,63 Milnacipran is not approved for MDD; levomilnacipran received approval in 2013.64
SRMs such as trazodone, nefazodone, vilazodone, and vortioxetine also function as serotonin reuptake inhibitors.14,15 Trazodone is FDA-approved for MDD. It has been used off-label to treat anxiety, Alzheimer disease, substance misuse, bulimia nervosa, insomnia, fibromyalgia, and PTSD when first-line SSRIs are ineffective. A notable AE of trazodone is orthostatic hypotension, which can lead to dizziness and increase the risk of falls, especially in geriatric patients.65-70 Nefazodone was discontinued in Europe in 2003 due to rare cases of liver toxicity but remains available in the US.71-74 Vilazodone and vortioxetine are FDA-approved.
The latest classes of antidepressants include SMRAs and NMDARAs.14 Agomelatine, an SMRA, was approved in Europe in 2009 but rejected by the FDA in 2011 due to liver toxicity.75 NMDARAs like esketamine and a combination of dextromethorphan and bupropion received FDA approval in 2019 and 2022, respectively.76,77
This retrospective study analyzes noncancer drugs used during systemic chemotherapy based on a dataset of 14 antineoplastic agents. It sought to identify the most dispensed noncancer drug groups, discuss findings, compare patients with and without antidepressant prescriptions, and examine trends in antidepressant use from 2002 to 2023. This analysis expands on prior research.78-81
Methods
The Walter Reed National Military Medical Center Institutional Review Board approved the study protocol and ensured compliance with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act as an exempt protocol. The Joint Pathology Center (JPC) of the US Department of Defense (DoD) Cancer Registry Program and Military Health System (MHS) data experts from the Comprehensive Ambulatory/Professional Encounter Record (CAPER) and Pharmacy Data Transaction Service (PDTS) provided data for the analysis.
Data Sources
The JPC DoD Cancer Registry Program contains data from 1998 to 2024. CAPER and PDTS are part of the MHS Data Repository/Management Analysis and Reporting Tool database. Each observation in CAPER represents an ambulatory encounter at a military treatment facility (MTF). CAPER records are available from 2003 to 2024. PDTS records are available from 2002 to 2004. Each observation in PDTS represents a prescription filled for an MHS beneficiary, excluding those filled at international civilian pharmacies and inpatient pharmacy prescriptions.
This cross-sectional analysis requested data extraction for specific cancer drugs from the DoD Cancer Registry, focusing on treatment details, diagnosis dates, patient demographics, and physicians’ comments on AEs. After identifying patients, CAPER was used to identify additional health conditions. PDTS was used to compile a list of prescription medications filled during systemic cancer treatment or < 2 years postdiagnosis.
The 2016 Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program Coding and Staging Manual and International Classification of Diseases for Oncology, 3rd edition, 1st revision, were used to decode disease and cancer types.82,83 Data sorting and analysis were performed using Microsoft Excel. The percentage for the total was calculated by using the number of patients or data available within the subgroup divided by the total number of patients or data variables. To compare the mean number of dispensed antidepressants to those without antidepressants, a 2-tailed, 2-sample z test was used to calculate the P value and determine statistical significance (P < .05) using socscistatistics.com.
Data were extracted 3 times between 2021 and 2023. The initial 2021 protocol focused on erlotinib and gefitinib. A modified protocol in 2022 added paclitaxel, cisplatin, docetaxel, pemetrexed, and crizotinib; further modification in 2023 included 8 new antineoplastic agents and 2 anticoagulants. Sotorasib has not been prescribed in the MHS, and JPC lacks records for noncancer drugs. The 2023 dataset comprised 2210 patients with cancer treated with 14 antineoplastic agents; 2104 had documented diagnoses and 2113 had recorded prescriptions. Data for erlotinib, gefitinib, and paclitaxel have been published previously.78,79
Results
Of 2113 patients with recorded prescriptions, 1297 patients (61.4%) received 109 cancer drugs, including 96 antineoplastics, 7 disease-modifying antirheumatic agents, 4 biologic response modifiers, and 2 calcitonin gene-related peptides. Fourteen antineoplastic agents had complete data from JPC, while others were noted for combination therapies or treatment switches from the PDTS (Table 1). Seventy-six cancer drugs were prescribed with antidepressants in 489 patients (eAppendix).

The JPC provided 2242 entries for 2210 patients, ranging in age from 2 months to 88 years (mean, 56 years), documenting treatment from September 1988 to January 2023. Thirty-two patients had duplicate entries due to multiple cancer locations or occurrences. Of the 2242 patients, 1541 (68.7%) were aged > 50 years, 975 patients (43.5%) had cancers that were stage III or IV, and 1267 (56.5%) had cancers that were stage 0, I, II, or not applicable/unknown. There were 51 different types of cancer: breast, lung, testicular, endometrial, and ovarian were most common (n ≥ 100 patients). Forty-two cancer types were documented among 750 patients prescribed antidepressants (Table 2).

The CAPER database recorded 8882 unique diagnoses for 2104 patients, while PDTS noted 1089 unique prescriptions within 273 therapeutic codes for 2113 patients. Nine therapeutic codes (opiate agonists, adrenals, cathartics-laxatives, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents, antihistamines for GI conditions, 5-HT3 receptor antagonists, analgesics and antipyretic miscellanea, antineoplastic agents, and proton-pump inhibitors) and 8 drugs (dexamethasone, prochlorperazine, ondansetron, docusate, acetaminophen, ibuprofen, oxycodone, and polyethylene glycol 3350) were associated with > 1000 patients (≥ 50%). Patients had between 1 and 275 unique health conditions and filled 1 to 108 prescriptions. The mean (SD) number of diagnoses and prescriptions was 50 (28) and 29 (12), respectively. Of the 273 therapeutic codes, 30 groups were analyzed, with others categorized into miscellaneous groups such as lotions, vaccines, and devices. Significant differences in mean number of prescriptions were found for patients taking antidepressants compared to those not (P < .05), except for anticonvulsants and antipsychotics (P = .12 and .09, respectively) (Table 3).

Antidepressants
Of the 2113 patients with recorded prescriptions, 750 (35.5%) were dispensed 17 different antidepressants. Among these 17 antidepressants, 183 (8.7%) patients received duloxetine, 158 (7.5%) received venlafaxine, 118 (5.6%) received trazodone, and 107 (5.1%) received sertraline (Figure 1, Table 4). Of the 750 patients, 509 (67.9%) received 1 antidepressant, 168 (22.4%) received 2, 60 (8.0%) received 3, and 13 (1.7%) received > 3. Combinations varied, but only duloxetine and trazodone were prescribed to > 10 patients.



Antidepressants were prescribed annually at an overall mean (SD) rate of 23% (5%) from 2003 to 2022 (Figure 2). Patients on antidepressants during systemic therapy had a greater number of diagnosed medical conditions and received more prescription medications compared to those not taking antidepressants (P < .001) (Figure 3). The 745 patients taking antidepressants in CAPER data had between 1 and 275 diagnosed medical issues, with a mean (SD) of 55 (31) vs a range of 1 to 209 and a mean (SD) of 46 (26) for the 1359 patients not taking antidepressants. The 750 patients on antidepressants in PDTS data had between 8 and 108 prescriptions dispensed, with a mean (SD) of 32 (12), vs a range of 1 to 65 prescriptions and a mean (SD) of 29 (12) for 1363 patients not taking antidepressants.


Discussion
The JPC DoD Cancer Registry includes information on cancer types, stages, treatment regimens, and physicians’ notes, while noncancer drugs are sourced from the PDTS database. The pharmacy uses a different documentation system, leading to varied classifications.
Database reliance has its drawbacks. For example, megestrol is coded as a cancer drug, although it’s primarily used for endometrial or gynecologic cancers. Many drugs have multiple therapeutic codes assigned to them, including 10 antineoplastic agents: diclofenac, Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG), megestrol acetate, tamoxifen, anastrozole, letrozole, leuprolide, goserelin, degarelix, and fluorouracil. Diclofenac, BCG, and mitomycin have been repurposed for cancer treatment.84-87 From 2003 to 2023, diclofenac was prescribed to 350 patients for mild-to-moderate pain, with only 2 patients receiving it for cancer in 2018. FDA-approved for bladder cancer in 1990, BCG was prescribed for cancer treatment for 1 patient in 2021 after being used for vaccines between 2003 and 2018. Tamoxifen, used for hormone receptor-positive breast cancer from 2004 to 2017 with 53 patients, switched to estrogen agonist-antagonists from 2017 to 2023 with 123 patients. Only a few of the 168 patients were prescribed tamoxifen using both codes.88-91 Anastrozole and letrozole were coded as antiestrogens for 7 and 18 patients, respectively, while leuprolide and goserelin were coded as gonadotropins for 59 and 18 patients. Degarelix was coded as antigonadotropins, fluorouracil as skin and mucous membrane agents miscellaneous, and megestrol acetate as progestins for 7, 6, and 3 patients, respectively. Duloxetine was given to 186 patients, primarily for depression from 2005 to 2023, with 7 patients treated for fibromyalgia from 2022 to 2023.
Antidepressants Observed
Tables 1 and 5 provide insight into the FDA approval of 14 antineoplastics and antidepressants and their CYP metabolic pathways.92-122 In Table 4, the most prescribed antidepressant classes are SNRIs, SRMs, SSRIs, TeCAs, NDRIs, and TCAs. This trend highlights a preference for newer medications with weak CYP inhibition. A total of 349 patients were prescribed SSRIs, 343 SNRIs, 119 SRMs, 109 TCAs, 83 TeCAs, and 79 NDRIs. MAOIs, SMRAs, and NMDARAs were not observed in this dataset. While there are instances of dextromethorphan-bupropion and sertraline-escitalopram being dispensed together, it remains unclear whether these were NMDARA combinations.
Among the 14 specific antineoplastic agents, 10 are metabolized by CYP isoenzymes, primarily CYP3A4. Duloxetine neither inhibits nor is metabolized by CYP3A4, a reason it is often recommended, following venlafaxine.
Both duloxetine and venlafaxine are used off-label for chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy related to paclitaxel and docetaxel. According to the CYP metabolized pathway, duloxetine tends to have more favorable DDIs than venlafaxine. In PDTS data, 371 patients were treated with paclitaxel and 180 with docetaxel, with respective antidepressant prescriptions of 156 and 70. Of the 156 patients dispensed paclitaxel, 62 (40%) were dispensed with duloxetine compared to 43 (28%) with venlafaxine. Of the 70 patients dispensed docetaxel, 23 (33%) received duloxetine vs 24 (34%) with venlafaxine.
Of 85 patients prescribed duloxetine, 75 received it with either paclitaxel or docetaxel (5 received both). Five patients had documented AEs (1 neuropathy related). Of 67 patients prescribed venlafaxine, 66 received it with either paclitaxel or docetaxel. Two patients had documented AEs (1 was neuropathy related, the same patient who received duloxetine). Of the 687 patients treated with paclitaxel and 337 with docetaxel in all databases, 4 experienced neuropathic AEs from both medications.79
Antidepressants can increase the risk of bleeding, especially when combined with blood thinners, and may elevate blood pressure, particularly alongside stimulants. Of the 554 patients prescribed 9 different anticoagulants, enoxaparin, apixaban, and rivaroxaban were the most common (each > 100 patients). Among these, 201 patients (36%) received both anticoagulants and antidepressants: duloxetine for 64 patients, venlafaxine for 30, trazodone for 35, and sertraline for 26. There were no data available to assess bleeding rates related to the evaluation of DDIs between these medication classes.
Antidepressants can be prescribed for erectile dysfunction. Of the 148 patients prescribed an antidepressant for erectile dysfunction, duloxetine, trazodone, and mirtazapine were the most common. Antidepressant preferences varied by cancer type. Duloxetine was the only antidepressant used for all types of cancer. Venlafaxine, duloxetine, trazodone, sertraline, and escitalopram were the most prescribed antidepressants for breast cancer, while duloxetine, mirtazapine, citalopram, sertraline, and trazodone were the most prescribed for lung cancer. Sertraline, duloxetine, trazodone, amitriptyline, and escitalopram were most common for testicular cancer. Duloxetine, venlafaxine, trazodone, amitriptyline, and sertraline were the most prescribed for endometrial cancer, while duloxetine, venlafaxine, amitriptyline, citalopram, and sertraline were most prescribed for ovarian cancer.
The broadness of International Statistical Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision codes made it challenging to identify nondepression diagnoses in the analyzed population. However, if all antidepressants were prescribed to treat depression, service members with cancer exhibited a higher depression rate (35%) than the general population (25%). Of 2104 patients, 191 (9.1%) had mood disorders, and 706 (33.6%) had mental disorders: 346 (49.0%) had 1 diagnosis, and 360 (51.0%) had multiple diagnoses. The percentage of diagnoses varied yearly, with notable drops in 2003, 2007, 2011, 2014, and 2018, and peaks in 2006, 2008, 2013, 2017, and 2022. This fluctuation was influenced by events like the establishment of PDTS in 2002, the 2008 economic recession, a hospital relocation in 2011, the 2014 Ebola outbreak, and the COVID-19 pandemic. Although the number of patients receiving antidepressants increased from 2019 to 2022, the overall percentage of patients receiving them did not significantly change from 2003 to 2022, aligning with previous research.5,125
Many medications have potential uses beyond what is detailed in the prescribing information. Antidepressants can relieve pain, while pain medications may help with depression. Opioids were once thought to effectively treat depression, but this perspective has changed with a greater understanding of their risks, including misuse.126-131 Pain is a severe and often unbearable AE of cancer. Of 2113 patients, 92% received opioids; 34% received both opioids and antidepressants; 2% received only antidepressants; and 7% received neither. This study didn’t clarify whether those on opioids alone recognized their depression or if those on both were aware of their dependence. While SSRIs are generally not addictive, they can lead to physical dependence, and any medication can be abused if not managed properly.132-134
Conclusions
This retrospective study analyzes data from antineoplastic agents used in systemic cancer treatment between 1988 and 2023, with a particular focus on the use of antidepressants. Data on antidepressant prescriptions are incomplete and specific to these agents, which means the findings cannot be generalized to all antidepressants. Hence, the results indicate that patients taking antidepressants had more diagnosed health issues and received more medications compared to patients who were not on these drugs.
This study underscores the need for further research into the effects of antidepressants on cancer treatment, utilizing all data from the DoD Cancer Registry. Future research should explore DDIs between antidepressants and other cancer and noncancer medications, as this study did not assess AE documentation, unlike in studies involving erlotinib, gefitinib, and paclitaxel.78,79 Further investigation is needed to evaluate the impact of discontinuing antidepressant use during cancer treatment. This comprehensive overview provides insights for clinicians to help them make informed decisions regarding the prescription of antidepressants in the context of cancer treatment.
- National Cancer Institute. Depression (PDQ)-Health Professional Version. Updated July 25, 2024. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/coping/feelings/depression-hp-pdq
- Krebber AM, Buffart LM, Kleijn G, et al. Prevalence of depression in cancer patients: a meta-analysis of diagnostic interviews and self-report instruments. Psychooncology. 2014;23(2):121-130. doi:10.1002/pon.3409
- Xiang X, An R, Gehlert S. Trends in antidepressant use among U.S. cancer survivors, 1999-2012. Psychiatr Serv. 2015;66(6):564. doi:10.1176/appi.ps.201500007
- Hartung TJ, Brähler E, Faller H, et al. The risk of being depressed is significantly higher in cancer patients than in the general population: Prevalence and severity of depressive symptoms across major cancer types. Eur J Cancer. 2017;72:46-53. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2016.11.017
- Walker J, Holm Hansen C, Martin P, et al. Prevalence of depression in adults with cancer: a systematic review. Ann Oncol. 2013;24(4):895-900. doi:10.1093/annonc/mds575
- Pitman A, Suleman S, Hyde N, Hodgkiss A. Depression and anxiety in patients with cancer. BMJ. 2018;361:k1415. doi:10.1136/bmj.k1415
- Kisely S, Alotiby MKN, Protani MM, Soole R, Arnautovska U, Siskind D. Breast cancer treatment disparities in patients with severe mental illness: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychooncology. 2023;32(5):651-662. doi:10.1002/pon.6120
- Massie MJ. Prevalence of depression in patients with cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 2004;(32):57-71. doi:10.1093/jncimonographs/lgh014
- Rodin G, Katz M, Lloyd N, Green E, Mackay JA, Wong RK. Treatment of depression in cancer patients. Curr Oncol. 2007;14(5):180-188. doi:10.3747/co.2007.146
- Wilson KG, Chochinov HM, Skirko MG, et al. Depression and anxiety disorders in palliative cancer care. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2007;33(2):118-129. doi:10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2006.07.016
- Moradi Y, Dowran B, Sepandi M. The global prevalence of depression, suicide ideation, and attempts in the military forces: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cross sectional studies. BMC Psychiatry. 2021;21(1):510. doi:10.1186/s12888-021-03526-2
- Lu CY, Zhang F, Lakoma MD, et al. Changes in antidepressant use by young people and suicidal behavior after FDA warnings and media coverage: quasi-experimental study. BMJ. 2014;348:g3596. doi:10.1136/bmj.g3596
- Friedman RA. Antidepressants’ black-box warning--10 years later. N Engl J Med. 2014;371(18):1666-1668. doi:10.1056/NEJMp1408480
- Sheffler ZM, Patel P, Abdijadid S. Antidepressants. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated May 26, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK538182/
- Miller JJ. Antidepressants, Part 1: 100 Years and Counting. Accessed April 4, 2025. Psychiatric Times. https:// www.psychiatrictimes.com/view/antidepressants-part-1-100-years-and-counting
- Hillhouse TM, Porter JH. A brief history of the development of antidepressant drugs: from monoamines to glutamate. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol. 2015;23(1):1-21. doi:10.1037/a0038550
- Mitchell PB, Mitchell MS. The management of depression. Part 2. The place of the new antidepressants. Aust Fam Physician. 1994;23(9):1771-1781.
- Sabri MA, Saber-Ayad MM. MAO Inhibitors. In: Stat- Pearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated June 5, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557395/
- Sub Laban T, Saadabadi A. Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOI). In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated July 17, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK539848/
- Fiedorowicz JG, Swartz KL. The role of monoamine oxidase inhibitors in current psychiatric practice. J Psychiatr Pract. 2004;10(4):239-248. doi:10.1097/00131746-200407000-00005
- Flockhart DA. Dietary restrictions and drug interactions with monoamine oxidase inhibitors: an update. J Clin Psychiatry. 2012;73 Suppl 1:17-24. doi:10.4088/JCP.11096su1c.03
- Moraczewski J, Awosika AO, Aedma KK. Tricyclic Antidepressants. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated August 17, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557791/
- Almasi A, Patel P, Meza CE. Doxepin. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated February 14, 2024. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK542306/
- Thour A, Marwaha R. Amitriptyline. In: StatPearls. Stat- Pearls Publishing. Updated July 18, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537225/
- Radley DC, Finkelstein SN, Stafford RS. Off-label prescribing among office-based physicians. Arch Intern Med. 2006;166(9):1021-1026. doi:10.1001/archinte.166.9.1021
- Tesfaye S, Sloan G, Petrie J, et al. Comparison of amitriptyline supplemented with pregabalin, pregabalin supplemented with amitriptyline, and duloxetine supplemented with pregabalin for the treatment of diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain (OPTION-DM): a multicentre, double-blind, randomised crossover trial. Lancet. 2022;400(10353):680- 690. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(22)01472-6
- Farag HM, Yunusa I, Goswami H, Sultan I, Doucette JA, Eguale T. Comparison of amitriptyline and US Food and Drug Administration-approved treatments for fibromyalgia: a systematic review and network metaanalysis. JAMA Netw Open. 2022;5(5):e2212939. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.12939
- Merwar G, Gibbons JR, Hosseini SA, Saadabadi A. Nortriptyline. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated June 5, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482214/
- Fayez R, Gupta V. Imipramine. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated May 22, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557656/
- Jilani TN, Gibbons JR, Faizy RM, Saadabadi A. Mirtazapine. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated August 28, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK519059/
- Nutt DJ. Tolerability and safety aspects of mirtazapine. Hum Psychopharmacol. 2002;17 Suppl 1:S37-S41. doi:10.1002/hup.388
- Gandotra K, Chen P, Jaskiw GE, Konicki PE, Strohl KP. Effective treatment of insomnia with mirtazapine attenuates concomitant suicidal ideation. J Clin Sleep Med. 2018;14(5):901-902. doi:10.5664/jcsm.7142
- Anttila SA, Leinonen EV. A review of the pharmacological and clinical profile of mirtazapine. CNS Drug Rev. 2001;7(3):249-264. doi:10.1111/j.1527-3458.2001.tb00198.x
- Wang SM, Han C, Bahk WM, et al. Addressing the side effects of contemporary antidepressant drugs: a comprehensive review. Chonnam Med J. 2018;54(2):101-112. doi:10.4068/cmj.2018.54.2.101
- Huecker MR, Smiley A, Saadabadi A. Bupropion. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated April 9, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470212/
- Hsieh MT, Tseng PT, Wu YC, et al. Effects of different pharmacologic smoking cessation treatments on body weight changes and success rates in patients with nicotine dependence: a network meta-analysis. Obes Rev. 2019;20(6):895- 905. doi:10.1111/obr.12835
- Hankosky ER, Bush HM, Dwoskin LP, et al. Retrospective analysis of health claims to evaluate pharmacotherapies with potential for repurposing: association of bupropion and stimulant use disorder remission. AMIA Annu Symp Proc. 2018;2018:1292-1299.
- Livingstone-Banks J, Norris E, Hartmann-Boyce J, West R, Jarvis M, Hajek P. Relapse prevention interventions for smoking cessation. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019; 2(2):CD003999. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003999.pub5
- Clayton AH, Kingsberg SA, Goldstein I. Evaluation and management of hypoactive sexual desire disorder. Sex Med. 2018;6(2):59-74. doi:10.1016/j.esxm.2018.01.004
- Verbeeck W, Bekkering GE, Van den Noortgate W, Kramers C. Bupropion for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017;10(10):CD009504. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD009504.pub2
- Ng QX. A systematic review of the use of bupropion for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents. J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol. 2017;27(2):112-116. doi:10.1089/cap.2016.0124
- Fava M, Rush AJ, Thase ME, et al. 15 years of clinical experience with bupropion HCl: from bupropion to bupropion SR to bupropion XL. Prim Care Companion J Clin Psychiatry. 2005;7(3):106-113. doi:10.4088/pcc.v07n0305
- Chu A, Wadhwa R. Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated May 1, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK554406/
- Singh HK, Saadabadi A. Sertraline. In: StatPearls. Stat- Pearls Publishing. Updated February 13, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK547689/
- MacQueen G, Born L, Steiner M. The selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor sertraline: its profile and use in psychiatric disorders. CNS Drug Rev. 2001;7(1):1-24. doi:10.1111/j.1527-3458.2001.tb00188.x
- Cipriani A, Furukawa TA, Salanti G, et al. Comparative efficacy and acceptability of 12 new-generation antidepressants: a multiple-treatments meta-analysis. Lancet. 2009;373(9665):746-758. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60046-5
- Nelson JC. The STAR*D study: a four-course meal that leaves us wanting more. Am J Psychiatry. 2006;163(11):1864-1866. doi:10.1176/ajp.2006.163.11.1864
- Sharbaf Shoar N, Fariba KA, Padhy RK. Citalopram. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated November 7, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482222/
- Landy K, Rosani A, Estevez R. Escitalopram. In: Stat- Pearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated November 10, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557734/
- Cavanah LR, Ray P, Goldhirsh JL, Huey LY, Piper BJ. Rise of escitalopram and the fall of citalopram. medRxiv. Preprint published online May 8, 2023. doi:10.1101/2023.05.07.23289632
- Sohel AJ, Shutter MC, Patel P, Molla M. Fluoxetine. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated July 4, 2022. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459223/
- Wong DT, Perry KW, Bymaster FP. Case history: the discovery of fluoxetine hydrochloride (Prozac). Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2005;4(9):764-774. doi:10.1038/nrd1821
- Shrestha P, Fariba KA, Abdijadid S. Paroxetine. In: Stat- Pearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated July 17, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK526022/
- Naseeruddin R, Rosani A, Marwaha R. Desvenlafaxine. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated July 10, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK534829
- Lieberman DZ, Massey SH. Desvenlafaxine in major depressive disorder: an evidence-based review of its place in therapy. Core Evid. 2010;4:67-82. doi:10.2147/ce.s5998
- Withdrawal assessment report for Ellefore (desvenlafaxine). European Medicine Agency. 2009. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/withdrawal-report/withdrawal-assessment-report-ellefore_en.pdf
- Dhaliwal JS, Spurling BC, Molla M. Duloxetine. In: Stat- Pearls. Statpearls Publishing. Updated May 29, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK549806/
- Hershman DL, Lacchetti C, Dworkin RH, et al. Prevention and management of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in survivors of adult cancers: American Society of Clinical Oncology clinical practice guideline. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32(18):1941-1967. doi:10.1200/JCO.2013.54.0914
- Sommer C, Häuser W, Alten R, et al. Medikamentöse Therapie des Fibromyalgiesyndroms. Systematische Übersicht und Metaanalyse [Drug therapy of fibromyalgia syndrome. Systematic review, meta-analysis and guideline]. Schmerz. 2012;26(3):297-310. doi:10.1007/s00482-012-1172-2
- Bril V, England J, Franklin GM, et al. Evidence-based guideline: treatment of painful diabetic neuropathy: report of the American Academy of Neurology, the American Association of Neuromuscular and Electrodiagnostic Medicine, and the American Academy of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. Neurology. 2011;76(20):1758-1765. doi:10.1212/WNL.0b013e3182166ebe
- Attal N, Cruccu G, Baron R, et al. EFNS guidelines on the pharmacological treatment of neuropathic pain: 2010 revision. Eur J Neurol. 2010;17(9):1113-e88. doi:10.1111/j.1468-1331.2010.02999.x
- Singh D, Saadabadi A. Venlafaxine. In: StatPearls. StatePearls Publishing. Updated February 26, 2024. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK535363/
- Sertraline and venlafaxine: new indication. Prevention of recurrent depression: no advance. Prescrire Int. 2005;14(75):19-20.
- Bruno A, Morabito P, S p i n a E , M u s c a t ello MRl. The role of levomilnacipran in the management of major depressive disorder: a comprehensive review. Curr Neuro pharmacol. 2016;14(2):191-199. doi:10.2174/1570159x14666151117122458
- Shin JJ, Saadabadi A. Trazodone. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated February 29, 2024. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470560/
- Khouzam HR. A review of trazodone use in psychiatric and medical conditions. Postgrad Med. 2017;129(1):140-148. doi:10.1080/00325481.2017.1249265
- Smales ET, Edwards BA, Deyoung PN, et al. Trazodone effects on obstructive sleep apnea and non-REM arousal threshold. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2015;12(5):758-764. doi:10.1513/AnnalsATS.201408-399OC
- Eckert DJ, Malhotra A, Wellman A, White DP. Trazodone increases the respiratory arousal threshold in patients with obstructive sleep apnea and a low arousal threshold. Sleep. 2014;37(4):811-819. doi:10.5665/sleep.3596
- Schatzberg AF, Nemeroff CB, eds. The American Psychiat ric Association Publishing Textbook of Psychopharmacology. 4th ed. American Psychiatric Publishing; 2009.
- Ruxton K, Woodman RJ, Mangoni AA. Drugs with anticholinergic effects and cognitive impairment, falls and allcause mortality in older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2015;80(2):209-220. doi:10.1111/bcp.12617
- Nefazodone. In: LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Updated March 6, 2020. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK548179/
- Drugs of Current Interest: Nefazodone. WHO Pharmaceuticals Newsletter:(1). 2003(1):7. https://web.archive.org/web/20150403165029/http:/apps.who.int/medicinedocs/en/d/Js4944e/3.html
- Choi S. Nefazodone (serzone) withdrawn because of hepatotoxicity. CMAJ. 2003;169(11):1187.
- Teva Nefazodone Statement. News release. Teva USA. December 20, 2021. Accessed April 4, 2025. https:// www.tevausa.com/news-and-media/press-releases/teva-nefazodone-statement/
- Levitan MN, Papelbaum M, Nardi AE. Profile of agomelatine and its potential in the treatment of generalized anxiety disorder. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2015;11:1149- 1155. doi:10.2147/NDT.S67470
- Fu DJ, Ionescu DF, Li X, et al. Esketamine nasal spray for rapid reduction of major depressive disorder symptoms in patients who have active suicidal ideation with intent: double-blind, randomized study (ASPIRE I). J Clin Psychiatry. 2020;81(3):19m13191. doi:10.4088/JCP.19m13191
- Iosifescu DV, Jones A, O’Gorman C, et al. Efficacy and safety of AXS-05 (dextromethorphan-bupropion) in patients with major depressive disorder: a phase 3 randomized clinical trial (GEMINI). J Clin Psychiatry. 2022;83(4): 21m14345. doi:10.4088/JCP.21m14345
- Luong TT, Powers CN, Reinhardt BJ, et al. Retrospective evaluation of drug-drug interactions with erlotinib and gefitinib use in the Military Health System. Fed Pract. 2023;40(Suppl 3):S24-S34. doi:10.12788/fp.0401
- Luong TT, Shou KJ, Reinhard BJ, Kigelman OF, Greenfield KM. Paclitaxel drug-drug interactions in the Military Health System. Fed Pract. 2024;41(Suppl 3):S70-S82. doi:10.12788/fp.0499
- Luong TT, Powers CN, Reinhardt BJ, Weina PJ. Preclinical drug-drug interactions (DDIs) of gefitinib with/without losartan and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs): citalopram, fluoxetine, fluvoxamine, paroxetine, sertraline, and venlafaxine. Curr Res Pharmacol Drug Discov. 2022;3:100112. doi:10.1016/j.crphar.2022.100112
- Luong TT, McAnulty MJ, Evers DL, Reinhardt BJ, Weina PJ. Pre-clinical drug-drug interaction (DDI) of gefitinib or erlotinib with cytochrome P450 (CYP) inhibiting drugs, fluoxetine and/or losartan. Curr Res Toxicol. 2021;2:217- 224. doi:10.1016/j.crtox.2021.05.006,
- Adamo M, Dickie L, Ruhl J. SEER program coding and staging manual 2016. National Cancer Institute; 2016. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://seer.cancer.gov/archive/manuals/2016/SPCSM_2016_maindoc.pdf
- World Health Organization. International classification of diseases for oncology (ICD-O). 3rd ed, 1st revision. World Health Organization; 2013. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/96612
- Simon S. FDA approves Jelmyto (mitomycin gel) for urothelial cancer. American Cancer Society. April 20, 2020. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/latest-news/fda-approves-jelmyto-mitomycin-gel-for-urothelial-cancer.html
- Pantziarka P, Sukhatme V, Bouche G, Meheus L, Sukhatme VP. Repurposing drugs in oncology (ReDO)- diclofenac as an anti-cancer agent. Ecancermedicalscience. 2016;10:610. doi:10.3332/ecancer.2016.610
- Choi S, Kim S, Park J, Lee SE, Kim C, Kang D. Diclofenac: a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug inducing cancer cell death by inhibiting microtubule polymerization and autophagy flux. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022;11(5):1009. doi:10.3390/antiox11051009
- Tontonoz M. The ABCs of BCG: oldest approved immunotherapy gets new explanation. Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center. July 17, 2020. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.mskcc.org/news/oldest-approved-immunotherapy-gets-new-explanation
- Jordan VC. Tamoxifen as the first targeted long-term adjuvant therapy for breast cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2014;21(3):R235-R246. doi:10.1530/ERC-14-0092
- Cole MP, Jones CT, Todd ID. A new anti-oestrogenic agent in late breast cancer. An early clinical appraisal of ICI46474. Br J Cancer. 1971;25(2):270-275. doi:10.1038/bjc.1971.33
- Jordan VC. Tamoxifen: a most unlikely pioneering medicine. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2003;2(3):205-213. doi:10.1038/nrd1031
- Maximov PY, McDaniel RE, Jordan VC. Tamoxifen: Pioneering Medicine in Breast Cancer. Springer Basel; 2013. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://link.springer.com/book/10.1007/978-3-0348-0664-0
- Taxol (paclitaxel). Prescribing information. Bristol-Myers Squibb Company; 2011. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2011/020262s049lbl.pdf
- Abraxane (paclitaxel). Prescribing information. Celgene Corporation; 2020. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/021660s047lbl.pdf
- Tarceva (erlotinib). Prescribing information. OSI Pharmaceuticals, LLC; 2016. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2016/021743s025lbl.pdf
- Docetaxel. Prescribing information. Sichuan Hyiyu Pharmaceutical Co.; 2022. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/215813s000lbl.pdf
- Alimta (pemetrexed). Prescribing information. Teva Pharmaceuticals; 2022. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/208419s004lbl.pdf
- Tagrisso (osimertinib). Prescribing information. Astra- Zeneca Pharmaceuticals; 2020. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/208065s021lbl.pdf
- Iressa (gefitinib). Prescribing information. AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals; 2018. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2018/206995s003lbl.pdf
- Kadcyla (ado-trastuzumab emtansine). Prescribing information. Genentech, Inc.; 2013. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2013/125427lbl.pdf
- Alecensa (alectinib). Prescribing information. Genetech, Inc.; 2017. Accessed April 4, 2025. https:// www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2017/208434s003lbl.pdf
- Xalkori (crizotinib). Prescribing information. Pfizer Laboratories; 2022. Accessed April 4, 2025. https:// www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/202570s033lbl.pdf
- Lorbrena (lorlatinib). Prescribing information. Pfizer Laboratories; 2018. Accessed April 14, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2018/210868s000lbl.pdf
- Alunbrig (brigatinib). Prescribing information. Takeda Pharmaceutical Company; 2020. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/208772s008lbl.pdf
- Rozlytrek (entrectinib). Prescribing information. Genentech, Inc.; 2019. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2019/212725s000lbl.pdf
- Herceptin (trastuzumab). Prescribing information. Genentech, Inc.; 2010. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2010/103792s5250lbl.pdf
- Cybalta (duloxetine). Prescribing information. Eli Lilly and Company; 2017. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2017/021427s049lbl.pdf
- Effexor XR (venlafaxine). Prescribing information. Pfizer Wyeth Pharmaceuticals Inc; 2022. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/020699s112lbl.pdf
- Desyrel (trazodone hydrochloride). Prescribing information. Pragma Pharmaceuticals; 2017. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2017/018207s032lbl.pdf
- Sertraline hydrochloride. Prescribing information. Almatica Pharma LLC; 2021. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2021/215133s000lbl.pdf
- Remeron (mirtazapine). Prescribing information. Merck & Co. Inc; 2020. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/020415s029,%20021208s019lbl.pdf
- Celexa (citalopram). Prescribing information. Allergan USA Inc; 2022. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/020822s041lbl.pdf
- information. GlaxoSmithKline; 2019. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/020358s066lbl.pdf
- Amitriptyline hydrochloride tablet. Prescribing information. Quality Care Products LLC; 2022. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/spl/data/0f12f50f-7087-46e7-a2e6-356b4c566c9f/0f12f50f-7087-46e7-a2e6-356b4c566c9f.xml
- Lexapro (escitalopram). Prescribing information. AbbVie Inc; 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2023/021323s055,021365s039lbl.pdf
- Fluoxetine. Prescribing information. Edgemont Pharmaceutical, LLC; 2017. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2017/202133s004s005lbl.pdf
- Paxil (paroxetine). Prescribing Information. Apotex Inc; 2021. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2021/020031s077lbl.pdf
- Pamelor (nortriptyline HCl). Prescribing information. Mallinckrodt, Inc; 2012. Accessed April 4, 2025. https:// www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2012/018012s029,018013s061lbl.pdf
- Silenor (doxepin). Prescribing information. Currax Pharmaceuticals; 2020. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/022036s006lbl.pdf
- Tofranil-PM (imipramine pamote). Prescribing information. Mallinckrodt, Inc; 2014. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2014/017090s078lbl.pdf
- Norpramin (desipramine hydrochloride). Prescribing information. Sanofi-aventis U.S. LLC; 2014. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2014/014399s069lbl.pdf
- Khedezla (desvenlafaxine). Prescribing information. Osmotical Pharmaceutical US LLC; 2019. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2019/204683s006lbl.pdf
- Nefazodone hydrochloride. Prescribing information. Bryant Ranch Prepack; 2022. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/spl/data/0bd4c34a-4f43-4c84-8b98-1d074cba97d5/0bd4c34a-4f43-4c84-8b98-1d074cba97d5.xml
- Grassi L, Nanni MG, Rodin G, Li M, Caruso R. The use of antidepressants in oncology: a review and practical tips for oncologists. Ann Oncol. 2018;29(1):101-111. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdx526
- Lee E, Park Y, Li D, Rodriguez-Fuguet A, Wang X, Zhang WC. Antidepressant use and lung cancer risk and survival: a meta-analysis of observational studies. Cancer Res Commun. 2023;3(6):1013-1025. doi:10.1158/2767-9764.CRC-23-0003
- Olfson M, Marcus SC. National patterns in antidepressant medication treatment. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2009;66(8):848 -856. doi:10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2009.81
- Grattan A, Sullivan MD, Saunders KW, Campbell CI, Von Korff MR. Depression and prescription opioid misuse among chronic opioid therapy recipients with no history of substance abuse. Ann Fam Med. 2012;10(4):304-311. doi:10.1370/afm.1371
- Cowan DT, Wilson-Barnett J, Griffiths P, Allan LG. A survey of chronic noncancer pain patients prescribed opioid analgesics. Pain Med. 2003;4(4):340-351. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4637.2003.03038.x
- Breckenridge J, Clark JD. Patient characteristics associated with opioid versus nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug management of chronic low back pain. J Pain. 2003;4(6):344-350. doi:10.1016/s1526-5900(03)00638-2
- Edlund MJ, Martin BC, Devries A, Fan MY, Braden JB, Sullivan MD. Trends in use of opioids for chronic noncancer pain among individuals with mental health and substance use disorders: the TROUP study. Clin J Pain. 2010;26(1):1-8. doi:10.1097/AJP.0b013e3181b99f35
- Sullivan MD, Edlund MJ, Fan MY, DeVries A, Braden JB, Martin BC. Risks for possible and probable opioid misuse among recipients of chronic opioid therapy in commercial and medicaid insurance plans: the TROUP study. Pain. 2010;150(2):332-339. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2010.05.020
- Dunn KM, Saunders KW, Rutter CM, et al. Opioid prescriptions for chronic pain and overdose: a cohort study. Ann Intern Med. 2010;152(2):85-92. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-152-2-201001190-00006
- Haddad P. Do antidepressants have any potential to cause addiction? J Psychopharmacol. 1999;13(3):300- 307. doi:10.1177/026988119901300321
- Lakeview Health Staff. America’s most abused antidepressants. Lakeview Health. January 24, 2004. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.lakeviewhealth.com/blog/us-most-abused-antidepressants/
- Greenhouse Treatment Center Editorial Staff. Addiction to antidepressants: is it possible? America Addiction Centers: Greenhouse Treatment Center. Updated April 23, 2024. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://greenhousetreatment.com/prescription-medication/antidepressants/
- National Cancer Institute. Depression (PDQ)-Health Professional Version. Updated July 25, 2024. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/coping/feelings/depression-hp-pdq
- Krebber AM, Buffart LM, Kleijn G, et al. Prevalence of depression in cancer patients: a meta-analysis of diagnostic interviews and self-report instruments. Psychooncology. 2014;23(2):121-130. doi:10.1002/pon.3409
- Xiang X, An R, Gehlert S. Trends in antidepressant use among U.S. cancer survivors, 1999-2012. Psychiatr Serv. 2015;66(6):564. doi:10.1176/appi.ps.201500007
- Hartung TJ, Brähler E, Faller H, et al. The risk of being depressed is significantly higher in cancer patients than in the general population: Prevalence and severity of depressive symptoms across major cancer types. Eur J Cancer. 2017;72:46-53. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2016.11.017
- Walker J, Holm Hansen C, Martin P, et al. Prevalence of depression in adults with cancer: a systematic review. Ann Oncol. 2013;24(4):895-900. doi:10.1093/annonc/mds575
- Pitman A, Suleman S, Hyde N, Hodgkiss A. Depression and anxiety in patients with cancer. BMJ. 2018;361:k1415. doi:10.1136/bmj.k1415
- Kisely S, Alotiby MKN, Protani MM, Soole R, Arnautovska U, Siskind D. Breast cancer treatment disparities in patients with severe mental illness: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychooncology. 2023;32(5):651-662. doi:10.1002/pon.6120
- Massie MJ. Prevalence of depression in patients with cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 2004;(32):57-71. doi:10.1093/jncimonographs/lgh014
- Rodin G, Katz M, Lloyd N, Green E, Mackay JA, Wong RK. Treatment of depression in cancer patients. Curr Oncol. 2007;14(5):180-188. doi:10.3747/co.2007.146
- Wilson KG, Chochinov HM, Skirko MG, et al. Depression and anxiety disorders in palliative cancer care. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2007;33(2):118-129. doi:10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2006.07.016
- Moradi Y, Dowran B, Sepandi M. The global prevalence of depression, suicide ideation, and attempts in the military forces: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cross sectional studies. BMC Psychiatry. 2021;21(1):510. doi:10.1186/s12888-021-03526-2
- Lu CY, Zhang F, Lakoma MD, et al. Changes in antidepressant use by young people and suicidal behavior after FDA warnings and media coverage: quasi-experimental study. BMJ. 2014;348:g3596. doi:10.1136/bmj.g3596
- Friedman RA. Antidepressants’ black-box warning--10 years later. N Engl J Med. 2014;371(18):1666-1668. doi:10.1056/NEJMp1408480
- Sheffler ZM, Patel P, Abdijadid S. Antidepressants. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated May 26, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK538182/
- Miller JJ. Antidepressants, Part 1: 100 Years and Counting. Accessed April 4, 2025. Psychiatric Times. https:// www.psychiatrictimes.com/view/antidepressants-part-1-100-years-and-counting
- Hillhouse TM, Porter JH. A brief history of the development of antidepressant drugs: from monoamines to glutamate. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol. 2015;23(1):1-21. doi:10.1037/a0038550
- Mitchell PB, Mitchell MS. The management of depression. Part 2. The place of the new antidepressants. Aust Fam Physician. 1994;23(9):1771-1781.
- Sabri MA, Saber-Ayad MM. MAO Inhibitors. In: Stat- Pearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated June 5, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557395/
- Sub Laban T, Saadabadi A. Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOI). In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated July 17, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK539848/
- Fiedorowicz JG, Swartz KL. The role of monoamine oxidase inhibitors in current psychiatric practice. J Psychiatr Pract. 2004;10(4):239-248. doi:10.1097/00131746-200407000-00005
- Flockhart DA. Dietary restrictions and drug interactions with monoamine oxidase inhibitors: an update. J Clin Psychiatry. 2012;73 Suppl 1:17-24. doi:10.4088/JCP.11096su1c.03
- Moraczewski J, Awosika AO, Aedma KK. Tricyclic Antidepressants. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated August 17, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557791/
- Almasi A, Patel P, Meza CE. Doxepin. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated February 14, 2024. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK542306/
- Thour A, Marwaha R. Amitriptyline. In: StatPearls. Stat- Pearls Publishing. Updated July 18, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537225/
- Radley DC, Finkelstein SN, Stafford RS. Off-label prescribing among office-based physicians. Arch Intern Med. 2006;166(9):1021-1026. doi:10.1001/archinte.166.9.1021
- Tesfaye S, Sloan G, Petrie J, et al. Comparison of amitriptyline supplemented with pregabalin, pregabalin supplemented with amitriptyline, and duloxetine supplemented with pregabalin for the treatment of diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain (OPTION-DM): a multicentre, double-blind, randomised crossover trial. Lancet. 2022;400(10353):680- 690. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(22)01472-6
- Farag HM, Yunusa I, Goswami H, Sultan I, Doucette JA, Eguale T. Comparison of amitriptyline and US Food and Drug Administration-approved treatments for fibromyalgia: a systematic review and network metaanalysis. JAMA Netw Open. 2022;5(5):e2212939. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.12939
- Merwar G, Gibbons JR, Hosseini SA, Saadabadi A. Nortriptyline. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated June 5, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482214/
- Fayez R, Gupta V. Imipramine. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated May 22, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557656/
- Jilani TN, Gibbons JR, Faizy RM, Saadabadi A. Mirtazapine. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated August 28, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK519059/
- Nutt DJ. Tolerability and safety aspects of mirtazapine. Hum Psychopharmacol. 2002;17 Suppl 1:S37-S41. doi:10.1002/hup.388
- Gandotra K, Chen P, Jaskiw GE, Konicki PE, Strohl KP. Effective treatment of insomnia with mirtazapine attenuates concomitant suicidal ideation. J Clin Sleep Med. 2018;14(5):901-902. doi:10.5664/jcsm.7142
- Anttila SA, Leinonen EV. A review of the pharmacological and clinical profile of mirtazapine. CNS Drug Rev. 2001;7(3):249-264. doi:10.1111/j.1527-3458.2001.tb00198.x
- Wang SM, Han C, Bahk WM, et al. Addressing the side effects of contemporary antidepressant drugs: a comprehensive review. Chonnam Med J. 2018;54(2):101-112. doi:10.4068/cmj.2018.54.2.101
- Huecker MR, Smiley A, Saadabadi A. Bupropion. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated April 9, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470212/
- Hsieh MT, Tseng PT, Wu YC, et al. Effects of different pharmacologic smoking cessation treatments on body weight changes and success rates in patients with nicotine dependence: a network meta-analysis. Obes Rev. 2019;20(6):895- 905. doi:10.1111/obr.12835
- Hankosky ER, Bush HM, Dwoskin LP, et al. Retrospective analysis of health claims to evaluate pharmacotherapies with potential for repurposing: association of bupropion and stimulant use disorder remission. AMIA Annu Symp Proc. 2018;2018:1292-1299.
- Livingstone-Banks J, Norris E, Hartmann-Boyce J, West R, Jarvis M, Hajek P. Relapse prevention interventions for smoking cessation. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019; 2(2):CD003999. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003999.pub5
- Clayton AH, Kingsberg SA, Goldstein I. Evaluation and management of hypoactive sexual desire disorder. Sex Med. 2018;6(2):59-74. doi:10.1016/j.esxm.2018.01.004
- Verbeeck W, Bekkering GE, Van den Noortgate W, Kramers C. Bupropion for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017;10(10):CD009504. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD009504.pub2
- Ng QX. A systematic review of the use of bupropion for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents. J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol. 2017;27(2):112-116. doi:10.1089/cap.2016.0124
- Fava M, Rush AJ, Thase ME, et al. 15 years of clinical experience with bupropion HCl: from bupropion to bupropion SR to bupropion XL. Prim Care Companion J Clin Psychiatry. 2005;7(3):106-113. doi:10.4088/pcc.v07n0305
- Chu A, Wadhwa R. Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated May 1, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK554406/
- Singh HK, Saadabadi A. Sertraline. In: StatPearls. Stat- Pearls Publishing. Updated February 13, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK547689/
- MacQueen G, Born L, Steiner M. The selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor sertraline: its profile and use in psychiatric disorders. CNS Drug Rev. 2001;7(1):1-24. doi:10.1111/j.1527-3458.2001.tb00188.x
- Cipriani A, Furukawa TA, Salanti G, et al. Comparative efficacy and acceptability of 12 new-generation antidepressants: a multiple-treatments meta-analysis. Lancet. 2009;373(9665):746-758. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60046-5
- Nelson JC. The STAR*D study: a four-course meal that leaves us wanting more. Am J Psychiatry. 2006;163(11):1864-1866. doi:10.1176/ajp.2006.163.11.1864
- Sharbaf Shoar N, Fariba KA, Padhy RK. Citalopram. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated November 7, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482222/
- Landy K, Rosani A, Estevez R. Escitalopram. In: Stat- Pearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated November 10, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557734/
- Cavanah LR, Ray P, Goldhirsh JL, Huey LY, Piper BJ. Rise of escitalopram and the fall of citalopram. medRxiv. Preprint published online May 8, 2023. doi:10.1101/2023.05.07.23289632
- Sohel AJ, Shutter MC, Patel P, Molla M. Fluoxetine. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated July 4, 2022. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459223/
- Wong DT, Perry KW, Bymaster FP. Case history: the discovery of fluoxetine hydrochloride (Prozac). Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2005;4(9):764-774. doi:10.1038/nrd1821
- Shrestha P, Fariba KA, Abdijadid S. Paroxetine. In: Stat- Pearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated July 17, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK526022/
- Naseeruddin R, Rosani A, Marwaha R. Desvenlafaxine. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated July 10, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK534829
- Lieberman DZ, Massey SH. Desvenlafaxine in major depressive disorder: an evidence-based review of its place in therapy. Core Evid. 2010;4:67-82. doi:10.2147/ce.s5998
- Withdrawal assessment report for Ellefore (desvenlafaxine). European Medicine Agency. 2009. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/withdrawal-report/withdrawal-assessment-report-ellefore_en.pdf
- Dhaliwal JS, Spurling BC, Molla M. Duloxetine. In: Stat- Pearls. Statpearls Publishing. Updated May 29, 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK549806/
- Hershman DL, Lacchetti C, Dworkin RH, et al. Prevention and management of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in survivors of adult cancers: American Society of Clinical Oncology clinical practice guideline. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32(18):1941-1967. doi:10.1200/JCO.2013.54.0914
- Sommer C, Häuser W, Alten R, et al. Medikamentöse Therapie des Fibromyalgiesyndroms. Systematische Übersicht und Metaanalyse [Drug therapy of fibromyalgia syndrome. Systematic review, meta-analysis and guideline]. Schmerz. 2012;26(3):297-310. doi:10.1007/s00482-012-1172-2
- Bril V, England J, Franklin GM, et al. Evidence-based guideline: treatment of painful diabetic neuropathy: report of the American Academy of Neurology, the American Association of Neuromuscular and Electrodiagnostic Medicine, and the American Academy of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. Neurology. 2011;76(20):1758-1765. doi:10.1212/WNL.0b013e3182166ebe
- Attal N, Cruccu G, Baron R, et al. EFNS guidelines on the pharmacological treatment of neuropathic pain: 2010 revision. Eur J Neurol. 2010;17(9):1113-e88. doi:10.1111/j.1468-1331.2010.02999.x
- Singh D, Saadabadi A. Venlafaxine. In: StatPearls. StatePearls Publishing. Updated February 26, 2024. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK535363/
- Sertraline and venlafaxine: new indication. Prevention of recurrent depression: no advance. Prescrire Int. 2005;14(75):19-20.
- Bruno A, Morabito P, S p i n a E , M u s c a t ello MRl. The role of levomilnacipran in the management of major depressive disorder: a comprehensive review. Curr Neuro pharmacol. 2016;14(2):191-199. doi:10.2174/1570159x14666151117122458
- Shin JJ, Saadabadi A. Trazodone. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated February 29, 2024. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470560/
- Khouzam HR. A review of trazodone use in psychiatric and medical conditions. Postgrad Med. 2017;129(1):140-148. doi:10.1080/00325481.2017.1249265
- Smales ET, Edwards BA, Deyoung PN, et al. Trazodone effects on obstructive sleep apnea and non-REM arousal threshold. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2015;12(5):758-764. doi:10.1513/AnnalsATS.201408-399OC
- Eckert DJ, Malhotra A, Wellman A, White DP. Trazodone increases the respiratory arousal threshold in patients with obstructive sleep apnea and a low arousal threshold. Sleep. 2014;37(4):811-819. doi:10.5665/sleep.3596
- Schatzberg AF, Nemeroff CB, eds. The American Psychiat ric Association Publishing Textbook of Psychopharmacology. 4th ed. American Psychiatric Publishing; 2009.
- Ruxton K, Woodman RJ, Mangoni AA. Drugs with anticholinergic effects and cognitive impairment, falls and allcause mortality in older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2015;80(2):209-220. doi:10.1111/bcp.12617
- Nefazodone. In: LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Updated March 6, 2020. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK548179/
- Drugs of Current Interest: Nefazodone. WHO Pharmaceuticals Newsletter:(1). 2003(1):7. https://web.archive.org/web/20150403165029/http:/apps.who.int/medicinedocs/en/d/Js4944e/3.html
- Choi S. Nefazodone (serzone) withdrawn because of hepatotoxicity. CMAJ. 2003;169(11):1187.
- Teva Nefazodone Statement. News release. Teva USA. December 20, 2021. Accessed April 4, 2025. https:// www.tevausa.com/news-and-media/press-releases/teva-nefazodone-statement/
- Levitan MN, Papelbaum M, Nardi AE. Profile of agomelatine and its potential in the treatment of generalized anxiety disorder. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2015;11:1149- 1155. doi:10.2147/NDT.S67470
- Fu DJ, Ionescu DF, Li X, et al. Esketamine nasal spray for rapid reduction of major depressive disorder symptoms in patients who have active suicidal ideation with intent: double-blind, randomized study (ASPIRE I). J Clin Psychiatry. 2020;81(3):19m13191. doi:10.4088/JCP.19m13191
- Iosifescu DV, Jones A, O’Gorman C, et al. Efficacy and safety of AXS-05 (dextromethorphan-bupropion) in patients with major depressive disorder: a phase 3 randomized clinical trial (GEMINI). J Clin Psychiatry. 2022;83(4): 21m14345. doi:10.4088/JCP.21m14345
- Luong TT, Powers CN, Reinhardt BJ, et al. Retrospective evaluation of drug-drug interactions with erlotinib and gefitinib use in the Military Health System. Fed Pract. 2023;40(Suppl 3):S24-S34. doi:10.12788/fp.0401
- Luong TT, Shou KJ, Reinhard BJ, Kigelman OF, Greenfield KM. Paclitaxel drug-drug interactions in the Military Health System. Fed Pract. 2024;41(Suppl 3):S70-S82. doi:10.12788/fp.0499
- Luong TT, Powers CN, Reinhardt BJ, Weina PJ. Preclinical drug-drug interactions (DDIs) of gefitinib with/without losartan and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs): citalopram, fluoxetine, fluvoxamine, paroxetine, sertraline, and venlafaxine. Curr Res Pharmacol Drug Discov. 2022;3:100112. doi:10.1016/j.crphar.2022.100112
- Luong TT, McAnulty MJ, Evers DL, Reinhardt BJ, Weina PJ. Pre-clinical drug-drug interaction (DDI) of gefitinib or erlotinib with cytochrome P450 (CYP) inhibiting drugs, fluoxetine and/or losartan. Curr Res Toxicol. 2021;2:217- 224. doi:10.1016/j.crtox.2021.05.006,
- Adamo M, Dickie L, Ruhl J. SEER program coding and staging manual 2016. National Cancer Institute; 2016. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://seer.cancer.gov/archive/manuals/2016/SPCSM_2016_maindoc.pdf
- World Health Organization. International classification of diseases for oncology (ICD-O). 3rd ed, 1st revision. World Health Organization; 2013. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/96612
- Simon S. FDA approves Jelmyto (mitomycin gel) for urothelial cancer. American Cancer Society. April 20, 2020. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/latest-news/fda-approves-jelmyto-mitomycin-gel-for-urothelial-cancer.html
- Pantziarka P, Sukhatme V, Bouche G, Meheus L, Sukhatme VP. Repurposing drugs in oncology (ReDO)- diclofenac as an anti-cancer agent. Ecancermedicalscience. 2016;10:610. doi:10.3332/ecancer.2016.610
- Choi S, Kim S, Park J, Lee SE, Kim C, Kang D. Diclofenac: a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug inducing cancer cell death by inhibiting microtubule polymerization and autophagy flux. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022;11(5):1009. doi:10.3390/antiox11051009
- Tontonoz M. The ABCs of BCG: oldest approved immunotherapy gets new explanation. Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center. July 17, 2020. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.mskcc.org/news/oldest-approved-immunotherapy-gets-new-explanation
- Jordan VC. Tamoxifen as the first targeted long-term adjuvant therapy for breast cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2014;21(3):R235-R246. doi:10.1530/ERC-14-0092
- Cole MP, Jones CT, Todd ID. A new anti-oestrogenic agent in late breast cancer. An early clinical appraisal of ICI46474. Br J Cancer. 1971;25(2):270-275. doi:10.1038/bjc.1971.33
- Jordan VC. Tamoxifen: a most unlikely pioneering medicine. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2003;2(3):205-213. doi:10.1038/nrd1031
- Maximov PY, McDaniel RE, Jordan VC. Tamoxifen: Pioneering Medicine in Breast Cancer. Springer Basel; 2013. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://link.springer.com/book/10.1007/978-3-0348-0664-0
- Taxol (paclitaxel). Prescribing information. Bristol-Myers Squibb Company; 2011. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2011/020262s049lbl.pdf
- Abraxane (paclitaxel). Prescribing information. Celgene Corporation; 2020. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/021660s047lbl.pdf
- Tarceva (erlotinib). Prescribing information. OSI Pharmaceuticals, LLC; 2016. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2016/021743s025lbl.pdf
- Docetaxel. Prescribing information. Sichuan Hyiyu Pharmaceutical Co.; 2022. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/215813s000lbl.pdf
- Alimta (pemetrexed). Prescribing information. Teva Pharmaceuticals; 2022. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/208419s004lbl.pdf
- Tagrisso (osimertinib). Prescribing information. Astra- Zeneca Pharmaceuticals; 2020. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/208065s021lbl.pdf
- Iressa (gefitinib). Prescribing information. AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals; 2018. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2018/206995s003lbl.pdf
- Kadcyla (ado-trastuzumab emtansine). Prescribing information. Genentech, Inc.; 2013. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2013/125427lbl.pdf
- Alecensa (alectinib). Prescribing information. Genetech, Inc.; 2017. Accessed April 4, 2025. https:// www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2017/208434s003lbl.pdf
- Xalkori (crizotinib). Prescribing information. Pfizer Laboratories; 2022. Accessed April 4, 2025. https:// www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/202570s033lbl.pdf
- Lorbrena (lorlatinib). Prescribing information. Pfizer Laboratories; 2018. Accessed April 14, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2018/210868s000lbl.pdf
- Alunbrig (brigatinib). Prescribing information. Takeda Pharmaceutical Company; 2020. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/208772s008lbl.pdf
- Rozlytrek (entrectinib). Prescribing information. Genentech, Inc.; 2019. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2019/212725s000lbl.pdf
- Herceptin (trastuzumab). Prescribing information. Genentech, Inc.; 2010. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2010/103792s5250lbl.pdf
- Cybalta (duloxetine). Prescribing information. Eli Lilly and Company; 2017. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2017/021427s049lbl.pdf
- Effexor XR (venlafaxine). Prescribing information. Pfizer Wyeth Pharmaceuticals Inc; 2022. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/020699s112lbl.pdf
- Desyrel (trazodone hydrochloride). Prescribing information. Pragma Pharmaceuticals; 2017. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2017/018207s032lbl.pdf
- Sertraline hydrochloride. Prescribing information. Almatica Pharma LLC; 2021. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2021/215133s000lbl.pdf
- Remeron (mirtazapine). Prescribing information. Merck & Co. Inc; 2020. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/020415s029,%20021208s019lbl.pdf
- Celexa (citalopram). Prescribing information. Allergan USA Inc; 2022. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/020822s041lbl.pdf
- information. GlaxoSmithKline; 2019. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/020358s066lbl.pdf
- Amitriptyline hydrochloride tablet. Prescribing information. Quality Care Products LLC; 2022. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/spl/data/0f12f50f-7087-46e7-a2e6-356b4c566c9f/0f12f50f-7087-46e7-a2e6-356b4c566c9f.xml
- Lexapro (escitalopram). Prescribing information. AbbVie Inc; 2023. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2023/021323s055,021365s039lbl.pdf
- Fluoxetine. Prescribing information. Edgemont Pharmaceutical, LLC; 2017. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2017/202133s004s005lbl.pdf
- Paxil (paroxetine). Prescribing Information. Apotex Inc; 2021. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2021/020031s077lbl.pdf
- Pamelor (nortriptyline HCl). Prescribing information. Mallinckrodt, Inc; 2012. Accessed April 4, 2025. https:// www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2012/018012s029,018013s061lbl.pdf
- Silenor (doxepin). Prescribing information. Currax Pharmaceuticals; 2020. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/022036s006lbl.pdf
- Tofranil-PM (imipramine pamote). Prescribing information. Mallinckrodt, Inc; 2014. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2014/017090s078lbl.pdf
- Norpramin (desipramine hydrochloride). Prescribing information. Sanofi-aventis U.S. LLC; 2014. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2014/014399s069lbl.pdf
- Khedezla (desvenlafaxine). Prescribing information. Osmotical Pharmaceutical US LLC; 2019. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2019/204683s006lbl.pdf
- Nefazodone hydrochloride. Prescribing information. Bryant Ranch Prepack; 2022. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/spl/data/0bd4c34a-4f43-4c84-8b98-1d074cba97d5/0bd4c34a-4f43-4c84-8b98-1d074cba97d5.xml
- Grassi L, Nanni MG, Rodin G, Li M, Caruso R. The use of antidepressants in oncology: a review and practical tips for oncologists. Ann Oncol. 2018;29(1):101-111. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdx526
- Lee E, Park Y, Li D, Rodriguez-Fuguet A, Wang X, Zhang WC. Antidepressant use and lung cancer risk and survival: a meta-analysis of observational studies. Cancer Res Commun. 2023;3(6):1013-1025. doi:10.1158/2767-9764.CRC-23-0003
- Olfson M, Marcus SC. National patterns in antidepressant medication treatment. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2009;66(8):848 -856. doi:10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2009.81
- Grattan A, Sullivan MD, Saunders KW, Campbell CI, Von Korff MR. Depression and prescription opioid misuse among chronic opioid therapy recipients with no history of substance abuse. Ann Fam Med. 2012;10(4):304-311. doi:10.1370/afm.1371
- Cowan DT, Wilson-Barnett J, Griffiths P, Allan LG. A survey of chronic noncancer pain patients prescribed opioid analgesics. Pain Med. 2003;4(4):340-351. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4637.2003.03038.x
- Breckenridge J, Clark JD. Patient characteristics associated with opioid versus nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug management of chronic low back pain. J Pain. 2003;4(6):344-350. doi:10.1016/s1526-5900(03)00638-2
- Edlund MJ, Martin BC, Devries A, Fan MY, Braden JB, Sullivan MD. Trends in use of opioids for chronic noncancer pain among individuals with mental health and substance use disorders: the TROUP study. Clin J Pain. 2010;26(1):1-8. doi:10.1097/AJP.0b013e3181b99f35
- Sullivan MD, Edlund MJ, Fan MY, DeVries A, Braden JB, Martin BC. Risks for possible and probable opioid misuse among recipients of chronic opioid therapy in commercial and medicaid insurance plans: the TROUP study. Pain. 2010;150(2):332-339. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2010.05.020
- Dunn KM, Saunders KW, Rutter CM, et al. Opioid prescriptions for chronic pain and overdose: a cohort study. Ann Intern Med. 2010;152(2):85-92. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-152-2-201001190-00006
- Haddad P. Do antidepressants have any potential to cause addiction? J Psychopharmacol. 1999;13(3):300- 307. doi:10.1177/026988119901300321
- Lakeview Health Staff. America’s most abused antidepressants. Lakeview Health. January 24, 2004. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.lakeviewhealth.com/blog/us-most-abused-antidepressants/
- Greenhouse Treatment Center Editorial Staff. Addiction to antidepressants: is it possible? America Addiction Centers: Greenhouse Treatment Center. Updated April 23, 2024. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://greenhousetreatment.com/prescription-medication/antidepressants/
Assessing the Impact of Antidepressants on Cancer Treatment: A Retrospective Analysis of 14 Antineoplastic Agents
Assessing the Impact of Antidepressants on Cancer Treatment: A Retrospective Analysis of 14 Antineoplastic Agents
Associations Between Prescreening Dietary Patterns and Longitudinal Colonoscopy Outcomes in Veterans
Associations Between Prescreening Dietary Patterns and Longitudinal Colonoscopy Outcomes in Veterans
Screening for colorectal cancer (CRC) with colonoscopy enables the identification and removal of CRC precursors (colonic adenomas) and has been associated with reduced risk of CRC incidence and mortality.1-3 Furthermore, there is consensus that diet and lifestyle may be associated with forestalling CRC pathogenesis at the intermediate adenoma stages.4-7 However, studies have shown that US veterans have poorer diet quality and a higher risk for neoplasia compared with nonveterans, reinforcing the need for tailored clinical approaches.8,9 Combining screening with conversations about modifiable environmental and lifestyle risk factors, such as poor diet, is a highly relevant and possibly easily leveraged prevention for those at high risk. However, there is limited evidence for any particular dietary patterns or dietary features that are most important over time.7
Several dietary components have been shown to be associated with CRC risk,10 either as potentially chemopreventive (fiber, fruits and vegetables,11 dairy,12 supplemental vitamin D,13 calcium,14 and multivitamins15) or carcinogenic (red meat16 and alcohol17). Previous studies of veterans have similarly shown that higher intake of fiber and vitamin D reduced risk, and red meat is associated with an increased risk for finding CRC precursors during colonoscopy.18 However, these dietary categories are often analyzed in isolation. Studying healthy dietary patterns in aggregate may be more clinically relevant and easier to implement for prevention of CRC and its precursors.19-21 Healthy dietary patterns, such as the US Dietary Guidelines for Americans represented by the Healthy Eating Index (HEI), the Mediterranean diet (MD), and the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet, have been associated with lower risk for chronic disease.22-24 Despite the extant literature, no known studies have compared these dietary patterns for associations with risk of CRC precursor or CRC development among US veterans undergoing long-term screening and follow-up after a baseline colonoscopy.
The objective of this study was to test for associations between baseline scores of healthy dietary patterns and the most severe colonoscopy findings (MSCFs) over ≥ 10 years following a baseline screening colonoscopy in veterans.
Methods
Participants in the Cooperative Studies Program (CSP) #380 cohort study included 3121 asymptomatic veterans aged 50 to 75 years at baseline who had consented to initial screening colonoscopy between 1994 and 1997, with subsequent follow-up and surveillance.25 Prior to their colonoscopy, all participants completed a baseline study survey that included questions about cancer risk factors including family history of CRC, diet, physical activity, and medication use.
Included in this cross-sectional analysis were data from a sample of veteran participants of the CSP #380 cohort with 1 baseline colonoscopy, follow-up surveillance through 2009, a cancer risk factor survey collected at baseline, and complete demographic and clinical indicator data. Excluded from the analysis were 67 participants with insufficient responses to the dietary food frequency questionnaire (FFQ) and 31 participants with missing body mass index (BMI), 3023 veterans.
Measures
MSCF. The outcome of interest in this study was the MSCF recorded across all participant colonoscopies during the study period. MSCF was categorized as either (1) no neoplasia; (2) < 2 nonadvanced adenomas, including small adenomas (diameter < 10 mm) with tubular histology; or (3) advanced neoplasia (AN), which is characterized by adenomas > 10 mm in diameter, with villous histology, with high-grade dysplasia, or CRC.
Dietary patterns. Dietary pattern scores representing dietary quality and calculated based on recommendations of the US Dietary Guidelines for Americans using the HEI, MD, and DASH diets were independent variables.26-28 These 3 dietary patterns were chosen for their hypothesized relationship with CRC risk, but each weighs food categories differently (Appendix 1).22-24,29 Dietary pattern scores were calculated using the CSP #380 self-reported responses to 129 baseline survey questions adapted from a well-established and previously validated semiquantitative FFQ.30 The form was administered by mail twice to a sample of 127 participants at baseline and at 1 year. During this interval, men completed 1-week diet records twice, spaced about 6 months apart. Mean values for intake of most nutrients assessed by the 2 methods were similar. Intraclass correlation coefficients for the baseline and 1-year FFQ-assessed nutrient intakes that ranged from 0.47 for vitamin E (without supplements) to 0.80 for vitamin C (with supplements). Correlation coefficients between the energy-adjusted nutrient intakes were measured by diet records and the 1-year FFQ, which asked about diet during the year encompassing the diet records. Higher raw and percent scores indicated better alignment with recommendations from each respective dietary pattern. Percent scores were calculated as a standardizing method and used in analyses for ease of comparing the dietary patterns. Scoring can be found in Appendix 2.
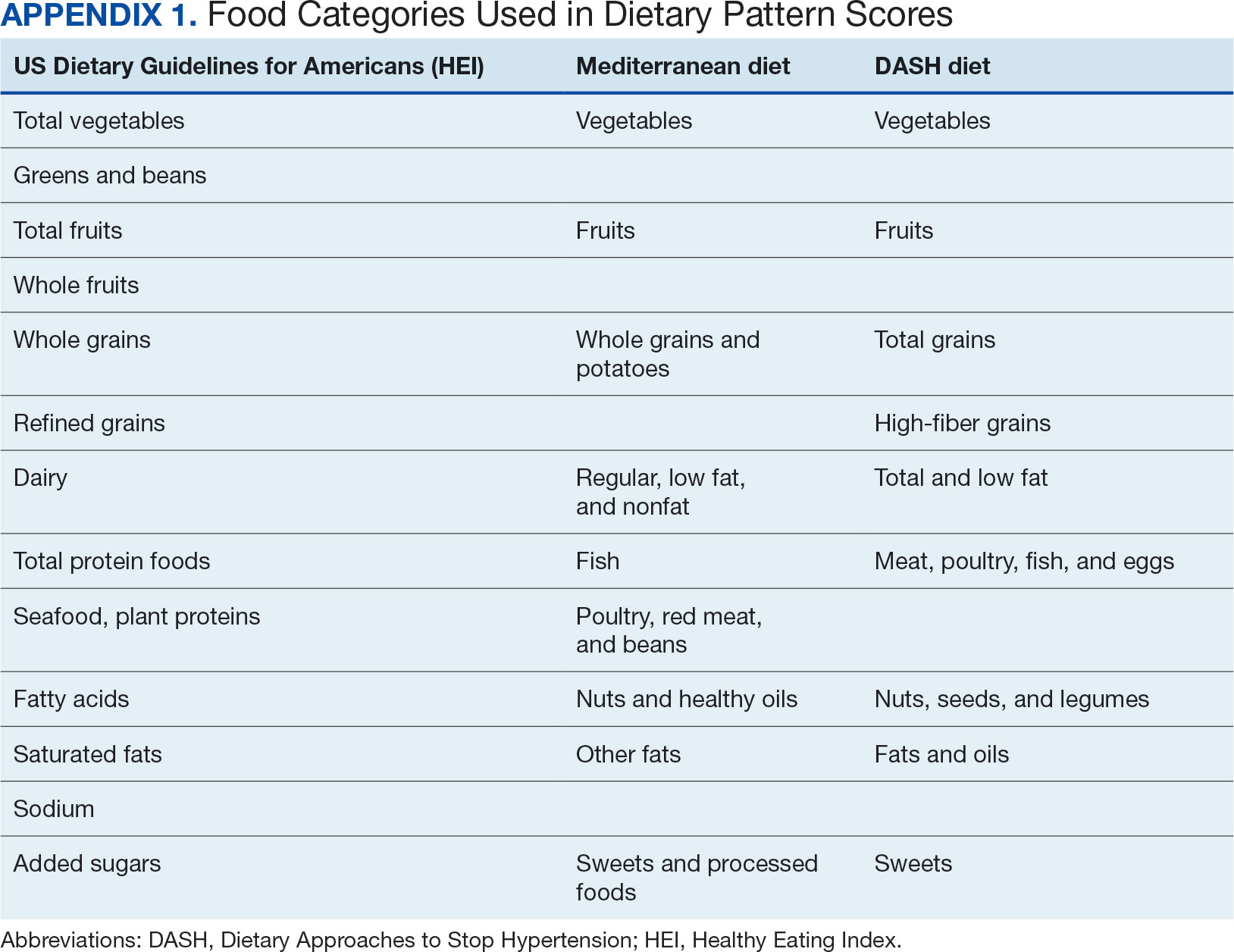
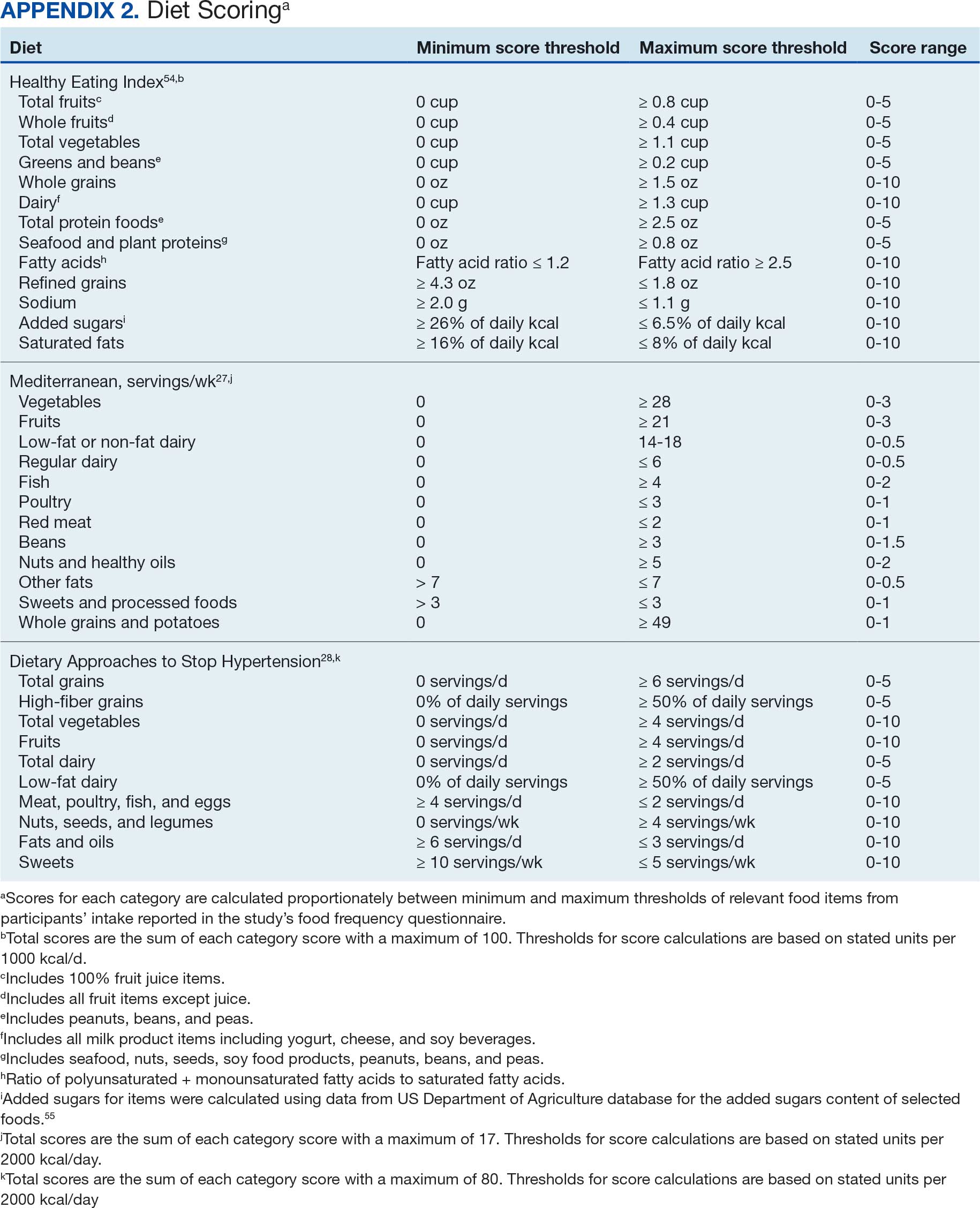
Demographic characteristics and clinical indicators. Demographic characteristics included age categories, sex, and race/ethnicity. Clinical indicators included BMI, the number of comorbid conditions used to calculate the Charlson Comorbidity Index, family history of CRC in first-degree relatives, number of follow-up colonoscopies across the study period, and food-based vitamin D intake.31 These variables were chosen for their applicability found in previous CSP #380 cohort studies.18,32,33 Self-reported race and ethnicity were collapsed due to small numbers in some groups. The authors acknowledge these are distinct concepts and the variable has limited utility other than for controlling for systemic racism in the model.
Statistical Analyses
Descriptive statistics were used to describe distributional assumptions for all variables, including demographics, clinical indicators, colonoscopy results, and dietary patterns. Pairwise correlations between the total dietary pattern scores and food category scores were calculated with Pearson correlation (r).
Multinomial logistic regression models were created using SAS procedure LOGISTIC with the outcome of the categorical MSCF (no neoplasia, nonadvanced adenoma, or AN).34 A model was created for each independent predictor variable of interest (ie, the HEI, MD, or DASH percentage-standardized dietary pattern score and each food category comprising each dietary pattern score). All models were adjusted for age, sex, race/ethnicity, BMI, number of comorbidities, family history of CRC, number of follow-up colonoscopies, and estimated daily food-derived vitamin D intake. The demographic and clinical indicators were included in the models as they are known to be associated with CRC risk.18 The number of colonoscopies was included to control for surveillance intensity presuming risk for AN is reduced as polyps are removed. Because colonoscopy findings from an initial screening have unique clinical implications compared with follow- up and surveillance, MSCF was observed in 2 ways in sensitivity analyses: (1) baseline and (2) aggregate follow-up and surveillance only, excluding baseline findings.
Adjusted odds ratios (aORs) and 95% CIs for each of the MSCF outcomes with a reference finding of no neoplasia for the models are presented. We chose not to adjust for multiple comparisons across the different dietary patterns given the correlation between dietary pattern total and category scores but did adjust for multiple comparisons for dietary categories within each dietary pattern. Tests for statistical significance used α= .05 for the dietary pattern total scores and P values for the dietary category scores for each dietary pattern controlled for false discovery rate using the MULTTEST SAS procedure.35 All data manipulations and analyses were performed using SAS version 9.4.
Results
The study included 3023 patients. All were aged 50 to 75 years, 2923 (96.7%) were male and 2532 (83.8%) were non-Hispanic White (Table 1). Most participants were overweight or obese (n = 2535 [83.8%]), 2024 (67.0%) had ≤ 2 comorbidities, and 2602 (86.1%) had no family history of CRC. The MSCF for 1628 patients (53.9%) was no neoplasia, 966 patients (32.0%) was nonadvanced adenoma, and 429 participants (14.2%) had AN.
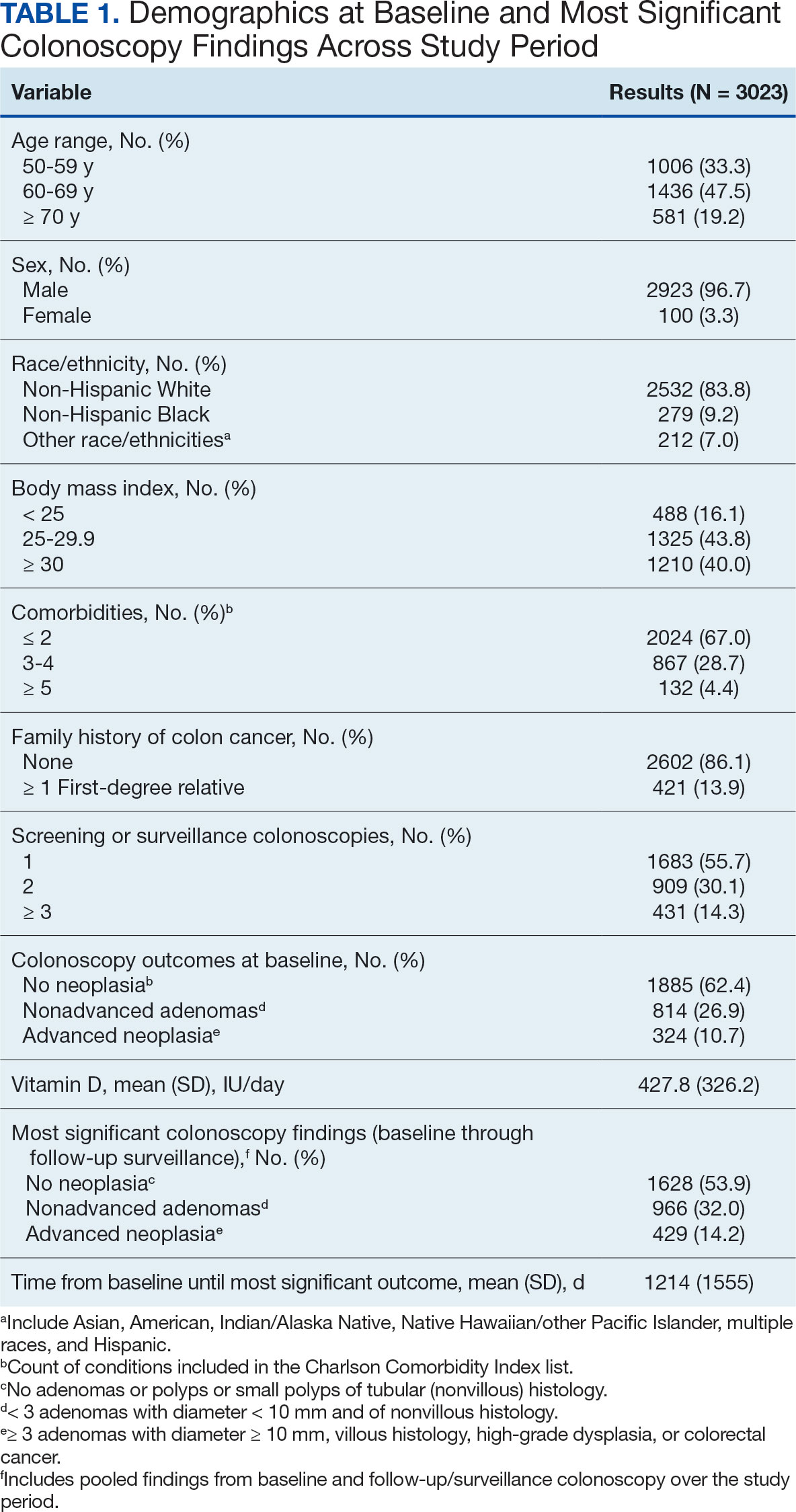
Mean percent scores were 58.5% for HEI, 38.2% for MD, and 63.1% for the DASH diet, with higher percentages indicating greater alignment with the recommendations for each diet (Table 2). All 3 dietary patterns scores standardized to percentages were strongly and significantly correlated in pairwise comparisons: HEI:MD, r = 0.62 (P < .001); HEI:DASH, r = 0.60 (P < .001); and MD:DASH, r = 0.72 (P < .001). Likewise, food category scores were significantly correlated across dietary patterns. For example, whole grain and fiber values from each dietary score were strongly correlated in pairwise comparisons: HEI Whole Grain:MD Grain, r = 0.64 (P < .001); HEI Whole Grain:DASH Fiber, r = 0.71 (P < .001); and MD Grain:DASH Fiber, r = 0.70 (P < .001).
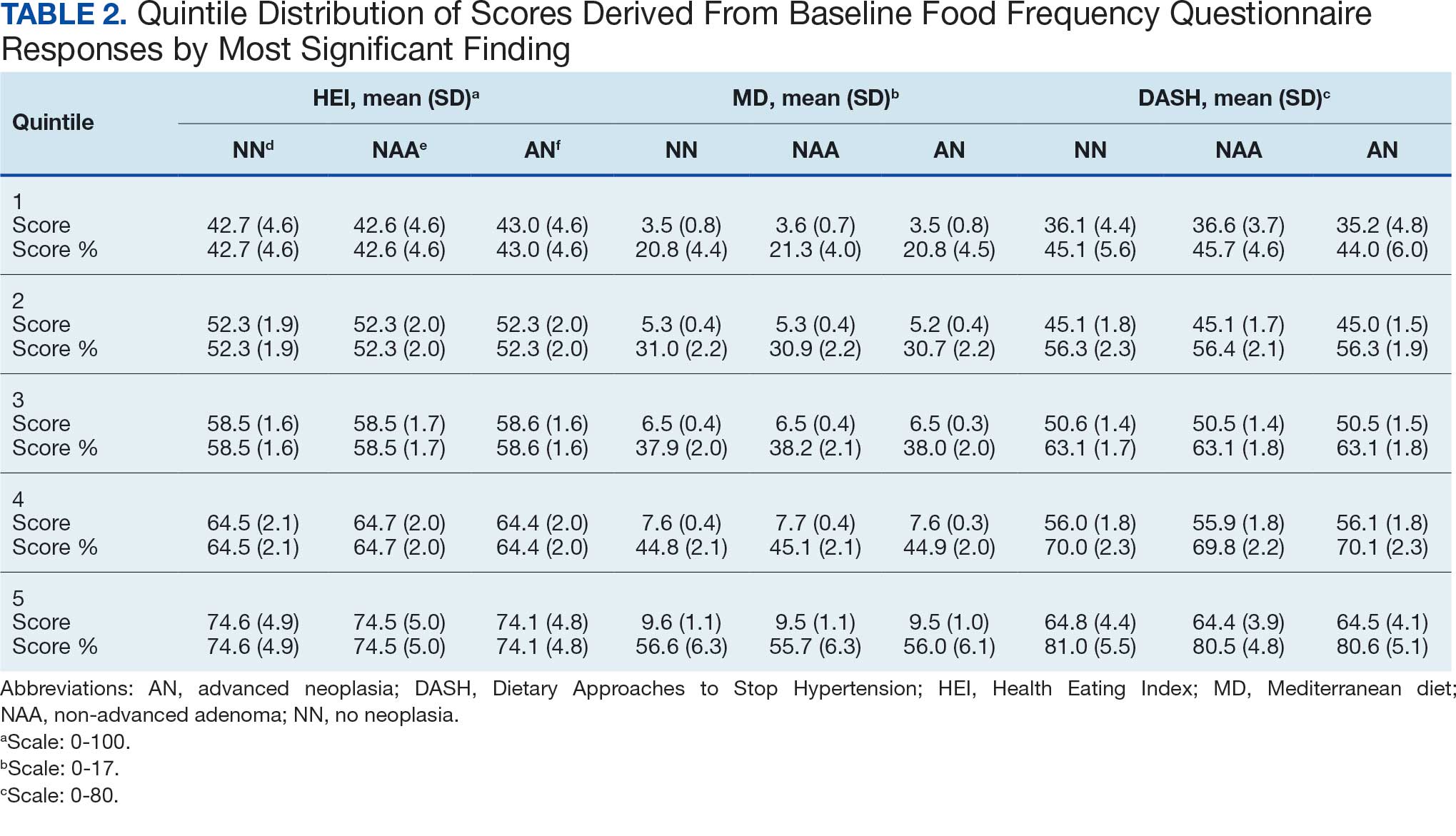
Associations between individual participants' dietary pattern scores and the outcome of their pooled MSCF from baseline screening and ≥ 10 years of surveillance are presented in Table 3. For each single-point increases in dietary pattern scores (reflecting better dietary quality), aORs for nonadvanced adenoma vs no neoplasia were slightly lower but not statistically significantly: HEI, aOR, 1.00 (95% CI, 0.99-1.01); MD, aOR, 0.98 (95% CI, 0.94-1.02); and DASH, aOR, 0.99 (95% CI, 0.99-1.00). aORs for AN vs no neoplasia were slightly lower for each dietary pattern assessed, and only the MD and DASH scores were significantly different from 1.00: HEI, aOR, 1.00 (95% CI, 0.99-1.01); MD, aOR, 0.95 (95% CI, 0.90-1.00); and DASH, aOR, 0.99 (95% CI, 0.98-1.00).
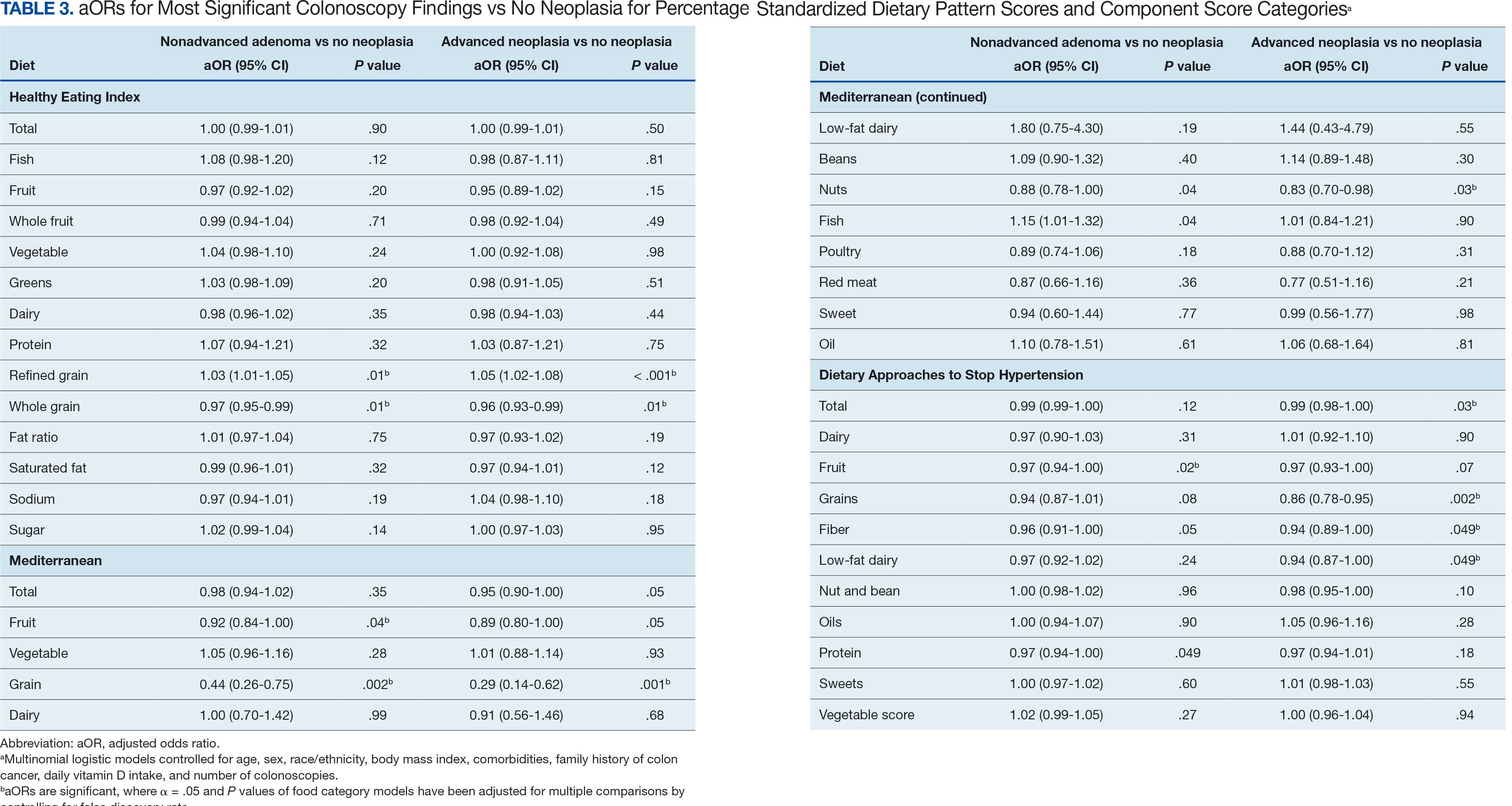
We observed lower odds for nonadvanced adenoma and AN among all these dietary patterns when there was greater alignment with the recommended intake of whole grains and fiber. In separate models conducted using food categories comprising the dietary patterns as independent variables and after correcting for multiple tests, higher scores for the HEI Refined Grain category were associated with higher odds for nonadvanced adenoma (aOR, 1.03 [95% CI, 1.01-1.05]; P = .01) and AN (aOR, 1.05 [95% CI, 1.02-1.08]; P < .001). Higher scores for the HEI Whole Grain category were associated with lower odds for nonadvanced adenoma (aOR, 0.97 [95% CI, 0.95-0.99]; P = .01) and AN (aOR, 0.96 [95% CI, 0.93-0.99]; P = .01). Higher scores for the MD Grain category were significantly associated with lower odds for nonadvanced adenoma (aOR, 0.44 [95% CI, 0.26-0.75]; P = .002) and AN (aOR, 0.29 [95% CI, 0.14-0.62]; P = .001). The DASH Grains category also was significantly associated with lower odds for AN (aOR, 0.86 [95% CI, 0.78-0.95]; P = .002).
Discussion
In this study of 3023 veterans undergoing first-time screening colonoscopy and ≥ 10 years of surveillance, we found that healthy dietary patterns, as assessed by the MD and DASH diet, were significantly associated with lower risk of AN. Additionally, we identified lower odds for AN and nonadvanced adenoma compared with no neoplasia for higher grain scores for all the dietary patterns studied. Other food categories that comprise the dietary pattern scores had mixed associations with the MSCF outcomes. Several other studies have examined associations between dietary patterns and risk for CRC but to our knowledge, no studies have explored these associations among US veterans.
These results also indicate study participants had better than average (based on a 50% threshold) dietary quality according to the HEI and DASH diet scoring methods we used, but poor dietary quality according to the MD scoring method. The mean HEI scores for the present study were higher than a US Department of Agriculture study by Dong et al that compared dietary quality between veterans and nonveterans using the HEI, for which veterans’ expected HEI score was 45.6 of 100.8 This could be explained by the fact that the participants needed to be healthy to be eligible and those with healthier behaviors overall may have self-selected into the study due to motivation for screening during a time when screening was not yet commonplace. 36 Similarly, participants of the present study had higher adherence to the DASH diet (63.1%) than adolescents with diabetes in a study by Günther et al. Conversely, firefighters who were coached to use a Mediterranean-style dietary pattern and dietary had higher adherence to MD than did participants in this study.27
A closer examination of specific food category component scores that comprise the 3 distinct dietary patterns revealed mixed results from the multinomial modeling, which may have to do with the guideline thresholds used to calculate the dietary scores. When analyzed separately in the logistic regression models for their associations with nonadvanced adenomas and AN compared with no neoplasia, higher MD and DASH fruit scores (but not HEI fruit scores) were found to be significant. Other studies have had mixed findings when attempting to test for associations of fruit intake with adenoma recurrence.10,37
This study had some unexpected findings. Vegetable intake was not associated with nonadvanced adenomas or AN risk. Studies of food categories have consistently found vegetable (specifically cruciferous ones) intake to be linked with lower odds for cancers.38 Likewise, the red meat category, which was only a unique food category in the MD score, was not associated with nonadvanced adenomas or AN. Despite consistent literature suggesting higher intake of red meat and processed meats increases CRC risk, in 2019 the Nutritional Recommendations Consortium indicated that the evidence was weak.39,40 This study showed higher DASH diet scores for low-fat dairy, which were maximized when participants reported at least 50% of their dairy servings per day as being low-fat, had lower odds for AN. Yet, the MD scores for low-fat dairy had no association with either outcome; their calculation was based on total number of servings per week. This difference in findings suggests the fat intake ratio may be more relevant to CRC risk than intake quantity.
The literature is mixed regarding fatty acid intake and CRC risk, which may be relevant to both dairy and meat intake. One systematic review and meta-analysis found dietary fat and types of fatty acid intake had no association with CRC risk.41 However, a more recent meta-analysis that assessed both dietary intake and plasma levels of fatty acids did find some statistically significant differences for various types of fatty acids and CRC risk.42
The findings in the present study that grain intake is associated with lower odds for more severe colonoscopy findings among veterans are notable.43 Lieberman et al, using the CSP #380 data, found that cereal fiber intake was associated with a lower odds for AN compared with hyperplastic polyps (OR, 0.98 [95% CI, 0.96- 1.00]).18 Similarly, Hullings et al determined that older adults in the highest quintile of cereal fiber intake had significantly lower odds of CRC than those in lower odds for CRC when compared with lowest quintile (OR, 0.89 [95% CI, 0.83- 0.96]; P < .001).44 These findings support existing guidance that prioritizes whole grains as a key source of dietary fiber for CRC prevention.
A recent literature review on fiber, fat, and CRC risk suggested a consensus regarding one protective mechanism: dietary fiber from grains modulates the gut microbiota by promoting butyrate synthesis.45 Butyrate is a short-chain fatty acid that supports energy production in colonocytes and has tumor-suppressing properties.46 Our findings suggest there could be more to learn about the relationship between butyrate production and reduction of CRC risk through metabolomic studies that use measurements of plasma butyrate. These studies may examine associations between not just a singular food or food category, but rather food patterns that include fruits, vegetables, nuts and seeds, and whole grains known to promote butyrate production and plasma butyrate.47
Improved understanding of mechanisms and risk-modifying lifestyle factors such as dietary patterns may enhance prevention strategies. Identifying the collective chemopreventive characteristics of a specific dietary pattern (eg, MD) will be helpful to clinicians and health care staff to promote healthy eating to reduce cancer risk. More studies are needed to understand whether such promotion is more clinically applicable and effective for patients, as compared with eating more or less of specific foods (eg, more whole grains, less red meat). Furthermore, considering important environmental factors collectively beyond dietary patterns may offer a way to better tailor screening and implement a variety of lifestyle interventions. In the literature, this is often referred to as a teachable moment when patients’ attentions are captured and may position them to be more receptive to guidance.48
Limitations
This study has several important limitations and leaves opportunities for future studies that explore the role of dietary patterns and AN or CRC risk. First, the FFQ data used to calculate dietary pattern scores used in analysis were only captured at baseline, and there are nearly 3 decades across the study period. However, it is widely assumed that the diets of older adults, like those included in this study, remain stable over time which is appropriate given our sample population was aged 50 to 75 years when the baseline FFQ data were collected.49-51 Additionally, while the HEI is a well-documented, standard scoring method for dietary quality, there are multitudes of dietary pattern scoring approaches for MD and DASH.23,52,53 Finally, findings from this study using the sample of veterans may not be generalizable to a broader population. Future longitudinal studies that test for a clinically significant change threshold are warranted.
Conclusion
Results of this study suggest future research should further explore the effects of dietary patterns, particularly intake of specific food groups in combination, as opposed to individual nutrients or food items, on AN and CRC risk. Possible studies might explore these dietary patterns for their mechanistic role in altering the microbiome metabolism, which may influence CRC outcomes or include diet in a more comprehensive, holistic risk score that could be used to predict colonic neoplasia risk or in intervention studies that assess the effects of dietary changes on long-term CRC prevention. We suggest there are differences in people’s dietary intake patterns that might be important to consider when implementing tailored approaches to CRC risk mitigation.
- Zauber AG, Winawer SJ, O’Brien MJ, et al. Colonoscopic polypectomy and long-term prevention of colorectalcancer deaths. N Engl J Med. 2012;366(8):687-696. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1100370
- Nishihara R, Wu K, Lochhead P, et al. Long-term colorectal-cancer incidence and mortality after lower endoscopy. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(12):1095-1105. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1301969
- Bretthauer M, Løberg M, Wieszczy P, et al. Effect of colonoscopy screening on risks of colorectal cancer and related death. N Engl J Med. 2022;387(17):1547-1556. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2208375
- Cottet V, Bonithon-Kopp C, Kronborg O, et al. Dietary patterns and the risk of colorectal adenoma recurrence in a European intervention trial. Eur J Cancer Prev. 2005;14(1):21.
- Miller PE, Lesko SM, Muscat JE, Lazarus P, Hartman TJ. Dietary patterns and colorectal adenoma and cancer risk: a review of the epidemiological evidence. Nutr Cancer. 2010;62(4):413-424. doi:10.1080/01635580903407114
- Godos J, Bella F, Torrisi A, Sciacca S, Galvano F, Grosso G. Dietary patterns and risk of colorectal adenoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. J Hum Nutr Diet Off J Br Diet Assoc. 2016;29(6):757-767. doi:10.1111/jhn.12395
- Haggar FA, Boushey RP. Colorectal cancer epidemiology: incidence, mortality, survival, and risk factors. Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 2009;22(4):191-197. doi:10.1055/s-0029-1242458
- Dong D, Stewart H, Carlson AC. An Examination of Veterans’ Diet Quality. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Economic Research Service; 2019:32.
- El-Halabi MM, Rex DK, Saito A, Eckert GJ, Kahi CJ. Defining adenoma detection rate benchmarks in average-risk male veterans. Gastrointest Endosc. 2019;89(1):137-143. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2018.08.021
- Alberts DS, Hess LM, eds. Fundamentals of Cancer Prevention. Springer International Publishing; 2019. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-15935-1
- Dahm CC, Keogh RH, Spencer EA, et al. Dietary fiber and colorectal cancer risk: a nested case-control study using food diaries. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2010;102(9):614-626. doi:10.1093/jnci/djq092
- Aune D, Lau R, Chan DSM, et al. Dairy products and colorectal cancer risk: a systematic review and metaanalysis of cohort studies. Ann Oncol. 2012;23(1):37-45. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdr269
- Lee JE, Li H, Chan AT, et al. Circulating levels of vitamin D and colon and rectal cancer: the Physicians’ Health Study and a meta-analysis of prospective studies. Cancer Prev Res Phila Pa. 2011;4(5):735-743. doi:10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-10-0289
- Carroll C, Cooper K, Papaioannou D, Hind D, Pilgrim H, Tappenden P. Supplemental calcium in the chemoprevention of colorectal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Ther. 2010;32(5):789-803. doi:10.1016/j.clinthera.2010.04.024
- Park Y, Spiegelman D, Hunter DJ, et al. Intakes of vitamins A, C, and E and use of multiple vitamin supplements and risk of colon cancer: a pooled analysis of prospective cohort studies. Cancer Causes Control CCC. 2010;21(11):1745- 1757. doi:10.1007/s10552-010-9549-y
- Alexander DD, Weed DL, Miller PE, Mohamed MA. Red meat and colorectal cancer: a quantitative update on the state of the epidemiologic science. J Am Coll Nutr. 2015;34(6):521-543. doi:10.1080/07315724.2014.992553
- Park SY, Wilkens LR, Setiawan VW, Monroe KR, Haiman CA, Le Marchand L. Alcohol intake and colorectal cancer risk in the multiethnic cohort study. Am J Epidemiol. 2019;188(1):67-76. doi:10.1093/aje/kwy208
- Lieberman DA. Risk Factors for advanced colonic neoplasia and hyperplastic polyps in asymptomatic individuals. JAMA. 2003;290(22):2959. doi:10.1001/jama.290.22.2959
- Archambault AN, Jeon J, Lin Y, et al. Risk stratification for early-onset colorectal cancer using a combination of genetic and environmental risk scores: an international multi-center study. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2022;114(4):528-539. doi:10.1093/jnci/djac003
- Carr PR, Weigl K, Edelmann D, et al. Estimation of absolute risk of colorectal cancer based on healthy lifestyle, genetic risk, and colonoscopy status in a populationbased study. Gastroenterology. 2020;159(1):129-138.e9. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2020.03.016
- Sullivan BA, Qin X, Miller C, et al. Screening colonoscopy findings are associated with noncolorectal cancer mortality. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2022;13(4):e00479. doi:10.14309/ctg.0000000000000479
- Erben V, Carr PR, Holleczek B, Stegmaier C, Hoffmeister M, Brenner H. Dietary patterns and risk of advanced colorectal neoplasms: A large population based screening study in Germany. Prev Med. 2018;111:101-109. doi:10.1016/j.ypmed.2018.02.025
- Donovan MG, Selmin OI, Doetschman TC, Romagnolo DF. Mediterranean diet: prevention of colorectal cancer. Front Nutr. 2017;4:59. doi:10.3389/fnut.2017.00059
- Mohseni R, Mohseni F, Alizadeh S, Abbasi S. The Association of Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet with the risk of colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis of observational studies.Nutr Cancer. 2020;72(5):778-790. doi:10.1080/01635581.2019.1651880
- Lieberman DA, Weiss DG, Bond JH, Ahnen DJ, Garewal H, Chejfec G. Use of colonoscopy to screen asymptomatic adults for colorectal cancer. Veterans Affairs Cooperative Study Group 380. N Engl J Med. 2000;343(3):162-168. doi:10.1056/NEJM200007203430301
- Developing the Healthy Eating Index (HEI) | EGRP/ DCCPS/NCI/NIH. Accessed July 22, 2025. https://epi.grants.cancer.gov/hei/developing.html#2015c
- Reeve E, Piccici F, Feairheller DL. Validation of a Mediterranean diet scoring system for intervention based research. J Nutr Med Diet Care. 2021;7(1):053. doi:10.23937/2572-3278/1510053
- Günther AL, Liese AD, Bell RA, et al. ASSOCIATION BETWEEN THE DIETARY APPROACHES TO HYPERTENSION (DASH) DIET AND HYPERTENSION IN YOUTH WITH DIABETES. Hypertens Dallas Tex 1979. 2009;53(1):6-12. doi:10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.108.116665
- Buckland G, Agudo A, Luján L, et al. Adherence to a Mediterranean diet and risk of gastric adenocarcinoma within the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC) cohort study. Am J Clin Nutr. 2010;91(2):381- 390. doi:10.3945/ajcn.2009.28209
- Rimm EB, Giovannucci EL, Stampfer MJ, Colditz GA, Litin LB, Willett WC. Reproducibility and validity of an expanded self-administered semiquantitative food frequency questionnaire among male health professionals. Am J Epidemiol. 1992;135(10):1114-1126. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a116211
- Charlson ME, Pompei P, Ales KL, MacKenzie CR. A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longitudinal studies: development and validation. J Chronic Dis. 1987;40(5):373-383. doi:10.1016/0021-9681(87)90171-8
- Lieberman DA, Weiss DG, Harford WV, et al. Fiveyear colon surveillance after screening colonoscopy. Gastroenterology. 2007;133(4):1077-1085. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2007.07.006
- Lieberman D, Sullivan BA, Hauser ER, et al. Baseline colonoscopy findings associated with 10-year outcomes in a screening cohort undergoing colonoscopy surveillance. Gastroenterology. 2020;158(4):862-874.e8. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2019.07.052
- PROC LOGISTIC: PROC LOGISTIC Statement : SAS/STAT(R) 9.22 User’s Guide. Accessed July 22, 2025. https://support.sas.com/documentation/cdl/en/statug/63347/HTML/default/viewer.htm#statug_logistic_sect004.htm
- PROC MULTTEST: PROC MULTTEST Statement : SAS/ STAT(R) 9.22 User’s Guide. Accessed July 22, 2025. https://support.sas.com/documentation/cdl/en/statug/63347/HTML/default/viewer.htm#statug_multtest_sect005.htm
- Elston DM. Participation bias, self-selection bias, and response bias. J Am Acad Dermatol. Published online June 18, 2021. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.06.025
- Sansbury LB, Wanke K, Albert PS, et al. The effect of strict adherence to a high-fiber, high-fruit and -vegetable, and low-fat eating pattern on adenoma recurrence. Am J Epidemiol. 2009;170(5):576-584. doi:10.1093/aje/kwp169
- Borgas P, Gonzalez G, Veselkov K, Mirnezami R. Phytochemically rich dietary components and the risk of colorectal cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. World J Clin Oncol. 2021;12(6):482- 499. doi:10.5306/wjco.v12.i6.482
- Papadimitriou N, Markozannes G, Kanellopoulou A, et al. An umbrella review of the evidence associating diet and cancer risk at 11 anatomical sites. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):4579. doi:10.1038/s41467-021-24861-8
- Johnston BC, Zeraatkar D, Han MA, et al. Unprocessed red meat and processed meat consumption: dietary guideline recommendations from the nutritional recommendations (NutriRECS) Consortium. Ann Intern Med. 2019;171(10):756-764. doi:10.7326/M19-1621
- Kim M, Park K. Dietary fat intake and risk of colorectal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective studies. Nutrients. 2018;10(12):1963. doi:10.3390/nu10121963
- Lu Y, Li D, Wang L, et al. Comprehensive investigation on associations between dietary intake and blood levels of fatty acids and colorectal cancer risk. Nutrients. 2023;15(3):730. doi:10.3390/nu15030730
- Gherasim A, Arhire LI, Ni.a O, Popa AD, Graur M, Mihalache L. The relationship between lifestyle components and dietary patterns. Proc Nutr Soc. 2020;79(3):311-323. doi:10.1017/S0029665120006898
- Hullings AG, Sinha R, Liao LM, Freedman ND, Graubard BI, Loftfield E. Whole grain and dietary fiber intake and risk of colorectal cancer in the NIH-AARP Diet and Health Study cohort. Am J Clin Nutr. 2020;112(3):603- 612. doi:10.1093/ajcn/nqaa161
- Ocvirk S, Wilson AS, Appolonia CN, Thomas TK, O’Keefe SJD. Fiber, fat, and colorectal cancer: new insight into modifiable dietary risk factors. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2019;21(11):62. doi:10.1007/s11894-019-0725-2
- O’Keefe SJD. Diet, microorganisms and their metabolites, and colon cancer. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;13(12):691-706. doi:10.1038/nrgastro.2016.165
- The health benefits and side effects of Butyrate Cleveland Clinic. July 11, 2022. Accessed July 22, 2025. https://health.clevelandclinic.org/butyrate-benefits/
- Knudsen MD, Wang L, Wang K, et al. Changes in lifestyle factors after endoscopic screening: a prospective study in the United States. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol Off ClinPract J Am Gastroenterol Assoc. 2022;20(6):e1240-e1249. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2021.07.014
- Thorpe MG, Milte CM, Crawford D, McNaughton SA. Education and lifestyle predict change in dietary patterns and diet quality of adults 55 years and over. Nutr J. 2019;18(1):67. doi:10.1186/s12937-019-0495-6
- Chapman K, Ogden J. How do people change their diet?: an exploration into mechanisms of dietary change. J Health Psychol. 2009;14(8):1229-1242. doi:10.1177/1359105309342289
- Djoussé L, Petrone AB, Weir NL, et al. Repeated versus single measurement of plasma omega-3 fatty acids and risk of heart failure. Eur J Nutr. 2014;53(6):1403-1408. doi:10.1007/s00394-013-0642-3
- Bach-Faig A, Berry EM, Lairon D, et al. Mediterranean diet pyramid today. Science and cultural updates. Public Health Nutr. 2011;14(12A):2274-2284. doi:10.1017/S1368980011002515
- Miller PE, Cross AJ, Subar AF, et al. Comparison of 4 established DASH diet indexes: examining associations of index scores and colorectal cancer123. Am J Clin Nutr. 2013;98(3):794-803. doi:10.3945/ajcn.113.063602
- Krebs-Smith SM, Pannucci TE, Subar AF, et al. Update of the Healthy Eating Index: HEI-2015. J Acad Nutr Diet. 2018;118(9):1591-1602. doi:10.1016/j.jand.2018.05.021
- P.R. Pehrsson, Cutrufelli RL, Gebhardt SE, et al. USDA Database for the Added Sugars Content of Selected Foods. USDA; 2005. www.ars.usda.gov/nutrientdata
Screening for colorectal cancer (CRC) with colonoscopy enables the identification and removal of CRC precursors (colonic adenomas) and has been associated with reduced risk of CRC incidence and mortality.1-3 Furthermore, there is consensus that diet and lifestyle may be associated with forestalling CRC pathogenesis at the intermediate adenoma stages.4-7 However, studies have shown that US veterans have poorer diet quality and a higher risk for neoplasia compared with nonveterans, reinforcing the need for tailored clinical approaches.8,9 Combining screening with conversations about modifiable environmental and lifestyle risk factors, such as poor diet, is a highly relevant and possibly easily leveraged prevention for those at high risk. However, there is limited evidence for any particular dietary patterns or dietary features that are most important over time.7
Several dietary components have been shown to be associated with CRC risk,10 either as potentially chemopreventive (fiber, fruits and vegetables,11 dairy,12 supplemental vitamin D,13 calcium,14 and multivitamins15) or carcinogenic (red meat16 and alcohol17). Previous studies of veterans have similarly shown that higher intake of fiber and vitamin D reduced risk, and red meat is associated with an increased risk for finding CRC precursors during colonoscopy.18 However, these dietary categories are often analyzed in isolation. Studying healthy dietary patterns in aggregate may be more clinically relevant and easier to implement for prevention of CRC and its precursors.19-21 Healthy dietary patterns, such as the US Dietary Guidelines for Americans represented by the Healthy Eating Index (HEI), the Mediterranean diet (MD), and the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet, have been associated with lower risk for chronic disease.22-24 Despite the extant literature, no known studies have compared these dietary patterns for associations with risk of CRC precursor or CRC development among US veterans undergoing long-term screening and follow-up after a baseline colonoscopy.
The objective of this study was to test for associations between baseline scores of healthy dietary patterns and the most severe colonoscopy findings (MSCFs) over ≥ 10 years following a baseline screening colonoscopy in veterans.
Methods
Participants in the Cooperative Studies Program (CSP) #380 cohort study included 3121 asymptomatic veterans aged 50 to 75 years at baseline who had consented to initial screening colonoscopy between 1994 and 1997, with subsequent follow-up and surveillance.25 Prior to their colonoscopy, all participants completed a baseline study survey that included questions about cancer risk factors including family history of CRC, diet, physical activity, and medication use.
Included in this cross-sectional analysis were data from a sample of veteran participants of the CSP #380 cohort with 1 baseline colonoscopy, follow-up surveillance through 2009, a cancer risk factor survey collected at baseline, and complete demographic and clinical indicator data. Excluded from the analysis were 67 participants with insufficient responses to the dietary food frequency questionnaire (FFQ) and 31 participants with missing body mass index (BMI), 3023 veterans.
Measures
MSCF. The outcome of interest in this study was the MSCF recorded across all participant colonoscopies during the study period. MSCF was categorized as either (1) no neoplasia; (2) < 2 nonadvanced adenomas, including small adenomas (diameter < 10 mm) with tubular histology; or (3) advanced neoplasia (AN), which is characterized by adenomas > 10 mm in diameter, with villous histology, with high-grade dysplasia, or CRC.
Dietary patterns. Dietary pattern scores representing dietary quality and calculated based on recommendations of the US Dietary Guidelines for Americans using the HEI, MD, and DASH diets were independent variables.26-28 These 3 dietary patterns were chosen for their hypothesized relationship with CRC risk, but each weighs food categories differently (Appendix 1).22-24,29 Dietary pattern scores were calculated using the CSP #380 self-reported responses to 129 baseline survey questions adapted from a well-established and previously validated semiquantitative FFQ.30 The form was administered by mail twice to a sample of 127 participants at baseline and at 1 year. During this interval, men completed 1-week diet records twice, spaced about 6 months apart. Mean values for intake of most nutrients assessed by the 2 methods were similar. Intraclass correlation coefficients for the baseline and 1-year FFQ-assessed nutrient intakes that ranged from 0.47 for vitamin E (without supplements) to 0.80 for vitamin C (with supplements). Correlation coefficients between the energy-adjusted nutrient intakes were measured by diet records and the 1-year FFQ, which asked about diet during the year encompassing the diet records. Higher raw and percent scores indicated better alignment with recommendations from each respective dietary pattern. Percent scores were calculated as a standardizing method and used in analyses for ease of comparing the dietary patterns. Scoring can be found in Appendix 2.


Demographic characteristics and clinical indicators. Demographic characteristics included age categories, sex, and race/ethnicity. Clinical indicators included BMI, the number of comorbid conditions used to calculate the Charlson Comorbidity Index, family history of CRC in first-degree relatives, number of follow-up colonoscopies across the study period, and food-based vitamin D intake.31 These variables were chosen for their applicability found in previous CSP #380 cohort studies.18,32,33 Self-reported race and ethnicity were collapsed due to small numbers in some groups. The authors acknowledge these are distinct concepts and the variable has limited utility other than for controlling for systemic racism in the model.
Statistical Analyses
Descriptive statistics were used to describe distributional assumptions for all variables, including demographics, clinical indicators, colonoscopy results, and dietary patterns. Pairwise correlations between the total dietary pattern scores and food category scores were calculated with Pearson correlation (r).
Multinomial logistic regression models were created using SAS procedure LOGISTIC with the outcome of the categorical MSCF (no neoplasia, nonadvanced adenoma, or AN).34 A model was created for each independent predictor variable of interest (ie, the HEI, MD, or DASH percentage-standardized dietary pattern score and each food category comprising each dietary pattern score). All models were adjusted for age, sex, race/ethnicity, BMI, number of comorbidities, family history of CRC, number of follow-up colonoscopies, and estimated daily food-derived vitamin D intake. The demographic and clinical indicators were included in the models as they are known to be associated with CRC risk.18 The number of colonoscopies was included to control for surveillance intensity presuming risk for AN is reduced as polyps are removed. Because colonoscopy findings from an initial screening have unique clinical implications compared with follow- up and surveillance, MSCF was observed in 2 ways in sensitivity analyses: (1) baseline and (2) aggregate follow-up and surveillance only, excluding baseline findings.
Adjusted odds ratios (aORs) and 95% CIs for each of the MSCF outcomes with a reference finding of no neoplasia for the models are presented. We chose not to adjust for multiple comparisons across the different dietary patterns given the correlation between dietary pattern total and category scores but did adjust for multiple comparisons for dietary categories within each dietary pattern. Tests for statistical significance used α= .05 for the dietary pattern total scores and P values for the dietary category scores for each dietary pattern controlled for false discovery rate using the MULTTEST SAS procedure.35 All data manipulations and analyses were performed using SAS version 9.4.
Results
The study included 3023 patients. All were aged 50 to 75 years, 2923 (96.7%) were male and 2532 (83.8%) were non-Hispanic White (Table 1). Most participants were overweight or obese (n = 2535 [83.8%]), 2024 (67.0%) had ≤ 2 comorbidities, and 2602 (86.1%) had no family history of CRC. The MSCF for 1628 patients (53.9%) was no neoplasia, 966 patients (32.0%) was nonadvanced adenoma, and 429 participants (14.2%) had AN.

Mean percent scores were 58.5% for HEI, 38.2% for MD, and 63.1% for the DASH diet, with higher percentages indicating greater alignment with the recommendations for each diet (Table 2). All 3 dietary patterns scores standardized to percentages were strongly and significantly correlated in pairwise comparisons: HEI:MD, r = 0.62 (P < .001); HEI:DASH, r = 0.60 (P < .001); and MD:DASH, r = 0.72 (P < .001). Likewise, food category scores were significantly correlated across dietary patterns. For example, whole grain and fiber values from each dietary score were strongly correlated in pairwise comparisons: HEI Whole Grain:MD Grain, r = 0.64 (P < .001); HEI Whole Grain:DASH Fiber, r = 0.71 (P < .001); and MD Grain:DASH Fiber, r = 0.70 (P < .001).

Associations between individual participants' dietary pattern scores and the outcome of their pooled MSCF from baseline screening and ≥ 10 years of surveillance are presented in Table 3. For each single-point increases in dietary pattern scores (reflecting better dietary quality), aORs for nonadvanced adenoma vs no neoplasia were slightly lower but not statistically significantly: HEI, aOR, 1.00 (95% CI, 0.99-1.01); MD, aOR, 0.98 (95% CI, 0.94-1.02); and DASH, aOR, 0.99 (95% CI, 0.99-1.00). aORs for AN vs no neoplasia were slightly lower for each dietary pattern assessed, and only the MD and DASH scores were significantly different from 1.00: HEI, aOR, 1.00 (95% CI, 0.99-1.01); MD, aOR, 0.95 (95% CI, 0.90-1.00); and DASH, aOR, 0.99 (95% CI, 0.98-1.00).

We observed lower odds for nonadvanced adenoma and AN among all these dietary patterns when there was greater alignment with the recommended intake of whole grains and fiber. In separate models conducted using food categories comprising the dietary patterns as independent variables and after correcting for multiple tests, higher scores for the HEI Refined Grain category were associated with higher odds for nonadvanced adenoma (aOR, 1.03 [95% CI, 1.01-1.05]; P = .01) and AN (aOR, 1.05 [95% CI, 1.02-1.08]; P < .001). Higher scores for the HEI Whole Grain category were associated with lower odds for nonadvanced adenoma (aOR, 0.97 [95% CI, 0.95-0.99]; P = .01) and AN (aOR, 0.96 [95% CI, 0.93-0.99]; P = .01). Higher scores for the MD Grain category were significantly associated with lower odds for nonadvanced adenoma (aOR, 0.44 [95% CI, 0.26-0.75]; P = .002) and AN (aOR, 0.29 [95% CI, 0.14-0.62]; P = .001). The DASH Grains category also was significantly associated with lower odds for AN (aOR, 0.86 [95% CI, 0.78-0.95]; P = .002).
Discussion
In this study of 3023 veterans undergoing first-time screening colonoscopy and ≥ 10 years of surveillance, we found that healthy dietary patterns, as assessed by the MD and DASH diet, were significantly associated with lower risk of AN. Additionally, we identified lower odds for AN and nonadvanced adenoma compared with no neoplasia for higher grain scores for all the dietary patterns studied. Other food categories that comprise the dietary pattern scores had mixed associations with the MSCF outcomes. Several other studies have examined associations between dietary patterns and risk for CRC but to our knowledge, no studies have explored these associations among US veterans.
These results also indicate study participants had better than average (based on a 50% threshold) dietary quality according to the HEI and DASH diet scoring methods we used, but poor dietary quality according to the MD scoring method. The mean HEI scores for the present study were higher than a US Department of Agriculture study by Dong et al that compared dietary quality between veterans and nonveterans using the HEI, for which veterans’ expected HEI score was 45.6 of 100.8 This could be explained by the fact that the participants needed to be healthy to be eligible and those with healthier behaviors overall may have self-selected into the study due to motivation for screening during a time when screening was not yet commonplace. 36 Similarly, participants of the present study had higher adherence to the DASH diet (63.1%) than adolescents with diabetes in a study by Günther et al. Conversely, firefighters who were coached to use a Mediterranean-style dietary pattern and dietary had higher adherence to MD than did participants in this study.27
A closer examination of specific food category component scores that comprise the 3 distinct dietary patterns revealed mixed results from the multinomial modeling, which may have to do with the guideline thresholds used to calculate the dietary scores. When analyzed separately in the logistic regression models for their associations with nonadvanced adenomas and AN compared with no neoplasia, higher MD and DASH fruit scores (but not HEI fruit scores) were found to be significant. Other studies have had mixed findings when attempting to test for associations of fruit intake with adenoma recurrence.10,37
This study had some unexpected findings. Vegetable intake was not associated with nonadvanced adenomas or AN risk. Studies of food categories have consistently found vegetable (specifically cruciferous ones) intake to be linked with lower odds for cancers.38 Likewise, the red meat category, which was only a unique food category in the MD score, was not associated with nonadvanced adenomas or AN. Despite consistent literature suggesting higher intake of red meat and processed meats increases CRC risk, in 2019 the Nutritional Recommendations Consortium indicated that the evidence was weak.39,40 This study showed higher DASH diet scores for low-fat dairy, which were maximized when participants reported at least 50% of their dairy servings per day as being low-fat, had lower odds for AN. Yet, the MD scores for low-fat dairy had no association with either outcome; their calculation was based on total number of servings per week. This difference in findings suggests the fat intake ratio may be more relevant to CRC risk than intake quantity.
The literature is mixed regarding fatty acid intake and CRC risk, which may be relevant to both dairy and meat intake. One systematic review and meta-analysis found dietary fat and types of fatty acid intake had no association with CRC risk.41 However, a more recent meta-analysis that assessed both dietary intake and plasma levels of fatty acids did find some statistically significant differences for various types of fatty acids and CRC risk.42
The findings in the present study that grain intake is associated with lower odds for more severe colonoscopy findings among veterans are notable.43 Lieberman et al, using the CSP #380 data, found that cereal fiber intake was associated with a lower odds for AN compared with hyperplastic polyps (OR, 0.98 [95% CI, 0.96- 1.00]).18 Similarly, Hullings et al determined that older adults in the highest quintile of cereal fiber intake had significantly lower odds of CRC than those in lower odds for CRC when compared with lowest quintile (OR, 0.89 [95% CI, 0.83- 0.96]; P < .001).44 These findings support existing guidance that prioritizes whole grains as a key source of dietary fiber for CRC prevention.
A recent literature review on fiber, fat, and CRC risk suggested a consensus regarding one protective mechanism: dietary fiber from grains modulates the gut microbiota by promoting butyrate synthesis.45 Butyrate is a short-chain fatty acid that supports energy production in colonocytes and has tumor-suppressing properties.46 Our findings suggest there could be more to learn about the relationship between butyrate production and reduction of CRC risk through metabolomic studies that use measurements of plasma butyrate. These studies may examine associations between not just a singular food or food category, but rather food patterns that include fruits, vegetables, nuts and seeds, and whole grains known to promote butyrate production and plasma butyrate.47
Improved understanding of mechanisms and risk-modifying lifestyle factors such as dietary patterns may enhance prevention strategies. Identifying the collective chemopreventive characteristics of a specific dietary pattern (eg, MD) will be helpful to clinicians and health care staff to promote healthy eating to reduce cancer risk. More studies are needed to understand whether such promotion is more clinically applicable and effective for patients, as compared with eating more or less of specific foods (eg, more whole grains, less red meat). Furthermore, considering important environmental factors collectively beyond dietary patterns may offer a way to better tailor screening and implement a variety of lifestyle interventions. In the literature, this is often referred to as a teachable moment when patients’ attentions are captured and may position them to be more receptive to guidance.48
Limitations
This study has several important limitations and leaves opportunities for future studies that explore the role of dietary patterns and AN or CRC risk. First, the FFQ data used to calculate dietary pattern scores used in analysis were only captured at baseline, and there are nearly 3 decades across the study period. However, it is widely assumed that the diets of older adults, like those included in this study, remain stable over time which is appropriate given our sample population was aged 50 to 75 years when the baseline FFQ data were collected.49-51 Additionally, while the HEI is a well-documented, standard scoring method for dietary quality, there are multitudes of dietary pattern scoring approaches for MD and DASH.23,52,53 Finally, findings from this study using the sample of veterans may not be generalizable to a broader population. Future longitudinal studies that test for a clinically significant change threshold are warranted.
Conclusion
Results of this study suggest future research should further explore the effects of dietary patterns, particularly intake of specific food groups in combination, as opposed to individual nutrients or food items, on AN and CRC risk. Possible studies might explore these dietary patterns for their mechanistic role in altering the microbiome metabolism, which may influence CRC outcomes or include diet in a more comprehensive, holistic risk score that could be used to predict colonic neoplasia risk or in intervention studies that assess the effects of dietary changes on long-term CRC prevention. We suggest there are differences in people’s dietary intake patterns that might be important to consider when implementing tailored approaches to CRC risk mitigation.
Screening for colorectal cancer (CRC) with colonoscopy enables the identification and removal of CRC precursors (colonic adenomas) and has been associated with reduced risk of CRC incidence and mortality.1-3 Furthermore, there is consensus that diet and lifestyle may be associated with forestalling CRC pathogenesis at the intermediate adenoma stages.4-7 However, studies have shown that US veterans have poorer diet quality and a higher risk for neoplasia compared with nonveterans, reinforcing the need for tailored clinical approaches.8,9 Combining screening with conversations about modifiable environmental and lifestyle risk factors, such as poor diet, is a highly relevant and possibly easily leveraged prevention for those at high risk. However, there is limited evidence for any particular dietary patterns or dietary features that are most important over time.7
Several dietary components have been shown to be associated with CRC risk,10 either as potentially chemopreventive (fiber, fruits and vegetables,11 dairy,12 supplemental vitamin D,13 calcium,14 and multivitamins15) or carcinogenic (red meat16 and alcohol17). Previous studies of veterans have similarly shown that higher intake of fiber and vitamin D reduced risk, and red meat is associated with an increased risk for finding CRC precursors during colonoscopy.18 However, these dietary categories are often analyzed in isolation. Studying healthy dietary patterns in aggregate may be more clinically relevant and easier to implement for prevention of CRC and its precursors.19-21 Healthy dietary patterns, such as the US Dietary Guidelines for Americans represented by the Healthy Eating Index (HEI), the Mediterranean diet (MD), and the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet, have been associated with lower risk for chronic disease.22-24 Despite the extant literature, no known studies have compared these dietary patterns for associations with risk of CRC precursor or CRC development among US veterans undergoing long-term screening and follow-up after a baseline colonoscopy.
The objective of this study was to test for associations between baseline scores of healthy dietary patterns and the most severe colonoscopy findings (MSCFs) over ≥ 10 years following a baseline screening colonoscopy in veterans.
Methods
Participants in the Cooperative Studies Program (CSP) #380 cohort study included 3121 asymptomatic veterans aged 50 to 75 years at baseline who had consented to initial screening colonoscopy between 1994 and 1997, with subsequent follow-up and surveillance.25 Prior to their colonoscopy, all participants completed a baseline study survey that included questions about cancer risk factors including family history of CRC, diet, physical activity, and medication use.
Included in this cross-sectional analysis were data from a sample of veteran participants of the CSP #380 cohort with 1 baseline colonoscopy, follow-up surveillance through 2009, a cancer risk factor survey collected at baseline, and complete demographic and clinical indicator data. Excluded from the analysis were 67 participants with insufficient responses to the dietary food frequency questionnaire (FFQ) and 31 participants with missing body mass index (BMI), 3023 veterans.
Measures
MSCF. The outcome of interest in this study was the MSCF recorded across all participant colonoscopies during the study period. MSCF was categorized as either (1) no neoplasia; (2) < 2 nonadvanced adenomas, including small adenomas (diameter < 10 mm) with tubular histology; or (3) advanced neoplasia (AN), which is characterized by adenomas > 10 mm in diameter, with villous histology, with high-grade dysplasia, or CRC.
Dietary patterns. Dietary pattern scores representing dietary quality and calculated based on recommendations of the US Dietary Guidelines for Americans using the HEI, MD, and DASH diets were independent variables.26-28 These 3 dietary patterns were chosen for their hypothesized relationship with CRC risk, but each weighs food categories differently (Appendix 1).22-24,29 Dietary pattern scores were calculated using the CSP #380 self-reported responses to 129 baseline survey questions adapted from a well-established and previously validated semiquantitative FFQ.30 The form was administered by mail twice to a sample of 127 participants at baseline and at 1 year. During this interval, men completed 1-week diet records twice, spaced about 6 months apart. Mean values for intake of most nutrients assessed by the 2 methods were similar. Intraclass correlation coefficients for the baseline and 1-year FFQ-assessed nutrient intakes that ranged from 0.47 for vitamin E (without supplements) to 0.80 for vitamin C (with supplements). Correlation coefficients between the energy-adjusted nutrient intakes were measured by diet records and the 1-year FFQ, which asked about diet during the year encompassing the diet records. Higher raw and percent scores indicated better alignment with recommendations from each respective dietary pattern. Percent scores were calculated as a standardizing method and used in analyses for ease of comparing the dietary patterns. Scoring can be found in Appendix 2.


Demographic characteristics and clinical indicators. Demographic characteristics included age categories, sex, and race/ethnicity. Clinical indicators included BMI, the number of comorbid conditions used to calculate the Charlson Comorbidity Index, family history of CRC in first-degree relatives, number of follow-up colonoscopies across the study period, and food-based vitamin D intake.31 These variables were chosen for their applicability found in previous CSP #380 cohort studies.18,32,33 Self-reported race and ethnicity were collapsed due to small numbers in some groups. The authors acknowledge these are distinct concepts and the variable has limited utility other than for controlling for systemic racism in the model.
Statistical Analyses
Descriptive statistics were used to describe distributional assumptions for all variables, including demographics, clinical indicators, colonoscopy results, and dietary patterns. Pairwise correlations between the total dietary pattern scores and food category scores were calculated with Pearson correlation (r).
Multinomial logistic regression models were created using SAS procedure LOGISTIC with the outcome of the categorical MSCF (no neoplasia, nonadvanced adenoma, or AN).34 A model was created for each independent predictor variable of interest (ie, the HEI, MD, or DASH percentage-standardized dietary pattern score and each food category comprising each dietary pattern score). All models were adjusted for age, sex, race/ethnicity, BMI, number of comorbidities, family history of CRC, number of follow-up colonoscopies, and estimated daily food-derived vitamin D intake. The demographic and clinical indicators were included in the models as they are known to be associated with CRC risk.18 The number of colonoscopies was included to control for surveillance intensity presuming risk for AN is reduced as polyps are removed. Because colonoscopy findings from an initial screening have unique clinical implications compared with follow- up and surveillance, MSCF was observed in 2 ways in sensitivity analyses: (1) baseline and (2) aggregate follow-up and surveillance only, excluding baseline findings.
Adjusted odds ratios (aORs) and 95% CIs for each of the MSCF outcomes with a reference finding of no neoplasia for the models are presented. We chose not to adjust for multiple comparisons across the different dietary patterns given the correlation between dietary pattern total and category scores but did adjust for multiple comparisons for dietary categories within each dietary pattern. Tests for statistical significance used α= .05 for the dietary pattern total scores and P values for the dietary category scores for each dietary pattern controlled for false discovery rate using the MULTTEST SAS procedure.35 All data manipulations and analyses were performed using SAS version 9.4.
Results
The study included 3023 patients. All were aged 50 to 75 years, 2923 (96.7%) were male and 2532 (83.8%) were non-Hispanic White (Table 1). Most participants were overweight or obese (n = 2535 [83.8%]), 2024 (67.0%) had ≤ 2 comorbidities, and 2602 (86.1%) had no family history of CRC. The MSCF for 1628 patients (53.9%) was no neoplasia, 966 patients (32.0%) was nonadvanced adenoma, and 429 participants (14.2%) had AN.

Mean percent scores were 58.5% for HEI, 38.2% for MD, and 63.1% for the DASH diet, with higher percentages indicating greater alignment with the recommendations for each diet (Table 2). All 3 dietary patterns scores standardized to percentages were strongly and significantly correlated in pairwise comparisons: HEI:MD, r = 0.62 (P < .001); HEI:DASH, r = 0.60 (P < .001); and MD:DASH, r = 0.72 (P < .001). Likewise, food category scores were significantly correlated across dietary patterns. For example, whole grain and fiber values from each dietary score were strongly correlated in pairwise comparisons: HEI Whole Grain:MD Grain, r = 0.64 (P < .001); HEI Whole Grain:DASH Fiber, r = 0.71 (P < .001); and MD Grain:DASH Fiber, r = 0.70 (P < .001).

Associations between individual participants' dietary pattern scores and the outcome of their pooled MSCF from baseline screening and ≥ 10 years of surveillance are presented in Table 3. For each single-point increases in dietary pattern scores (reflecting better dietary quality), aORs for nonadvanced adenoma vs no neoplasia were slightly lower but not statistically significantly: HEI, aOR, 1.00 (95% CI, 0.99-1.01); MD, aOR, 0.98 (95% CI, 0.94-1.02); and DASH, aOR, 0.99 (95% CI, 0.99-1.00). aORs for AN vs no neoplasia were slightly lower for each dietary pattern assessed, and only the MD and DASH scores were significantly different from 1.00: HEI, aOR, 1.00 (95% CI, 0.99-1.01); MD, aOR, 0.95 (95% CI, 0.90-1.00); and DASH, aOR, 0.99 (95% CI, 0.98-1.00).

We observed lower odds for nonadvanced adenoma and AN among all these dietary patterns when there was greater alignment with the recommended intake of whole grains and fiber. In separate models conducted using food categories comprising the dietary patterns as independent variables and after correcting for multiple tests, higher scores for the HEI Refined Grain category were associated with higher odds for nonadvanced adenoma (aOR, 1.03 [95% CI, 1.01-1.05]; P = .01) and AN (aOR, 1.05 [95% CI, 1.02-1.08]; P < .001). Higher scores for the HEI Whole Grain category were associated with lower odds for nonadvanced adenoma (aOR, 0.97 [95% CI, 0.95-0.99]; P = .01) and AN (aOR, 0.96 [95% CI, 0.93-0.99]; P = .01). Higher scores for the MD Grain category were significantly associated with lower odds for nonadvanced adenoma (aOR, 0.44 [95% CI, 0.26-0.75]; P = .002) and AN (aOR, 0.29 [95% CI, 0.14-0.62]; P = .001). The DASH Grains category also was significantly associated with lower odds for AN (aOR, 0.86 [95% CI, 0.78-0.95]; P = .002).
Discussion
In this study of 3023 veterans undergoing first-time screening colonoscopy and ≥ 10 years of surveillance, we found that healthy dietary patterns, as assessed by the MD and DASH diet, were significantly associated with lower risk of AN. Additionally, we identified lower odds for AN and nonadvanced adenoma compared with no neoplasia for higher grain scores for all the dietary patterns studied. Other food categories that comprise the dietary pattern scores had mixed associations with the MSCF outcomes. Several other studies have examined associations between dietary patterns and risk for CRC but to our knowledge, no studies have explored these associations among US veterans.
These results also indicate study participants had better than average (based on a 50% threshold) dietary quality according to the HEI and DASH diet scoring methods we used, but poor dietary quality according to the MD scoring method. The mean HEI scores for the present study were higher than a US Department of Agriculture study by Dong et al that compared dietary quality between veterans and nonveterans using the HEI, for which veterans’ expected HEI score was 45.6 of 100.8 This could be explained by the fact that the participants needed to be healthy to be eligible and those with healthier behaviors overall may have self-selected into the study due to motivation for screening during a time when screening was not yet commonplace. 36 Similarly, participants of the present study had higher adherence to the DASH diet (63.1%) than adolescents with diabetes in a study by Günther et al. Conversely, firefighters who were coached to use a Mediterranean-style dietary pattern and dietary had higher adherence to MD than did participants in this study.27
A closer examination of specific food category component scores that comprise the 3 distinct dietary patterns revealed mixed results from the multinomial modeling, which may have to do with the guideline thresholds used to calculate the dietary scores. When analyzed separately in the logistic regression models for their associations with nonadvanced adenomas and AN compared with no neoplasia, higher MD and DASH fruit scores (but not HEI fruit scores) were found to be significant. Other studies have had mixed findings when attempting to test for associations of fruit intake with adenoma recurrence.10,37
This study had some unexpected findings. Vegetable intake was not associated with nonadvanced adenomas or AN risk. Studies of food categories have consistently found vegetable (specifically cruciferous ones) intake to be linked with lower odds for cancers.38 Likewise, the red meat category, which was only a unique food category in the MD score, was not associated with nonadvanced adenomas or AN. Despite consistent literature suggesting higher intake of red meat and processed meats increases CRC risk, in 2019 the Nutritional Recommendations Consortium indicated that the evidence was weak.39,40 This study showed higher DASH diet scores for low-fat dairy, which were maximized when participants reported at least 50% of their dairy servings per day as being low-fat, had lower odds for AN. Yet, the MD scores for low-fat dairy had no association with either outcome; their calculation was based on total number of servings per week. This difference in findings suggests the fat intake ratio may be more relevant to CRC risk than intake quantity.
The literature is mixed regarding fatty acid intake and CRC risk, which may be relevant to both dairy and meat intake. One systematic review and meta-analysis found dietary fat and types of fatty acid intake had no association with CRC risk.41 However, a more recent meta-analysis that assessed both dietary intake and plasma levels of fatty acids did find some statistically significant differences for various types of fatty acids and CRC risk.42
The findings in the present study that grain intake is associated with lower odds for more severe colonoscopy findings among veterans are notable.43 Lieberman et al, using the CSP #380 data, found that cereal fiber intake was associated with a lower odds for AN compared with hyperplastic polyps (OR, 0.98 [95% CI, 0.96- 1.00]).18 Similarly, Hullings et al determined that older adults in the highest quintile of cereal fiber intake had significantly lower odds of CRC than those in lower odds for CRC when compared with lowest quintile (OR, 0.89 [95% CI, 0.83- 0.96]; P < .001).44 These findings support existing guidance that prioritizes whole grains as a key source of dietary fiber for CRC prevention.
A recent literature review on fiber, fat, and CRC risk suggested a consensus regarding one protective mechanism: dietary fiber from grains modulates the gut microbiota by promoting butyrate synthesis.45 Butyrate is a short-chain fatty acid that supports energy production in colonocytes and has tumor-suppressing properties.46 Our findings suggest there could be more to learn about the relationship between butyrate production and reduction of CRC risk through metabolomic studies that use measurements of plasma butyrate. These studies may examine associations between not just a singular food or food category, but rather food patterns that include fruits, vegetables, nuts and seeds, and whole grains known to promote butyrate production and plasma butyrate.47
Improved understanding of mechanisms and risk-modifying lifestyle factors such as dietary patterns may enhance prevention strategies. Identifying the collective chemopreventive characteristics of a specific dietary pattern (eg, MD) will be helpful to clinicians and health care staff to promote healthy eating to reduce cancer risk. More studies are needed to understand whether such promotion is more clinically applicable and effective for patients, as compared with eating more or less of specific foods (eg, more whole grains, less red meat). Furthermore, considering important environmental factors collectively beyond dietary patterns may offer a way to better tailor screening and implement a variety of lifestyle interventions. In the literature, this is often referred to as a teachable moment when patients’ attentions are captured and may position them to be more receptive to guidance.48
Limitations
This study has several important limitations and leaves opportunities for future studies that explore the role of dietary patterns and AN or CRC risk. First, the FFQ data used to calculate dietary pattern scores used in analysis were only captured at baseline, and there are nearly 3 decades across the study period. However, it is widely assumed that the diets of older adults, like those included in this study, remain stable over time which is appropriate given our sample population was aged 50 to 75 years when the baseline FFQ data were collected.49-51 Additionally, while the HEI is a well-documented, standard scoring method for dietary quality, there are multitudes of dietary pattern scoring approaches for MD and DASH.23,52,53 Finally, findings from this study using the sample of veterans may not be generalizable to a broader population. Future longitudinal studies that test for a clinically significant change threshold are warranted.
Conclusion
Results of this study suggest future research should further explore the effects of dietary patterns, particularly intake of specific food groups in combination, as opposed to individual nutrients or food items, on AN and CRC risk. Possible studies might explore these dietary patterns for their mechanistic role in altering the microbiome metabolism, which may influence CRC outcomes or include diet in a more comprehensive, holistic risk score that could be used to predict colonic neoplasia risk or in intervention studies that assess the effects of dietary changes on long-term CRC prevention. We suggest there are differences in people’s dietary intake patterns that might be important to consider when implementing tailored approaches to CRC risk mitigation.
- Zauber AG, Winawer SJ, O’Brien MJ, et al. Colonoscopic polypectomy and long-term prevention of colorectalcancer deaths. N Engl J Med. 2012;366(8):687-696. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1100370
- Nishihara R, Wu K, Lochhead P, et al. Long-term colorectal-cancer incidence and mortality after lower endoscopy. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(12):1095-1105. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1301969
- Bretthauer M, Løberg M, Wieszczy P, et al. Effect of colonoscopy screening on risks of colorectal cancer and related death. N Engl J Med. 2022;387(17):1547-1556. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2208375
- Cottet V, Bonithon-Kopp C, Kronborg O, et al. Dietary patterns and the risk of colorectal adenoma recurrence in a European intervention trial. Eur J Cancer Prev. 2005;14(1):21.
- Miller PE, Lesko SM, Muscat JE, Lazarus P, Hartman TJ. Dietary patterns and colorectal adenoma and cancer risk: a review of the epidemiological evidence. Nutr Cancer. 2010;62(4):413-424. doi:10.1080/01635580903407114
- Godos J, Bella F, Torrisi A, Sciacca S, Galvano F, Grosso G. Dietary patterns and risk of colorectal adenoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. J Hum Nutr Diet Off J Br Diet Assoc. 2016;29(6):757-767. doi:10.1111/jhn.12395
- Haggar FA, Boushey RP. Colorectal cancer epidemiology: incidence, mortality, survival, and risk factors. Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 2009;22(4):191-197. doi:10.1055/s-0029-1242458
- Dong D, Stewart H, Carlson AC. An Examination of Veterans’ Diet Quality. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Economic Research Service; 2019:32.
- El-Halabi MM, Rex DK, Saito A, Eckert GJ, Kahi CJ. Defining adenoma detection rate benchmarks in average-risk male veterans. Gastrointest Endosc. 2019;89(1):137-143. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2018.08.021
- Alberts DS, Hess LM, eds. Fundamentals of Cancer Prevention. Springer International Publishing; 2019. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-15935-1
- Dahm CC, Keogh RH, Spencer EA, et al. Dietary fiber and colorectal cancer risk: a nested case-control study using food diaries. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2010;102(9):614-626. doi:10.1093/jnci/djq092
- Aune D, Lau R, Chan DSM, et al. Dairy products and colorectal cancer risk: a systematic review and metaanalysis of cohort studies. Ann Oncol. 2012;23(1):37-45. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdr269
- Lee JE, Li H, Chan AT, et al. Circulating levels of vitamin D and colon and rectal cancer: the Physicians’ Health Study and a meta-analysis of prospective studies. Cancer Prev Res Phila Pa. 2011;4(5):735-743. doi:10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-10-0289
- Carroll C, Cooper K, Papaioannou D, Hind D, Pilgrim H, Tappenden P. Supplemental calcium in the chemoprevention of colorectal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Ther. 2010;32(5):789-803. doi:10.1016/j.clinthera.2010.04.024
- Park Y, Spiegelman D, Hunter DJ, et al. Intakes of vitamins A, C, and E and use of multiple vitamin supplements and risk of colon cancer: a pooled analysis of prospective cohort studies. Cancer Causes Control CCC. 2010;21(11):1745- 1757. doi:10.1007/s10552-010-9549-y
- Alexander DD, Weed DL, Miller PE, Mohamed MA. Red meat and colorectal cancer: a quantitative update on the state of the epidemiologic science. J Am Coll Nutr. 2015;34(6):521-543. doi:10.1080/07315724.2014.992553
- Park SY, Wilkens LR, Setiawan VW, Monroe KR, Haiman CA, Le Marchand L. Alcohol intake and colorectal cancer risk in the multiethnic cohort study. Am J Epidemiol. 2019;188(1):67-76. doi:10.1093/aje/kwy208
- Lieberman DA. Risk Factors for advanced colonic neoplasia and hyperplastic polyps in asymptomatic individuals. JAMA. 2003;290(22):2959. doi:10.1001/jama.290.22.2959
- Archambault AN, Jeon J, Lin Y, et al. Risk stratification for early-onset colorectal cancer using a combination of genetic and environmental risk scores: an international multi-center study. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2022;114(4):528-539. doi:10.1093/jnci/djac003
- Carr PR, Weigl K, Edelmann D, et al. Estimation of absolute risk of colorectal cancer based on healthy lifestyle, genetic risk, and colonoscopy status in a populationbased study. Gastroenterology. 2020;159(1):129-138.e9. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2020.03.016
- Sullivan BA, Qin X, Miller C, et al. Screening colonoscopy findings are associated with noncolorectal cancer mortality. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2022;13(4):e00479. doi:10.14309/ctg.0000000000000479
- Erben V, Carr PR, Holleczek B, Stegmaier C, Hoffmeister M, Brenner H. Dietary patterns and risk of advanced colorectal neoplasms: A large population based screening study in Germany. Prev Med. 2018;111:101-109. doi:10.1016/j.ypmed.2018.02.025
- Donovan MG, Selmin OI, Doetschman TC, Romagnolo DF. Mediterranean diet: prevention of colorectal cancer. Front Nutr. 2017;4:59. doi:10.3389/fnut.2017.00059
- Mohseni R, Mohseni F, Alizadeh S, Abbasi S. The Association of Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet with the risk of colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis of observational studies.Nutr Cancer. 2020;72(5):778-790. doi:10.1080/01635581.2019.1651880
- Lieberman DA, Weiss DG, Bond JH, Ahnen DJ, Garewal H, Chejfec G. Use of colonoscopy to screen asymptomatic adults for colorectal cancer. Veterans Affairs Cooperative Study Group 380. N Engl J Med. 2000;343(3):162-168. doi:10.1056/NEJM200007203430301
- Developing the Healthy Eating Index (HEI) | EGRP/ DCCPS/NCI/NIH. Accessed July 22, 2025. https://epi.grants.cancer.gov/hei/developing.html#2015c
- Reeve E, Piccici F, Feairheller DL. Validation of a Mediterranean diet scoring system for intervention based research. J Nutr Med Diet Care. 2021;7(1):053. doi:10.23937/2572-3278/1510053
- Günther AL, Liese AD, Bell RA, et al. ASSOCIATION BETWEEN THE DIETARY APPROACHES TO HYPERTENSION (DASH) DIET AND HYPERTENSION IN YOUTH WITH DIABETES. Hypertens Dallas Tex 1979. 2009;53(1):6-12. doi:10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.108.116665
- Buckland G, Agudo A, Luján L, et al. Adherence to a Mediterranean diet and risk of gastric adenocarcinoma within the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC) cohort study. Am J Clin Nutr. 2010;91(2):381- 390. doi:10.3945/ajcn.2009.28209
- Rimm EB, Giovannucci EL, Stampfer MJ, Colditz GA, Litin LB, Willett WC. Reproducibility and validity of an expanded self-administered semiquantitative food frequency questionnaire among male health professionals. Am J Epidemiol. 1992;135(10):1114-1126. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a116211
- Charlson ME, Pompei P, Ales KL, MacKenzie CR. A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longitudinal studies: development and validation. J Chronic Dis. 1987;40(5):373-383. doi:10.1016/0021-9681(87)90171-8
- Lieberman DA, Weiss DG, Harford WV, et al. Fiveyear colon surveillance after screening colonoscopy. Gastroenterology. 2007;133(4):1077-1085. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2007.07.006
- Lieberman D, Sullivan BA, Hauser ER, et al. Baseline colonoscopy findings associated with 10-year outcomes in a screening cohort undergoing colonoscopy surveillance. Gastroenterology. 2020;158(4):862-874.e8. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2019.07.052
- PROC LOGISTIC: PROC LOGISTIC Statement : SAS/STAT(R) 9.22 User’s Guide. Accessed July 22, 2025. https://support.sas.com/documentation/cdl/en/statug/63347/HTML/default/viewer.htm#statug_logistic_sect004.htm
- PROC MULTTEST: PROC MULTTEST Statement : SAS/ STAT(R) 9.22 User’s Guide. Accessed July 22, 2025. https://support.sas.com/documentation/cdl/en/statug/63347/HTML/default/viewer.htm#statug_multtest_sect005.htm
- Elston DM. Participation bias, self-selection bias, and response bias. J Am Acad Dermatol. Published online June 18, 2021. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.06.025
- Sansbury LB, Wanke K, Albert PS, et al. The effect of strict adherence to a high-fiber, high-fruit and -vegetable, and low-fat eating pattern on adenoma recurrence. Am J Epidemiol. 2009;170(5):576-584. doi:10.1093/aje/kwp169
- Borgas P, Gonzalez G, Veselkov K, Mirnezami R. Phytochemically rich dietary components and the risk of colorectal cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. World J Clin Oncol. 2021;12(6):482- 499. doi:10.5306/wjco.v12.i6.482
- Papadimitriou N, Markozannes G, Kanellopoulou A, et al. An umbrella review of the evidence associating diet and cancer risk at 11 anatomical sites. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):4579. doi:10.1038/s41467-021-24861-8
- Johnston BC, Zeraatkar D, Han MA, et al. Unprocessed red meat and processed meat consumption: dietary guideline recommendations from the nutritional recommendations (NutriRECS) Consortium. Ann Intern Med. 2019;171(10):756-764. doi:10.7326/M19-1621
- Kim M, Park K. Dietary fat intake and risk of colorectal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective studies. Nutrients. 2018;10(12):1963. doi:10.3390/nu10121963
- Lu Y, Li D, Wang L, et al. Comprehensive investigation on associations between dietary intake and blood levels of fatty acids and colorectal cancer risk. Nutrients. 2023;15(3):730. doi:10.3390/nu15030730
- Gherasim A, Arhire LI, Ni.a O, Popa AD, Graur M, Mihalache L. The relationship between lifestyle components and dietary patterns. Proc Nutr Soc. 2020;79(3):311-323. doi:10.1017/S0029665120006898
- Hullings AG, Sinha R, Liao LM, Freedman ND, Graubard BI, Loftfield E. Whole grain and dietary fiber intake and risk of colorectal cancer in the NIH-AARP Diet and Health Study cohort. Am J Clin Nutr. 2020;112(3):603- 612. doi:10.1093/ajcn/nqaa161
- Ocvirk S, Wilson AS, Appolonia CN, Thomas TK, O’Keefe SJD. Fiber, fat, and colorectal cancer: new insight into modifiable dietary risk factors. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2019;21(11):62. doi:10.1007/s11894-019-0725-2
- O’Keefe SJD. Diet, microorganisms and their metabolites, and colon cancer. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;13(12):691-706. doi:10.1038/nrgastro.2016.165
- The health benefits and side effects of Butyrate Cleveland Clinic. July 11, 2022. Accessed July 22, 2025. https://health.clevelandclinic.org/butyrate-benefits/
- Knudsen MD, Wang L, Wang K, et al. Changes in lifestyle factors after endoscopic screening: a prospective study in the United States. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol Off ClinPract J Am Gastroenterol Assoc. 2022;20(6):e1240-e1249. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2021.07.014
- Thorpe MG, Milte CM, Crawford D, McNaughton SA. Education and lifestyle predict change in dietary patterns and diet quality of adults 55 years and over. Nutr J. 2019;18(1):67. doi:10.1186/s12937-019-0495-6
- Chapman K, Ogden J. How do people change their diet?: an exploration into mechanisms of dietary change. J Health Psychol. 2009;14(8):1229-1242. doi:10.1177/1359105309342289
- Djoussé L, Petrone AB, Weir NL, et al. Repeated versus single measurement of plasma omega-3 fatty acids and risk of heart failure. Eur J Nutr. 2014;53(6):1403-1408. doi:10.1007/s00394-013-0642-3
- Bach-Faig A, Berry EM, Lairon D, et al. Mediterranean diet pyramid today. Science and cultural updates. Public Health Nutr. 2011;14(12A):2274-2284. doi:10.1017/S1368980011002515
- Miller PE, Cross AJ, Subar AF, et al. Comparison of 4 established DASH diet indexes: examining associations of index scores and colorectal cancer123. Am J Clin Nutr. 2013;98(3):794-803. doi:10.3945/ajcn.113.063602
- Krebs-Smith SM, Pannucci TE, Subar AF, et al. Update of the Healthy Eating Index: HEI-2015. J Acad Nutr Diet. 2018;118(9):1591-1602. doi:10.1016/j.jand.2018.05.021
- P.R. Pehrsson, Cutrufelli RL, Gebhardt SE, et al. USDA Database for the Added Sugars Content of Selected Foods. USDA; 2005. www.ars.usda.gov/nutrientdata
- Zauber AG, Winawer SJ, O’Brien MJ, et al. Colonoscopic polypectomy and long-term prevention of colorectalcancer deaths. N Engl J Med. 2012;366(8):687-696. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1100370
- Nishihara R, Wu K, Lochhead P, et al. Long-term colorectal-cancer incidence and mortality after lower endoscopy. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(12):1095-1105. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1301969
- Bretthauer M, Løberg M, Wieszczy P, et al. Effect of colonoscopy screening on risks of colorectal cancer and related death. N Engl J Med. 2022;387(17):1547-1556. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2208375
- Cottet V, Bonithon-Kopp C, Kronborg O, et al. Dietary patterns and the risk of colorectal adenoma recurrence in a European intervention trial. Eur J Cancer Prev. 2005;14(1):21.
- Miller PE, Lesko SM, Muscat JE, Lazarus P, Hartman TJ. Dietary patterns and colorectal adenoma and cancer risk: a review of the epidemiological evidence. Nutr Cancer. 2010;62(4):413-424. doi:10.1080/01635580903407114
- Godos J, Bella F, Torrisi A, Sciacca S, Galvano F, Grosso G. Dietary patterns and risk of colorectal adenoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. J Hum Nutr Diet Off J Br Diet Assoc. 2016;29(6):757-767. doi:10.1111/jhn.12395
- Haggar FA, Boushey RP. Colorectal cancer epidemiology: incidence, mortality, survival, and risk factors. Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 2009;22(4):191-197. doi:10.1055/s-0029-1242458
- Dong D, Stewart H, Carlson AC. An Examination of Veterans’ Diet Quality. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Economic Research Service; 2019:32.
- El-Halabi MM, Rex DK, Saito A, Eckert GJ, Kahi CJ. Defining adenoma detection rate benchmarks in average-risk male veterans. Gastrointest Endosc. 2019;89(1):137-143. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2018.08.021
- Alberts DS, Hess LM, eds. Fundamentals of Cancer Prevention. Springer International Publishing; 2019. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-15935-1
- Dahm CC, Keogh RH, Spencer EA, et al. Dietary fiber and colorectal cancer risk: a nested case-control study using food diaries. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2010;102(9):614-626. doi:10.1093/jnci/djq092
- Aune D, Lau R, Chan DSM, et al. Dairy products and colorectal cancer risk: a systematic review and metaanalysis of cohort studies. Ann Oncol. 2012;23(1):37-45. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdr269
- Lee JE, Li H, Chan AT, et al. Circulating levels of vitamin D and colon and rectal cancer: the Physicians’ Health Study and a meta-analysis of prospective studies. Cancer Prev Res Phila Pa. 2011;4(5):735-743. doi:10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-10-0289
- Carroll C, Cooper K, Papaioannou D, Hind D, Pilgrim H, Tappenden P. Supplemental calcium in the chemoprevention of colorectal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Ther. 2010;32(5):789-803. doi:10.1016/j.clinthera.2010.04.024
- Park Y, Spiegelman D, Hunter DJ, et al. Intakes of vitamins A, C, and E and use of multiple vitamin supplements and risk of colon cancer: a pooled analysis of prospective cohort studies. Cancer Causes Control CCC. 2010;21(11):1745- 1757. doi:10.1007/s10552-010-9549-y
- Alexander DD, Weed DL, Miller PE, Mohamed MA. Red meat and colorectal cancer: a quantitative update on the state of the epidemiologic science. J Am Coll Nutr. 2015;34(6):521-543. doi:10.1080/07315724.2014.992553
- Park SY, Wilkens LR, Setiawan VW, Monroe KR, Haiman CA, Le Marchand L. Alcohol intake and colorectal cancer risk in the multiethnic cohort study. Am J Epidemiol. 2019;188(1):67-76. doi:10.1093/aje/kwy208
- Lieberman DA. Risk Factors for advanced colonic neoplasia and hyperplastic polyps in asymptomatic individuals. JAMA. 2003;290(22):2959. doi:10.1001/jama.290.22.2959
- Archambault AN, Jeon J, Lin Y, et al. Risk stratification for early-onset colorectal cancer using a combination of genetic and environmental risk scores: an international multi-center study. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2022;114(4):528-539. doi:10.1093/jnci/djac003
- Carr PR, Weigl K, Edelmann D, et al. Estimation of absolute risk of colorectal cancer based on healthy lifestyle, genetic risk, and colonoscopy status in a populationbased study. Gastroenterology. 2020;159(1):129-138.e9. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2020.03.016
- Sullivan BA, Qin X, Miller C, et al. Screening colonoscopy findings are associated with noncolorectal cancer mortality. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2022;13(4):e00479. doi:10.14309/ctg.0000000000000479
- Erben V, Carr PR, Holleczek B, Stegmaier C, Hoffmeister M, Brenner H. Dietary patterns and risk of advanced colorectal neoplasms: A large population based screening study in Germany. Prev Med. 2018;111:101-109. doi:10.1016/j.ypmed.2018.02.025
- Donovan MG, Selmin OI, Doetschman TC, Romagnolo DF. Mediterranean diet: prevention of colorectal cancer. Front Nutr. 2017;4:59. doi:10.3389/fnut.2017.00059
- Mohseni R, Mohseni F, Alizadeh S, Abbasi S. The Association of Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet with the risk of colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis of observational studies.Nutr Cancer. 2020;72(5):778-790. doi:10.1080/01635581.2019.1651880
- Lieberman DA, Weiss DG, Bond JH, Ahnen DJ, Garewal H, Chejfec G. Use of colonoscopy to screen asymptomatic adults for colorectal cancer. Veterans Affairs Cooperative Study Group 380. N Engl J Med. 2000;343(3):162-168. doi:10.1056/NEJM200007203430301
- Developing the Healthy Eating Index (HEI) | EGRP/ DCCPS/NCI/NIH. Accessed July 22, 2025. https://epi.grants.cancer.gov/hei/developing.html#2015c
- Reeve E, Piccici F, Feairheller DL. Validation of a Mediterranean diet scoring system for intervention based research. J Nutr Med Diet Care. 2021;7(1):053. doi:10.23937/2572-3278/1510053
- Günther AL, Liese AD, Bell RA, et al. ASSOCIATION BETWEEN THE DIETARY APPROACHES TO HYPERTENSION (DASH) DIET AND HYPERTENSION IN YOUTH WITH DIABETES. Hypertens Dallas Tex 1979. 2009;53(1):6-12. doi:10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.108.116665
- Buckland G, Agudo A, Luján L, et al. Adherence to a Mediterranean diet and risk of gastric adenocarcinoma within the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC) cohort study. Am J Clin Nutr. 2010;91(2):381- 390. doi:10.3945/ajcn.2009.28209
- Rimm EB, Giovannucci EL, Stampfer MJ, Colditz GA, Litin LB, Willett WC. Reproducibility and validity of an expanded self-administered semiquantitative food frequency questionnaire among male health professionals. Am J Epidemiol. 1992;135(10):1114-1126. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a116211
- Charlson ME, Pompei P, Ales KL, MacKenzie CR. A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longitudinal studies: development and validation. J Chronic Dis. 1987;40(5):373-383. doi:10.1016/0021-9681(87)90171-8
- Lieberman DA, Weiss DG, Harford WV, et al. Fiveyear colon surveillance after screening colonoscopy. Gastroenterology. 2007;133(4):1077-1085. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2007.07.006
- Lieberman D, Sullivan BA, Hauser ER, et al. Baseline colonoscopy findings associated with 10-year outcomes in a screening cohort undergoing colonoscopy surveillance. Gastroenterology. 2020;158(4):862-874.e8. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2019.07.052
- PROC LOGISTIC: PROC LOGISTIC Statement : SAS/STAT(R) 9.22 User’s Guide. Accessed July 22, 2025. https://support.sas.com/documentation/cdl/en/statug/63347/HTML/default/viewer.htm#statug_logistic_sect004.htm
- PROC MULTTEST: PROC MULTTEST Statement : SAS/ STAT(R) 9.22 User’s Guide. Accessed July 22, 2025. https://support.sas.com/documentation/cdl/en/statug/63347/HTML/default/viewer.htm#statug_multtest_sect005.htm
- Elston DM. Participation bias, self-selection bias, and response bias. J Am Acad Dermatol. Published online June 18, 2021. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.06.025
- Sansbury LB, Wanke K, Albert PS, et al. The effect of strict adherence to a high-fiber, high-fruit and -vegetable, and low-fat eating pattern on adenoma recurrence. Am J Epidemiol. 2009;170(5):576-584. doi:10.1093/aje/kwp169
- Borgas P, Gonzalez G, Veselkov K, Mirnezami R. Phytochemically rich dietary components and the risk of colorectal cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. World J Clin Oncol. 2021;12(6):482- 499. doi:10.5306/wjco.v12.i6.482
- Papadimitriou N, Markozannes G, Kanellopoulou A, et al. An umbrella review of the evidence associating diet and cancer risk at 11 anatomical sites. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):4579. doi:10.1038/s41467-021-24861-8
- Johnston BC, Zeraatkar D, Han MA, et al. Unprocessed red meat and processed meat consumption: dietary guideline recommendations from the nutritional recommendations (NutriRECS) Consortium. Ann Intern Med. 2019;171(10):756-764. doi:10.7326/M19-1621
- Kim M, Park K. Dietary fat intake and risk of colorectal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective studies. Nutrients. 2018;10(12):1963. doi:10.3390/nu10121963
- Lu Y, Li D, Wang L, et al. Comprehensive investigation on associations between dietary intake and blood levels of fatty acids and colorectal cancer risk. Nutrients. 2023;15(3):730. doi:10.3390/nu15030730
- Gherasim A, Arhire LI, Ni.a O, Popa AD, Graur M, Mihalache L. The relationship between lifestyle components and dietary patterns. Proc Nutr Soc. 2020;79(3):311-323. doi:10.1017/S0029665120006898
- Hullings AG, Sinha R, Liao LM, Freedman ND, Graubard BI, Loftfield E. Whole grain and dietary fiber intake and risk of colorectal cancer in the NIH-AARP Diet and Health Study cohort. Am J Clin Nutr. 2020;112(3):603- 612. doi:10.1093/ajcn/nqaa161
- Ocvirk S, Wilson AS, Appolonia CN, Thomas TK, O’Keefe SJD. Fiber, fat, and colorectal cancer: new insight into modifiable dietary risk factors. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2019;21(11):62. doi:10.1007/s11894-019-0725-2
- O’Keefe SJD. Diet, microorganisms and their metabolites, and colon cancer. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;13(12):691-706. doi:10.1038/nrgastro.2016.165
- The health benefits and side effects of Butyrate Cleveland Clinic. July 11, 2022. Accessed July 22, 2025. https://health.clevelandclinic.org/butyrate-benefits/
- Knudsen MD, Wang L, Wang K, et al. Changes in lifestyle factors after endoscopic screening: a prospective study in the United States. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol Off ClinPract J Am Gastroenterol Assoc. 2022;20(6):e1240-e1249. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2021.07.014
- Thorpe MG, Milte CM, Crawford D, McNaughton SA. Education and lifestyle predict change in dietary patterns and diet quality of adults 55 years and over. Nutr J. 2019;18(1):67. doi:10.1186/s12937-019-0495-6
- Chapman K, Ogden J. How do people change their diet?: an exploration into mechanisms of dietary change. J Health Psychol. 2009;14(8):1229-1242. doi:10.1177/1359105309342289
- Djoussé L, Petrone AB, Weir NL, et al. Repeated versus single measurement of plasma omega-3 fatty acids and risk of heart failure. Eur J Nutr. 2014;53(6):1403-1408. doi:10.1007/s00394-013-0642-3
- Bach-Faig A, Berry EM, Lairon D, et al. Mediterranean diet pyramid today. Science and cultural updates. Public Health Nutr. 2011;14(12A):2274-2284. doi:10.1017/S1368980011002515
- Miller PE, Cross AJ, Subar AF, et al. Comparison of 4 established DASH diet indexes: examining associations of index scores and colorectal cancer123. Am J Clin Nutr. 2013;98(3):794-803. doi:10.3945/ajcn.113.063602
- Krebs-Smith SM, Pannucci TE, Subar AF, et al. Update of the Healthy Eating Index: HEI-2015. J Acad Nutr Diet. 2018;118(9):1591-1602. doi:10.1016/j.jand.2018.05.021
- P.R. Pehrsson, Cutrufelli RL, Gebhardt SE, et al. USDA Database for the Added Sugars Content of Selected Foods. USDA; 2005. www.ars.usda.gov/nutrientdata
Associations Between Prescreening Dietary Patterns and Longitudinal Colonoscopy Outcomes in Veterans
Associations Between Prescreening Dietary Patterns and Longitudinal Colonoscopy Outcomes in Veterans
Chemotherapy Linked to Brain Atrophy in Patients With Breast Cancer
Patients with breast cancer who undergo chemotherapy may face an increased risk for brain atrophy and cognitive decline, new findings from a pilot study suggest.
Memory problems in patients with cancer may not stem solely from stress or anxiety related to their diagnosis but could reflect underlying changes in brain structure, study investigator Paul Edison, PhD, MPhil, professor of neuroscience and clinical professor of neurology at Imperial College London, England, told this news organization.
While the findings suggest that chemotherapy may contribute to neuronal damage, the researchers noted that many aspects of the relationship between treatment and brain changes remain unclear.
Edison highlighted three key areas that require further investigation — uncovering the mechanisms driving brain atrophy, determining the proportion of patients affected, and identifying effective prevention strategies.
Another investigator on the study, Laura Kenny, MD, PhD, associate professor and consultant medical oncologist at Imperial College London, noted that the issue has received limited attention to date but expressed hope that the findings will raise awareness and encourage further research, given its clinical importance.
The findings were presented on July 29 at the Alzheimer’s Association International Conference (AAIC) 2025.
Investigating Cognitive Impact
Advances in chemotherapeutic agents have improved survival rates in patients with cancer. However, challenges persist regarding the long-term impact of these drugs.
Chemotherapy-associated cognitive impairment, often referred to as “brain fog” or “chemobrain,” affects approximately one third of patients with breast cancer following treatment.
While cognitive decline resolves within 12 months for some patients, others experience persistent effects that may elevate the risk for neurodegenerative conditions, Edison explained.
To evaluate the impact of chemotherapy on the brain, investigators studied 328 women with nonmetastatic breast cancer who had undergone chemotherapy within the past 12 months.
Patients received either anthracycline — a drug derived from the Streptomyces peucetius bacterium — or taxanes such as docetaxel and paclitaxel, both commonly used in breast cancer treatment, or a combination of these agents. In addition, some patients may also have had hormone therapy at some point during treatment, said Kenny.
Participants completed neurocognitive prescreening tests every 3 months using a specialized artificial intelligence–driven platform, allowing them to take detailed memory assessments online from home.
Among those prescreened, 18 individuals with lower neurocognitive scores (mean age, 55 years) and 19 cognitively normal control individuals without breast cancer (mean age, 67 years) underwent comprehensive, in-person, neurocognitive evaluations and MRI scans.
Researchers analyzed the scans using region of interest (ROI) and voxel-based morphometry (VBM), which uses sophisticated computer software, to assess gray matter volumes and surface areas.
The ROI analysis revealed significant reductions in gray matter volume (measured in mm3) and surface area (measured in mm2) among patients experiencing chemobrain, particularly affecting the isthmus cingulate and pars opercularis, with changes extending into the orbitofrontal and temporal regions.
Significant Atrophy
The VBM analysis confirmed significant atrophy in the frontal, parietal, and cingulate regions of patients with chemobrain compared with control individuals (P < .05). Edison noted that this pattern overlaps with brain changes typically observed in Alzheimer’s disease and vascular cognitive impairment.
For both analyses, “we demonstrated there is some amount of shrinkage in the brain among patients with chemobrain,” he said. “The fact that controls are older means the results are even more significant as there’s more brain atrophy as people age.”
Some of the affected brain regions may be linked to impaired memory, a hallmark of Alzheimer’s disease, but Edison cautioned that given the small sample size this finding should be interpreted with caution.
While the analysis demonstrated overall lower brain volumes in patients with “chemobrain” compared with controls, Edison emphasized that this finding reflects a single time point and does not indicate brain shrinkage over time.
Other events, including stroke — can also cause brain changes.
Edison highlighted the importance of determining the significance of these brain changes, how they affect patients and whether they can be prevented.
In-person neurocognitive testing revealed significantly reduced semantic and verbal fluency, as well as lower Mini-Mental State Examination scores in patients with chemobrain. Edison noted that these results support the MRI findings.
The team plans to follow patients to track brain changes and memory recovery, Kenny said. While patients with breast cancer are a common focus, the researchers intend to expand the study to other cancers in both men and women, said Kenny.
Based on discussions with her oncology colleagues, Kenny noted that many patients anecdotally report experiencing memory problems during chemotherapy.
More Research Needed
Commenting for this news organization, Rebecca M. Edelmayer, PhD, vice president, scientific engagement, at the Alzheimer’s Association, said the research may help shed light on why women are more likely to develop dementia than men.
For years now, experts have been trying to figure out what puts women at higher risk for AD and other dementias, said Edelmayer.
“We still don’t understand whether this involves biologically driven risk factors or socially driven risk factors.”
Research linking treatments for other health conditions to increased memory problems may offer some clues, she noted, suggesting a potential avenue for further investigation into the intersection of chemotherapy and neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s.
However, Edelmayer emphasized that this line of research is still in its infancy. Much more work is needed to determine whether there is a direct cause-and-effect relationship with specific chemotherapy drugs, and whether some patients may already be predisposed or at higher risk for cognitive decline, she said.
Also commenting for this news organization, Eric Brown, MD, associate scientist and associate chief of geriatric psychiatry at the Centre for Addiction and Mental Health in Toronto, raised concerns about the study’s design.
One issue, he noted, is that the researchers did not image all patients who received chemotherapy but instead selected those with the most significant cognitive impairment. As a result, the findings may not have reflected outcomes in the average post-chemotherapy patients but rather represent the most severely affected subgroup.
Brown pointed out that the study did not clarify whether this subgroup had comorbid conditions. It’s possible, he said, that some individuals may have had Alzheimer’s disease or other forms of dementia unrelated to chemotherapy.
He agreed that tracking longitudinal changes in both cognitive scores and neuroimaging — comparing patients who receive chemotherapy with those who do not — would be a valuable next step.
The investigators, Edelmayer, and Brown reported no relevant conflicts of interest. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients with breast cancer who undergo chemotherapy may face an increased risk for brain atrophy and cognitive decline, new findings from a pilot study suggest.
Memory problems in patients with cancer may not stem solely from stress or anxiety related to their diagnosis but could reflect underlying changes in brain structure, study investigator Paul Edison, PhD, MPhil, professor of neuroscience and clinical professor of neurology at Imperial College London, England, told this news organization.
While the findings suggest that chemotherapy may contribute to neuronal damage, the researchers noted that many aspects of the relationship between treatment and brain changes remain unclear.
Edison highlighted three key areas that require further investigation — uncovering the mechanisms driving brain atrophy, determining the proportion of patients affected, and identifying effective prevention strategies.
Another investigator on the study, Laura Kenny, MD, PhD, associate professor and consultant medical oncologist at Imperial College London, noted that the issue has received limited attention to date but expressed hope that the findings will raise awareness and encourage further research, given its clinical importance.
The findings were presented on July 29 at the Alzheimer’s Association International Conference (AAIC) 2025.
Investigating Cognitive Impact
Advances in chemotherapeutic agents have improved survival rates in patients with cancer. However, challenges persist regarding the long-term impact of these drugs.
Chemotherapy-associated cognitive impairment, often referred to as “brain fog” or “chemobrain,” affects approximately one third of patients with breast cancer following treatment.
While cognitive decline resolves within 12 months for some patients, others experience persistent effects that may elevate the risk for neurodegenerative conditions, Edison explained.
To evaluate the impact of chemotherapy on the brain, investigators studied 328 women with nonmetastatic breast cancer who had undergone chemotherapy within the past 12 months.
Patients received either anthracycline — a drug derived from the Streptomyces peucetius bacterium — or taxanes such as docetaxel and paclitaxel, both commonly used in breast cancer treatment, or a combination of these agents. In addition, some patients may also have had hormone therapy at some point during treatment, said Kenny.
Participants completed neurocognitive prescreening tests every 3 months using a specialized artificial intelligence–driven platform, allowing them to take detailed memory assessments online from home.
Among those prescreened, 18 individuals with lower neurocognitive scores (mean age, 55 years) and 19 cognitively normal control individuals without breast cancer (mean age, 67 years) underwent comprehensive, in-person, neurocognitive evaluations and MRI scans.
Researchers analyzed the scans using region of interest (ROI) and voxel-based morphometry (VBM), which uses sophisticated computer software, to assess gray matter volumes and surface areas.
The ROI analysis revealed significant reductions in gray matter volume (measured in mm3) and surface area (measured in mm2) among patients experiencing chemobrain, particularly affecting the isthmus cingulate and pars opercularis, with changes extending into the orbitofrontal and temporal regions.
Significant Atrophy
The VBM analysis confirmed significant atrophy in the frontal, parietal, and cingulate regions of patients with chemobrain compared with control individuals (P < .05). Edison noted that this pattern overlaps with brain changes typically observed in Alzheimer’s disease and vascular cognitive impairment.
For both analyses, “we demonstrated there is some amount of shrinkage in the brain among patients with chemobrain,” he said. “The fact that controls are older means the results are even more significant as there’s more brain atrophy as people age.”
Some of the affected brain regions may be linked to impaired memory, a hallmark of Alzheimer’s disease, but Edison cautioned that given the small sample size this finding should be interpreted with caution.
While the analysis demonstrated overall lower brain volumes in patients with “chemobrain” compared with controls, Edison emphasized that this finding reflects a single time point and does not indicate brain shrinkage over time.
Other events, including stroke — can also cause brain changes.
Edison highlighted the importance of determining the significance of these brain changes, how they affect patients and whether they can be prevented.
In-person neurocognitive testing revealed significantly reduced semantic and verbal fluency, as well as lower Mini-Mental State Examination scores in patients with chemobrain. Edison noted that these results support the MRI findings.
The team plans to follow patients to track brain changes and memory recovery, Kenny said. While patients with breast cancer are a common focus, the researchers intend to expand the study to other cancers in both men and women, said Kenny.
Based on discussions with her oncology colleagues, Kenny noted that many patients anecdotally report experiencing memory problems during chemotherapy.
More Research Needed
Commenting for this news organization, Rebecca M. Edelmayer, PhD, vice president, scientific engagement, at the Alzheimer’s Association, said the research may help shed light on why women are more likely to develop dementia than men.
For years now, experts have been trying to figure out what puts women at higher risk for AD and other dementias, said Edelmayer.
“We still don’t understand whether this involves biologically driven risk factors or socially driven risk factors.”
Research linking treatments for other health conditions to increased memory problems may offer some clues, she noted, suggesting a potential avenue for further investigation into the intersection of chemotherapy and neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s.
However, Edelmayer emphasized that this line of research is still in its infancy. Much more work is needed to determine whether there is a direct cause-and-effect relationship with specific chemotherapy drugs, and whether some patients may already be predisposed or at higher risk for cognitive decline, she said.
Also commenting for this news organization, Eric Brown, MD, associate scientist and associate chief of geriatric psychiatry at the Centre for Addiction and Mental Health in Toronto, raised concerns about the study’s design.
One issue, he noted, is that the researchers did not image all patients who received chemotherapy but instead selected those with the most significant cognitive impairment. As a result, the findings may not have reflected outcomes in the average post-chemotherapy patients but rather represent the most severely affected subgroup.
Brown pointed out that the study did not clarify whether this subgroup had comorbid conditions. It’s possible, he said, that some individuals may have had Alzheimer’s disease or other forms of dementia unrelated to chemotherapy.
He agreed that tracking longitudinal changes in both cognitive scores and neuroimaging — comparing patients who receive chemotherapy with those who do not — would be a valuable next step.
The investigators, Edelmayer, and Brown reported no relevant conflicts of interest. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients with breast cancer who undergo chemotherapy may face an increased risk for brain atrophy and cognitive decline, new findings from a pilot study suggest.
Memory problems in patients with cancer may not stem solely from stress or anxiety related to their diagnosis but could reflect underlying changes in brain structure, study investigator Paul Edison, PhD, MPhil, professor of neuroscience and clinical professor of neurology at Imperial College London, England, told this news organization.
While the findings suggest that chemotherapy may contribute to neuronal damage, the researchers noted that many aspects of the relationship between treatment and brain changes remain unclear.
Edison highlighted three key areas that require further investigation — uncovering the mechanisms driving brain atrophy, determining the proportion of patients affected, and identifying effective prevention strategies.
Another investigator on the study, Laura Kenny, MD, PhD, associate professor and consultant medical oncologist at Imperial College London, noted that the issue has received limited attention to date but expressed hope that the findings will raise awareness and encourage further research, given its clinical importance.
The findings were presented on July 29 at the Alzheimer’s Association International Conference (AAIC) 2025.
Investigating Cognitive Impact
Advances in chemotherapeutic agents have improved survival rates in patients with cancer. However, challenges persist regarding the long-term impact of these drugs.
Chemotherapy-associated cognitive impairment, often referred to as “brain fog” or “chemobrain,” affects approximately one third of patients with breast cancer following treatment.
While cognitive decline resolves within 12 months for some patients, others experience persistent effects that may elevate the risk for neurodegenerative conditions, Edison explained.
To evaluate the impact of chemotherapy on the brain, investigators studied 328 women with nonmetastatic breast cancer who had undergone chemotherapy within the past 12 months.
Patients received either anthracycline — a drug derived from the Streptomyces peucetius bacterium — or taxanes such as docetaxel and paclitaxel, both commonly used in breast cancer treatment, or a combination of these agents. In addition, some patients may also have had hormone therapy at some point during treatment, said Kenny.
Participants completed neurocognitive prescreening tests every 3 months using a specialized artificial intelligence–driven platform, allowing them to take detailed memory assessments online from home.
Among those prescreened, 18 individuals with lower neurocognitive scores (mean age, 55 years) and 19 cognitively normal control individuals without breast cancer (mean age, 67 years) underwent comprehensive, in-person, neurocognitive evaluations and MRI scans.
Researchers analyzed the scans using region of interest (ROI) and voxel-based morphometry (VBM), which uses sophisticated computer software, to assess gray matter volumes and surface areas.
The ROI analysis revealed significant reductions in gray matter volume (measured in mm3) and surface area (measured in mm2) among patients experiencing chemobrain, particularly affecting the isthmus cingulate and pars opercularis, with changes extending into the orbitofrontal and temporal regions.
Significant Atrophy
The VBM analysis confirmed significant atrophy in the frontal, parietal, and cingulate regions of patients with chemobrain compared with control individuals (P < .05). Edison noted that this pattern overlaps with brain changes typically observed in Alzheimer’s disease and vascular cognitive impairment.
For both analyses, “we demonstrated there is some amount of shrinkage in the brain among patients with chemobrain,” he said. “The fact that controls are older means the results are even more significant as there’s more brain atrophy as people age.”
Some of the affected brain regions may be linked to impaired memory, a hallmark of Alzheimer’s disease, but Edison cautioned that given the small sample size this finding should be interpreted with caution.
While the analysis demonstrated overall lower brain volumes in patients with “chemobrain” compared with controls, Edison emphasized that this finding reflects a single time point and does not indicate brain shrinkage over time.
Other events, including stroke — can also cause brain changes.
Edison highlighted the importance of determining the significance of these brain changes, how they affect patients and whether they can be prevented.
In-person neurocognitive testing revealed significantly reduced semantic and verbal fluency, as well as lower Mini-Mental State Examination scores in patients with chemobrain. Edison noted that these results support the MRI findings.
The team plans to follow patients to track brain changes and memory recovery, Kenny said. While patients with breast cancer are a common focus, the researchers intend to expand the study to other cancers in both men and women, said Kenny.
Based on discussions with her oncology colleagues, Kenny noted that many patients anecdotally report experiencing memory problems during chemotherapy.
More Research Needed
Commenting for this news organization, Rebecca M. Edelmayer, PhD, vice president, scientific engagement, at the Alzheimer’s Association, said the research may help shed light on why women are more likely to develop dementia than men.
For years now, experts have been trying to figure out what puts women at higher risk for AD and other dementias, said Edelmayer.
“We still don’t understand whether this involves biologically driven risk factors or socially driven risk factors.”
Research linking treatments for other health conditions to increased memory problems may offer some clues, she noted, suggesting a potential avenue for further investigation into the intersection of chemotherapy and neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s.
However, Edelmayer emphasized that this line of research is still in its infancy. Much more work is needed to determine whether there is a direct cause-and-effect relationship with specific chemotherapy drugs, and whether some patients may already be predisposed or at higher risk for cognitive decline, she said.
Also commenting for this news organization, Eric Brown, MD, associate scientist and associate chief of geriatric psychiatry at the Centre for Addiction and Mental Health in Toronto, raised concerns about the study’s design.
One issue, he noted, is that the researchers did not image all patients who received chemotherapy but instead selected those with the most significant cognitive impairment. As a result, the findings may not have reflected outcomes in the average post-chemotherapy patients but rather represent the most severely affected subgroup.
Brown pointed out that the study did not clarify whether this subgroup had comorbid conditions. It’s possible, he said, that some individuals may have had Alzheimer’s disease or other forms of dementia unrelated to chemotherapy.
He agreed that tracking longitudinal changes in both cognitive scores and neuroimaging — comparing patients who receive chemotherapy with those who do not — would be a valuable next step.
The investigators, Edelmayer, and Brown reported no relevant conflicts of interest. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AAIC 2025
These Two Simple Interventions May Cut Colorectal Cancer Recurrence Risk
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
New guidelines have lowered the age to begin screening for colon cancer to 45 years old. Although this change is positive, we’re still seeing advanced cancer in younger patients who haven’t been screened in time.
Once diagnosed, these patients undergo surgery and chemotherapy and often return to us asking, “What can I do now to help myself?”
Two recent studies highlight interventions that are simple, affordable, and actionable today: exercise and aspirin. Let’s take a closer look at the results.
Exercise’s Risk Reduction Potential
The idea that exercise reduces cancer recurrence and mortality is supported by observational data. The mechanistic effects behind this have been ascribed to metabolic growth factors, inflammatory changes, immune function changes, and perhaps even positive impact on sleep.
A study just published in The New England Journal of Medicine examined structured exercise after adjuvant chemotherapy for colon cancer. The phase 3 randomized CHALLENGE trial, mostly conducted at Canadian and Australian centers, recruited patients with resected stage II or III colon cancer (9.8% and 90.2%, respectively) who had completed adjuvant chemotherapy. Patients with recurrences within a year of diagnosis were excluded, as they were more likely to have highly aggressive, biologically active disease.
Patients were randomized to receive healthcare education materials alone or in conjunction with a structured exercise program over a 3-year follow-up period.
The exercise intervention, delivered in person or virtually, focused on increasing recreational aerobic activity over baseline by at least 10 metabolic equivalent task (MET). An increment of 10 MET hours per week is not too vigorous. It is essentially the equivalent of adding about 45-60 minutes of brisk walking or 25-30 minutes of jogging 3-4 times a week.
Patients were asked to increase MET over the first 6 months and then maintain or further increase the amount over the next 2.5 years. They were permitted to structure their own exercise program by choosing the type, frequency, intensity, and duration of aerobic exercise.
The primary endpoint was disease-free survival, with secondary endpoints assessing overall survival, patient-reported outcomes, and other outcomes. Although designed to detect differences at 3 years, follow-up was also performed out to 5 and 8 years.
At a median follow-up of 7.9 years, exercise reduced the relative risk of disease recurrence, new primary cancer, or death by 28% (P = .02). This benefit persisted — and even strengthened — over time, with disease-free survival increasing by 6.4 and 7.1 percentage points at 5 and 8 years, respectively.
Musculoskeletal adverse events were slightly higher in the exercise group compared with the health education group (18.5% vs 11.5%, respectively), but only 10% were directly attributed to the exercise.
There are considerations when interpreting these results. First, there was an attrition over time for compliance and training. It would be interesting to see whether that impacted the results. Second, it’s unclear whether patient pedigree or a genomic pathway may predispose to a benefit here for the exercise group.
But overall, this phase 3 trial provides class 1 evidence supporting exercise as a low-cost, high-impact intervention to reduce cancer recurrence.
Adjuvant Aspirin in Colon Cancer Subset
That’s a perfect segue into another recent study looking at the effects of adjuvant aspirin on the prevention of recurrence.
The ALASCCA trial— conducted across centers in Sweden, Denmark, Finland, and Norway — assessed patients with stage I-III rectal cancer or stage II-III colon cancer. It focused on a subset of patients with an oncogenic abnormality called PIK3CA (phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit alpha).
PIK3CA occurs in approximately a third of colon cancers and is associated with significant chemotherapy resistance and a higher rate of disease progression.
Of the included patients, 1103 (37%) had alterations in the PIK3CA pathway. Researchers randomized patients to receive either 160 mg of aspirin or placebo daily for 3 years, starting within 3 months of surgery.
Among patients with PIK3CA mutations, aspirin dramatically reduced the risk for time to recurrence by nearly 50% at 3 years (P = .044). Adverse events associated with aspirin were minimal, including one case each of gastrointestinal bleeding, hematoma, and allergic reaction.
There is no evidence that higher aspirin doses provide greater prevention of colorectal cancer recurrence. The 160-mg use in the current study is fairly normal, roughly equivalent to two low-dose (81-mg) aspirin tablets.
Now, it’s worth noting that the use of aspirin for the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease was initially recommended by the US Preventive Services Task Force in 2016. This recommendation was then recanted in 2022, when the same group reported limited net benefit to this approach.
Two Proactive Actions
These studies highlight 2 interventions — exercise and aspirin — that are low cost, accessible, and appeal to patients eager to help prevent their cancer from recurring.
Exercise is broadly beneficial and can be recommended immediately.
For aspirin, patients should work with their oncologist to determine their PIK3CA mutation status, as this subgroup appears to benefit the most.
These findings offer patients meaningful, proactive interventions they can apply to support their recovery and reduce the risk of recurrence. Hopefully these new findings will help guide your clinical conversations.
Johnson is a regular contributor to Medscape. He is professor of medicine and chief of gastroenterology at Eastern Virginia Medical School in Norfolk, and a past president of the American College of Gastroenterology. His primary focus is the clinical practice of gastroenterology. He has published extensively in the internal medicine/gastroenterology literature, with principal research interests in esophageal and colon disease, and more recently in sleep and microbiome effects on gastrointestinal health and disease. He disclosed that he is an adviser for ISOThrive.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
New guidelines have lowered the age to begin screening for colon cancer to 45 years old. Although this change is positive, we’re still seeing advanced cancer in younger patients who haven’t been screened in time.
Once diagnosed, these patients undergo surgery and chemotherapy and often return to us asking, “What can I do now to help myself?”
Two recent studies highlight interventions that are simple, affordable, and actionable today: exercise and aspirin. Let’s take a closer look at the results.
Exercise’s Risk Reduction Potential
The idea that exercise reduces cancer recurrence and mortality is supported by observational data. The mechanistic effects behind this have been ascribed to metabolic growth factors, inflammatory changes, immune function changes, and perhaps even positive impact on sleep.
A study just published in The New England Journal of Medicine examined structured exercise after adjuvant chemotherapy for colon cancer. The phase 3 randomized CHALLENGE trial, mostly conducted at Canadian and Australian centers, recruited patients with resected stage II or III colon cancer (9.8% and 90.2%, respectively) who had completed adjuvant chemotherapy. Patients with recurrences within a year of diagnosis were excluded, as they were more likely to have highly aggressive, biologically active disease.
Patients were randomized to receive healthcare education materials alone or in conjunction with a structured exercise program over a 3-year follow-up period.
The exercise intervention, delivered in person or virtually, focused on increasing recreational aerobic activity over baseline by at least 10 metabolic equivalent task (MET). An increment of 10 MET hours per week is not too vigorous. It is essentially the equivalent of adding about 45-60 minutes of brisk walking or 25-30 minutes of jogging 3-4 times a week.
Patients were asked to increase MET over the first 6 months and then maintain or further increase the amount over the next 2.5 years. They were permitted to structure their own exercise program by choosing the type, frequency, intensity, and duration of aerobic exercise.
The primary endpoint was disease-free survival, with secondary endpoints assessing overall survival, patient-reported outcomes, and other outcomes. Although designed to detect differences at 3 years, follow-up was also performed out to 5 and 8 years.
At a median follow-up of 7.9 years, exercise reduced the relative risk of disease recurrence, new primary cancer, or death by 28% (P = .02). This benefit persisted — and even strengthened — over time, with disease-free survival increasing by 6.4 and 7.1 percentage points at 5 and 8 years, respectively.
Musculoskeletal adverse events were slightly higher in the exercise group compared with the health education group (18.5% vs 11.5%, respectively), but only 10% were directly attributed to the exercise.
There are considerations when interpreting these results. First, there was an attrition over time for compliance and training. It would be interesting to see whether that impacted the results. Second, it’s unclear whether patient pedigree or a genomic pathway may predispose to a benefit here for the exercise group.
But overall, this phase 3 trial provides class 1 evidence supporting exercise as a low-cost, high-impact intervention to reduce cancer recurrence.
Adjuvant Aspirin in Colon Cancer Subset
That’s a perfect segue into another recent study looking at the effects of adjuvant aspirin on the prevention of recurrence.
The ALASCCA trial— conducted across centers in Sweden, Denmark, Finland, and Norway — assessed patients with stage I-III rectal cancer or stage II-III colon cancer. It focused on a subset of patients with an oncogenic abnormality called PIK3CA (phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit alpha).
PIK3CA occurs in approximately a third of colon cancers and is associated with significant chemotherapy resistance and a higher rate of disease progression.
Of the included patients, 1103 (37%) had alterations in the PIK3CA pathway. Researchers randomized patients to receive either 160 mg of aspirin or placebo daily for 3 years, starting within 3 months of surgery.
Among patients with PIK3CA mutations, aspirin dramatically reduced the risk for time to recurrence by nearly 50% at 3 years (P = .044). Adverse events associated with aspirin were minimal, including one case each of gastrointestinal bleeding, hematoma, and allergic reaction.
There is no evidence that higher aspirin doses provide greater prevention of colorectal cancer recurrence. The 160-mg use in the current study is fairly normal, roughly equivalent to two low-dose (81-mg) aspirin tablets.
Now, it’s worth noting that the use of aspirin for the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease was initially recommended by the US Preventive Services Task Force in 2016. This recommendation was then recanted in 2022, when the same group reported limited net benefit to this approach.
Two Proactive Actions
These studies highlight 2 interventions — exercise and aspirin — that are low cost, accessible, and appeal to patients eager to help prevent their cancer from recurring.
Exercise is broadly beneficial and can be recommended immediately.
For aspirin, patients should work with their oncologist to determine their PIK3CA mutation status, as this subgroup appears to benefit the most.
These findings offer patients meaningful, proactive interventions they can apply to support their recovery and reduce the risk of recurrence. Hopefully these new findings will help guide your clinical conversations.
Johnson is a regular contributor to Medscape. He is professor of medicine and chief of gastroenterology at Eastern Virginia Medical School in Norfolk, and a past president of the American College of Gastroenterology. His primary focus is the clinical practice of gastroenterology. He has published extensively in the internal medicine/gastroenterology literature, with principal research interests in esophageal and colon disease, and more recently in sleep and microbiome effects on gastrointestinal health and disease. He disclosed that he is an adviser for ISOThrive.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
New guidelines have lowered the age to begin screening for colon cancer to 45 years old. Although this change is positive, we’re still seeing advanced cancer in younger patients who haven’t been screened in time.
Once diagnosed, these patients undergo surgery and chemotherapy and often return to us asking, “What can I do now to help myself?”
Two recent studies highlight interventions that are simple, affordable, and actionable today: exercise and aspirin. Let’s take a closer look at the results.
Exercise’s Risk Reduction Potential
The idea that exercise reduces cancer recurrence and mortality is supported by observational data. The mechanistic effects behind this have been ascribed to metabolic growth factors, inflammatory changes, immune function changes, and perhaps even positive impact on sleep.
A study just published in The New England Journal of Medicine examined structured exercise after adjuvant chemotherapy for colon cancer. The phase 3 randomized CHALLENGE trial, mostly conducted at Canadian and Australian centers, recruited patients with resected stage II or III colon cancer (9.8% and 90.2%, respectively) who had completed adjuvant chemotherapy. Patients with recurrences within a year of diagnosis were excluded, as they were more likely to have highly aggressive, biologically active disease.
Patients were randomized to receive healthcare education materials alone or in conjunction with a structured exercise program over a 3-year follow-up period.
The exercise intervention, delivered in person or virtually, focused on increasing recreational aerobic activity over baseline by at least 10 metabolic equivalent task (MET). An increment of 10 MET hours per week is not too vigorous. It is essentially the equivalent of adding about 45-60 minutes of brisk walking or 25-30 minutes of jogging 3-4 times a week.
Patients were asked to increase MET over the first 6 months and then maintain or further increase the amount over the next 2.5 years. They were permitted to structure their own exercise program by choosing the type, frequency, intensity, and duration of aerobic exercise.
The primary endpoint was disease-free survival, with secondary endpoints assessing overall survival, patient-reported outcomes, and other outcomes. Although designed to detect differences at 3 years, follow-up was also performed out to 5 and 8 years.
At a median follow-up of 7.9 years, exercise reduced the relative risk of disease recurrence, new primary cancer, or death by 28% (P = .02). This benefit persisted — and even strengthened — over time, with disease-free survival increasing by 6.4 and 7.1 percentage points at 5 and 8 years, respectively.
Musculoskeletal adverse events were slightly higher in the exercise group compared with the health education group (18.5% vs 11.5%, respectively), but only 10% were directly attributed to the exercise.
There are considerations when interpreting these results. First, there was an attrition over time for compliance and training. It would be interesting to see whether that impacted the results. Second, it’s unclear whether patient pedigree or a genomic pathway may predispose to a benefit here for the exercise group.
But overall, this phase 3 trial provides class 1 evidence supporting exercise as a low-cost, high-impact intervention to reduce cancer recurrence.
Adjuvant Aspirin in Colon Cancer Subset
That’s a perfect segue into another recent study looking at the effects of adjuvant aspirin on the prevention of recurrence.
The ALASCCA trial— conducted across centers in Sweden, Denmark, Finland, and Norway — assessed patients with stage I-III rectal cancer or stage II-III colon cancer. It focused on a subset of patients with an oncogenic abnormality called PIK3CA (phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit alpha).
PIK3CA occurs in approximately a third of colon cancers and is associated with significant chemotherapy resistance and a higher rate of disease progression.
Of the included patients, 1103 (37%) had alterations in the PIK3CA pathway. Researchers randomized patients to receive either 160 mg of aspirin or placebo daily for 3 years, starting within 3 months of surgery.
Among patients with PIK3CA mutations, aspirin dramatically reduced the risk for time to recurrence by nearly 50% at 3 years (P = .044). Adverse events associated with aspirin were minimal, including one case each of gastrointestinal bleeding, hematoma, and allergic reaction.
There is no evidence that higher aspirin doses provide greater prevention of colorectal cancer recurrence. The 160-mg use in the current study is fairly normal, roughly equivalent to two low-dose (81-mg) aspirin tablets.
Now, it’s worth noting that the use of aspirin for the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease was initially recommended by the US Preventive Services Task Force in 2016. This recommendation was then recanted in 2022, when the same group reported limited net benefit to this approach.
Two Proactive Actions
These studies highlight 2 interventions — exercise and aspirin — that are low cost, accessible, and appeal to patients eager to help prevent their cancer from recurring.
Exercise is broadly beneficial and can be recommended immediately.
For aspirin, patients should work with their oncologist to determine their PIK3CA mutation status, as this subgroup appears to benefit the most.
These findings offer patients meaningful, proactive interventions they can apply to support their recovery and reduce the risk of recurrence. Hopefully these new findings will help guide your clinical conversations.
Johnson is a regular contributor to Medscape. He is professor of medicine and chief of gastroenterology at Eastern Virginia Medical School in Norfolk, and a past president of the American College of Gastroenterology. His primary focus is the clinical practice of gastroenterology. He has published extensively in the internal medicine/gastroenterology literature, with principal research interests in esophageal and colon disease, and more recently in sleep and microbiome effects on gastrointestinal health and disease. He disclosed that he is an adviser for ISOThrive.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Endometrial Cancer: 5 Things to Know
Endometrial cancer is a common type of gynecologic cancer, and its incidence is rising steadily in the United States and globally. Most cases are endometrioid adenocarcinomas, arising from the inner lining of the uterus — the endometrium. While many patients are diagnosed early because of noticeable symptoms like abnormal bleeding, trends in both incidence and mortality are concerning, especially given the persistent racial and socioeconomic disparities in outcomes.
In addition to being the most common uterine malignancy, endometrial cancer is at the forefront of precision oncology in gynecology. The traditional classification systems based on histology and hormone dependence are now being augmented by molecular subtyping that better informs prognosis and treatment. As diagnostic tools, genetic testing, and therapeutic strategies advance, the management of endometrial cancer is becoming increasingly personalized.
Here are five things to know about endometrial cancer:
1. Endometrial cancer is one of the few cancers with increasing mortality.
Endometrial cancer accounts for the majority of uterine cancers in the United States with an overall lifetime risk for women of about 1 in 40. Since the mid-2000s, incidence rates have risen steadily, by > 1% per year, reflecting both lifestyle and environmental factors. Importantly, the disease tends to be diagnosed at an early stage due to the presence of warning signs like postmenopausal bleeding, which contributes to relatively favorable survival outcomes when caught early.
However, mortality trends continue to evolve. From 1999 to 2013, death rates from endometrial cancer in the US declined slightly, but since 2013, they have increased sharply — by > 8% annually — according to recent data. This upward trend in mortality disproportionately affects non-Hispanic Black women, who experience the highest mortality rate (4.7 per 100,000) among all racial and ethnic groups. This disparity is likely caused by a complex interplay of factors, including delays in diagnosis, more aggressive tumor biology, and inequities in access to care. Addressing these disparities remains a key priority in improving outcomes.
2. Risk factors go beyond hormones and age.
Risk factors for endometrial cancer include prolonged exposure to unopposed estrogen, which can result from estrogen-only hormone replacement therapy, higher BMI, and early menarche or late menopause. Nulliparity (having never been pregnant) and older age also increase risk, as does tamoxifen use — a medication commonly prescribed for breast cancer prevention. These factors cumulatively increase endometrial proliferation and the potential for atypical cellular changes. Endometrial hyperplasia, a known precursor to cancer, is often linked to these hormonal imbalances and may require surveillance or treatment.
Beyond estrogen’s influence, a growing body of research is uncovering additional risk contributors. Women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), metabolic syndrome, or diabetes face elevated risk of developing endometrial cancer. Genetic syndromes, particularly Lynch and Cowden syndromes, are associated with significantly increased lifetime risks of endometrial cancer. Environmental exposures, such as the use of hair relaxers, are being investigated as emerging risk factors. Additionally, race remains a risk marker, with Black women not only experiencing higher mortality but also more aggressive subtypes of the disease. These complex, overlapping risks highlight the importance of individualized risk assessment and early intervention strategies.
3. Postmenopausal bleeding is the hallmark symptom — but not the only one.
In endometrial cancer, the majority of cases are diagnosed at an early stage, largely because of the hallmark symptom of postmenopausal bleeding. In addition to bleeding, patients may present with vaginal discharge, pyometra, and even pain and abdominal distension in advanced disease. Any bleeding in a postmenopausal woman should prompt evaluation, as it may signal endometrial hyperplasia or carcinoma. In premenopausal women, irregular or heavy menstrual bleeding may raise suspicion, particularly when accompanied by risk factors such as PCOS.
The diagnostic workup for suspected endometrial cancer in women, particularly those presenting with postmenopausal bleeding, begins with a focused clinical assessment and frequently includes transvaginal ultrasound (TVUS) to evaluate the endometrium. While TVUS can aid in identifying structural abnormalities or suggest malignancy, endometrial sampling is warranted in all postmenopausal women with abnormal bleeding, regardless of endometrial thickness. Office-based biopsy is the preferred initial approach due to its convenience and diagnostic yield; however, if the sample is nondiagnostic or technically difficult to obtain, hysteroscopy with directed biopsy or dilation and curettage should be pursued.
4. Classification systems are evolving to include molecular subtypes.
Historically, endometrial cancers were classified using the World Health Organization system based on histology and by hormone dependence: Type 1 (estrogen-dependent, typically endometrioid and low grade) and Type 2 (non-estrogen dependent, often serous and high grade). Type 1 cancers tend to have a better prognosis and slower progression, while Type 2 cancers are more aggressive and require intensive treatment. While helpful, this binary classification does not fully capture the biological diversity or treatment responsiveness of the disease.
The field is now moving toward molecular classification, which offers a more nuanced understanding. The four main molecular subtypes include: polymerase epsilon (POLE)-mutant, mismatch repair (MMR)-deficient, p53-abnormal, and no specific molecular profile (NSMP). These groups differ in prognosis and therapeutic implications. POLE-mutant tumors with extremely high mutational burdens generally have excellent outcomes and may not require aggressive adjuvant therapy. In contrast, p53-abnormal tumors are associated with chromosomal instability, TP53 mutations, and poor outcomes, necessitating more aggressive multimodal treatment. MMR-deficient tumors are particularly responsive to immunotherapy. These molecular distinctions are changing how clinicians approach risk stratification and management in patients with endometrial cancer.
5. Treatment is increasingly personalized — and immunotherapy is expanding.
The cornerstone of treatment for early-stage endometrial cancer is surgical: total hysterectomy with bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy, often with sentinel node mapping or lymphadenectomy. Adjuvant therapy depends on factors such as stage, grade, histology, and molecular subtype. Fertility-sparing management with progestin therapy is an option for highly selected patients with early-stage, low-grade tumors. Clinical guidelines recommend that fertility desires be addressed prior to initiating treatment, as standard surgical management typically results in loss of reproductive capacity.
For advanced or recurrent disease, treatment becomes more complex and increasingly individualized. Chemotherapy, often with carboplatin and paclitaxel, is standard for stage III/IV and recurrent disease. Molecular findings now guide additional therapy: For instance, MMR-deficient tumors may respond to checkpoint inhibitors. As targeted agents and combination regimens continue to emerge, treatment of endometrial is increasingly focused on precision medicine.
Markman is professor of medical oncology and therapeutics research and President of Medicine & Science at City of Hope in Atlanta and Chicago. He has disclosed relevant financial relationships with AstraZeneca, GSK and Myriad.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Endometrial cancer is a common type of gynecologic cancer, and its incidence is rising steadily in the United States and globally. Most cases are endometrioid adenocarcinomas, arising from the inner lining of the uterus — the endometrium. While many patients are diagnosed early because of noticeable symptoms like abnormal bleeding, trends in both incidence and mortality are concerning, especially given the persistent racial and socioeconomic disparities in outcomes.
In addition to being the most common uterine malignancy, endometrial cancer is at the forefront of precision oncology in gynecology. The traditional classification systems based on histology and hormone dependence are now being augmented by molecular subtyping that better informs prognosis and treatment. As diagnostic tools, genetic testing, and therapeutic strategies advance, the management of endometrial cancer is becoming increasingly personalized.
Here are five things to know about endometrial cancer:
1. Endometrial cancer is one of the few cancers with increasing mortality.
Endometrial cancer accounts for the majority of uterine cancers in the United States with an overall lifetime risk for women of about 1 in 40. Since the mid-2000s, incidence rates have risen steadily, by > 1% per year, reflecting both lifestyle and environmental factors. Importantly, the disease tends to be diagnosed at an early stage due to the presence of warning signs like postmenopausal bleeding, which contributes to relatively favorable survival outcomes when caught early.
However, mortality trends continue to evolve. From 1999 to 2013, death rates from endometrial cancer in the US declined slightly, but since 2013, they have increased sharply — by > 8% annually — according to recent data. This upward trend in mortality disproportionately affects non-Hispanic Black women, who experience the highest mortality rate (4.7 per 100,000) among all racial and ethnic groups. This disparity is likely caused by a complex interplay of factors, including delays in diagnosis, more aggressive tumor biology, and inequities in access to care. Addressing these disparities remains a key priority in improving outcomes.
2. Risk factors go beyond hormones and age.
Risk factors for endometrial cancer include prolonged exposure to unopposed estrogen, which can result from estrogen-only hormone replacement therapy, higher BMI, and early menarche or late menopause. Nulliparity (having never been pregnant) and older age also increase risk, as does tamoxifen use — a medication commonly prescribed for breast cancer prevention. These factors cumulatively increase endometrial proliferation and the potential for atypical cellular changes. Endometrial hyperplasia, a known precursor to cancer, is often linked to these hormonal imbalances and may require surveillance or treatment.
Beyond estrogen’s influence, a growing body of research is uncovering additional risk contributors. Women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), metabolic syndrome, or diabetes face elevated risk of developing endometrial cancer. Genetic syndromes, particularly Lynch and Cowden syndromes, are associated with significantly increased lifetime risks of endometrial cancer. Environmental exposures, such as the use of hair relaxers, are being investigated as emerging risk factors. Additionally, race remains a risk marker, with Black women not only experiencing higher mortality but also more aggressive subtypes of the disease. These complex, overlapping risks highlight the importance of individualized risk assessment and early intervention strategies.
3. Postmenopausal bleeding is the hallmark symptom — but not the only one.
In endometrial cancer, the majority of cases are diagnosed at an early stage, largely because of the hallmark symptom of postmenopausal bleeding. In addition to bleeding, patients may present with vaginal discharge, pyometra, and even pain and abdominal distension in advanced disease. Any bleeding in a postmenopausal woman should prompt evaluation, as it may signal endometrial hyperplasia or carcinoma. In premenopausal women, irregular or heavy menstrual bleeding may raise suspicion, particularly when accompanied by risk factors such as PCOS.
The diagnostic workup for suspected endometrial cancer in women, particularly those presenting with postmenopausal bleeding, begins with a focused clinical assessment and frequently includes transvaginal ultrasound (TVUS) to evaluate the endometrium. While TVUS can aid in identifying structural abnormalities or suggest malignancy, endometrial sampling is warranted in all postmenopausal women with abnormal bleeding, regardless of endometrial thickness. Office-based biopsy is the preferred initial approach due to its convenience and diagnostic yield; however, if the sample is nondiagnostic or technically difficult to obtain, hysteroscopy with directed biopsy or dilation and curettage should be pursued.
4. Classification systems are evolving to include molecular subtypes.
Historically, endometrial cancers were classified using the World Health Organization system based on histology and by hormone dependence: Type 1 (estrogen-dependent, typically endometrioid and low grade) and Type 2 (non-estrogen dependent, often serous and high grade). Type 1 cancers tend to have a better prognosis and slower progression, while Type 2 cancers are more aggressive and require intensive treatment. While helpful, this binary classification does not fully capture the biological diversity or treatment responsiveness of the disease.
The field is now moving toward molecular classification, which offers a more nuanced understanding. The four main molecular subtypes include: polymerase epsilon (POLE)-mutant, mismatch repair (MMR)-deficient, p53-abnormal, and no specific molecular profile (NSMP). These groups differ in prognosis and therapeutic implications. POLE-mutant tumors with extremely high mutational burdens generally have excellent outcomes and may not require aggressive adjuvant therapy. In contrast, p53-abnormal tumors are associated with chromosomal instability, TP53 mutations, and poor outcomes, necessitating more aggressive multimodal treatment. MMR-deficient tumors are particularly responsive to immunotherapy. These molecular distinctions are changing how clinicians approach risk stratification and management in patients with endometrial cancer.
5. Treatment is increasingly personalized — and immunotherapy is expanding.
The cornerstone of treatment for early-stage endometrial cancer is surgical: total hysterectomy with bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy, often with sentinel node mapping or lymphadenectomy. Adjuvant therapy depends on factors such as stage, grade, histology, and molecular subtype. Fertility-sparing management with progestin therapy is an option for highly selected patients with early-stage, low-grade tumors. Clinical guidelines recommend that fertility desires be addressed prior to initiating treatment, as standard surgical management typically results in loss of reproductive capacity.
For advanced or recurrent disease, treatment becomes more complex and increasingly individualized. Chemotherapy, often with carboplatin and paclitaxel, is standard for stage III/IV and recurrent disease. Molecular findings now guide additional therapy: For instance, MMR-deficient tumors may respond to checkpoint inhibitors. As targeted agents and combination regimens continue to emerge, treatment of endometrial is increasingly focused on precision medicine.
Markman is professor of medical oncology and therapeutics research and President of Medicine & Science at City of Hope in Atlanta and Chicago. He has disclosed relevant financial relationships with AstraZeneca, GSK and Myriad.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Endometrial cancer is a common type of gynecologic cancer, and its incidence is rising steadily in the United States and globally. Most cases are endometrioid adenocarcinomas, arising from the inner lining of the uterus — the endometrium. While many patients are diagnosed early because of noticeable symptoms like abnormal bleeding, trends in both incidence and mortality are concerning, especially given the persistent racial and socioeconomic disparities in outcomes.
In addition to being the most common uterine malignancy, endometrial cancer is at the forefront of precision oncology in gynecology. The traditional classification systems based on histology and hormone dependence are now being augmented by molecular subtyping that better informs prognosis and treatment. As diagnostic tools, genetic testing, and therapeutic strategies advance, the management of endometrial cancer is becoming increasingly personalized.
Here are five things to know about endometrial cancer:
1. Endometrial cancer is one of the few cancers with increasing mortality.
Endometrial cancer accounts for the majority of uterine cancers in the United States with an overall lifetime risk for women of about 1 in 40. Since the mid-2000s, incidence rates have risen steadily, by > 1% per year, reflecting both lifestyle and environmental factors. Importantly, the disease tends to be diagnosed at an early stage due to the presence of warning signs like postmenopausal bleeding, which contributes to relatively favorable survival outcomes when caught early.
However, mortality trends continue to evolve. From 1999 to 2013, death rates from endometrial cancer in the US declined slightly, but since 2013, they have increased sharply — by > 8% annually — according to recent data. This upward trend in mortality disproportionately affects non-Hispanic Black women, who experience the highest mortality rate (4.7 per 100,000) among all racial and ethnic groups. This disparity is likely caused by a complex interplay of factors, including delays in diagnosis, more aggressive tumor biology, and inequities in access to care. Addressing these disparities remains a key priority in improving outcomes.
2. Risk factors go beyond hormones and age.
Risk factors for endometrial cancer include prolonged exposure to unopposed estrogen, which can result from estrogen-only hormone replacement therapy, higher BMI, and early menarche or late menopause. Nulliparity (having never been pregnant) and older age also increase risk, as does tamoxifen use — a medication commonly prescribed for breast cancer prevention. These factors cumulatively increase endometrial proliferation and the potential for atypical cellular changes. Endometrial hyperplasia, a known precursor to cancer, is often linked to these hormonal imbalances and may require surveillance or treatment.
Beyond estrogen’s influence, a growing body of research is uncovering additional risk contributors. Women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), metabolic syndrome, or diabetes face elevated risk of developing endometrial cancer. Genetic syndromes, particularly Lynch and Cowden syndromes, are associated with significantly increased lifetime risks of endometrial cancer. Environmental exposures, such as the use of hair relaxers, are being investigated as emerging risk factors. Additionally, race remains a risk marker, with Black women not only experiencing higher mortality but also more aggressive subtypes of the disease. These complex, overlapping risks highlight the importance of individualized risk assessment and early intervention strategies.
3. Postmenopausal bleeding is the hallmark symptom — but not the only one.
In endometrial cancer, the majority of cases are diagnosed at an early stage, largely because of the hallmark symptom of postmenopausal bleeding. In addition to bleeding, patients may present with vaginal discharge, pyometra, and even pain and abdominal distension in advanced disease. Any bleeding in a postmenopausal woman should prompt evaluation, as it may signal endometrial hyperplasia or carcinoma. In premenopausal women, irregular or heavy menstrual bleeding may raise suspicion, particularly when accompanied by risk factors such as PCOS.
The diagnostic workup for suspected endometrial cancer in women, particularly those presenting with postmenopausal bleeding, begins with a focused clinical assessment and frequently includes transvaginal ultrasound (TVUS) to evaluate the endometrium. While TVUS can aid in identifying structural abnormalities or suggest malignancy, endometrial sampling is warranted in all postmenopausal women with abnormal bleeding, regardless of endometrial thickness. Office-based biopsy is the preferred initial approach due to its convenience and diagnostic yield; however, if the sample is nondiagnostic or technically difficult to obtain, hysteroscopy with directed biopsy or dilation and curettage should be pursued.
4. Classification systems are evolving to include molecular subtypes.
Historically, endometrial cancers were classified using the World Health Organization system based on histology and by hormone dependence: Type 1 (estrogen-dependent, typically endometrioid and low grade) and Type 2 (non-estrogen dependent, often serous and high grade). Type 1 cancers tend to have a better prognosis and slower progression, while Type 2 cancers are more aggressive and require intensive treatment. While helpful, this binary classification does not fully capture the biological diversity or treatment responsiveness of the disease.
The field is now moving toward molecular classification, which offers a more nuanced understanding. The four main molecular subtypes include: polymerase epsilon (POLE)-mutant, mismatch repair (MMR)-deficient, p53-abnormal, and no specific molecular profile (NSMP). These groups differ in prognosis and therapeutic implications. POLE-mutant tumors with extremely high mutational burdens generally have excellent outcomes and may not require aggressive adjuvant therapy. In contrast, p53-abnormal tumors are associated with chromosomal instability, TP53 mutations, and poor outcomes, necessitating more aggressive multimodal treatment. MMR-deficient tumors are particularly responsive to immunotherapy. These molecular distinctions are changing how clinicians approach risk stratification and management in patients with endometrial cancer.
5. Treatment is increasingly personalized — and immunotherapy is expanding.
The cornerstone of treatment for early-stage endometrial cancer is surgical: total hysterectomy with bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy, often with sentinel node mapping or lymphadenectomy. Adjuvant therapy depends on factors such as stage, grade, histology, and molecular subtype. Fertility-sparing management with progestin therapy is an option for highly selected patients with early-stage, low-grade tumors. Clinical guidelines recommend that fertility desires be addressed prior to initiating treatment, as standard surgical management typically results in loss of reproductive capacity.
For advanced or recurrent disease, treatment becomes more complex and increasingly individualized. Chemotherapy, often with carboplatin and paclitaxel, is standard for stage III/IV and recurrent disease. Molecular findings now guide additional therapy: For instance, MMR-deficient tumors may respond to checkpoint inhibitors. As targeted agents and combination regimens continue to emerge, treatment of endometrial is increasingly focused on precision medicine.
Markman is professor of medical oncology and therapeutics research and President of Medicine & Science at City of Hope in Atlanta and Chicago. He has disclosed relevant financial relationships with AstraZeneca, GSK and Myriad.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Older Patients With Breast Cancer Face Inconsistent Bone Health Management Across Centres
TOPLINE:
Bone health management for older women with breast cancer receiving aromatase inhibitors (AIs) varied substantially across 5 UK hospitals. Despite the higher risk for fractures, women aged > 80 years were less likely to receive DEXA scans or bisphosphonates, highlighting the urgent need for standardised bone monitoring and treatment in frail older patients.
METHODOLOGY:
- This secondary analysis of the multicentre Age Gap study included 529 women (age ≥ 70 years) with oestrogen receptor-positive early breast cancer who received AIs, either as primary or adjuvant treatment, at five hospitals in the UK.
- Researchers collected comprehensive data including the type of endocrine therapy, DEXA scan results, bisphosphonate usage, calcium and vitamin D supplementation, and the incidence of fractures during or after AI therapy.
- Frailty was assessed using a modified Rockwood Frailty Index, with scores being calculated across 75 variables to categorise patients as robust (< 0.08), prefrail (0.08-0.25), or frail (> 0.25).
TAKEAWAY:
- Overall, 67% of patients had baseline DEXA scans. Of these, 42% were osteopenic and 18% osteoporotic. Scans were more common in 70- to 79-year-olds than in those aged ≥ 80 years and in women undergoing surgery than in those undergoing primary endocrine therapy, with marked variation across centres (P < .001 for all).
- Among patients receiving AI therapy, 43% were prescribed bisphosphonates, especially those who had surgery (hazard ratio [HR], 1.36; P = .04) and those aged 70-79 years (HR, 1.31; P = .02); 33% had vitamin D plus calcium along with bisphosphonates.
- During follow-up, 23% of patients had fractures, with significant variation across centres (P = .02), and 38% of these patients had received prior bisphosphonates.
- Although 94% of patients were frail or prefrail, frailty did not correlate with baseline hip (P = .10) or spine (P = .89) T scores. Bisphosphonates plus AIs were prescribed in 70% of nonfrail participants vs 43% of prefrail and 47% of frail participants (P = .02).
IN PRACTICE:
“Patient’s age and general health influence bone health decision making, with older and frailer patients often receiving non-standard care. Despite national and international recommendations, there is still wide variation in bone health management, highlighting the need for further education and standardised bone health care in older women with breast cancer,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Elisavet Theodoulou, University of Sheffield, Sheffield, England. It was published online, in the Journal of Geriatric Oncology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s inclusion of only 5 hospital sites limited the ability to draw broader conclusions about bone health management practices across a wider range of centres. Additionally, the interpretation of the results was complicated by the introduction of adjuvant bisphosphonates during the study period, making the cohort unstable in terms of bisphosphonate usage indications.
DISCLOSURES:
The Age Gap study was supported by the National Institute for Health and Care Research Programme Grants for Applied Research. The authors declared having no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Bone health management for older women with breast cancer receiving aromatase inhibitors (AIs) varied substantially across 5 UK hospitals. Despite the higher risk for fractures, women aged > 80 years were less likely to receive DEXA scans or bisphosphonates, highlighting the urgent need for standardised bone monitoring and treatment in frail older patients.
METHODOLOGY:
- This secondary analysis of the multicentre Age Gap study included 529 women (age ≥ 70 years) with oestrogen receptor-positive early breast cancer who received AIs, either as primary or adjuvant treatment, at five hospitals in the UK.
- Researchers collected comprehensive data including the type of endocrine therapy, DEXA scan results, bisphosphonate usage, calcium and vitamin D supplementation, and the incidence of fractures during or after AI therapy.
- Frailty was assessed using a modified Rockwood Frailty Index, with scores being calculated across 75 variables to categorise patients as robust (< 0.08), prefrail (0.08-0.25), or frail (> 0.25).
TAKEAWAY:
- Overall, 67% of patients had baseline DEXA scans. Of these, 42% were osteopenic and 18% osteoporotic. Scans were more common in 70- to 79-year-olds than in those aged ≥ 80 years and in women undergoing surgery than in those undergoing primary endocrine therapy, with marked variation across centres (P < .001 for all).
- Among patients receiving AI therapy, 43% were prescribed bisphosphonates, especially those who had surgery (hazard ratio [HR], 1.36; P = .04) and those aged 70-79 years (HR, 1.31; P = .02); 33% had vitamin D plus calcium along with bisphosphonates.
- During follow-up, 23% of patients had fractures, with significant variation across centres (P = .02), and 38% of these patients had received prior bisphosphonates.
- Although 94% of patients were frail or prefrail, frailty did not correlate with baseline hip (P = .10) or spine (P = .89) T scores. Bisphosphonates plus AIs were prescribed in 70% of nonfrail participants vs 43% of prefrail and 47% of frail participants (P = .02).
IN PRACTICE:
“Patient’s age and general health influence bone health decision making, with older and frailer patients often receiving non-standard care. Despite national and international recommendations, there is still wide variation in bone health management, highlighting the need for further education and standardised bone health care in older women with breast cancer,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Elisavet Theodoulou, University of Sheffield, Sheffield, England. It was published online, in the Journal of Geriatric Oncology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s inclusion of only 5 hospital sites limited the ability to draw broader conclusions about bone health management practices across a wider range of centres. Additionally, the interpretation of the results was complicated by the introduction of adjuvant bisphosphonates during the study period, making the cohort unstable in terms of bisphosphonate usage indications.
DISCLOSURES:
The Age Gap study was supported by the National Institute for Health and Care Research Programme Grants for Applied Research. The authors declared having no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Bone health management for older women with breast cancer receiving aromatase inhibitors (AIs) varied substantially across 5 UK hospitals. Despite the higher risk for fractures, women aged > 80 years were less likely to receive DEXA scans or bisphosphonates, highlighting the urgent need for standardised bone monitoring and treatment in frail older patients.
METHODOLOGY:
- This secondary analysis of the multicentre Age Gap study included 529 women (age ≥ 70 years) with oestrogen receptor-positive early breast cancer who received AIs, either as primary or adjuvant treatment, at five hospitals in the UK.
- Researchers collected comprehensive data including the type of endocrine therapy, DEXA scan results, bisphosphonate usage, calcium and vitamin D supplementation, and the incidence of fractures during or after AI therapy.
- Frailty was assessed using a modified Rockwood Frailty Index, with scores being calculated across 75 variables to categorise patients as robust (< 0.08), prefrail (0.08-0.25), or frail (> 0.25).
TAKEAWAY:
- Overall, 67% of patients had baseline DEXA scans. Of these, 42% were osteopenic and 18% osteoporotic. Scans were more common in 70- to 79-year-olds than in those aged ≥ 80 years and in women undergoing surgery than in those undergoing primary endocrine therapy, with marked variation across centres (P < .001 for all).
- Among patients receiving AI therapy, 43% were prescribed bisphosphonates, especially those who had surgery (hazard ratio [HR], 1.36; P = .04) and those aged 70-79 years (HR, 1.31; P = .02); 33% had vitamin D plus calcium along with bisphosphonates.
- During follow-up, 23% of patients had fractures, with significant variation across centres (P = .02), and 38% of these patients had received prior bisphosphonates.
- Although 94% of patients were frail or prefrail, frailty did not correlate with baseline hip (P = .10) or spine (P = .89) T scores. Bisphosphonates plus AIs were prescribed in 70% of nonfrail participants vs 43% of prefrail and 47% of frail participants (P = .02).
IN PRACTICE:
“Patient’s age and general health influence bone health decision making, with older and frailer patients often receiving non-standard care. Despite national and international recommendations, there is still wide variation in bone health management, highlighting the need for further education and standardised bone health care in older women with breast cancer,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Elisavet Theodoulou, University of Sheffield, Sheffield, England. It was published online, in the Journal of Geriatric Oncology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s inclusion of only 5 hospital sites limited the ability to draw broader conclusions about bone health management practices across a wider range of centres. Additionally, the interpretation of the results was complicated by the introduction of adjuvant bisphosphonates during the study period, making the cohort unstable in terms of bisphosphonate usage indications.
DISCLOSURES:
The Age Gap study was supported by the National Institute for Health and Care Research Programme Grants for Applied Research. The authors declared having no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Ovarian Cancer Risk Rises Soon After IBS Diagnosis
TOPLINE:
Women with a new diagnosis of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) have a significantly higher risk for ovarian cancer at 3 months and 6 months post-diagnosis, but this risk is no longer elevated beyond 8 months.
METHODOLOGY:
- Ovarian cancer often presents with nonspecific symptoms overlapping those of IBS. The frequency of misdiagnosis remains unknown, and not all IBS guidelines recommend screening for ovarian cancer.
- Researchers conducted a retrospective cohort study using US administrative claims data to compare ovarian cancer incidence in adult women with and without a new IBS diagnosis.
- Diagnostic codes were used to identify cases of IBS and ovarian cancer.
TAKEAWAY:
- The cohort comprised 9804 women with IBS and 79,804 women without IBS, identified between January 2017 and December 2020.
- Women with IBS had a significantly higher risk for ovarian cancer at 3 months (hazard ratio [HR], 1.71; P = .02) and 6 months (HR, 1.43; P = .02), but not beyond 8 months post-diagnosis.
- Women with both IBS and endometriosis had an even greater risk for ovarian cancer at 3 months (HR, 4.20; P = .01), 6 months (HR, 3.52; P = .01), and after 1 year (HR, 2.67; P = .04).
- Increasing age was significantly associated with higher ovarian cancer incidence only in women younger than 50 years (HR, 1.07; P < .01), regardless of IBS status.
IN PRACTICE:
“Identifying patient-specific risk factors, such as chronic pelvic pain or endometriosis, could help develop tailored risk profiles and improve the approach to personalized care in women with IBS-type symptoms,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Andrea Shin, Vatche and Tamar Manoukian Division of Digestive Diseases, University of California, Los Angeles. It was published online in Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics.
LIMITATIONS:
The use of diagnostic codes for identifying IBS may have led to misclassification or reflected symptoms rather than confirmed and validated diagnosis.
DISCLOSURES:
This study received support from the National Institutes of Health. Some authors reported serving as consultants, advisors, and/or receiving research support from pharmaceutical and healthcare companies; one author reported having stock options.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Women with a new diagnosis of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) have a significantly higher risk for ovarian cancer at 3 months and 6 months post-diagnosis, but this risk is no longer elevated beyond 8 months.
METHODOLOGY:
- Ovarian cancer often presents with nonspecific symptoms overlapping those of IBS. The frequency of misdiagnosis remains unknown, and not all IBS guidelines recommend screening for ovarian cancer.
- Researchers conducted a retrospective cohort study using US administrative claims data to compare ovarian cancer incidence in adult women with and without a new IBS diagnosis.
- Diagnostic codes were used to identify cases of IBS and ovarian cancer.
TAKEAWAY:
- The cohort comprised 9804 women with IBS and 79,804 women without IBS, identified between January 2017 and December 2020.
- Women with IBS had a significantly higher risk for ovarian cancer at 3 months (hazard ratio [HR], 1.71; P = .02) and 6 months (HR, 1.43; P = .02), but not beyond 8 months post-diagnosis.
- Women with both IBS and endometriosis had an even greater risk for ovarian cancer at 3 months (HR, 4.20; P = .01), 6 months (HR, 3.52; P = .01), and after 1 year (HR, 2.67; P = .04).
- Increasing age was significantly associated with higher ovarian cancer incidence only in women younger than 50 years (HR, 1.07; P < .01), regardless of IBS status.
IN PRACTICE:
“Identifying patient-specific risk factors, such as chronic pelvic pain or endometriosis, could help develop tailored risk profiles and improve the approach to personalized care in women with IBS-type symptoms,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Andrea Shin, Vatche and Tamar Manoukian Division of Digestive Diseases, University of California, Los Angeles. It was published online in Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics.
LIMITATIONS:
The use of diagnostic codes for identifying IBS may have led to misclassification or reflected symptoms rather than confirmed and validated diagnosis.
DISCLOSURES:
This study received support from the National Institutes of Health. Some authors reported serving as consultants, advisors, and/or receiving research support from pharmaceutical and healthcare companies; one author reported having stock options.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Women with a new diagnosis of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) have a significantly higher risk for ovarian cancer at 3 months and 6 months post-diagnosis, but this risk is no longer elevated beyond 8 months.
METHODOLOGY:
- Ovarian cancer often presents with nonspecific symptoms overlapping those of IBS. The frequency of misdiagnosis remains unknown, and not all IBS guidelines recommend screening for ovarian cancer.
- Researchers conducted a retrospective cohort study using US administrative claims data to compare ovarian cancer incidence in adult women with and without a new IBS diagnosis.
- Diagnostic codes were used to identify cases of IBS and ovarian cancer.
TAKEAWAY:
- The cohort comprised 9804 women with IBS and 79,804 women without IBS, identified between January 2017 and December 2020.
- Women with IBS had a significantly higher risk for ovarian cancer at 3 months (hazard ratio [HR], 1.71; P = .02) and 6 months (HR, 1.43; P = .02), but not beyond 8 months post-diagnosis.
- Women with both IBS and endometriosis had an even greater risk for ovarian cancer at 3 months (HR, 4.20; P = .01), 6 months (HR, 3.52; P = .01), and after 1 year (HR, 2.67; P = .04).
- Increasing age was significantly associated with higher ovarian cancer incidence only in women younger than 50 years (HR, 1.07; P < .01), regardless of IBS status.
IN PRACTICE:
“Identifying patient-specific risk factors, such as chronic pelvic pain or endometriosis, could help develop tailored risk profiles and improve the approach to personalized care in women with IBS-type symptoms,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Andrea Shin, Vatche and Tamar Manoukian Division of Digestive Diseases, University of California, Los Angeles. It was published online in Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics.
LIMITATIONS:
The use of diagnostic codes for identifying IBS may have led to misclassification or reflected symptoms rather than confirmed and validated diagnosis.
DISCLOSURES:
This study received support from the National Institutes of Health. Some authors reported serving as consultants, advisors, and/or receiving research support from pharmaceutical and healthcare companies; one author reported having stock options.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.