User login
MDR Candida auris is on the move
MADRID – The anticipated global emergence of multidrug resistant Candida auris is now an established fact, but a case study presented at the European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases annual congress demonstrates just how devastating an outbreak can be to a medical facility and its surgical ICU patients.
The dangerous invasive infection is spreading through Asia, Europe, and the Americas, causing potentially fatal candidemias and proving devilishly difficult to eradicate in health care facilities once it becomes established.
Several multidrug resistant (MDR) C. auris outbreaks were reported at the ECCMID meeting. Most troubling: a continuing outbreak in a hospital in Valencia, Spain, in which 17 patients have died – a 41% fatality rate among those who developed a fulminant C. auris candidemia, Javier Pemán, MD, said at the meeting. The strain appeared to be a clonal population not previously identified in published reports.
“C. auris is hard to remove from the hospital environment,” once it becomes established, said Dr. Pemán of La Fe University and Polytechnic Hospital, Valencia. “When an outbreak lasts for months, as ours has, it is difficult, but necessary, to maintain control measures, identify it early in the lab, and isolate and treat patients early with combination therapy.”
He and his team have relied primarily on a combination of amphotericin B and echinocandin (AMB+ECN), although, he added, the optimal dosing and treatment time aren’t known, and many C. auris isolates are echinocandin resistant.
MDR C. auris first appearedin Tokyo in 2009. It then spread to South Korea around 2011, and then appeared across Asia and Western Europe. Its first appearance in Spain was the 2016 Le Fe outbreak.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, single cases have appeared in Austria, Belgium, Malaysia, Norway, and the United Arab Emirates. Canada, Colombia, France, Germany, India, Israel, Japan, Kenya, Kuwait, Oman, Pakistan, Panama, South Korea, South Africa, Spain, the United Arab Emirates, the United Kingdom, and Venezuela have experienced multiple outbreaks.
The CDC has recorded 257 confirmed and 30 probable cases of MDR C. auris in the United States as of March 31, 2018. Most of these occurred in New York City and New Jersey; a number of patients had recent stays in hospitals in India, Pakistan, South Africa, the UAE, and Venezuela.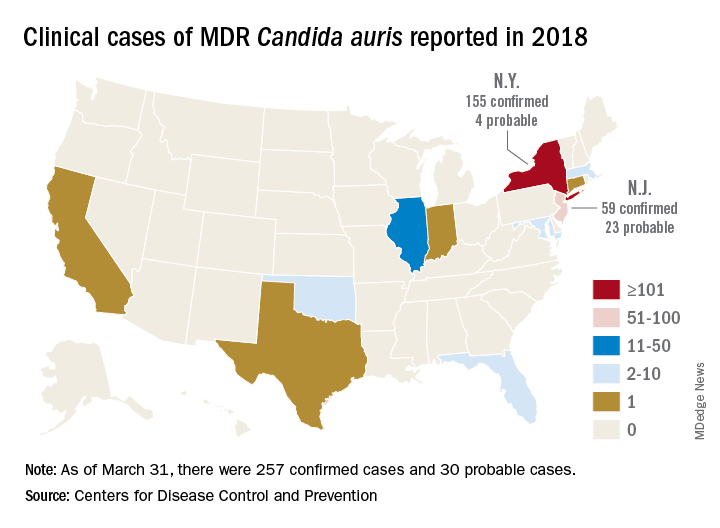
Jacques Meis, MD, of the department of medical microbiology and infectious diseases at Canisius Wilhelmina Hospital, Nijmegen, the Netherlands, set the stage for an extended discussion of C. auris at the meeting.
“This is a multidrug resistant yeast that has emerged in the last decade. Some rare isolates are resistant to all three major antifungal classes. Unlike other Candida species, it seems to persist for prolonged periods in health care environments and to colonize patients’ skin. It behaves rather like resistant bacteria.”
Once established in a health care setting – often an intensive care ward – C. auris poses major infection controls challenges and can be very hard to identify and eradicate, said Dr. Meis.
The identification problem is well known. The 2016 CDC alert noted that “commercially available biochemical-based tests, including API strips and VITEK-2, used in many U.S. laboratories to identify fungi, cannot differentiate C. auris from related species. Because of these challenges, clinical laboratories have misidentified the organism as C. haemulonii and Saccharomyces cerevisiae.”
“It’s often misidentified as other Candida species or as Saccharomyces when we investigate with biochemical methods. C. auris is best identified using Matrix Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization time of flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF),” said Dr. Meis.
Among the presentations at ECCMID were a report of a U.K. outbreak that affected 70 patients in a neuroscience ICU. It was traced to axillary skin-surface temperature probes, and eradicated only after those probes were removed. More than 90% of the isolates were resistant to fluconazole, voriconazole, and posaconazole; 18% were amphotericin resistant.
A poster described the microbiological characteristics of 50 C. auris isolates taken from 11 hospitals in Korea.
Dr. Pemán described the outbreak in Valencia, which began in April 2016; the report was simultaneously published in the online journal Mycoses (2018 Apr 14. doi: 10.1111/myc.12781).
The index case was a 66-year-old man with hepatocellular carcinoma who underwent a liver resection at Hospital Le Fe in April 2016. During his stay in the surgical ICU (SICU), he developed a fungal infection from an unknown, highly fluconazole-resistant yeast. The pathogen was twice misidentified, first as C. haemulonii and then as S. cerevisiae.
Three weeks later, the patient in the adjacent bed developed a similar infection. Sequencing of the internal transcribed spacer confirmed both as a Candida isolate – an organism previously unknown in Spain.
The SICU setup was apparently very conducive to the C. auris life cycle, Dr. Pemán said. It’s a relatively open ward divided into three rooms with 12 beds in each. There are no isolation beds, and dozens of workers have access to the ward every day, including clinical and cleaning staff.
After identifying the second isolate, Dr. Pemán said, infection control staff went into action. They instituted contact precautions in the SICU, and took regular cultures from newly admitted patients and cultures of every SICU patient every 7 days.
“We also started an intense search for more cases throughout the hospital and in 101 SICU workers. Of 305 samples from hands and ears, we found nothing.” They reviewed all the prior fluconazole-resistant Candida isolates; C. auris was not present in the hospital before the index case.
Three weeks after case 2, six new SICU patients tested positive for C. auris (two blood cultures, one vascular line, one respiratory specimen, two rectal swabs, and one urinary tract sample).
“We reinforced contact precautions in colonized and infected patients and started a twice-daily environmental cleaning practice with quaternary ammonium around them,” said Dr. Pemán. They instituted a proactive hospital-wide hand hygiene campaign and spread the word about the outbreak.
By July, there were 11 new colonized patients, 3 of whom developed candidemia. These patients were grouped in the same SICU ward and underwent daily skin treatments with 4% aqueous chlorhexidine wipes.
The environmental inspection found C. auris on beds, tables, walls, and the floor all around infected patients. The pathogen also was living on IV pumps, computer keyboards, and bedside tables. Blood pressure cuffs were a favorite haunt: 19 of 36 samples in the adjacent ICU were positive. These data were separately reported at ECCMID.
Despite all of these efforts at eradication, infections continued to rise. By November, there were 24 newly colonized patients and nine new candidemia episodes in SICU and regular ICU patients. In December, a new infection control bundle began: A surveillance nurse in the C. auris SICU ward was in charge of compliance; any patient with any yeast growth in culture was isolated, and staff used 2% alcohol chlorhexidine wipes before and after IV catheter handling. Staff also washed down all surfaces three times daily with a disinfectant.
Patients could leave isolation after three consecutive C. auris–negative cultures. After discharge, an ultraviolet light decontamination procedure disinfected each patient room.
The pathogen was almost unbelievably resilient, Dr. Pemán noted in the Mycoses article. “In some cases, C. auris was recovered from walls after cleaning with cationic surface–active products ... it was not known until very recently that these products, as well as quaternary ammonium disinfectants, cannot effectively remove C. auris from surfaces.”
As a result of the previous measures, the outbreak slowed down during December 2016, with two new candidemia cases, but by February, the outbreak resumed with 50 new cases and 18 candidemias detected. Cases continued to emerge throughout 2017.
By September 2017, 250 patients had been colonized; 116 of these were included in the Mycoses report. There were 30 episodes of candidemia (26%); of these, 17 died by 30 days (41.4%). Spondylodiscitis and endocarditis each developed in two patients and one developed ventriculitis.
A separate poster by Dr. Pemán and his colleagues gave more details:
• A 52-year-old woman with C. auris–induced endocarditis died after 4 weeks of treatment with AMB+ECN and flucytosine. She had undergone a prosthetic heart valve placement for Ebstein’s anomaly.
• A 71-year-old man with hydrocephalus developed a C. auris–induced infection of his ventriculoperitoneal shunt; he also had undergone cardiovascular surgery and had an ischemic cardiomyopathy. He died despite shunt removal and 8 weeks of AMB+ECN.
• A 71-year-old man who underwent cardiovascular surgery and received a prosthetic heart valve developed endocarditis. He is alive and at last report, on week 26 of AMB+ECN, flucytosine, and isavuconazole.
• A 68-year-old man who underwent abdominal surgery for hepatocellular carcinoma developed spondylodiscitis and is alive after 24 weeks of AMB+ECN.
• A 48-year old female multiple trauma patient developed spondylodiscitis and is alive after 48 weeks of treatment with AMB+ECN.
A multivariate analysis determined that antibacterial treatment increased the risk of candidemia by almost 30 times (odds ratio, 29.59). The next highest risk was neutropenia (OR, 20.7) and then simply being a hospital and SICU patient. Dr. Pemán’s poster said, “In the 16 months before the index case, La Fe recorded 89 candidemias, none caused by C. auris. In the 16 months afterward, there were 154 candidemias, largely C. auris. Before April 2016, C. parapsilosis accounted for the largest portion of candidemias (46%) followed by C. albicans. After the index case, C. auris accounted for 42%, followed by C. parapsilosis (21%) and C. albicans (18%).”
Because of its fluconazole resistance, patients with C. auris received a combined antifungal treatment of liposomal amphotericin B 3 mg/kg per day for 5 days, and a standard dose of echinocandin for 3 weeks. Many C. auris strains are echinocandin resistant, Dr. Pemán noted. This particular strain was clonal, different from any other previously reported, he said.
“Our results confirm those previously reported by other authors, that C. auris is grouped in different independent clusters according to its geographical origin. Although all Spanish isolates were genotypically distinct from Indian, Omani, U.K., and Venezuelan isolates, there seems to be some connection with South African isolates.”
Hospital Le Fe continues to struggle with C. auris. As of March, 335 patients have tested positive for the pathogen, and 80 have developed candidemias.
“We feel we may be approaching the end of this episode, but it’s really not possible to be sure,” he said.
Dr. Pemán had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: ECCMID 2018 Peman et al. S0067.
MADRID – The anticipated global emergence of multidrug resistant Candida auris is now an established fact, but a case study presented at the European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases annual congress demonstrates just how devastating an outbreak can be to a medical facility and its surgical ICU patients.
The dangerous invasive infection is spreading through Asia, Europe, and the Americas, causing potentially fatal candidemias and proving devilishly difficult to eradicate in health care facilities once it becomes established.
Several multidrug resistant (MDR) C. auris outbreaks were reported at the ECCMID meeting. Most troubling: a continuing outbreak in a hospital in Valencia, Spain, in which 17 patients have died – a 41% fatality rate among those who developed a fulminant C. auris candidemia, Javier Pemán, MD, said at the meeting. The strain appeared to be a clonal population not previously identified in published reports.
“C. auris is hard to remove from the hospital environment,” once it becomes established, said Dr. Pemán of La Fe University and Polytechnic Hospital, Valencia. “When an outbreak lasts for months, as ours has, it is difficult, but necessary, to maintain control measures, identify it early in the lab, and isolate and treat patients early with combination therapy.”
He and his team have relied primarily on a combination of amphotericin B and echinocandin (AMB+ECN), although, he added, the optimal dosing and treatment time aren’t known, and many C. auris isolates are echinocandin resistant.
MDR C. auris first appearedin Tokyo in 2009. It then spread to South Korea around 2011, and then appeared across Asia and Western Europe. Its first appearance in Spain was the 2016 Le Fe outbreak.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, single cases have appeared in Austria, Belgium, Malaysia, Norway, and the United Arab Emirates. Canada, Colombia, France, Germany, India, Israel, Japan, Kenya, Kuwait, Oman, Pakistan, Panama, South Korea, South Africa, Spain, the United Arab Emirates, the United Kingdom, and Venezuela have experienced multiple outbreaks.
The CDC has recorded 257 confirmed and 30 probable cases of MDR C. auris in the United States as of March 31, 2018. Most of these occurred in New York City and New Jersey; a number of patients had recent stays in hospitals in India, Pakistan, South Africa, the UAE, and Venezuela.
Jacques Meis, MD, of the department of medical microbiology and infectious diseases at Canisius Wilhelmina Hospital, Nijmegen, the Netherlands, set the stage for an extended discussion of C. auris at the meeting.
“This is a multidrug resistant yeast that has emerged in the last decade. Some rare isolates are resistant to all three major antifungal classes. Unlike other Candida species, it seems to persist for prolonged periods in health care environments and to colonize patients’ skin. It behaves rather like resistant bacteria.”
Once established in a health care setting – often an intensive care ward – C. auris poses major infection controls challenges and can be very hard to identify and eradicate, said Dr. Meis.
The identification problem is well known. The 2016 CDC alert noted that “commercially available biochemical-based tests, including API strips and VITEK-2, used in many U.S. laboratories to identify fungi, cannot differentiate C. auris from related species. Because of these challenges, clinical laboratories have misidentified the organism as C. haemulonii and Saccharomyces cerevisiae.”
“It’s often misidentified as other Candida species or as Saccharomyces when we investigate with biochemical methods. C. auris is best identified using Matrix Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization time of flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF),” said Dr. Meis.
Among the presentations at ECCMID were a report of a U.K. outbreak that affected 70 patients in a neuroscience ICU. It was traced to axillary skin-surface temperature probes, and eradicated only after those probes were removed. More than 90% of the isolates were resistant to fluconazole, voriconazole, and posaconazole; 18% were amphotericin resistant.
A poster described the microbiological characteristics of 50 C. auris isolates taken from 11 hospitals in Korea.
Dr. Pemán described the outbreak in Valencia, which began in April 2016; the report was simultaneously published in the online journal Mycoses (2018 Apr 14. doi: 10.1111/myc.12781).
The index case was a 66-year-old man with hepatocellular carcinoma who underwent a liver resection at Hospital Le Fe in April 2016. During his stay in the surgical ICU (SICU), he developed a fungal infection from an unknown, highly fluconazole-resistant yeast. The pathogen was twice misidentified, first as C. haemulonii and then as S. cerevisiae.
Three weeks later, the patient in the adjacent bed developed a similar infection. Sequencing of the internal transcribed spacer confirmed both as a Candida isolate – an organism previously unknown in Spain.
The SICU setup was apparently very conducive to the C. auris life cycle, Dr. Pemán said. It’s a relatively open ward divided into three rooms with 12 beds in each. There are no isolation beds, and dozens of workers have access to the ward every day, including clinical and cleaning staff.
After identifying the second isolate, Dr. Pemán said, infection control staff went into action. They instituted contact precautions in the SICU, and took regular cultures from newly admitted patients and cultures of every SICU patient every 7 days.
“We also started an intense search for more cases throughout the hospital and in 101 SICU workers. Of 305 samples from hands and ears, we found nothing.” They reviewed all the prior fluconazole-resistant Candida isolates; C. auris was not present in the hospital before the index case.
Three weeks after case 2, six new SICU patients tested positive for C. auris (two blood cultures, one vascular line, one respiratory specimen, two rectal swabs, and one urinary tract sample).
“We reinforced contact precautions in colonized and infected patients and started a twice-daily environmental cleaning practice with quaternary ammonium around them,” said Dr. Pemán. They instituted a proactive hospital-wide hand hygiene campaign and spread the word about the outbreak.
By July, there were 11 new colonized patients, 3 of whom developed candidemia. These patients were grouped in the same SICU ward and underwent daily skin treatments with 4% aqueous chlorhexidine wipes.
The environmental inspection found C. auris on beds, tables, walls, and the floor all around infected patients. The pathogen also was living on IV pumps, computer keyboards, and bedside tables. Blood pressure cuffs were a favorite haunt: 19 of 36 samples in the adjacent ICU were positive. These data were separately reported at ECCMID.
Despite all of these efforts at eradication, infections continued to rise. By November, there were 24 newly colonized patients and nine new candidemia episodes in SICU and regular ICU patients. In December, a new infection control bundle began: A surveillance nurse in the C. auris SICU ward was in charge of compliance; any patient with any yeast growth in culture was isolated, and staff used 2% alcohol chlorhexidine wipes before and after IV catheter handling. Staff also washed down all surfaces three times daily with a disinfectant.
Patients could leave isolation after three consecutive C. auris–negative cultures. After discharge, an ultraviolet light decontamination procedure disinfected each patient room.
The pathogen was almost unbelievably resilient, Dr. Pemán noted in the Mycoses article. “In some cases, C. auris was recovered from walls after cleaning with cationic surface–active products ... it was not known until very recently that these products, as well as quaternary ammonium disinfectants, cannot effectively remove C. auris from surfaces.”
As a result of the previous measures, the outbreak slowed down during December 2016, with two new candidemia cases, but by February, the outbreak resumed with 50 new cases and 18 candidemias detected. Cases continued to emerge throughout 2017.
By September 2017, 250 patients had been colonized; 116 of these were included in the Mycoses report. There were 30 episodes of candidemia (26%); of these, 17 died by 30 days (41.4%). Spondylodiscitis and endocarditis each developed in two patients and one developed ventriculitis.
A separate poster by Dr. Pemán and his colleagues gave more details:
• A 52-year-old woman with C. auris–induced endocarditis died after 4 weeks of treatment with AMB+ECN and flucytosine. She had undergone a prosthetic heart valve placement for Ebstein’s anomaly.
• A 71-year-old man with hydrocephalus developed a C. auris–induced infection of his ventriculoperitoneal shunt; he also had undergone cardiovascular surgery and had an ischemic cardiomyopathy. He died despite shunt removal and 8 weeks of AMB+ECN.
• A 71-year-old man who underwent cardiovascular surgery and received a prosthetic heart valve developed endocarditis. He is alive and at last report, on week 26 of AMB+ECN, flucytosine, and isavuconazole.
• A 68-year-old man who underwent abdominal surgery for hepatocellular carcinoma developed spondylodiscitis and is alive after 24 weeks of AMB+ECN.
• A 48-year old female multiple trauma patient developed spondylodiscitis and is alive after 48 weeks of treatment with AMB+ECN.
A multivariate analysis determined that antibacterial treatment increased the risk of candidemia by almost 30 times (odds ratio, 29.59). The next highest risk was neutropenia (OR, 20.7) and then simply being a hospital and SICU patient. Dr. Pemán’s poster said, “In the 16 months before the index case, La Fe recorded 89 candidemias, none caused by C. auris. In the 16 months afterward, there were 154 candidemias, largely C. auris. Before April 2016, C. parapsilosis accounted for the largest portion of candidemias (46%) followed by C. albicans. After the index case, C. auris accounted for 42%, followed by C. parapsilosis (21%) and C. albicans (18%).”
Because of its fluconazole resistance, patients with C. auris received a combined antifungal treatment of liposomal amphotericin B 3 mg/kg per day for 5 days, and a standard dose of echinocandin for 3 weeks. Many C. auris strains are echinocandin resistant, Dr. Pemán noted. This particular strain was clonal, different from any other previously reported, he said.
“Our results confirm those previously reported by other authors, that C. auris is grouped in different independent clusters according to its geographical origin. Although all Spanish isolates were genotypically distinct from Indian, Omani, U.K., and Venezuelan isolates, there seems to be some connection with South African isolates.”
Hospital Le Fe continues to struggle with C. auris. As of March, 335 patients have tested positive for the pathogen, and 80 have developed candidemias.
“We feel we may be approaching the end of this episode, but it’s really not possible to be sure,” he said.
Dr. Pemán had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: ECCMID 2018 Peman et al. S0067.
MADRID – The anticipated global emergence of multidrug resistant Candida auris is now an established fact, but a case study presented at the European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases annual congress demonstrates just how devastating an outbreak can be to a medical facility and its surgical ICU patients.
The dangerous invasive infection is spreading through Asia, Europe, and the Americas, causing potentially fatal candidemias and proving devilishly difficult to eradicate in health care facilities once it becomes established.
Several multidrug resistant (MDR) C. auris outbreaks were reported at the ECCMID meeting. Most troubling: a continuing outbreak in a hospital in Valencia, Spain, in which 17 patients have died – a 41% fatality rate among those who developed a fulminant C. auris candidemia, Javier Pemán, MD, said at the meeting. The strain appeared to be a clonal population not previously identified in published reports.
“C. auris is hard to remove from the hospital environment,” once it becomes established, said Dr. Pemán of La Fe University and Polytechnic Hospital, Valencia. “When an outbreak lasts for months, as ours has, it is difficult, but necessary, to maintain control measures, identify it early in the lab, and isolate and treat patients early with combination therapy.”
He and his team have relied primarily on a combination of amphotericin B and echinocandin (AMB+ECN), although, he added, the optimal dosing and treatment time aren’t known, and many C. auris isolates are echinocandin resistant.
MDR C. auris first appearedin Tokyo in 2009. It then spread to South Korea around 2011, and then appeared across Asia and Western Europe. Its first appearance in Spain was the 2016 Le Fe outbreak.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, single cases have appeared in Austria, Belgium, Malaysia, Norway, and the United Arab Emirates. Canada, Colombia, France, Germany, India, Israel, Japan, Kenya, Kuwait, Oman, Pakistan, Panama, South Korea, South Africa, Spain, the United Arab Emirates, the United Kingdom, and Venezuela have experienced multiple outbreaks.
The CDC has recorded 257 confirmed and 30 probable cases of MDR C. auris in the United States as of March 31, 2018. Most of these occurred in New York City and New Jersey; a number of patients had recent stays in hospitals in India, Pakistan, South Africa, the UAE, and Venezuela.
Jacques Meis, MD, of the department of medical microbiology and infectious diseases at Canisius Wilhelmina Hospital, Nijmegen, the Netherlands, set the stage for an extended discussion of C. auris at the meeting.
“This is a multidrug resistant yeast that has emerged in the last decade. Some rare isolates are resistant to all three major antifungal classes. Unlike other Candida species, it seems to persist for prolonged periods in health care environments and to colonize patients’ skin. It behaves rather like resistant bacteria.”
Once established in a health care setting – often an intensive care ward – C. auris poses major infection controls challenges and can be very hard to identify and eradicate, said Dr. Meis.
The identification problem is well known. The 2016 CDC alert noted that “commercially available biochemical-based tests, including API strips and VITEK-2, used in many U.S. laboratories to identify fungi, cannot differentiate C. auris from related species. Because of these challenges, clinical laboratories have misidentified the organism as C. haemulonii and Saccharomyces cerevisiae.”
“It’s often misidentified as other Candida species or as Saccharomyces when we investigate with biochemical methods. C. auris is best identified using Matrix Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization time of flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF),” said Dr. Meis.
Among the presentations at ECCMID were a report of a U.K. outbreak that affected 70 patients in a neuroscience ICU. It was traced to axillary skin-surface temperature probes, and eradicated only after those probes were removed. More than 90% of the isolates were resistant to fluconazole, voriconazole, and posaconazole; 18% were amphotericin resistant.
A poster described the microbiological characteristics of 50 C. auris isolates taken from 11 hospitals in Korea.
Dr. Pemán described the outbreak in Valencia, which began in April 2016; the report was simultaneously published in the online journal Mycoses (2018 Apr 14. doi: 10.1111/myc.12781).
The index case was a 66-year-old man with hepatocellular carcinoma who underwent a liver resection at Hospital Le Fe in April 2016. During his stay in the surgical ICU (SICU), he developed a fungal infection from an unknown, highly fluconazole-resistant yeast. The pathogen was twice misidentified, first as C. haemulonii and then as S. cerevisiae.
Three weeks later, the patient in the adjacent bed developed a similar infection. Sequencing of the internal transcribed spacer confirmed both as a Candida isolate – an organism previously unknown in Spain.
The SICU setup was apparently very conducive to the C. auris life cycle, Dr. Pemán said. It’s a relatively open ward divided into three rooms with 12 beds in each. There are no isolation beds, and dozens of workers have access to the ward every day, including clinical and cleaning staff.
After identifying the second isolate, Dr. Pemán said, infection control staff went into action. They instituted contact precautions in the SICU, and took regular cultures from newly admitted patients and cultures of every SICU patient every 7 days.
“We also started an intense search for more cases throughout the hospital and in 101 SICU workers. Of 305 samples from hands and ears, we found nothing.” They reviewed all the prior fluconazole-resistant Candida isolates; C. auris was not present in the hospital before the index case.
Three weeks after case 2, six new SICU patients tested positive for C. auris (two blood cultures, one vascular line, one respiratory specimen, two rectal swabs, and one urinary tract sample).
“We reinforced contact precautions in colonized and infected patients and started a twice-daily environmental cleaning practice with quaternary ammonium around them,” said Dr. Pemán. They instituted a proactive hospital-wide hand hygiene campaign and spread the word about the outbreak.
By July, there were 11 new colonized patients, 3 of whom developed candidemia. These patients were grouped in the same SICU ward and underwent daily skin treatments with 4% aqueous chlorhexidine wipes.
The environmental inspection found C. auris on beds, tables, walls, and the floor all around infected patients. The pathogen also was living on IV pumps, computer keyboards, and bedside tables. Blood pressure cuffs were a favorite haunt: 19 of 36 samples in the adjacent ICU were positive. These data were separately reported at ECCMID.
Despite all of these efforts at eradication, infections continued to rise. By November, there were 24 newly colonized patients and nine new candidemia episodes in SICU and regular ICU patients. In December, a new infection control bundle began: A surveillance nurse in the C. auris SICU ward was in charge of compliance; any patient with any yeast growth in culture was isolated, and staff used 2% alcohol chlorhexidine wipes before and after IV catheter handling. Staff also washed down all surfaces three times daily with a disinfectant.
Patients could leave isolation after three consecutive C. auris–negative cultures. After discharge, an ultraviolet light decontamination procedure disinfected each patient room.
The pathogen was almost unbelievably resilient, Dr. Pemán noted in the Mycoses article. “In some cases, C. auris was recovered from walls after cleaning with cationic surface–active products ... it was not known until very recently that these products, as well as quaternary ammonium disinfectants, cannot effectively remove C. auris from surfaces.”
As a result of the previous measures, the outbreak slowed down during December 2016, with two new candidemia cases, but by February, the outbreak resumed with 50 new cases and 18 candidemias detected. Cases continued to emerge throughout 2017.
By September 2017, 250 patients had been colonized; 116 of these were included in the Mycoses report. There were 30 episodes of candidemia (26%); of these, 17 died by 30 days (41.4%). Spondylodiscitis and endocarditis each developed in two patients and one developed ventriculitis.
A separate poster by Dr. Pemán and his colleagues gave more details:
• A 52-year-old woman with C. auris–induced endocarditis died after 4 weeks of treatment with AMB+ECN and flucytosine. She had undergone a prosthetic heart valve placement for Ebstein’s anomaly.
• A 71-year-old man with hydrocephalus developed a C. auris–induced infection of his ventriculoperitoneal shunt; he also had undergone cardiovascular surgery and had an ischemic cardiomyopathy. He died despite shunt removal and 8 weeks of AMB+ECN.
• A 71-year-old man who underwent cardiovascular surgery and received a prosthetic heart valve developed endocarditis. He is alive and at last report, on week 26 of AMB+ECN, flucytosine, and isavuconazole.
• A 68-year-old man who underwent abdominal surgery for hepatocellular carcinoma developed spondylodiscitis and is alive after 24 weeks of AMB+ECN.
• A 48-year old female multiple trauma patient developed spondylodiscitis and is alive after 48 weeks of treatment with AMB+ECN.
A multivariate analysis determined that antibacterial treatment increased the risk of candidemia by almost 30 times (odds ratio, 29.59). The next highest risk was neutropenia (OR, 20.7) and then simply being a hospital and SICU patient. Dr. Pemán’s poster said, “In the 16 months before the index case, La Fe recorded 89 candidemias, none caused by C. auris. In the 16 months afterward, there were 154 candidemias, largely C. auris. Before April 2016, C. parapsilosis accounted for the largest portion of candidemias (46%) followed by C. albicans. After the index case, C. auris accounted for 42%, followed by C. parapsilosis (21%) and C. albicans (18%).”
Because of its fluconazole resistance, patients with C. auris received a combined antifungal treatment of liposomal amphotericin B 3 mg/kg per day for 5 days, and a standard dose of echinocandin for 3 weeks. Many C. auris strains are echinocandin resistant, Dr. Pemán noted. This particular strain was clonal, different from any other previously reported, he said.
“Our results confirm those previously reported by other authors, that C. auris is grouped in different independent clusters according to its geographical origin. Although all Spanish isolates were genotypically distinct from Indian, Omani, U.K., and Venezuelan isolates, there seems to be some connection with South African isolates.”
Hospital Le Fe continues to struggle with C. auris. As of March, 335 patients have tested positive for the pathogen, and 80 have developed candidemias.
“We feel we may be approaching the end of this episode, but it’s really not possible to be sure,” he said.
Dr. Pemán had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: ECCMID 2018 Peman et al. S0067.
REPORTING FROM ECCMID 2018
For Gram-negative bacteremias, 7 days of antibiotics is enough
MADRID – Seven days of antibiotic therapy was just as effective as 14 days for patients with Gram-negative bacteremias.
The shorter course was associated with similar cure rates and a faster return to normal activities, Dafna Yahav, MD, said at the European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases annual congress.
“In patients hospitalized with Gram-negative bacteremia and sepsis, a course of 7 antibiotic days was not inferior to 14 days, and resulted in a more rapid return to baseline activity, “ said Dr. Yahav of the Rabin Medical Center, Petah Tikva, Israel. “This could lead to a change in accepted management algorithms and shortened antibiotic therapy. Potentially, though we did not show this in our trial, it may lead to reduced cost, reduced development of resistance, and fewer adverse events.”
During the past few years, a new dogma has emerged in antibiotic treatment paradigms, she said: Shorter is better. Brad Spellberg, MD, described this concept in his 2016 editorial in JAMA Internal Medicine, “The new antibiotic mantra” (Sep 1;176[9]:1254-5).
In it, Dr. Spellberg, of the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, addressed the long-held view that a full 10- or 14-day course of antibiotics was necessary to decrease the risk of creating a resistant strain, even if clinical symptoms were long resolved.
However, he noted, there is little evidence supporting the idea that longer courses suppress the rise of resistance – and, in fact, some data support the opposite.
“To the contrary, specifically for pneumonia, studies have shown that longer courses of therapy result in more emergence of antibiotic resistance, which is consistent with everything we know about natural selection, the driver of antibiotic resistance,” he noted. “In only a few types of infections does resistance emerge at the site of infection; rather, resistance typically emerges off target, among colonizing flora away from the site of infection. Thus, all that is achieved by treating an infection with antibiotics for longer than the patient has symptoms is increased selective pressure driving antibiotic resistance among our colonizing microbial flora.”
The European Union and Infectious Diseases Society of America and the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America have all recently updated their antibiotic stewardship guidelines to include a strong recommendation for the shortest effective duration of antimicrobial therapy.
However, most of the supporting data were drawn from randomized, controlled studies of patients with lung, skin, and kidney infections. Short-course treatments have not been adequately studied in bacteremia patients, Dr. Yahav said.
The aim of her study, which was investigator initiated and received no external funding, was to demonstrate the noninferiority of 7 days of antibiotic therapy, compared with 14 days, in patients with bacteremia arising from Gram-negative infections.
The randomized, open-label study comprised 604 patients in three hospitals: two in Israel and one in Italy. Patients were eligible if they had an aerobic Gram-negative bacteremia of any infection source that was either community- or hospital acquired. The medication choice was left up to the treating physician. Patients were assessed at discharge, and at days 30 and 90.
The primary outcome was a composite 90-day endpoint of all-cause mortality, clinical failure (relapse, new local complications, or distant complications), and readmission or hospital stay longer than 14 days. There were a number of secondary outcomes, including new infection, emergence of antibiotic resistance, total hospital and total antibiotic days, time to return to baseline activity, and adverse events.
The cohort was a mean of 71 years old. About 60% were functionally independent, and the mean Charlson comorbidity score was 2. Most of the infections (90%) were nosocomial. The urinary tract was the largest source of infection (69%). Other sources were abdominal, respiratory, central venous catheter, and skin or soft tissue.
Escherichia coli was the most common infective organism (62%), followed by Klebsiella species and Enterobacteriaceae. A small number of patients had Acinetobacter and Pseudomonas infections.
In the intent-to-treat analysis, the primary composite outcome of all-cause mortality or extended hospital stay occurred in 46% of the 7-day group and 50% of the 14-day group – not significantly different. The results were nearly identical in the per-protocol analysis (46% vs. 49.6%).
Likewise, none of the secondary outcomes posted a significant difference in favor of one treatment arm, including relapse (2.9% vs. 2.7%) and resistance development (10.8% vs. 9.7%).
Dr. Yahav pointed out that total antibiotic-use days were significantly less in the 7-day group, (5 days) than in the 14-day group (10 days). Patients in the short-duration group returned to their normal activities a day earlier than those in the longer-term group (2 days vs. 3 days), a difference that was statistically significant.
The total hospital stay from randomization to day 90 was only half a day shorter in the short-term group (mean, 3 days vs. 3.5 days). That was not a significant finding.
There were some differences in adverse events, although none was statistically significant. The short-duration arm had slightly more cases of kidney injury (0.5%), fewer cases of liver function abnormalities (–1.5%), and half as many rashes (two vs. four). There were two cases of Clostridium difficile in the short-use arm and one in the long-use arm, also not a significant difference.
A subgroup analysis looked at outcomes among the different sources of infection (urinary tract vs. other), whether empirical antibiotics were used, and whether the induced resistance was multdrug or non–multidrug. All of those differences hovered close to the null, but generally favored short antibiotic treatment, Dr. Yahav noted.
“I would conclude from these data that is generally safe to stop antibiotics after 7 days of covering antibiotics for Gram-negative bacteremia patients, if they are hemodynamically stable and nonneutropenic at 7 days, and have no uncontrolled source of infection,” she concluded.
The investigator-initiated study had no outside funding.
SOURCE: Yahav D et al. ECCMID 2018. Oral abstract O1120.
MADRID – Seven days of antibiotic therapy was just as effective as 14 days for patients with Gram-negative bacteremias.
The shorter course was associated with similar cure rates and a faster return to normal activities, Dafna Yahav, MD, said at the European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases annual congress.
“In patients hospitalized with Gram-negative bacteremia and sepsis, a course of 7 antibiotic days was not inferior to 14 days, and resulted in a more rapid return to baseline activity, “ said Dr. Yahav of the Rabin Medical Center, Petah Tikva, Israel. “This could lead to a change in accepted management algorithms and shortened antibiotic therapy. Potentially, though we did not show this in our trial, it may lead to reduced cost, reduced development of resistance, and fewer adverse events.”
During the past few years, a new dogma has emerged in antibiotic treatment paradigms, she said: Shorter is better. Brad Spellberg, MD, described this concept in his 2016 editorial in JAMA Internal Medicine, “The new antibiotic mantra” (Sep 1;176[9]:1254-5).
In it, Dr. Spellberg, of the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, addressed the long-held view that a full 10- or 14-day course of antibiotics was necessary to decrease the risk of creating a resistant strain, even if clinical symptoms were long resolved.
However, he noted, there is little evidence supporting the idea that longer courses suppress the rise of resistance – and, in fact, some data support the opposite.
“To the contrary, specifically for pneumonia, studies have shown that longer courses of therapy result in more emergence of antibiotic resistance, which is consistent with everything we know about natural selection, the driver of antibiotic resistance,” he noted. “In only a few types of infections does resistance emerge at the site of infection; rather, resistance typically emerges off target, among colonizing flora away from the site of infection. Thus, all that is achieved by treating an infection with antibiotics for longer than the patient has symptoms is increased selective pressure driving antibiotic resistance among our colonizing microbial flora.”
The European Union and Infectious Diseases Society of America and the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America have all recently updated their antibiotic stewardship guidelines to include a strong recommendation for the shortest effective duration of antimicrobial therapy.
However, most of the supporting data were drawn from randomized, controlled studies of patients with lung, skin, and kidney infections. Short-course treatments have not been adequately studied in bacteremia patients, Dr. Yahav said.
The aim of her study, which was investigator initiated and received no external funding, was to demonstrate the noninferiority of 7 days of antibiotic therapy, compared with 14 days, in patients with bacteremia arising from Gram-negative infections.
The randomized, open-label study comprised 604 patients in three hospitals: two in Israel and one in Italy. Patients were eligible if they had an aerobic Gram-negative bacteremia of any infection source that was either community- or hospital acquired. The medication choice was left up to the treating physician. Patients were assessed at discharge, and at days 30 and 90.
The primary outcome was a composite 90-day endpoint of all-cause mortality, clinical failure (relapse, new local complications, or distant complications), and readmission or hospital stay longer than 14 days. There were a number of secondary outcomes, including new infection, emergence of antibiotic resistance, total hospital and total antibiotic days, time to return to baseline activity, and adverse events.
The cohort was a mean of 71 years old. About 60% were functionally independent, and the mean Charlson comorbidity score was 2. Most of the infections (90%) were nosocomial. The urinary tract was the largest source of infection (69%). Other sources were abdominal, respiratory, central venous catheter, and skin or soft tissue.
Escherichia coli was the most common infective organism (62%), followed by Klebsiella species and Enterobacteriaceae. A small number of patients had Acinetobacter and Pseudomonas infections.
In the intent-to-treat analysis, the primary composite outcome of all-cause mortality or extended hospital stay occurred in 46% of the 7-day group and 50% of the 14-day group – not significantly different. The results were nearly identical in the per-protocol analysis (46% vs. 49.6%).
Likewise, none of the secondary outcomes posted a significant difference in favor of one treatment arm, including relapse (2.9% vs. 2.7%) and resistance development (10.8% vs. 9.7%).
Dr. Yahav pointed out that total antibiotic-use days were significantly less in the 7-day group, (5 days) than in the 14-day group (10 days). Patients in the short-duration group returned to their normal activities a day earlier than those in the longer-term group (2 days vs. 3 days), a difference that was statistically significant.
The total hospital stay from randomization to day 90 was only half a day shorter in the short-term group (mean, 3 days vs. 3.5 days). That was not a significant finding.
There were some differences in adverse events, although none was statistically significant. The short-duration arm had slightly more cases of kidney injury (0.5%), fewer cases of liver function abnormalities (–1.5%), and half as many rashes (two vs. four). There were two cases of Clostridium difficile in the short-use arm and one in the long-use arm, also not a significant difference.
A subgroup analysis looked at outcomes among the different sources of infection (urinary tract vs. other), whether empirical antibiotics were used, and whether the induced resistance was multdrug or non–multidrug. All of those differences hovered close to the null, but generally favored short antibiotic treatment, Dr. Yahav noted.
“I would conclude from these data that is generally safe to stop antibiotics after 7 days of covering antibiotics for Gram-negative bacteremia patients, if they are hemodynamically stable and nonneutropenic at 7 days, and have no uncontrolled source of infection,” she concluded.
The investigator-initiated study had no outside funding.
SOURCE: Yahav D et al. ECCMID 2018. Oral abstract O1120.
MADRID – Seven days of antibiotic therapy was just as effective as 14 days for patients with Gram-negative bacteremias.
The shorter course was associated with similar cure rates and a faster return to normal activities, Dafna Yahav, MD, said at the European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases annual congress.
“In patients hospitalized with Gram-negative bacteremia and sepsis, a course of 7 antibiotic days was not inferior to 14 days, and resulted in a more rapid return to baseline activity, “ said Dr. Yahav of the Rabin Medical Center, Petah Tikva, Israel. “This could lead to a change in accepted management algorithms and shortened antibiotic therapy. Potentially, though we did not show this in our trial, it may lead to reduced cost, reduced development of resistance, and fewer adverse events.”
During the past few years, a new dogma has emerged in antibiotic treatment paradigms, she said: Shorter is better. Brad Spellberg, MD, described this concept in his 2016 editorial in JAMA Internal Medicine, “The new antibiotic mantra” (Sep 1;176[9]:1254-5).
In it, Dr. Spellberg, of the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, addressed the long-held view that a full 10- or 14-day course of antibiotics was necessary to decrease the risk of creating a resistant strain, even if clinical symptoms were long resolved.
However, he noted, there is little evidence supporting the idea that longer courses suppress the rise of resistance – and, in fact, some data support the opposite.
“To the contrary, specifically for pneumonia, studies have shown that longer courses of therapy result in more emergence of antibiotic resistance, which is consistent with everything we know about natural selection, the driver of antibiotic resistance,” he noted. “In only a few types of infections does resistance emerge at the site of infection; rather, resistance typically emerges off target, among colonizing flora away from the site of infection. Thus, all that is achieved by treating an infection with antibiotics for longer than the patient has symptoms is increased selective pressure driving antibiotic resistance among our colonizing microbial flora.”
The European Union and Infectious Diseases Society of America and the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America have all recently updated their antibiotic stewardship guidelines to include a strong recommendation for the shortest effective duration of antimicrobial therapy.
However, most of the supporting data were drawn from randomized, controlled studies of patients with lung, skin, and kidney infections. Short-course treatments have not been adequately studied in bacteremia patients, Dr. Yahav said.
The aim of her study, which was investigator initiated and received no external funding, was to demonstrate the noninferiority of 7 days of antibiotic therapy, compared with 14 days, in patients with bacteremia arising from Gram-negative infections.
The randomized, open-label study comprised 604 patients in three hospitals: two in Israel and one in Italy. Patients were eligible if they had an aerobic Gram-negative bacteremia of any infection source that was either community- or hospital acquired. The medication choice was left up to the treating physician. Patients were assessed at discharge, and at days 30 and 90.
The primary outcome was a composite 90-day endpoint of all-cause mortality, clinical failure (relapse, new local complications, or distant complications), and readmission or hospital stay longer than 14 days. There were a number of secondary outcomes, including new infection, emergence of antibiotic resistance, total hospital and total antibiotic days, time to return to baseline activity, and adverse events.
The cohort was a mean of 71 years old. About 60% were functionally independent, and the mean Charlson comorbidity score was 2. Most of the infections (90%) were nosocomial. The urinary tract was the largest source of infection (69%). Other sources were abdominal, respiratory, central venous catheter, and skin or soft tissue.
Escherichia coli was the most common infective organism (62%), followed by Klebsiella species and Enterobacteriaceae. A small number of patients had Acinetobacter and Pseudomonas infections.
In the intent-to-treat analysis, the primary composite outcome of all-cause mortality or extended hospital stay occurred in 46% of the 7-day group and 50% of the 14-day group – not significantly different. The results were nearly identical in the per-protocol analysis (46% vs. 49.6%).
Likewise, none of the secondary outcomes posted a significant difference in favor of one treatment arm, including relapse (2.9% vs. 2.7%) and resistance development (10.8% vs. 9.7%).
Dr. Yahav pointed out that total antibiotic-use days were significantly less in the 7-day group, (5 days) than in the 14-day group (10 days). Patients in the short-duration group returned to their normal activities a day earlier than those in the longer-term group (2 days vs. 3 days), a difference that was statistically significant.
The total hospital stay from randomization to day 90 was only half a day shorter in the short-term group (mean, 3 days vs. 3.5 days). That was not a significant finding.
There were some differences in adverse events, although none was statistically significant. The short-duration arm had slightly more cases of kidney injury (0.5%), fewer cases of liver function abnormalities (–1.5%), and half as many rashes (two vs. four). There were two cases of Clostridium difficile in the short-use arm and one in the long-use arm, also not a significant difference.
A subgroup analysis looked at outcomes among the different sources of infection (urinary tract vs. other), whether empirical antibiotics were used, and whether the induced resistance was multdrug or non–multidrug. All of those differences hovered close to the null, but generally favored short antibiotic treatment, Dr. Yahav noted.
“I would conclude from these data that is generally safe to stop antibiotics after 7 days of covering antibiotics for Gram-negative bacteremia patients, if they are hemodynamically stable and nonneutropenic at 7 days, and have no uncontrolled source of infection,” she concluded.
The investigator-initiated study had no outside funding.
SOURCE: Yahav D et al. ECCMID 2018. Oral abstract O1120.
REPORTING FROM ECCMID 2018
Key clinical point: Two weeks of antibiotic treatment conferred no benefits over 7 days of treatment in patients with Gram-negative bacteremias.
Major finding: All-cause mortality and extended hospital stay occurred in 46% of the 7-day group and 50% of the 14-day group – not significantly different.
Study details: The randomized, open-label trial comprised 604 patients.
Disclosures: The investigator-initiated study had no external funding. Dr. Yahav had no financial disclosures.
Source: Yahav D et al. ECCMID 2018. Oral Abstract O1120.
Three days of beta-lactam beat clinically stable CAP
MADRID – Three days of beta-lactam therapy was just as effective as 8 days for clinically stable patients presenting with community-acquired pneumonia.
In a randomized, placebo-controlled trial, 15-day cure rates were 69.9% in patients who took 3 days of antibiotics and 61.2% in those who took 8 days – a nonsignificant difference, Aurélien Dinh, MD, said at the European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases annual congress.
“Reducing treatment time now appears to be manageable and effective in a number of infectious diseases,” Dr. Dinh explained. “Although there are some limits, surely, this change in practice might lead to reduced rates of multidrug-resistant bacteria, fewer adverse events, and surely lower costs.”
The French PTC Trial (Short Duration Treatment of Non-Severe Community-Acquired Pneumonia) randomized 310 patients (mean age, 73.5 years) to either short- or long-course treatment with a beta-lactam antibiotic. Patients were eligible for the study if they were admitted to the hospital for community-acquired pneumonia based on respiratory signs, fever of 38° C or higher, and evidence of new infiltrate on chest radiograph.
All patients were treated with 3 days of amoxicillin/clavulanic acid (Augmentin) or third-generation cephalosporin. Those who had responded clinically by day 3 entered the 5-day randomization period, receiving placebo or 5 more days of active therapy with the same agent.
Clinical requirements for randomization included being afebrile with stable heart and respiratory rate, a systolic blood pressure of at least 90 mm Hg, and oxygen saturation of at least 90%.
The primary endpoint was clinical cure at day 15: no fever, absence of or improvement in respiratory symptoms (dyspnea, cough, purulent sputum, and cackles), and no need for additional antibiotic treatment for any indication.
Secondary endpoints were cure at day 30, 30-day mortality, adverse events, length of stay, return to usual activities by day 30, and quality of life at day 30.
Many of the generally elderly patient cohort had comorbid illnesses, including diabetes (about 20%), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (about 35%), and coronary insufficiency (about 14%). About 20% were active smokers. Less than 10% had gotten a pneumococcal vaccine in the past 5 years.
At admission, more than half of patients were dyspneic, 80% had cough, and 39% had purulent sputum. The median PSI/PORT Score was 82.
After 3 days of treatment, clinical cure was not significantly different between the 3- and 8-day groups, either in the intent-to-treat analysis (69.9% vs. 61.2%) or in the per-protocol analysis (75.7% vs. 68.7%).
Because the trial had closed days before the ECCMID meeting, only the primary endpoints were available for discussion, Dr. Dinh said. Investigators are analyzing the secondary endpoint data, which he said would be published at a later date.
Despite the positive results, Dr. Dinh cautioned against using the study as justification for a one-size-fits-all treatment for community-acquired pneumonia.
“Although I think we demonstrated that 3 days of treatment with beta-lactam is not inferior to 8 days, this cannot be imposed without regard to individual patient status,” he cautioned. Such a treatment paradigm would not be advisable for patients with moderately severe pneumonia, who were excluded from the study, or those with compromised immune systems.
Nor does Dr. Dinh expect wholesale clinical embracing of the encouraging results, which bolster the ever-accumulating data in favor of shorter courses of antibiotics for some infectious diseases.
“I think there is a chance that clinicians who normally treat for 9 or 10 days may now feel comfortable reducing to 7,” he said with a chuckle.
The French Ministry of Health sponsored the study. Dr. Dinh had no competing financial interests.
SOURCE: Dinh et al. ECCMID 2018, Oral Abstract O1126.
MADRID – Three days of beta-lactam therapy was just as effective as 8 days for clinically stable patients presenting with community-acquired pneumonia.
In a randomized, placebo-controlled trial, 15-day cure rates were 69.9% in patients who took 3 days of antibiotics and 61.2% in those who took 8 days – a nonsignificant difference, Aurélien Dinh, MD, said at the European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases annual congress.
“Reducing treatment time now appears to be manageable and effective in a number of infectious diseases,” Dr. Dinh explained. “Although there are some limits, surely, this change in practice might lead to reduced rates of multidrug-resistant bacteria, fewer adverse events, and surely lower costs.”
The French PTC Trial (Short Duration Treatment of Non-Severe Community-Acquired Pneumonia) randomized 310 patients (mean age, 73.5 years) to either short- or long-course treatment with a beta-lactam antibiotic. Patients were eligible for the study if they were admitted to the hospital for community-acquired pneumonia based on respiratory signs, fever of 38° C or higher, and evidence of new infiltrate on chest radiograph.
All patients were treated with 3 days of amoxicillin/clavulanic acid (Augmentin) or third-generation cephalosporin. Those who had responded clinically by day 3 entered the 5-day randomization period, receiving placebo or 5 more days of active therapy with the same agent.
Clinical requirements for randomization included being afebrile with stable heart and respiratory rate, a systolic blood pressure of at least 90 mm Hg, and oxygen saturation of at least 90%.
The primary endpoint was clinical cure at day 15: no fever, absence of or improvement in respiratory symptoms (dyspnea, cough, purulent sputum, and cackles), and no need for additional antibiotic treatment for any indication.
Secondary endpoints were cure at day 30, 30-day mortality, adverse events, length of stay, return to usual activities by day 30, and quality of life at day 30.
Many of the generally elderly patient cohort had comorbid illnesses, including diabetes (about 20%), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (about 35%), and coronary insufficiency (about 14%). About 20% were active smokers. Less than 10% had gotten a pneumococcal vaccine in the past 5 years.
At admission, more than half of patients were dyspneic, 80% had cough, and 39% had purulent sputum. The median PSI/PORT Score was 82.
After 3 days of treatment, clinical cure was not significantly different between the 3- and 8-day groups, either in the intent-to-treat analysis (69.9% vs. 61.2%) or in the per-protocol analysis (75.7% vs. 68.7%).
Because the trial had closed days before the ECCMID meeting, only the primary endpoints were available for discussion, Dr. Dinh said. Investigators are analyzing the secondary endpoint data, which he said would be published at a later date.
Despite the positive results, Dr. Dinh cautioned against using the study as justification for a one-size-fits-all treatment for community-acquired pneumonia.
“Although I think we demonstrated that 3 days of treatment with beta-lactam is not inferior to 8 days, this cannot be imposed without regard to individual patient status,” he cautioned. Such a treatment paradigm would not be advisable for patients with moderately severe pneumonia, who were excluded from the study, or those with compromised immune systems.
Nor does Dr. Dinh expect wholesale clinical embracing of the encouraging results, which bolster the ever-accumulating data in favor of shorter courses of antibiotics for some infectious diseases.
“I think there is a chance that clinicians who normally treat for 9 or 10 days may now feel comfortable reducing to 7,” he said with a chuckle.
The French Ministry of Health sponsored the study. Dr. Dinh had no competing financial interests.
SOURCE: Dinh et al. ECCMID 2018, Oral Abstract O1126.
MADRID – Three days of beta-lactam therapy was just as effective as 8 days for clinically stable patients presenting with community-acquired pneumonia.
In a randomized, placebo-controlled trial, 15-day cure rates were 69.9% in patients who took 3 days of antibiotics and 61.2% in those who took 8 days – a nonsignificant difference, Aurélien Dinh, MD, said at the European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases annual congress.
“Reducing treatment time now appears to be manageable and effective in a number of infectious diseases,” Dr. Dinh explained. “Although there are some limits, surely, this change in practice might lead to reduced rates of multidrug-resistant bacteria, fewer adverse events, and surely lower costs.”
The French PTC Trial (Short Duration Treatment of Non-Severe Community-Acquired Pneumonia) randomized 310 patients (mean age, 73.5 years) to either short- or long-course treatment with a beta-lactam antibiotic. Patients were eligible for the study if they were admitted to the hospital for community-acquired pneumonia based on respiratory signs, fever of 38° C or higher, and evidence of new infiltrate on chest radiograph.
All patients were treated with 3 days of amoxicillin/clavulanic acid (Augmentin) or third-generation cephalosporin. Those who had responded clinically by day 3 entered the 5-day randomization period, receiving placebo or 5 more days of active therapy with the same agent.
Clinical requirements for randomization included being afebrile with stable heart and respiratory rate, a systolic blood pressure of at least 90 mm Hg, and oxygen saturation of at least 90%.
The primary endpoint was clinical cure at day 15: no fever, absence of or improvement in respiratory symptoms (dyspnea, cough, purulent sputum, and cackles), and no need for additional antibiotic treatment for any indication.
Secondary endpoints were cure at day 30, 30-day mortality, adverse events, length of stay, return to usual activities by day 30, and quality of life at day 30.
Many of the generally elderly patient cohort had comorbid illnesses, including diabetes (about 20%), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (about 35%), and coronary insufficiency (about 14%). About 20% were active smokers. Less than 10% had gotten a pneumococcal vaccine in the past 5 years.
At admission, more than half of patients were dyspneic, 80% had cough, and 39% had purulent sputum. The median PSI/PORT Score was 82.
After 3 days of treatment, clinical cure was not significantly different between the 3- and 8-day groups, either in the intent-to-treat analysis (69.9% vs. 61.2%) or in the per-protocol analysis (75.7% vs. 68.7%).
Because the trial had closed days before the ECCMID meeting, only the primary endpoints were available for discussion, Dr. Dinh said. Investigators are analyzing the secondary endpoint data, which he said would be published at a later date.
Despite the positive results, Dr. Dinh cautioned against using the study as justification for a one-size-fits-all treatment for community-acquired pneumonia.
“Although I think we demonstrated that 3 days of treatment with beta-lactam is not inferior to 8 days, this cannot be imposed without regard to individual patient status,” he cautioned. Such a treatment paradigm would not be advisable for patients with moderately severe pneumonia, who were excluded from the study, or those with compromised immune systems.
Nor does Dr. Dinh expect wholesale clinical embracing of the encouraging results, which bolster the ever-accumulating data in favor of shorter courses of antibiotics for some infectious diseases.
“I think there is a chance that clinicians who normally treat for 9 or 10 days may now feel comfortable reducing to 7,” he said with a chuckle.
The French Ministry of Health sponsored the study. Dr. Dinh had no competing financial interests.
SOURCE: Dinh et al. ECCMID 2018, Oral Abstract O1126.
REPORTING FROM ECCMID 2018
Key clinical point: Three days of beta-lactam treatment were as effective as 8 days in curing clinically stable patients with community-acquired pneumonia.
Major finding: Cure rates at 15 days were 69.9% in the 3-day group, compared with 61.2% in the 8-day group, a nonsignificant difference.
Study details: The placebo-controlled study randomized 310 patients to treatment.
Disclosures: The French Ministry of Health sponsored the trial. Dr. Dinh had no financial disclosures.
Source: Dinh et al. ECCMID 2018, oral abstract O1126.
ESBL-B before colorectal surgery ups risk of surgical site infection
MADRID – Patients who are carriers of , despite a standard prophylactic antibiotic regimen.
Surgical site infections (SSIs) occurred in 23% of those who tested positive for the pathogens preoperatively, compared with 10.5% of ESBL-B–negative patients – a significant increased risk of 2.25, Yehuda Carmeli, MD, said at the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases annual congress.
ESBL-B was not the infective pathogen in most infection cases, but being a carrier increased the likelihood of an ESBL-B SSI. ESBL-B was the pathogen in 7.2% of the carriers and 1.6% of the noncarriers. However, investigators are still working to determine if the species present in the wound infection are the same as the ones present at baseline, said Dr. Carmeli of Tel Aviv Medical Center.
All of these results are emerging from the WP4 study, which was carried out in three hospitals in Serbia, Switzerland, and Israel. Designed as a before-and-after trial, it tested the theory that identifying ESBL carriers and targeting presurgical antibiotic prophylaxis could improve their surgical outcomes.
WP4 was one of five studies in the multinational R-GNOSIS project. “Resistance in Gram-Negative Organisms: Studying Intervention Strategies” is a 12-million-euro, 5-year European collaborative research project designed to identify effective interventions for reducing the carriage, infection, and spread of multi-drug resistant Gram-negative bacteria. From 2012 to 2017, WP4 enrolled almost 4,000 adults scheduled to undergo colorectal surgery (excluding appendectomy or minor anorectal procedures).
Several of the studies were reported at ECCMID 2018.
This portion of R-GNOSIS was intended to investigate the relationship between ESBL-B carriage and postoperative surgical site infections among colorectal surgery patients.
The study comprised 3,626 patients who were preoperatively screened for ESBL-B within 2 weeks of colorectal surgery. The ESBL-B carriage rate was 15.3% overall, but ranged from 12% to 20% by site. Of the carriers, 222 were included in this study sample. They were randomly matched with 444 noncarriers.
Anywhere from 2 weeks to 2 days before surgery, all of the patients received a standard prophylactic antibiotic. This was most often an infusion of 1.5 g cefuroxime plus 500 mg metronidazole. Other cephalosporins were allowed at the clinician’s discretion.
Patients were a mean of 62 years old. Nearly half (48%) had cardiovascular disease and about a third had undergone a prior colorectal surgical procedure. Cancer was the surgical indication in about 70%. Other indications were inflammatory bowel disease and diverticular disease.
A multivariate analysis controlled for age, cardiovascular disease, indication for surgery, and whether the procedure included a rectal resection, retention of drain at the surgical site, or stoma. The model also controlled for National Nosocomial Infection Surveillance score, a three-point scale that estimates surgical infection risk. Among this cohort, 48% were at low risk, 43% at moderate risk, and 10% at high risk.
Dr. Carmeli made no financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Carmeli et al, ECCMID 2018, Oral Abstract O1133.
MADRID – Patients who are carriers of , despite a standard prophylactic antibiotic regimen.
Surgical site infections (SSIs) occurred in 23% of those who tested positive for the pathogens preoperatively, compared with 10.5% of ESBL-B–negative patients – a significant increased risk of 2.25, Yehuda Carmeli, MD, said at the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases annual congress.
ESBL-B was not the infective pathogen in most infection cases, but being a carrier increased the likelihood of an ESBL-B SSI. ESBL-B was the pathogen in 7.2% of the carriers and 1.6% of the noncarriers. However, investigators are still working to determine if the species present in the wound infection are the same as the ones present at baseline, said Dr. Carmeli of Tel Aviv Medical Center.
All of these results are emerging from the WP4 study, which was carried out in three hospitals in Serbia, Switzerland, and Israel. Designed as a before-and-after trial, it tested the theory that identifying ESBL carriers and targeting presurgical antibiotic prophylaxis could improve their surgical outcomes.
WP4 was one of five studies in the multinational R-GNOSIS project. “Resistance in Gram-Negative Organisms: Studying Intervention Strategies” is a 12-million-euro, 5-year European collaborative research project designed to identify effective interventions for reducing the carriage, infection, and spread of multi-drug resistant Gram-negative bacteria. From 2012 to 2017, WP4 enrolled almost 4,000 adults scheduled to undergo colorectal surgery (excluding appendectomy or minor anorectal procedures).
Several of the studies were reported at ECCMID 2018.
This portion of R-GNOSIS was intended to investigate the relationship between ESBL-B carriage and postoperative surgical site infections among colorectal surgery patients.
The study comprised 3,626 patients who were preoperatively screened for ESBL-B within 2 weeks of colorectal surgery. The ESBL-B carriage rate was 15.3% overall, but ranged from 12% to 20% by site. Of the carriers, 222 were included in this study sample. They were randomly matched with 444 noncarriers.
Anywhere from 2 weeks to 2 days before surgery, all of the patients received a standard prophylactic antibiotic. This was most often an infusion of 1.5 g cefuroxime plus 500 mg metronidazole. Other cephalosporins were allowed at the clinician’s discretion.
Patients were a mean of 62 years old. Nearly half (48%) had cardiovascular disease and about a third had undergone a prior colorectal surgical procedure. Cancer was the surgical indication in about 70%. Other indications were inflammatory bowel disease and diverticular disease.
A multivariate analysis controlled for age, cardiovascular disease, indication for surgery, and whether the procedure included a rectal resection, retention of drain at the surgical site, or stoma. The model also controlled for National Nosocomial Infection Surveillance score, a three-point scale that estimates surgical infection risk. Among this cohort, 48% were at low risk, 43% at moderate risk, and 10% at high risk.
Dr. Carmeli made no financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Carmeli et al, ECCMID 2018, Oral Abstract O1133.
MADRID – Patients who are carriers of , despite a standard prophylactic antibiotic regimen.
Surgical site infections (SSIs) occurred in 23% of those who tested positive for the pathogens preoperatively, compared with 10.5% of ESBL-B–negative patients – a significant increased risk of 2.25, Yehuda Carmeli, MD, said at the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases annual congress.
ESBL-B was not the infective pathogen in most infection cases, but being a carrier increased the likelihood of an ESBL-B SSI. ESBL-B was the pathogen in 7.2% of the carriers and 1.6% of the noncarriers. However, investigators are still working to determine if the species present in the wound infection are the same as the ones present at baseline, said Dr. Carmeli of Tel Aviv Medical Center.
All of these results are emerging from the WP4 study, which was carried out in three hospitals in Serbia, Switzerland, and Israel. Designed as a before-and-after trial, it tested the theory that identifying ESBL carriers and targeting presurgical antibiotic prophylaxis could improve their surgical outcomes.
WP4 was one of five studies in the multinational R-GNOSIS project. “Resistance in Gram-Negative Organisms: Studying Intervention Strategies” is a 12-million-euro, 5-year European collaborative research project designed to identify effective interventions for reducing the carriage, infection, and spread of multi-drug resistant Gram-negative bacteria. From 2012 to 2017, WP4 enrolled almost 4,000 adults scheduled to undergo colorectal surgery (excluding appendectomy or minor anorectal procedures).
Several of the studies were reported at ECCMID 2018.
This portion of R-GNOSIS was intended to investigate the relationship between ESBL-B carriage and postoperative surgical site infections among colorectal surgery patients.
The study comprised 3,626 patients who were preoperatively screened for ESBL-B within 2 weeks of colorectal surgery. The ESBL-B carriage rate was 15.3% overall, but ranged from 12% to 20% by site. Of the carriers, 222 were included in this study sample. They were randomly matched with 444 noncarriers.
Anywhere from 2 weeks to 2 days before surgery, all of the patients received a standard prophylactic antibiotic. This was most often an infusion of 1.5 g cefuroxime plus 500 mg metronidazole. Other cephalosporins were allowed at the clinician’s discretion.
Patients were a mean of 62 years old. Nearly half (48%) had cardiovascular disease and about a third had undergone a prior colorectal surgical procedure. Cancer was the surgical indication in about 70%. Other indications were inflammatory bowel disease and diverticular disease.
A multivariate analysis controlled for age, cardiovascular disease, indication for surgery, and whether the procedure included a rectal resection, retention of drain at the surgical site, or stoma. The model also controlled for National Nosocomial Infection Surveillance score, a three-point scale that estimates surgical infection risk. Among this cohort, 48% were at low risk, 43% at moderate risk, and 10% at high risk.
Dr. Carmeli made no financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Carmeli et al, ECCMID 2018, Oral Abstract O1133.
REPORTING FROM ECCMID 2018
Key clinical point: ESBL-B colonization increased the risk of surgical site infections after colorectal surgery, despite use of standard preoperative antibiotics.
Major finding: ESBL-B carriage more than doubled the risk of a colorectal surgical site infection by (OR 2.25).
Study details: The prospective study comprised 222 carriers and 444 noncarriers.
Disclosures: The study is part of the R-GNOSIS project, a 12-million-euro, 5-year European collaborative research project designed to identify effective interventions for reducing the carriage, infection, and spread of multi-drug resistant Gram-negative bacteria.
Source: Carmeli Y et al. ECCMID 2018, Oral Abstract O1130.
ESBL-resistant bacteria spread in hospital despite strict contact precautions
MADRID – even when staff employed an active surveillance screening protocol to identify every carrier at admission.
The failure of precautions may have root in two thorny issues, said Friederike Maechler, MD, who presented the data at the the European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases annual congress.
“Adherence to strict contact isolation and hand hygiene is never 100% in a real-life scenario,” said Dr. Maechler, of Charite University Hospital, Berlin. Also, she said, contact isolation can only be effective in a ward if all, or at least most, of the ESBL-E carriers are identified. “Even with an extensive surveillance screening program established, many carriers remained unknown to the health care staff.”
The 25-month study, dubbed R-Gnosis, was conducted in 20 Western European hospitals in Madrid, Berlin, Utrecht, and Geneva. It compared 12 months of contact precaution with standard precaution infection control strategies in medical and surgical non-ICUs.
The entire study hinged on a strict protocol to identify as many ESBL-E carriers as possible. This was done by screening upon admission to the unit, screening once per week during the hospital stay, and screening on discharge. Each patient underwent deep rectal swabs that were cultured on agar and screened for resistance.
The crossover design trial randomized each unit to either contact precautions or standard precautions for 12 months, followed by a 1-month washout period, after which they began the other protocol.
In all, 50,870 patients were entered into the study. By the end, Dr. Maechler had data on 11,367 patients with full screening and follow-up.
Standard precautions did not require a private bedroom, with gloves, gowns, and apron needed for direct contact to body fluids or wounds only, and consistent hand hygiene. Contact precautions required a private bedroom and strict hand hygiene, with gloves, gowns, and aprons used for any patient contact. Study staff monitored compliance with these procedures monthly.
The primary outcome was the ESBL-E acquisition rate per 1,000 patient days. This was defined as a new ESBL-E detection after the patient had a prior negative screen. Dr. Maechler noted that by epidemiological definition, acquisition does not necessarily imply cross-transmission from other patients.
Adherence to the study protocols was good, she said. Adherence to both contact and standard precautions was about 85%, while adherence to hand hygiene was less at around 62%.
Admission ESBL-E screenings revealed that about 12% of the study population was colonized with the strain at admission. The proportion was nearly identical in the contact and standard precaution groups (11.6%, 12.2%).
The incidence density of ward-acquired ESBL-E per 1,000 patient-days at risk was 4.6 in both intervention periods, regardless of the type of precaution taken. Contact precautions appeared to be slightly less effective for Escherichia coli (3.6 per 1,000 patient-days in contact precautions vs. 3.5 in standard), compared with Klebsiella pneumoniae (1.8 vs. 2.2).
A multivariate analysis controlled for screening compliance, colonization pressure, and length of stay, study site, and season of year. It showed that strict contact precautions did not reduce the risk of ward-acquired ESBL-E carriage.
Dr. Maechler had no financial disclosures. The R-Gnosis study was funded by the European Community’s Seventh Framework Programme.
SOURCE: Maechler F et al. ECCMID 2018, Oral Abstract O1130.
MADRID – even when staff employed an active surveillance screening protocol to identify every carrier at admission.
The failure of precautions may have root in two thorny issues, said Friederike Maechler, MD, who presented the data at the the European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases annual congress.
“Adherence to strict contact isolation and hand hygiene is never 100% in a real-life scenario,” said Dr. Maechler, of Charite University Hospital, Berlin. Also, she said, contact isolation can only be effective in a ward if all, or at least most, of the ESBL-E carriers are identified. “Even with an extensive surveillance screening program established, many carriers remained unknown to the health care staff.”
The 25-month study, dubbed R-Gnosis, was conducted in 20 Western European hospitals in Madrid, Berlin, Utrecht, and Geneva. It compared 12 months of contact precaution with standard precaution infection control strategies in medical and surgical non-ICUs.
The entire study hinged on a strict protocol to identify as many ESBL-E carriers as possible. This was done by screening upon admission to the unit, screening once per week during the hospital stay, and screening on discharge. Each patient underwent deep rectal swabs that were cultured on agar and screened for resistance.
The crossover design trial randomized each unit to either contact precautions or standard precautions for 12 months, followed by a 1-month washout period, after which they began the other protocol.
In all, 50,870 patients were entered into the study. By the end, Dr. Maechler had data on 11,367 patients with full screening and follow-up.
Standard precautions did not require a private bedroom, with gloves, gowns, and apron needed for direct contact to body fluids or wounds only, and consistent hand hygiene. Contact precautions required a private bedroom and strict hand hygiene, with gloves, gowns, and aprons used for any patient contact. Study staff monitored compliance with these procedures monthly.
The primary outcome was the ESBL-E acquisition rate per 1,000 patient days. This was defined as a new ESBL-E detection after the patient had a prior negative screen. Dr. Maechler noted that by epidemiological definition, acquisition does not necessarily imply cross-transmission from other patients.
Adherence to the study protocols was good, she said. Adherence to both contact and standard precautions was about 85%, while adherence to hand hygiene was less at around 62%.
Admission ESBL-E screenings revealed that about 12% of the study population was colonized with the strain at admission. The proportion was nearly identical in the contact and standard precaution groups (11.6%, 12.2%).
The incidence density of ward-acquired ESBL-E per 1,000 patient-days at risk was 4.6 in both intervention periods, regardless of the type of precaution taken. Contact precautions appeared to be slightly less effective for Escherichia coli (3.6 per 1,000 patient-days in contact precautions vs. 3.5 in standard), compared with Klebsiella pneumoniae (1.8 vs. 2.2).
A multivariate analysis controlled for screening compliance, colonization pressure, and length of stay, study site, and season of year. It showed that strict contact precautions did not reduce the risk of ward-acquired ESBL-E carriage.
Dr. Maechler had no financial disclosures. The R-Gnosis study was funded by the European Community’s Seventh Framework Programme.
SOURCE: Maechler F et al. ECCMID 2018, Oral Abstract O1130.
MADRID – even when staff employed an active surveillance screening protocol to identify every carrier at admission.
The failure of precautions may have root in two thorny issues, said Friederike Maechler, MD, who presented the data at the the European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases annual congress.
“Adherence to strict contact isolation and hand hygiene is never 100% in a real-life scenario,” said Dr. Maechler, of Charite University Hospital, Berlin. Also, she said, contact isolation can only be effective in a ward if all, or at least most, of the ESBL-E carriers are identified. “Even with an extensive surveillance screening program established, many carriers remained unknown to the health care staff.”
The 25-month study, dubbed R-Gnosis, was conducted in 20 Western European hospitals in Madrid, Berlin, Utrecht, and Geneva. It compared 12 months of contact precaution with standard precaution infection control strategies in medical and surgical non-ICUs.
The entire study hinged on a strict protocol to identify as many ESBL-E carriers as possible. This was done by screening upon admission to the unit, screening once per week during the hospital stay, and screening on discharge. Each patient underwent deep rectal swabs that were cultured on agar and screened for resistance.
The crossover design trial randomized each unit to either contact precautions or standard precautions for 12 months, followed by a 1-month washout period, after which they began the other protocol.
In all, 50,870 patients were entered into the study. By the end, Dr. Maechler had data on 11,367 patients with full screening and follow-up.
Standard precautions did not require a private bedroom, with gloves, gowns, and apron needed for direct contact to body fluids or wounds only, and consistent hand hygiene. Contact precautions required a private bedroom and strict hand hygiene, with gloves, gowns, and aprons used for any patient contact. Study staff monitored compliance with these procedures monthly.
The primary outcome was the ESBL-E acquisition rate per 1,000 patient days. This was defined as a new ESBL-E detection after the patient had a prior negative screen. Dr. Maechler noted that by epidemiological definition, acquisition does not necessarily imply cross-transmission from other patients.
Adherence to the study protocols was good, she said. Adherence to both contact and standard precautions was about 85%, while adherence to hand hygiene was less at around 62%.
Admission ESBL-E screenings revealed that about 12% of the study population was colonized with the strain at admission. The proportion was nearly identical in the contact and standard precaution groups (11.6%, 12.2%).
The incidence density of ward-acquired ESBL-E per 1,000 patient-days at risk was 4.6 in both intervention periods, regardless of the type of precaution taken. Contact precautions appeared to be slightly less effective for Escherichia coli (3.6 per 1,000 patient-days in contact precautions vs. 3.5 in standard), compared with Klebsiella pneumoniae (1.8 vs. 2.2).
A multivariate analysis controlled for screening compliance, colonization pressure, and length of stay, study site, and season of year. It showed that strict contact precautions did not reduce the risk of ward-acquired ESBL-E carriage.
Dr. Maechler had no financial disclosures. The R-Gnosis study was funded by the European Community’s Seventh Framework Programme.
SOURCE: Maechler F et al. ECCMID 2018, Oral Abstract O1130.
REPORTING FROM ECCMID 2018
Key clinical point: A protocol of strict contact precautions and hand hygiene was no better than standard contact precautions at preventing the spread of extended-spectrum, beta-lactamase–resistant Enterobacteriaceae.
Major finding: The incidence density of ward-acquired ESBL-E per 1,000 patient-days at risk was 4.6, regardless of precaution.
Study details: The 25-month crossover trial comprised more than 11,000 patients.
Disclosures: Dr. Maechler had no financial disclosures. The R-Gnosis study was funded by the European Community’s Seventh Framework Programme.
Source: Maechler F et al. ECCMID 2018, Oral Abstract O1130.
CAZ-AVI appears safe, effective in pediatric complicated UTI, intra-abdominal infections
MADRID – Two randomized phase 2b trials show the combination of ceftazidime-avibactam (CAZ-AVI) is safe and effective in children with complicated intra-abdominal infections or complicated urinary tract infections (UTIs).
The combination already is approved for these conditions in adults, said John Bradley, MD, who presented the studies at the European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases annual congress.
However, Pfizer, which recently acquired the drug combination from AstraZeneca as part of its small-molecule anti-infectives sell-off, intends to go for a pediatric approval for these two indications. The studies, which had secondary efficacy endpoints, will be used as part of the application package to the Food and Drug Administration and the European Medicines Agency, said Dr. Bradley, professor of clinical pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego.
“For those of you who take care of adults and use these drugs, this seems like old news, but those of us who take care of children can rejoice, because these are the first pediatric data presented. And – no surprise – the combination appears to be as safe and effective in children as it is in adults.”
Both studies concluded in late 2017. “We have the data locked and it’s being cleaned and soon will be submitted to regulatory agencies,” Dr. Bradley said. “However, we do not yet have approval so if you do use it, it will still be considered an off-label use until regulatory agencies work with the sponsor to achieve approval.”
Both studies were international, conducted in the United States, Europe, Russia, South Korea, Taiwan, and Turkey.
The first study included 83 children, mean age 10 years, who had complicated intra-abdominal infections precipitated by ruptured appendicitis. About 90% already had been treated with other antibiotics. In this trial, the CAZ-AVI combination was augmented with metronidazole, and compared to meropenem, in 72-hour infusions. The microbiologic test of cure was conducted at 8-15 days with a late follow-up at 20-36 days after the last infusion.
Most of the patents (83%) had an infective organism identified; it was most often Escherichia coli or Pseudomonas aeruginosa. All pathogens were susceptible to the study drugs.
Five children in the combination group experienced a serious adverse event. These included one case each of ileus, intestinal obstruction, large intestine perforation, renal colic, and urethra meatus stenosis. There was one case of ileus in the meropenem group.
There was one case of diarrhea in the combination group. There were three allergic reactions in each group (cough, pruritus, and rash). The meropenem group also had two cases of anemia.
At the test-of-cure point, clinical response was similar in the combination and meropenem groups, both in clinical evidence (93% vs. 95%) and microbiological response (90% vs. 95%) At last follow-up, 100% of each group was clinically cured. The microbiological cure rates were 90% and 95%, respectively.
Success for complicated UTI
The complicated UTI study was likewise good news for CAZ-AVI, this time without metronidazole. This study included 95 children, mean age 6 years, in the same globally gathered cohorts. All of the children were hospitalized; they were randomized to CAZ-AVI at age-specific doses or cefepime, less than 2,000 mg/infusion for 72 hours. The test of cure was conducted at 8-15 days with a late follow-up at 20-36 days after the last infusion.
Most patients (83%) had acute pyelonephritis. About a quarter had at least one complicating factor, including obstructive uropathies due to functional or anatomic abnormalities of the urogenital tract, recurrent UTI, vesicoureteral reflex, or intermittent catheterization. About 20% of the group had a urological abnormality and 40% had been on a systemic antibiotic in the 2 weeks before study entry.
The most common infective organism was E. coli, (92%) followed by Klebsiella pneumoniae, Proteus mirabilis, and Enterobacter cloacae.
Again, about half of each group had at least one adverse event. Serious adverse events occurred in 12% of the combination group and 7% of the cefepime group. Three patients taking the combination discontinued because of the reaction.
There were eight serious events in the combination group, including abdominal pain, constipation, cystitis, acute pyelonephritis, UTI (not considered related to the study drug) viral infection, nervous system disorder, and nephrolithiasis. There were two serious adverse events in the cefepime group (cystitis and acute pyelonephritis).
Favorable clinical outcomes occurred in 89% of the combination group and 82.6% of the cefepime group. A microbiological cure was evident in 79.6% and 60.9%, respectively.
The combination was more effective than was cefepime at eradicating E. coli (79.6% vs. 59.1%), although no statistical analysis was presented. The other, less-frequent pathogens did not co-occur in both groups, so comparisons were not made. However, the combination eradicated P. mirabilis in both patients who had it, and 50% of K. pneumoniae infections.
A sustained clinical cure occurred in 81% of the combination group and 82.6% of the cefepime group.
Dr. Bradley said the University of California, San Diego, received fees from both Pfizer or AstraZeneca relating to the studies.
SOURCE: Bradley J et al. ECCMID 2018 oral abstracts O1123 and O1124.
MADRID – Two randomized phase 2b trials show the combination of ceftazidime-avibactam (CAZ-AVI) is safe and effective in children with complicated intra-abdominal infections or complicated urinary tract infections (UTIs).
The combination already is approved for these conditions in adults, said John Bradley, MD, who presented the studies at the European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases annual congress.
However, Pfizer, which recently acquired the drug combination from AstraZeneca as part of its small-molecule anti-infectives sell-off, intends to go for a pediatric approval for these two indications. The studies, which had secondary efficacy endpoints, will be used as part of the application package to the Food and Drug Administration and the European Medicines Agency, said Dr. Bradley, professor of clinical pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego.
“For those of you who take care of adults and use these drugs, this seems like old news, but those of us who take care of children can rejoice, because these are the first pediatric data presented. And – no surprise – the combination appears to be as safe and effective in children as it is in adults.”
Both studies concluded in late 2017. “We have the data locked and it’s being cleaned and soon will be submitted to regulatory agencies,” Dr. Bradley said. “However, we do not yet have approval so if you do use it, it will still be considered an off-label use until regulatory agencies work with the sponsor to achieve approval.”
Both studies were international, conducted in the United States, Europe, Russia, South Korea, Taiwan, and Turkey.
The first study included 83 children, mean age 10 years, who had complicated intra-abdominal infections precipitated by ruptured appendicitis. About 90% already had been treated with other antibiotics. In this trial, the CAZ-AVI combination was augmented with metronidazole, and compared to meropenem, in 72-hour infusions. The microbiologic test of cure was conducted at 8-15 days with a late follow-up at 20-36 days after the last infusion.
Most of the patents (83%) had an infective organism identified; it was most often Escherichia coli or Pseudomonas aeruginosa. All pathogens were susceptible to the study drugs.
Five children in the combination group experienced a serious adverse event. These included one case each of ileus, intestinal obstruction, large intestine perforation, renal colic, and urethra meatus stenosis. There was one case of ileus in the meropenem group.
There was one case of diarrhea in the combination group. There were three allergic reactions in each group (cough, pruritus, and rash). The meropenem group also had two cases of anemia.
At the test-of-cure point, clinical response was similar in the combination and meropenem groups, both in clinical evidence (93% vs. 95%) and microbiological response (90% vs. 95%) At last follow-up, 100% of each group was clinically cured. The microbiological cure rates were 90% and 95%, respectively.
Success for complicated UTI
The complicated UTI study was likewise good news for CAZ-AVI, this time without metronidazole. This study included 95 children, mean age 6 years, in the same globally gathered cohorts. All of the children were hospitalized; they were randomized to CAZ-AVI at age-specific doses or cefepime, less than 2,000 mg/infusion for 72 hours. The test of cure was conducted at 8-15 days with a late follow-up at 20-36 days after the last infusion.
Most patients (83%) had acute pyelonephritis. About a quarter had at least one complicating factor, including obstructive uropathies due to functional or anatomic abnormalities of the urogenital tract, recurrent UTI, vesicoureteral reflex, or intermittent catheterization. About 20% of the group had a urological abnormality and 40% had been on a systemic antibiotic in the 2 weeks before study entry.
The most common infective organism was E. coli, (92%) followed by Klebsiella pneumoniae, Proteus mirabilis, and Enterobacter cloacae.
Again, about half of each group had at least one adverse event. Serious adverse events occurred in 12% of the combination group and 7% of the cefepime group. Three patients taking the combination discontinued because of the reaction.
There were eight serious events in the combination group, including abdominal pain, constipation, cystitis, acute pyelonephritis, UTI (not considered related to the study drug) viral infection, nervous system disorder, and nephrolithiasis. There were two serious adverse events in the cefepime group (cystitis and acute pyelonephritis).
Favorable clinical outcomes occurred in 89% of the combination group and 82.6% of the cefepime group. A microbiological cure was evident in 79.6% and 60.9%, respectively.
The combination was more effective than was cefepime at eradicating E. coli (79.6% vs. 59.1%), although no statistical analysis was presented. The other, less-frequent pathogens did not co-occur in both groups, so comparisons were not made. However, the combination eradicated P. mirabilis in both patients who had it, and 50% of K. pneumoniae infections.
A sustained clinical cure occurred in 81% of the combination group and 82.6% of the cefepime group.
Dr. Bradley said the University of California, San Diego, received fees from both Pfizer or AstraZeneca relating to the studies.
SOURCE: Bradley J et al. ECCMID 2018 oral abstracts O1123 and O1124.
MADRID – Two randomized phase 2b trials show the combination of ceftazidime-avibactam (CAZ-AVI) is safe and effective in children with complicated intra-abdominal infections or complicated urinary tract infections (UTIs).
The combination already is approved for these conditions in adults, said John Bradley, MD, who presented the studies at the European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases annual congress.
However, Pfizer, which recently acquired the drug combination from AstraZeneca as part of its small-molecule anti-infectives sell-off, intends to go for a pediatric approval for these two indications. The studies, which had secondary efficacy endpoints, will be used as part of the application package to the Food and Drug Administration and the European Medicines Agency, said Dr. Bradley, professor of clinical pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego.
“For those of you who take care of adults and use these drugs, this seems like old news, but those of us who take care of children can rejoice, because these are the first pediatric data presented. And – no surprise – the combination appears to be as safe and effective in children as it is in adults.”
Both studies concluded in late 2017. “We have the data locked and it’s being cleaned and soon will be submitted to regulatory agencies,” Dr. Bradley said. “However, we do not yet have approval so if you do use it, it will still be considered an off-label use until regulatory agencies work with the sponsor to achieve approval.”
Both studies were international, conducted in the United States, Europe, Russia, South Korea, Taiwan, and Turkey.
The first study included 83 children, mean age 10 years, who had complicated intra-abdominal infections precipitated by ruptured appendicitis. About 90% already had been treated with other antibiotics. In this trial, the CAZ-AVI combination was augmented with metronidazole, and compared to meropenem, in 72-hour infusions. The microbiologic test of cure was conducted at 8-15 days with a late follow-up at 20-36 days after the last infusion.
Most of the patents (83%) had an infective organism identified; it was most often Escherichia coli or Pseudomonas aeruginosa. All pathogens were susceptible to the study drugs.
Five children in the combination group experienced a serious adverse event. These included one case each of ileus, intestinal obstruction, large intestine perforation, renal colic, and urethra meatus stenosis. There was one case of ileus in the meropenem group.
There was one case of diarrhea in the combination group. There were three allergic reactions in each group (cough, pruritus, and rash). The meropenem group also had two cases of anemia.
At the test-of-cure point, clinical response was similar in the combination and meropenem groups, both in clinical evidence (93% vs. 95%) and microbiological response (90% vs. 95%) At last follow-up, 100% of each group was clinically cured. The microbiological cure rates were 90% and 95%, respectively.
Success for complicated UTI
The complicated UTI study was likewise good news for CAZ-AVI, this time without metronidazole. This study included 95 children, mean age 6 years, in the same globally gathered cohorts. All of the children were hospitalized; they were randomized to CAZ-AVI at age-specific doses or cefepime, less than 2,000 mg/infusion for 72 hours. The test of cure was conducted at 8-15 days with a late follow-up at 20-36 days after the last infusion.
Most patients (83%) had acute pyelonephritis. About a quarter had at least one complicating factor, including obstructive uropathies due to functional or anatomic abnormalities of the urogenital tract, recurrent UTI, vesicoureteral reflex, or intermittent catheterization. About 20% of the group had a urological abnormality and 40% had been on a systemic antibiotic in the 2 weeks before study entry.
The most common infective organism was E. coli, (92%) followed by Klebsiella pneumoniae, Proteus mirabilis, and Enterobacter cloacae.
Again, about half of each group had at least one adverse event. Serious adverse events occurred in 12% of the combination group and 7% of the cefepime group. Three patients taking the combination discontinued because of the reaction.
There were eight serious events in the combination group, including abdominal pain, constipation, cystitis, acute pyelonephritis, UTI (not considered related to the study drug) viral infection, nervous system disorder, and nephrolithiasis. There were two serious adverse events in the cefepime group (cystitis and acute pyelonephritis).
Favorable clinical outcomes occurred in 89% of the combination group and 82.6% of the cefepime group. A microbiological cure was evident in 79.6% and 60.9%, respectively.
The combination was more effective than was cefepime at eradicating E. coli (79.6% vs. 59.1%), although no statistical analysis was presented. The other, less-frequent pathogens did not co-occur in both groups, so comparisons were not made. However, the combination eradicated P. mirabilis in both patients who had it, and 50% of K. pneumoniae infections.
A sustained clinical cure occurred in 81% of the combination group and 82.6% of the cefepime group.
Dr. Bradley said the University of California, San Diego, received fees from both Pfizer or AstraZeneca relating to the studies.
SOURCE: Bradley J et al. ECCMID 2018 oral abstracts O1123 and O1124.
REPORTING FROM ECCMID 2018
Key clinical point: The CAZ-AVI combination was as good as the standard comparator drug in both studies.
Major finding: The combination cured close to 90% of infections in both studies.
Study details: Together, the phase 2b studies comprised 178 children.
Disclosures: Pfizer sponsored the studies.
Source: Bradley J et al. ECCMID 2018 oral abstracts O1123 and O1124.
Don’t shorten therapy for older, sicker cellulitis patients
MADRID – An attempt to balance effective treatment with good antibiotic stewardship fell short when patients with cellulitis who got 6 days of flucloxacillin relapsed significantly sooner and more frequently than did those who received the standard 12 days of treatment.
While cellulitis cure rates at 14 and 28 days were similar between the two groups, 90-day relapse rates were significantly higher for those who took the 6-day course (23.5% vs. 6%), Duncan R. Cranendonk, MD, said at the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases annual conference. The cohort demographics perhaps played into this finding: Most of the group was elderly, hospitalized, and had comorbid conditions.
“However, this is the population clinicians are most likely to see,” said Dr Cranendonk of the University of Amsterdam. “It appears that therapy cannot be safely shortened in this population.”
In light of recent antibiotic trials showing that shorter courses can be as effective as prolonged treatment, Dr. Cranendonk and his colleagues conducted the DANCE (Duration of Antibiotic Therapy for Cellulitis) trial. The study investigated the efficacy of an abbreviated course of intravenous flucloxacillin among 248 patients with cellulitis admitted to 11 Dutch hospitals. At treatment day 6, those who had clinically improved after their initial treatment were randomized to 6 additional days of IV flucloxacillin or to placebo. The primary outcome was cure by day 14 without relapse by day 28.
A 2004 study successfully paved the way for DANCE, Dr. Cranendonk noted. That trial examined 5 versus 10 days of levofloxacin 500 mg for uncomplicated cellulitis in 87 patients. The outcome was positive: There was no significant difference in clinical outcome between the two arms, with a 98% cure rate in both groups.
However, Dr. Cranendonk noted, there were some important differences between the patients in that study and the DANCE cohort. They were, on the whole, younger and generally in better overall health. Also, only 15% of those patients were hospitalized for their infections, while all of the DANCE subjects were treated in the hospital.
Patients enrolled in DANCE were a mean of 62 years old, with a median 28 kg/m2 body mass index. About 40% had experienced cellulitis before, and 25% had diabetes. Most infections were on the leg (84%) and involved the lower leg or the lower leg and the foot. Fever was present in half of the group, lymphadenopathy in a third, and leukocytosis in 70%.
Upon enrollment, all 248 patients received 6 days of 1,000 mg/day IV flucloxacillin, with the option of a step-down to oral treatment (500 mg four times per day) at the treating physician’s discretion. At day 6, patients who were clinically improved (afebrile, no need to an antibiotic switch, no growth in blood culture, and improved symptoms of pain, ulceration, discharge, and fluctuance) were randomized to either another 6 days of flucloxacillin or placebo.
The primary endpoint was cure by day 14, with no relapse and no need for new antibiotics by day 28. The secondary endpoint was relapse by 90 days after initial cure.
After initial treatment, 151 patients entered the randomization phase. At 28 days, relapse-free cure rates were nearly identical: 49% of the 12-day group and 50% of the 6-day group. However, by 90 days, a significant difference became apparent: Patients who had received the 6-day course of flucloxacillin were significantly more likely to have experienced a relapse of cellulitis in the same region (23.5% vs. 6% in the 12-day group). A Kaplan-Meier analysis showed that these patients began to relapse as early as 35 days after the end of therapy. Most relapses occurred during days 60-90. The few relapses in the 12-day group occurred toward the end of the follow-up period, from day 75 onward.
Dr. Cranendonk said the investigation shows that older, less-healthy cellulitis patients can probably benefit from the longer course of antibiotics. “Short-term outcomes aren’t everything,” he noted.
He had no financial disclosures.
A video interview of Dr. Cranendock by ECCMID 2018 is available.
SOURCE: Cranendonk et al. ECCMID 2018, Abstract O1122
MADRID – An attempt to balance effective treatment with good antibiotic stewardship fell short when patients with cellulitis who got 6 days of flucloxacillin relapsed significantly sooner and more frequently than did those who received the standard 12 days of treatment.
While cellulitis cure rates at 14 and 28 days were similar between the two groups, 90-day relapse rates were significantly higher for those who took the 6-day course (23.5% vs. 6%), Duncan R. Cranendonk, MD, said at the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases annual conference. The cohort demographics perhaps played into this finding: Most of the group was elderly, hospitalized, and had comorbid conditions.
“However, this is the population clinicians are most likely to see,” said Dr Cranendonk of the University of Amsterdam. “It appears that therapy cannot be safely shortened in this population.”
In light of recent antibiotic trials showing that shorter courses can be as effective as prolonged treatment, Dr. Cranendonk and his colleagues conducted the DANCE (Duration of Antibiotic Therapy for Cellulitis) trial. The study investigated the efficacy of an abbreviated course of intravenous flucloxacillin among 248 patients with cellulitis admitted to 11 Dutch hospitals. At treatment day 6, those who had clinically improved after their initial treatment were randomized to 6 additional days of IV flucloxacillin or to placebo. The primary outcome was cure by day 14 without relapse by day 28.
A 2004 study successfully paved the way for DANCE, Dr. Cranendonk noted. That trial examined 5 versus 10 days of levofloxacin 500 mg for uncomplicated cellulitis in 87 patients. The outcome was positive: There was no significant difference in clinical outcome between the two arms, with a 98% cure rate in both groups.
However, Dr. Cranendonk noted, there were some important differences between the patients in that study and the DANCE cohort. They were, on the whole, younger and generally in better overall health. Also, only 15% of those patients were hospitalized for their infections, while all of the DANCE subjects were treated in the hospital.
Patients enrolled in DANCE were a mean of 62 years old, with a median 28 kg/m2 body mass index. About 40% had experienced cellulitis before, and 25% had diabetes. Most infections were on the leg (84%) and involved the lower leg or the lower leg and the foot. Fever was present in half of the group, lymphadenopathy in a third, and leukocytosis in 70%.
Upon enrollment, all 248 patients received 6 days of 1,000 mg/day IV flucloxacillin, with the option of a step-down to oral treatment (500 mg four times per day) at the treating physician’s discretion. At day 6, patients who were clinically improved (afebrile, no need to an antibiotic switch, no growth in blood culture, and improved symptoms of pain, ulceration, discharge, and fluctuance) were randomized to either another 6 days of flucloxacillin or placebo.
The primary endpoint was cure by day 14, with no relapse and no need for new antibiotics by day 28. The secondary endpoint was relapse by 90 days after initial cure.
After initial treatment, 151 patients entered the randomization phase. At 28 days, relapse-free cure rates were nearly identical: 49% of the 12-day group and 50% of the 6-day group. However, by 90 days, a significant difference became apparent: Patients who had received the 6-day course of flucloxacillin were significantly more likely to have experienced a relapse of cellulitis in the same region (23.5% vs. 6% in the 12-day group). A Kaplan-Meier analysis showed that these patients began to relapse as early as 35 days after the end of therapy. Most relapses occurred during days 60-90. The few relapses in the 12-day group occurred toward the end of the follow-up period, from day 75 onward.
Dr. Cranendonk said the investigation shows that older, less-healthy cellulitis patients can probably benefit from the longer course of antibiotics. “Short-term outcomes aren’t everything,” he noted.
He had no financial disclosures.
A video interview of Dr. Cranendock by ECCMID 2018 is available.
SOURCE: Cranendonk et al. ECCMID 2018, Abstract O1122
MADRID – An attempt to balance effective treatment with good antibiotic stewardship fell short when patients with cellulitis who got 6 days of flucloxacillin relapsed significantly sooner and more frequently than did those who received the standard 12 days of treatment.
While cellulitis cure rates at 14 and 28 days were similar between the two groups, 90-day relapse rates were significantly higher for those who took the 6-day course (23.5% vs. 6%), Duncan R. Cranendonk, MD, said at the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases annual conference. The cohort demographics perhaps played into this finding: Most of the group was elderly, hospitalized, and had comorbid conditions.
“However, this is the population clinicians are most likely to see,” said Dr Cranendonk of the University of Amsterdam. “It appears that therapy cannot be safely shortened in this population.”
In light of recent antibiotic trials showing that shorter courses can be as effective as prolonged treatment, Dr. Cranendonk and his colleagues conducted the DANCE (Duration of Antibiotic Therapy for Cellulitis) trial. The study investigated the efficacy of an abbreviated course of intravenous flucloxacillin among 248 patients with cellulitis admitted to 11 Dutch hospitals. At treatment day 6, those who had clinically improved after their initial treatment were randomized to 6 additional days of IV flucloxacillin or to placebo. The primary outcome was cure by day 14 without relapse by day 28.
A 2004 study successfully paved the way for DANCE, Dr. Cranendonk noted. That trial examined 5 versus 10 days of levofloxacin 500 mg for uncomplicated cellulitis in 87 patients. The outcome was positive: There was no significant difference in clinical outcome between the two arms, with a 98% cure rate in both groups.
However, Dr. Cranendonk noted, there were some important differences between the patients in that study and the DANCE cohort. They were, on the whole, younger and generally in better overall health. Also, only 15% of those patients were hospitalized for their infections, while all of the DANCE subjects were treated in the hospital.
Patients enrolled in DANCE were a mean of 62 years old, with a median 28 kg/m2 body mass index. About 40% had experienced cellulitis before, and 25% had diabetes. Most infections were on the leg (84%) and involved the lower leg or the lower leg and the foot. Fever was present in half of the group, lymphadenopathy in a third, and leukocytosis in 70%.
Upon enrollment, all 248 patients received 6 days of 1,000 mg/day IV flucloxacillin, with the option of a step-down to oral treatment (500 mg four times per day) at the treating physician’s discretion. At day 6, patients who were clinically improved (afebrile, no need to an antibiotic switch, no growth in blood culture, and improved symptoms of pain, ulceration, discharge, and fluctuance) were randomized to either another 6 days of flucloxacillin or placebo.
The primary endpoint was cure by day 14, with no relapse and no need for new antibiotics by day 28. The secondary endpoint was relapse by 90 days after initial cure.
After initial treatment, 151 patients entered the randomization phase. At 28 days, relapse-free cure rates were nearly identical: 49% of the 12-day group and 50% of the 6-day group. However, by 90 days, a significant difference became apparent: Patients who had received the 6-day course of flucloxacillin were significantly more likely to have experienced a relapse of cellulitis in the same region (23.5% vs. 6% in the 12-day group). A Kaplan-Meier analysis showed that these patients began to relapse as early as 35 days after the end of therapy. Most relapses occurred during days 60-90. The few relapses in the 12-day group occurred toward the end of the follow-up period, from day 75 onward.
Dr. Cranendonk said the investigation shows that older, less-healthy cellulitis patients can probably benefit from the longer course of antibiotics. “Short-term outcomes aren’t everything,” he noted.
He had no financial disclosures.
A video interview of Dr. Cranendock by ECCMID 2018 is available.
SOURCE: Cranendonk et al. ECCMID 2018, Abstract O1122
REPORTING FROM ECCMID 2018
Key clinical point: Elderly patients with cellulitis and comorbid conditions probably need a full 12-day course of treatment.
Major finding: Three-month relapse rates were significantly higher in those who received 6 days of flucloxacillin than they were among those who received 12 days (23.5% vs. 6%).
Study details: Patients who improved on 6 days of treatment were randomized to either placebo or another 6 days of therapy.
Disclosures: Dr. Cranendonk had no financial disclosures.
Source: Cranendonk DR et al. ECCMID 2018, Abstract O1122
Piperacillin-tazobactam tripled risk of death for patients with cephalosporin-resistant septicemia
MADRID – A study designed to test the benefit of piperacillin-tazobactam in cephalosporin-resistant bloodstream infections has showed just the opposite: The combination can be fatal for these patients, conferring a threefold increased risk of death compared with meropenem.
The piperacillin-tazobactam combination (PTZ) was associated with a significantly higher 30-day mortality than that of meropenem (12.3% vs. 3.7%; RR 3.4), Patrick Harris, MD, said at the European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases annual congress.
The number needed to harm with PTZ treatment was 12, said Dr. Harris of the University of Queensland, Australia.
“This was really not the result we wanted. We were expecting to show noninferiority, but the answer we did get was quite compelling. We have to say that in patients with these kinds of bloodstream infections, the use of piperacillin-tazobactam is definitely not supported.”
The signal came on strongly and quickly in the 32-country MERINO trial, he said. An independent data safety monitoring board stopped the study at 75% recruitment after reviewing the alarming interim results last summer.
The trial was designed to test a seemingly sound hypothesis. PTZ is an effective weapon against increasingly extended spectrum beta-lactamase–producing (ESBL) Escherichia coli and Klebsiella infections. These have long been treated with carbapenems, including meropenem, but the widespread global use of that class is putting heavy environmental pressure on these bacteria and creating carbapenem resistance, Dr. Harris said.
“Carbapenems have for many years been the top therapy for these infections, but it may well be a strong selection driver for carbapenem resistance in Gram negative bacilli. We should be thinking about carbapenem-sparing therapy, and it seemed that piperacillin-tazobactam could be useful here.”
Some observational studies do suggest a use for it in this setting but the combination had never been formally investigated. MERINO was designed to do so; investigators hoped to show that PTZ would be noninferior to meropenem in patients with septicemias caused by ESBL E. coli and K. pneumoniae.
The enrollment target for MERINO was 454 patients. Between 2014 and 2017, the study enrolled 391, of whom 379 were included in the final analysis. Patients had to start treatment with the study drugs within 72 hours of confirmatory blood culture. Both arms underwent 4 days of treatment with either PTZ 4.5 g every 6 hours or meropenem 1 g every 8 hours.
The study’s primary outcome was 30-day all-cause mortality. Secondary outcomes were days to clinical and microbiological resolution, clinical and microbiological success at day 4, relapsing septicemia or secondary infection with a PTZ- or meropenem-resistant organism, or Clostridium difficile infection.
The mean age of the patients was 66 years. Most (86%) were infected with resistant strains of E. coli; the rest had K. pneumoniae. About 60% of the infections were acquired in a health care or hospital setting, and about 50% originated in the urinary tract. APACHE II scores were different between the meropenem and PTZ groups (21 vs. 17.9). More patients in PTZ arm had immune compromise (27% vs. 21%).
By 30 days, 23 of those randomized to the combination therapy (12.3%) and seven (3.7%) of those randomized to meropenem had died – a significant 8.6% difference. This translated to more than a threefold increase in the risk of death for those taking the combination (RR 3.4; P = .002). The number needed to harm was just 12.
All of the secondary endpoints also favored meropenem, although the differences were not statistically significant. Patients taking meropenem experienced clinical and microbiological improvement a mean of 1 day sooner (2 vs. 3 days). Microbiological relapse occurred in 2% of those taking meropenem compared with 4.8% of those taking PTZ. The meropenem group was also less likely to develop a multidrug resistant organism or C. difficile infection (4.2% vs. 8%).
The investigators performed several subgroup analyses looking for other trends in 30-day mortality. The difference remained significant no matter how the groups were analyzed.
“Patients with urinary tract infections had a slightly lower risk of mortality, but even after adjusting for risk in several multivariate regression models, the increased risk of 30-day mortality remained,” Dr. Harris said.
The Australasian Society for Antimicrobials and the International Society for Chemotherapy funded the work. Dr. Harris reported having no financial declarations.
MADRID – A study designed to test the benefit of piperacillin-tazobactam in cephalosporin-resistant bloodstream infections has showed just the opposite: The combination can be fatal for these patients, conferring a threefold increased risk of death compared with meropenem.
The piperacillin-tazobactam combination (PTZ) was associated with a significantly higher 30-day mortality than that of meropenem (12.3% vs. 3.7%; RR 3.4), Patrick Harris, MD, said at the European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases annual congress.
The number needed to harm with PTZ treatment was 12, said Dr. Harris of the University of Queensland, Australia.
“This was really not the result we wanted. We were expecting to show noninferiority, but the answer we did get was quite compelling. We have to say that in patients with these kinds of bloodstream infections, the use of piperacillin-tazobactam is definitely not supported.”
The signal came on strongly and quickly in the 32-country MERINO trial, he said. An independent data safety monitoring board stopped the study at 75% recruitment after reviewing the alarming interim results last summer.
The trial was designed to test a seemingly sound hypothesis. PTZ is an effective weapon against increasingly extended spectrum beta-lactamase–producing (ESBL) Escherichia coli and Klebsiella infections. These have long been treated with carbapenems, including meropenem, but the widespread global use of that class is putting heavy environmental pressure on these bacteria and creating carbapenem resistance, Dr. Harris said.
“Carbapenems have for many years been the top therapy for these infections, but it may well be a strong selection driver for carbapenem resistance in Gram negative bacilli. We should be thinking about carbapenem-sparing therapy, and it seemed that piperacillin-tazobactam could be useful here.”
Some observational studies do suggest a use for it in this setting but the combination had never been formally investigated. MERINO was designed to do so; investigators hoped to show that PTZ would be noninferior to meropenem in patients with septicemias caused by ESBL E. coli and K. pneumoniae.
The enrollment target for MERINO was 454 patients. Between 2014 and 2017, the study enrolled 391, of whom 379 were included in the final analysis. Patients had to start treatment with the study drugs within 72 hours of confirmatory blood culture. Both arms underwent 4 days of treatment with either PTZ 4.5 g every 6 hours or meropenem 1 g every 8 hours.
The study’s primary outcome was 30-day all-cause mortality. Secondary outcomes were days to clinical and microbiological resolution, clinical and microbiological success at day 4, relapsing septicemia or secondary infection with a PTZ- or meropenem-resistant organism, or Clostridium difficile infection.
The mean age of the patients was 66 years. Most (86%) were infected with resistant strains of E. coli; the rest had K. pneumoniae. About 60% of the infections were acquired in a health care or hospital setting, and about 50% originated in the urinary tract. APACHE II scores were different between the meropenem and PTZ groups (21 vs. 17.9). More patients in PTZ arm had immune compromise (27% vs. 21%).
By 30 days, 23 of those randomized to the combination therapy (12.3%) and seven (3.7%) of those randomized to meropenem had died – a significant 8.6% difference. This translated to more than a threefold increase in the risk of death for those taking the combination (RR 3.4; P = .002). The number needed to harm was just 12.
All of the secondary endpoints also favored meropenem, although the differences were not statistically significant. Patients taking meropenem experienced clinical and microbiological improvement a mean of 1 day sooner (2 vs. 3 days). Microbiological relapse occurred in 2% of those taking meropenem compared with 4.8% of those taking PTZ. The meropenem group was also less likely to develop a multidrug resistant organism or C. difficile infection (4.2% vs. 8%).
The investigators performed several subgroup analyses looking for other trends in 30-day mortality. The difference remained significant no matter how the groups were analyzed.
“Patients with urinary tract infections had a slightly lower risk of mortality, but even after adjusting for risk in several multivariate regression models, the increased risk of 30-day mortality remained,” Dr. Harris said.
The Australasian Society for Antimicrobials and the International Society for Chemotherapy funded the work. Dr. Harris reported having no financial declarations.
MADRID – A study designed to test the benefit of piperacillin-tazobactam in cephalosporin-resistant bloodstream infections has showed just the opposite: The combination can be fatal for these patients, conferring a threefold increased risk of death compared with meropenem.
The piperacillin-tazobactam combination (PTZ) was associated with a significantly higher 30-day mortality than that of meropenem (12.3% vs. 3.7%; RR 3.4), Patrick Harris, MD, said at the European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases annual congress.
The number needed to harm with PTZ treatment was 12, said Dr. Harris of the University of Queensland, Australia.
“This was really not the result we wanted. We were expecting to show noninferiority, but the answer we did get was quite compelling. We have to say that in patients with these kinds of bloodstream infections, the use of piperacillin-tazobactam is definitely not supported.”
The signal came on strongly and quickly in the 32-country MERINO trial, he said. An independent data safety monitoring board stopped the study at 75% recruitment after reviewing the alarming interim results last summer.
The trial was designed to test a seemingly sound hypothesis. PTZ is an effective weapon against increasingly extended spectrum beta-lactamase–producing (ESBL) Escherichia coli and Klebsiella infections. These have long been treated with carbapenems, including meropenem, but the widespread global use of that class is putting heavy environmental pressure on these bacteria and creating carbapenem resistance, Dr. Harris said.
“Carbapenems have for many years been the top therapy for these infections, but it may well be a strong selection driver for carbapenem resistance in Gram negative bacilli. We should be thinking about carbapenem-sparing therapy, and it seemed that piperacillin-tazobactam could be useful here.”
Some observational studies do suggest a use for it in this setting but the combination had never been formally investigated. MERINO was designed to do so; investigators hoped to show that PTZ would be noninferior to meropenem in patients with septicemias caused by ESBL E. coli and K. pneumoniae.
The enrollment target for MERINO was 454 patients. Between 2014 and 2017, the study enrolled 391, of whom 379 were included in the final analysis. Patients had to start treatment with the study drugs within 72 hours of confirmatory blood culture. Both arms underwent 4 days of treatment with either PTZ 4.5 g every 6 hours or meropenem 1 g every 8 hours.
The study’s primary outcome was 30-day all-cause mortality. Secondary outcomes were days to clinical and microbiological resolution, clinical and microbiological success at day 4, relapsing septicemia or secondary infection with a PTZ- or meropenem-resistant organism, or Clostridium difficile infection.
The mean age of the patients was 66 years. Most (86%) were infected with resistant strains of E. coli; the rest had K. pneumoniae. About 60% of the infections were acquired in a health care or hospital setting, and about 50% originated in the urinary tract. APACHE II scores were different between the meropenem and PTZ groups (21 vs. 17.9). More patients in PTZ arm had immune compromise (27% vs. 21%).
By 30 days, 23 of those randomized to the combination therapy (12.3%) and seven (3.7%) of those randomized to meropenem had died – a significant 8.6% difference. This translated to more than a threefold increase in the risk of death for those taking the combination (RR 3.4; P = .002). The number needed to harm was just 12.
All of the secondary endpoints also favored meropenem, although the differences were not statistically significant. Patients taking meropenem experienced clinical and microbiological improvement a mean of 1 day sooner (2 vs. 3 days). Microbiological relapse occurred in 2% of those taking meropenem compared with 4.8% of those taking PTZ. The meropenem group was also less likely to develop a multidrug resistant organism or C. difficile infection (4.2% vs. 8%).
The investigators performed several subgroup analyses looking for other trends in 30-day mortality. The difference remained significant no matter how the groups were analyzed.
“Patients with urinary tract infections had a slightly lower risk of mortality, but even after adjusting for risk in several multivariate regression models, the increased risk of 30-day mortality remained,” Dr. Harris said.
The Australasian Society for Antimicrobials and the International Society for Chemotherapy funded the work. Dr. Harris reported having no financial declarations.
REPORTING FROM ECCMID 2018
Key clinical point: PTZ more than tripled the risk of 30-day mortality in patients with cephalosporin-resistant bloodstream infections.
Major finding: Compared with meropenem, PZT increased the risk of death by 3.4, with a number needed to harm of 12.
Study details: The study randomized 391 patients.
Disclosures: The Australasian Society for Antimicrobials and the International Society for Chemotherapy funded the work. Dr. Harris has no financial declarations.
Source: Harris et al. ECCMID 2018, abstract O1121.
Ertapenem slashes surgical site infections in carriers of ESBL-producing bacteria
MADRID – A targeted antibiotic strategy that employed ertapenem in carriers of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase–producing Enterobacteriaceae reduced infections after colorectal surgery by 41%, compared with routine treatment with cefuroxime and metronidazole.
The strategy was even more effective at preventing surgical site infections caused by ESBL-producing bacteria, cutting the rate by 87%, Amir Nutman, MD, said at the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases.
He presented the results of the WP4 study, which was carried out in three hospitals in Serbia, Switzerland, and Israel. Designed as a before-and-after trial, it tested the theory that identifying ESBL carriers and targeting presurgical antibiotic prophylaxis could improve their surgical outcomes.
WP4 was one of five studies in the multinational R-GNOSIS project. “Resistance in gram-negative organisms: Studying intervention strategies” is a 12 million euro, 5-year European collaborative research project designed to identify effective interventions for reducing the carriage, infection, and spread of multidrug resistant Gram-negative bacteria. Several of the studies reported at ECCMID 2018.
During 2012-2017, WP4 enrolled almost 4,000 adults scheduled to undergo colorectal surgery (excluding appendectomy or minor anorectal procedures). All patients were screened for ESBL-producing bacteria from 2 weeks to 2 days before their operation. In the first phase, carriers were treated with the standard presurgical prophylaxis of 1.5 g cefuroxime and 500 mg metronidazole intravenously. In phase 2, carriers received targeted prophylaxis with IV ertapenem 1 g. Both interventions were given 30 minutes before surgery commenced.
All patients underwent regular surgical site infection surveillance until hospital discharge, then followed up 30 days later by phone or in person.
The primary outcome was surgical site infection at 30 days. Secondary outcomes were the type of any surgical site infection (superficial, deep, or organ/space), and infections caused by ESBL-producing bacteria.
ESBL screening was carried out on 3,626 patients; carriage prevalence was 13.8%, but varied by center from 9% to 29%. Of the carriers, 468 were included in the study; 247 received routine prophylaxis and 221 received ertapenem.
Patients were a mean of 63 years old; 98% were living at home before admission. About 20% had diabetes; 5% had some type of immunodeficiency. The most common surgical indication was colon cancer (68%), and about a third had undergone prior colon surgery. Most of the surgeries were open, and about half involved a colectomy.
Patients in the ertapenem group had overall better scores on the National Nosocomial Infections Surveillance Basic SSI Risk Index and were less likely to have an intraoperative finding of colon dilation (20.8% vs. 27%).There were no other clinically compelling intraoperative differences between the two groups, including bleeding, bowel spillage, the need for drains, or stoma placement.
Patients who received prophylactic ertapenem had significantly better 30-day outcomes on all measures of infection than did patients who had standard prophylaxis, Dr. Nutman said.
There were 34 surgical site infections in the routine prophylaxis group and 19 in the ertapenem group. Among these, 17 in the routine group and three in the ertapenem group were caused by ESBL-producing bacteria. The ESBL-positive infections were as follows:
- E. coli (thirteen in the routine and one in the ertapenem group).
- Klebsiella species (four and one, respectively).
- Proteus species (one in the ertapenem group).
Other infections were caused by ESBL-nonproducers, including E. coli, Klebsiella, Proteus, Enterococci, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus aureus, and other unspecified organisms. Polymicrobial infections occurred in 25 patients.
In an analysis that controlled for National Nosocomial Infections Surveillance score and colon dilation, patients who received ertapenem were 41% less likely to develop any surgical site infection (15.8% vs. 22.7%; odds ratio, 0.59); 17% less likely to develop a deep infection (9.5% vs. 11.3%; OR, 0.83); and 87% less likely to develop an infection caused by an ESBL-producing bacteria (0.9% vs. 6.5%; OR, 0.13).
Dr. Nutman made no financial declarations.
SOURCE: Nutman et al. ECCMID 2018, Abstract O1129.
MADRID – A targeted antibiotic strategy that employed ertapenem in carriers of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase–producing Enterobacteriaceae reduced infections after colorectal surgery by 41%, compared with routine treatment with cefuroxime and metronidazole.
The strategy was even more effective at preventing surgical site infections caused by ESBL-producing bacteria, cutting the rate by 87%, Amir Nutman, MD, said at the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases.
He presented the results of the WP4 study, which was carried out in three hospitals in Serbia, Switzerland, and Israel. Designed as a before-and-after trial, it tested the theory that identifying ESBL carriers and targeting presurgical antibiotic prophylaxis could improve their surgical outcomes.
WP4 was one of five studies in the multinational R-GNOSIS project. “Resistance in gram-negative organisms: Studying intervention strategies” is a 12 million euro, 5-year European collaborative research project designed to identify effective interventions for reducing the carriage, infection, and spread of multidrug resistant Gram-negative bacteria. Several of the studies reported at ECCMID 2018.
During 2012-2017, WP4 enrolled almost 4,000 adults scheduled to undergo colorectal surgery (excluding appendectomy or minor anorectal procedures). All patients were screened for ESBL-producing bacteria from 2 weeks to 2 days before their operation. In the first phase, carriers were treated with the standard presurgical prophylaxis of 1.5 g cefuroxime and 500 mg metronidazole intravenously. In phase 2, carriers received targeted prophylaxis with IV ertapenem 1 g. Both interventions were given 30 minutes before surgery commenced.
All patients underwent regular surgical site infection surveillance until hospital discharge, then followed up 30 days later by phone or in person.
The primary outcome was surgical site infection at 30 days. Secondary outcomes were the type of any surgical site infection (superficial, deep, or organ/space), and infections caused by ESBL-producing bacteria.
ESBL screening was carried out on 3,626 patients; carriage prevalence was 13.8%, but varied by center from 9% to 29%. Of the carriers, 468 were included in the study; 247 received routine prophylaxis and 221 received ertapenem.
Patients were a mean of 63 years old; 98% were living at home before admission. About 20% had diabetes; 5% had some type of immunodeficiency. The most common surgical indication was colon cancer (68%), and about a third had undergone prior colon surgery. Most of the surgeries were open, and about half involved a colectomy.
Patients in the ertapenem group had overall better scores on the National Nosocomial Infections Surveillance Basic SSI Risk Index and were less likely to have an intraoperative finding of colon dilation (20.8% vs. 27%).There were no other clinically compelling intraoperative differences between the two groups, including bleeding, bowel spillage, the need for drains, or stoma placement.
Patients who received prophylactic ertapenem had significantly better 30-day outcomes on all measures of infection than did patients who had standard prophylaxis, Dr. Nutman said.
There were 34 surgical site infections in the routine prophylaxis group and 19 in the ertapenem group. Among these, 17 in the routine group and three in the ertapenem group were caused by ESBL-producing bacteria. The ESBL-positive infections were as follows:
- E. coli (thirteen in the routine and one in the ertapenem group).
- Klebsiella species (four and one, respectively).
- Proteus species (one in the ertapenem group).
Other infections were caused by ESBL-nonproducers, including E. coli, Klebsiella, Proteus, Enterococci, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus aureus, and other unspecified organisms. Polymicrobial infections occurred in 25 patients.
In an analysis that controlled for National Nosocomial Infections Surveillance score and colon dilation, patients who received ertapenem were 41% less likely to develop any surgical site infection (15.8% vs. 22.7%; odds ratio, 0.59); 17% less likely to develop a deep infection (9.5% vs. 11.3%; OR, 0.83); and 87% less likely to develop an infection caused by an ESBL-producing bacteria (0.9% vs. 6.5%; OR, 0.13).
Dr. Nutman made no financial declarations.
SOURCE: Nutman et al. ECCMID 2018, Abstract O1129.
MADRID – A targeted antibiotic strategy that employed ertapenem in carriers of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase–producing Enterobacteriaceae reduced infections after colorectal surgery by 41%, compared with routine treatment with cefuroxime and metronidazole.
The strategy was even more effective at preventing surgical site infections caused by ESBL-producing bacteria, cutting the rate by 87%, Amir Nutman, MD, said at the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases.
He presented the results of the WP4 study, which was carried out in three hospitals in Serbia, Switzerland, and Israel. Designed as a before-and-after trial, it tested the theory that identifying ESBL carriers and targeting presurgical antibiotic prophylaxis could improve their surgical outcomes.
WP4 was one of five studies in the multinational R-GNOSIS project. “Resistance in gram-negative organisms: Studying intervention strategies” is a 12 million euro, 5-year European collaborative research project designed to identify effective interventions for reducing the carriage, infection, and spread of multidrug resistant Gram-negative bacteria. Several of the studies reported at ECCMID 2018.
During 2012-2017, WP4 enrolled almost 4,000 adults scheduled to undergo colorectal surgery (excluding appendectomy or minor anorectal procedures). All patients were screened for ESBL-producing bacteria from 2 weeks to 2 days before their operation. In the first phase, carriers were treated with the standard presurgical prophylaxis of 1.5 g cefuroxime and 500 mg metronidazole intravenously. In phase 2, carriers received targeted prophylaxis with IV ertapenem 1 g. Both interventions were given 30 minutes before surgery commenced.
All patients underwent regular surgical site infection surveillance until hospital discharge, then followed up 30 days later by phone or in person.
The primary outcome was surgical site infection at 30 days. Secondary outcomes were the type of any surgical site infection (superficial, deep, or organ/space), and infections caused by ESBL-producing bacteria.
ESBL screening was carried out on 3,626 patients; carriage prevalence was 13.8%, but varied by center from 9% to 29%. Of the carriers, 468 were included in the study; 247 received routine prophylaxis and 221 received ertapenem.
Patients were a mean of 63 years old; 98% were living at home before admission. About 20% had diabetes; 5% had some type of immunodeficiency. The most common surgical indication was colon cancer (68%), and about a third had undergone prior colon surgery. Most of the surgeries were open, and about half involved a colectomy.
Patients in the ertapenem group had overall better scores on the National Nosocomial Infections Surveillance Basic SSI Risk Index and were less likely to have an intraoperative finding of colon dilation (20.8% vs. 27%).There were no other clinically compelling intraoperative differences between the two groups, including bleeding, bowel spillage, the need for drains, or stoma placement.
Patients who received prophylactic ertapenem had significantly better 30-day outcomes on all measures of infection than did patients who had standard prophylaxis, Dr. Nutman said.
There were 34 surgical site infections in the routine prophylaxis group and 19 in the ertapenem group. Among these, 17 in the routine group and three in the ertapenem group were caused by ESBL-producing bacteria. The ESBL-positive infections were as follows:
- E. coli (thirteen in the routine and one in the ertapenem group).
- Klebsiella species (four and one, respectively).
- Proteus species (one in the ertapenem group).
Other infections were caused by ESBL-nonproducers, including E. coli, Klebsiella, Proteus, Enterococci, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus aureus, and other unspecified organisms. Polymicrobial infections occurred in 25 patients.
In an analysis that controlled for National Nosocomial Infections Surveillance score and colon dilation, patients who received ertapenem were 41% less likely to develop any surgical site infection (15.8% vs. 22.7%; odds ratio, 0.59); 17% less likely to develop a deep infection (9.5% vs. 11.3%; OR, 0.83); and 87% less likely to develop an infection caused by an ESBL-producing bacteria (0.9% vs. 6.5%; OR, 0.13).
Dr. Nutman made no financial declarations.
SOURCE: Nutman et al. ECCMID 2018, Abstract O1129.
REPORTING FROM ECCMID 2018
Key clinical point: A targeted presurgical antibiotic prophylaxis significantly cut rates of surgical site infections in carriers of extended beta-lactamase–producing bacteria.
Major finding: Ertapenem reduced the rate of surgical site infection by 41% , and the rate of ESBL-producing infections by 87%, compared to routine prophylaxis.
Study details: The study comprised 468 patients.
Disclosures: The study was funded by the European Commission under the Seventh Framework Programme (FP7) for Research and Technology. Dr. Nutman had no financial disclosures.
Source: Nutman A et al. ECCMID 2018, Abstract O1129
Nitrofurantoin beats fosfomycin for uncomplicated UTI
MADRID – (UTIs), a randomized study has determined.
By 28 days, clinical resolution had occurred in 70% of those who took nitrofurantoin and 58% of those who took fosfomycin – a statistically significant 12% difference, Angela Huttner, MD, said at the European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases annual congress.
But the benefit was even more pronounced in women whose infections were caused by Escherichia coli, with a 28% spread in clinical resolution, (78% vs. 50%) and a 14-point spread in microbiological cure (72% vs. 58%), said Dr. Huttner of Geneva University, Switzerland.
The results were simultaneously published online in JAMA (2018 Apr 22. doi: 10.1001/jama.2018.3627).
Despite its success, nitrofurantoin did not live up to its purported 96% UTI cure rate – an established number based on study data from the 1950s-1970s.
Such efficacy was probably a false finding, she said. Studies of that era were much less rigorous than they are today, Dr. Huttner pointed out. The primary endpoint in those studies was typically defined not as complete resolution of symptoms – as it was in her study – but as resolution or improvement.
“Also, improvement was often defined microbiologically, often something like a decrease from 105 colony-forming units to 104, which is never something we would use today.”
The study was conducted in Geneva, Poland, and Israel. It randomized 512 women with an uncomplicated lower UTI to either 5 days of thrice-daily nitrofurantoin 100 mg or to a single 3-gram dose of fosfomycin. The women returned for clinical exam and urine culture at 14 and 28 days after they completed their treatment.
The primary outcome was 28-day clinical response. Success was defined as complete resolution of symptoms, a characterization that Dr. Huttner and her colleagues chose carefully. Many UTI studies include “improvement” in the clinical picture as part of a successful response. Dr. Huttner disagreed with that. “Our patients don’t want a partial response. They don’t want just an improvement. They want complete resolution of their symptoms.”
Failure was defined as the need for additional antibiotics or a change in antibiotic treatment. There was also an “indeterminate” category, for the small minority of patients who still felt some mild symptoms but were without microbiological signs of infection.
The mean age of the women was 44 years. All had an uncomplicated UTI characterized by dysuria, urgency, frequency, or suprapubic tenderness; 73% had a positive baseline urine culture. E. coli was the most common infective organism (about 60%) followed by different Klebsiella species, Proteus, and Enterococci. A few women had mixed pathogen infections. Only six patients had infective pathogens that were resistant to either of the study drugs.
After 28 days of treatment, a clinical cure was determined in 70% of those taking nitrofurantoin and 58% of those taking fosfomycin – an absolute difference of 12 points.
“The difference was obvious at 14 days,” Dr. Huttner noted. At that point, 75% of those taking nitrofurantoin and 66% of those taking fosfomycin reported resolution of their symptoms.
Pathology reflected the improving clinical picture: Microbiologic resolution occurred in 74% of the nitrofurantoin group and 63% of the fosfomycin group.
A post hoc analysis looked at results among the 214 women with confirmed E. coli infections.
The difference in clinical response was “even more pronounced” in these patients, Dr. Huttner said. Through day 28, clinical resolution occurred in 78% of those taking nitrofurantoin and 50% of those taking fosfomycin – a significant difference of 28 points.
Patients with E. coli infections were 4.48 times more likely to fail treatment if they received fosfomycin than if they received nitrofurantoin.
Adverse events were few and primarily gastrointestinal. The most common were mild to moderate nausea and diarrhea (less than 4% in each group).
Both of the antibiotics were popular from the 1950s on, but gradually fell out of favor as more powerful therapies were developed. However, as antibiotic resistance began to develop, infectious disease specialists began to support bringing nitrofurantoin and fosfomycin out of mothballs. In 2011, a panel of international experts convened by the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) and the European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ESCMID) recommended both of the medications as first-line therapy for women with acute uncomplicated cystitis and pyelonephritis.
The group recommended fosfomycin in a single 3-gram dose and a nitrofurantoin regimen of 100 mg twice daily for 5 days. The fosfomycin recommendation is clearly inadequate, Dr. Huttner said.
“Fosfomycin is not a bad drug. I just think it’s underdosed in this setting,” she said.
Dr. Huttner had no financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Huttner A et al. ECCMID 2018. Abstract O0479.
MADRID – (UTIs), a randomized study has determined.
By 28 days, clinical resolution had occurred in 70% of those who took nitrofurantoin and 58% of those who took fosfomycin – a statistically significant 12% difference, Angela Huttner, MD, said at the European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases annual congress.
But the benefit was even more pronounced in women whose infections were caused by Escherichia coli, with a 28% spread in clinical resolution, (78% vs. 50%) and a 14-point spread in microbiological cure (72% vs. 58%), said Dr. Huttner of Geneva University, Switzerland.
The results were simultaneously published online in JAMA (2018 Apr 22. doi: 10.1001/jama.2018.3627).
Despite its success, nitrofurantoin did not live up to its purported 96% UTI cure rate – an established number based on study data from the 1950s-1970s.
Such efficacy was probably a false finding, she said. Studies of that era were much less rigorous than they are today, Dr. Huttner pointed out. The primary endpoint in those studies was typically defined not as complete resolution of symptoms – as it was in her study – but as resolution or improvement.
“Also, improvement was often defined microbiologically, often something like a decrease from 105 colony-forming units to 104, which is never something we would use today.”
The study was conducted in Geneva, Poland, and Israel. It randomized 512 women with an uncomplicated lower UTI to either 5 days of thrice-daily nitrofurantoin 100 mg or to a single 3-gram dose of fosfomycin. The women returned for clinical exam and urine culture at 14 and 28 days after they completed their treatment.
The primary outcome was 28-day clinical response. Success was defined as complete resolution of symptoms, a characterization that Dr. Huttner and her colleagues chose carefully. Many UTI studies include “improvement” in the clinical picture as part of a successful response. Dr. Huttner disagreed with that. “Our patients don’t want a partial response. They don’t want just an improvement. They want complete resolution of their symptoms.”
Failure was defined as the need for additional antibiotics or a change in antibiotic treatment. There was also an “indeterminate” category, for the small minority of patients who still felt some mild symptoms but were without microbiological signs of infection.
The mean age of the women was 44 years. All had an uncomplicated UTI characterized by dysuria, urgency, frequency, or suprapubic tenderness; 73% had a positive baseline urine culture. E. coli was the most common infective organism (about 60%) followed by different Klebsiella species, Proteus, and Enterococci. A few women had mixed pathogen infections. Only six patients had infective pathogens that were resistant to either of the study drugs.
After 28 days of treatment, a clinical cure was determined in 70% of those taking nitrofurantoin and 58% of those taking fosfomycin – an absolute difference of 12 points.
“The difference was obvious at 14 days,” Dr. Huttner noted. At that point, 75% of those taking nitrofurantoin and 66% of those taking fosfomycin reported resolution of their symptoms.
Pathology reflected the improving clinical picture: Microbiologic resolution occurred in 74% of the nitrofurantoin group and 63% of the fosfomycin group.
A post hoc analysis looked at results among the 214 women with confirmed E. coli infections.
The difference in clinical response was “even more pronounced” in these patients, Dr. Huttner said. Through day 28, clinical resolution occurred in 78% of those taking nitrofurantoin and 50% of those taking fosfomycin – a significant difference of 28 points.
Patients with E. coli infections were 4.48 times more likely to fail treatment if they received fosfomycin than if they received nitrofurantoin.
Adverse events were few and primarily gastrointestinal. The most common were mild to moderate nausea and diarrhea (less than 4% in each group).
Both of the antibiotics were popular from the 1950s on, but gradually fell out of favor as more powerful therapies were developed. However, as antibiotic resistance began to develop, infectious disease specialists began to support bringing nitrofurantoin and fosfomycin out of mothballs. In 2011, a panel of international experts convened by the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) and the European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ESCMID) recommended both of the medications as first-line therapy for women with acute uncomplicated cystitis and pyelonephritis.
The group recommended fosfomycin in a single 3-gram dose and a nitrofurantoin regimen of 100 mg twice daily for 5 days. The fosfomycin recommendation is clearly inadequate, Dr. Huttner said.
“Fosfomycin is not a bad drug. I just think it’s underdosed in this setting,” she said.
Dr. Huttner had no financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Huttner A et al. ECCMID 2018. Abstract O0479.
MADRID – (UTIs), a randomized study has determined.
By 28 days, clinical resolution had occurred in 70% of those who took nitrofurantoin and 58% of those who took fosfomycin – a statistically significant 12% difference, Angela Huttner, MD, said at the European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases annual congress.
But the benefit was even more pronounced in women whose infections were caused by Escherichia coli, with a 28% spread in clinical resolution, (78% vs. 50%) and a 14-point spread in microbiological cure (72% vs. 58%), said Dr. Huttner of Geneva University, Switzerland.
The results were simultaneously published online in JAMA (2018 Apr 22. doi: 10.1001/jama.2018.3627).
Despite its success, nitrofurantoin did not live up to its purported 96% UTI cure rate – an established number based on study data from the 1950s-1970s.
Such efficacy was probably a false finding, she said. Studies of that era were much less rigorous than they are today, Dr. Huttner pointed out. The primary endpoint in those studies was typically defined not as complete resolution of symptoms – as it was in her study – but as resolution or improvement.
“Also, improvement was often defined microbiologically, often something like a decrease from 105 colony-forming units to 104, which is never something we would use today.”
The study was conducted in Geneva, Poland, and Israel. It randomized 512 women with an uncomplicated lower UTI to either 5 days of thrice-daily nitrofurantoin 100 mg or to a single 3-gram dose of fosfomycin. The women returned for clinical exam and urine culture at 14 and 28 days after they completed their treatment.
The primary outcome was 28-day clinical response. Success was defined as complete resolution of symptoms, a characterization that Dr. Huttner and her colleagues chose carefully. Many UTI studies include “improvement” in the clinical picture as part of a successful response. Dr. Huttner disagreed with that. “Our patients don’t want a partial response. They don’t want just an improvement. They want complete resolution of their symptoms.”
Failure was defined as the need for additional antibiotics or a change in antibiotic treatment. There was also an “indeterminate” category, for the small minority of patients who still felt some mild symptoms but were without microbiological signs of infection.
The mean age of the women was 44 years. All had an uncomplicated UTI characterized by dysuria, urgency, frequency, or suprapubic tenderness; 73% had a positive baseline urine culture. E. coli was the most common infective organism (about 60%) followed by different Klebsiella species, Proteus, and Enterococci. A few women had mixed pathogen infections. Only six patients had infective pathogens that were resistant to either of the study drugs.
After 28 days of treatment, a clinical cure was determined in 70% of those taking nitrofurantoin and 58% of those taking fosfomycin – an absolute difference of 12 points.
“The difference was obvious at 14 days,” Dr. Huttner noted. At that point, 75% of those taking nitrofurantoin and 66% of those taking fosfomycin reported resolution of their symptoms.
Pathology reflected the improving clinical picture: Microbiologic resolution occurred in 74% of the nitrofurantoin group and 63% of the fosfomycin group.
A post hoc analysis looked at results among the 214 women with confirmed E. coli infections.
The difference in clinical response was “even more pronounced” in these patients, Dr. Huttner said. Through day 28, clinical resolution occurred in 78% of those taking nitrofurantoin and 50% of those taking fosfomycin – a significant difference of 28 points.
Patients with E. coli infections were 4.48 times more likely to fail treatment if they received fosfomycin than if they received nitrofurantoin.
Adverse events were few and primarily gastrointestinal. The most common were mild to moderate nausea and diarrhea (less than 4% in each group).
Both of the antibiotics were popular from the 1950s on, but gradually fell out of favor as more powerful therapies were developed. However, as antibiotic resistance began to develop, infectious disease specialists began to support bringing nitrofurantoin and fosfomycin out of mothballs. In 2011, a panel of international experts convened by the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) and the European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ESCMID) recommended both of the medications as first-line therapy for women with acute uncomplicated cystitis and pyelonephritis.
The group recommended fosfomycin in a single 3-gram dose and a nitrofurantoin regimen of 100 mg twice daily for 5 days. The fosfomycin recommendation is clearly inadequate, Dr. Huttner said.
“Fosfomycin is not a bad drug. I just think it’s underdosed in this setting,” she said.
Dr. Huttner had no financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Huttner A et al. ECCMID 2018. Abstract O0479.
REPORTING FROM ECCMID 2018
Key clinical point: Nitrofurantoin was significantly more effective than was fosfomycin for a clinical and microbiological cure of uncomplicated UTI in women.
Major finding: By 28 days, clinical resolution had occurred in 70% of those who took nitrofurantoin and 58% of those who took fosfomycin .
Study details: The prospective study randomized 512 women.
Disclosures: Dr. Huttner had no financial disclosures.
Source: Huttner A et al. ECCMID 2018. Abstract O0479.