User login
THE COMPARISON
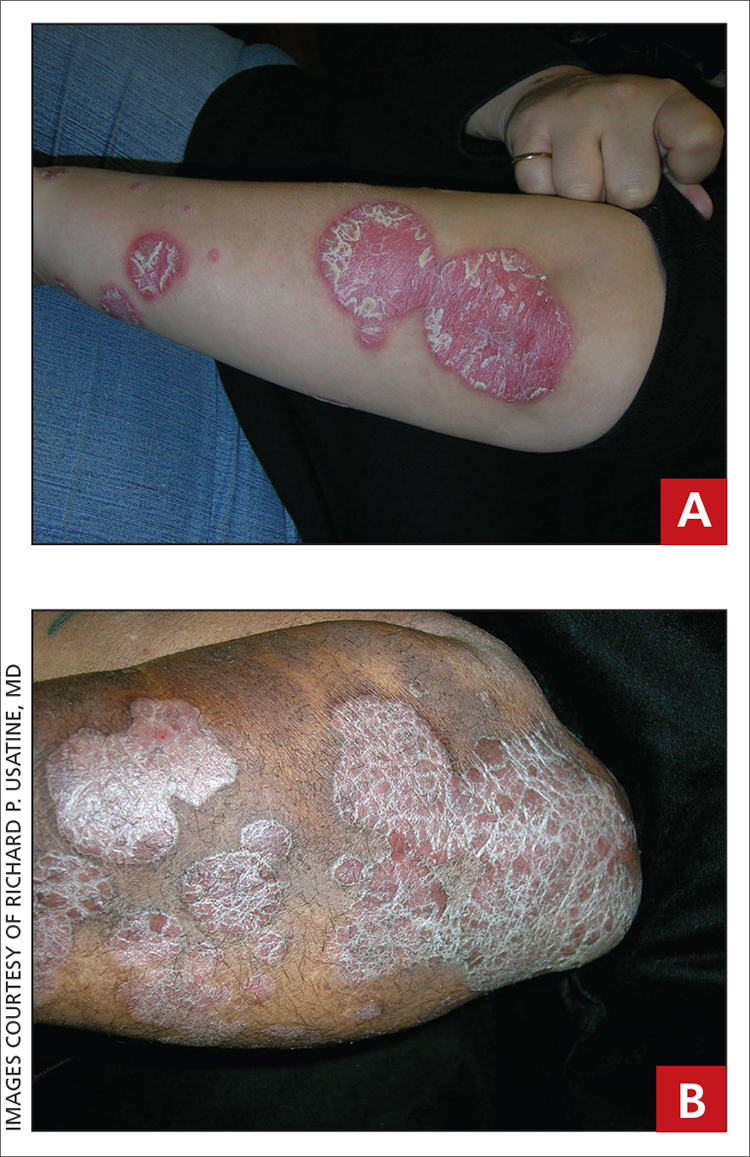
A Elbow and forearm with erythematous, well-demarcated, pink plaques with mild micaceous scale in a 42-year-old White woman.
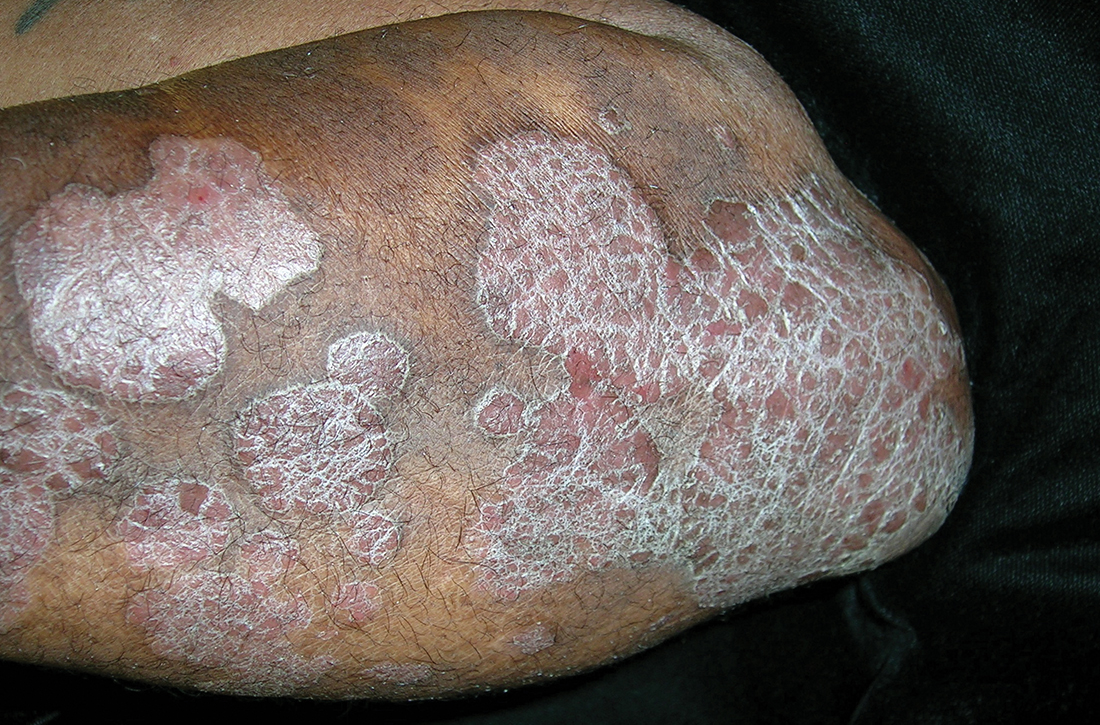
B Elbow and forearm with violaceous, well-demarcated plaques with micaceous scale and hyperpigmented patches around the active plaques in a 58-year-old Black man.
Epidemiology
Psoriasis prevalence in the United States has been estimated at 3.7%.1-3 If broken down by race or ethnicity, the prevalence of psoriasis varies: 2.5% to 3.7% in White adults1-4; 1.3% to 2% in Black adults1-4; 1.6% in Hispanics/other adults1-3; 1% in children overall; 0.29% in White children1,5; and 0.06% in Black children.1,5
Key clinical features in people with darker skin tones include:
- plaques that may appear more violaceous in color instead of pink or erythematous
- higher body surface area of involvement4 and thicker, more scaly plaques6
- increased likelihood of postinflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH).
Worth noting
Although individuals of all skin tones may experience the psychosocial impact of psoriasis, quality-of-life measures have been found to be worse in those with skin of color (SOC) compared to White patients. 1,4 This may be due to the lingering PIH and hypopigmentation that occurs even after inflammatory plaques are treated. Of course, lack of access to care contributes to greater disease burden and more devastating psychological impact.
Health disparity highlight
Psoriasis may be underreported and underdiagnosed in individuals with SOC, as factors contributing to health care disparities may play a role, such as access to health care in general,1,7 and access to clinicians proficient in diagnosing cutaneous diseases in SOC may be delayed.8
Biologic medications are used less often in Black patients than in White patients, despite biologic medications being very efficacious for treatment of psoriasis.1,9,10
1. Kaufman BP, Alexis AF. Psoriasis in skin of color: insights into the epidemiology, clinical presentation, genetics, quality-of-life impact, and treatment of psoriasis in non-white racial/ethnic groups. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2018;19:405-423.
2. Rachakonda TD, Schupp CW, Armstrong AW. Psoriasis prevalence among adults in the United States. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:512-516.
3. Helmick CG, Lee-Han H, Hirsch SC, et al. Prevalence of psoriasis among adults in the U.S.: 2003-2006 and 2009-2010 National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys. Am J Prev Med. 2014;47:37-45.
4. Gelfand JM, Stern RS, Nijsten T, et al. The prevalence of psoriasis in African Americans: results from a population-based study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;52:23-26.
5. Wu JJ, Black MH, Smith N, et al. Low prevalence of psoriasis among children and adolescents in a large multiethnic cohort in southern California. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;65:957-964.
6. Davis SA, Narahari S, Feldman SR, et al. Top dermatologic conditions in patients of color: an analysis of nationally representative data. J Drugs Dermatol. 2012;11:466-473.
7. Alexis AF, Blackcloud P. Psoriasis in skin of color: epidemiology, genetics, clinical presentation, and treatment nuances. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2014;7:16-24.
8. Mundluru SN, Ramalingam ND, Tran HN. Addressing internal medicine residents’ discomfort with basic dermatology in persons of color in the primary care clinic. Am J Med Qual. 2019;34:513-513.
9. Kerr GS, Qaiyumi S, Richards J, et al. Psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis in African-American patients—the need to measure disease burden. Clin Rheumatol. 2015;34:1753-1759.
10. Takeshita J, Gelfand JM, Li P, et al. Psoriasis in the US Medicare population: prevalence, treatment, and factors associated with biologic use. J Invest Dermatol. 2015;135:2955-2963.
THE COMPARISON
A Elbow and forearm with erythematous, well-demarcated, pink plaques with mild micaceous scale in a 42-year-old White woman.
B Elbow and forearm with violaceous, well-demarcated plaques with micaceous scale and hyperpigmented patches around the active plaques in a 58-year-old Black man.

Epidemiology
Psoriasis prevalence in the United States has been estimated at 3.7%.1-3 If broken down by race or ethnicity, the prevalence of psoriasis varies: 2.5% to 3.7% in White adults1-4; 1.3% to 2% in Black adults1-4; 1.6% in Hispanics/other adults1-3; 1% in children overall; 0.29% in White children1,5; and 0.06% in Black children.1,5
Key clinical features in people with darker skin tones include:
- plaques that may appear more violaceous in color instead of pink or erythematous
- higher body surface area of involvement4 and thicker, more scaly plaques6
- increased likelihood of postinflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH).
Worth noting
Although individuals of all skin tones may experience the psychosocial impact of psoriasis, quality-of-life measures have been found to be worse in those with skin of color (SOC) compared to White patients. 1,4 This may be due to the lingering PIH and hypopigmentation that occurs even after inflammatory plaques are treated. Of course, lack of access to care contributes to greater disease burden and more devastating psychological impact.
Health disparity highlight
Psoriasis may be underreported and underdiagnosed in individuals with SOC, as factors contributing to health care disparities may play a role, such as access to health care in general,1,7 and access to clinicians proficient in diagnosing cutaneous diseases in SOC may be delayed.8
Biologic medications are used less often in Black patients than in White patients, despite biologic medications being very efficacious for treatment of psoriasis.1,9,10
THE COMPARISON
A Elbow and forearm with erythematous, well-demarcated, pink plaques with mild micaceous scale in a 42-year-old White woman.
B Elbow and forearm with violaceous, well-demarcated plaques with micaceous scale and hyperpigmented patches around the active plaques in a 58-year-old Black man.

Epidemiology
Psoriasis prevalence in the United States has been estimated at 3.7%.1-3 If broken down by race or ethnicity, the prevalence of psoriasis varies: 2.5% to 3.7% in White adults1-4; 1.3% to 2% in Black adults1-4; 1.6% in Hispanics/other adults1-3; 1% in children overall; 0.29% in White children1,5; and 0.06% in Black children.1,5
Key clinical features in people with darker skin tones include:
- plaques that may appear more violaceous in color instead of pink or erythematous
- higher body surface area of involvement4 and thicker, more scaly plaques6
- increased likelihood of postinflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH).
Worth noting
Although individuals of all skin tones may experience the psychosocial impact of psoriasis, quality-of-life measures have been found to be worse in those with skin of color (SOC) compared to White patients. 1,4 This may be due to the lingering PIH and hypopigmentation that occurs even after inflammatory plaques are treated. Of course, lack of access to care contributes to greater disease burden and more devastating psychological impact.
Health disparity highlight
Psoriasis may be underreported and underdiagnosed in individuals with SOC, as factors contributing to health care disparities may play a role, such as access to health care in general,1,7 and access to clinicians proficient in diagnosing cutaneous diseases in SOC may be delayed.8
Biologic medications are used less often in Black patients than in White patients, despite biologic medications being very efficacious for treatment of psoriasis.1,9,10
1. Kaufman BP, Alexis AF. Psoriasis in skin of color: insights into the epidemiology, clinical presentation, genetics, quality-of-life impact, and treatment of psoriasis in non-white racial/ethnic groups. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2018;19:405-423.
2. Rachakonda TD, Schupp CW, Armstrong AW. Psoriasis prevalence among adults in the United States. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:512-516.
3. Helmick CG, Lee-Han H, Hirsch SC, et al. Prevalence of psoriasis among adults in the U.S.: 2003-2006 and 2009-2010 National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys. Am J Prev Med. 2014;47:37-45.
4. Gelfand JM, Stern RS, Nijsten T, et al. The prevalence of psoriasis in African Americans: results from a population-based study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;52:23-26.
5. Wu JJ, Black MH, Smith N, et al. Low prevalence of psoriasis among children and adolescents in a large multiethnic cohort in southern California. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;65:957-964.
6. Davis SA, Narahari S, Feldman SR, et al. Top dermatologic conditions in patients of color: an analysis of nationally representative data. J Drugs Dermatol. 2012;11:466-473.
7. Alexis AF, Blackcloud P. Psoriasis in skin of color: epidemiology, genetics, clinical presentation, and treatment nuances. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2014;7:16-24.
8. Mundluru SN, Ramalingam ND, Tran HN. Addressing internal medicine residents’ discomfort with basic dermatology in persons of color in the primary care clinic. Am J Med Qual. 2019;34:513-513.
9. Kerr GS, Qaiyumi S, Richards J, et al. Psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis in African-American patients—the need to measure disease burden. Clin Rheumatol. 2015;34:1753-1759.
10. Takeshita J, Gelfand JM, Li P, et al. Psoriasis in the US Medicare population: prevalence, treatment, and factors associated with biologic use. J Invest Dermatol. 2015;135:2955-2963.
1. Kaufman BP, Alexis AF. Psoriasis in skin of color: insights into the epidemiology, clinical presentation, genetics, quality-of-life impact, and treatment of psoriasis in non-white racial/ethnic groups. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2018;19:405-423.
2. Rachakonda TD, Schupp CW, Armstrong AW. Psoriasis prevalence among adults in the United States. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:512-516.
3. Helmick CG, Lee-Han H, Hirsch SC, et al. Prevalence of psoriasis among adults in the U.S.: 2003-2006 and 2009-2010 National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys. Am J Prev Med. 2014;47:37-45.
4. Gelfand JM, Stern RS, Nijsten T, et al. The prevalence of psoriasis in African Americans: results from a population-based study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;52:23-26.
5. Wu JJ, Black MH, Smith N, et al. Low prevalence of psoriasis among children and adolescents in a large multiethnic cohort in southern California. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;65:957-964.
6. Davis SA, Narahari S, Feldman SR, et al. Top dermatologic conditions in patients of color: an analysis of nationally representative data. J Drugs Dermatol. 2012;11:466-473.
7. Alexis AF, Blackcloud P. Psoriasis in skin of color: epidemiology, genetics, clinical presentation, and treatment nuances. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2014;7:16-24.
8. Mundluru SN, Ramalingam ND, Tran HN. Addressing internal medicine residents’ discomfort with basic dermatology in persons of color in the primary care clinic. Am J Med Qual. 2019;34:513-513.
9. Kerr GS, Qaiyumi S, Richards J, et al. Psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis in African-American patients—the need to measure disease burden. Clin Rheumatol. 2015;34:1753-1759.
10. Takeshita J, Gelfand JM, Li P, et al. Psoriasis in the US Medicare population: prevalence, treatment, and factors associated with biologic use. J Invest Dermatol. 2015;135:2955-2963.