User login
Top questions answered about COVID-19 boosters for your patients
Confusion continues to circulate in the wake of decisions on booster doses of the Pfizer/BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine, all announced within 1 week. Many people – including those now eligible and those who officially have to wait for their shot at a third dose – have questions.
Multiple agencies are involved in the booster decisions, and they have put out multiple – and sometimes conflicting – messages about booster doses, leaving more questions than answers for many people.
On Sept. 22, the Food and Drug Administration granted an emergency use authorization (EUA) for a booster dose of the Pfizer mRNA COVID-19 vaccine for those 65 and older and those at high risk for severe illness from the coronavirus, including essential workers whose jobs increase their risk for infection – such as frontline health care workers.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, then overruled advice from the agency’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) to recommend boosters for essential workers such as those working on the front lines during the pandemic.
As it stands now, the CDC recommends that the following groups should get a third dose of the Pfizer vaccine:
- People aged 65 years and older.
- People aged 18 years and older in long-term care settings.
- People aged 50-64 years with underlying medical conditions.
The CDC also recommends that the following groups may receive a booster shot of the Pfizer vaccine, based on their individual benefits and risks:
- People aged 18-49 years with underlying medical conditions.
- People aged 18-64 years at increased risk for COVID-19 exposure and transmission because of occupational or institutional setting.
The CDC currently considers the following groups at increased risk for COVID-19:
- First responders (health care workers, firefighters, police, congregate care staff).
- Education staff (teachers, support staff, day care workers).
- Food and agriculture workers.
- Manufacturing workers.
- Corrections workers.
- U.S. Postal Service workers.
- Public transit workers.
- Grocery store workers.
Health care professionals, among the most trusted sources of COVID-19 information, are likely to encounter a number of patients wondering how all this will work.
“It’s fantastic that boosters will be available for those who the data supports need [them],” Rachael Piltch-Loeb, PhD, said during a media briefing on Sept. 23, held between the FDA and CDC decisions.
“But we’re really in a place where we have a lot more questions and answers about what the next phase of the vaccine availability and updates are going to be in the United States,” added Dr. Piltch-Loeb, preparedness fellow in the division of policy translation and leadership development and a research associate in the department of biostatistics at the Harvard T. H. Chan School of Public Health in Boston.
1. What is the biggest concern you are hearing from patients about getting a booster?
“The biggest concerns are that everyone wants it and they don’t know where to get it. In health care’s defense, the CDC just figured out what to do,” said Janet Englund, MD, professor of pediatric infectious diseases and an infectious disease and virology expert at Seattle Children’s Hospital in Washington.
“Everyone thinks they should be eligible for a booster ... people in their 50s who are not yet 65+, people with young grandchildren, etc.,” she added. “I’m at Seattle Children’s Hospital, so people are asking about booster shots and about getting their children vaccinated.”
Boosters for all COVID-19 vaccines are completely free.
“All COVID-19 vaccines, including booster doses, will be provided free of charge to the U.S. population,” the CDC has said.
2. Will patients need to prove they meet eligibility criteria for a booster shot or will it be the honor system?
“No, patients will only need to attest that they fall into one of the high-risk groups for whom a booster vaccine is authorized,” said Robert Atmar, MD, professor of infectious diseases at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston.
Dr. Piltch-Loeb agreed. “It is likely to be an honor system. It is very unlikely that there will be punishments or other ramifications ... if doses are administered, beyond the approved usage.”
3. If a patient who had the Moderna or the Johnson and Johnson vaccination requests a booster, can health care workers give them Pfizer?
The short answer is no. “This only applies to individuals who have received the Pfizer vaccine,” Dr. Piltch-Loeb said.
More data will be needed before other vaccine boosters are authorized, she added.
“My understanding is the Moderna people have just recently submitted their information, all of their data to the FDA and J&J is in line to do that very shortly,” said William Schaffner, MD, professor of preventive medicine and infectious diseases at Vanderbilt University in Nashville, Tenn. “I would hope that within the next month to 6 weeks, we will get information about both of those vaccines,” Dr. Schaffner said.
4. When are the “mix-and-match” vaccine study results expected to come out?
“We expect that data from the study will be available in the coming weeks,” said Dr. Atmar, who is the national co-principal investigator of a mix-and-match booster trial launched in June 2021.
5. Are side effects of a booster vaccine expected to be about the same as what people experienced during their first or second immunization?
“I’m expecting the side effects will be similar to the second dose,” Dr. Englund said.
“The data presented ... at ACIP suggests that the side effects from the third shot are either the same or actually less than the first two shots,” said Carlos del Rio, MD, distinguished professor of medicine, epidemiology, and global health, and executive associate dean of Emory University School of Medicine at Grady Health System in Atlanta.
”Everyone reacts very differently to vaccines, regardless of vaccine type,” said Eric Ascher, MD, a family medicine physician at Lenox Hill Hospital in New York City. “I have had patients (as well as personal experience) where there were none to minimal symptoms, and others who felt they had a mild flu for 24 hours.”
“I expect no side effects greater than what was felt with you prior doses,” he said. “The vaccine is very safe and the benefit of vaccination outweighs the risks of any mild side effects.”
6. Is it unethical to give a booster to someone outside the approved groups if there are doses remaining at the end of the day in an open vial?
“Offering a booster shot to someone outside of approved groups if remaining doses will go to waste at the end of the day seems like a prudent decision, and relatively harmless action,” said Faith Fletcher, PhD, assistant professor at the Center for Medical Ethics and Health Policy at Baylor College of Medicine.
“However, if doses continue to fall in the laps of unapproved groups, we must evaluate the vaccine systems and structures that advantage some groups and disadvantage others,” she added. “We know that the distribution of COVID-19 vaccines has not been equitable – and some groups have been left behind.”
“I am not an ethicist and there are many competing concerns that this question addresses,” Dr. Atmar said. For example, “there is not a limitation of vaccine supply in the U.S., so that using leftover vaccine to prevent waste is no longer a major concern in the U.S.”
It could be more of a legal than ethical question, Dr. Atmar said. For an individual outside the authorized groups, legally, the FDA’s EUA for boosting does not allow the vaccine to be administered to this person, he said.
“The rationale for the restricted use in the EUA is that at this time the safety and risks associated with such administration are not known, and the benefits also have not been determined,” Dr. Atmar said. “Members of the ACIP raised concerns about other individuals who may potentially benefit from a booster but are not eligible and the importance of making boosters available to them, but from a legal standpoint – I am also not a lawyer, so this is my understanding – administration of the vaccine is limited to those identified in the EUA.”
7. What is the likelihood that one shot will combine COVID and flu protection in the near future?
It is not likely, Dr. Englund said. “The reason is that the flu vaccine changes so much, and it already has four different antigens. This is assuming we keep the same method of making the flu vaccine – the answer could be different if the flu vaccine becomes an mRNA vaccine in the future.”
Companies such as Moderna and Novavax are testing single-dose shots for COVID-19 and influenza, but they are still far from having anything ready for this flu season in the United States.
8. Is there any chance a booster shot distributed now will need to be redesigned for a future variant?
“Absolutely,” Dr. Englund said. “And a booster dose is the time we may want to consider re-engineering a vaccine.”
9. Do you think the FDA/CDC limitations on who is eligible for a booster was in any way influenced by the World Health Organization call for prioritizing shots for the unvaccinated in lower-resource countries?
“This is absolutely still a global problem,” Dr. Piltch-Loeb said. “We need to get more vaccine to more countries and more people as soon as possible, because if there’s anything we’ve seen about the variants it is that ... they can come from all different places.”
“That being said, I think that it is unlikely to change the course of action in the U.S.,” she added, when it comes to comparing the global need with the domestic policy priorities of the administration.
Dr. Atmar was more direct. “No,” he said. “The WHO recommends against boosting of anyone. The U.S. decisions about boosting those in this country who are eligible are aimed toward addressing perceived needs domestically at the same time that vaccines are being provided to other countries.
“The philosophy is to address both ‘needs’ at the same time,” Dr. Atmar said.
10. What does the future hold for booster shots?
“Predicting the future is really hard, especially when it involves COVID,” Dr. del Rio said.
“Having said that, COVID is not the flu, so I doubt there will be need for annual boosters. I think the population eligible for boosters will be expanded ... and the major population not addressed at this point is the people that received either Moderna or J&J [vaccines].”
Kelly Davis contributed to this feature. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Confusion continues to circulate in the wake of decisions on booster doses of the Pfizer/BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine, all announced within 1 week. Many people – including those now eligible and those who officially have to wait for their shot at a third dose – have questions.
Multiple agencies are involved in the booster decisions, and they have put out multiple – and sometimes conflicting – messages about booster doses, leaving more questions than answers for many people.
On Sept. 22, the Food and Drug Administration granted an emergency use authorization (EUA) for a booster dose of the Pfizer mRNA COVID-19 vaccine for those 65 and older and those at high risk for severe illness from the coronavirus, including essential workers whose jobs increase their risk for infection – such as frontline health care workers.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, then overruled advice from the agency’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) to recommend boosters for essential workers such as those working on the front lines during the pandemic.
As it stands now, the CDC recommends that the following groups should get a third dose of the Pfizer vaccine:
- People aged 65 years and older.
- People aged 18 years and older in long-term care settings.
- People aged 50-64 years with underlying medical conditions.
The CDC also recommends that the following groups may receive a booster shot of the Pfizer vaccine, based on their individual benefits and risks:
- People aged 18-49 years with underlying medical conditions.
- People aged 18-64 years at increased risk for COVID-19 exposure and transmission because of occupational or institutional setting.
The CDC currently considers the following groups at increased risk for COVID-19:
- First responders (health care workers, firefighters, police, congregate care staff).
- Education staff (teachers, support staff, day care workers).
- Food and agriculture workers.
- Manufacturing workers.
- Corrections workers.
- U.S. Postal Service workers.
- Public transit workers.
- Grocery store workers.
Health care professionals, among the most trusted sources of COVID-19 information, are likely to encounter a number of patients wondering how all this will work.
“It’s fantastic that boosters will be available for those who the data supports need [them],” Rachael Piltch-Loeb, PhD, said during a media briefing on Sept. 23, held between the FDA and CDC decisions.
“But we’re really in a place where we have a lot more questions and answers about what the next phase of the vaccine availability and updates are going to be in the United States,” added Dr. Piltch-Loeb, preparedness fellow in the division of policy translation and leadership development and a research associate in the department of biostatistics at the Harvard T. H. Chan School of Public Health in Boston.
1. What is the biggest concern you are hearing from patients about getting a booster?
“The biggest concerns are that everyone wants it and they don’t know where to get it. In health care’s defense, the CDC just figured out what to do,” said Janet Englund, MD, professor of pediatric infectious diseases and an infectious disease and virology expert at Seattle Children’s Hospital in Washington.
“Everyone thinks they should be eligible for a booster ... people in their 50s who are not yet 65+, people with young grandchildren, etc.,” she added. “I’m at Seattle Children’s Hospital, so people are asking about booster shots and about getting their children vaccinated.”
Boosters for all COVID-19 vaccines are completely free.
“All COVID-19 vaccines, including booster doses, will be provided free of charge to the U.S. population,” the CDC has said.
2. Will patients need to prove they meet eligibility criteria for a booster shot or will it be the honor system?
“No, patients will only need to attest that they fall into one of the high-risk groups for whom a booster vaccine is authorized,” said Robert Atmar, MD, professor of infectious diseases at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston.
Dr. Piltch-Loeb agreed. “It is likely to be an honor system. It is very unlikely that there will be punishments or other ramifications ... if doses are administered, beyond the approved usage.”
3. If a patient who had the Moderna or the Johnson and Johnson vaccination requests a booster, can health care workers give them Pfizer?
The short answer is no. “This only applies to individuals who have received the Pfizer vaccine,” Dr. Piltch-Loeb said.
More data will be needed before other vaccine boosters are authorized, she added.
“My understanding is the Moderna people have just recently submitted their information, all of their data to the FDA and J&J is in line to do that very shortly,” said William Schaffner, MD, professor of preventive medicine and infectious diseases at Vanderbilt University in Nashville, Tenn. “I would hope that within the next month to 6 weeks, we will get information about both of those vaccines,” Dr. Schaffner said.
4. When are the “mix-and-match” vaccine study results expected to come out?
“We expect that data from the study will be available in the coming weeks,” said Dr. Atmar, who is the national co-principal investigator of a mix-and-match booster trial launched in June 2021.
5. Are side effects of a booster vaccine expected to be about the same as what people experienced during their first or second immunization?
“I’m expecting the side effects will be similar to the second dose,” Dr. Englund said.
“The data presented ... at ACIP suggests that the side effects from the third shot are either the same or actually less than the first two shots,” said Carlos del Rio, MD, distinguished professor of medicine, epidemiology, and global health, and executive associate dean of Emory University School of Medicine at Grady Health System in Atlanta.
”Everyone reacts very differently to vaccines, regardless of vaccine type,” said Eric Ascher, MD, a family medicine physician at Lenox Hill Hospital in New York City. “I have had patients (as well as personal experience) where there were none to minimal symptoms, and others who felt they had a mild flu for 24 hours.”
“I expect no side effects greater than what was felt with you prior doses,” he said. “The vaccine is very safe and the benefit of vaccination outweighs the risks of any mild side effects.”
6. Is it unethical to give a booster to someone outside the approved groups if there are doses remaining at the end of the day in an open vial?
“Offering a booster shot to someone outside of approved groups if remaining doses will go to waste at the end of the day seems like a prudent decision, and relatively harmless action,” said Faith Fletcher, PhD, assistant professor at the Center for Medical Ethics and Health Policy at Baylor College of Medicine.
“However, if doses continue to fall in the laps of unapproved groups, we must evaluate the vaccine systems and structures that advantage some groups and disadvantage others,” she added. “We know that the distribution of COVID-19 vaccines has not been equitable – and some groups have been left behind.”
“I am not an ethicist and there are many competing concerns that this question addresses,” Dr. Atmar said. For example, “there is not a limitation of vaccine supply in the U.S., so that using leftover vaccine to prevent waste is no longer a major concern in the U.S.”
It could be more of a legal than ethical question, Dr. Atmar said. For an individual outside the authorized groups, legally, the FDA’s EUA for boosting does not allow the vaccine to be administered to this person, he said.
“The rationale for the restricted use in the EUA is that at this time the safety and risks associated with such administration are not known, and the benefits also have not been determined,” Dr. Atmar said. “Members of the ACIP raised concerns about other individuals who may potentially benefit from a booster but are not eligible and the importance of making boosters available to them, but from a legal standpoint – I am also not a lawyer, so this is my understanding – administration of the vaccine is limited to those identified in the EUA.”
7. What is the likelihood that one shot will combine COVID and flu protection in the near future?
It is not likely, Dr. Englund said. “The reason is that the flu vaccine changes so much, and it already has four different antigens. This is assuming we keep the same method of making the flu vaccine – the answer could be different if the flu vaccine becomes an mRNA vaccine in the future.”
Companies such as Moderna and Novavax are testing single-dose shots for COVID-19 and influenza, but they are still far from having anything ready for this flu season in the United States.
8. Is there any chance a booster shot distributed now will need to be redesigned for a future variant?
“Absolutely,” Dr. Englund said. “And a booster dose is the time we may want to consider re-engineering a vaccine.”
9. Do you think the FDA/CDC limitations on who is eligible for a booster was in any way influenced by the World Health Organization call for prioritizing shots for the unvaccinated in lower-resource countries?
“This is absolutely still a global problem,” Dr. Piltch-Loeb said. “We need to get more vaccine to more countries and more people as soon as possible, because if there’s anything we’ve seen about the variants it is that ... they can come from all different places.”
“That being said, I think that it is unlikely to change the course of action in the U.S.,” she added, when it comes to comparing the global need with the domestic policy priorities of the administration.
Dr. Atmar was more direct. “No,” he said. “The WHO recommends against boosting of anyone. The U.S. decisions about boosting those in this country who are eligible are aimed toward addressing perceived needs domestically at the same time that vaccines are being provided to other countries.
“The philosophy is to address both ‘needs’ at the same time,” Dr. Atmar said.
10. What does the future hold for booster shots?
“Predicting the future is really hard, especially when it involves COVID,” Dr. del Rio said.
“Having said that, COVID is not the flu, so I doubt there will be need for annual boosters. I think the population eligible for boosters will be expanded ... and the major population not addressed at this point is the people that received either Moderna or J&J [vaccines].”
Kelly Davis contributed to this feature. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Confusion continues to circulate in the wake of decisions on booster doses of the Pfizer/BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine, all announced within 1 week. Many people – including those now eligible and those who officially have to wait for their shot at a third dose – have questions.
Multiple agencies are involved in the booster decisions, and they have put out multiple – and sometimes conflicting – messages about booster doses, leaving more questions than answers for many people.
On Sept. 22, the Food and Drug Administration granted an emergency use authorization (EUA) for a booster dose of the Pfizer mRNA COVID-19 vaccine for those 65 and older and those at high risk for severe illness from the coronavirus, including essential workers whose jobs increase their risk for infection – such as frontline health care workers.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, then overruled advice from the agency’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) to recommend boosters for essential workers such as those working on the front lines during the pandemic.
As it stands now, the CDC recommends that the following groups should get a third dose of the Pfizer vaccine:
- People aged 65 years and older.
- People aged 18 years and older in long-term care settings.
- People aged 50-64 years with underlying medical conditions.
The CDC also recommends that the following groups may receive a booster shot of the Pfizer vaccine, based on their individual benefits and risks:
- People aged 18-49 years with underlying medical conditions.
- People aged 18-64 years at increased risk for COVID-19 exposure and transmission because of occupational or institutional setting.
The CDC currently considers the following groups at increased risk for COVID-19:
- First responders (health care workers, firefighters, police, congregate care staff).
- Education staff (teachers, support staff, day care workers).
- Food and agriculture workers.
- Manufacturing workers.
- Corrections workers.
- U.S. Postal Service workers.
- Public transit workers.
- Grocery store workers.
Health care professionals, among the most trusted sources of COVID-19 information, are likely to encounter a number of patients wondering how all this will work.
“It’s fantastic that boosters will be available for those who the data supports need [them],” Rachael Piltch-Loeb, PhD, said during a media briefing on Sept. 23, held between the FDA and CDC decisions.
“But we’re really in a place where we have a lot more questions and answers about what the next phase of the vaccine availability and updates are going to be in the United States,” added Dr. Piltch-Loeb, preparedness fellow in the division of policy translation and leadership development and a research associate in the department of biostatistics at the Harvard T. H. Chan School of Public Health in Boston.
1. What is the biggest concern you are hearing from patients about getting a booster?
“The biggest concerns are that everyone wants it and they don’t know where to get it. In health care’s defense, the CDC just figured out what to do,” said Janet Englund, MD, professor of pediatric infectious diseases and an infectious disease and virology expert at Seattle Children’s Hospital in Washington.
“Everyone thinks they should be eligible for a booster ... people in their 50s who are not yet 65+, people with young grandchildren, etc.,” she added. “I’m at Seattle Children’s Hospital, so people are asking about booster shots and about getting their children vaccinated.”
Boosters for all COVID-19 vaccines are completely free.
“All COVID-19 vaccines, including booster doses, will be provided free of charge to the U.S. population,” the CDC has said.
2. Will patients need to prove they meet eligibility criteria for a booster shot or will it be the honor system?
“No, patients will only need to attest that they fall into one of the high-risk groups for whom a booster vaccine is authorized,” said Robert Atmar, MD, professor of infectious diseases at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston.
Dr. Piltch-Loeb agreed. “It is likely to be an honor system. It is very unlikely that there will be punishments or other ramifications ... if doses are administered, beyond the approved usage.”
3. If a patient who had the Moderna or the Johnson and Johnson vaccination requests a booster, can health care workers give them Pfizer?
The short answer is no. “This only applies to individuals who have received the Pfizer vaccine,” Dr. Piltch-Loeb said.
More data will be needed before other vaccine boosters are authorized, she added.
“My understanding is the Moderna people have just recently submitted their information, all of their data to the FDA and J&J is in line to do that very shortly,” said William Schaffner, MD, professor of preventive medicine and infectious diseases at Vanderbilt University in Nashville, Tenn. “I would hope that within the next month to 6 weeks, we will get information about both of those vaccines,” Dr. Schaffner said.
4. When are the “mix-and-match” vaccine study results expected to come out?
“We expect that data from the study will be available in the coming weeks,” said Dr. Atmar, who is the national co-principal investigator of a mix-and-match booster trial launched in June 2021.
5. Are side effects of a booster vaccine expected to be about the same as what people experienced during their first or second immunization?
“I’m expecting the side effects will be similar to the second dose,” Dr. Englund said.
“The data presented ... at ACIP suggests that the side effects from the third shot are either the same or actually less than the first two shots,” said Carlos del Rio, MD, distinguished professor of medicine, epidemiology, and global health, and executive associate dean of Emory University School of Medicine at Grady Health System in Atlanta.
”Everyone reacts very differently to vaccines, regardless of vaccine type,” said Eric Ascher, MD, a family medicine physician at Lenox Hill Hospital in New York City. “I have had patients (as well as personal experience) where there were none to minimal symptoms, and others who felt they had a mild flu for 24 hours.”
“I expect no side effects greater than what was felt with you prior doses,” he said. “The vaccine is very safe and the benefit of vaccination outweighs the risks of any mild side effects.”
6. Is it unethical to give a booster to someone outside the approved groups if there are doses remaining at the end of the day in an open vial?
“Offering a booster shot to someone outside of approved groups if remaining doses will go to waste at the end of the day seems like a prudent decision, and relatively harmless action,” said Faith Fletcher, PhD, assistant professor at the Center for Medical Ethics and Health Policy at Baylor College of Medicine.
“However, if doses continue to fall in the laps of unapproved groups, we must evaluate the vaccine systems and structures that advantage some groups and disadvantage others,” she added. “We know that the distribution of COVID-19 vaccines has not been equitable – and some groups have been left behind.”
“I am not an ethicist and there are many competing concerns that this question addresses,” Dr. Atmar said. For example, “there is not a limitation of vaccine supply in the U.S., so that using leftover vaccine to prevent waste is no longer a major concern in the U.S.”
It could be more of a legal than ethical question, Dr. Atmar said. For an individual outside the authorized groups, legally, the FDA’s EUA for boosting does not allow the vaccine to be administered to this person, he said.
“The rationale for the restricted use in the EUA is that at this time the safety and risks associated with such administration are not known, and the benefits also have not been determined,” Dr. Atmar said. “Members of the ACIP raised concerns about other individuals who may potentially benefit from a booster but are not eligible and the importance of making boosters available to them, but from a legal standpoint – I am also not a lawyer, so this is my understanding – administration of the vaccine is limited to those identified in the EUA.”
7. What is the likelihood that one shot will combine COVID and flu protection in the near future?
It is not likely, Dr. Englund said. “The reason is that the flu vaccine changes so much, and it already has four different antigens. This is assuming we keep the same method of making the flu vaccine – the answer could be different if the flu vaccine becomes an mRNA vaccine in the future.”
Companies such as Moderna and Novavax are testing single-dose shots for COVID-19 and influenza, but they are still far from having anything ready for this flu season in the United States.
8. Is there any chance a booster shot distributed now will need to be redesigned for a future variant?
“Absolutely,” Dr. Englund said. “And a booster dose is the time we may want to consider re-engineering a vaccine.”
9. Do you think the FDA/CDC limitations on who is eligible for a booster was in any way influenced by the World Health Organization call for prioritizing shots for the unvaccinated in lower-resource countries?
“This is absolutely still a global problem,” Dr. Piltch-Loeb said. “We need to get more vaccine to more countries and more people as soon as possible, because if there’s anything we’ve seen about the variants it is that ... they can come from all different places.”
“That being said, I think that it is unlikely to change the course of action in the U.S.,” she added, when it comes to comparing the global need with the domestic policy priorities of the administration.
Dr. Atmar was more direct. “No,” he said. “The WHO recommends against boosting of anyone. The U.S. decisions about boosting those in this country who are eligible are aimed toward addressing perceived needs domestically at the same time that vaccines are being provided to other countries.
“The philosophy is to address both ‘needs’ at the same time,” Dr. Atmar said.
10. What does the future hold for booster shots?
“Predicting the future is really hard, especially when it involves COVID,” Dr. del Rio said.
“Having said that, COVID is not the flu, so I doubt there will be need for annual boosters. I think the population eligible for boosters will be expanded ... and the major population not addressed at this point is the people that received either Moderna or J&J [vaccines].”
Kelly Davis contributed to this feature. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Gastroenterology Data Trends 2021
Contents Include:
- Digital health in managing GI diseases
- Emergence of live biotherapeutic products for C. difficile and beyond
- AI and machine learning in GI practice
- Eosinophilic esophagitis: Addressing the rise in incidence and treatment options
- Racial and social diversity in GI practice
- The gut-brain connection in IBS
- Managing IBD in the backdrop of COVID-19
- Noncardia gastric cancer risk: Racial/ethnic disparity, gastric precancerous changes, and refractory H. pylori
- Rethinking management of alcohol-associated liver disease: The other fatty liver epidemic
- Endoscopic bariatric and metabolic therapies for weight loss
- The weight loss journey at University of Michigan
Contents Include:
- Digital health in managing GI diseases
- Emergence of live biotherapeutic products for C. difficile and beyond
- AI and machine learning in GI practice
- Eosinophilic esophagitis: Addressing the rise in incidence and treatment options
- Racial and social diversity in GI practice
- The gut-brain connection in IBS
- Managing IBD in the backdrop of COVID-19
- Noncardia gastric cancer risk: Racial/ethnic disparity, gastric precancerous changes, and refractory H. pylori
- Rethinking management of alcohol-associated liver disease: The other fatty liver epidemic
- Endoscopic bariatric and metabolic therapies for weight loss
- The weight loss journey at University of Michigan
Contents Include:
- Digital health in managing GI diseases
- Emergence of live biotherapeutic products for C. difficile and beyond
- AI and machine learning in GI practice
- Eosinophilic esophagitis: Addressing the rise in incidence and treatment options
- Racial and social diversity in GI practice
- The gut-brain connection in IBS
- Managing IBD in the backdrop of COVID-19
- Noncardia gastric cancer risk: Racial/ethnic disparity, gastric precancerous changes, and refractory H. pylori
- Rethinking management of alcohol-associated liver disease: The other fatty liver epidemic
- Endoscopic bariatric and metabolic therapies for weight loss
- The weight loss journey at University of Michigan
Bone density gains are lost following stop of denosumab in glucocorticoid-treated RA
Patients with rheumatoid arthritis who were taking glucocorticoids and received short-term denosumab (Prolia) had lost any gains in bone mineral density at the spine or hip as well as any improvements in bone turnover markers a year later, according to findings from a post-hoc analysis of a phase 2 trial.
That is, stopping denosumab after a 12-month course resulted in a gradual increase in bone turnover markers and a concurrent return to baseline lumbar spine and total hip bone mineral density, Kenneth G. Saag, MD, professor of medicine and division director of clinical immunology and rheumatology at the University of Alabama at Birmingham, and colleagues reported in an article published online Sept. 17, 2021 in Arthritis & Rheumatology.
“These results provide further support for recommendations that patients discontinuing denosumab should transition to follow-on osteoporosis therapy to prevent or minimize remodeling-induced bone loss,” they concluded.
Like all nonbisphosphonate medications for osteoporosis, Dr. Saag and colleagues wrote, the pharmacologic effects of denosumab are readily reversible after discontinuation.
The current findings in glucocorticoid-treated patients are consistent with those observed in postmenopausal women 2 years after discontinuing denosumab therapy for osteoporosis. Denosumab is typically given for a longer time in such patients, compared with patients receiving glucocorticoids.
Invited to comment, Karen E. Hansen, MD, a rheumatologist and associate professor at the University of Wisconsin, Madison, who was not involved with the study, agreed that the results “highlight the need to prescribe another osteoporosis medication after stopping denosumab, in hopes of preventing loss of bone mineral density.”
Dr. Hansen, a coauthor of a review and meta-analysis of denosumab in the treatment of glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis, noted that the American College of Rheumatology guideline for the prevention and treatment of glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis suggests the use of denosumab as fourth-line therapy, after oral bisphosphonates, intravenous bisphosphonates, and teriparatide (Forteo).
“Its use is particularly relevant in patients who have contraindications or side effects from bisphosphonates or anabolic therapy, or when patient compliance must be ensured,” she said in an interview.
“The type, timing, and effect of therapy after denosumab discontinuation, however, remain controversial,” Dr. Saag and colleagues noted.
However, ongoing trials that are investigating the optimal medication and dosing needed to prevent such losses in bone mineral density after stopping denosumab should provide greater insight, Dr. Hansen said.
Bone health after stopping denosumab
Patients with rheumatoid arthritis often have bone loss that can be worsened by their frequent use of glucocorticoids, leading to an increased risk of fragility fractures.
Denosumab, a monoclonal antibody that inhibits receptor activator of nuclear factor kappaB ligand (RANKL), was approved by the Food and Drug Administration in 2018 for treating patients with glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis and a high risk of fracture.
Dr. Saag and colleagues performed a post-hoc analysis of a subgroup of 82 patients receiving glucocorticoids who were part of a larger phase 2 clinical trial of 218 patients with rheumatoid arthritis.
The patients had been randomized to receive placebo (n = 26), 60 mg denosumab (the approved dose, n = 27), or 180 mg denosumab (n = 29), given as two subcutaneous 6-month injections at baseline and 6 months, followed by 12 months without any bone-loss prevention therapy.
The patients had a mean age of 55, and 62% were women.
While receiving denosumab, their serum levels of the bone resorption marker C-terminal telopeptide of type I collagen (CTX) and the bone formation marker procollagen type I N-terminal propeptide (P1NP) decreased significantly from baseline.
In patients who received the 60-mg dose of denosumab, CTX levels had returned to baseline levels 6 months and 12 months after denosumab was discontinued.
Median levels of P1NP in these patients were 0.16% lower than baseline and 15% higher than baseline at 6 months and 12 months after denosumab was stopped, respectively.
In patients who received the 180-mg dose of denosumab, CTX levels also had returned to baseline levels 6 months and 12 months after denosumab was discontinued.
Median levels of P1NP in these patients were 9% and 76% higher than baseline levels, at 6 months and 12 months after denosumab was stopped, respectively.
Bone mineral density at the lumbar spine and total hip increased during the 12 months of denosumab treatment and then returned to baseline after 12 months of discontinuation of both doses of denosumab.
No osteoporotic fractures were reported during the 12-month denosumab treatment or the 12-month follow-up.
The study was funded by Amgen, which markets denosumab. Dr. Saag is an investigator with Amgen, Mereo, and Radius, and a consultant for Amgen and Roche. Four coauthors are employees of Amgen. The other six coauthors all reported a financial relationship with Amgen.
Patients with rheumatoid arthritis who were taking glucocorticoids and received short-term denosumab (Prolia) had lost any gains in bone mineral density at the spine or hip as well as any improvements in bone turnover markers a year later, according to findings from a post-hoc analysis of a phase 2 trial.
That is, stopping denosumab after a 12-month course resulted in a gradual increase in bone turnover markers and a concurrent return to baseline lumbar spine and total hip bone mineral density, Kenneth G. Saag, MD, professor of medicine and division director of clinical immunology and rheumatology at the University of Alabama at Birmingham, and colleagues reported in an article published online Sept. 17, 2021 in Arthritis & Rheumatology.
“These results provide further support for recommendations that patients discontinuing denosumab should transition to follow-on osteoporosis therapy to prevent or minimize remodeling-induced bone loss,” they concluded.
Like all nonbisphosphonate medications for osteoporosis, Dr. Saag and colleagues wrote, the pharmacologic effects of denosumab are readily reversible after discontinuation.
The current findings in glucocorticoid-treated patients are consistent with those observed in postmenopausal women 2 years after discontinuing denosumab therapy for osteoporosis. Denosumab is typically given for a longer time in such patients, compared with patients receiving glucocorticoids.
Invited to comment, Karen E. Hansen, MD, a rheumatologist and associate professor at the University of Wisconsin, Madison, who was not involved with the study, agreed that the results “highlight the need to prescribe another osteoporosis medication after stopping denosumab, in hopes of preventing loss of bone mineral density.”
Dr. Hansen, a coauthor of a review and meta-analysis of denosumab in the treatment of glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis, noted that the American College of Rheumatology guideline for the prevention and treatment of glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis suggests the use of denosumab as fourth-line therapy, after oral bisphosphonates, intravenous bisphosphonates, and teriparatide (Forteo).
“Its use is particularly relevant in patients who have contraindications or side effects from bisphosphonates or anabolic therapy, or when patient compliance must be ensured,” she said in an interview.
“The type, timing, and effect of therapy after denosumab discontinuation, however, remain controversial,” Dr. Saag and colleagues noted.
However, ongoing trials that are investigating the optimal medication and dosing needed to prevent such losses in bone mineral density after stopping denosumab should provide greater insight, Dr. Hansen said.
Bone health after stopping denosumab
Patients with rheumatoid arthritis often have bone loss that can be worsened by their frequent use of glucocorticoids, leading to an increased risk of fragility fractures.
Denosumab, a monoclonal antibody that inhibits receptor activator of nuclear factor kappaB ligand (RANKL), was approved by the Food and Drug Administration in 2018 for treating patients with glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis and a high risk of fracture.
Dr. Saag and colleagues performed a post-hoc analysis of a subgroup of 82 patients receiving glucocorticoids who were part of a larger phase 2 clinical trial of 218 patients with rheumatoid arthritis.
The patients had been randomized to receive placebo (n = 26), 60 mg denosumab (the approved dose, n = 27), or 180 mg denosumab (n = 29), given as two subcutaneous 6-month injections at baseline and 6 months, followed by 12 months without any bone-loss prevention therapy.
The patients had a mean age of 55, and 62% were women.
While receiving denosumab, their serum levels of the bone resorption marker C-terminal telopeptide of type I collagen (CTX) and the bone formation marker procollagen type I N-terminal propeptide (P1NP) decreased significantly from baseline.
In patients who received the 60-mg dose of denosumab, CTX levels had returned to baseline levels 6 months and 12 months after denosumab was discontinued.
Median levels of P1NP in these patients were 0.16% lower than baseline and 15% higher than baseline at 6 months and 12 months after denosumab was stopped, respectively.
In patients who received the 180-mg dose of denosumab, CTX levels also had returned to baseline levels 6 months and 12 months after denosumab was discontinued.
Median levels of P1NP in these patients were 9% and 76% higher than baseline levels, at 6 months and 12 months after denosumab was stopped, respectively.
Bone mineral density at the lumbar spine and total hip increased during the 12 months of denosumab treatment and then returned to baseline after 12 months of discontinuation of both doses of denosumab.
No osteoporotic fractures were reported during the 12-month denosumab treatment or the 12-month follow-up.
The study was funded by Amgen, which markets denosumab. Dr. Saag is an investigator with Amgen, Mereo, and Radius, and a consultant for Amgen and Roche. Four coauthors are employees of Amgen. The other six coauthors all reported a financial relationship with Amgen.
Patients with rheumatoid arthritis who were taking glucocorticoids and received short-term denosumab (Prolia) had lost any gains in bone mineral density at the spine or hip as well as any improvements in bone turnover markers a year later, according to findings from a post-hoc analysis of a phase 2 trial.
That is, stopping denosumab after a 12-month course resulted in a gradual increase in bone turnover markers and a concurrent return to baseline lumbar spine and total hip bone mineral density, Kenneth G. Saag, MD, professor of medicine and division director of clinical immunology and rheumatology at the University of Alabama at Birmingham, and colleagues reported in an article published online Sept. 17, 2021 in Arthritis & Rheumatology.
“These results provide further support for recommendations that patients discontinuing denosumab should transition to follow-on osteoporosis therapy to prevent or minimize remodeling-induced bone loss,” they concluded.
Like all nonbisphosphonate medications for osteoporosis, Dr. Saag and colleagues wrote, the pharmacologic effects of denosumab are readily reversible after discontinuation.
The current findings in glucocorticoid-treated patients are consistent with those observed in postmenopausal women 2 years after discontinuing denosumab therapy for osteoporosis. Denosumab is typically given for a longer time in such patients, compared with patients receiving glucocorticoids.
Invited to comment, Karen E. Hansen, MD, a rheumatologist and associate professor at the University of Wisconsin, Madison, who was not involved with the study, agreed that the results “highlight the need to prescribe another osteoporosis medication after stopping denosumab, in hopes of preventing loss of bone mineral density.”
Dr. Hansen, a coauthor of a review and meta-analysis of denosumab in the treatment of glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis, noted that the American College of Rheumatology guideline for the prevention and treatment of glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis suggests the use of denosumab as fourth-line therapy, after oral bisphosphonates, intravenous bisphosphonates, and teriparatide (Forteo).
“Its use is particularly relevant in patients who have contraindications or side effects from bisphosphonates or anabolic therapy, or when patient compliance must be ensured,” she said in an interview.
“The type, timing, and effect of therapy after denosumab discontinuation, however, remain controversial,” Dr. Saag and colleagues noted.
However, ongoing trials that are investigating the optimal medication and dosing needed to prevent such losses in bone mineral density after stopping denosumab should provide greater insight, Dr. Hansen said.
Bone health after stopping denosumab
Patients with rheumatoid arthritis often have bone loss that can be worsened by their frequent use of glucocorticoids, leading to an increased risk of fragility fractures.
Denosumab, a monoclonal antibody that inhibits receptor activator of nuclear factor kappaB ligand (RANKL), was approved by the Food and Drug Administration in 2018 for treating patients with glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis and a high risk of fracture.
Dr. Saag and colleagues performed a post-hoc analysis of a subgroup of 82 patients receiving glucocorticoids who were part of a larger phase 2 clinical trial of 218 patients with rheumatoid arthritis.
The patients had been randomized to receive placebo (n = 26), 60 mg denosumab (the approved dose, n = 27), or 180 mg denosumab (n = 29), given as two subcutaneous 6-month injections at baseline and 6 months, followed by 12 months without any bone-loss prevention therapy.
The patients had a mean age of 55, and 62% were women.
While receiving denosumab, their serum levels of the bone resorption marker C-terminal telopeptide of type I collagen (CTX) and the bone formation marker procollagen type I N-terminal propeptide (P1NP) decreased significantly from baseline.
In patients who received the 60-mg dose of denosumab, CTX levels had returned to baseline levels 6 months and 12 months after denosumab was discontinued.
Median levels of P1NP in these patients were 0.16% lower than baseline and 15% higher than baseline at 6 months and 12 months after denosumab was stopped, respectively.
In patients who received the 180-mg dose of denosumab, CTX levels also had returned to baseline levels 6 months and 12 months after denosumab was discontinued.
Median levels of P1NP in these patients were 9% and 76% higher than baseline levels, at 6 months and 12 months after denosumab was stopped, respectively.
Bone mineral density at the lumbar spine and total hip increased during the 12 months of denosumab treatment and then returned to baseline after 12 months of discontinuation of both doses of denosumab.
No osteoporotic fractures were reported during the 12-month denosumab treatment or the 12-month follow-up.
The study was funded by Amgen, which markets denosumab. Dr. Saag is an investigator with Amgen, Mereo, and Radius, and a consultant for Amgen and Roche. Four coauthors are employees of Amgen. The other six coauthors all reported a financial relationship with Amgen.
FROM ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATOLOGY
Concomitant laparoscopic and vaginal excision of duplicated collecting system
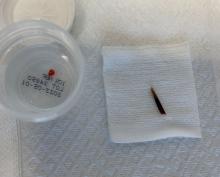
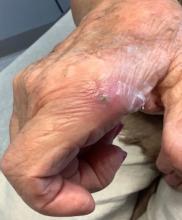
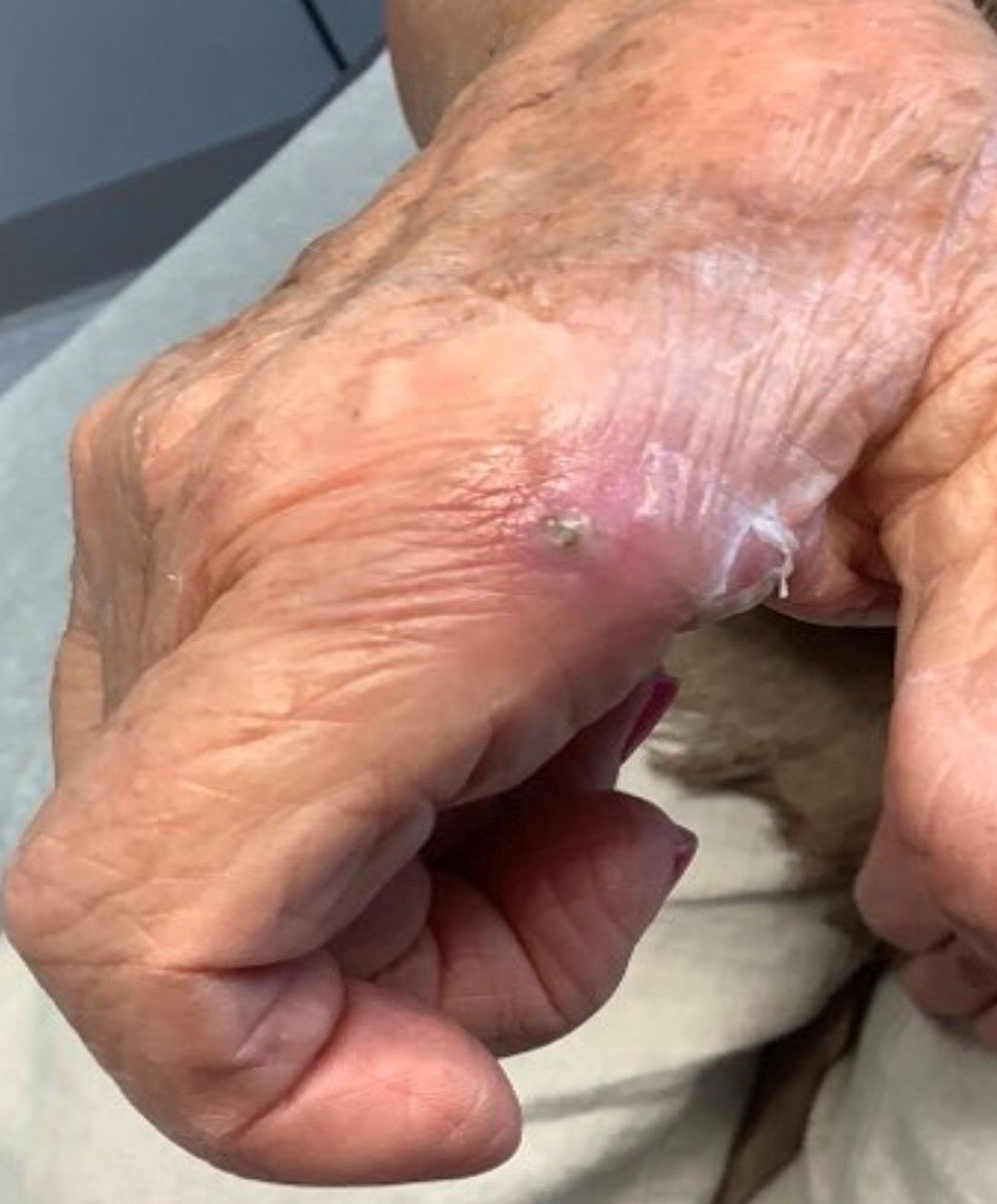
An 80-year-old female developed a painful purulent nodule a day after gardening
. There are more than 100 species of dematiaceous fungi that can cause phaeohyphomycosis, including Alternaria, Exophiala, Phialophora, Wangiella, Bipolaris, Curvularia, and Exserohilum.1,2 The causative fungi are found in plants and soil, so they are commonly seen after activities such as gardening or walking barefoot. Trauma, such as a splinter, typically incites the infection. Infections can present with superficial, cutaneous and subcutaneous involvement.
Sporotrichosis, also called Rose gardener’s disease, is a mycosis caused by Sporothrix schenckii. A typical presentation is when a gardener gets pricked by a rose thorn. Classically, a pustule will develop at the site of inoculation, with additional lesions forming along the path of lymphatic drainage (called a “sporotrichoid” pattern) weeks later. Atypical mycobacterial infections, mainly Mycobacterium marinum, may also present in this way. Histopathology and tissue cultures help to differentiate the two.
An incision and drainage with pathology was performed in the office. Upon opening the nodule, a large wood splinter was extracted. Both the foreign body and a punch biopsy of skin were sent in for examination. Pathology revealed polarizable foreign material in association with suppurative inflammation and dematiaceous fungi. PAS (Periodic-acid Schiff) and GMS (Grocott methenamine silver) stain highlighted fungal forms. Cultures were negative.
Local disease may be treated with excision alone. Oral antifungals, such as itraconazole, fluconazole, or ketoconazole may be used, although may require long treatment courses for months. Amphotericin B and flucytosine may be required in systemic cases. Almost all cases of disseminated disease occur in immunocompromised patients. Our patient’s hand resolved after removal of the causative thorn.
This case and these photos were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. Kradin R. Diagnostic Pathology of Infectious Disease, 1st edition (Saunders, Feb. 2, 2010).
2. Bolognia J et al. Dermatology (St. Louis: Mosby/Elsevier, 2008).
. There are more than 100 species of dematiaceous fungi that can cause phaeohyphomycosis, including Alternaria, Exophiala, Phialophora, Wangiella, Bipolaris, Curvularia, and Exserohilum.1,2 The causative fungi are found in plants and soil, so they are commonly seen after activities such as gardening or walking barefoot. Trauma, such as a splinter, typically incites the infection. Infections can present with superficial, cutaneous and subcutaneous involvement.
Sporotrichosis, also called Rose gardener’s disease, is a mycosis caused by Sporothrix schenckii. A typical presentation is when a gardener gets pricked by a rose thorn. Classically, a pustule will develop at the site of inoculation, with additional lesions forming along the path of lymphatic drainage (called a “sporotrichoid” pattern) weeks later. Atypical mycobacterial infections, mainly Mycobacterium marinum, may also present in this way. Histopathology and tissue cultures help to differentiate the two.
An incision and drainage with pathology was performed in the office. Upon opening the nodule, a large wood splinter was extracted. Both the foreign body and a punch biopsy of skin were sent in for examination. Pathology revealed polarizable foreign material in association with suppurative inflammation and dematiaceous fungi. PAS (Periodic-acid Schiff) and GMS (Grocott methenamine silver) stain highlighted fungal forms. Cultures were negative.
Local disease may be treated with excision alone. Oral antifungals, such as itraconazole, fluconazole, or ketoconazole may be used, although may require long treatment courses for months. Amphotericin B and flucytosine may be required in systemic cases. Almost all cases of disseminated disease occur in immunocompromised patients. Our patient’s hand resolved after removal of the causative thorn.
This case and these photos were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. Kradin R. Diagnostic Pathology of Infectious Disease, 1st edition (Saunders, Feb. 2, 2010).
2. Bolognia J et al. Dermatology (St. Louis: Mosby/Elsevier, 2008).
. There are more than 100 species of dematiaceous fungi that can cause phaeohyphomycosis, including Alternaria, Exophiala, Phialophora, Wangiella, Bipolaris, Curvularia, and Exserohilum.1,2 The causative fungi are found in plants and soil, so they are commonly seen after activities such as gardening or walking barefoot. Trauma, such as a splinter, typically incites the infection. Infections can present with superficial, cutaneous and subcutaneous involvement.
Sporotrichosis, also called Rose gardener’s disease, is a mycosis caused by Sporothrix schenckii. A typical presentation is when a gardener gets pricked by a rose thorn. Classically, a pustule will develop at the site of inoculation, with additional lesions forming along the path of lymphatic drainage (called a “sporotrichoid” pattern) weeks later. Atypical mycobacterial infections, mainly Mycobacterium marinum, may also present in this way. Histopathology and tissue cultures help to differentiate the two.
An incision and drainage with pathology was performed in the office. Upon opening the nodule, a large wood splinter was extracted. Both the foreign body and a punch biopsy of skin were sent in for examination. Pathology revealed polarizable foreign material in association with suppurative inflammation and dematiaceous fungi. PAS (Periodic-acid Schiff) and GMS (Grocott methenamine silver) stain highlighted fungal forms. Cultures were negative.
Local disease may be treated with excision alone. Oral antifungals, such as itraconazole, fluconazole, or ketoconazole may be used, although may require long treatment courses for months. Amphotericin B and flucytosine may be required in systemic cases. Almost all cases of disseminated disease occur in immunocompromised patients. Our patient’s hand resolved after removal of the causative thorn.
This case and these photos were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. Kradin R. Diagnostic Pathology of Infectious Disease, 1st edition (Saunders, Feb. 2, 2010).
2. Bolognia J et al. Dermatology (St. Louis: Mosby/Elsevier, 2008).
Outreach Finds Veterans Unaware of Service Connection
The US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Northeast Ohio Healthcare System has been eaching out directly by postal mail to hundreds of veterans with cancer who may have been exposed to Agent Orange or contaminated water at Camp Lejeune in North Carolina. Advocates say they’ve connected dozens to “service-connected” benefits that pay for 100% of the veterans’ care and can potentially provide support to their spouses after they pass away.
The details and outcomes of the outreach project were presented at the 2021 annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology (AVAHO) being held virtually and in person in Denver, Colorado, from September 24 to September 26, 2021.
“Once you get a devastating diagnosis like cancer, you’ve got enough going on in your head. You shouldn’t have to worry about what the next step is in the benefit process,” said VA Northeast Ohio Healthcare System outreach coordinator Willie J. Berry in an interview. “We want you to focus on your care and not have to worry about anything else.”
Agent Orange, made up of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin, was used to defoliate forests and kill crops during the Vietnam War. Through “100% service connection” the VA fully covers benefits for certain cancers and other diseases for veterans who are considered to have been exposed to Agent Orange in Vietnam and elsewhere.
Veterans do not need to pay copays in these cases, Berry said, and care outside the VA may be fully funded once arrangements are made.
The VA also fully covers benefits for a similar list of diseases, also including some types of cancer, for veterans who are considered to have been exposed to a contaminated water supply at Camp Lejeune in the early 1980s.
Vietnam War veterans may not be aware of the Agent Orange benefits due to a negative perception of the VA, Berry said. “They were treated poorly [by the VA] and didn’t want to have anything to do with it.”
In the first phase of the project, the VA Northeast Ohio Healthcare System tried to reach potentially eligible veterans with both cancer and possible Agent Orange exposure via phone. Seventy veterans were referred to outreach coordinators, and 16 received 100% service connection after 6 months. The latter number later grew to 34.
“The most inefficient thing were doing was calling veterans one by one,” Berry said. “We felt a mailer would be more efficient in order to reach more people.”
For the second phase, in 2021, coordinators sent informational “Dear veteran” mailers to 427 veterans with cancer who may be eligible for special Agent Orange/Camp Lejeune benefits based on their service history.
The Agent Orange letters began this way: “Through a recent medical diagnosis, VA has identified you as possibly being impacted by a change in Agent Orange Exposure legislation.” The letters then list the eligible conditions, which as of 2021 now include bladder cancer, hyperthyroidism and parkinsonism.
The letters also note that “claims often enhance a veteran’s VA compensation and reduce their cost of care. Additionally, if a veteran were to succumb to a diagnosis that they were service connected for, their spouse might be able to receive both VA health care (until the age of Medicare eligibility) as well as financial benefits for the rest of their life.”
If veterans were terminally ill, the application process for the special benefits could be expedited, Berry said. The number of veterans who received 100% service connection in the second phase of the project was not provided.
No study funding is reported. Berry has no disclosures.
The US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Northeast Ohio Healthcare System has been eaching out directly by postal mail to hundreds of veterans with cancer who may have been exposed to Agent Orange or contaminated water at Camp Lejeune in North Carolina. Advocates say they’ve connected dozens to “service-connected” benefits that pay for 100% of the veterans’ care and can potentially provide support to their spouses after they pass away.
The details and outcomes of the outreach project were presented at the 2021 annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology (AVAHO) being held virtually and in person in Denver, Colorado, from September 24 to September 26, 2021.
“Once you get a devastating diagnosis like cancer, you’ve got enough going on in your head. You shouldn’t have to worry about what the next step is in the benefit process,” said VA Northeast Ohio Healthcare System outreach coordinator Willie J. Berry in an interview. “We want you to focus on your care and not have to worry about anything else.”
Agent Orange, made up of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin, was used to defoliate forests and kill crops during the Vietnam War. Through “100% service connection” the VA fully covers benefits for certain cancers and other diseases for veterans who are considered to have been exposed to Agent Orange in Vietnam and elsewhere.
Veterans do not need to pay copays in these cases, Berry said, and care outside the VA may be fully funded once arrangements are made.
The VA also fully covers benefits for a similar list of diseases, also including some types of cancer, for veterans who are considered to have been exposed to a contaminated water supply at Camp Lejeune in the early 1980s.
Vietnam War veterans may not be aware of the Agent Orange benefits due to a negative perception of the VA, Berry said. “They were treated poorly [by the VA] and didn’t want to have anything to do with it.”
In the first phase of the project, the VA Northeast Ohio Healthcare System tried to reach potentially eligible veterans with both cancer and possible Agent Orange exposure via phone. Seventy veterans were referred to outreach coordinators, and 16 received 100% service connection after 6 months. The latter number later grew to 34.
“The most inefficient thing were doing was calling veterans one by one,” Berry said. “We felt a mailer would be more efficient in order to reach more people.”
For the second phase, in 2021, coordinators sent informational “Dear veteran” mailers to 427 veterans with cancer who may be eligible for special Agent Orange/Camp Lejeune benefits based on their service history.
The Agent Orange letters began this way: “Through a recent medical diagnosis, VA has identified you as possibly being impacted by a change in Agent Orange Exposure legislation.” The letters then list the eligible conditions, which as of 2021 now include bladder cancer, hyperthyroidism and parkinsonism.
The letters also note that “claims often enhance a veteran’s VA compensation and reduce their cost of care. Additionally, if a veteran were to succumb to a diagnosis that they were service connected for, their spouse might be able to receive both VA health care (until the age of Medicare eligibility) as well as financial benefits for the rest of their life.”
If veterans were terminally ill, the application process for the special benefits could be expedited, Berry said. The number of veterans who received 100% service connection in the second phase of the project was not provided.
No study funding is reported. Berry has no disclosures.
The US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Northeast Ohio Healthcare System has been eaching out directly by postal mail to hundreds of veterans with cancer who may have been exposed to Agent Orange or contaminated water at Camp Lejeune in North Carolina. Advocates say they’ve connected dozens to “service-connected” benefits that pay for 100% of the veterans’ care and can potentially provide support to their spouses after they pass away.
The details and outcomes of the outreach project were presented at the 2021 annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology (AVAHO) being held virtually and in person in Denver, Colorado, from September 24 to September 26, 2021.
“Once you get a devastating diagnosis like cancer, you’ve got enough going on in your head. You shouldn’t have to worry about what the next step is in the benefit process,” said VA Northeast Ohio Healthcare System outreach coordinator Willie J. Berry in an interview. “We want you to focus on your care and not have to worry about anything else.”
Agent Orange, made up of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin, was used to defoliate forests and kill crops during the Vietnam War. Through “100% service connection” the VA fully covers benefits for certain cancers and other diseases for veterans who are considered to have been exposed to Agent Orange in Vietnam and elsewhere.
Veterans do not need to pay copays in these cases, Berry said, and care outside the VA may be fully funded once arrangements are made.
The VA also fully covers benefits for a similar list of diseases, also including some types of cancer, for veterans who are considered to have been exposed to a contaminated water supply at Camp Lejeune in the early 1980s.
Vietnam War veterans may not be aware of the Agent Orange benefits due to a negative perception of the VA, Berry said. “They were treated poorly [by the VA] and didn’t want to have anything to do with it.”
In the first phase of the project, the VA Northeast Ohio Healthcare System tried to reach potentially eligible veterans with both cancer and possible Agent Orange exposure via phone. Seventy veterans were referred to outreach coordinators, and 16 received 100% service connection after 6 months. The latter number later grew to 34.
“The most inefficient thing were doing was calling veterans one by one,” Berry said. “We felt a mailer would be more efficient in order to reach more people.”
For the second phase, in 2021, coordinators sent informational “Dear veteran” mailers to 427 veterans with cancer who may be eligible for special Agent Orange/Camp Lejeune benefits based on their service history.
The Agent Orange letters began this way: “Through a recent medical diagnosis, VA has identified you as possibly being impacted by a change in Agent Orange Exposure legislation.” The letters then list the eligible conditions, which as of 2021 now include bladder cancer, hyperthyroidism and parkinsonism.
The letters also note that “claims often enhance a veteran’s VA compensation and reduce their cost of care. Additionally, if a veteran were to succumb to a diagnosis that they were service connected for, their spouse might be able to receive both VA health care (until the age of Medicare eligibility) as well as financial benefits for the rest of their life.”
If veterans were terminally ill, the application process for the special benefits could be expedited, Berry said. The number of veterans who received 100% service connection in the second phase of the project was not provided.
No study funding is reported. Berry has no disclosures.
Duty to Assist: Assisting Veterans with Exposures to Hazardous Materials
Community outreach coordinators identified Veterans who were not aware of their entitlement to service-connected benefits. Veterans were also unaware of the importance of adding new presumptive diagnoses to their existing service connection and were unaware of new conditions that were added to the presumptive lists. Many Veterans, unaware of the Agent Orange/Camp Lejeune presumptive conditions, were paying out of pocket for their oncology care. A project was developed between community outreach and oncology to identify, and contact Veterans newly diagnosed with cancers on the presumptive list for Vietnam and Camp Lejeune. The goals for the project were to: Increase presumptive condition awareness, assist Veterans in navigating the VHA, VBA and VSC (Veteran Service Commission) and provide a VA resource for the Veterans for assistance. Oncology team reviewed the cancer registry each month and identified Veterans who served during the Vietnam Era or the Marine Corps and contacted them to screen for military history. If a Veteran met the time and location qualifications, the Veteran was referred to the community outreach coordinators. The coordinators then further screened the Veterans for eligibility, assisted the Veterans in initiating their claims applications and connected the Veterans with their local VSC. At the six month follow up, 74 Veterans had been referred to community outreach, and 16 Veterans had received 100% service connection. It is important to note, the benefits application process can take several months to complete under normal circumstances. Since implementation the project has been revised. The project team developed mailers to alert Veterans of: Potential benefits eligibility, importance for filing claims, contact information for their local VSC and contact information for VA Outreach for additional assistance. Informatics was recruited to assist with identifying Veterans who met the service criteria and providing their addresses. The Veterans identified were then sent mailers, which expedited the process, allowing the project team to reach more Veterans in a shorter timeframe. Since project initiation, 74 Veterans were contacted directly by outreach coordinators, 273 mailers have been sent to potentially eligible Veterans, and 34 have received 100% service connection to date. al center will continue this practice moving forward.
Community outreach coordinators identified Veterans who were not aware of their entitlement to service-connected benefits. Veterans were also unaware of the importance of adding new presumptive diagnoses to their existing service connection and were unaware of new conditions that were added to the presumptive lists. Many Veterans, unaware of the Agent Orange/Camp Lejeune presumptive conditions, were paying out of pocket for their oncology care. A project was developed between community outreach and oncology to identify, and contact Veterans newly diagnosed with cancers on the presumptive list for Vietnam and Camp Lejeune. The goals for the project were to: Increase presumptive condition awareness, assist Veterans in navigating the VHA, VBA and VSC (Veteran Service Commission) and provide a VA resource for the Veterans for assistance. Oncology team reviewed the cancer registry each month and identified Veterans who served during the Vietnam Era or the Marine Corps and contacted them to screen for military history. If a Veteran met the time and location qualifications, the Veteran was referred to the community outreach coordinators. The coordinators then further screened the Veterans for eligibility, assisted the Veterans in initiating their claims applications and connected the Veterans with their local VSC. At the six month follow up, 74 Veterans had been referred to community outreach, and 16 Veterans had received 100% service connection. It is important to note, the benefits application process can take several months to complete under normal circumstances. Since implementation the project has been revised. The project team developed mailers to alert Veterans of: Potential benefits eligibility, importance for filing claims, contact information for their local VSC and contact information for VA Outreach for additional assistance. Informatics was recruited to assist with identifying Veterans who met the service criteria and providing their addresses. The Veterans identified were then sent mailers, which expedited the process, allowing the project team to reach more Veterans in a shorter timeframe. Since project initiation, 74 Veterans were contacted directly by outreach coordinators, 273 mailers have been sent to potentially eligible Veterans, and 34 have received 100% service connection to date. al center will continue this practice moving forward.
Community outreach coordinators identified Veterans who were not aware of their entitlement to service-connected benefits. Veterans were also unaware of the importance of adding new presumptive diagnoses to their existing service connection and were unaware of new conditions that were added to the presumptive lists. Many Veterans, unaware of the Agent Orange/Camp Lejeune presumptive conditions, were paying out of pocket for their oncology care. A project was developed between community outreach and oncology to identify, and contact Veterans newly diagnosed with cancers on the presumptive list for Vietnam and Camp Lejeune. The goals for the project were to: Increase presumptive condition awareness, assist Veterans in navigating the VHA, VBA and VSC (Veteran Service Commission) and provide a VA resource for the Veterans for assistance. Oncology team reviewed the cancer registry each month and identified Veterans who served during the Vietnam Era or the Marine Corps and contacted them to screen for military history. If a Veteran met the time and location qualifications, the Veteran was referred to the community outreach coordinators. The coordinators then further screened the Veterans for eligibility, assisted the Veterans in initiating their claims applications and connected the Veterans with their local VSC. At the six month follow up, 74 Veterans had been referred to community outreach, and 16 Veterans had received 100% service connection. It is important to note, the benefits application process can take several months to complete under normal circumstances. Since implementation the project has been revised. The project team developed mailers to alert Veterans of: Potential benefits eligibility, importance for filing claims, contact information for their local VSC and contact information for VA Outreach for additional assistance. Informatics was recruited to assist with identifying Veterans who met the service criteria and providing their addresses. The Veterans identified were then sent mailers, which expedited the process, allowing the project team to reach more Veterans in a shorter timeframe. Since project initiation, 74 Veterans were contacted directly by outreach coordinators, 273 mailers have been sent to potentially eligible Veterans, and 34 have received 100% service connection to date. al center will continue this practice moving forward.
One in three children fall short of sleep recommendations
Just over one-third of children in the United States get less sleep than recommended, with higher rates occurring among several racial/ethnic and socioeconomic groups, according to a report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
, Anne G. Wheaton, PhD, and Angelika H. Claussen, PhD, said in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
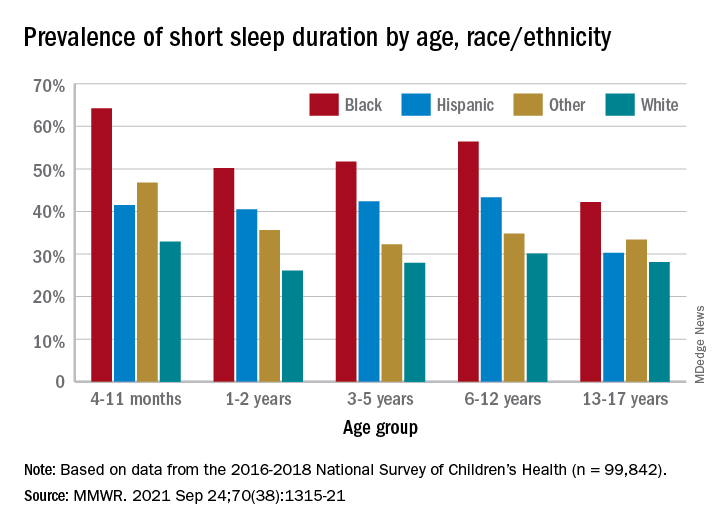
Unlike previous reports, this analysis showed that adolescents were less likely than infants to have short sleep duration, 31.2% vs. 40.3%. These latest data are based on the 2016-2018 editions of the National Survey of Children’s Health, and the “difference might be explained by NSCH’s reliance on parent report rather than self-report with Youth Risk Behavior Surveys,” they suggested.
Black children had the highest prevalence of any group included in the study, as parents reported that 50.8% of all ages were not getting the recommended amount of sleep, compared with 39.1% among Hispanics, 34.6% for other races, and 28.8% for Whites. The figure for Black infants was 64.2%, almost double the prevalence for White infants (32.9%), said Dr. Wheaton and Dr. Claussen of the CDC.
Short sleep duration also was more common in children from lower-income families and among those with less educated parents. Geography had an effect as well, with prevalence “highest in the Southeast, similar to geographic variation in adequate sleep observed for adults,” they noted.
Previous research has shown that “sleep disparity was associated with various social determinants of health (e.g., poverty, food insecurity, and perceived racism), which can increase chronic and acute stress and result in environmental and psychological factors that negatively affect sleep duration and can compound long-term health risks,” the investigators wrote.
Short sleep duration by age group was defined as less the following amounts: Twelve hours for infants (4-11 months), 11 hours for children aged 1-2 years, 10 hours for children aged 3-5 years, 9 hours for children aged 6-12, and 8 hours for adolescents (13-17 years), they explained. Responses for the survey’s sleep-duration question totaled 99,842 for the 3 years included.
Just over one-third of children in the United States get less sleep than recommended, with higher rates occurring among several racial/ethnic and socioeconomic groups, according to a report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

, Anne G. Wheaton, PhD, and Angelika H. Claussen, PhD, said in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
Unlike previous reports, this analysis showed that adolescents were less likely than infants to have short sleep duration, 31.2% vs. 40.3%. These latest data are based on the 2016-2018 editions of the National Survey of Children’s Health, and the “difference might be explained by NSCH’s reliance on parent report rather than self-report with Youth Risk Behavior Surveys,” they suggested.
Black children had the highest prevalence of any group included in the study, as parents reported that 50.8% of all ages were not getting the recommended amount of sleep, compared with 39.1% among Hispanics, 34.6% for other races, and 28.8% for Whites. The figure for Black infants was 64.2%, almost double the prevalence for White infants (32.9%), said Dr. Wheaton and Dr. Claussen of the CDC.
Short sleep duration also was more common in children from lower-income families and among those with less educated parents. Geography had an effect as well, with prevalence “highest in the Southeast, similar to geographic variation in adequate sleep observed for adults,” they noted.
Previous research has shown that “sleep disparity was associated with various social determinants of health (e.g., poverty, food insecurity, and perceived racism), which can increase chronic and acute stress and result in environmental and psychological factors that negatively affect sleep duration and can compound long-term health risks,” the investigators wrote.
Short sleep duration by age group was defined as less the following amounts: Twelve hours for infants (4-11 months), 11 hours for children aged 1-2 years, 10 hours for children aged 3-5 years, 9 hours for children aged 6-12, and 8 hours for adolescents (13-17 years), they explained. Responses for the survey’s sleep-duration question totaled 99,842 for the 3 years included.
Just over one-third of children in the United States get less sleep than recommended, with higher rates occurring among several racial/ethnic and socioeconomic groups, according to a report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

, Anne G. Wheaton, PhD, and Angelika H. Claussen, PhD, said in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
Unlike previous reports, this analysis showed that adolescents were less likely than infants to have short sleep duration, 31.2% vs. 40.3%. These latest data are based on the 2016-2018 editions of the National Survey of Children’s Health, and the “difference might be explained by NSCH’s reliance on parent report rather than self-report with Youth Risk Behavior Surveys,” they suggested.
Black children had the highest prevalence of any group included in the study, as parents reported that 50.8% of all ages were not getting the recommended amount of sleep, compared with 39.1% among Hispanics, 34.6% for other races, and 28.8% for Whites. The figure for Black infants was 64.2%, almost double the prevalence for White infants (32.9%), said Dr. Wheaton and Dr. Claussen of the CDC.
Short sleep duration also was more common in children from lower-income families and among those with less educated parents. Geography had an effect as well, with prevalence “highest in the Southeast, similar to geographic variation in adequate sleep observed for adults,” they noted.
Previous research has shown that “sleep disparity was associated with various social determinants of health (e.g., poverty, food insecurity, and perceived racism), which can increase chronic and acute stress and result in environmental and psychological factors that negatively affect sleep duration and can compound long-term health risks,” the investigators wrote.
Short sleep duration by age group was defined as less the following amounts: Twelve hours for infants (4-11 months), 11 hours for children aged 1-2 years, 10 hours for children aged 3-5 years, 9 hours for children aged 6-12, and 8 hours for adolescents (13-17 years), they explained. Responses for the survey’s sleep-duration question totaled 99,842 for the 3 years included.
FROM MMWR
RA: Treatment escalation to biologics vs. csDMARD more effective in clinical remission
Key clinical point: In patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in clinical remission, treat-to-target-based treatment escalations to biologics were more effective than escalation to conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (csDMARD) in improving magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) inflammation, physical function, and clinical disease activity.
Major finding: Escalation to first biologic vs. csDMARD escalation effectively reduced MRI osteitis (difference between least squares means [∆LSM] 1.8; 95% CI 1.0-2.6), Health Assessment Questionnaire score (∆LSM 0.08; 95% CI 0.03-0.1), MRI combined inflammation (∆LSM 2.5; 95% CI 0.9-4.1), and Simplified Disease Activity Index scores (∆LSM 2.7; 95% CI 1.9-3.5).
Study details: This study evaluated the impact of treatment intensification with csDMARDs and biologics in 100 patients with established RA in clinical remission from the IMAGINE-RA trial, who were randomly assigned to MRI treat-to-target strategy.
Disclosures: This research was funded by AbbVie. Some of the authors reported receiving grants and personal fees from various sources including AbbVie.
Source: Møller-Bisgaard S et al. Scand J Rheumatol. 2021 Sep 2. doi: 10.1080/03009742.2021.1935312.
Key clinical point: In patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in clinical remission, treat-to-target-based treatment escalations to biologics were more effective than escalation to conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (csDMARD) in improving magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) inflammation, physical function, and clinical disease activity.
Major finding: Escalation to first biologic vs. csDMARD escalation effectively reduced MRI osteitis (difference between least squares means [∆LSM] 1.8; 95% CI 1.0-2.6), Health Assessment Questionnaire score (∆LSM 0.08; 95% CI 0.03-0.1), MRI combined inflammation (∆LSM 2.5; 95% CI 0.9-4.1), and Simplified Disease Activity Index scores (∆LSM 2.7; 95% CI 1.9-3.5).
Study details: This study evaluated the impact of treatment intensification with csDMARDs and biologics in 100 patients with established RA in clinical remission from the IMAGINE-RA trial, who were randomly assigned to MRI treat-to-target strategy.
Disclosures: This research was funded by AbbVie. Some of the authors reported receiving grants and personal fees from various sources including AbbVie.
Source: Møller-Bisgaard S et al. Scand J Rheumatol. 2021 Sep 2. doi: 10.1080/03009742.2021.1935312.
Key clinical point: In patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in clinical remission, treat-to-target-based treatment escalations to biologics were more effective than escalation to conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (csDMARD) in improving magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) inflammation, physical function, and clinical disease activity.
Major finding: Escalation to first biologic vs. csDMARD escalation effectively reduced MRI osteitis (difference between least squares means [∆LSM] 1.8; 95% CI 1.0-2.6), Health Assessment Questionnaire score (∆LSM 0.08; 95% CI 0.03-0.1), MRI combined inflammation (∆LSM 2.5; 95% CI 0.9-4.1), and Simplified Disease Activity Index scores (∆LSM 2.7; 95% CI 1.9-3.5).
Study details: This study evaluated the impact of treatment intensification with csDMARDs and biologics in 100 patients with established RA in clinical remission from the IMAGINE-RA trial, who were randomly assigned to MRI treat-to-target strategy.
Disclosures: This research was funded by AbbVie. Some of the authors reported receiving grants and personal fees from various sources including AbbVie.
Source: Møller-Bisgaard S et al. Scand J Rheumatol. 2021 Sep 2. doi: 10.1080/03009742.2021.1935312.
Abatacept beneficial in csDMARD-refractory RA
Key clinical point: Abatacept appeared to be more efficacious and safer than adding or switching to conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (csDMARD) in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) of any age who were refractory to csDMARDs.
Major finding: At 24 weeks, European League Against Rheumatism good or moderate response was achieved by a significantly higher proportion of older patients aged 65 years or above (odds ratio [OR] 7.770; P < .0001) and younger patients (OR 4.089; P = .005) receiving abatacept vs. csDMARDs. Few serious adverse events were reported.
Study details: This was a prospective, multicenter study involving 202 bio-naive, csDMARD-refractory patients with RA. The patients were categorized into older (n=67) and younger (n=47) patients receiving abatacept and older (n=48) and younger (n=40) patients receiving csDMARDs.
Disclosures: This study was supported by Bristol Myers Squibb K.K. and Ono Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. The authors including the lead author reported receiving grants and personal/consultancy/speakers’ fees from various sources including Bristol Myers Squibb K.K. and Ono Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.
Source: Muraoka S et al. Rheumatol Ther. 2021 Aug 26. doi: 10.1007/s40744-021-00356-2.
Key clinical point: Abatacept appeared to be more efficacious and safer than adding or switching to conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (csDMARD) in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) of any age who were refractory to csDMARDs.
Major finding: At 24 weeks, European League Against Rheumatism good or moderate response was achieved by a significantly higher proportion of older patients aged 65 years or above (odds ratio [OR] 7.770; P < .0001) and younger patients (OR 4.089; P = .005) receiving abatacept vs. csDMARDs. Few serious adverse events were reported.
Study details: This was a prospective, multicenter study involving 202 bio-naive, csDMARD-refractory patients with RA. The patients were categorized into older (n=67) and younger (n=47) patients receiving abatacept and older (n=48) and younger (n=40) patients receiving csDMARDs.
Disclosures: This study was supported by Bristol Myers Squibb K.K. and Ono Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. The authors including the lead author reported receiving grants and personal/consultancy/speakers’ fees from various sources including Bristol Myers Squibb K.K. and Ono Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.
Source: Muraoka S et al. Rheumatol Ther. 2021 Aug 26. doi: 10.1007/s40744-021-00356-2.
Key clinical point: Abatacept appeared to be more efficacious and safer than adding or switching to conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (csDMARD) in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) of any age who were refractory to csDMARDs.
Major finding: At 24 weeks, European League Against Rheumatism good or moderate response was achieved by a significantly higher proportion of older patients aged 65 years or above (odds ratio [OR] 7.770; P < .0001) and younger patients (OR 4.089; P = .005) receiving abatacept vs. csDMARDs. Few serious adverse events were reported.
Study details: This was a prospective, multicenter study involving 202 bio-naive, csDMARD-refractory patients with RA. The patients were categorized into older (n=67) and younger (n=47) patients receiving abatacept and older (n=48) and younger (n=40) patients receiving csDMARDs.
Disclosures: This study was supported by Bristol Myers Squibb K.K. and Ono Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. The authors including the lead author reported receiving grants and personal/consultancy/speakers’ fees from various sources including Bristol Myers Squibb K.K. and Ono Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.
Source: Muraoka S et al. Rheumatol Ther. 2021 Aug 26. doi: 10.1007/s40744-021-00356-2.