User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
Powered by CHEST Physician, Clinician Reviews, MDedge Family Medicine, Internal Medicine News, and The Journal of Clinical Outcomes Management.
Even those who just test positive at more risk for long COVID: CDC
Long-term symptoms, like those linked with COVID-19, were common in people who had even just a single positive test, new Centers for Disease Control and Prevention data show.
The data show that symptoms in this group – including fatigue, cough, and headache – tended to last for more than a month.
Frequency of symptoms in people with a positive test was 1.5 times higher, compared with people whose tests had always been negative, according to the research published in the CDC’s latest Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
Lead author Valentine Wanga, PhD, with the CDC’s COVID-19 response team, and colleagues conducted a non–probability-based internet panel survey of about 6,000 U.S. adults to assess long-term symptoms often associated with COVID-19 among those who had ever tested positive or always tested negative for COVID-19 between January 2020 and April 2021.
William Schaffner, MD, an infectious disease expert at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., said in an interview that this research “establishes more securely than before that you don’t have to be hospitalized with COVID in order to develop long COVID symptoms.”
That’s better known among infectious disease experts, he said, but added that “this survey really gives a firm database for that.”
Study results
The study’s results showed that, compared with respondents who had a negative test result, those who received a positive result reported a significantly higher prevalence of any long-term symptom (65.9% vs. 42.9%), fatigue (22.5% vs. 12.0%), change in sense of smell or taste (17.3% vs. 1.7%), shortness of breath (15.5% vs. 5.2%), cough (14.5% vs. 4.9%), and headache (13.8% vs. 9.9%).
More people who had a positive test result (76.2%) reported persistence for more than a month of at least one initially occurring symptom, compared with those whose test results were always negative (69.6%).
The numbers are further proof, Dr. Schaffner said, that COVID not only will be an acute stressor on the health care system but patients with long COVID will need help with managing care for the long term.
“We still don’t know what the COVID virus does that results in these long COVID symptoms,” he said. Vanderbilt and many other institutions have developed “long COVID” centers as a testament to how important the problem is.
Long COVID symptoms are not well understood and most studies have looked at the effects from patients who had been hospitalized with COVID-19.
In this survey, respondents self-reported whether they had ever had a positive SARS-CoV-2 test result (698), always received a negative test result (2,437), or never were tested for SARS-CoV-2 (2,750).
Compared with those who always tested negative, a larger proportion of those who tested positive (28.7% vs. 15.7%) reported believing that receiving a COVID-19 vaccine made their long-term symptoms better. No difference was found in reported beliefs that a vaccine made long-term symptoms worse.
Dr. Schaffner said he found that survey result interesting, but said that is not backed up by current data and would need further study.
“I would treat that with great caution,” he said. “I’m not dismissing it, but you can’t take that at face value. All of us who get sick and those of us who care for people who are sick – if there’s an intervention, we all hope for the best. We’re being optimistic. It’s when you do a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study that you can find out whether your instincts or hopes were correct.”
The authors said that findings can inform public health preparedness, help guide care for people with post-COVID conditions, and help make the case for vaccines.
The study authors and Dr. Schaffner disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Long-term symptoms, like those linked with COVID-19, were common in people who had even just a single positive test, new Centers for Disease Control and Prevention data show.
The data show that symptoms in this group – including fatigue, cough, and headache – tended to last for more than a month.
Frequency of symptoms in people with a positive test was 1.5 times higher, compared with people whose tests had always been negative, according to the research published in the CDC’s latest Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
Lead author Valentine Wanga, PhD, with the CDC’s COVID-19 response team, and colleagues conducted a non–probability-based internet panel survey of about 6,000 U.S. adults to assess long-term symptoms often associated with COVID-19 among those who had ever tested positive or always tested negative for COVID-19 between January 2020 and April 2021.
William Schaffner, MD, an infectious disease expert at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., said in an interview that this research “establishes more securely than before that you don’t have to be hospitalized with COVID in order to develop long COVID symptoms.”
That’s better known among infectious disease experts, he said, but added that “this survey really gives a firm database for that.”
Study results
The study’s results showed that, compared with respondents who had a negative test result, those who received a positive result reported a significantly higher prevalence of any long-term symptom (65.9% vs. 42.9%), fatigue (22.5% vs. 12.0%), change in sense of smell or taste (17.3% vs. 1.7%), shortness of breath (15.5% vs. 5.2%), cough (14.5% vs. 4.9%), and headache (13.8% vs. 9.9%).
More people who had a positive test result (76.2%) reported persistence for more than a month of at least one initially occurring symptom, compared with those whose test results were always negative (69.6%).
The numbers are further proof, Dr. Schaffner said, that COVID not only will be an acute stressor on the health care system but patients with long COVID will need help with managing care for the long term.
“We still don’t know what the COVID virus does that results in these long COVID symptoms,” he said. Vanderbilt and many other institutions have developed “long COVID” centers as a testament to how important the problem is.
Long COVID symptoms are not well understood and most studies have looked at the effects from patients who had been hospitalized with COVID-19.
In this survey, respondents self-reported whether they had ever had a positive SARS-CoV-2 test result (698), always received a negative test result (2,437), or never were tested for SARS-CoV-2 (2,750).
Compared with those who always tested negative, a larger proportion of those who tested positive (28.7% vs. 15.7%) reported believing that receiving a COVID-19 vaccine made their long-term symptoms better. No difference was found in reported beliefs that a vaccine made long-term symptoms worse.
Dr. Schaffner said he found that survey result interesting, but said that is not backed up by current data and would need further study.
“I would treat that with great caution,” he said. “I’m not dismissing it, but you can’t take that at face value. All of us who get sick and those of us who care for people who are sick – if there’s an intervention, we all hope for the best. We’re being optimistic. It’s when you do a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study that you can find out whether your instincts or hopes were correct.”
The authors said that findings can inform public health preparedness, help guide care for people with post-COVID conditions, and help make the case for vaccines.
The study authors and Dr. Schaffner disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Long-term symptoms, like those linked with COVID-19, were common in people who had even just a single positive test, new Centers for Disease Control and Prevention data show.
The data show that symptoms in this group – including fatigue, cough, and headache – tended to last for more than a month.
Frequency of symptoms in people with a positive test was 1.5 times higher, compared with people whose tests had always been negative, according to the research published in the CDC’s latest Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
Lead author Valentine Wanga, PhD, with the CDC’s COVID-19 response team, and colleagues conducted a non–probability-based internet panel survey of about 6,000 U.S. adults to assess long-term symptoms often associated with COVID-19 among those who had ever tested positive or always tested negative for COVID-19 between January 2020 and April 2021.
William Schaffner, MD, an infectious disease expert at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., said in an interview that this research “establishes more securely than before that you don’t have to be hospitalized with COVID in order to develop long COVID symptoms.”
That’s better known among infectious disease experts, he said, but added that “this survey really gives a firm database for that.”
Study results
The study’s results showed that, compared with respondents who had a negative test result, those who received a positive result reported a significantly higher prevalence of any long-term symptom (65.9% vs. 42.9%), fatigue (22.5% vs. 12.0%), change in sense of smell or taste (17.3% vs. 1.7%), shortness of breath (15.5% vs. 5.2%), cough (14.5% vs. 4.9%), and headache (13.8% vs. 9.9%).
More people who had a positive test result (76.2%) reported persistence for more than a month of at least one initially occurring symptom, compared with those whose test results were always negative (69.6%).
The numbers are further proof, Dr. Schaffner said, that COVID not only will be an acute stressor on the health care system but patients with long COVID will need help with managing care for the long term.
“We still don’t know what the COVID virus does that results in these long COVID symptoms,” he said. Vanderbilt and many other institutions have developed “long COVID” centers as a testament to how important the problem is.
Long COVID symptoms are not well understood and most studies have looked at the effects from patients who had been hospitalized with COVID-19.
In this survey, respondents self-reported whether they had ever had a positive SARS-CoV-2 test result (698), always received a negative test result (2,437), or never were tested for SARS-CoV-2 (2,750).
Compared with those who always tested negative, a larger proportion of those who tested positive (28.7% vs. 15.7%) reported believing that receiving a COVID-19 vaccine made their long-term symptoms better. No difference was found in reported beliefs that a vaccine made long-term symptoms worse.
Dr. Schaffner said he found that survey result interesting, but said that is not backed up by current data and would need further study.
“I would treat that with great caution,” he said. “I’m not dismissing it, but you can’t take that at face value. All of us who get sick and those of us who care for people who are sick – if there’s an intervention, we all hope for the best. We’re being optimistic. It’s when you do a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study that you can find out whether your instincts or hopes were correct.”
The authors said that findings can inform public health preparedness, help guide care for people with post-COVID conditions, and help make the case for vaccines.
The study authors and Dr. Schaffner disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
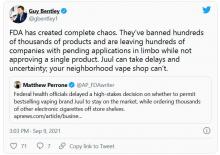
FDA moves to block some vape products, delays action on Juul
The agency had a court-ordered deadline of Sept. 9 to review more than 6.5 million applications for approval of what are considered new tobacco products – the vast majority of which are e-cigarettes and liquids, none of which have gone through FDA review before.
The FDA reviewed 93% of those applications in the past year, acting FDA Commissioner Janet Woodcock, MD, and Mitch Zeller, director of the FDA’s Center for Tobacco Products, said in a statement.
Of those reviewed, the agency rejected more than 946,000 flavored vape products, “because their applications lacked sufficient evidence that they have a benefit to adult smokers sufficient to overcome the public health threat posed by the well-documented, alarming levels of youth use of such products,” Dr. Woodcock and Mr. Zeller said.
The pair said more work is needed to finish the reviews to “ensure that we continue taking appropriate action to protect our nation’s youth from the dangers of all tobacco products, including e-cigarettes, which remain the most commonly used tobacco product by youth in the United States.”
No e-cigarette product has been given official FDA approval to be sold, meaning all e-cigarette products technically are on the market illegally, the agency said in 2020, but federal officials decided only to begin enforcing rules against flavored products, which surveys show are more often used by children. Tobacco-flavored and menthol e-cigarette products – which some adults use to quit smoking cigarettes – were exempted.
The American Cancer Society and other advocacy groups slammed the FDA’s decision to withhold action on major e-cigarette manufacturers, including Juul.
“The FDA’s failure today to act on applications by Juul, the manufacturer with the single biggest e-cigarette market share, is extremely disappointing and will allow the industry to further endanger public health and hook more kids on their highly addictive products,” Lisa Lacasse, president of ACS CAN, said in a statement, according to CNN.
“The FDA has had ample time to review the applications and allowing additional delays is unconscionable. There is overwhelming data to demonstrate the negative impact these kinds of flavored products have had on public health and their role in the youth e-cigarette epidemic. The time to act is now,” Ms. Lacasse added.
E-cigarette use among high school students rose from 11.7% in 2017 to 19.6% in 2020, the American Cancer Society said. Nearly 5% of middle schoolers reported using them in 2020.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The agency had a court-ordered deadline of Sept. 9 to review more than 6.5 million applications for approval of what are considered new tobacco products – the vast majority of which are e-cigarettes and liquids, none of which have gone through FDA review before.
The FDA reviewed 93% of those applications in the past year, acting FDA Commissioner Janet Woodcock, MD, and Mitch Zeller, director of the FDA’s Center for Tobacco Products, said in a statement.
Of those reviewed, the agency rejected more than 946,000 flavored vape products, “because their applications lacked sufficient evidence that they have a benefit to adult smokers sufficient to overcome the public health threat posed by the well-documented, alarming levels of youth use of such products,” Dr. Woodcock and Mr. Zeller said.
The pair said more work is needed to finish the reviews to “ensure that we continue taking appropriate action to protect our nation’s youth from the dangers of all tobacco products, including e-cigarettes, which remain the most commonly used tobacco product by youth in the United States.”
No e-cigarette product has been given official FDA approval to be sold, meaning all e-cigarette products technically are on the market illegally, the agency said in 2020, but federal officials decided only to begin enforcing rules against flavored products, which surveys show are more often used by children. Tobacco-flavored and menthol e-cigarette products – which some adults use to quit smoking cigarettes – were exempted.
The American Cancer Society and other advocacy groups slammed the FDA’s decision to withhold action on major e-cigarette manufacturers, including Juul.
“The FDA’s failure today to act on applications by Juul, the manufacturer with the single biggest e-cigarette market share, is extremely disappointing and will allow the industry to further endanger public health and hook more kids on their highly addictive products,” Lisa Lacasse, president of ACS CAN, said in a statement, according to CNN.
“The FDA has had ample time to review the applications and allowing additional delays is unconscionable. There is overwhelming data to demonstrate the negative impact these kinds of flavored products have had on public health and their role in the youth e-cigarette epidemic. The time to act is now,” Ms. Lacasse added.
E-cigarette use among high school students rose from 11.7% in 2017 to 19.6% in 2020, the American Cancer Society said. Nearly 5% of middle schoolers reported using them in 2020.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The agency had a court-ordered deadline of Sept. 9 to review more than 6.5 million applications for approval of what are considered new tobacco products – the vast majority of which are e-cigarettes and liquids, none of which have gone through FDA review before.
The FDA reviewed 93% of those applications in the past year, acting FDA Commissioner Janet Woodcock, MD, and Mitch Zeller, director of the FDA’s Center for Tobacco Products, said in a statement.
Of those reviewed, the agency rejected more than 946,000 flavored vape products, “because their applications lacked sufficient evidence that they have a benefit to adult smokers sufficient to overcome the public health threat posed by the well-documented, alarming levels of youth use of such products,” Dr. Woodcock and Mr. Zeller said.
The pair said more work is needed to finish the reviews to “ensure that we continue taking appropriate action to protect our nation’s youth from the dangers of all tobacco products, including e-cigarettes, which remain the most commonly used tobacco product by youth in the United States.”
No e-cigarette product has been given official FDA approval to be sold, meaning all e-cigarette products technically are on the market illegally, the agency said in 2020, but federal officials decided only to begin enforcing rules against flavored products, which surveys show are more often used by children. Tobacco-flavored and menthol e-cigarette products – which some adults use to quit smoking cigarettes – were exempted.
The American Cancer Society and other advocacy groups slammed the FDA’s decision to withhold action on major e-cigarette manufacturers, including Juul.
“The FDA’s failure today to act on applications by Juul, the manufacturer with the single biggest e-cigarette market share, is extremely disappointing and will allow the industry to further endanger public health and hook more kids on their highly addictive products,” Lisa Lacasse, president of ACS CAN, said in a statement, according to CNN.
“The FDA has had ample time to review the applications and allowing additional delays is unconscionable. There is overwhelming data to demonstrate the negative impact these kinds of flavored products have had on public health and their role in the youth e-cigarette epidemic. The time to act is now,” Ms. Lacasse added.
E-cigarette use among high school students rose from 11.7% in 2017 to 19.6% in 2020, the American Cancer Society said. Nearly 5% of middle schoolers reported using them in 2020.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
COVID-19 spares lung function in young adults
Here’s some encouraging news for once regarding SARS-CoV-2 infections: A study of young adults for whom prepandemic spirometry data were available showed that COVID-19 did not have a significant impact on lung function, even among patients with asthma.
Among 853 Swedish men and women (mean age, 22 years) who were part of a birth cohort study, there were no significant differences in either forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) or in the ratio of FEV1 to forced vital capacity, reported Ida Mogensen, MD, PhD, a postdoctoral fellow at the Karolinska Institute in Stockholm.
“We found no effect of COVID-19 on spirometric lung function in generally healthy adults,” she said in an oral abstract presented at the European Respiratory Society 2021 International Congress.
The findings echo those of a small study that involved 73 children and adolescents with COVID-19 and 45 uninfected control persons. The investigators in that study, which was also presented at ERS 2021, found that there were no significant differences in the frequency of abnormal pulmonary function measures between case patients and control patients (abstract OA1303).
“The findings from these two studies provide important reassurance about the impact of COVID infection on lung function in children and young adults,” commented Anita Simonds, MD, an honorary consultant in respiratory and sleep medicine at the Royal Brompton Hospital, London.
“We know already that this group is less likely to suffer severe illness if they contract the virus, and these studies, which importantly include comparator groups without COVID-19, show that they are also less likely to suffer long-term consequences with respect to lung function,” she said. Dr. Simonds was not involved in either study.
Young adult study
Dr. Mogenson and colleagues assessed data on 853 participants in the BAMSE Project, a prospective birth cohort study that included 4,089 children born in Stockholm from 1994 to 1996. Of the participants, 147 had asthma. They have been regularly followed with questionnaires on respiratory symptoms and medications. In addition, at 8 and 16 years’ follow-up, spirometry measures and fractional exhaled nitric oxide (FeNO) levels were assessed, allergic sensitization tests were administered, and blood eosinophil levels were measured.
In 2020 and 2021, during the pandemic, the participants underwent spirometry testing and were assessed for antibodies against SARS-CoV-2, and they self-reported use of inhaled corticosteroids.
The investigators defined asthma as any physician diagnosis and asthma symptoms and/or asthma medication use within the previous year. Participants were determined to be COVID-19 seropositive if they had IgG antibodies to the SARS-CoV-2 spike greater than 25.09 AU/mL, IgM antibodies greater than 14.42 AU/mL, or IgA antibodies greater than 2.61 AU/mL, as measured with enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
Participants who had been vaccinated against COVID-19 were excluded.
No significant decreases
A total of 243 participants, including 38 with asthma, were seropositive for SARS-CoV-2 antibodies. The mean change in lung function from before the pandemic to the study end date during the pandemic were not significantly different between seropositive participants and seronegative participants or IgM-positive participants and seronegative participants.
Similarly, there were no significant differences in lung function between seropositive and seronegative participants in an analysis that was adjusted for sex, body mass index, smoking status, or prepandemic lung function.
Although there was a trend toward slightly lower function among seropositive participants with asthma in comparison with seronegative patients with asthma, it was not statistically significant, Dr. Mogenson said.
There were also no significant decreases in lung function from the prepandemic measure to the present in any of the inflammatory parameters, including blood eosinophil levels, FeNO, allergic sensitization, or inhaled corticosteroid use.
Potential misclassification
In the question-and-answer period that followed the presentation, session comoderator Sam Bayat, MD, PhD, from the University of Grenoble (France), who was not involved in the study, noted that “some subjects can have positive serology without any symptoms, while others can have symptomatic disease and a couple of months later they have negative serology.”
He asked Dr. Mogenson whether they had included in their study participants with symptomatic COVID-19 and whether that would change the findings.
“We did not have access to RNA testing, so we only had serology, and of course some participants could be wrongly classified to have disease – probably around 15%,” she acknowledged.
She noted that there were no significant changes in lung function among patients who reported having respiratory symptoms.
The study was funded by the Swedish Research Council, the Swedish Heart-Lung Foundation, the Swedish Research Council for Health, Working Life and Welfare, the Karolinska Institutet, Formas, the European Research Council, and Region Stockholm. Dr. Mogenson, Dr. Simonds, and Dr. Bayat disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Here’s some encouraging news for once regarding SARS-CoV-2 infections: A study of young adults for whom prepandemic spirometry data were available showed that COVID-19 did not have a significant impact on lung function, even among patients with asthma.
Among 853 Swedish men and women (mean age, 22 years) who were part of a birth cohort study, there were no significant differences in either forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) or in the ratio of FEV1 to forced vital capacity, reported Ida Mogensen, MD, PhD, a postdoctoral fellow at the Karolinska Institute in Stockholm.
“We found no effect of COVID-19 on spirometric lung function in generally healthy adults,” she said in an oral abstract presented at the European Respiratory Society 2021 International Congress.
The findings echo those of a small study that involved 73 children and adolescents with COVID-19 and 45 uninfected control persons. The investigators in that study, which was also presented at ERS 2021, found that there were no significant differences in the frequency of abnormal pulmonary function measures between case patients and control patients (abstract OA1303).
“The findings from these two studies provide important reassurance about the impact of COVID infection on lung function in children and young adults,” commented Anita Simonds, MD, an honorary consultant in respiratory and sleep medicine at the Royal Brompton Hospital, London.
“We know already that this group is less likely to suffer severe illness if they contract the virus, and these studies, which importantly include comparator groups without COVID-19, show that they are also less likely to suffer long-term consequences with respect to lung function,” she said. Dr. Simonds was not involved in either study.
Young adult study
Dr. Mogenson and colleagues assessed data on 853 participants in the BAMSE Project, a prospective birth cohort study that included 4,089 children born in Stockholm from 1994 to 1996. Of the participants, 147 had asthma. They have been regularly followed with questionnaires on respiratory symptoms and medications. In addition, at 8 and 16 years’ follow-up, spirometry measures and fractional exhaled nitric oxide (FeNO) levels were assessed, allergic sensitization tests were administered, and blood eosinophil levels were measured.
In 2020 and 2021, during the pandemic, the participants underwent spirometry testing and were assessed for antibodies against SARS-CoV-2, and they self-reported use of inhaled corticosteroids.
The investigators defined asthma as any physician diagnosis and asthma symptoms and/or asthma medication use within the previous year. Participants were determined to be COVID-19 seropositive if they had IgG antibodies to the SARS-CoV-2 spike greater than 25.09 AU/mL, IgM antibodies greater than 14.42 AU/mL, or IgA antibodies greater than 2.61 AU/mL, as measured with enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
Participants who had been vaccinated against COVID-19 were excluded.
No significant decreases
A total of 243 participants, including 38 with asthma, were seropositive for SARS-CoV-2 antibodies. The mean change in lung function from before the pandemic to the study end date during the pandemic were not significantly different between seropositive participants and seronegative participants or IgM-positive participants and seronegative participants.
Similarly, there were no significant differences in lung function between seropositive and seronegative participants in an analysis that was adjusted for sex, body mass index, smoking status, or prepandemic lung function.
Although there was a trend toward slightly lower function among seropositive participants with asthma in comparison with seronegative patients with asthma, it was not statistically significant, Dr. Mogenson said.
There were also no significant decreases in lung function from the prepandemic measure to the present in any of the inflammatory parameters, including blood eosinophil levels, FeNO, allergic sensitization, or inhaled corticosteroid use.
Potential misclassification
In the question-and-answer period that followed the presentation, session comoderator Sam Bayat, MD, PhD, from the University of Grenoble (France), who was not involved in the study, noted that “some subjects can have positive serology without any symptoms, while others can have symptomatic disease and a couple of months later they have negative serology.”
He asked Dr. Mogenson whether they had included in their study participants with symptomatic COVID-19 and whether that would change the findings.
“We did not have access to RNA testing, so we only had serology, and of course some participants could be wrongly classified to have disease – probably around 15%,” she acknowledged.
She noted that there were no significant changes in lung function among patients who reported having respiratory symptoms.
The study was funded by the Swedish Research Council, the Swedish Heart-Lung Foundation, the Swedish Research Council for Health, Working Life and Welfare, the Karolinska Institutet, Formas, the European Research Council, and Region Stockholm. Dr. Mogenson, Dr. Simonds, and Dr. Bayat disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Here’s some encouraging news for once regarding SARS-CoV-2 infections: A study of young adults for whom prepandemic spirometry data were available showed that COVID-19 did not have a significant impact on lung function, even among patients with asthma.
Among 853 Swedish men and women (mean age, 22 years) who were part of a birth cohort study, there were no significant differences in either forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) or in the ratio of FEV1 to forced vital capacity, reported Ida Mogensen, MD, PhD, a postdoctoral fellow at the Karolinska Institute in Stockholm.
“We found no effect of COVID-19 on spirometric lung function in generally healthy adults,” she said in an oral abstract presented at the European Respiratory Society 2021 International Congress.
The findings echo those of a small study that involved 73 children and adolescents with COVID-19 and 45 uninfected control persons. The investigators in that study, which was also presented at ERS 2021, found that there were no significant differences in the frequency of abnormal pulmonary function measures between case patients and control patients (abstract OA1303).
“The findings from these two studies provide important reassurance about the impact of COVID infection on lung function in children and young adults,” commented Anita Simonds, MD, an honorary consultant in respiratory and sleep medicine at the Royal Brompton Hospital, London.
“We know already that this group is less likely to suffer severe illness if they contract the virus, and these studies, which importantly include comparator groups without COVID-19, show that they are also less likely to suffer long-term consequences with respect to lung function,” she said. Dr. Simonds was not involved in either study.
Young adult study
Dr. Mogenson and colleagues assessed data on 853 participants in the BAMSE Project, a prospective birth cohort study that included 4,089 children born in Stockholm from 1994 to 1996. Of the participants, 147 had asthma. They have been regularly followed with questionnaires on respiratory symptoms and medications. In addition, at 8 and 16 years’ follow-up, spirometry measures and fractional exhaled nitric oxide (FeNO) levels were assessed, allergic sensitization tests were administered, and blood eosinophil levels were measured.
In 2020 and 2021, during the pandemic, the participants underwent spirometry testing and were assessed for antibodies against SARS-CoV-2, and they self-reported use of inhaled corticosteroids.
The investigators defined asthma as any physician diagnosis and asthma symptoms and/or asthma medication use within the previous year. Participants were determined to be COVID-19 seropositive if they had IgG antibodies to the SARS-CoV-2 spike greater than 25.09 AU/mL, IgM antibodies greater than 14.42 AU/mL, or IgA antibodies greater than 2.61 AU/mL, as measured with enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
Participants who had been vaccinated against COVID-19 were excluded.
No significant decreases
A total of 243 participants, including 38 with asthma, were seropositive for SARS-CoV-2 antibodies. The mean change in lung function from before the pandemic to the study end date during the pandemic were not significantly different between seropositive participants and seronegative participants or IgM-positive participants and seronegative participants.
Similarly, there were no significant differences in lung function between seropositive and seronegative participants in an analysis that was adjusted for sex, body mass index, smoking status, or prepandemic lung function.
Although there was a trend toward slightly lower function among seropositive participants with asthma in comparison with seronegative patients with asthma, it was not statistically significant, Dr. Mogenson said.
There were also no significant decreases in lung function from the prepandemic measure to the present in any of the inflammatory parameters, including blood eosinophil levels, FeNO, allergic sensitization, or inhaled corticosteroid use.
Potential misclassification
In the question-and-answer period that followed the presentation, session comoderator Sam Bayat, MD, PhD, from the University of Grenoble (France), who was not involved in the study, noted that “some subjects can have positive serology without any symptoms, while others can have symptomatic disease and a couple of months later they have negative serology.”
He asked Dr. Mogenson whether they had included in their study participants with symptomatic COVID-19 and whether that would change the findings.
“We did not have access to RNA testing, so we only had serology, and of course some participants could be wrongly classified to have disease – probably around 15%,” she acknowledged.
She noted that there were no significant changes in lung function among patients who reported having respiratory symptoms.
The study was funded by the Swedish Research Council, the Swedish Heart-Lung Foundation, the Swedish Research Council for Health, Working Life and Welfare, the Karolinska Institutet, Formas, the European Research Council, and Region Stockholm. Dr. Mogenson, Dr. Simonds, and Dr. Bayat disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Sweeping new vaccine mandates will impact most U.S. workers
, including sweeping vaccine mandates that will affect 100 million American workers, nearly two-thirds of the country’s workforce.
“As your president, I’m announcing tonight a new plan to get more Americans vaccinated to combat those blocking public health,” he said Sept. 9.
As part of a six-part plan unveiled in a speech from the State Dining Room of the White House, President Biden said he would require vaccinations for nearly 4 million federal workers and the employees of companies that contract with the federal government.
He has also directed the Occupational Safety and Health Administration to develop a rule that will require large employers -- those with at least 100 employees -- to ensure their workers are vaccinated or tested weekly.
Nearly 17 million health care workers will face new vaccine mandates as part of the conditions of participation in the Medicare and Medicaid programs.
President Biden said the federal government will require staff at federally funded Head Start programs and schools to be vaccinated. He’s also calling on all states to mandate vaccines for teachers.
“A distinct minority of Americans, supported by a distinct minority of elected officials, are keeping us from turning the corner,” PresidentBiden said. “These pandemic politics, as I refer to them, are making people sick, causing unvaccinated people to die.”
One public health official said he was glad to see the president’s bold action.
“What I saw today was the federal government trying to use its powers to create greater safety in the American population,” said Ashish K. Jha, MD, dean of the school of public health at Brown University, Providence, R.I., in a call with reporters after the speech.
National Nurses United, the largest union of registered nurses in the United States, issued a statement in support of President Biden’s new vaccination requirements, but pushed back on his language.
“…as advocates for public health, registered nurses want to be extremely clear: There is no such thing as a pandemic of only the unvaccinated. The science of epidemiology tells us there is just one deadly, global pandemic that has not yet ended, and we are all in it together. To get out of it, we must act together. All of us,” the statement says.
A host of other professional groups, including the American Medical Association and the Association of State and Territorial Health Officials, also issued statements of support for President Biden’s plan.
But the plan was not well received by all.
“I will pursue every legal option available to the state of Georgia to stop this blatantly unlawful overreach by the Biden Administration,” said Georgia Governor Brian Kemp, a Republican, in a Tweet.
The National Council for Occupational Safety and Health called the plan “a missed opportunity” because it failed to include workplace protections for essential workers such as grocery, postal, and transit workers.
“Social distancing, improved ventilation, shift rotation, and protective equipment to reduce exposure are important components of an overall plan to reduce risk and stop the virus. These tools are missing from the new steps President Biden announced today,” said Jessica Martinez, co-executive director of the group.
In addition to the new vaccination requirements, President Biden said extra doses would be on the way for people who have already been fully vaccinated in order to protect against waning immunity, starting on Sept. 20. But he noted that those plans would be contingent on the Food and Drug Administration’s approval for third doses and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s recommendation of the shots.
President Biden pledged to use the Defense Production Act to ramp up production of at-home tests, which have been selling out across the nation as the Delta variant spreads.
He also announced plans to expand access to COVID-19 testing, including offering testing for free at thousands of pharmacies nationwide and getting major retailers to sell at-home COVID-19 tests at cost.
The BinaxNow test kit, which currently retails for $23.99, will now cost about $15 for two tests at Kroger, Amazon, and Walmart, according to the White House. Food banks and community health centers will get free tests, too.
He called on states to set up COVID-19 testing programs at all schools.
Jha said that in his view, the big, game-changing news out of the president’s speech was the expansion of testing.
“Our country has failed to deploy tests in a way that can really bring this pandemic under control,” Jha said. “There are plenty of reasons, data, experience to indicate that if these were widely available, it would make a dramatic difference in reducing infection numbers across our country.”.
Dr. Jha said the private market had not worked effectively to make testing more widely available, so it was “absolutely a requirement of the federal government to step in and make testing more widely available,” he said.
President Biden also announced new economic stimulus programs, saying he’s expanding loan programs to small businesses and streamlining the loan forgiveness process.
President Biden said he’s boosting help for overburdened hospitals, doubling the number of federal surge response teams sent to hard-hit areas to reduce the strain on local health care workers. He said he would increase the pace of antibody treatments to states by 50%.
“We made so much progress during the past 7 months of this pandemic. Even so, we remain at a critical moment, a critical time,” he said. “We have the tools. Now, we just have to finish the job with truth, with science, with confidence and together as one nation.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
, including sweeping vaccine mandates that will affect 100 million American workers, nearly two-thirds of the country’s workforce.
“As your president, I’m announcing tonight a new plan to get more Americans vaccinated to combat those blocking public health,” he said Sept. 9.
As part of a six-part plan unveiled in a speech from the State Dining Room of the White House, President Biden said he would require vaccinations for nearly 4 million federal workers and the employees of companies that contract with the federal government.
He has also directed the Occupational Safety and Health Administration to develop a rule that will require large employers -- those with at least 100 employees -- to ensure their workers are vaccinated or tested weekly.
Nearly 17 million health care workers will face new vaccine mandates as part of the conditions of participation in the Medicare and Medicaid programs.
President Biden said the federal government will require staff at federally funded Head Start programs and schools to be vaccinated. He’s also calling on all states to mandate vaccines for teachers.
“A distinct minority of Americans, supported by a distinct minority of elected officials, are keeping us from turning the corner,” PresidentBiden said. “These pandemic politics, as I refer to them, are making people sick, causing unvaccinated people to die.”
One public health official said he was glad to see the president’s bold action.
“What I saw today was the federal government trying to use its powers to create greater safety in the American population,” said Ashish K. Jha, MD, dean of the school of public health at Brown University, Providence, R.I., in a call with reporters after the speech.
National Nurses United, the largest union of registered nurses in the United States, issued a statement in support of President Biden’s new vaccination requirements, but pushed back on his language.
“…as advocates for public health, registered nurses want to be extremely clear: There is no such thing as a pandemic of only the unvaccinated. The science of epidemiology tells us there is just one deadly, global pandemic that has not yet ended, and we are all in it together. To get out of it, we must act together. All of us,” the statement says.
A host of other professional groups, including the American Medical Association and the Association of State and Territorial Health Officials, also issued statements of support for President Biden’s plan.
But the plan was not well received by all.
“I will pursue every legal option available to the state of Georgia to stop this blatantly unlawful overreach by the Biden Administration,” said Georgia Governor Brian Kemp, a Republican, in a Tweet.
The National Council for Occupational Safety and Health called the plan “a missed opportunity” because it failed to include workplace protections for essential workers such as grocery, postal, and transit workers.
“Social distancing, improved ventilation, shift rotation, and protective equipment to reduce exposure are important components of an overall plan to reduce risk and stop the virus. These tools are missing from the new steps President Biden announced today,” said Jessica Martinez, co-executive director of the group.
In addition to the new vaccination requirements, President Biden said extra doses would be on the way for people who have already been fully vaccinated in order to protect against waning immunity, starting on Sept. 20. But he noted that those plans would be contingent on the Food and Drug Administration’s approval for third doses and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s recommendation of the shots.
President Biden pledged to use the Defense Production Act to ramp up production of at-home tests, which have been selling out across the nation as the Delta variant spreads.
He also announced plans to expand access to COVID-19 testing, including offering testing for free at thousands of pharmacies nationwide and getting major retailers to sell at-home COVID-19 tests at cost.
The BinaxNow test kit, which currently retails for $23.99, will now cost about $15 for two tests at Kroger, Amazon, and Walmart, according to the White House. Food banks and community health centers will get free tests, too.
He called on states to set up COVID-19 testing programs at all schools.
Jha said that in his view, the big, game-changing news out of the president’s speech was the expansion of testing.
“Our country has failed to deploy tests in a way that can really bring this pandemic under control,” Jha said. “There are plenty of reasons, data, experience to indicate that if these were widely available, it would make a dramatic difference in reducing infection numbers across our country.”.
Dr. Jha said the private market had not worked effectively to make testing more widely available, so it was “absolutely a requirement of the federal government to step in and make testing more widely available,” he said.
President Biden also announced new economic stimulus programs, saying he’s expanding loan programs to small businesses and streamlining the loan forgiveness process.
President Biden said he’s boosting help for overburdened hospitals, doubling the number of federal surge response teams sent to hard-hit areas to reduce the strain on local health care workers. He said he would increase the pace of antibody treatments to states by 50%.
“We made so much progress during the past 7 months of this pandemic. Even so, we remain at a critical moment, a critical time,” he said. “We have the tools. Now, we just have to finish the job with truth, with science, with confidence and together as one nation.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
, including sweeping vaccine mandates that will affect 100 million American workers, nearly two-thirds of the country’s workforce.
“As your president, I’m announcing tonight a new plan to get more Americans vaccinated to combat those blocking public health,” he said Sept. 9.
As part of a six-part plan unveiled in a speech from the State Dining Room of the White House, President Biden said he would require vaccinations for nearly 4 million federal workers and the employees of companies that contract with the federal government.
He has also directed the Occupational Safety and Health Administration to develop a rule that will require large employers -- those with at least 100 employees -- to ensure their workers are vaccinated or tested weekly.
Nearly 17 million health care workers will face new vaccine mandates as part of the conditions of participation in the Medicare and Medicaid programs.
President Biden said the federal government will require staff at federally funded Head Start programs and schools to be vaccinated. He’s also calling on all states to mandate vaccines for teachers.
“A distinct minority of Americans, supported by a distinct minority of elected officials, are keeping us from turning the corner,” PresidentBiden said. “These pandemic politics, as I refer to them, are making people sick, causing unvaccinated people to die.”
One public health official said he was glad to see the president’s bold action.
“What I saw today was the federal government trying to use its powers to create greater safety in the American population,” said Ashish K. Jha, MD, dean of the school of public health at Brown University, Providence, R.I., in a call with reporters after the speech.
National Nurses United, the largest union of registered nurses in the United States, issued a statement in support of President Biden’s new vaccination requirements, but pushed back on his language.
“…as advocates for public health, registered nurses want to be extremely clear: There is no such thing as a pandemic of only the unvaccinated. The science of epidemiology tells us there is just one deadly, global pandemic that has not yet ended, and we are all in it together. To get out of it, we must act together. All of us,” the statement says.
A host of other professional groups, including the American Medical Association and the Association of State and Territorial Health Officials, also issued statements of support for President Biden’s plan.
But the plan was not well received by all.
“I will pursue every legal option available to the state of Georgia to stop this blatantly unlawful overreach by the Biden Administration,” said Georgia Governor Brian Kemp, a Republican, in a Tweet.
The National Council for Occupational Safety and Health called the plan “a missed opportunity” because it failed to include workplace protections for essential workers such as grocery, postal, and transit workers.
“Social distancing, improved ventilation, shift rotation, and protective equipment to reduce exposure are important components of an overall plan to reduce risk and stop the virus. These tools are missing from the new steps President Biden announced today,” said Jessica Martinez, co-executive director of the group.
In addition to the new vaccination requirements, President Biden said extra doses would be on the way for people who have already been fully vaccinated in order to protect against waning immunity, starting on Sept. 20. But he noted that those plans would be contingent on the Food and Drug Administration’s approval for third doses and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s recommendation of the shots.
President Biden pledged to use the Defense Production Act to ramp up production of at-home tests, which have been selling out across the nation as the Delta variant spreads.
He also announced plans to expand access to COVID-19 testing, including offering testing for free at thousands of pharmacies nationwide and getting major retailers to sell at-home COVID-19 tests at cost.
The BinaxNow test kit, which currently retails for $23.99, will now cost about $15 for two tests at Kroger, Amazon, and Walmart, according to the White House. Food banks and community health centers will get free tests, too.
He called on states to set up COVID-19 testing programs at all schools.
Jha said that in his view, the big, game-changing news out of the president’s speech was the expansion of testing.
“Our country has failed to deploy tests in a way that can really bring this pandemic under control,” Jha said. “There are plenty of reasons, data, experience to indicate that if these were widely available, it would make a dramatic difference in reducing infection numbers across our country.”.
Dr. Jha said the private market had not worked effectively to make testing more widely available, so it was “absolutely a requirement of the federal government to step in and make testing more widely available,” he said.
President Biden also announced new economic stimulus programs, saying he’s expanding loan programs to small businesses and streamlining the loan forgiveness process.
President Biden said he’s boosting help for overburdened hospitals, doubling the number of federal surge response teams sent to hard-hit areas to reduce the strain on local health care workers. He said he would increase the pace of antibody treatments to states by 50%.
“We made so much progress during the past 7 months of this pandemic. Even so, we remain at a critical moment, a critical time,” he said. “We have the tools. Now, we just have to finish the job with truth, with science, with confidence and together as one nation.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
United States reaches 5 million cases of child COVID
Cases of child COVID-19 set a new 1-week record and the total number of children infected during the pandemic passed 5 million, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
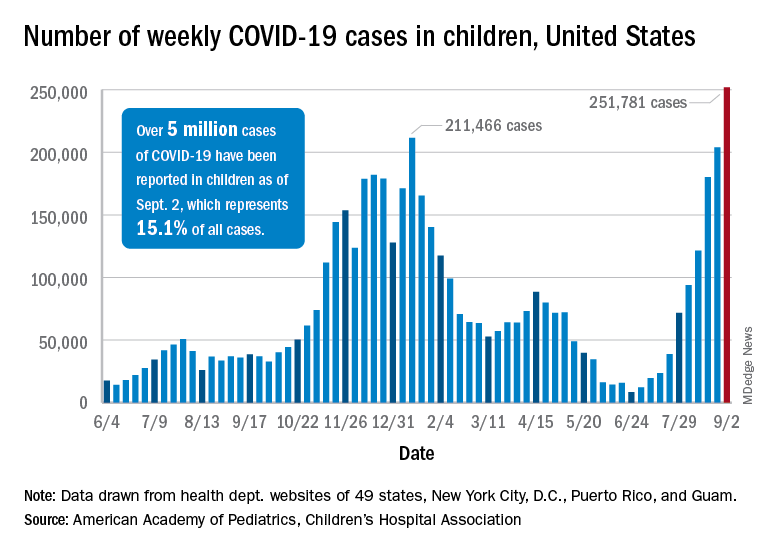
The nearly 282,000 new cases reported in the United States during the week ending Sept. 2 broke the record of 211,000 set in mid-January and brought the cumulative count to 5,049,465 children with COVID-19 since the pandemic began, the AAP and the CHA said in their weekly COVID report.
Hospitalizations in children aged 0-17 years have also reached record levels in recent days. The highest daily admission rate since the pandemic began, 0.51 per 100,000 population, was recorded on Sept. 2, less than 2 months after the nation saw its lowest child COVID admission rate for 1 day: 0.07 per 100,000 on July 4. That’s an increase of 629%, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Vaccinations in children, however, did not follow suit. New vaccinations in children aged 12-17 years dropped by 4.5% for the week ending Sept. 6, compared with the week before. Initiations were actually up almost 12% for children aged 16-17, but that was not enough to overcome the continued decline among 12- to 15-year-olds, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
Despite the decline in new vaccinations, those younger children passed a noteworthy group milestone: 50.9% of all 12- to 15-year-olds now have received at least one dose, with 38.6% having completed the regimen. The 16- to 17-year-olds got an earlier start and have reached 58.9% coverage for one dose and 47.6% for two, the CDC said.
A total of 12.2 million children aged 12-17 years had received at least one dose of COVID vaccine as of Sept. 6, of whom almost 9.5 million are fully vaccinated, based on the CDC data.
At the state level, Vermont has the highest rates for vaccine initiation (75%) and full vaccination (65%), with Massachusetts (75%/62%) and Connecticut (73%/59%) just behind. The other end of the scale is occupied by Wyoming (28% initiation/19% full vaccination), Alabama (32%/19%), and North Dakota (32%/23%), the AAP said in a separate report.
In a recent letter to the Food and Drug Administration, AAP President Lee Savio Beers, MD, said that the “Delta variant is surging at extremely alarming rates in every region of America. This surge is seriously impacting all populations, including children.” Dr. Beers urged the FDA to work “aggressively toward authorizing safe and effective COVID-19 vaccines for children under age 12 as soon as possible.”
Cases of child COVID-19 set a new 1-week record and the total number of children infected during the pandemic passed 5 million, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

The nearly 282,000 new cases reported in the United States during the week ending Sept. 2 broke the record of 211,000 set in mid-January and brought the cumulative count to 5,049,465 children with COVID-19 since the pandemic began, the AAP and the CHA said in their weekly COVID report.
Hospitalizations in children aged 0-17 years have also reached record levels in recent days. The highest daily admission rate since the pandemic began, 0.51 per 100,000 population, was recorded on Sept. 2, less than 2 months after the nation saw its lowest child COVID admission rate for 1 day: 0.07 per 100,000 on July 4. That’s an increase of 629%, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Vaccinations in children, however, did not follow suit. New vaccinations in children aged 12-17 years dropped by 4.5% for the week ending Sept. 6, compared with the week before. Initiations were actually up almost 12% for children aged 16-17, but that was not enough to overcome the continued decline among 12- to 15-year-olds, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
Despite the decline in new vaccinations, those younger children passed a noteworthy group milestone: 50.9% of all 12- to 15-year-olds now have received at least one dose, with 38.6% having completed the regimen. The 16- to 17-year-olds got an earlier start and have reached 58.9% coverage for one dose and 47.6% for two, the CDC said.
A total of 12.2 million children aged 12-17 years had received at least one dose of COVID vaccine as of Sept. 6, of whom almost 9.5 million are fully vaccinated, based on the CDC data.
At the state level, Vermont has the highest rates for vaccine initiation (75%) and full vaccination (65%), with Massachusetts (75%/62%) and Connecticut (73%/59%) just behind. The other end of the scale is occupied by Wyoming (28% initiation/19% full vaccination), Alabama (32%/19%), and North Dakota (32%/23%), the AAP said in a separate report.
In a recent letter to the Food and Drug Administration, AAP President Lee Savio Beers, MD, said that the “Delta variant is surging at extremely alarming rates in every region of America. This surge is seriously impacting all populations, including children.” Dr. Beers urged the FDA to work “aggressively toward authorizing safe and effective COVID-19 vaccines for children under age 12 as soon as possible.”
Cases of child COVID-19 set a new 1-week record and the total number of children infected during the pandemic passed 5 million, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

The nearly 282,000 new cases reported in the United States during the week ending Sept. 2 broke the record of 211,000 set in mid-January and brought the cumulative count to 5,049,465 children with COVID-19 since the pandemic began, the AAP and the CHA said in their weekly COVID report.
Hospitalizations in children aged 0-17 years have also reached record levels in recent days. The highest daily admission rate since the pandemic began, 0.51 per 100,000 population, was recorded on Sept. 2, less than 2 months after the nation saw its lowest child COVID admission rate for 1 day: 0.07 per 100,000 on July 4. That’s an increase of 629%, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Vaccinations in children, however, did not follow suit. New vaccinations in children aged 12-17 years dropped by 4.5% for the week ending Sept. 6, compared with the week before. Initiations were actually up almost 12% for children aged 16-17, but that was not enough to overcome the continued decline among 12- to 15-year-olds, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
Despite the decline in new vaccinations, those younger children passed a noteworthy group milestone: 50.9% of all 12- to 15-year-olds now have received at least one dose, with 38.6% having completed the regimen. The 16- to 17-year-olds got an earlier start and have reached 58.9% coverage for one dose and 47.6% for two, the CDC said.
A total of 12.2 million children aged 12-17 years had received at least one dose of COVID vaccine as of Sept. 6, of whom almost 9.5 million are fully vaccinated, based on the CDC data.
At the state level, Vermont has the highest rates for vaccine initiation (75%) and full vaccination (65%), with Massachusetts (75%/62%) and Connecticut (73%/59%) just behind. The other end of the scale is occupied by Wyoming (28% initiation/19% full vaccination), Alabama (32%/19%), and North Dakota (32%/23%), the AAP said in a separate report.
In a recent letter to the Food and Drug Administration, AAP President Lee Savio Beers, MD, said that the “Delta variant is surging at extremely alarming rates in every region of America. This surge is seriously impacting all populations, including children.” Dr. Beers urged the FDA to work “aggressively toward authorizing safe and effective COVID-19 vaccines for children under age 12 as soon as possible.”
Changing minds: What moves the needle for the unvaccinated?
Not so long ago, Heather Simpson of Dallas was known as the anti-vaccine mom who dressed as “the measles” for Halloween. She painted red spots on her face and posted her photo on Facebook, joking: “Was trying to think of the least scary thing I could be for Halloween … so I became the measles.” It went viral with the anti-vaccine crowd.
But between that Halloween and today, a series of “aha” moments transformed Ms. Simpson’s attitudes toward vaccines.
In January 2021, one of those moments involved her daughter, now 4, who was scratched by a feral cat, raising concerns about tetanus. Her daughter had been bitten by a dog when she was just 1, and Ms. Simpson turned down advice then to get a tetanus shot. “I was convinced the tetanus shot would kill her faster than the tetanus.”
After the cat incident, the anxiety was so exhausting, she listened to the nurse practitioner at the clinic, whom she trusted. The nurse gently reassured Ms. Simpson that the shot was less risky than the possibility of tetanus – but did not bombard her with statistics – and that won over Ms. Simpson and triggered an overall rethinking of her vaccine stance.
Fast-forward to February, and that “aha” turned into action when Ms. Simpson launched a “Back to the Vax” effort with a fellow former vaccine opponent. Through their website, Facebook page, and podcasts, they now encourage people to get the COVID-19 vaccine, as well as other immunizations.
Challenge: Reaching the rest
With just over 52% of those eligible in the United States fully vaccinated as of Sept. 1,
Recent data and a poll show some movement in the right direction, as immunizations are increasing and hesitancy is declining among certain groups. According to federal officials, about 14 million people in the United States got their first dose in August, an increase of 4 million, compared to the numbers who got it in July.
And a new poll from the Axios-IPSOS Coronavirus Index found only one in five Americans, or 20%, say they are not likely to get the vaccine, while “hard opposition,” those not at all likely, has dropped to 14% of those adults.
But there is still a lot of work to do. So, how do medical professionals or concerned citizens reach those who haven’t gotten vaccinated yet, whatever their reason?
Many experts in communication and persuasion that this news organization talked to agree that throwing statistics at people hesitant to get the COVID-19 vaccine is generally useless and often backfires.
So what does work, according to these experts?
- Emphasizing the trends of more people getting vaccinated.
- Focusing on everyone’s freedom of choice.
- Listening to concerns without judgment.
- Offering credible information.
- Correcting myths when necessary.
- Helping them fit vaccination into their “world view.”
Stories over statistics
Talking about the trends of vaccinations can definitely change minds about getting vaccinated, said Robert Cialdini, PhD, regents professor emeritus of psychology and marketing at Arizona State University, Tempe, and author of the recently updated book, “Influence: The Psychology of Persuasion,” which has sold over 5 million copies since it was first published in 1984.
Face-to-face with a hesitant patient, a doctor can say: “More and more people are being vaccinated every day,” Dr. Cialdini says. “The reason you say more and more is [that] it conveys a trend. When people see a trend, they project it into the future that it is going to get even larger.”
A focus on choice can also help people change their minds and accept the vaccine, he says. “A lot of conspiracy theorists claim they don’t want to do it because they are being pushed or forced by the government, and they are resisting that.”
If that’s the case, presenting people with new information, such as the increased infectiousness of the Delta variant, and suggesting that a decision be made based on the new information, can work, Dr. Cialdini says, but be sure to end with: “It’s completely up to you.”
“This removes all their sense of being pushed. It says, ‘Here is all the evidence.’ ” At this point, a doctor’s personal recommendation with a patient who trusts him or her may sway them, Dr. Cialdini said. “I think you have to personalize the communication in both directions. That is, to say, ‘For someone in your situation, I would personally recommend that you get the vaccine.’ ” A health care professional’s authority and expertise can carry the day, he says, although “not always.”
This approach worked, Dr. Cialdini says, with a friend of the family hesitant about the COVID-19 vaccine. “I told him: ‘We have gotten it. You trust us, right?’ ” He waited for the person to say yes.
Then: “For someone in your position, my personal recommendation is to get vaccinated. There is new information about the vaccine, and more and more people are getting vaccinated. And of course, it is completely up to you.”
The person decided to get the vaccine.
‘Live in that space’
“People develop negative attitudes [about vaccines] by accessing alternative sources of information, anecdotes, and personal stories,” said Matthew Seeger, PhD, dean of the College of Fine, Performing, and Communication Arts and codirector of the Center for Emerging Infectious Diseases at Wayne State University in Detroit.
“If we are going to change their opinion, we need to live in that space.” That means listening first, he says. Ask: “Where did you get that information? How credible do you think the sources are? What do you mean about the vaccine changing DNA?”
Then, you might respond, he said, by addressing that specific information, such as, “We have no cases of DNA being changed.”
Dr. Seeger recalls that his mother would simply talk louder when she couldn’t understand someone who wasn’t a native English speaker. “That’s what we are trying to do with the vaccine-hesitant,” he says. “In some cases, we are yelling at them.” Instead, he says, probe their sources of information.
For some who are vaccine-hesitant, Dr. Seeger said, it is not just about the vaccine. The attitude about vaccines is tied in, often, with a distrust of government and feelings about personal freedom. “That’s one reason it’s so hard to change the attitude.” For some, getting the vaccine in a family against the vaccine might also disrupt their social structure or even get them ostracized.
For these people, a health care provider might give opportunities to get the vaccine without affecting either what they see as their political stance or upsetting family harmony. “There are places you can go, make an appointment, get a vaccine, and nobody knows,” Dr. Seeger said.
One Missouri doctor told CNN that some people calling for a vaccine appointment do request privacy, such as going through a drive-thru or having the shot as they sit in their cars. She said the hospital tries to accommodate them, reasoning that every additional vaccine shot is a win.
Dr. Seeger agrees. “Of course there are still public records,” he says, “but you can still claim you are a vaccine denier. It’s very difficult to persuade people to give up their whole world. Vaccine denial is part of that world. At this point, we need to do whatever we can to get people vaccinated.”
From peer to peer
A theme that runs through many of these persuasion techniques is peer pressure.
One example, while a bit more profane and confrontational than some groups, is COVIDAteMyFace, a subgroup, or “subreddit,” of the popular online site Reddit, which hosts numerous forums inviting users to share news and comments on a variety of topics. The subreddit has over 20,000 members. Its purpose, says the sub’s creator, “was to document the folks who denied COVID, then got bitten in the ass by it.” Reports are of actual cases.
“It’s interesting and powerful that Reddit users are taking this on,” Dr. Seeger said. And this kind of peer pressure, or peer-to-peer information, can be persuasive, he says. “We often seek consensual validation from peers about risk messages and risk behaviors.”
For instance, hurricane evacuation notices are more effective, he said, when people learn their neighbors are leaving.
Peer information – “the number of others who are doing or believing or responding to something – definitely persuades people,” agreed Dr. Cialdini. “When a lot of others are responding in a particular way – for example, getting vaccinated – people follow for three reasons: The action seems more appropriate or correct, it appears more feasible to perform, and it avoids social disapproval from those others.”
Let them talk, give them time
Gladys Jimenez is a contact tracer and “vaccine ambassador” for Tracing Health, a partnership between the Oregon Public Health Institute and the Public Health Institute that has nearly 300 bilingual contract tracers who serve the ethnic communities they’re from. During a typical week, she talks to 50 people or more, and promoting the vaccine is top of mind.
The conversations, Ms. Jimenez said, are like a dance. She presents information, then steps back and lets them talk. “I want to hear the person talk, where they are coming from, where they are at.” Depending on what they say, she gives them more information or corrects their misinformation. “They often will say, ‘Oh, I didn’t know that.’ ”
It’s rarely one conversation that convinces hesitant people, she said. “I’m planting this seed in their brain. ... people want someone to listen to them ... they want to vent.”
Once you let them do that, Ms. Jimenez said, “I can tell the person is in a different state of mind.” She also knows that people “will make the decision in their own time.”
With time, people can change their minds, as a Southern California woman who resisted at first (and asked to remain anonymous) can attest. “When the vaccine first came out, I remember thinking [that] it was a quick fix to a very big problem,” she said. The lack of full FDA approval, which has since been granted, was also an issue. She doesn’t oppose vaccines, she said, but was leery just of the COVID-19 vaccine.
When her longtime partner got his vaccine, he urged her to go right away for hers. She stalled. He got his second dose and grew impatient with her hesitancy. It began to wear on the relationship. Finally, the woman talked to two health care professionals she knew socially. They both follow the science, and “they both could explain vaccination to me in a way that resonated. The information was coming from sources I already trusted.”
Those conversations are what convinced her to get vaccinated this summer.
Simpson’s transformation
Ms. Simpson of Back to the Vax got her first COVID-19 immunization April 16. She had an allergic reaction, including severe itchiness and a bad headache, and needed emergency care, she said. Even so, she scheduled her second shot appointment.
Like many who turned against vaccines as adults, Ms. Simpson had all her childhood vaccines, but she developed a distrust after watching a lengthy documentary series that warned of vaccine dangers as an adult.
Looking back at that documentary, she thought about how it seems to blame everything – childhood cancer, ADHD, autism, allergies – on vaccinations. That suddenly seemed like sketchy science to her.
So did the claim from a family friend who said she knew someone who got the flu shot and began walking backward. She researched on her own, and with time, she decided to be pro-vaccines.
These days, she continues to find that stories, not statistics, are changing the minds of many who decide to get vaccinated. If the nurse practitioner urging the tetanus shot for her daughter had told her that the tetanus shot is linked with problems in one of a specific number of people who get it, no matter how large that second number was, Ms. Simpson said she would have thought: “What if she is that one?”
So she relies on stories that point out how universally vulnerable people are to COVID-19 first, facts next.
“Facts help once you are already moved,” Ms. Simpson said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Not so long ago, Heather Simpson of Dallas was known as the anti-vaccine mom who dressed as “the measles” for Halloween. She painted red spots on her face and posted her photo on Facebook, joking: “Was trying to think of the least scary thing I could be for Halloween … so I became the measles.” It went viral with the anti-vaccine crowd.
But between that Halloween and today, a series of “aha” moments transformed Ms. Simpson’s attitudes toward vaccines.
In January 2021, one of those moments involved her daughter, now 4, who was scratched by a feral cat, raising concerns about tetanus. Her daughter had been bitten by a dog when she was just 1, and Ms. Simpson turned down advice then to get a tetanus shot. “I was convinced the tetanus shot would kill her faster than the tetanus.”
After the cat incident, the anxiety was so exhausting, she listened to the nurse practitioner at the clinic, whom she trusted. The nurse gently reassured Ms. Simpson that the shot was less risky than the possibility of tetanus – but did not bombard her with statistics – and that won over Ms. Simpson and triggered an overall rethinking of her vaccine stance.
Fast-forward to February, and that “aha” turned into action when Ms. Simpson launched a “Back to the Vax” effort with a fellow former vaccine opponent. Through their website, Facebook page, and podcasts, they now encourage people to get the COVID-19 vaccine, as well as other immunizations.
Challenge: Reaching the rest
With just over 52% of those eligible in the United States fully vaccinated as of Sept. 1,
Recent data and a poll show some movement in the right direction, as immunizations are increasing and hesitancy is declining among certain groups. According to federal officials, about 14 million people in the United States got their first dose in August, an increase of 4 million, compared to the numbers who got it in July.
And a new poll from the Axios-IPSOS Coronavirus Index found only one in five Americans, or 20%, say they are not likely to get the vaccine, while “hard opposition,” those not at all likely, has dropped to 14% of those adults.
But there is still a lot of work to do. So, how do medical professionals or concerned citizens reach those who haven’t gotten vaccinated yet, whatever their reason?
Many experts in communication and persuasion that this news organization talked to agree that throwing statistics at people hesitant to get the COVID-19 vaccine is generally useless and often backfires.
So what does work, according to these experts?
- Emphasizing the trends of more people getting vaccinated.
- Focusing on everyone’s freedom of choice.
- Listening to concerns without judgment.
- Offering credible information.
- Correcting myths when necessary.
- Helping them fit vaccination into their “world view.”
Stories over statistics
Talking about the trends of vaccinations can definitely change minds about getting vaccinated, said Robert Cialdini, PhD, regents professor emeritus of psychology and marketing at Arizona State University, Tempe, and author of the recently updated book, “Influence: The Psychology of Persuasion,” which has sold over 5 million copies since it was first published in 1984.
Face-to-face with a hesitant patient, a doctor can say: “More and more people are being vaccinated every day,” Dr. Cialdini says. “The reason you say more and more is [that] it conveys a trend. When people see a trend, they project it into the future that it is going to get even larger.”
A focus on choice can also help people change their minds and accept the vaccine, he says. “A lot of conspiracy theorists claim they don’t want to do it because they are being pushed or forced by the government, and they are resisting that.”
If that’s the case, presenting people with new information, such as the increased infectiousness of the Delta variant, and suggesting that a decision be made based on the new information, can work, Dr. Cialdini says, but be sure to end with: “It’s completely up to you.”
“This removes all their sense of being pushed. It says, ‘Here is all the evidence.’ ” At this point, a doctor’s personal recommendation with a patient who trusts him or her may sway them, Dr. Cialdini said. “I think you have to personalize the communication in both directions. That is, to say, ‘For someone in your situation, I would personally recommend that you get the vaccine.’ ” A health care professional’s authority and expertise can carry the day, he says, although “not always.”
This approach worked, Dr. Cialdini says, with a friend of the family hesitant about the COVID-19 vaccine. “I told him: ‘We have gotten it. You trust us, right?’ ” He waited for the person to say yes.
Then: “For someone in your position, my personal recommendation is to get vaccinated. There is new information about the vaccine, and more and more people are getting vaccinated. And of course, it is completely up to you.”
The person decided to get the vaccine.
‘Live in that space’
“People develop negative attitudes [about vaccines] by accessing alternative sources of information, anecdotes, and personal stories,” said Matthew Seeger, PhD, dean of the College of Fine, Performing, and Communication Arts and codirector of the Center for Emerging Infectious Diseases at Wayne State University in Detroit.
“If we are going to change their opinion, we need to live in that space.” That means listening first, he says. Ask: “Where did you get that information? How credible do you think the sources are? What do you mean about the vaccine changing DNA?”
Then, you might respond, he said, by addressing that specific information, such as, “We have no cases of DNA being changed.”
Dr. Seeger recalls that his mother would simply talk louder when she couldn’t understand someone who wasn’t a native English speaker. “That’s what we are trying to do with the vaccine-hesitant,” he says. “In some cases, we are yelling at them.” Instead, he says, probe their sources of information.
For some who are vaccine-hesitant, Dr. Seeger said, it is not just about the vaccine. The attitude about vaccines is tied in, often, with a distrust of government and feelings about personal freedom. “That’s one reason it’s so hard to change the attitude.” For some, getting the vaccine in a family against the vaccine might also disrupt their social structure or even get them ostracized.
For these people, a health care provider might give opportunities to get the vaccine without affecting either what they see as their political stance or upsetting family harmony. “There are places you can go, make an appointment, get a vaccine, and nobody knows,” Dr. Seeger said.
One Missouri doctor told CNN that some people calling for a vaccine appointment do request privacy, such as going through a drive-thru or having the shot as they sit in their cars. She said the hospital tries to accommodate them, reasoning that every additional vaccine shot is a win.
Dr. Seeger agrees. “Of course there are still public records,” he says, “but you can still claim you are a vaccine denier. It’s very difficult to persuade people to give up their whole world. Vaccine denial is part of that world. At this point, we need to do whatever we can to get people vaccinated.”
From peer to peer
A theme that runs through many of these persuasion techniques is peer pressure.
One example, while a bit more profane and confrontational than some groups, is COVIDAteMyFace, a subgroup, or “subreddit,” of the popular online site Reddit, which hosts numerous forums inviting users to share news and comments on a variety of topics. The subreddit has over 20,000 members. Its purpose, says the sub’s creator, “was to document the folks who denied COVID, then got bitten in the ass by it.” Reports are of actual cases.
“It’s interesting and powerful that Reddit users are taking this on,” Dr. Seeger said. And this kind of peer pressure, or peer-to-peer information, can be persuasive, he says. “We often seek consensual validation from peers about risk messages and risk behaviors.”
For instance, hurricane evacuation notices are more effective, he said, when people learn their neighbors are leaving.
Peer information – “the number of others who are doing or believing or responding to something – definitely persuades people,” agreed Dr. Cialdini. “When a lot of others are responding in a particular way – for example, getting vaccinated – people follow for three reasons: The action seems more appropriate or correct, it appears more feasible to perform, and it avoids social disapproval from those others.”
Let them talk, give them time
Gladys Jimenez is a contact tracer and “vaccine ambassador” for Tracing Health, a partnership between the Oregon Public Health Institute and the Public Health Institute that has nearly 300 bilingual contract tracers who serve the ethnic communities they’re from. During a typical week, she talks to 50 people or more, and promoting the vaccine is top of mind.
The conversations, Ms. Jimenez said, are like a dance. She presents information, then steps back and lets them talk. “I want to hear the person talk, where they are coming from, where they are at.” Depending on what they say, she gives them more information or corrects their misinformation. “They often will say, ‘Oh, I didn’t know that.’ ”
It’s rarely one conversation that convinces hesitant people, she said. “I’m planting this seed in their brain. ... people want someone to listen to them ... they want to vent.”
Once you let them do that, Ms. Jimenez said, “I can tell the person is in a different state of mind.” She also knows that people “will make the decision in their own time.”
With time, people can change their minds, as a Southern California woman who resisted at first (and asked to remain anonymous) can attest. “When the vaccine first came out, I remember thinking [that] it was a quick fix to a very big problem,” she said. The lack of full FDA approval, which has since been granted, was also an issue. She doesn’t oppose vaccines, she said, but was leery just of the COVID-19 vaccine.
When her longtime partner got his vaccine, he urged her to go right away for hers. She stalled. He got his second dose and grew impatient with her hesitancy. It began to wear on the relationship. Finally, the woman talked to two health care professionals she knew socially. They both follow the science, and “they both could explain vaccination to me in a way that resonated. The information was coming from sources I already trusted.”
Those conversations are what convinced her to get vaccinated this summer.
Simpson’s transformation
Ms. Simpson of Back to the Vax got her first COVID-19 immunization April 16. She had an allergic reaction, including severe itchiness and a bad headache, and needed emergency care, she said. Even so, she scheduled her second shot appointment.
Like many who turned against vaccines as adults, Ms. Simpson had all her childhood vaccines, but she developed a distrust after watching a lengthy documentary series that warned of vaccine dangers as an adult.
Looking back at that documentary, she thought about how it seems to blame everything – childhood cancer, ADHD, autism, allergies – on vaccinations. That suddenly seemed like sketchy science to her.
So did the claim from a family friend who said she knew someone who got the flu shot and began walking backward. She researched on her own, and with time, she decided to be pro-vaccines.
These days, she continues to find that stories, not statistics, are changing the minds of many who decide to get vaccinated. If the nurse practitioner urging the tetanus shot for her daughter had told her that the tetanus shot is linked with problems in one of a specific number of people who get it, no matter how large that second number was, Ms. Simpson said she would have thought: “What if she is that one?”
So she relies on stories that point out how universally vulnerable people are to COVID-19 first, facts next.
“Facts help once you are already moved,” Ms. Simpson said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Not so long ago, Heather Simpson of Dallas was known as the anti-vaccine mom who dressed as “the measles” for Halloween. She painted red spots on her face and posted her photo on Facebook, joking: “Was trying to think of the least scary thing I could be for Halloween … so I became the measles.” It went viral with the anti-vaccine crowd.
But between that Halloween and today, a series of “aha” moments transformed Ms. Simpson’s attitudes toward vaccines.
In January 2021, one of those moments involved her daughter, now 4, who was scratched by a feral cat, raising concerns about tetanus. Her daughter had been bitten by a dog when she was just 1, and Ms. Simpson turned down advice then to get a tetanus shot. “I was convinced the tetanus shot would kill her faster than the tetanus.”
After the cat incident, the anxiety was so exhausting, she listened to the nurse practitioner at the clinic, whom she trusted. The nurse gently reassured Ms. Simpson that the shot was less risky than the possibility of tetanus – but did not bombard her with statistics – and that won over Ms. Simpson and triggered an overall rethinking of her vaccine stance.
Fast-forward to February, and that “aha” turned into action when Ms. Simpson launched a “Back to the Vax” effort with a fellow former vaccine opponent. Through their website, Facebook page, and podcasts, they now encourage people to get the COVID-19 vaccine, as well as other immunizations.
Challenge: Reaching the rest
With just over 52% of those eligible in the United States fully vaccinated as of Sept. 1,
Recent data and a poll show some movement in the right direction, as immunizations are increasing and hesitancy is declining among certain groups. According to federal officials, about 14 million people in the United States got their first dose in August, an increase of 4 million, compared to the numbers who got it in July.
And a new poll from the Axios-IPSOS Coronavirus Index found only one in five Americans, or 20%, say they are not likely to get the vaccine, while “hard opposition,” those not at all likely, has dropped to 14% of those adults.
But there is still a lot of work to do. So, how do medical professionals or concerned citizens reach those who haven’t gotten vaccinated yet, whatever their reason?
Many experts in communication and persuasion that this news organization talked to agree that throwing statistics at people hesitant to get the COVID-19 vaccine is generally useless and often backfires.
So what does work, according to these experts?
- Emphasizing the trends of more people getting vaccinated.
- Focusing on everyone’s freedom of choice.
- Listening to concerns without judgment.
- Offering credible information.
- Correcting myths when necessary.
- Helping them fit vaccination into their “world view.”
Stories over statistics
Talking about the trends of vaccinations can definitely change minds about getting vaccinated, said Robert Cialdini, PhD, regents professor emeritus of psychology and marketing at Arizona State University, Tempe, and author of the recently updated book, “Influence: The Psychology of Persuasion,” which has sold over 5 million copies since it was first published in 1984.
Face-to-face with a hesitant patient, a doctor can say: “More and more people are being vaccinated every day,” Dr. Cialdini says. “The reason you say more and more is [that] it conveys a trend. When people see a trend, they project it into the future that it is going to get even larger.”
A focus on choice can also help people change their minds and accept the vaccine, he says. “A lot of conspiracy theorists claim they don’t want to do it because they are being pushed or forced by the government, and they are resisting that.”
If that’s the case, presenting people with new information, such as the increased infectiousness of the Delta variant, and suggesting that a decision be made based on the new information, can work, Dr. Cialdini says, but be sure to end with: “It’s completely up to you.”
“This removes all their sense of being pushed. It says, ‘Here is all the evidence.’ ” At this point, a doctor’s personal recommendation with a patient who trusts him or her may sway them, Dr. Cialdini said. “I think you have to personalize the communication in both directions. That is, to say, ‘For someone in your situation, I would personally recommend that you get the vaccine.’ ” A health care professional’s authority and expertise can carry the day, he says, although “not always.”
This approach worked, Dr. Cialdini says, with a friend of the family hesitant about the COVID-19 vaccine. “I told him: ‘We have gotten it. You trust us, right?’ ” He waited for the person to say yes.
Then: “For someone in your position, my personal recommendation is to get vaccinated. There is new information about the vaccine, and more and more people are getting vaccinated. And of course, it is completely up to you.”
The person decided to get the vaccine.
‘Live in that space’
“People develop negative attitudes [about vaccines] by accessing alternative sources of information, anecdotes, and personal stories,” said Matthew Seeger, PhD, dean of the College of Fine, Performing, and Communication Arts and codirector of the Center for Emerging Infectious Diseases at Wayne State University in Detroit.
“If we are going to change their opinion, we need to live in that space.” That means listening first, he says. Ask: “Where did you get that information? How credible do you think the sources are? What do you mean about the vaccine changing DNA?”
Then, you might respond, he said, by addressing that specific information, such as, “We have no cases of DNA being changed.”
Dr. Seeger recalls that his mother would simply talk louder when she couldn’t understand someone who wasn’t a native English speaker. “That’s what we are trying to do with the vaccine-hesitant,” he says. “In some cases, we are yelling at them.” Instead, he says, probe their sources of information.
For some who are vaccine-hesitant, Dr. Seeger said, it is not just about the vaccine. The attitude about vaccines is tied in, often, with a distrust of government and feelings about personal freedom. “That’s one reason it’s so hard to change the attitude.” For some, getting the vaccine in a family against the vaccine might also disrupt their social structure or even get them ostracized.
For these people, a health care provider might give opportunities to get the vaccine without affecting either what they see as their political stance or upsetting family harmony. “There are places you can go, make an appointment, get a vaccine, and nobody knows,” Dr. Seeger said.
One Missouri doctor told CNN that some people calling for a vaccine appointment do request privacy, such as going through a drive-thru or having the shot as they sit in their cars. She said the hospital tries to accommodate them, reasoning that every additional vaccine shot is a win.
Dr. Seeger agrees. “Of course there are still public records,” he says, “but you can still claim you are a vaccine denier. It’s very difficult to persuade people to give up their whole world. Vaccine denial is part of that world. At this point, we need to do whatever we can to get people vaccinated.”
From peer to peer
A theme that runs through many of these persuasion techniques is peer pressure.
One example, while a bit more profane and confrontational than some groups, is COVIDAteMyFace, a subgroup, or “subreddit,” of the popular online site Reddit, which hosts numerous forums inviting users to share news and comments on a variety of topics. The subreddit has over 20,000 members. Its purpose, says the sub’s creator, “was to document the folks who denied COVID, then got bitten in the ass by it.” Reports are of actual cases.
“It’s interesting and powerful that Reddit users are taking this on,” Dr. Seeger said. And this kind of peer pressure, or peer-to-peer information, can be persuasive, he says. “We often seek consensual validation from peers about risk messages and risk behaviors.”
For instance, hurricane evacuation notices are more effective, he said, when people learn their neighbors are leaving.
Peer information – “the number of others who are doing or believing or responding to something – definitely persuades people,” agreed Dr. Cialdini. “When a lot of others are responding in a particular way – for example, getting vaccinated – people follow for three reasons: The action seems more appropriate or correct, it appears more feasible to perform, and it avoids social disapproval from those others.”
Let them talk, give them time
Gladys Jimenez is a contact tracer and “vaccine ambassador” for Tracing Health, a partnership between the Oregon Public Health Institute and the Public Health Institute that has nearly 300 bilingual contract tracers who serve the ethnic communities they’re from. During a typical week, she talks to 50 people or more, and promoting the vaccine is top of mind.
The conversations, Ms. Jimenez said, are like a dance. She presents information, then steps back and lets them talk. “I want to hear the person talk, where they are coming from, where they are at.” Depending on what they say, she gives them more information or corrects their misinformation. “They often will say, ‘Oh, I didn’t know that.’ ”
It’s rarely one conversation that convinces hesitant people, she said. “I’m planting this seed in their brain. ... people want someone to listen to them ... they want to vent.”
Once you let them do that, Ms. Jimenez said, “I can tell the person is in a different state of mind.” She also knows that people “will make the decision in their own time.”
With time, people can change their minds, as a Southern California woman who resisted at first (and asked to remain anonymous) can attest. “When the vaccine first came out, I remember thinking [that] it was a quick fix to a very big problem,” she said. The lack of full FDA approval, which has since been granted, was also an issue. She doesn’t oppose vaccines, she said, but was leery just of the COVID-19 vaccine.
When her longtime partner got his vaccine, he urged her to go right away for hers. She stalled. He got his second dose and grew impatient with her hesitancy. It began to wear on the relationship. Finally, the woman talked to two health care professionals she knew socially. They both follow the science, and “they both could explain vaccination to me in a way that resonated. The information was coming from sources I already trusted.”
Those conversations are what convinced her to get vaccinated this summer.
Simpson’s transformation
Ms. Simpson of Back to the Vax got her first COVID-19 immunization April 16. She had an allergic reaction, including severe itchiness and a bad headache, and needed emergency care, she said. Even so, she scheduled her second shot appointment.
Like many who turned against vaccines as adults, Ms. Simpson had all her childhood vaccines, but she developed a distrust after watching a lengthy documentary series that warned of vaccine dangers as an adult.
Looking back at that documentary, she thought about how it seems to blame everything – childhood cancer, ADHD, autism, allergies – on vaccinations. That suddenly seemed like sketchy science to her.
So did the claim from a family friend who said she knew someone who got the flu shot and began walking backward. She researched on her own, and with time, she decided to be pro-vaccines.
These days, she continues to find that stories, not statistics, are changing the minds of many who decide to get vaccinated. If the nurse practitioner urging the tetanus shot for her daughter had told her that the tetanus shot is linked with problems in one of a specific number of people who get it, no matter how large that second number was, Ms. Simpson said she would have thought: “What if she is that one?”
So she relies on stories that point out how universally vulnerable people are to COVID-19 first, facts next.
“Facts help once you are already moved,” Ms. Simpson said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
WHO tracking new COVID-19 variant called Mu
The variant, also known as B.1.621, was first identified in Colombia in January. It has now been detected in 43 countries and was added to the WHO’s “variant of interest” list Aug. 30.
“The Mu variant has a constellation of mutations that indicate potential properties of immune escape,” the WHO wrote in its weekly COVID-19 update on Aug 31.
Preliminary data suggests that the Mu variant may be able to evade antibodies at levels similar to the Beta variant, the WHO wrote, though more studies are needed. The Beta variant, also known as B.1.351, was first detected in South Africa and has shown some ability to evade vaccines.
As of Aug. 29, the global prevalence of the Mu variant appears to be less than 0.1%. But its prevalence in South America has “consistently increased,” the WHO wrote, now making up 39% of cases in Colombia and 13% of cases in Ecuador.
More than 4,700 cases of the Mu variant have been identified worldwide through genomic sequencing, according to Outbreak.info, an open-source database operated by Scripps Research. The United States has identified 2,011 of these cases, with 348 in California. As of Sept. 2, only one state -- Nebraska -- had not yet reported a Mu case.
“At the moment, it looks like there’s genuine cause for concern in USA, Central America, and South America, but as we saw with Delta, a potent variant can traverse the globe in the blink of an eye,” Danny Altmann, PhD, an immunologist at Imperial College London, told The Telegraph.
The WHO is monitoring nine variants with genetic mutations that could make them more transmissible, lead to more severe disease, and help them evade vaccines. The Delta variant, which is now a dominant form of the virus in the United States and worldwide, has led to a surge in cases and hospitalizations this summer.
In its report, the WHO said it would monitor the Mu variant for changes, “particularly with the co-circulation of the Delta variant.”
“Mu looks potentially good at immune evasion,” Dr. Altmann told The Telegraph. “For my taste, it’s a stark reminder that this isn’t by any means over. On a planet of 4.4 million-plus new infections per week, there are new variants popping up all the time, and little reason to feel complacent.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The variant, also known as B.1.621, was first identified in Colombia in January. It has now been detected in 43 countries and was added to the WHO’s “variant of interest” list Aug. 30.
“The Mu variant has a constellation of mutations that indicate potential properties of immune escape,” the WHO wrote in its weekly COVID-19 update on Aug 31.
Preliminary data suggests that the Mu variant may be able to evade antibodies at levels similar to the Beta variant, the WHO wrote, though more studies are needed. The Beta variant, also known as B.1.351, was first detected in South Africa and has shown some ability to evade vaccines.
As of Aug. 29, the global prevalence of the Mu variant appears to be less than 0.1%. But its prevalence in South America has “consistently increased,” the WHO wrote, now making up 39% of cases in Colombia and 13% of cases in Ecuador.
More than 4,700 cases of the Mu variant have been identified worldwide through genomic sequencing, according to Outbreak.info, an open-source database operated by Scripps Research. The United States has identified 2,011 of these cases, with 348 in California. As of Sept. 2, only one state -- Nebraska -- had not yet reported a Mu case.
“At the moment, it looks like there’s genuine cause for concern in USA, Central America, and South America, but as we saw with Delta, a potent variant can traverse the globe in the blink of an eye,” Danny Altmann, PhD, an immunologist at Imperial College London, told The Telegraph.
The WHO is monitoring nine variants with genetic mutations that could make them more transmissible, lead to more severe disease, and help them evade vaccines. The Delta variant, which is now a dominant form of the virus in the United States and worldwide, has led to a surge in cases and hospitalizations this summer.
In its report, the WHO said it would monitor the Mu variant for changes, “particularly with the co-circulation of the Delta variant.”
“Mu looks potentially good at immune evasion,” Dr. Altmann told The Telegraph. “For my taste, it’s a stark reminder that this isn’t by any means over. On a planet of 4.4 million-plus new infections per week, there are new variants popping up all the time, and little reason to feel complacent.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The variant, also known as B.1.621, was first identified in Colombia in January. It has now been detected in 43 countries and was added to the WHO’s “variant of interest” list Aug. 30.
“The Mu variant has a constellation of mutations that indicate potential properties of immune escape,” the WHO wrote in its weekly COVID-19 update on Aug 31.
Preliminary data suggests that the Mu variant may be able to evade antibodies at levels similar to the Beta variant, the WHO wrote, though more studies are needed. The Beta variant, also known as B.1.351, was first detected in South Africa and has shown some ability to evade vaccines.
As of Aug. 29, the global prevalence of the Mu variant appears to be less than 0.1%. But its prevalence in South America has “consistently increased,” the WHO wrote, now making up 39% of cases in Colombia and 13% of cases in Ecuador.
More than 4,700 cases of the Mu variant have been identified worldwide through genomic sequencing, according to Outbreak.info, an open-source database operated by Scripps Research. The United States has identified 2,011 of these cases, with 348 in California. As of Sept. 2, only one state -- Nebraska -- had not yet reported a Mu case.
“At the moment, it looks like there’s genuine cause for concern in USA, Central America, and South America, but as we saw with Delta, a potent variant can traverse the globe in the blink of an eye,” Danny Altmann, PhD, an immunologist at Imperial College London, told The Telegraph.
The WHO is monitoring nine variants with genetic mutations that could make them more transmissible, lead to more severe disease, and help them evade vaccines. The Delta variant, which is now a dominant form of the virus in the United States and worldwide, has led to a surge in cases and hospitalizations this summer.
In its report, the WHO said it would monitor the Mu variant for changes, “particularly with the co-circulation of the Delta variant.”
“Mu looks potentially good at immune evasion,” Dr. Altmann told The Telegraph. “For my taste, it’s a stark reminder that this isn’t by any means over. On a planet of 4.4 million-plus new infections per week, there are new variants popping up all the time, and little reason to feel complacent.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Even highly allergic adults unlikely to react to COVID-19 vaccine
published Aug. 31, 2021, in JAMA Network Open. Symptoms resolved in a few hours with medication, and no patients required hospitalization.
Risk for allergic reaction has been one of several obstacles in global vaccination efforts, the authors, led by Nancy Agmon-Levin, MD, of the Sheba Medical Center, Ramat Gan, Israel, wrote. Clinical trials for the Moderna and Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccines excluded individuals with allergies to any component of the vaccine or with previous allergies to other vaccines. Early reports of anaphylaxis in reaction to the vaccines caused concern among patients and practitioners. Soon after, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and other authorities released guidance on preparing for allergic reactions. “Despite these recommendations, uncertainty remains, particularly among patients with a history of anaphylaxis and/or multiple allergies,” the authors added.
In response to early concerns, the Sheba Medical Center opened a COVID-19 referral center to address safety questions and to conduct assessments of allergy risk for the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine, the first COVID-19 vaccine approved in Israel. From Dec. 27, 2020, to Feb. 22, 2021, the referral center assessed 8,102 patients with allergies. Those who were not clearly at low risk filled out a questionnaire about prior allergic or anaphylactic reactions to drugs or vaccines, other allergies, and other relevant medical history. Patients were considered to be at high risk for allergic reactions if they met at least one of the following criteria: previous anaphylactic reaction to any drug or vaccine, multiple drug allergies, multiple other allergies, and mast cell disorders. Individuals were also classified as high risk if their health care practitioner deferred vaccination because of allergy concerns.
Nearly 95% of the cohort (7,668 individuals) were classified as low risk and received both Pfizer vaccine doses at standard immunization sites and underwent 30 minutes of observation after immunization. Although the study did not follow these lower-risk patients, “no serious allergic reactions were reported back to our referral center by patients or their general practitioner after immunization in the regular settings,” the authors wrote.
Five patients were considered ineligible for immunization because of known sensitivity to polyethylene glycol or multiple anaphylactic reactions to different injectable drugs, following recommendations from the Ministry of Health of Israel at the time. The remaining 429 individuals were deemed high risk and underwent observation for 2 hours from a dedicated allergy team after immunization. For these high-risk patients, both vaccine doses were administered in the same setting. Patients also reported any adverse reactions in the 21 days between the first and second dose.
Women made up most of the high-risk cohort (70.9%). The average age of participants was 52 years. Of the high-risk individuals, 63.2% reported prior anaphylaxis, 32.9% had multiple drug allergies, and 30.3% had multiple other allergies.
During the first 2 hours following immunization, nine individuals (2.1%), all women, experienced allergic reactions. Six individuals (1.4%) experienced minor reactions, including skin flushing, tongue or uvula swelling, or a cough that resolved with antihistamine treatment during the observation period. Three patients (0.7%) had anaphylactic reactions that occurred 10 to 20 minutes after injection. All three patients experienced significant bronchospasm, skin eruption, itching, and shortness of breath. Two patients experienced angioedema, and one patient had gastrointestinal symptoms. They were treated with adrenaline, antihistamines, and an inhaled bronchodilator. All symptoms resolved within 2-6 hours, and no patient required hospitalization.
In the days following vaccination, patients commonly reported pain at the injection site, fatigue, muscle pain, and headache; 14.7% of patients reported skin eruption, itching, or urticaria.
As of Feb. 22, 2021, 218 patients from this highly allergic cohort received their second dose of the vaccine. Four patients (1.8%) had mild allergic reactions. All four developed flushing, and one patient also developed a cough that resolved with antihistamine treatment. Three of these patients had experienced mild allergic reactions to the first dose and were premedicated for the second dose. One patient only reacted to the second dose.
The findings should be “very reassuring” to individuals hesitant to receive the vaccine, Elizabeth Phillips, MD, the director of the Center for Drug Safety and Immunology at Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tenn., said in an interview. She was not involved with the research and wrote an invited commentary on the study. “The rates of anaphylaxis and allergic reactions are truly quite low,” she said. Although about 2% of the high-risk group developed allergic reactions to immunization, the overall percentage for the entire cohort would be much lower.
The study did not investigate specific risk factors for and mechanisms of allergic reactions to COVID-19 vaccines, Dr. Phillips said, which is a study limitation that the authors also acknowledge. The National Institute for Allergy and Infectious Diseases is currently trying to answer some of these questions with a multisite, randomized, double-blinded study. The study is intended to help understand why people have these allergic reactions, Dr. Phillips added. Vanderbilt is one of the sites for the study.
While researchers continue to hunt for answers, the algorithm developed by the authors provides “a great strategy to get people that are at higher risk vaccinated in a monitored setting,” she said. The results show that “people should not be avoiding vaccination because of a history of anaphylaxis.”
Dr. Phillips has received institutional grants from the National Institutes of Health and the National Health and Medical Research Council; royalties from UpToDate and Lexicomp; and consulting fees from Janssen, Vertex, Biocryst, and Regeneron.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
published Aug. 31, 2021, in JAMA Network Open. Symptoms resolved in a few hours with medication, and no patients required hospitalization.
Risk for allergic reaction has been one of several obstacles in global vaccination efforts, the authors, led by Nancy Agmon-Levin, MD, of the Sheba Medical Center, Ramat Gan, Israel, wrote. Clinical trials for the Moderna and Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccines excluded individuals with allergies to any component of the vaccine or with previous allergies to other vaccines. Early reports of anaphylaxis in reaction to the vaccines caused concern among patients and practitioners. Soon after, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and other authorities released guidance on preparing for allergic reactions. “Despite these recommendations, uncertainty remains, particularly among patients with a history of anaphylaxis and/or multiple allergies,” the authors added.
In response to early concerns, the Sheba Medical Center opened a COVID-19 referral center to address safety questions and to conduct assessments of allergy risk for the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine, the first COVID-19 vaccine approved in Israel. From Dec. 27, 2020, to Feb. 22, 2021, the referral center assessed 8,102 patients with allergies. Those who were not clearly at low risk filled out a questionnaire about prior allergic or anaphylactic reactions to drugs or vaccines, other allergies, and other relevant medical history. Patients were considered to be at high risk for allergic reactions if they met at least one of the following criteria: previous anaphylactic reaction to any drug or vaccine, multiple drug allergies, multiple other allergies, and mast cell disorders. Individuals were also classified as high risk if their health care practitioner deferred vaccination because of allergy concerns.
Nearly 95% of the cohort (7,668 individuals) were classified as low risk and received both Pfizer vaccine doses at standard immunization sites and underwent 30 minutes of observation after immunization. Although the study did not follow these lower-risk patients, “no serious allergic reactions were reported back to our referral center by patients or their general practitioner after immunization in the regular settings,” the authors wrote.
Five patients were considered ineligible for immunization because of known sensitivity to polyethylene glycol or multiple anaphylactic reactions to different injectable drugs, following recommendations from the Ministry of Health of Israel at the time. The remaining 429 individuals were deemed high risk and underwent observation for 2 hours from a dedicated allergy team after immunization. For these high-risk patients, both vaccine doses were administered in the same setting. Patients also reported any adverse reactions in the 21 days between the first and second dose.
Women made up most of the high-risk cohort (70.9%). The average age of participants was 52 years. Of the high-risk individuals, 63.2% reported prior anaphylaxis, 32.9% had multiple drug allergies, and 30.3% had multiple other allergies.
During the first 2 hours following immunization, nine individuals (2.1%), all women, experienced allergic reactions. Six individuals (1.4%) experienced minor reactions, including skin flushing, tongue or uvula swelling, or a cough that resolved with antihistamine treatment during the observation period. Three patients (0.7%) had anaphylactic reactions that occurred 10 to 20 minutes after injection. All three patients experienced significant bronchospasm, skin eruption, itching, and shortness of breath. Two patients experienced angioedema, and one patient had gastrointestinal symptoms. They were treated with adrenaline, antihistamines, and an inhaled bronchodilator. All symptoms resolved within 2-6 hours, and no patient required hospitalization.
In the days following vaccination, patients commonly reported pain at the injection site, fatigue, muscle pain, and headache; 14.7% of patients reported skin eruption, itching, or urticaria.
As of Feb. 22, 2021, 218 patients from this highly allergic cohort received their second dose of the vaccine. Four patients (1.8%) had mild allergic reactions. All four developed flushing, and one patient also developed a cough that resolved with antihistamine treatment. Three of these patients had experienced mild allergic reactions to the first dose and were premedicated for the second dose. One patient only reacted to the second dose.
The findings should be “very reassuring” to individuals hesitant to receive the vaccine, Elizabeth Phillips, MD, the director of the Center for Drug Safety and Immunology at Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tenn., said in an interview. She was not involved with the research and wrote an invited commentary on the study. “The rates of anaphylaxis and allergic reactions are truly quite low,” she said. Although about 2% of the high-risk group developed allergic reactions to immunization, the overall percentage for the entire cohort would be much lower.
The study did not investigate specific risk factors for and mechanisms of allergic reactions to COVID-19 vaccines, Dr. Phillips said, which is a study limitation that the authors also acknowledge. The National Institute for Allergy and Infectious Diseases is currently trying to answer some of these questions with a multisite, randomized, double-blinded study. The study is intended to help understand why people have these allergic reactions, Dr. Phillips added. Vanderbilt is one of the sites for the study.
While researchers continue to hunt for answers, the algorithm developed by the authors provides “a great strategy to get people that are at higher risk vaccinated in a monitored setting,” she said. The results show that “people should not be avoiding vaccination because of a history of anaphylaxis.”
Dr. Phillips has received institutional grants from the National Institutes of Health and the National Health and Medical Research Council; royalties from UpToDate and Lexicomp; and consulting fees from Janssen, Vertex, Biocryst, and Regeneron.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
published Aug. 31, 2021, in JAMA Network Open. Symptoms resolved in a few hours with medication, and no patients required hospitalization.
Risk for allergic reaction has been one of several obstacles in global vaccination efforts, the authors, led by Nancy Agmon-Levin, MD, of the Sheba Medical Center, Ramat Gan, Israel, wrote. Clinical trials for the Moderna and Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccines excluded individuals with allergies to any component of the vaccine or with previous allergies to other vaccines. Early reports of anaphylaxis in reaction to the vaccines caused concern among patients and practitioners. Soon after, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and other authorities released guidance on preparing for allergic reactions. “Despite these recommendations, uncertainty remains, particularly among patients with a history of anaphylaxis and/or multiple allergies,” the authors added.
In response to early concerns, the Sheba Medical Center opened a COVID-19 referral center to address safety questions and to conduct assessments of allergy risk for the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine, the first COVID-19 vaccine approved in Israel. From Dec. 27, 2020, to Feb. 22, 2021, the referral center assessed 8,102 patients with allergies. Those who were not clearly at low risk filled out a questionnaire about prior allergic or anaphylactic reactions to drugs or vaccines, other allergies, and other relevant medical history. Patients were considered to be at high risk for allergic reactions if they met at least one of the following criteria: previous anaphylactic reaction to any drug or vaccine, multiple drug allergies, multiple other allergies, and mast cell disorders. Individuals were also classified as high risk if their health care practitioner deferred vaccination because of allergy concerns.
Nearly 95% of the cohort (7,668 individuals) were classified as low risk and received both Pfizer vaccine doses at standard immunization sites and underwent 30 minutes of observation after immunization. Although the study did not follow these lower-risk patients, “no serious allergic reactions were reported back to our referral center by patients or their general practitioner after immunization in the regular settings,” the authors wrote.
Five patients were considered ineligible for immunization because of known sensitivity to polyethylene glycol or multiple anaphylactic reactions to different injectable drugs, following recommendations from the Ministry of Health of Israel at the time. The remaining 429 individuals were deemed high risk and underwent observation for 2 hours from a dedicated allergy team after immunization. For these high-risk patients, both vaccine doses were administered in the same setting. Patients also reported any adverse reactions in the 21 days between the first and second dose.
Women made up most of the high-risk cohort (70.9%). The average age of participants was 52 years. Of the high-risk individuals, 63.2% reported prior anaphylaxis, 32.9% had multiple drug allergies, and 30.3% had multiple other allergies.
During the first 2 hours following immunization, nine individuals (2.1%), all women, experienced allergic reactions. Six individuals (1.4%) experienced minor reactions, including skin flushing, tongue or uvula swelling, or a cough that resolved with antihistamine treatment during the observation period. Three patients (0.7%) had anaphylactic reactions that occurred 10 to 20 minutes after injection. All three patients experienced significant bronchospasm, skin eruption, itching, and shortness of breath. Two patients experienced angioedema, and one patient had gastrointestinal symptoms. They were treated with adrenaline, antihistamines, and an inhaled bronchodilator. All symptoms resolved within 2-6 hours, and no patient required hospitalization.
In the days following vaccination, patients commonly reported pain at the injection site, fatigue, muscle pain, and headache; 14.7% of patients reported skin eruption, itching, or urticaria.
As of Feb. 22, 2021, 218 patients from this highly allergic cohort received their second dose of the vaccine. Four patients (1.8%) had mild allergic reactions. All four developed flushing, and one patient also developed a cough that resolved with antihistamine treatment. Three of these patients had experienced mild allergic reactions to the first dose and were premedicated for the second dose. One patient only reacted to the second dose.
The findings should be “very reassuring” to individuals hesitant to receive the vaccine, Elizabeth Phillips, MD, the director of the Center for Drug Safety and Immunology at Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tenn., said in an interview. She was not involved with the research and wrote an invited commentary on the study. “The rates of anaphylaxis and allergic reactions are truly quite low,” she said. Although about 2% of the high-risk group developed allergic reactions to immunization, the overall percentage for the entire cohort would be much lower.
The study did not investigate specific risk factors for and mechanisms of allergic reactions to COVID-19 vaccines, Dr. Phillips said, which is a study limitation that the authors also acknowledge. The National Institute for Allergy and Infectious Diseases is currently trying to answer some of these questions with a multisite, randomized, double-blinded study. The study is intended to help understand why people have these allergic reactions, Dr. Phillips added. Vanderbilt is one of the sites for the study.
While researchers continue to hunt for answers, the algorithm developed by the authors provides “a great strategy to get people that are at higher risk vaccinated in a monitored setting,” she said. The results show that “people should not be avoiding vaccination because of a history of anaphylaxis.”
Dr. Phillips has received institutional grants from the National Institutes of Health and the National Health and Medical Research Council; royalties from UpToDate and Lexicomp; and consulting fees from Janssen, Vertex, Biocryst, and Regeneron.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Another COVID-19 patient to get ivermectin after court order
Another case, another state, another judge ordering a hospital to give a patient a controversial horse deworming drug to treat a severe case of COVID-19.
, according to the Ohio Capital Journal. Judge Gregory Howard’s ruling comes after Mr. Smith’s wife sued to force the hospital to provide the controversial drug to her husband, who has been hospitalized since July 15.
Julie Smith has gotten Fred Wagshul, MD, to agree to administer ivermectin to her husband. Dr. Wagshul is known as a member of a group of doctors who say the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the Food and Drug Administration are lying about ivermectin’s usefulness in fighting COVID-19. Both agencies have warned against using the drug to treat COVID-19, saying there is no evidence it works and that it can be dangerous in large amounts.
According to the Ohio Capital Journal, Dr. Wagshul accused the CDC and FDA of engaging in a “conspiracy” to prevent ivermectin’s use.
But Arthur L. Caplan, MD, professor of bioethics at New York University’s Langone Medical Center, said, “it is absurd that this order was issued,” according to an interview in Ars Technica. “If I were these doctors, I simply wouldn’t do it.”
It is not the first time a judge has ordered ivermectin’s use against a hospital’s wishes.
A 68-year-old woman with COVID-19 in an Illinois hospital started receiving the controversial drug in May after her family sued the hospital to have someone administer it.
Nurije Fype’s daughter, Desareta, filed suit against Elmhurst Hospital, part of Edward-Elmhurst Health, asking that her mother receive the treatment, which is approved as an antiparasitic drug but not approved for the treatment of COVID-19. Desareta Fype was granted temporary guardianship of her mother.
The FDA has published guidance titled “Why You Should Not Use Ivermectin to Treat or Prevent COVID-19” on its website. The National Institutes of Health said there is not enough data to recommend either for or against its use in treating COVID-19.
But DuPage County Judge James Orel ruled Ms. Fype should be allowed to get the treatment.
Three days later, according to the Daily Herald, the lawyer for the hospital, Joseph Monahan, argued the hospital could not find a hospital-affiliated doctor to administer the ivermectin.
The Herald reported the judge told the hospital to “get out of the way” and allow any board-certified doctor to administer the drug.
When Ms. Fype’s doctor was unable to administer it, the legal team found another doctor, Alan Bain, DO, to do it. Mr. Monahan said Dr. Bain was granted credentials to work at the hospital so he could administer it.
Judge Orel denied a request from Desareta Fype’s lawyer to order the hospital’s nurses to administer further doses. The judge also denied a request to hold the hospital in contempt of court.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Another case, another state, another judge ordering a hospital to give a patient a controversial horse deworming drug to treat a severe case of COVID-19.
, according to the Ohio Capital Journal. Judge Gregory Howard’s ruling comes after Mr. Smith’s wife sued to force the hospital to provide the controversial drug to her husband, who has been hospitalized since July 15.
Julie Smith has gotten Fred Wagshul, MD, to agree to administer ivermectin to her husband. Dr. Wagshul is known as a member of a group of doctors who say the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the Food and Drug Administration are lying about ivermectin’s usefulness in fighting COVID-19. Both agencies have warned against using the drug to treat COVID-19, saying there is no evidence it works and that it can be dangerous in large amounts.
According to the Ohio Capital Journal, Dr. Wagshul accused the CDC and FDA of engaging in a “conspiracy” to prevent ivermectin’s use.
But Arthur L. Caplan, MD, professor of bioethics at New York University’s Langone Medical Center, said, “it is absurd that this order was issued,” according to an interview in Ars Technica. “If I were these doctors, I simply wouldn’t do it.”
It is not the first time a judge has ordered ivermectin’s use against a hospital’s wishes.
A 68-year-old woman with COVID-19 in an Illinois hospital started receiving the controversial drug in May after her family sued the hospital to have someone administer it.
Nurije Fype’s daughter, Desareta, filed suit against Elmhurst Hospital, part of Edward-Elmhurst Health, asking that her mother receive the treatment, which is approved as an antiparasitic drug but not approved for the treatment of COVID-19. Desareta Fype was granted temporary guardianship of her mother.
The FDA has published guidance titled “Why You Should Not Use Ivermectin to Treat or Prevent COVID-19” on its website. The National Institutes of Health said there is not enough data to recommend either for or against its use in treating COVID-19.
But DuPage County Judge James Orel ruled Ms. Fype should be allowed to get the treatment.
Three days later, according to the Daily Herald, the lawyer for the hospital, Joseph Monahan, argued the hospital could not find a hospital-affiliated doctor to administer the ivermectin.
The Herald reported the judge told the hospital to “get out of the way” and allow any board-certified doctor to administer the drug.
When Ms. Fype’s doctor was unable to administer it, the legal team found another doctor, Alan Bain, DO, to do it. Mr. Monahan said Dr. Bain was granted credentials to work at the hospital so he could administer it.
Judge Orel denied a request from Desareta Fype’s lawyer to order the hospital’s nurses to administer further doses. The judge also denied a request to hold the hospital in contempt of court.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Another case, another state, another judge ordering a hospital to give a patient a controversial horse deworming drug to treat a severe case of COVID-19.
, according to the Ohio Capital Journal. Judge Gregory Howard’s ruling comes after Mr. Smith’s wife sued to force the hospital to provide the controversial drug to her husband, who has been hospitalized since July 15.
Julie Smith has gotten Fred Wagshul, MD, to agree to administer ivermectin to her husband. Dr. Wagshul is known as a member of a group of doctors who say the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the Food and Drug Administration are lying about ivermectin’s usefulness in fighting COVID-19. Both agencies have warned against using the drug to treat COVID-19, saying there is no evidence it works and that it can be dangerous in large amounts.
According to the Ohio Capital Journal, Dr. Wagshul accused the CDC and FDA of engaging in a “conspiracy” to prevent ivermectin’s use.
But Arthur L. Caplan, MD, professor of bioethics at New York University’s Langone Medical Center, said, “it is absurd that this order was issued,” according to an interview in Ars Technica. “If I were these doctors, I simply wouldn’t do it.”
It is not the first time a judge has ordered ivermectin’s use against a hospital’s wishes.
A 68-year-old woman with COVID-19 in an Illinois hospital started receiving the controversial drug in May after her family sued the hospital to have someone administer it.
Nurije Fype’s daughter, Desareta, filed suit against Elmhurst Hospital, part of Edward-Elmhurst Health, asking that her mother receive the treatment, which is approved as an antiparasitic drug but not approved for the treatment of COVID-19. Desareta Fype was granted temporary guardianship of her mother.
The FDA has published guidance titled “Why You Should Not Use Ivermectin to Treat or Prevent COVID-19” on its website. The National Institutes of Health said there is not enough data to recommend either for or against its use in treating COVID-19.
But DuPage County Judge James Orel ruled Ms. Fype should be allowed to get the treatment.
Three days later, according to the Daily Herald, the lawyer for the hospital, Joseph Monahan, argued the hospital could not find a hospital-affiliated doctor to administer the ivermectin.
The Herald reported the judge told the hospital to “get out of the way” and allow any board-certified doctor to administer the drug.
When Ms. Fype’s doctor was unable to administer it, the legal team found another doctor, Alan Bain, DO, to do it. Mr. Monahan said Dr. Bain was granted credentials to work at the hospital so he could administer it.
Judge Orel denied a request from Desareta Fype’s lawyer to order the hospital’s nurses to administer further doses. The judge also denied a request to hold the hospital in contempt of court.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
COVID-clogged ICUs ‘terrify’ those with chronic or emergency illness
Jessica Gosnell, MD, 41, from Portland, Oregon, lives daily with the knowledge that her rare disease — a form of hereditary angioedema — could cause a sudden, severe swelling in her throat that could require quick intubation and land her in an intensive care unit (ICU) for days.
“I’ve been hospitalized for throat swells three times in the last year,” she said in an interview.
Dr. Gosnell no longer practices medicine because of a combination of illnesses, but lives with her husband, Andrew, and two young children, and said they are all “terrified” she will have to go to the hospital amid a COVID-19 surge that had shrunk the number of available ICU beds to 152 from 780 in Oregon as of Aug. 30. Thirty percent of the beds are in use for patients with COVID-19.
She said her life depends on being near hospitals that have ICUs and having access to highly specialized medications, one of which can cost up to $50,000 for the rescue dose.
Her fear has her “literally living bedbound.” In addition to hereditary angioedema, she has Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, which weakens connective tissue. She wears a cervical collar 24/7 to keep from tearing tissues, as any tissue injury can trigger a swell.
Patients worry there won’t be room
As ICU beds in most states are filling with COVID-19 patients as the Delta variant spreads, fears are rising among people like Dr. Gosnell, who have chronic conditions and diseases with unpredictable emergency visits, who worry that if they need emergency care there won’t be room.
As of Aug. 30, in the United States, 79% of ICU beds nationally were in use, 30% of them for COVID-19 patients, according to the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
In individual states, the picture is dire. Alabama has fewer than 10% of its ICU beds open across the entire state. In Florida, 93% of ICU beds are filled, 53% of them with COVID patients. In Louisiana, 87% of beds were already in use, 45% of them with COVID patients, just as category 4 hurricane Ida smashed into the coastline on Aug. 29.
News reports have told of people transported and airlifted as hospitals reach capacity.
In Bellville, Tex., U.S. Army veteran Daniel Wilkinson needed advanced care for gallstone pancreatitis that normally would take 30 minutes to treat, his Bellville doctor, Hasan Kakli, MD, told CBS News.
Mr. Wilkinson’s house was three doors from Bellville Hospital, but the hospital was not equipped to treat the condition. Calls to other hospitals found the same answer: no empty ICU beds. After a 7-hour wait on a stretcher, he was airlifted to a Veterans Affairs hospital in Houston, but it was too late. He died on August 22 at age 46.
Dr. Kakli said, “I’ve never lost a patient with this diagnosis. Ever. I’m scared that the next patient I see is someone that I can’t get to where they need to get to. We are playing musical chairs with 100 people and 10 chairs. When the music stops, what happens?”
Also in Texas in August, Joe Valdez, who was shot six times as an unlucky bystander in a domestic dispute, waited for more than a week for surgery at Ben Taub Hospital in Houston, which was over capacity with COVID patients, the Washington Post reported.
Others with chronic diseases fear needing emergency services or even entering a hospital for regular care with the COVID surge.
Nicole Seefeldt, 44, from Easton, Penn., who had a double-lung transplant in 2016, said that she hasn’t been able to see her lung transplant specialists in Philadelphia — an hour-and-a-half drive — for almost 2 years because of fear of contracting COVID. Before the pandemic, she made the trip almost weekly.
“I protect my lungs like they’re children,” she said.
She relies on her local hospital for care, but has put off some needed care, such as a colonoscopy, and has relied on telemedicine because she wants to limit her hospital exposure.
Ms. Seefeldt now faces an eventual kidney transplant, as her kidney function has been reduced to 20%. In the meantime, she worries she will need emergency care for either her lungs or kidneys.
“For those of us who are chronically ill or disabled, what if we have an emergency that is not COVID-related? Are we going to be able to get a bed? Are we going to be able to get treatment? It’s not just COVID patients who come to the [emergency room],” she said.
A pandemic problem
Paul E. Casey, MD, MBA, chief medical officer at Rush University Medical Center in Chicago, said that high vaccination rates in Chicago have helped Rush continue to accommodate both non-COVID and COVID patients in the emergency department.
Though the hospital treated a large volume of COVID patients, “The vast majority of people we see and did see through the pandemic were non-COVID patents,” he said.
Dr. Casey said that in the first wave the hospital noticed a concerning drop in patients coming in for strokes and heart attacks — “things we knew hadn’t gone away.”
And the data backs it up. Over the course of the pandemic, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s National Health Interview Survey found that the percentage of Americans who reported seeing a doctor or health professional fell from 85% at the end of 2019 to about 80% in the first three months of 2021. The survey did not differentiate between in-person visits and telehealth appointments.
Medical practices and patients themselves postponed elective procedures and delayed routine visits during the early months of the crisis.
Patients also reported staying away from hospitals’ emergency departments throughout the pandemic. At the end of 2019, 22% of respondents reported visiting an emergency department in the past year. That dropped to 17% by the end of 2020, and was at 17.7% in the first 3 months of 2021.
Dr. Casey said that, in his hospital’s case, clear messaging became very important to assure patients it was safe to come back. And the message is still critical.
“We want to be loud and clear that patients should continue to seek care for those conditions,” Dr. Casey said. “Deferring healthcare only comes with the long-term sequelae of disease left untreated so we want people to be as proactive in seeking care as they always would be.”
In some cases, fears of entering emergency rooms because of excess patients and risk for infection are keeping some patients from seeking necessary care for minor injuries.
Jim Rickert, MD, an orthopedic surgeon with Indiana University Health in Bloomington, said that some of his patients have expressed fears of coming into the hospital for fractures.
Some patients, particularly elderly patients, he said, are having falls and fractures and wearing slings or braces at home rather than going into the hospital for injuries that need immediate attention.
Bones start healing incorrectly, Dr. Rickert said, and the correction becomes much more difficult.
Plea for vaccinations
Dr. Gosnell made a plea posted on her neighborhood news forum for people to get COVID vaccinations.
“It seems to me it’s easy for other people who are not in bodies like mine to take health for granted,” she said. “But there are a lot of us who live in very fragile bodies and our entire life is at the intersection of us and getting healthcare treatment. Small complications to getting treatment can be life altering.”
Dr. Gosnell, Ms. Seefeldt, Dr. Casey, and Dr. Rickert reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Jessica Gosnell, MD, 41, from Portland, Oregon, lives daily with the knowledge that her rare disease — a form of hereditary angioedema — could cause a sudden, severe swelling in her throat that could require quick intubation and land her in an intensive care unit (ICU) for days.
“I’ve been hospitalized for throat swells three times in the last year,” she said in an interview.
Dr. Gosnell no longer practices medicine because of a combination of illnesses, but lives with her husband, Andrew, and two young children, and said they are all “terrified” she will have to go to the hospital amid a COVID-19 surge that had shrunk the number of available ICU beds to 152 from 780 in Oregon as of Aug. 30. Thirty percent of the beds are in use for patients with COVID-19.
She said her life depends on being near hospitals that have ICUs and having access to highly specialized medications, one of which can cost up to $50,000 for the rescue dose.
Her fear has her “literally living bedbound.” In addition to hereditary angioedema, she has Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, which weakens connective tissue. She wears a cervical collar 24/7 to keep from tearing tissues, as any tissue injury can trigger a swell.
Patients worry there won’t be room
As ICU beds in most states are filling with COVID-19 patients as the Delta variant spreads, fears are rising among people like Dr. Gosnell, who have chronic conditions and diseases with unpredictable emergency visits, who worry that if they need emergency care there won’t be room.
As of Aug. 30, in the United States, 79% of ICU beds nationally were in use, 30% of them for COVID-19 patients, according to the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
In individual states, the picture is dire. Alabama has fewer than 10% of its ICU beds open across the entire state. In Florida, 93% of ICU beds are filled, 53% of them with COVID patients. In Louisiana, 87% of beds were already in use, 45% of them with COVID patients, just as category 4 hurricane Ida smashed into the coastline on Aug. 29.
News reports have told of people transported and airlifted as hospitals reach capacity.
In Bellville, Tex., U.S. Army veteran Daniel Wilkinson needed advanced care for gallstone pancreatitis that normally would take 30 minutes to treat, his Bellville doctor, Hasan Kakli, MD, told CBS News.
Mr. Wilkinson’s house was three doors from Bellville Hospital, but the hospital was not equipped to treat the condition. Calls to other hospitals found the same answer: no empty ICU beds. After a 7-hour wait on a stretcher, he was airlifted to a Veterans Affairs hospital in Houston, but it was too late. He died on August 22 at age 46.
Dr. Kakli said, “I’ve never lost a patient with this diagnosis. Ever. I’m scared that the next patient I see is someone that I can’t get to where they need to get to. We are playing musical chairs with 100 people and 10 chairs. When the music stops, what happens?”
Also in Texas in August, Joe Valdez, who was shot six times as an unlucky bystander in a domestic dispute, waited for more than a week for surgery at Ben Taub Hospital in Houston, which was over capacity with COVID patients, the Washington Post reported.
Others with chronic diseases fear needing emergency services or even entering a hospital for regular care with the COVID surge.
Nicole Seefeldt, 44, from Easton, Penn., who had a double-lung transplant in 2016, said that she hasn’t been able to see her lung transplant specialists in Philadelphia — an hour-and-a-half drive — for almost 2 years because of fear of contracting COVID. Before the pandemic, she made the trip almost weekly.
“I protect my lungs like they’re children,” she said.
She relies on her local hospital for care, but has put off some needed care, such as a colonoscopy, and has relied on telemedicine because she wants to limit her hospital exposure.
Ms. Seefeldt now faces an eventual kidney transplant, as her kidney function has been reduced to 20%. In the meantime, she worries she will need emergency care for either her lungs or kidneys.
“For those of us who are chronically ill or disabled, what if we have an emergency that is not COVID-related? Are we going to be able to get a bed? Are we going to be able to get treatment? It’s not just COVID patients who come to the [emergency room],” she said.
A pandemic problem
Paul E. Casey, MD, MBA, chief medical officer at Rush University Medical Center in Chicago, said that high vaccination rates in Chicago have helped Rush continue to accommodate both non-COVID and COVID patients in the emergency department.
Though the hospital treated a large volume of COVID patients, “The vast majority of people we see and did see through the pandemic were non-COVID patents,” he said.
Dr. Casey said that in the first wave the hospital noticed a concerning drop in patients coming in for strokes and heart attacks — “things we knew hadn’t gone away.”
And the data backs it up. Over the course of the pandemic, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s National Health Interview Survey found that the percentage of Americans who reported seeing a doctor or health professional fell from 85% at the end of 2019 to about 80% in the first three months of 2021. The survey did not differentiate between in-person visits and telehealth appointments.
Medical practices and patients themselves postponed elective procedures and delayed routine visits during the early months of the crisis.
Patients also reported staying away from hospitals’ emergency departments throughout the pandemic. At the end of 2019, 22% of respondents reported visiting an emergency department in the past year. That dropped to 17% by the end of 2020, and was at 17.7% in the first 3 months of 2021.
Dr. Casey said that, in his hospital’s case, clear messaging became very important to assure patients it was safe to come back. And the message is still critical.
“We want to be loud and clear that patients should continue to seek care for those conditions,” Dr. Casey said. “Deferring healthcare only comes with the long-term sequelae of disease left untreated so we want people to be as proactive in seeking care as they always would be.”
In some cases, fears of entering emergency rooms because of excess patients and risk for infection are keeping some patients from seeking necessary care for minor injuries.
Jim Rickert, MD, an orthopedic surgeon with Indiana University Health in Bloomington, said that some of his patients have expressed fears of coming into the hospital for fractures.
Some patients, particularly elderly patients, he said, are having falls and fractures and wearing slings or braces at home rather than going into the hospital for injuries that need immediate attention.
Bones start healing incorrectly, Dr. Rickert said, and the correction becomes much more difficult.
Plea for vaccinations
Dr. Gosnell made a plea posted on her neighborhood news forum for people to get COVID vaccinations.
“It seems to me it’s easy for other people who are not in bodies like mine to take health for granted,” she said. “But there are a lot of us who live in very fragile bodies and our entire life is at the intersection of us and getting healthcare treatment. Small complications to getting treatment can be life altering.”
Dr. Gosnell, Ms. Seefeldt, Dr. Casey, and Dr. Rickert reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Jessica Gosnell, MD, 41, from Portland, Oregon, lives daily with the knowledge that her rare disease — a form of hereditary angioedema — could cause a sudden, severe swelling in her throat that could require quick intubation and land her in an intensive care unit (ICU) for days.
“I’ve been hospitalized for throat swells three times in the last year,” she said in an interview.
Dr. Gosnell no longer practices medicine because of a combination of illnesses, but lives with her husband, Andrew, and two young children, and said they are all “terrified” she will have to go to the hospital amid a COVID-19 surge that had shrunk the number of available ICU beds to 152 from 780 in Oregon as of Aug. 30. Thirty percent of the beds are in use for patients with COVID-19.
She said her life depends on being near hospitals that have ICUs and having access to highly specialized medications, one of which can cost up to $50,000 for the rescue dose.
Her fear has her “literally living bedbound.” In addition to hereditary angioedema, she has Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, which weakens connective tissue. She wears a cervical collar 24/7 to keep from tearing tissues, as any tissue injury can trigger a swell.
Patients worry there won’t be room
As ICU beds in most states are filling with COVID-19 patients as the Delta variant spreads, fears are rising among people like Dr. Gosnell, who have chronic conditions and diseases with unpredictable emergency visits, who worry that if they need emergency care there won’t be room.
As of Aug. 30, in the United States, 79% of ICU beds nationally were in use, 30% of them for COVID-19 patients, according to the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
In individual states, the picture is dire. Alabama has fewer than 10% of its ICU beds open across the entire state. In Florida, 93% of ICU beds are filled, 53% of them with COVID patients. In Louisiana, 87% of beds were already in use, 45% of them with COVID patients, just as category 4 hurricane Ida smashed into the coastline on Aug. 29.
News reports have told of people transported and airlifted as hospitals reach capacity.
In Bellville, Tex., U.S. Army veteran Daniel Wilkinson needed advanced care for gallstone pancreatitis that normally would take 30 minutes to treat, his Bellville doctor, Hasan Kakli, MD, told CBS News.
Mr. Wilkinson’s house was three doors from Bellville Hospital, but the hospital was not equipped to treat the condition. Calls to other hospitals found the same answer: no empty ICU beds. After a 7-hour wait on a stretcher, he was airlifted to a Veterans Affairs hospital in Houston, but it was too late. He died on August 22 at age 46.
Dr. Kakli said, “I’ve never lost a patient with this diagnosis. Ever. I’m scared that the next patient I see is someone that I can’t get to where they need to get to. We are playing musical chairs with 100 people and 10 chairs. When the music stops, what happens?”
Also in Texas in August, Joe Valdez, who was shot six times as an unlucky bystander in a domestic dispute, waited for more than a week for surgery at Ben Taub Hospital in Houston, which was over capacity with COVID patients, the Washington Post reported.
Others with chronic diseases fear needing emergency services or even entering a hospital for regular care with the COVID surge.
Nicole Seefeldt, 44, from Easton, Penn., who had a double-lung transplant in 2016, said that she hasn’t been able to see her lung transplant specialists in Philadelphia — an hour-and-a-half drive — for almost 2 years because of fear of contracting COVID. Before the pandemic, she made the trip almost weekly.
“I protect my lungs like they’re children,” she said.
She relies on her local hospital for care, but has put off some needed care, such as a colonoscopy, and has relied on telemedicine because she wants to limit her hospital exposure.
Ms. Seefeldt now faces an eventual kidney transplant, as her kidney function has been reduced to 20%. In the meantime, she worries she will need emergency care for either her lungs or kidneys.
“For those of us who are chronically ill or disabled, what if we have an emergency that is not COVID-related? Are we going to be able to get a bed? Are we going to be able to get treatment? It’s not just COVID patients who come to the [emergency room],” she said.
A pandemic problem
Paul E. Casey, MD, MBA, chief medical officer at Rush University Medical Center in Chicago, said that high vaccination rates in Chicago have helped Rush continue to accommodate both non-COVID and COVID patients in the emergency department.
Though the hospital treated a large volume of COVID patients, “The vast majority of people we see and did see through the pandemic were non-COVID patents,” he said.
Dr. Casey said that in the first wave the hospital noticed a concerning drop in patients coming in for strokes and heart attacks — “things we knew hadn’t gone away.”
And the data backs it up. Over the course of the pandemic, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s National Health Interview Survey found that the percentage of Americans who reported seeing a doctor or health professional fell from 85% at the end of 2019 to about 80% in the first three months of 2021. The survey did not differentiate between in-person visits and telehealth appointments.
Medical practices and patients themselves postponed elective procedures and delayed routine visits during the early months of the crisis.
Patients also reported staying away from hospitals’ emergency departments throughout the pandemic. At the end of 2019, 22% of respondents reported visiting an emergency department in the past year. That dropped to 17% by the end of 2020, and was at 17.7% in the first 3 months of 2021.
Dr. Casey said that, in his hospital’s case, clear messaging became very important to assure patients it was safe to come back. And the message is still critical.
“We want to be loud and clear that patients should continue to seek care for those conditions,” Dr. Casey said. “Deferring healthcare only comes with the long-term sequelae of disease left untreated so we want people to be as proactive in seeking care as they always would be.”
In some cases, fears of entering emergency rooms because of excess patients and risk for infection are keeping some patients from seeking necessary care for minor injuries.
Jim Rickert, MD, an orthopedic surgeon with Indiana University Health in Bloomington, said that some of his patients have expressed fears of coming into the hospital for fractures.
Some patients, particularly elderly patients, he said, are having falls and fractures and wearing slings or braces at home rather than going into the hospital for injuries that need immediate attention.
Bones start healing incorrectly, Dr. Rickert said, and the correction becomes much more difficult.
Plea for vaccinations
Dr. Gosnell made a plea posted on her neighborhood news forum for people to get COVID vaccinations.
“It seems to me it’s easy for other people who are not in bodies like mine to take health for granted,” she said. “But there are a lot of us who live in very fragile bodies and our entire life is at the intersection of us and getting healthcare treatment. Small complications to getting treatment can be life altering.”
Dr. Gosnell, Ms. Seefeldt, Dr. Casey, and Dr. Rickert reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.