User login
Recognizing Contributions Physician Personalities Make to the Greater Good
My family and I recently took a spring break trip out west to see a few national parks. During the trip, we stayed on a family ranch in Utah. It had a wide variety of livestock, including a large number of mules and horses.
During our stay at this family-owned ranch, two things really stood out and made me think:
- The guesthouse we stayed in had an inordinate volume of collections dedicated to the science and art of raising horses and mules. Everywhere one looked you could find a wall-mounted picture, poem, or coffee table book about these species. My favorite, written by the owner of the ranch, John Hauer, was The Natural Superiority of Mules.1
- The second thing I noticed was that every member of the ranch-owning family had fairly strong opinions about which was better—horse or mule. Just to recap the biology, a horse is the product of two horses, whereas a mule is the progeny of a male donkey and a female horse. It turns out that their physical structure and demeanors are very different.
One of the oldest members of the ranch family (who I believe was a “distant uncle”) had a very strong opinion about the superiority of the mule. His opinion was based on selected facts, including that mules are “steadier on their feet” in unstable ground, require less volume and less frequent food and water, and very rarely became ill or need costly veterinary care.
Another mule-favoring family member told us how mules get a “bad rap” for being stubborn when they actually are much smarter and better decision makers than horses. She recalled a famous folklore of a farmer who took his mule out to gather materials from across a field. When the farmer and the mule approached a wooden bridge, the mule absolutely refused to cross the bridge. After much back and forth between the farmer and the mule (involving both coaxing and cussing), the farmer gave up and returned to the farm with the mule. He then took his horse on the same errand. When they came to the same bridge, the horse also hesitated but required little bargaining from the farmer to coax it to cross the bridge. When barely halfway across, a rotten board in the bridge gave way, almost sending both the horse and the farmer to their deaths in the ravine below.
The moral of the folklore is that mules cannot be coaxed (or cussed) into performing behaviors that will put themselves or those around them at risk of injury or death. Mules will stop when exhausted or profoundly dehydrated, for example, whereas a horse will continue on if ordered by their farmer, even to the point of running themselves to their eventual demise.
One of the younger members of the family-owned ranch, however, had very strong opinions on the superiority of the horse. Horses are loyal and unwavering in their dedication to please those that they serve. They will put the needs of others before themselves in most situations and therefore almost always “outperform” a mule in all respects. They are willing and (usually) able to perform in uncertain conditions, even despite some reservations. They are loyal and loving, and they have unique and inquisitive personalities, which makes them fun to raise and to ride any day.
Test Drives
Our family of four went on a ride with some of these animals and randomly got two horses and two mules. Interestingly, during our ride, we all did indeed notice the differences between the horses and the mules.
The horses were seemingly easygoing and quick to please, easily following cues to change direction or course. The mules were more hesitant and seemed to need to understand why they were being asked to do something before they acquiesced to the demand.
And when we approached a narrow rocky downslope, the mules were slow, steady, and confident, whereas the horses were seemingly uncomfortable and less agile. And, indeed in researching mules, they seem to have gotten a very bad rap over time (as evidenced by the term “stubborn as a mule”).
Charles Darwin actually categorized mules as an example of “hybrid vigor,” which is a rare example of when an offspring is actually better in most ways than either of its parents. Compared to its parental species, mules have more intelligence, endurance, longevity, health, speed, height, and agility. Also to their advantage, they have harder skin and hooves, allowing them to weather and endure more treacherous conditions.
With all of this newfound knowledge of the mule, it struck me what remarkable similarity some physicians have with mules and the role that these mules are likely serving within our organizations. These physicians are probably labeled as stubborn, obstinate, resistant, or impatient. But maybe they are actually intelligent, agile, and appropriately cautious. Maybe the resistance they express in the organization is serving to warn others about the rotten wooden bridges.
HM Takeaway
Similar to a ranch, most hospitals probably function best with a healthy combination of horses and mules. So if you get an opportunity, next time you encounter physicians at your hospital acting like mules, you should congratulate them and appreciate their mule-like characteristics. Recognize the contribution these types of physicians are making, in their own way, to the greater good of the organization.
After all, we can’t—and shouldn’t—all be horses. TH
Reference
1. Hauer J. The Natural Superiority of Mules: A Celebration of One of the Most Intelligent, Sure-footed, and Misunderstood Animals in the World. New York, NY: Skyhorse Publishing; 2006.

My family and I recently took a spring break trip out west to see a few national parks. During the trip, we stayed on a family ranch in Utah. It had a wide variety of livestock, including a large number of mules and horses.
During our stay at this family-owned ranch, two things really stood out and made me think:
- The guesthouse we stayed in had an inordinate volume of collections dedicated to the science and art of raising horses and mules. Everywhere one looked you could find a wall-mounted picture, poem, or coffee table book about these species. My favorite, written by the owner of the ranch, John Hauer, was The Natural Superiority of Mules.1
- The second thing I noticed was that every member of the ranch-owning family had fairly strong opinions about which was better—horse or mule. Just to recap the biology, a horse is the product of two horses, whereas a mule is the progeny of a male donkey and a female horse. It turns out that their physical structure and demeanors are very different.
One of the oldest members of the ranch family (who I believe was a “distant uncle”) had a very strong opinion about the superiority of the mule. His opinion was based on selected facts, including that mules are “steadier on their feet” in unstable ground, require less volume and less frequent food and water, and very rarely became ill or need costly veterinary care.
Another mule-favoring family member told us how mules get a “bad rap” for being stubborn when they actually are much smarter and better decision makers than horses. She recalled a famous folklore of a farmer who took his mule out to gather materials from across a field. When the farmer and the mule approached a wooden bridge, the mule absolutely refused to cross the bridge. After much back and forth between the farmer and the mule (involving both coaxing and cussing), the farmer gave up and returned to the farm with the mule. He then took his horse on the same errand. When they came to the same bridge, the horse also hesitated but required little bargaining from the farmer to coax it to cross the bridge. When barely halfway across, a rotten board in the bridge gave way, almost sending both the horse and the farmer to their deaths in the ravine below.
The moral of the folklore is that mules cannot be coaxed (or cussed) into performing behaviors that will put themselves or those around them at risk of injury or death. Mules will stop when exhausted or profoundly dehydrated, for example, whereas a horse will continue on if ordered by their farmer, even to the point of running themselves to their eventual demise.
One of the younger members of the family-owned ranch, however, had very strong opinions on the superiority of the horse. Horses are loyal and unwavering in their dedication to please those that they serve. They will put the needs of others before themselves in most situations and therefore almost always “outperform” a mule in all respects. They are willing and (usually) able to perform in uncertain conditions, even despite some reservations. They are loyal and loving, and they have unique and inquisitive personalities, which makes them fun to raise and to ride any day.
Test Drives
Our family of four went on a ride with some of these animals and randomly got two horses and two mules. Interestingly, during our ride, we all did indeed notice the differences between the horses and the mules.
The horses were seemingly easygoing and quick to please, easily following cues to change direction or course. The mules were more hesitant and seemed to need to understand why they were being asked to do something before they acquiesced to the demand.
And when we approached a narrow rocky downslope, the mules were slow, steady, and confident, whereas the horses were seemingly uncomfortable and less agile. And, indeed in researching mules, they seem to have gotten a very bad rap over time (as evidenced by the term “stubborn as a mule”).
Charles Darwin actually categorized mules as an example of “hybrid vigor,” which is a rare example of when an offspring is actually better in most ways than either of its parents. Compared to its parental species, mules have more intelligence, endurance, longevity, health, speed, height, and agility. Also to their advantage, they have harder skin and hooves, allowing them to weather and endure more treacherous conditions.
With all of this newfound knowledge of the mule, it struck me what remarkable similarity some physicians have with mules and the role that these mules are likely serving within our organizations. These physicians are probably labeled as stubborn, obstinate, resistant, or impatient. But maybe they are actually intelligent, agile, and appropriately cautious. Maybe the resistance they express in the organization is serving to warn others about the rotten wooden bridges.
HM Takeaway
Similar to a ranch, most hospitals probably function best with a healthy combination of horses and mules. So if you get an opportunity, next time you encounter physicians at your hospital acting like mules, you should congratulate them and appreciate their mule-like characteristics. Recognize the contribution these types of physicians are making, in their own way, to the greater good of the organization.
After all, we can’t—and shouldn’t—all be horses. TH
Reference
1. Hauer J. The Natural Superiority of Mules: A Celebration of One of the Most Intelligent, Sure-footed, and Misunderstood Animals in the World. New York, NY: Skyhorse Publishing; 2006.

My family and I recently took a spring break trip out west to see a few national parks. During the trip, we stayed on a family ranch in Utah. It had a wide variety of livestock, including a large number of mules and horses.
During our stay at this family-owned ranch, two things really stood out and made me think:
- The guesthouse we stayed in had an inordinate volume of collections dedicated to the science and art of raising horses and mules. Everywhere one looked you could find a wall-mounted picture, poem, or coffee table book about these species. My favorite, written by the owner of the ranch, John Hauer, was The Natural Superiority of Mules.1
- The second thing I noticed was that every member of the ranch-owning family had fairly strong opinions about which was better—horse or mule. Just to recap the biology, a horse is the product of two horses, whereas a mule is the progeny of a male donkey and a female horse. It turns out that their physical structure and demeanors are very different.
One of the oldest members of the ranch family (who I believe was a “distant uncle”) had a very strong opinion about the superiority of the mule. His opinion was based on selected facts, including that mules are “steadier on their feet” in unstable ground, require less volume and less frequent food and water, and very rarely became ill or need costly veterinary care.
Another mule-favoring family member told us how mules get a “bad rap” for being stubborn when they actually are much smarter and better decision makers than horses. She recalled a famous folklore of a farmer who took his mule out to gather materials from across a field. When the farmer and the mule approached a wooden bridge, the mule absolutely refused to cross the bridge. After much back and forth between the farmer and the mule (involving both coaxing and cussing), the farmer gave up and returned to the farm with the mule. He then took his horse on the same errand. When they came to the same bridge, the horse also hesitated but required little bargaining from the farmer to coax it to cross the bridge. When barely halfway across, a rotten board in the bridge gave way, almost sending both the horse and the farmer to their deaths in the ravine below.
The moral of the folklore is that mules cannot be coaxed (or cussed) into performing behaviors that will put themselves or those around them at risk of injury or death. Mules will stop when exhausted or profoundly dehydrated, for example, whereas a horse will continue on if ordered by their farmer, even to the point of running themselves to their eventual demise.
One of the younger members of the family-owned ranch, however, had very strong opinions on the superiority of the horse. Horses are loyal and unwavering in their dedication to please those that they serve. They will put the needs of others before themselves in most situations and therefore almost always “outperform” a mule in all respects. They are willing and (usually) able to perform in uncertain conditions, even despite some reservations. They are loyal and loving, and they have unique and inquisitive personalities, which makes them fun to raise and to ride any day.
Test Drives
Our family of four went on a ride with some of these animals and randomly got two horses and two mules. Interestingly, during our ride, we all did indeed notice the differences between the horses and the mules.
The horses were seemingly easygoing and quick to please, easily following cues to change direction or course. The mules were more hesitant and seemed to need to understand why they were being asked to do something before they acquiesced to the demand.
And when we approached a narrow rocky downslope, the mules were slow, steady, and confident, whereas the horses were seemingly uncomfortable and less agile. And, indeed in researching mules, they seem to have gotten a very bad rap over time (as evidenced by the term “stubborn as a mule”).
Charles Darwin actually categorized mules as an example of “hybrid vigor,” which is a rare example of when an offspring is actually better in most ways than either of its parents. Compared to its parental species, mules have more intelligence, endurance, longevity, health, speed, height, and agility. Also to their advantage, they have harder skin and hooves, allowing them to weather and endure more treacherous conditions.
With all of this newfound knowledge of the mule, it struck me what remarkable similarity some physicians have with mules and the role that these mules are likely serving within our organizations. These physicians are probably labeled as stubborn, obstinate, resistant, or impatient. But maybe they are actually intelligent, agile, and appropriately cautious. Maybe the resistance they express in the organization is serving to warn others about the rotten wooden bridges.
HM Takeaway
Similar to a ranch, most hospitals probably function best with a healthy combination of horses and mules. So if you get an opportunity, next time you encounter physicians at your hospital acting like mules, you should congratulate them and appreciate their mule-like characteristics. Recognize the contribution these types of physicians are making, in their own way, to the greater good of the organization.
After all, we can’t—and shouldn’t—all be horses. TH
Reference
1. Hauer J. The Natural Superiority of Mules: A Celebration of One of the Most Intelligent, Sure-footed, and Misunderstood Animals in the World. New York, NY: Skyhorse Publishing; 2006.

Standardized Clinical Pathways’ Effects on Outcomes
Clinical question: What are the effects of implementing standardized clinical pathways on length of stay, cost, readmissions, and patient quality of life?
Background: As payment models shift from volume- to value-based models, standardized clinical pathways are one option to simultaneously provide high-value care, improve quality, and control costs. Studies of individual clinical pathways suggest that they may be helpful in decreasing utilization, but the measured impact has varied significantly. It is unknown how much of the measured effect is due to the pathway and how much is due to the clinical factors of the disease or patient population studied. No prior studies have evaluated a suite of clinical pathways in pediatric populations.
Study design: Retrospective cohort study.
Setting: Single, 250-bed, tertiary care, freestanding children’s hospital.
Synopsis: Over four years, 15 clinical pathways were created for common pediatric medical, surgical, and psychiatric complaints (urinary tract infection, diabetes, both diabetic ketoacidosis [DKA] and non-DKA, fractures, spinal surgery, croup, neonatal jaundice, neonatal fever, depressive disorders, pyloric stenosis, pneumonia, tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy, disruptive behavior, and cellulitis/abscess).
The pathways were implemented when they were complete, with guidelines coming online throughout the study period. Implementation included an order set in the electronic medical record that included relevant literature references and decision support, online training, and integration into the clinical workflow for providers and nurses. Use of the pathways was monitored, and they were reviewed on at least a quarterly basis and revised, if necessary.
The authors examined pathway use for eligible patients, hospital costs, length of stay, 30-day readmissions, and parent-reported quality of life, both before and after pathway implementation. Patients meeting criteria for complex chronic conditions were excluded from the study.
Before implementation, 3,808 admissions fulfilled pathway criteria, and 2,902 fulfilled criteria after implementation. The pathway for depressive disorders was the most used pathway, with 411 admissions and 95% of eligible patients on the pathway. Both pyloric stenosis and neonatal jaundice had 100% pathway use.
The lowest rate of pathway use was for urinary tract infection (20%). Pathway implementation slowed the rate of rise of hospital costs. Prior to study implementation, the costs were increasing by $126 per month. Following implementation, costs decreased by $29 per month (95% CI, $100 decrease to $34 increase; P=.001). Post-implementation, the length of stay for pathway-eligible patients began a statistically significant downward trend at a rate that yielded a decrease in length of stay of 8.6 hours over a year (P=0.02). There were no differences in 30-day readmissions or parent-reported quality of life.
Bottom line: Systematic development and implementation of clinical pathways for a variety of conditions can contain costs and decrease length of stay while maintaining clinical outcomes and not increasing readmissions.
Citation: Lion KC, Wright DR, Spencer S, Zhou C, Del Beccaro M, Mangione-Smith R. Standardized clinical pathways for hospitalized children and outcomes. Pediatrics. 2016;137(4). pii:e20151202. doi:10.1542/peds.2015-1202.
Dr. Stubblefield is a pediatric hospitalist at Nemours/Alfred I. Dupont Hospital for Children in Wilmington, Del., and clinical assistant professor of pediatrics at Sidney Kimmel Medical College at Thomas Jefferson University in Philadelphia.
Clinical question: What are the effects of implementing standardized clinical pathways on length of stay, cost, readmissions, and patient quality of life?
Background: As payment models shift from volume- to value-based models, standardized clinical pathways are one option to simultaneously provide high-value care, improve quality, and control costs. Studies of individual clinical pathways suggest that they may be helpful in decreasing utilization, but the measured impact has varied significantly. It is unknown how much of the measured effect is due to the pathway and how much is due to the clinical factors of the disease or patient population studied. No prior studies have evaluated a suite of clinical pathways in pediatric populations.
Study design: Retrospective cohort study.
Setting: Single, 250-bed, tertiary care, freestanding children’s hospital.
Synopsis: Over four years, 15 clinical pathways were created for common pediatric medical, surgical, and psychiatric complaints (urinary tract infection, diabetes, both diabetic ketoacidosis [DKA] and non-DKA, fractures, spinal surgery, croup, neonatal jaundice, neonatal fever, depressive disorders, pyloric stenosis, pneumonia, tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy, disruptive behavior, and cellulitis/abscess).
The pathways were implemented when they were complete, with guidelines coming online throughout the study period. Implementation included an order set in the electronic medical record that included relevant literature references and decision support, online training, and integration into the clinical workflow for providers and nurses. Use of the pathways was monitored, and they were reviewed on at least a quarterly basis and revised, if necessary.
The authors examined pathway use for eligible patients, hospital costs, length of stay, 30-day readmissions, and parent-reported quality of life, both before and after pathway implementation. Patients meeting criteria for complex chronic conditions were excluded from the study.
Before implementation, 3,808 admissions fulfilled pathway criteria, and 2,902 fulfilled criteria after implementation. The pathway for depressive disorders was the most used pathway, with 411 admissions and 95% of eligible patients on the pathway. Both pyloric stenosis and neonatal jaundice had 100% pathway use.
The lowest rate of pathway use was for urinary tract infection (20%). Pathway implementation slowed the rate of rise of hospital costs. Prior to study implementation, the costs were increasing by $126 per month. Following implementation, costs decreased by $29 per month (95% CI, $100 decrease to $34 increase; P=.001). Post-implementation, the length of stay for pathway-eligible patients began a statistically significant downward trend at a rate that yielded a decrease in length of stay of 8.6 hours over a year (P=0.02). There were no differences in 30-day readmissions or parent-reported quality of life.
Bottom line: Systematic development and implementation of clinical pathways for a variety of conditions can contain costs and decrease length of stay while maintaining clinical outcomes and not increasing readmissions.
Citation: Lion KC, Wright DR, Spencer S, Zhou C, Del Beccaro M, Mangione-Smith R. Standardized clinical pathways for hospitalized children and outcomes. Pediatrics. 2016;137(4). pii:e20151202. doi:10.1542/peds.2015-1202.
Dr. Stubblefield is a pediatric hospitalist at Nemours/Alfred I. Dupont Hospital for Children in Wilmington, Del., and clinical assistant professor of pediatrics at Sidney Kimmel Medical College at Thomas Jefferson University in Philadelphia.
Clinical question: What are the effects of implementing standardized clinical pathways on length of stay, cost, readmissions, and patient quality of life?
Background: As payment models shift from volume- to value-based models, standardized clinical pathways are one option to simultaneously provide high-value care, improve quality, and control costs. Studies of individual clinical pathways suggest that they may be helpful in decreasing utilization, but the measured impact has varied significantly. It is unknown how much of the measured effect is due to the pathway and how much is due to the clinical factors of the disease or patient population studied. No prior studies have evaluated a suite of clinical pathways in pediatric populations.
Study design: Retrospective cohort study.
Setting: Single, 250-bed, tertiary care, freestanding children’s hospital.
Synopsis: Over four years, 15 clinical pathways were created for common pediatric medical, surgical, and psychiatric complaints (urinary tract infection, diabetes, both diabetic ketoacidosis [DKA] and non-DKA, fractures, spinal surgery, croup, neonatal jaundice, neonatal fever, depressive disorders, pyloric stenosis, pneumonia, tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy, disruptive behavior, and cellulitis/abscess).
The pathways were implemented when they were complete, with guidelines coming online throughout the study period. Implementation included an order set in the electronic medical record that included relevant literature references and decision support, online training, and integration into the clinical workflow for providers and nurses. Use of the pathways was monitored, and they were reviewed on at least a quarterly basis and revised, if necessary.
The authors examined pathway use for eligible patients, hospital costs, length of stay, 30-day readmissions, and parent-reported quality of life, both before and after pathway implementation. Patients meeting criteria for complex chronic conditions were excluded from the study.
Before implementation, 3,808 admissions fulfilled pathway criteria, and 2,902 fulfilled criteria after implementation. The pathway for depressive disorders was the most used pathway, with 411 admissions and 95% of eligible patients on the pathway. Both pyloric stenosis and neonatal jaundice had 100% pathway use.
The lowest rate of pathway use was for urinary tract infection (20%). Pathway implementation slowed the rate of rise of hospital costs. Prior to study implementation, the costs were increasing by $126 per month. Following implementation, costs decreased by $29 per month (95% CI, $100 decrease to $34 increase; P=.001). Post-implementation, the length of stay for pathway-eligible patients began a statistically significant downward trend at a rate that yielded a decrease in length of stay of 8.6 hours over a year (P=0.02). There were no differences in 30-day readmissions or parent-reported quality of life.
Bottom line: Systematic development and implementation of clinical pathways for a variety of conditions can contain costs and decrease length of stay while maintaining clinical outcomes and not increasing readmissions.
Citation: Lion KC, Wright DR, Spencer S, Zhou C, Del Beccaro M, Mangione-Smith R. Standardized clinical pathways for hospitalized children and outcomes. Pediatrics. 2016;137(4). pii:e20151202. doi:10.1542/peds.2015-1202.
Dr. Stubblefield is a pediatric hospitalist at Nemours/Alfred I. Dupont Hospital for Children in Wilmington, Del., and clinical assistant professor of pediatrics at Sidney Kimmel Medical College at Thomas Jefferson University in Philadelphia.
Use the Teach-Back Method to Confirm Patient Understanding
Editor’s note: “Everything We Say and Do” is an informational series developed by SHM’s Patient Experience Committee to provide readers with thoughtful and actionable communication tactics that have great potential to positively impact patients’ experience of care. Each article will focus on how the contributor applies one or more of the “key communication” tactics in practice to maintain provider accountability for “everything we say and do that affects our patients’ thoughts, feelings, and well-being.”
View a chart outlining key communication tactics
What I Say and Do
I use the teach-back method to confirm my patients’ understanding.
Why I Do It
Teach-back allows me to address my patients’ uncertainty about the plan and clarify any misunderstandings.
As doctors, one of our most important jobs is explaining in ways our patients understand. It doesn’t matter how brilliant our treatment plan is if our patients do not understand it. We all want to feel like we’re making a difference in our patients’ lives. Yet it’s hard for our patients to do what we recommend if they don’t understand.
Unfortunately, many patients are too embarrassed to ask questions, or they simply do not know what to ask. Patients will also say they understand everything even when they do not because they fear appearing uneducated.
This is why the teach-back method is so valuable. The teach-back method allows you to better assess your patients’ understanding of their medical problems. It allows you to uncover and clarify any misunderstandings your patients may have about the plan. It also helps you to engage in a more collaborative relationship with your patients.
How I Do It
Teach-back helps me to test my effectiveness as a teacher by allowing me to assess whether my patient understands; if not, I explain in a different way.
One of the common mistakes clinicians make when assessing for understanding is asking, “Do you have any questions?” or “Does this make sense?” The problem with these questions is that they are closed-ended. The only responses are yes or no. Your patients may say they understand even when they do not. In reality, it does not matter how brilliant your treatment plans are if patients do not follow them because they do not understand.
Teach-back encourages the doctor to check for understanding by using open-ended instead of closed-ended questions.
Example one: “This is a new diagnosis for you, so I want to make sure you understand. Will you tell me in your own words what congestive heart failure is?”
Example two: “I want to make sure I explained this clearly. I know your daughter helps you manage your health. What will you tell her about the changes we made to your blood pressure medication?”
Teach-back steps:
- I explain the concept to my patients, avoiding medical jargon.
- I assess my patients’ understanding by asking them to explain the concept in their own words.
- I clarify anything my patients did not understand and reassess their understanding.
- If my patients still do not understand, I find a new way to explain the concept.
- I repeat the process of explaining and assessing for understanding until my patients are able to accurately state their understanding.
There are a few key things to remember as you perform teach-back. The first is to ensure you use a caring tone when speaking with your patients. Next, if you have several concepts you want to teach, break it into small pieces. Use teach-back for the first concept before moving on to the next. Finally, one of the most common questions I get from other doctors about teach-back is how to assess patients’ understanding without sounding condescending. I address this by making it about me and my effectiveness as a teacher. I tell my patients it is my responsibility to explain things in a way they understand, so if they do not, I will explain it in a different way. When I frame it this way, patients are not offended by my asking them to perform teach-back because they realize I’m doing it as a test of my effectiveness as a teacher.
Example: “Mr. Johnson, as your doctor, one of my top priorities is to ensure I’m explaining things in a way you understand. I want to make sure my instructions about how to take your new medication are clear. Would you mind telling me in your own words how you will take this new medication?”
Now that you know what teach-back is and understand how helpful it can be, start incorporating it into your practice. Think about a few concepts that you teach again and again, such as disease management, medication changes, and self-care instructions. Next, think about how you could use teach-back in these scenarios. Practice what you will say when you ask patients to engage in teach-back. Finally, commit to using teach-back with your next few patients. The more you practice, the easier it becomes.
For more information on teach-back, visit www.teachbacktraining.org.
Dr. Dorrah is regional medical director for quality and the patient experience, Baylor Scott & White Health, Round Rock, Texas.
Editor’s note: “Everything We Say and Do” is an informational series developed by SHM’s Patient Experience Committee to provide readers with thoughtful and actionable communication tactics that have great potential to positively impact patients’ experience of care. Each article will focus on how the contributor applies one or more of the “key communication” tactics in practice to maintain provider accountability for “everything we say and do that affects our patients’ thoughts, feelings, and well-being.”
View a chart outlining key communication tactics
What I Say and Do
I use the teach-back method to confirm my patients’ understanding.
Why I Do It
Teach-back allows me to address my patients’ uncertainty about the plan and clarify any misunderstandings.
As doctors, one of our most important jobs is explaining in ways our patients understand. It doesn’t matter how brilliant our treatment plan is if our patients do not understand it. We all want to feel like we’re making a difference in our patients’ lives. Yet it’s hard for our patients to do what we recommend if they don’t understand.
Unfortunately, many patients are too embarrassed to ask questions, or they simply do not know what to ask. Patients will also say they understand everything even when they do not because they fear appearing uneducated.
This is why the teach-back method is so valuable. The teach-back method allows you to better assess your patients’ understanding of their medical problems. It allows you to uncover and clarify any misunderstandings your patients may have about the plan. It also helps you to engage in a more collaborative relationship with your patients.
How I Do It
Teach-back helps me to test my effectiveness as a teacher by allowing me to assess whether my patient understands; if not, I explain in a different way.
One of the common mistakes clinicians make when assessing for understanding is asking, “Do you have any questions?” or “Does this make sense?” The problem with these questions is that they are closed-ended. The only responses are yes or no. Your patients may say they understand even when they do not. In reality, it does not matter how brilliant your treatment plans are if patients do not follow them because they do not understand.
Teach-back encourages the doctor to check for understanding by using open-ended instead of closed-ended questions.
Example one: “This is a new diagnosis for you, so I want to make sure you understand. Will you tell me in your own words what congestive heart failure is?”
Example two: “I want to make sure I explained this clearly. I know your daughter helps you manage your health. What will you tell her about the changes we made to your blood pressure medication?”
Teach-back steps:
- I explain the concept to my patients, avoiding medical jargon.
- I assess my patients’ understanding by asking them to explain the concept in their own words.
- I clarify anything my patients did not understand and reassess their understanding.
- If my patients still do not understand, I find a new way to explain the concept.
- I repeat the process of explaining and assessing for understanding until my patients are able to accurately state their understanding.
There are a few key things to remember as you perform teach-back. The first is to ensure you use a caring tone when speaking with your patients. Next, if you have several concepts you want to teach, break it into small pieces. Use teach-back for the first concept before moving on to the next. Finally, one of the most common questions I get from other doctors about teach-back is how to assess patients’ understanding without sounding condescending. I address this by making it about me and my effectiveness as a teacher. I tell my patients it is my responsibility to explain things in a way they understand, so if they do not, I will explain it in a different way. When I frame it this way, patients are not offended by my asking them to perform teach-back because they realize I’m doing it as a test of my effectiveness as a teacher.
Example: “Mr. Johnson, as your doctor, one of my top priorities is to ensure I’m explaining things in a way you understand. I want to make sure my instructions about how to take your new medication are clear. Would you mind telling me in your own words how you will take this new medication?”
Now that you know what teach-back is and understand how helpful it can be, start incorporating it into your practice. Think about a few concepts that you teach again and again, such as disease management, medication changes, and self-care instructions. Next, think about how you could use teach-back in these scenarios. Practice what you will say when you ask patients to engage in teach-back. Finally, commit to using teach-back with your next few patients. The more you practice, the easier it becomes.
For more information on teach-back, visit www.teachbacktraining.org.
Dr. Dorrah is regional medical director for quality and the patient experience, Baylor Scott & White Health, Round Rock, Texas.
Editor’s note: “Everything We Say and Do” is an informational series developed by SHM’s Patient Experience Committee to provide readers with thoughtful and actionable communication tactics that have great potential to positively impact patients’ experience of care. Each article will focus on how the contributor applies one or more of the “key communication” tactics in practice to maintain provider accountability for “everything we say and do that affects our patients’ thoughts, feelings, and well-being.”
View a chart outlining key communication tactics
What I Say and Do
I use the teach-back method to confirm my patients’ understanding.
Why I Do It
Teach-back allows me to address my patients’ uncertainty about the plan and clarify any misunderstandings.
As doctors, one of our most important jobs is explaining in ways our patients understand. It doesn’t matter how brilliant our treatment plan is if our patients do not understand it. We all want to feel like we’re making a difference in our patients’ lives. Yet it’s hard for our patients to do what we recommend if they don’t understand.
Unfortunately, many patients are too embarrassed to ask questions, or they simply do not know what to ask. Patients will also say they understand everything even when they do not because they fear appearing uneducated.
This is why the teach-back method is so valuable. The teach-back method allows you to better assess your patients’ understanding of their medical problems. It allows you to uncover and clarify any misunderstandings your patients may have about the plan. It also helps you to engage in a more collaborative relationship with your patients.
How I Do It
Teach-back helps me to test my effectiveness as a teacher by allowing me to assess whether my patient understands; if not, I explain in a different way.
One of the common mistakes clinicians make when assessing for understanding is asking, “Do you have any questions?” or “Does this make sense?” The problem with these questions is that they are closed-ended. The only responses are yes or no. Your patients may say they understand even when they do not. In reality, it does not matter how brilliant your treatment plans are if patients do not follow them because they do not understand.
Teach-back encourages the doctor to check for understanding by using open-ended instead of closed-ended questions.
Example one: “This is a new diagnosis for you, so I want to make sure you understand. Will you tell me in your own words what congestive heart failure is?”
Example two: “I want to make sure I explained this clearly. I know your daughter helps you manage your health. What will you tell her about the changes we made to your blood pressure medication?”
Teach-back steps:
- I explain the concept to my patients, avoiding medical jargon.
- I assess my patients’ understanding by asking them to explain the concept in their own words.
- I clarify anything my patients did not understand and reassess their understanding.
- If my patients still do not understand, I find a new way to explain the concept.
- I repeat the process of explaining and assessing for understanding until my patients are able to accurately state their understanding.
There are a few key things to remember as you perform teach-back. The first is to ensure you use a caring tone when speaking with your patients. Next, if you have several concepts you want to teach, break it into small pieces. Use teach-back for the first concept before moving on to the next. Finally, one of the most common questions I get from other doctors about teach-back is how to assess patients’ understanding without sounding condescending. I address this by making it about me and my effectiveness as a teacher. I tell my patients it is my responsibility to explain things in a way they understand, so if they do not, I will explain it in a different way. When I frame it this way, patients are not offended by my asking them to perform teach-back because they realize I’m doing it as a test of my effectiveness as a teacher.
Example: “Mr. Johnson, as your doctor, one of my top priorities is to ensure I’m explaining things in a way you understand. I want to make sure my instructions about how to take your new medication are clear. Would you mind telling me in your own words how you will take this new medication?”
Now that you know what teach-back is and understand how helpful it can be, start incorporating it into your practice. Think about a few concepts that you teach again and again, such as disease management, medication changes, and self-care instructions. Next, think about how you could use teach-back in these scenarios. Practice what you will say when you ask patients to engage in teach-back. Finally, commit to using teach-back with your next few patients. The more you practice, the easier it becomes.
For more information on teach-back, visit www.teachbacktraining.org.
Dr. Dorrah is regional medical director for quality and the patient experience, Baylor Scott & White Health, Round Rock, Texas.
VIDEO: Locum Tenens in Hospital Medicine
Dr. Geeta Arora is a locum tenens hospitalist; James Levy is a PA who hires locums as the VP of Human Resources for Indigo Health Partners in Northern Michigan. They share their experiences navigating "freelance hospital medicine," from both the medical practice and business perspective.
The video associated with this article is no longer available on this site. Please view all of our videos on the MDedge YouTube channel
Dr. Geeta Arora is a locum tenens hospitalist; James Levy is a PA who hires locums as the VP of Human Resources for Indigo Health Partners in Northern Michigan. They share their experiences navigating "freelance hospital medicine," from both the medical practice and business perspective.
The video associated with this article is no longer available on this site. Please view all of our videos on the MDedge YouTube channel
Dr. Geeta Arora is a locum tenens hospitalist; James Levy is a PA who hires locums as the VP of Human Resources for Indigo Health Partners in Northern Michigan. They share their experiences navigating "freelance hospital medicine," from both the medical practice and business perspective.
The video associated with this article is no longer available on this site. Please view all of our videos on the MDedge YouTube channel
Does Preoperative Hypercapnia Predict Postoperative Complications in Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea?
Clinical question: Are patients with obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) and preoperative hypercapnia more likely to experience postoperative complications than those without?
Background: Obesity hypoventilation syndrome (OHS) is known to increase medical morbidity in patients with OSA, but its impact on postoperative outcome is unknown.
Study design: Retrospective cohort study.
Setting: Single tertiary-care center.
Synopsis: The study examined 1,800 patients with body mass index (BMI) ≥30 who underwent polysomnography, elective non-cardiac surgery (NCS), and had a blood gas performed. Of those, 194 patients were identified as having OSA with hypercapnia, and 325 were identified as having only OSA. Investigators found that the presence of hypercapnia in patients with OSA, whether from OHS, COPD, or another cause, was associated with worse postoperative outcomes. They found a statistically significant increase in postoperative respiratory failure (21% versus 2%), heart failure (8% versus 0%), tracheostomy (2% versus 1%), and ICU transfer (21% versus 6%). Mortality data did not reach significance.
The major limitation to the study is that hypercapnia is underrecognized in this patient population, and as a result, only patients who had a blood gas were included; many hypercapnic patients may have had elective NCS without receiving a blood gas and were thus excluded.
Bottom line: Consider performing a preoperative blood gas in patients with OSA undergoing elective NCS to help with postoperative complication risk assessment.
Citation: Kaw R, Bhateja P, Paz y Mar H, et al. Postoperative complications in patients with unrecognized obesity hypoventilation syndrome undergoing elective noncardiac surgery. Chest. 2016;149(1):84-91 doi:10.1378/chest.14-3216.
Clinical question: Are patients with obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) and preoperative hypercapnia more likely to experience postoperative complications than those without?
Background: Obesity hypoventilation syndrome (OHS) is known to increase medical morbidity in patients with OSA, but its impact on postoperative outcome is unknown.
Study design: Retrospective cohort study.
Setting: Single tertiary-care center.
Synopsis: The study examined 1,800 patients with body mass index (BMI) ≥30 who underwent polysomnography, elective non-cardiac surgery (NCS), and had a blood gas performed. Of those, 194 patients were identified as having OSA with hypercapnia, and 325 were identified as having only OSA. Investigators found that the presence of hypercapnia in patients with OSA, whether from OHS, COPD, or another cause, was associated with worse postoperative outcomes. They found a statistically significant increase in postoperative respiratory failure (21% versus 2%), heart failure (8% versus 0%), tracheostomy (2% versus 1%), and ICU transfer (21% versus 6%). Mortality data did not reach significance.
The major limitation to the study is that hypercapnia is underrecognized in this patient population, and as a result, only patients who had a blood gas were included; many hypercapnic patients may have had elective NCS without receiving a blood gas and were thus excluded.
Bottom line: Consider performing a preoperative blood gas in patients with OSA undergoing elective NCS to help with postoperative complication risk assessment.
Citation: Kaw R, Bhateja P, Paz y Mar H, et al. Postoperative complications in patients with unrecognized obesity hypoventilation syndrome undergoing elective noncardiac surgery. Chest. 2016;149(1):84-91 doi:10.1378/chest.14-3216.
Clinical question: Are patients with obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) and preoperative hypercapnia more likely to experience postoperative complications than those without?
Background: Obesity hypoventilation syndrome (OHS) is known to increase medical morbidity in patients with OSA, but its impact on postoperative outcome is unknown.
Study design: Retrospective cohort study.
Setting: Single tertiary-care center.
Synopsis: The study examined 1,800 patients with body mass index (BMI) ≥30 who underwent polysomnography, elective non-cardiac surgery (NCS), and had a blood gas performed. Of those, 194 patients were identified as having OSA with hypercapnia, and 325 were identified as having only OSA. Investigators found that the presence of hypercapnia in patients with OSA, whether from OHS, COPD, or another cause, was associated with worse postoperative outcomes. They found a statistically significant increase in postoperative respiratory failure (21% versus 2%), heart failure (8% versus 0%), tracheostomy (2% versus 1%), and ICU transfer (21% versus 6%). Mortality data did not reach significance.
The major limitation to the study is that hypercapnia is underrecognized in this patient population, and as a result, only patients who had a blood gas were included; many hypercapnic patients may have had elective NCS without receiving a blood gas and were thus excluded.
Bottom line: Consider performing a preoperative blood gas in patients with OSA undergoing elective NCS to help with postoperative complication risk assessment.
Citation: Kaw R, Bhateja P, Paz y Mar H, et al. Postoperative complications in patients with unrecognized obesity hypoventilation syndrome undergoing elective noncardiac surgery. Chest. 2016;149(1):84-91 doi:10.1378/chest.14-3216.
Rapid Immunoassays for Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia Offer Fast Screening Possibilities
Clinical question: How useful are rapid immunoassays (RIs) compared to other tests for heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT)?
Background: HIT is a clinicopathologic diagnosis, which traditionally requires clinical criteria and laboratory confirmation through initial testing with enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and “gold standard” testing with washed platelet functional assays when available. There are an increasing number of RIs available, which have lab turnaround times of less than one hour. Their clinical utility is not well understood.
Study design: Meta-analysis.
Setting: Twenty-three studies.
Synopsis: The authors found 23 articles to include for review. These studies included 5,637 unique patients and included heterogeneous (medical, surgical, non-ICU) populations. These articles examined six different rapid immunoassays, which have been developed in recent years. All RIs examined had excellent negative predictive values (NPVs) ranging from 0.99 to 1.00, though positive predictive values (PPVs) had much wider variation (0.42–0.71). The greatest limitation in this meta-analysis is that 17 of the studies were marked as “high risk of bias” because they did not compare the RIs to the “gold standard” assay.
Bottom line: RIs for the diagnosis of HIT have very high NPVs and may be usefully incorporated into the diagnostic algorithm for HIT, but they cannot take the place of “gold standard” washed platelet functional assays.
Citation: Sun L, Gimotty PA, Lakshmanan S, Cuker A. Diagnostic accuracy of rapid immunoassays for heparin-induced thrombocytopenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis [published online ahead of print January 14, 2016]. Thromb Haemost. doi:10.1160/TH15-06-0523.
Clinical question: How useful are rapid immunoassays (RIs) compared to other tests for heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT)?
Background: HIT is a clinicopathologic diagnosis, which traditionally requires clinical criteria and laboratory confirmation through initial testing with enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and “gold standard” testing with washed platelet functional assays when available. There are an increasing number of RIs available, which have lab turnaround times of less than one hour. Their clinical utility is not well understood.
Study design: Meta-analysis.
Setting: Twenty-three studies.
Synopsis: The authors found 23 articles to include for review. These studies included 5,637 unique patients and included heterogeneous (medical, surgical, non-ICU) populations. These articles examined six different rapid immunoassays, which have been developed in recent years. All RIs examined had excellent negative predictive values (NPVs) ranging from 0.99 to 1.00, though positive predictive values (PPVs) had much wider variation (0.42–0.71). The greatest limitation in this meta-analysis is that 17 of the studies were marked as “high risk of bias” because they did not compare the RIs to the “gold standard” assay.
Bottom line: RIs for the diagnosis of HIT have very high NPVs and may be usefully incorporated into the diagnostic algorithm for HIT, but they cannot take the place of “gold standard” washed platelet functional assays.
Citation: Sun L, Gimotty PA, Lakshmanan S, Cuker A. Diagnostic accuracy of rapid immunoassays for heparin-induced thrombocytopenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis [published online ahead of print January 14, 2016]. Thromb Haemost. doi:10.1160/TH15-06-0523.
Clinical question: How useful are rapid immunoassays (RIs) compared to other tests for heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT)?
Background: HIT is a clinicopathologic diagnosis, which traditionally requires clinical criteria and laboratory confirmation through initial testing with enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and “gold standard” testing with washed platelet functional assays when available. There are an increasing number of RIs available, which have lab turnaround times of less than one hour. Their clinical utility is not well understood.
Study design: Meta-analysis.
Setting: Twenty-three studies.
Synopsis: The authors found 23 articles to include for review. These studies included 5,637 unique patients and included heterogeneous (medical, surgical, non-ICU) populations. These articles examined six different rapid immunoassays, which have been developed in recent years. All RIs examined had excellent negative predictive values (NPVs) ranging from 0.99 to 1.00, though positive predictive values (PPVs) had much wider variation (0.42–0.71). The greatest limitation in this meta-analysis is that 17 of the studies were marked as “high risk of bias” because they did not compare the RIs to the “gold standard” assay.
Bottom line: RIs for the diagnosis of HIT have very high NPVs and may be usefully incorporated into the diagnostic algorithm for HIT, but they cannot take the place of “gold standard” washed platelet functional assays.
Citation: Sun L, Gimotty PA, Lakshmanan S, Cuker A. Diagnostic accuracy of rapid immunoassays for heparin-induced thrombocytopenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis [published online ahead of print January 14, 2016]. Thromb Haemost. doi:10.1160/TH15-06-0523.
Does U.S. Healthcare Need More Diverse Leadership?
Throughout its history, the United States has been a nation of immigrants. From the early colonial settlements to the mid-20th century, most immigrants came from Western European countries. Since 1965, when the Immigration and Nationality Act abolished national-origin quotas, the diversity of immigrants has increased. “By the year 2043,” says Tomás León, president and CEO of the Institute for Diversity in Health Management in Chicago, “we will be a country where the majority of our population is comprised of racial and ethnic minorities.”
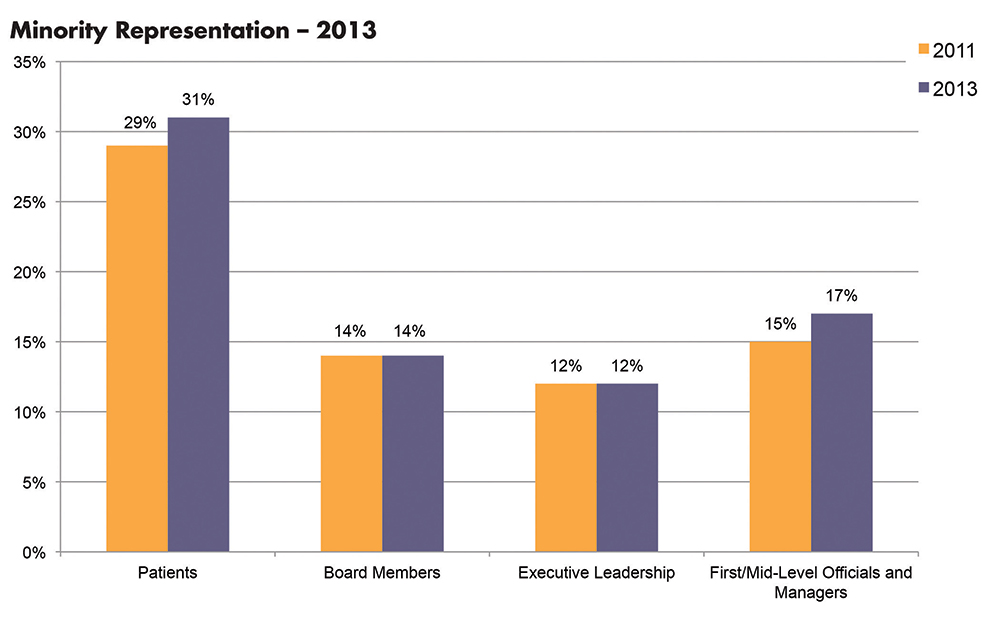
Those changing demographics, cited from the U.S. Census Bureau’s projections, already are evidenced in hospital patient populations. According to a benchmarking survey sponsored by the institute, which is an affiliate of the American Hospital Association, the percentage of minority patients seen in hospitals grew from 29% to 31% of patient census between 2011 and 2013.1 And yet, the survey found this increasing diversity is not currently reflected in leadership positions. During the same time period, underrepresented racial and ethnic minorities (UREM) on hospital boards of directors (14%) and in C-suite positions (14%) remained flat (see Figure 1).
Gender disparities in healthcare and academic leadership also have been slow to change. Periodic surveys conducted by the American College of Healthcare Executives indicate that women comprise only 11% of healthcare CEOs in the U.S.2 And despite the fact that women make up half of all medical students (and one-third of full-time faculty), the Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC) finds that women still trail men when it comes to attaining full professorship and decanal positions at their academic institutions.3
The Hospitalist interviewed medical directors, researchers, diversity management professionals, and hospitalists to ascertain current solutions being pursued to narrow the gaps in leadership diversity.
Why Diversity in Leadership Matters
Eric E. Howell, MD, MHM, chief of the Division of Hospital Medicine at Johns Hopkins Bayview Medical Center in the Hopkins School of Medicine in Baltimore, believes there is a need to encourage the advancement to leadership positions for female and UREM physicians.
“In medicine, it’s really about service. If we are really here for our patients, we need representation of diversity in our faculty and leadership,” says Dr. Howell, a past SHM president and faculty member of SHM’s Leadership Academy since its inception in 2005. In addition, he says, “Diversity adds incredible strength to an organization and adds to the richness of the ideas and solutions to overcome challenging problems.”
With the implementation of the Affordable Care Act, formerly uninsured people are now accessing the healthcare system; many are bilingual and bicultural, notes George A. Zeppenfeldt-Cestero, president and CEO, Association of Hispanic Healthcare Executives.
“You want to make sure that providers, whether they are physicians, nurses, dentists, or health executives that drive policy issues, are also reflective of that population throughout the organization,” he says. “The real definition of diversity is making sure you have diversity in all layers of the workforce, including the C-suite.”
León points to the coming “seismic demographic shifts” and wonders if healthcare is ready to become more reflective of the communities it serves.
“Increasing diversity in healthcare leadership and governance is essential for the delivery and provision of culturally competent care,” León says. “Now, more than ever, it’s important that we collectively accelerate progress in this area.”
Advancing in Academic and Hospital Medicine
Might hospital medicine offer additional opportunities for women and minorities to advance into leadership positions? Hospitalist Flora Kisuule, MD, SFHM, assistant professor of medicine at Johns Hopkins School of Medicine and associate division director of the Collaborative Inpatient Medicine Service (CIMS) at Johns Hopkins Bayview Medical Center, believes this may be the case. She was with Dr. Howell’s group when he needed to fill the associate director position.
“My advancement speaks to hospital medicine and the fact that we are growing as a field,” she says. “Because of that, opportunities are presenting themselves.”
Dr. Kisuule’s ability to thrive in her position speaks to her professionalism but also to a number of other intentional factors: Dr. Howell’s continuing sponsorship to include her in leadership opportunities, an emergency call system for parents with sick children, and a women’s task force whose agenda calls for transparency in hiring and advancement.
Intentional Structure Change
Cardiologist Hannah A. Valantine, MD, recognizes the importance of addressing the lack of women and people from unrepresented groups in the Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics (STEM) workforce. While at Stanford University School of Medicine, she developed and put into place a set of strategies to understand and mitigate the drivers of gender imbalance. Since then, Dr. Valantine was recruited to bring her expertise to the National Institutes of Health in Bethesda, Md., where she is the inaugural chief officer for scientific workforce diversity. In this role, she is committed “to promoting biomedical workforce diversity as an opportunity, not a problem.”
Dr. Valantine is pushing NIH to pursue a wide range of evidence-based programming to eliminate career-transition barriers that keep women and individuals from underrepresented groups from attaining spots in the top echelons of science and health leadership. She believes that applying scientific rigor to the issue of workforce diversity can lead to quantifiable, translatable, and repeatable methods for recruitment and retention of talent in the biomedical workforce (see “Building Blocks").
Before joining NIH, Dr. Valantine and her colleagues at Stanford surveyed gender composition and faculty satisfaction several years after initiating a multifaceted intervention to boost recruitment and development of women faculty.4 After making a visible commitment of resources to support faculty, with special attention to women, Stanford rose from below to above national benchmarks in the representation of women among faculty. Yet significant work remains to be done, Dr. Valantine says. Her work predicts that the estimated time to achieve 50% occupancy of full professorships by women nationally approaches 50 years—“far too long using current approaches.”
In a separate review article, Dr. Valantine and co-author Christy Sandborg, MD, described the Stanford University School of Medicine Academic Biomedical Career Customization (ABCC) model, which was adapted from Deloitte’s Mass Career Customization framework and allows for development of individual career plans that span a faculty member’s total career, not just a year or two at a time. Long-term planning can enable better alignment between the work culture and values of the workforce, which will improve the outlook for women faculty, Dr. Valantine says.
The issues of work-life balance may actually be generational, Dr. Valantine explains. Veteran hospitalist Janet Nagamine, MD, BSN, SFHM, of Santa Clara, Calif., agrees.
“Nowadays, men as well as women are looking for work-life balance,” she says.
In hospital medicine, Dr. Nagamine points out, the structural changes required to effect a work-life balance for hospital leaders are often difficult to achieve.
“As productivity surveys show, HM group leaders are putting in as many RVUs as the staff,” the former SHM board member says. “There is no dedicated time for administrative duties.”
Construct a Pipeline
Barriers to advancement often are particular to characteristics of diverse populations. For example, the AAMC’s report on the U.S. physician workforce documents that in African-American physicians 40 and younger, women outnumber their male counterparts. Therefore, in the association’s Diversity in Medical Education: Facts and Figures 2012 report, the executive summary points out the need to strengthen the medical education pipeline to increase the number of African-American males who enter the premed track.
Despite the fast-growing percentage of Latino and Hispanic populations in the United States, the shortage of Latino/Hispanic physicians increased from 1980 to 2010. Latinos/Hispanics are greatly underrepresented in the medical student, resident, and faculty populations, according to John Paul Sánchez, MD, MPH, assistant dean for diversity and inclusion in the Office for Diversity and Community Engagement at Rutgers, The State University of New Jersey. Likewise, Zeppenfeldt-Cestero believes that efforts must begin much earlier with Latino and other minority and underrepresented students.
“We have to make sure our students pursue the STEM disciplines and that they also later have the education and preparation to be competitive at the MBA or MPH levels,” he says.
Dr. Sánchez, an associate professor of emergency medicine and a diversity activist since his med school days, is the recipient of last year’s Association of Hispanic Healthcare Executives’ academic leader of the year award. Since September 2014, he has been involved with Building the Next Generation of Academic Physicians Inc., which collaborates with more than 40 medical schools across the country. The initiative offers conferences designed to develop diverse medical students’ and residents’ interest in pursuing academic medicine. Open to all medical students and residents, the conference curriculum is tailored for women, UREMs, and trainees who identify as lesbian, gay, bisexual, or transgender (LGBT), he says. Seven conferences were held in 2015, 10 are planned for this year, and seven for 2017.
Healthcare Leadership Gaps
Despite their omnipresence in healthcare, there is a dearth of women in chief executive and governance roles, as has been noted by both the American College of Healthcare Executives and the National Center for Healthcare Leadership. As with academic leadership positions, the leadership gap in the administrative sector does not seem to be due to a lack of women entering graduate programs in health administration. On the contrary, since the mid-1980s women have comprised 50% to 60% of graduate students.
“This is absolutely not a pipeline issue,” says Christy Harris Lemak, PhD, FACHE, professor and chair of the Department of Health Services Administration at the University of Alabama at Birmingham School of Health Professions and lead investigator of the National Center for Healthcare Leadership’s study of women in healthcare executive positions. Other factors come into play.
In the study, she and her co-authors queried female healthcare CEOs to ascertain the critical career inflection points that led to their success.6 Those who were strategic about their careers, sought out mentors, and voiced their intentions about pursuing leadership positions were more likely to be successful in those efforts. However, individual career efforts must be coupled with overall organizational commitment to fostering inclusion (see “Path to the Top: Strategic Advice for Women").
Hospitals and healthcare organizations must pursue the development of human capital (and the diversity of their leaders) in a systematic way. “We recommended [in the study] that organizations set expectations that leaders who mentor other potential leaders be rewarded in the same way as those who hit financial targets or readmission rate targets,” Dr. Lemak says.
Leadership matters, agrees Deborah J. Bowen, FACHE, CAE, president and CEO of Chicago-based American College of Healthcare Executives.
“I think we’re getting a little smarter. Organizational leaders and trustees have a better understanding that talent development is one of the most important jobs,” she says. “If you don’t have the right people in the right places making good decisions on behalf of the patients and the populations in the communities they’re serving, the rest falls apart.”
Nuances of Mentoring
Many conversations about encouraging diversity in healthcare leadership converge around the role of effective mentoring and sponsorship. A substantial body of research supports the impact of mentoring on retention, research productivity, career satisfaction, and career development for women. It’s important to ensure that the institutional culture is geared toward mentoring junior faculty, says Jessie Kimbrough Marshall, MD, MPH, assistant professor in the Division of General Medicine Hospitalist Program at the University of Michigan Health System in Ann Arbor (UMHS).
Several of our sources pointed out that leaders must learn how to be effective mentors. More attention is being given to enhancing leaders’ mentorship skills. One example is at the Institute for Diversity in Health Management, which conducts an intensive 12-month certificate in diversity management program for practitioners. León says the program fosters ongoing networking and support through the American Leadership Council on Diversity in Healthcare by building leadership competencies.
Dr. Valantine points out that mentoring is hardly a one-style-fits-all proposition but that it is a crucial element to creating and retaining diversity. She says it should be viewed “much more broadly than it is today, and it should focus beyond the trainer-trainee relationship.”
The process is a two-way street. Denege Ward, MD, hospitalist, assistant professor of internal medicine, and director of the medical short stay unit at UMHS, says minorities need to be ready to take a leap of faith.
“Underrepresented faculty and staff should take the risk of possible failure in challenging situations but learn from it and do better and not succumb to fear in face of challenges,” Dr. Ward says.
Although mentoring is one important component in building diversity in academic medicine, Dr. Sánchez asserts that role models, champions, and sponsors are equally important.
“In addition and separate from role models, there must be in place policies and procedures that promote a climate for diverse individuals to succeed,” he says. “What’s needed is an institutional vision and strategic plan that recognizes the importance of diversity. [It] has to become a core principle.”
Dr. Marshall echoes that refrain, noting the recruitment and retention of a diverse set of leaders will take time and intentionality. She is actively engaged in organizing annual meeting mentoring panels at the Society of General Internal Medicine.
“There are still quite a few barriers for women and minorities to advance into hospital leadership roles,” she says. “We still have a long way to go. However, I’m seeing more women and people of color get into these positions. The numbers are increasing, and that encourages me.” TH
Gretchen Henkel is a freelance writer in California.
References
- Institute for Diversity in Health Management. The state of health care diversity and disparities: a benchmarking study of U.S. hospitals. Available at: http://www.diversityconnection.org/diversityconnection/leadership-conferences/Benchmarking-Survey.jsp?fll=S11.
- Top issues confronting hospitals in 2015. American College of Healthcare Executives website. Available at: https://www.ache.org/pubs/research/ceoissues.cfm. Accessed March 5, 2016.
- Association of American Medical Colleges. Diversity in the physician workforce: facts & figures 2014. Available at: http://aamcdiversityfactsandfigures.org/.
- Valantine HA, Grewal D, Ku MC, et al. The gender gap in academic medicine: comparing results from a multifaceted intervention for Stanford faculty to peer and national cohorts. Acad Med. 2014;89(6):904-911.
- Valantine H, Sandborg CI. Changing the culture of academic medicine to eliminate the gender leadership gap: 50/50 by 2020. Acad Med. 2013;88(10):1411-1413.
- Sexton DW, Lemak CH, Wainio JA. Career inflection points of women who successfully achieved the hospital CEO position. J Healthc Manag. 2014;59(5):367-383.
Throughout its history, the United States has been a nation of immigrants. From the early colonial settlements to the mid-20th century, most immigrants came from Western European countries. Since 1965, when the Immigration and Nationality Act abolished national-origin quotas, the diversity of immigrants has increased. “By the year 2043,” says Tomás León, president and CEO of the Institute for Diversity in Health Management in Chicago, “we will be a country where the majority of our population is comprised of racial and ethnic minorities.”
Those changing demographics, cited from the U.S. Census Bureau’s projections, already are evidenced in hospital patient populations. According to a benchmarking survey sponsored by the institute, which is an affiliate of the American Hospital Association, the percentage of minority patients seen in hospitals grew from 29% to 31% of patient census between 2011 and 2013.1 And yet, the survey found this increasing diversity is not currently reflected in leadership positions. During the same time period, underrepresented racial and ethnic minorities (UREM) on hospital boards of directors (14%) and in C-suite positions (14%) remained flat (see Figure 1).
Gender disparities in healthcare and academic leadership also have been slow to change. Periodic surveys conducted by the American College of Healthcare Executives indicate that women comprise only 11% of healthcare CEOs in the U.S.2 And despite the fact that women make up half of all medical students (and one-third of full-time faculty), the Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC) finds that women still trail men when it comes to attaining full professorship and decanal positions at their academic institutions.3
The Hospitalist interviewed medical directors, researchers, diversity management professionals, and hospitalists to ascertain current solutions being pursued to narrow the gaps in leadership diversity.
Why Diversity in Leadership Matters
Eric E. Howell, MD, MHM, chief of the Division of Hospital Medicine at Johns Hopkins Bayview Medical Center in the Hopkins School of Medicine in Baltimore, believes there is a need to encourage the advancement to leadership positions for female and UREM physicians.
“In medicine, it’s really about service. If we are really here for our patients, we need representation of diversity in our faculty and leadership,” says Dr. Howell, a past SHM president and faculty member of SHM’s Leadership Academy since its inception in 2005. In addition, he says, “Diversity adds incredible strength to an organization and adds to the richness of the ideas and solutions to overcome challenging problems.”
With the implementation of the Affordable Care Act, formerly uninsured people are now accessing the healthcare system; many are bilingual and bicultural, notes George A. Zeppenfeldt-Cestero, president and CEO, Association of Hispanic Healthcare Executives.
“You want to make sure that providers, whether they are physicians, nurses, dentists, or health executives that drive policy issues, are also reflective of that population throughout the organization,” he says. “The real definition of diversity is making sure you have diversity in all layers of the workforce, including the C-suite.”
León points to the coming “seismic demographic shifts” and wonders if healthcare is ready to become more reflective of the communities it serves.
“Increasing diversity in healthcare leadership and governance is essential for the delivery and provision of culturally competent care,” León says. “Now, more than ever, it’s important that we collectively accelerate progress in this area.”
Advancing in Academic and Hospital Medicine
Might hospital medicine offer additional opportunities for women and minorities to advance into leadership positions? Hospitalist Flora Kisuule, MD, SFHM, assistant professor of medicine at Johns Hopkins School of Medicine and associate division director of the Collaborative Inpatient Medicine Service (CIMS) at Johns Hopkins Bayview Medical Center, believes this may be the case. She was with Dr. Howell’s group when he needed to fill the associate director position.
“My advancement speaks to hospital medicine and the fact that we are growing as a field,” she says. “Because of that, opportunities are presenting themselves.”
Dr. Kisuule’s ability to thrive in her position speaks to her professionalism but also to a number of other intentional factors: Dr. Howell’s continuing sponsorship to include her in leadership opportunities, an emergency call system for parents with sick children, and a women’s task force whose agenda calls for transparency in hiring and advancement.
Intentional Structure Change
Cardiologist Hannah A. Valantine, MD, recognizes the importance of addressing the lack of women and people from unrepresented groups in the Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics (STEM) workforce. While at Stanford University School of Medicine, she developed and put into place a set of strategies to understand and mitigate the drivers of gender imbalance. Since then, Dr. Valantine was recruited to bring her expertise to the National Institutes of Health in Bethesda, Md., where she is the inaugural chief officer for scientific workforce diversity. In this role, she is committed “to promoting biomedical workforce diversity as an opportunity, not a problem.”
Dr. Valantine is pushing NIH to pursue a wide range of evidence-based programming to eliminate career-transition barriers that keep women and individuals from underrepresented groups from attaining spots in the top echelons of science and health leadership. She believes that applying scientific rigor to the issue of workforce diversity can lead to quantifiable, translatable, and repeatable methods for recruitment and retention of talent in the biomedical workforce (see “Building Blocks").
Before joining NIH, Dr. Valantine and her colleagues at Stanford surveyed gender composition and faculty satisfaction several years after initiating a multifaceted intervention to boost recruitment and development of women faculty.4 After making a visible commitment of resources to support faculty, with special attention to women, Stanford rose from below to above national benchmarks in the representation of women among faculty. Yet significant work remains to be done, Dr. Valantine says. Her work predicts that the estimated time to achieve 50% occupancy of full professorships by women nationally approaches 50 years—“far too long using current approaches.”
In a separate review article, Dr. Valantine and co-author Christy Sandborg, MD, described the Stanford University School of Medicine Academic Biomedical Career Customization (ABCC) model, which was adapted from Deloitte’s Mass Career Customization framework and allows for development of individual career plans that span a faculty member’s total career, not just a year or two at a time. Long-term planning can enable better alignment between the work culture and values of the workforce, which will improve the outlook for women faculty, Dr. Valantine says.
The issues of work-life balance may actually be generational, Dr. Valantine explains. Veteran hospitalist Janet Nagamine, MD, BSN, SFHM, of Santa Clara, Calif., agrees.
“Nowadays, men as well as women are looking for work-life balance,” she says.
In hospital medicine, Dr. Nagamine points out, the structural changes required to effect a work-life balance for hospital leaders are often difficult to achieve.
“As productivity surveys show, HM group leaders are putting in as many RVUs as the staff,” the former SHM board member says. “There is no dedicated time for administrative duties.”
Construct a Pipeline
Barriers to advancement often are particular to characteristics of diverse populations. For example, the AAMC’s report on the U.S. physician workforce documents that in African-American physicians 40 and younger, women outnumber their male counterparts. Therefore, in the association’s Diversity in Medical Education: Facts and Figures 2012 report, the executive summary points out the need to strengthen the medical education pipeline to increase the number of African-American males who enter the premed track.
Despite the fast-growing percentage of Latino and Hispanic populations in the United States, the shortage of Latino/Hispanic physicians increased from 1980 to 2010. Latinos/Hispanics are greatly underrepresented in the medical student, resident, and faculty populations, according to John Paul Sánchez, MD, MPH, assistant dean for diversity and inclusion in the Office for Diversity and Community Engagement at Rutgers, The State University of New Jersey. Likewise, Zeppenfeldt-Cestero believes that efforts must begin much earlier with Latino and other minority and underrepresented students.
“We have to make sure our students pursue the STEM disciplines and that they also later have the education and preparation to be competitive at the MBA or MPH levels,” he says.
Dr. Sánchez, an associate professor of emergency medicine and a diversity activist since his med school days, is the recipient of last year’s Association of Hispanic Healthcare Executives’ academic leader of the year award. Since September 2014, he has been involved with Building the Next Generation of Academic Physicians Inc., which collaborates with more than 40 medical schools across the country. The initiative offers conferences designed to develop diverse medical students’ and residents’ interest in pursuing academic medicine. Open to all medical students and residents, the conference curriculum is tailored for women, UREMs, and trainees who identify as lesbian, gay, bisexual, or transgender (LGBT), he says. Seven conferences were held in 2015, 10 are planned for this year, and seven for 2017.
Healthcare Leadership Gaps
Despite their omnipresence in healthcare, there is a dearth of women in chief executive and governance roles, as has been noted by both the American College of Healthcare Executives and the National Center for Healthcare Leadership. As with academic leadership positions, the leadership gap in the administrative sector does not seem to be due to a lack of women entering graduate programs in health administration. On the contrary, since the mid-1980s women have comprised 50% to 60% of graduate students.
“This is absolutely not a pipeline issue,” says Christy Harris Lemak, PhD, FACHE, professor and chair of the Department of Health Services Administration at the University of Alabama at Birmingham School of Health Professions and lead investigator of the National Center for Healthcare Leadership’s study of women in healthcare executive positions. Other factors come into play.
In the study, she and her co-authors queried female healthcare CEOs to ascertain the critical career inflection points that led to their success.6 Those who were strategic about their careers, sought out mentors, and voiced their intentions about pursuing leadership positions were more likely to be successful in those efforts. However, individual career efforts must be coupled with overall organizational commitment to fostering inclusion (see “Path to the Top: Strategic Advice for Women").
Hospitals and healthcare organizations must pursue the development of human capital (and the diversity of their leaders) in a systematic way. “We recommended [in the study] that organizations set expectations that leaders who mentor other potential leaders be rewarded in the same way as those who hit financial targets or readmission rate targets,” Dr. Lemak says.
Leadership matters, agrees Deborah J. Bowen, FACHE, CAE, president and CEO of Chicago-based American College of Healthcare Executives.
“I think we’re getting a little smarter. Organizational leaders and trustees have a better understanding that talent development is one of the most important jobs,” she says. “If you don’t have the right people in the right places making good decisions on behalf of the patients and the populations in the communities they’re serving, the rest falls apart.”
Nuances of Mentoring
Many conversations about encouraging diversity in healthcare leadership converge around the role of effective mentoring and sponsorship. A substantial body of research supports the impact of mentoring on retention, research productivity, career satisfaction, and career development for women. It’s important to ensure that the institutional culture is geared toward mentoring junior faculty, says Jessie Kimbrough Marshall, MD, MPH, assistant professor in the Division of General Medicine Hospitalist Program at the University of Michigan Health System in Ann Arbor (UMHS).
Several of our sources pointed out that leaders must learn how to be effective mentors. More attention is being given to enhancing leaders’ mentorship skills. One example is at the Institute for Diversity in Health Management, which conducts an intensive 12-month certificate in diversity management program for practitioners. León says the program fosters ongoing networking and support through the American Leadership Council on Diversity in Healthcare by building leadership competencies.
Dr. Valantine points out that mentoring is hardly a one-style-fits-all proposition but that it is a crucial element to creating and retaining diversity. She says it should be viewed “much more broadly than it is today, and it should focus beyond the trainer-trainee relationship.”
The process is a two-way street. Denege Ward, MD, hospitalist, assistant professor of internal medicine, and director of the medical short stay unit at UMHS, says minorities need to be ready to take a leap of faith.
“Underrepresented faculty and staff should take the risk of possible failure in challenging situations but learn from it and do better and not succumb to fear in face of challenges,” Dr. Ward says.
Although mentoring is one important component in building diversity in academic medicine, Dr. Sánchez asserts that role models, champions, and sponsors are equally important.
“In addition and separate from role models, there must be in place policies and procedures that promote a climate for diverse individuals to succeed,” he says. “What’s needed is an institutional vision and strategic plan that recognizes the importance of diversity. [It] has to become a core principle.”
Dr. Marshall echoes that refrain, noting the recruitment and retention of a diverse set of leaders will take time and intentionality. She is actively engaged in organizing annual meeting mentoring panels at the Society of General Internal Medicine.
“There are still quite a few barriers for women and minorities to advance into hospital leadership roles,” she says. “We still have a long way to go. However, I’m seeing more women and people of color get into these positions. The numbers are increasing, and that encourages me.” TH
Gretchen Henkel is a freelance writer in California.
References
- Institute for Diversity in Health Management. The state of health care diversity and disparities: a benchmarking study of U.S. hospitals. Available at: http://www.diversityconnection.org/diversityconnection/leadership-conferences/Benchmarking-Survey.jsp?fll=S11.
- Top issues confronting hospitals in 2015. American College of Healthcare Executives website. Available at: https://www.ache.org/pubs/research/ceoissues.cfm. Accessed March 5, 2016.
- Association of American Medical Colleges. Diversity in the physician workforce: facts & figures 2014. Available at: http://aamcdiversityfactsandfigures.org/.
- Valantine HA, Grewal D, Ku MC, et al. The gender gap in academic medicine: comparing results from a multifaceted intervention for Stanford faculty to peer and national cohorts. Acad Med. 2014;89(6):904-911.
- Valantine H, Sandborg CI. Changing the culture of academic medicine to eliminate the gender leadership gap: 50/50 by 2020. Acad Med. 2013;88(10):1411-1413.
- Sexton DW, Lemak CH, Wainio JA. Career inflection points of women who successfully achieved the hospital CEO position. J Healthc Manag. 2014;59(5):367-383.
Throughout its history, the United States has been a nation of immigrants. From the early colonial settlements to the mid-20th century, most immigrants came from Western European countries. Since 1965, when the Immigration and Nationality Act abolished national-origin quotas, the diversity of immigrants has increased. “By the year 2043,” says Tomás León, president and CEO of the Institute for Diversity in Health Management in Chicago, “we will be a country where the majority of our population is comprised of racial and ethnic minorities.”
Those changing demographics, cited from the U.S. Census Bureau’s projections, already are evidenced in hospital patient populations. According to a benchmarking survey sponsored by the institute, which is an affiliate of the American Hospital Association, the percentage of minority patients seen in hospitals grew from 29% to 31% of patient census between 2011 and 2013.1 And yet, the survey found this increasing diversity is not currently reflected in leadership positions. During the same time period, underrepresented racial and ethnic minorities (UREM) on hospital boards of directors (14%) and in C-suite positions (14%) remained flat (see Figure 1).
Gender disparities in healthcare and academic leadership also have been slow to change. Periodic surveys conducted by the American College of Healthcare Executives indicate that women comprise only 11% of healthcare CEOs in the U.S.2 And despite the fact that women make up half of all medical students (and one-third of full-time faculty), the Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC) finds that women still trail men when it comes to attaining full professorship and decanal positions at their academic institutions.3
The Hospitalist interviewed medical directors, researchers, diversity management professionals, and hospitalists to ascertain current solutions being pursued to narrow the gaps in leadership diversity.
Why Diversity in Leadership Matters
Eric E. Howell, MD, MHM, chief of the Division of Hospital Medicine at Johns Hopkins Bayview Medical Center in the Hopkins School of Medicine in Baltimore, believes there is a need to encourage the advancement to leadership positions for female and UREM physicians.
“In medicine, it’s really about service. If we are really here for our patients, we need representation of diversity in our faculty and leadership,” says Dr. Howell, a past SHM president and faculty member of SHM’s Leadership Academy since its inception in 2005. In addition, he says, “Diversity adds incredible strength to an organization and adds to the richness of the ideas and solutions to overcome challenging problems.”
With the implementation of the Affordable Care Act, formerly uninsured people are now accessing the healthcare system; many are bilingual and bicultural, notes George A. Zeppenfeldt-Cestero, president and CEO, Association of Hispanic Healthcare Executives.
“You want to make sure that providers, whether they are physicians, nurses, dentists, or health executives that drive policy issues, are also reflective of that population throughout the organization,” he says. “The real definition of diversity is making sure you have diversity in all layers of the workforce, including the C-suite.”
León points to the coming “seismic demographic shifts” and wonders if healthcare is ready to become more reflective of the communities it serves.
“Increasing diversity in healthcare leadership and governance is essential for the delivery and provision of culturally competent care,” León says. “Now, more than ever, it’s important that we collectively accelerate progress in this area.”
Advancing in Academic and Hospital Medicine
Might hospital medicine offer additional opportunities for women and minorities to advance into leadership positions? Hospitalist Flora Kisuule, MD, SFHM, assistant professor of medicine at Johns Hopkins School of Medicine and associate division director of the Collaborative Inpatient Medicine Service (CIMS) at Johns Hopkins Bayview Medical Center, believes this may be the case. She was with Dr. Howell’s group when he needed to fill the associate director position.
“My advancement speaks to hospital medicine and the fact that we are growing as a field,” she says. “Because of that, opportunities are presenting themselves.”
Dr. Kisuule’s ability to thrive in her position speaks to her professionalism but also to a number of other intentional factors: Dr. Howell’s continuing sponsorship to include her in leadership opportunities, an emergency call system for parents with sick children, and a women’s task force whose agenda calls for transparency in hiring and advancement.
Intentional Structure Change
Cardiologist Hannah A. Valantine, MD, recognizes the importance of addressing the lack of women and people from unrepresented groups in the Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics (STEM) workforce. While at Stanford University School of Medicine, she developed and put into place a set of strategies to understand and mitigate the drivers of gender imbalance. Since then, Dr. Valantine was recruited to bring her expertise to the National Institutes of Health in Bethesda, Md., where she is the inaugural chief officer for scientific workforce diversity. In this role, she is committed “to promoting biomedical workforce diversity as an opportunity, not a problem.”
Dr. Valantine is pushing NIH to pursue a wide range of evidence-based programming to eliminate career-transition barriers that keep women and individuals from underrepresented groups from attaining spots in the top echelons of science and health leadership. She believes that applying scientific rigor to the issue of workforce diversity can lead to quantifiable, translatable, and repeatable methods for recruitment and retention of talent in the biomedical workforce (see “Building Blocks").
Before joining NIH, Dr. Valantine and her colleagues at Stanford surveyed gender composition and faculty satisfaction several years after initiating a multifaceted intervention to boost recruitment and development of women faculty.4 After making a visible commitment of resources to support faculty, with special attention to women, Stanford rose from below to above national benchmarks in the representation of women among faculty. Yet significant work remains to be done, Dr. Valantine says. Her work predicts that the estimated time to achieve 50% occupancy of full professorships by women nationally approaches 50 years—“far too long using current approaches.”
In a separate review article, Dr. Valantine and co-author Christy Sandborg, MD, described the Stanford University School of Medicine Academic Biomedical Career Customization (ABCC) model, which was adapted from Deloitte’s Mass Career Customization framework and allows for development of individual career plans that span a faculty member’s total career, not just a year or two at a time. Long-term planning can enable better alignment between the work culture and values of the workforce, which will improve the outlook for women faculty, Dr. Valantine says.
The issues of work-life balance may actually be generational, Dr. Valantine explains. Veteran hospitalist Janet Nagamine, MD, BSN, SFHM, of Santa Clara, Calif., agrees.
“Nowadays, men as well as women are looking for work-life balance,” she says.
In hospital medicine, Dr. Nagamine points out, the structural changes required to effect a work-life balance for hospital leaders are often difficult to achieve.
“As productivity surveys show, HM group leaders are putting in as many RVUs as the staff,” the former SHM board member says. “There is no dedicated time for administrative duties.”
Construct a Pipeline
Barriers to advancement often are particular to characteristics of diverse populations. For example, the AAMC’s report on the U.S. physician workforce documents that in African-American physicians 40 and younger, women outnumber their male counterparts. Therefore, in the association’s Diversity in Medical Education: Facts and Figures 2012 report, the executive summary points out the need to strengthen the medical education pipeline to increase the number of African-American males who enter the premed track.
Despite the fast-growing percentage of Latino and Hispanic populations in the United States, the shortage of Latino/Hispanic physicians increased from 1980 to 2010. Latinos/Hispanics are greatly underrepresented in the medical student, resident, and faculty populations, according to John Paul Sánchez, MD, MPH, assistant dean for diversity and inclusion in the Office for Diversity and Community Engagement at Rutgers, The State University of New Jersey. Likewise, Zeppenfeldt-Cestero believes that efforts must begin much earlier with Latino and other minority and underrepresented students.
“We have to make sure our students pursue the STEM disciplines and that they also later have the education and preparation to be competitive at the MBA or MPH levels,” he says.
Dr. Sánchez, an associate professor of emergency medicine and a diversity activist since his med school days, is the recipient of last year’s Association of Hispanic Healthcare Executives’ academic leader of the year award. Since September 2014, he has been involved with Building the Next Generation of Academic Physicians Inc., which collaborates with more than 40 medical schools across the country. The initiative offers conferences designed to develop diverse medical students’ and residents’ interest in pursuing academic medicine. Open to all medical students and residents, the conference curriculum is tailored for women, UREMs, and trainees who identify as lesbian, gay, bisexual, or transgender (LGBT), he says. Seven conferences were held in 2015, 10 are planned for this year, and seven for 2017.
Healthcare Leadership Gaps
Despite their omnipresence in healthcare, there is a dearth of women in chief executive and governance roles, as has been noted by both the American College of Healthcare Executives and the National Center for Healthcare Leadership. As with academic leadership positions, the leadership gap in the administrative sector does not seem to be due to a lack of women entering graduate programs in health administration. On the contrary, since the mid-1980s women have comprised 50% to 60% of graduate students.
“This is absolutely not a pipeline issue,” says Christy Harris Lemak, PhD, FACHE, professor and chair of the Department of Health Services Administration at the University of Alabama at Birmingham School of Health Professions and lead investigator of the National Center for Healthcare Leadership’s study of women in healthcare executive positions. Other factors come into play.
In the study, she and her co-authors queried female healthcare CEOs to ascertain the critical career inflection points that led to their success.6 Those who were strategic about their careers, sought out mentors, and voiced their intentions about pursuing leadership positions were more likely to be successful in those efforts. However, individual career efforts must be coupled with overall organizational commitment to fostering inclusion (see “Path to the Top: Strategic Advice for Women").
Hospitals and healthcare organizations must pursue the development of human capital (and the diversity of their leaders) in a systematic way. “We recommended [in the study] that organizations set expectations that leaders who mentor other potential leaders be rewarded in the same way as those who hit financial targets or readmission rate targets,” Dr. Lemak says.
Leadership matters, agrees Deborah J. Bowen, FACHE, CAE, president and CEO of Chicago-based American College of Healthcare Executives.
“I think we’re getting a little smarter. Organizational leaders and trustees have a better understanding that talent development is one of the most important jobs,” she says. “If you don’t have the right people in the right places making good decisions on behalf of the patients and the populations in the communities they’re serving, the rest falls apart.”
Nuances of Mentoring
Many conversations about encouraging diversity in healthcare leadership converge around the role of effective mentoring and sponsorship. A substantial body of research supports the impact of mentoring on retention, research productivity, career satisfaction, and career development for women. It’s important to ensure that the institutional culture is geared toward mentoring junior faculty, says Jessie Kimbrough Marshall, MD, MPH, assistant professor in the Division of General Medicine Hospitalist Program at the University of Michigan Health System in Ann Arbor (UMHS).
Several of our sources pointed out that leaders must learn how to be effective mentors. More attention is being given to enhancing leaders’ mentorship skills. One example is at the Institute for Diversity in Health Management, which conducts an intensive 12-month certificate in diversity management program for practitioners. León says the program fosters ongoing networking and support through the American Leadership Council on Diversity in Healthcare by building leadership competencies.
Dr. Valantine points out that mentoring is hardly a one-style-fits-all proposition but that it is a crucial element to creating and retaining diversity. She says it should be viewed “much more broadly than it is today, and it should focus beyond the trainer-trainee relationship.”
The process is a two-way street. Denege Ward, MD, hospitalist, assistant professor of internal medicine, and director of the medical short stay unit at UMHS, says minorities need to be ready to take a leap of faith.
“Underrepresented faculty and staff should take the risk of possible failure in challenging situations but learn from it and do better and not succumb to fear in face of challenges,” Dr. Ward says.
Although mentoring is one important component in building diversity in academic medicine, Dr. Sánchez asserts that role models, champions, and sponsors are equally important.
“In addition and separate from role models, there must be in place policies and procedures that promote a climate for diverse individuals to succeed,” he says. “What’s needed is an institutional vision and strategic plan that recognizes the importance of diversity. [It] has to become a core principle.”
Dr. Marshall echoes that refrain, noting the recruitment and retention of a diverse set of leaders will take time and intentionality. She is actively engaged in organizing annual meeting mentoring panels at the Society of General Internal Medicine.
“There are still quite a few barriers for women and minorities to advance into hospital leadership roles,” she says. “We still have a long way to go. However, I’m seeing more women and people of color get into these positions. The numbers are increasing, and that encourages me.” TH
Gretchen Henkel is a freelance writer in California.
References
- Institute for Diversity in Health Management. The state of health care diversity and disparities: a benchmarking study of U.S. hospitals. Available at: http://www.diversityconnection.org/diversityconnection/leadership-conferences/Benchmarking-Survey.jsp?fll=S11.
- Top issues confronting hospitals in 2015. American College of Healthcare Executives website. Available at: https://www.ache.org/pubs/research/ceoissues.cfm. Accessed March 5, 2016.
- Association of American Medical Colleges. Diversity in the physician workforce: facts & figures 2014. Available at: http://aamcdiversityfactsandfigures.org/.
- Valantine HA, Grewal D, Ku MC, et al. The gender gap in academic medicine: comparing results from a multifaceted intervention for Stanford faculty to peer and national cohorts. Acad Med. 2014;89(6):904-911.
- Valantine H, Sandborg CI. Changing the culture of academic medicine to eliminate the gender leadership gap: 50/50 by 2020. Acad Med. 2013;88(10):1411-1413.
- Sexton DW, Lemak CH, Wainio JA. Career inflection points of women who successfully achieved the hospital CEO position. J Healthc Manag. 2014;59(5):367-383.
Impact of Delayed Discharge Summary Completion on Hospital Readmission
Clinical question: Is a delay in completion of hospital discharge summary associated with hospital readmissions?
Background: Inpatient discharge summaries serve as a communication tool to future care providers. Previous studies have shown mixed impact on the timeliness of discharge summaries on hospital readmissions.
Study design: Retrospective cohort study.
Setting: Adult medical patients at Johns Hopkins University Hospital, Baltimore.
Synopsis: Study authors examined the time between hospital discharge and discharge summary completion on 87,994 hospitalizations to assess whether a delay increased the odds of hospital readmission. In those hospitalizations, 14,248 patients (16.2%) were readmitted within 30 days of discharge. There was a statistically significant adjusted odds ratio of 1.09 (P=0.001) for readmission associated with discharge summaries completed more than three days after discharge.
The main advantage of the study is that the investigators reviewed a large number of hospitalizations. The major limitation is that deaths or admissions to other hospitals within 30 days of discharge were not measured.
Bottom line: Completing a discharge summary within three days of discharge may decrease the risk of 30-day readmission.
Citation: Hoyer EH, Odonkor CA, Bhatia SN, Leung C, Deutschendorf A, Brotman DJ. Association between days to complete inpatient discharge summaries with all-payer hospital readmissions in Maryland [published online ahead of print February 23, 2016]. J Hosp Med. doi:10.1002/jhm.2556
Short Take
Effectiveness of Rapid Response Teams
A meta-analysis of 30 eligible studies evaluating the impact of rapid response teams (RRTs) from 2000 to 2016 found that RRTs are effective at reducing both in-hospital cardiac arrest and hospital mortality.
Citation: Solomon RS, Corwin GS, Barclay DC, Quddusi SF, Dannenberg MD. Effectiveness of rapid response teams on rates of in-hospital cardiopulmonary arrest and mortality: a systematic review and meta-analysis [published online ahead of print Febraury 1, 2016]. J Hosp Med. doi:10.1002/jhm.2554.
Clinical question: Is a delay in completion of hospital discharge summary associated with hospital readmissions?
Background: Inpatient discharge summaries serve as a communication tool to future care providers. Previous studies have shown mixed impact on the timeliness of discharge summaries on hospital readmissions.
Study design: Retrospective cohort study.
Setting: Adult medical patients at Johns Hopkins University Hospital, Baltimore.
Synopsis: Study authors examined the time between hospital discharge and discharge summary completion on 87,994 hospitalizations to assess whether a delay increased the odds of hospital readmission. In those hospitalizations, 14,248 patients (16.2%) were readmitted within 30 days of discharge. There was a statistically significant adjusted odds ratio of 1.09 (P=0.001) for readmission associated with discharge summaries completed more than three days after discharge.
The main advantage of the study is that the investigators reviewed a large number of hospitalizations. The major limitation is that deaths or admissions to other hospitals within 30 days of discharge were not measured.
Bottom line: Completing a discharge summary within three days of discharge may decrease the risk of 30-day readmission.
Citation: Hoyer EH, Odonkor CA, Bhatia SN, Leung C, Deutschendorf A, Brotman DJ. Association between days to complete inpatient discharge summaries with all-payer hospital readmissions in Maryland [published online ahead of print February 23, 2016]. J Hosp Med. doi:10.1002/jhm.2556
Short Take
Effectiveness of Rapid Response Teams
A meta-analysis of 30 eligible studies evaluating the impact of rapid response teams (RRTs) from 2000 to 2016 found that RRTs are effective at reducing both in-hospital cardiac arrest and hospital mortality.
Citation: Solomon RS, Corwin GS, Barclay DC, Quddusi SF, Dannenberg MD. Effectiveness of rapid response teams on rates of in-hospital cardiopulmonary arrest and mortality: a systematic review and meta-analysis [published online ahead of print Febraury 1, 2016]. J Hosp Med. doi:10.1002/jhm.2554.
Clinical question: Is a delay in completion of hospital discharge summary associated with hospital readmissions?
Background: Inpatient discharge summaries serve as a communication tool to future care providers. Previous studies have shown mixed impact on the timeliness of discharge summaries on hospital readmissions.
Study design: Retrospective cohort study.
Setting: Adult medical patients at Johns Hopkins University Hospital, Baltimore.
Synopsis: Study authors examined the time between hospital discharge and discharge summary completion on 87,994 hospitalizations to assess whether a delay increased the odds of hospital readmission. In those hospitalizations, 14,248 patients (16.2%) were readmitted within 30 days of discharge. There was a statistically significant adjusted odds ratio of 1.09 (P=0.001) for readmission associated with discharge summaries completed more than three days after discharge.
The main advantage of the study is that the investigators reviewed a large number of hospitalizations. The major limitation is that deaths or admissions to other hospitals within 30 days of discharge were not measured.
Bottom line: Completing a discharge summary within three days of discharge may decrease the risk of 30-day readmission.
Citation: Hoyer EH, Odonkor CA, Bhatia SN, Leung C, Deutschendorf A, Brotman DJ. Association between days to complete inpatient discharge summaries with all-payer hospital readmissions in Maryland [published online ahead of print February 23, 2016]. J Hosp Med. doi:10.1002/jhm.2556
Short Take
Effectiveness of Rapid Response Teams
A meta-analysis of 30 eligible studies evaluating the impact of rapid response teams (RRTs) from 2000 to 2016 found that RRTs are effective at reducing both in-hospital cardiac arrest and hospital mortality.
Citation: Solomon RS, Corwin GS, Barclay DC, Quddusi SF, Dannenberg MD. Effectiveness of rapid response teams on rates of in-hospital cardiopulmonary arrest and mortality: a systematic review and meta-analysis [published online ahead of print Febraury 1, 2016]. J Hosp Med. doi:10.1002/jhm.2554.
Effects of Assigning Medical Teams to Nursing Units on Patient Care
Clinical question: Does assigning a single medical team to a nursing unit (regionalizing) improve communication and prevent adverse events?
Background: Many factors impact communication in healthcare delivery. Failures in communication are a known source of adverse events in hospital care. Previous studies of the impact of regionalized care (assigning medical physician teams to nursing units) on communication and outcomes have had mixed results.
Study design: Pre-post intervention cohort analysis.
Setting: Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston.
Synopsis: Three medical teams were assigned to 15-bed nursing units with structured multidisciplinary meeting times for one year. Assessments of concordance of care plan and adverse event detection (with a focus on adverse drug events and poor glycemic control) were performed before and after this assignment. Regionalization of care in the study site improved recognition of care team members (0.56 versus 0.86; P<0.001), discussion of care plan (0.73 versus 0.88; P<0.001), and agreement on estimated discharge date (0.56 versus 0.68; P<0.003). However, it did not significantly improve nurse and physician concordance of the plan or reduce the odds of preventable adverse events.
This study may not have captured an impact on more subtle adverse events or other aspects of interprofessional relationships that enhance patient care.
Bottom line: Regionalization effectively promotes communication but may not lead to patient safety improvements.
Citation: Mueller SK, Schnipper JL, Giannelli K, Roy CL, Boxer R. Impact of regionalized care on concordance of plan and preventable adverse events on general medicine services [published online ahead of print February 24, 2016]. J Hosp Med. doi:10.1002/jhm.2566.
Clinical question: Does assigning a single medical team to a nursing unit (regionalizing) improve communication and prevent adverse events?
Background: Many factors impact communication in healthcare delivery. Failures in communication are a known source of adverse events in hospital care. Previous studies of the impact of regionalized care (assigning medical physician teams to nursing units) on communication and outcomes have had mixed results.
Study design: Pre-post intervention cohort analysis.
Setting: Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston.
Synopsis: Three medical teams were assigned to 15-bed nursing units with structured multidisciplinary meeting times for one year. Assessments of concordance of care plan and adverse event detection (with a focus on adverse drug events and poor glycemic control) were performed before and after this assignment. Regionalization of care in the study site improved recognition of care team members (0.56 versus 0.86; P<0.001), discussion of care plan (0.73 versus 0.88; P<0.001), and agreement on estimated discharge date (0.56 versus 0.68; P<0.003). However, it did not significantly improve nurse and physician concordance of the plan or reduce the odds of preventable adverse events.
This study may not have captured an impact on more subtle adverse events or other aspects of interprofessional relationships that enhance patient care.
Bottom line: Regionalization effectively promotes communication but may not lead to patient safety improvements.
Citation: Mueller SK, Schnipper JL, Giannelli K, Roy CL, Boxer R. Impact of regionalized care on concordance of plan and preventable adverse events on general medicine services [published online ahead of print February 24, 2016]. J Hosp Med. doi:10.1002/jhm.2566.
Clinical question: Does assigning a single medical team to a nursing unit (regionalizing) improve communication and prevent adverse events?
Background: Many factors impact communication in healthcare delivery. Failures in communication are a known source of adverse events in hospital care. Previous studies of the impact of regionalized care (assigning medical physician teams to nursing units) on communication and outcomes have had mixed results.
Study design: Pre-post intervention cohort analysis.
Setting: Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston.
Synopsis: Three medical teams were assigned to 15-bed nursing units with structured multidisciplinary meeting times for one year. Assessments of concordance of care plan and adverse event detection (with a focus on adverse drug events and poor glycemic control) were performed before and after this assignment. Regionalization of care in the study site improved recognition of care team members (0.56 versus 0.86; P<0.001), discussion of care plan (0.73 versus 0.88; P<0.001), and agreement on estimated discharge date (0.56 versus 0.68; P<0.003). However, it did not significantly improve nurse and physician concordance of the plan or reduce the odds of preventable adverse events.
This study may not have captured an impact on more subtle adverse events or other aspects of interprofessional relationships that enhance patient care.
Bottom line: Regionalization effectively promotes communication but may not lead to patient safety improvements.
Citation: Mueller SK, Schnipper JL, Giannelli K, Roy CL, Boxer R. Impact of regionalized care on concordance of plan and preventable adverse events on general medicine services [published online ahead of print February 24, 2016]. J Hosp Med. doi:10.1002/jhm.2566.
Hospitals Not Utilizing More Observation Services to Avoid Readmission Penalties: Study
Concern that the Hospital Readmissions Reduction Program (HRRP) has led to more observation stays in an effort by hospitals to avoid readmission penalties can be put to rest.
A study published in late February in the New England Journal of Medicine shows that while readmission rates dropped dramatically with the passage of the Affordable Care Act (ACA) in 2010, this drop was not correlated with an increase in observation services within the nearly 4,000 individual hospitals assessed.1
“I think we were all really happy to see this paper because it’s really well done and it confirms what our gut feeling was as hospitalists—that the readmissions rate falling wasn’t linked to the increase in the use of observation stays,” says Ann Sheehy, MD, MS, FHM, a hospitalist at the University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health and member of SHM’s Public Policy Committee. “The paper definitively shows that hospitals are not gaming the system to avoid readmission penalties.”
Potentially avoidable hospital readmissions within 30 days of discharge were estimated in 2009 to cost Medicare more than $17 billion annually and are considered a mark of poor-quality care.2 The ACA established HRRP to penalize hospitals with higher-than-expected 30-day readmission rates for several targeted conditions: heart failure, pneumonia, COPD, acute myocardial infarction, total hip and knee replacement, and coronary artery bypass graft surgery.
“Readmission rates had been rock stable for years and years, and coincidentally they came down as observation status rose,” says Ashish Jha, MD, MPH, hospitalist at the VA Boston Healthcare System and professor of health policy at the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health. “The concerning part was that we thought we were making care better by reducing readmissions, but if we were just shifting readmissions to observation, that’s not a change in care pattern—that’s a change in the classification of billing data.”
Earlier data, including an article and an analysis in the Health Affairs blog, also suggested hospitals were trading observation for readmissions, Dr. Jha says.3,4 But the new data have assuaged his concern.
“They did it right,” he says. “Previous studies lumped hospitals together in categories and were not carefully teasing apart what individual hospitals were doing, and when they looked at the individual level, we see no correlation.”
The study’s lead author, Rachael Zuckerman, an economist in the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services (HHS) Office of the Assistant Secretary for Planning and Evaluation (ASPE), writes in a blog post that approximately 565,000 readmissions were likely prevented for the program’s original targeted conditions—heart failure, pneumonia, and acute myocardial infarction—between 2010 and 2015, compared to the readmission rates in the year before passage of the ACA.5
The study examined within-hospital rates of readmission and observation stays among Medicare beneficiaries from October 2007 through May 2015. Within hospitals, there was no correlation between the decline in readmission rates and an uptick in observation stays based on more than 7 million and 45 million index stays for targeted conditions and non-targeted conditions, respectively.
Readmission rates for HRRP’s original target conditions dropped from 21.5% to 17.8%, while non-targeted conditions dropped from 15.3% to 13.1%.
The most rapid drop for targeted and non-targeted conditions occurred shortly after the ACA’s passage, from March 2010 until October 2012, particularly within the six-month window from March through September 2010. Readmission penalties began in October 2012, based on three year’s worth of baseline data.
“Hospitals were reporting readmission rates and CMS was publishing them before the ACA was passed,” says study co-author Steven Sheingold, APSE director of healthcare financing policy. “Hospitals had a good idea a year or two earlier whether they might be in a penalty situation.”
Meanwhile, between 2007 and 2015, observation stays for targeted conditions increased from 2.6% to 4.7% and from 2.5% to 4.2% for non-targeted conditions. There was a steady increase across the entire analysis period, with no significant change pre- and post-ACA.
“Readmissions seem to be more related to passage of the Affordable Care Act than observation,” Zuckerman says. Changes in observation rate are likely due to other factors, such as confusion over Medicare recovery audit contractors, the study authors conclude.
Whether the drop in readmission rates without related increase in observation is tied to improved patient health is still unknown, as Dr. Jha explains in his blog, An Ounce of Evidence. He believes it is “flatly incorrect” to assume lower readmission rates mean better patient outcomes “because readmissions are a utilization measure, a measure of integration and accountability, not a patient outcome measure, not a state of health,” he explains.
While the current study does not address this, Zuckerman says her team is interested in understanding whether overall health measures are changing.
“A hospital is not always a bad thing,” Dr. Jha says. “Sometimes they’re just what a patient needs.”
Dr. Sheehy is particularly interested in why, after October 2012, the steep drop in readmissions slowed down. Probably, she says, much of the low hanging fruit was plucked. But it suggests there is still a population of patients facing higher-than-expected readmissions, and researchers would be wise to understand who they are and how they might be better served.
“The next step is looking at people who are still being readmitted,” she says. TH
Kelly April Tyrell is a freelance writer in Madison, Wis.
References
- Zuckerman RB, Sheingold SH, Orav EJ, Ruhter J, Epstein AM. Readmissions, observation, and the Hospital Readmissions Reduction Program [published online ahead of print April 21, 2016]. N Engl J Med. doi:10.1056/NEJMsa1513024.
- Jencks SF, Williams MV, Coleman EA. Rehospitalizations among patients in the Medicare fee-for-service program. N Engl J Med. 2009;360(14):1418-1428.
- Himmelstein D, Woolhandler S. Quality improvement: ‘become good at cheating and you never need to become good at anything else.’ Available at: http://healthaffairs.org/blog/2015/08/27/quality-improvement-become-good-at-cheating-and-you-never-need-to-become-good-at-anything-else/. Published August 27, 2015. Accessed April 15, 2016.
- Noel-Miller C, Lind K. Is observation status substituting for hospital readmission? Available at: http://healthaffairs.org/blog/2015/10/28/is-observation-status-substituting-for-hospital-readmission/. Published October 25, 2016. Accessed April 15, 2016.
- Zuckerman R. Reducing avoidable hospital readmissions to create a better, safer health care system. Available at: http://www.hhs.gov/blog/2016/02/24/reducing-avoidable-hospital-readmissions.html. Published February 24, 2016. Accessed April 15, 2016.
Concern that the Hospital Readmissions Reduction Program (HRRP) has led to more observation stays in an effort by hospitals to avoid readmission penalties can be put to rest.
A study published in late February in the New England Journal of Medicine shows that while readmission rates dropped dramatically with the passage of the Affordable Care Act (ACA) in 2010, this drop was not correlated with an increase in observation services within the nearly 4,000 individual hospitals assessed.1
“I think we were all really happy to see this paper because it’s really well done and it confirms what our gut feeling was as hospitalists—that the readmissions rate falling wasn’t linked to the increase in the use of observation stays,” says Ann Sheehy, MD, MS, FHM, a hospitalist at the University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health and member of SHM’s Public Policy Committee. “The paper definitively shows that hospitals are not gaming the system to avoid readmission penalties.”
Potentially avoidable hospital readmissions within 30 days of discharge were estimated in 2009 to cost Medicare more than $17 billion annually and are considered a mark of poor-quality care.2 The ACA established HRRP to penalize hospitals with higher-than-expected 30-day readmission rates for several targeted conditions: heart failure, pneumonia, COPD, acute myocardial infarction, total hip and knee replacement, and coronary artery bypass graft surgery.
“Readmission rates had been rock stable for years and years, and coincidentally they came down as observation status rose,” says Ashish Jha, MD, MPH, hospitalist at the VA Boston Healthcare System and professor of health policy at the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health. “The concerning part was that we thought we were making care better by reducing readmissions, but if we were just shifting readmissions to observation, that’s not a change in care pattern—that’s a change in the classification of billing data.”
Earlier data, including an article and an analysis in the Health Affairs blog, also suggested hospitals were trading observation for readmissions, Dr. Jha says.3,4 But the new data have assuaged his concern.
“They did it right,” he says. “Previous studies lumped hospitals together in categories and were not carefully teasing apart what individual hospitals were doing, and when they looked at the individual level, we see no correlation.”
The study’s lead author, Rachael Zuckerman, an economist in the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services (HHS) Office of the Assistant Secretary for Planning and Evaluation (ASPE), writes in a blog post that approximately 565,000 readmissions were likely prevented for the program’s original targeted conditions—heart failure, pneumonia, and acute myocardial infarction—between 2010 and 2015, compared to the readmission rates in the year before passage of the ACA.5
The study examined within-hospital rates of readmission and observation stays among Medicare beneficiaries from October 2007 through May 2015. Within hospitals, there was no correlation between the decline in readmission rates and an uptick in observation stays based on more than 7 million and 45 million index stays for targeted conditions and non-targeted conditions, respectively.
Readmission rates for HRRP’s original target conditions dropped from 21.5% to 17.8%, while non-targeted conditions dropped from 15.3% to 13.1%.
The most rapid drop for targeted and non-targeted conditions occurred shortly after the ACA’s passage, from March 2010 until October 2012, particularly within the six-month window from March through September 2010. Readmission penalties began in October 2012, based on three year’s worth of baseline data.
“Hospitals were reporting readmission rates and CMS was publishing them before the ACA was passed,” says study co-author Steven Sheingold, APSE director of healthcare financing policy. “Hospitals had a good idea a year or two earlier whether they might be in a penalty situation.”
Meanwhile, between 2007 and 2015, observation stays for targeted conditions increased from 2.6% to 4.7% and from 2.5% to 4.2% for non-targeted conditions. There was a steady increase across the entire analysis period, with no significant change pre- and post-ACA.
“Readmissions seem to be more related to passage of the Affordable Care Act than observation,” Zuckerman says. Changes in observation rate are likely due to other factors, such as confusion over Medicare recovery audit contractors, the study authors conclude.
Whether the drop in readmission rates without related increase in observation is tied to improved patient health is still unknown, as Dr. Jha explains in his blog, An Ounce of Evidence. He believes it is “flatly incorrect” to assume lower readmission rates mean better patient outcomes “because readmissions are a utilization measure, a measure of integration and accountability, not a patient outcome measure, not a state of health,” he explains.
While the current study does not address this, Zuckerman says her team is interested in understanding whether overall health measures are changing.
“A hospital is not always a bad thing,” Dr. Jha says. “Sometimes they’re just what a patient needs.”
Dr. Sheehy is particularly interested in why, after October 2012, the steep drop in readmissions slowed down. Probably, she says, much of the low hanging fruit was plucked. But it suggests there is still a population of patients facing higher-than-expected readmissions, and researchers would be wise to understand who they are and how they might be better served.
“The next step is looking at people who are still being readmitted,” she says. TH
Kelly April Tyrell is a freelance writer in Madison, Wis.
References
- Zuckerman RB, Sheingold SH, Orav EJ, Ruhter J, Epstein AM. Readmissions, observation, and the Hospital Readmissions Reduction Program [published online ahead of print April 21, 2016]. N Engl J Med. doi:10.1056/NEJMsa1513024.
- Jencks SF, Williams MV, Coleman EA. Rehospitalizations among patients in the Medicare fee-for-service program. N Engl J Med. 2009;360(14):1418-1428.
- Himmelstein D, Woolhandler S. Quality improvement: ‘become good at cheating and you never need to become good at anything else.’ Available at: http://healthaffairs.org/blog/2015/08/27/quality-improvement-become-good-at-cheating-and-you-never-need-to-become-good-at-anything-else/. Published August 27, 2015. Accessed April 15, 2016.
- Noel-Miller C, Lind K. Is observation status substituting for hospital readmission? Available at: http://healthaffairs.org/blog/2015/10/28/is-observation-status-substituting-for-hospital-readmission/. Published October 25, 2016. Accessed April 15, 2016.
- Zuckerman R. Reducing avoidable hospital readmissions to create a better, safer health care system. Available at: http://www.hhs.gov/blog/2016/02/24/reducing-avoidable-hospital-readmissions.html. Published February 24, 2016. Accessed April 15, 2016.
Concern that the Hospital Readmissions Reduction Program (HRRP) has led to more observation stays in an effort by hospitals to avoid readmission penalties can be put to rest.
A study published in late February in the New England Journal of Medicine shows that while readmission rates dropped dramatically with the passage of the Affordable Care Act (ACA) in 2010, this drop was not correlated with an increase in observation services within the nearly 4,000 individual hospitals assessed.1
“I think we were all really happy to see this paper because it’s really well done and it confirms what our gut feeling was as hospitalists—that the readmissions rate falling wasn’t linked to the increase in the use of observation stays,” says Ann Sheehy, MD, MS, FHM, a hospitalist at the University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health and member of SHM’s Public Policy Committee. “The paper definitively shows that hospitals are not gaming the system to avoid readmission penalties.”
Potentially avoidable hospital readmissions within 30 days of discharge were estimated in 2009 to cost Medicare more than $17 billion annually and are considered a mark of poor-quality care.2 The ACA established HRRP to penalize hospitals with higher-than-expected 30-day readmission rates for several targeted conditions: heart failure, pneumonia, COPD, acute myocardial infarction, total hip and knee replacement, and coronary artery bypass graft surgery.
“Readmission rates had been rock stable for years and years, and coincidentally they came down as observation status rose,” says Ashish Jha, MD, MPH, hospitalist at the VA Boston Healthcare System and professor of health policy at the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health. “The concerning part was that we thought we were making care better by reducing readmissions, but if we were just shifting readmissions to observation, that’s not a change in care pattern—that’s a change in the classification of billing data.”
Earlier data, including an article and an analysis in the Health Affairs blog, also suggested hospitals were trading observation for readmissions, Dr. Jha says.3,4 But the new data have assuaged his concern.
“They did it right,” he says. “Previous studies lumped hospitals together in categories and were not carefully teasing apart what individual hospitals were doing, and when they looked at the individual level, we see no correlation.”
The study’s lead author, Rachael Zuckerman, an economist in the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services (HHS) Office of the Assistant Secretary for Planning and Evaluation (ASPE), writes in a blog post that approximately 565,000 readmissions were likely prevented for the program’s original targeted conditions—heart failure, pneumonia, and acute myocardial infarction—between 2010 and 2015, compared to the readmission rates in the year before passage of the ACA.5
The study examined within-hospital rates of readmission and observation stays among Medicare beneficiaries from October 2007 through May 2015. Within hospitals, there was no correlation between the decline in readmission rates and an uptick in observation stays based on more than 7 million and 45 million index stays for targeted conditions and non-targeted conditions, respectively.
Readmission rates for HRRP’s original target conditions dropped from 21.5% to 17.8%, while non-targeted conditions dropped from 15.3% to 13.1%.
The most rapid drop for targeted and non-targeted conditions occurred shortly after the ACA’s passage, from March 2010 until October 2012, particularly within the six-month window from March through September 2010. Readmission penalties began in October 2012, based on three year’s worth of baseline data.
“Hospitals were reporting readmission rates and CMS was publishing them before the ACA was passed,” says study co-author Steven Sheingold, APSE director of healthcare financing policy. “Hospitals had a good idea a year or two earlier whether they might be in a penalty situation.”
Meanwhile, between 2007 and 2015, observation stays for targeted conditions increased from 2.6% to 4.7% and from 2.5% to 4.2% for non-targeted conditions. There was a steady increase across the entire analysis period, with no significant change pre- and post-ACA.
“Readmissions seem to be more related to passage of the Affordable Care Act than observation,” Zuckerman says. Changes in observation rate are likely due to other factors, such as confusion over Medicare recovery audit contractors, the study authors conclude.
Whether the drop in readmission rates without related increase in observation is tied to improved patient health is still unknown, as Dr. Jha explains in his blog, An Ounce of Evidence. He believes it is “flatly incorrect” to assume lower readmission rates mean better patient outcomes “because readmissions are a utilization measure, a measure of integration and accountability, not a patient outcome measure, not a state of health,” he explains.
While the current study does not address this, Zuckerman says her team is interested in understanding whether overall health measures are changing.
“A hospital is not always a bad thing,” Dr. Jha says. “Sometimes they’re just what a patient needs.”
Dr. Sheehy is particularly interested in why, after October 2012, the steep drop in readmissions slowed down. Probably, she says, much of the low hanging fruit was plucked. But it suggests there is still a population of patients facing higher-than-expected readmissions, and researchers would be wise to understand who they are and how they might be better served.
“The next step is looking at people who are still being readmitted,” she says. TH
Kelly April Tyrell is a freelance writer in Madison, Wis.
References
- Zuckerman RB, Sheingold SH, Orav EJ, Ruhter J, Epstein AM. Readmissions, observation, and the Hospital Readmissions Reduction Program [published online ahead of print April 21, 2016]. N Engl J Med. doi:10.1056/NEJMsa1513024.
- Jencks SF, Williams MV, Coleman EA. Rehospitalizations among patients in the Medicare fee-for-service program. N Engl J Med. 2009;360(14):1418-1428.
- Himmelstein D, Woolhandler S. Quality improvement: ‘become good at cheating and you never need to become good at anything else.’ Available at: http://healthaffairs.org/blog/2015/08/27/quality-improvement-become-good-at-cheating-and-you-never-need-to-become-good-at-anything-else/. Published August 27, 2015. Accessed April 15, 2016.
- Noel-Miller C, Lind K. Is observation status substituting for hospital readmission? Available at: http://healthaffairs.org/blog/2015/10/28/is-observation-status-substituting-for-hospital-readmission/. Published October 25, 2016. Accessed April 15, 2016.
- Zuckerman R. Reducing avoidable hospital readmissions to create a better, safer health care system. Available at: http://www.hhs.gov/blog/2016/02/24/reducing-avoidable-hospital-readmissions.html. Published February 24, 2016. Accessed April 15, 2016.